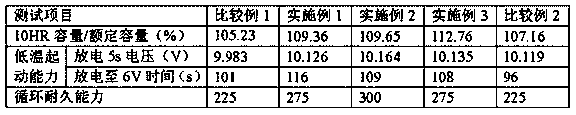
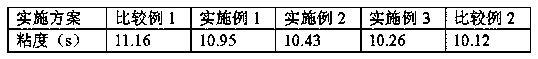
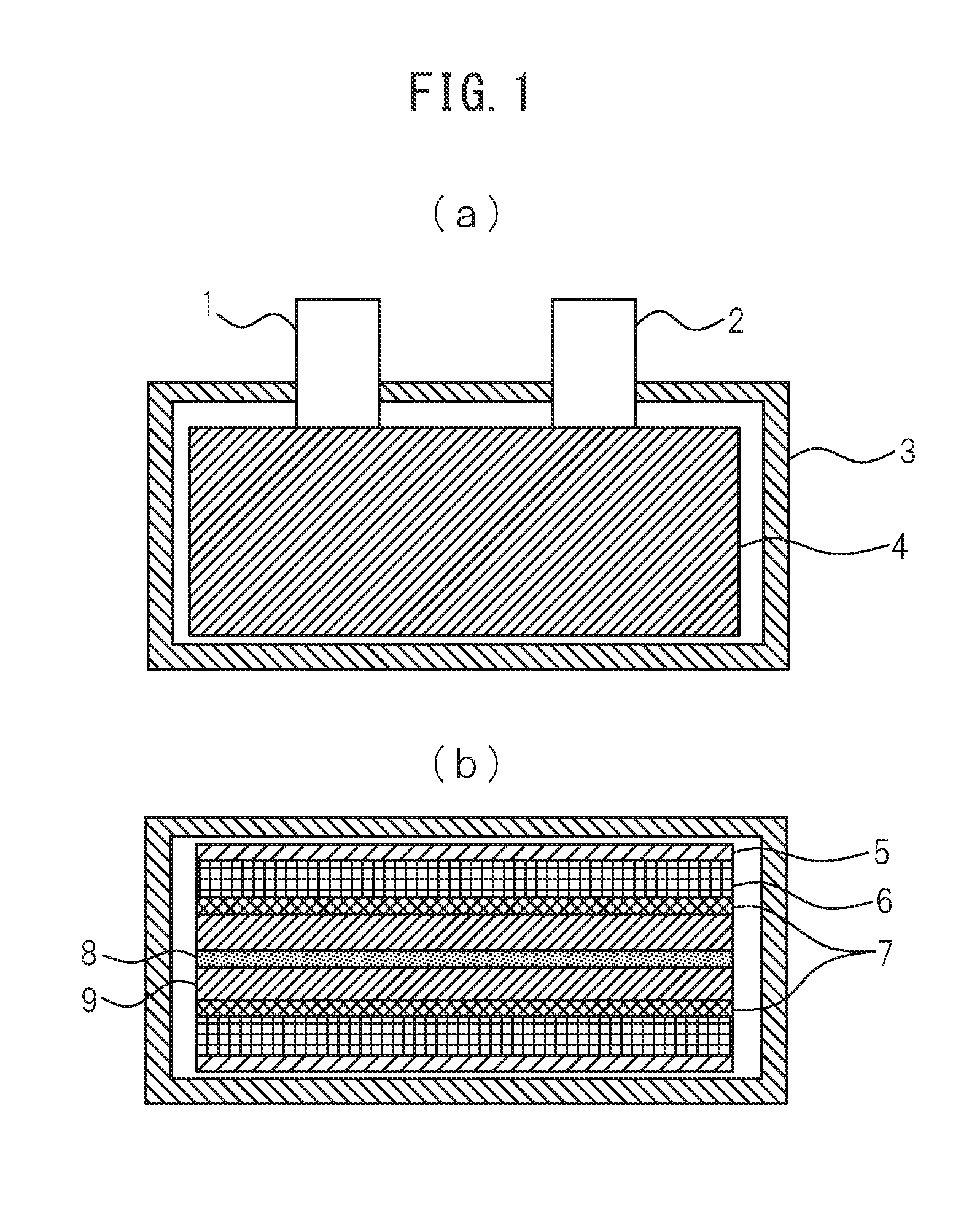
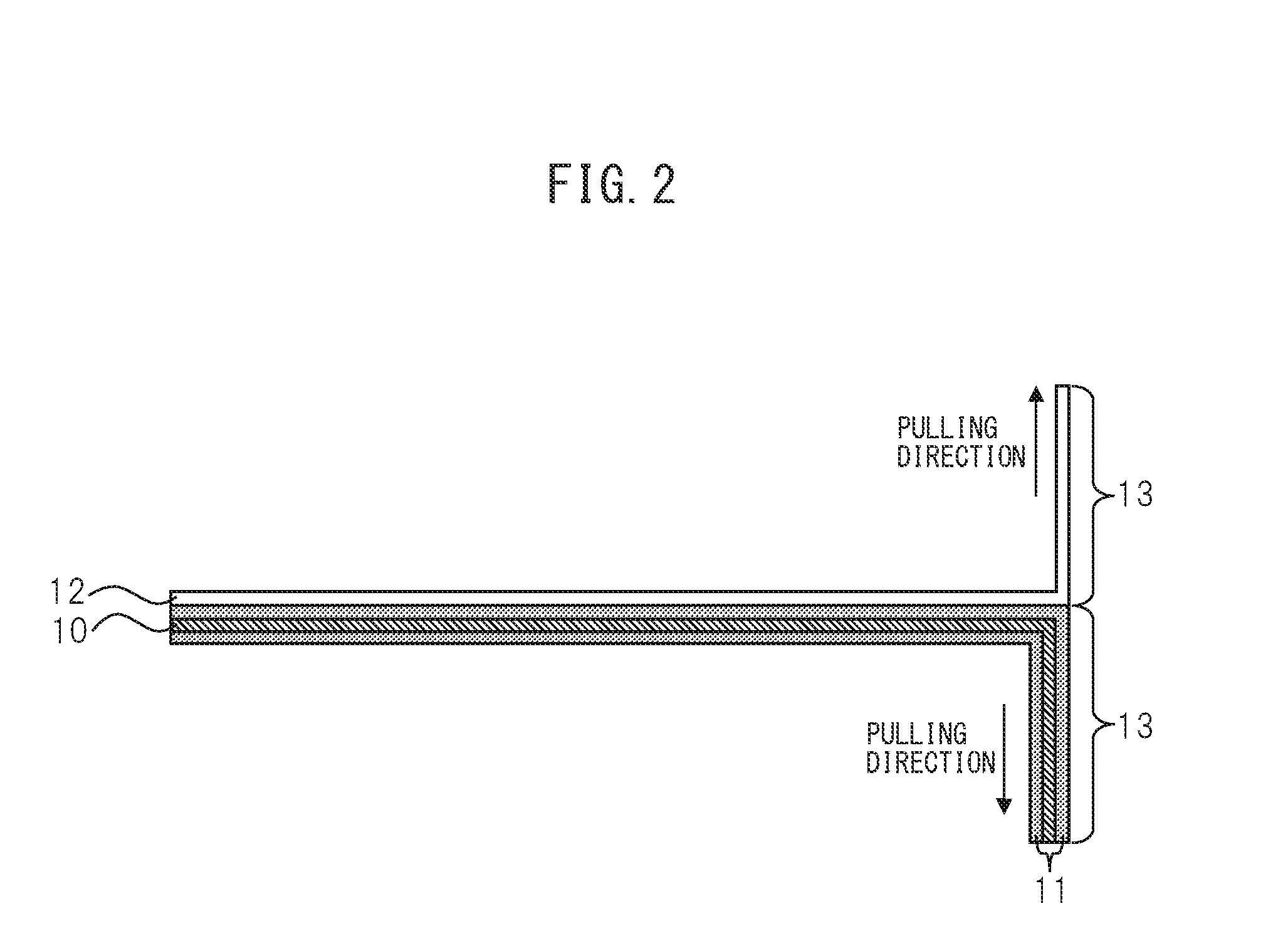
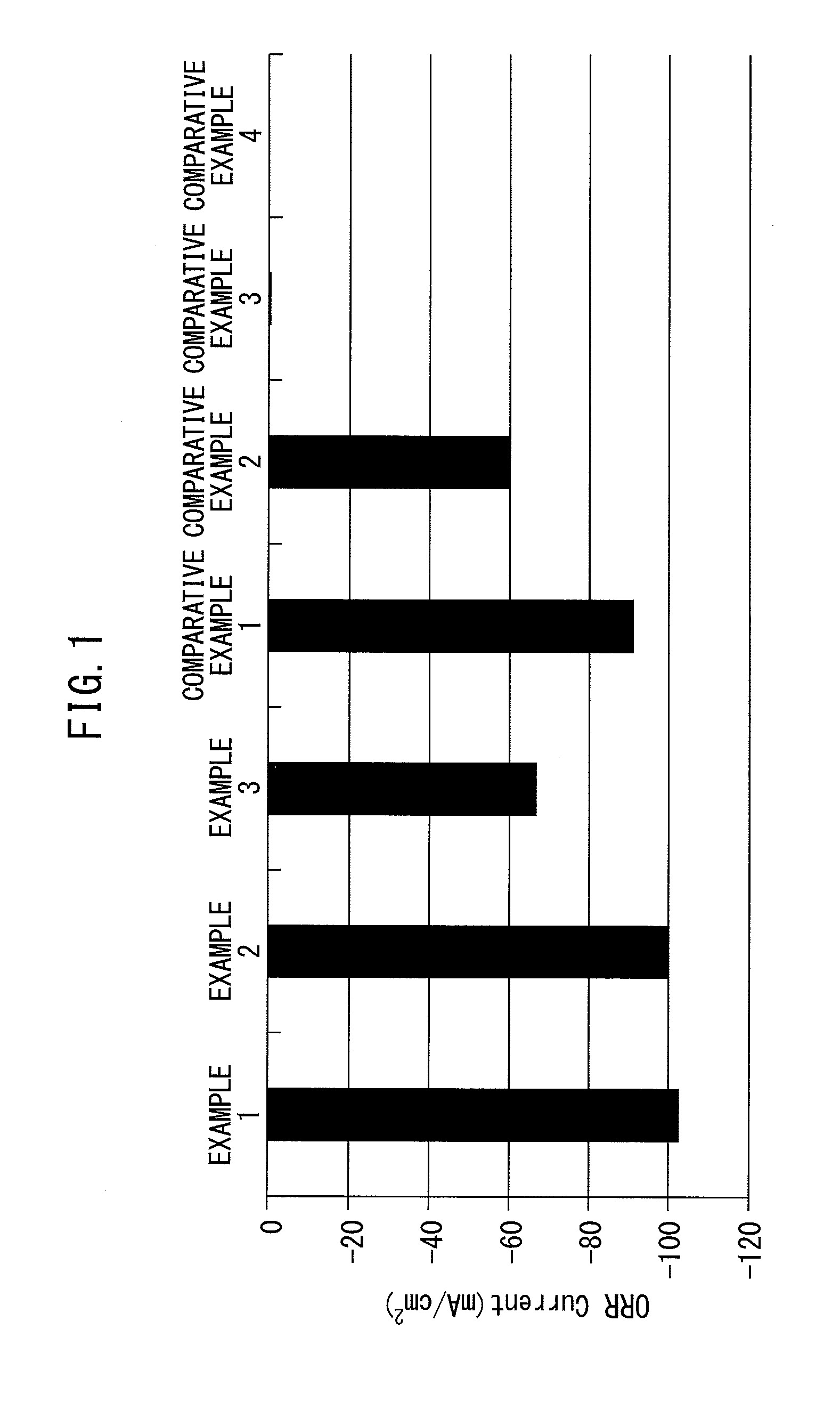
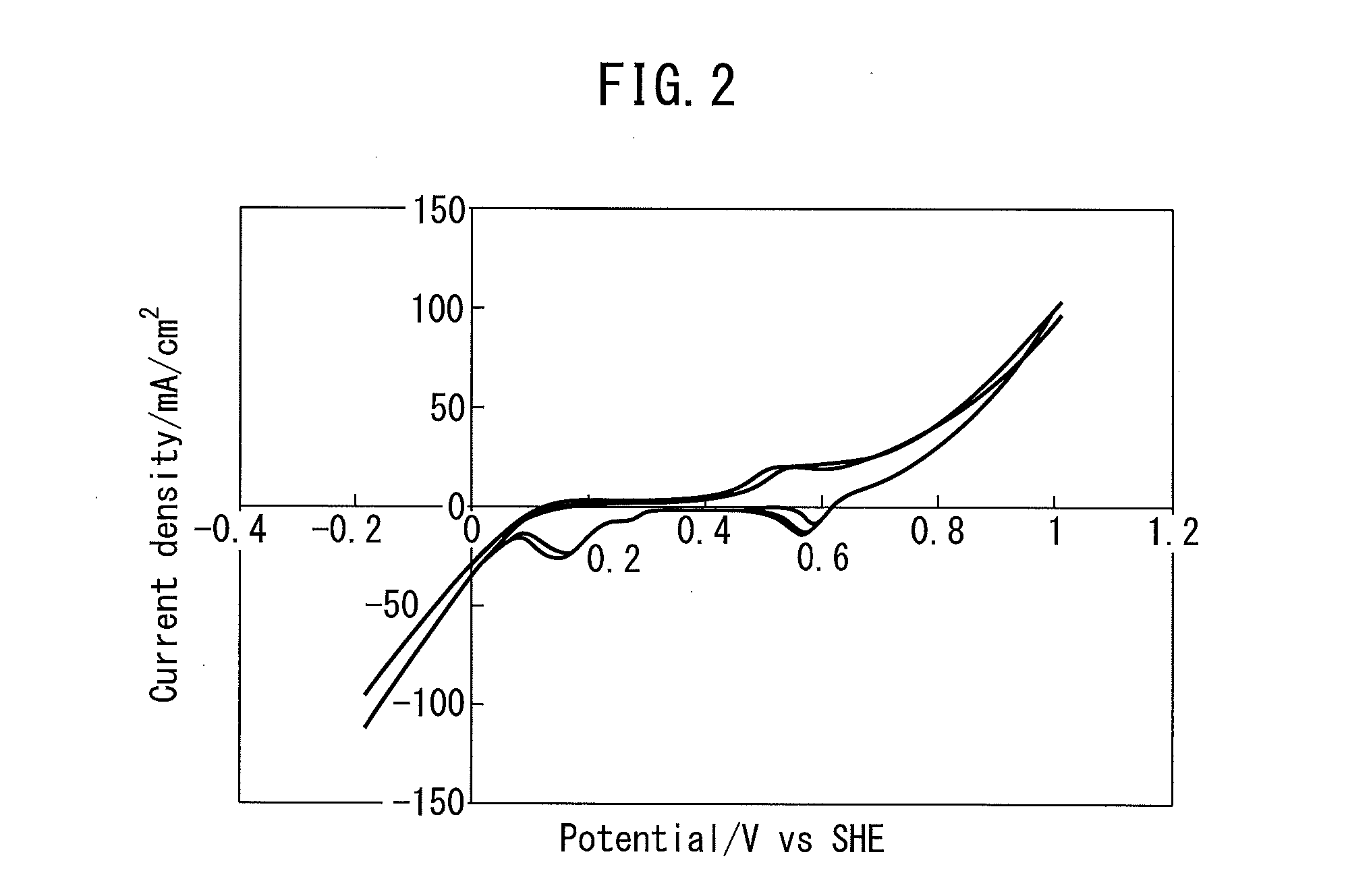
Patents
Literature
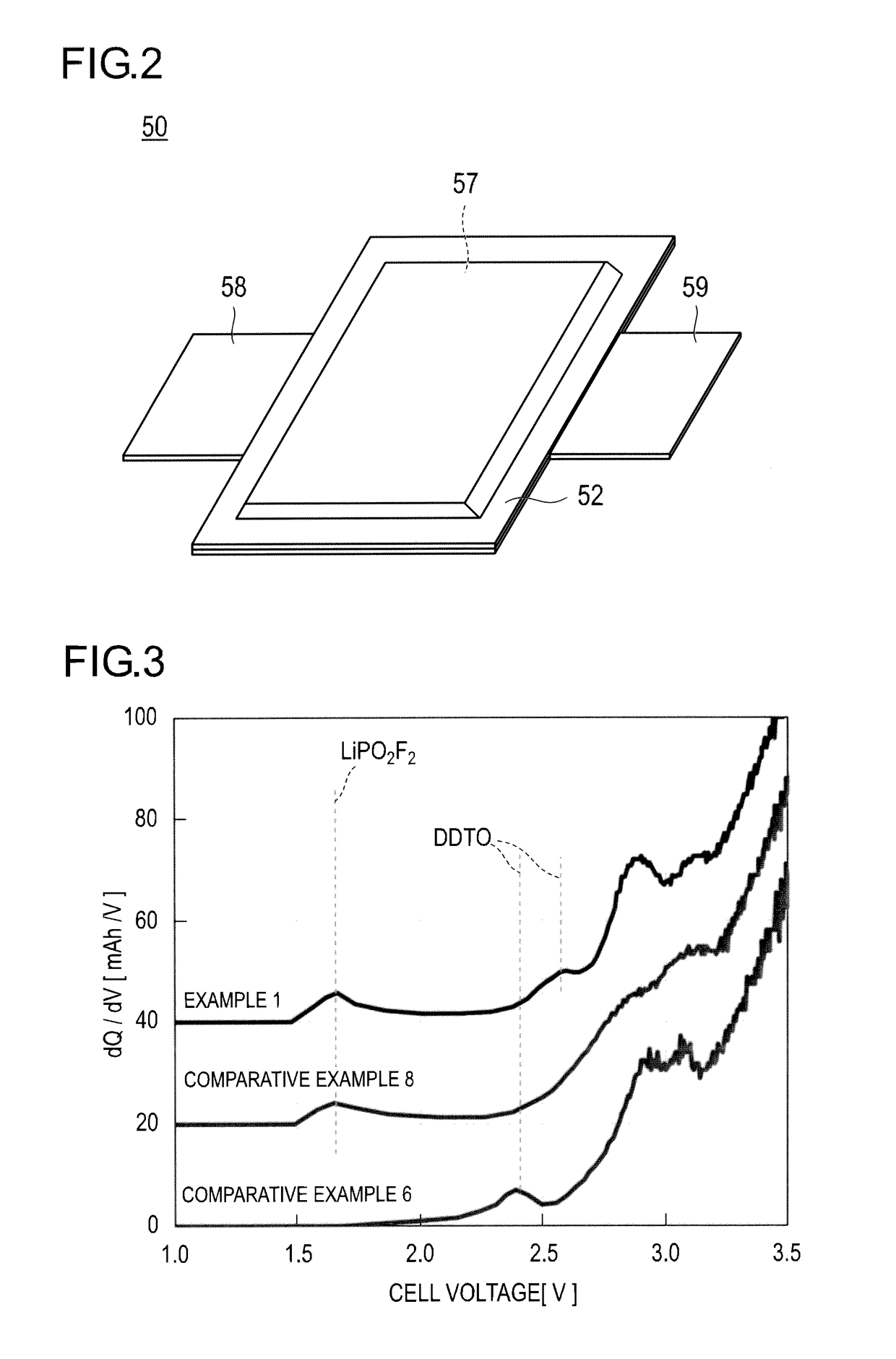
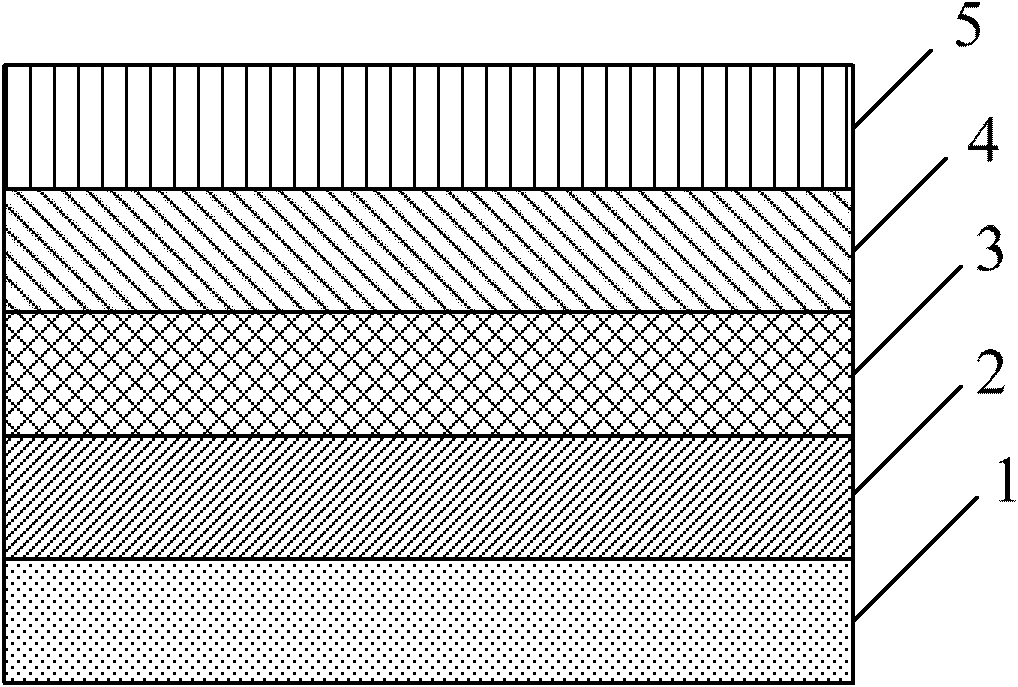
71results about How to "High cycle durability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Negative electrode material for secondary battery with non-aqueous electrolyte, method for manufacturing negative electrode material for secondary battery with non-aqueous electrolyte, and lithium ion secondary battery
ActiveUS20110244334A1Large capacityHigh cycle durabilityFinal product manufactureLi-accumulatorsCarbon coatingX-ray
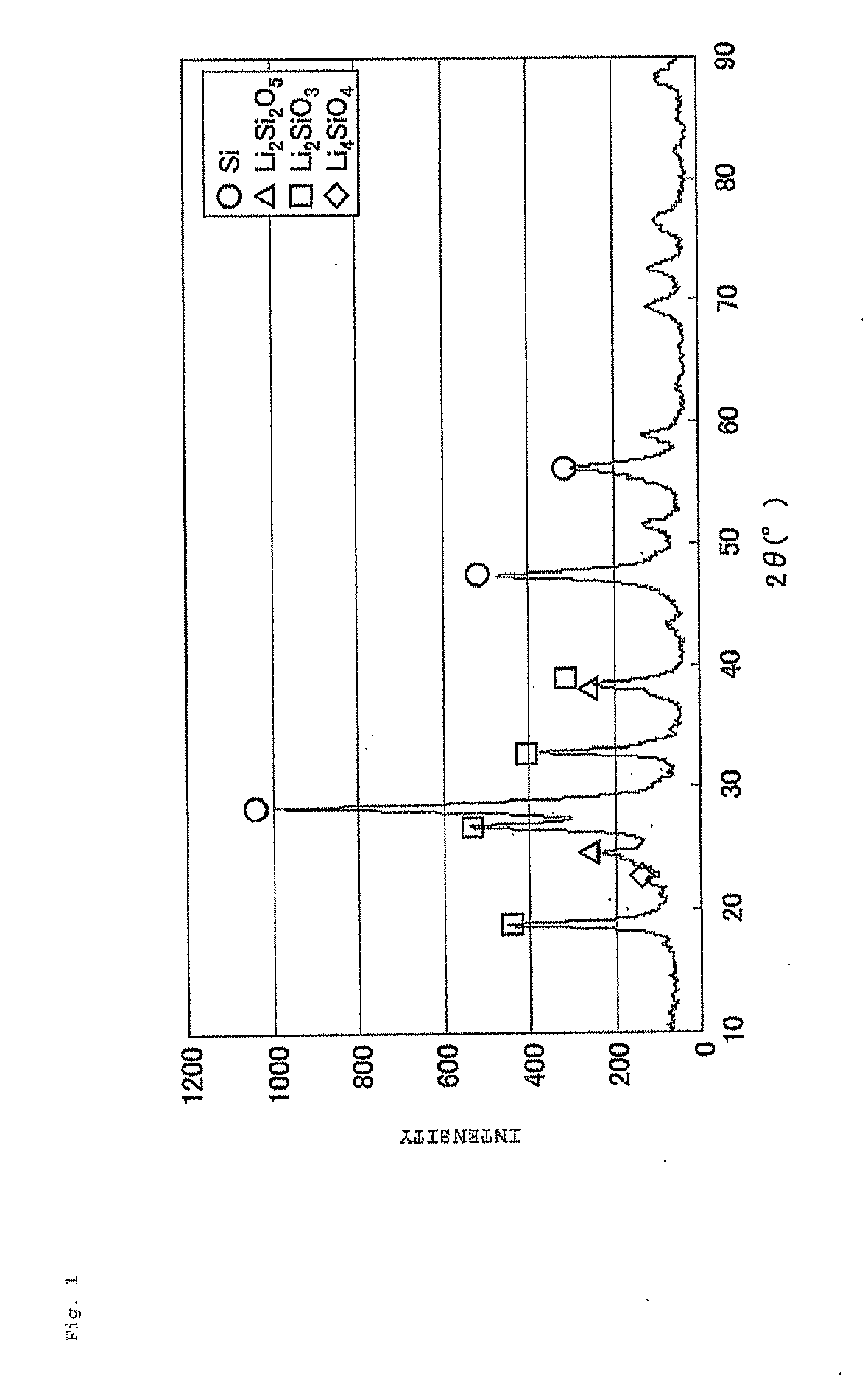
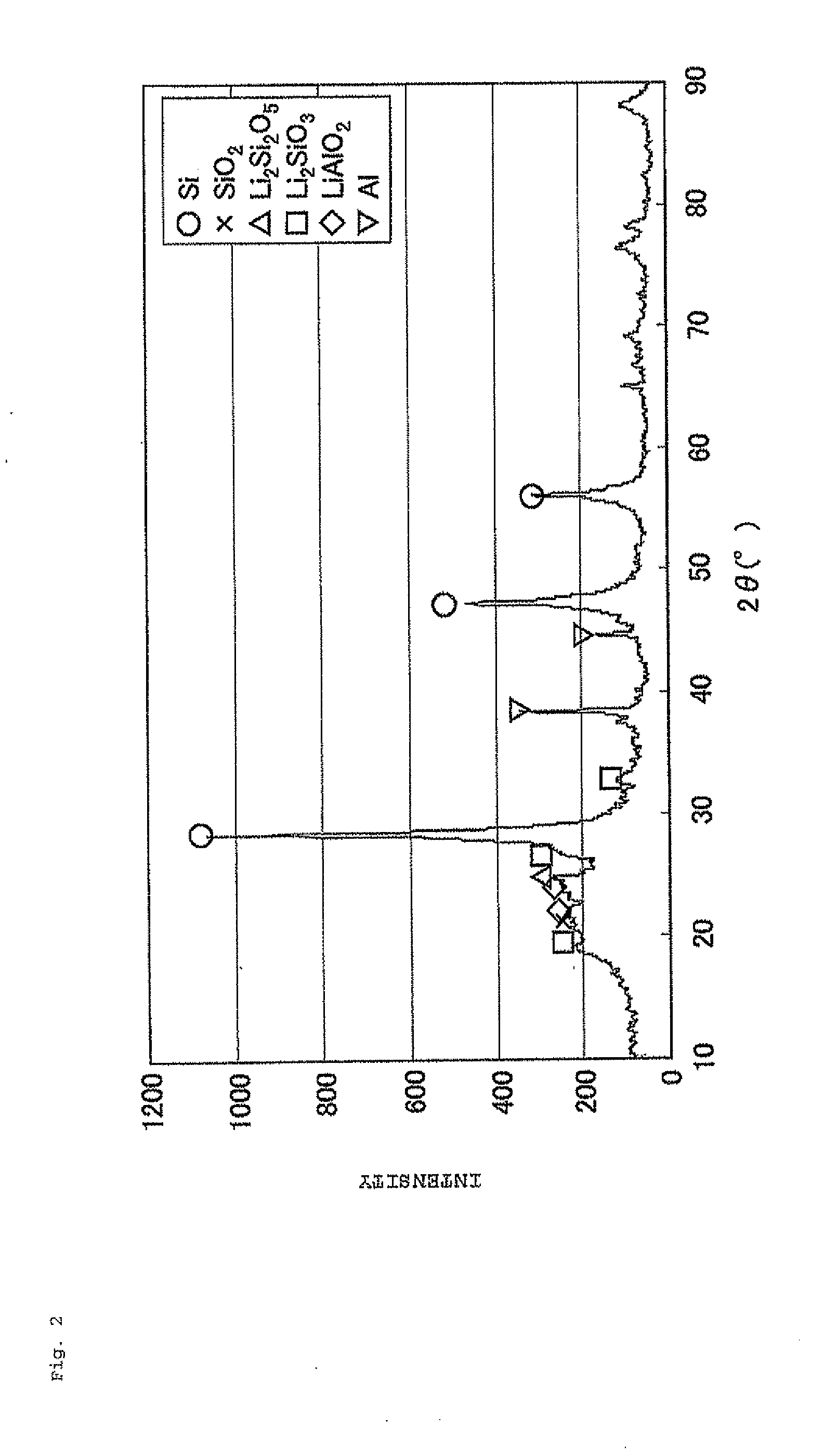
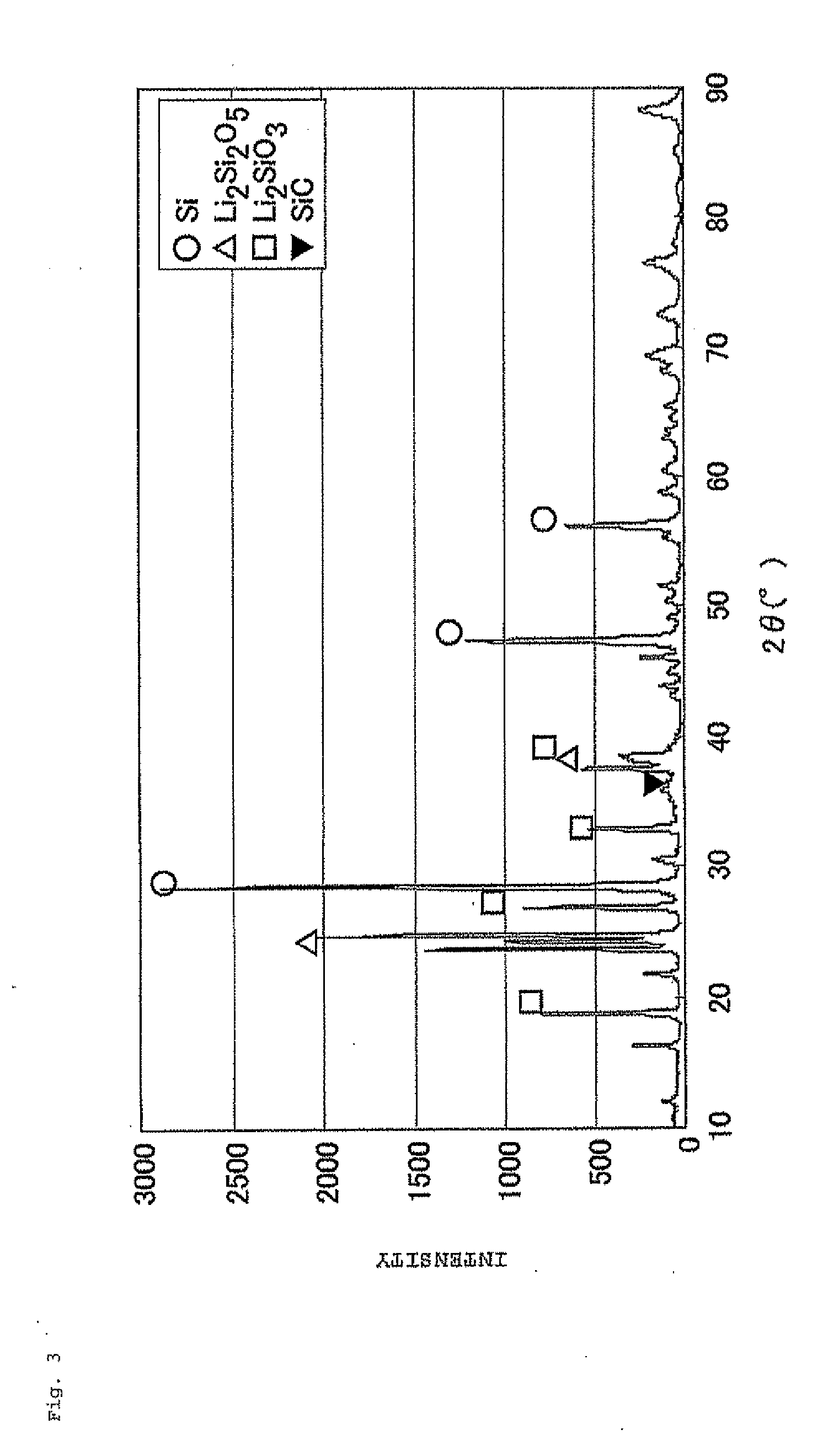
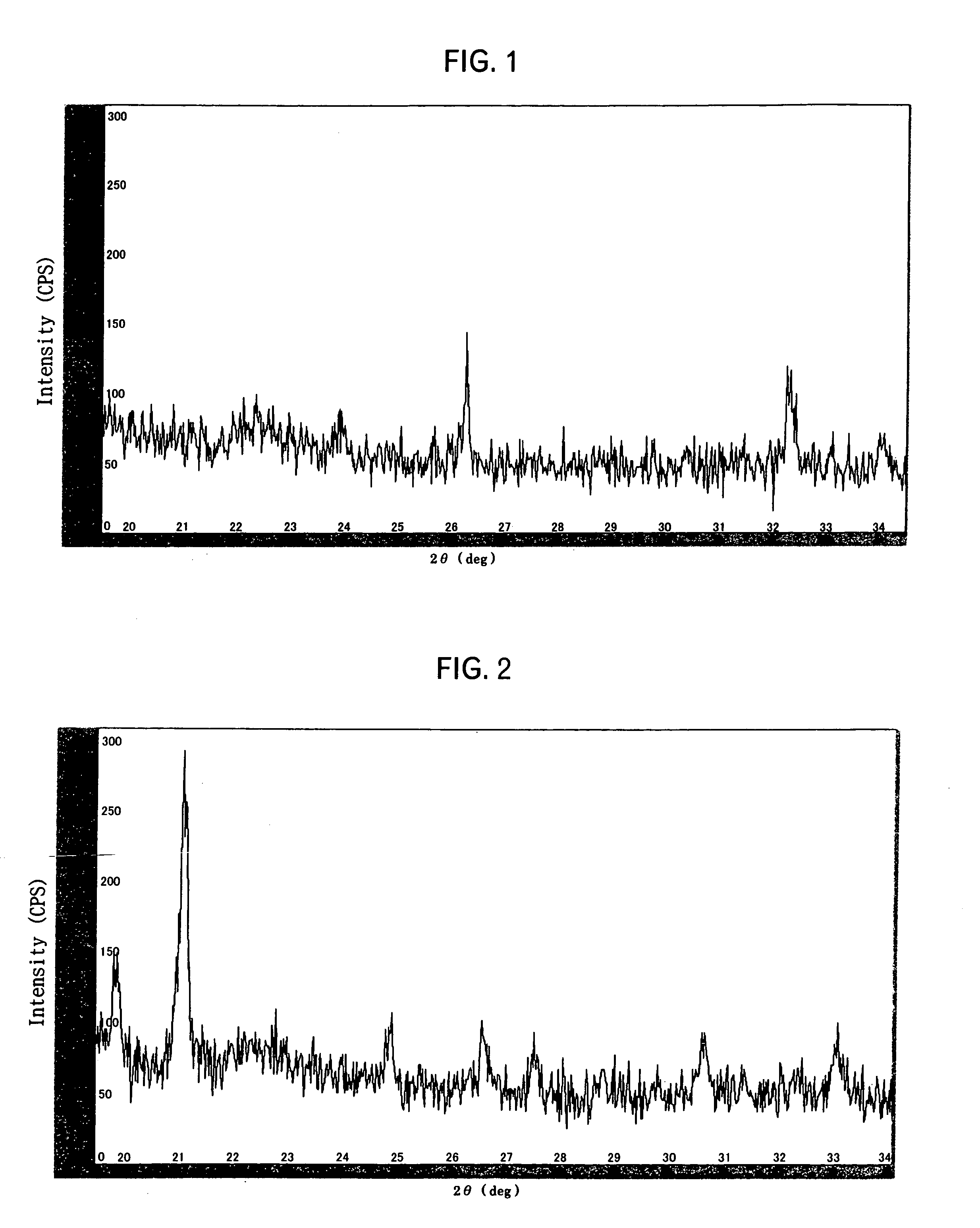
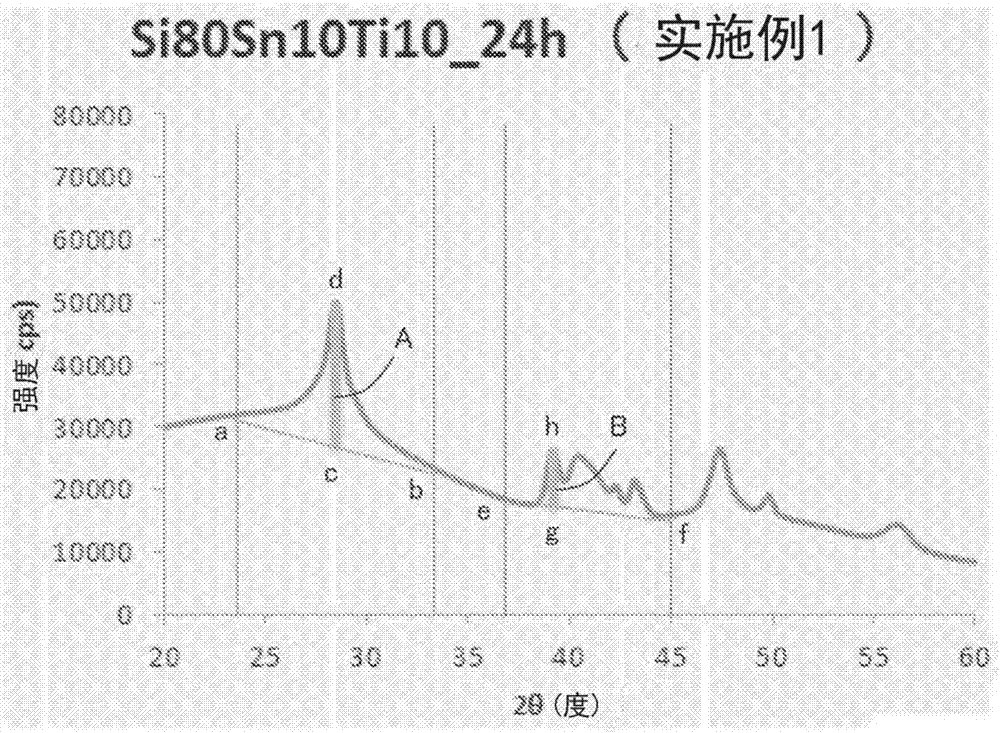
The present invention is a negative electrode material for a secondary battery with a non-aqueous electrolyte comprising at least a silicon-silicon oxide composite and a carbon coating formed on a surface of the silicon-silicon oxide composite, wherein at least the silicon-silicon oxide composite is doped with lithium, and a ratio I(SiC) / I(Si) of a peak intensity I(SiC) attributable to SiC of 2θ=35.8±0.2° to a peak intensity I(Si) attributable to Si of 2θ=28.4±0.2° satisfies a relation of I(SiC) / I(Si)≦0.03, when x-ray diffraction using Cu—Kα ray. As a result, there is provided a negative electrode material for a secondary battery with a non-aqueous electrolyte that is superior in first efficiency and cycle durability to a conventional negative electrode material.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
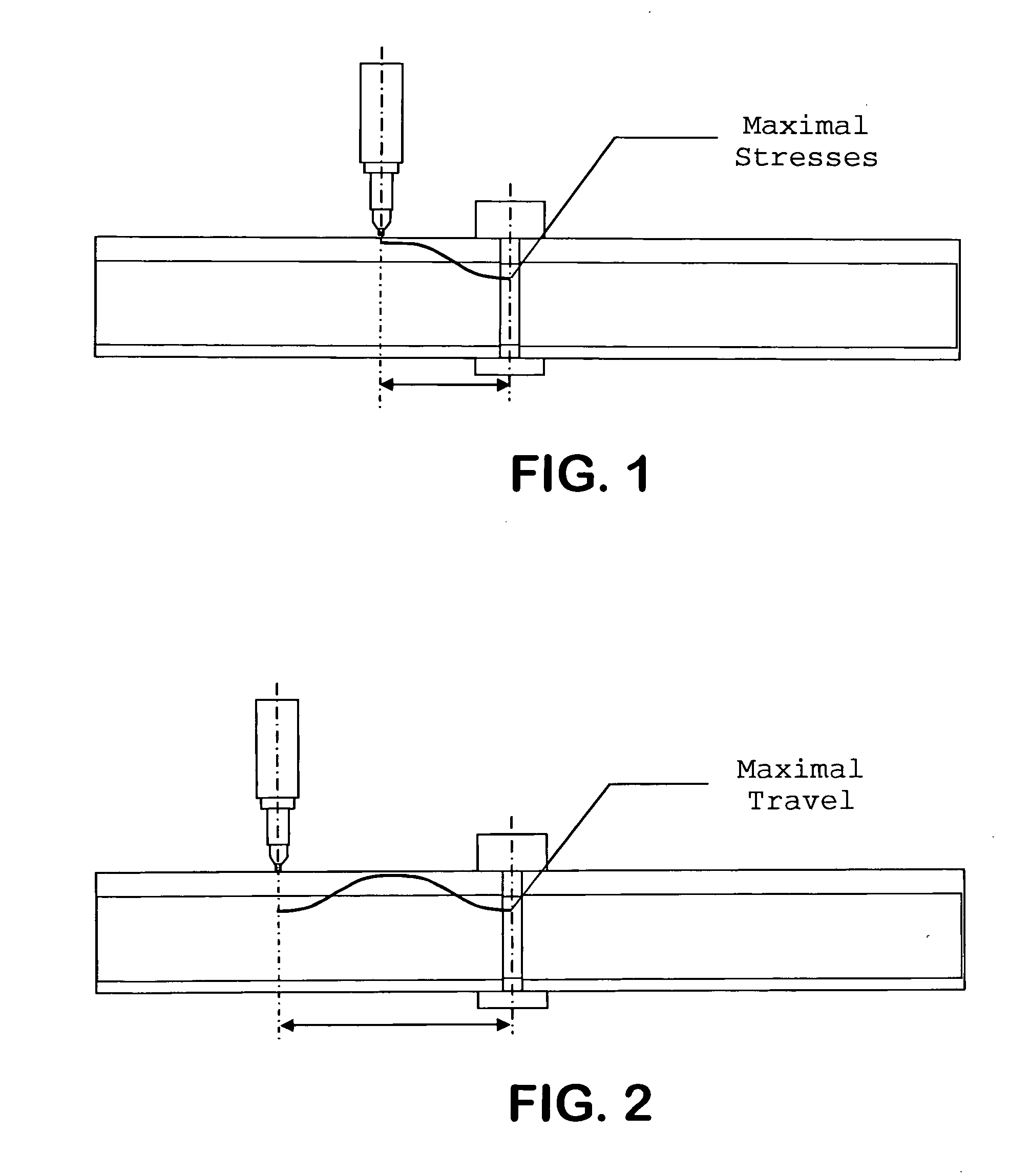
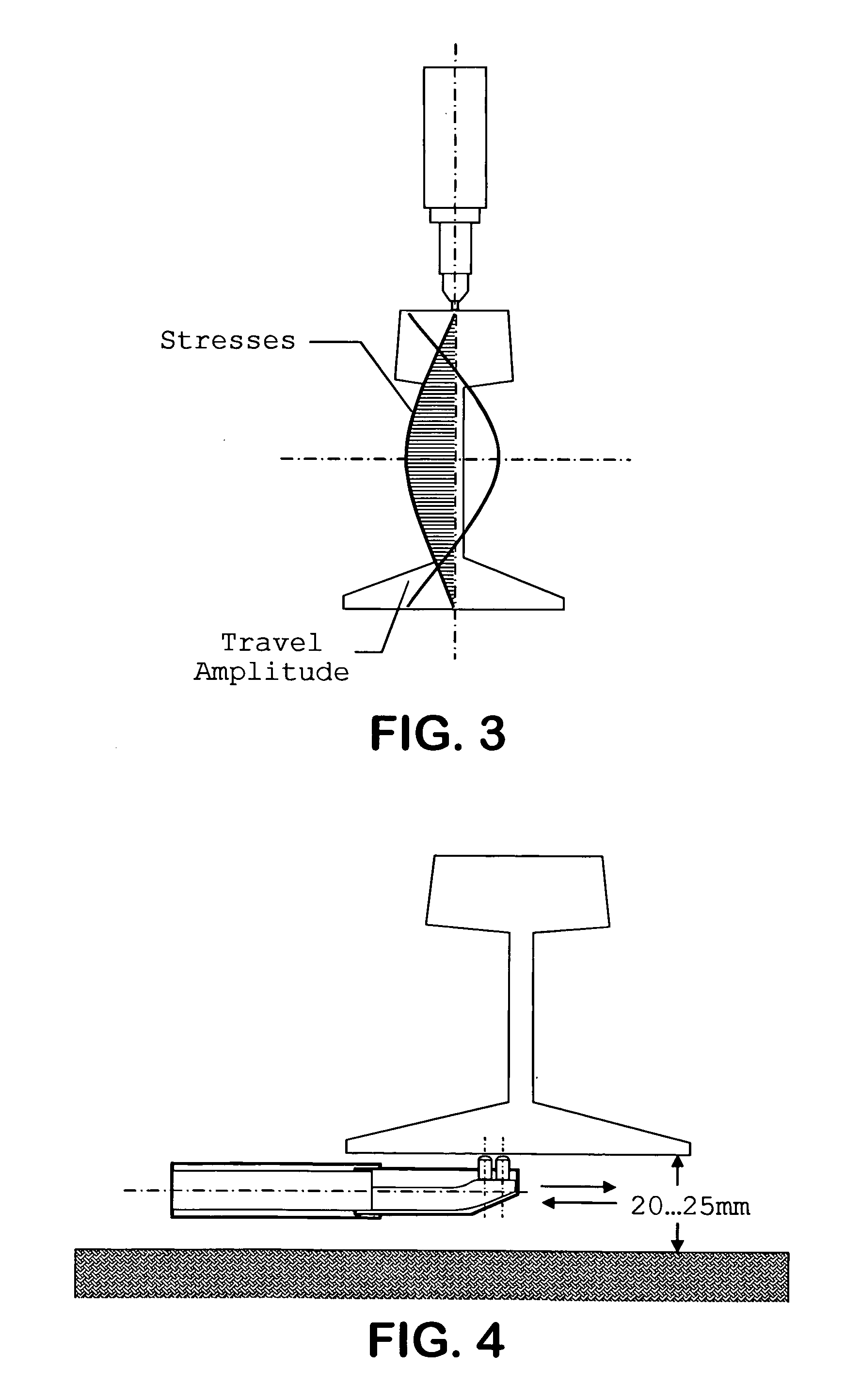
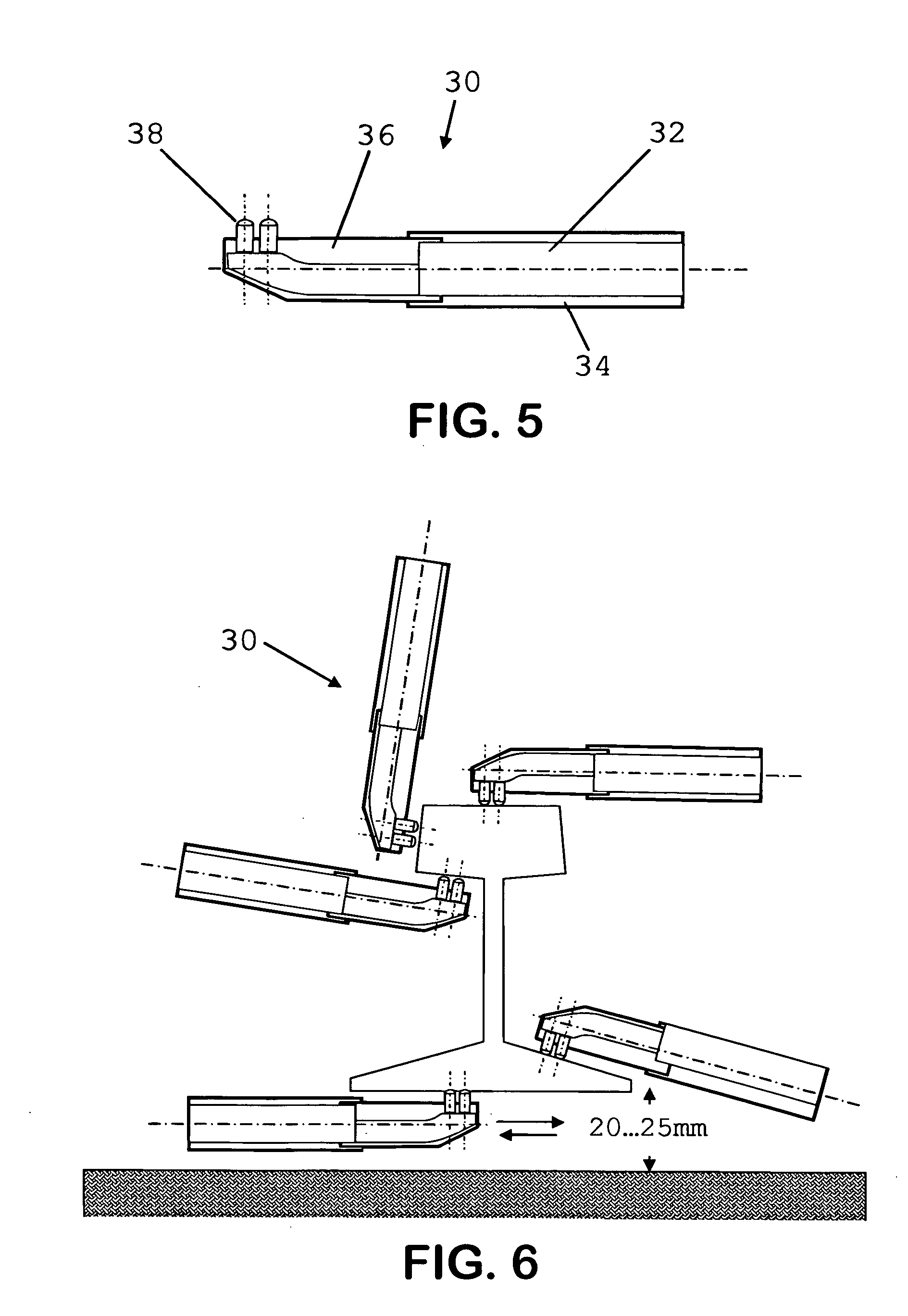
Method of improving quality and reliability of welded rail joint properties by ultrasonic impact treatment
InactiveUS20060016858A1Improving statistical reliabilitySolution to short lifeRailsCooking-vessel materialsIncreased fatiguePulse energy
