Patents
Literature
212results about How to "Suppress light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
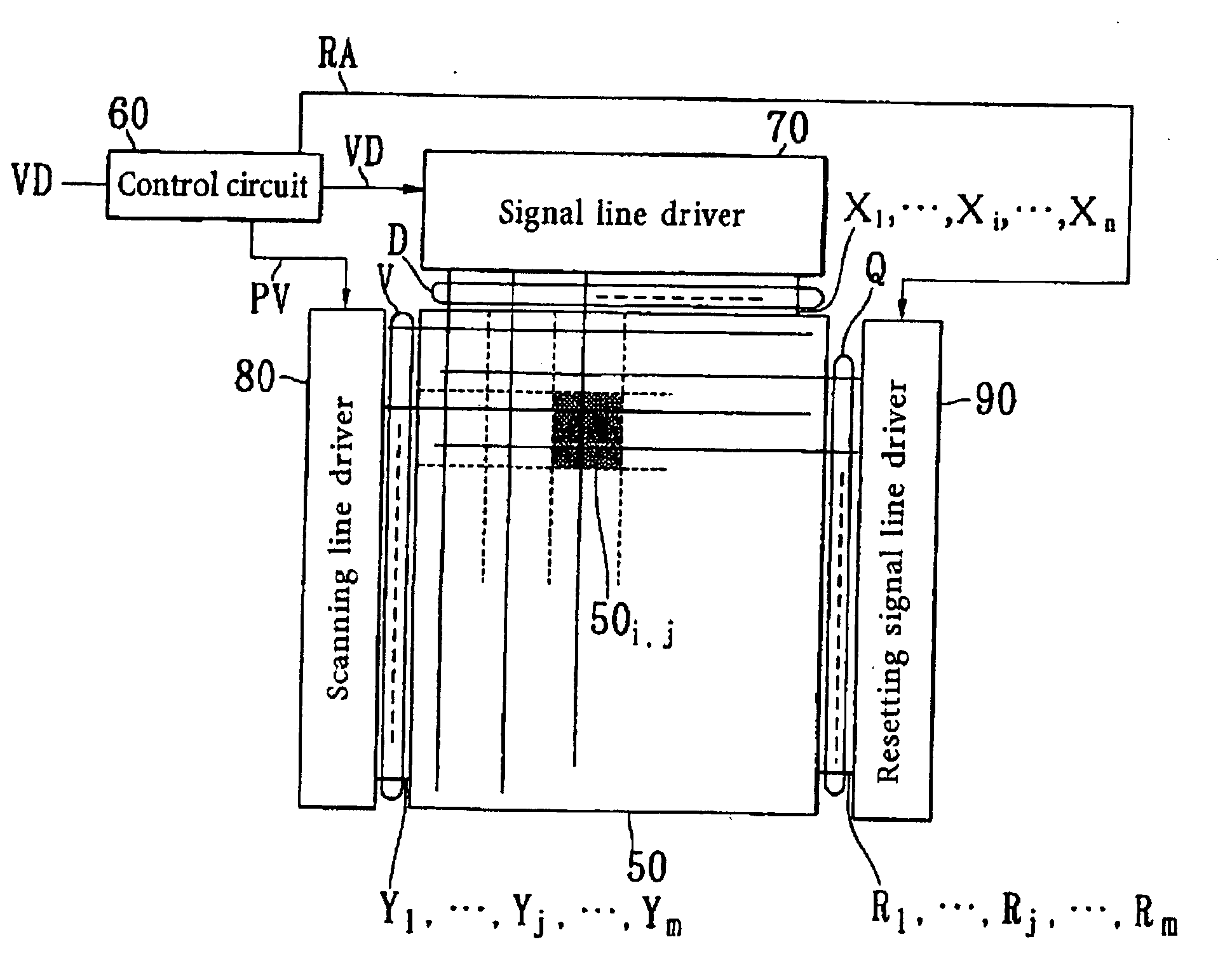
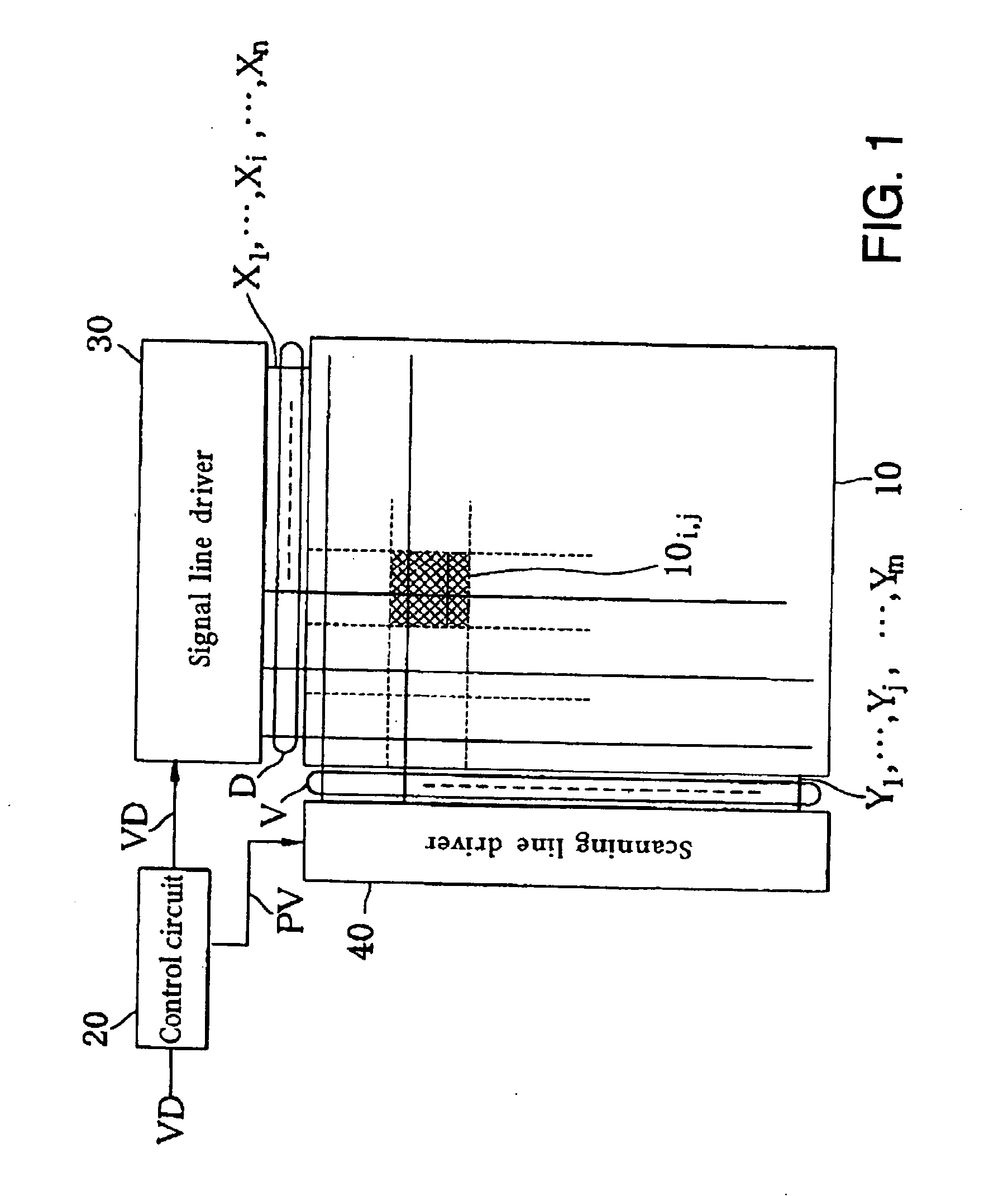
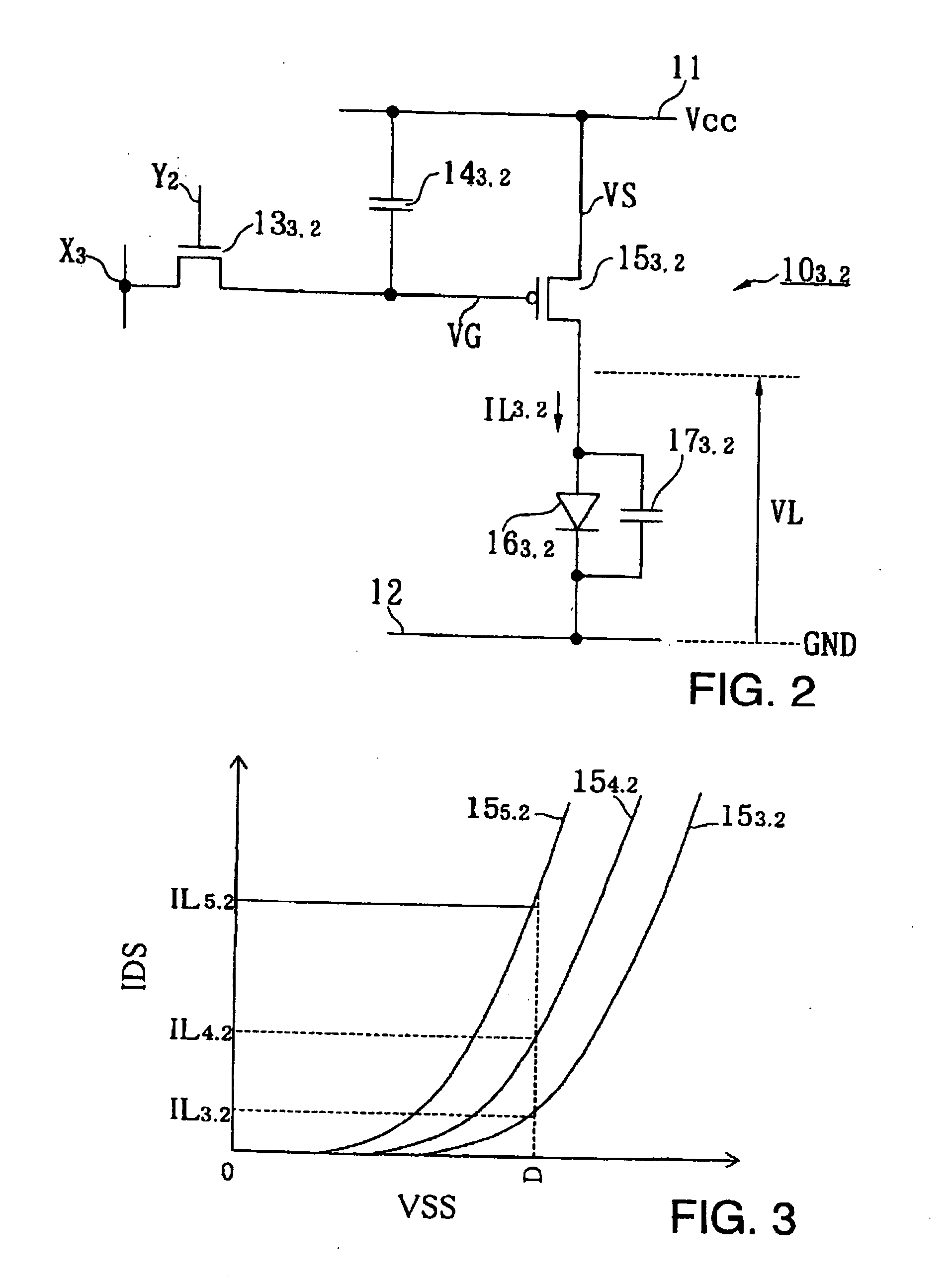
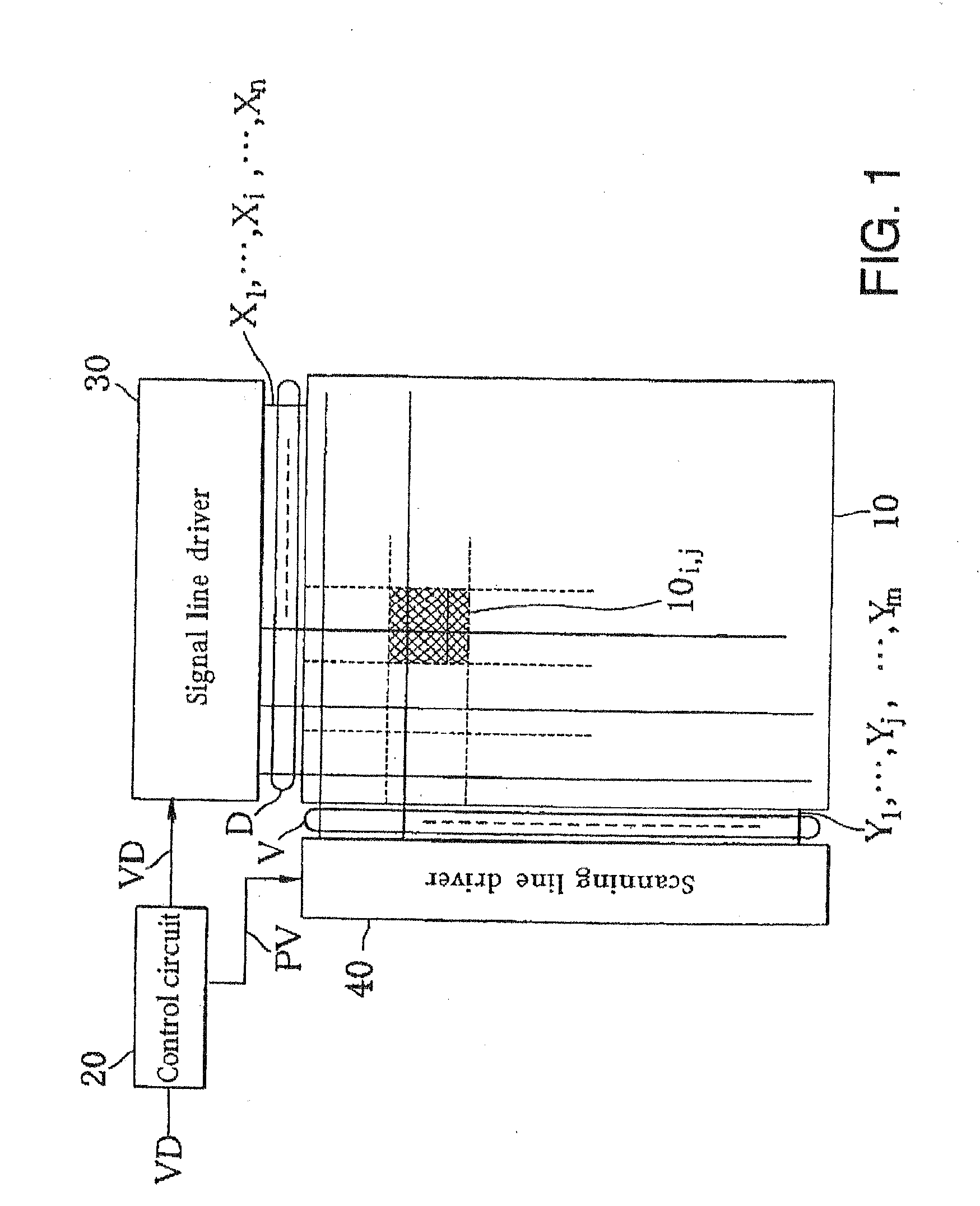
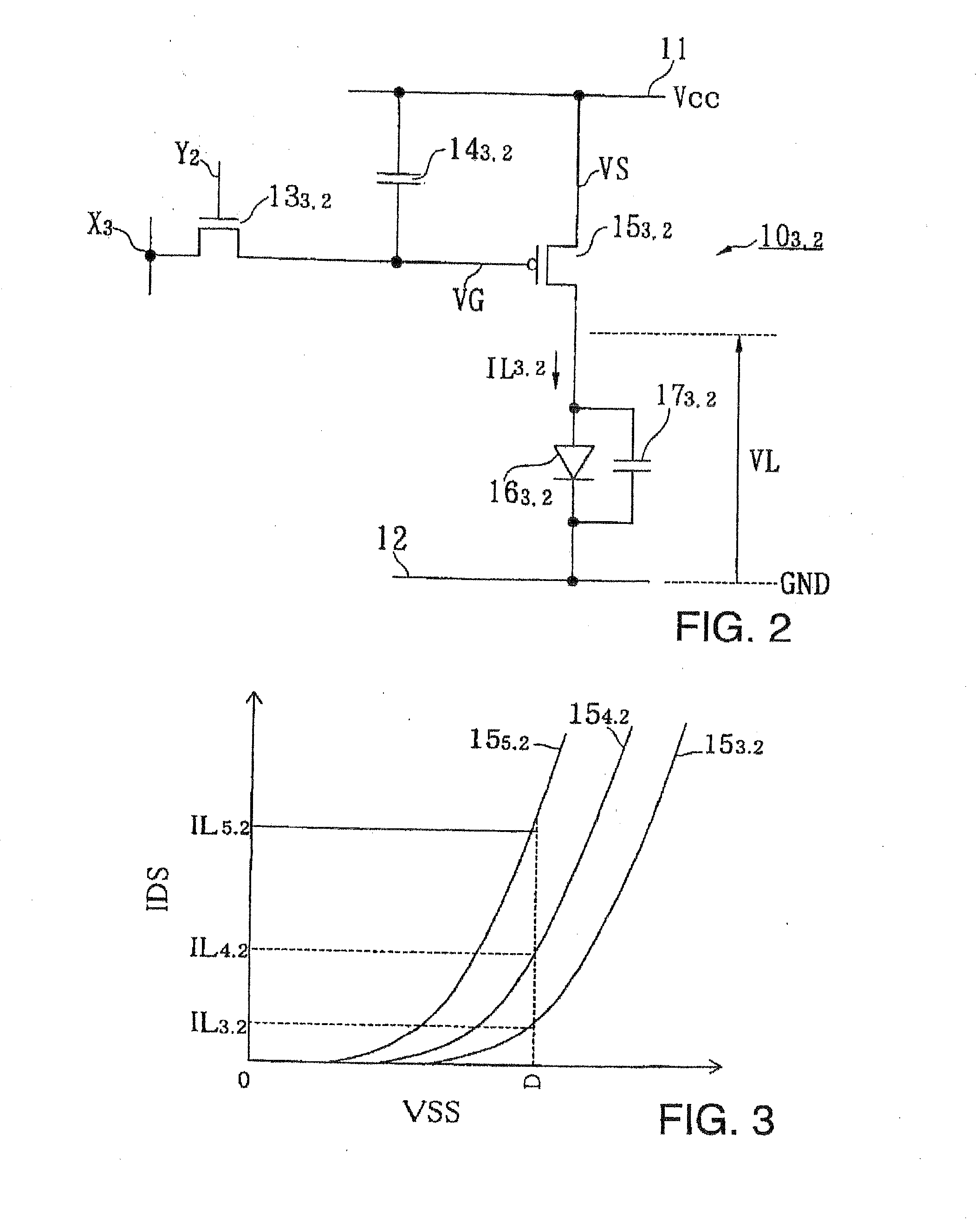
Image display and Its control method
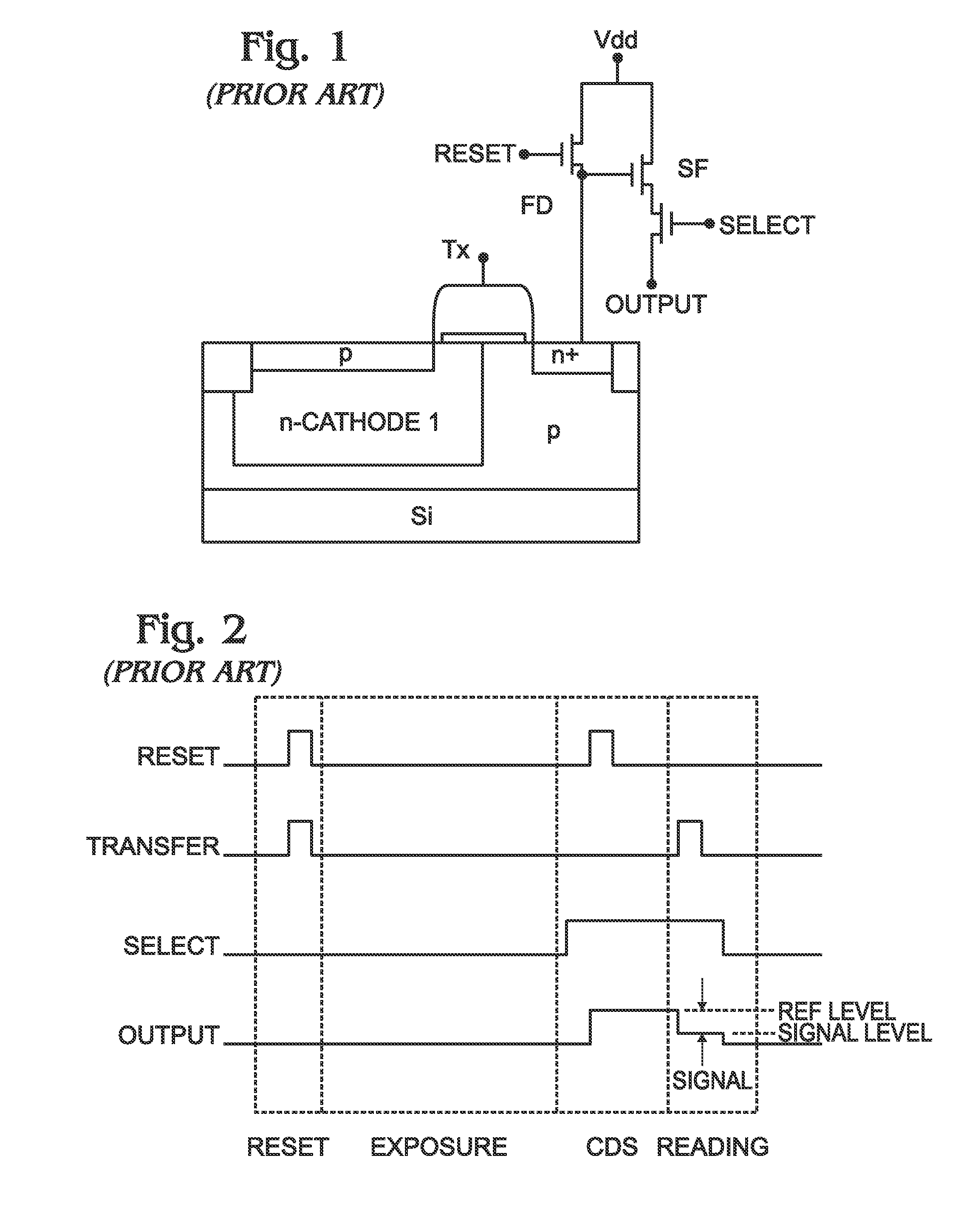
ActiveUS20050206590A1Quality improvementSuppress lightCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingData storingCapacitor
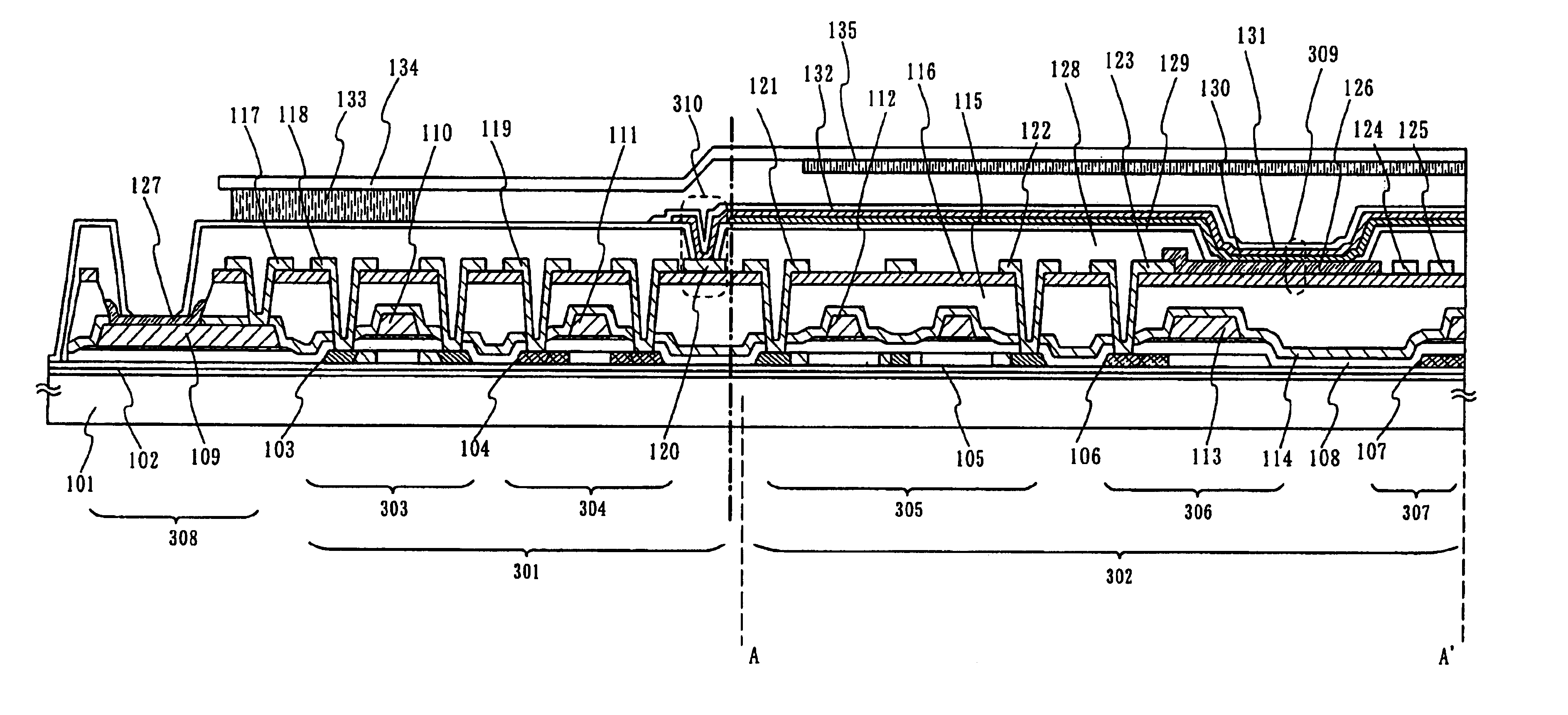
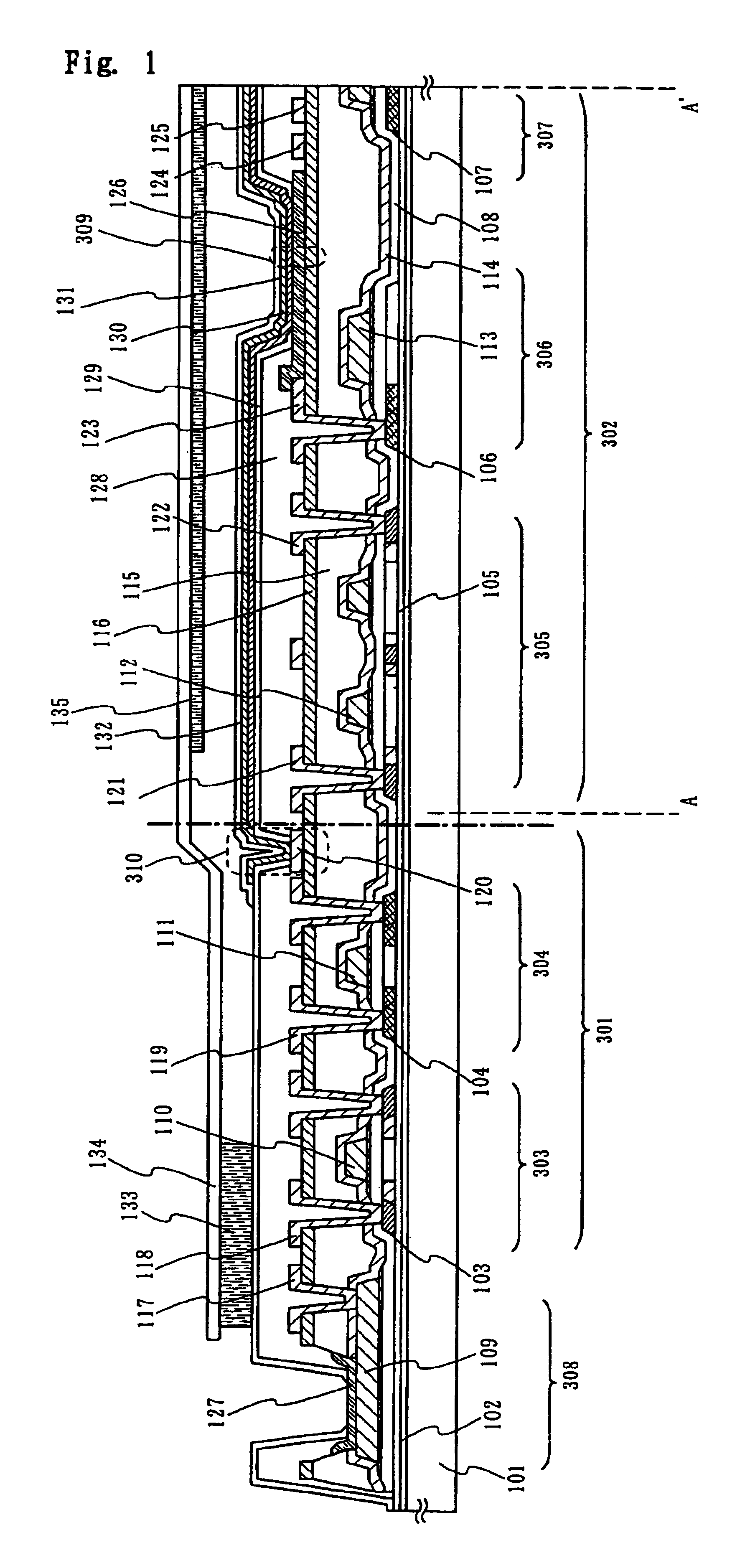
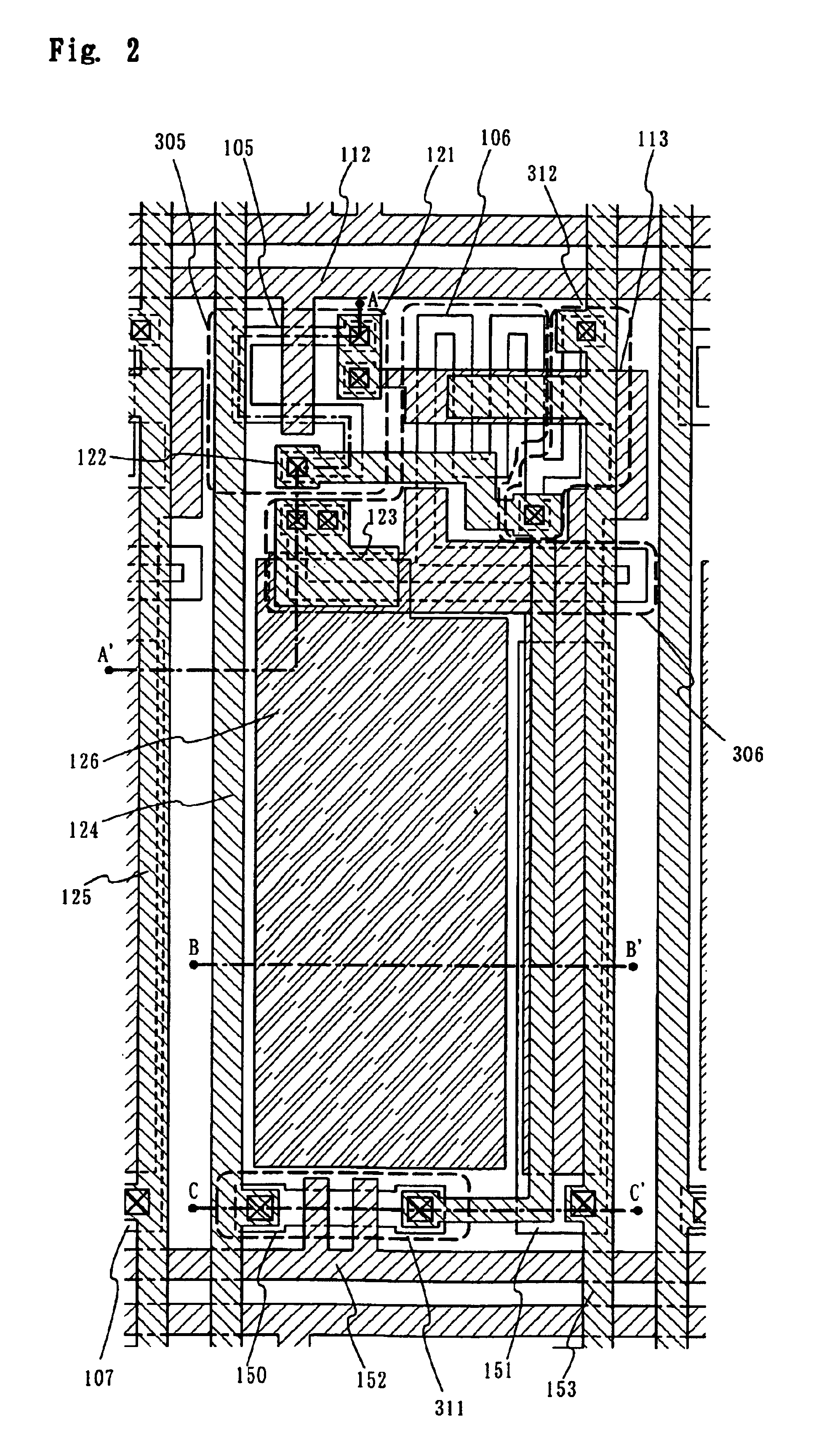
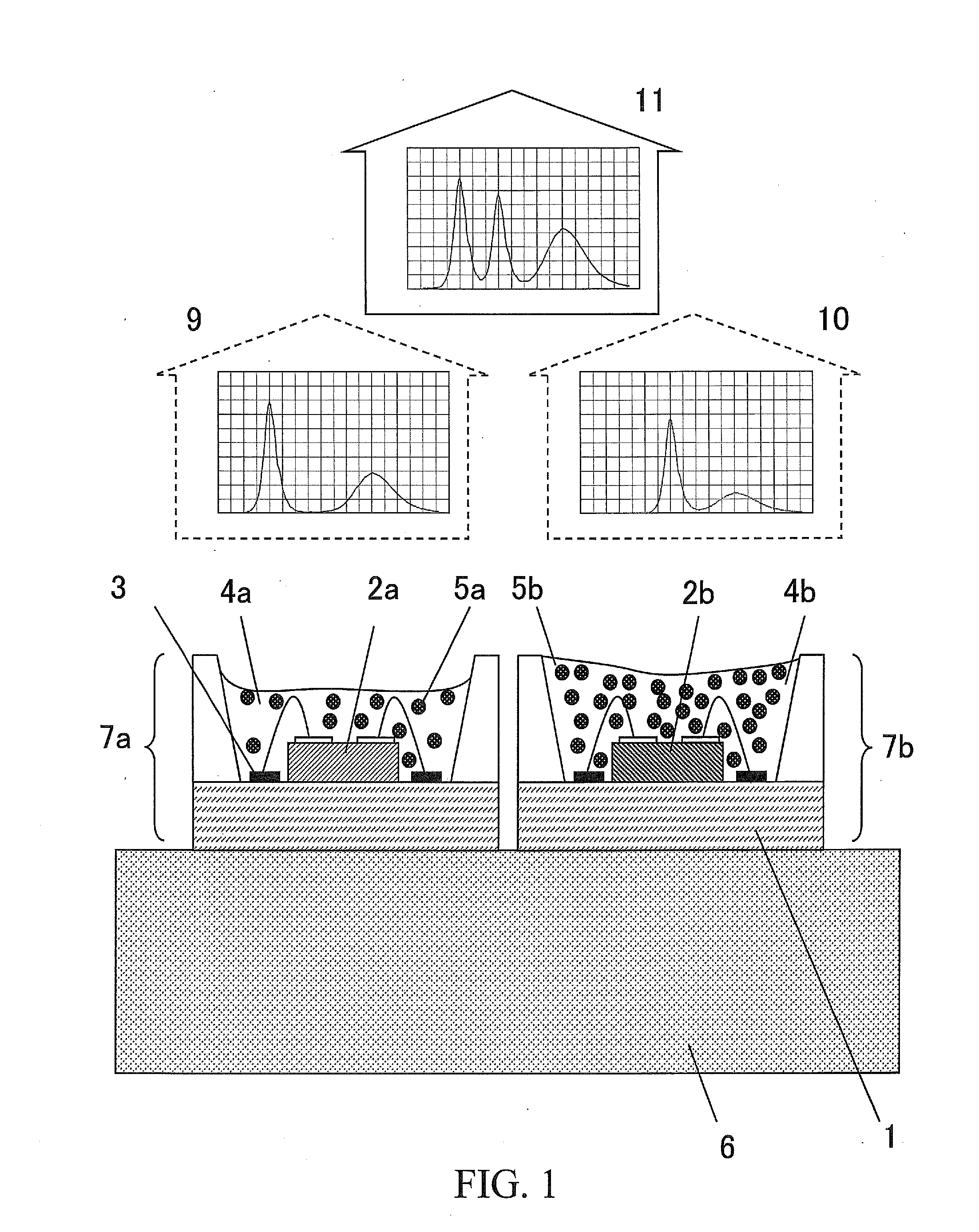
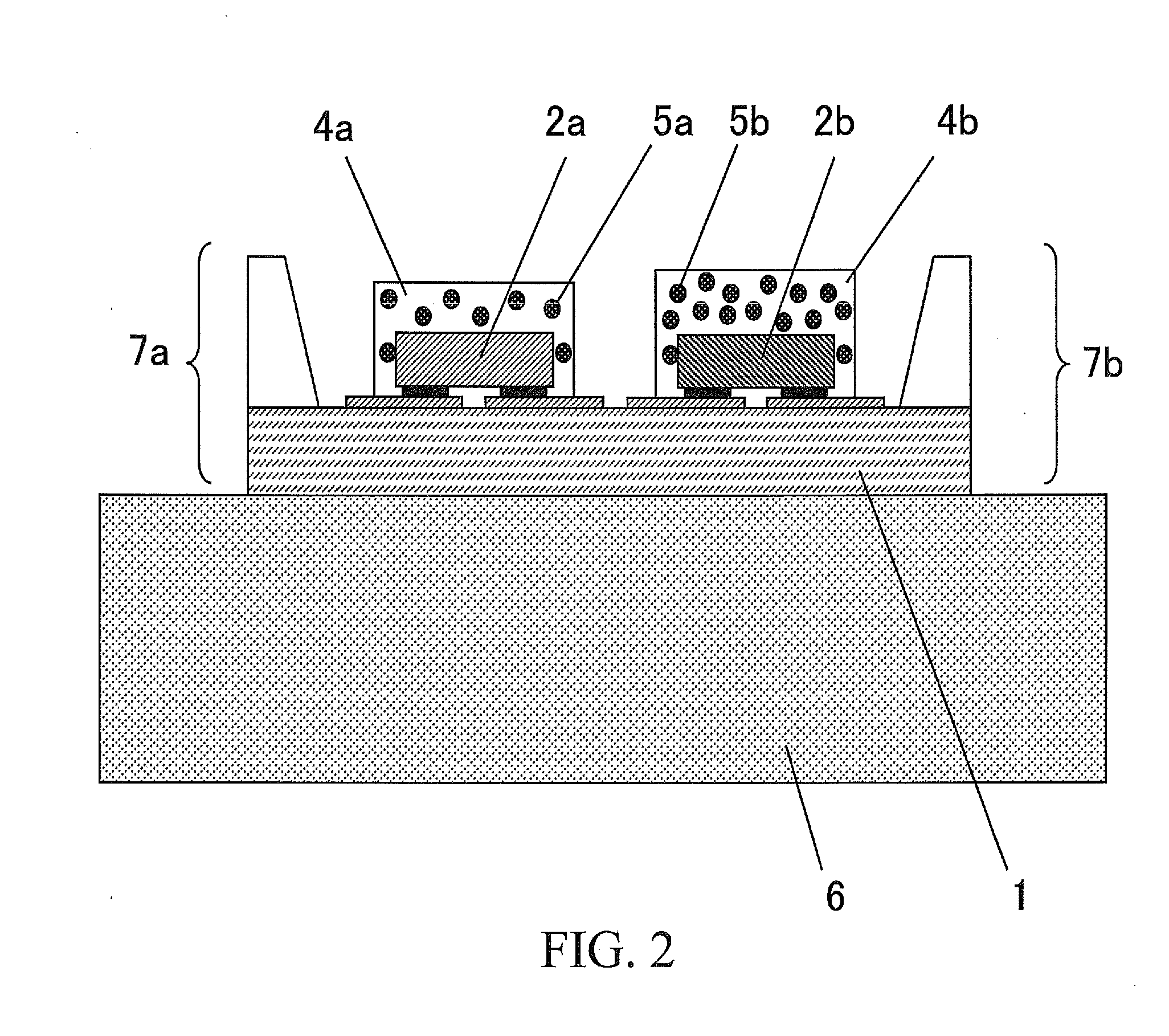
An image display apparatus comprises a pixel having a drive transistor and a pixel display element which are connected in series between a first power line and a second power line, a holding capacitor connected to a gate electrode of the drive transistor, and a selection transistor connected between a signal line and the gate electrode of the drive transistor. When the selection transistor is turned on, gradation pixel data is written in the holding capacitor from the signal line. The charge of gradation pixel data written in the holding capacitor is discharged for a certain period through the drive transistor, thereafter the charge of the gradation pixel data stored in the holding capacitor is held by floating the gate electrode of the drive transistor.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
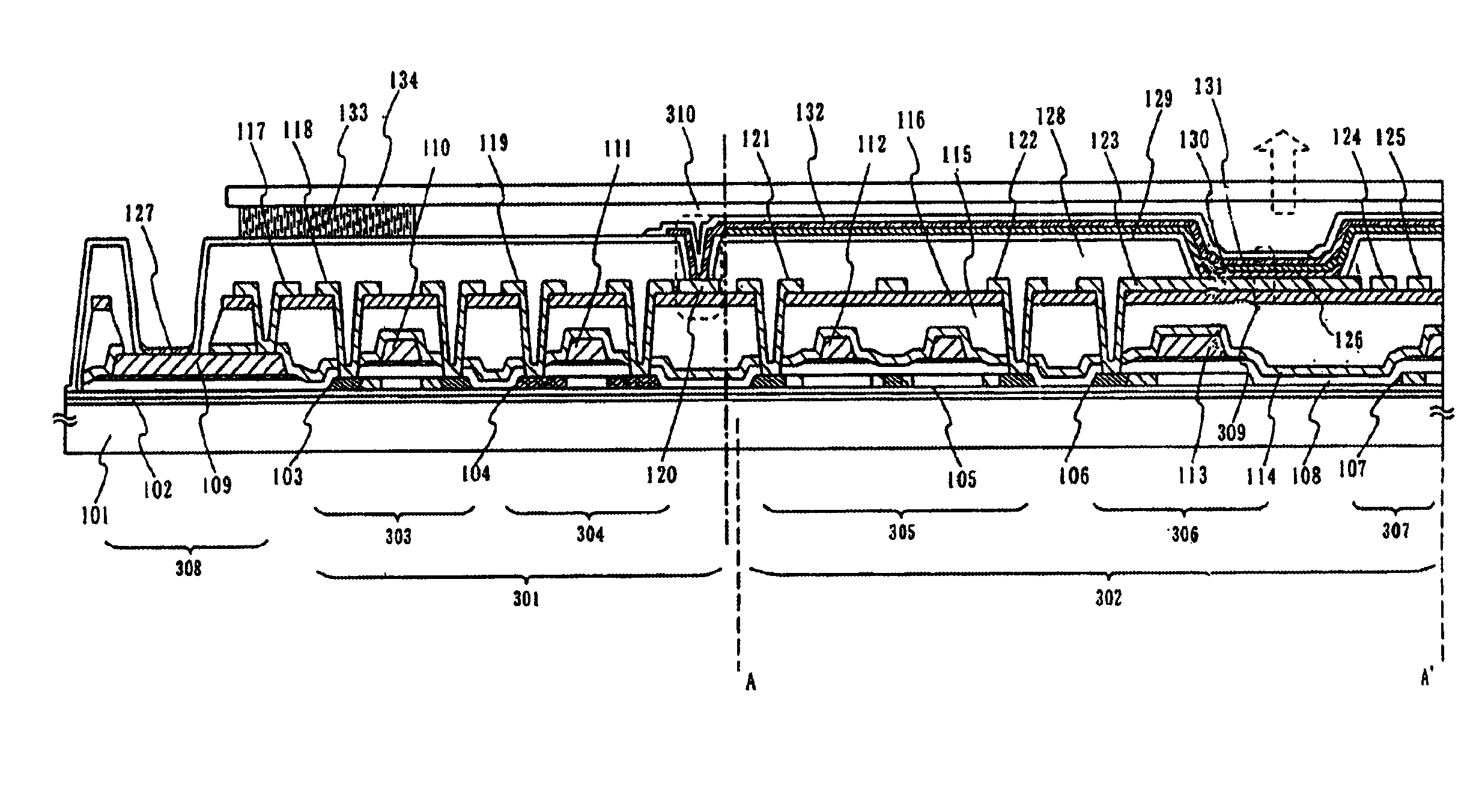
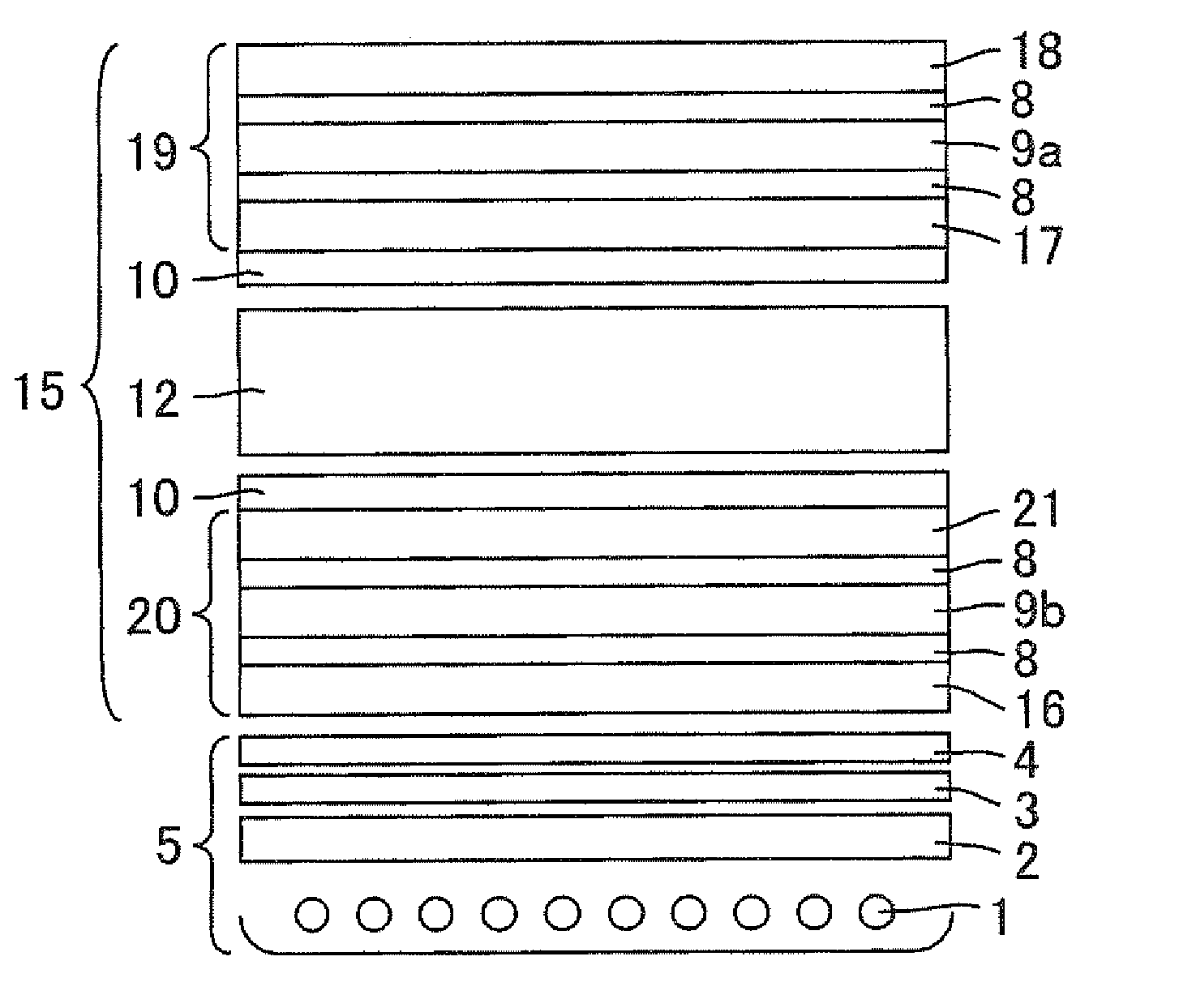
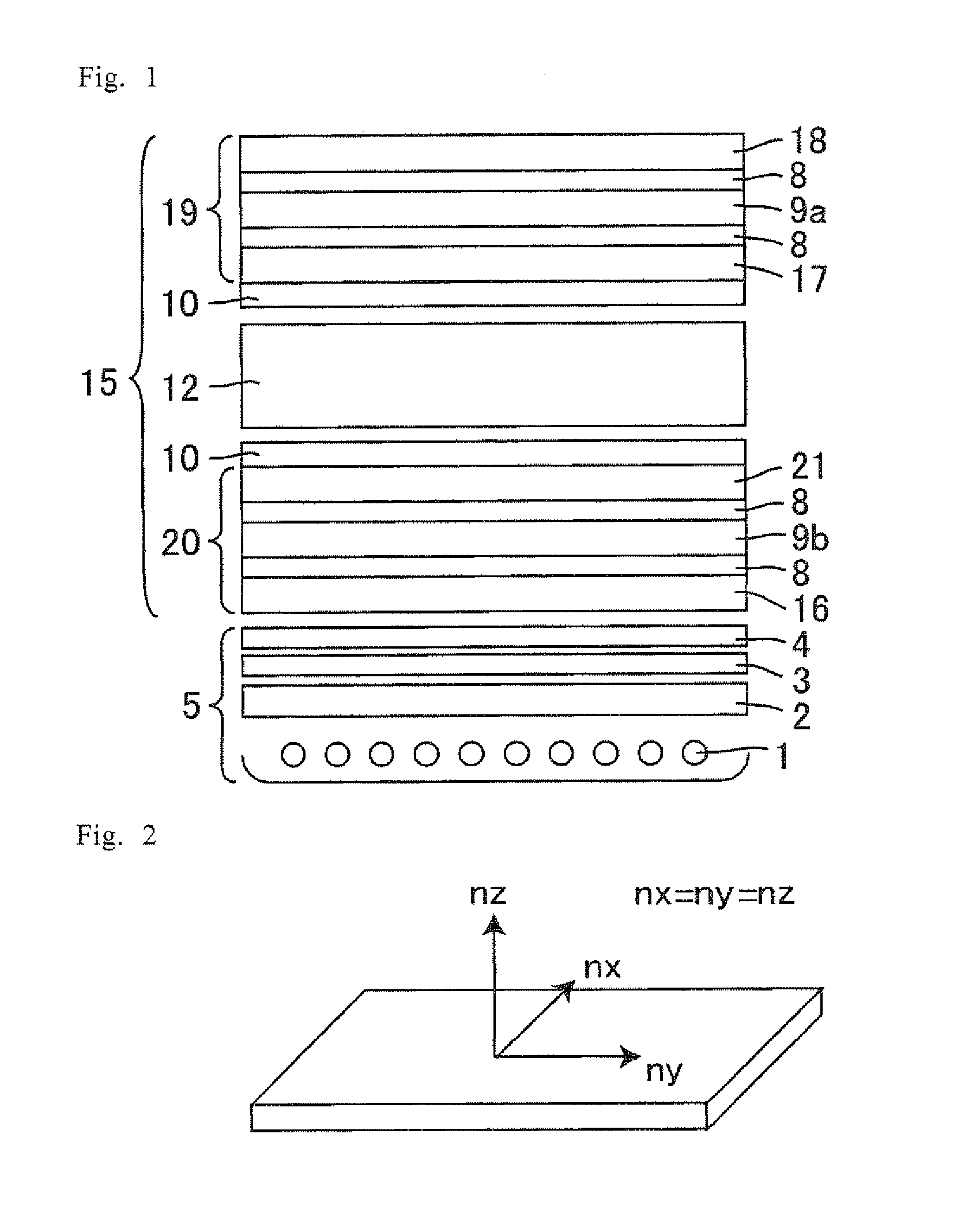
Light emitting apparatus and method for manufacturing the same
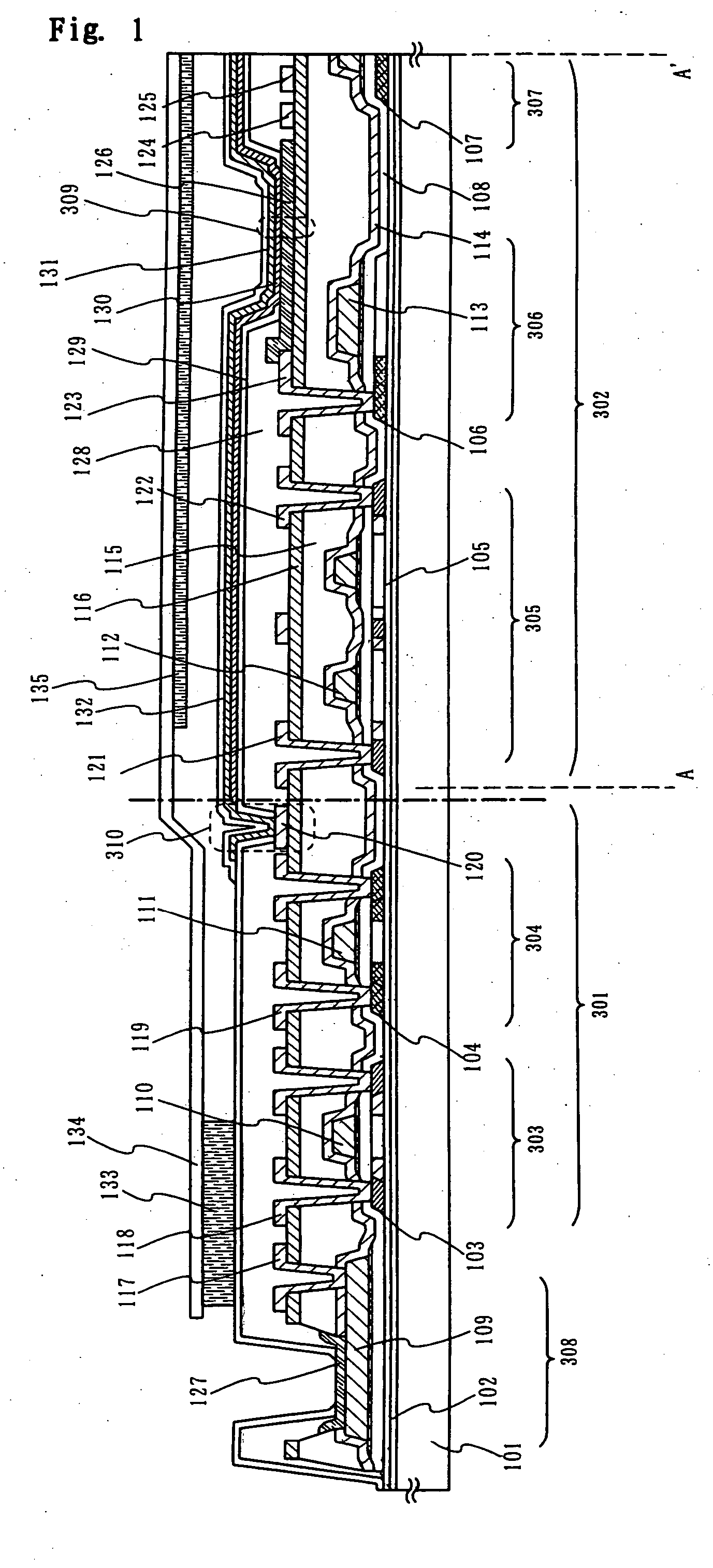
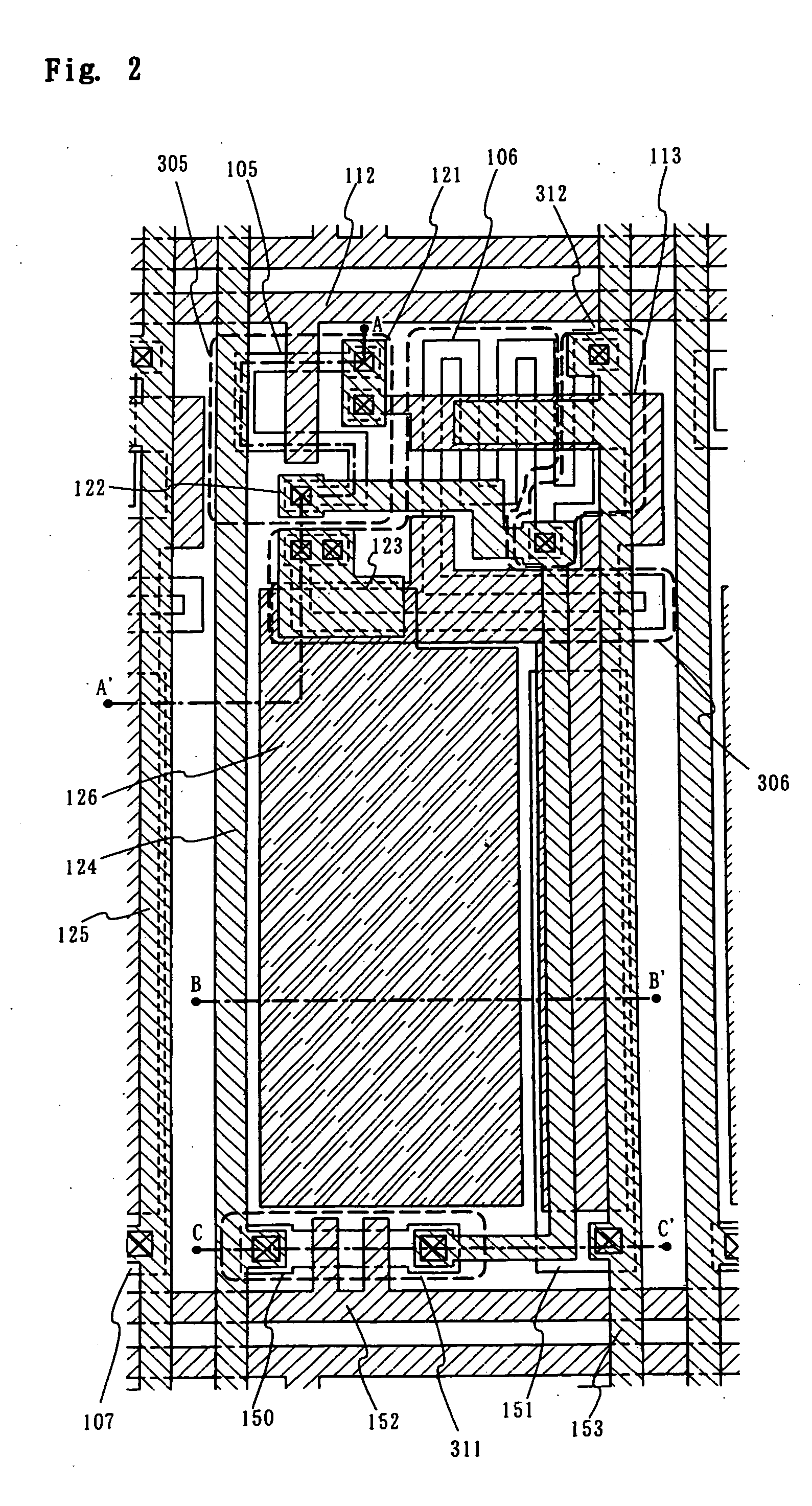
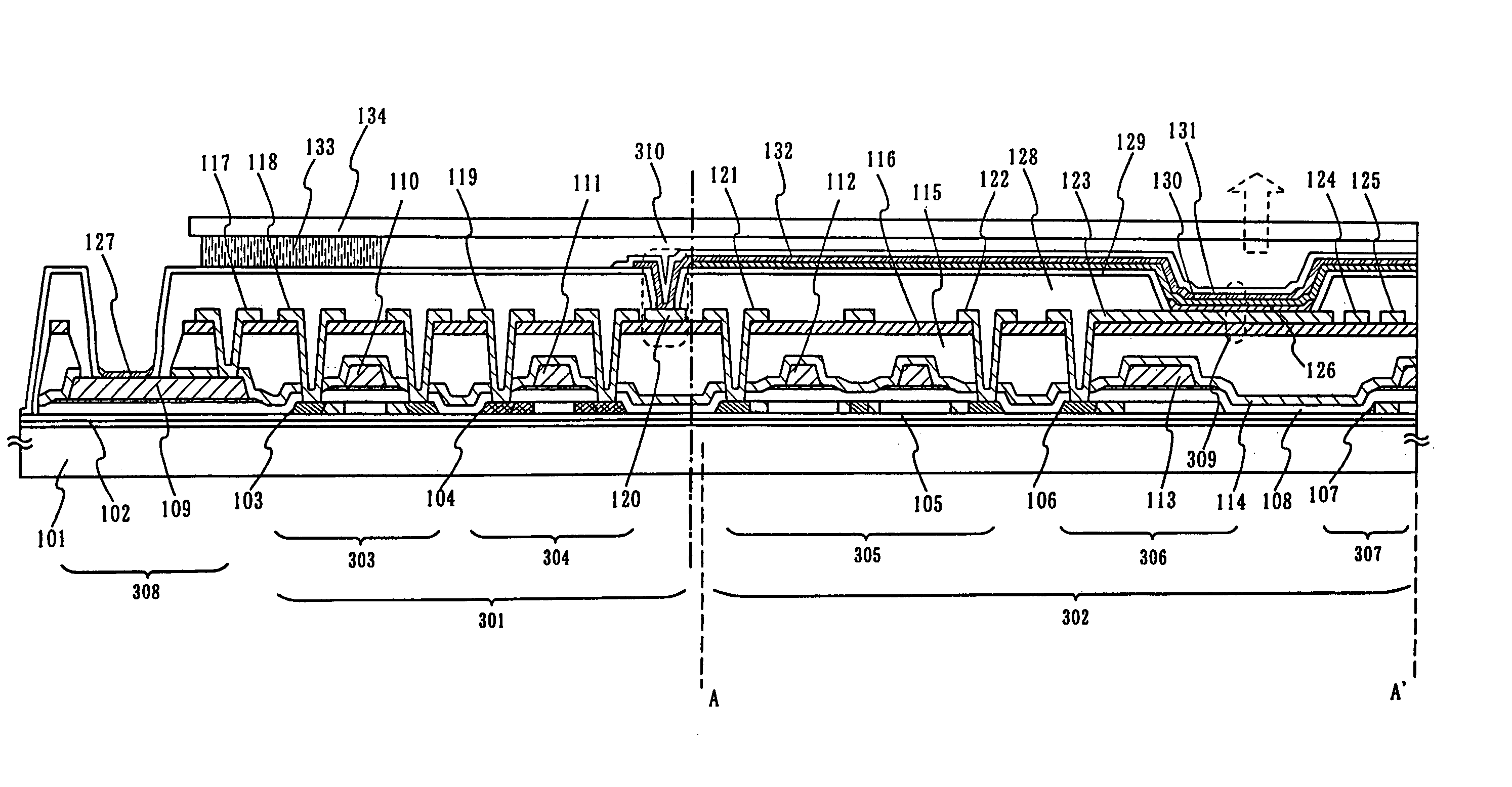
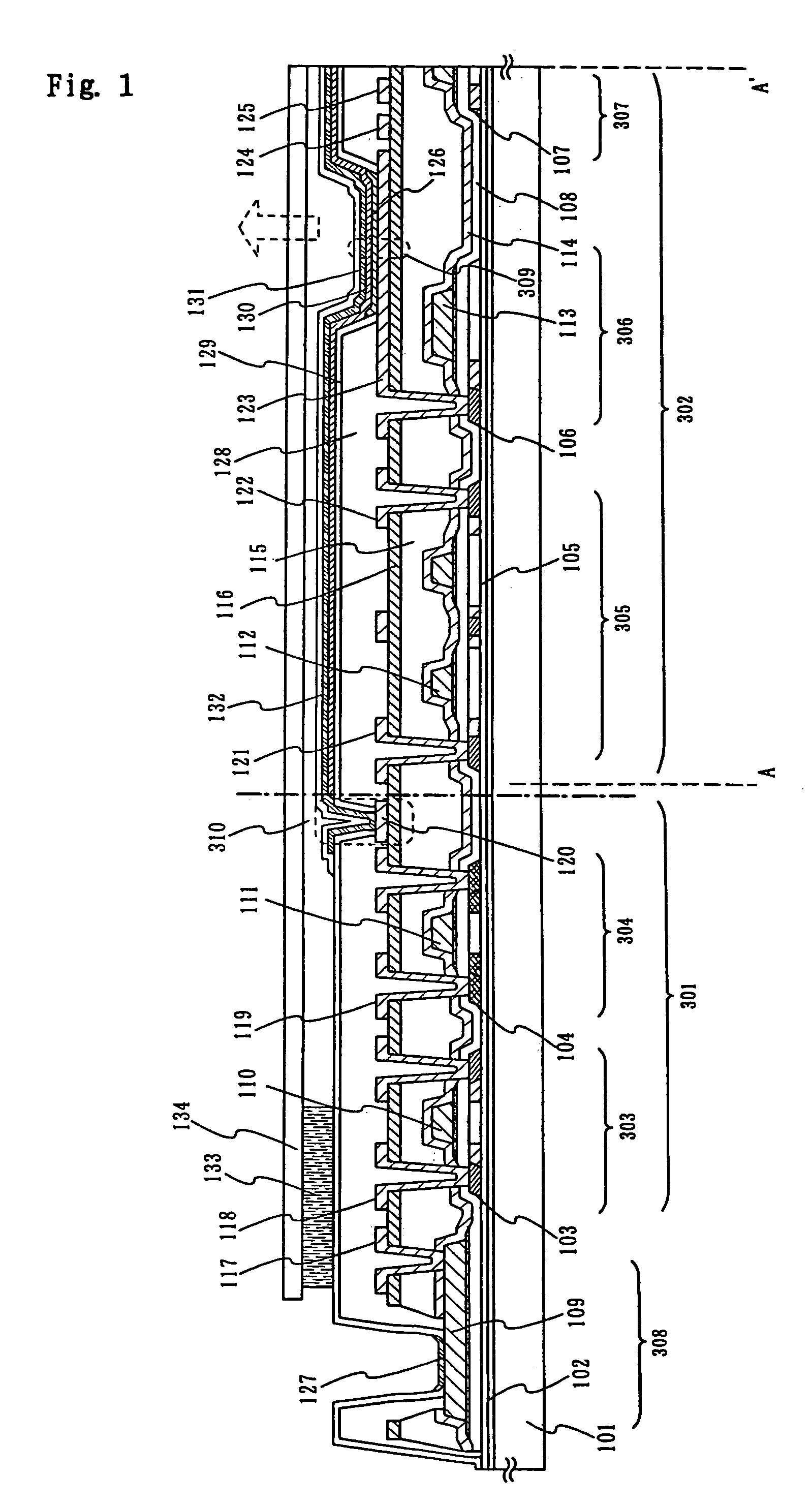
InactiveUS6903377B2Improve reliabilityInhibit deteriorationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon nitrideAluminium
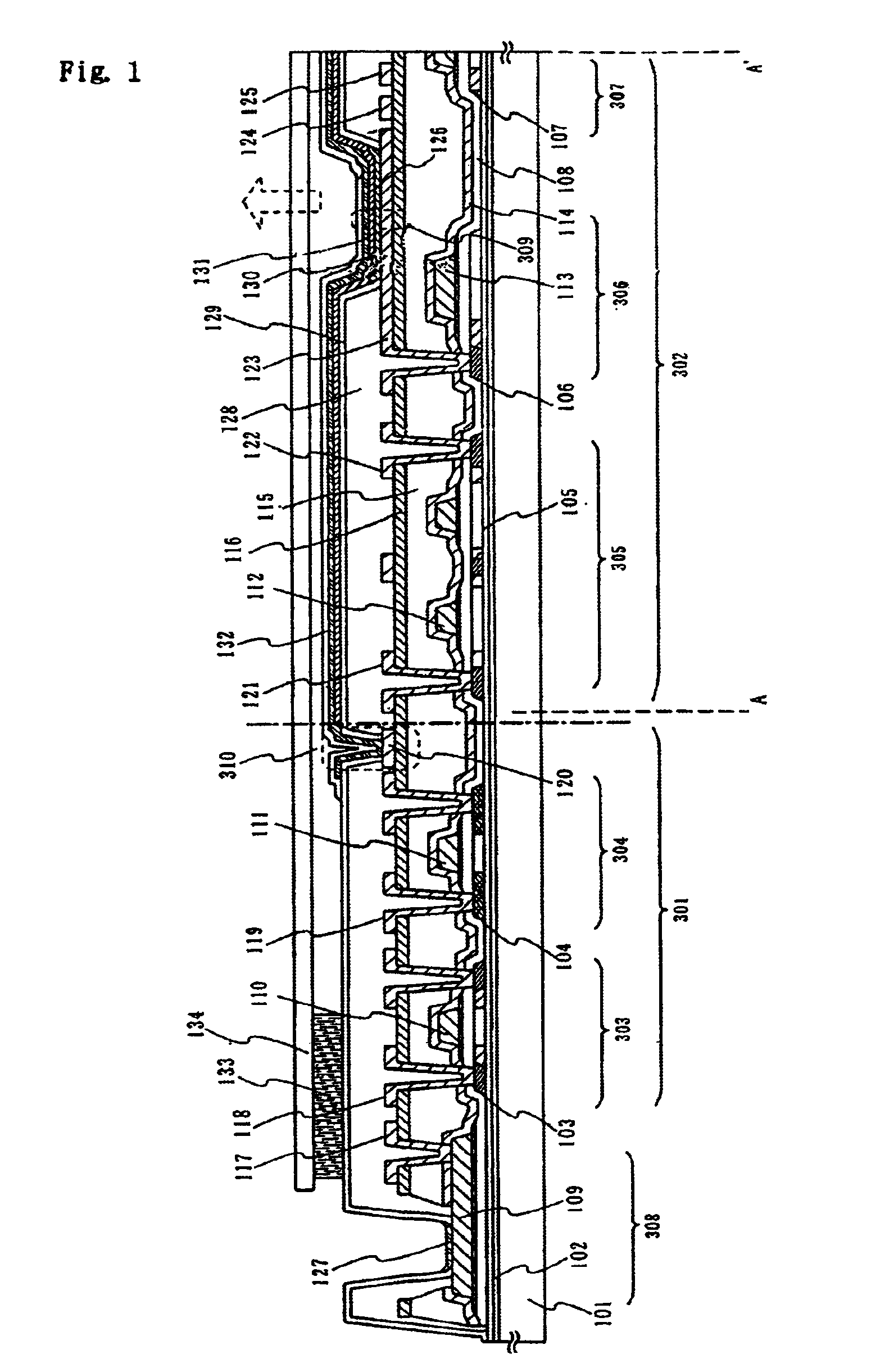
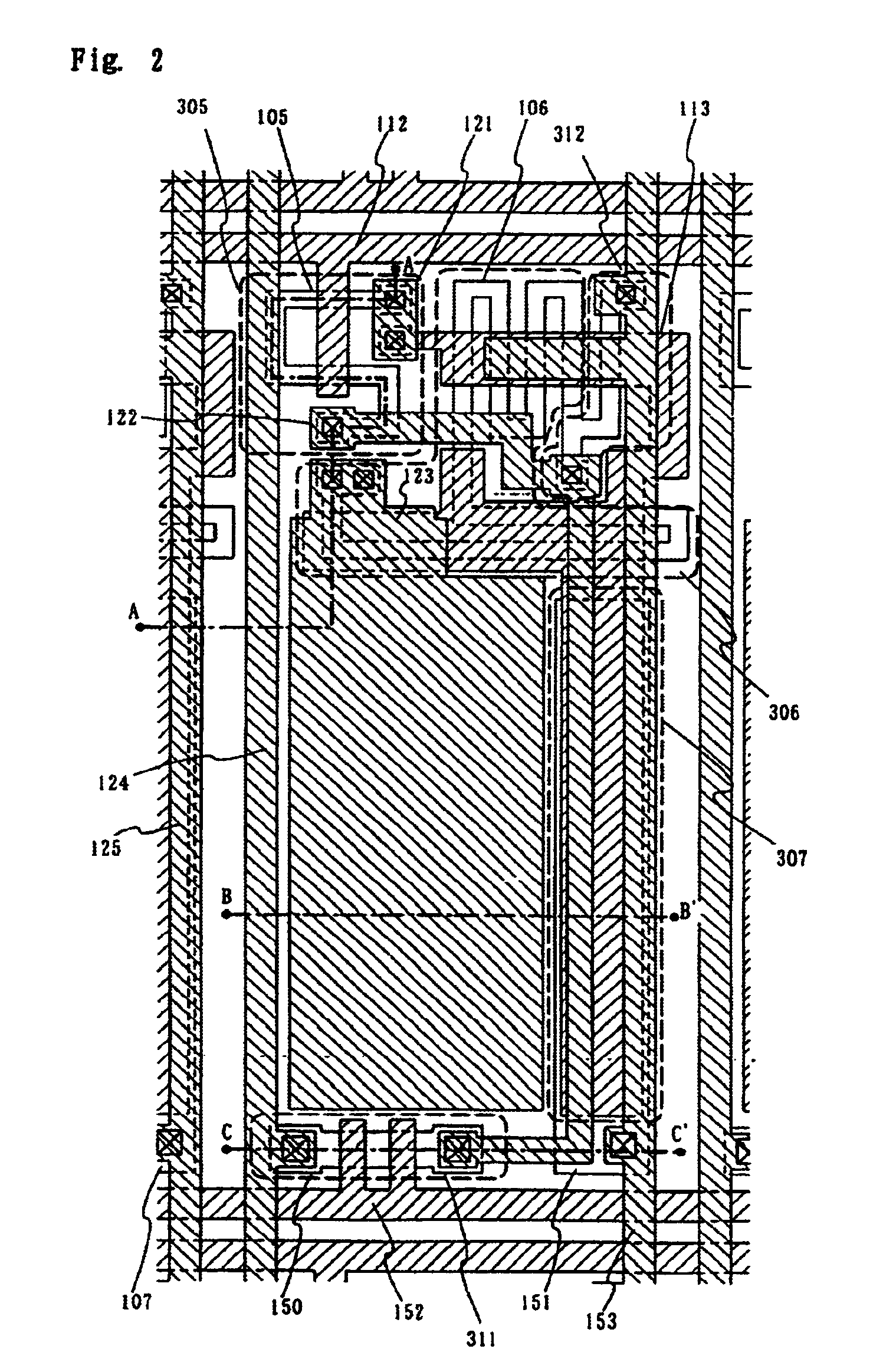
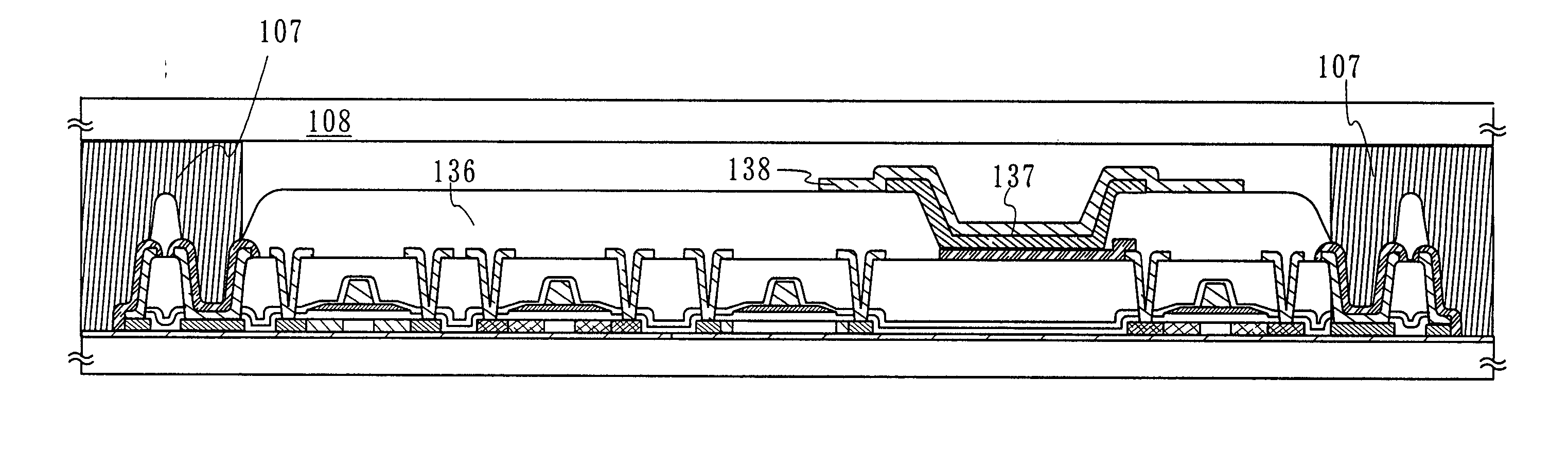
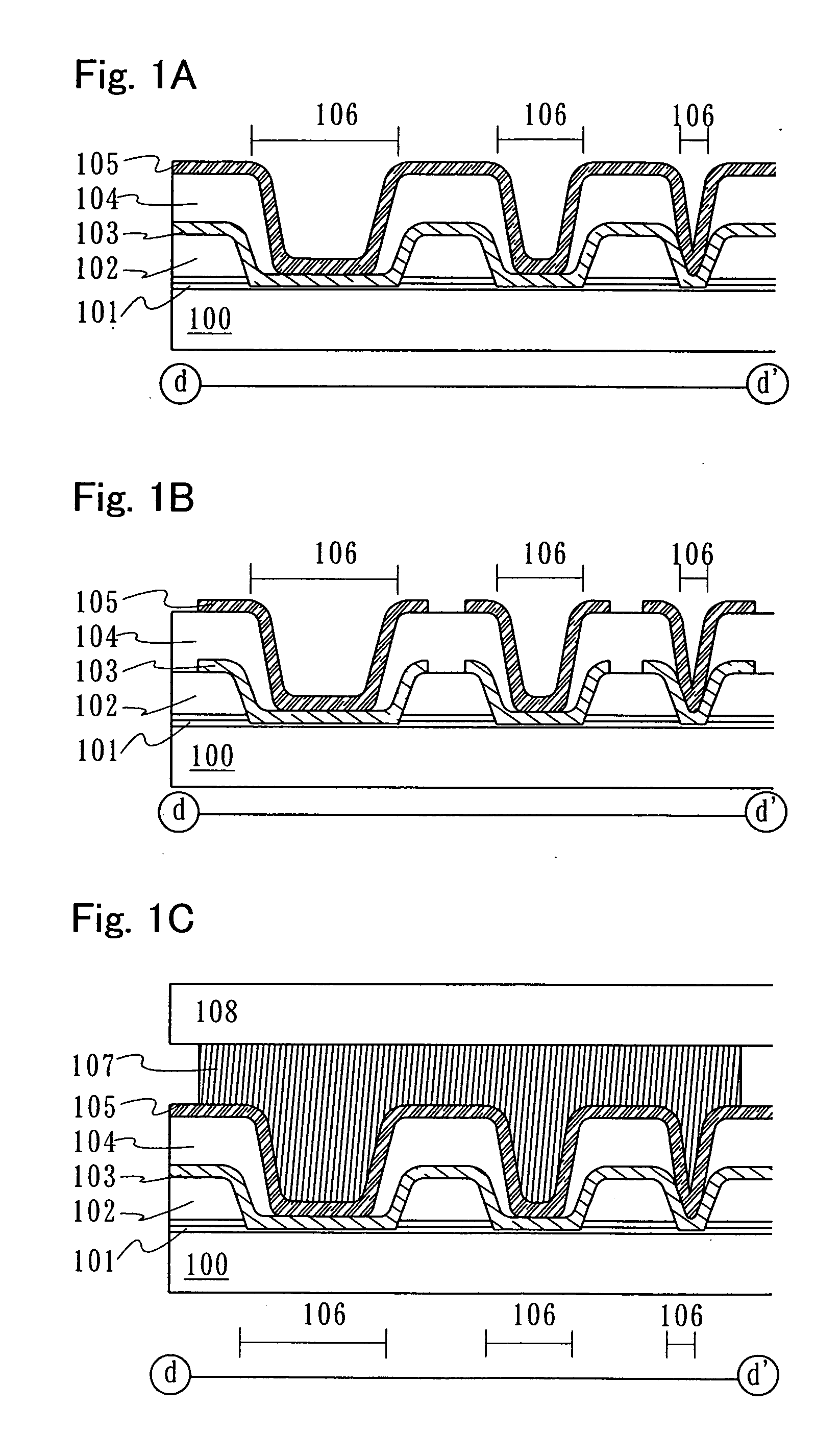
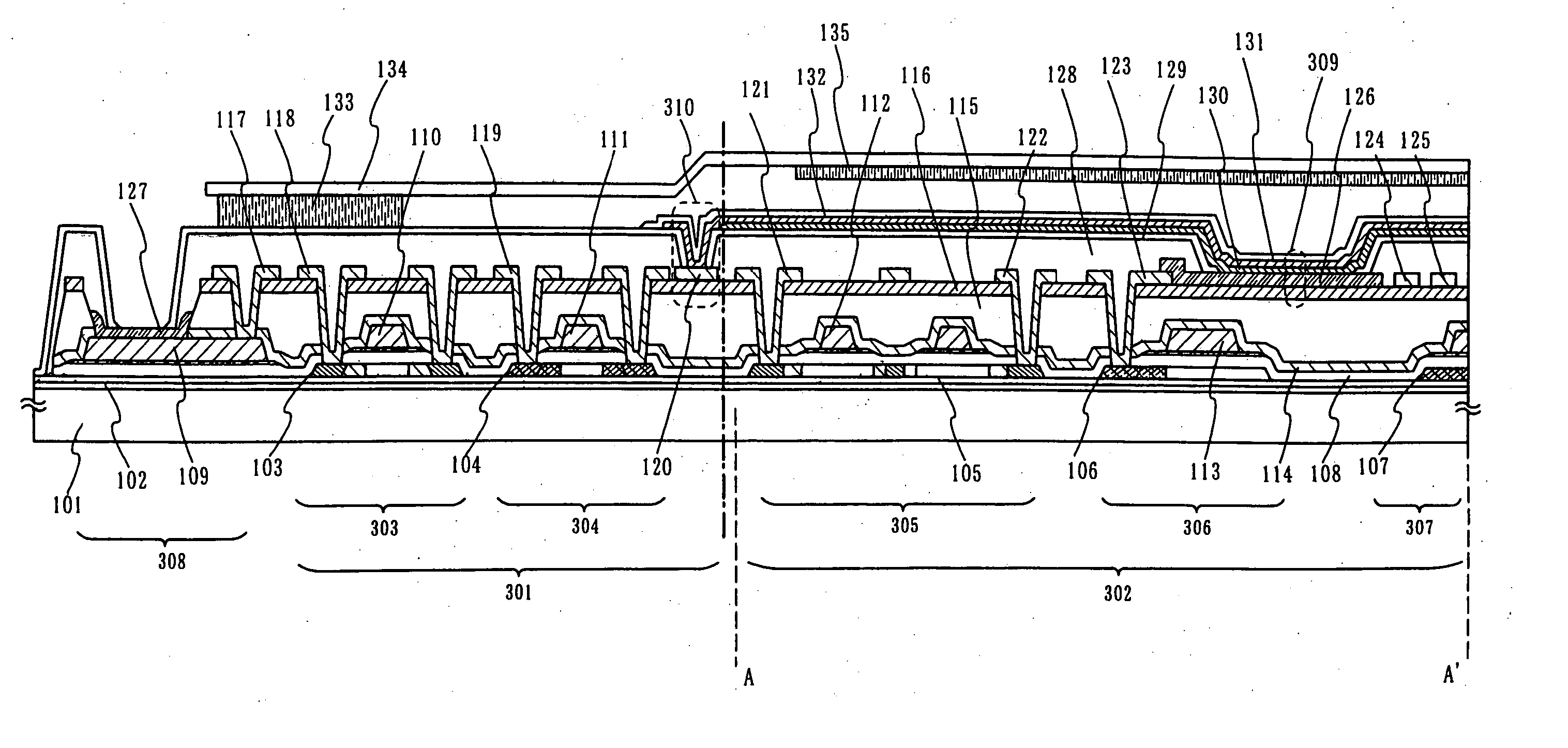
