Method for producing astaxanthin by using transgenic plant
A technology of transgenic plants and astaxanthin, which is applied in the field of plant genetic engineering and can solve problems such as low-cost industrial production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Cloning, transformation and analysis of Chlamydomonas β-carotene oxygenase in bacterial expression system:
[0027] (1) Cloning of Chlamydomonas carotene oxygenase:
[0028] Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cc-124 was provided by Chamydomonas Center (Duke University, USA). Chlamydomonas was cultured with TAP medium / medium. TRI extraction solution (Molecular research center, Cincinnati, OH, USA) was used for total RNA extraction, and about 10 8 The total RNA was extracted from Chlamydomonas cells, and the method was referred to the steps in the manual. Synthesis of cDNA using SuperScript TM III One-Step RT-PCR system (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), cDNA was synthesized at 50°C for 15 minutes. Using the Chlamydomonas cDNA as a template, use the following pair of primers for PCR amplification to obtain the carotene oxygenase gene. After sequencing to confirm that there is no mutation, the fragment obtained by digesting with HindIII and XbaI is connected to the corresponding...
Embodiment 2
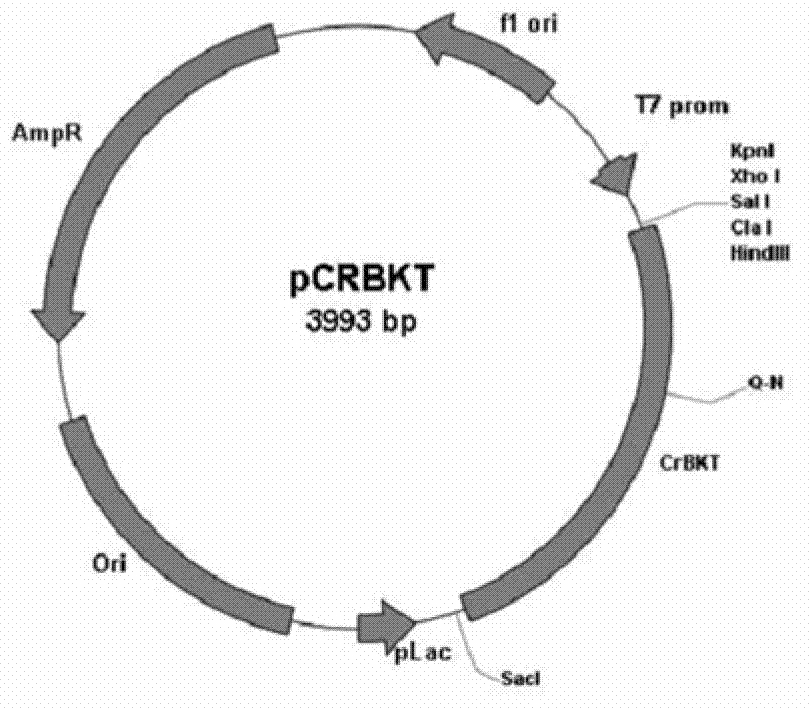
[0041] Construction of plant expression vectors containing Chlamydomonas carotene oxygenase:
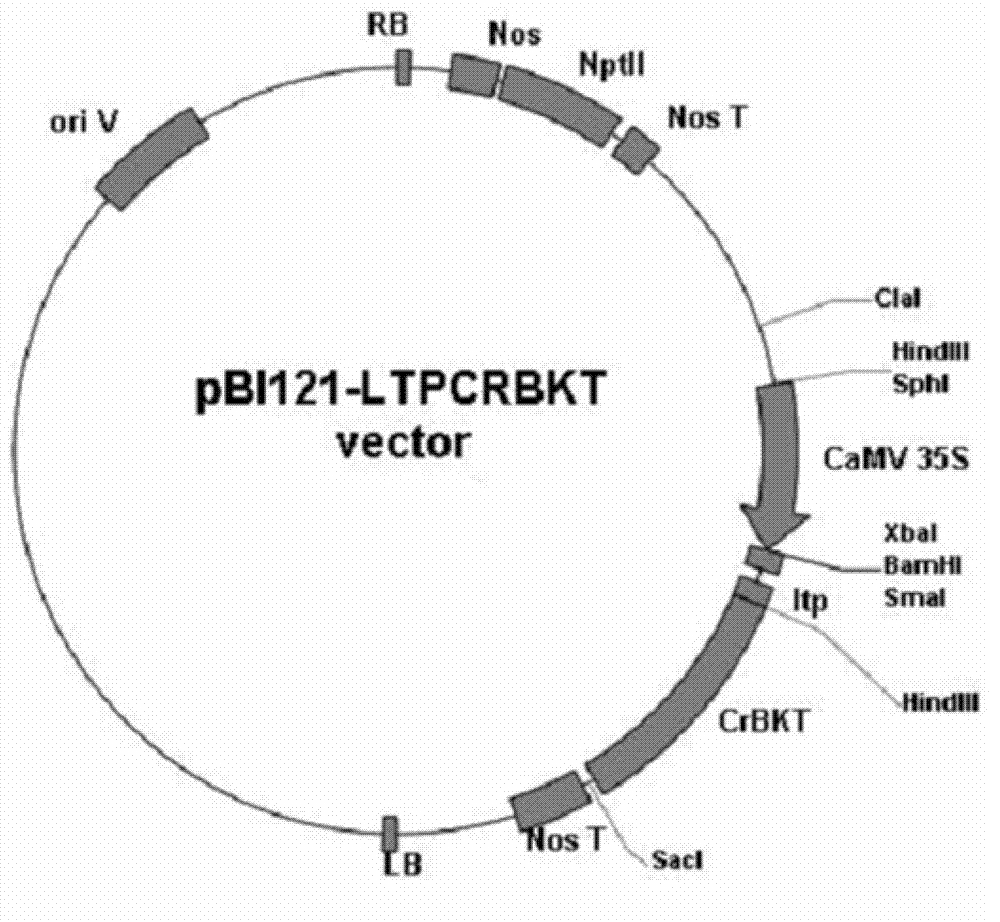
[0042] (1) One of the vectors, pBI121-LTPCRBKT, was constructed from pBI121-CRBKT (zhong et al, Journal of Experimental Botany 62:3659-69, 2011). The RBCS1 signal peptide derived from Arabidopsis in pBI121-CRBKT was replaced with the RBCS signal peptide of tomato (NCBI accession number: M15236). The tomato RBCS signal peptide was amplified using the total tomato DNA as a template, and the following pair of primers were used for PCR amplification to obtain the tomato RBCS signal peptide (LTP). After sequencing, it was confirmed that there was no mutation, and the fragment obtained by digestion with SmaI and HindIII was ligated into pBI121- The vector product obtained from the corresponding restriction site of CRBKT is pBI121-LTPCRBKT.