A method for improving the performance of sections of rails joined together by welding by reworking welded joints utilizing an ultrasonic impact treatment (UIT) process either before welding, during welding, after welding or during repairs of used rails, including treatment of a joint, around a joint and / or length of a rail, in order to increasing fatigue life and / or other properties of welded rail sections is disclosed. The method provides reduction of stress defects and redistribution of internal stress patterns in the vicinity of weld seams of rails. The UIT provides periodic pulse energy impact treatment with surfaces in welded rails to induce internal compression waves inducing a metal plasticity state in the vicinity of the weld seam of the rail or in the rail itself.
Owner:UIT LLC
Positive electrode active material for lithium secondary battery and method for producing same
InactiveUS20070117014A1Improve securityLarge capacityNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsActive material electrodesParticulatesLithium-ion battery
It is to provide a cathode active material for a lithium ion secondary battery, which has high safety, a high discharge voltage, a large capacity and excellent cyclic durability, and a process for producing it. A cathode active material for a lithium secondary battery, characterized by comprising a particulate lithium cobalt composite oxide represented by the formula LiaCobAlcMgdAeOfFg (1) (wherein A is Ti, Nb or Ta, O.90≦a≦1.10, 0.97≦b≦1.00, 0.000l≦c≦0.02, 0.000l≦d≦0.02, 0.000l≦e≦0.01, 1.98≦f≦2.02, 0≦g≦0.02, and 0.0003≦c+d+e≦0.03).
Owner:AGC SEIMI CHEM CO LTD
Positive electrode material for lithium secondary cell and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20060222951A1High cycle durabilityImprove securityElectrode manufacturing processesFluoride preparationLithiumHigh pressure
A positive electrode material for a lithium secondary battery for high voltage high capacity use exhibiting high cycle durability and high safety. The positive electrode material is composed of particles having a composition represented by the general formula: LiaCObMgcAdOeFf (A is the group 6 transition element or the group 14 element, 0.90≦a≦1.10, 0.97≦b≦1.00, 0.0001≦c>0.03, 0.0001≦d≦0.03, 1.98≦e≦2.02, 0≦f≦0.02 and 0.0001≦c+d≦0.03), and magnesium, the element A and fluorine exist uniformly in the vicinity of the surfaces of the particles.
