Patents
Literature
195 results about "Geometrical optics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
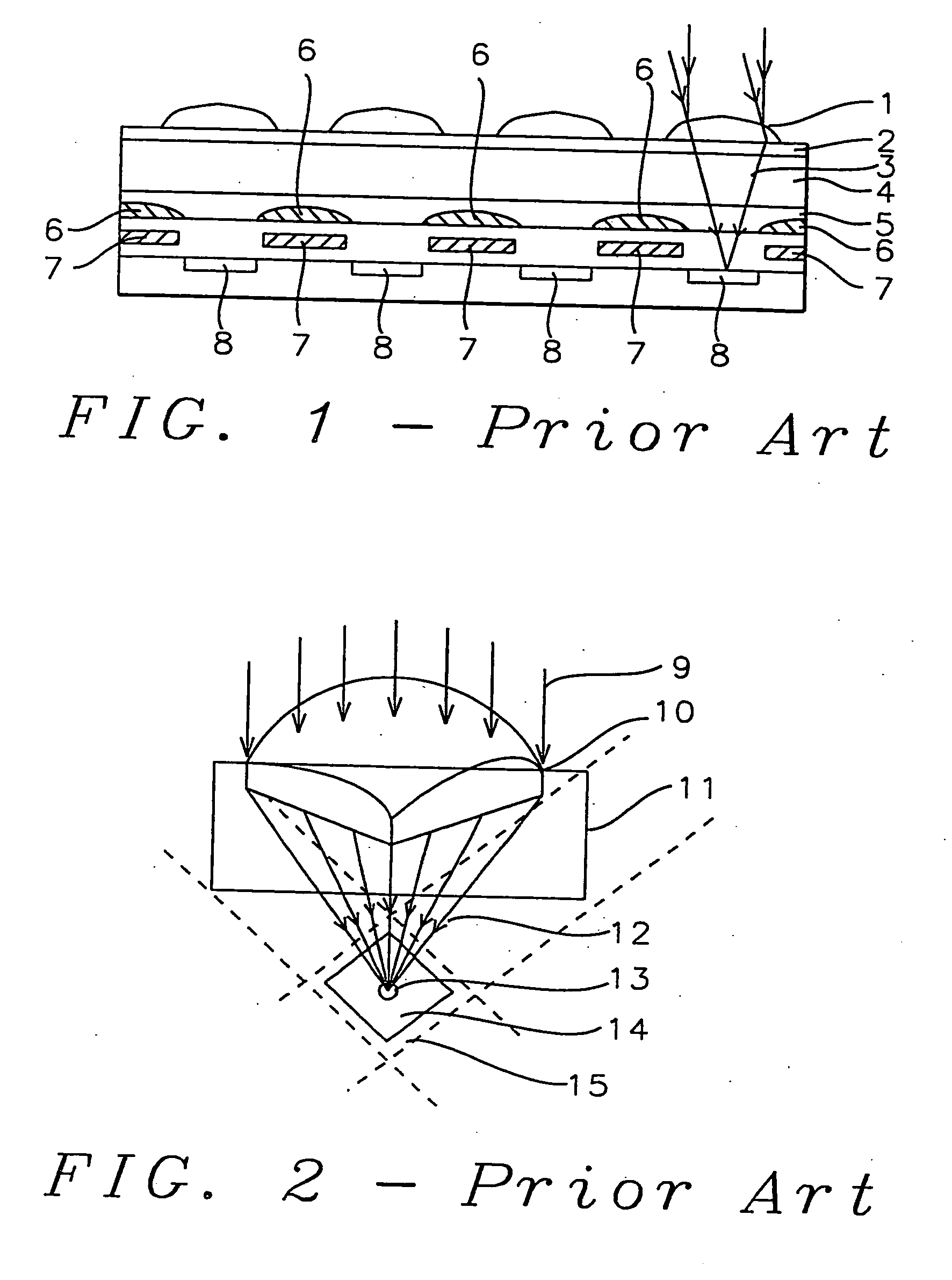
Geometrical optics, or ray optics, is a model of optics that describes light propagation in terms of rays. The ray in geometric optics is an abstraction useful for approximating the paths along which light propagates under certain circumstances.
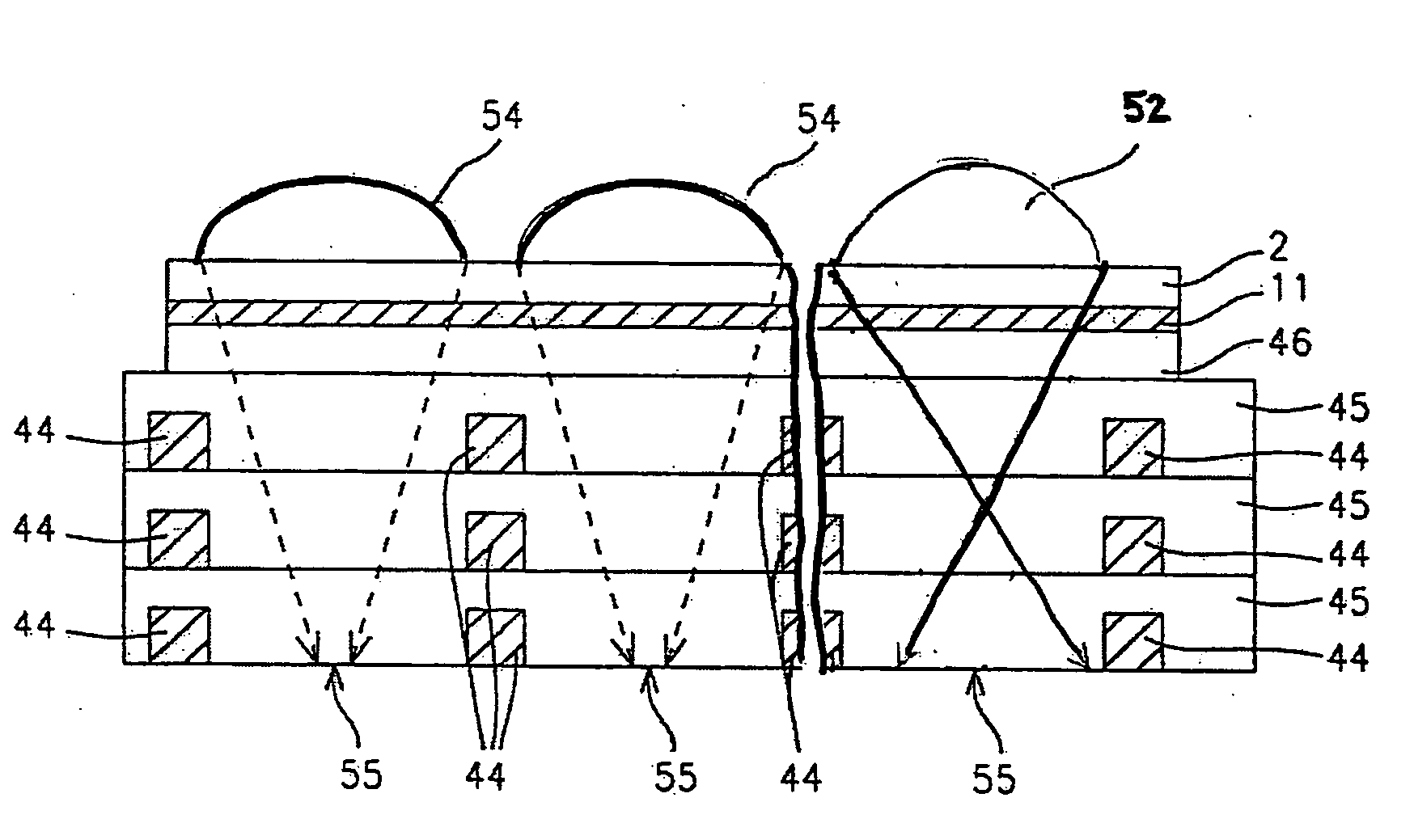
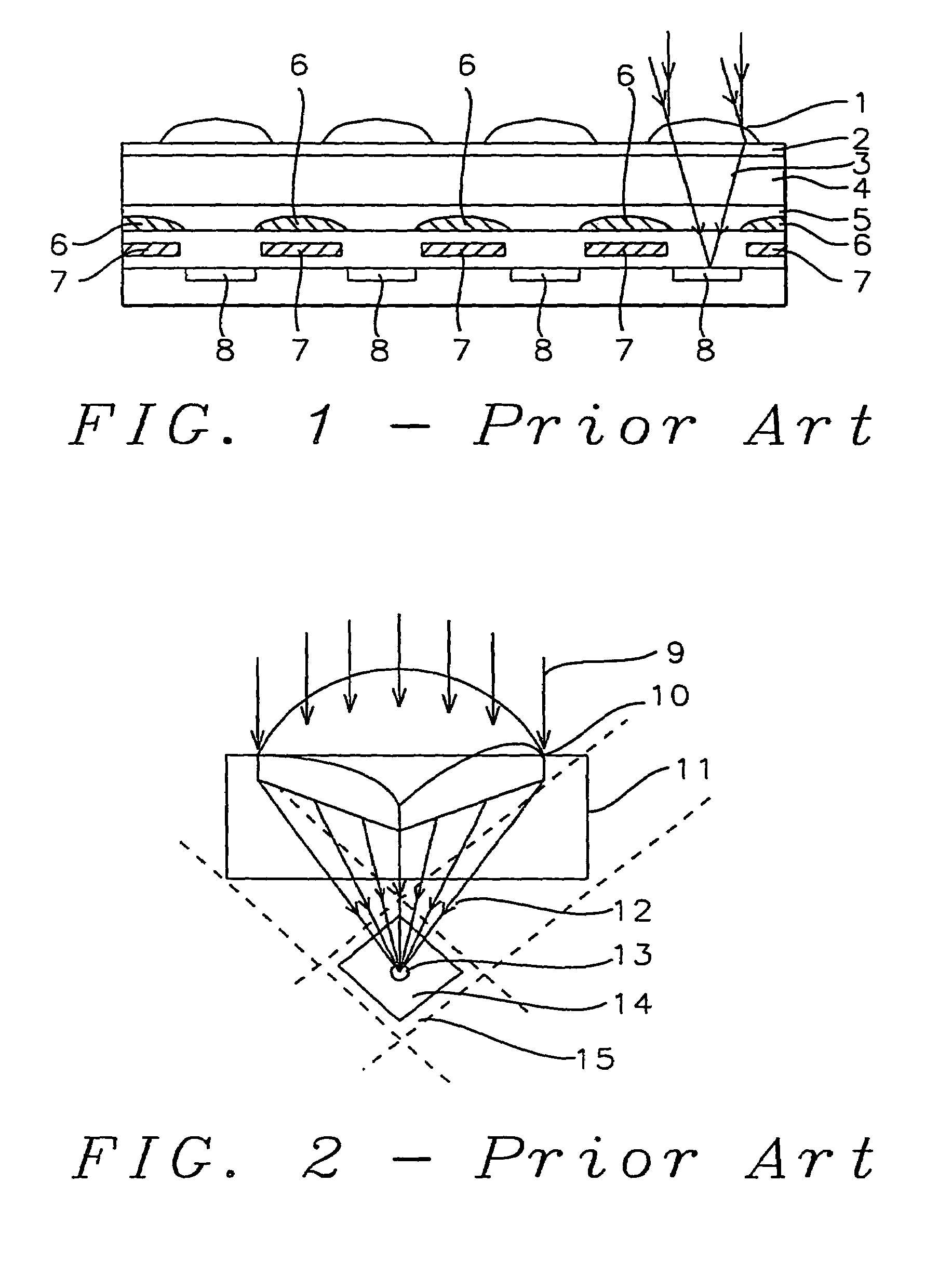
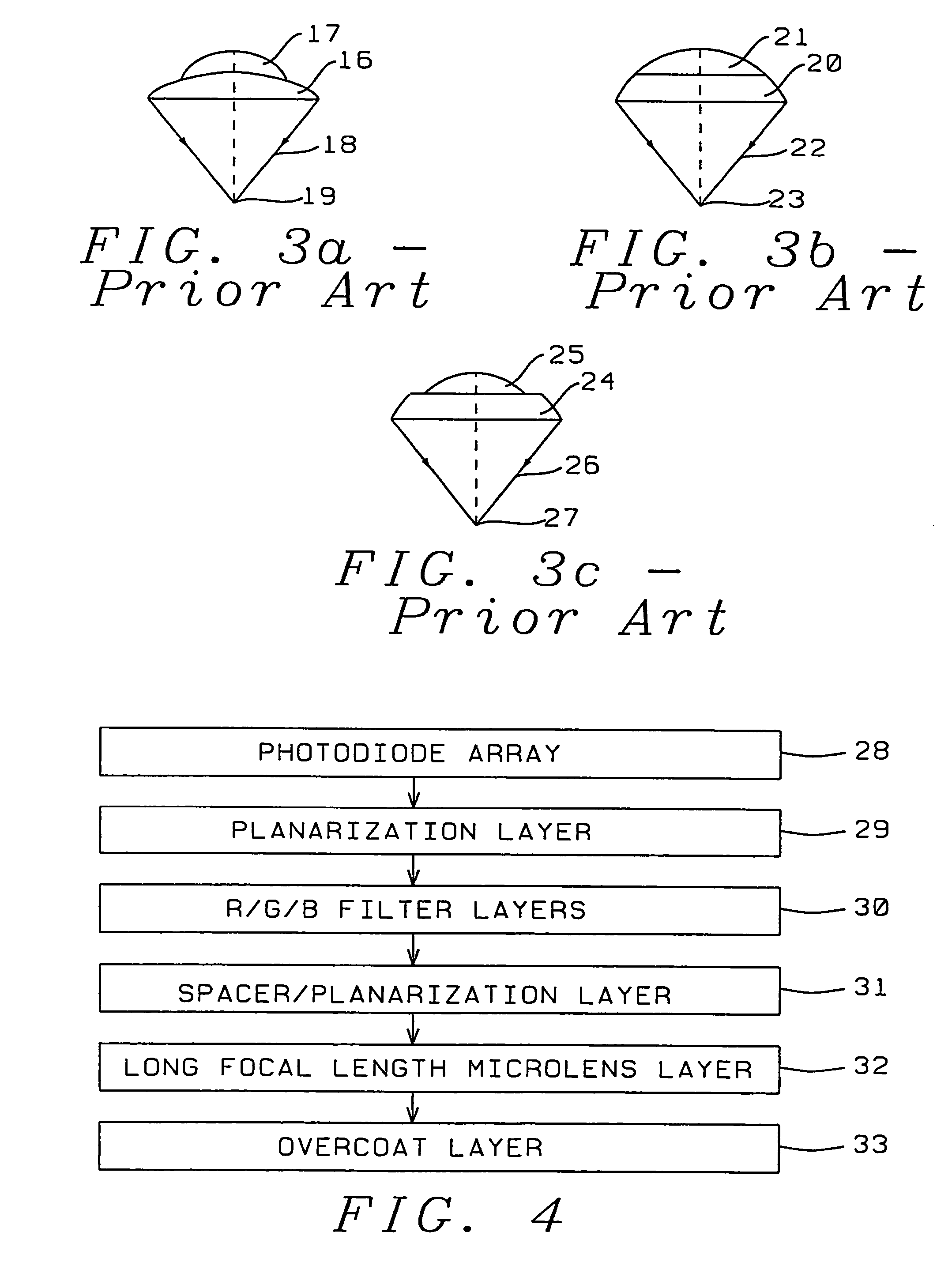
High transmittance overcoat for microlens arrays in semiconductor color imagers
InactiveUS20050041296A1Improve focus performanceHigh light transmittanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSHigh volume manufacturing
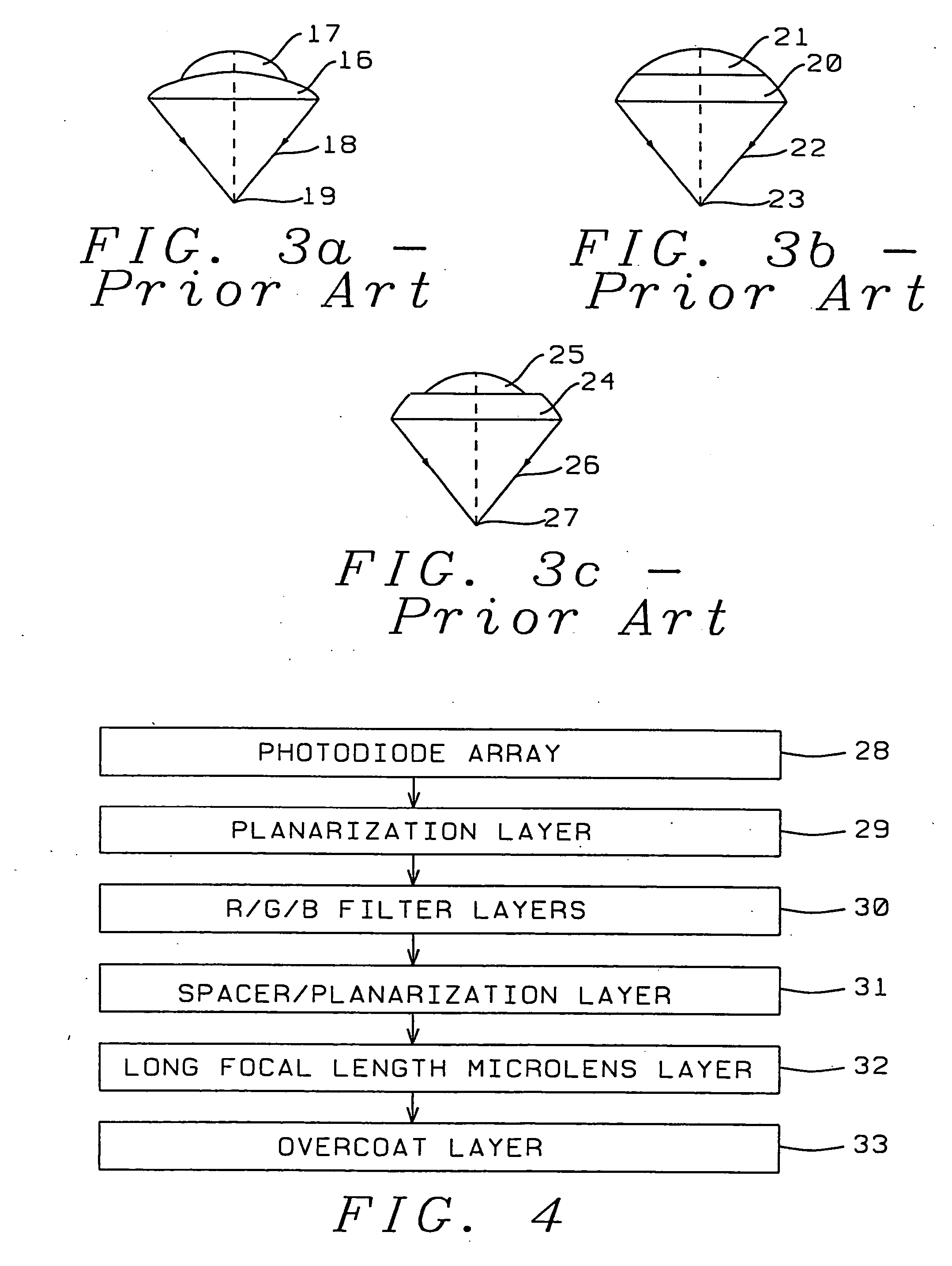
A transmittance overcoat with effectively planar top surface and specified optical and materials properties is applied above a microlens layer to extend the focal length and enhance the performance of long focal length microlenses for semiconductor array color imaging devices. The geometrical optics design factors and microelectric fabrication sequence to achieve optimized long focal length microlens performance are disclosed. The principal advantages of the adaptive process taught in the present invention is shown to enable real-time compensation adjustments for process and material variations. The overcoat process enables simplified single-layer integrated microlens optics for low-cost, high volume manufacturing of CMOS and CCD color video cameras.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Film having low refractive index film and method for producing the same, Anti-relection film and method for producing the same, coating liquid set for low refractive index film, substrate having microparticle-laminated thin film and method for producing the same, and optical member