The purpose of the invention is to improve reliability of a light emitting apparatus including a TFT and organic light emitting elements. The light emitting apparatus according to the invention having a thin film transistor and a light emitting element includes a first inorganic insulation layer on the lower surface of a semiconductor layer, a second inorganic insulation layer on the upper surface of a gate electrode, a first organic insulation layer on the second inorganic insulation layer, a third inorganic insulation layer on the first organic insulation layer, a wiring layer extending on the third inorganic insulation layer, a second organic insulation layer overlapped with the end of the wiring layer and having an inclination angle of 35 to 45 degrees, a fourth inorganic insulation layer formed on the upper surface and side surface of the second organic insulation layer and having an opening over the wiring layer, a cathode layer formed in contact with the wiring layer and having side end overlapped with the fourth inorganic insulation layer, and an organic compound layer formed in contact with the cathode layer and the fourth inorganic insulation layer and including light emitting material, and an anode layer formed in contact with the organic compound layer including the light emitting material, wherein the third inorganic insulation layer and the fourth inorganic insulation layer are formed with silicon nitride or aluminum nitride.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Display device and method for manufacturing the same
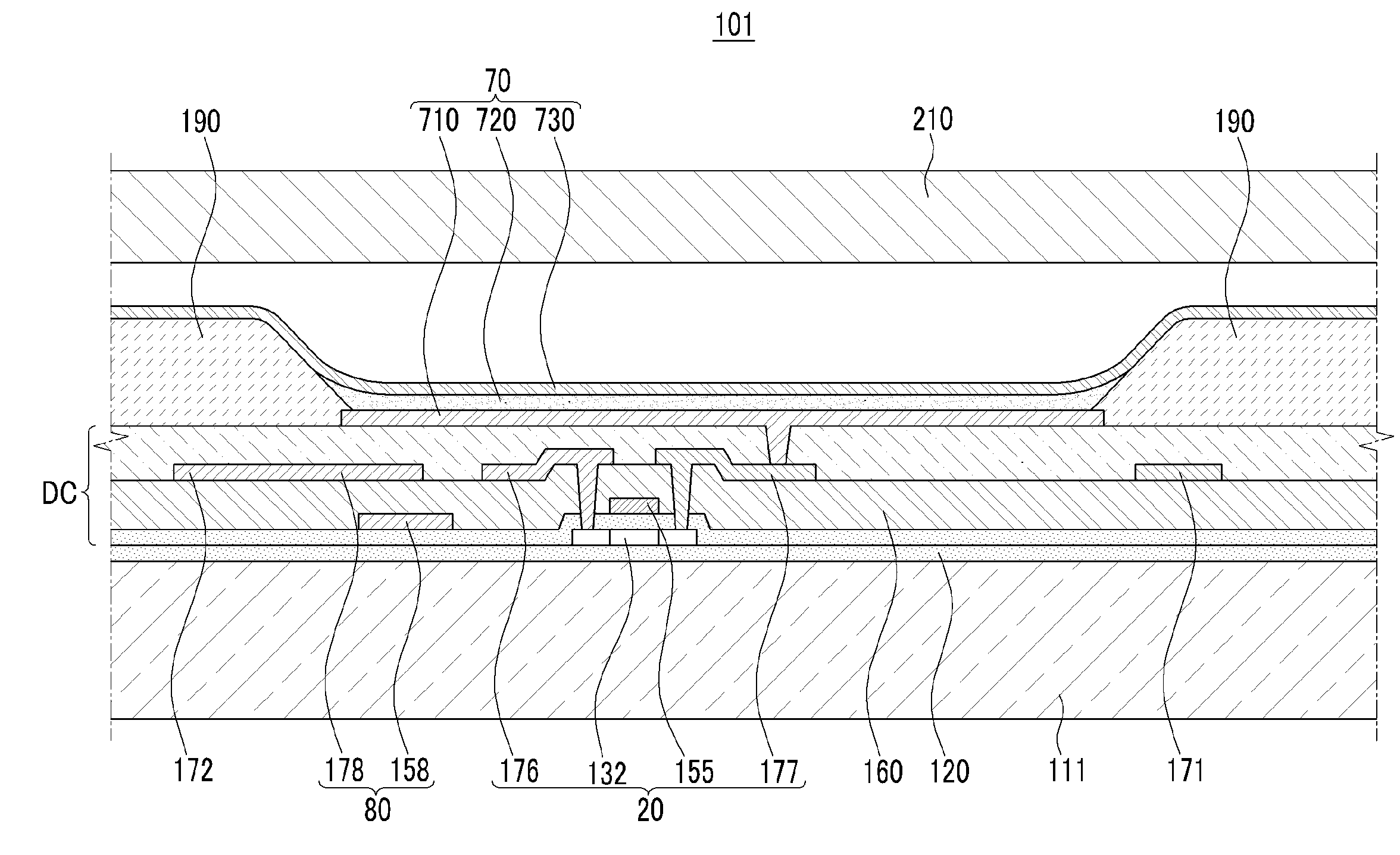
ActiveUS20050046346A1Solve the lack of reliabilityAvoid enteringDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceWater entry
An object of the present invention is to provide such a sealing structure that a material to be a deterioration factor such as water or oxygen is prevented from entering from external and sufficient reliability is obtained in a display using an organic or inorganic electroluminescent element. In view of the above object, focusing on permeability of an interlayer insulating film, deterioration of an electroluminescent element is suppressed and sufficient reliability is obtained by preventing water entry from an interlayer insulating film according to the present invention.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light emitting device