Owner:AGC SEIMI CHEM CO LTD
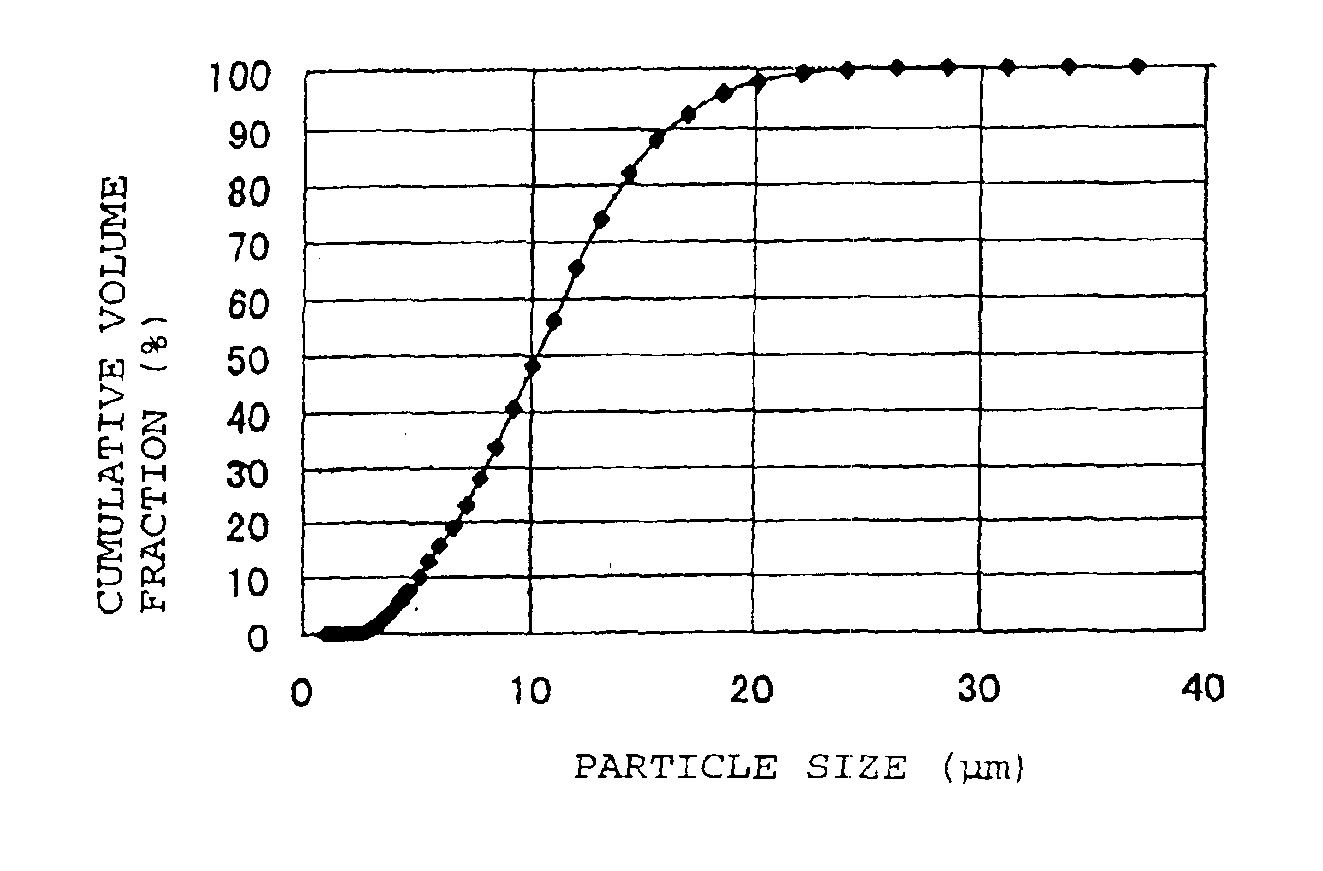
Lithium-transition metal composite oxide
InactiveUS6929883B2Large volume capacity densityImprove securityAlkali titanatesOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideAlkaline earth metalMetallurgy
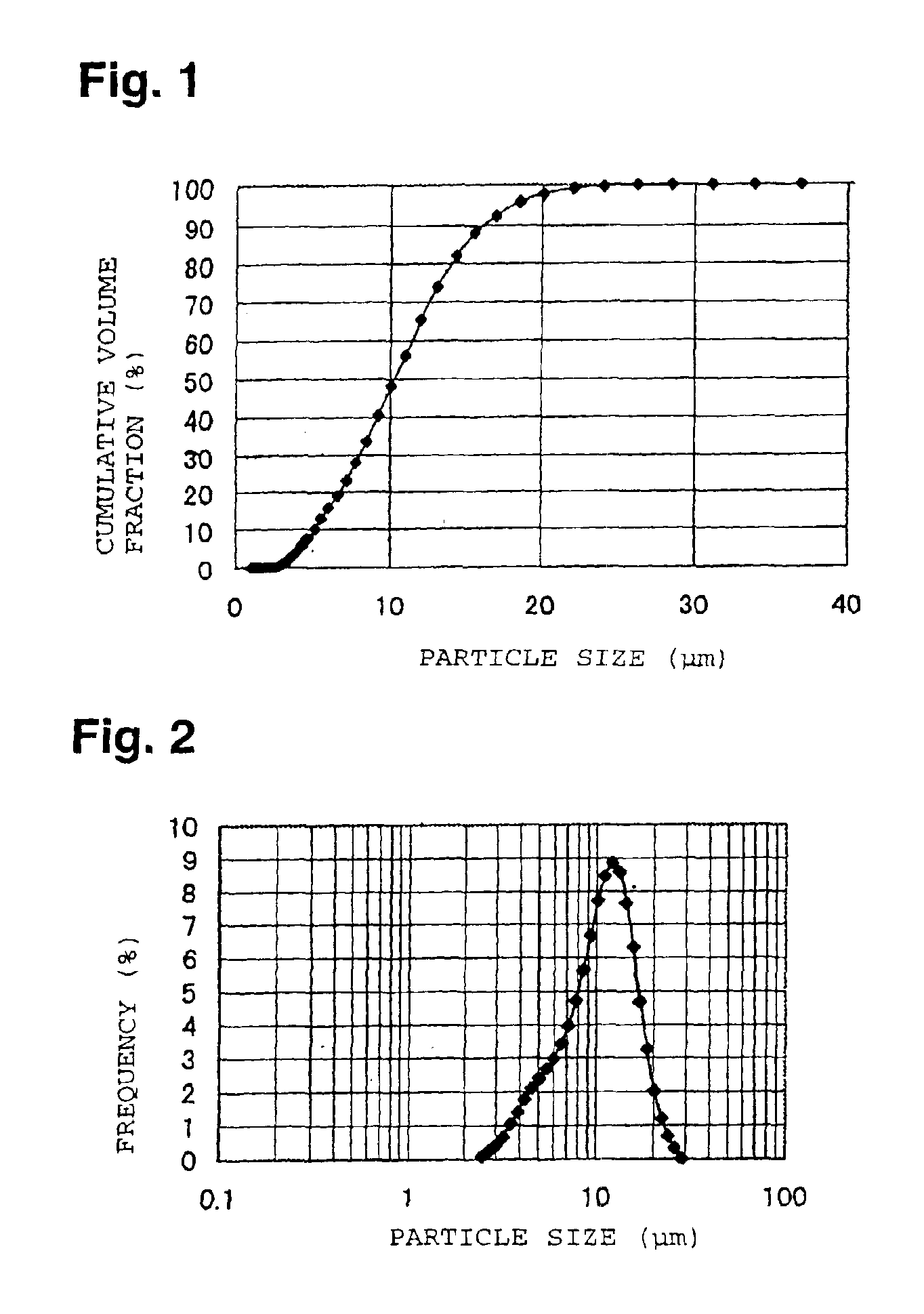
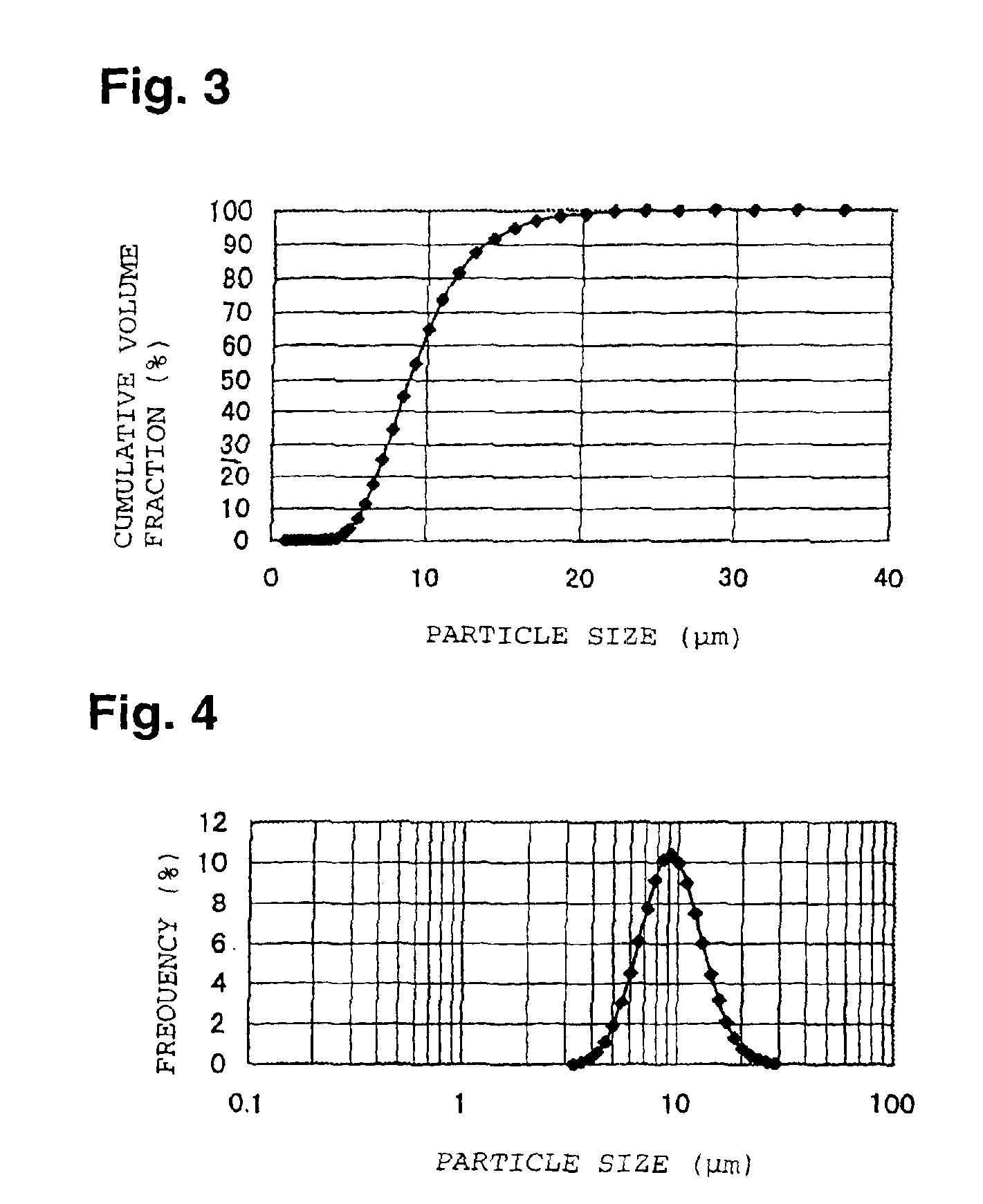
The present invention provides a lithium-transition metal composite oxide having a large volume capacity density, high safety, excellent coating uniformity, excellent charge / discharge cycle durability and excellent low temperature characteristics, and suitable as a positive electrode active material for a lithium secondary cell.A lithium-transition metal composite oxide which is represented by the formula LixM1−yNyO2 (wherein 0.2≦x≦1.2, 0≦y≦0.7, M is a transition metal element, and N is a transition metal element other than M or an alkaline earth metal element), wherein in the distribution curve of the cumulative volume particle size of said lithium composite oxide, the inclination of the curve at a cumulative volume fraction of 20% and 80% are at most 9% / μm and at least 3% / μm, respectively, and the average particle size is from 3 to 20 μm.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Si ALLOY NEGATIVE ELECTRODE ACTIVE MATERIAL FOR ELECTRIC DEVICE
ActiveUS20120175551A1Suppressing amorphous-crystal phase transitionImprove cycle lifeVapour deposition manufacturingSilicon alloyEngineering
[Problem]Provided is a negative electrode active material for an electric device which exhibits a well-balanced property of maintaining a high cycle property and attaining a high initial capacity.[Technical solution]The negative electrode active material for an electric device comprising an alloy having a composition formula SixZnyAlz (where each of x, y, and z represents amass percent value, satisfying (1) x+y+z=100, (2) 21≦x<100, (3) 0<y<79, and (4) 0<z<79).