ActiveUS20110195239A1Low refractive indexImprove adhesionMaterial nanotechnologyCladded optical fibrePolymer scienceSilanes
Provided is a film having a low refractive index, which can be formed under normal temperature and pressure while obtaining a lower refractive index, has excellent adhesion with a solid substrate, and does not lose geometric optical properties, such as the diffusibility or light-harvesting capability attributed to the microstructure. Also disclosed is a method for producing the same. The film having a low refractive index is obtained by causing an electrolyte polymer and microparticles to be alternately adsorbed on the surface of a solid substrate and bringing the resulting microparticle-laminated film into contact with a silicon compound solution in order to bond the solid substrate with microparticles and microparticles with microparticles. The silicon compound solution is selected from (1) the hydrolysis product of alkoxysilane (I) wherein the functional groups are formed from hydrolyzable groups and non-hydrolyzable organic groups, and the condensation reaction product thereof, (2) the hydrolysis product of a mixture of alkoxysilane (I) and alkoxysilane (II) wherein the functional groups are formed from hydrolyzable groups alone, and the condensation reaction product thereof; and (3) a mixture of hydrolysis product and condensation product thereof according to (1) and alkoxysilane (II).
Owner:RESONAC CORP
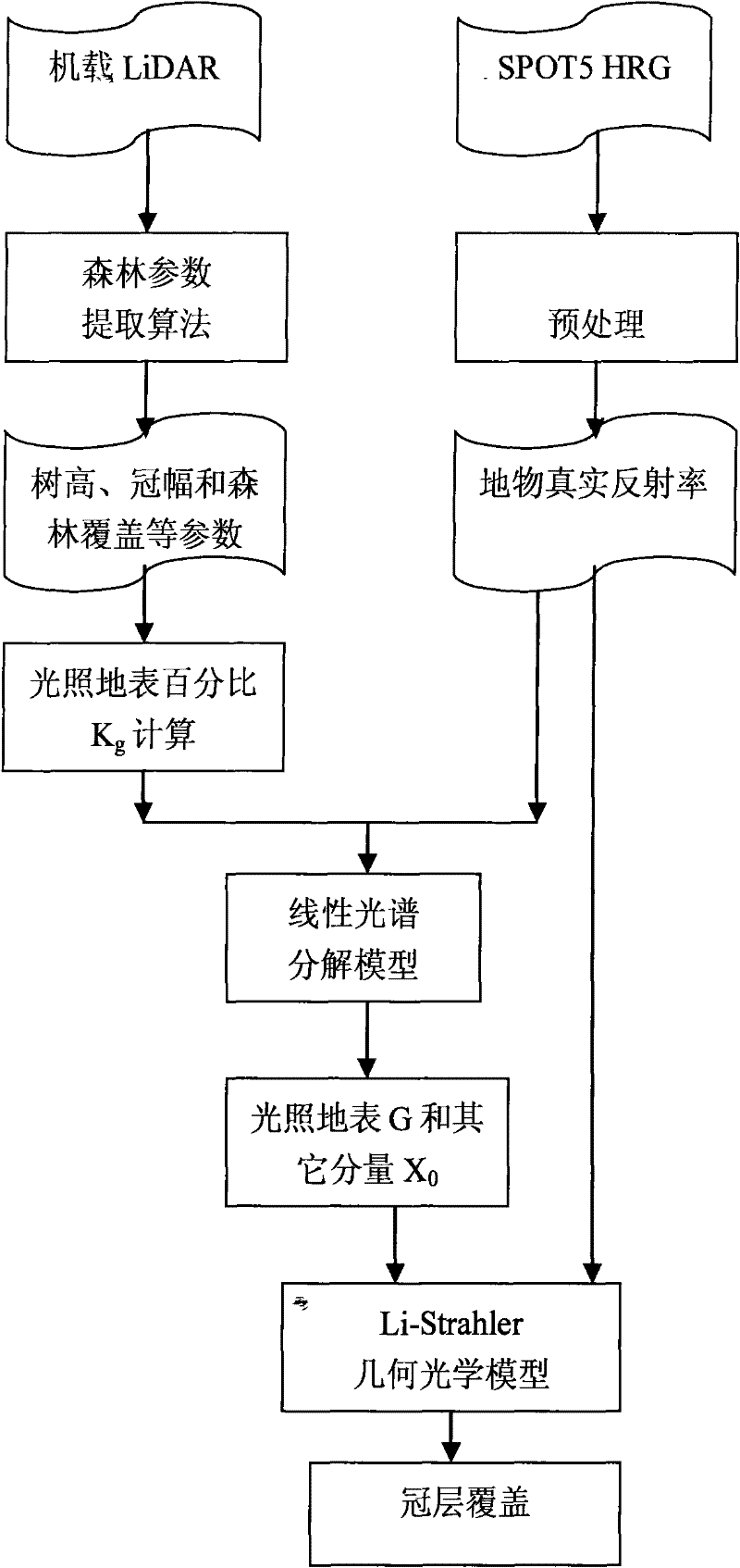
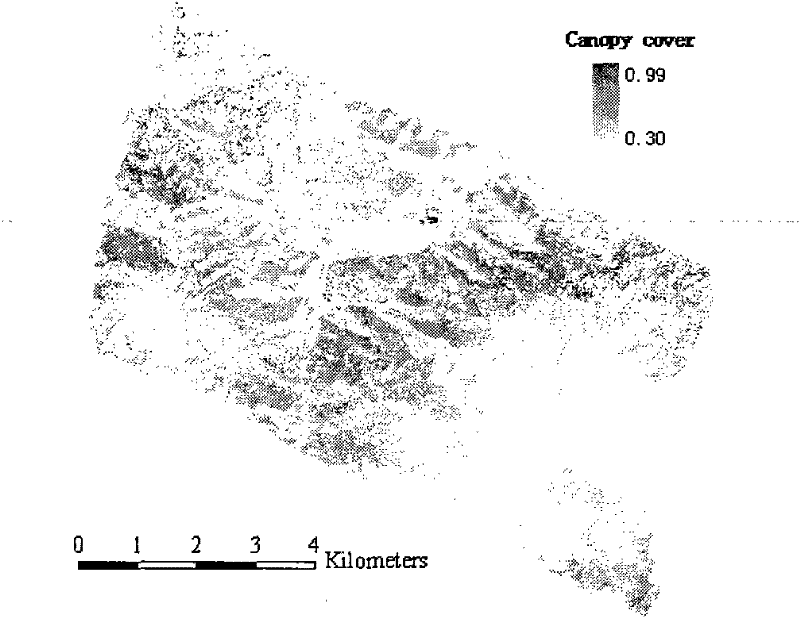
An Active-Passive Synergistic Inversion Method for Forest Coverage and Effective Leaf Area Index
InactiveCN102269576AReduce uncertaintyHigh precisionPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryUsing optical meansReduced modelDecomposition
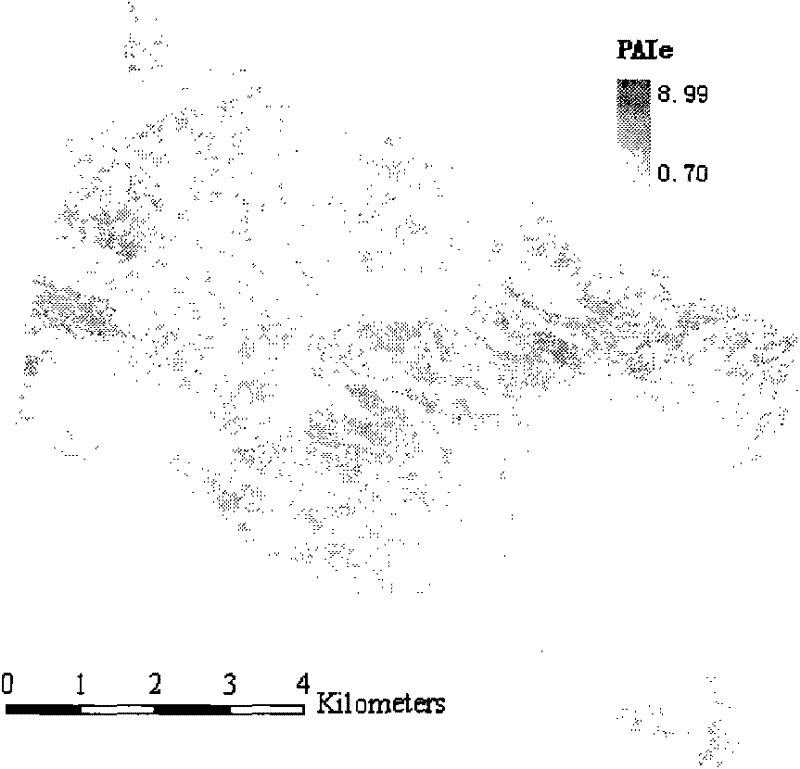
The invention provides an active-passive collaborative inversion method of forest coverage and effective leaf area index, the method comprising steps: 1) based on the forest parameters in the sample area obtained according to the airborne laser radar, obtained by the Li-Strahler geometrical optics model The percentage of illuminated surface area Kg of each mixed pixel; 2) According to the Kg value of each mixed pixel and the real reflectance of the pixel obtained from the optical remote sensing image, the linear spectral decomposition model is used to obtain the Li-Strahler geometric optics model The reflectance G of the illuminated surface and the average reflectance X0 of other components; 3) The two reflectances G and reflectance X0 obtained in 2) are used to obtain each real pixel on the entire image through the simplified model of Li-Strahler geometric optics The percentage of illuminated surface area Kg', and then get the canopy cover m and effective plant area index PAIe of each pixel. The invention utilizes the combination of the laser radar and the optical remote sensing data to reduce the influence of the mixed pixel and improve the accuracy of the optical remote sensing data inversion of the forest parameters.
