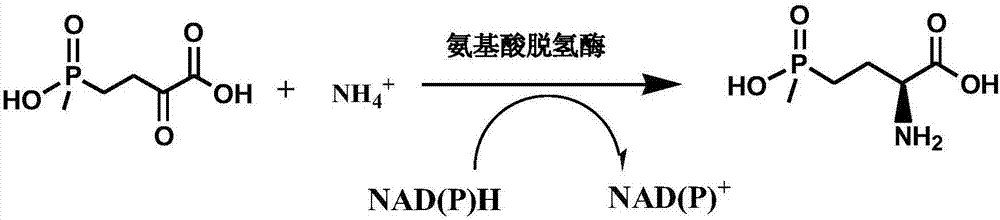
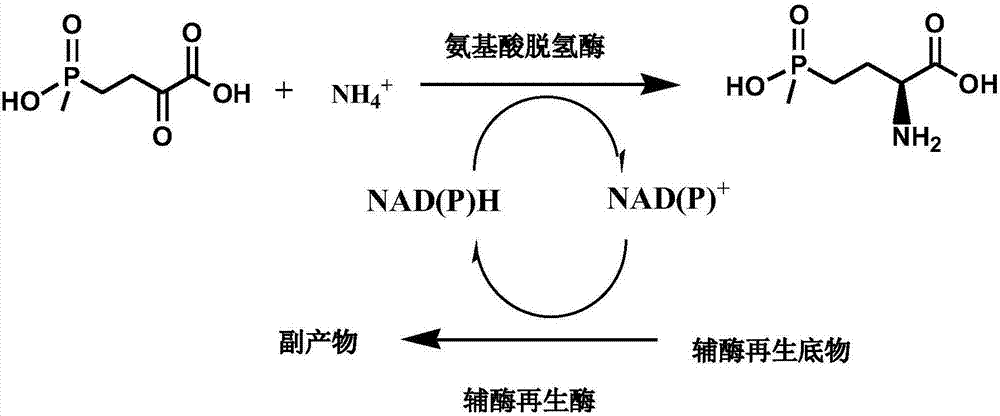
Method for preparing L-glufosinate-ammonium by use of amino acid dehydrogenase
A technology of glutamate dehydrogenase and dehydrogenase, which is applied in the production of chiral pure L-glufosinate-ammonium and the field of optically pure L-glufosinate-ammonium, can solve complex process, expensive chiral resolution reagents, L-glufosinate-ammonium separation troubles and other problems, to achieve the effect of easy separation and purification, high conversion rate of raw materials, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] The construction of embodiment 1 amino acid dehydrogenase
[0065] 1. Activation of wild bacteria and genome extraction
[0066] All wild bacteria were activated and cultured with LB medium, the formula was: peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L, dissolved in deionized water and then sterilized at 121°C for 20min, ready for use. The solid medium is LB medium with 2% agar added.
[0067] Streak the glycerol tube containing the wild bacteria onto a plate containing LB solid medium, and culture it statically at 30°C for 2-3 days. Pick colonies from the plates and transfer them into Erlenmeyer flasks containing 50 mL of LB medium, and culture them at 30°C and 200 rpm for 2 to 3 days. After obtaining the culture medium, the whole genome was extracted according to the operating instructions of the genome extraction kit. The obtained genome can be directly used for the amplification of the target gene or stored at -20°C for a long time.
[0068] 2. Amplification of ...
Embodiment 2
[0097] The cultivation of embodiment 2 thalline and the preparation of crude enzyme liquid
[0098] 1. Bacteria culture
[0099] Composition of LB liquid medium: peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L, dissolved in deionized water and then constant volume, sterilized at 121°C for 20min, ready for use.
[0100] After the engineering bacteria containing the amino acid dehydrogenase gene were activated by streaking on a plate, a single colony was picked and inoculated into 5 mL LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL kanamycin, and cultured with shaking at 37°C for 12 hours. Transfer to 50mL fresh LB liquid medium also containing 50μg / ml Kan at 2% inoculum size, shake culture to OD at 37°C 600 When it reaches about 0.8, add IPTG to its final concentration of 0.5mM, and induce culture at 18°C for 16h. After the cultivation, the culture solution was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min, the supernatant was discarded, the bacteria were collected, and stored in a -80°C ultra-l...
Embodiment 3
[0103] The mensuration of embodiment 3 enzyme storehouse enzyme activity
[0104] Standard enzyme activity detection system: 25g / L wet bacteria (ultrasonic disruption), 10mM substrate, 20mM coenzyme (NADH or NADPH), 750mM NH 4 Cl, the total system volume is 400 μL, and the reaction medium is pH 8.0 phosphate buffer. Definition of unit enzyme activity: under standard reaction conditions, the amount of enzyme required to generate 1 μmol L-glufosinate-ammonium per minute.
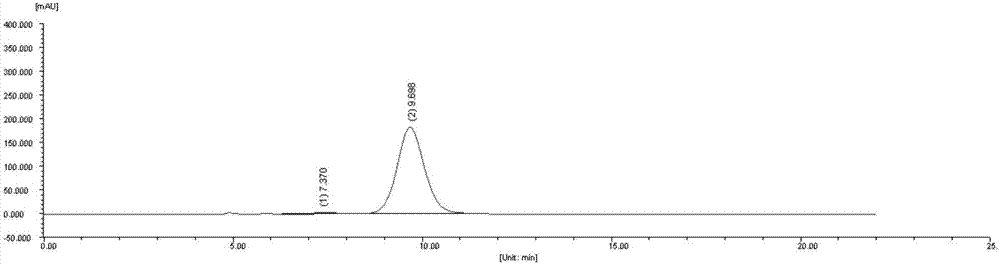
[0105] The reaction solution was prepared according to the above-mentioned standard enzyme activity detection system, reacted in a metal bath shaking reactor at 30°C for 6 hours, added 40 μL of 5M NaOH to terminate the reaction, and stored on ice. After the sample was diluted by a certain number of times, the concentration of L-glufosinate-ammonium was detected by pre-column derivatization high-performance liquid chromatography, and the enzyme activity was calculated.
[0106] Table 4 enzyme library enzyme a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-denatured | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Extend | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com