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Colloidal electrolyte of lead acid storage battery, and preparation method for colloidal electrolyte
ActiveCN105514503AGood gelReduce contentLead-acid accumulatorsElectrolyte immobilisation/gelificationLithium hydroxideGas phase
The invention discloses a colloidal electrolyte which is good in liquidity, easy to perfuse and capable of improving the high-current discharge performance of a battery at a low temperature and prolonging a cycle service life of the battery, and a preparation method for the colloidal electrolyte. The colloidal electrolyte comprises sulfuric acid, gas-phase silicon dioxide, silica sol, lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, polyacrylamide, stannous mono-sulphate, cerous sulfate, sodium of plyaspartic acid or salt of sodium of plyaspartic acid, and the balance of deionized water, wherein the total content of silicon dioxide in a mixed solution is 2.8-3.2%. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a gas-phase silicon dioxide mother liquid, secondly, preparing dilute sulphuric acid electrolyte, adding the gas-phase silicon dioxide mother liquid into the dilute sulphuric acid electrolyte, and thirdly, adding silica sol to obtain the colloidal electrolyte of a lead acid storage battery.
Owner:GUANGDONG DYNAVOLT NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Battery manufacturing method (as amended)
ActiveUS20130202781A1Good adhesivenessImprove quality stabilityFinal product manufactureSecondary cellsSolventAqueous solution
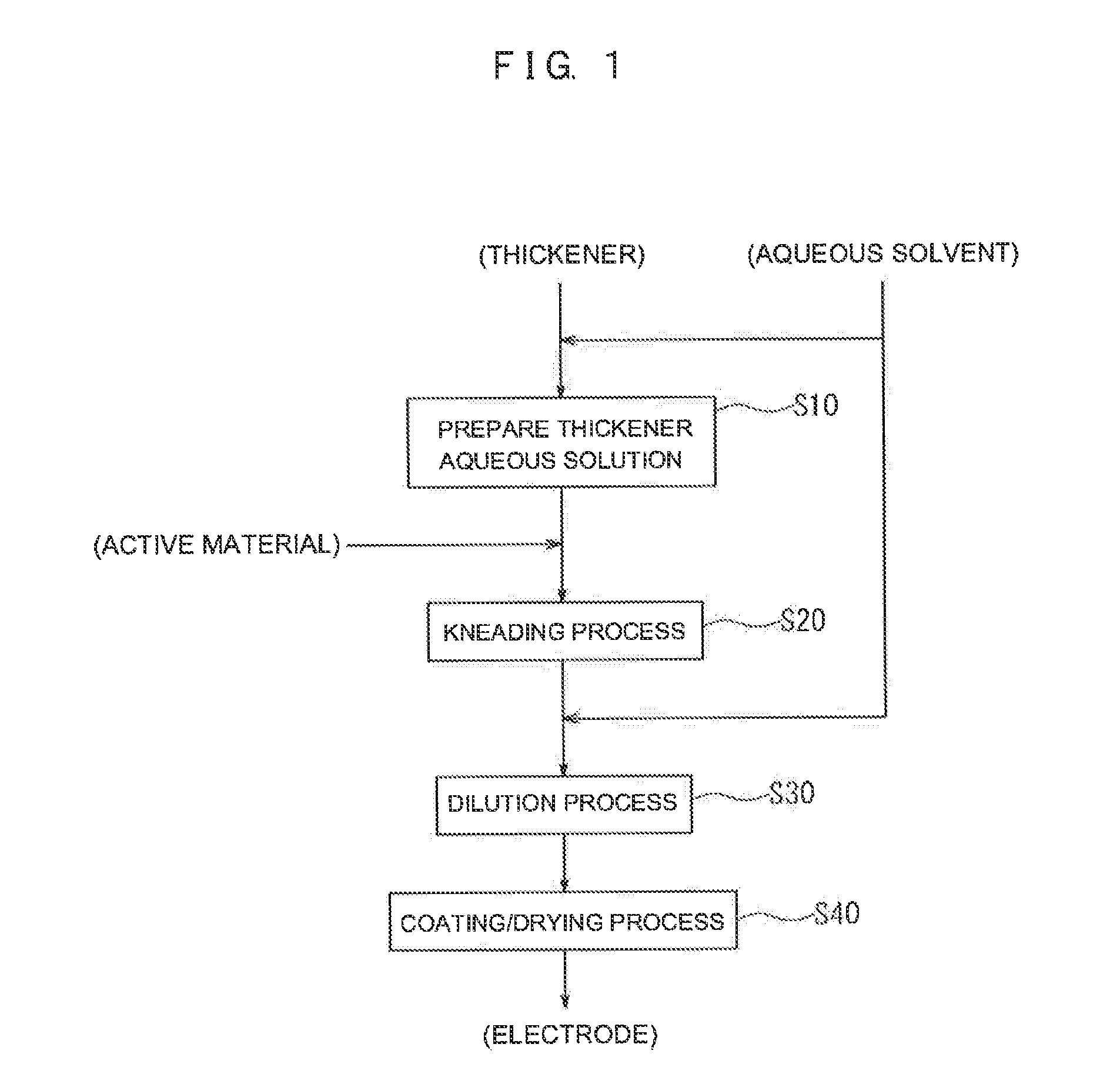
The present invention provides a battery manufacturing method including: a step of preparing a thickener aqueous solution by dissolving a thickener in an aqueous solvent (S10); a kneading step of introducing an active material into the prepared thickener aqueous solution and kneading a result (S20); a diluting step of adding an aqueous solvent to a kneaded material resulting from the kneading step such that the kneaded material is diluted, whereby an active material layer forming paste is obtained from the kneaded material (S30); and a step of obtaining an electrode in which an active material layer is formed on a current collector by coating the current collector with the active material layer forming paste and then drying the paste (S40).
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Positive electrode material for lithium secondary cell and process for producing the same
InactiveUS7615315B2High cycle durabilityImprove performanceElectrode manufacturing processesFluoride preparationLithiumHigh pressure
A positive electrode material for a lithium secondary battery for high voltage high capacity use exhibiting high cycle durability and high safety. The positive electrode material is composed of particles having a composition represented by the general formula: LiaCobMgcAdOeFf (A is the group 6 transition element or the group 14 element, 0.90≦a≦1.10, 0.97≦b≦1.00, 0.0001≦c≦0.03, 0.0001≦d≦0.03, 1.98≦e≦2.02, 0≦f≦0.02 and 0.0001≦c+d≦0.03), and magnesium, the element A and fluorine exist uniformly in the vicinity of the surfaces of the particles.
Owner:AGC SEIMI CHEM CO LTD
Si ALLOY NEGATIVE ELECTRODE ACTIVE MATERIAL FOR ELECTRIC DEVICE
ActiveUS20120153220A1Suppressing amorphous-crystal phase transitionImprove cycle lifeCell electrodesSecondary cellsAlloyElectron
[Problem]Provided is a negative electrode active material for an electric device which exhibits a well-balanced property of maintaining a high cycle property and attaining a high initial capacity.[Technical solution]The negative electrode active material for an electric device comprising an alloy having a composition formula SixTiyZnz (where each of x, y, and z represents amass percent value, satisfying (1) x+y+z=100, (2) 38≦x<100, (3) 0<y<62, and (4) 0<z<62).
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Lead plaster composition for manufacturing negative plate of lead-acid battery, negative plate of lead-acid battery, and lead-acid battery
ActiveCN103390749AIncrease profitExtend your lifeLead-acid accumulatorsLead-acid accumulator electrodesFiberSulfate
The invention provides a lead plaster composition for manufacturing a negative plate of a lead-acid battery. The lead plaster composition comprises the following components in percentage by weight (based on the weight of lead powder): 10.5-11.5% of water, 11.5-12.5% of dilute sulphuric acid, 0.7-0.9% of barium sulfate, 0.2-0.3% of carbon black, 0.07-0.09% of short fiber, 0.4-1.6% of gallium sulfate or germanium sulfate, and the lead powder. In the lead plaster composition, due to addition of the gallium sulfate or the germanium sulfate, the growth of lead granules can be inhibited, a mixed crystal is easily formed, the compact passivation phenomenon on the surface of an electrode during large-current discharge is effectively avoided, the cycle life under large-current discharge of the battery is greatly prolonged. The invention also provides the negative plate of the lead-acid battery, manufactured by adopting the lead plaster composition, as well as the lead-acid battery assembled by the negative plate of the lead-acid battery.
Owner:YANCHENG SILU INFORMATION TECH SERVICE CO LTD
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN104247130AInhibit deteriorationHigh cycle durabilityFinal product manufacturePositive electrodesOrganic solventAlloy
The present invention provides a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell in which degradation of the electrolytic solution or the negative electrode active material is minimized and excellent cycle durability achieved, and a method for manufacturing the same. This non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell is provided with: a positive electrode capable of doping and de-doping lithium ions; a negative electrode capable of occluding and releasing lithium ions, lithium, or a lithium alloy; and an electrolytic solution containing an organic solvent, a lithium salt electrolyte, and an additive. The positive electrode active material of the positive electrode contains a layered lithium-containing transition metal oxide represented by formula (1) Li1.5[NiaCobMnc[Li]d]O3 (where a, b, c, and d satisfy 0 < a < 1.4, 0 <=b< 1.4, 0< c< 1.4, 0< d<= 0.5, a + b + c + d = 1.5, and 1.0<= a + b + c< 1.5), and a spinel phase present in a part thereof. The negative electrode active material of the negative electrode contains a carbon-based material in which all or part of the surface thereof is covered with a coating derived from an additive.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Electrical device
