DP-TBD-based maneuvering target detecting and tracking method
A DP-TBD, maneuvering target technology, used in radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as increased influence, overlapping search ranges, acceleration, turning, and U-turn targets cannot be effectively detected and tracked. State estimation, effective detection and tracking, and the effect of improving state search efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034]The present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
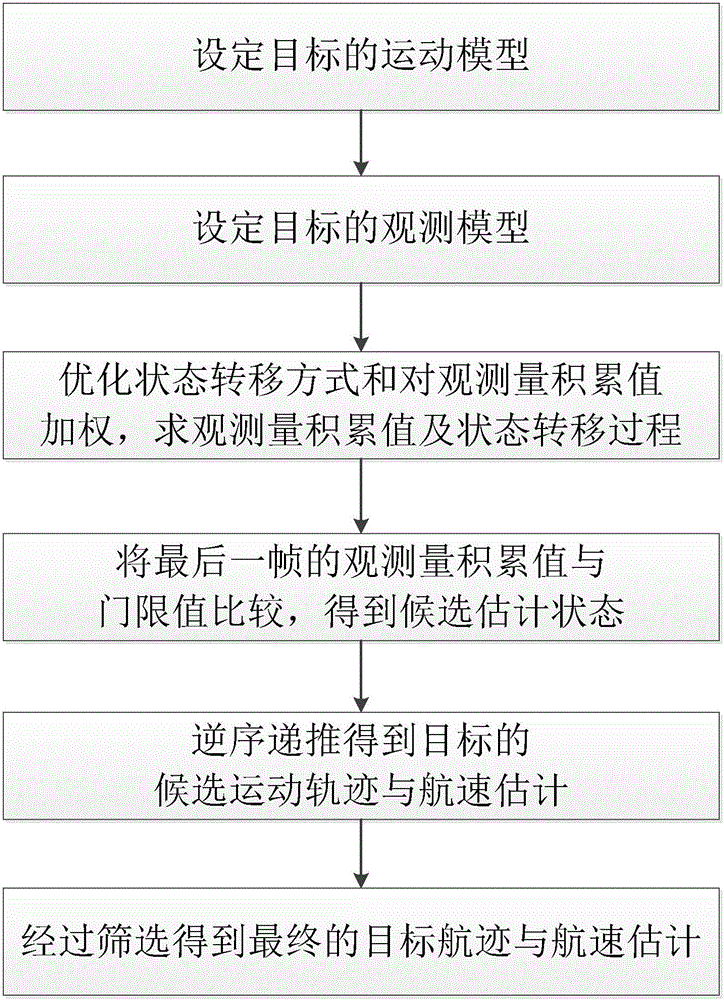
[0035] refer to figure 1 , the mobile target detection and tracking method based on DP-TBD of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0036] Step 1. Set the motion model of the target.
[0037] Assuming that the target moves in the X-Y plane, the state equation is: in is the target motion state, including the position and speed of the target at time k, F is the state transition matrix of the target motion trend, W k is the perturbation matrix of the observation error and quantization error in the simulated motion process.
[0038] Step 2, set the observation model of the target.
[0039] (2a) Consider an observation range including N resolution units, the resolution unit size is set as Δ, the speed resolution unit is set as Δv, and the observation frame interval is set as T, so T·Δv=Δ;
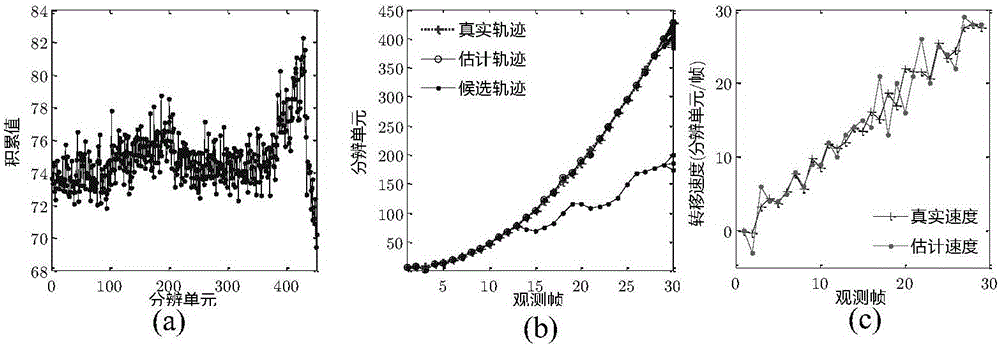
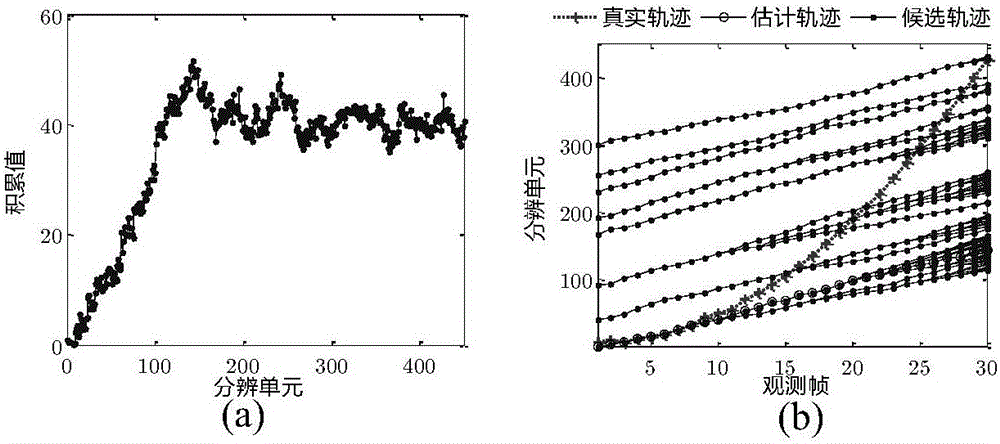
[0040] (2b) with X k Repre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com