Glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof to synthetizing L- glufosinate-ammonium
A mutant, glufosinate-ammonium technology, applied in the production field of chiral pure L-glufosinate-ammonium, can solve the problems of low reduction activity and low substrate concentration, and achieve easy separation and purification, high yield and simple process Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] The construction of embodiment 1 expression vector and engineering bacterium
[0037] Based on literature reports and gene sequence homology, four strains of dehydrogenases were selected from the NCBI database, which were derived from Pseudomonas, Pseudomonas extremaustralis, Pseudomonas moorei and Pseudomonassaudiphocaensis respectively. Or WP_037025837.1, and carry out whole gene synthesis, respectively obtain the glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase E1 (nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, aminoacid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2) derived from Pseudomonas, Glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase E2 derived from Pseudomonasextremaustralis (the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.3, and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.4), the glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase E3 derived from Pseudomonas moorei (nuclear The nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.5, the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.6) and the glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase E4 d...
Embodiment 2
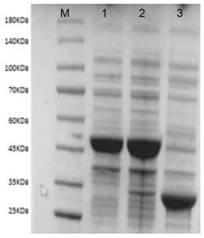
[0051] Embodiment 2: Induced expression of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase, glucose dehydrogenase, SDS-PAGE analysis
[0052] 1. Wet cells containing glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase: the recombinant Escherichia coli E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDHE1, E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1- PPTGDHE2, E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDHE3, E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDHE4, inoculated into LB liquid medium containing 50 μg / mL ampicillin resistance, 37°C, Cultivate at 200rpm for 12h, then inoculate 1% (v / v) inoculum into fresh LB liquid medium containing 50μg / mL ampicillin resistance, and cultivate at 37°C and 150rpm until the OD600 of the bacteria reaches 0.6- 0.8, add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.1mM, induce culture at 18°C for 16h, centrifuge at 8000rpm at 4°C for 20min, discard the supernatant, collect the precipitate, and wash twice with pH 7.5, 20mM phosphate buffer saline (PBS) , that is, to obtain Escherichia coli E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-PPTGDHE1, E.coli BL21(DE...
Embodiment 3
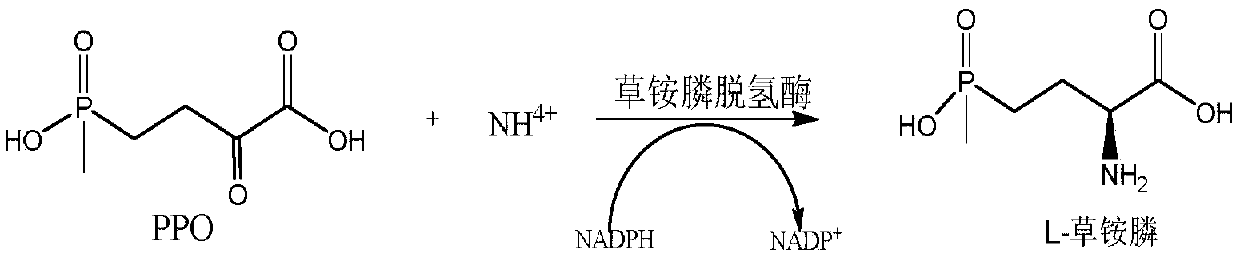
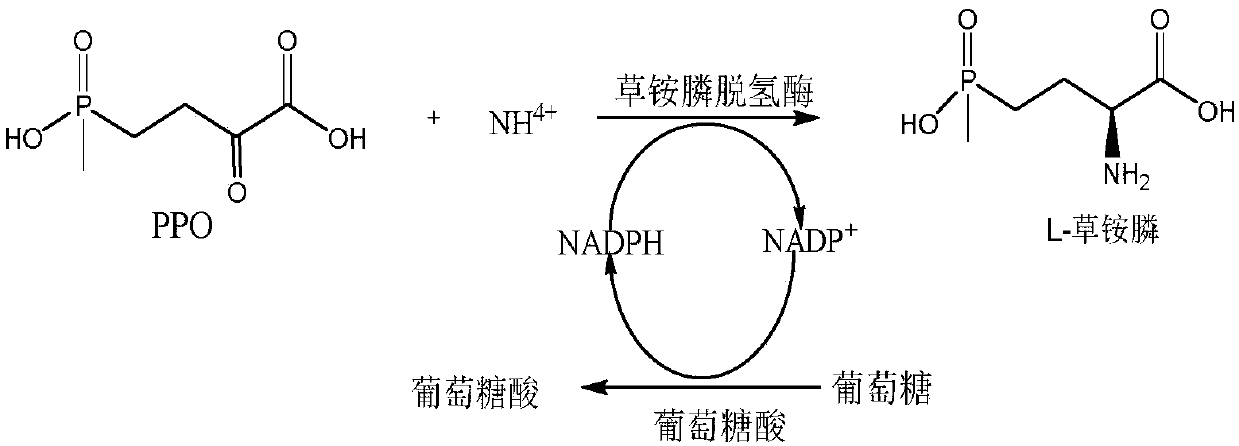
[0066] Example 3 Glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase catalyzes PPO to prepare L-glufosinate-ammonium
[0067] Crude enzyme solution: add the wet cells containing glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase and the wet cells containing glucose dehydrogenase prepared by the method in Example 2 to resuspend the cells in PBS with pH 7.5 and 100 mM, and put them on the ice-water mixture Ultrasonic crushing for 10 min, ultrasonic crushing conditions: power 400W, crushing for 1 s, pausing for 5 s, to obtain crude enzyme solution.
[0068] In 30mL PBS buffer (100mM, pH 7.5), add the crude enzyme solution of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase (the amount of bacteria is 25g / L buffer), 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethylphosphinyl)-butyl Acid (final concentration 100mmol / L), inorganic amino donor (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4(final concentration 500mM), glucose (final concentration 120mmol / L), NADPH (final concentration 1mmol / L), GDH crude enzyme solution (the amount of bacteria is 50g / L buffer) constitute the reacti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| catalytic efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com