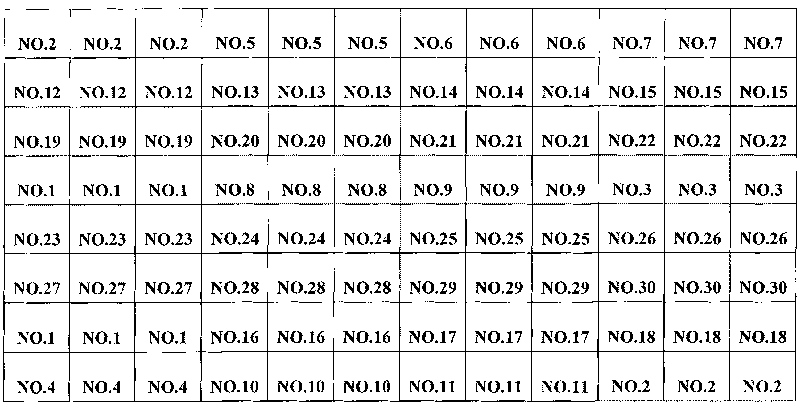Gene chip for detecting pathogens of lower respiratory tract and reagent kit
A gene chip and pathogenic bacteria technology, applied in the field of gene chips and kits for detecting pathogenic bacteria of the lower respiratory tract, can solve problems such as identification difficulties, and achieve the effects of simple operation, strong repeatability and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Design and preparation of embodiment 1 probe
[0033] 1. Sequence acquisition:
[0034] (1) Acquisition of bacterial 16s rDNA sequences: eight species of bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, pneumoniae) were downloaded from the GenBank public database. Streptococcus, Legionella pneumophila and Moraxella catarrhalis) all 16s rDNA sequences.
[0035] (2) Acquisition of 16S-23S rDNA interregional sequences: download all 16S-23S rDNA interregional regions of Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii and their relatives from the GenBank public database sequence.
[0036]There are only 21 interval sequences of 9 strains in the public database of Klebsiella pneumoniae, and only 1 sequence of 1 strain of Klebsiella oxytoca, which cannot meet the requirements of screening specificity detection. needle needs. 22 strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae, 3 strains ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Design and preparation of embodiment 2 primers
[0052] 1. Sequence acquisition: the same as the sequence of the designed probe.
[0053] 2. Design primers:
[0054] (1) Design of primers for amplifying the interregional sequence: After comparing the 16S rDNA of 8 species of bacteria downloaded from the public database NCBI with the sequence alignment software Glustal X, a 16S rDNA conserved sequence close to the interregional region was selected as the upstream primer , the length conforms to T m Value: 50°C±5°C, length: 17bp±2bp, Hairpin: NONE, Dimer: NONE, False Priming: NONE, Cross Dimer: NONE, and contains bacterial universal probe sequence.
[0055] (2) Design of primers for amplifying the copB gene sequence: compare the above-mentioned catamorra copB gene sequence downloaded from the GenBank public database with the sequence alignment software Glustal X to find the conserved segment of the gene, and then identify the conserved segment of the gene. The segmen...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Gene Chip Preparation——Chip Spotting
[0063] 1. Dissolving probes: the probes synthesized in Example 1 were respectively dissolved in 50% DMSO solution, and diluted so that the final concentration of the probes reached 1 μg / μl.
[0064] 2. Adding plate: Add the dissolved probe to the corresponding position of the 384-well plate, 10 μl per well.
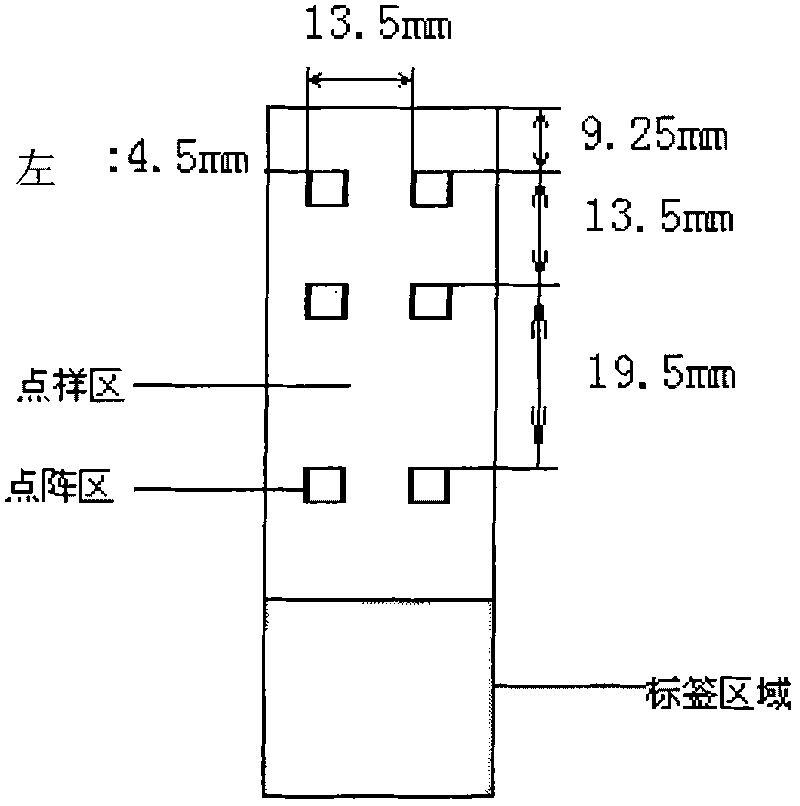
[0065] 3. Spotting: as figure 1The shown 57.5mm × 25.5mm × 1mm (length × width × height) clean aldehydated glass slide (CELAssociates, Inc.) was placed on the stage of the chip spotter (Spotarray 72), using the SpotArray Control software (Tele chem SMP3 stealth pin), run the program, press figure 2 The arrangement shown is spotted on the aldehydeized glass slide in the spotting area of 4.5 mm×4.5 mm to form a medium-low density DNA micro-array, and the array arrangement rules in the six dot matrix areas on the glass slide are the same. The size of the dot matrix area is 3mm×2.25mm, the dot pitch in the dot ma...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com