[0043] The PCR primers are as follows: (SalI-SmaI and HindIII sites are designed for the upstream and downstream primers respectively)
[0044] Forw...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Construction of transgenic plants:
[0056] (1) Preparation of Agrobacterium containing plant expression vector:
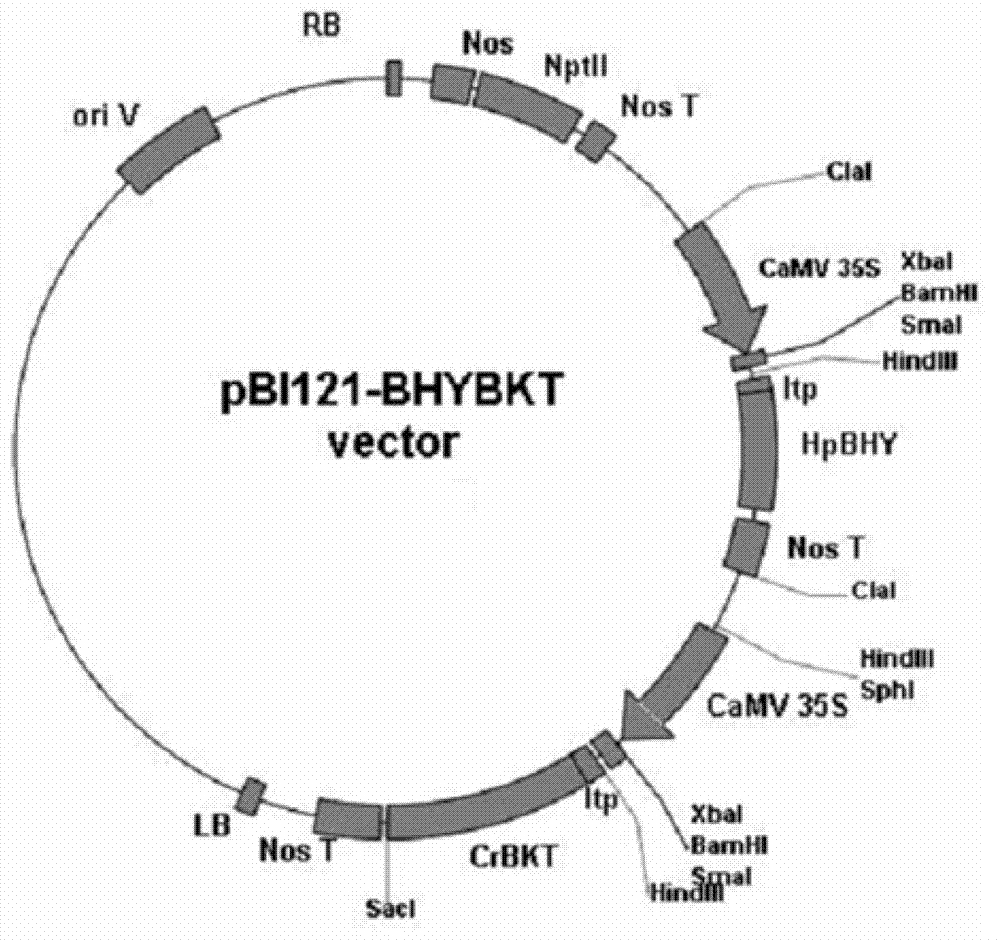
[0057] Add 2 microliters of the pBI121-CRBKT and pBI121-BHYBKT plasmids prepared in Example 2 to 200 microliters of the competent cells obtained in Example 1, mix gently, and place on ice for 30 minutes. Then the bacterial suspension was heat-shocked in a water bath at 42°C for 60 seconds, and quickly moved to ice for 5 minutes to cool down. Add 800 microliters of LB liquid medium to the bacterial suspension, and recover at 28°C for 3 hours. Take an appropriate amount of bacterial suspension and spread it on an LB plate containing 50 mg / L streptomycin and 50 mg / L kanamycin, and place the plate in a warm bath at 28°C for 2 days. Pick a single colony from the plate, identify it by PCR and expand it, extract the plasmid and identify it by digestion. Agrobacteria containing the corresponding plasmids are used for plant transformation. First, 100 microliters...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com