InactiveUS6891203B2Improve efficiencyIncrease brightnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesLength waveNitride
According to the invention, a Group III nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting element is provided with a light-emitting layer comprising two layers of different in ratio of AlGaInN composition, and emitting light with an emission peak wavelength in an ultraviolet region and light with an emission peak wavelength in a visible region. The light-emitting element and a fluorescent material excited by light in the ultraviolet region are combined to configure a light emitting device.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Light emitting apparatus and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7042024B2Improve reliabilityInhibit deteriorationTransistorSolid-state devicesInsulation layerOrganic compound
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light emitting apparatus, method for driving the light emitting apparatus, and display apparatus including the light emitting apparatus
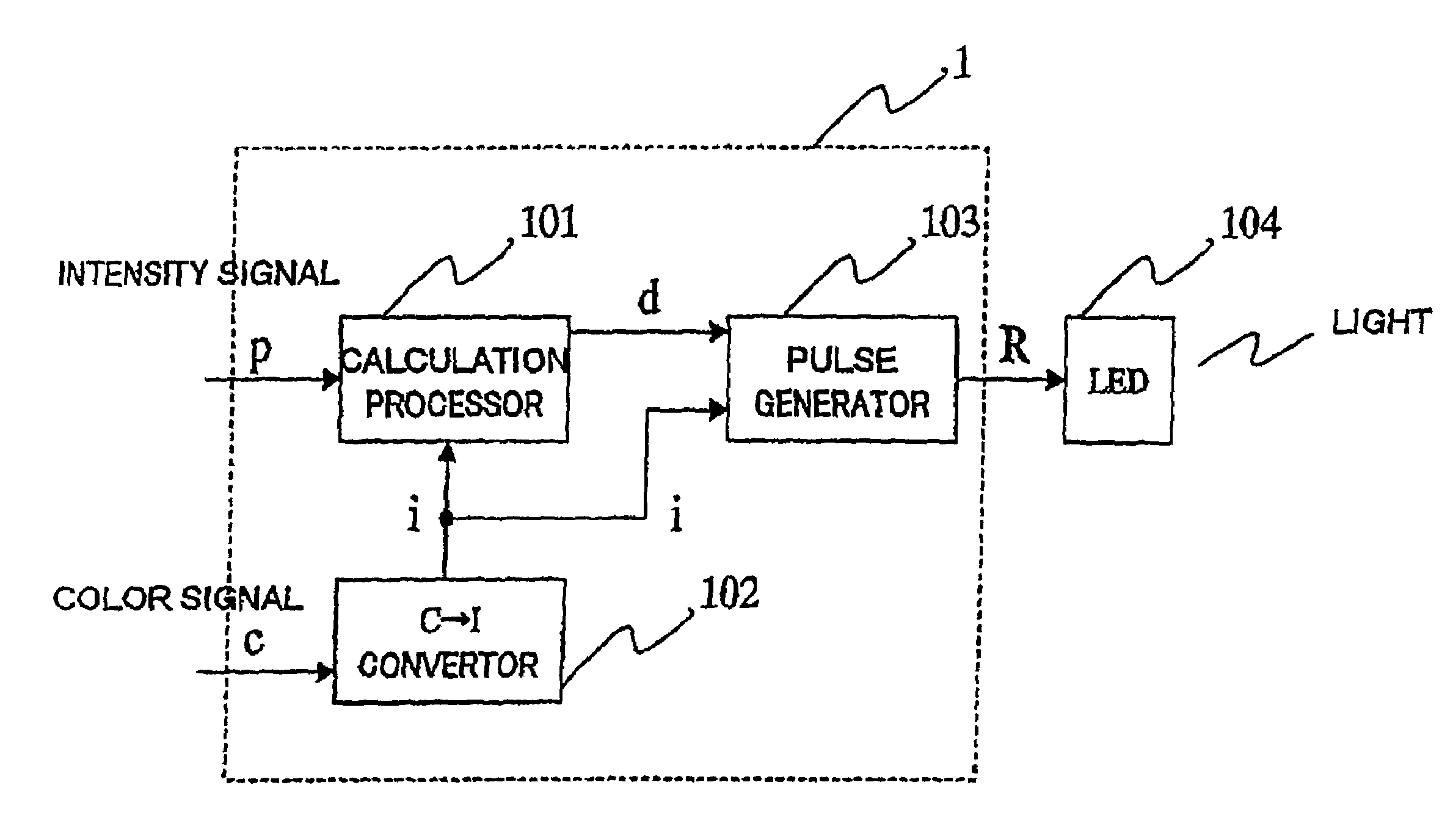
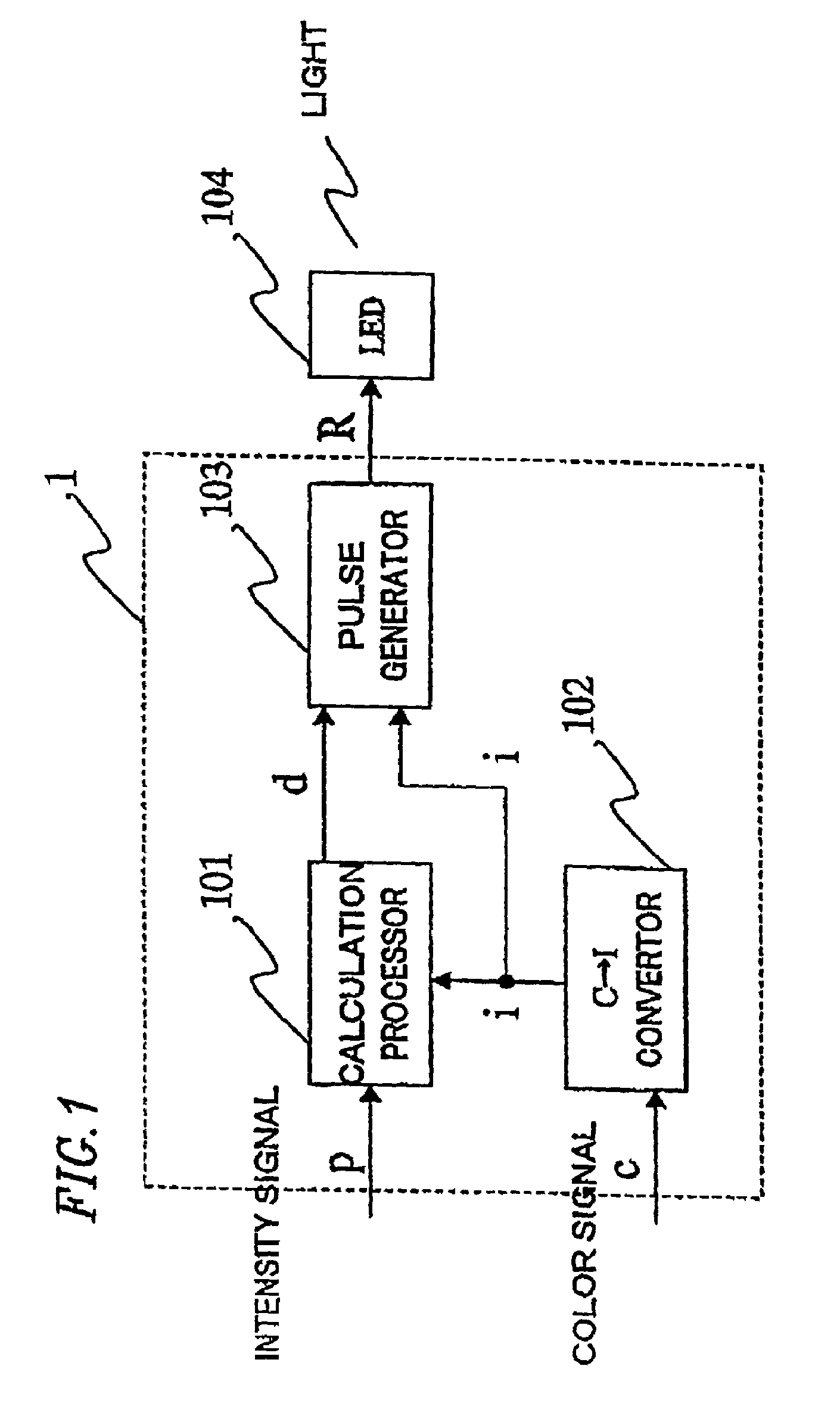
InactiveUS7180487B2Intensity can be suppressedSuppress lightElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesDriving currentLight emitting device
A light emitting apparatus comprises a light emitting section for emitting light, a color of the light being changed with a value of a driving current, and a driving section for driving the light emitting section so that the light emitting section emits light having a desired color and a desired intensity, by generating the driving current based on a signal designating the desired color and a signal designating the desired intensity and by applying the driving current to the light emitting section.
Owner:SHARP KK
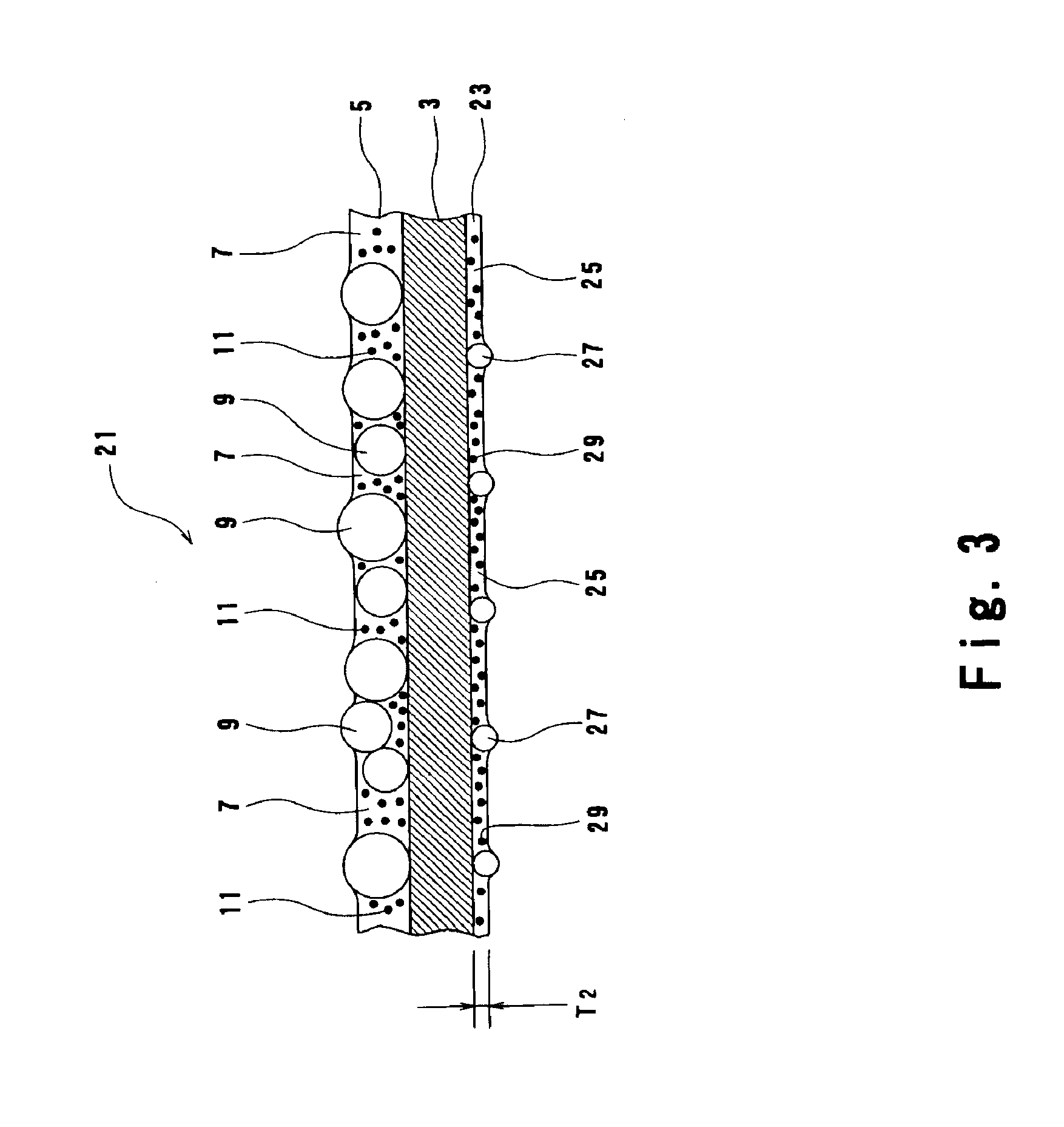
Photodiffusion sheet and backlight unit using this
InactiveUS6852396B1Preferable sticking-proof abilityHeat resistantMechanical apparatusMirrorsColloidal silicaMicrometer
