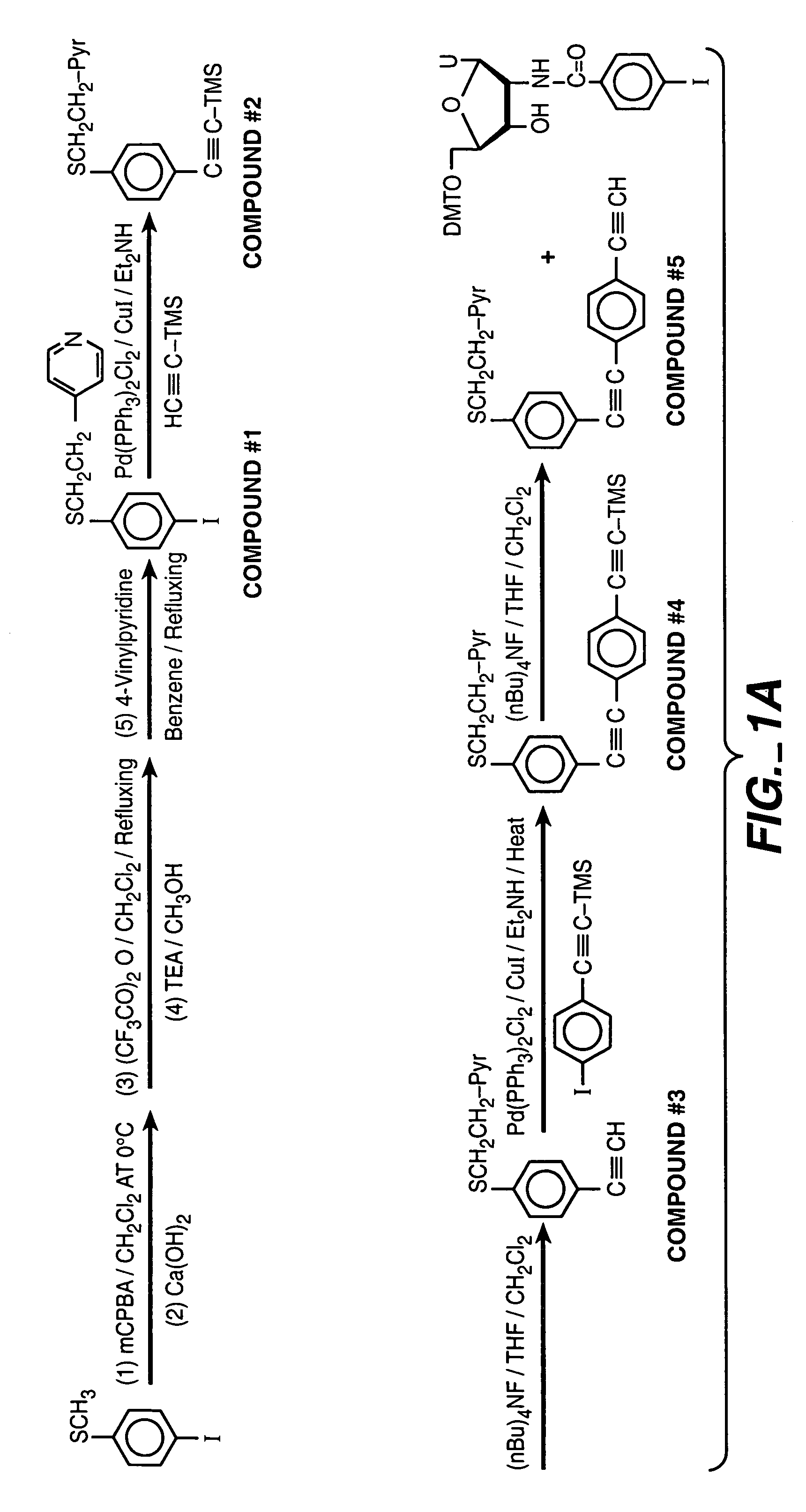
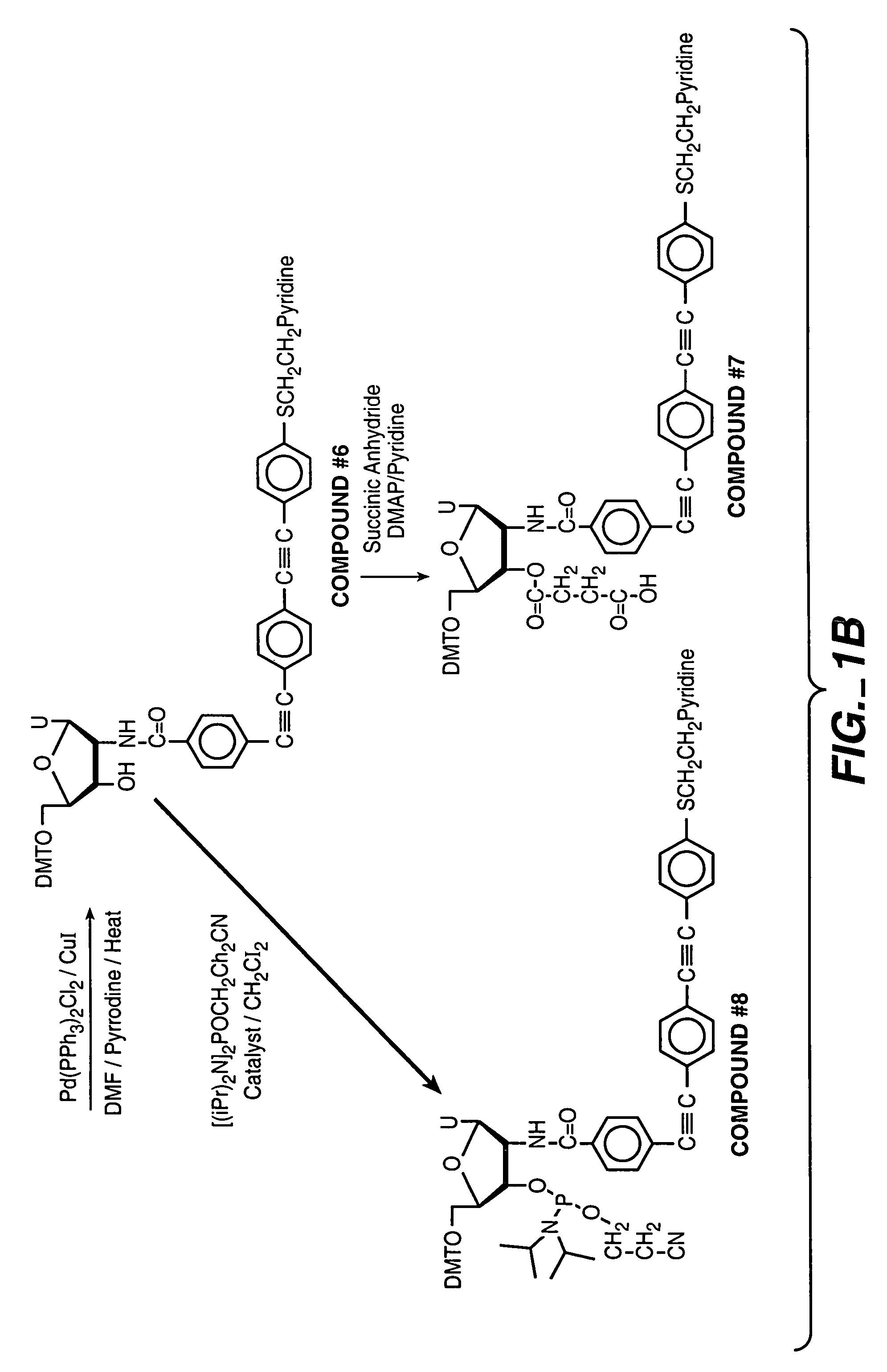
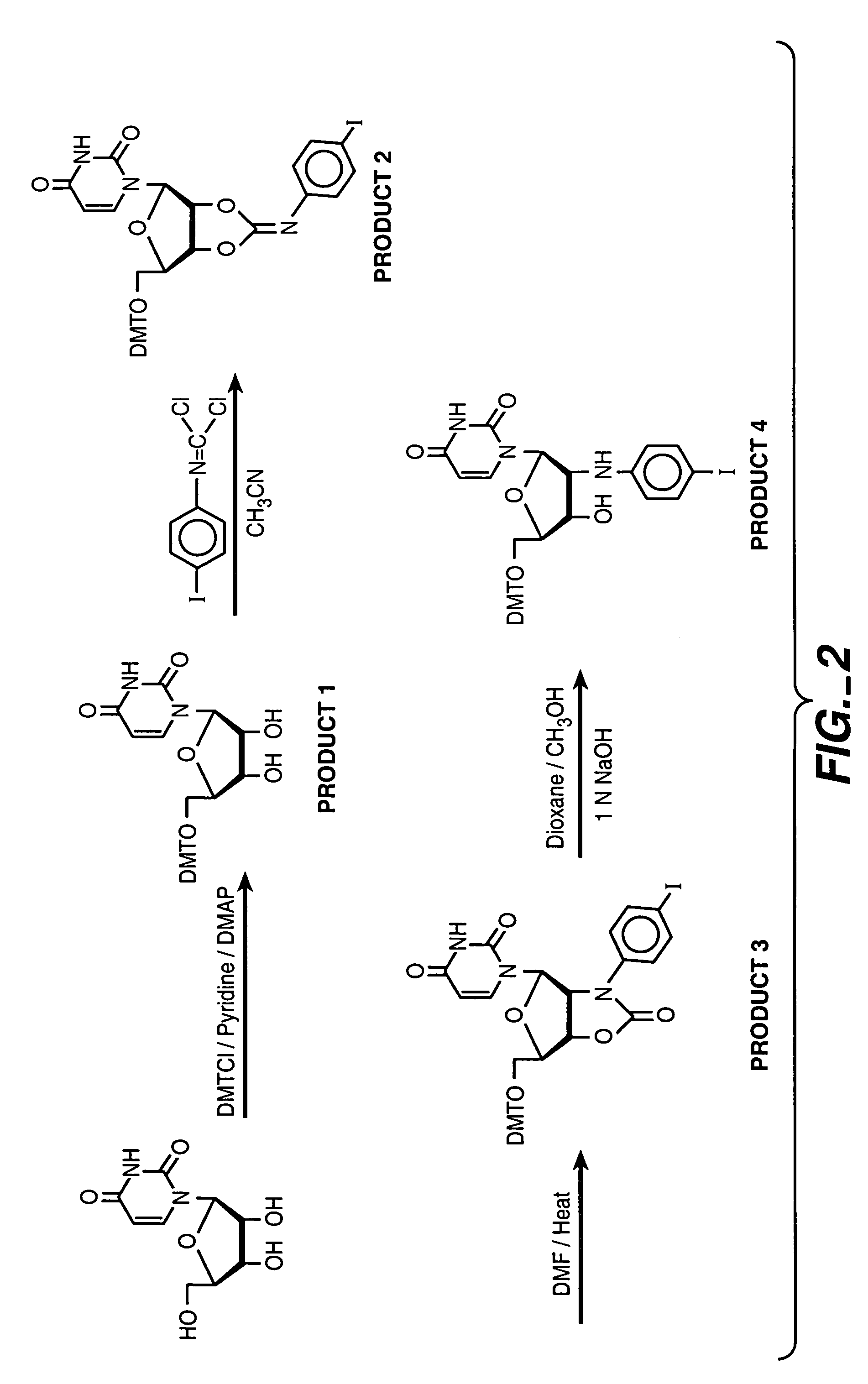
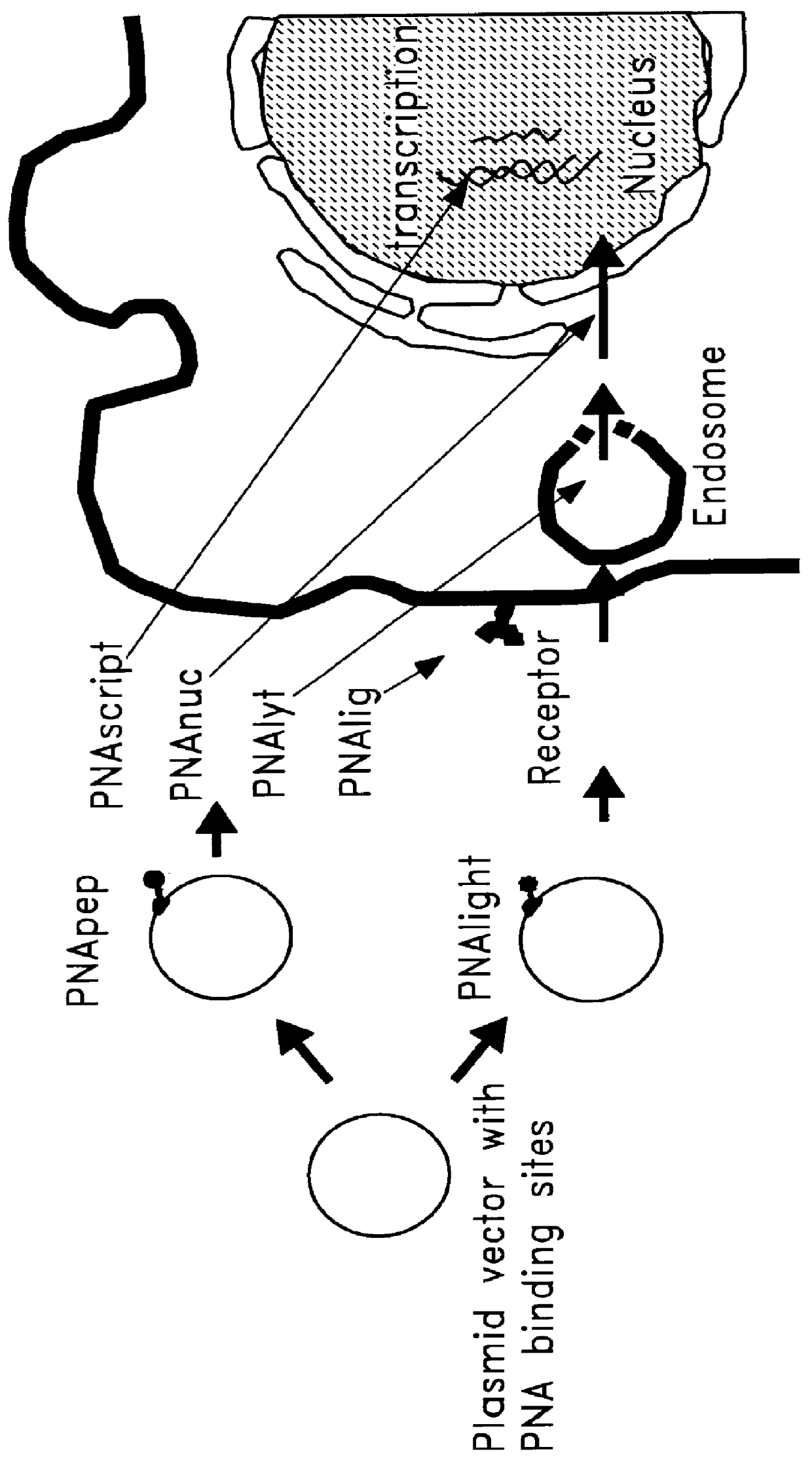
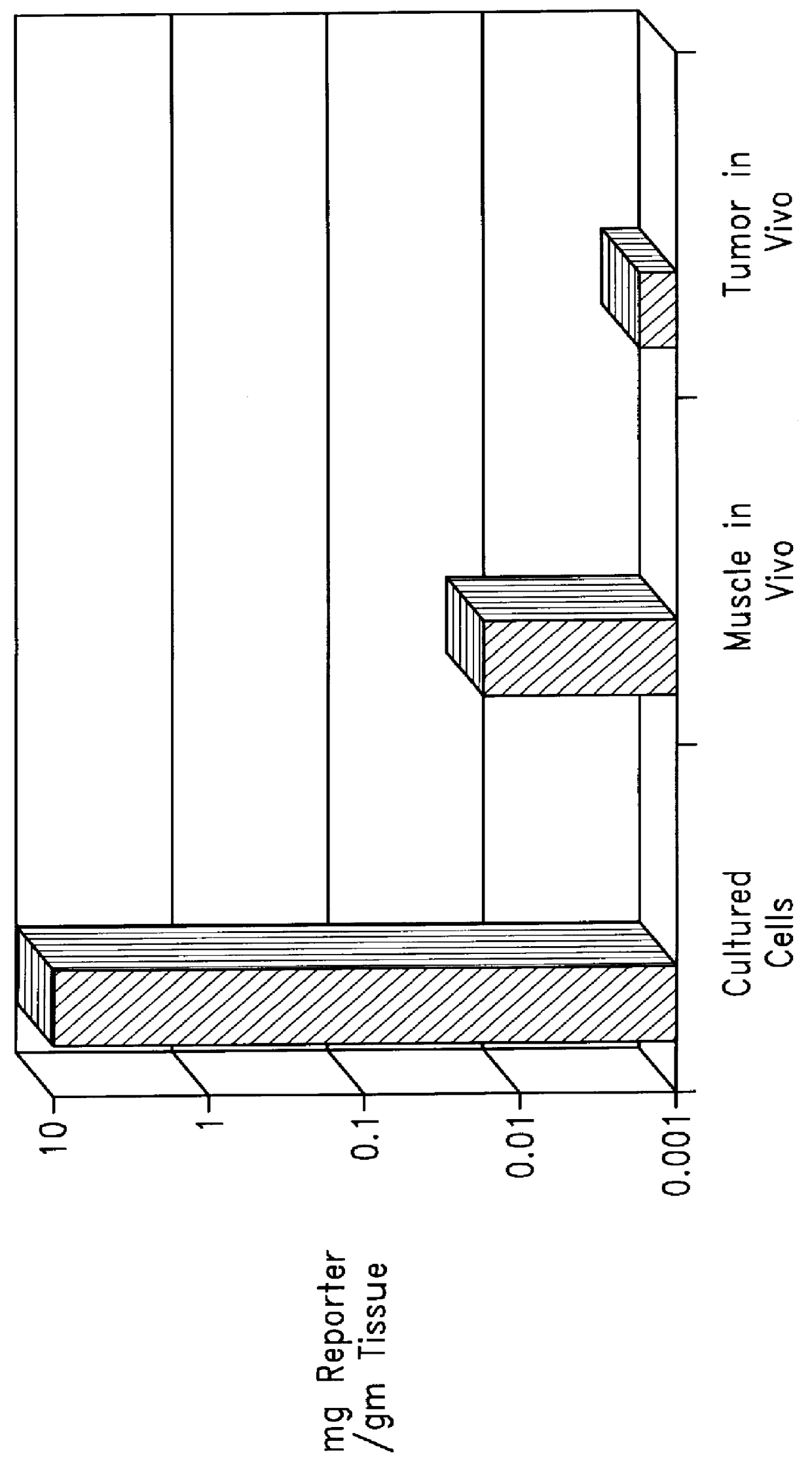
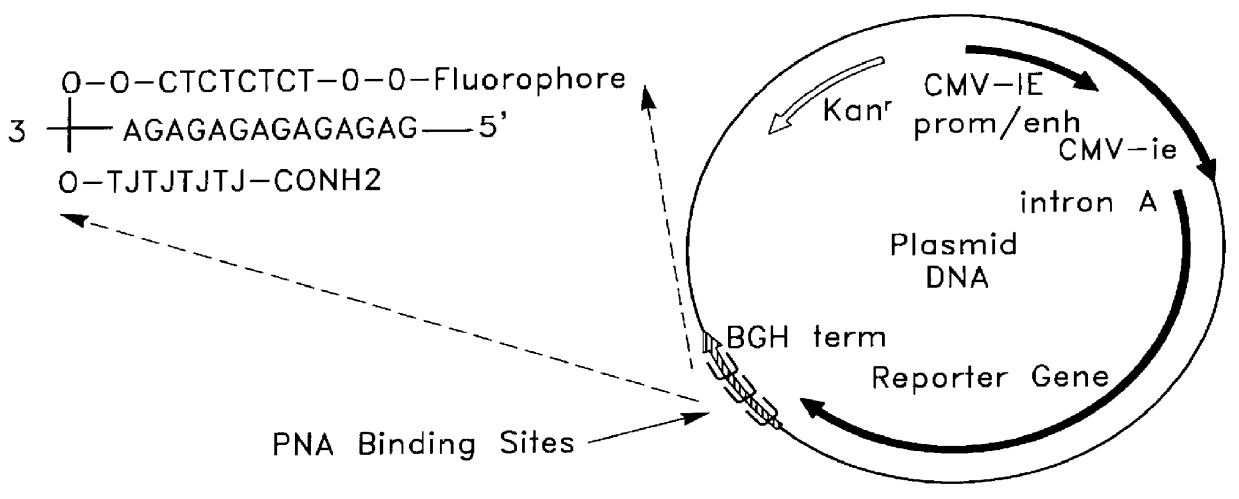
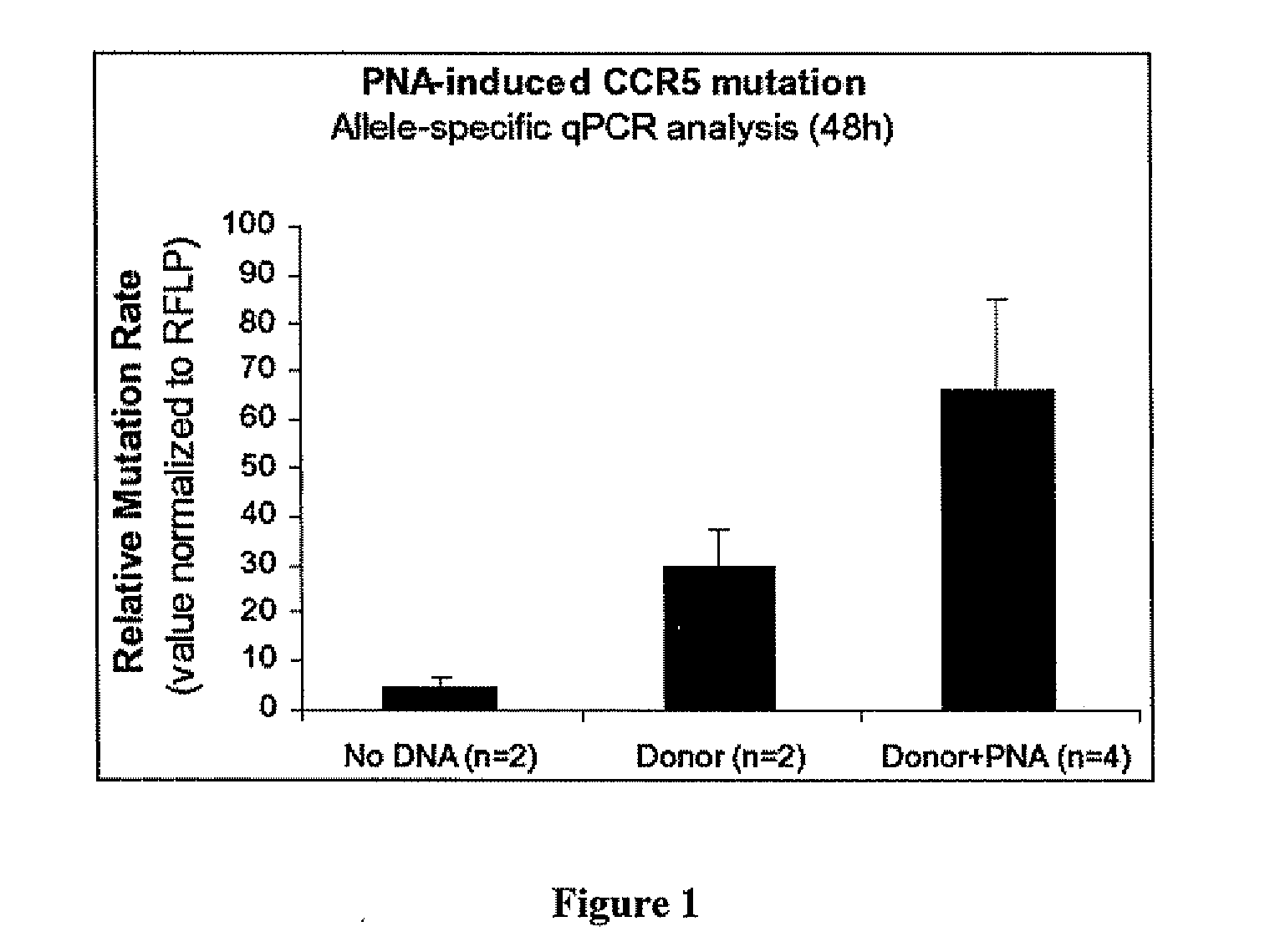
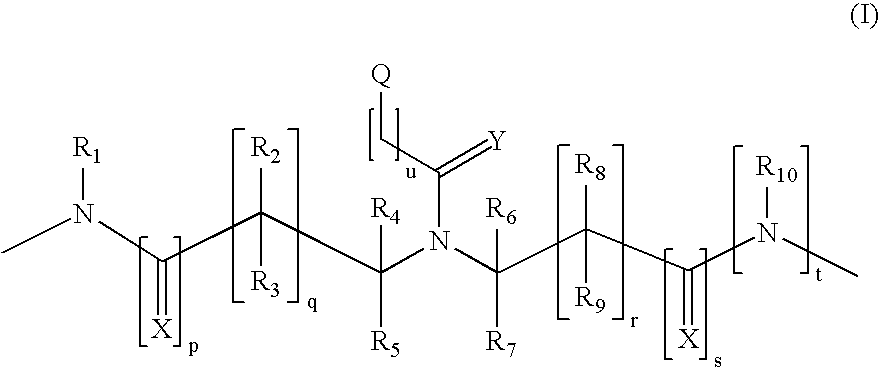
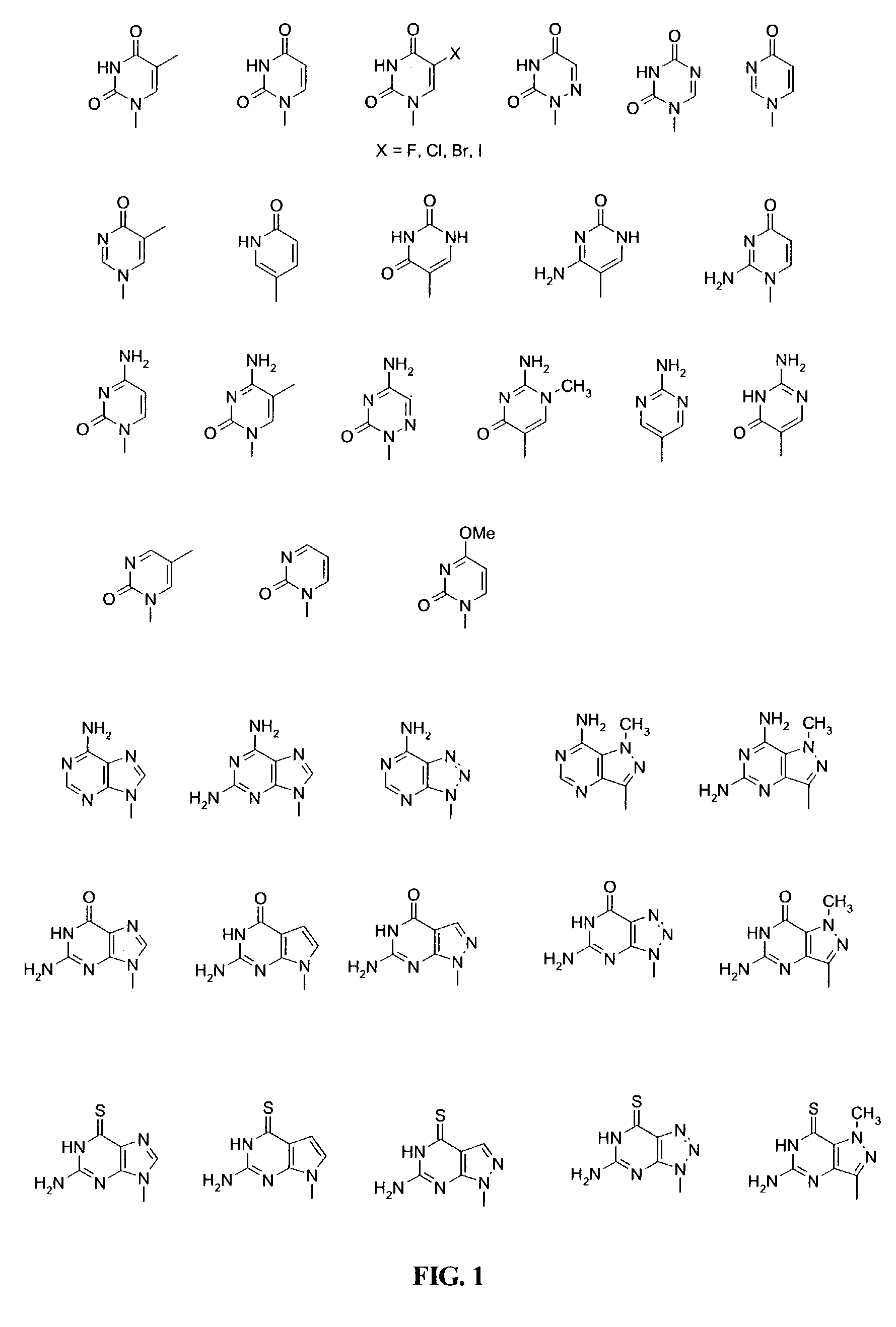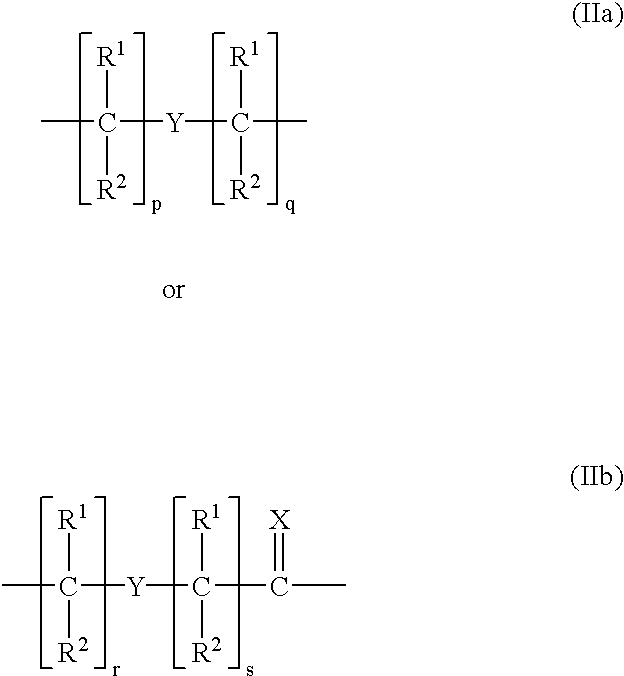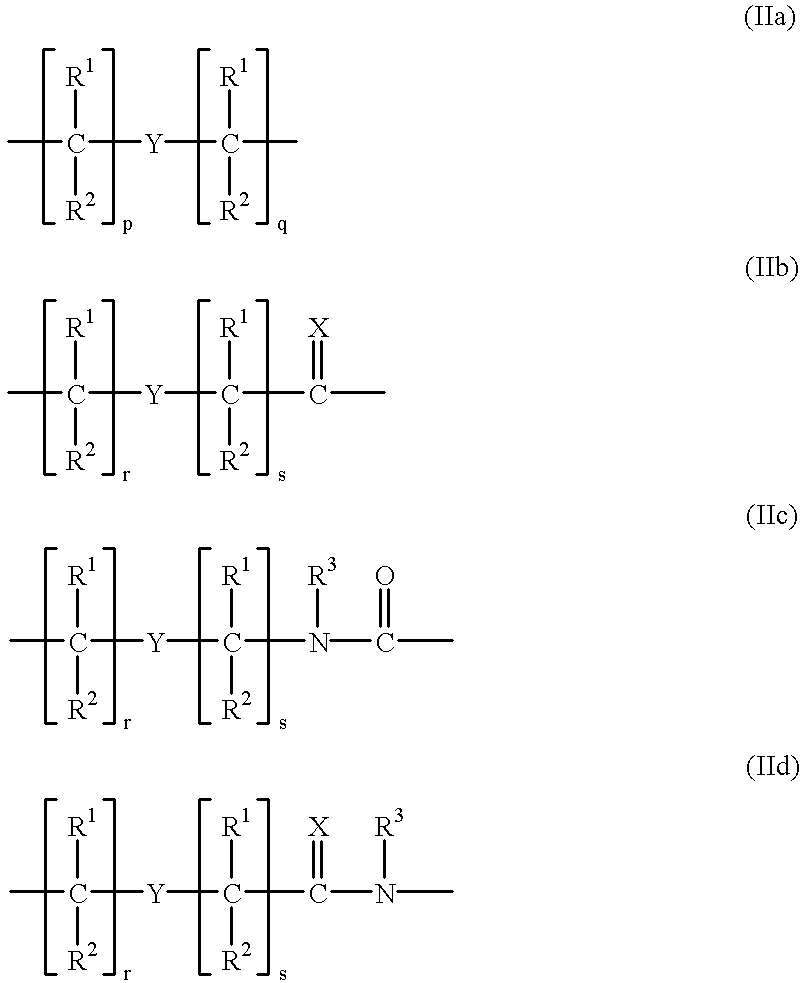Patents
Literature
566 results about "Peptide nucleic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Peptide nucleic acid (PNA) is an artificially synthesized polymer similar to DNA or RNA. It was invented by Peter E. Nielsen (Univ. Copenhagen), Michael Egholm (Univ. Copenhagen), Rolf H. Berg (Risø National Lab), and Ole Buchardt (Univ. Copenhagen) in 1991.
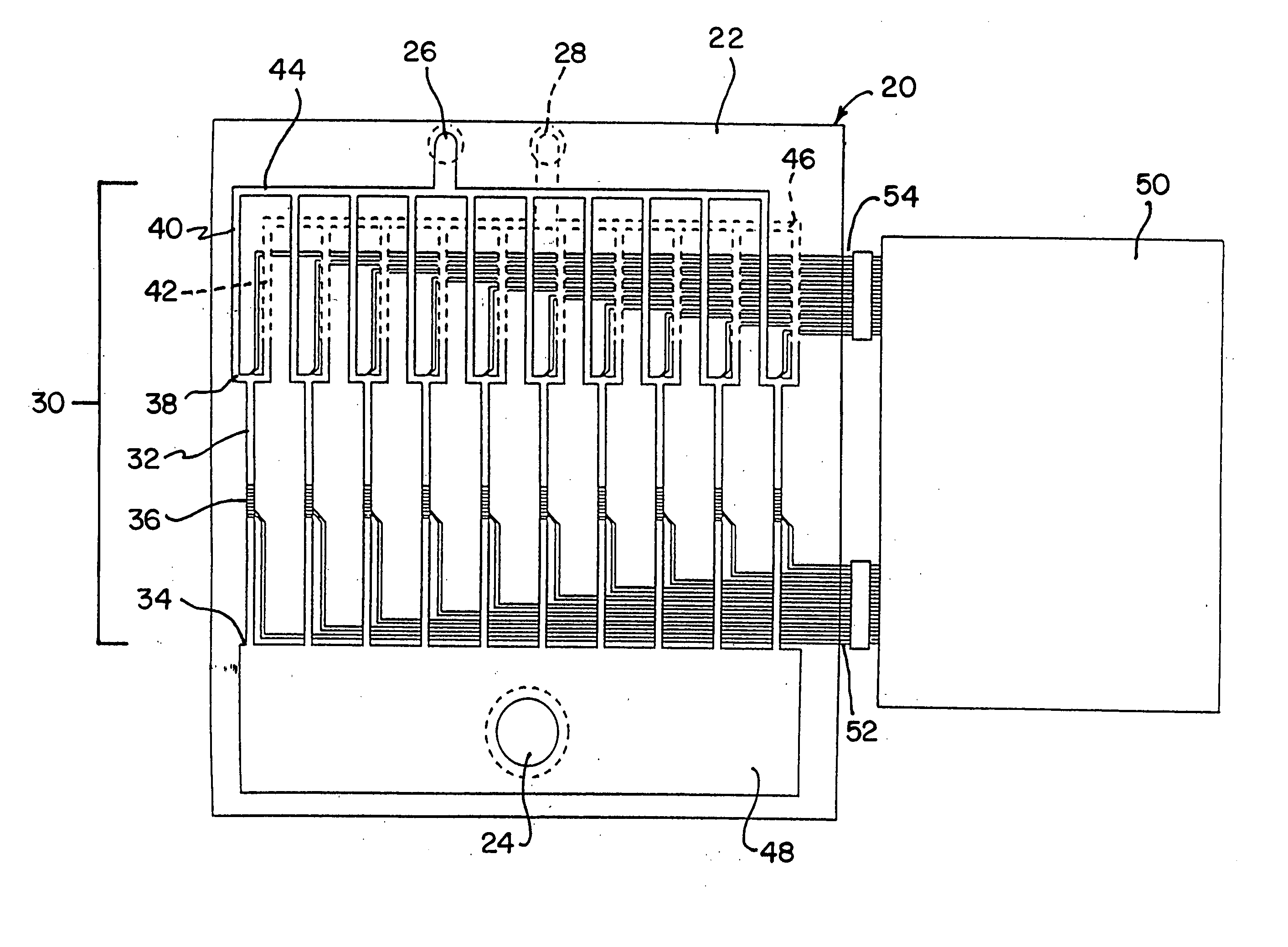
Integrated active flux microfluidic devices and methods
InactiveUS6767706B2Rapid and complete exposureQuick and accurate and inexpensive analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFlow mixersAntigenHybridization probe
The invention relates to a microfabricated device for the rapid detection of DNA, proteins or other molecules associated with a particular disease. The devices and methods of the invention can be used for the simultaneous diagnosis of multiple diseases by detecting molecules (e.g. amounts of molecules), such as polynucleotides (e.g., DNA) or proteins (e.g., antibodies), by measuring the signal of a detectable reporter associated with hybridized polynucleotides or antigen / antibody complex. In the microfabricated device according to the invention, detection of the presence of molecules (i.e., polynucleotides, proteins, or antigen / antibody complexes) are correlated to a hybridization signal from an optically-detectable (e.g. fluorescent) reporter associated with the bound molecules. These hybridization signals can be detected by any suitable means, for