Owner:曹春香 +2
Patterned sheeting with periodic rotated patterned regions
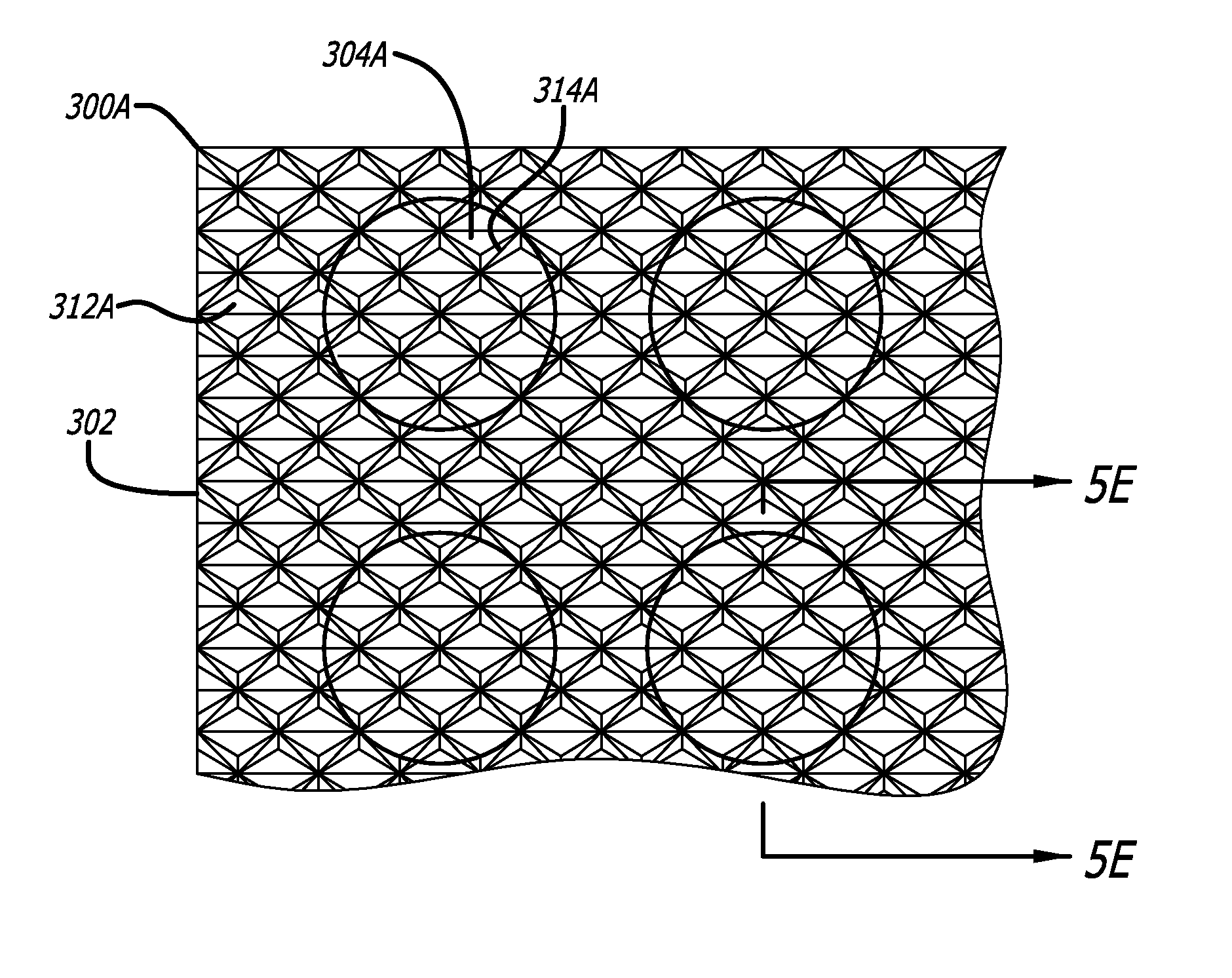
In one embodiment of the invention, retro-reflective sheeting is disclosed. The retro-reflective sheeting comprises a flexible optical material film or substrate having a geometric optical surface opposite a base surface. The geometric optical surface includes a background pattern region of corner cubes arranged at a first orientation with respect to an edge of the retro-reflective sheeting; and an array of circular corner cube regions periodically interrupting the background pattern region of corner cubes. Each of the circular corner cube regions has a second orientation with respect to the edge of the retro-reflective sheeting. The array of the plurality of circular corner cube regions reflects incident light differently than the background pattern region of corner cubes.