It is an object of the present invention to provide a light diffusing sheet that has a less tendency to be deflected due to heat generated by a lamp and a back light unit using this. The light diffusing sheet of the present invention comprises a base sheet and a light diffusing layer provided on a surface of the base sheet. The light diffusing layer is formed by dispersing resinous beads and a fine inorganic filler into a binder. It is preferable that the fine inorganic filler has an averaged particle diameter of not smaller than 5 nanometers and smaller than 1 micrometer. It is preferable that the amount of the fine inorganic filler to be mixed is 10 parts to 500 parts by weight for 100 parts by weight of a polymer component in the binder. As the fine inorganic filler, colloidal silica is used.
Owner:KEIWA INCORPORATED
Display device
ActiveUS20110148944A1Increase the number ofIncrease manufacturing costSolid-state devicesDiodeDisplay deviceDriven element
A display device includes a light emitting functional layer disposed between a first and second substrates; a first pixel which emits light to the second substrate and has a first pixel electrode disposed between the light emitting functional layer and the first substrate, a second electrode disposed between the light emitting functional layer and the second substrate, and a first reflecting layer disposed between the first pixel electrode and the first substrate; a second pixel which emits light to the first substrate side and has a second pixel electrode disposed between the light emitting functional layer and the first substrate, a second electrode disposed between the light emitting functional layer and the second substrate, and a second reflecting layer disposed between the second electrode and the second substrate; and a driving element which drives the first and second pixel electrodes is disposed above first substrate.
Owner:ELEMENT CAPITAL COMMERCIAL CO PTE LTD
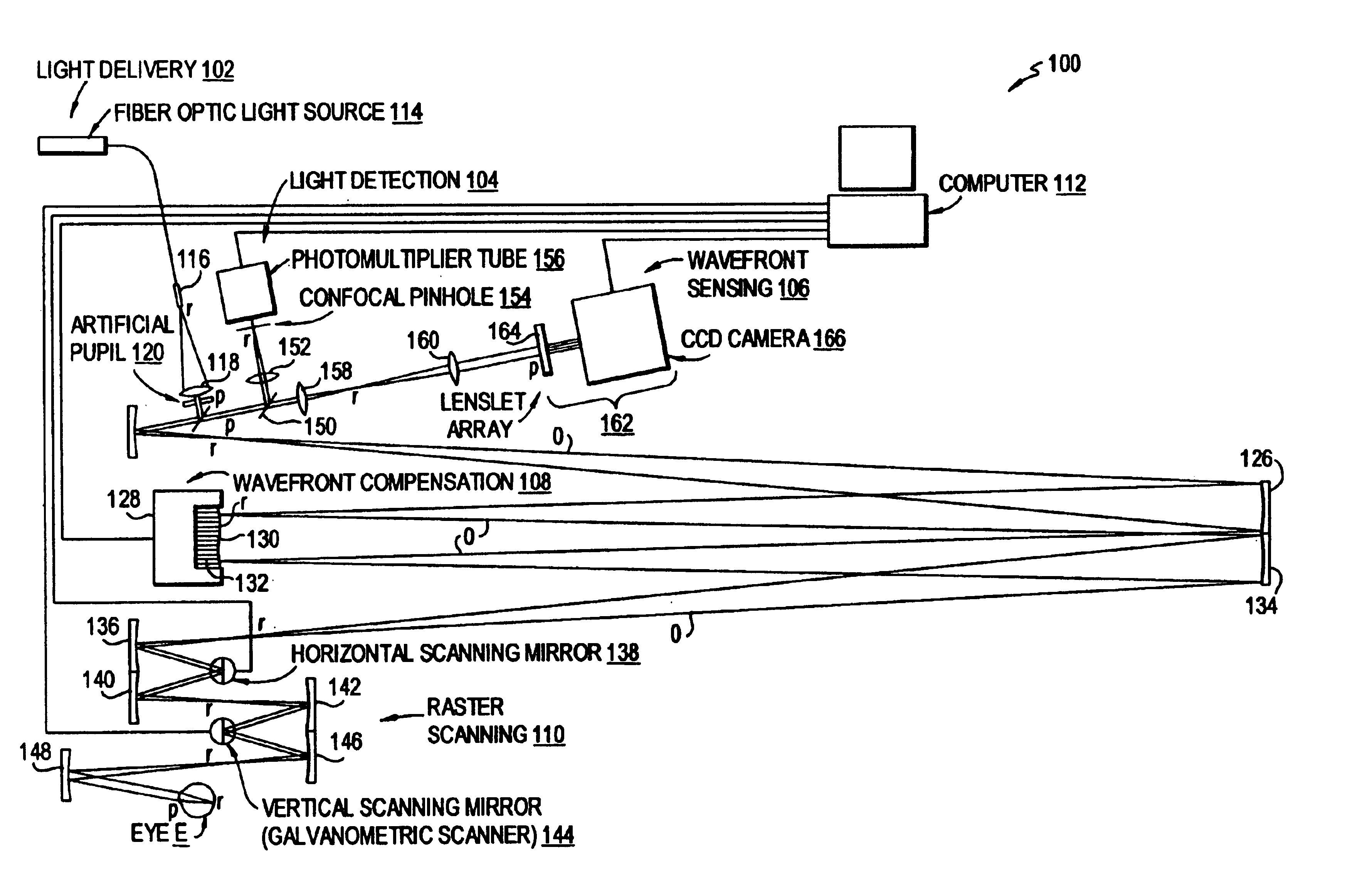
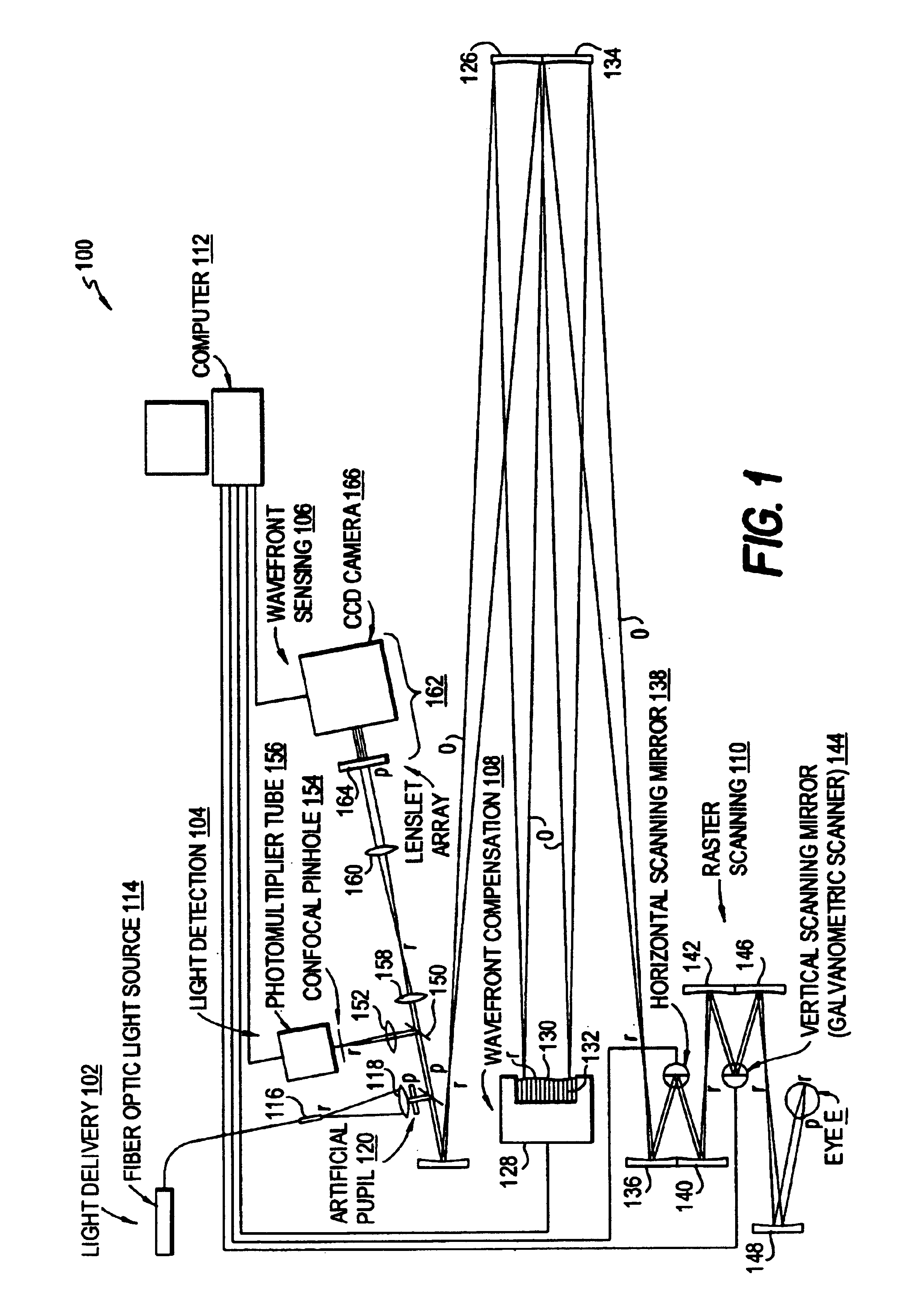
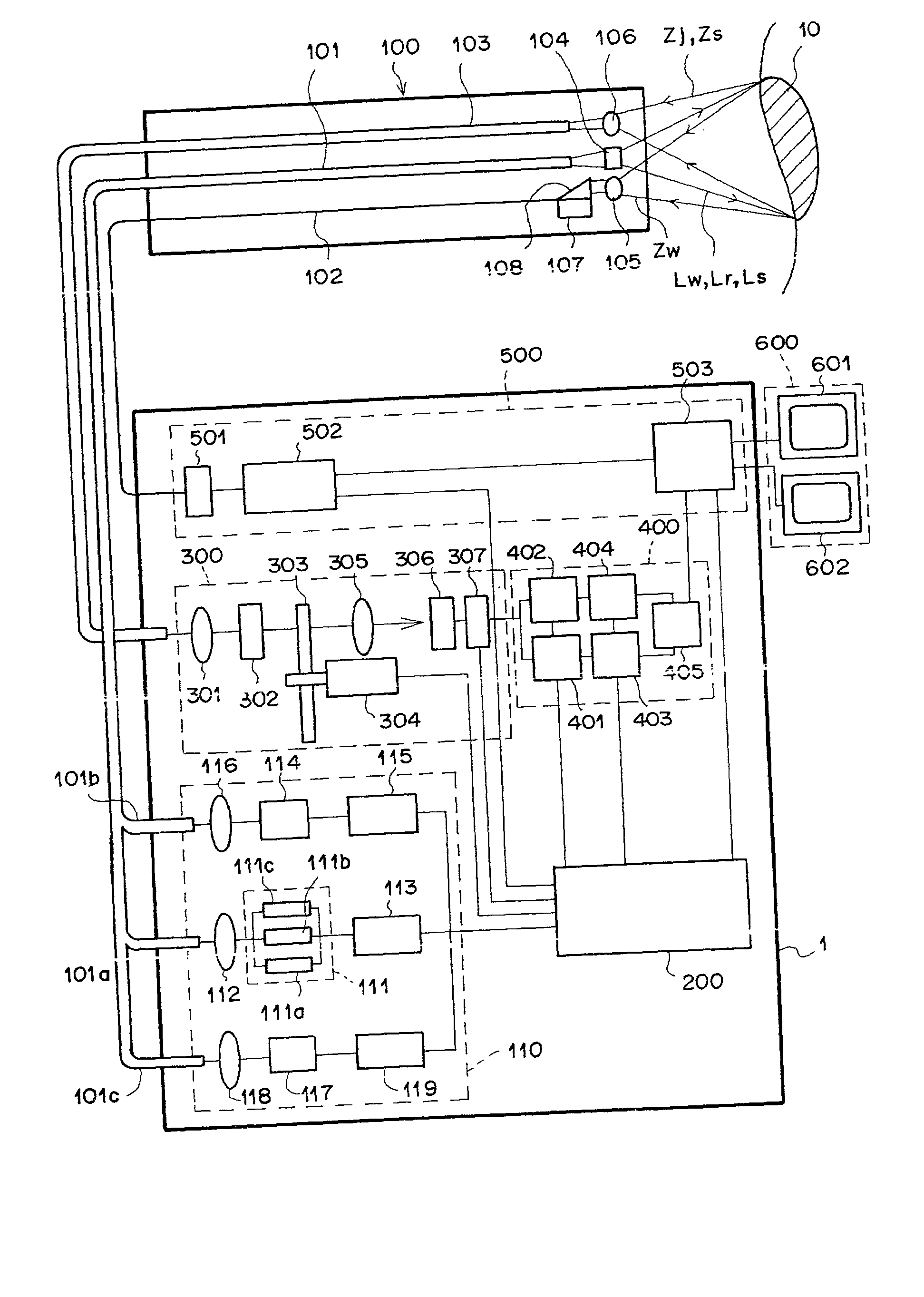
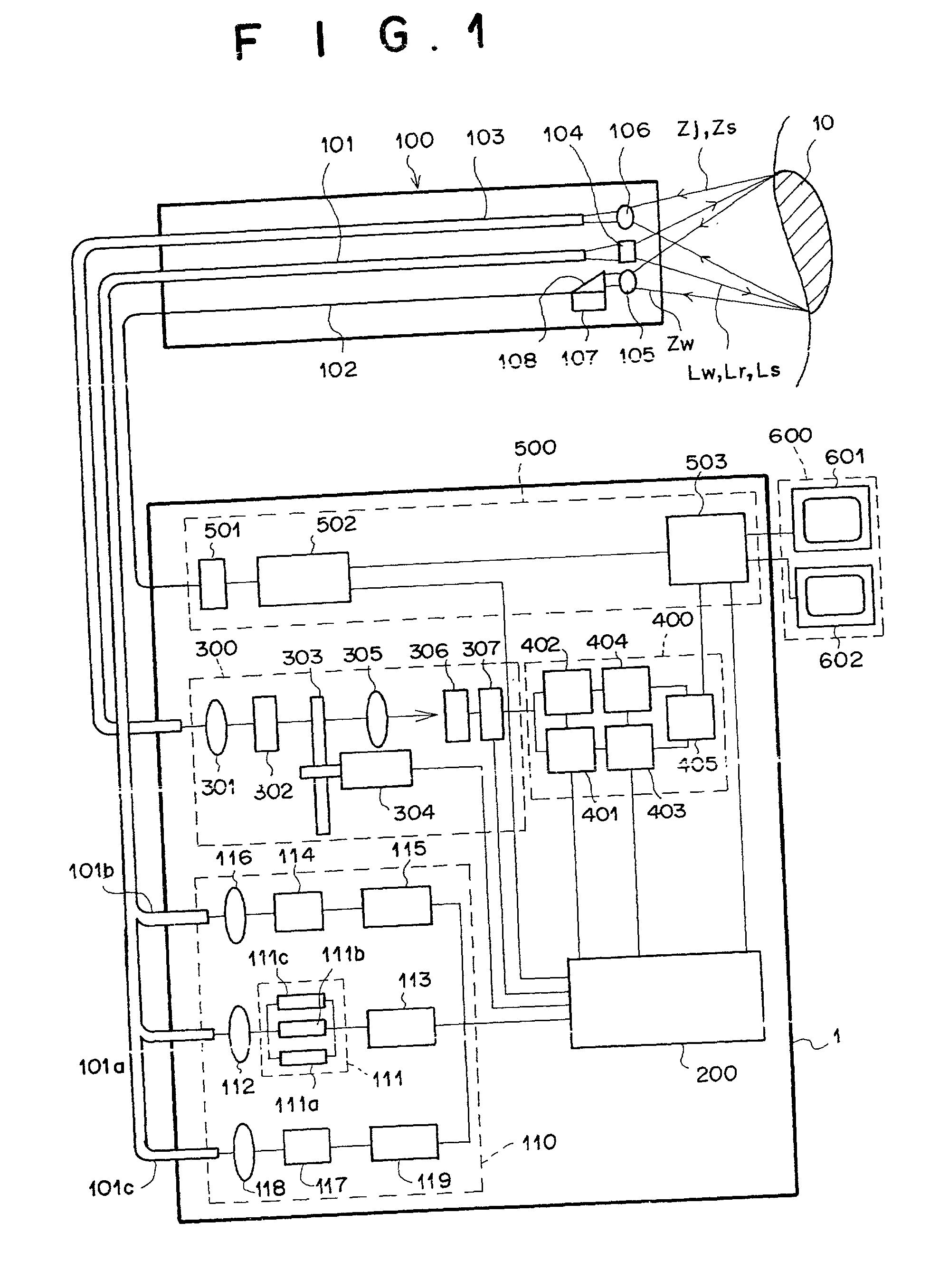
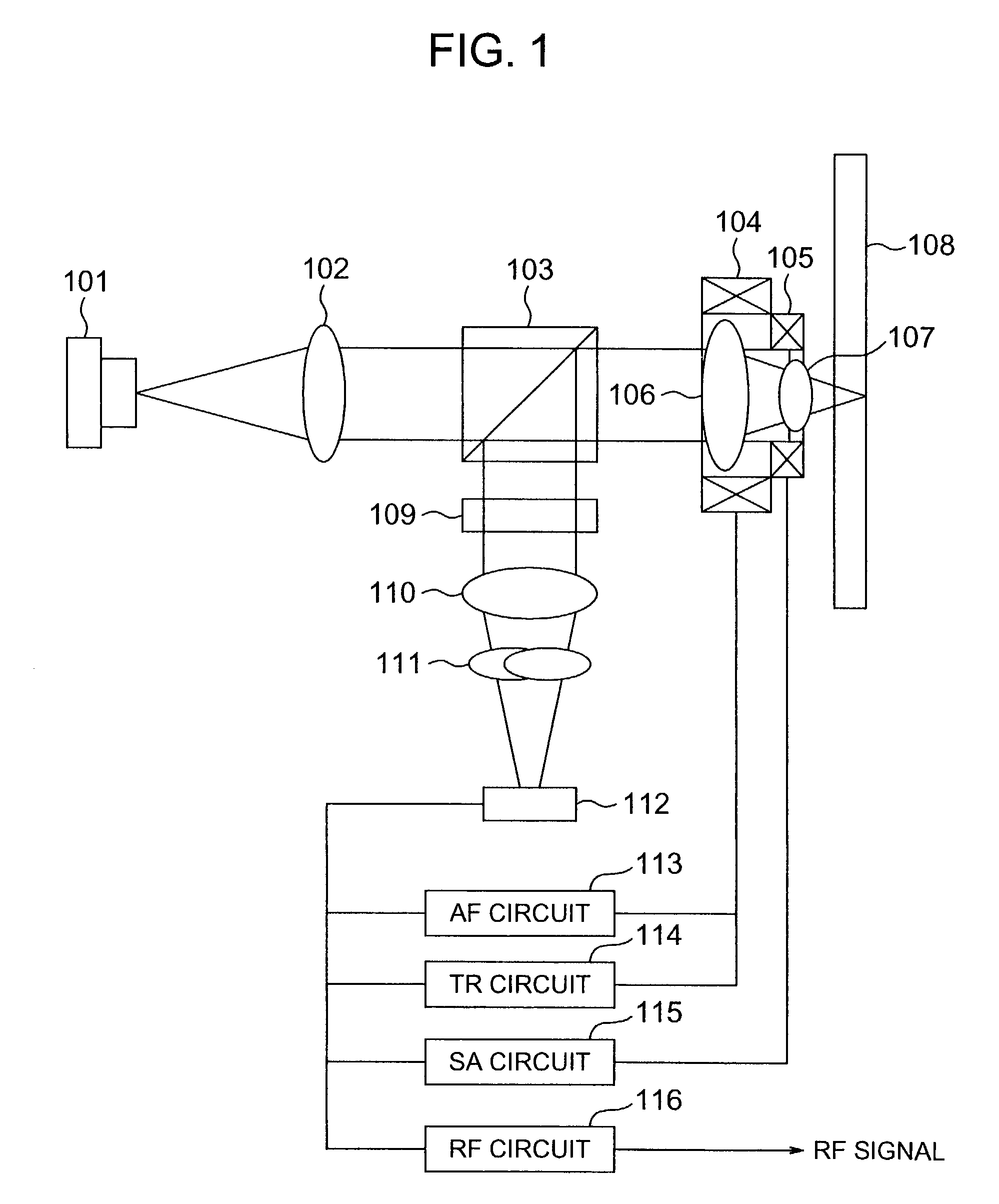
Method and apparatus for using adaptive optics in a scanning laser ophthalmoscope
InactiveUS6890076B2Efficient and effective implementationImprove abilitiesOptical measurementsOthalmoscopesScanning laser ophthalmoscopeEyewear