InactiveUS9954252B2High cycle durabilityEasy to set upCell electrodesSecondary cellsLithiumElectrical devices
To provide a means capable of further improving cycle durability in an electrical device such as a lithium ion secondary battery containing a positive electrode using a solid solution positive electrode active material. An electrical device has a power generating element containing a positive electrode in which a positive electrode active material layer containing a positive electrode active material is formed on a surface of a positive electrode current collector, a negative electrode in which a negative electrode active material layer containing a negative electrode active material is formed on a surface of a negative electrode current collector, and a separator impregnated with an electrolytic solution. The negative electrode active material layer contains a negative electrode active material represented by formula (1). The positive electrode active material layer contains a positive electrode active material (solid solution positive electrode active material) represented by formula (2). As the solid solution positive electrode active material contained in the positive electrode active material layer, a material having a composition represented by formula (3) as a basic structure is used. The electrolytic solution contains a predetermined additive.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Oxide resistor storage device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102148328AGood reliabilitySimple preparation processElectrical apparatusControl layerData retention
The invention discloses an oxide resistor storage device, which comprises a substrate, a bottom electrode positioned on the substrate, an oxide control layer positioned on the bottom electrode, an oxide resistance change layer positioned on the oxide control layer, and a top electrode positioned on the oxide resistance change layer. The device is simple in preparation process and reliable in performance, the circulating durability of the resistance change of an oxide resistance change storage is improved and the data retention performance is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Hydrogen storage alloy, preparation process thereof, and hydrogen storage device
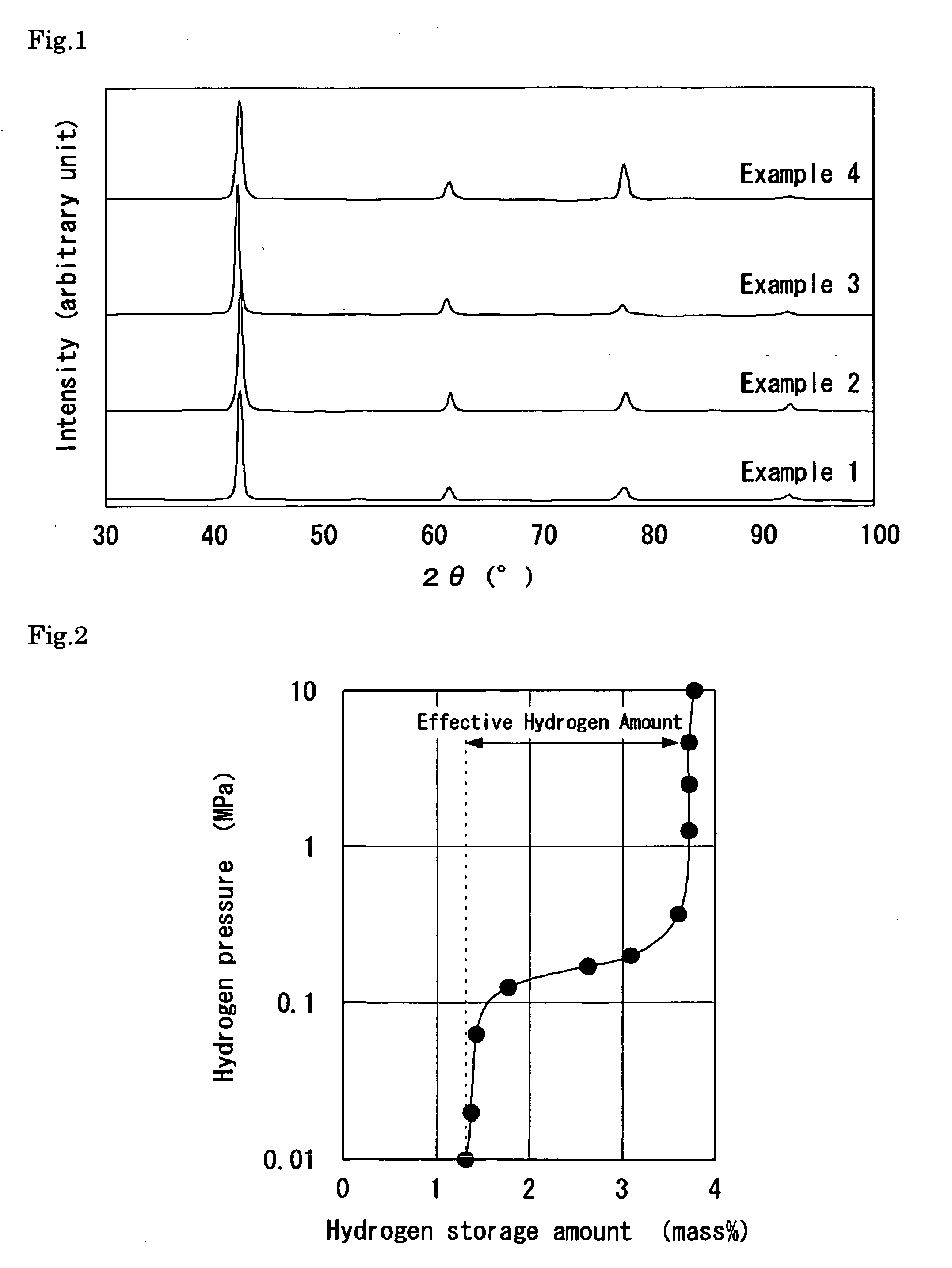
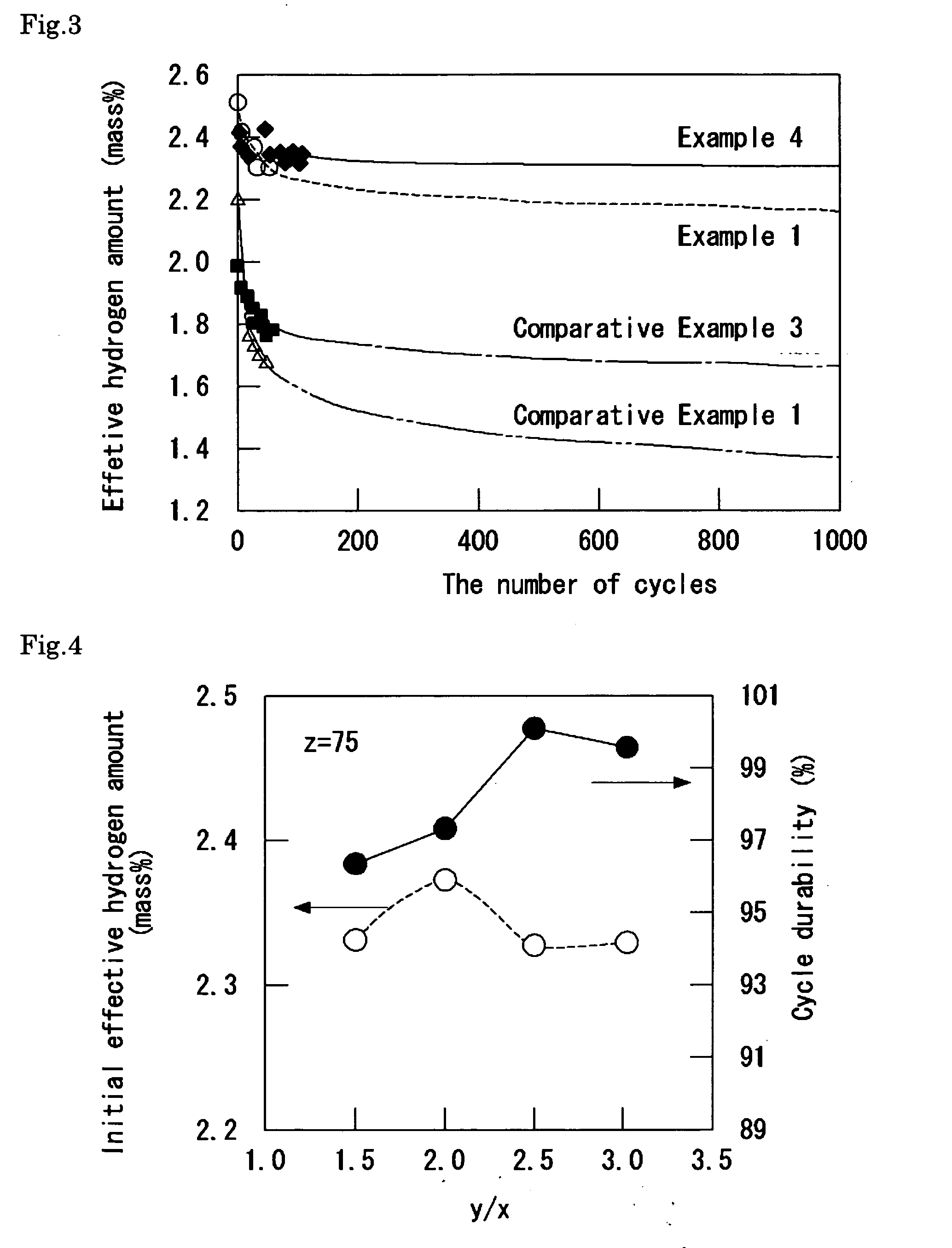
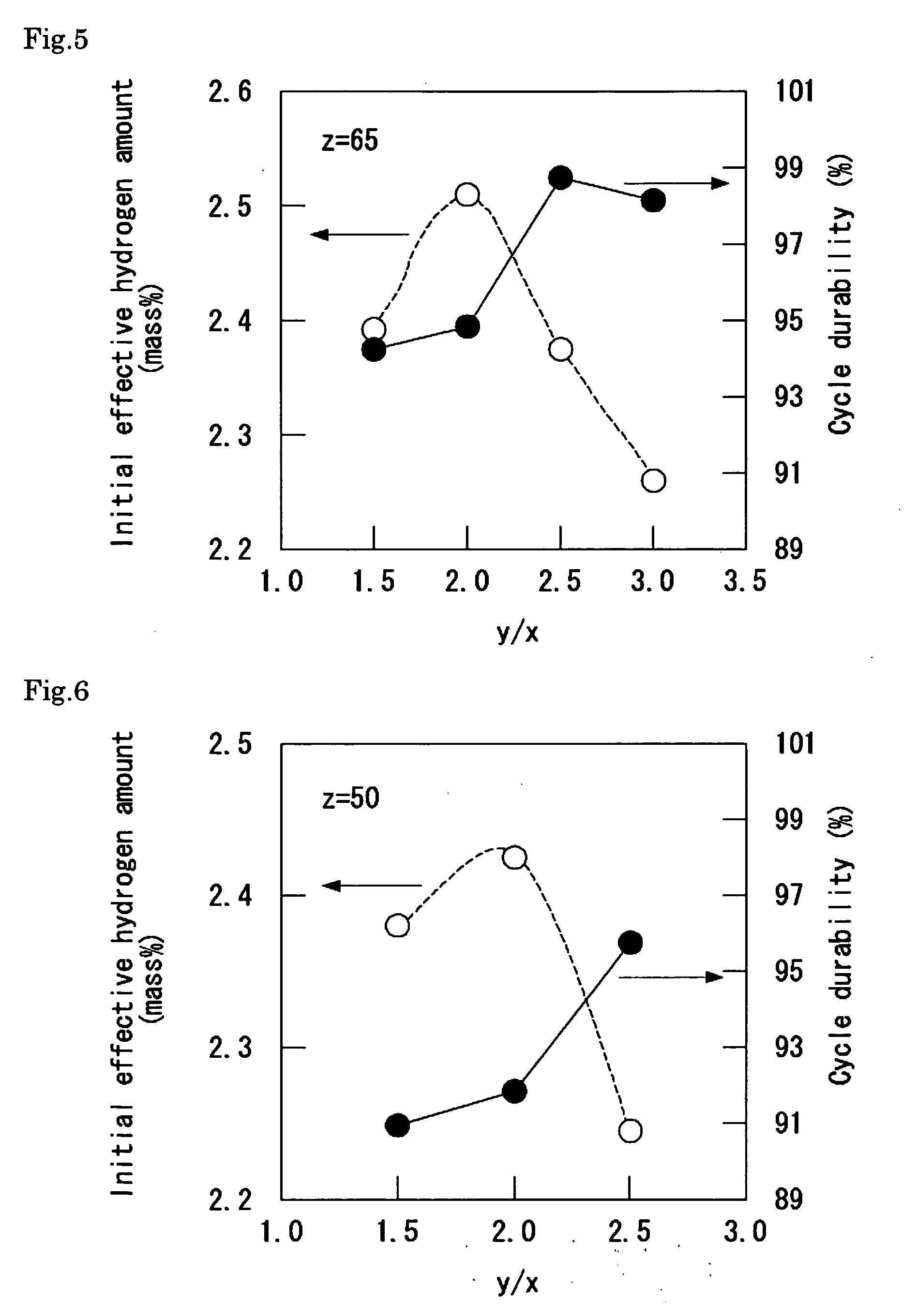
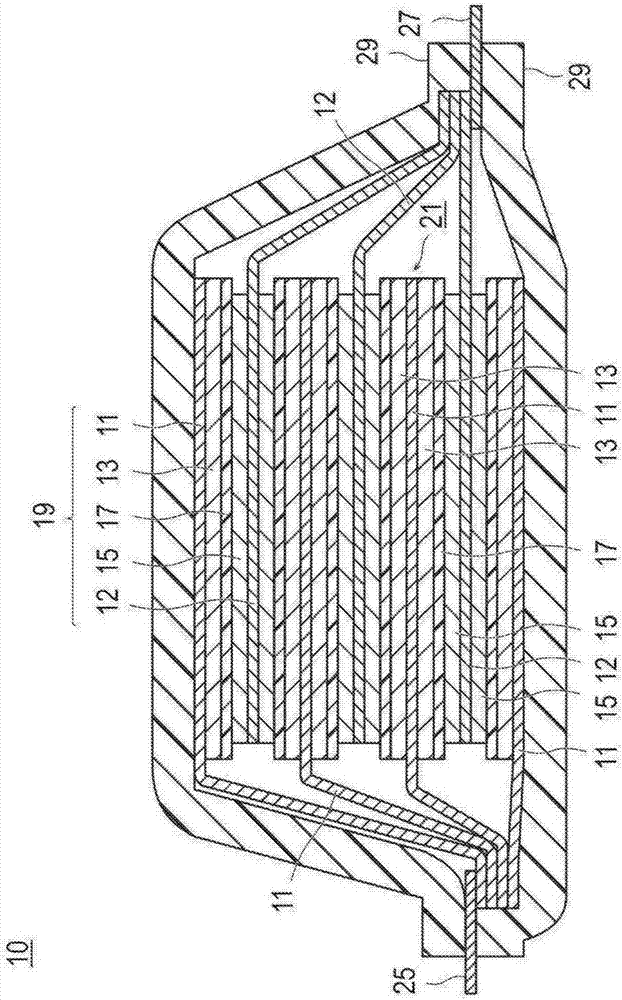
InactiveUS20100230299A1High initial effective hydrogen amountHigh cycle durabilityHydrogenFoundry mouldsIngotHeat treating
The hydrogen storage alloy has, as a main phase thereof, a bcc structure phase having a composition represented by TixCryVzXw wherein 3 / 2≦y / x≦3 / 1, 50≦z≦75 mol %, 0≦w≦5 mol %, and x+y+z+w=100 mol %, and X represents any one or more selected from Al, Si, and Fe. The hydrogen storage device is a device using the alloy. The preparation process of a hydrogen storage alloy includes the steps of: melting / casting raw materials mixed to give the composition represented by TixCryVzXw; heat-treating an ingot obtained in the melting / casting step; and subjecting the heat-treated ingot to a hydrogen storing / releasing treatment at least once to activate the ingot.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Negative-electrode active material for electrical device, and electrical device using same
ActiveCN107112518AAvoid expansion and contractionHigh cycle durabilityNegative electrodesLi-accumulatorsX-rayElectrical devices
The invention provides a means capable of improving the cycle durability of an electrical device such as a lithium-ion secondary battery. [Solution] Using, for an electrical device, a negative-electrode active material made of a silicon-containing alloy that has a predetermined composition and has a structure in which silicide phases including a silicide of a transition metal are dispersed in a matrix phase including amorphous or low-crystalline silicon as a main component, wherein, in an X-ray diffraction measurement of said silicon-containing alloy using a CuKalpha1 beam, the value of the ratio (B / A) of the diffraction peak intensity B of the transition metal silicide in the range 2 [theta] = 37 to 45 degrees to the diffraction peak intensity A of the (111) plane of Si in the range 2 [theta] = 24 to 33 degrees is 0.41 or greater.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Method for manufacturing battery electrode
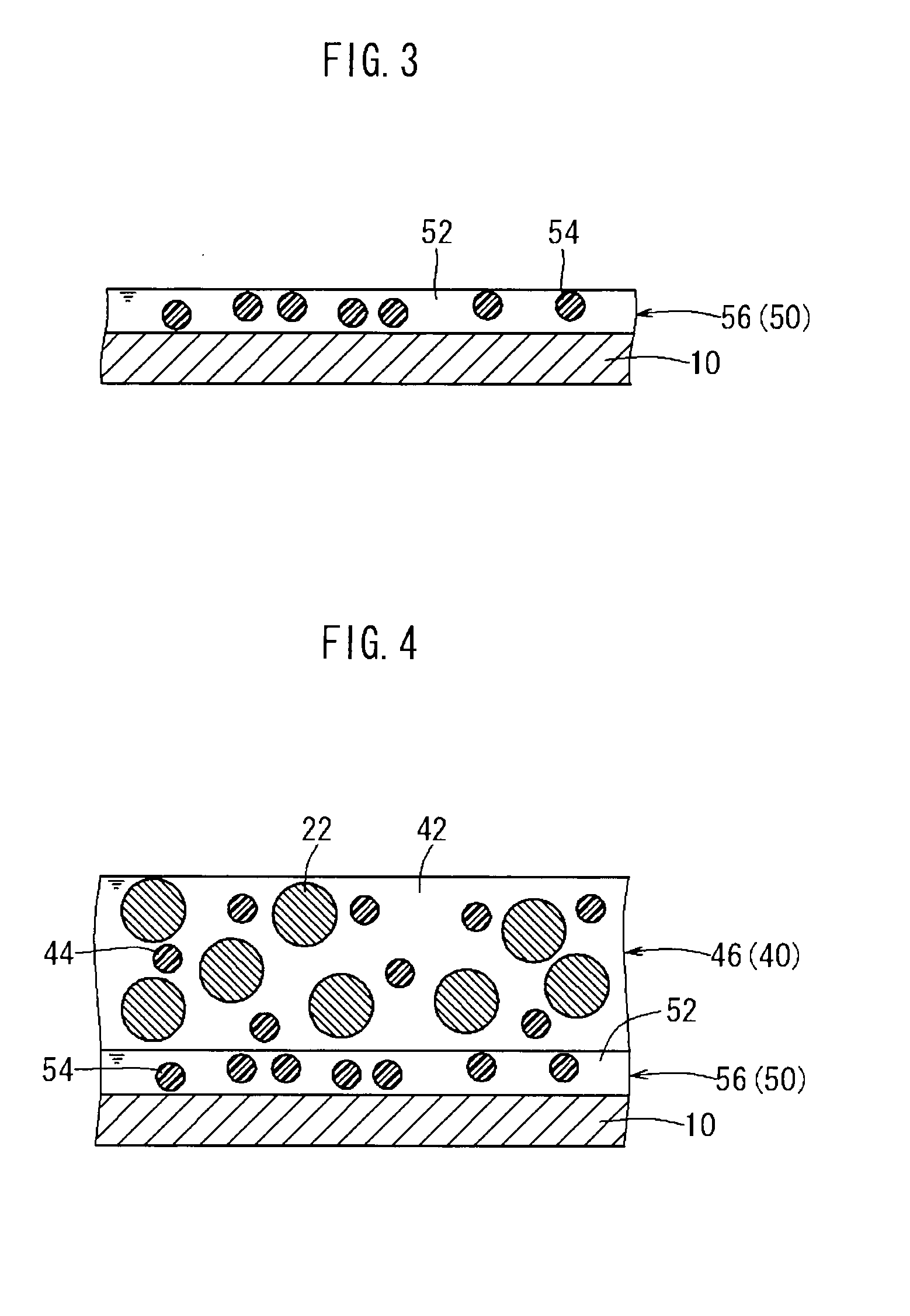
ActiveUS20130004855A1Reduce the amount requiredAdhesive strengthFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsMetallurgyMixed materials
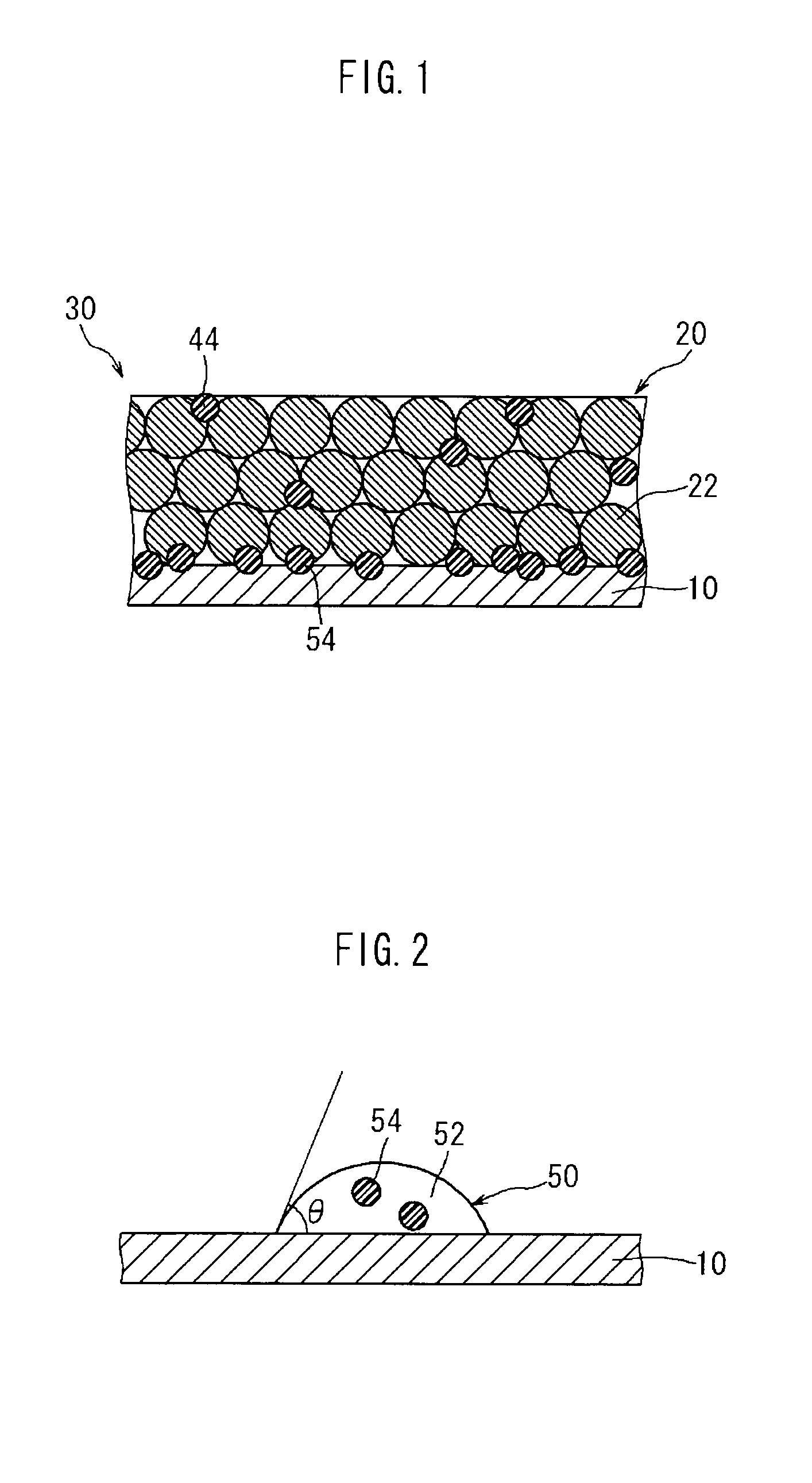
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a battery electrode. This method comprises the steps of applying a binder solution 50 that contains a binder 54 and is adjusted so that the contact angle of the binder solution 50 with the surface of a current collector 10 is 73° or less, to form a binder solution layer 56; applying a mixed material paste 40 containing an active material 22 on top of the binder solution layer 56, to deposit both the binder solution layer 56 and a mixed material paste layer 46 on the current collector 10; and obtaining an electrode 30 in which a mixed material layer 20 is formed on the current collector 10, by drying the deposited binder solution layer 56 and mixed material paste layer 46 together.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Solid storage battery having solid and liquid phase electrolyte
InactiveCN1702900AWill not harmImprove liquidityLead-acid accumulatorsFinal product manufactureElectrochemical responseFiber
This invention relates to a second battery with different electrolytes, which solves the problems of the solid storage battery with low capacity when entering the activity subject holes and capillary. The invention relates adopts abio-compound fiber material package electrode board as isolation board and filling the hydraulic electrolytes between the electrode and the isolation board. The invention overcomes the above shortcomings and has a battery with good quality and solid electrode board.