example optical, and can be stored for example in a computer as a representation of the presence of a particular gene. Hybridization probes can be immobilized on a substrate that forms part of or is exposed to a channel or channels of the device that form a closed loop, for circulation of sample to actively contact complementary probes. Universal chips according to the invention can be fabricated not only with DNA but also with other molecules such as RNA, proteins, peptide nucleic acid (PNA) and polyamide molecules.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
PNA-DNA-PNA chimeric macromolecules
InactiveUS6277603B1Increase resistanceHigh affinitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological bodyResearch purpose
Macromolecules are provided that have increased nuclease resistance, increasing binding affinity to a complementary strand, and that activate RNase H enzyme. The macromolecules have the structure PNA-DNA-PNA where the DNA portion is composed of subunits of 2'-deoxy-erythro-pento-furanosyl nucleotides and the PNA portions are composed of subunits of peptide nucleic acids. Such macromolecules are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to therapeutics.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
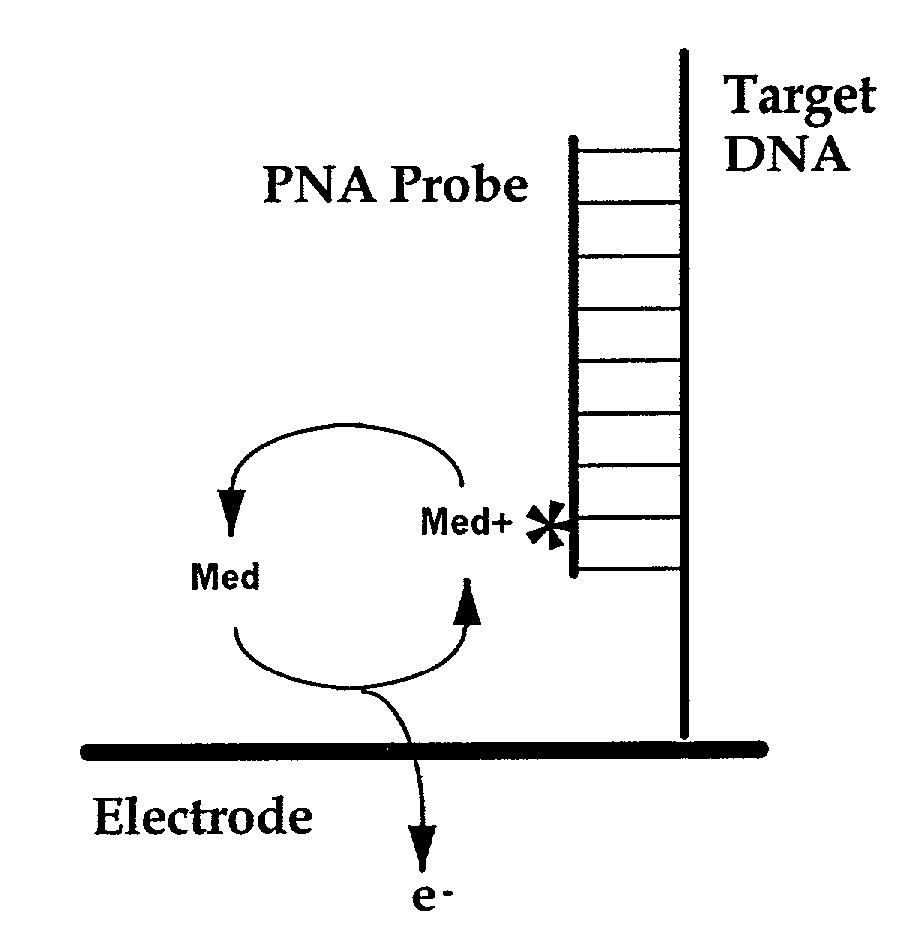
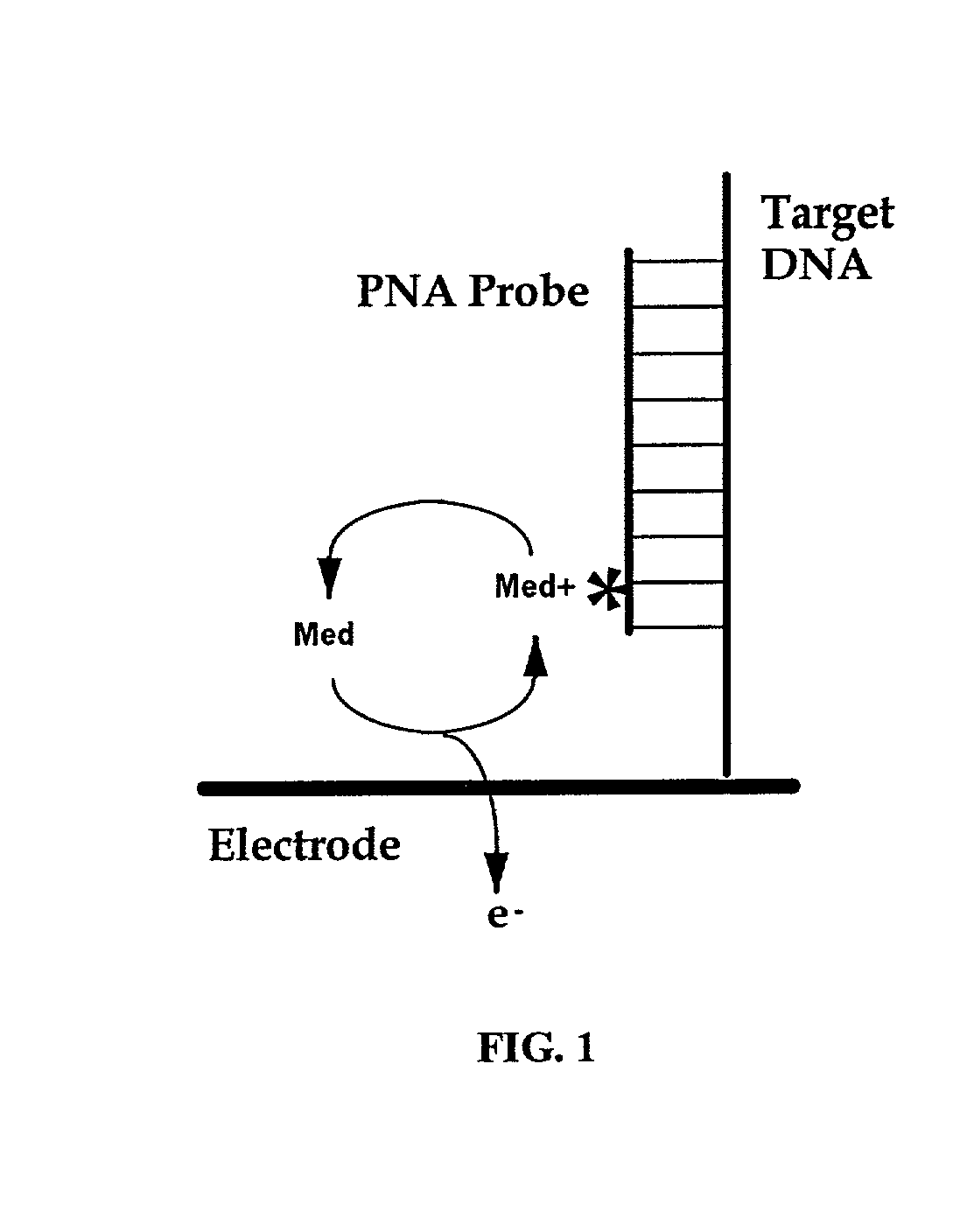
Electrochemical detection of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS6391558B1Quick checkComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionNucleic acid sequencing
An electrochemical detection system which specifically detects selected nucleic acid segments is described. The system utilizes biological probes such as nucleic acid or peptide nucleic acid probes which are complementary to and specifically hybridize with selected nucleic acid segments in order to generate a measurable current when an amperometric potential is applied. The electrochemical signal can be quantified.