A scanning laser ophthalmoscope incorporates adaptive optics to compensate for wavefront aberrations in the eye. Light from a light source is scanned onto the retina. Light reflected from the retina is detected for imaging and is also used for wavefront sensing. The sensed wavefront aberrations are used to control an adaptive optic device, such as a deformable mirror, disposed in the path of the light from the source in order to compensate for the aberrations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Image display apparatus and control method therefor
InactiveUS20100328294A1Quality improvementSuppress lightCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringData storing
An image display apparatus comprises a pixel having a drive transistor and a pixel display element which are connected in series between a first power line and a second power line, a holding capacitor connected to a gate electrode of the drive transistor, and a selection transistor connected between a signal line and the gate electrode of the drive transistor. When the selection transistor is turned on, gradation pixel data is written in the holding capacitor from the signal line. The charge of gradation pixel data written in the holding capacitor is discharged for a certain period through the drive transistor, thereafter the charge of the gradation pixel data stored in the holding capacitor is held by floating the gate electrode of the drive transistor.
Owner:SASAKI ISAO +1
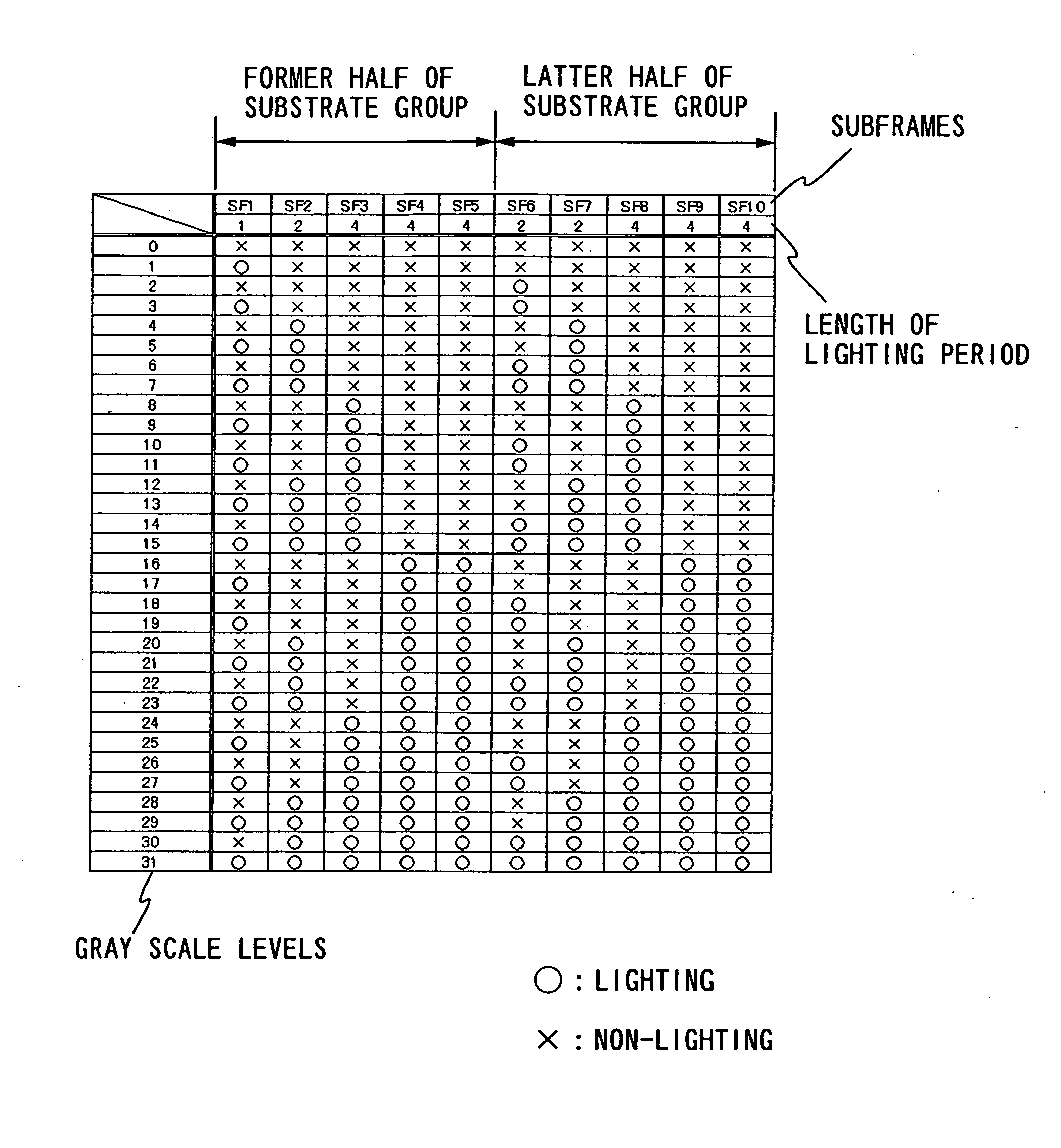
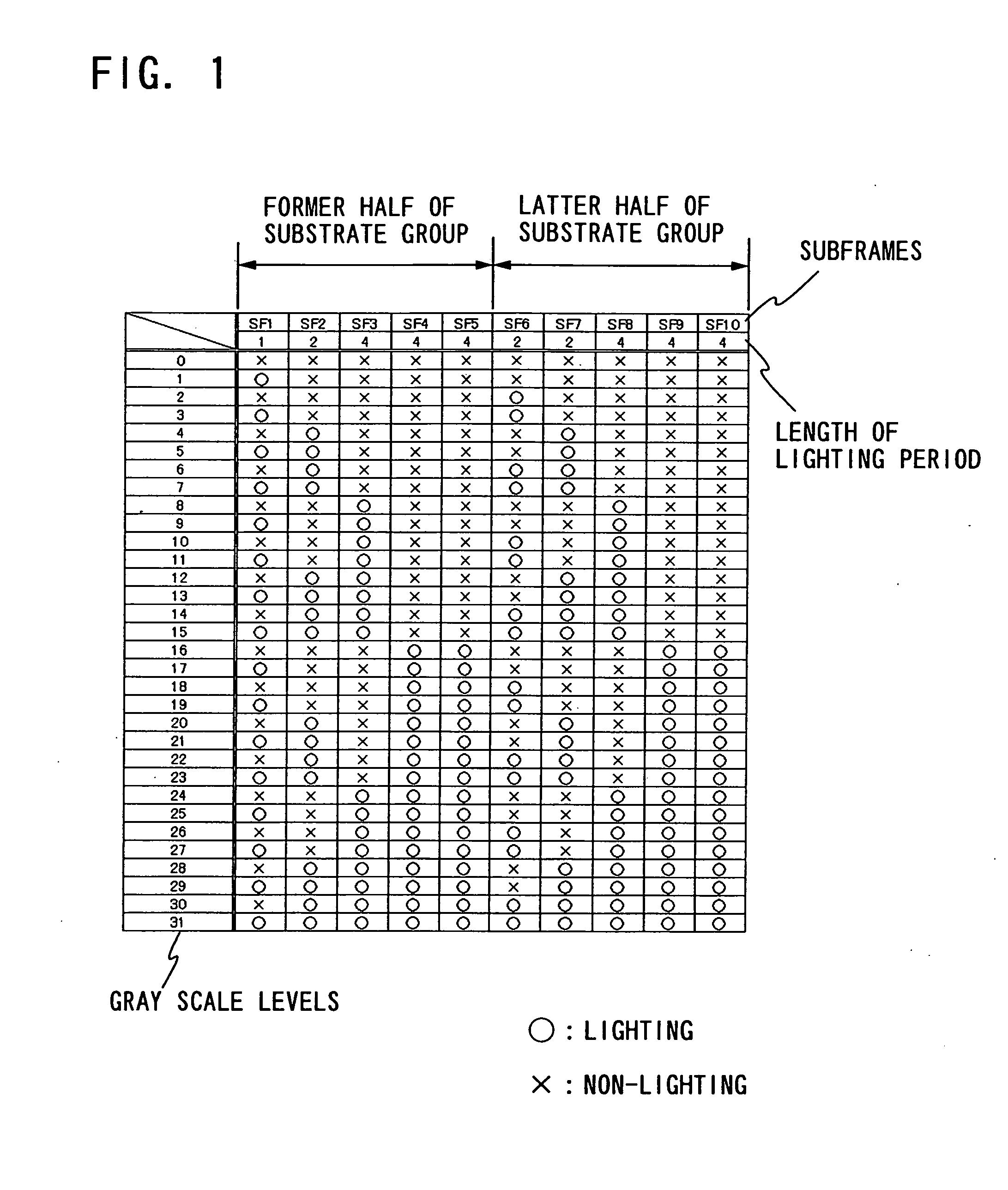
Display device, driving method of the display device, and electronic device
ActiveUS20060232600A1Clear imagingImprove image qualityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceComputer science
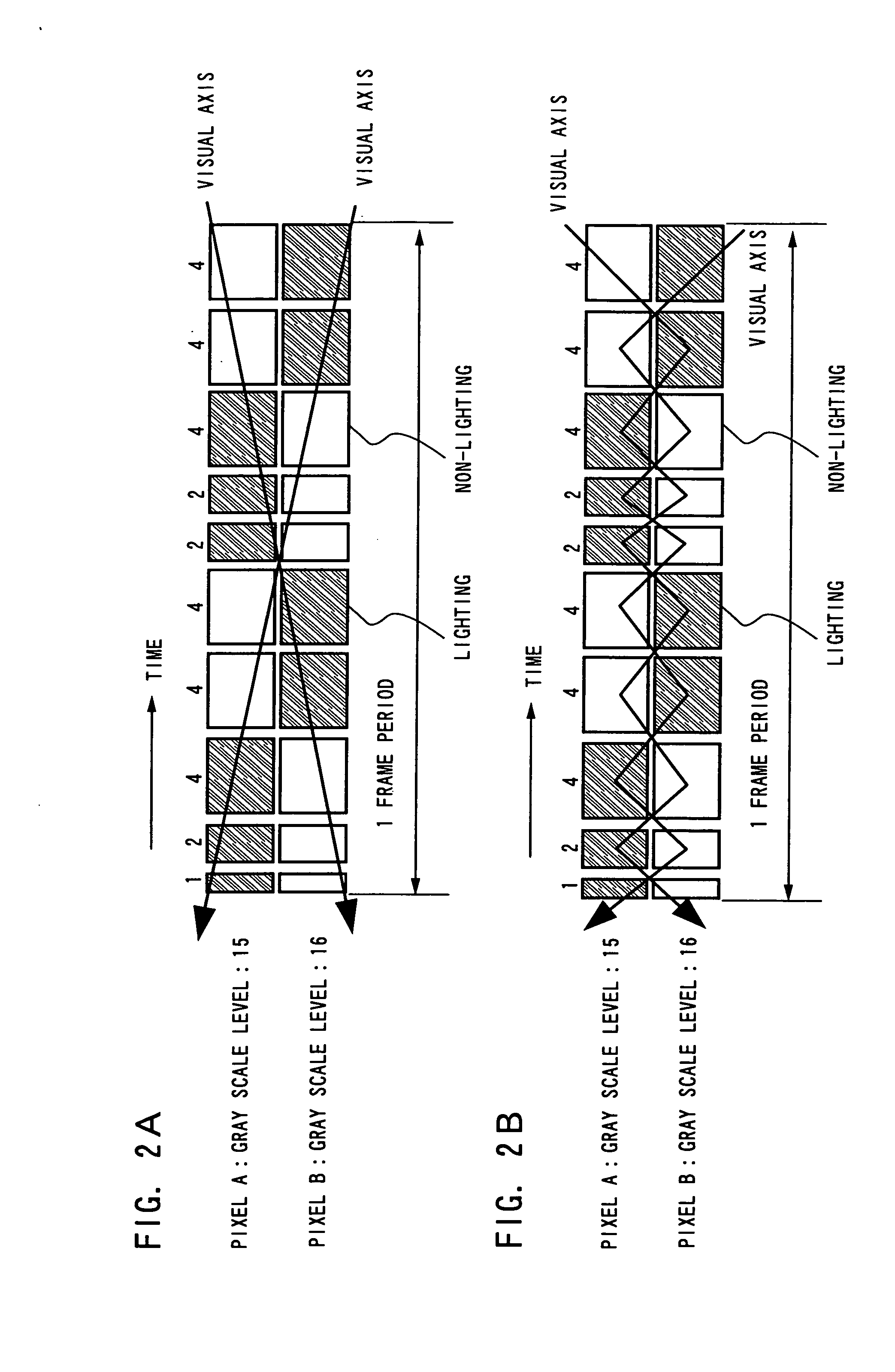
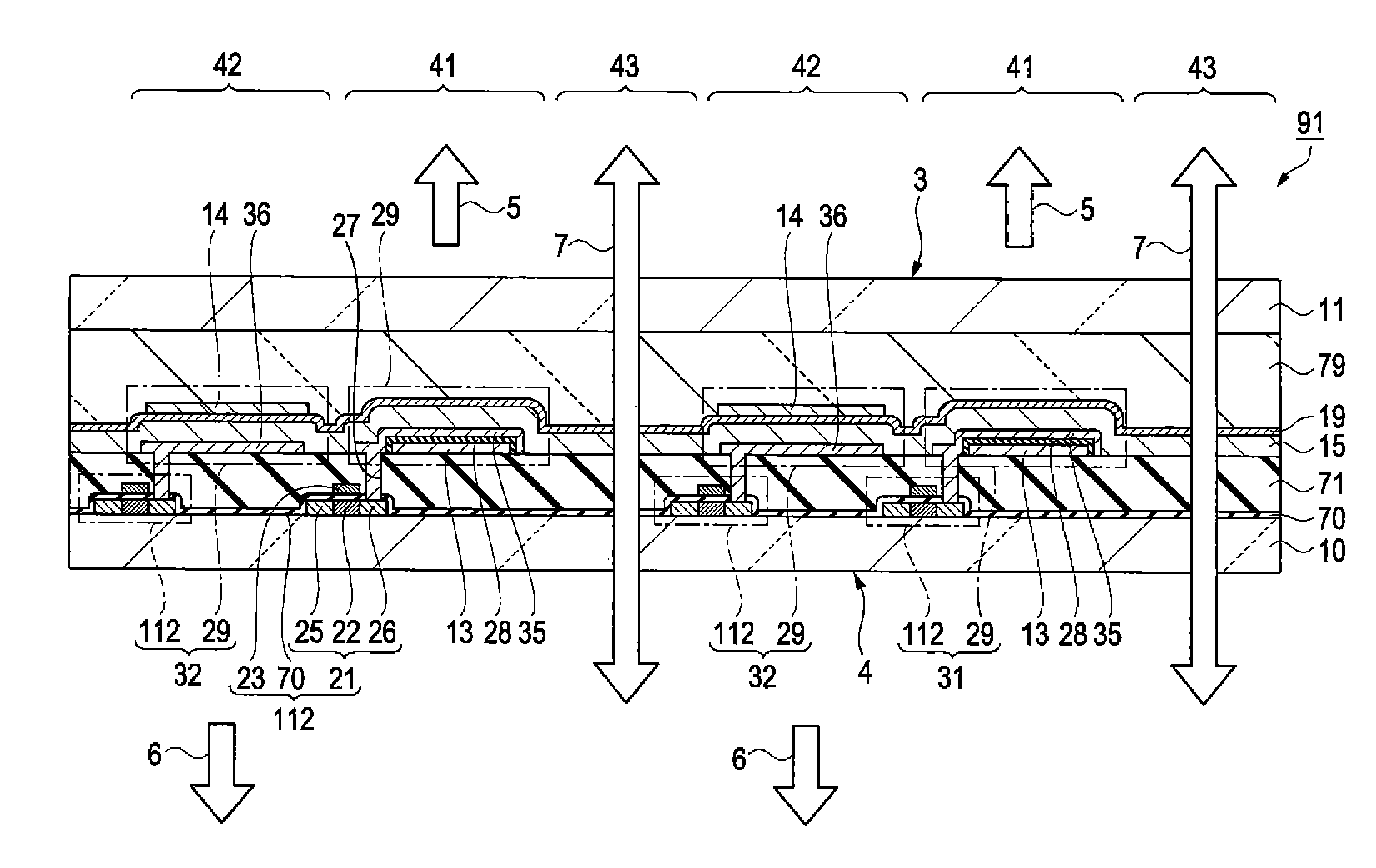
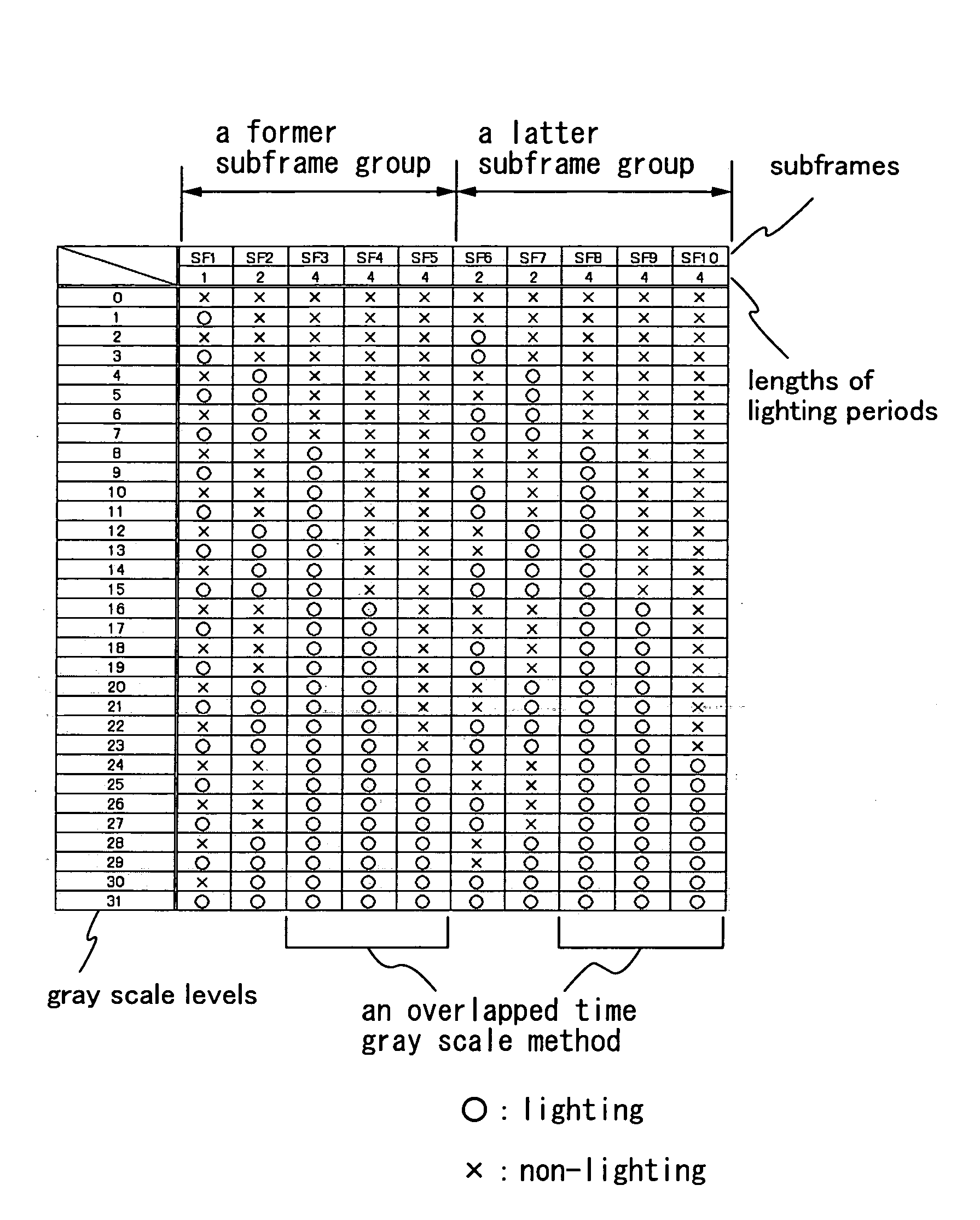
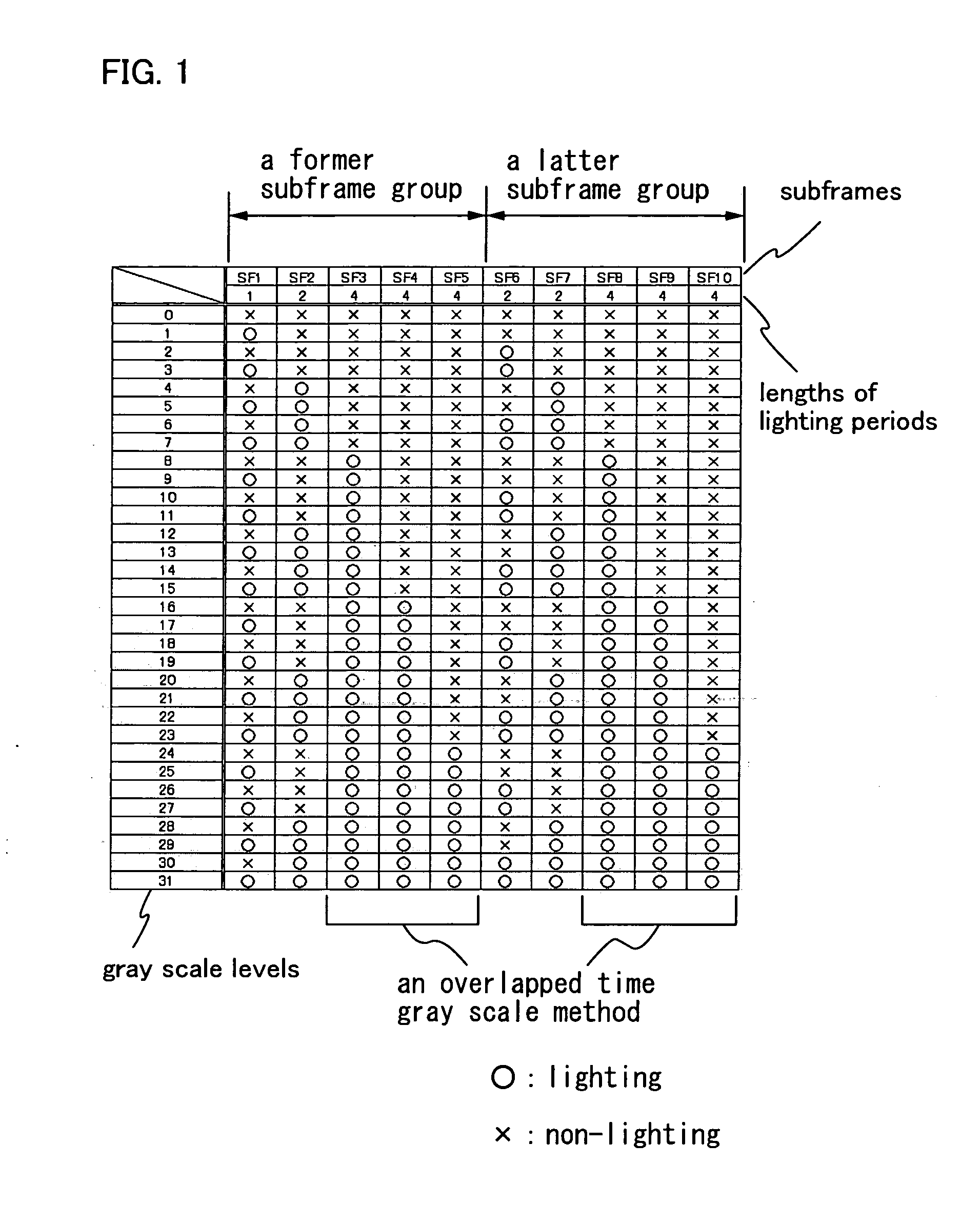
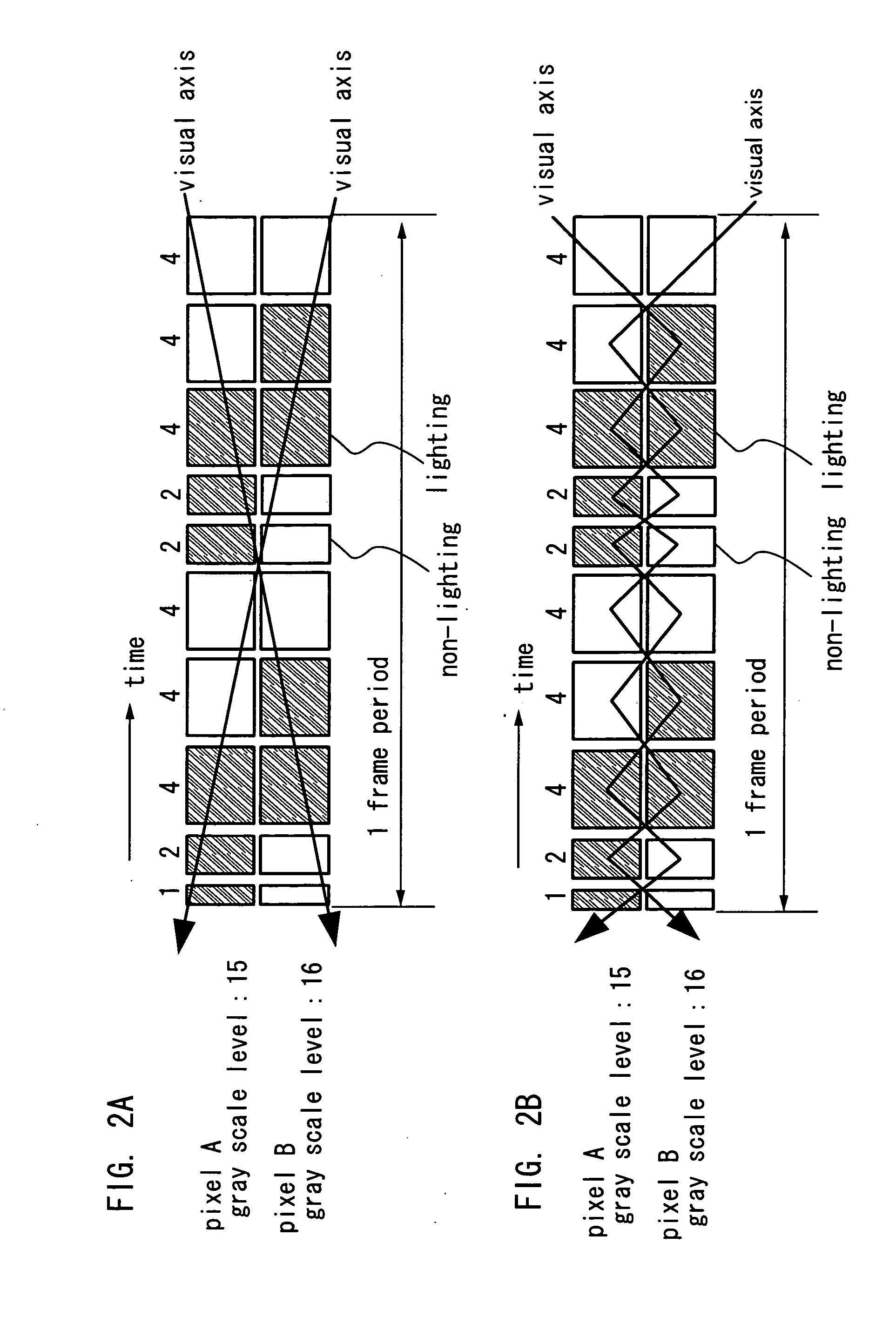
To reduce a pseudo contour which occurs when displaying by a time gray scale method. When gradation is expressed with an n bit, the bits are divided into three bit groups, and one frame is divided into two subframe groups. Then, a (0<a<n) subframes corresponding to bits belonging to a first bit group are divided into three or more, each about half of which is arranged in each subframe group; b (0<b<n) subframes corresponding to bits belonging to a second bit group are divided into two, each one of which is arranged in each the subframe group; and c (0≦c<n and a+b+c=n) subframes corresponding to bits belonging to a third bit group are arranged in at least one of the subframe groups.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Organic light emitting diode display