Owner:ORAFOL EURO
Measurement sensor for inhalable dust concentration
InactiveCN101487786AImprove signal-to-noise ratioEvenly distributedScattering properties measurementsParticle suspension analysisLaser lightOpto electronic
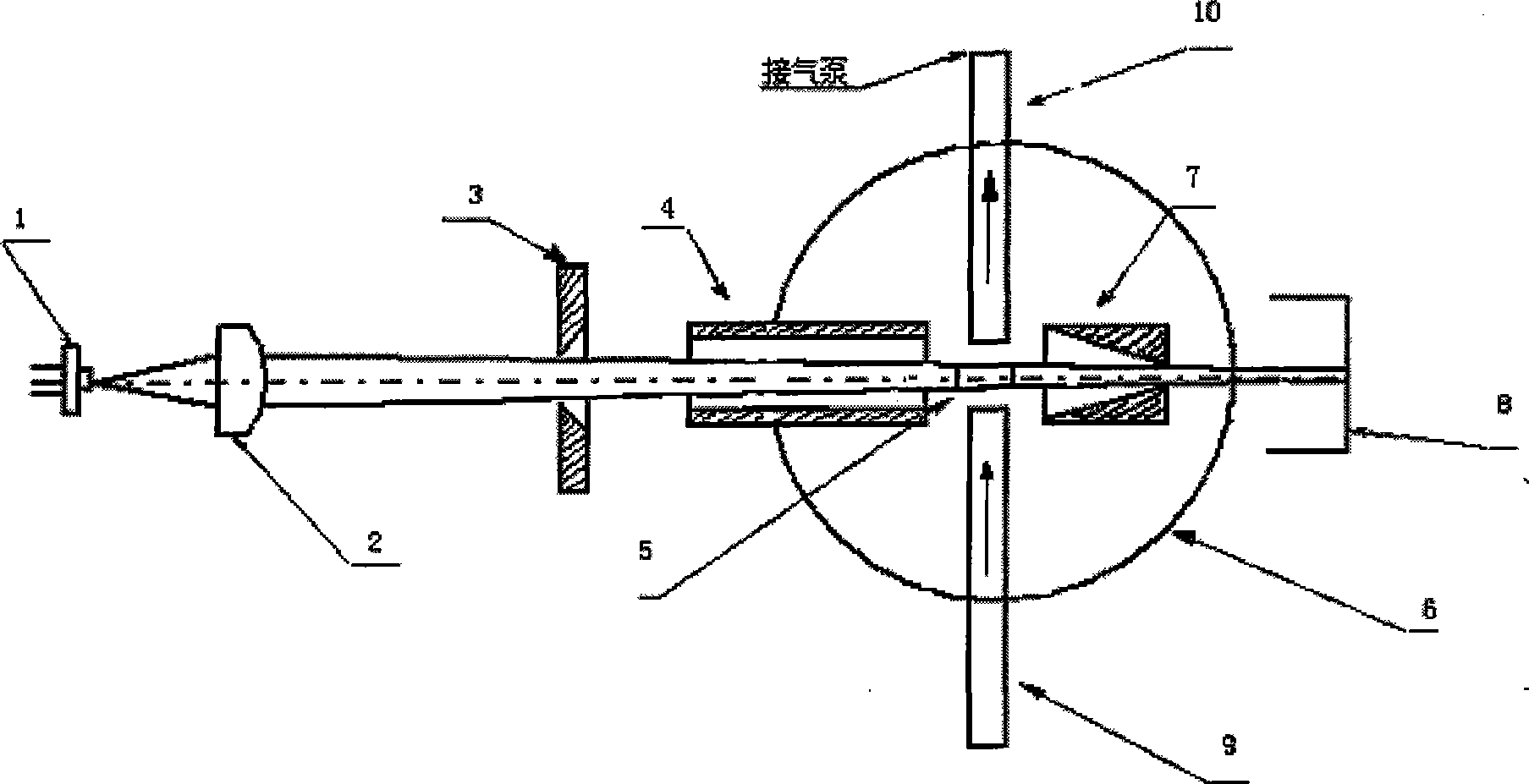
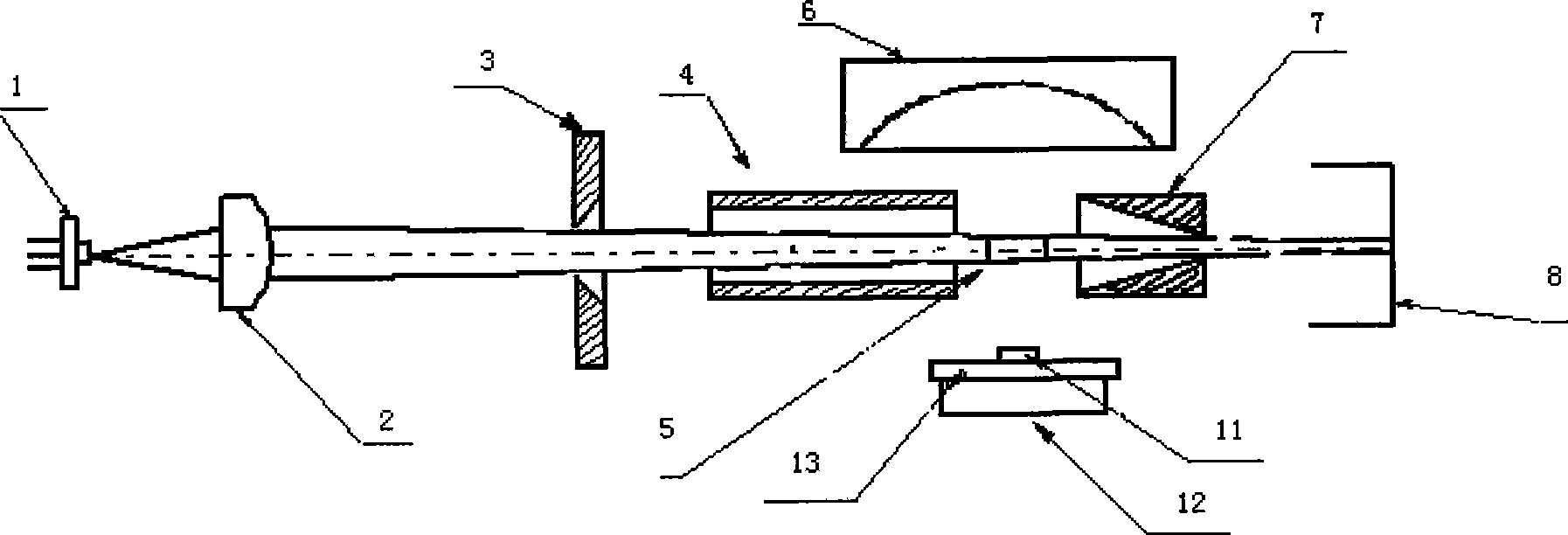
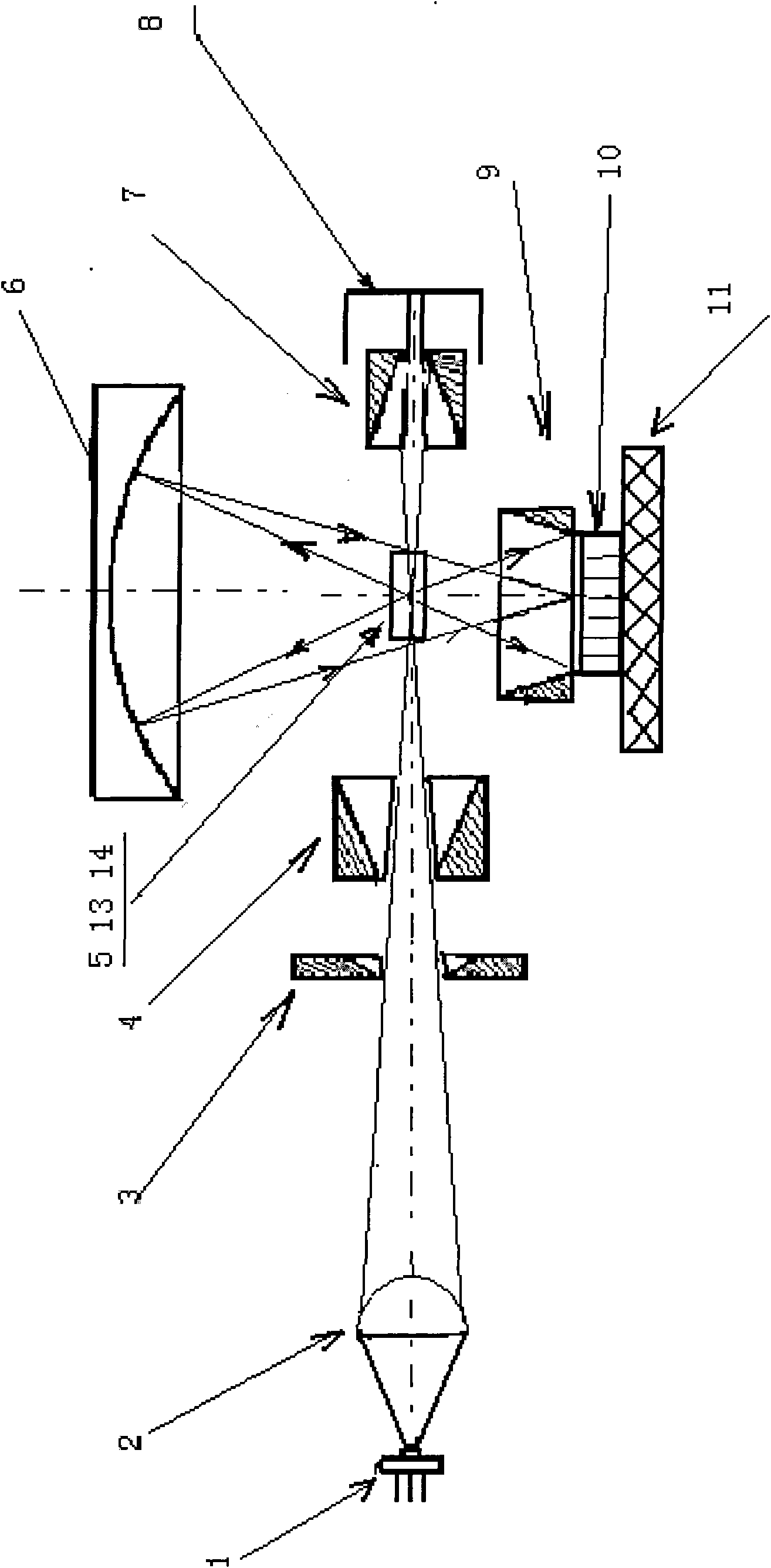
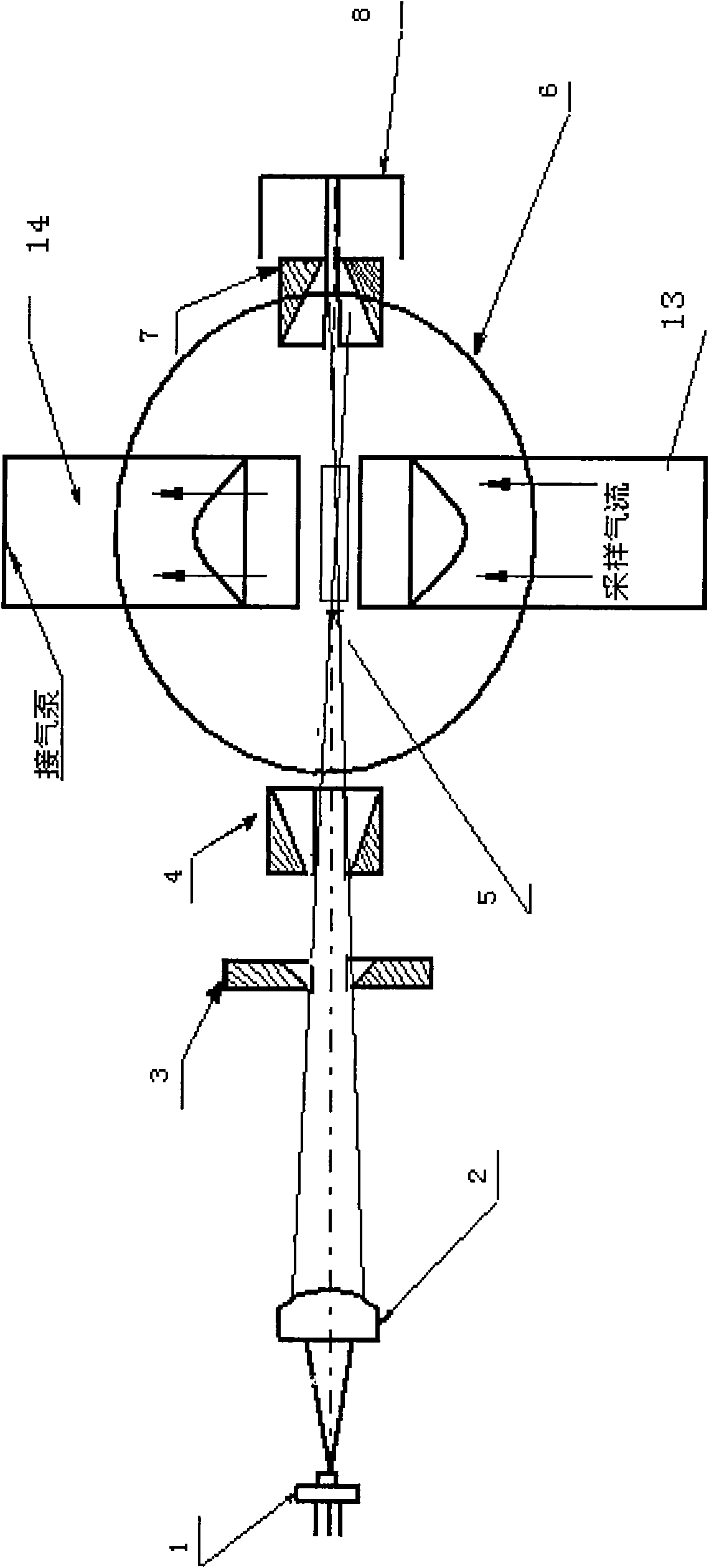
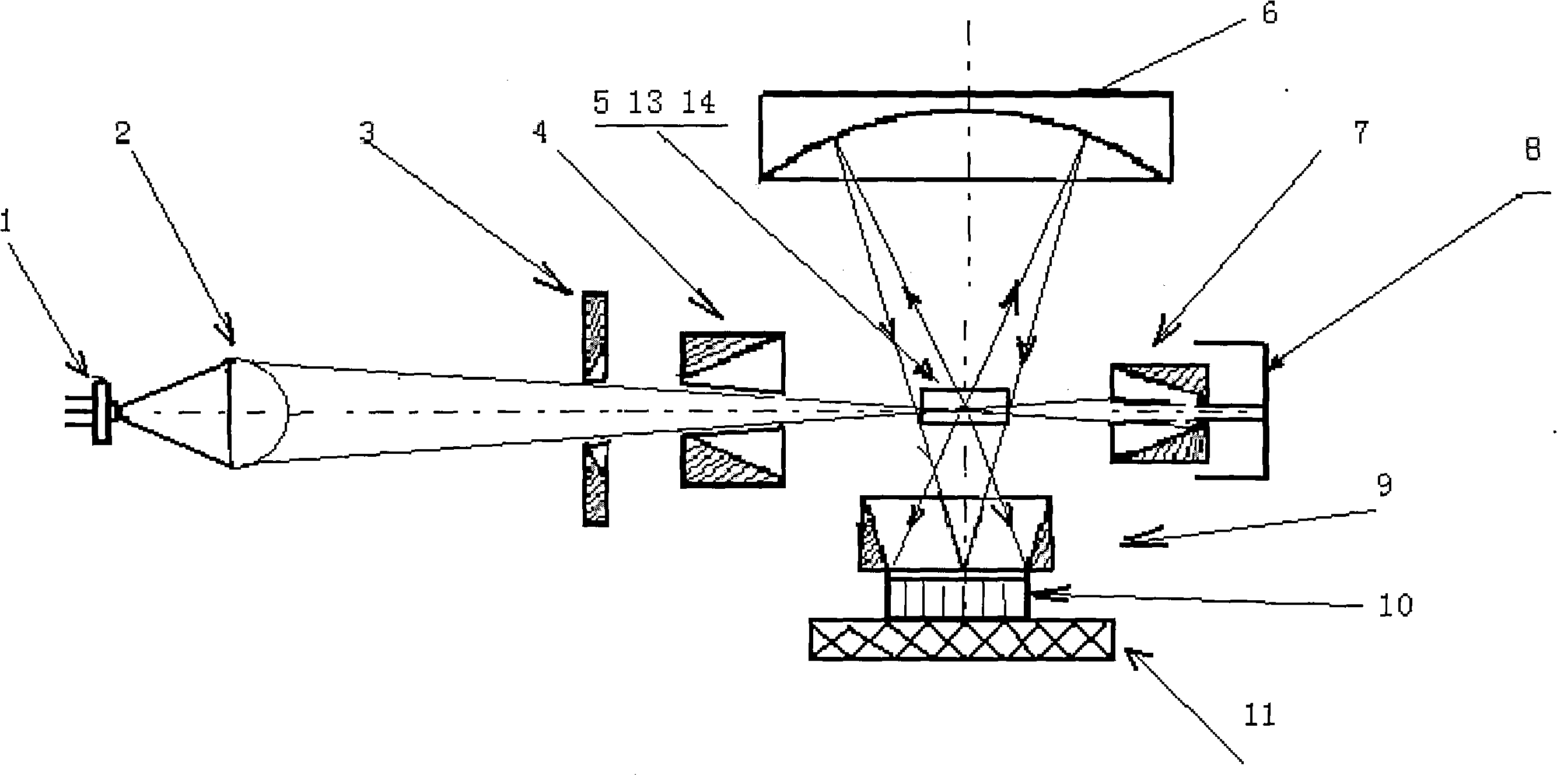
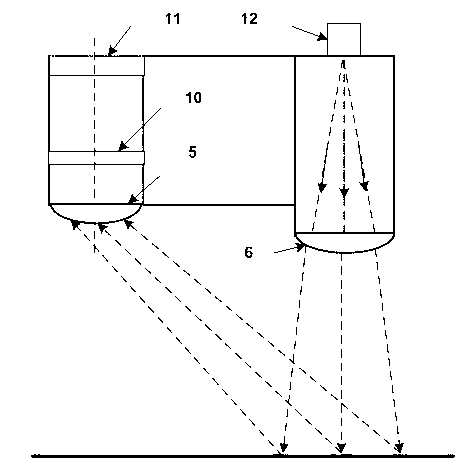
The invention discloses an inhalable dust concentration measuring sensor, comprising: a semiconductor laser light source. An aspherical mirror, an incidence diaphragm, an extinction diaphragm, a photosensitive area, a spherical reflecting mirror, an emergent diaphragm and a light trap are arranged in turn in the forward direction of the beam. The extinction diaphragm is of a long tube shape, and the opening of the diaphragm is close to the photosensitive area; the spherical reflecting mirror located at the right side of the extinction diaphragm ensures that the photosensitive area and the photosensitive surface of a photoelectric detector are respectively located at the two sides near the spherical center of the spherical reflecting mirror and the physical image relation in geometrical optics is met; the photoelectric detector is a high-sensitivity photoelectric diode; and the sampling nozzles in the gas path are distributed with respect to the photosensitive area. In the invention, the measurement is more accurate as the quality concentration of the inhalable dust is calculated by the energy sum of scattered lights in the particle swarm, and the measuring sensor has wide application as being free from the limit of the total particle number in a unit volume; the signal-to-noise ratio of the sensor is greatly improved as the light path is provided with three diaphragms; and the noise is low, and the measurement is more accurate and stable as the concentration measuring circuit adopts an integral method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High transmittance overcoat for microlens arrays in semiconductor color imagers
