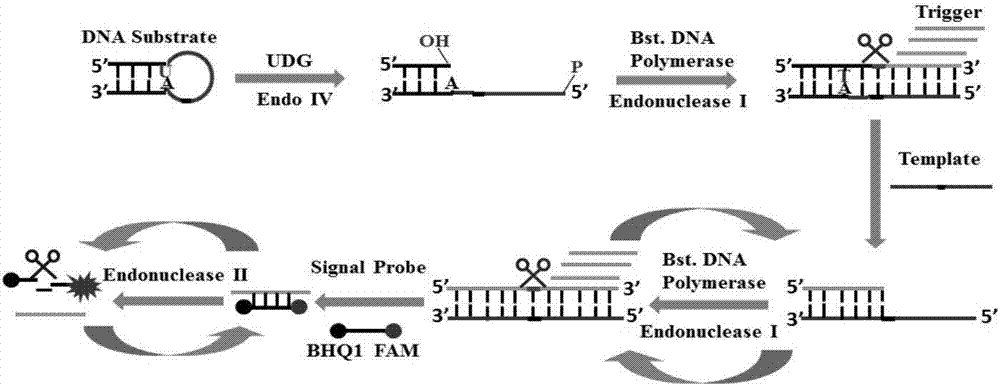
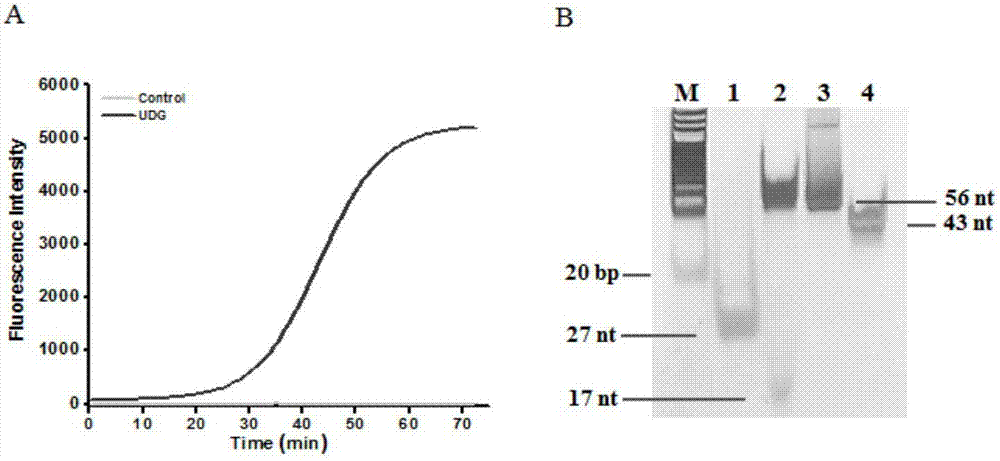
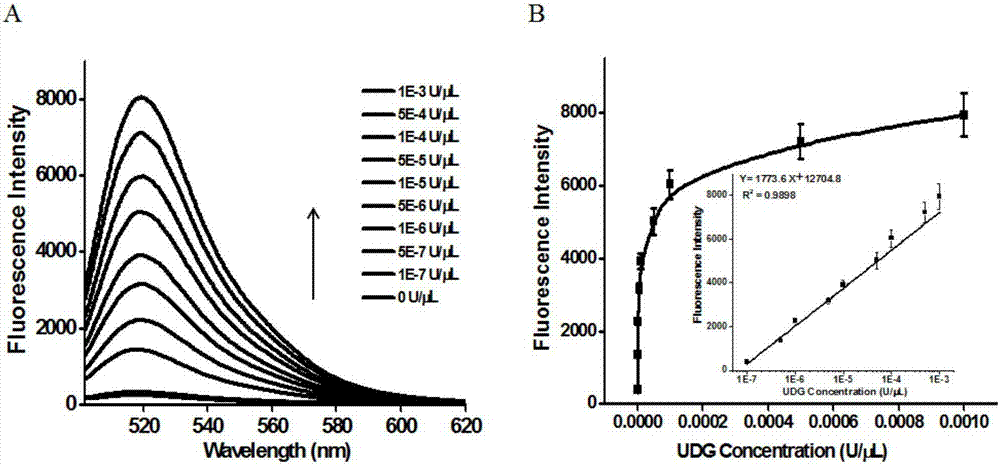
Method of detecting UDG activity by enzyme-mediated two-step serial signal amplification based on excision repair
A signal amplification, enzyme-mediated technology, applied in the field of biological analysis, can solve the problems of low detection sensitivity, long loss time, time-consuming and laborious, etc., and achieve the effects of high sensitivity, simple operation and high specificity
Active Publication Date: 2017-07-07
SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
View PDF3 Cites 15 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Among them, the colorimetric analysis method uses hydrogen peroxide to oxidize 2,2'-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS 2- ) produces colored ABTS - , to visualize the activity of uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG), but its detection sensitivity cannot be compared with electrochemical and fluorescent methods
The electrochemical analysis method improves the detection sensitivity to a certain extent, but it needs to immobilize the capture probe on the solidified carrier and prepare the graphene electrode in advance, which is time-consuming and laborious.
The fluorescence method is simple in design and easy to operate, but it cannot avoid the disadvantages of low detection sensitivity and unstable signal
In summary, although these methods for detecting uracil DNA glycosylase (UDG) activity are effective, they still have shortcomings such as low sensitivity, long loss time, and cumbersome operations.
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
[0053] Cell lysis buffer preparation: 10 millimoles per liter of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane-hydrochloric acid (Tris-HCl) (pH 8.0), 150 millimoles per liter of sodium chloride, 1% (mass / volume) Ethyl phenyl polyethylene glycol (NP-40), 0.25 millimoles per liter of sodium deoxycholate, 1% (mass / volume) glycerol, 0.1 millimoles per liter of 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzene Sulfonyl Fluoride Hydrochloride
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