Owner:MAGELLAN DIAGNOSTICS
Integrated active flux microfluidic devices and methods
InactiveUS20040248167A1Increase speedImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFlow mixersAntigenHybridization probe
The invention relates to a microfabricated device for the rapid detection of DNA, proteins or other molecules associated with a particular disease. The devices and methods of the invention can be used for the simultaneous diagnosis of multiple diseases by detecting molecules (e.g. amounts of molecules), such as polynucleotides (e.g., DNA) or proteins (e.g., antibodies), by measuring the signal of a detectable reporter associated with hybridized polynucleotides or antigen / antibody complex. In the microfabricated device according to the invention, detection of the presence of molecules (i.e., polynucleotides, proteins, or antigen / antibody complexes) are correlated to a hybridization signal from an optically-detectable (e.g. fluorescent) reporter associated with the bound molecules. These hybridization signals can be detected by any suitable means, for example optical, and can be stored for example in a computer as a representation of the presence of a particular gene. Hybridization probes can be immobilized on a substrate that forms part of or is exposed to a channel or channels of the device that form a closed loop, for circulation of sample to actively contact complementary probes. Universal chips according to the invention can be fabricated not only with DNA but also with other molecules such as RNA, proteins, peptide nucleic acid (PNA) and polyamide molecules.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
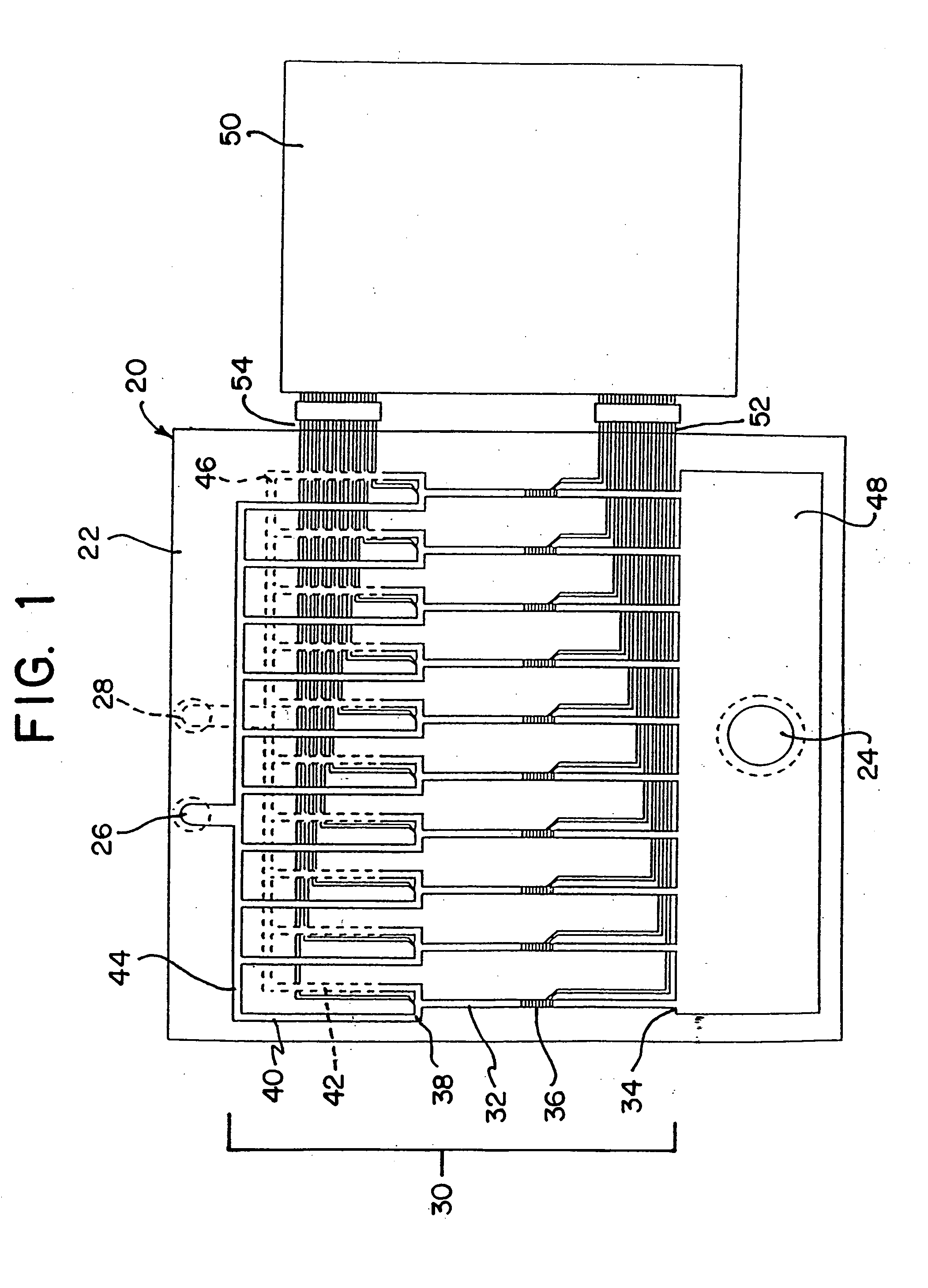
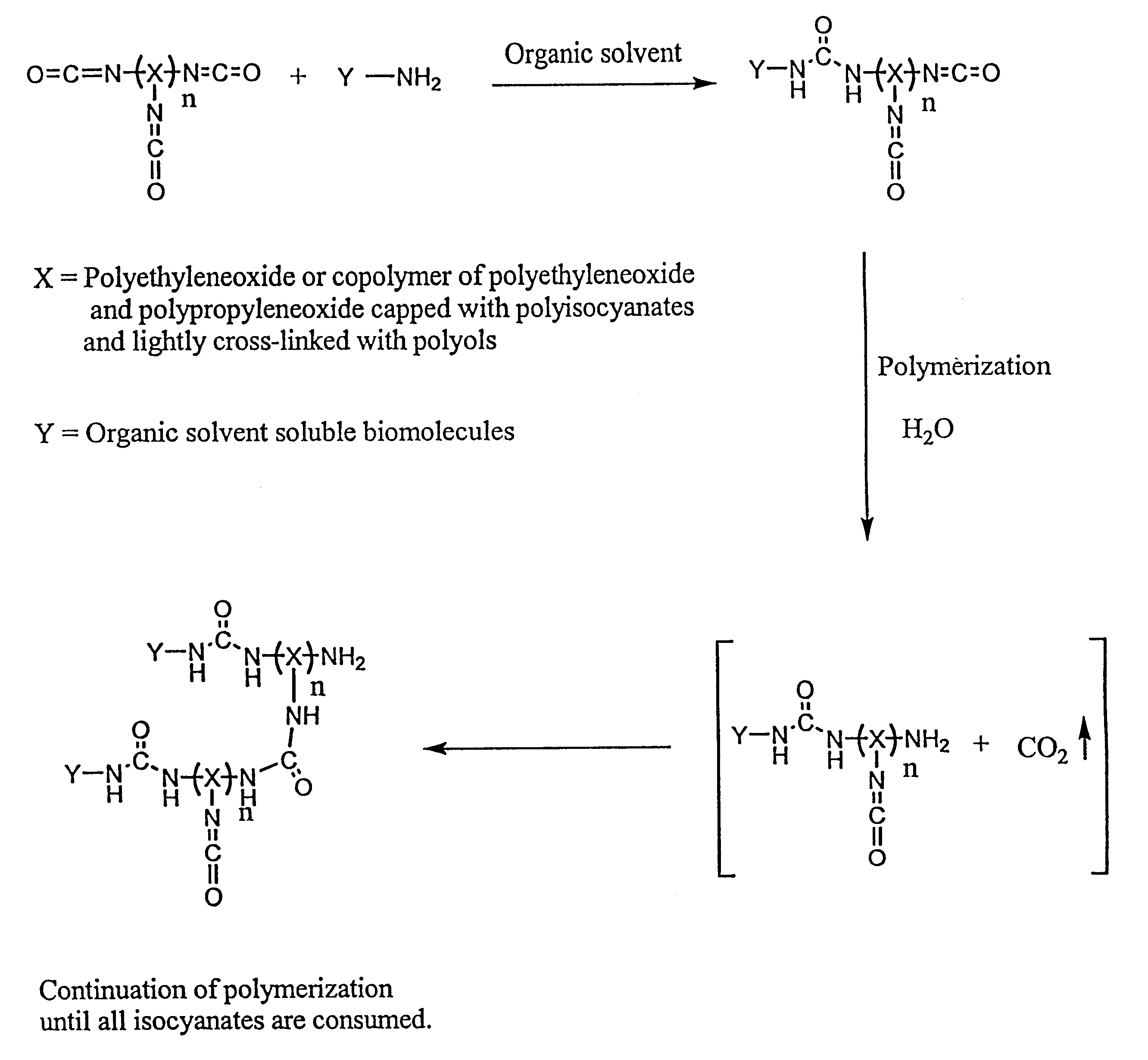
Method of making biochips and the biochips resulting therefrom
InactiveUS6174683B1Rapid and simple and cost-effective methodHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSodium bicarbonateSolid substrate
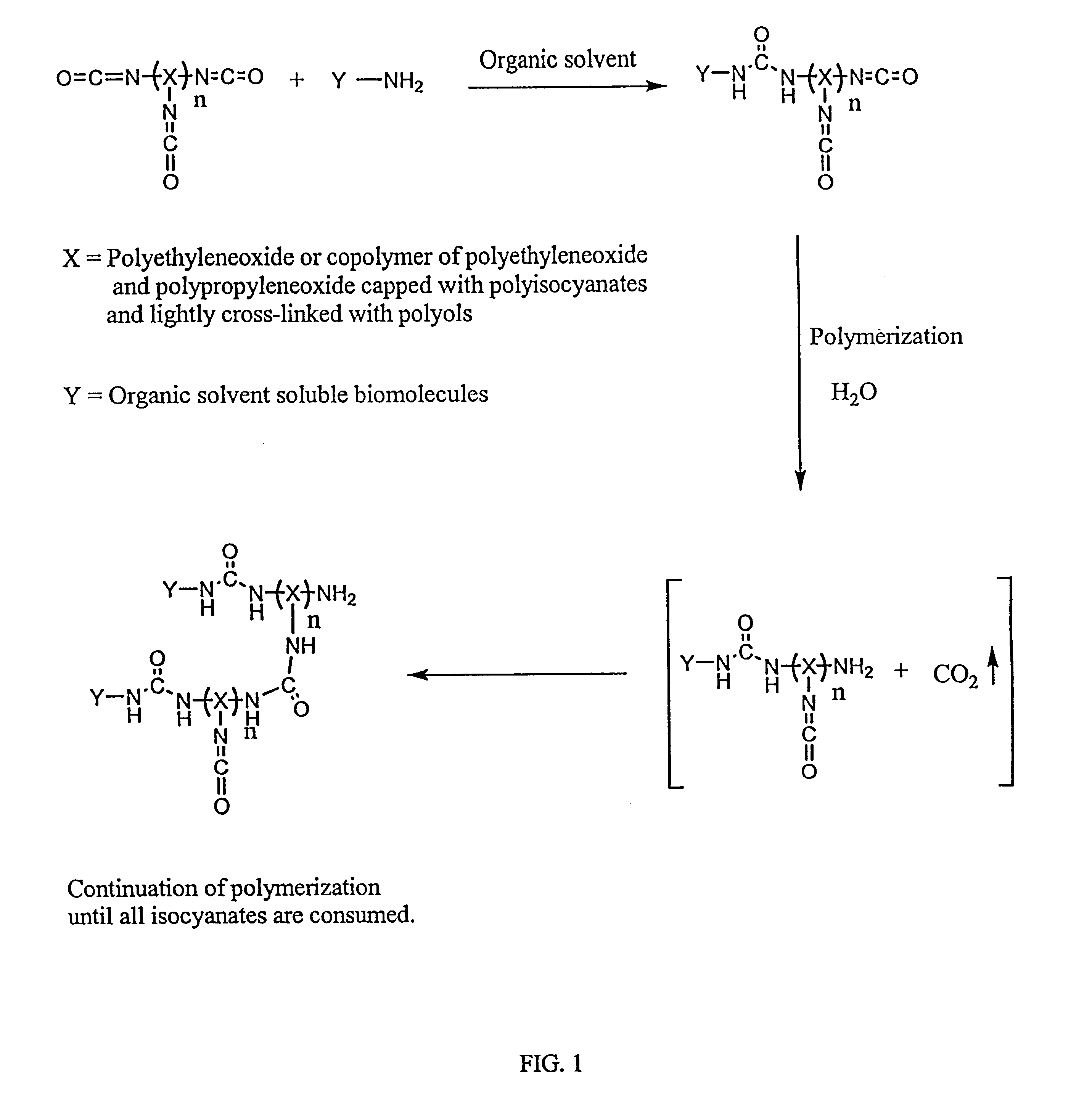
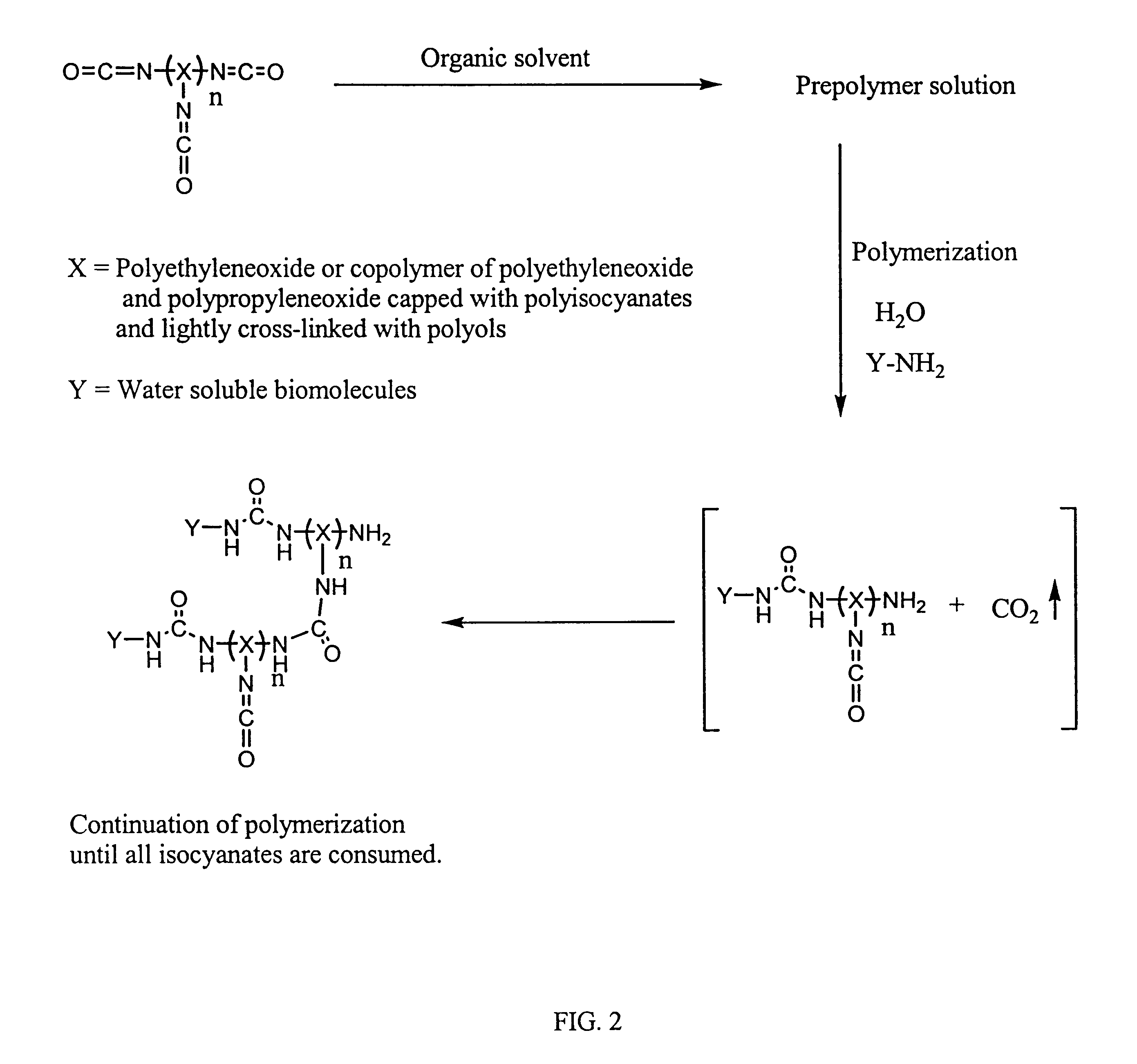
Methods for preparing a biochip are provided herein wherein the biomolecular probe to be used with the biochip is alternatively bound to a hydrogel prepolymer prior to or simultaneously with polymerization of the prepolymer. In particularly preferred embodiments, a polyurethane-based hydrogel prepolymer is derivatized with an organic solvent soluble biomolecule, such as a peptide nucleic acid probe in aprotic, organic solvent. Following derivatization of the prepolymer, an aqueous solution, for example sodium bicarbonate, preferably buffered to a pH of about 7.2 to about 9.5, is added to the derivatized prepolymer solution to initiate polymerization of the hydrogel. Alternatively, a water soluble biomolecule, such as DNA or other oligonucleotide, is prepared in an aqueous solution and added to the polyurethane-based hydrogel prepolymer such that derivatization and polymerization occur, essentially, simultaneously. While the hydrogel is polymerizing, it is microspotted onto a solid substrate, preferably a silanated glass substrate, to which the hydrogel microdroplet becomes covalently bound. Most preferably the hydrogel microdroplets are at least about 30 mum thick, for example about 50 mum to about 100 mum thick. The resulting biochips are particularly useful for gene discovery, gene characterization, functional gene analysis and related studies.
