Patents
Literature
497 results about "Laser application" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
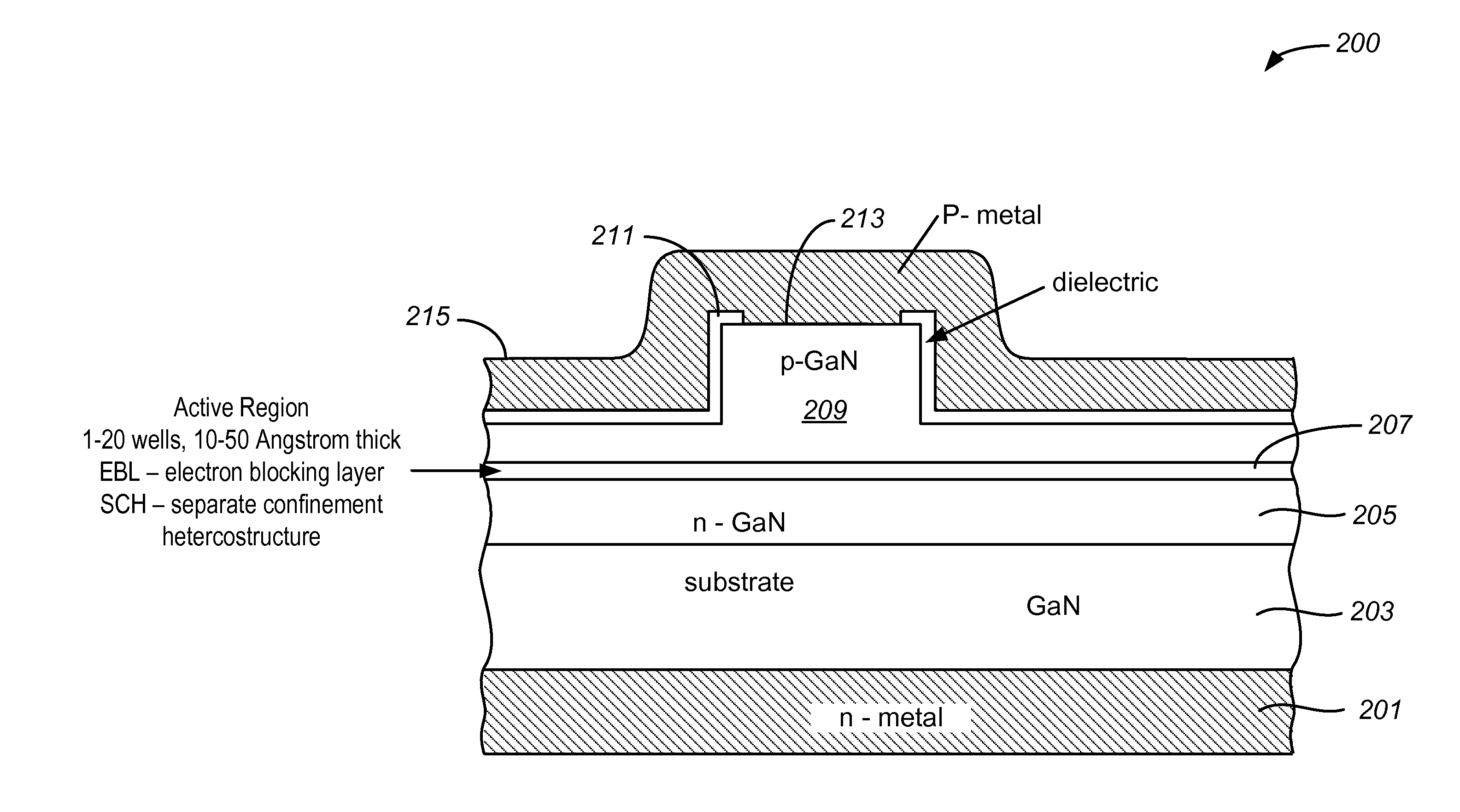
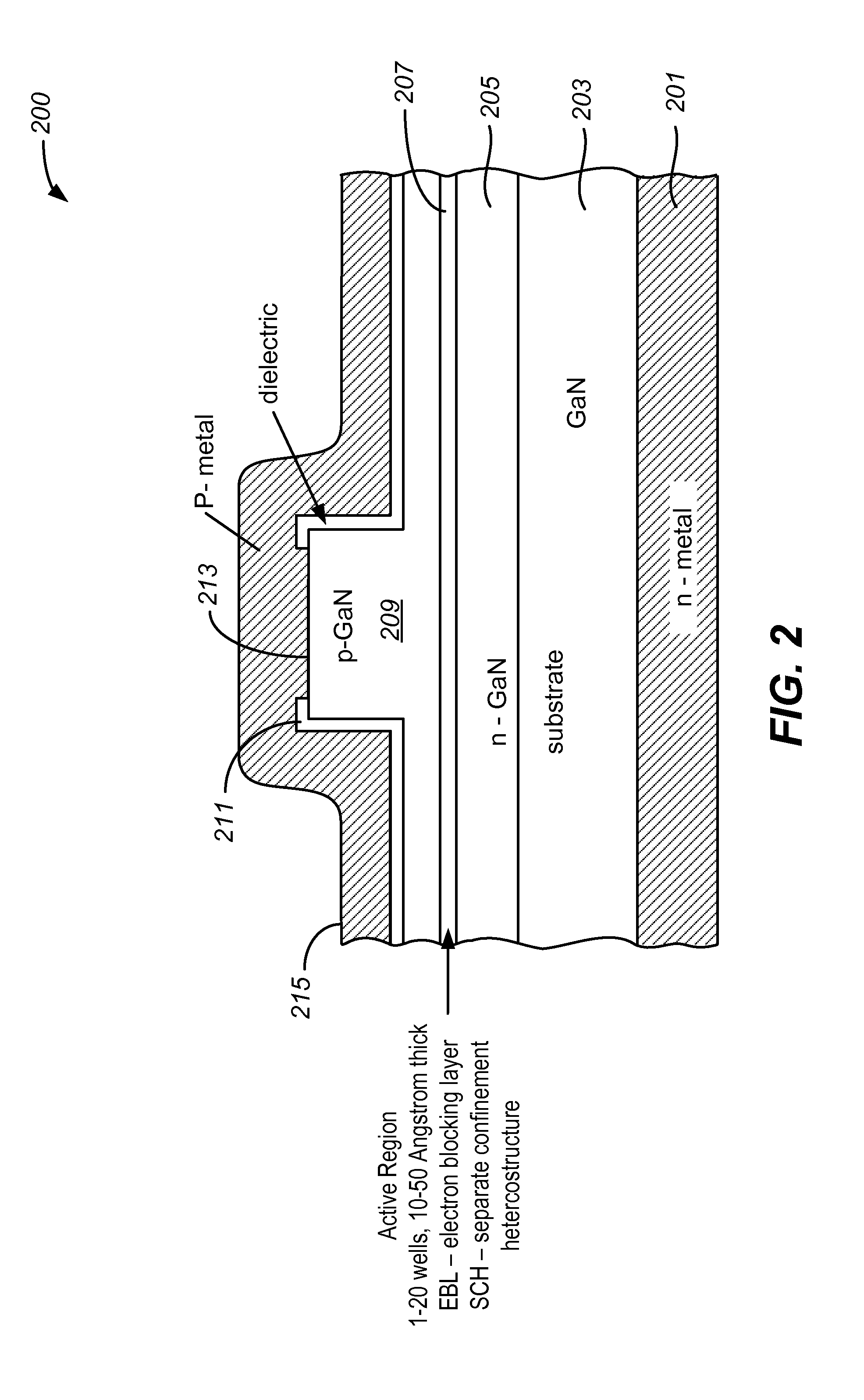
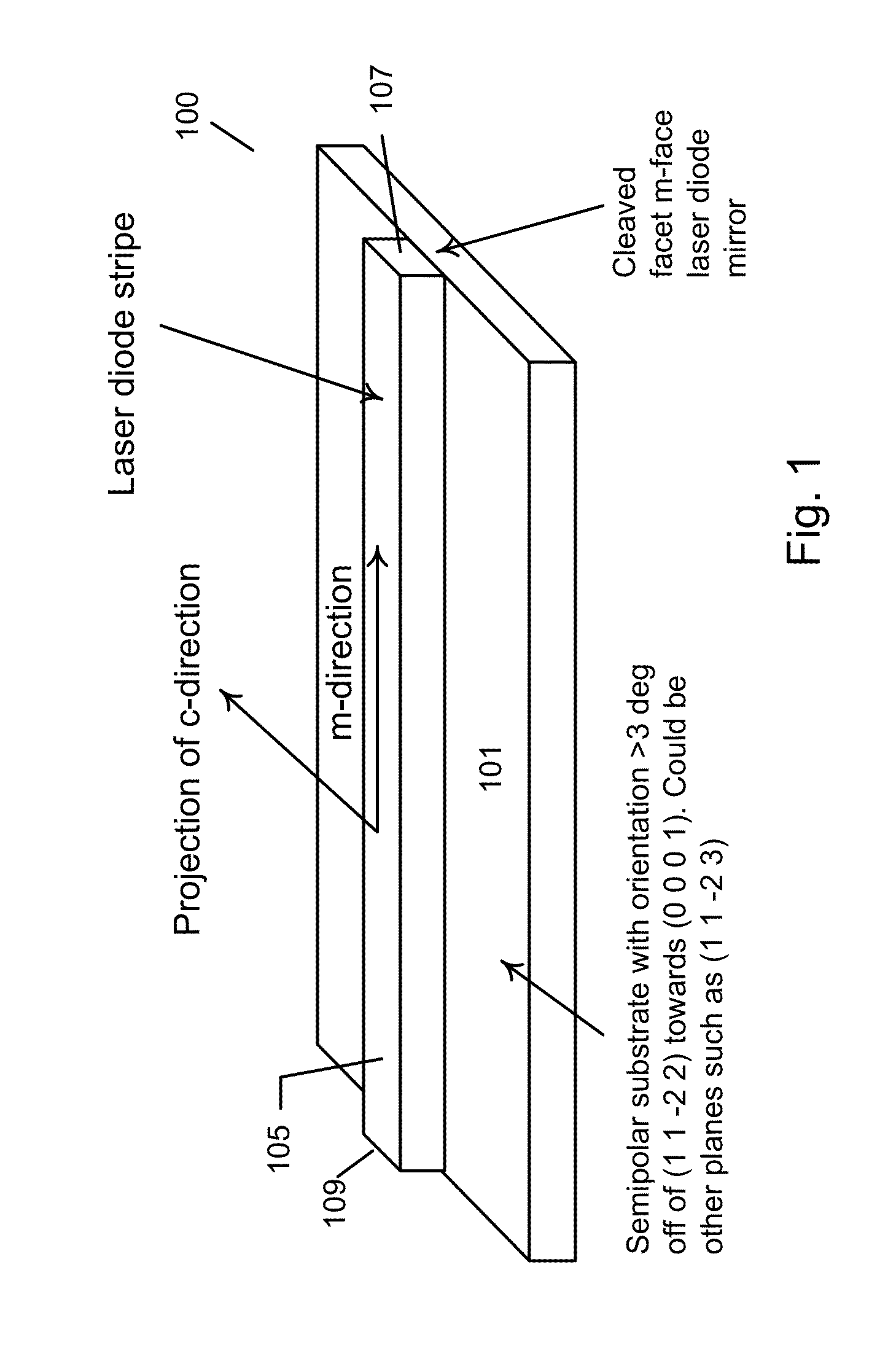
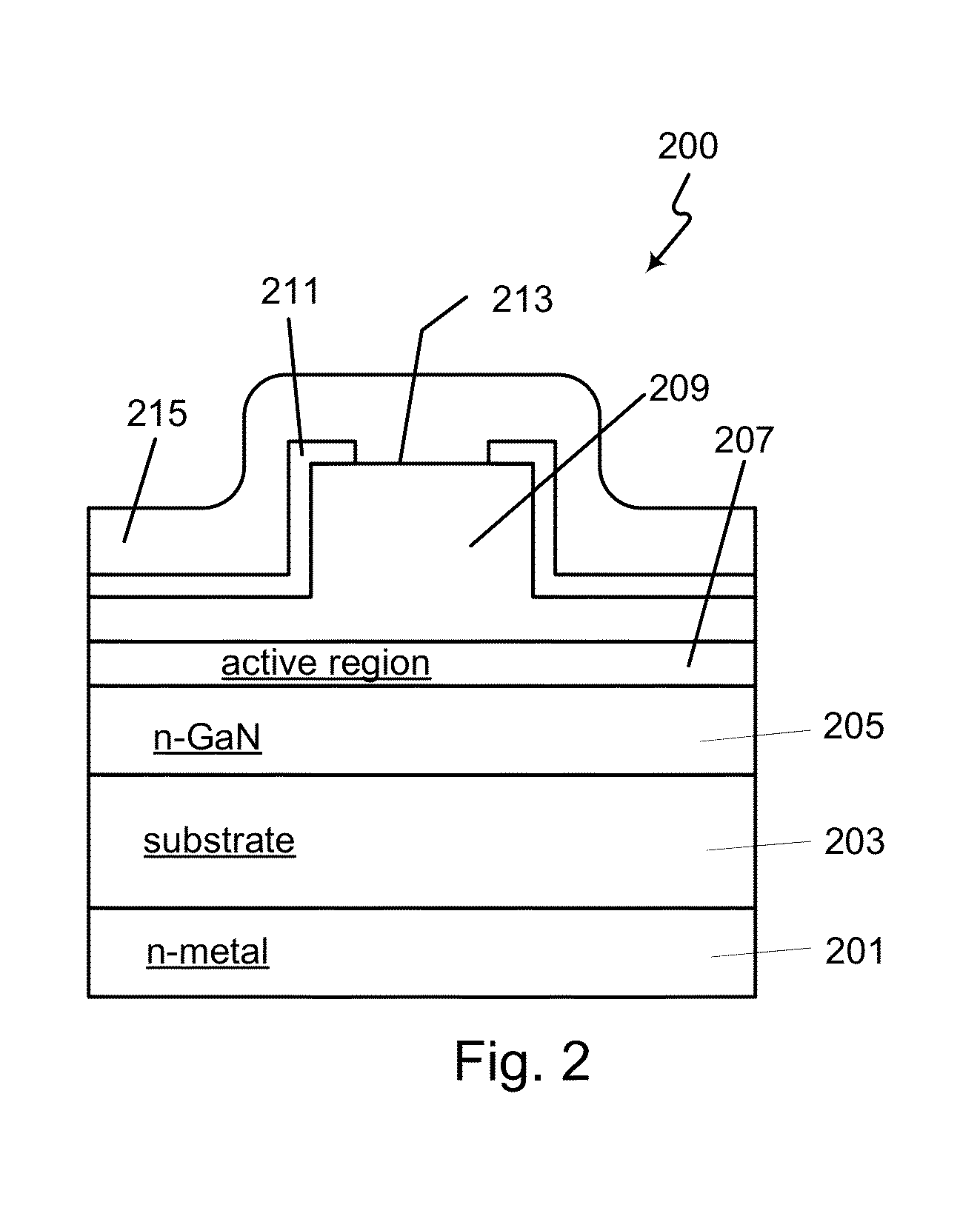
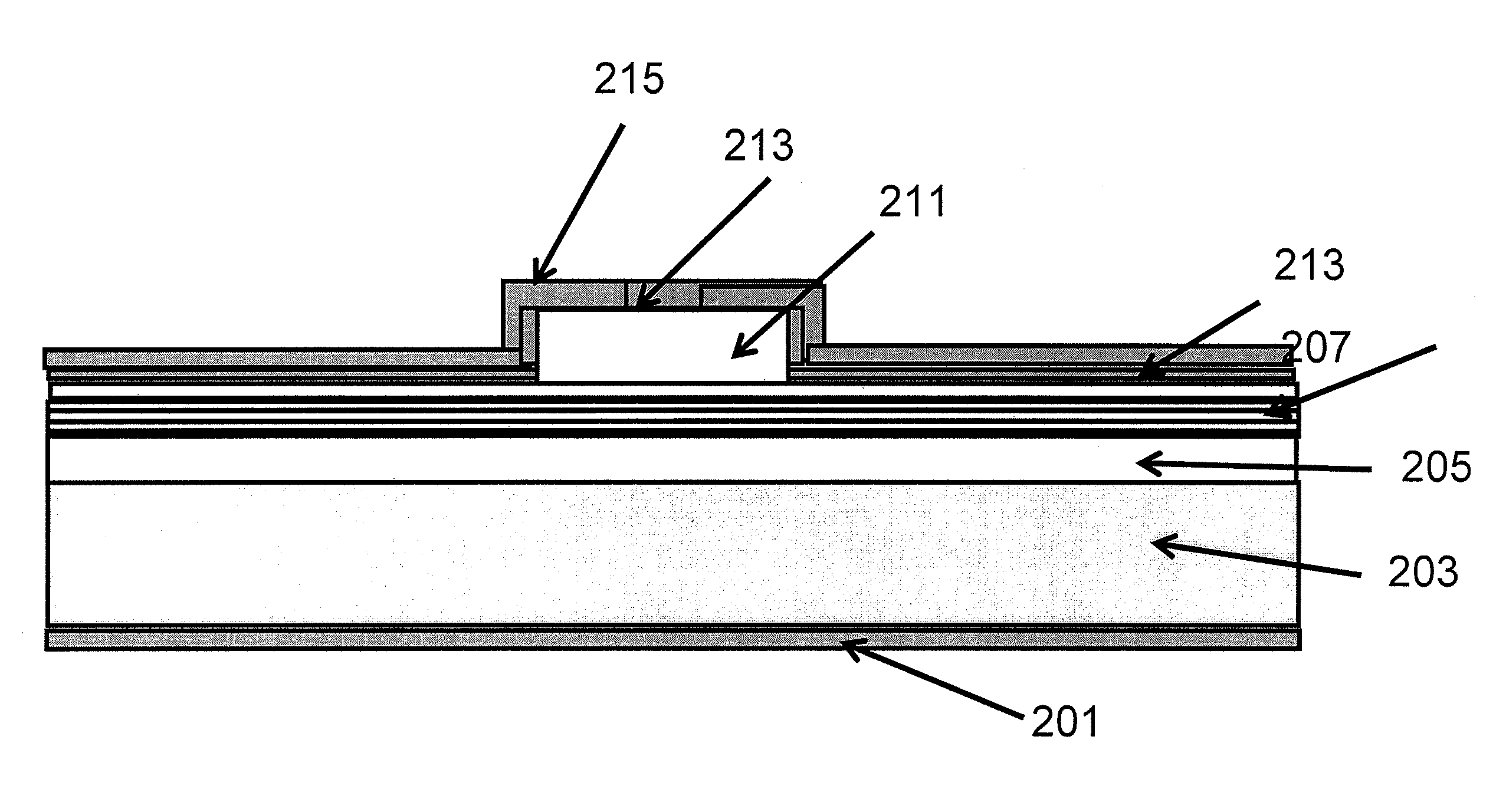
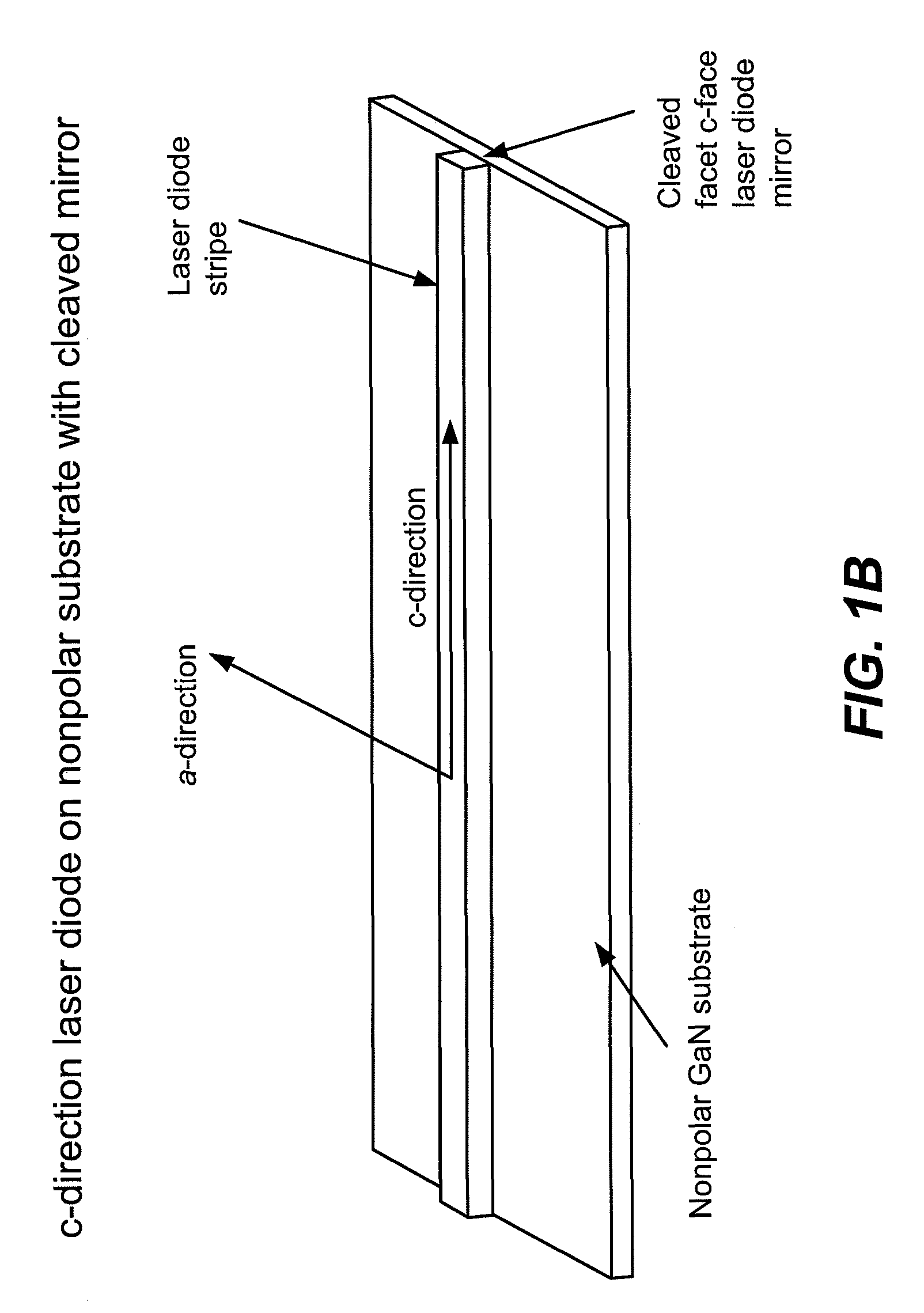
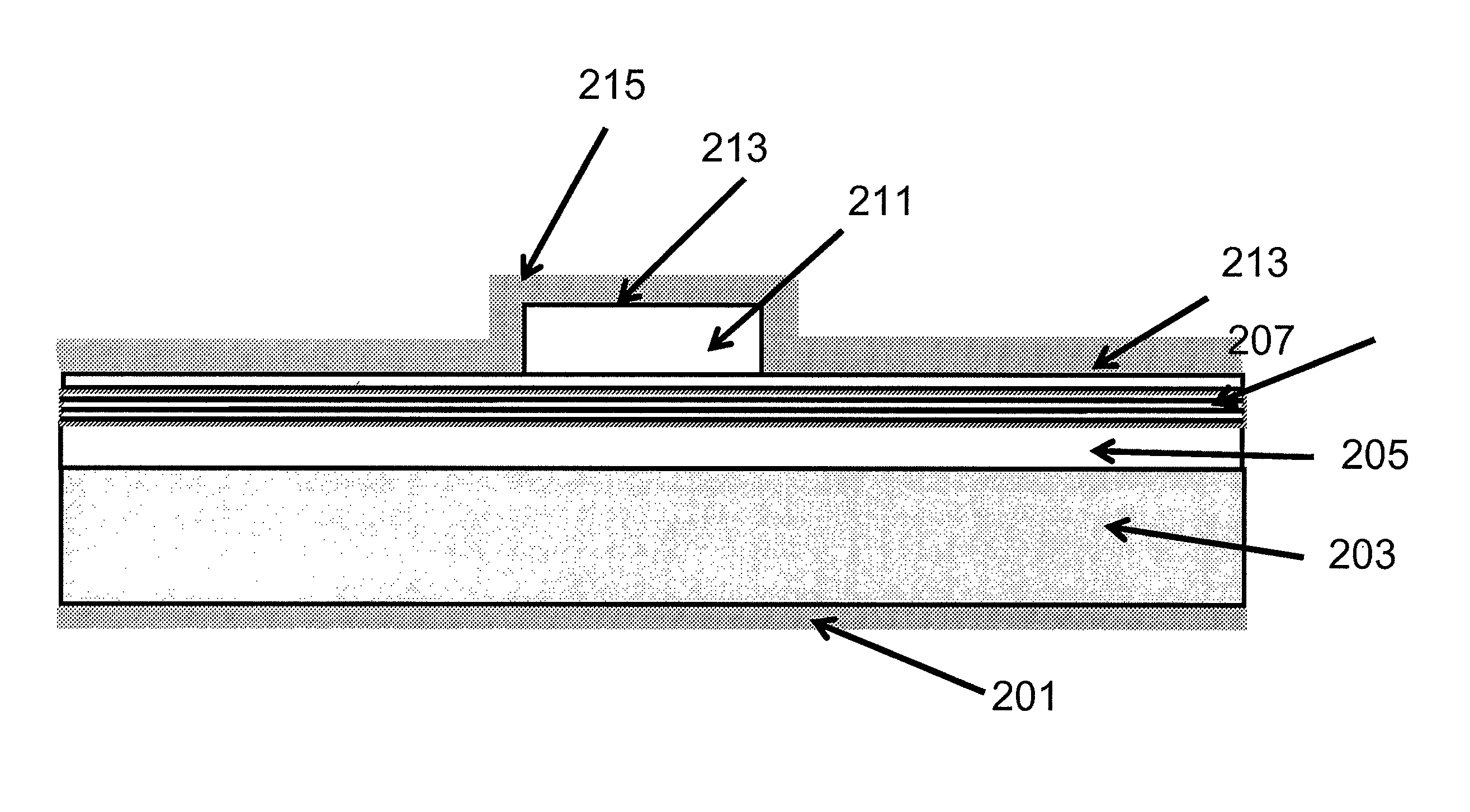
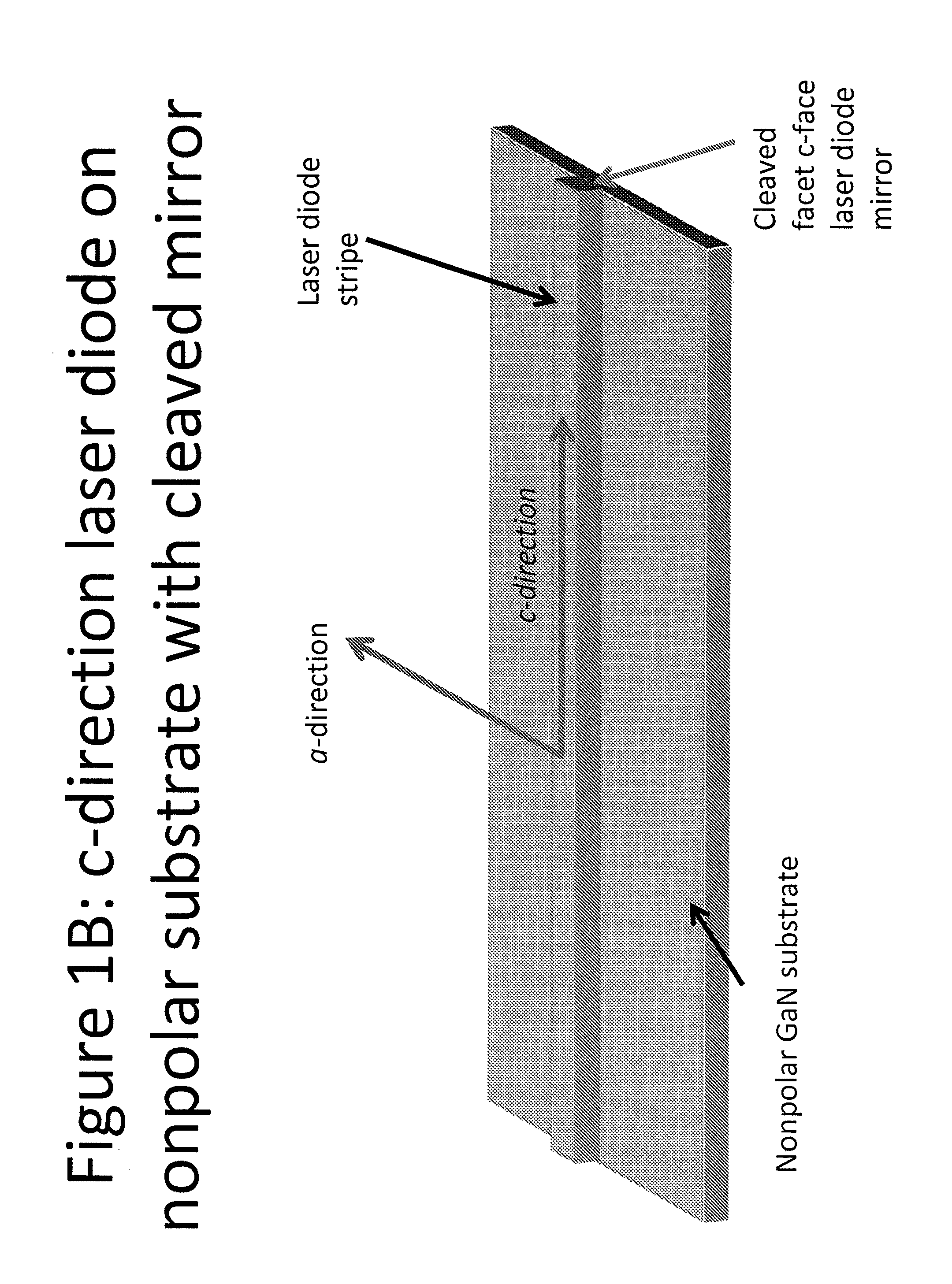
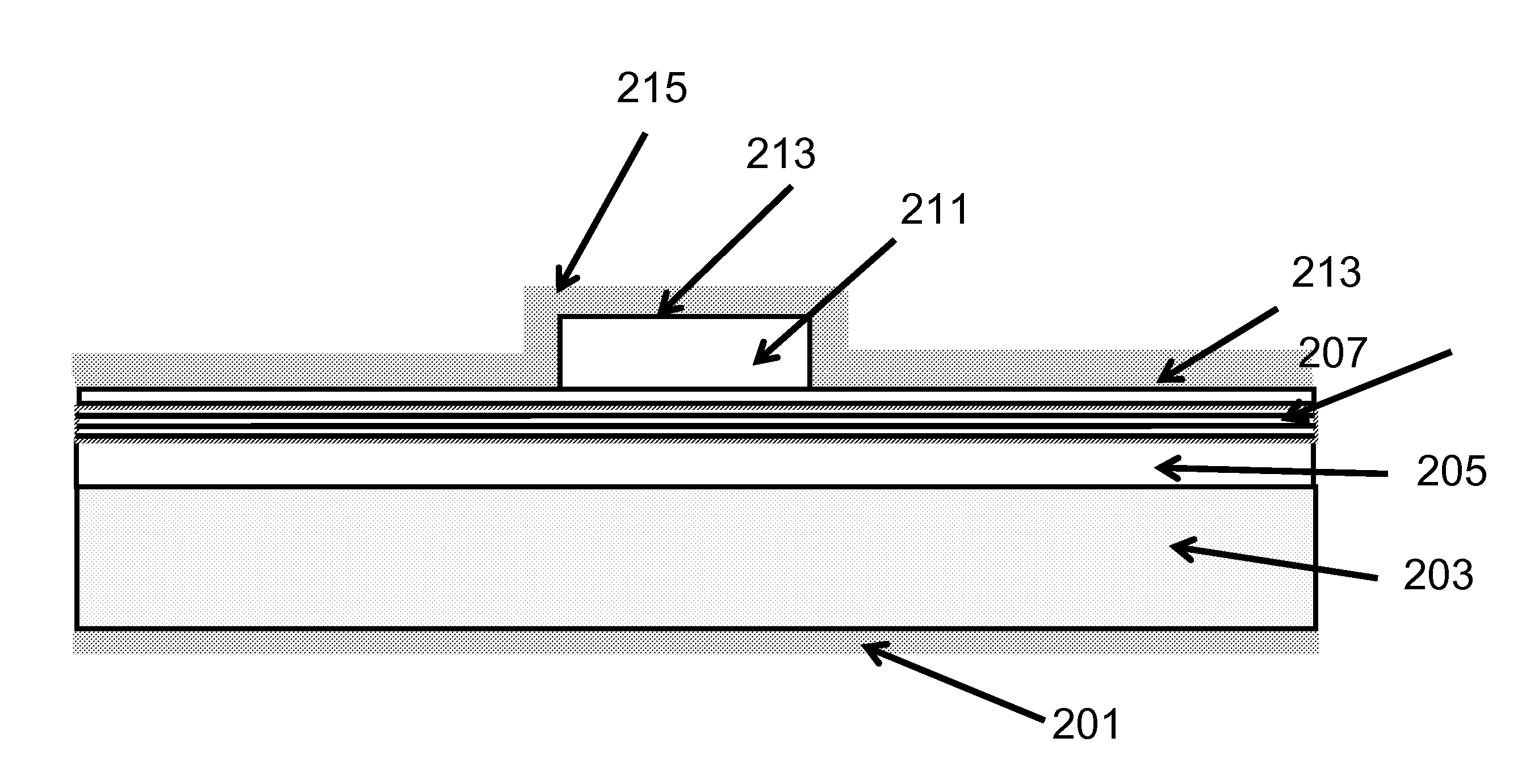
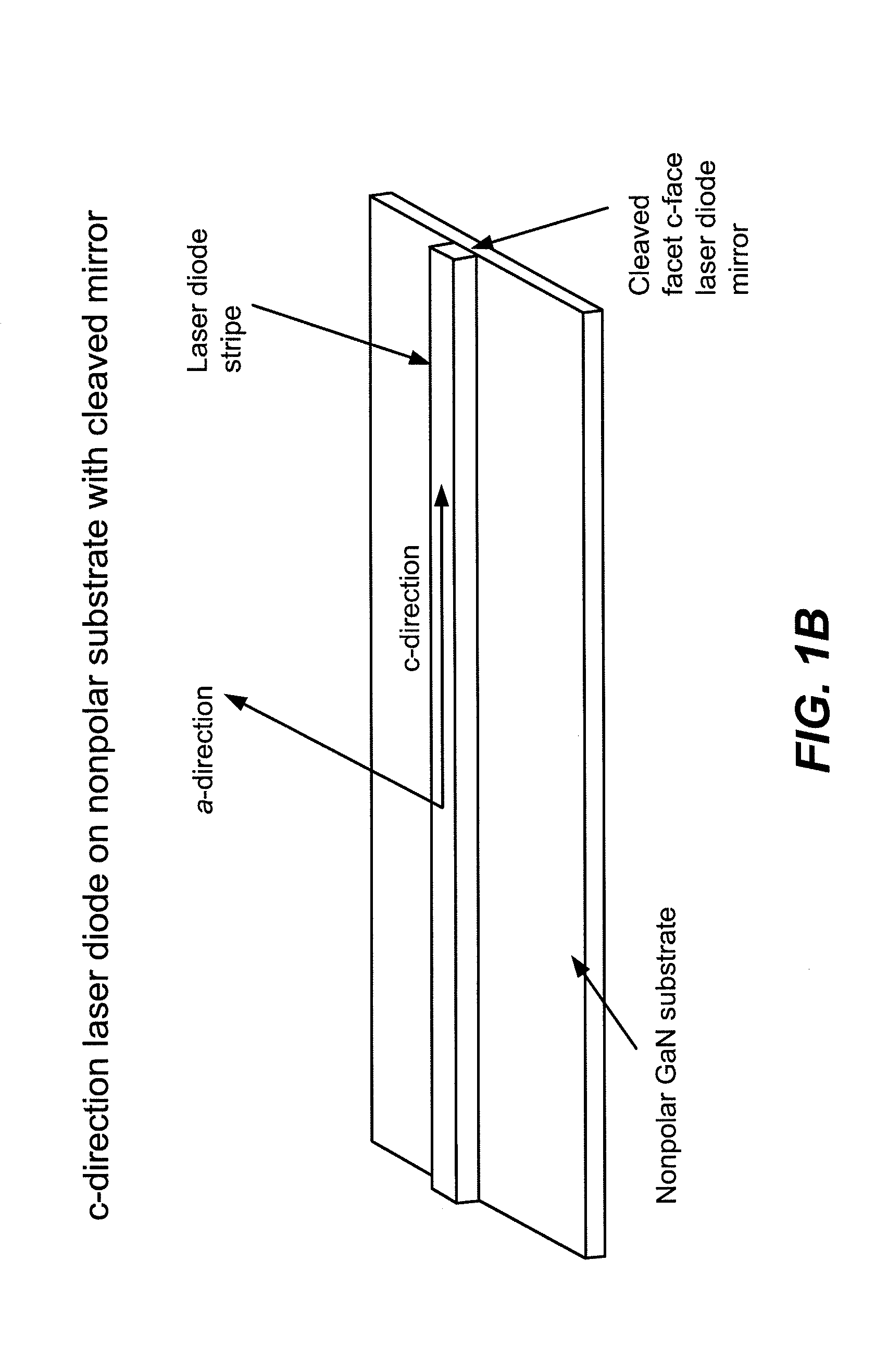
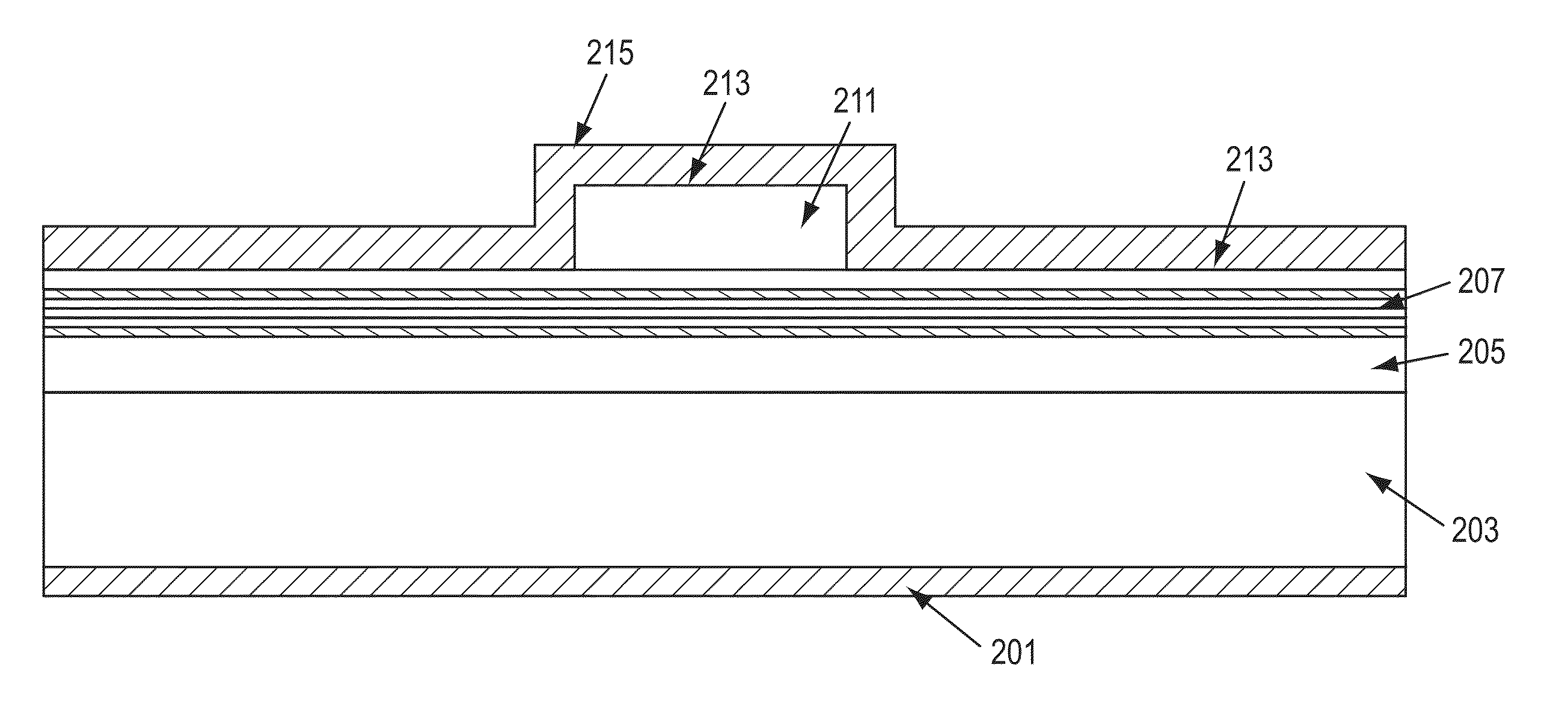
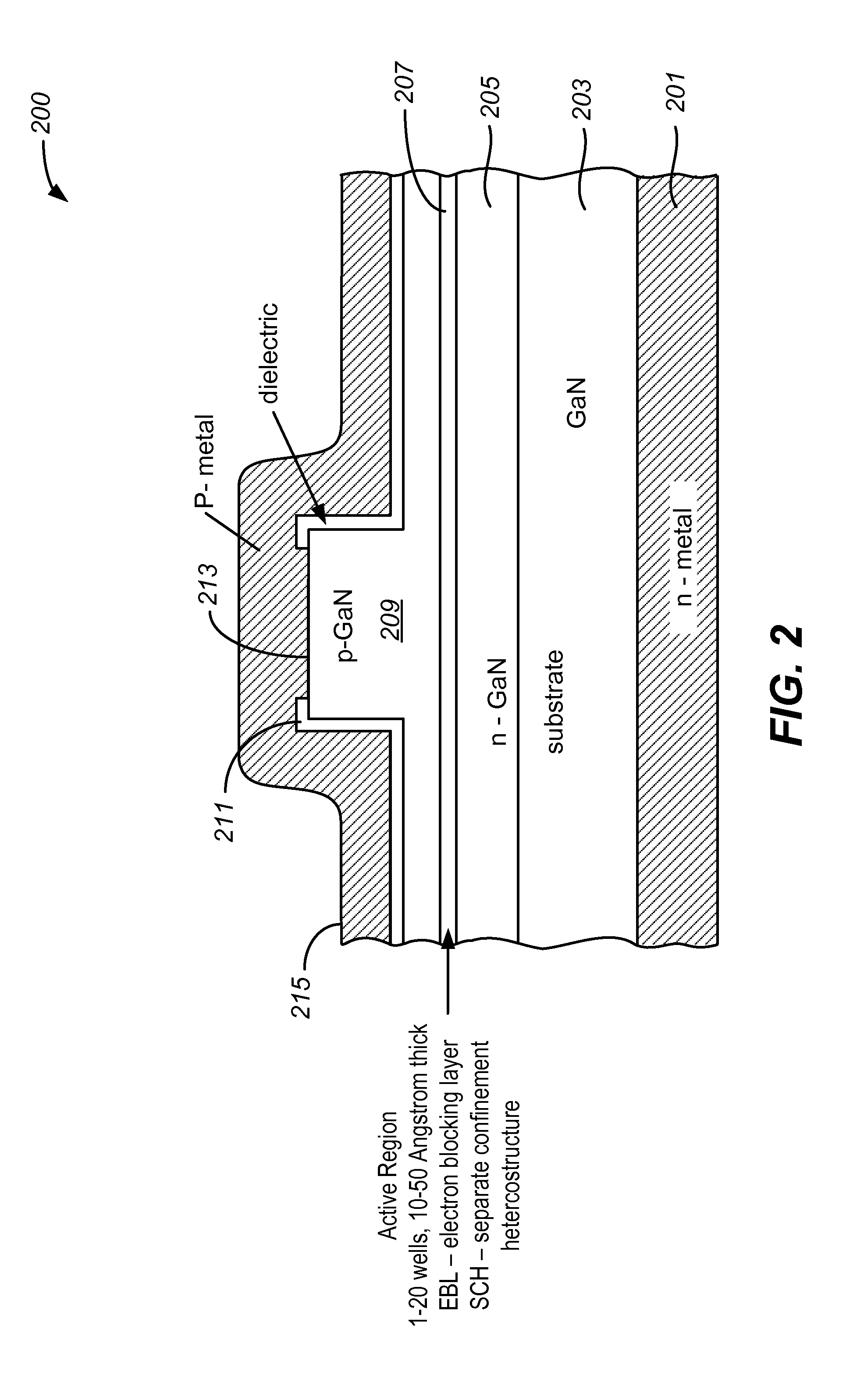
Optical Device Structure Using GaN Substrates for Laser Applications
ActiveUS20100316075A1Simple and cost-effectiveAchieve benefitsLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGallium nitrideLaser application
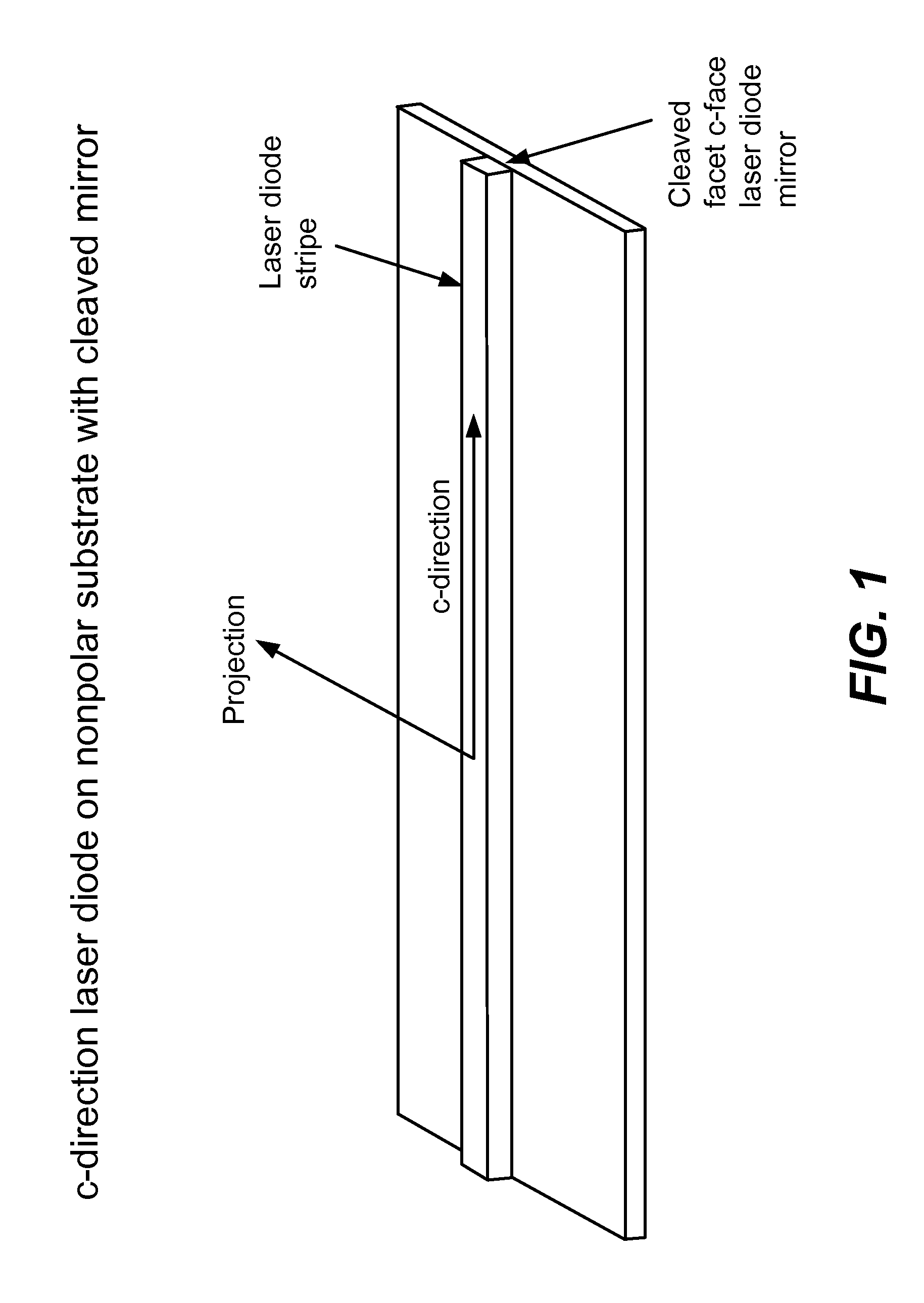
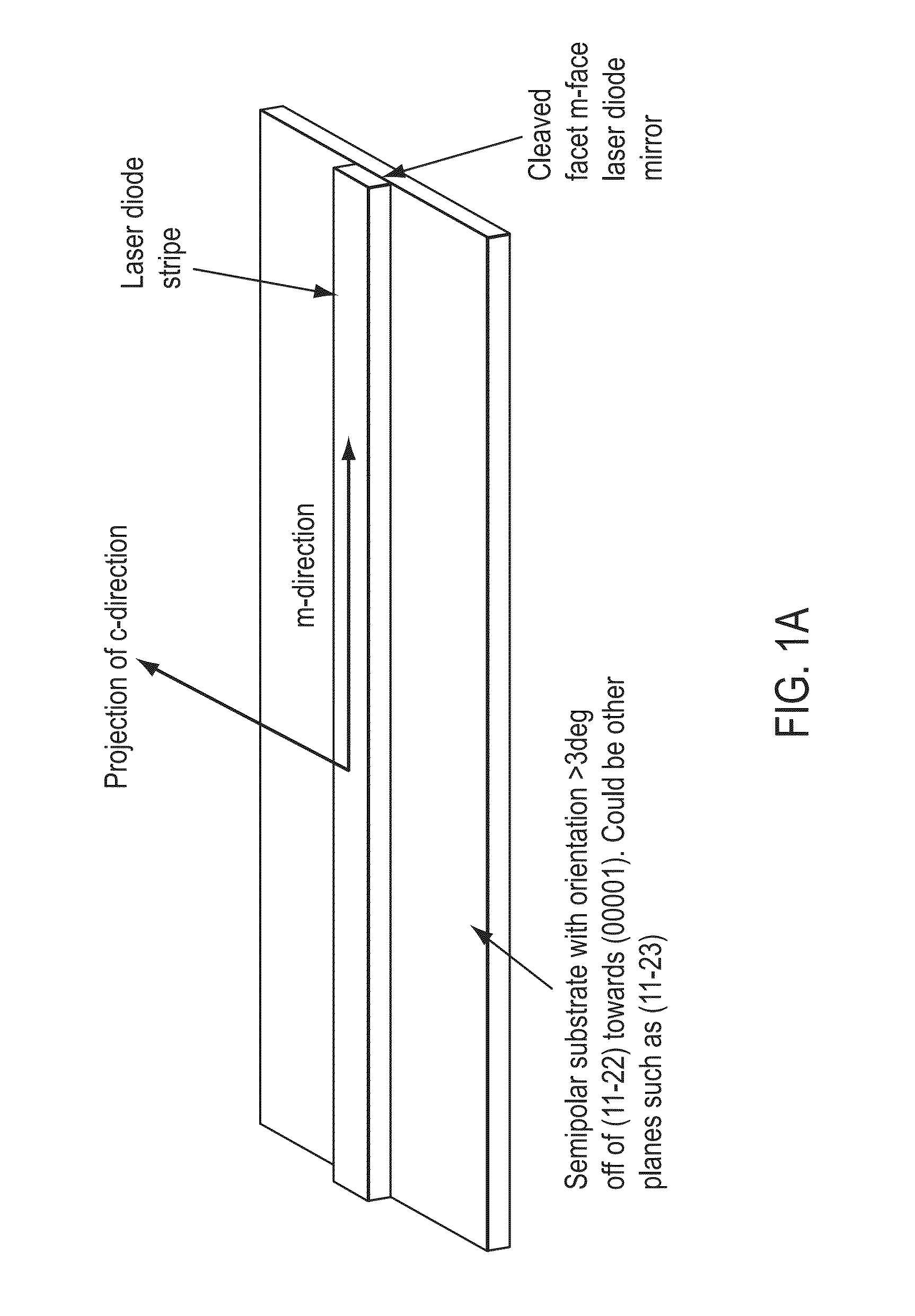
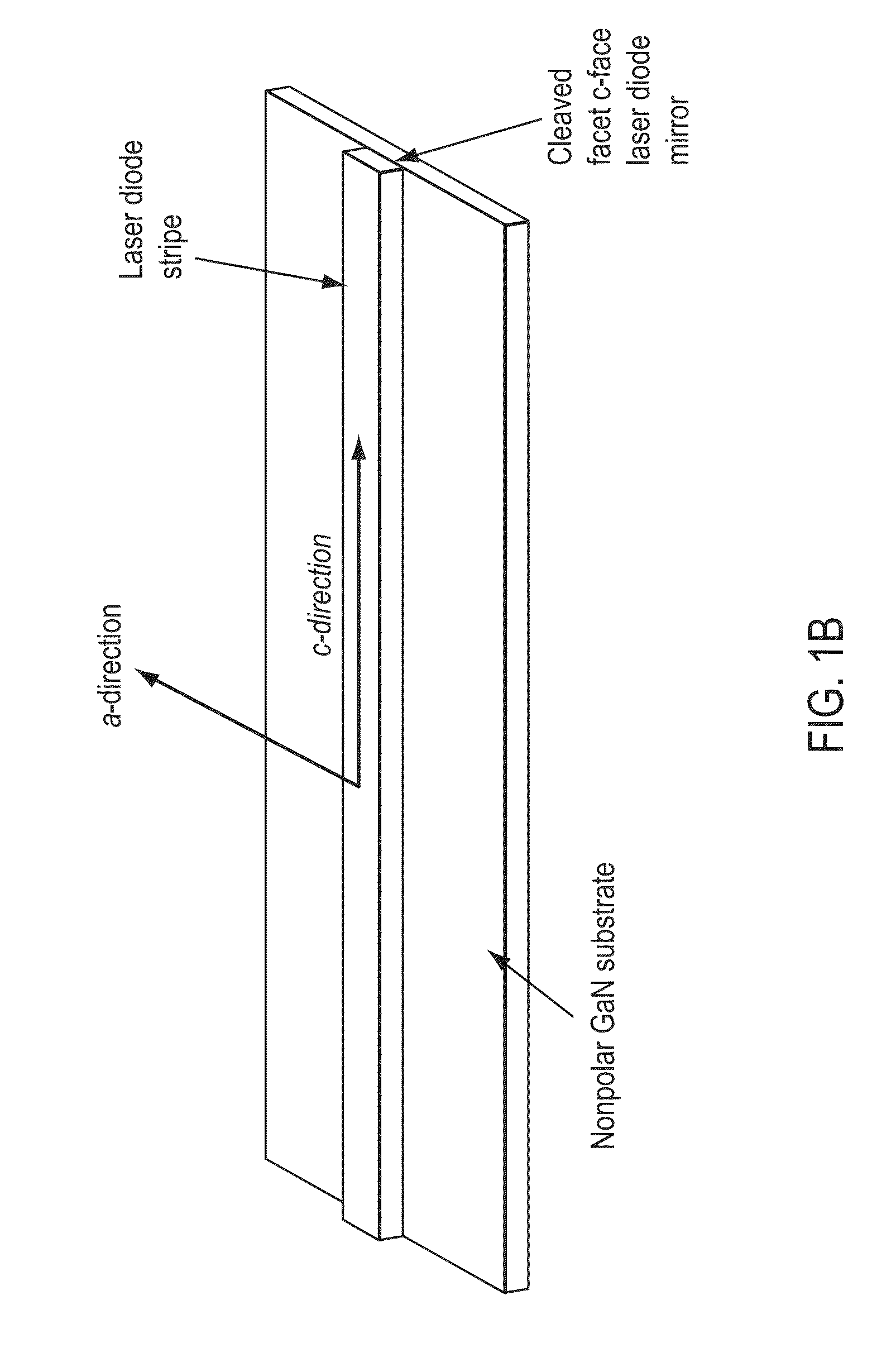
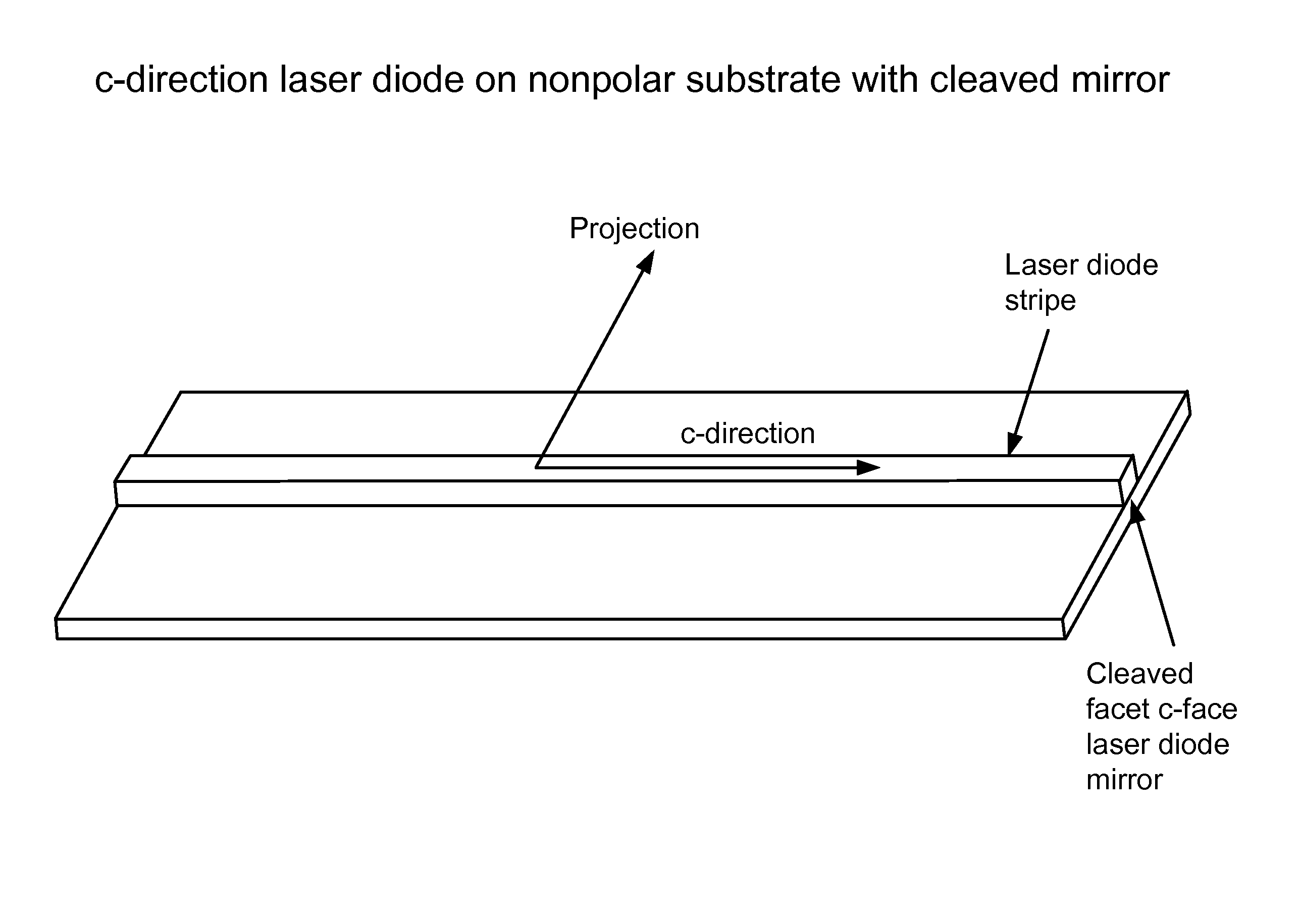
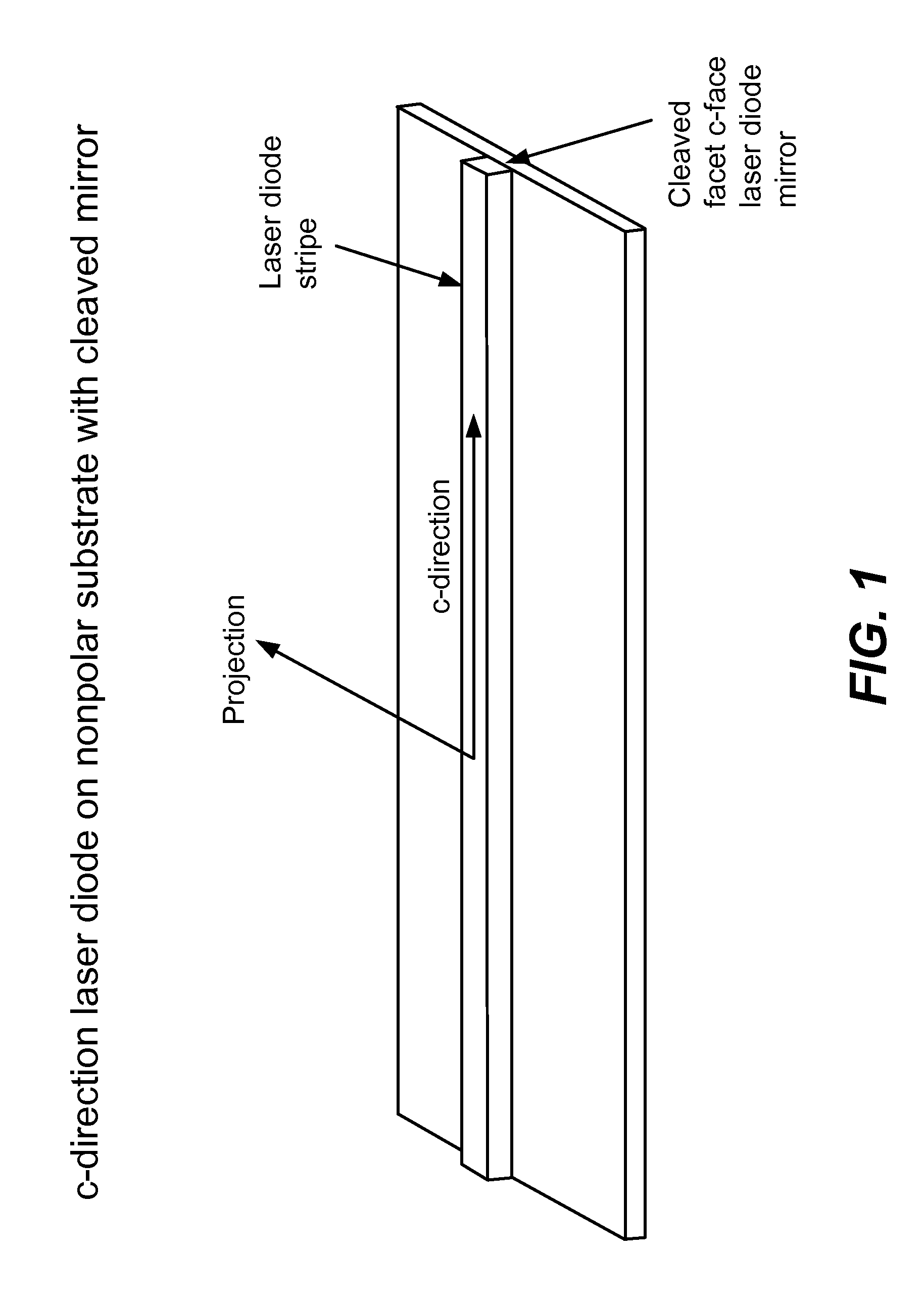
An optical device includes a gallium nitride substrate member having an m-plane nonpolar crystalline surface region characterized by an orientation of about −2 degrees to about 2 degrees towards (000-1) and less than about 0.5 degrees towards (11-20). The device also has a laser stripe region formed overlying a portion of the m-plane nonpolar crystalline orientation surface region. A first cleaved c-face facet is provided on one end of the laser stripe region, and a second cleaved c-face facet is provided on the other end of the laser stripe region.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
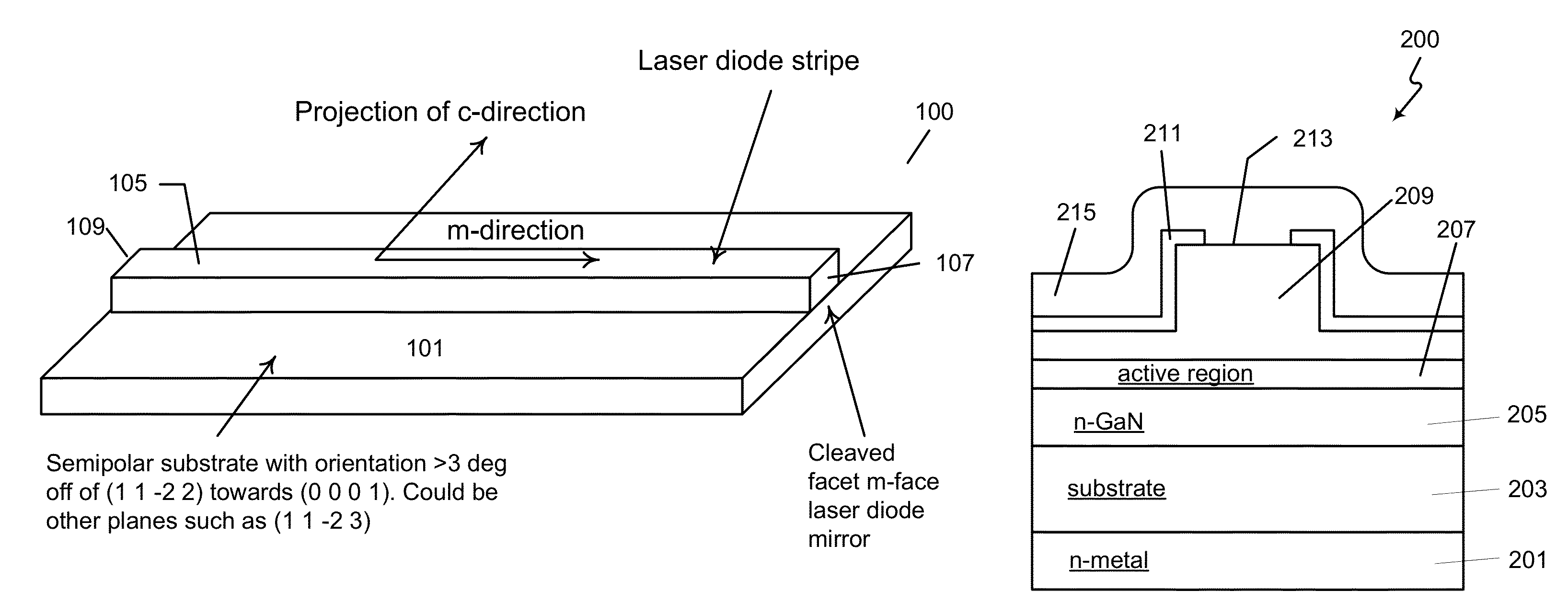
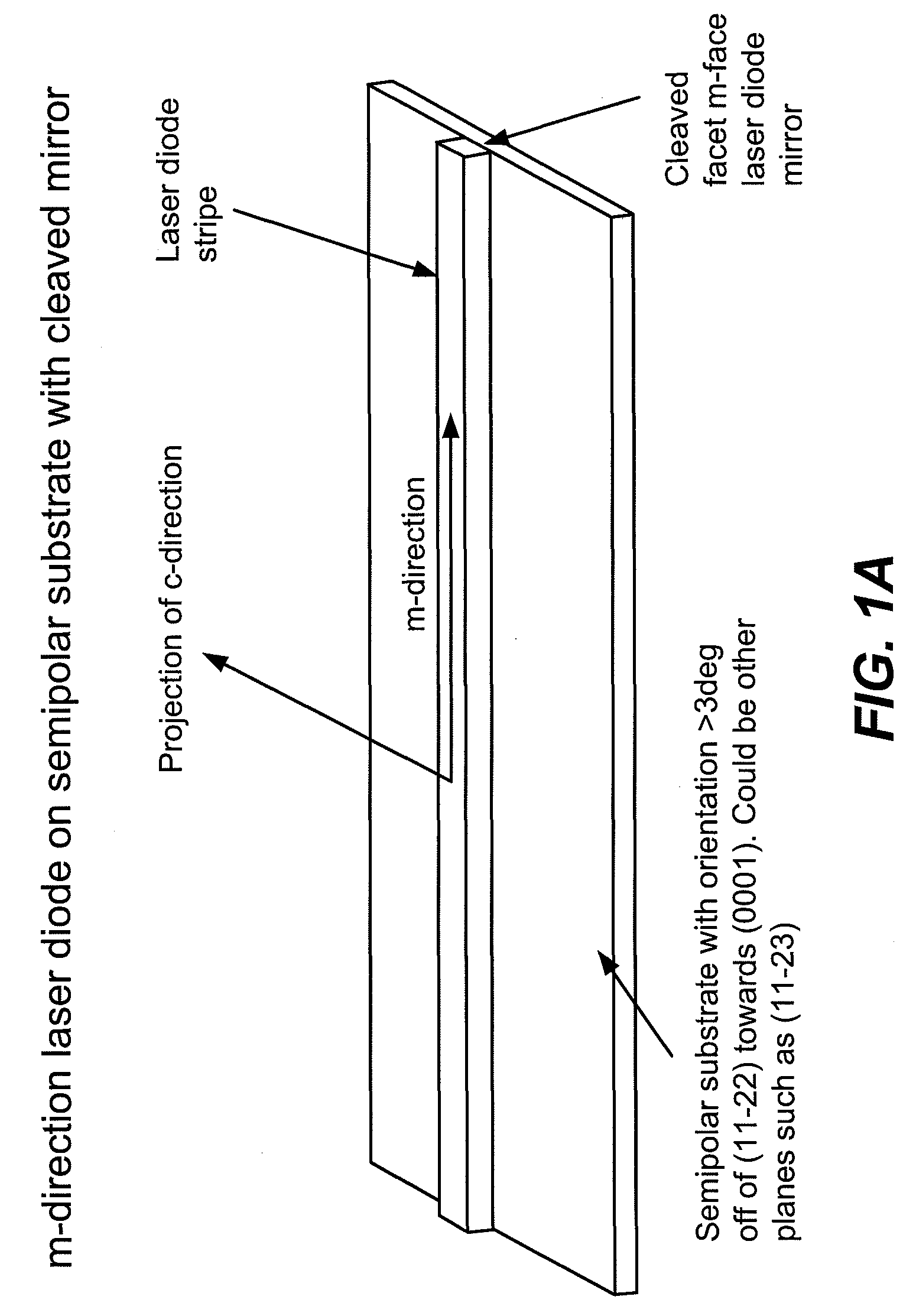
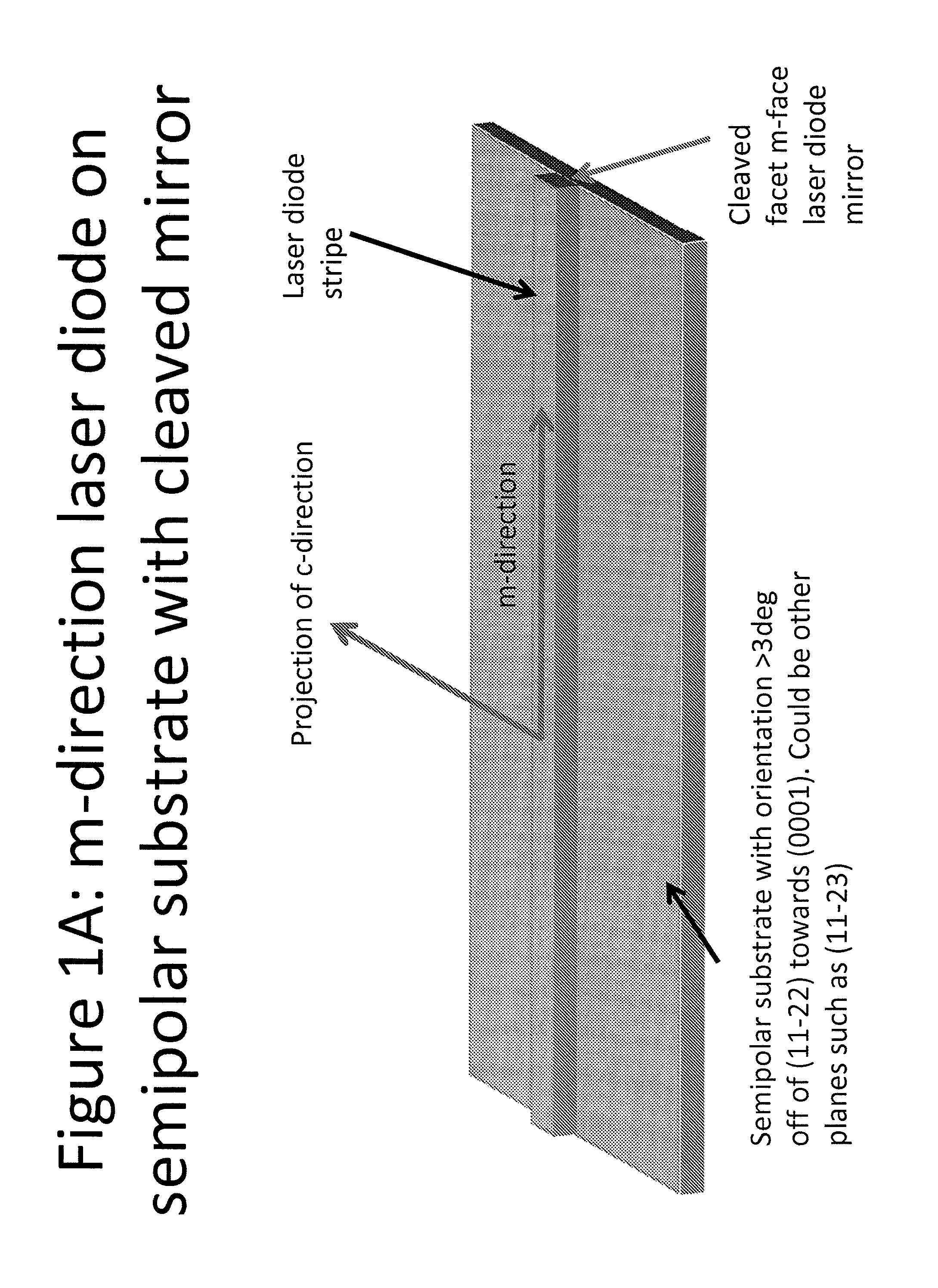
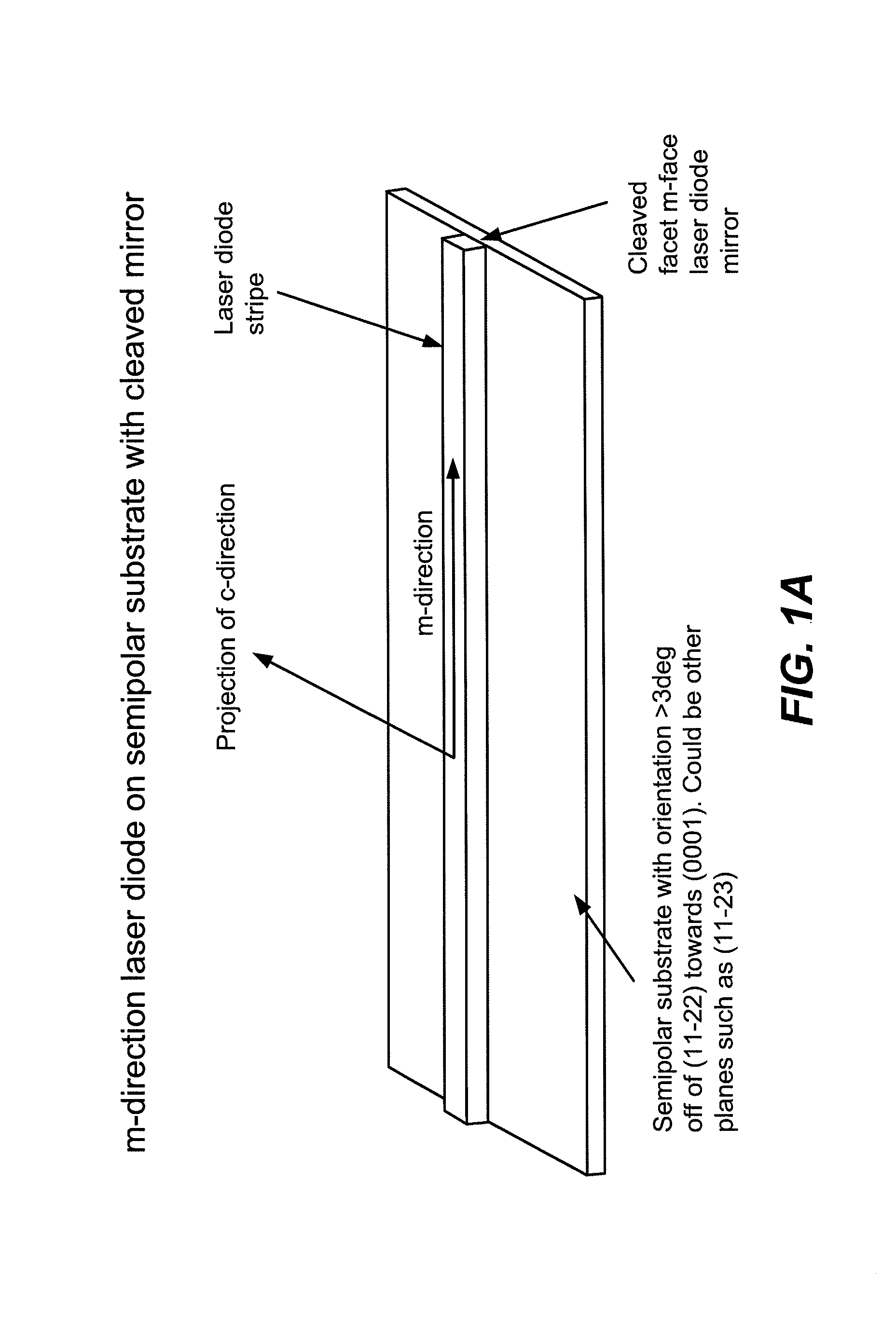
Optical device structure using miscut GaN substrates for laser applications
ActiveUS8422525B1Simple and cost-effectiveAchieve benefitsNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersLength waveGallium nitride
An optical device capable of emitting light having a wavelength ranging from about 490 to about 580 nanometers has a gallium nitride substrate with a semipolar crystalline surface region characterized by an orientation of greater than 3 degrees from (11-22) towards (0001) but less than about 50 degrees. A laser stripe formed on the substrate has a cavity orientation substantially parallel to the m-direction.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Optical device structure using GaN substrates and growth structures for laser applications of emissions of 500 nm and greater