InactiveUS7009772B2Improve focus performanceHigh light transmittanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSHigh volume manufacturing
A transmittance overcoat with effectively planar top surface and specified optical and materials properties is applied above a microlens layer to extend the focal length and enhance the performance of long focal length microlenses for semiconductor array color imaging devices. The geometrical optics design factors and microelectric fabrication sequence to achieve optimized long focal length microlens performance are disclosed. The principal advantages of the adaptive process taught in the present invention is shown to enable real-time compensation adjustments for process and material variations. The overcoat process enables simplified single-layer integrated microlens optics for low-cost, high volume manufacturing of CMOS and CCD color video cameras.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Micro optical sensor for laser dust particle counter
ActiveCN1570604AIncrease light intensityImprove light uniformityIndividual particle analysisCounting efficiencyLong axis
A micro optical sensor of laser dust particle counter, which is characterized by its components, which comprises the following: there is cylinder mirror, spherical mirror and light trap located orderly in the direction of light beam of laser source components. The spherical mirror is located in the right side of the cylinder mirror and light-sensitive area and that of light-electricity detector are located on both sides around the sphere center of spherical mirror, which satisfies the image relationship of geometry optics; vision diaphragm which is suited for the shape of light sensitive-area is located in front of light-electricity detector; the light-electricity detector employs photoelectric diode of high sensitivity or micro photoelectric multiplier tube sealed with metal; A band pass preposition enlarging circuit is fixed in the shell of scatter body of optics sensor with the same width of pulse frequency of scattering light.