Owner:BIOCEPT INC
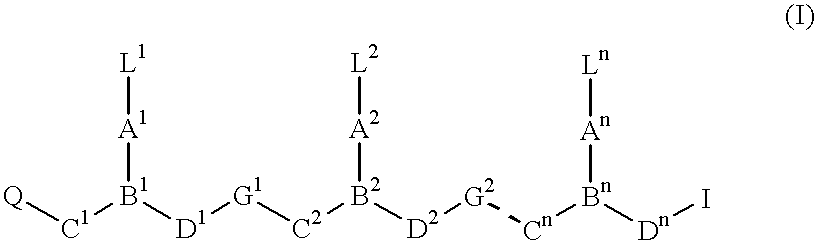
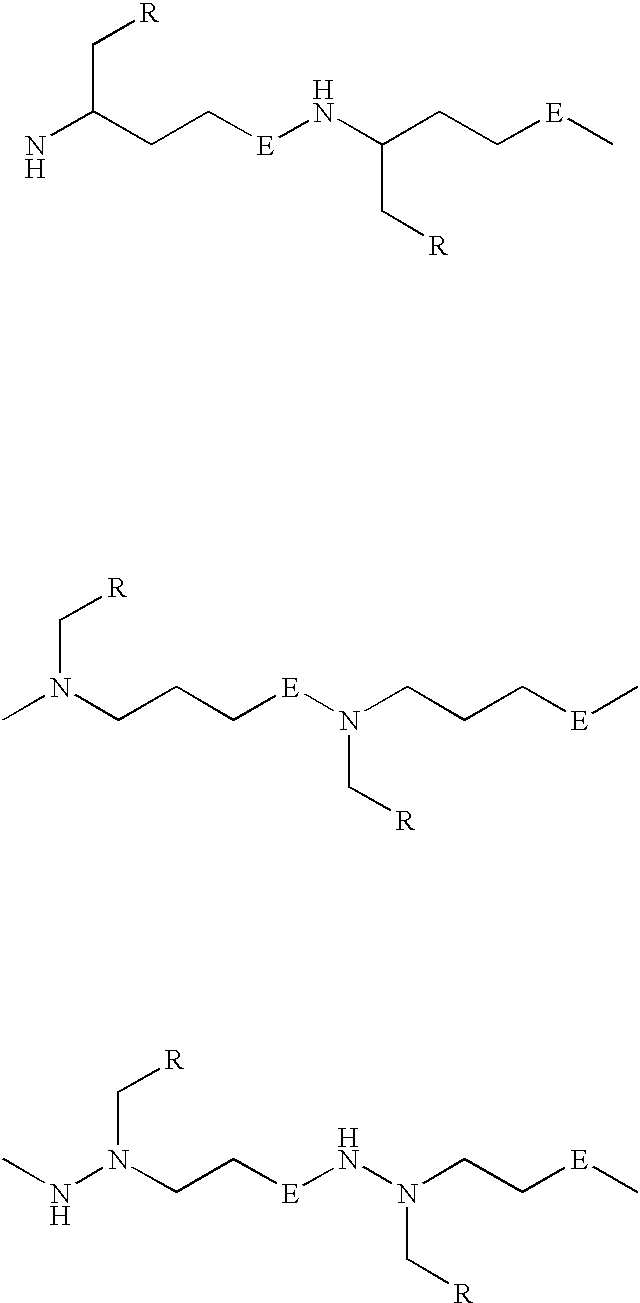
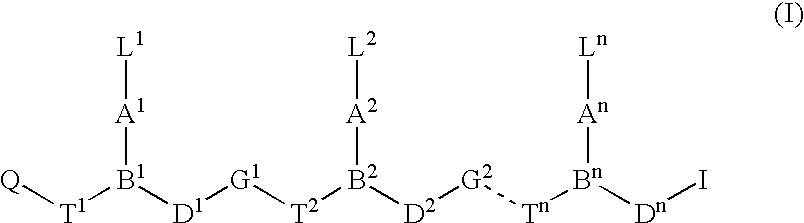
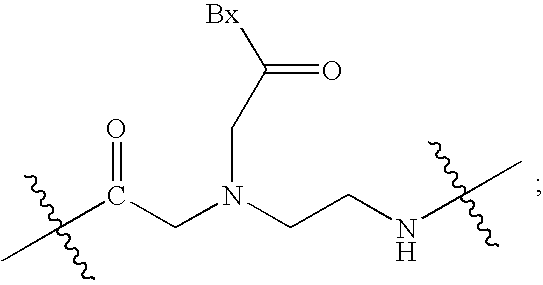
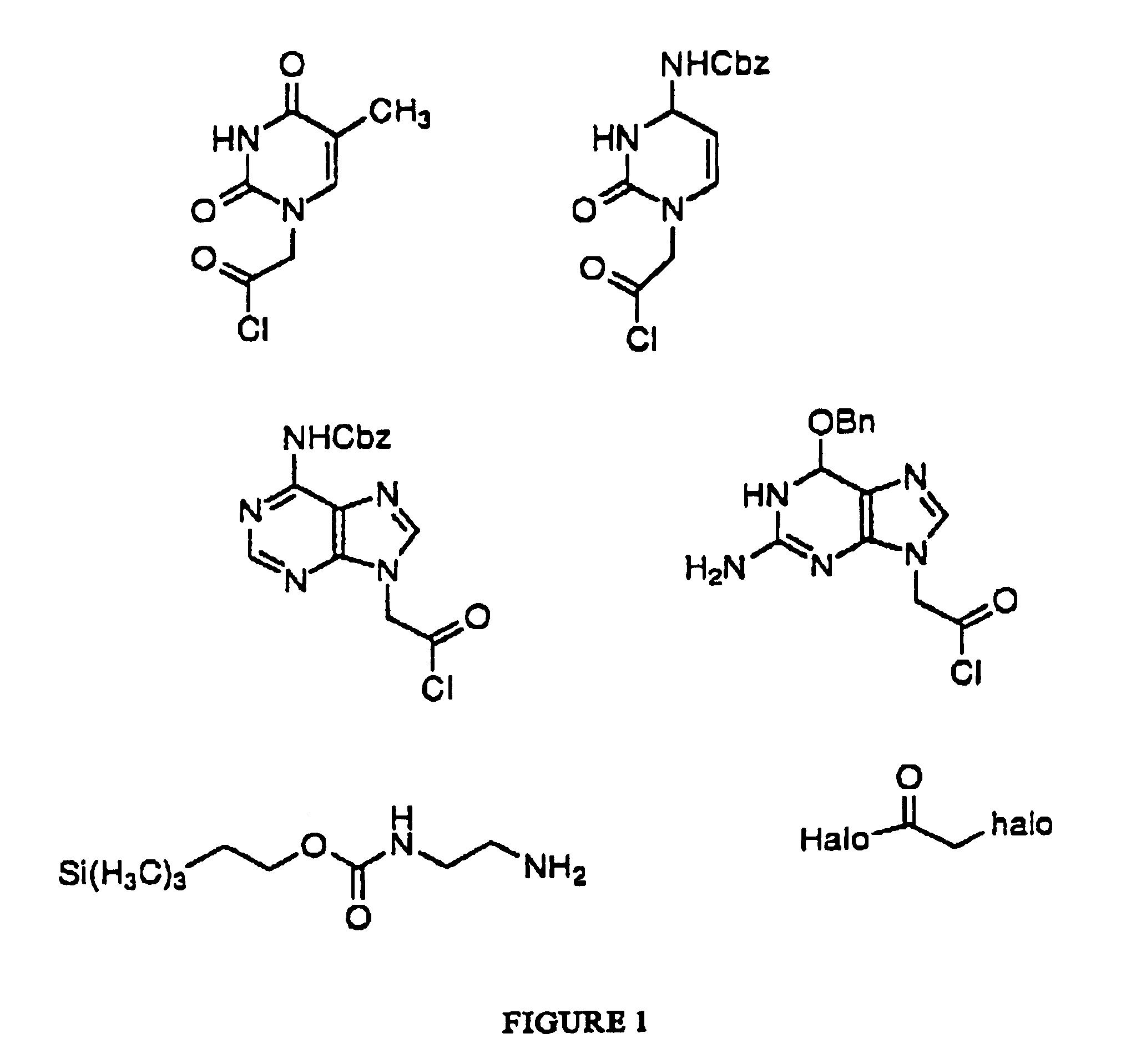
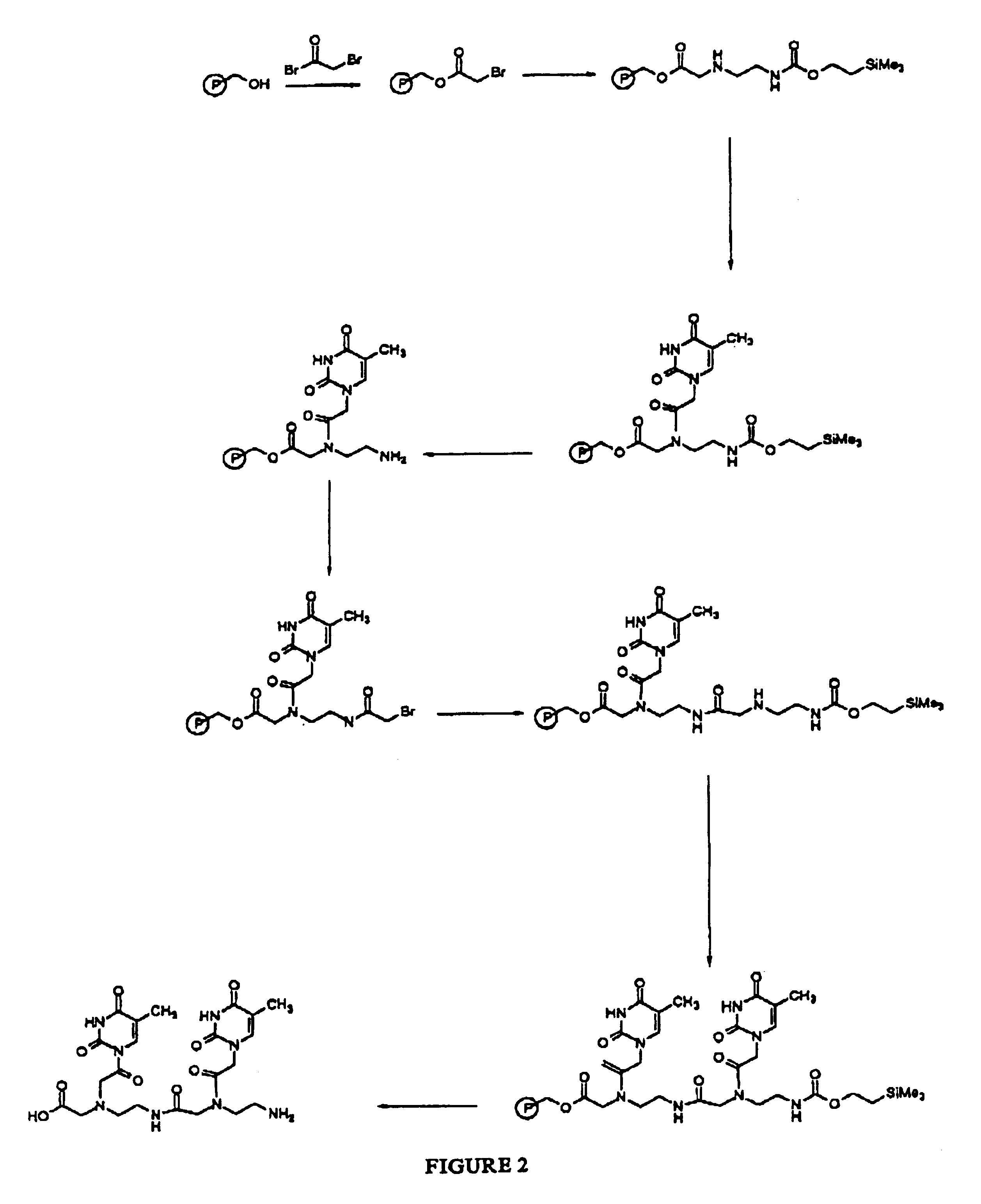
PNA monomer and precursor
InactiveUS7022851B2Improve efficiencyImprove convenienceSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBase JOligomer
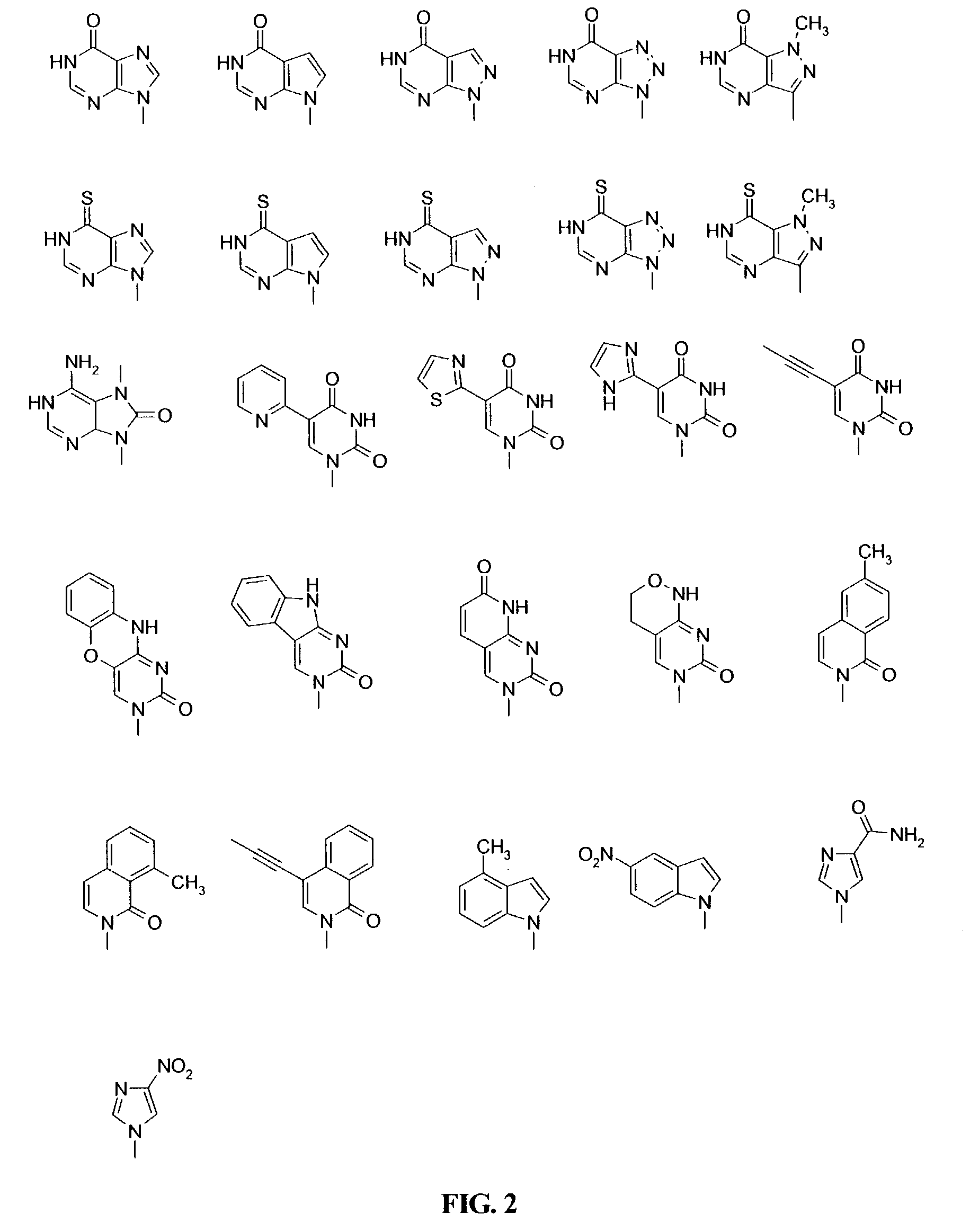
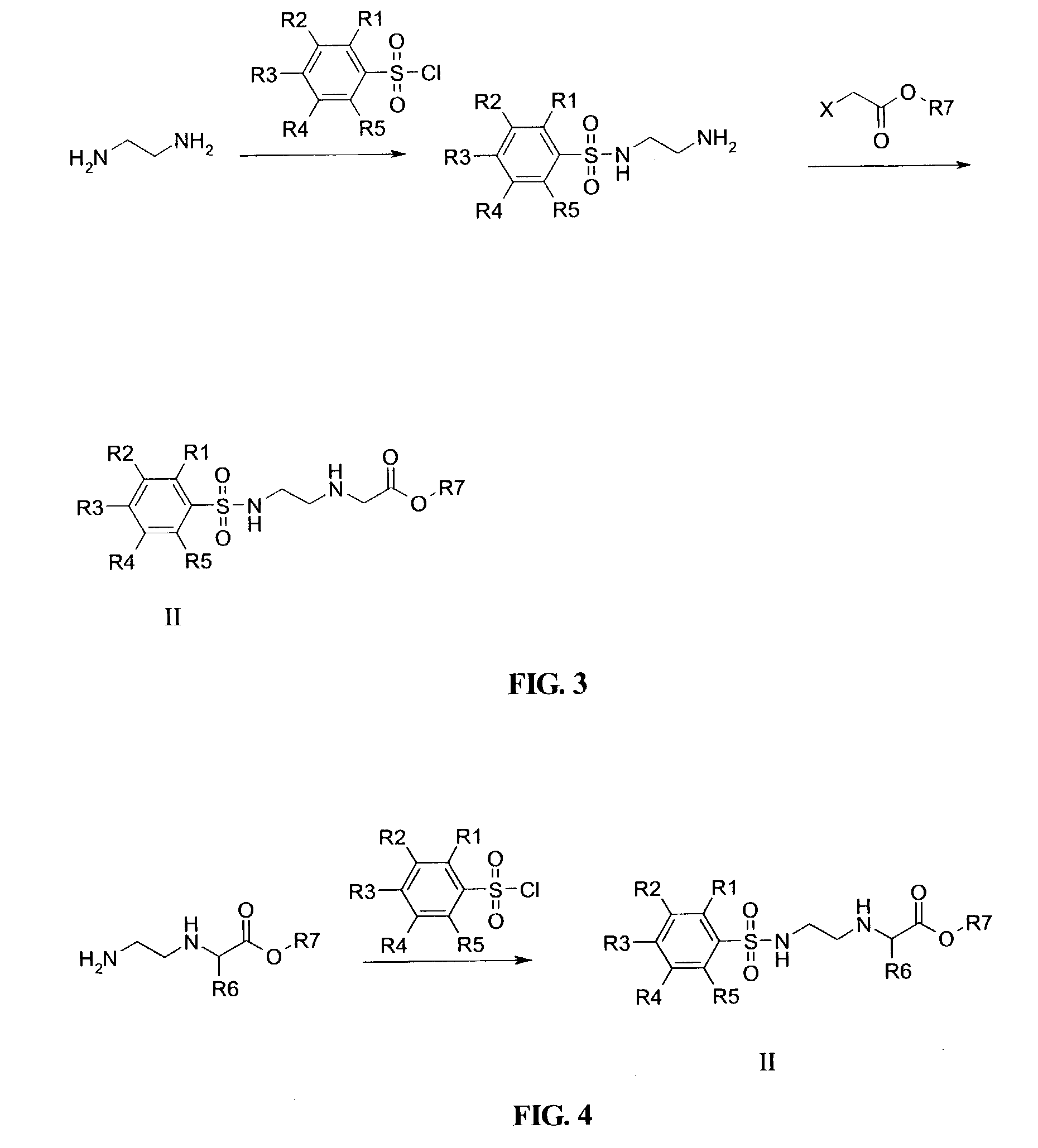
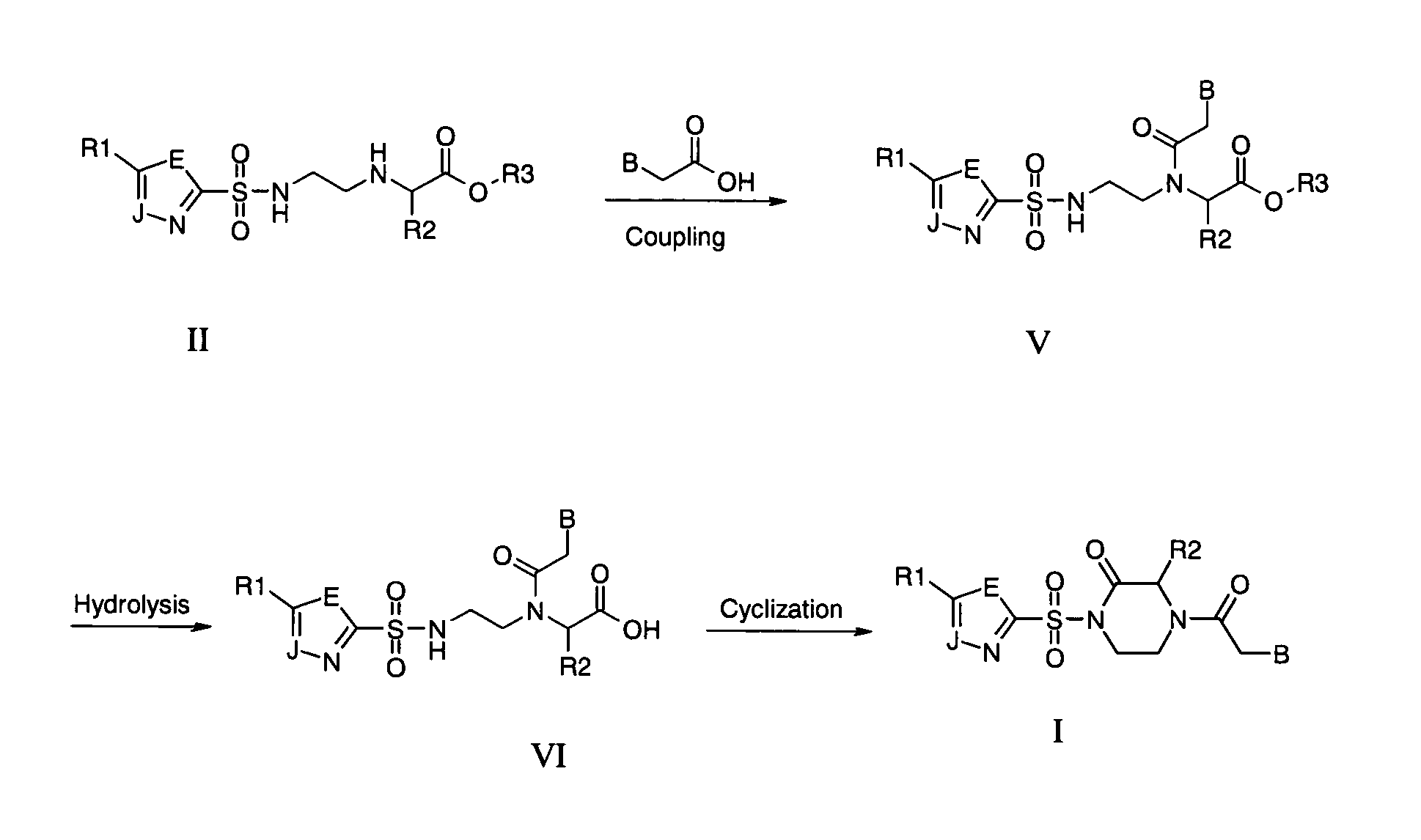
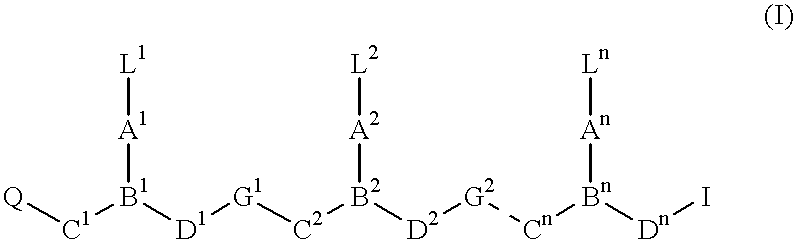
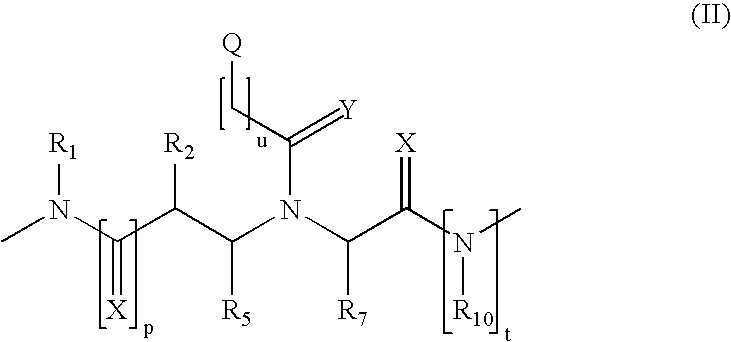
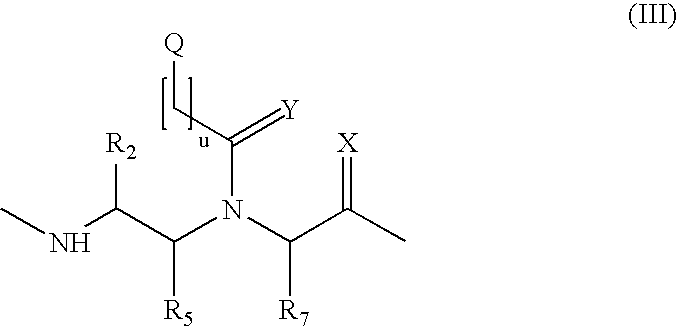
This application relates to monomers of the general formula (I) for the preparation of PNA (peptide nucleic acid) oligomers and provides method for the synthesis of both predefined sequence PNA oligomers and random sequence PNA oligomers: whereinR1, R2, R3, R4, R5 is independently H, halogen, C1–C4 alkyl, nitro, nitrile, C1–C4 alkoxy, halogenated C1–C4 alkyl, or halogenated C1–C4 alkoxy, wherein at least one of R1, R3, and R5 is nitro;R6 is H or protected or unprotected side chain of natural or unnatural α-amino acid; andB is a natural or unnatural nucleobase, wherein when said nucleobase has an exocyclic amino function, said function is protected by protecting group which is labile to acids but stable to weak to medium bases.