The invention discloses a method of detecting the UDG activity by enzyme-mediated two-step serial signal amplification based on excision repair. The method comprises the following steps: (1) adding a UDG active substrate in an excision reaction buffer solution to carry out excision repair reaction, excising a uracil base of the UDG active substrate, and leaving an abasic site; and (2) adding an excision repair reaction product in an amplification reaction buffer solution to carry out enzyme-assisted two-step serial signal amplification reaction, namely inducing strand displacement reaction and index amplification reaction, generating strengthened fluorescence signals in a circulation manner, and determining the UDG activity through weakness of the fluorescence signals. According to the method provided by the invention, ultrahigh sensitive detection to the activity of uracil DNA glycosylase (UDG) is realized by utilizing high amplification efficiency of constant-temperature index amplification reaction and specific circulation digestion of ribonuclease H.
Description
Technical field [0001] The present invention relates to the technical field of bioanalysis, in particular to a method for detecting UDG activity based on excision repair and enzyme-mediated two-step series signal amplification. Background technique [0002] The genome is composed of specifically paired A:T / G:C bases, and its accuracy and stability are of great significance to the maintenance of life. But in real life, the structure of genomic DNA bases often suffers from external factors (such as ultraviolet rays, ionizing radiation, toxic chemicals) and endogenous active factors (such as superoxide anions, hydroxyl radicals, hydrogen peroxide, etc.) The damage caused by DNA single-strand and double-strand breaks, mismatches, base deletions, etc., destroys the integrity of the genome, causes genome instability, induces cancer, and affects the survival of species. In order to reduce the damage of genomic DNA in the body, a variety of damage repair mechanisms have evolved in organ...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Applications(China)
IPC IPC(8): C12Q1/34G01N21/64
CPCC12Q1/34G01N21/6486
Inventor 张春阳王黎娟任明
Owner SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com