ActiveUS8126024B1Simple and cost-effectiveAchieve benefitsLaser detailsNanoopticsLength waveLight emission
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Optical device structure using GaN substrates and growth structures for laser applications
ActiveUS8294179B1Simple and cost-effectiveCost-effectiveOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsWavelengthLight emission
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Optical device structure using GaN substrates and growth structure for laser applications
ActiveUS8416825B1Simple and cost-effectiveCost-effectiveLaser detailsNanoopticsWavelengthLight emission
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
Optical Device Structure Using GaN Substrates and Growth Structures for Laser Applications
ActiveUS20130044782A1Improve efficiencyIncrease costLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLength waveLight emission
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
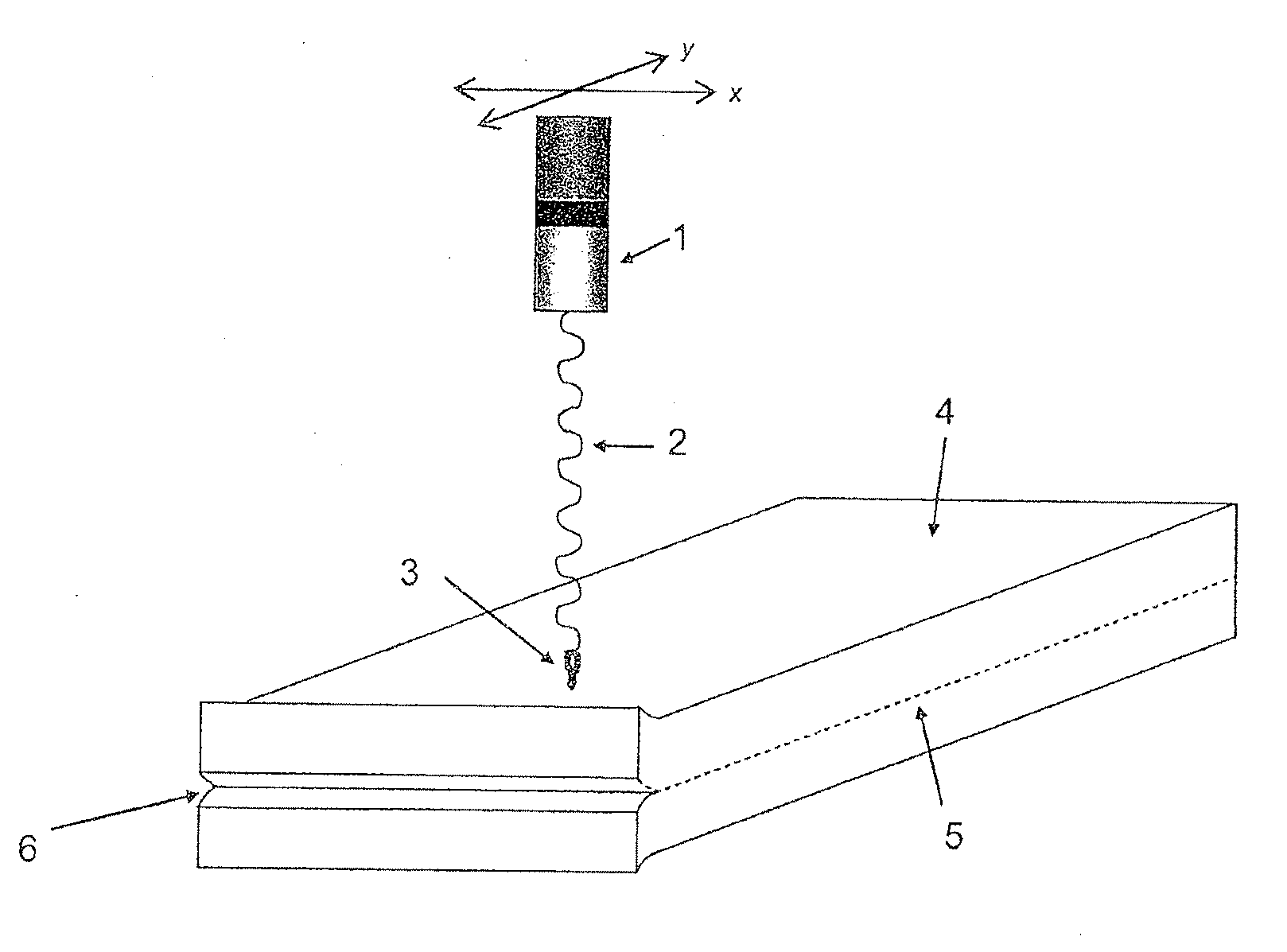
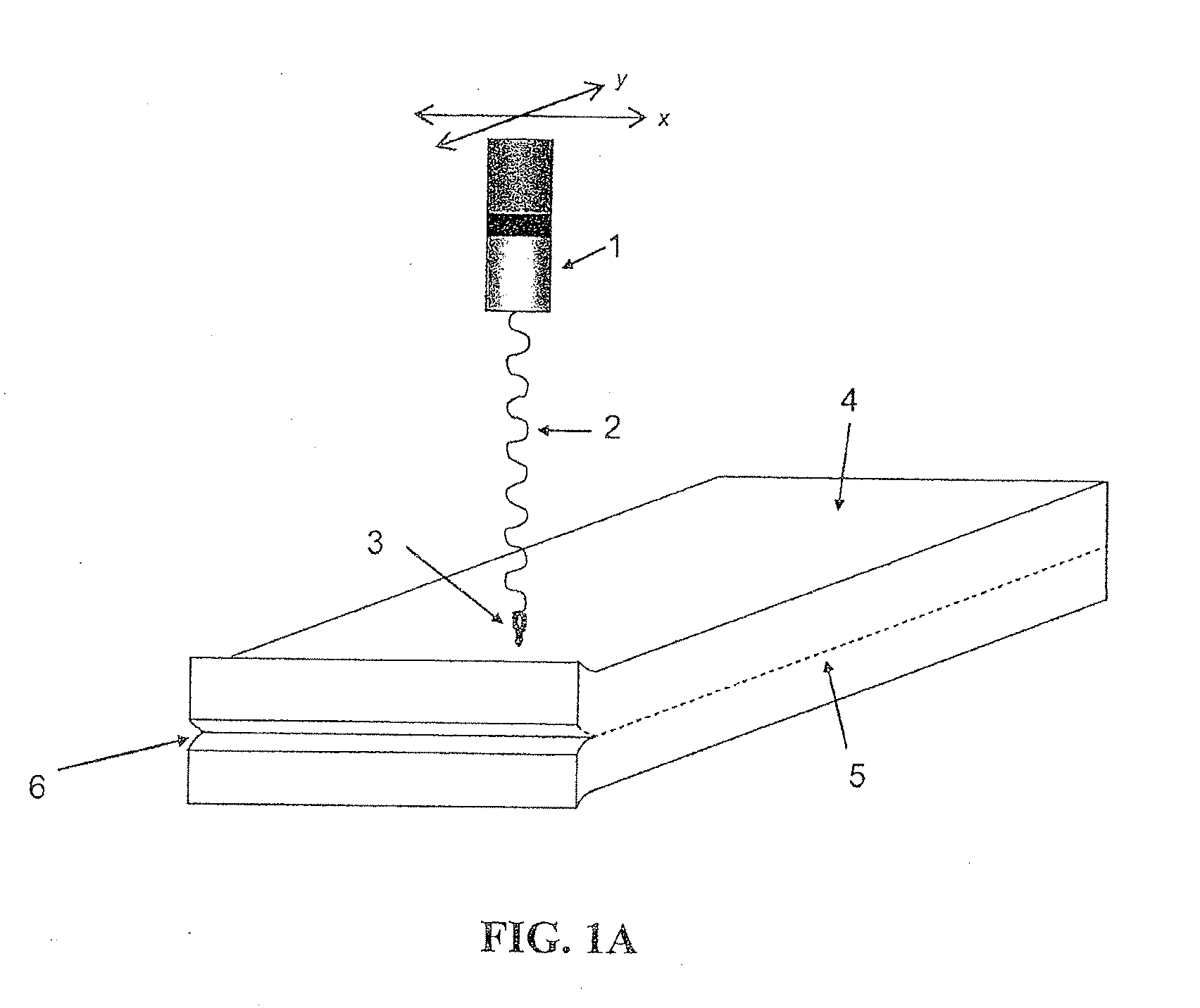
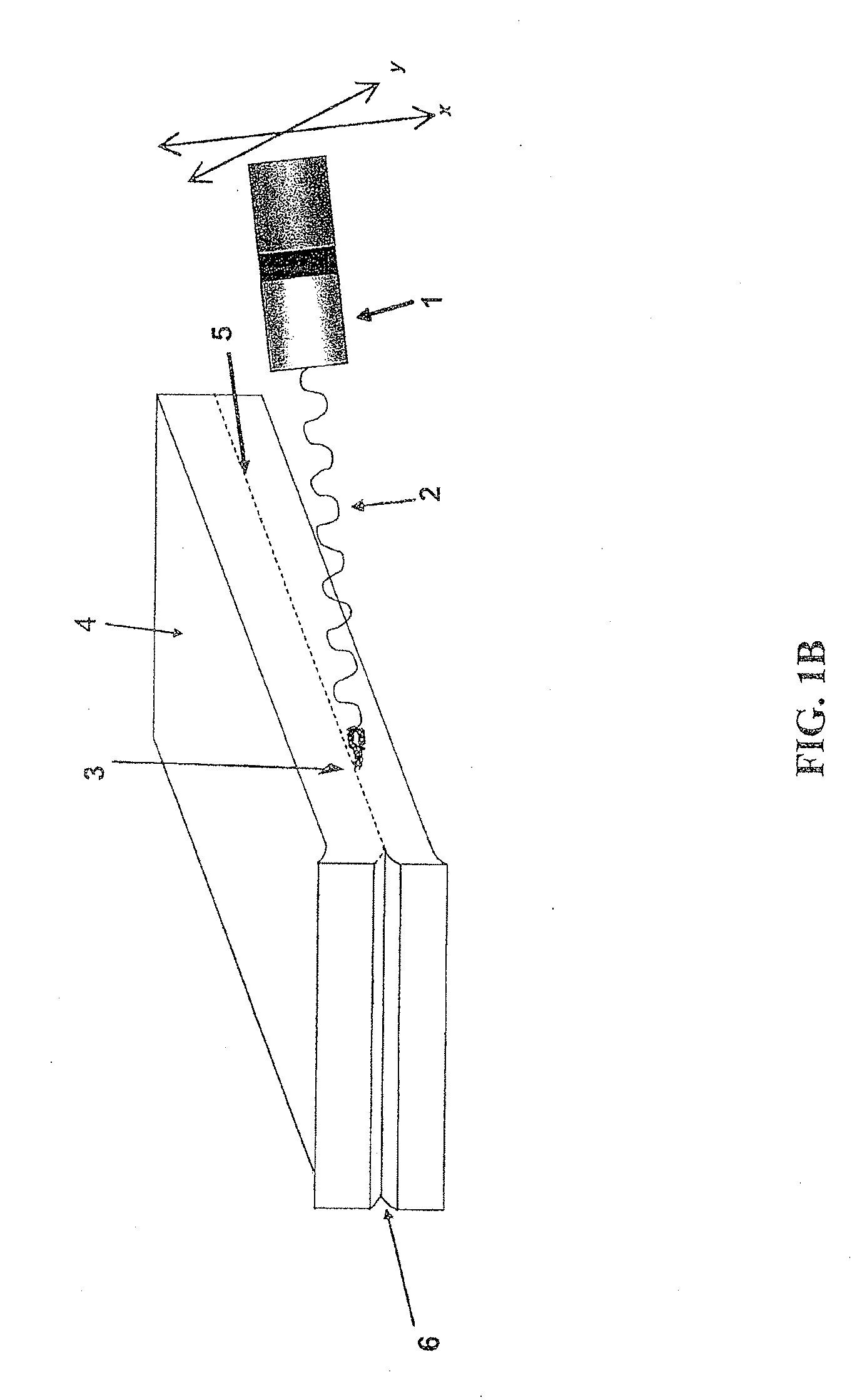
Lamp for laser applications
ActiveUS20120026721A1Reduce heat buildupGood optical performanceVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourceOptical radiationOptoelectronics
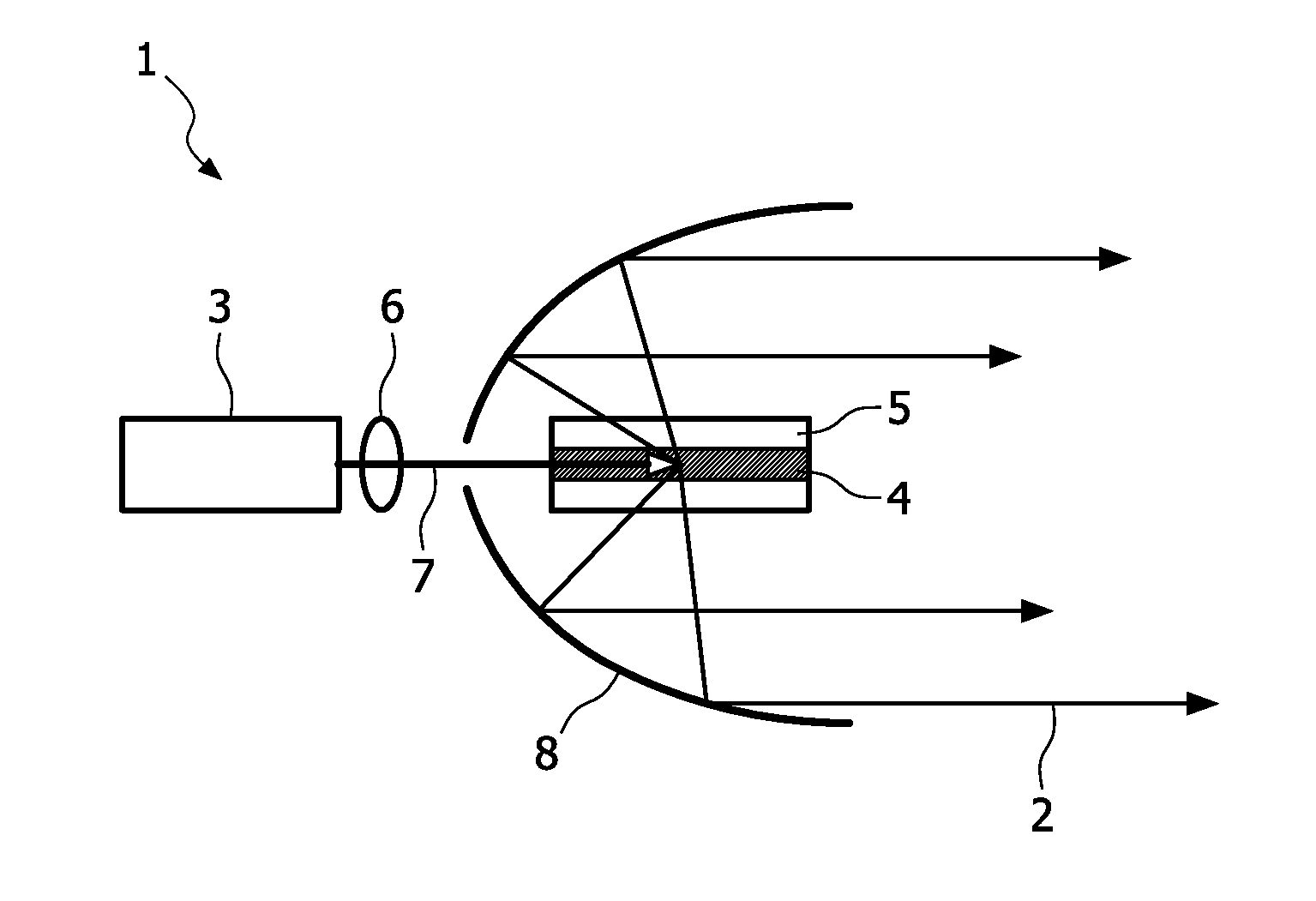
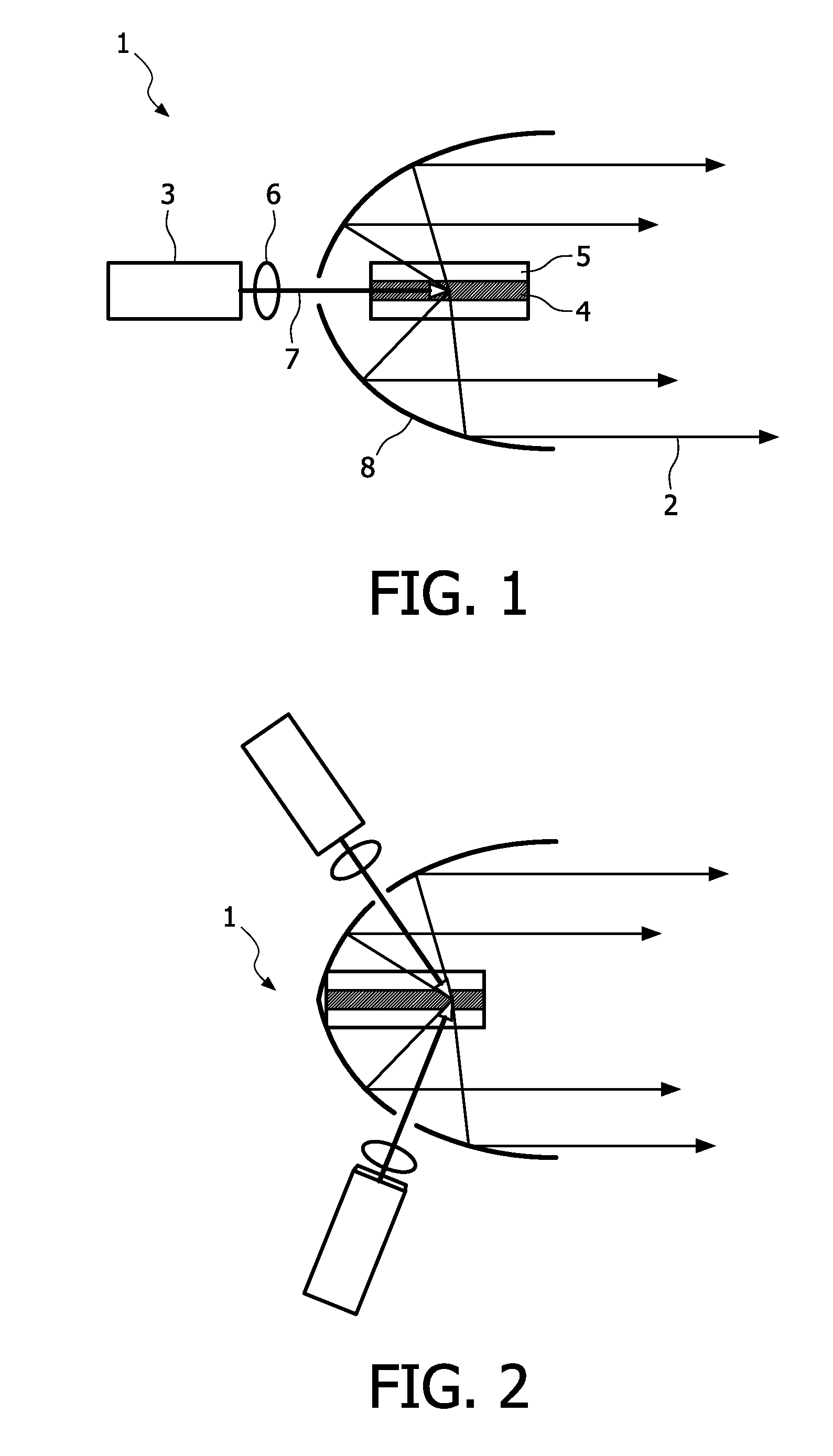
The invention relates to a lamp and a method, preferably adapted for generating high power in laser applications. The lamp (1) comprises a source (3) adapted for emitting optical radiation along an optical path and a holder (5) comprising a fluorescent body (4), wherein the holder (5) is arranged in the optical path, a collecting unit (8) is provided which is adapted for transmitting at least a portion of optical radiation emitted by the fluorescent body (4) to an output of the lamp (1), and the fluorescent body (4) comprises a shape being elongated in a predetermined direction. In this way, a small spot and little divergence is provided in conjunction with good heat dissipation leading to a high optical performance.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
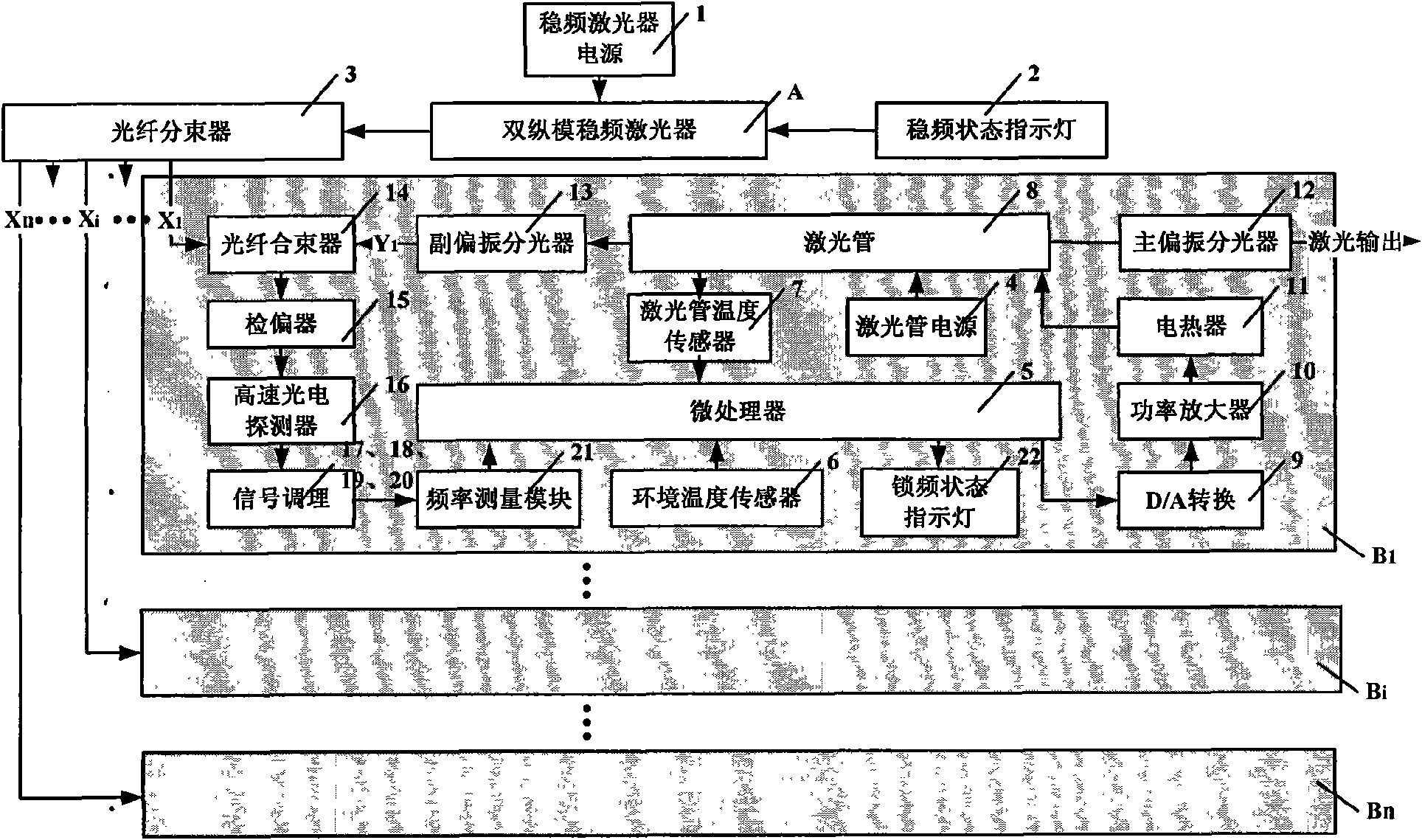
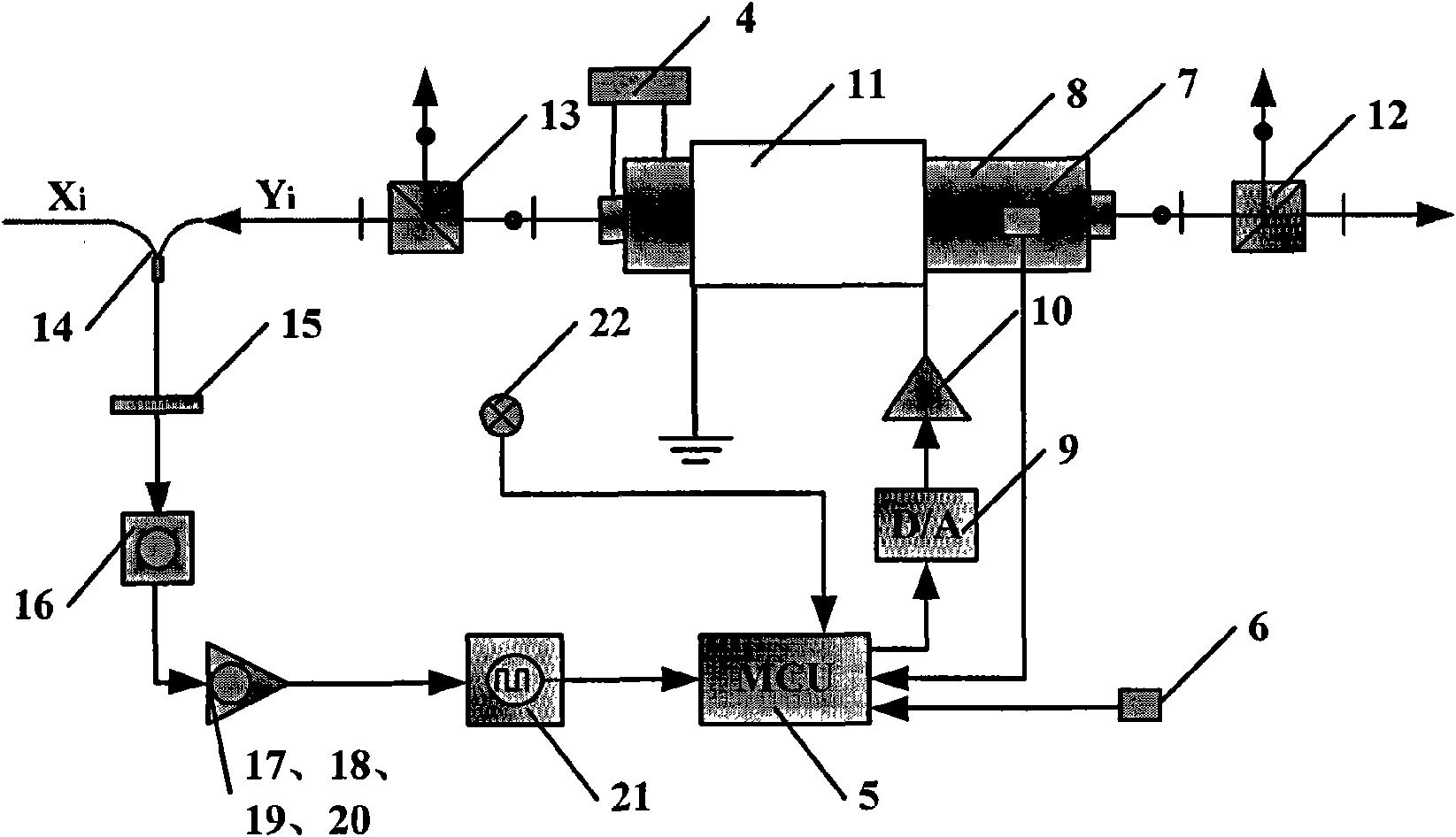
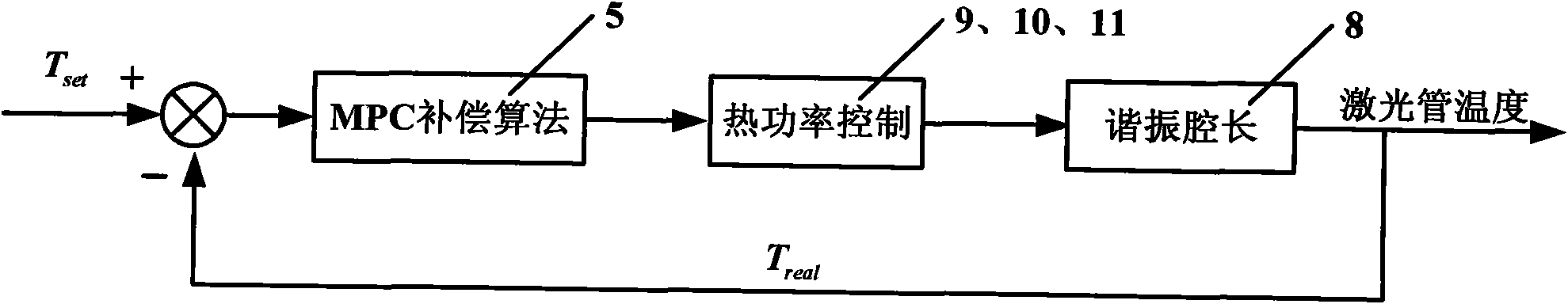