Owner:PANAGENE INC
PNA monomer and precursor
ActiveUS7211668B2Improve efficiencyImprove convenienceOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSide chainNucleobase
Owner:PANAGENE INC
Cell penetrating peptide conjugates for delivering of nucleic acids into a cell
InactiveUS20130137644A1Good curative effectLarge indexNervous disorderAntipyreticHydrophilic polymersPolyethylene glycol
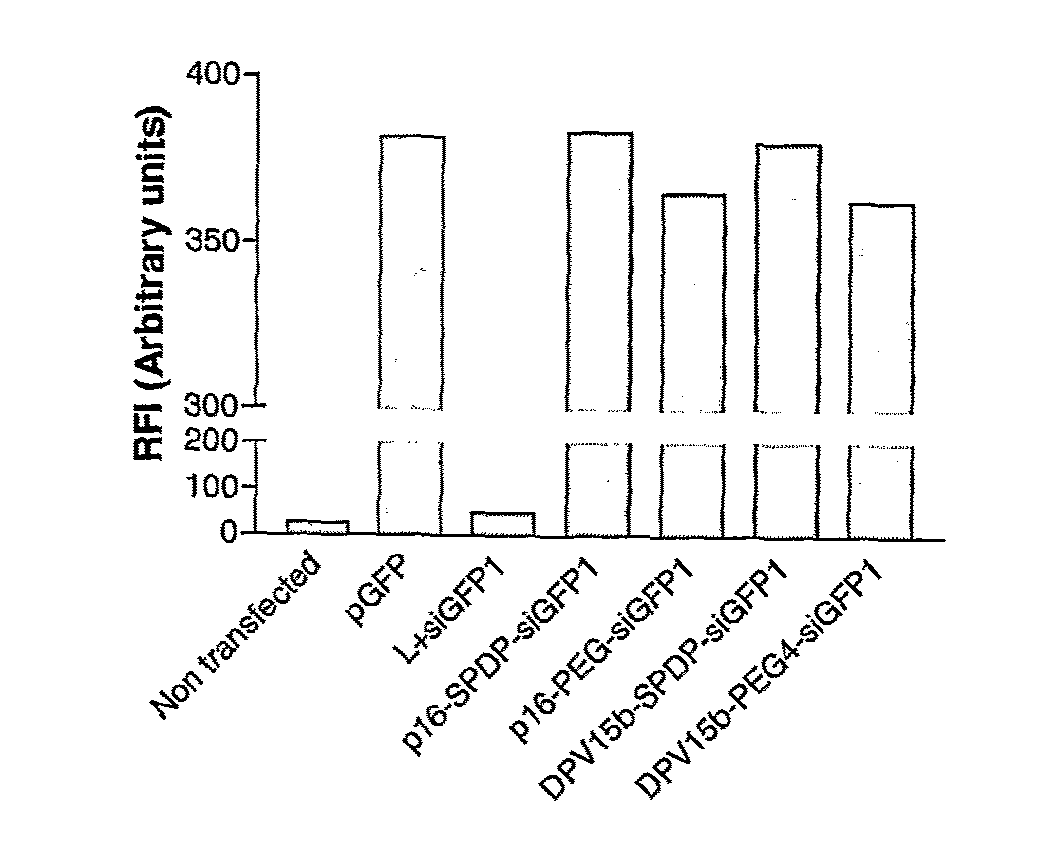
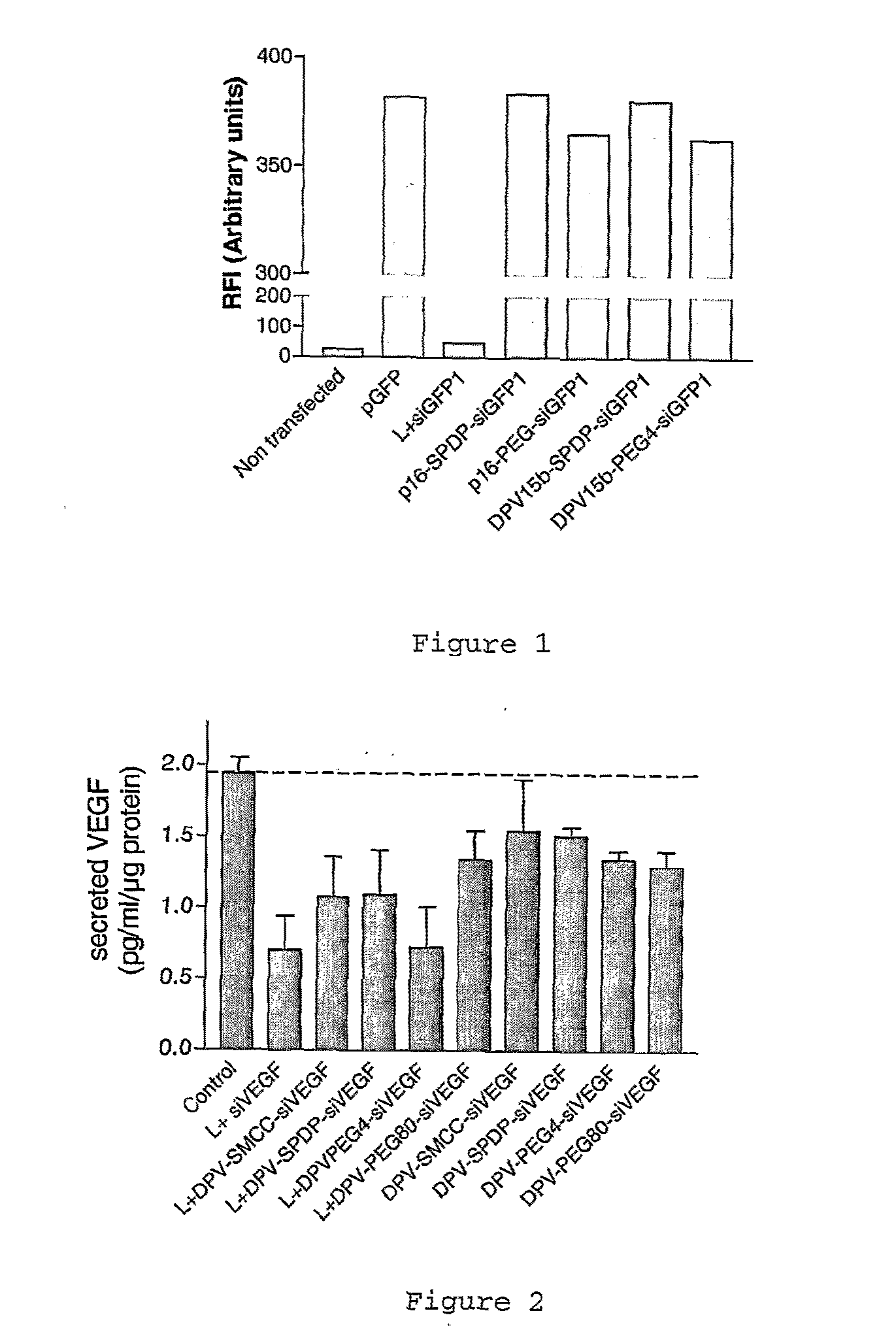
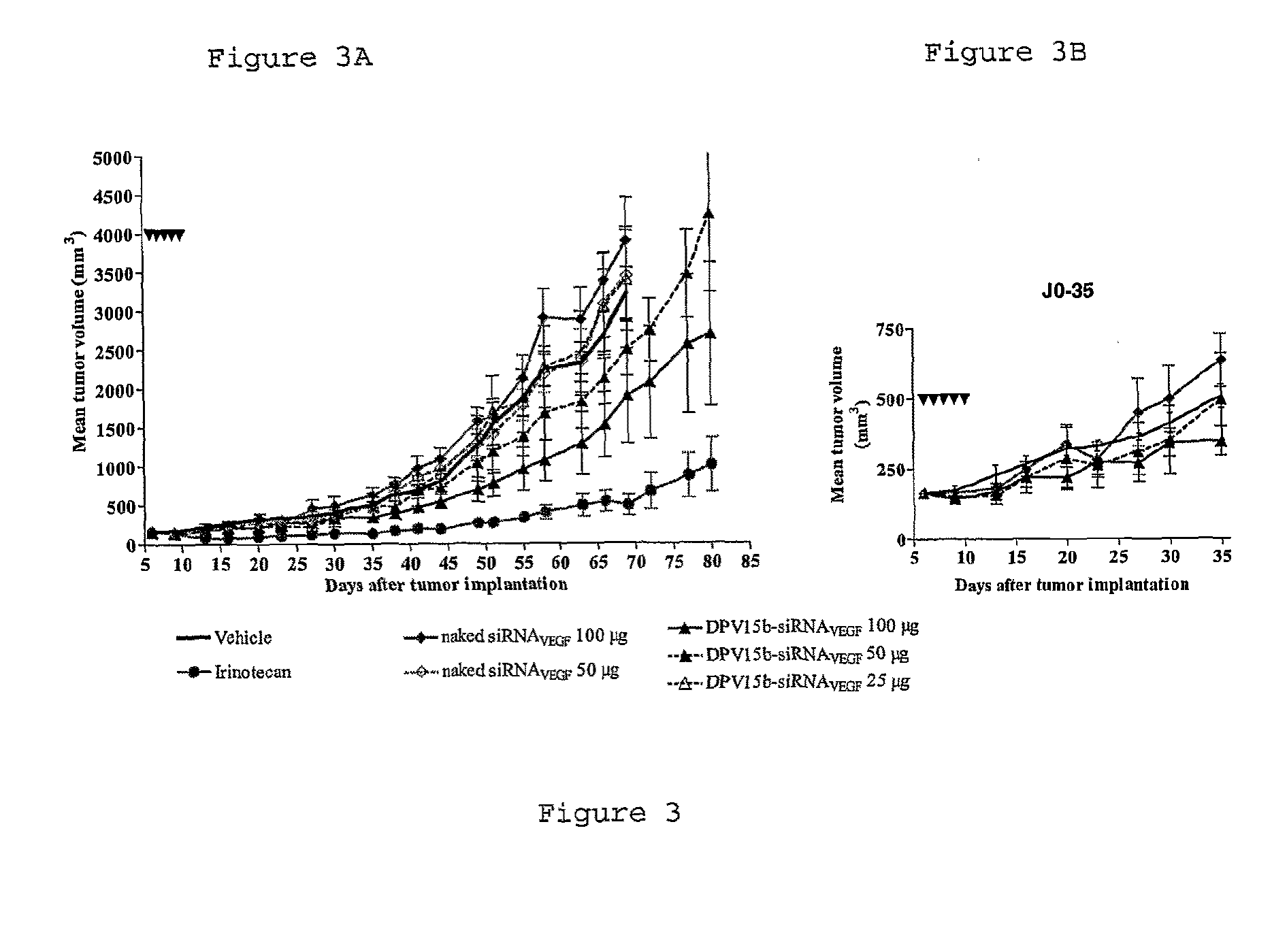
The invention provides cell penetrating peptide-nucleic acid conjugates having the formula P-L-N, wherein P is a cell penetrating peptide, N is a nucleic acid, preferably an oligonucleotide and more preferably a siRNA, and L is a hydrophilic polymer, preferably a polyethylene glycol (PEG)-based linker linking P and N together. Compositions, methods of use and methods for producing such conjugates are also disclosed.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
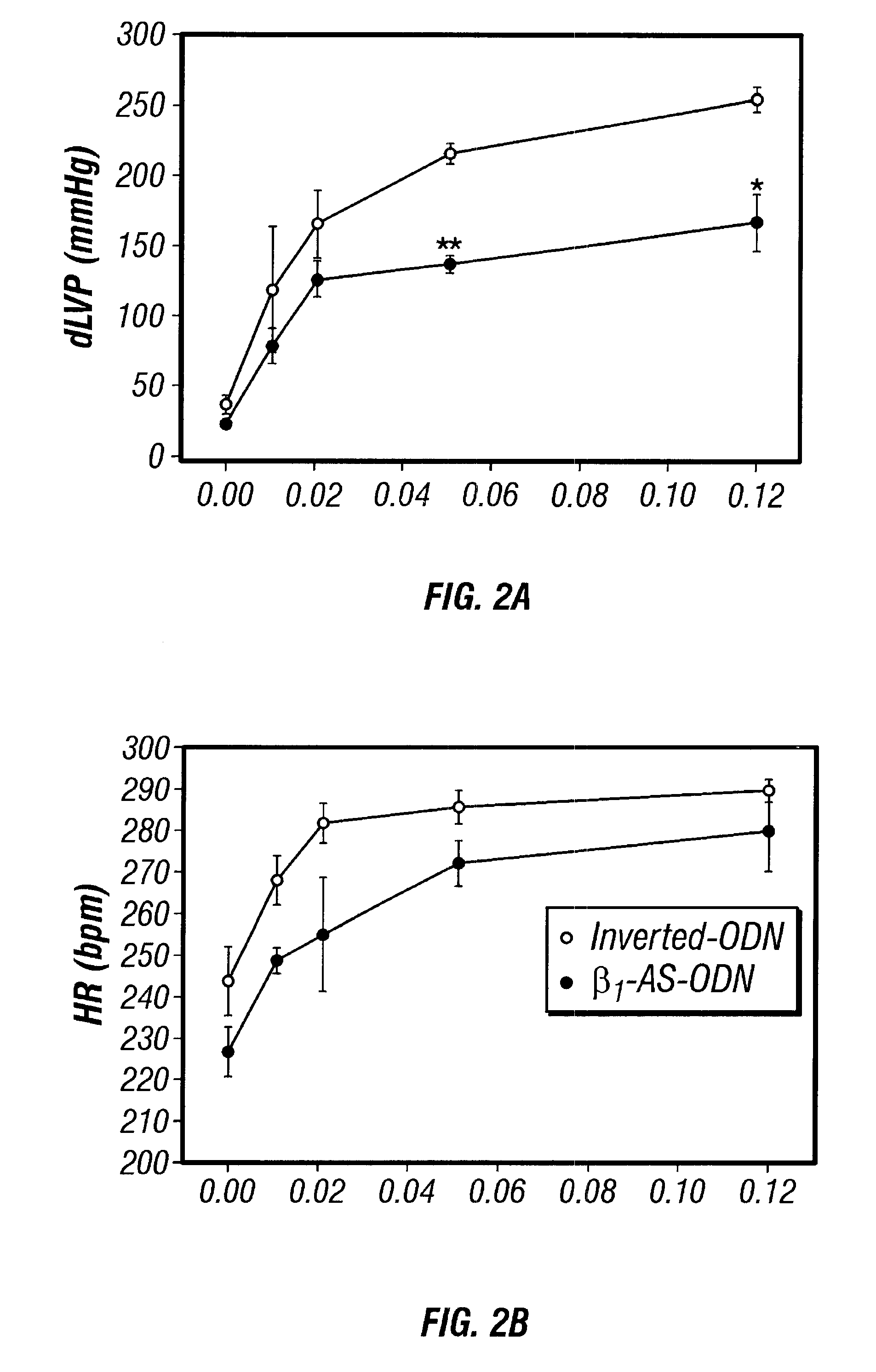
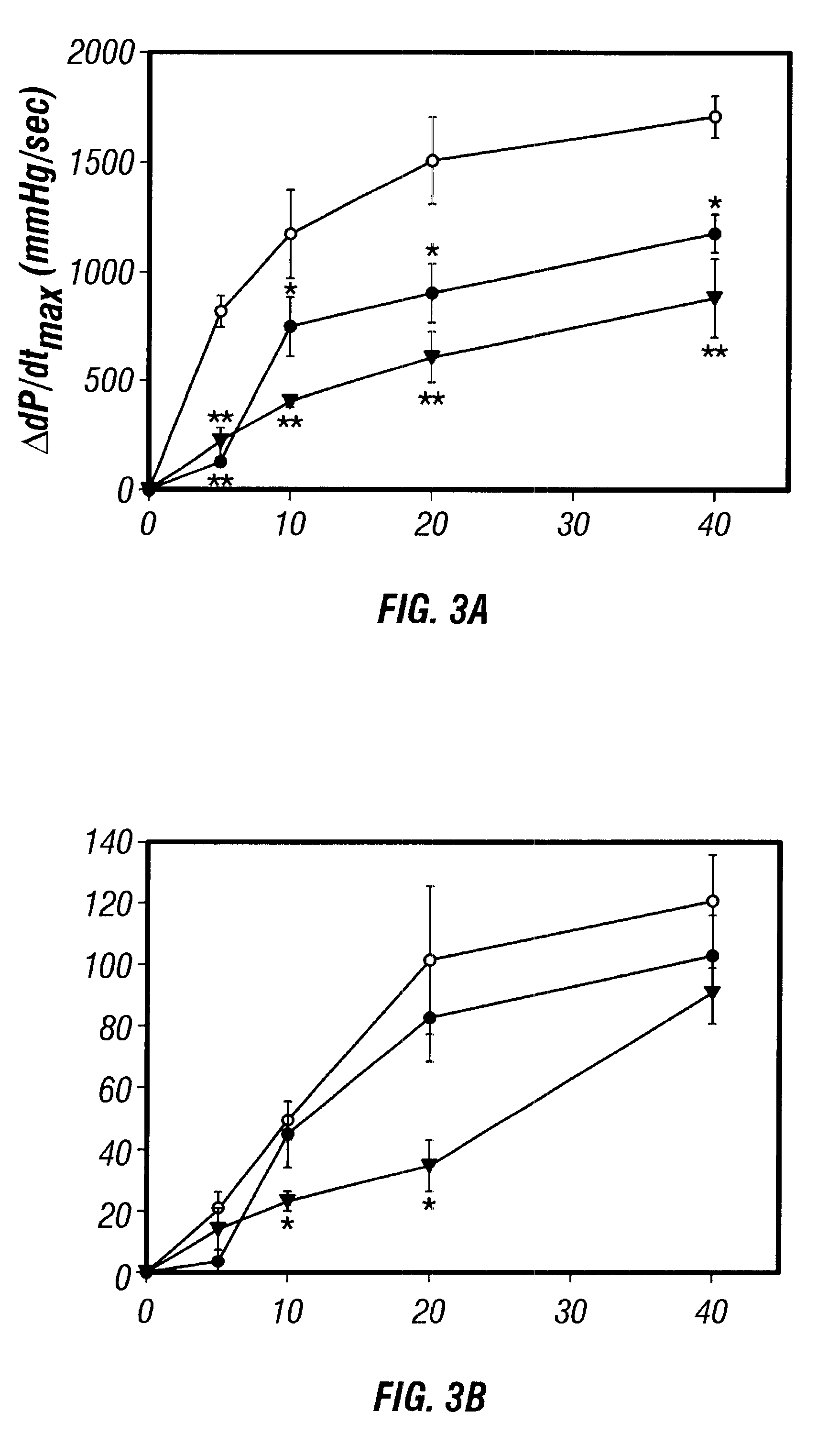
Antisense compositions targeted to beta1-adrenoceptor-specific mRNA and methods of use
InactiveUS6489307B1Reduce inhibitionInhibit and reduce expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsEccentric hypertrophyMammal
Disclosed are antisense oligonucleotide, polynucleotide, and peptide nucleic acid compounds that specifically bind to mammalian mRNA encoding a beta1-adrenoceptor polypeptide and that are useful in the control and / or treatment of cardiac dysfunction, hypertension, hypertrophy, myocardial ischemia, and other cardiovascular diseases in an affected mammal, and preferably, in a human subject. The antisense compounds disclosed herein, and pharmaceutical formulations thereof, provide sustained control of beta1-adrenoceptor expression over prolonged periods, and achieve therapeutic effects from as little as a single dose. Administration of these antisense compositions to approved animal models resulted in a decrease in blood pressure, but no significant change in heart rate. Use of such antisense compositions in the reduction of beta1-adrenoceptor polypeptides in a host cell expressing beta1-adrenoceptor-specific mRNA, and in the preparation of medicaments for treating human and animal diseases, and in particular, hypertension and other cardiac dysfunction is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
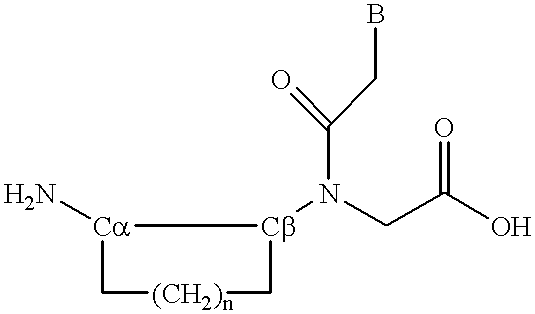
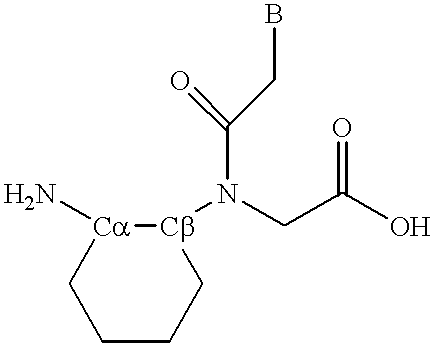
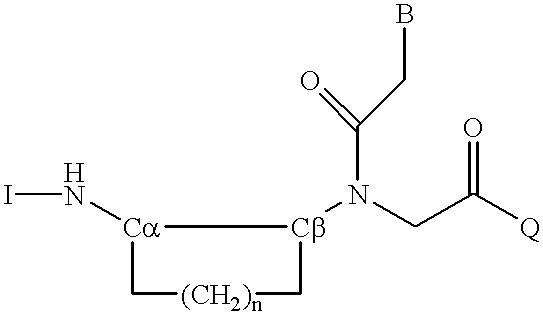
Peptide nucleic acids
InactiveUS6395474B1Remove complicationsAvoid less flexibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPeptide backboneRNA
Owner:BUCHARDT OLE +3
Nanopore sequencing using charge blockade labels
ActiveUS8652779B2Different levelDifferent modulus propertySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementNucleotidePolymerase L
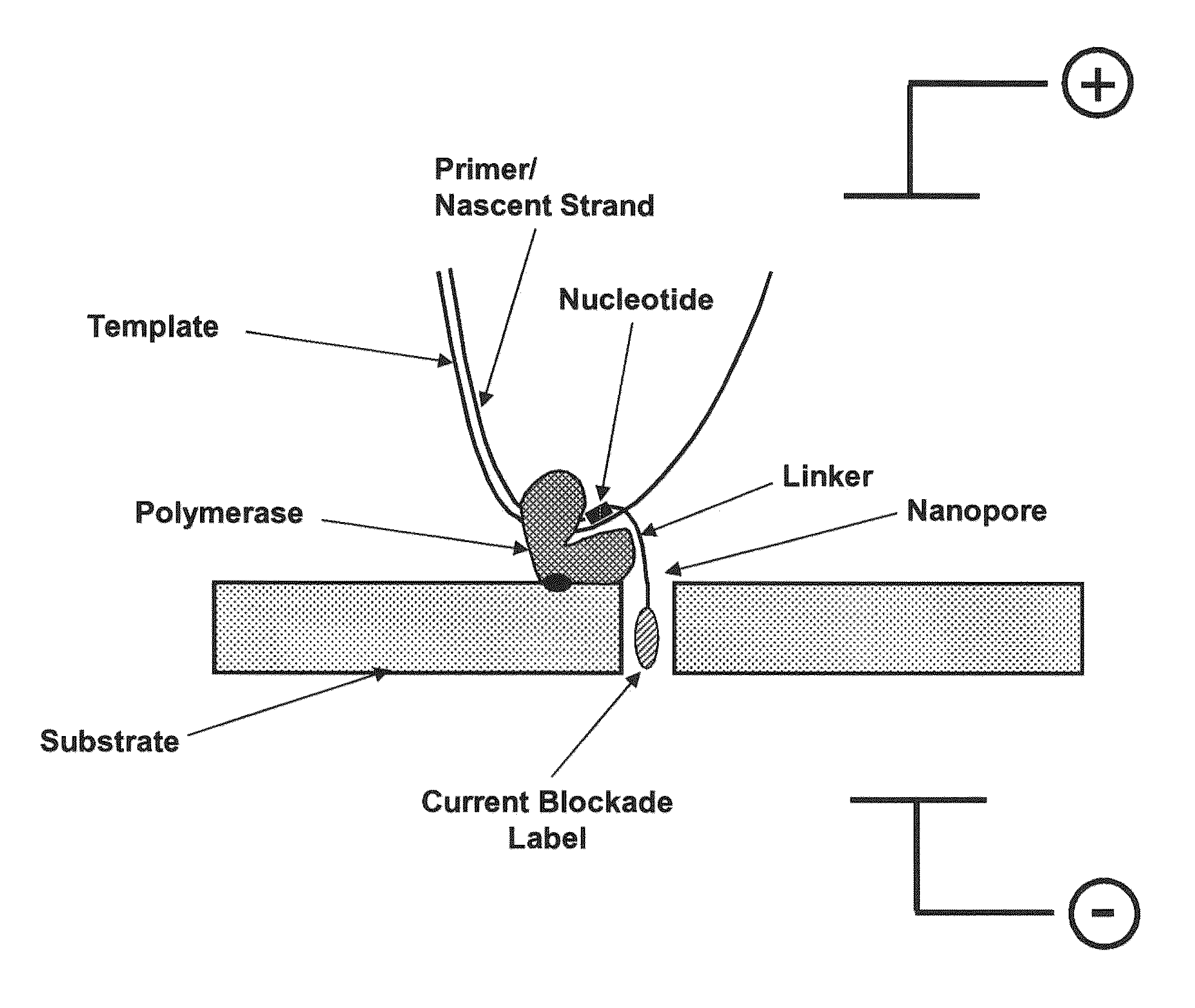
The invention relates to devices and methods for nanopore sequencing. The invention includes compositions and methods of nucleic acid sequencing using a single polymerase enzyme complex comprising a polymerase enzyme and a template nucleic acid attached proximal to a nanopore, and nucleotide analogs in solution comprising charge blockade label that are attached to the polyphosphate portion of the nucleotide analog such that the charge blockade labels are cleaved when the nucleotide analog is incorporated into a growing nucleic acid and the charge blockade label is detected by the nanopore to determine the presence and identity of the incorporated nucleotide and thereby determine the sequence of a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Cell Penetrating Peptide Conjugates for Delivering of Nucleic Acids into a Cell
InactiveUS20090186802A1Improve propertiesGood curative effectNervous disorderAntipyreticPolyethylene glycolOligonucleotide
The invention provides cell penetrating peptide-nucleic acid conjugates having the formula P-L-N, wherein P is a cell penetrating peptide, N is a nucleic acid, preferably an oligonucleotide and more preferably a siRNA, and L is a hydrophilic polymer, preferably a polyethylene glycol (PEG)-based linker linking P and N together. Compositions, methods of use and methods for producing such conjugates are also disclosed.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Measurement of concentrations and binding energetics
