Glucosamine synthase producing bacterium based on CRISPR-Cas9 technology and construction method and application of glucosamine synthase producing bacterium
A technology for producing bacteria and ammonia sugar, which is applied in the field of building and producing bacteria for ammonia sugar synthase, which can solve the problems of high GlcN accumulation concentration and difficulty in obtaining it, and achieve the effects of reducing inhibition, low production cost and short fermentation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
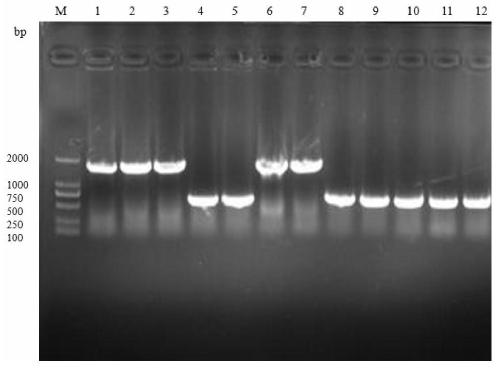
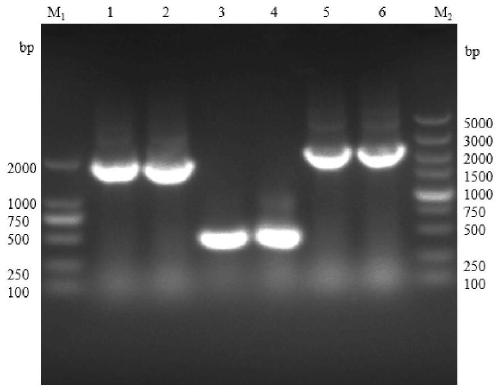
[0041] Example 1: CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology to knock out the genes mannX and naggE
[0042] Using E.coli BL21(DE3) as the starting strain, the gene editing technology mediated by CRISPR-Cas9 was used to knock out the target gene of the starting strain. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0043] (1) Add the pCas9 plasmid to a centrifuge tube containing 100 μL of E.coli BL21(DE3) competent, quickly maintain it in an ice bath for 30 minutes, then heat shock it in a water bath at 42°C for 90 seconds, and put it on ice immediately after the heat shock Cool in the bath for 5 min. Take out the centrifuge tube from ice, add 800 μL of LB medium to the centrifuge tube, place it on a shaker for activation and culture for 45 min. Take out the centrifuge tube and centrifuge it at 8000r / min for 5min. After centrifugation, suck off 800μL supernatant on the ultra-clean bench, blow and mix the bacteria and spread it on LB containing the corresponding antibiotic at a fina...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Exploration of carbon sources available for Escherichia coli with double gene deletion
[0054] Two kinds of bacteria were inoculated in the M9+glucosamine Glc (final concentration 0.5%) of 50mL respectively with the same inoculum size, M9+glucosamine GlcN (final concentration 0.5%), in M9+acetylglucosamine GlcNAc (final concentration 0.5%) liquid medium, Cultivate at 220rpm, 37°C under the same conditions at the same time, take samples regularly, and measure OD 600 , draw the growth curves of the two bacteria in different liquid media to explore whether the double gene deletion Escherichia coli can utilize glucosamine and acetylglucosamine.
Embodiment 3
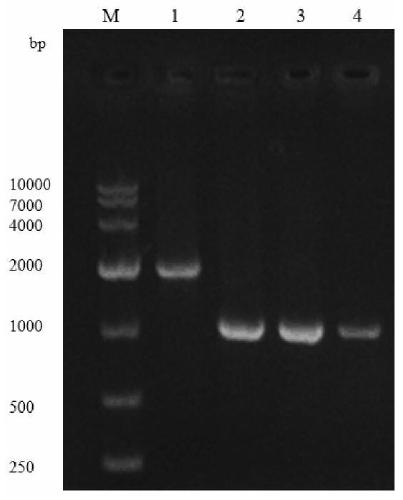
[0055] Embodiment 3: Construction of recombinant expression plasmid pET-28a / gnal / glms
[0056] The primer sequences needed to amplify the gene of interest in Table 3 Example 3
[0057]
[0058] The design of the primers for the glucosamine synthase gene in Table 3 is mainly based on the glms sequence of the glucosamine synthase gene in the NCBI genome of Escherichia colistr.K-12 substr.MG1655, and the design of the primers for the glucosamine acetylase gene is mainly based on the optimized The gnal sequence of the glucosamine acetylase gene derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae was used as a standard, and was designed using SnapGene software.
[0059] (1) Primer STAR HS DNA polymerase has good fidelity, so it is used to amplify the target gene. The PCR reaction program was: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 10 min, denaturation at 95°C for 0.5 min, annealing at 60°C for 0.75 min, extension at 72°C for 2 min, final extension at 72°C for 10 min, and repeated for 34 cycles. The P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com