Double-longitudinal-mode laser heat frequency stabilization method and device based on iodine frequency stabilization reference light
InactiveCN101615755AGood effectOvercome environmental problemsLaser detailsPulse automatic controlFrequency stabilizationCenter frequency
A double-longitudinal-mode laser heat frequency stabilization method and a device based on the iodine frequency stabilization reference light belong to the application technical field, the invention takes the center frequency of the iodine frequency stabilization laser with a relative frequency accuracy being 10<-11> as a reference frequency, and leads the frequency of laser output by multi-double-longitudinal-mode lasers to keep one fixed difference with the reference frequency through regulating cavity length, so that the relative frequency accuracy of the double-longitudinal-mode laser is improved from 10<-7>-10<-8> to 10<-9>, the frequency consistency of multi-double-longitudinal-mode lasers is improved from 10<-7> to 10<-9>, therefore, the problems that the relative frequency accuracy of the double-longitudinal-mode laser can not exceed 10<-8> and the frequency consistency of multi-double-longitudinal-mode lasers is poor are solved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
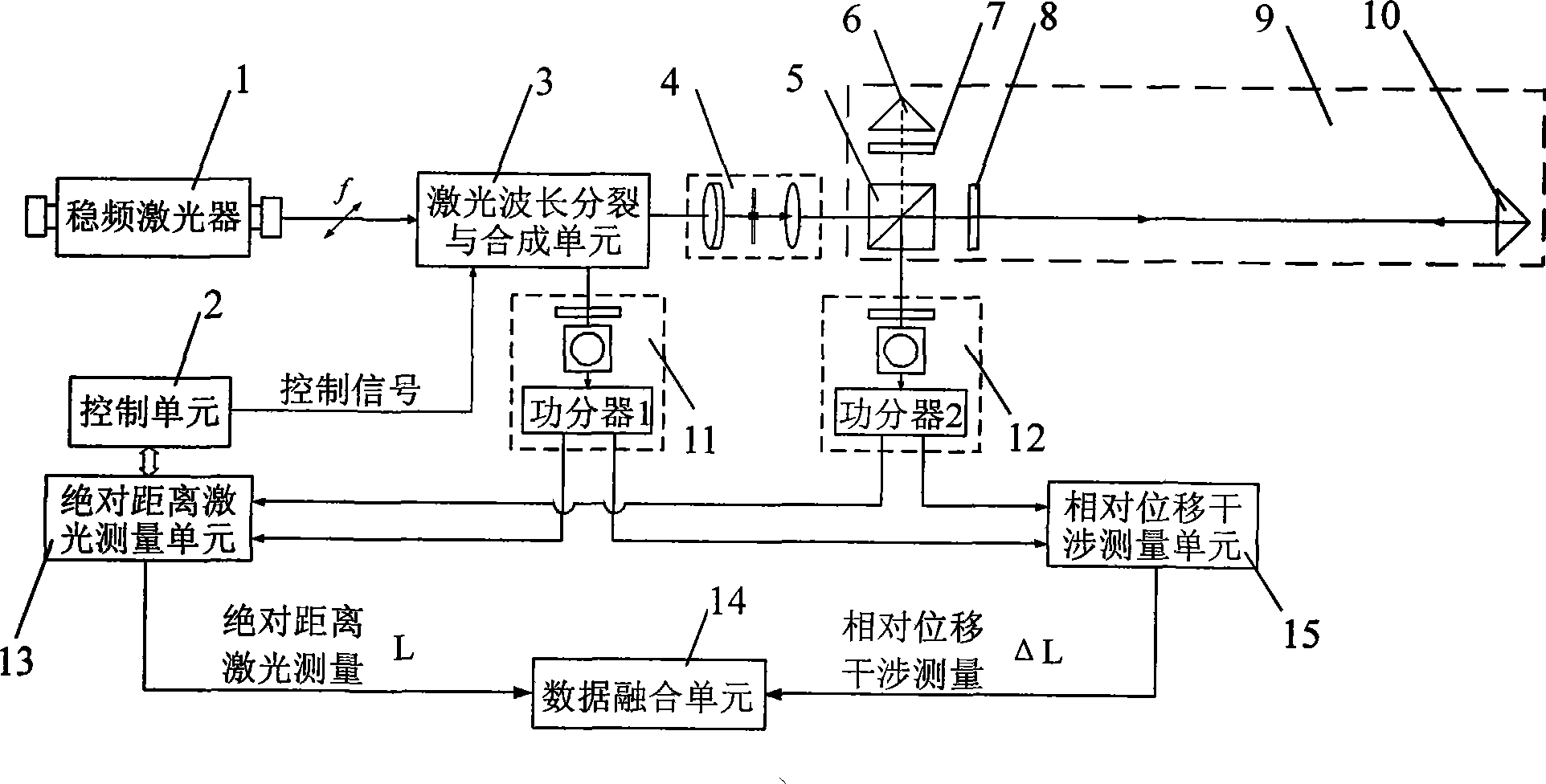
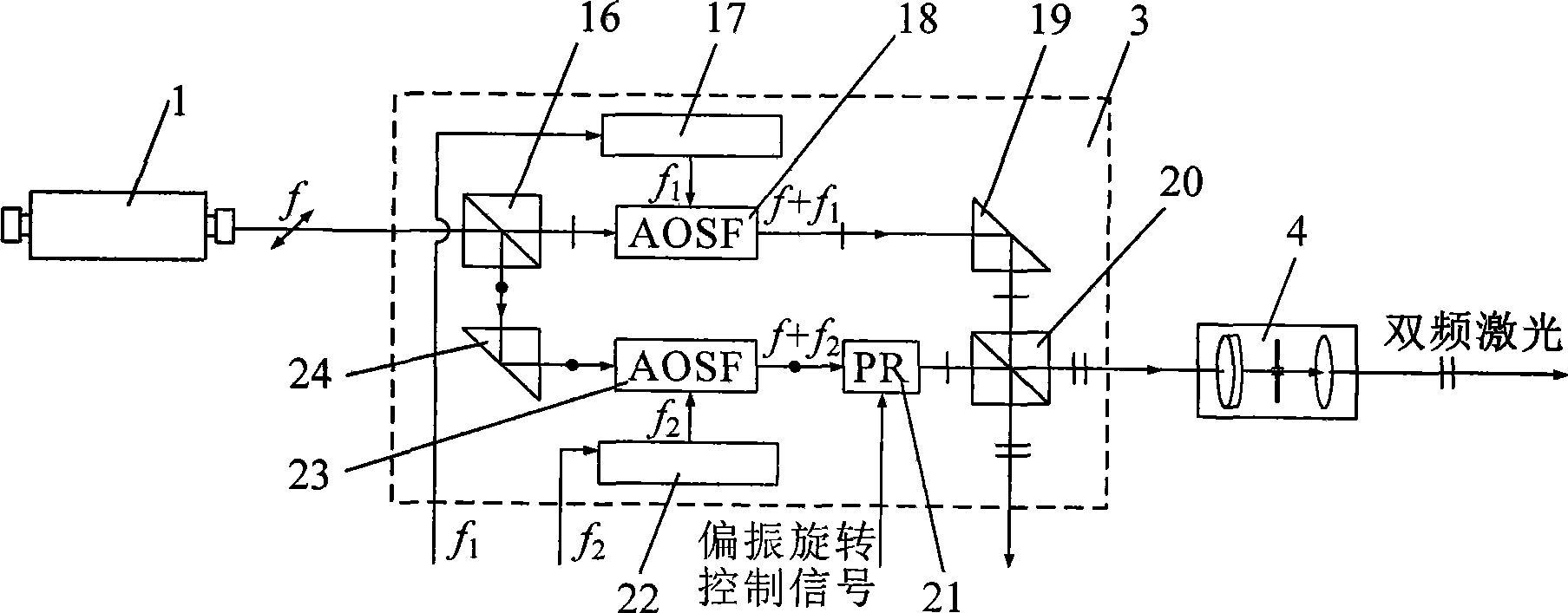
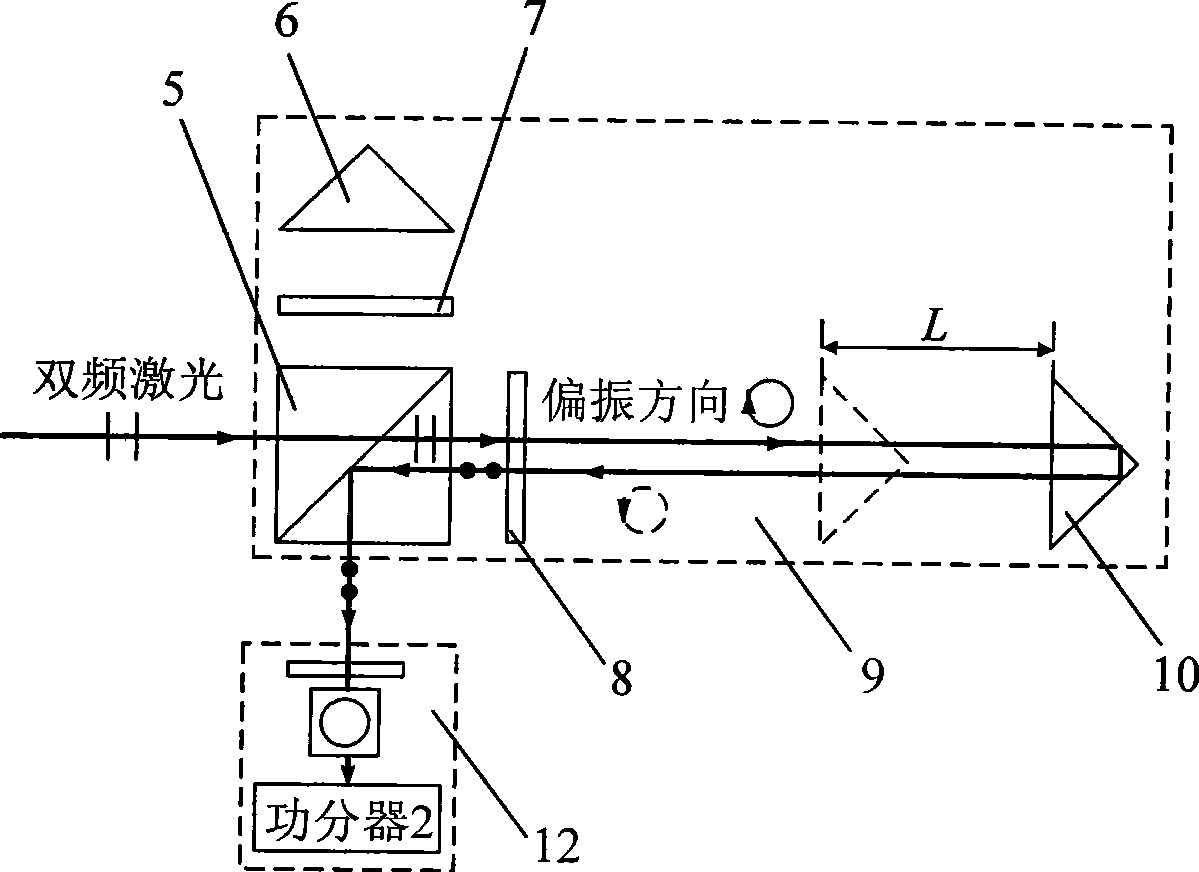
Dual-frequency laser ranging method and device based on polarization state regulation and wavelength synthesis
ActiveCN101533096AGood effectSimple structureElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingDual frequency
A dual-frequency laser ranging method and a device based on polarization state regulation and wavelength synthesis belong to the technical field of laser application. In absolute distance measurement and relative displacement measurement, the method adopts the same frequency stabilized laser as a measuring light source, realizes organic integration of absolute distance measurement and relative displacement dynamic measurement through the control of a polarization rotator and wavelength tuning of acoustooptic frequency shifters and simultaneously meets the requirements on extra long distance precise measurement and fast local displacement ultraprecise monitoring. The device comprises an acoustooptic frequency shifter A and an acoustooptic frequency shifter B, a reflecting mirror A and a reflecting mirror B, a frequency control unit A and a frequency control unit B, a polarization rotator, a polarization splitter B and a laser wavelength split and synthesis unit formed by partial optical splitters. The invention has the advantages of both extra long distance ultraprecise measurement capability and integral formation, etc.