ActiveUS20040038426A1Eliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBio moleculesBiological organism
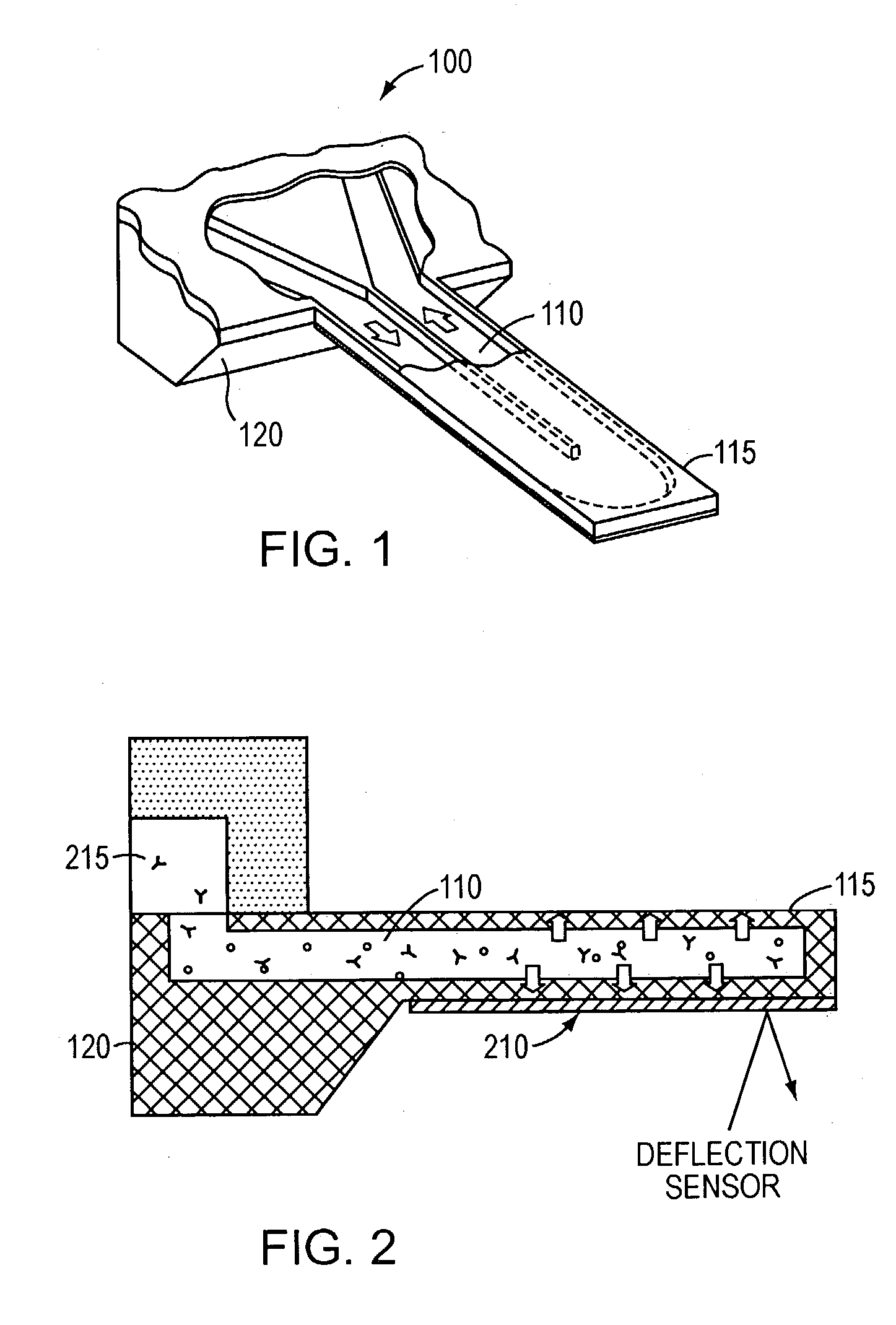
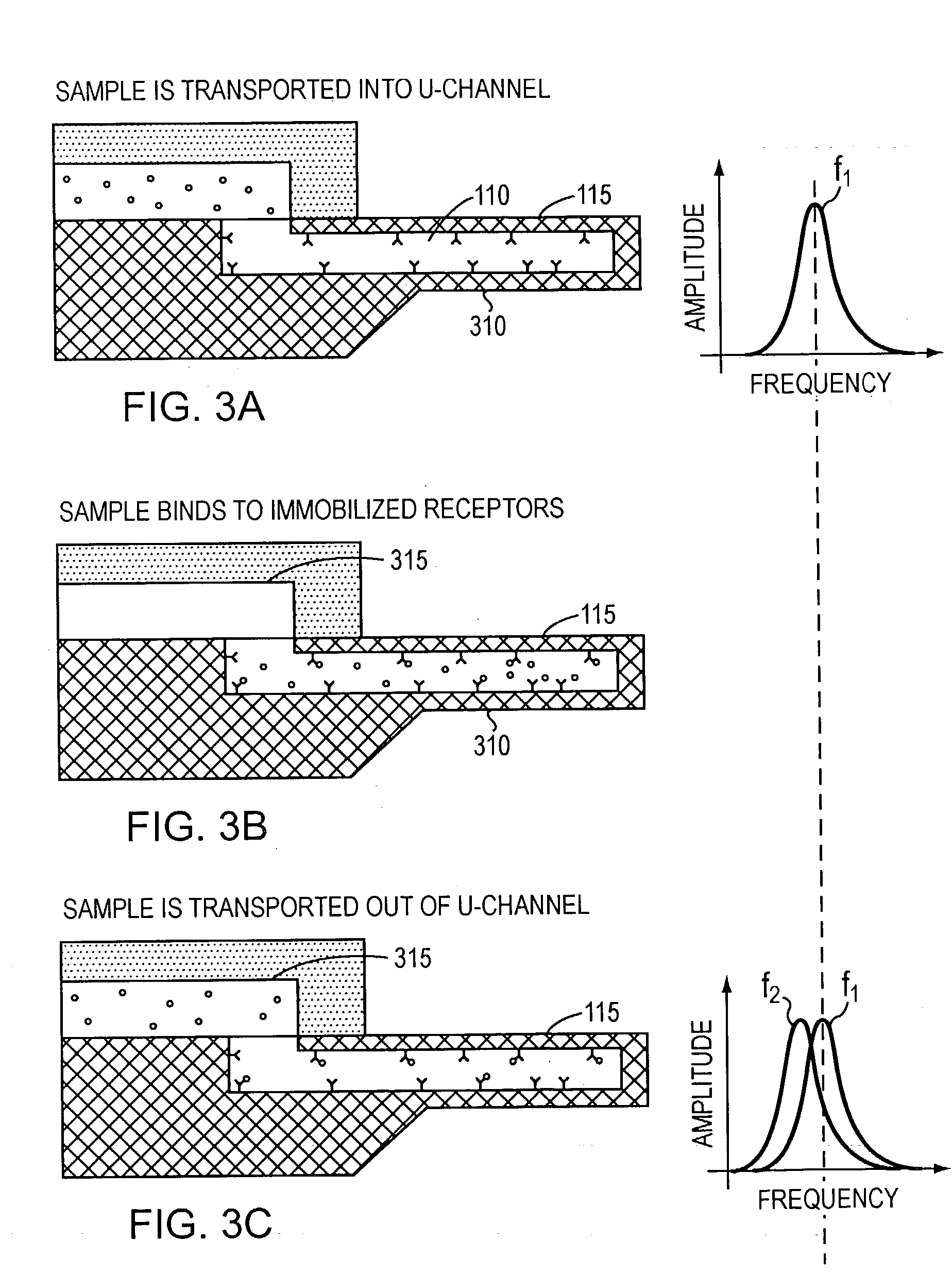
Free-standing microfluidic channels are used to both transport and analyze molecules of interest. In a biochemical context, such molecules may be polypeptides, nucleic acids, or other biomolecules. The free-standing channels provide a real-time readout of concentration without the need for labeling with reporter molecules. The channels can also measure enthalpy values and equilibrium constants by detecting heat released from or absorbed by the sample.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Double-stranded peptide nucleic acids
InactiveUS6228982B1Inhibit bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDouble strandOrganic chemistry
Owner:NIELSEN PETER E
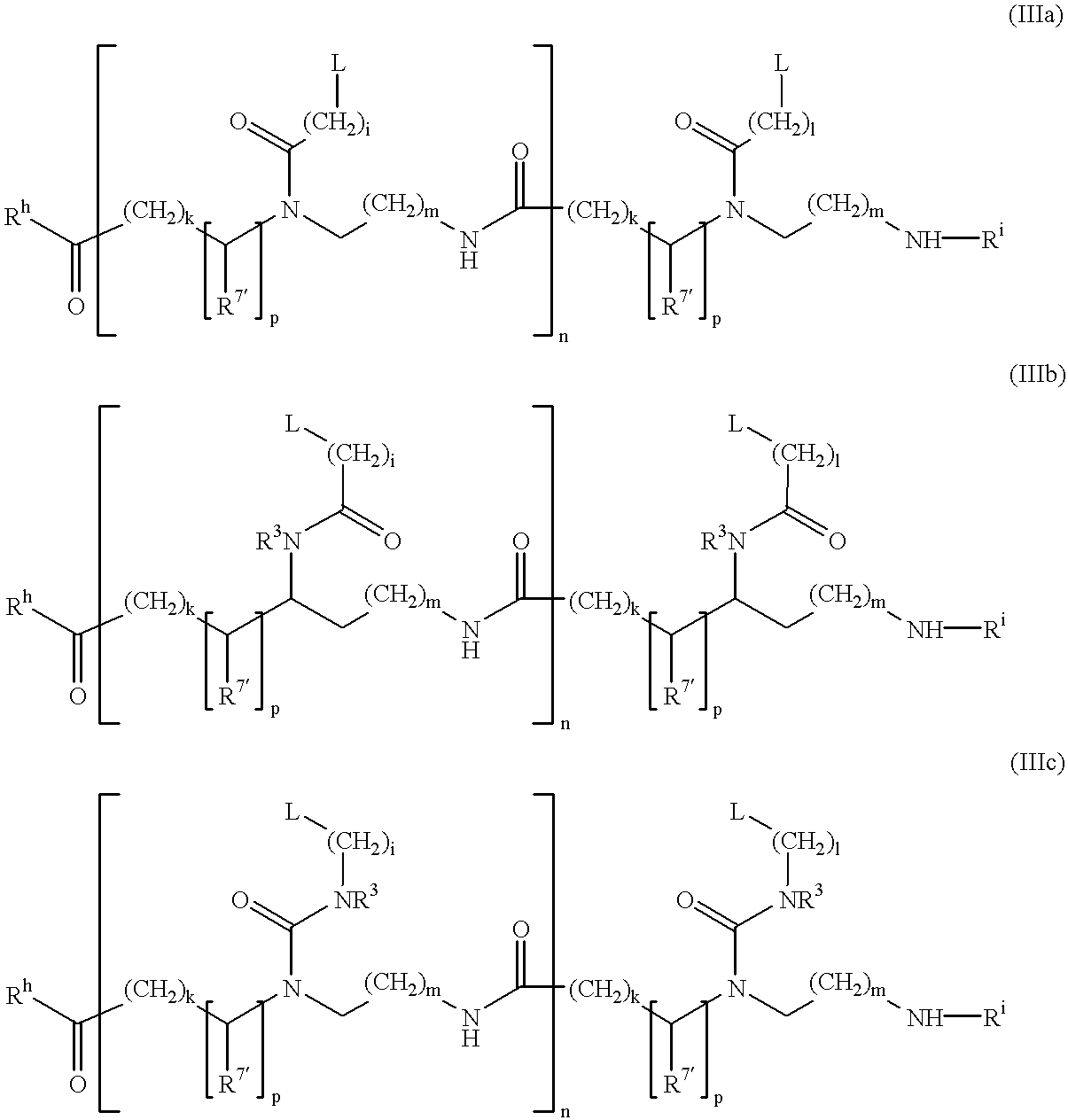
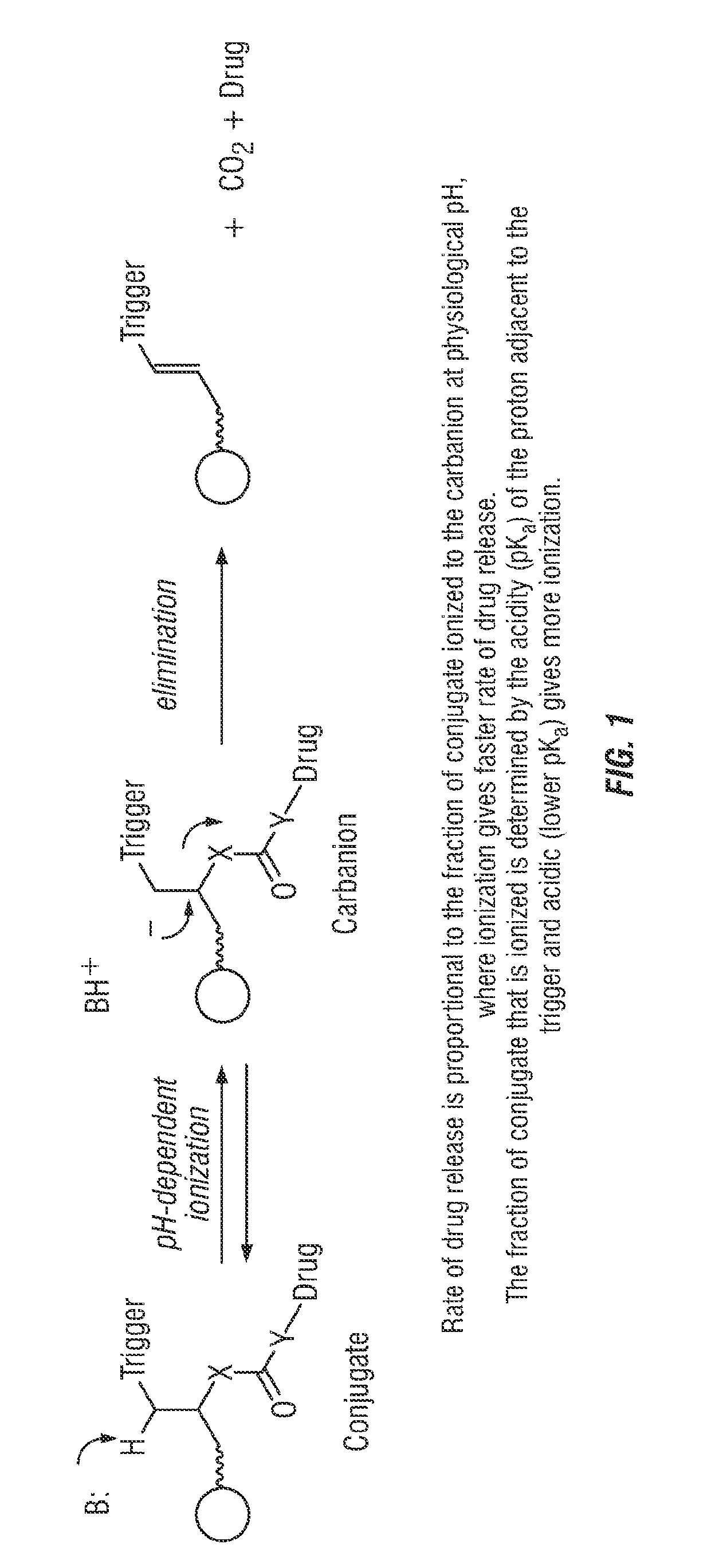
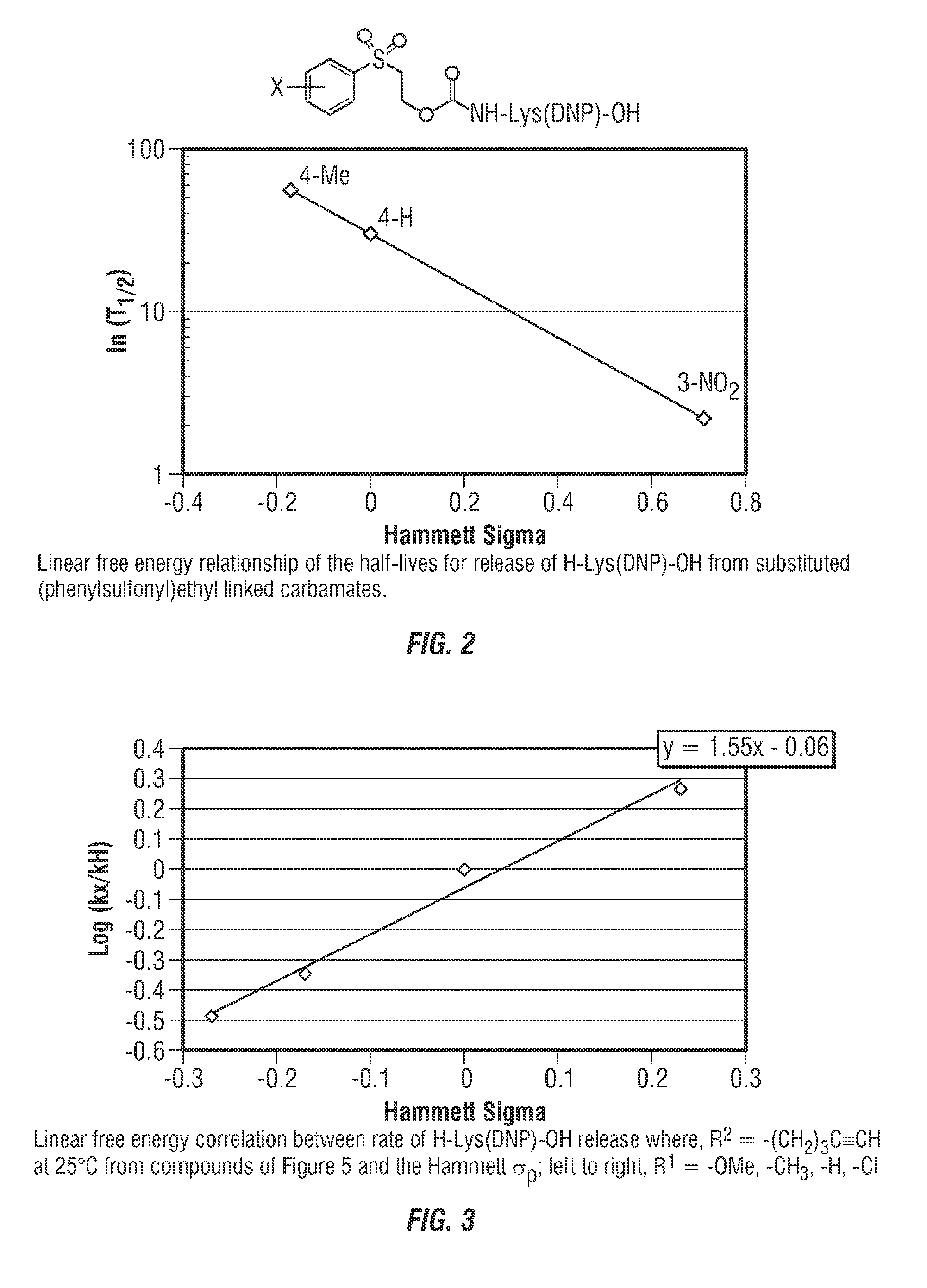
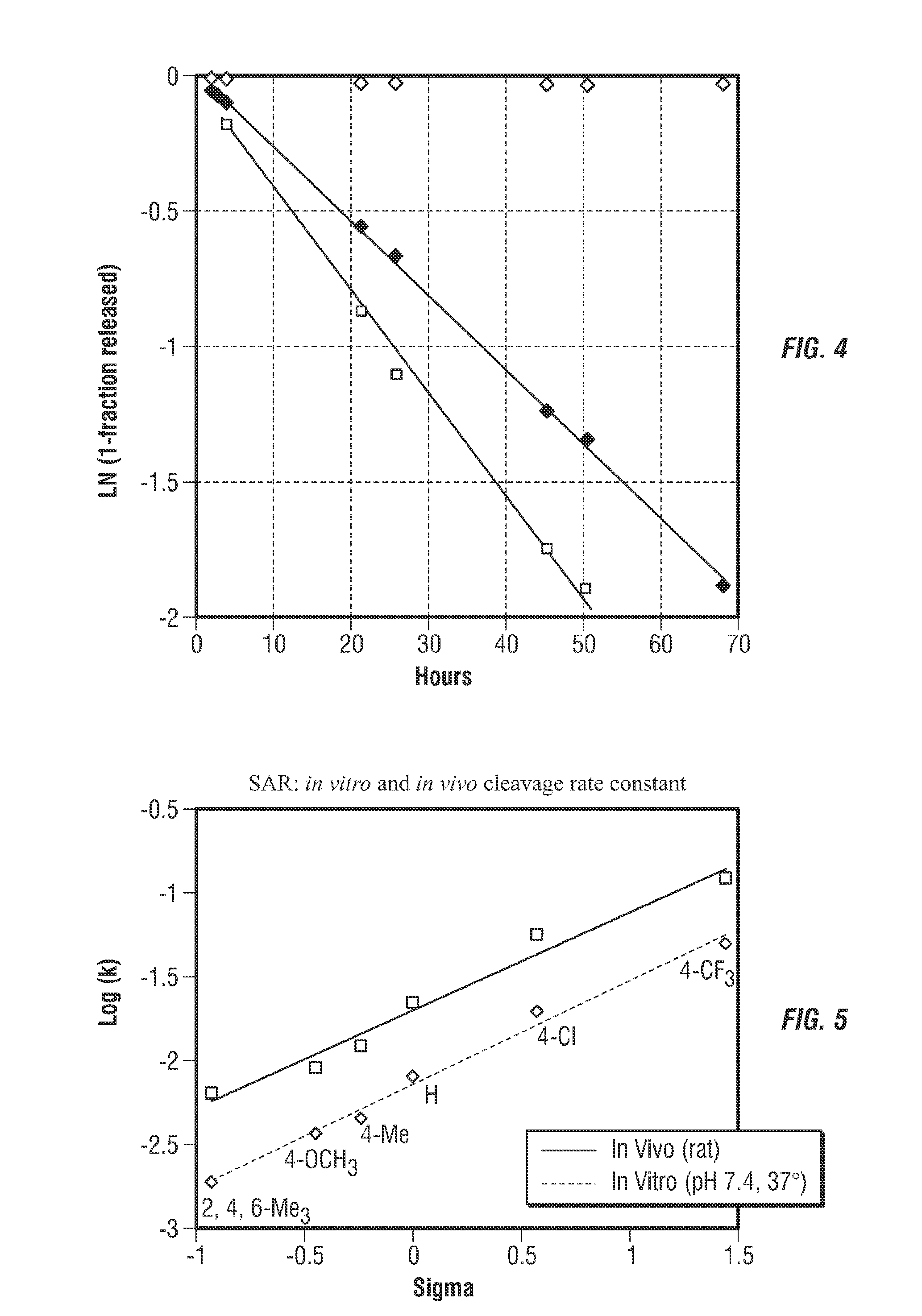
Controlled release from solid supports
The invention relates to solid supports useful in medical applications that provide controlled release of drugs, such as peptides, nucleic acids and small molecules. The drugs are covalently coupled to the solid support through a linkage that releases the drug or a prodrug through controlled beta elimination.
Owner:PROLYNX LLC
Peptide nucleic acid incorporating a chiral backbone
A novel class of peptide nucleic acid monomers are synthesized having chirality in the backbone. Peptide nucleic acid oligomers are synthesized to incorporate these chiral monomers.
Owner:PETER E NIELSEN
Electrochemical detection of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20040072158A1Conveniently accomplishedEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingOrganic chemistry
An electrochemical detection system which specifically detects selected nucleic acid segments is described. The system utilizes biological probes such as nucleic acid or peptide nucleic acid probes which are complementary to and specifically hybridize with selected nucleic acid segments in order to generate a measurable current when an amperometric potential is applied. The electrochemical signal can be quantified.
Owner:MAGELLAN DIAGNOSTICS
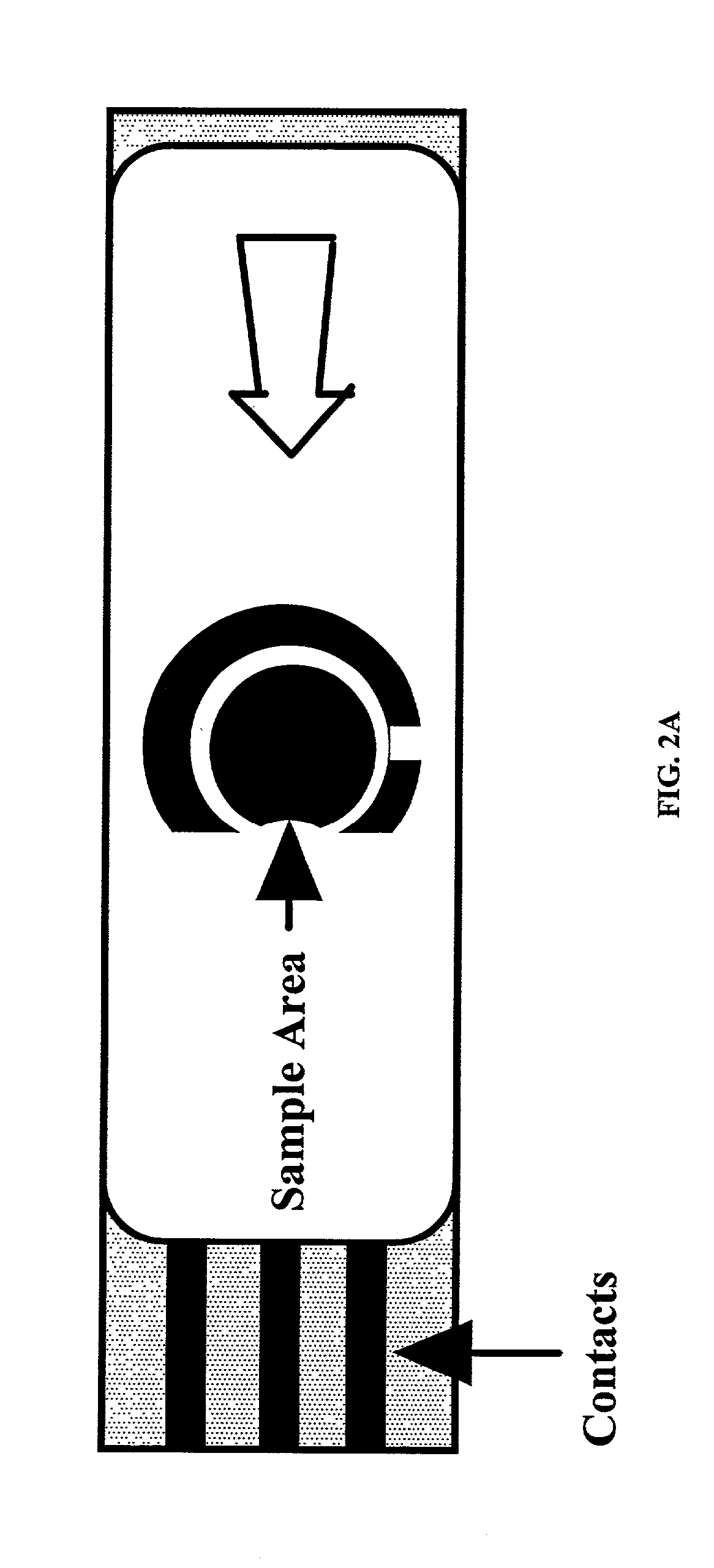
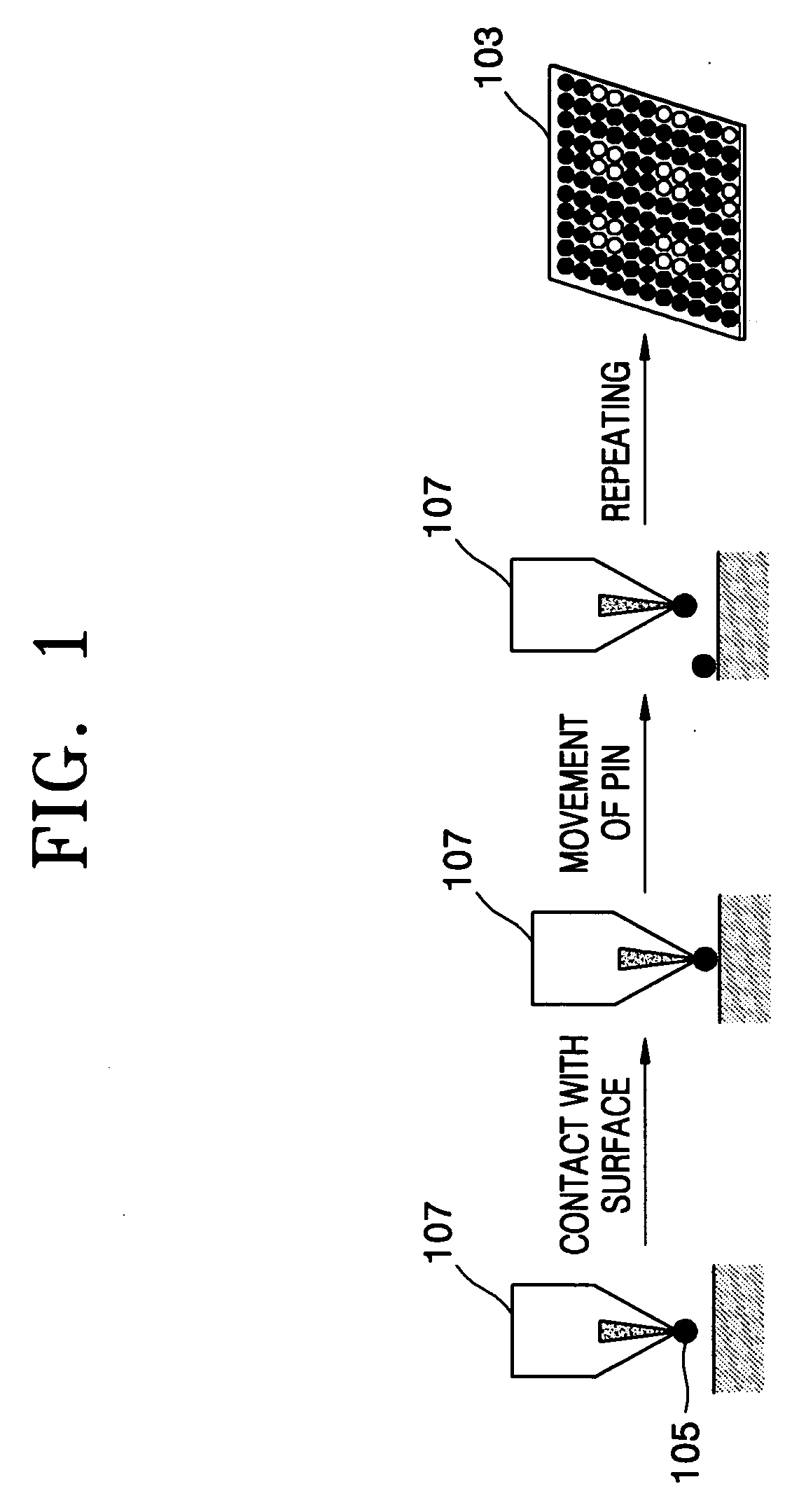
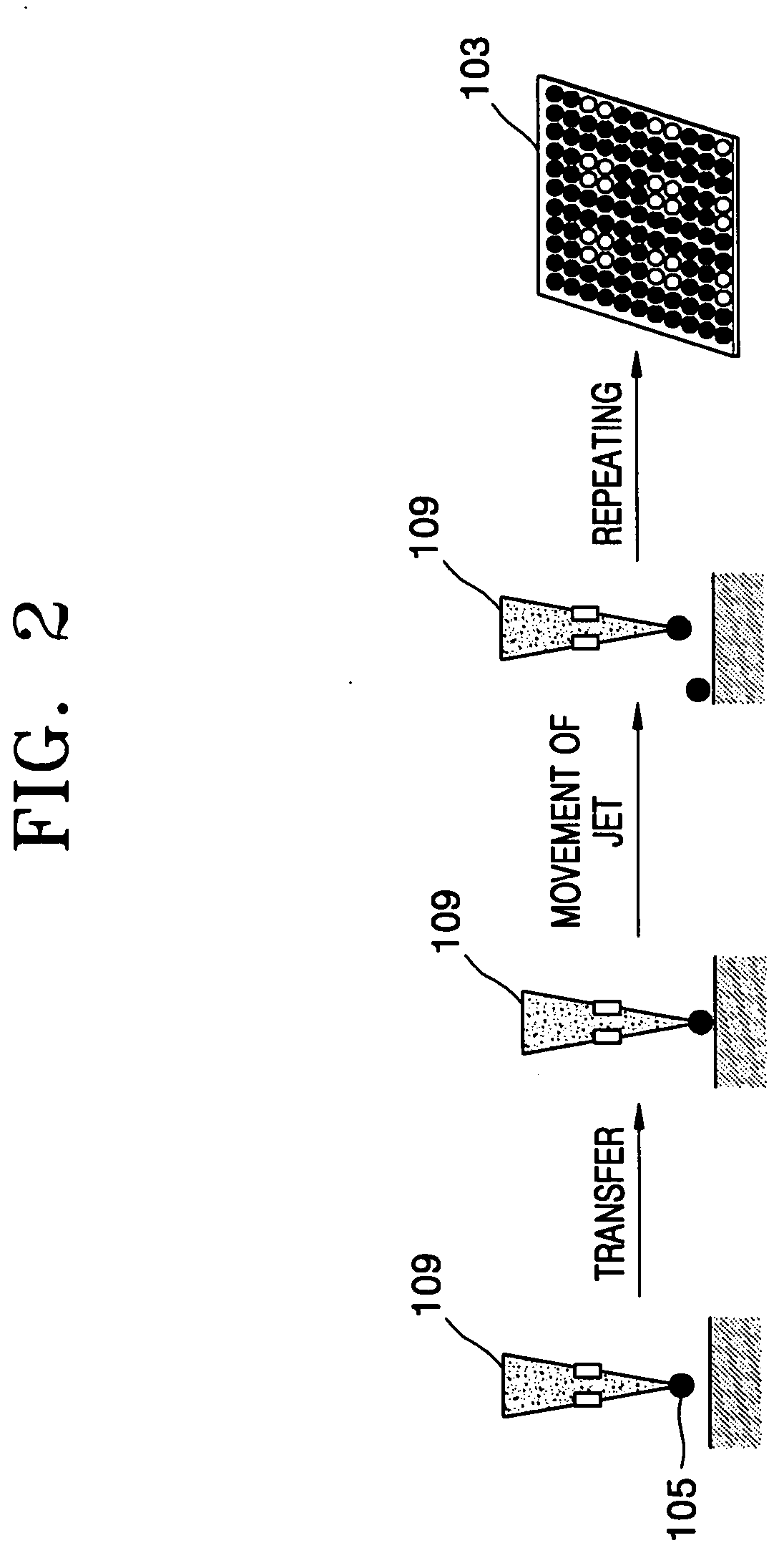
Spotting device for manufacturing DNA microarray and spotting method using the same
InactiveUS20050158755A1Shorten production timeUniform shapeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyCross-linkDNA microarray
A spotting device for manufacturing a DNA microarray and a spotting method using the same are provided. The spotting device for dropping and immobilizing a solution of biomolecules, for example nucleic acids such as probe DNA, mRNA, and peptide nucleic acid (PNA), and proteins on a DNA microarray surface to manufacture a DNA microarray, includes a first microchannel with a tube shape; a supplying unit supplying the solution of biomolecules to the first microchannel; a biomolecule solution droplet forming unit cross-linked to the first microchannel and forming biomolecule solution droplets with a predetermined size by periodically jetting a gas toward the biomolecule solution flowing in the first microchannel; a second microchannel linked to the first microchannel and having a greater diameter than the first microchannel; a cooling unit surrounding at least a part of the second microchannel to freeze the biomolecule solution droplets which pass through the second microchannel; and a spotting unit thawing the frozen biomolecule solution droplets and dropping the thawed biomolecule solution droplets on a surface of the DNA microarray. The spotting device can form spots with uniform shape, minimize an effect of temperature on biomolecules, and easily manipulate biomolecules when manufacturing a DNA microarray.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Novel immunogenic epitope for immunotherapy
ActiveUS20090136528A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAdditive ingredientWilms' tumor
The present invention relates to peptides, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumour-associated T-helper cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumour-associated peptides that serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions which stimulate anti-tumour immune responses. The present invention relates to novel peptide sequences and their variants derived from HLA class I and class II molecules of human tumour cells which can be used in vaccine compositions for eliciting anti-tumour immune responses.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Electronic transfer moieties attached to peptide nucleic acids