Owner:胡延强
Electrical device
InactiveUS20170012320A1High cycle durabilityEasy to set upCell electrodesSecondary cellsLithiumEngineering
To provide a means capable of further improving cycle durability in an electrical device such as a lithium ion secondary battery containing a positive electrode using a solid solution positive electrode active material.An electrical device has a power generating element containing a positive electrode in which a positive electrode active material layer containing a positive electrode active material is formed on a surface of a positive electrode current collector, a negative electrode in which a negative electrode active material layer containing a negative electrode active material is formed on a surface of a negative electrode current collector, and a separator impregnated with an electrolytic solution. The negative electrode active material layer contains a negative electrode active material represented by formula (1). The positive electrode active material layer contains a positive electrode active material (solid solution positive electrode active material) represented by formula (2). As the solid solution positive electrode active material contained in the positive electrode active material layer, a material having a composition represented by formula (3) as a basic structure is used. The electrolytic solution contains a predetermined additive.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Method of manufacturing negative electrode for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery
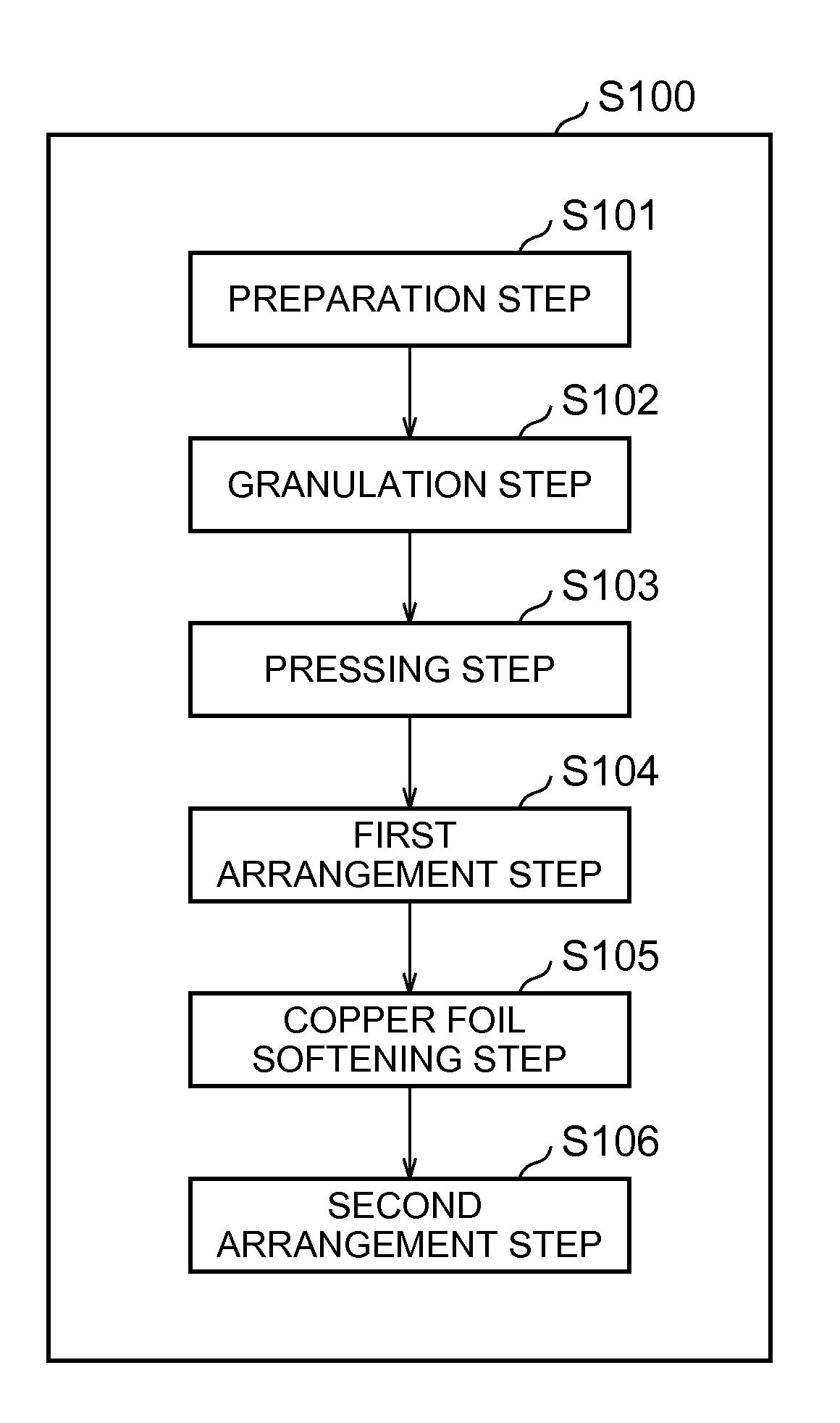
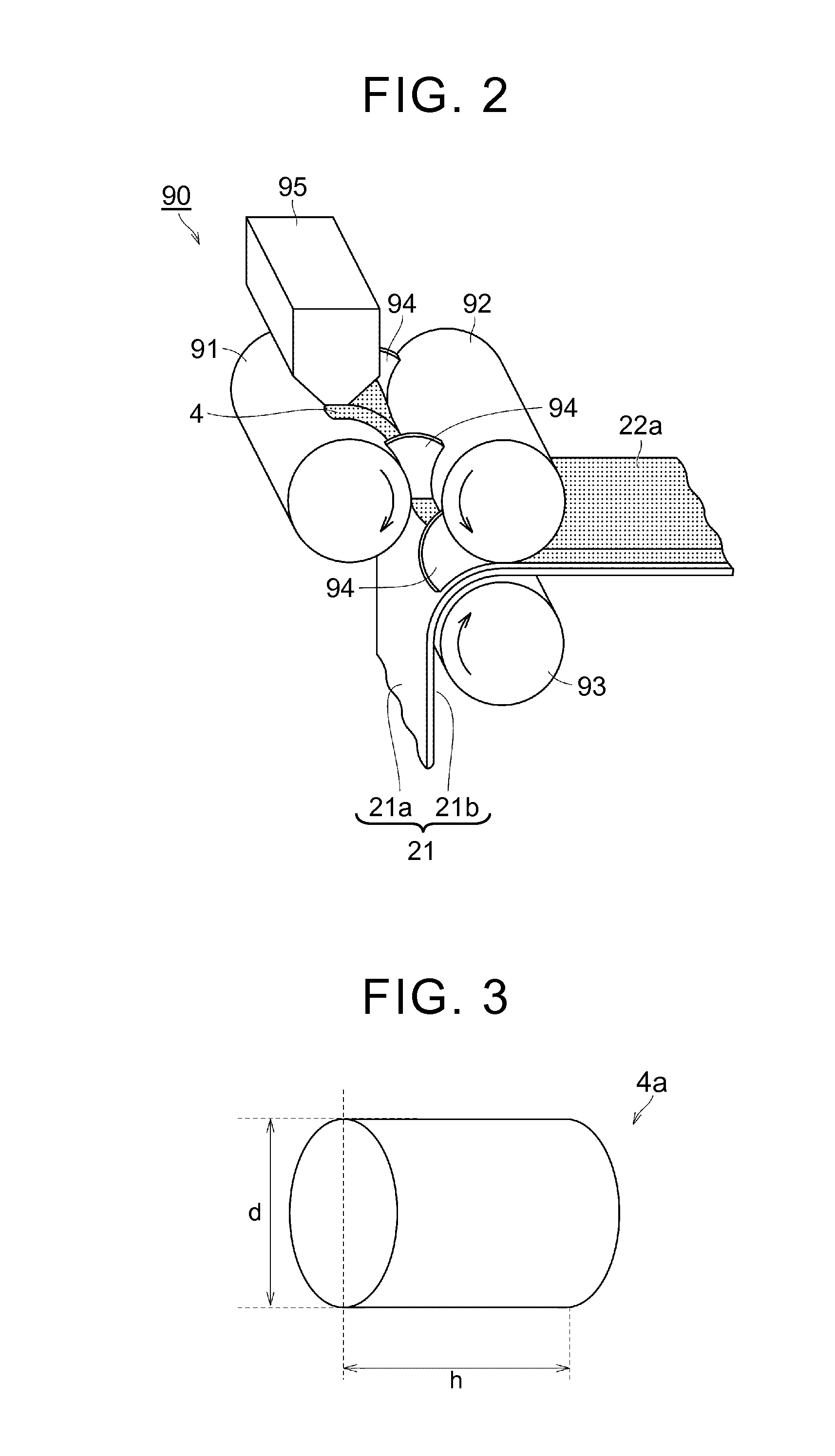
ActiveUS20160141597A1Superior in cycle durabilityHigh cycle durabilityElectrode rolling/calenderingElectrode thermal treatmentSolventCopper foil
A method of manufacturing a negative electrode for a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery includes: preparing a copper foil having a first main surface and a second main surface that are opposite sides of the copper foil; obtaining a granulated body by mixing a negative electrode active material, a thickener, a binder, and a solvent with each other to obtain a mixture and by granulating the mixture; obtaining a first negative electrode mixture layer by pressing the granulated body; arranging the first negative electrode mixture layer on the first main surface; and softening the copper foil by bringing the second main surface into contact with a heated roller in a state where the first negative electrode mixture layer is arranged on the first main surface. A temperature of the heated roller is a recrystallization temperature of the copper foil or higher.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Lithium Ion Capacitor
ActiveUS20160300666A1High characteristic highIncrease energy densityHybrid capacitor electrolytesHybrid capacitor electrodesCarbon compositesNon aqueous electrolytes
This lithium ion capacitor results from housing an electrode laminate body, which comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode, and a separator, and a non-aqueous electrolyte, which contains a lithium-ion-containing electrolyte, in an external body, wherein the negative electrode has a negative electrode current collector and a negative electrode active material layer containing a negative electrode active material that can occlude and release lithium ions on one or both surfaces of the negative electrode current collector, and the following (i) to (iii) are all satisfied: (i) the negative electrode active material is a carbon composite material containing carbon black and a carbonaceous material; (ii) the negative electrode is doped with lithium ion at between 1,050 mAh / g and 2,500 mAh / g, inclusive, per unit mass of the negative electrode active material; and (iii) the thickness of the negative electrode active material layer is between 10 μm and 60 μm, inclusive, per side.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
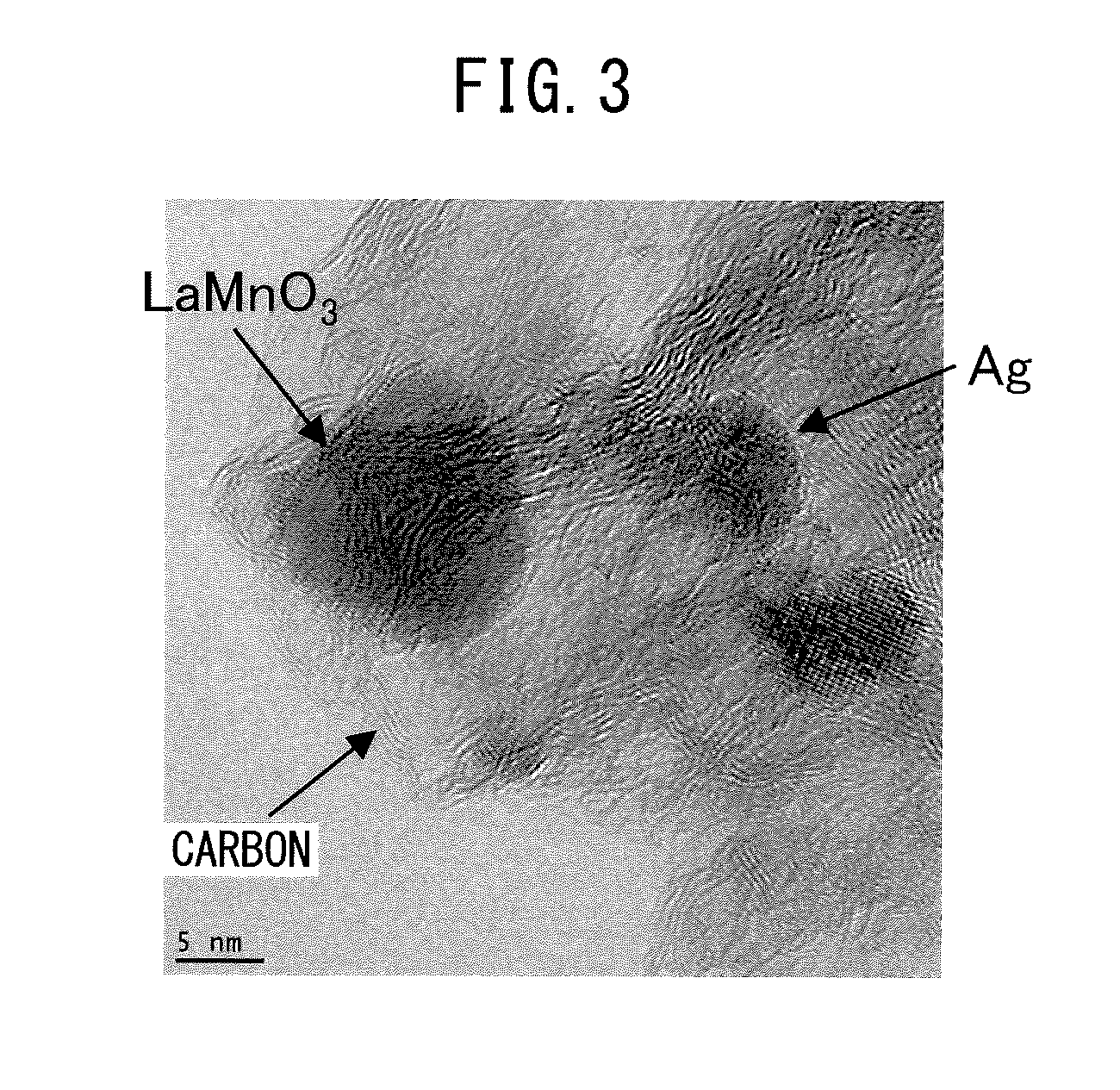
Electrode catalyst
InactiveUS20160104897A1Increase ORR activityHigh oxygen dissociation capacityFuel and primary cellsHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsMetal catalystManganese
An electrode catalyst includes a carbon (C) carrier; a perovskite-type oxide catalyst containing lanthanum (La), manganese (Mn), and oxygen (O) elements; and a metal catalyst containing a silver (Ag) element. The perovskite-type oxide catalyst is located on the carrier and the metal catalyst is also located on the carrier.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
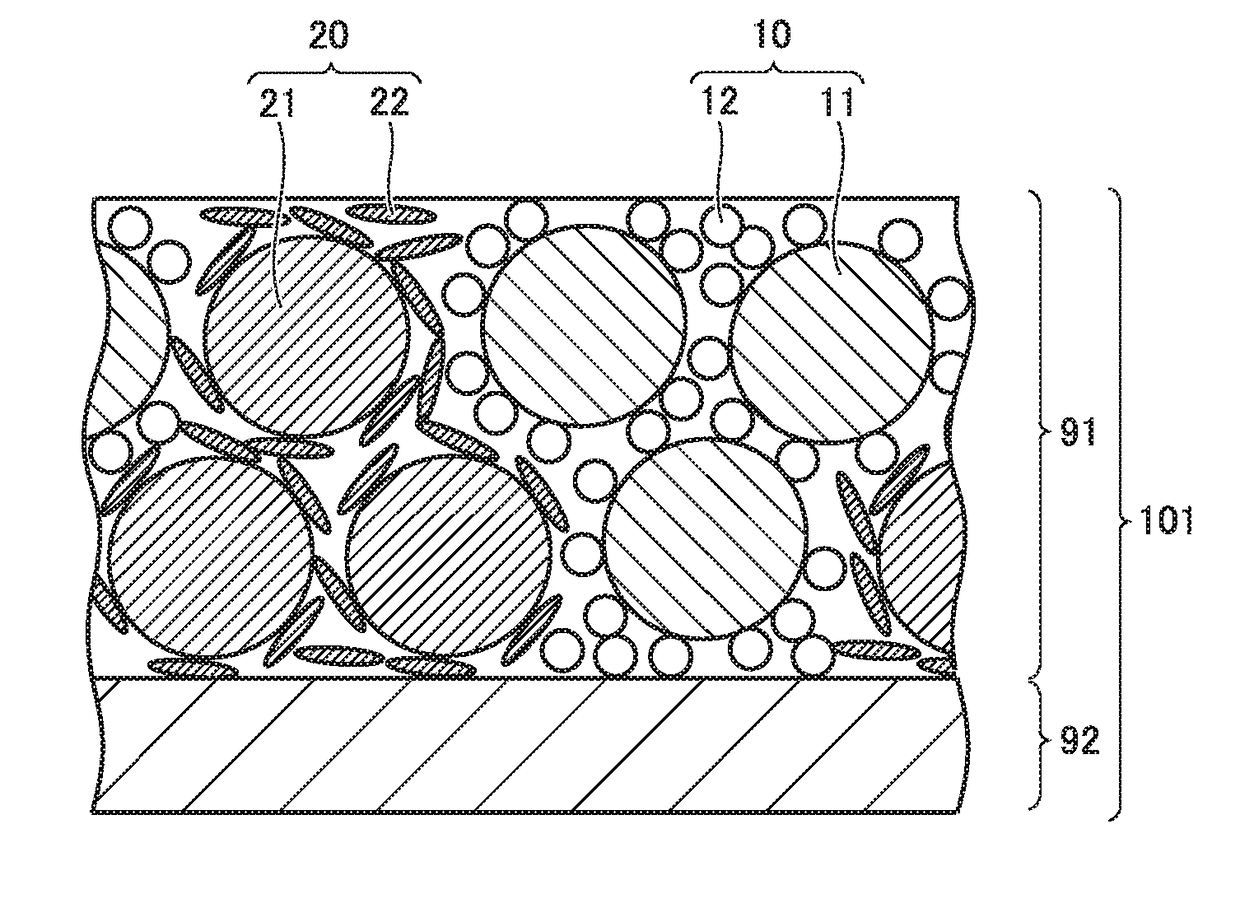
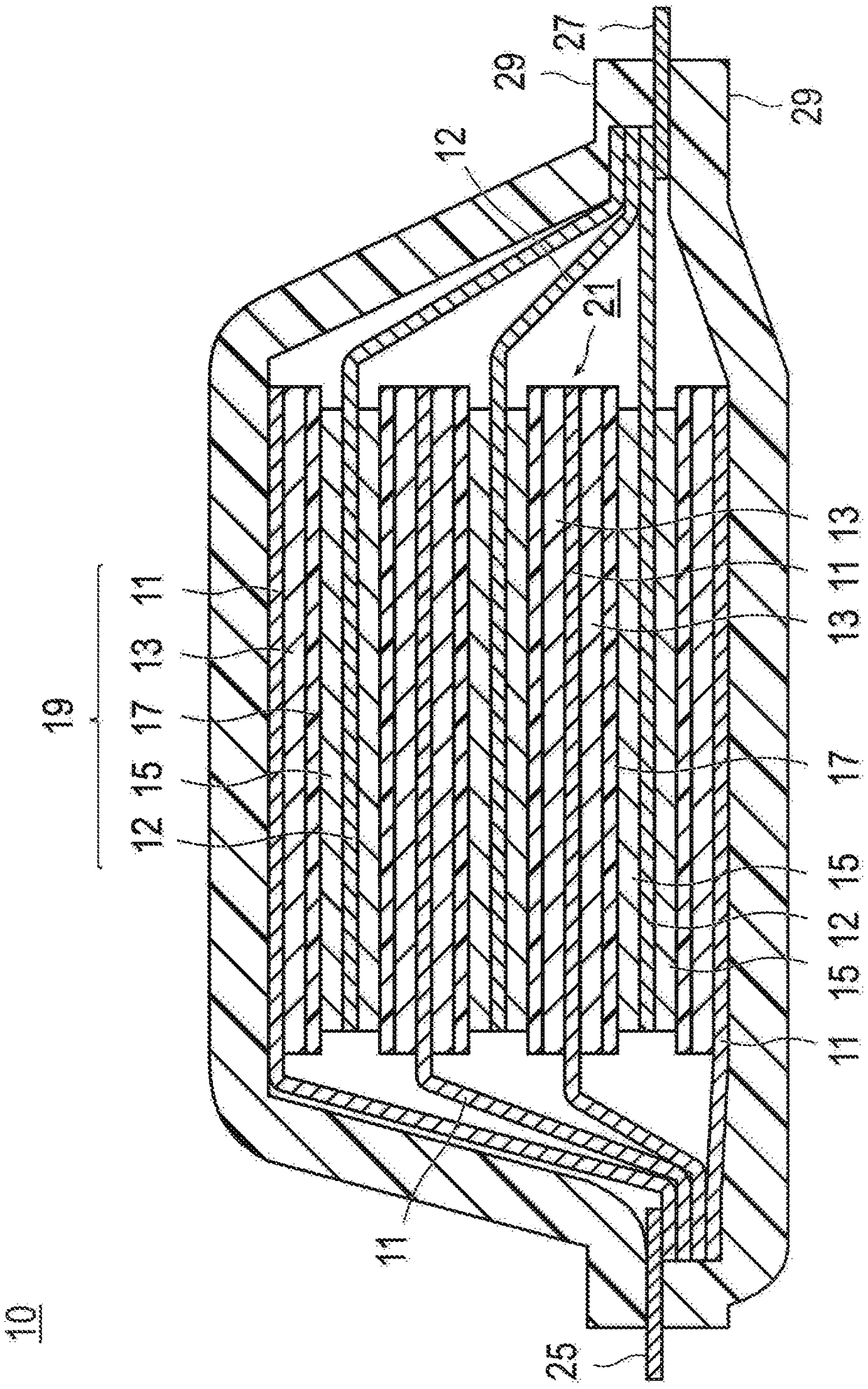
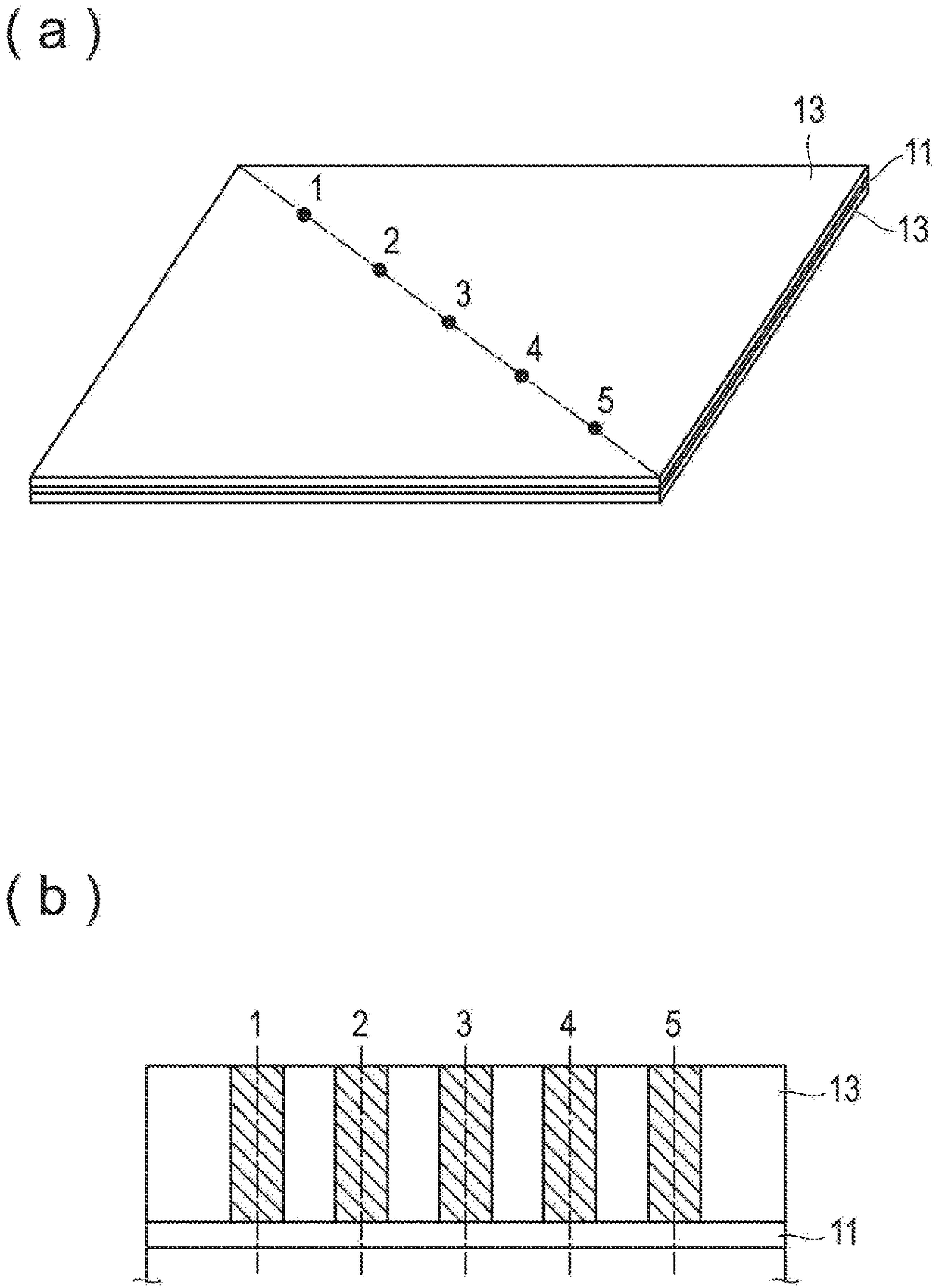
ActiveCN109075376ASuppression of unevenness in the distance between electrodesExcellent cycle durabilityFinal product manufactureNegative electrodesChemistryAqueous electrolyte