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Apparatus for implementing orbit angular momentum state super position and modulation
InactiveCN101251655AAchieve overlayGood for long-distance transmissionDiffraction gratingsNon-linear opticsBeam splittingPolarizer
The invention relates to a device for realizing superposition and modulation of orbital angular momentum states of light beams, belonging to the laser application technical field. The invention consists of a laser, a polarizer, a one-fourth wave plate, a diffraction grating, a Fourier lens, a polarized beam-splitting prism, two Dove prisms, three holophotes and a pinhole diaphragm, wherein, firstly, an optical system which takes the diffraction grating and the Fourier lens as core elements is adopted to generate a plurality of bundles of light beams which are equidistantly distributed on the circumference which takes an optical axis of incident light as the center and are positioned in different orbital angular momentum states; secondly, an optical system which consists of the polarized beam-splitting prism, the holophotes and the rotatable Dove prisms is adopted to decompose an optical field into field components which rotate towards the opposite direction; thirdly, the field components are superposed, and superposition of required orbital angular momentum states is realized and then superposition and modulation of the orbital angular momentum states are realized. The device for realizing superposition and modulation of the orbital angular momentum states of the light beams has application value in the free space optical communication field.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
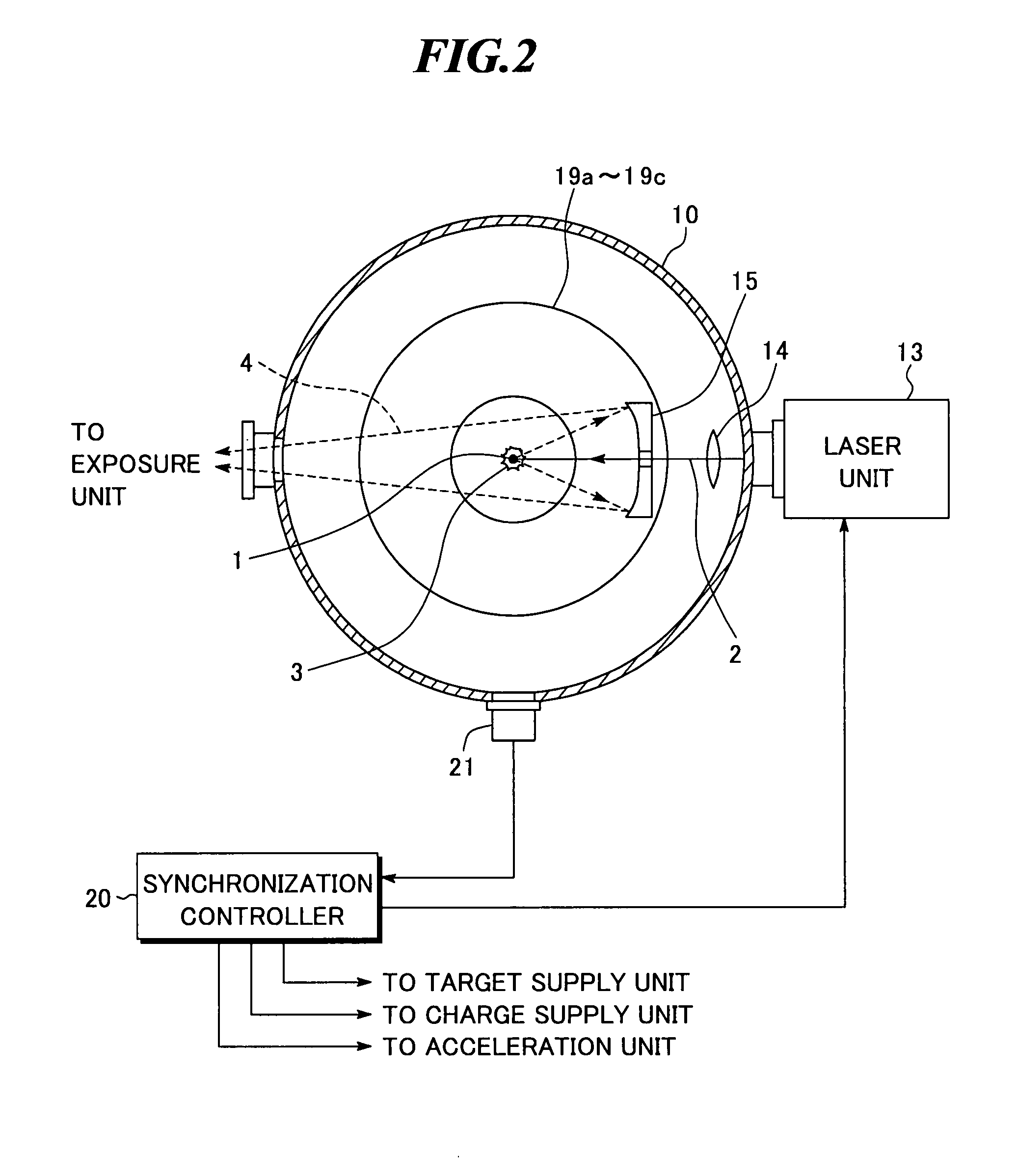
Extreme ultra violet light source device
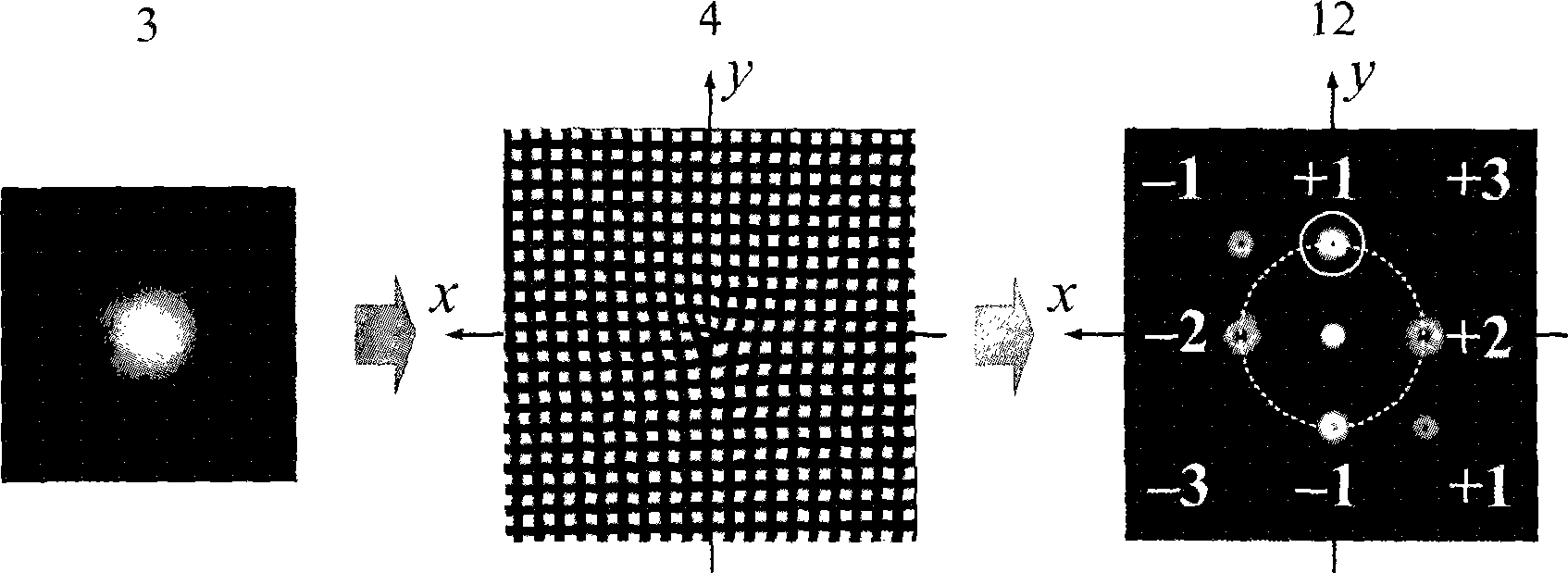
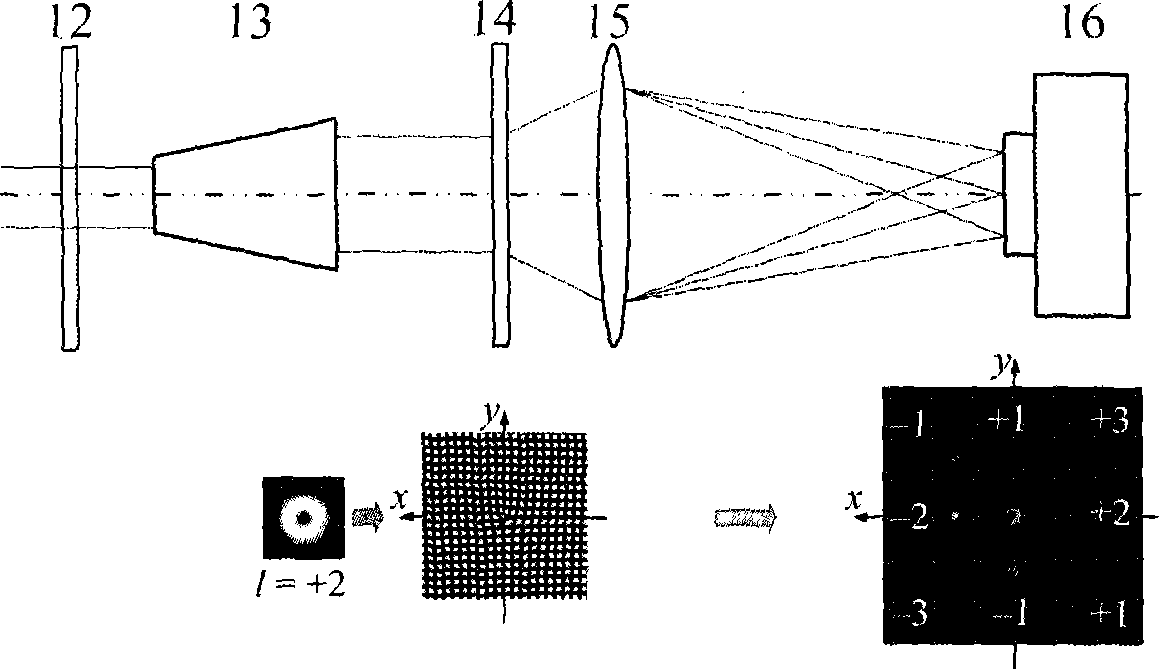
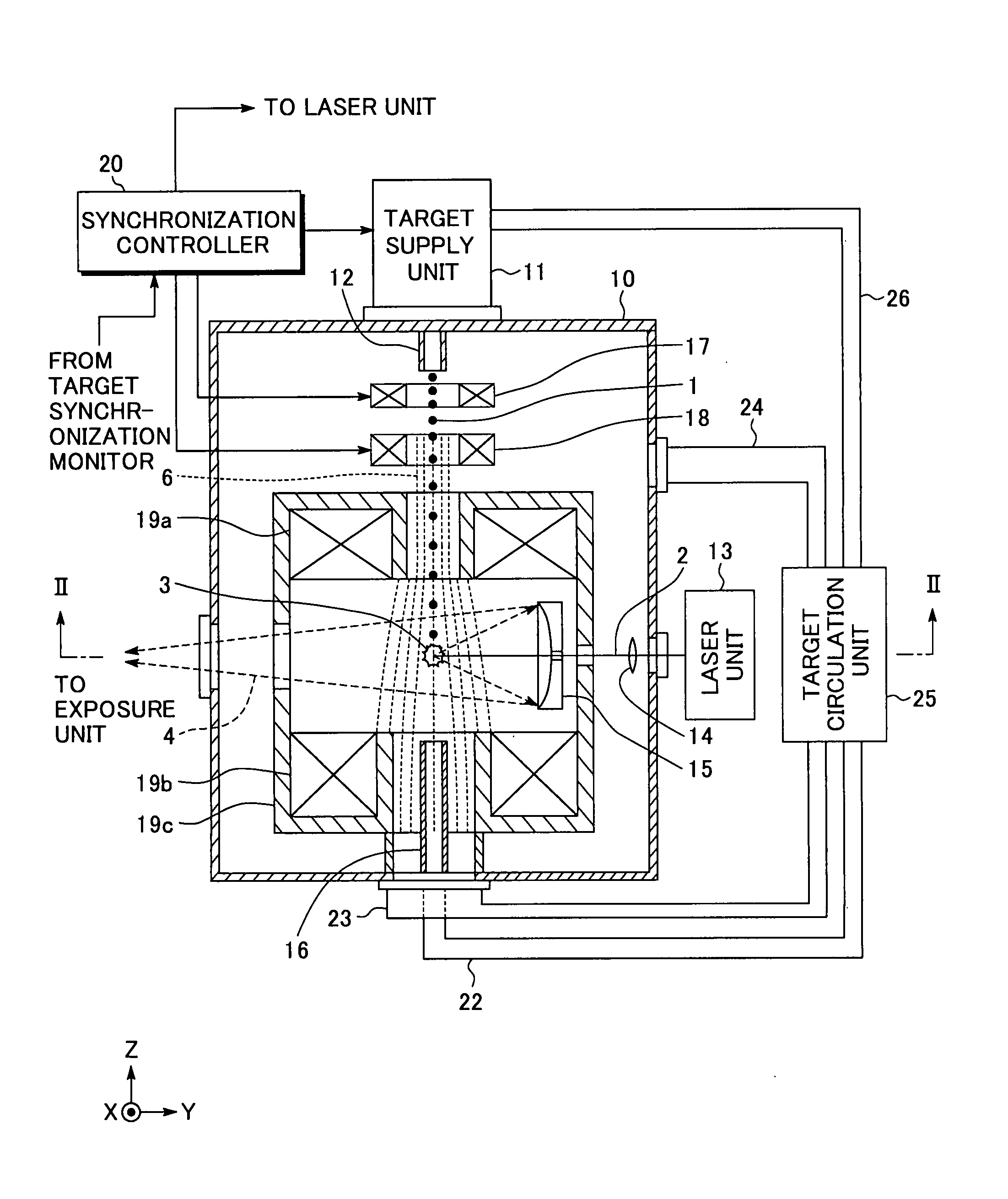
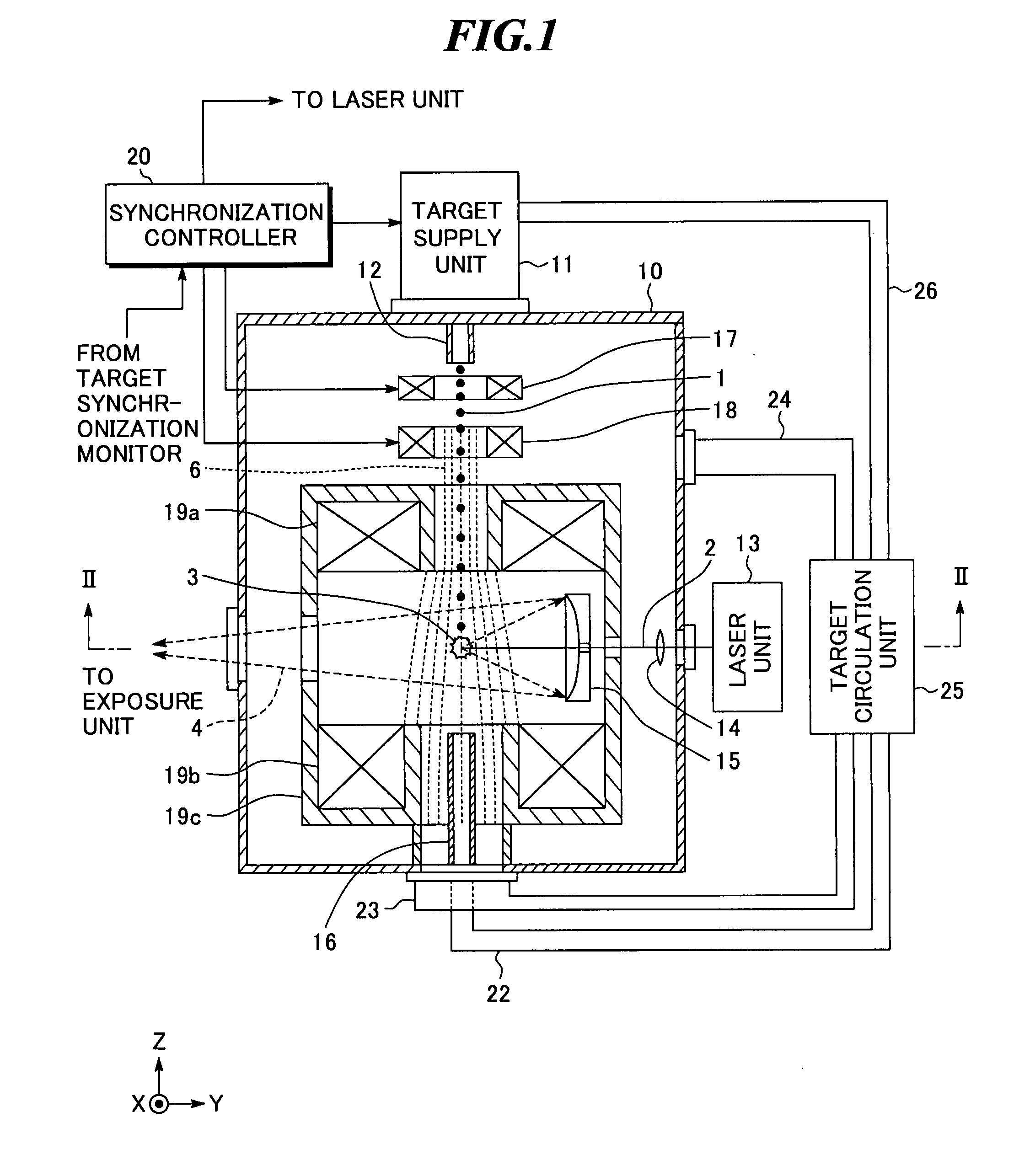
InactiveUS20080035865A1Increase speedAvoid changeRadiation pyrometryLight therapyMagnetic fluxAtomic physics