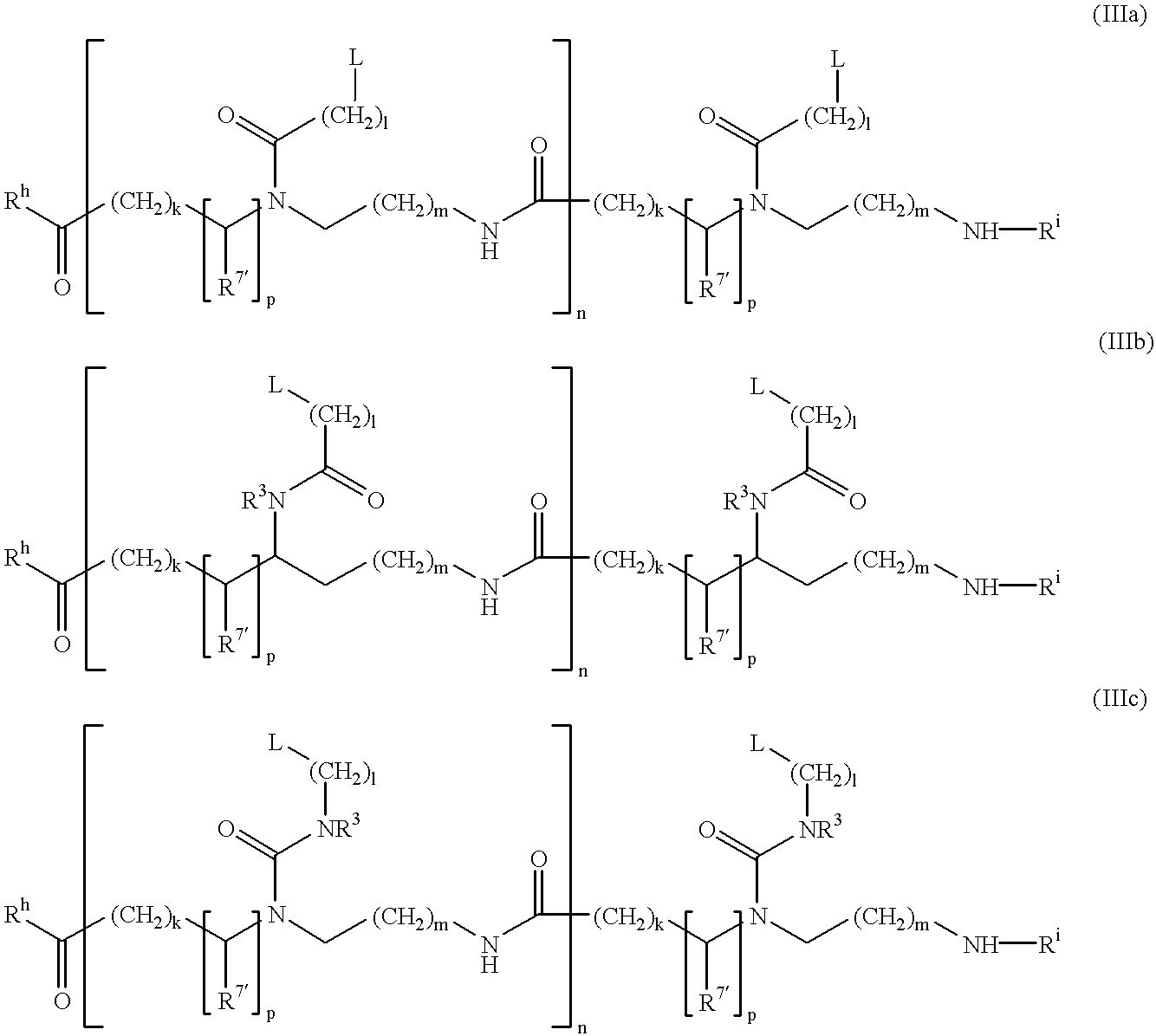
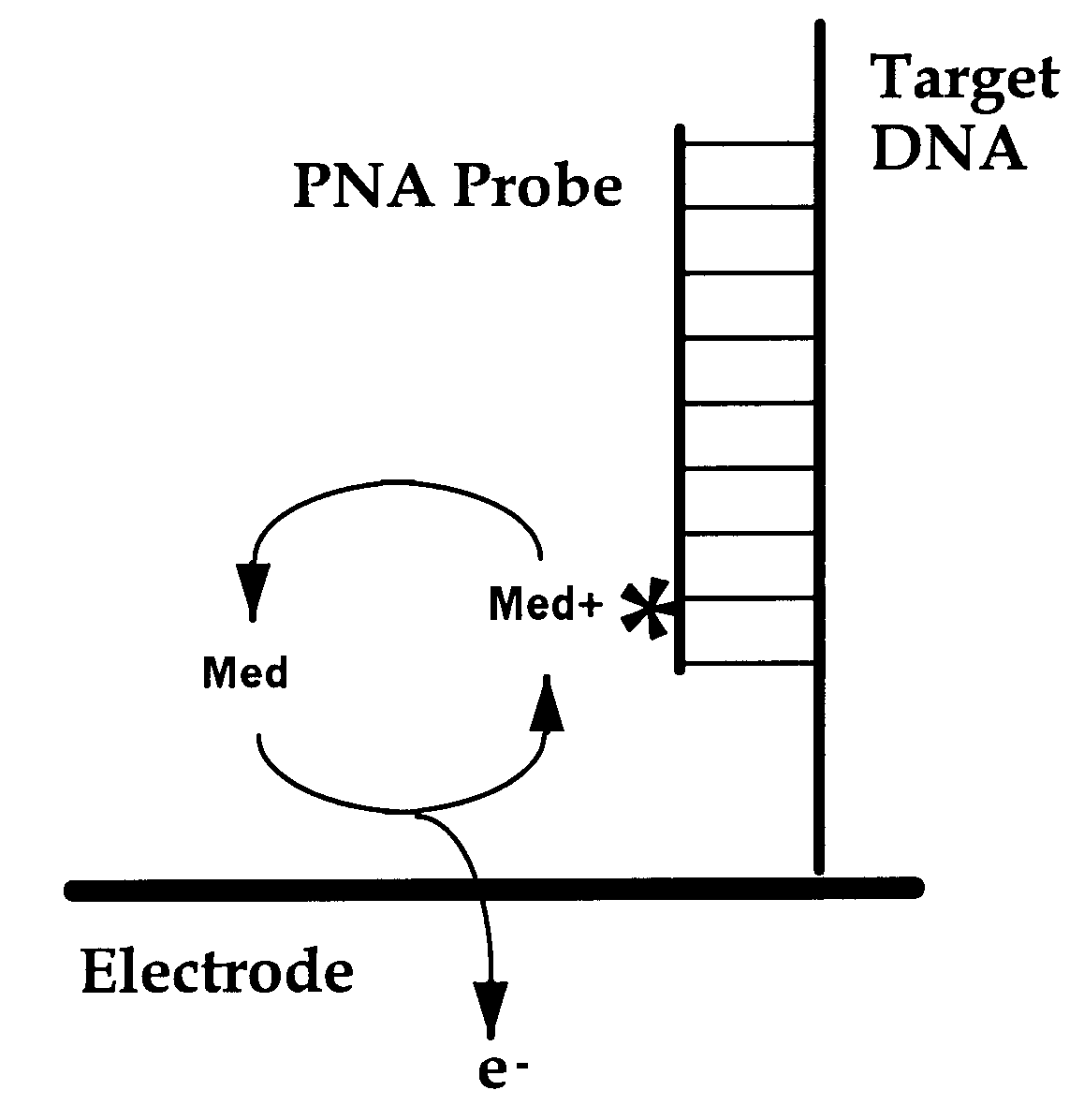
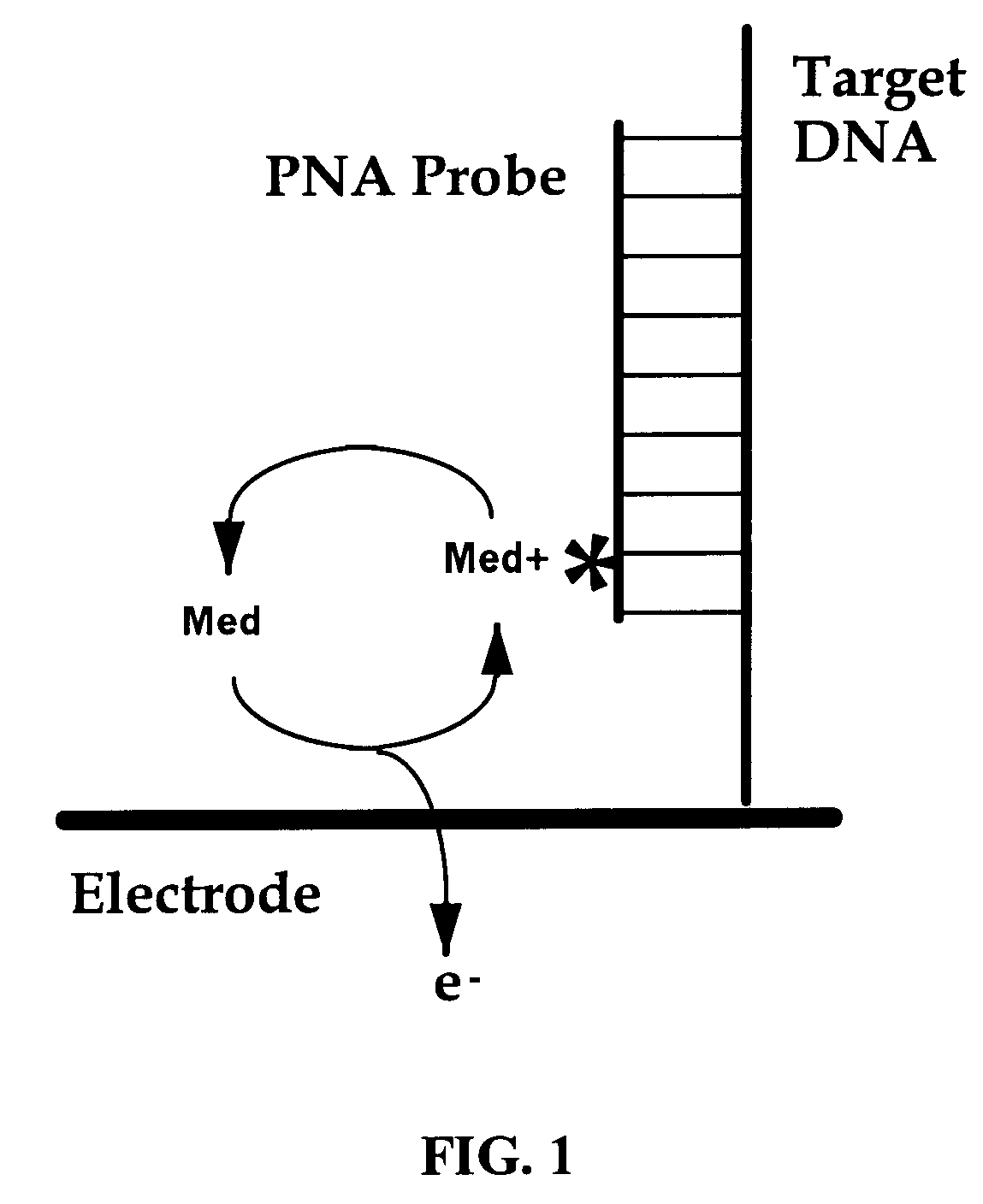
InactiveUS7045285B1Simple compositionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyOligomerConductive polymer
The invention relates to nucleic acids covalently coupled to electrodes via conductive oligomers. More particularly, the invention is directed to the site-selective modification of nucleic acids with electron transfer moieties and electrodes to produce a new class of biomaterials, and to methods of making and using them.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC +1
Chemical modification of DNA using peptide nucleic acid conjugates
InactiveUS6165720AReduce deliveryHigh transfection efficiencyFungiBacteriaEukaryotic plasmidsBiological activation
Complexes comprising a nucleic acid molecule and a conjugated peptide nucleic acid (PNA). The PNA may be labeled or conjugated to a protein, peptide, carbohydrate moiety or receptor ligand. These complexes are used to transfect cells to monitoring plasmid biodistribution, promote nuclear localization, induce transcriptional activation, lyse the endosomal compartment and facilitate transfection. These complexes increase the efficiency of expression of a particular gene.
Owner:GENE THERAPY SYST +1
Compositions and methods for targeted inactivation of HIV cell surface receptors
InactiveUS20100172882A1Avoid infectionReduce viral loadAntibacterial agentsBiocideImmunodeficiency virusReceptor degradation
Compositions for targeted mutagenesis of cell surface receptors for HIV and methods of their use are provided herein. The compositions include triplex-forming molecules that bind to duplex DNA in a sequence specific manner at target sites to form triple-stranded structures. The triplex-forming molecules can be triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) or peptide nucleic acids (PNAs). The triplex-forming molecules are useful to induce site-specific homologous recombination in mammalian cells when used in combination with donor oligonucleotides. The triplex-forming molecules target sites within or adjacent to genes that encodes cell surface receptors for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This binding stimulates homologous recombination of a donor oligonucleotide to cause mutations in HIV cell surface receptor genes that result in one or more deficiencies in the ability of the encoded receptor to bind to HIV and allow its transport into the cell. Methods for ex vivo and in vivo prophylaxis and therapy of HIV infection using the disclosed compositions are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method and probes for the detection of chromosome aberrations
InactiveUS7105294B2Lower melting temperatureRaise the ratioSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ hybridisationHybridization probe
A novel method for detecting chromosome aberrations is disclosed. More specifically, chromosome aberrations are detected by in situ hybridisation using at least two sets of hybridisation probes, at least one set comprising one or more peptide nucleic acid probes capable of hybridising to specific nucleic acid sequences related to a potential aberration in a chromosome, and at least one set comprising two or more peptide nucleic acid probes capable of hybridising to specific nucleic acid sequences related to another potential aberration in a chromosome. In particular, the method may be used for detecting chromosome aberrations in the form of breakpoints.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Polypeptides from Neisseria meningitidis
InactiveUS8039007B2Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Various specific meningococcal proteins are disclosed. The invention provides related polypeptides, nucleic acids, antibodies and methods. These can all be used in medicine for treating or preventing disease and / or infection caused by meningococcus, such as bacterial meningitis.
Owner:J CRAIG VENTER INST +1
Process for identification of genes encoding proteins having cell proliferation-promoting activity
InactiveUS20020019005A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingADAMTS ProteinsSelection system