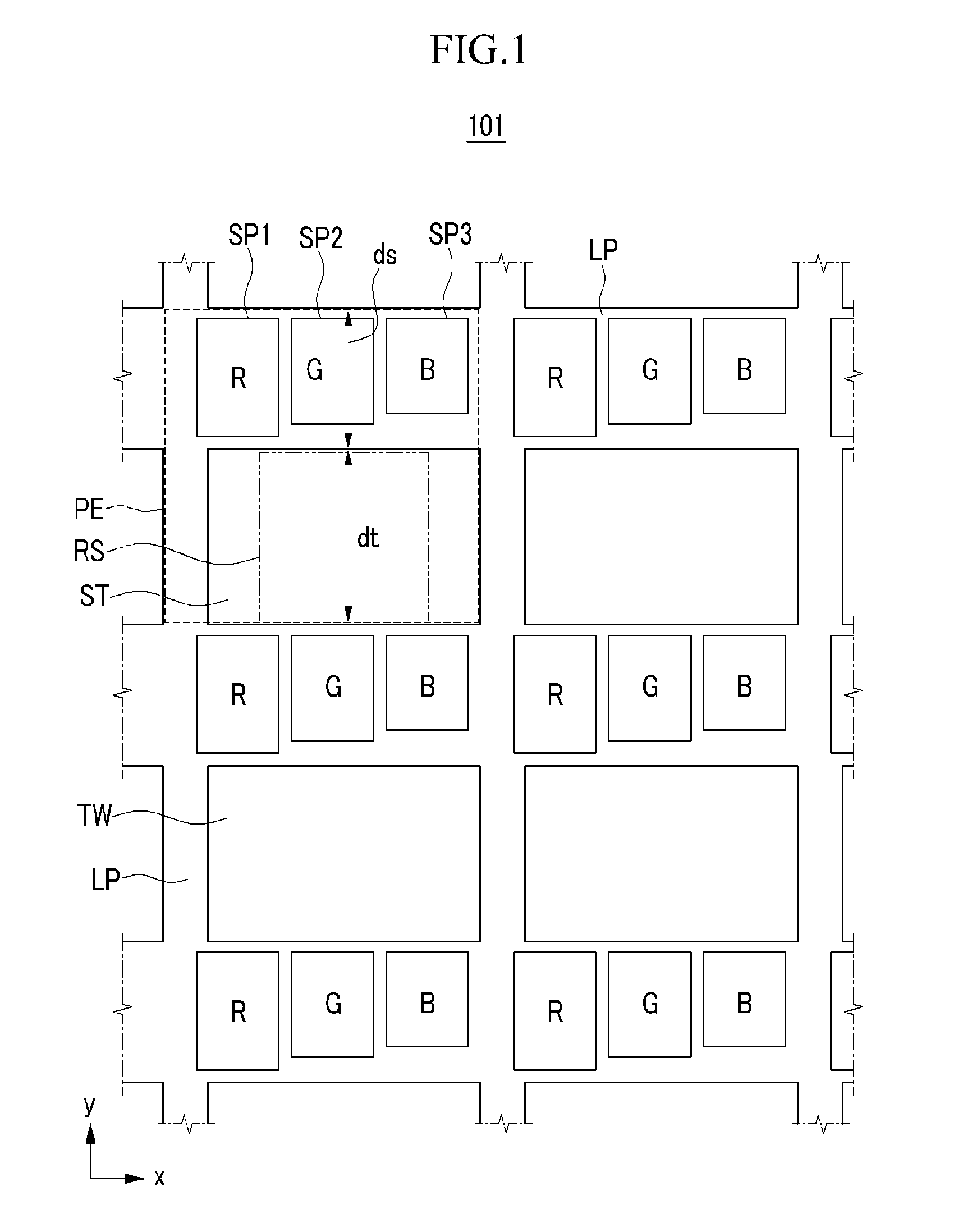
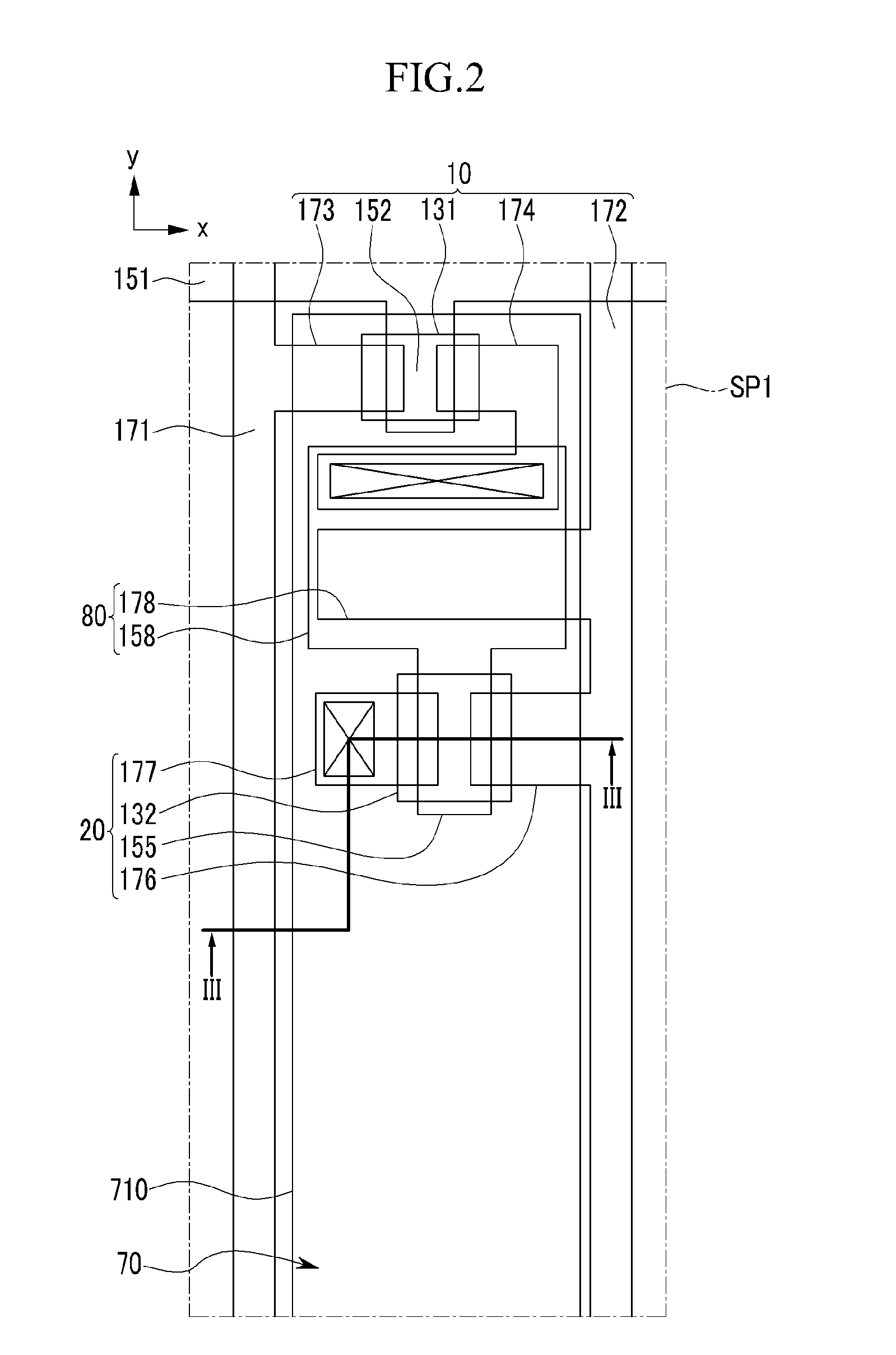
ActiveUS20110147770A1Minimize image distortionSuppressing of passing lightSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
An organic light emitting diode display includes: a substrate main body having a plurality of pixel regions, each including an opaque region and a transparent region; and organic light emitting diodes, thin film transistors, and conductive lines that are formed in the opaque region of the substrate main body. The transparent region includes a transparent square space that has an area that is at least 15% of the entire area of the pixel region.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
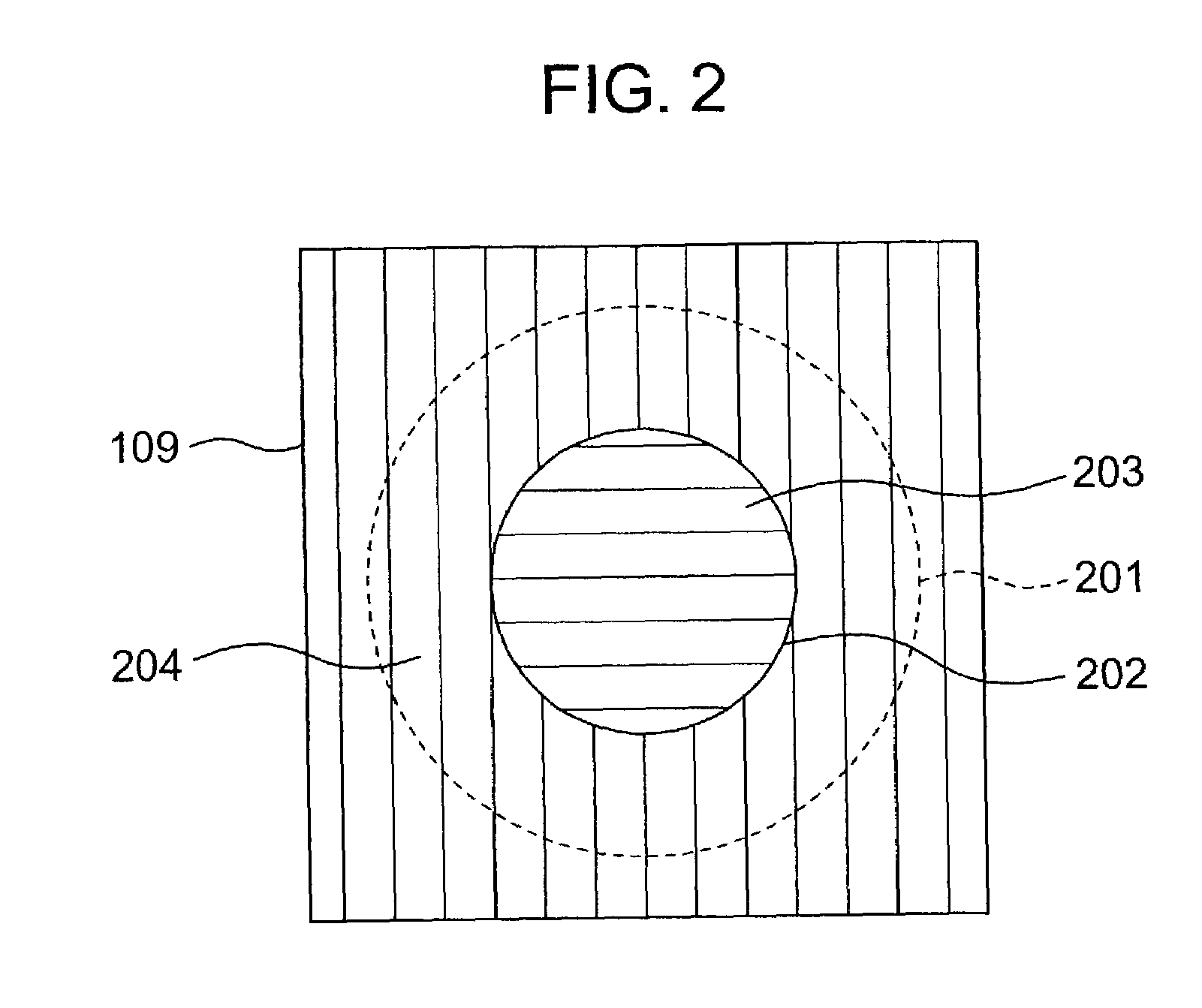
Full Color CMOS Imager Filter
ActiveUS20090200584A1Improve color separationSuppress lightSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesCMOSCheckerboard pattern
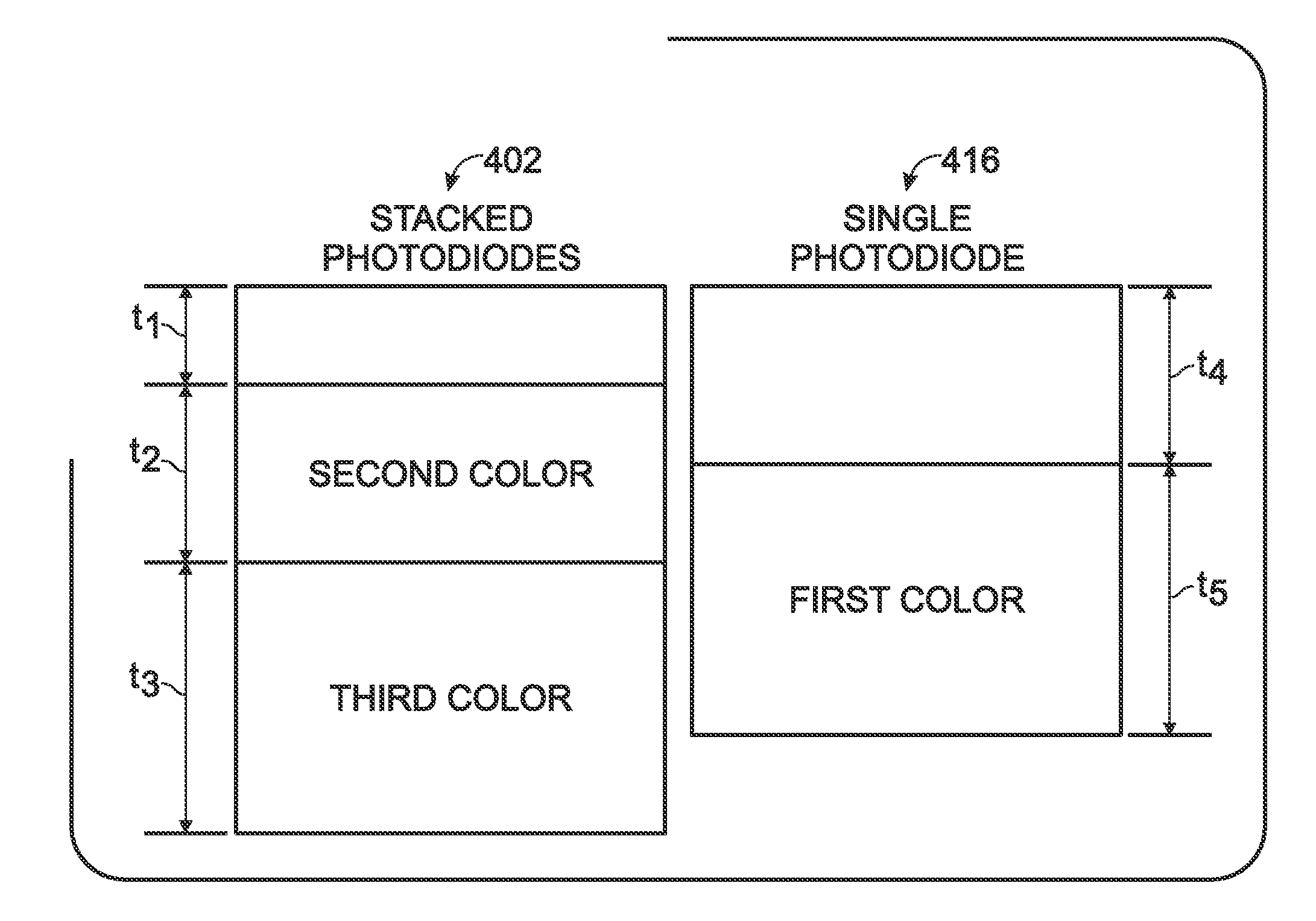
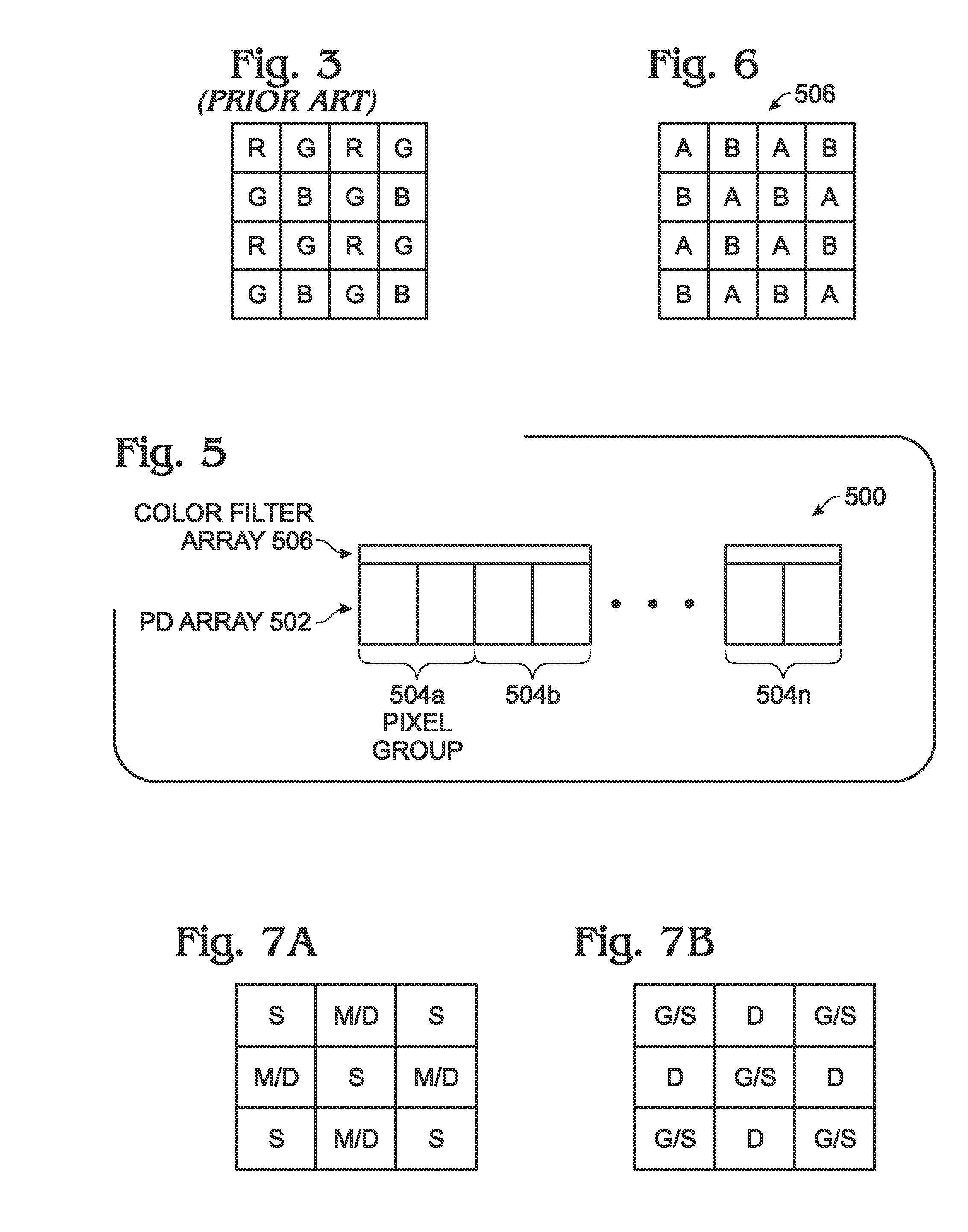
A full color complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) imaging circuit is provided. The imaging circuit comprises an array of photodiodes including a plurality of pixel groups. Each pixel group supplies 3 electrical color signals, corresponding to 3 detectable colors. The circuit also includes a color filter array overlying the photodiode array employing less than 3 separate filter colors. Each pixel group may be enabled as a dual-pixel including a single photodiode (PD) to supply a first color signal and stacked PDs to supply a second and third color signal. In one aspect, the color filter array employs 1 filter color per pixel group. In another aspect, the color filter array employees 2 filter colors per pixel group. In either aspect, the color filter array forms a checkerboard pattern of color filter pixels. For example, a magenta color filter may overlie the stacked PDs of each dual-pixel, to name one variation.