An extreme ultra violet light source apparatus in which both a mechanism of supplying a droplet target to a laser application position at a high speed and a mechanism of trapping charged particles generated from plasma are managed without disturbing a track of the target. The apparatus includes: a target nozzle that injects a target material toward a plasma generation point; an electric charge supply unit that charges the injected target material; an acceleration unit that accelerates the charged target material; a laser oscillator that applies a laser beam to the target material at the plasma generation point to generate plasma; and electromagnets that form a magnetic field at the plasma generation point such that the magnetic field has substantially straight lines of magnetic flux in substantially parallel with a traveling direction of the target material in the track of the target material.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Double-longitudinal-mode laser frequency-offset- lock method and device based on cavity length thermal regulation
InactiveCN101615756AGood effectShorten warm-up timeLaser detailsPulse automatic controlFrequency stabilizationPower balancing
A double-longitudinal-mode laser frequency-offset-lock method and a device based on cavity length thermal regulation belong to the application technical field; the invention takes the frequency of laser output by a power balanced type double-longitudinal-mode frequency stabilization laser A as a reference frequency, and simultaneously leads the frequency of laser output by the double-longitudinal-mode laser A with n being more than or equal to B1, B2,..., Bn to keep one fixed difference with the reference frequency, thus ensuring that the laser output by the double-longitudinal-mode laser B1, B2,..., Bn has uniform frequency value, the frequency stability and frequency consistency of the double-longitudinal-mode laser can reach 10<-8>, thereby overcoming the shortcoming that the frequency consistency between frequency stabilization lasers only reaches 10<-6>-10<-7> in the traditional frequency stabilization lasers.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Gauss laser beam shaping method and device and precise laser micropore processing device
ActiveCN104570363AIncrease profitImprove processing efficiencyMountingsLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