The present invention is directed to selection systems for the identification of cell proliferation genes based on functional analysis. More specifically, the invention is directed to a process for the identification of a cell proliferation promoting activity, the isolation of genes involved in such cell proliferation promoting activity, and the use of the so identified genes for the diagnosis or treatment of a disease associated with excessive cell proliferation. The invention further is directed to the design and development of antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids, and other compounds which specifically interfere with the function of the identified gene and / or its gene product, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds, for the treatment of diseases associated with inappropriate or unregulated cell proliferation.
Owner:DELTAGEN PROTEOMICS
Human bikunin
InactiveUS7019123B2Prolongation in clot timeIncrease concentrationAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderPlacental bikuninNucleic acid sequencing
The instant invention provides for proteins, polypeptides, nucleic acid sequences, constructs, expression vectors, host cells, pharmaceutical compositions of, and methods for using human placental bikunin, serine protease inhibitor domains, and fragments thereof
Owner:BAYER CORPORATION
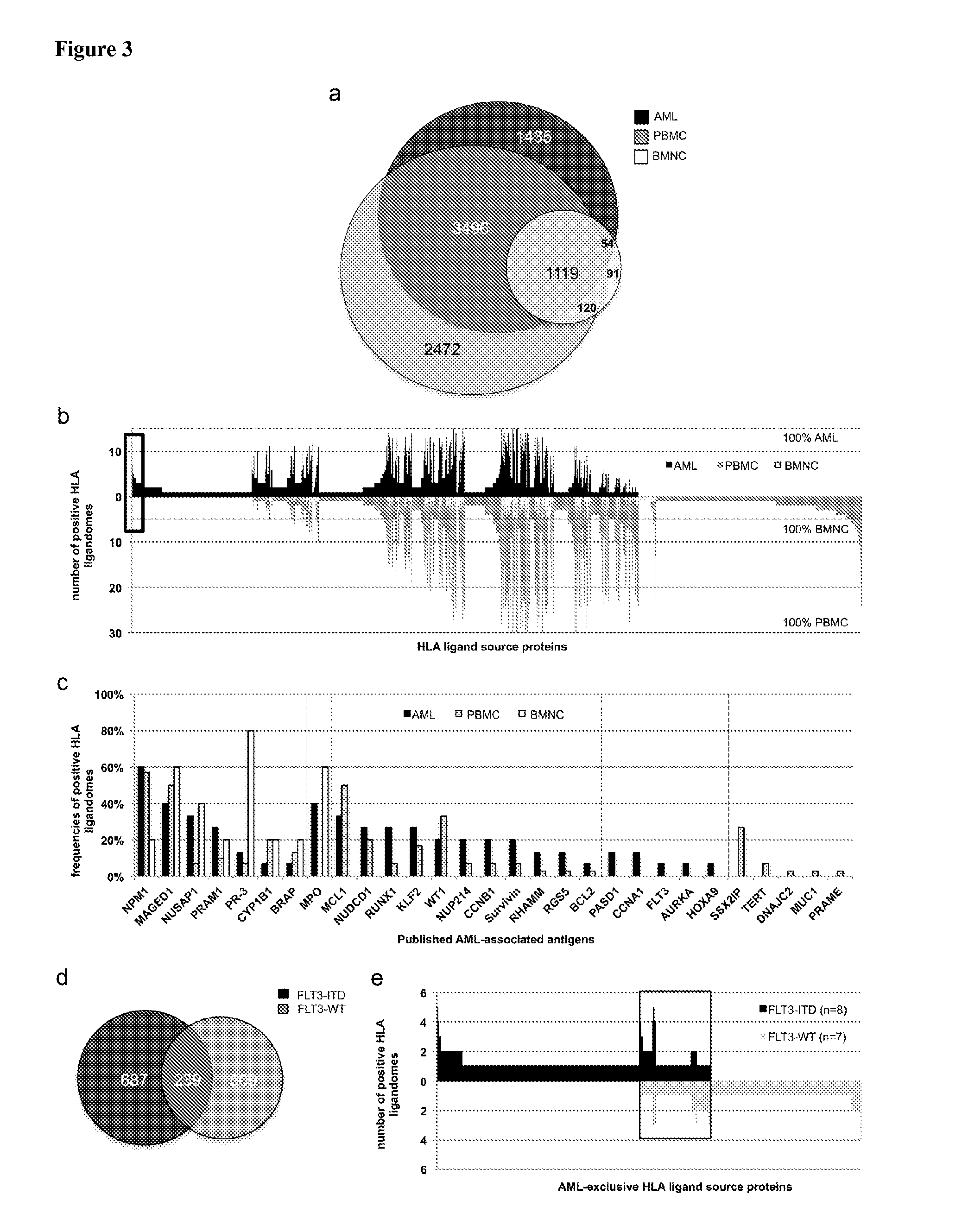
Novel immunotherapy against several tumors of the blood, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
The present invention relates to peptides, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated cytotoxic T cell (CTL) peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses. The present invention relates to several novel peptide sequences and their variants derived from HLA class I and HLA class II molecules of human tumor cells that can be used in vaccine compositions for eliciting anti-tumor immune responses.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Peptide nucleic acid combinatorial libraries and improved methods of synthesis
InactiveUS6756199B1Increase diversityIncrease transcriptionPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsOligomerAmino acid
New sub-monomer synthetic methods for the preparation of peptide nucleic acid oligomeric structures are disclosed that provide for the synthesis of both predefined sequence peptide nucleic acid oligomers as well as random sequence peptide nucleic acid oligomers. Further these methods also provide for the incorporation of peptide nucleic acid units or strings of such units with amino acids or strings of amino acids in chimeric peptide nucleic acid-amino acid compounds. Further disclosed are method of making random libraries of peptide nucleic acids using the fully preformed monomers. Chimeric oligomers and libraries of the same are also disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Chimerical peptide-nucleic acid fragment, process for producing the same and its for appropriately introducing nucleic acids into cell organelles and cells
InactiveUS20010008771A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsMolecular biologyBiophysics
This invention relates to a chimerical peptide-nucleic acid fragment, the process for producing the same and its use for appropriately introducing nucleic acids into cell organelles and cells.
Owner:SEIBEL PETER
Nucleic acid transcription method
ActiveUS20150152409A1Less biasOptimization orderNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotide PrimerComputational biology
The present invention relates to methods for generating an amplified nucleic acid portion of a template nucleic acid, comprising obtaining said template nucleic acid, annealing at least one oligonucleotide primer to said template nucleic acid, annealing at least one oligonucleotide stopper to said template nucleic acid, elongating the at least one oligonucleotide primer in a template specific manner until the elongating product nucleic acid reaches the position of an annealed oligonucleotide stopper, whereby the elongation reaction is stopped, wherein in said elongation reaction said oligonucleotide stopper is not elongated, and wherein the elongated product nucleic acid is ligated to the 3′ end of said oligonucleotide stopper—said stopper may also be a primer itself and uses and kits for performing said method.
Owner:LEXOGEN GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com