The invention is to provide a means for achieving adequate charge / discharge cycle characteristics in a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery having large capacity and a large area even when a mixture of a high-capacity Si material and a carbon material that swells little is used as a negative electrode active material. A non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery in which the value of the ratioof the battery volume (the product of the thickness of the battery and the projected area of the battery including a battery exterior body) with respect to the rated capacity is 10 cm<3> / Ah or less and the rated capacity is 3 Ah or more, said non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery comprising a power generation element that includes: a positive electrode in which a positive electrode active material layer including a positive electrode active material is formed on the surface of a positive electrode current collector; a negative electrode in which a negative electrode active material layerincluding a negative electrode active material is formed on the surface of a negative electrode current collector; and a separator. The non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery is characterized in that: the negative electrode active material layer contains a negative electrode active material represented by formula (1) alpha (Si material) and beta (carbon material) (in the formula, the Si material is one or more substances selected from the group consisting of Si-containing alloys and SiOx (x represents the number of oxygen atoms satisfying the valence of Si) that is a mixture of amorphous SiO2 particles and Si particles, the carbon material is one or more substances selected from the group consisting of graphite, hardly graphitizable carbon, and amorphous carbon, alpha and beta representthe mass% of the individual components in the negative electrode active material layer, 80 <= alpha + beta <= 98, 0.1 <= alpha <= 40, and 58 <= beta <= 97.9); and when a plurality of discretionary locations within the plane of the negative electrode active material layer are selected and the area ratios (%) of the Si material and the carbon material in the area of the field of view in each of images of a cross section of the negative electrode active material layer are denoted respectively as S (%) and (100-S) (%), the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value of S is within5%.
Owner:ENVISION AESC JAPAN LTD
Preparation method of multivalent lithium manganese oxide
The invention relates to a preparation method of multivalent lithium manganese oxide, and belongs to the field of electrochemical engineering and industry. Multivalent lithium manganese oxide is prepared by a high-temperature hydrothermal or high-temperature sintering method by controlling a manganese source, a lithium source and a mixing mode of the manganese source and the lithium source; a chemical formula of an obtained product is LixMn2Oy; x is greater than or equal to 2 and less than or equal to 4; and y is greater than or equal to 4 and less than or equal to 5. Manganese in multivalent lithium manganese oxide prepared by the method is in a lower valent state, contains multiple available lithium ions, and is high in specific capacity. The preparation method has the characteristics of simple technology, low cost and low pollution. A multivalent lithium manganese oxide material prepared by the method can be used in a battery system with an organic electrolyte or a neutral aqueous solution, is an appropriate active electrode material, is high in specific capacity, low in cost and high in activity, and has a wide application prospect in energy storage of an electric tool, an electromobile, a power grid and the like.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG SMARTGRID FANGHUA ELECTRICAL ENERGY STORAGE RES INST +1
Positive lead paste for lead-acid storage batteries and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110165197AIncrease manufacturing costTightly boundLead-acid accumulatorsCell electrodesFiberAntimony trioxide
The invention discloses a positive lead paste for lead-acid storage batteries, which contains the following substances in mass percentage: 71%-79% of lead powder, 8%-12% of a sulfuric acid solution, 10%-12% of deionized water, 2%-5% of red lead, 0.1%-0.3% of sodium perborate, 0.06%-0.18% of antimony oxide, 0.15%-0.2% of graphite powder and 0.07%-0.08% of fibers. According to the positive lead paste for lead-acid storage batteries, red lead is added on the basis of introducing boron and antimony elements, and the amount of antimony oxide is controlled, thereby reducing the amount of antimony while ensuring the excellent corrosion resistance of the lead paste, enhancing the electric conductivity of the batteries and preventing significant voltage drop, improving the high temperature resistance of startup lead-acid storage batteries, and thus achieving the purpose of simultaneously improving he corrosion resistance and service life of the startup lead-acid storage batteries.
Owner:JUJIANG POWER TECH CO LTD
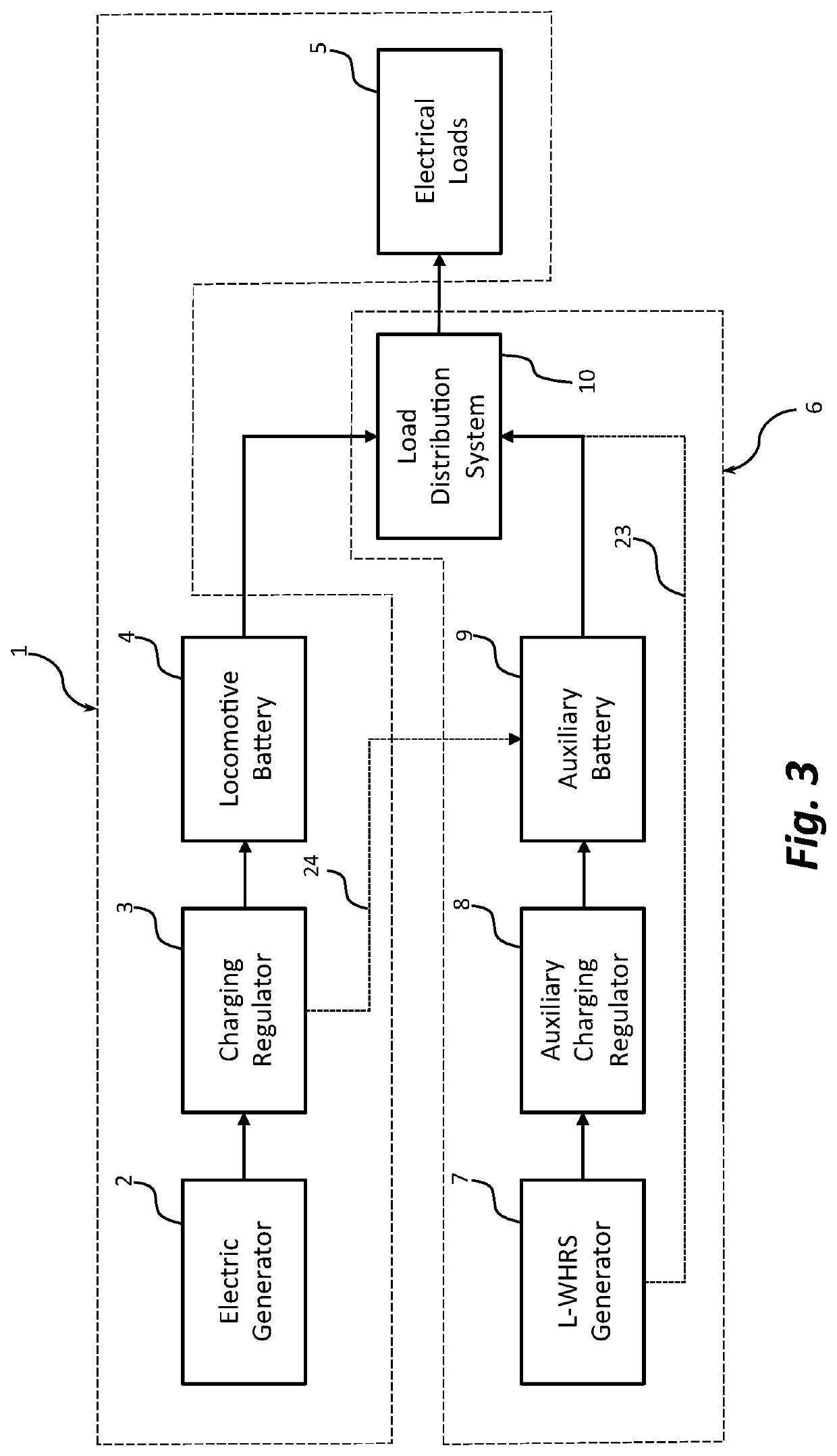
Locomotive waste heat recovery system and related methods
InactiveUS20200189625A1Large drainageAdd equipmentBatteries circuit arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesStart stopElectrical battery
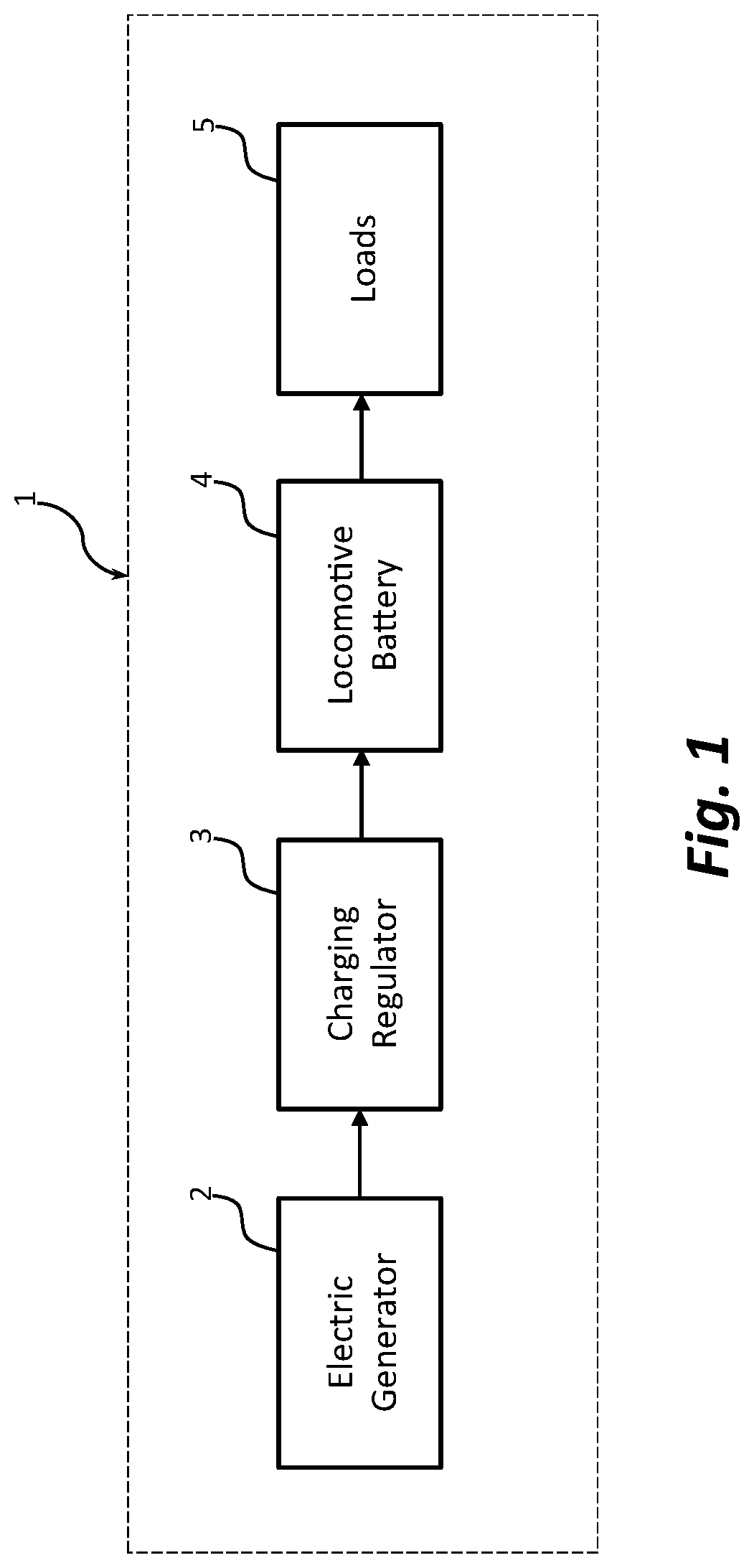
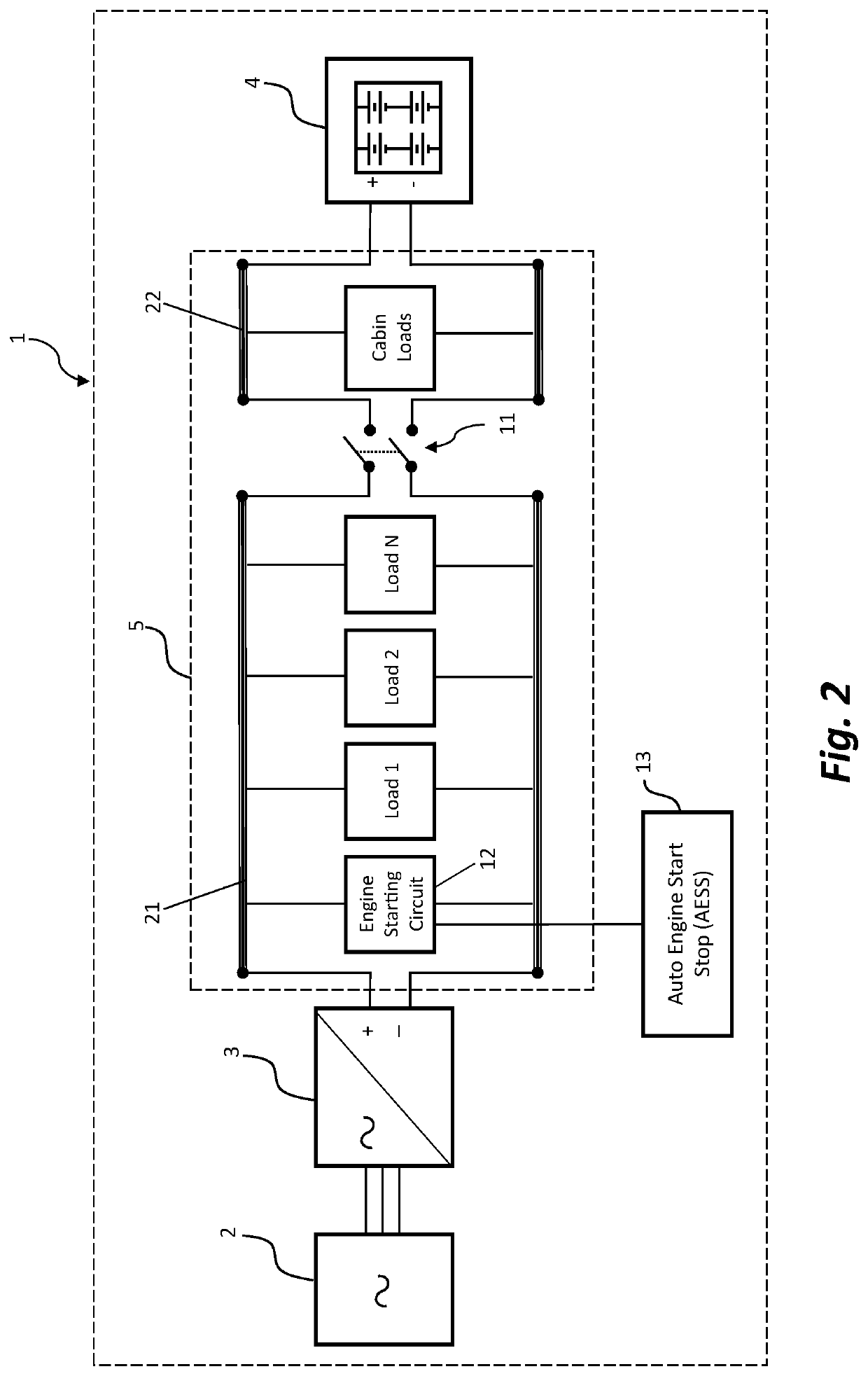
Various embodiments of a locomotive waste heat recovery system for charging an auxiliary battery, independent of the locomotive electric generator, are disclosed. The auxiliary battery is charged by a locomotive waste heat recovery system to supplement and supply the electric power normally provided by the locomotive battery during a shutdown condition caused by a locomotive auto engine start stop (AESS) system. The auxiliary battery is charged by recovery and conversion of waste thermal energy during locomotive engine operations, and its stored electric power is utilized to supply selected electrical loads during a prolonged engine shutdown condition. Accordingly, the locomotive battery can preserve its stored power to be exclusively utilized for locomotive engine start, which may decrease operational disruptions and increase the life of the locomotive battery, and thereby reducing the overall operating costs associated with the battery maintenance efforts.