The invention relates to the field of laser application, and in particular relates to a Gauss laser beam shaping method and a Gauss laser beam shaping device and a precise laser micropore processing device. A beam expanding device, a shaping device, an initial focusing lens, a hole diaphragm, a collimation device, a light beam deflection device and a focusing lens are sequentially arranged along the light path, wherein the Gauss laser beam is shaped as a flat laser beam by the shaping device after being expanded through the beam expanding device, the flat laser beam is collimated by the collimation device after being intercepted by the hole diaphragm and initially focused by the initial focusing lens, a transmission direction of the flat laser beam is changed through the light beam deflection device, and then the flat laser beam is focused through the focusing lens to obtain the laser beam for micropore processing. The Gauss laser beam is output after being shaped as the flat laser beam, the utilization rate and the processing efficiency of the laser are improved, and the energy loss is reduced; meanwhile, when the flat laser beam obtained through the focusing of the focusing lens is used for micropore processing, the hole margin of each of a through hole and a blind hole is smooth, the taper of the hole is reduced, the bottom damage of the blind hole is avoided, and the blind hole with a flat bottom is obtained.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD
Image processing method and image processing apparatus
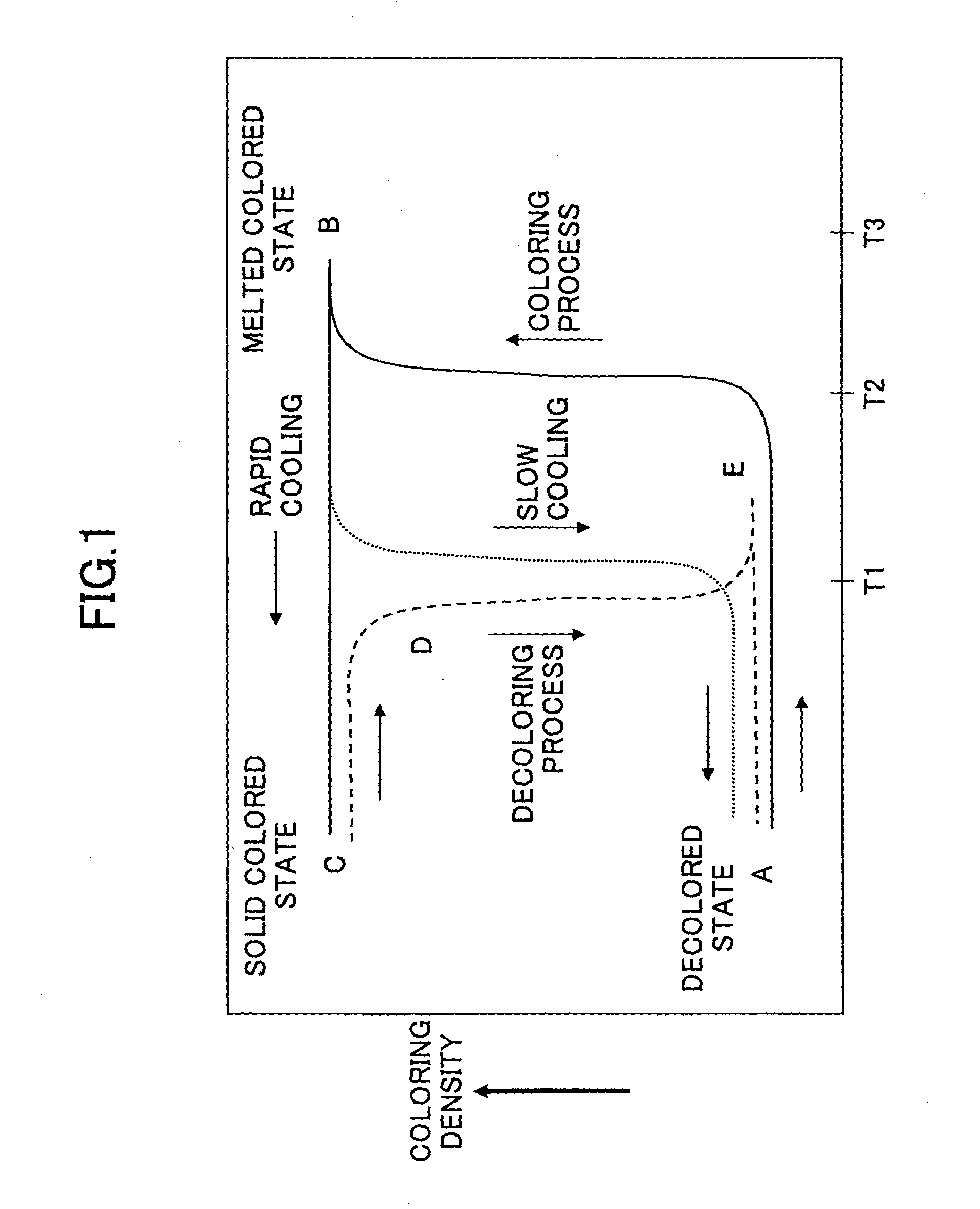
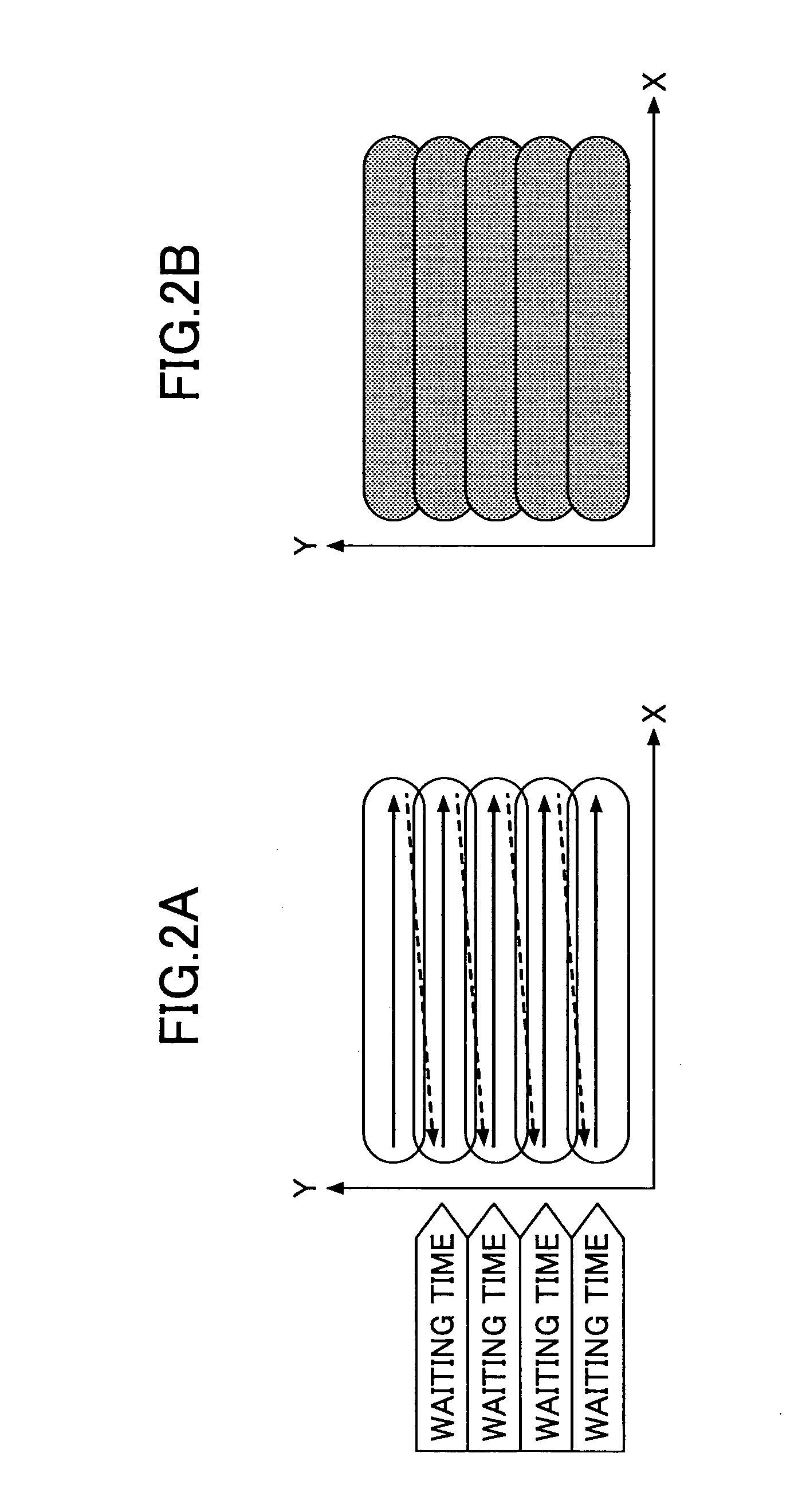
InactiveUS20070225162A1High cycle durabilityImprove erasabilityAblative recordingPrinting after-treatmentImaging processingImage recording
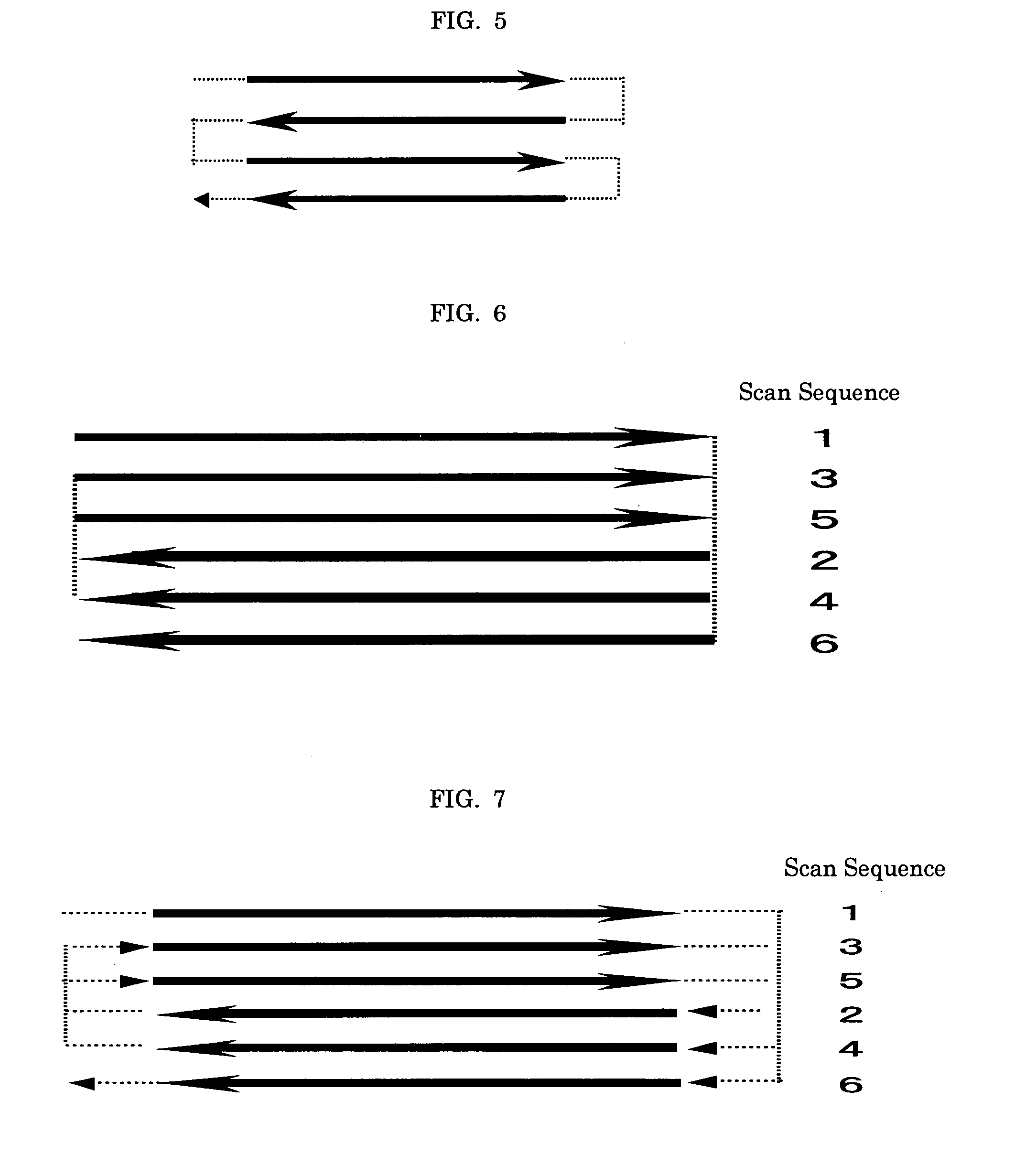
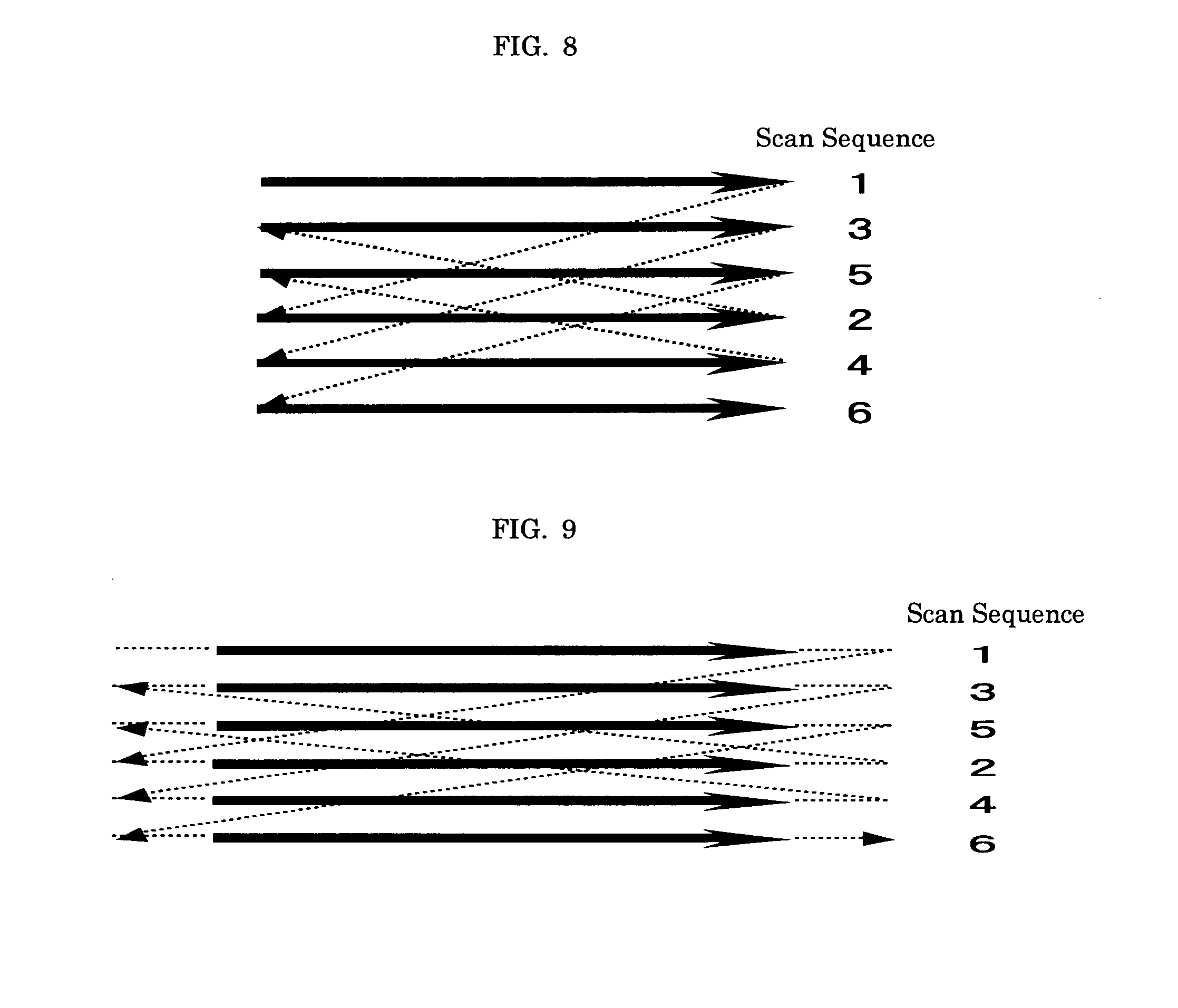
To provide an image processing method including at least one of an image recording step and an image erasing step, wherein (1) laser beams are swept in the same direction and laser scanning involves a period where laser application is discontinued, (2) laser beams are swept in alternating directions and the laser scanning involves a period where laser application is discontinued, (3) laser beams are swept in alternating directions and laser scanning involves a period where laser application is discontinued, wherein the period involves no laser beam application from first laser scanning end point to second laser scanning point, or (4) laser beams are applied in alternating directions while avoiding continuous laser irradiation of nearby portions between adjacent laser beam lines, and laser scanning involves a period where laser application is discontinued.