Owner:SHARP KK
Light emitting apparatus and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060006424A1Improve reliabilityInhibit deteriorationTransistorSolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsContact formation
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light emitting apparatus and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050224820A1Improve reliabilityInhibit deteriorationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSimple Organic CompoundsInsulation layer
The light emitting apparatus according to the invention having a thin film transistor and a light emitting element, comprises; a first inorganic insulation layer on the lower surface of a semiconductor layer, a second inorganic insulation layer on the upper surface of a gate electrode, a first organic insulation layer on the second inorganic insulation layer, a third inorganic insulation layer on the first organic insulation layer, a wiring layer extending on the third inorganic insulation layer, a second organic insulation layer overlapped with the end of the wiring layer and having an inclination angle of 35 to 45 degrees, a fourth inorganic insulation layer formed on the upper surface and side surface of the second organic insulation layer and having an opening over the wiring layer, a cathode layer formed in contact with the wiring layer and having side end overlapped with the fourth inorganic insulation layer, and an organic compound layer formed in contact with the cathode layer and the fourth inorganic insulation layer and comprising light emitting material, and an anode layer formed in contact with the organic compound layer comprising the light emitting material, wherein the third inorganic insulation layer and the fourth inorganic insulation layer are formed with silicon nitride or aluminum nitride.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Organic light emitting diode display
ActiveUS20110012816A1Avoid distortionSuppressing of transmitted lightStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceLight-emitting diode
An organic light emitting diode display including a plurality of pixel areas and a transparent area interposed between the plurality of pixel areas, the display includes a substrate member, thin film transistors and capacitor elements on the substrate member, the thin film transistor and the capacitor elements overlapping with the pixel areas, a gate line, a data line, and a common power supply line on the substrate member, the gate line, the data line, and the common power supply line overlapping with the pixel areas and the transparent area, and being connected to corresponding ones of the thin film transistors and / or the capacitor elements, and pixel electrodes on the substrate member, the pixel electrodes overlapping with all of the thin film transistors and capacitor elements, and with respective portions of the gate line, the data line, and the common power supply line that overlap with the pixel areas.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Endoscope system having multiaxial-mode laser-light source or substantially producing multiaxial-mode laser light from single-axial-mode laser light
InactiveUS20020038074A1Clearer diagnostic imageSmall sizeLaser detailsSurgeryDriving currentFluorescence
In an endoscope system including: a light emission unit emits laser light as illumination light or excitation light; a light guide unit guides the illumination light or the excitation light to an object; and an image pickup unit picks up a normal image formed with reflection light generated by reflection of the illumination light from the object or a fluorescence image emitted from the object in response to the excitation light. The laser light is multiaxial-mode laser light, or the light emission unit includes a plurality of laser-light sources which emit single-axial-mode laser beams having different wavelengths or phases. Alternatively, a vibration unit which vibrates the light guide unit is provided, or a high-frequency signal is superimposed on a driving current of the light emission unit, so that the wavelength of the laser light is shifted among a plurality of values.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
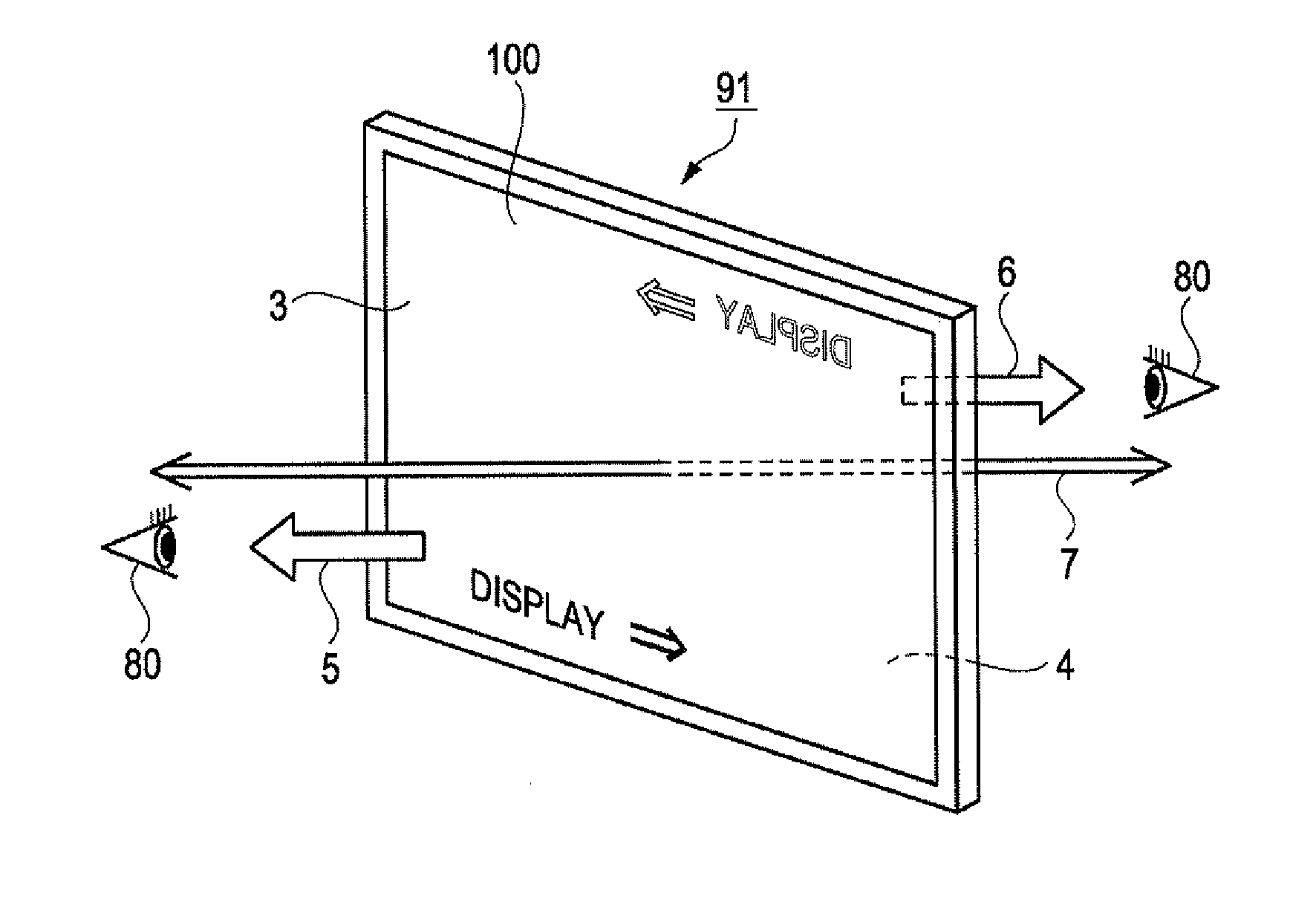
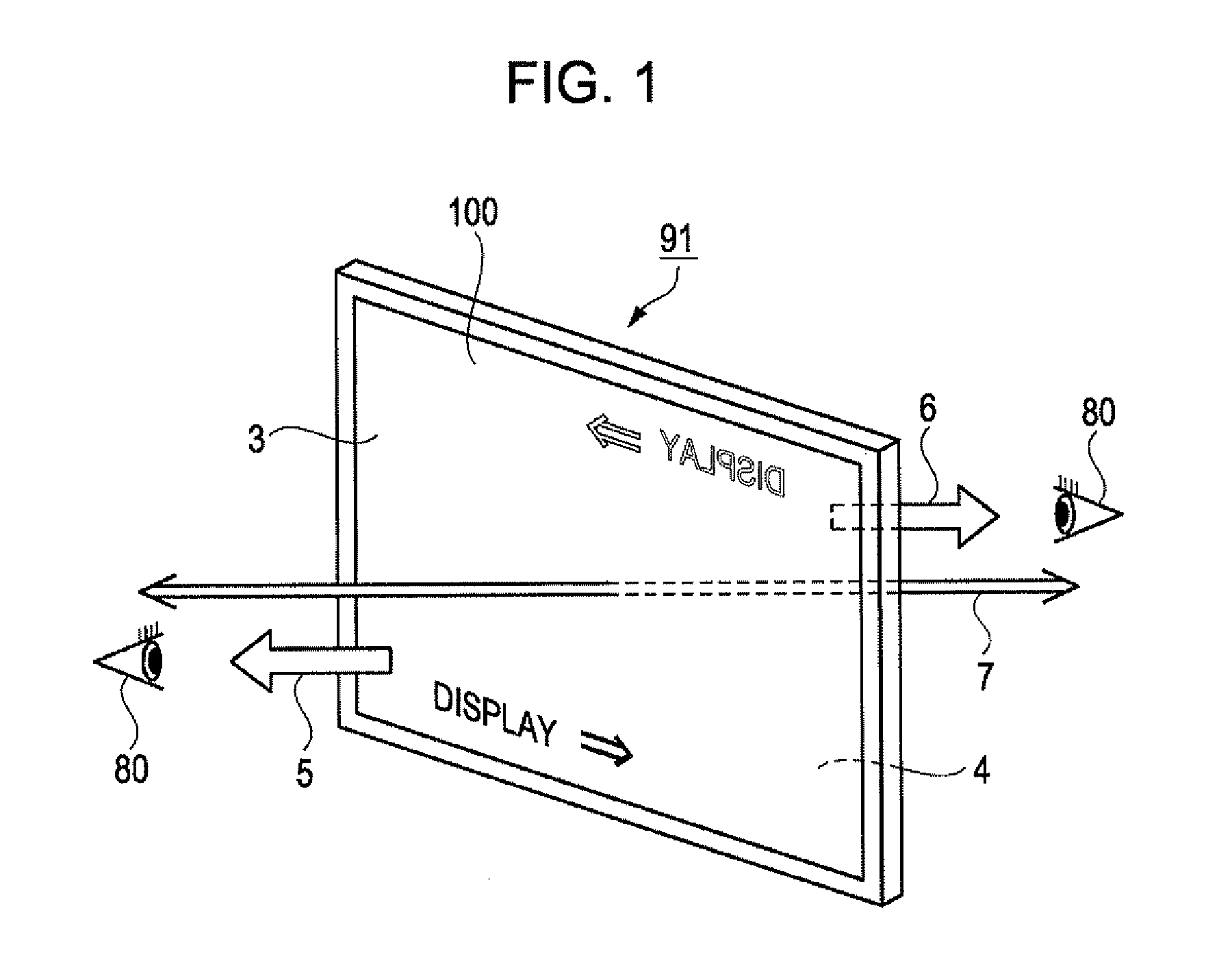
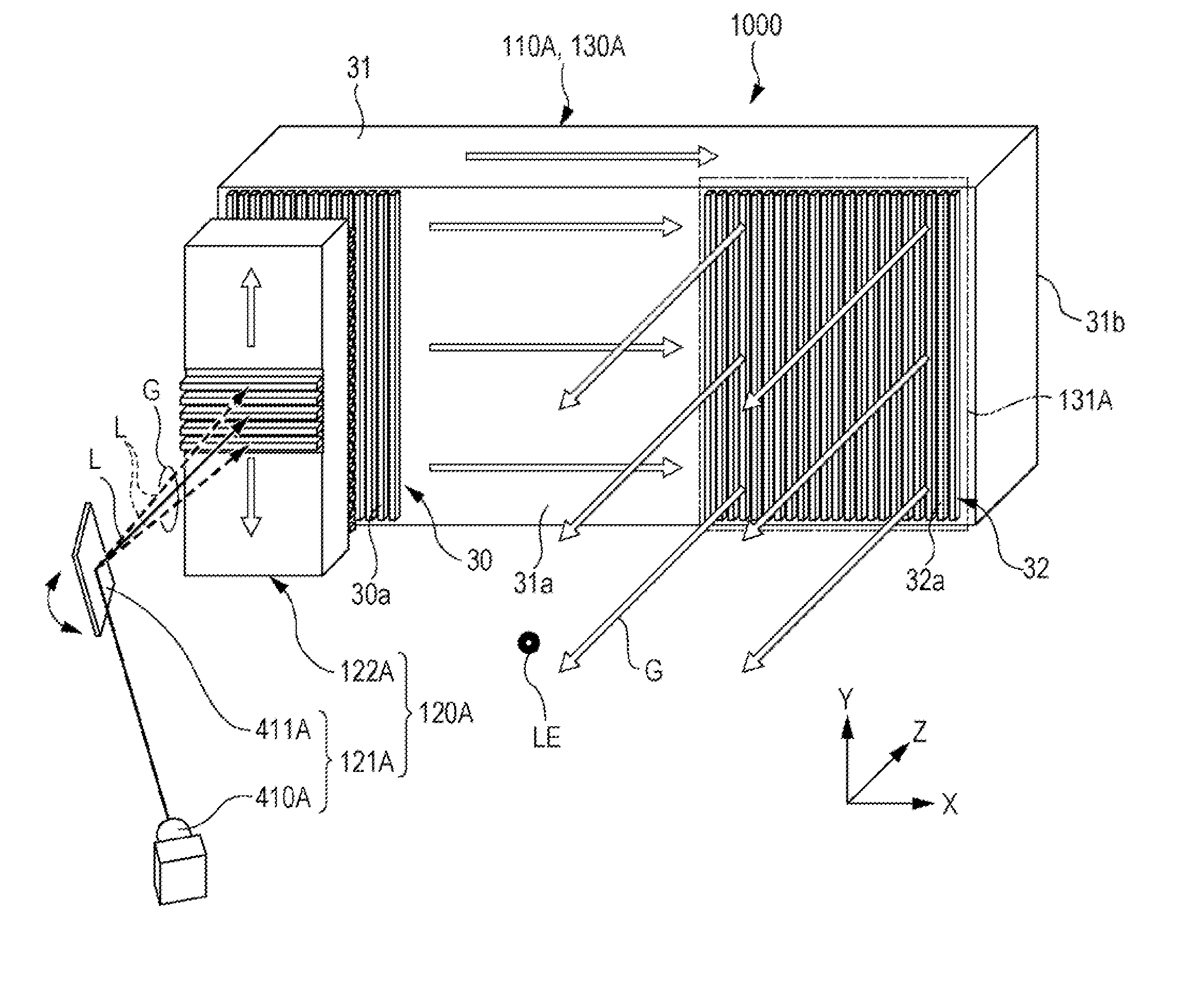
Optical element, electro-optical device, and mounted display apparatus
ActiveUS20160124229A1Improve display qualityImprove usabilityDiffraction gratingsPlanar/plate-like light guidesGratingLight guide
An optical element includes a light guide is provided with a incidence section and a emission section, a semitransmissive reflective film is provided in the inside of the light guide, a first diffraction element is provided in the incidence section, and is provided with a plurality of gratings, a second diffraction element is provided in the emission section, and is provided with a plurality of gratings, and a reflective film is provided in the incidence section in a periphery of the first diffraction element, in which the pitch of the plurality of gratings of the first diffraction element is equivalent to the pitch of the plurality of gratings of the second diffraction element, and each extension direction of the plurality of gratings of the first diffraction element is the same direction as each extension direction of the plurality of gratings of the second diffraction element.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Reflection suppression for an optical fiber
ActiveUS20050053350A1Suppresses internal reflectionSuppresses back reflectionCoupling light guidesFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringReturn loss
Forming a plurality of loops in an optical fiber around a spool adjacent to an exposed end face can suppress internal reflections from the exposed end face. The radius of the loops can attenuate light that is propagating to and from the end face by causing light to leak out of the optical fiber's core and into its cladding. The radius can be selected to control physical stress in the optical fiber and promote reliability. The radius and the number of loops can be selected to meet a return loss specification. The loops can be formed by coiling the optical fiber around a spool that includes a slot for holding the optical fiber until it is put into service.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS
Semiconductor light emitting device, image display unit, lighting apparatus, and method of fabricating semiconductor light emitting device
InactiveUS7087934B2High crystallinityLarge quantity of light emissionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLight equipmentActive layer
A semiconductor light emitting device includes a crystal growth layer, and a crystal layer composed of a first conductive type layer, an active layer, and a second conductive type layer. The crystal layer is provided on the upper side of the crystal growth layer. In this device, a back plane of the crystal growth layer has irregularities. Since light generated in the device is prevented from being totally reflected from the back plane of the crystal growth layer, the light emergence efficiency of the device can be increased.
Owner:SONY CORP
Light emitting device, and illumination light source, display unit and electronic apparatus including the light emitting device
InactiveUS20110211336A1No lot-to-lot variationColor tone is easilySolid-state devicesIlluminated signsOptical fluorescencePeak value
A light emitting device includes: a first semiconductor light emitting element having a solid-state blue light emitting element that emits blue light with a light emission peak in a wavelength range from 420 nm to less than 480 nm, and a first red phosphor layer that covers the solid-state blue light emitting element and includes a first red phosphor that emits red light with a light emission peak in a wavelength range from 600 nm to less than 680 nm; and a second semiconductor light emitting element having a solid-state green light emitting element that emits green light with a light emission peak in a wavelength range from 500 nm to less than 550 nm, and a second red phosphor layer that covers the solid-state green light emitting element and includes a second red phosphor that emits red light with a light emission peak in a wavelength range from 600 nm to less than 680 nm.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical modulator
ActiveUS20080002926A1Efficient separationSuppress lightOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsOptical modulatorLight wave
Provided is an optical modulator capable of efficiently separating radiation light and propagation light from each other or removing the radiation light in the optical modulator to suppress loss of the optical modulator and deterioration of an extinction ratio. In the optical modulator including a thin plate made of a material having an electrooptic effect and having a thickness of 20 μm or less; an optical waveguide formed in a top surface or a bottom surface of the thin plate; and a modulation electrode which is formed in the top surface of the thin plate to modulate light which propagates in the optical waveguide, the optical waveguide has an optical junction portion in which a plurality of optical waveguide portions are joined together and a shielding means for shielding a portion of radiation light radiated from the optical junction portion. The shielding means is a concave portion or a thorough-hole formed in the thin plate, a shortest distance from the waveguide to the shielding means is 5 to 10 μm, and the length of the shielding means in a direction perpendicular to the waveguide is at least 0.5 times the diameter of a fiber.
Owner:SUMITOMO OSAKA CEMENT CO LTD
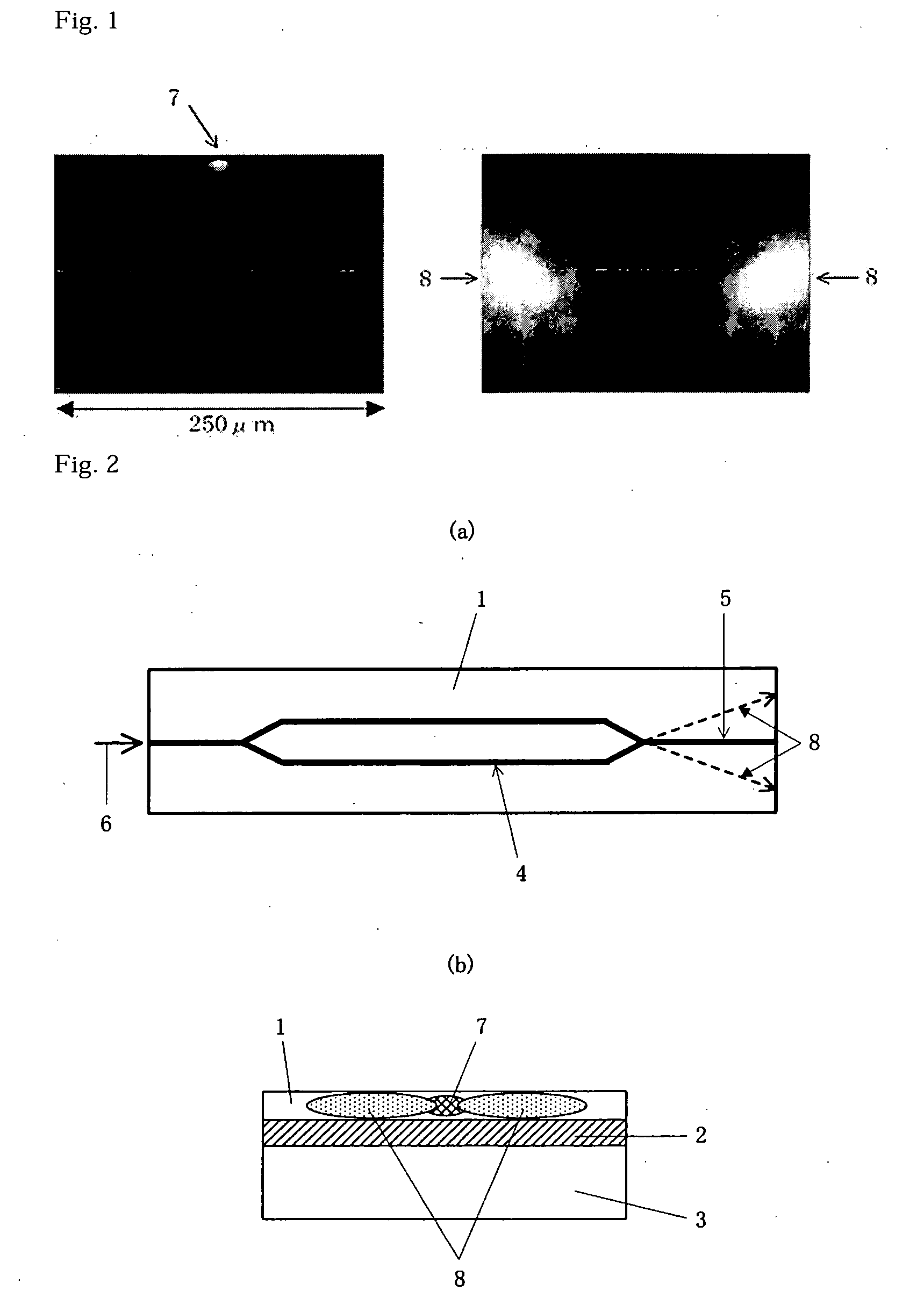
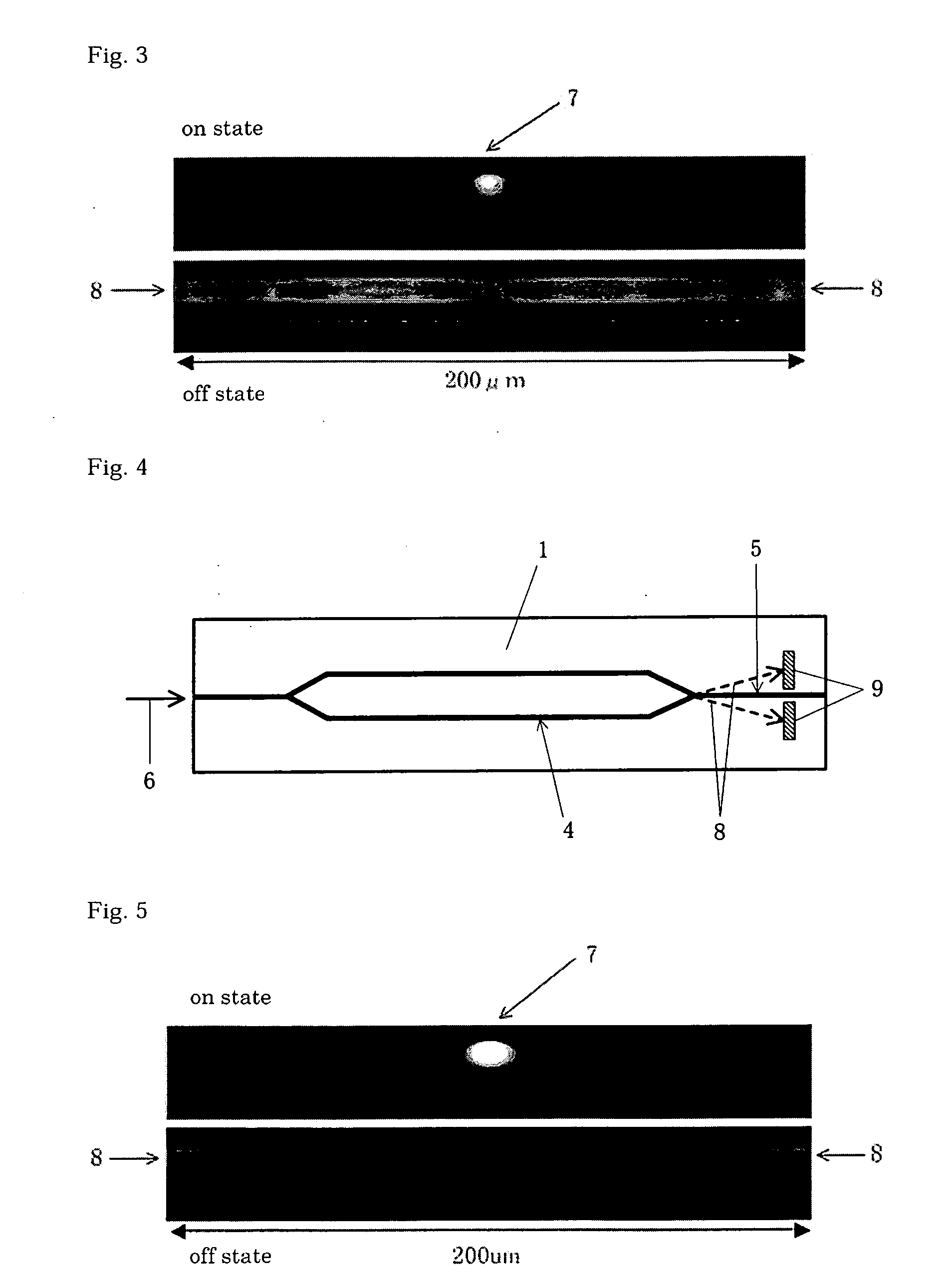
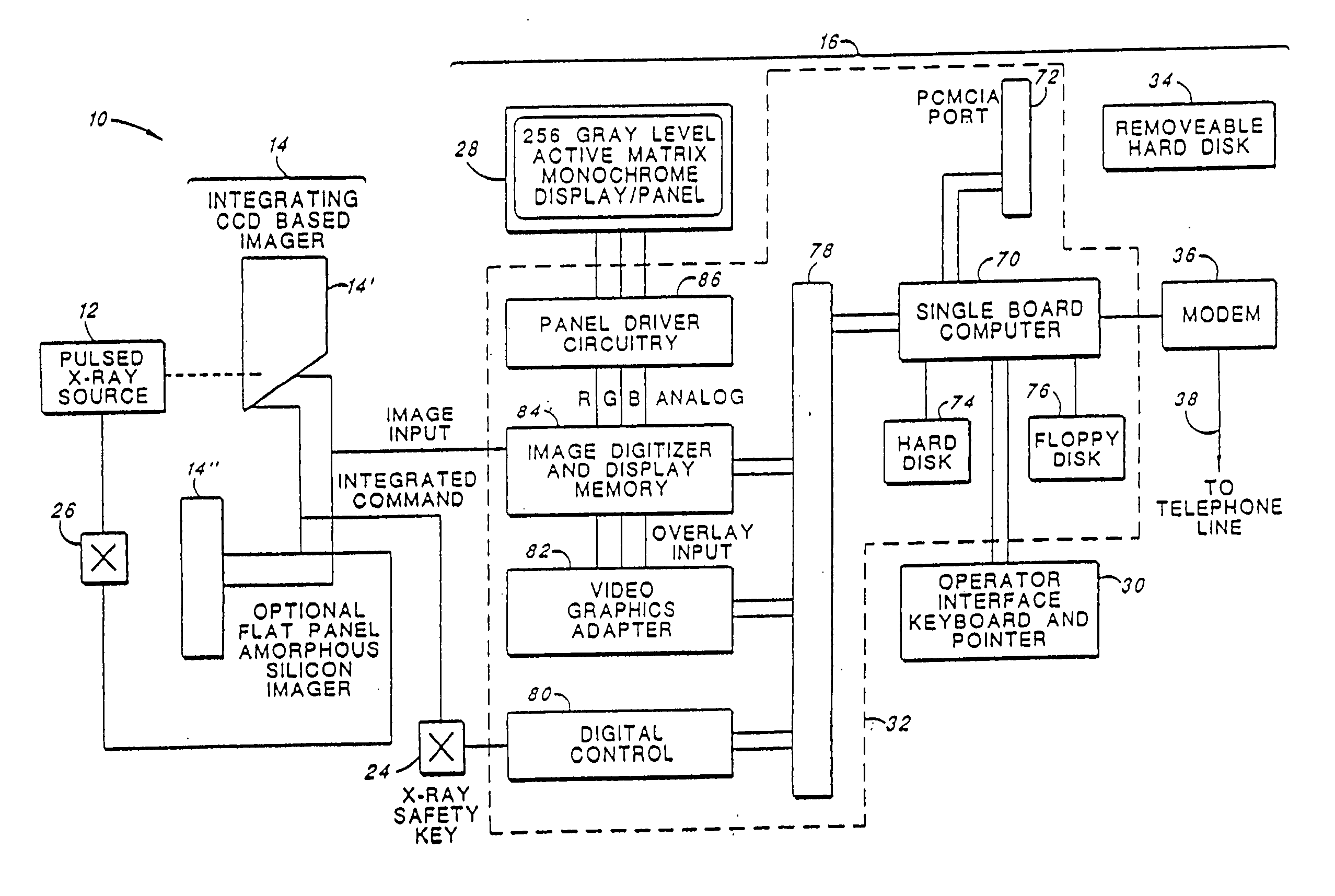
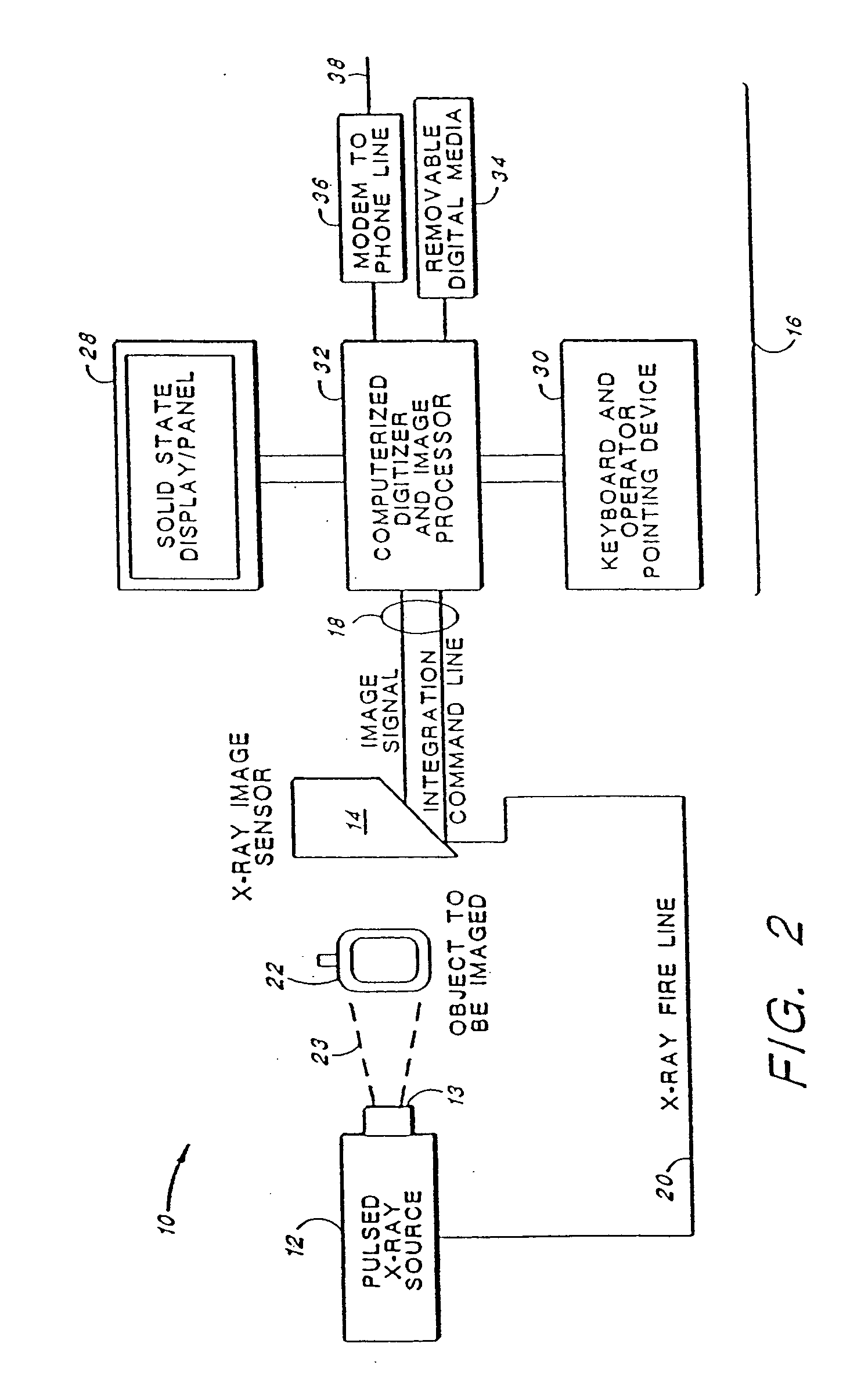
Portable, digital X-ray apparatus for producing, storing, and displaying electronic radioscopic images
InactiveUS20050276379A1Enhances the optical portion, or “imager”,Increasing fractionMaterial analysis by optical meansX-ray apparatusLow voltageX-ray
A portable, self-contained, electronic radioscopic imaging system uses a pulsed X-ray source, a remote X-ray sensor, and a self-contained, display and controller unit to produce, store, and / or display digital radioscopic images of an object under investigation in low voltage imaging environments such as medical applications including mammography and tissue imaging, and industrial radiography of low-density structures, or the like. The radiographic system uses an X-ray converter screen for converting impinging X-ray radiation to visible light, and thus each point impinged on the screen by X-ray radiation scintillates visible light emissions diverging from the screen. An image sensor, i.e., a CCD camera, is configured to sense the visible light from the screen. An aspheric objective lens operable with the CCD camera spatially senses visible light within a collection cone directed outwardly from the image sensor. An emission modification lens layer, e.g., a prismatic brightness enhancement film or a sprayed on transmissive layer, through which the visible light emitted from the screen is transmitted is superposed with the screen and positioned in an optical path between the aspheric lens and the screen for generally focusing the diverging visible light as a restricted cone of illumination propagating outwardly from each point impinged on the screen to increase the fraction of light directed into the collection cone of the first lens and reducing the amount of scattered visible light from the screen.