Owner:FILIPPONE CLAUDIO
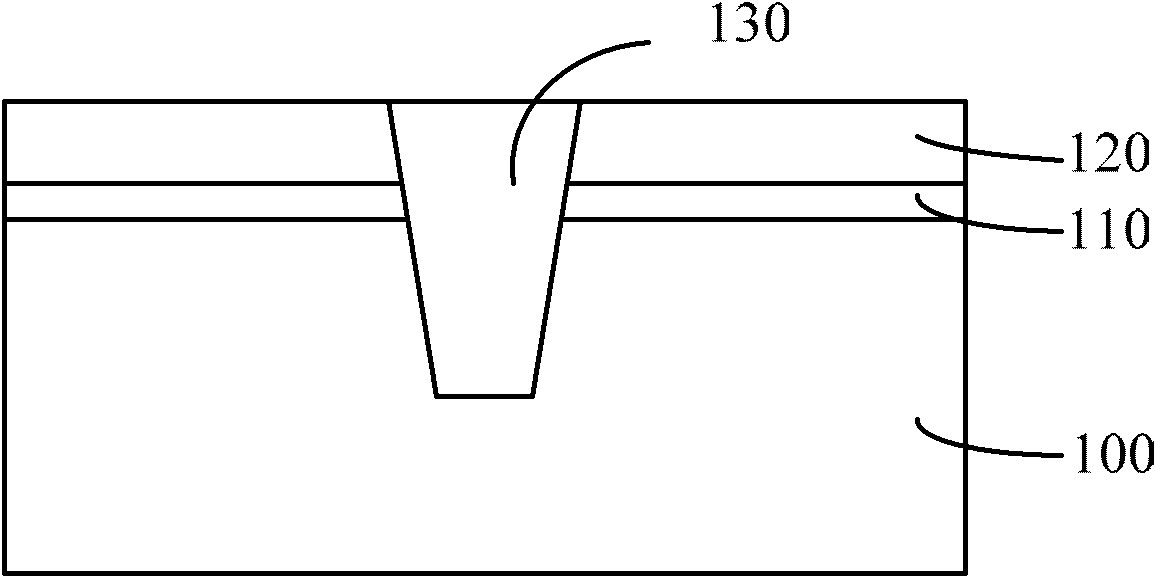
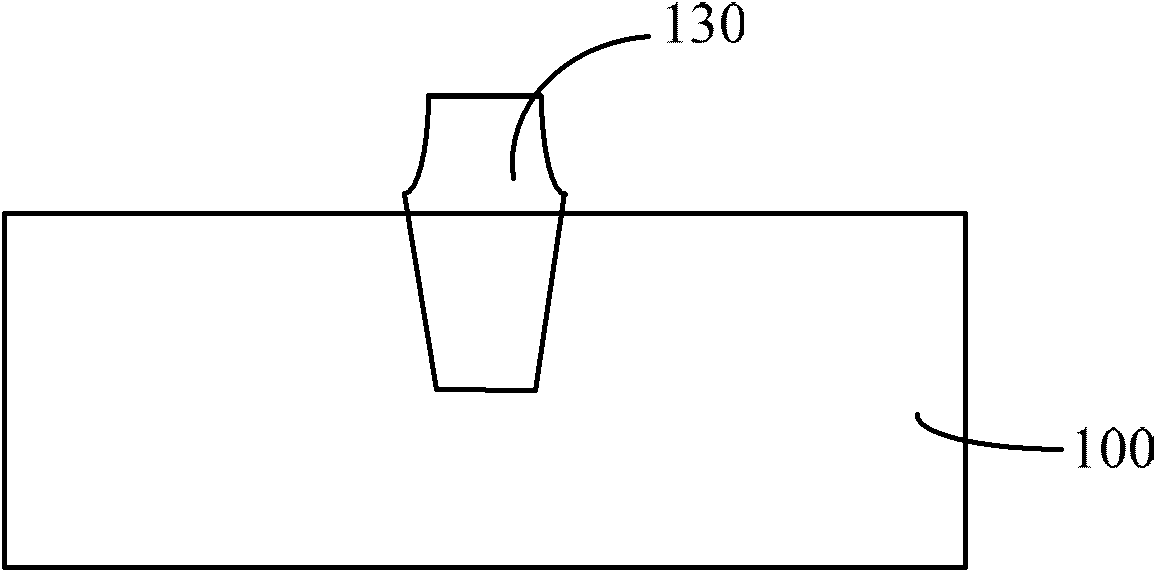
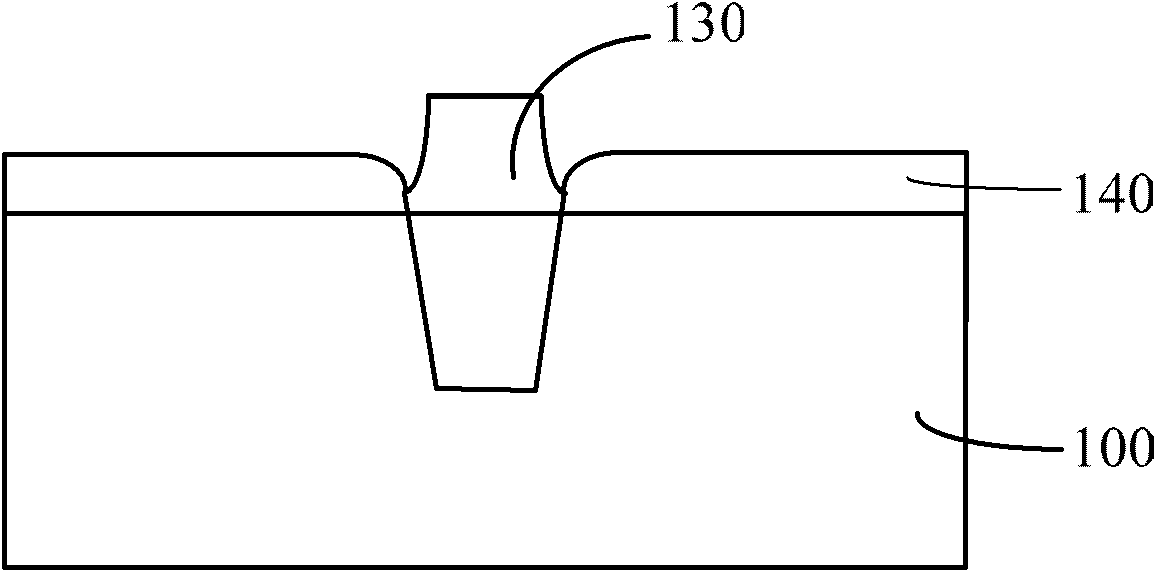
Flash memory unit forming method
ActiveCN102569078AUniform thicknessImprove ladder coverageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringChemical vapor deposition
A flash memory unit forming method comprises the steps as follows: a substrate is provided; a liner oxidation layer and an etching stop layer are formed sequentially on the surface of the substrate; at least two active areas are included in the substrate, and the adjacent active areas are isolated by a shallow trench isolation structure; the etching stop layer and the liner oxidation layer on the surface of the substrate are sequentially removed; a tunneling oxidation layer is formed on the surface of the substrate by a chemical vapor deposition method; and the tunneling oxidation layer is subjected to later stage oxidizing annealing treatment. The flash memory unit forming method provided by the invention avoids the double-hump effect and the reverse narrow channel effect, and the flash memory unit is better in period durability.
Owner:SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING INTERNATIONAL (BEIJING) CORP
Horizontal lead-acid storage battery formation method
ActiveCN113471560AImprove charge acceptanceHigh cycle durabilityFinal product manufactureSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectrolytic agentCharge current
The invention belongs to the technical field of lead-acid storage battery manufacturing, and particularly relates to a horizontal lead-acid storage battery formation method, which comprises the following steps: 1, injecting an electrolytic solution into a storage battery through a liquid adding hole; and 2, carrying out formation according to the following method that by taking charging once and discharging once as one stage, the charging current is calculated according to battery capacity multiplying power, charging is carried out at 0.1 C for the initial stage of the formation stage, then increasing is carried out at 0.05 C, when the charging current reaches 0.3 C, decreasing is carried out at 0.05 C until the last charging current reaches 0.05 C, the charging time is decreased by 1 h every other stage, the discharging current is 50% of the charging current of the stage, and the discharging time of each stage is 0.5 h. According to the invention, the current is controlled to be the optimal current in the process of converting active substances such as unformed electrode plates Pb, PbO, 3PbO.PbSO4, 4PbO.PbSO4 and the like into positive electrode plate PbO2 and negative electrode plate spongy Pb, discharging is reasonably and timely arranged, and conversion of the active substances in the formation process is facilitated.
Owner:浙江巨江电源制造有限公司
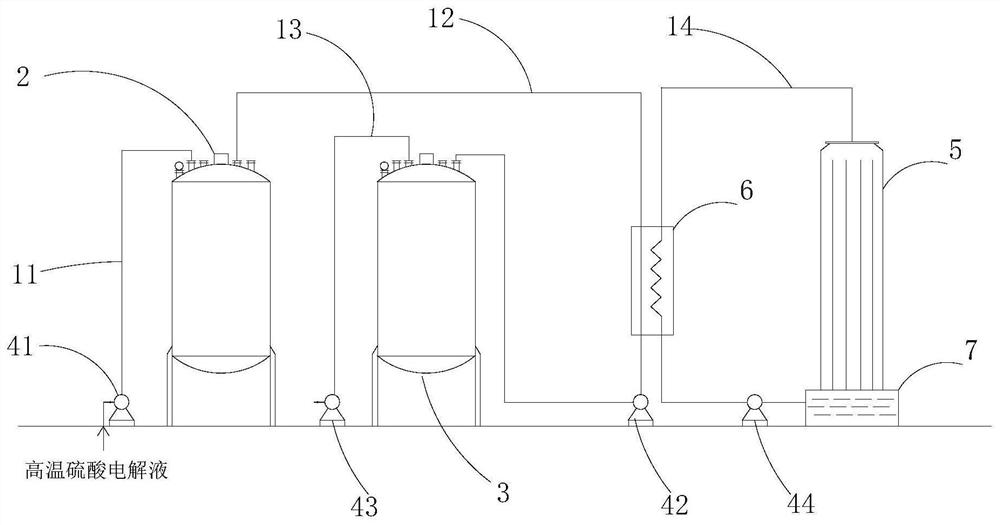
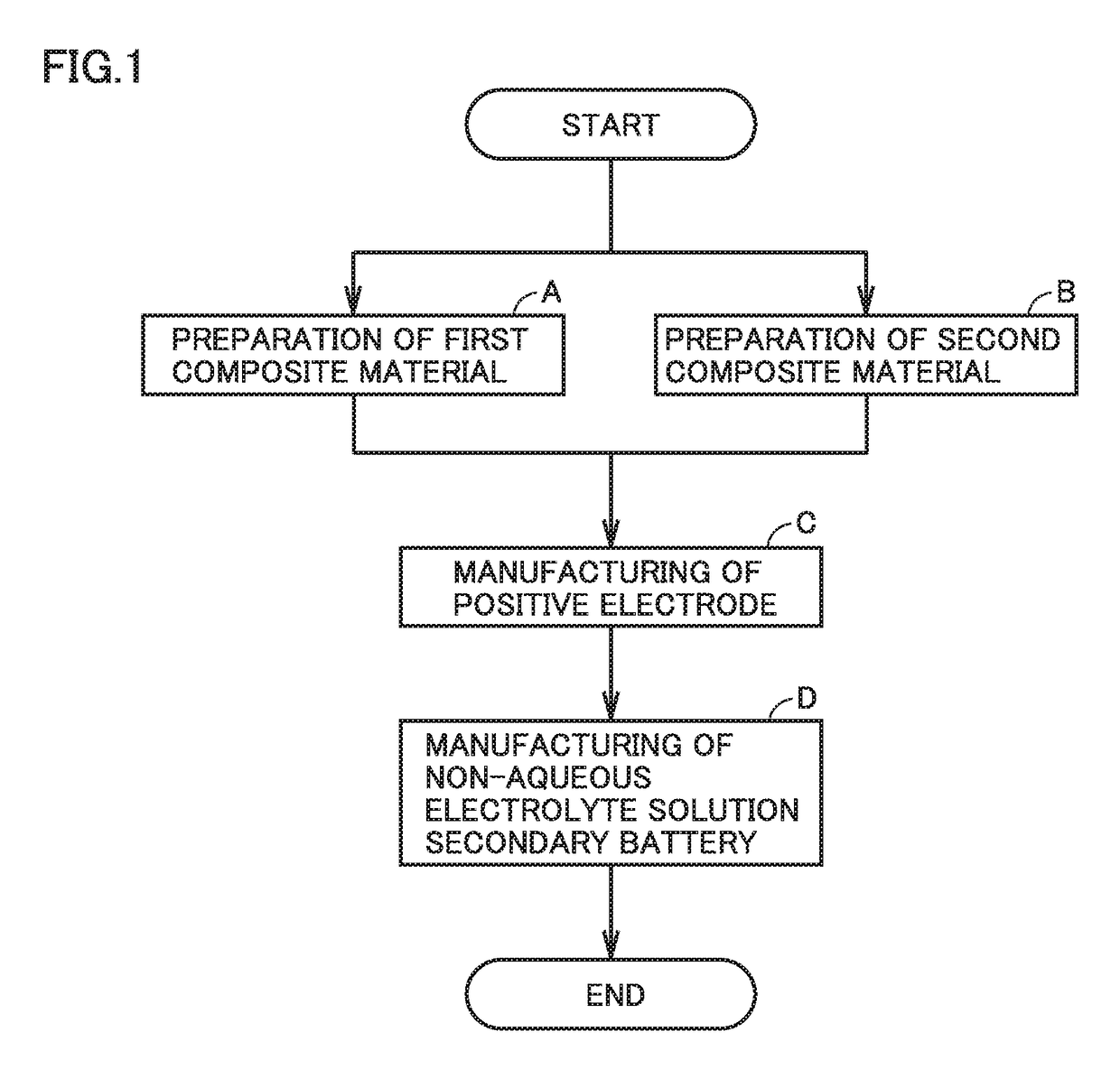
Method of manufacturing non-aqueous electrolyte solution secondary battery and non-aqueous electrolyte solution secondary battery
ActiveUS20180076450A1Increase productionHigh cycle durabilityElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureConductive materialsMaterials science
A method of manufacturing a non-aqueous electrolyte solution secondary battery includes: (A) preparing a first composite material by mixing a first positive electrode active material, a first conductive material and a first binder; (B) preparing a second composite material by mixing a second positive electrode active material, a second conductive material and a second binder; and (C) manufacturing a positive electrode by forming a positive electrode composite layer including the first composite material and the second composite material. The first positive electrode active material has an average discharge potential lower than that of the second positive electrode active material. The first conductive material has a first OAN. The second conductive material has a second OAN. A ratio of the second OAN to the first OAN is 1.3 or more and 2.1 or less. A sum of the first OAN and the second OAN is 31.64 ml / 100 g or less.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
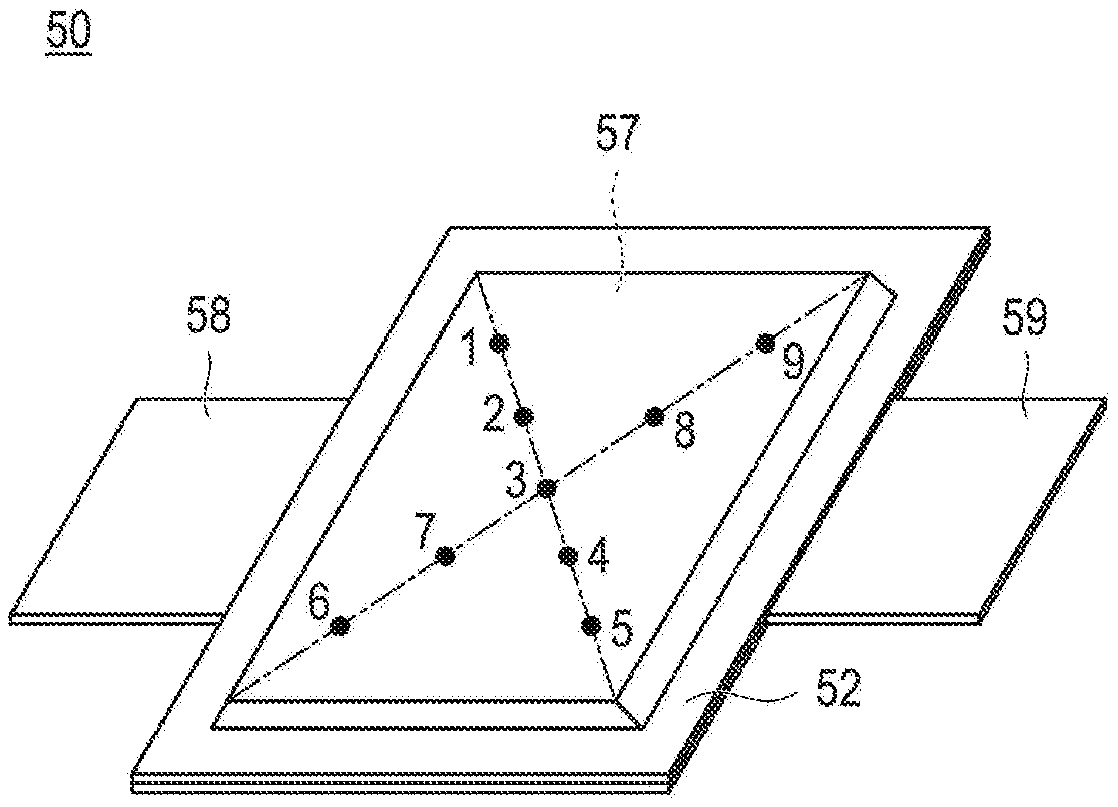
ActiveCN109075377AInhibit sheddingHigh cycle durabilityLi-accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesElectrical batteryEngineering
To provide a means for achieving adequate charge / discharge cycle characteristics in a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery having large capacity and a large area even when a mixture of a high-capacity Si material and a carbon material that swells little is used as a negative electrode active material. A non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery in which the value of the ratio of the battery volume with respect to the rated capacity is 10 cm3 / Ah or less and the rated capacity is 3 Ah or more, the non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery comprising a power generation element that includes:a positive electrode in which a positive electrode active material layer including a positive electrode active material is formed on the surface of a positive electrode current collector; a negativeelectrode in which a negative electrode active material layer including a negative electrode active material is formed on the surface of a negative electrode current collector; and a separator. The non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery is characterized in that: the negative electrode active material layer contains a negative electrode active material represented by formula (1), namely, [alpha](Si material) + [beta](carbon material) (in the formula, the Si material is one or more substances selected from the group consisting of Si-containing alloys and SiOx (x represents the number of oxygen atoms satisfying the valence of Si) that is a mixture of amorphous SiO2 particles and Si particles, the carbon material is one or more substances selected from the group consisting of graphite, hardly graphitizable carbon, and amorphous carbon, [alpha] and [beta] represent the mass% of the individual components in the negative electrode active material layer, 80 <= [alpha] + [beta] <= 98, 0.1 <=[alpha] <= 40, and 58 <= [beta] <= 97.9); and when a plurality of discretionary locations within the plane of the negative electrode active material layer are selected, the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value of the area ratio (%) occupied by a binder in the field of view of each of images of a cross section of the negative electrode active material layer is within 10%.
Owner:ENVISION AESC JAPAN LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com