Owner:RICOH KK
Device and method for laser shot blasting reinforcement of hard and brittle material
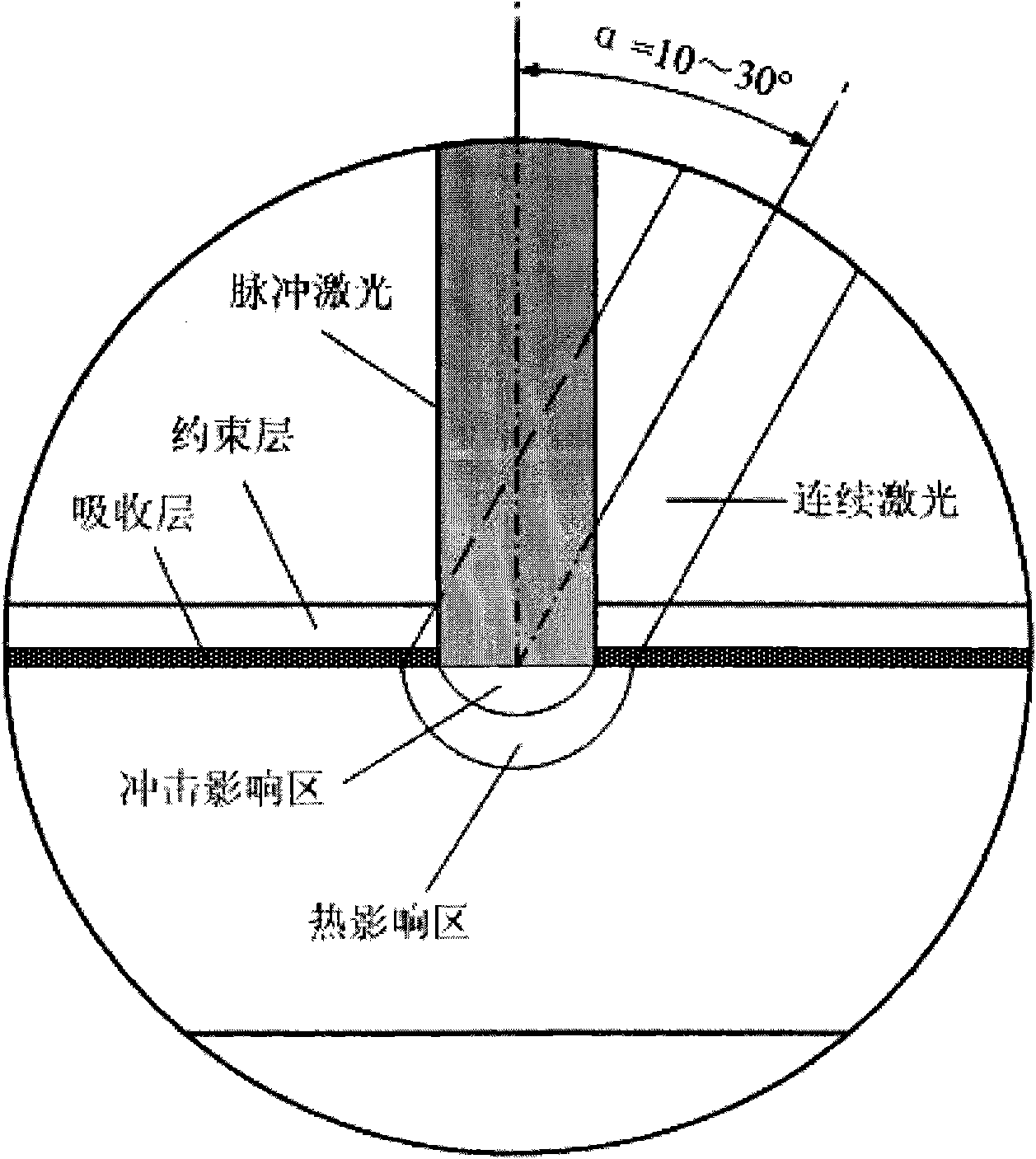
The invention discloses a device and a method for laser shot blasting reinforcement of a hard and brittle material, and relates to the field of mechanical manufacture of hard and brittle material processing and laser application. The device comprises a laser aid heating system, a laser shot blasting reinforcement system, a workpiece clamp system, a computer numerical control system, a measurement feedback system and a protective gas circulating system. The method comprises a laser aid heating stage and a laser shot blasting reinforcement stage, namely performing aid heating treatment on the area to be reinforced by adopting high-power continuous laser, wherein for most metal materials, the plastic performance is improved along with the rise of temperature; and after the temperature of the heating area reaches a predetermined heating temperature, implementing laser shot blasting reinforcement treatment by adopting high-power pulse laser. The device and the method can implement the laser shot blasting reinforcement on the hard and brittle material so as to broaden the application range of the laser shot blasting reinforcement technology, and meanwhile compound the advantages of continuous laser and pulse laser so as to broaden the application field and the application prospect of laser manufacture.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
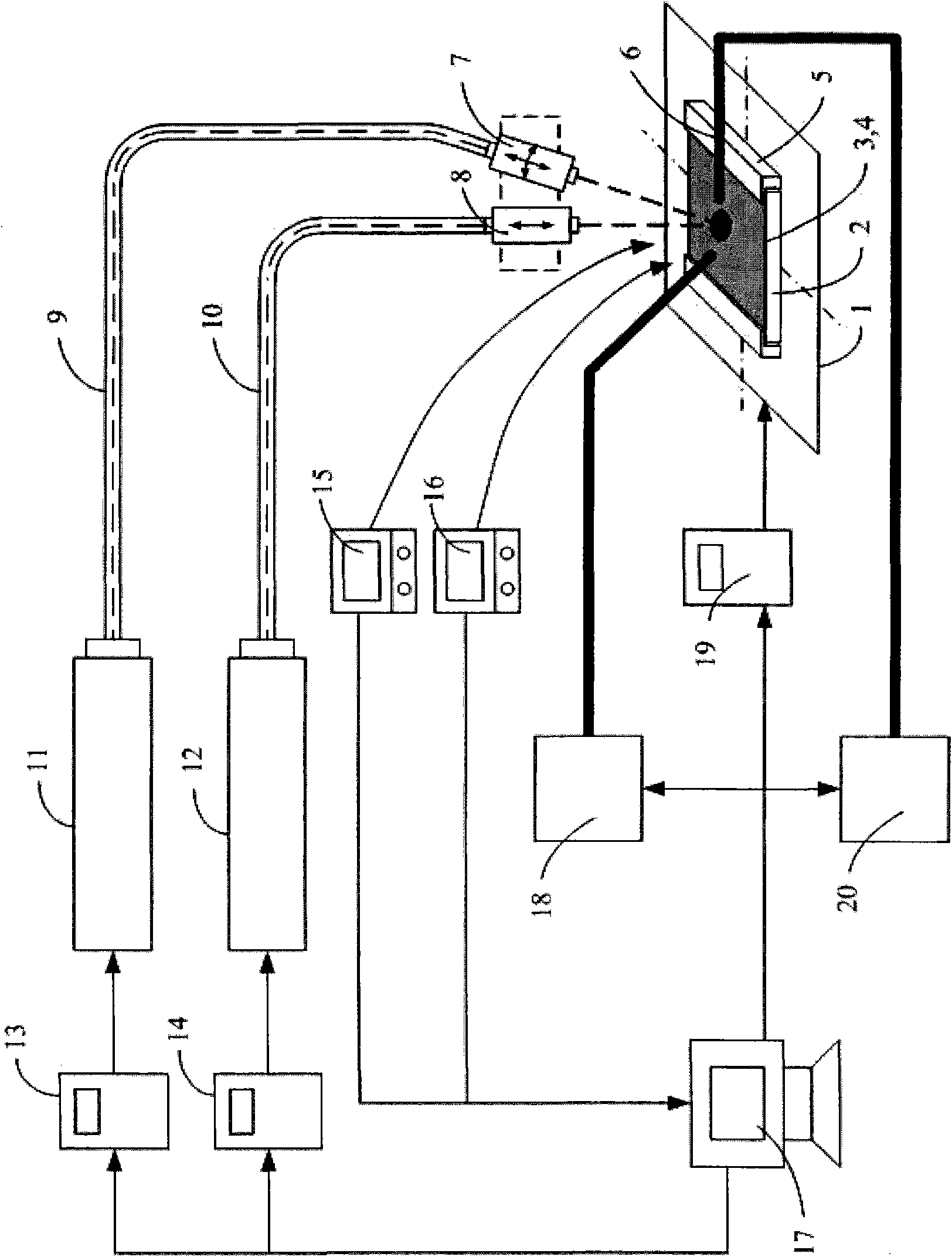
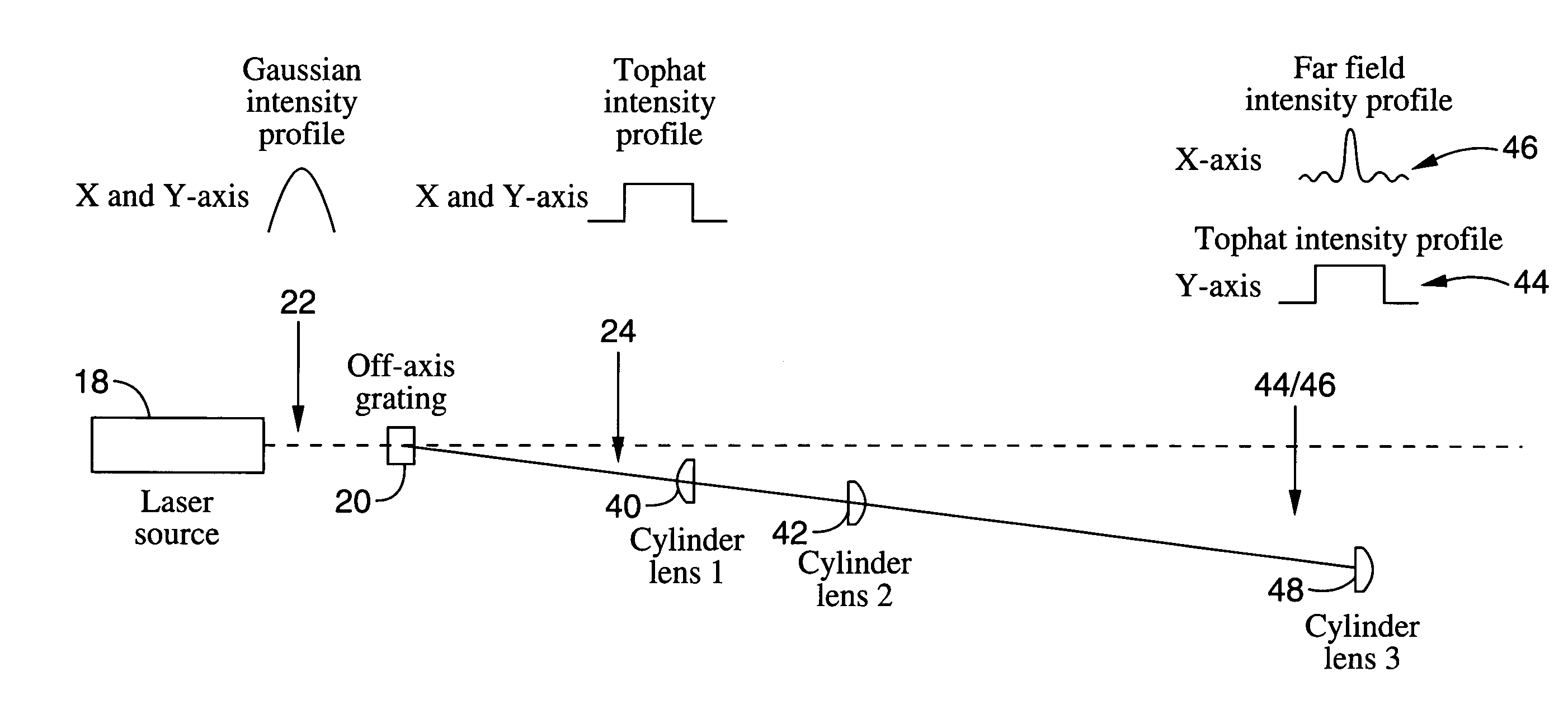
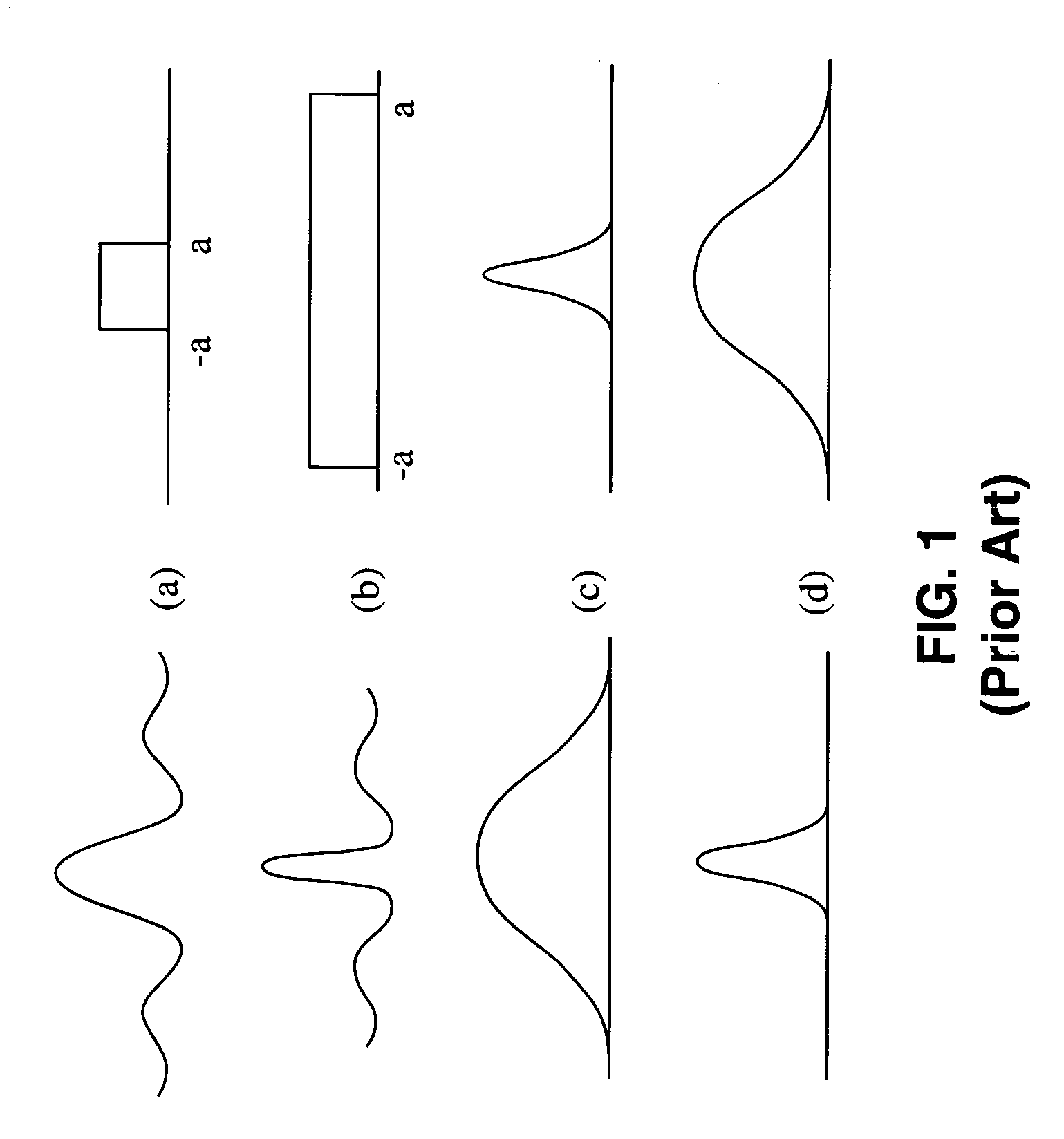
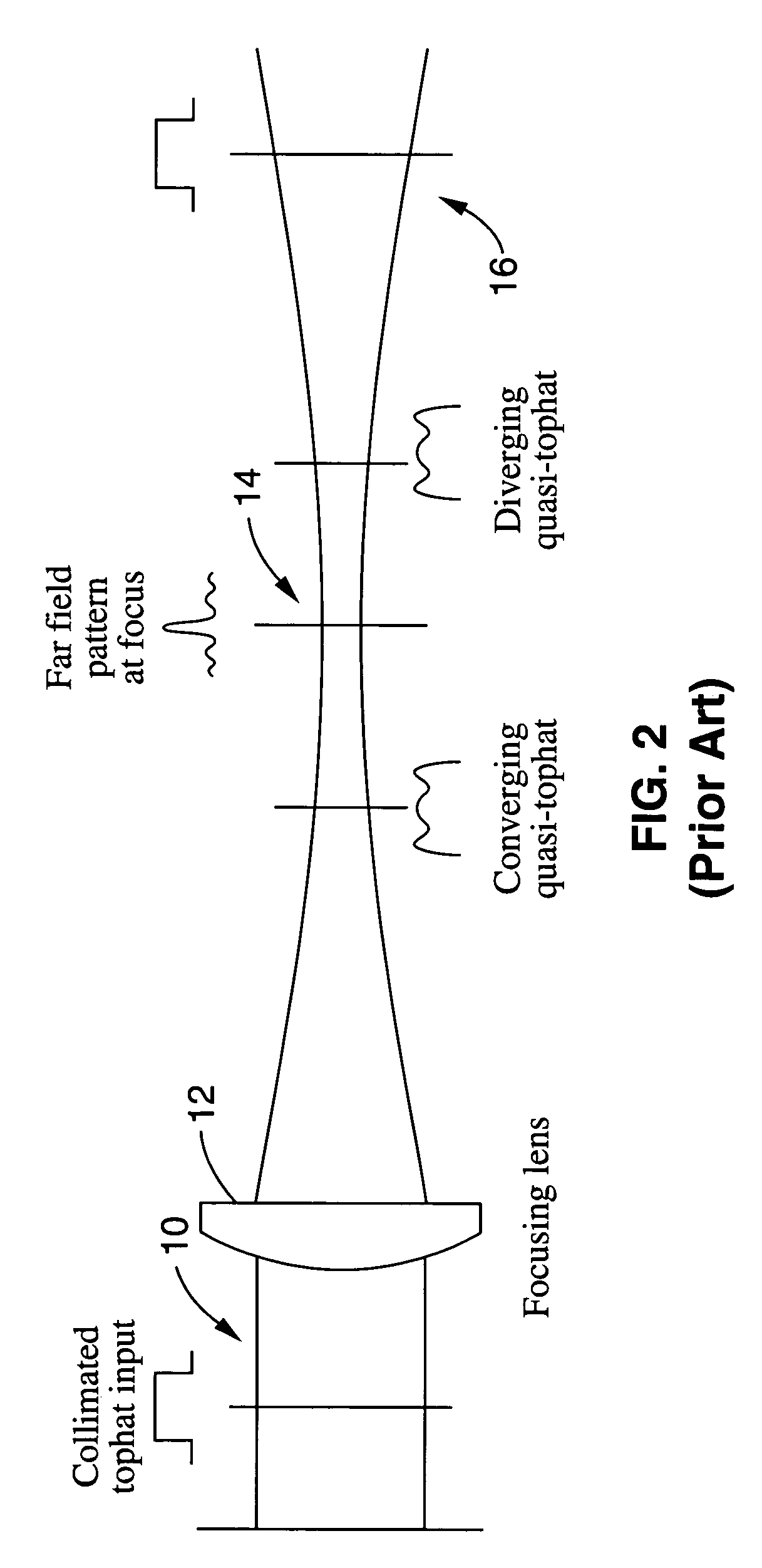
Method and apparatus for transformation of a gaussian laser beam to a far field diffraction pattern
InactiveUS6975458B1Optical resonator shape and constructionDiffraction gratingsGaussian beamFourier transform on finite groups
A method and apparatus for converting a Gaussian laser beam into a propagating far field diffraction pattern using an off-axis diffractive optic. This propagating far field pattern is focused by a lens to obtain a flattop intensity at the focal plane. The technique is based on the idea of Fourier transform pairs and produces a small spot diameter with a useable depth of field. A focused uniform intensity profile can be useful for many laser applications.