Owner:LEIDOS
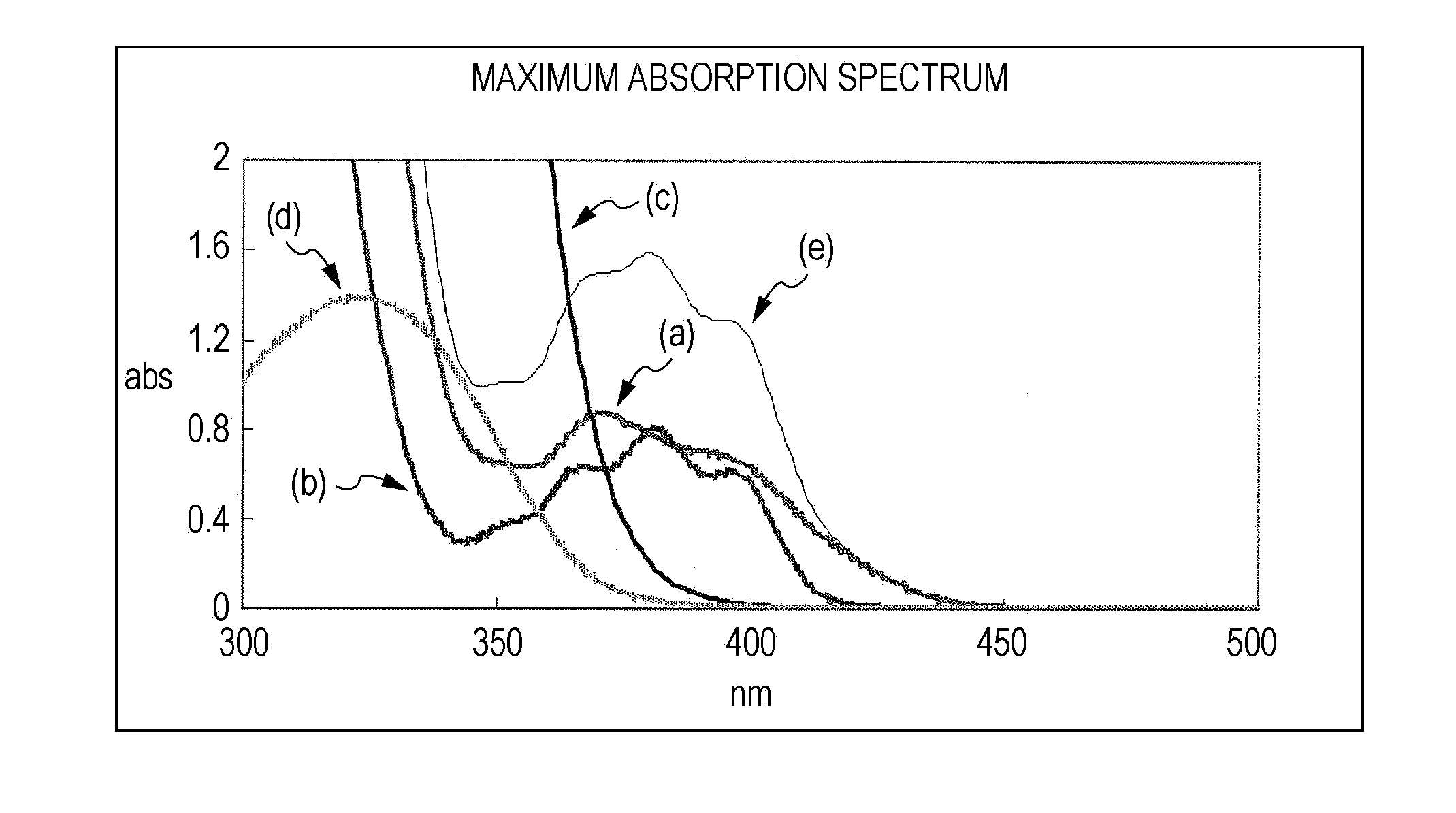
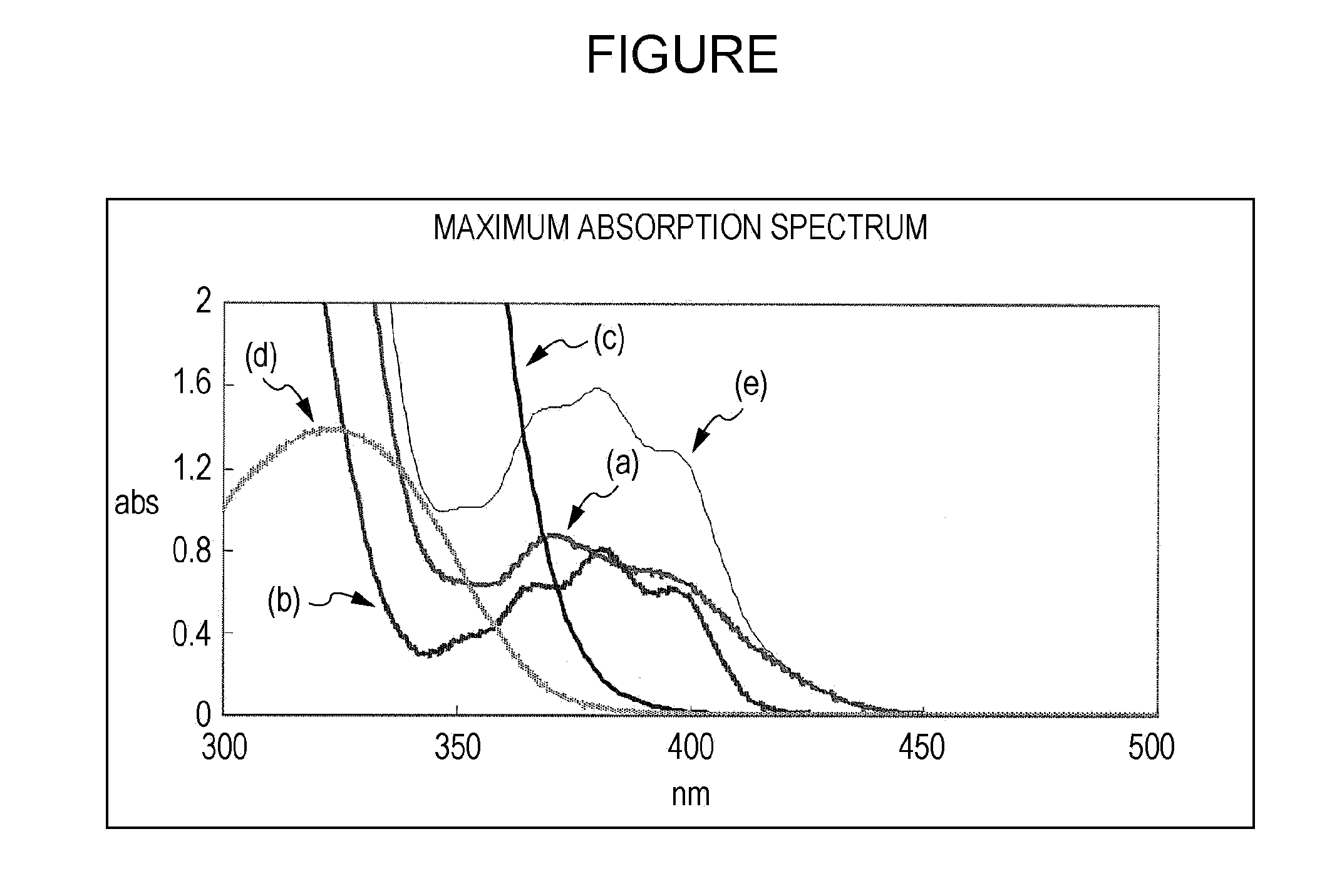
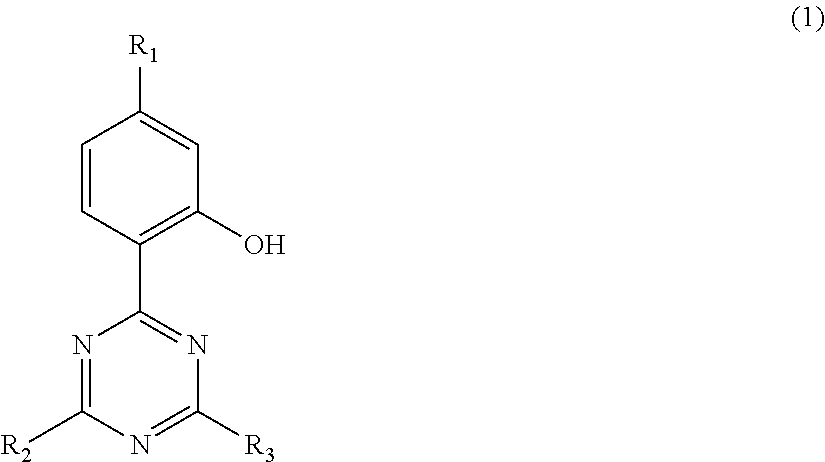
Photocurable ink composition and ink jet recording method
InactiveUS20110183081A1Excellent lightfastness and curing propertySuppress lightDuplicating/marking methodsInksHindered amine light stabilizersOrganic group
A photocurable ink composition includes (A) a polymerizable compound, (B) an acylphosphine oxide-based photopolymerization initiator, and (C) at least one compound selected from a hindered amine-based compound with a mass-average molecular weight of 2000 to 4000 and a hydroxyphenyltriazine-based compound of formula (1):(wherein R1, R2, and R3 each independently represent an organic group). The proportion of the component (C) is in the range of 0.2% by mass to 2.0% by mass.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical information recording/reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20070217300A1Prevent mixingSuppress lightCombination recordingRecord information storageLuminous fluxPupil
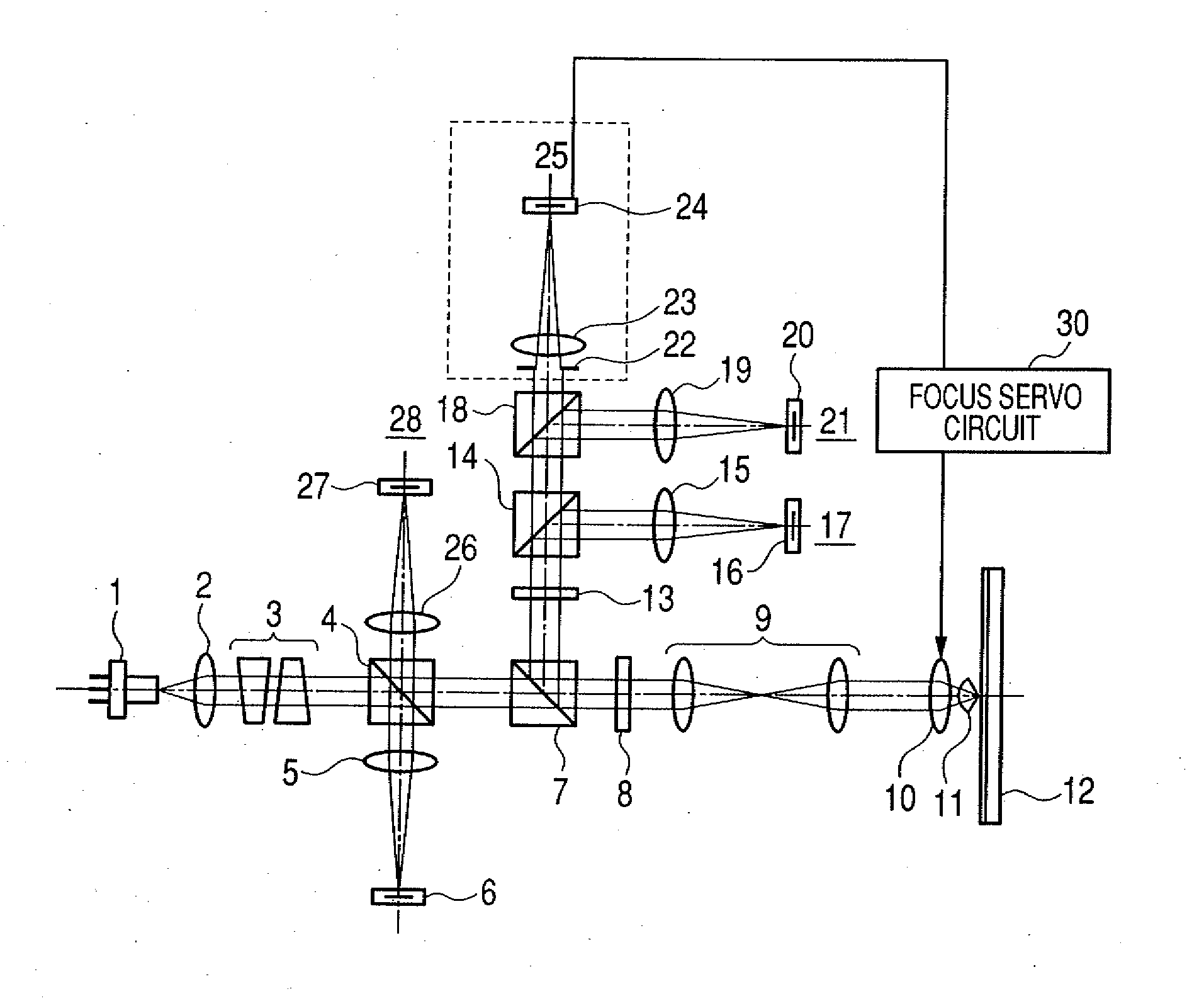
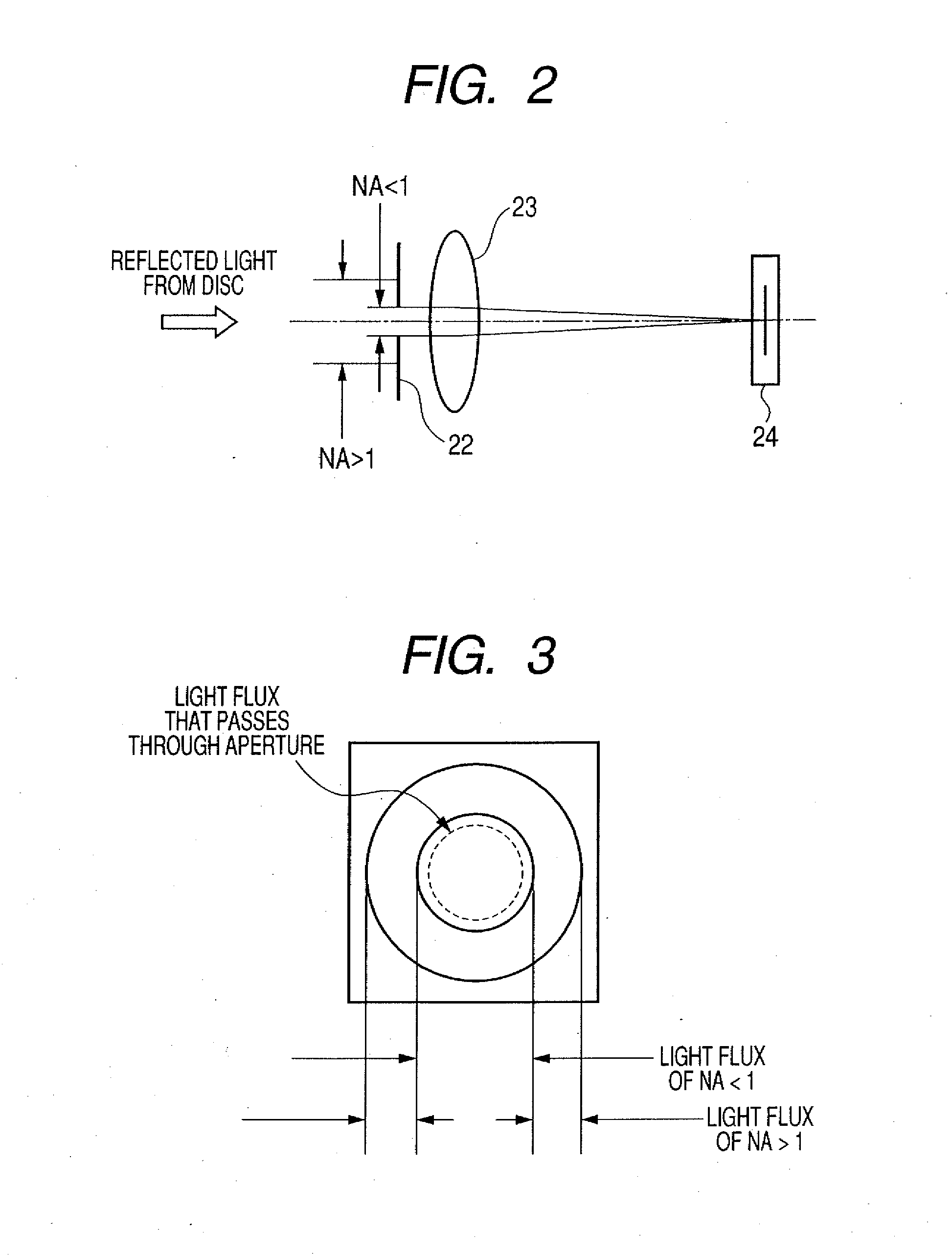
There is provided an optical information recording / reproducing apparatus including a unit for detecting the focus error signal from the reflected light flux from a recording layer of an optical recording medium, and a unit for focusing the light flux on the recording layer of the optical disk on the basis of the focus error signal. In the case of detecting the focus error signal, the light flux of the effective numeric aperture NAeff<1 due to an objective lens and the SIL within a pupil is obtained by a splitting device as the focus error signal, whereby it is possible to suppress the reflected light from the bottom surface of the SIL from being mixed into the focus error signal as a noise.
Owner:CANON KK
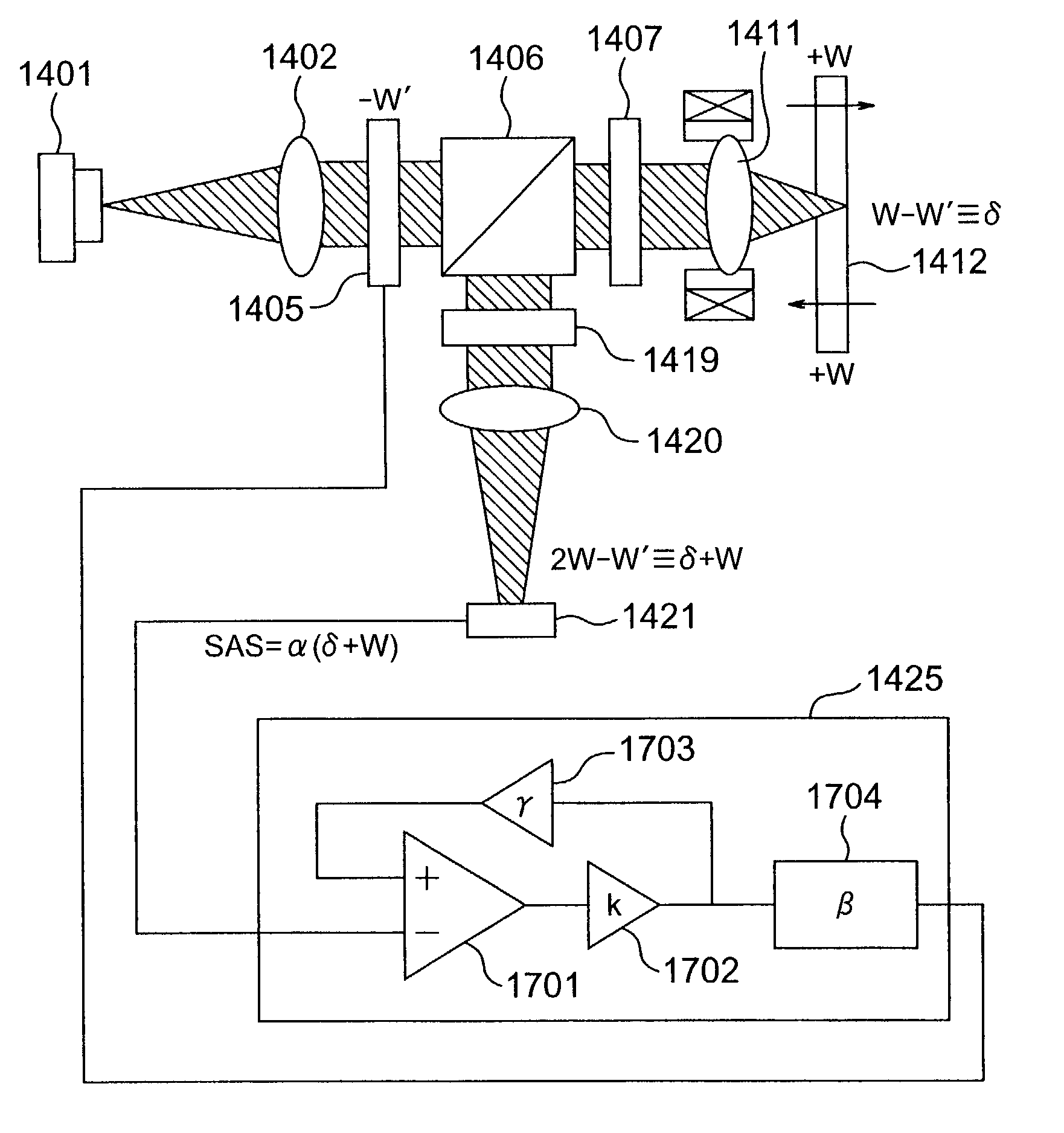
Optical disk apparatus using focal shift signals to control spherical aberration
InactiveUS7012875B2Suppress lightIntegrated optical head arrangementsOptical detectorsComputational physicsLuminous flux
In the past there has been a problem that on a detection surface the influence of interference causes a defocusing signal to degrade, narrowing the range in which spherical aberration can be stably detected. Accordingly, a diffraction grating is used to focus the inner and outer sides of luminous flux on separate optical detectors before the optical flux is focused on an optical detector and defocusing signals are independently calculated to find the difference therebetween, thereby providing a spherical aberration signal. This makes it possible to detect spherical aberation signals more stably.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Liquid crystal display device and polarization plate
InactiveUS20100188605A1Suppress light obtainedIncrease brightnessNon-linear opticsOptical elementsIn planeTectorial membrane
The present invention has an object to provide high-luminance liquid crystal display device and polarizer, each including a reflection and polarization sheet. The present invention is a liquid crystal display device including: a backlight system including a reflection and polarization sheet; a back polarizer; a liquid crystal cell; and a front polarizer, stacked in this order, wherein the liquid crystal display device includes a protective film that protects a back face of the back polarizer, the protective film has no retardation in a thickness direction thereof, and when the protective film is viewed in plane, an optic axis of the protective film in an in-plane direction thereof is parallel to an absorption axis of the back polarizer.
Owner:SHARP KK
Optical scan apparatus and image formation apparatus
InactiveUS20080284838A1Low running costSuppress lightVisual presentationPrintingOptoelectronicsLight source
An optical scan apparatus which deflects a plurality of light beams to scan a write region on a scan surface in a main scan direction is configured to include a light source which has a plurality of emission portions emitting the plurality of light beams arranged two-dimensionally on a plane in parallel to the main scan direction and a sub scan direction perpendicular to the main scan direction; a deflector which deflects the plurality of light beams from the plurality of emission portions; a light receiving element which receives the light beams and outputs a synchronous detection signal in accordance with the received light beams; and a control unit which selectively controls any one of the emission portions to emit a light beam upon each scanning and allows the light beam from the selected emission portion to be incident on the light receiving element via the deflector.
Owner:RICOH KK
Display device
InactiveUS20140252336A1Improve display qualitySuppress lightStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceDriven element
A display device includes a light emitting functional layer disposed between a first and second substrates; a first pixel which emits light to the second substrate and has a first pixel electrode disposed between the light emitting functional layer and the first substrate, a second electrode disposed between the light emitting functional layer and the second substrate, and a first reflecting layer disposed between the first pixel electrode and the first substrate; a second pixel which emits light to the first substrate side and has a second pixel electrode disposed between the light emitting functional layer and the first substrate, a second electrode disposed between the light emitting functional layer and the second substrate, and a second reflecting layer disposed between the second electrode and the second substrate; and a driving element which drives the first and second pixel electrodes is disposed above first substrate.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Display device, and driving method and electronic apparatus of the display device
InactiveUS20060232601A1Duty ratio be improveReduce light emissionTelevision system detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceSubframe
To reduce a pseudo contour which occurs when displaying by a time gray scale method. When gradation is expressed with an n bit, bits each of which is shown by a binary of the gray scales are divided into three bit groups, and one frame is divided into two subframe groups. Then, a (0<a<n) subframes corresponding to bits belonging to a first bit group are divided into three or more, each about half of which is arranged in each subframe group; b (0<b<n) subframes corresponding to bits belonging to a second bit group are divided into two, each one of which is arranged in each the subframe group; and c (0≦c<n and a+b+c=n) subframes corresponding to bits belonging to a third bit group are arranged in at least one of the subframe groups. And then, an overlapped time gray scale method is applied in each subframe group to express gradation.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com