Owner:KANZLER KURT
Optical device structure using GaN substrates for laser applications
ActiveUS9531164B2Cost-effectiveSimple and cost-effectiveOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsGallium nitrideLaser application
An optical device includes a gallium nitride substrate member having an m-plane nonpolar crystalline surface region characterized by an orientation of about −2 degrees to about 2 degrees towards (000-1) and less than about 0.5 degrees towards (11-20). The device also has a laser stripe region formed overlying a portion of the m-plane nonpolar crystalline orientation surface region. A first cleaved c-face facet is provided on one end of the laser stripe region, and a second cleaved c-face facet is provided on the other end of the laser stripe region.
Owner:KYOCERA SLD LASER INC
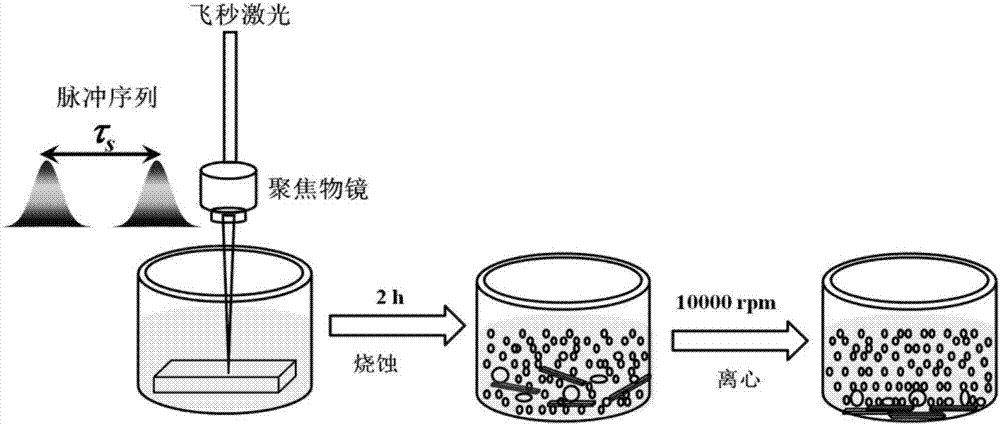
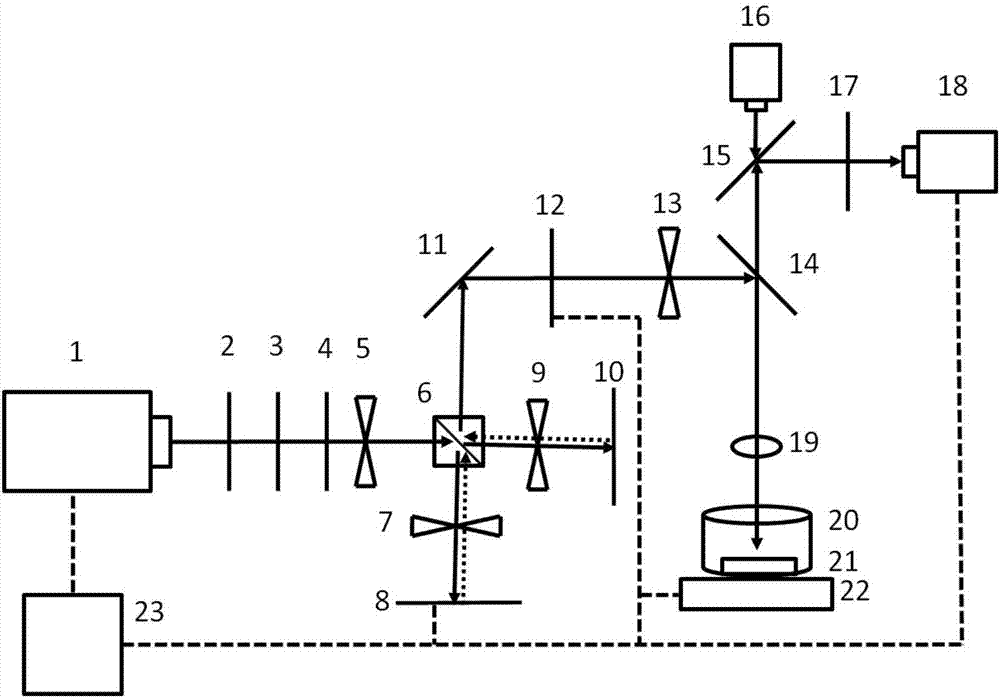
Method for processing micro array on glass surface via femtosecond laser pulse sequence
The invention relates to a method for processing a micro array on glass surface via femtosecond laser pulse sequence belonging to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. The method comprises the following steps: (1) modulating the conventional femtosecond laser into the femtosecond laser pulse sequence including two sub-pulses on a time domain via a pulse shaping method, wherein the time interval range of two sub-pulses is 50fs-2ps, and the energy ratio range of two sub-pulses is 0.2-5; (2) focusing the femtosecond laser pulse sequence on the surface of glass material, scanning the required micro array configuration pattern on the glass surface according to the relative movement between the glass material and the laser focal point; (3) immersing the glass material with micro array configuration pattern obtained in the step (2) in a hydrofluoric acid solution with the concentration being 1-10%, carrying out reaction on the micro array configuration pattern region and the hydrofluoric acid solution so as to from a concave micro array structure. The modification degree of the femtosecond laser irradiation region is increased and the etching efficiency of the irradiation region is finally improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Femtosecond laser-controlled silicon surface nanopillar preparation method based on dual-wavelength electronic dynamic control
ActiveCN105499792AEfficient and precise preparationAchieve optimal controlLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoNanopillar
The invention relates to a femtosecond laser-controlled silicon surface nanopillar preparation method based on dual-wavelength electronic dynamic control, and belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. The method comprises the steps that on the basis of local instant electronic exciting dynamic control, the wave length of the fundamental frequency laser is converted into 400 nm from 800 nm through a frequency doubling technology, and the surface micro-nano structural morphology is controlled by adopting a dual-wavelength femtosecond laser, wherein a first beam generates a generic plasma lens structure (PL) on the surface of a material, a second beam generates surface plasma along the edge of the generic PL structure and generates a gradient field distributed along the center of a light spot, and then the material generates the force extruding towards the center under the action of the pulse to form a convex nanopillar structure; preparation of large-area uniform nanopillar arrays is achieved through control over a procedure of a processing platform. Compared with an existing method, the preparation method has the advantages that the nanopillar processing precision and processing efficiency are effectively improved, efficient and precise control over the crystalline silicon surface nano structure is achieved, and the application value on the aspects such as information storage and solar cells is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for efficiently processing high-quality micro hole with large ratio of pit-depth to pit-diameter through femtosecond laser
InactiveCN103878496AAspect ratioQuality improvementWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusUltrasound attenuationMichelson interferometer
The invention relates to the field of laser application, in particular to a method for efficiently processing a high-quality micro hole with a large ratio of pit-depth to pit-diameter through a femtosecond laser. According to the method, the wavelength of a near-infrared femtosecond laser monopulse is regulated by a femtosecond laser optical parameter amplifier, so that the near-infrared femtosecond laser monopulse becomes visible light. Afterwards, an optical path of a Michelson interferometer is used for modulating the visible light to be laser double impulses and the overall energy of the laser double impulses is regulated with a continuous attenuation sheet. The obtained visible light double impulses penetrate through an optical shutter and are perpendicularly focused on the upper surface of a sample to be processed through an objective lens. Finally, the optical shutter is used for controlling the exposure time of the visible light double impulses and therefore the number of laser impulses which irradiates the surface of the sample to be processed is regulated until the depth of the processed hole is saturated. According to the processing method, the ratio of pit-depth to pit-diameter and the quality in processing the micro hole can be effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Crystal silicon surface femtosecond laser selective ablation method based on electron dynamic control
ActiveCN103658993AImprove machining accuracyImprove processing efficiencyWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoNano structuring
The invention relates to a crystal silicon surface femtosecond laser selective ablation method based on electron dynamic control, and belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. The crystal silicon surface femtosecond laser selective ablation method based on the electron dynamic control enables laser polarization parameters and crystal lattice properties of crystal silicon materials to be integrated, through the operation that femtosecond laser rays or the included angel of elliptic polarization and monocrystal silicon is adjusted effectively, the selective induction generation of crystal silicon surface periodical ripple micro nano structures is controlled by regulating and controlling material surface instant electron excitation dynamic states, and the induction generation of the crystal silicon surface periodical ripple micro nano structures can be achieved effectively and accurately according to preliminary design. According to the crystal silicon face femtosecond laser selective ablation method based on the electron dynamic control, selective ablation control is carried out on the silicon surface periodic ripple nano structures with diamond lattice structures from the aspect of static laser irradiation and the aspect of laser direct writing, the processing accuracy and the processing efficiency of the surface processing of the silicon surface periodic ripple nano structures are improved greatly, and the application value of the method on the aspects such as information storage is high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
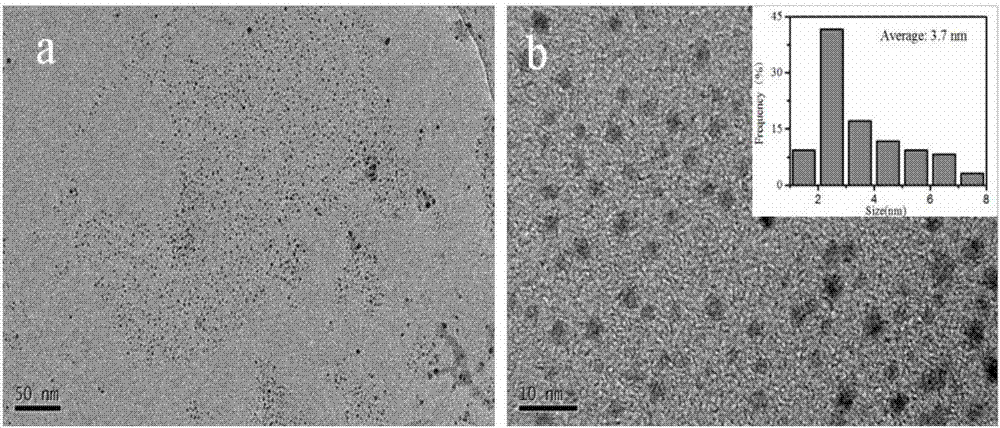
Method for preparing monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots based on electronic dynamic regulation and control
ActiveCN106905966AHigh yieldPromote absorptionCatalyst activation/preparationNanotechnologyPhotoablationLaser scanning
The invention relates to a method for preparing monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots based on electronic dynamic regulation and control, in particular to a method for obtaining the monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots with uniform particle sizes by obtaining molybdenum disulfide suspension and then centrifugally separating and belongs to the field of femtosecond laser application. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: aiming at the characteristics of a molybdenum disulfide material, carrying out pulse shaping on traditional femtosecond laser monopulse by using a Michelson interferometer to form a pulse sequence; adjusting energy of the pulse sequence, delay among sub pulses, laser scanning speed and scanning intervals; ablating blocky molybdenum disulfide in water and further regulating and controlling local transient electronic dynamics in the interaction process of laser and the material to form multistage photoablation monolayer molybdenum, and obtaining the monolayer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots with the uniform particle sizes; carrying out laser-induced water dissociation to enhance light absorption and improve the yield of the molybdenum disulfide quantum dots. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of no need of special chemical environment or chemical reagent, greenness, no pollution, and simple and flexible operation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Ultrashort pulse laser applications
The invention relates to methods of processing biological tissue using an ultrashort pulse (USP) laser. In one embodiment, the invention relates to a method of separating transverse layers or portions of a biological tissue using USP laser. In an alternative embodiment, the invention relates to a method of cutting biological tissue using USP laser. In another embodiment, the invention relates to a method of removing unwanted material from the surface of a biological tissue comprising application of the USP laser to the tissue surface.
Owner:GUO ZHIXIONG +3
Device and method to stabilize beam shape and symmetry for high energy pulsed laser applications
ActiveUS20070279747A1Increasing intensity symmetryIncrease intensity symmetryOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialMixed beamHigh energy
A beam mixer for increasing intensity symmetry along a selected axis of a beam (wherein the beam extends from a first edge to a second edge along the axis) is disclosed and may include a plurality of mirrors establishing a spatially inverting path. For the beam mixer, the inverting path may have a beginning and an end and may be characterized in that a part of the beam near the first beam edge at the beginning of the path translates to the second beam edge at the end of the path. For this aspect, the beam mixer may further include an optic dividing the beam into first and second beam portions, the optic placing the first portion onto the inverting path and recombining the first and second portions onto a common path after the first portion has traveled along the inverting path thereby mixing the beam.
Owner:CYMER INC
Method for inducting two-dimensional periodic structure on surface of material through femtosecond laser
InactiveCN103934576AUniform two-dimensional periodic structureLaser beam welding apparatusOptical parametric amplifierOptical polarization
The invention relates to the field of laser application, in particular to a method for inducting a two-dimensional periodic structure on the surface of a material through a femtosecond laser. According to the method, near-infrared femtosecond laser single pulses are generated by a femtosecond laser device. The wavelengths of the near-infrared femtosecond laser single pulses are adjusted within the range between 290 nm and 2600 nm through a femtosecond laser optical parametric amplifier; the laser single pulses are modulated to laser double pulses perpendicular to the polarization direction through a laser path of a Michelson interface instrument structure and the total energy of the laser double pulses is adjusted to the degree not lower than an erosion threshold value of a sample to be machined through a continuous attenuation piece; the laser path is adjusted, so that the double pulses with the changed wave length are focused in the vertical direction after passing through a planoconvex lens and the sample to be machined is moved to enable the laser focus point to be located on the upper surface of the sample, wherein the double pulses are perpendicular to the polarization direction; finally, the sample to be machined is controlled to move horizontally at a set speed, and therefore the two-dimensional periodic structure can be obtained by scanning the surface of the sample. The even two-dimensional periodic structure with various sub-wavelengths can be induced on the surface of the material.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for improving machining efficiency of micro-channel preparation through femtosecond laser
InactiveCN102601529AImprove processing efficiencyImprove production efficiencyLaser beam welding apparatusFemtosecond pulsed laserPolarizer
The invention relates to a method for improving the machining efficiency of micro-channel preparation through femtosecond laser, which belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. The method includes the steps: firstly, generating the femtosecond pulse laser by the aid of a femtosecond laser system, adjusting energy by means of combination of a half wave plate and a polarizing film and modulating the femtosecond laser into femtosecond interval pulse sequence by the aid of a pulse shaper; secondly, reflecting the pulse sequence laser obtained in the first step to an objective lens for focusing through a reflector, realizing imaging by the aid of a CCD (charge coupled device) and a lighting source, moving a six-dimensional precision electric control platform and positioning a laser focus on the lower surface of a sample horizontally placed on the six-dimensional precision electric control platform; and thirdly, controlling the six-dimensional precision electric control platform to move along a laser propagation direction by the aid of a computer to machine a micro-channel on the sample. As the femtosecond laser is modulated into the femtosecond interval pulse sequence by the aid of the pulse shaper, the micro-channel preparation efficiency is improved. Moreover, introduction of a vibration source is omitted, so that controllability of precision machining cannot be reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Femtosecond laser array micropore machining system based on spatial beam shaping
InactiveCN110238546AImprove uniformityQuality improvementLaser beam welding apparatusLaser arrayBeam splitting
The invention relates to a femtosecond laser array micropore machining system based on spatial beam shaping and belongs to the technical field of laser application. According to the machining system provided by the invention, a spatial light modulator (SLM) is utilized, by designing different phase positions, a single femtosecond laser beam is shaped into a plurality of array light fields featuring specific spatial distribution, the laser repeat frequency, the laser beam waist radius and the laser pulse energy are adjusted, finally, a light path is established through optical elements so as to focalize the shaped femtosecond laser to the surface of a sample, high-quality, no-contact, high-efficiency and large-area array micropore machining on multiple types of materials is achieved, and the repeatability and flexibility are high. When the system is applied to array micropore machining, beam splitting nonuniformity caused by Gaussian distribution of the laser is effectively avoided, and the array micropore uniformity and quality are improved. The quantity and distribution of array micropores can be freely adjusted and controlled through SLM load phase position variations, multiple types of elements do not need to be configured, and adjustability is high.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
System and method for preparing patterned metal thin layer through pulse laser-induced forward transfer
ActiveCN106825915APrecise Control of Local MetastasisPrecise Control of DepositionLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsManufacturing cost reductionOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a system and method for preparing a patterned metal thin layer through pulse laser-induced forward transfer, and belongs to the technical field of laser application and printing electronics. The system comprises a laser light source, a light path adjusting system and a two-dimensional precise motion system, wherein the laser light source is connected with the light path adjusting system; the two-dimensional precise motion system is located below the light path adjusting system; the laser light source is a pulse laser device; the light path adjusting system comprises a collimating beam expander lens assembly and a light splitting element connected with the collimating beam expander lens assembly; the light splitting element is connected with two reflectors at 90 degrees separately; the two reflectors are connected with a beam combiner separately; the beam combiner is connected with an objective lens through a focusing lens; the two-dimensional precise motion system comprises an electric platform, a motion controller and a computer; the computer is connected with an electric platform through the motion controller; and the electric platform is used for putting an initial substrate and a receiving substrate. Fast, high-precision and large-format pattern transfer can be achieved, the manufacturing cost is greatly reduced and the manufacturing cycle is greatly shortened.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
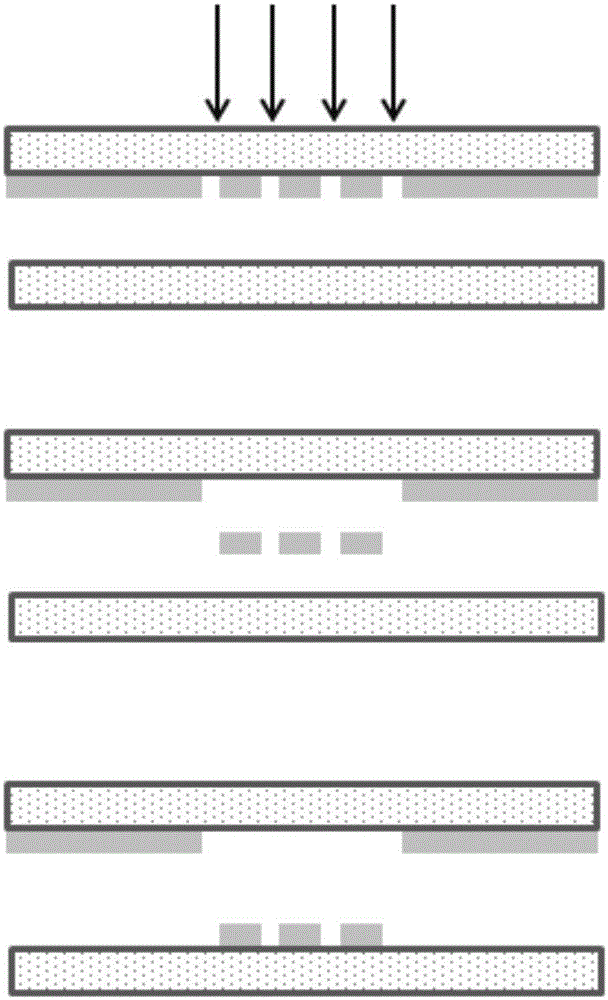
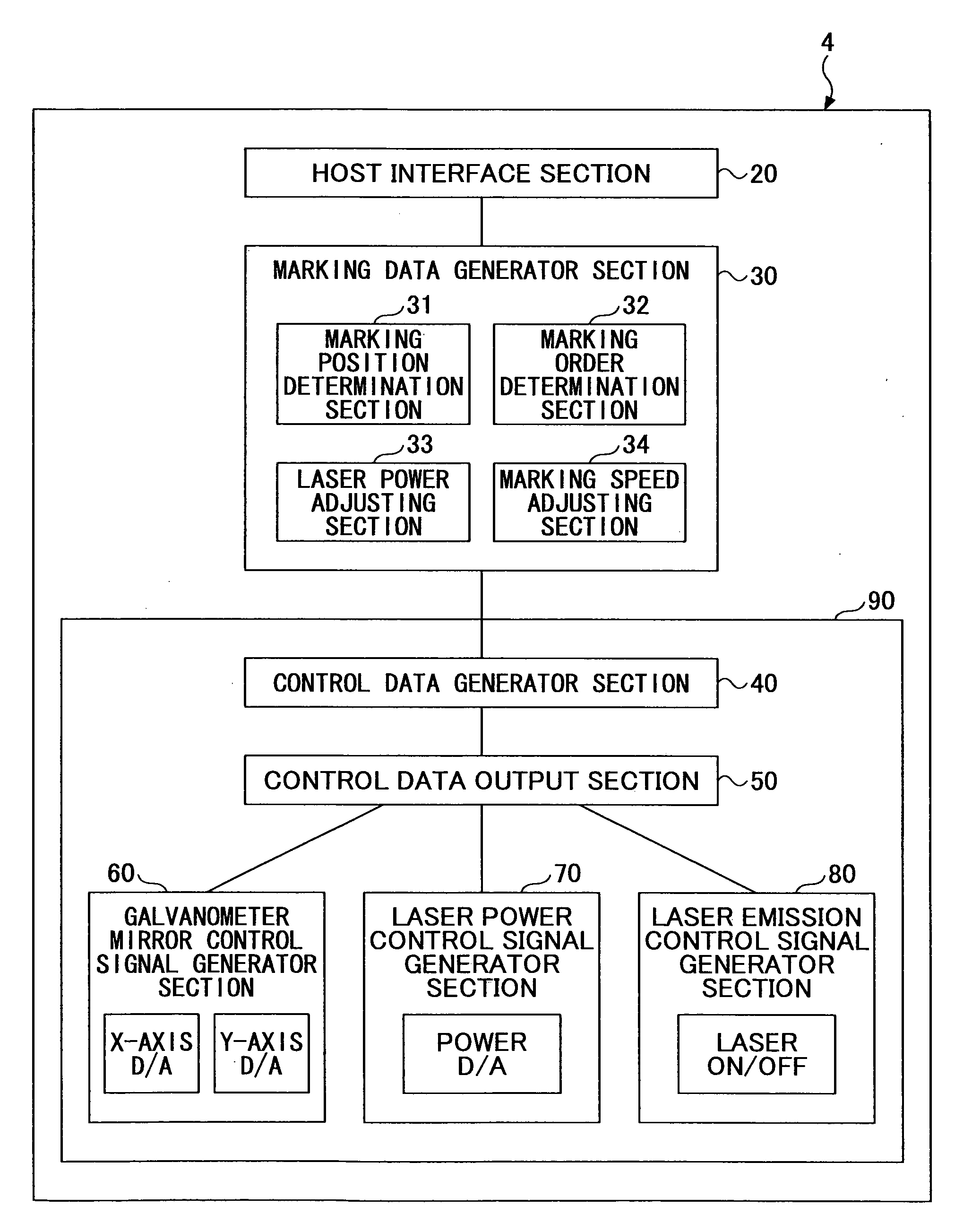
Marking control device, laser application device, marking control method, and computer-readable recording medium having marking control program
InactiveUS20120212564A1Quality improvementWide image erasable energy widthRecording apparatusVisual representation by thermal printersEngineeringLaser beams
A disclosed marking control device controls a marking device to mark a target image on a thermoreversible recording medium by applying a laser beam includes a marking position determination unit dividing the image into plural marking lines, and determining their marking positions; a marking order determination unit determining a marking order to mark the marking lines in mutually opposite directions; an adjusting unit adjusting a distance between a first ending point and a second starting point to be longer than a distance between a first starting point and a second ending point, or adjusting laser power applied to a second starting point side of the second marking line to be lower than the laser power applied to a second ending point side of the second marking line; and a marking instruction generator unit generating marking instructions including the marking positions of the marking lines and the marking order thereof.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical lens applied to ultraviolet laser
The invention discloses an ultraviolet laser-applied f-theta optical lens. The optical lens comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lend and a fourth lens which are positioned in the incident directions of light beams and arranged in order, wherein the first lens is a biconcave lens; the second lens is a meniscus lens, of which the curved surface bends towards the incident directions of the light beams; and the third lens is a planoconvex lens; and the fourth lens is a biconvex lens, wherein the optical lens is applied to the ultraviolet laser with the angle of vision of the lens of 50 degrees, the focal distance of 100mm, and the wavelength of 355nm in a processing range of 50mm*50mm. The ultraviolet laser has small focal spot and concentrated energy through the lens, and can mark or carve some processed special materials with superfine effects.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com