Owner:上海镭慎光电科技有限公司 +1
Method for detecting geometrical-optical aberrations
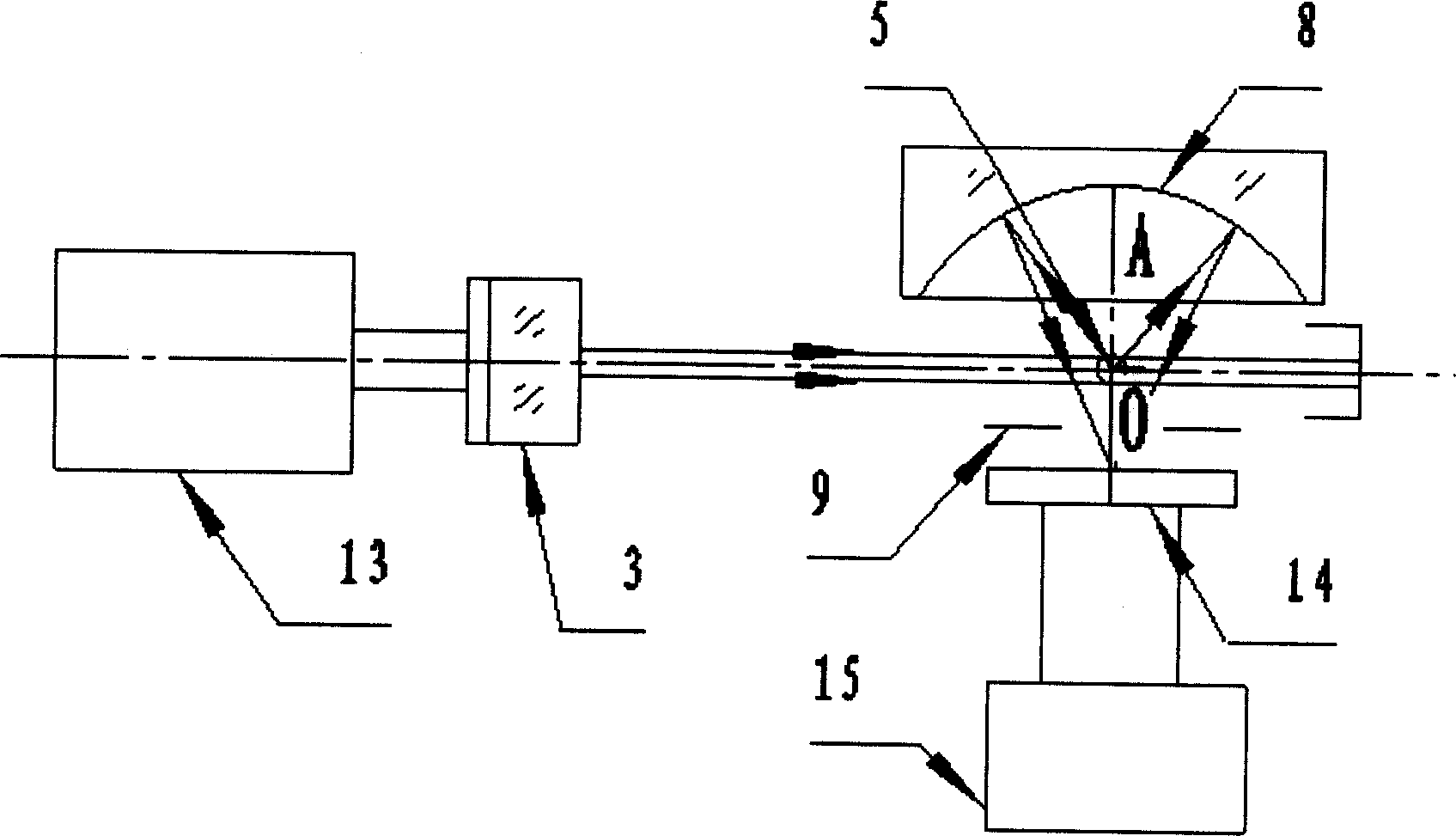
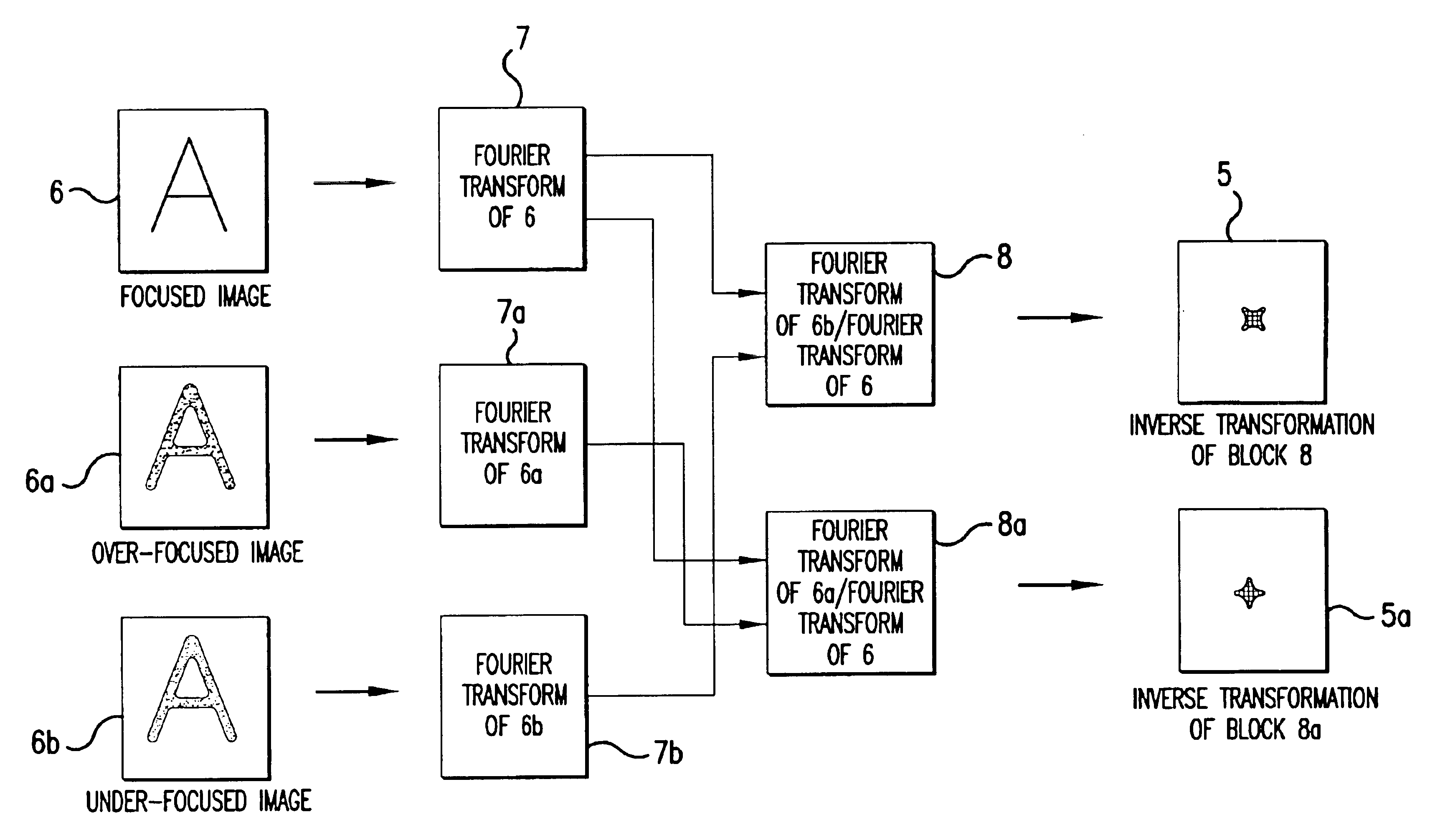
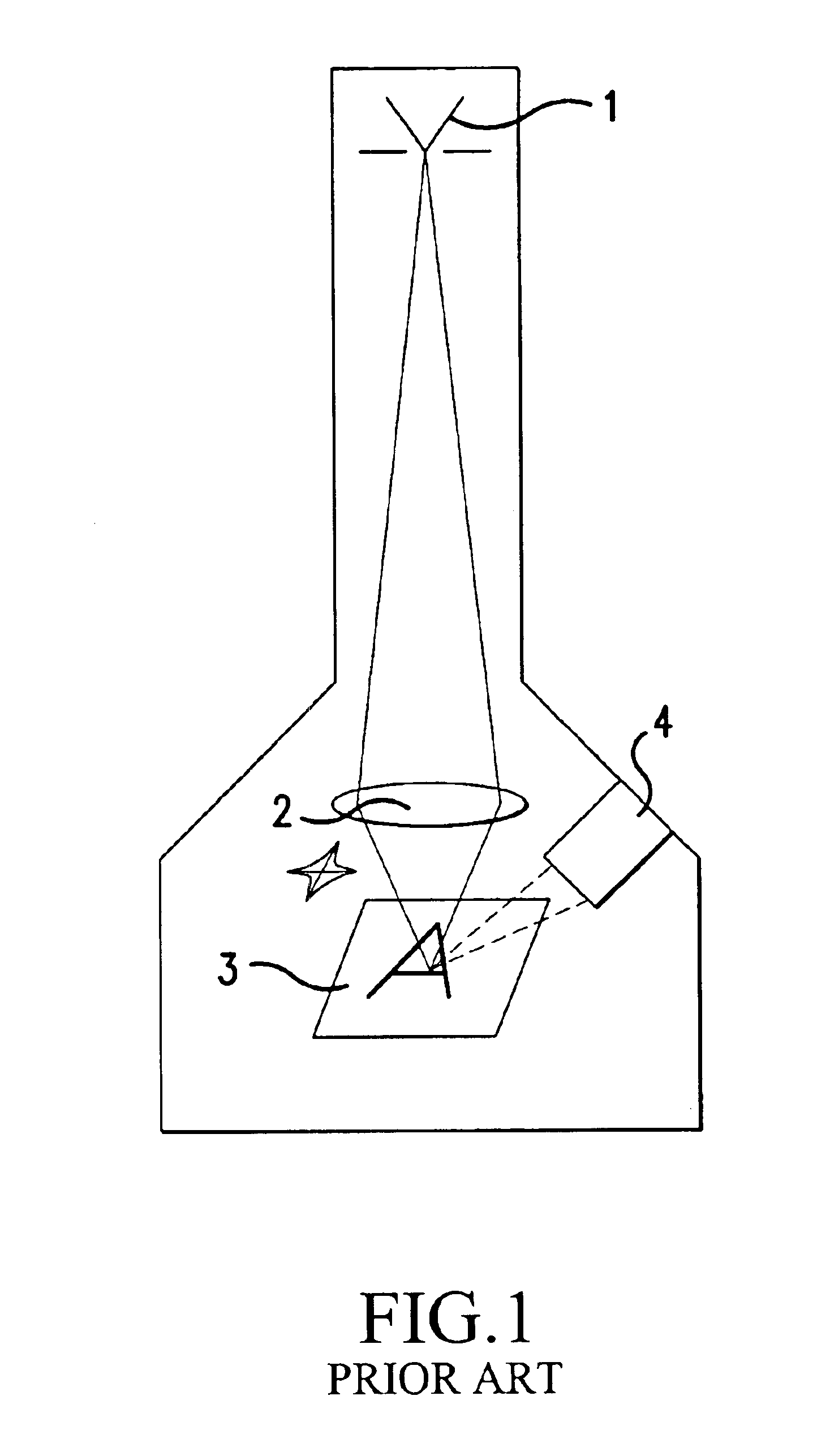
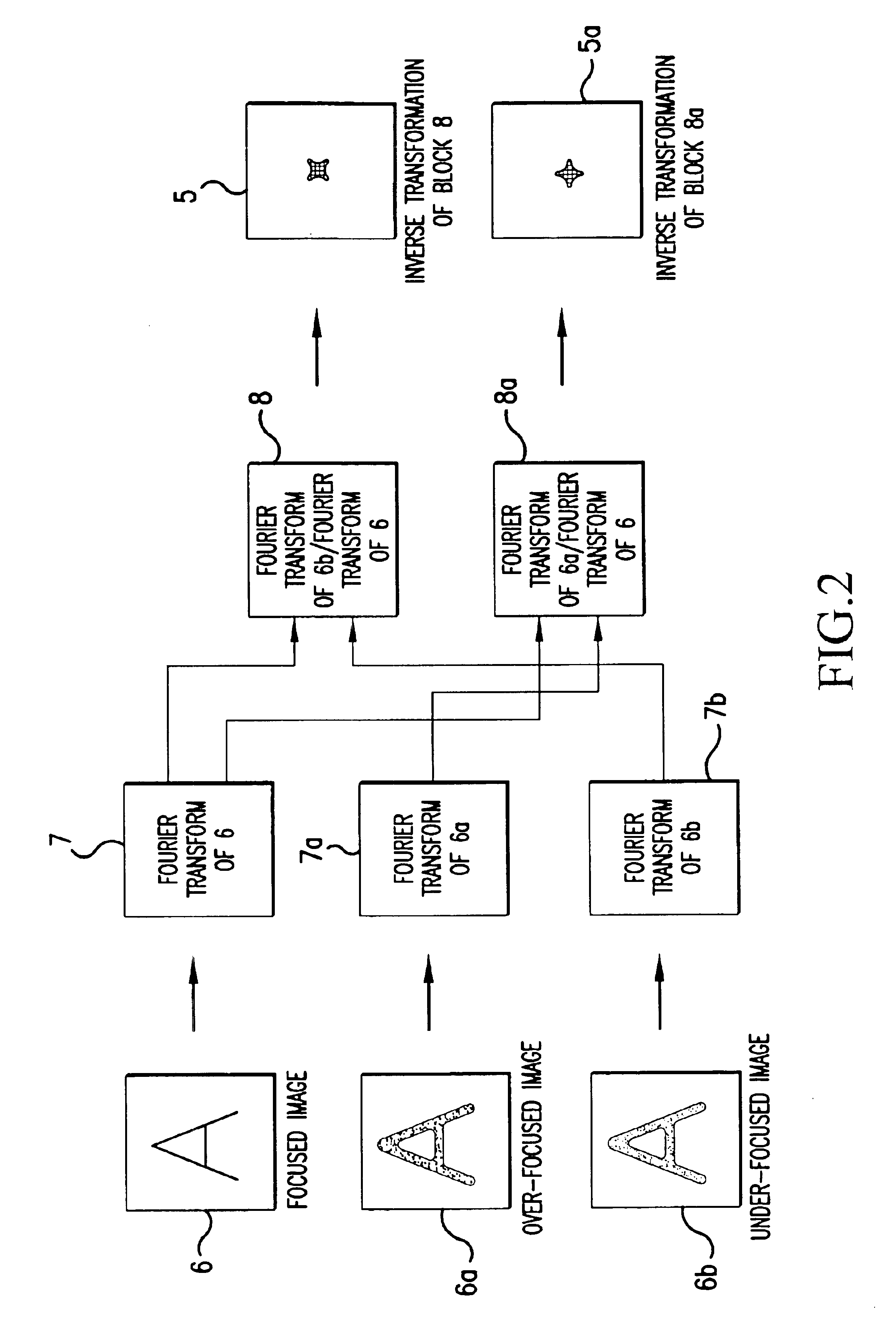
InactiveUS6858844B2Clear imagingAberration compensationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesScanning electron microscopeImage segmentation
The invention relates to a method for determining geometrical-optical aberrations up to and including 3rd order in particle-optical, probe-forming systems, in particular scanning electron microscopes, comprising an essentially punctiform source, lenses, an object, and a detector, the image being recorded, the process being repeated with an overfocussed and an underfocussed beam, the images being transformed in Fourier space, the transformation of the overfocussed image, and the underfocussed image is divided by the transformed focussed image. The results are reverse transformed, and the brightness profiles of the probes, the images of the source, are determined in overfocus and underfocus. The asymmetry, the width and / or the curvature of the profile being determined in the center, and the image aberration being determined from the differences.
Owner:ZACH JOACHIM
Invisible apparatus and design based on geometrical optics
InactiveCN101299079AAchieve optical invisibilitySimple structureBundled fibre light guidePhysical opticsImage transfer
The present invention provides a concealing device which is based on geometric optics and a design thereof, and relates to the field of optical concealing technique. According to the principle of physical optics, the light beams are converged with a convex lens. The cross-sectional area of the light beam is changed. The incidence light at the front of the object can be converged through the convex lens and transferred to the backside of the object through an image transferring channel, and is changed to the former incidence ray through radiation. The effect of concealing the visible light is obtained. The core of the device is that the concealing device is composed of at least one group of object group 1 which can be permeated with light and focus the light, a light beam transmission component 2 which is provided between the focusing object group 1 and a concealing area 3. The device is designed with an imaging formula of the convex lens to obtain the effect of optical concealing the visible light. The concealing state of the device is sustained without exterior power. The exterior exposed part of the device is fewer. Compared with the optical physical concealing device, the concealing device according to the invention has the characteristics of simple structure, easy manufacture, low cost and wide application area.
Owner:上海市第二中学
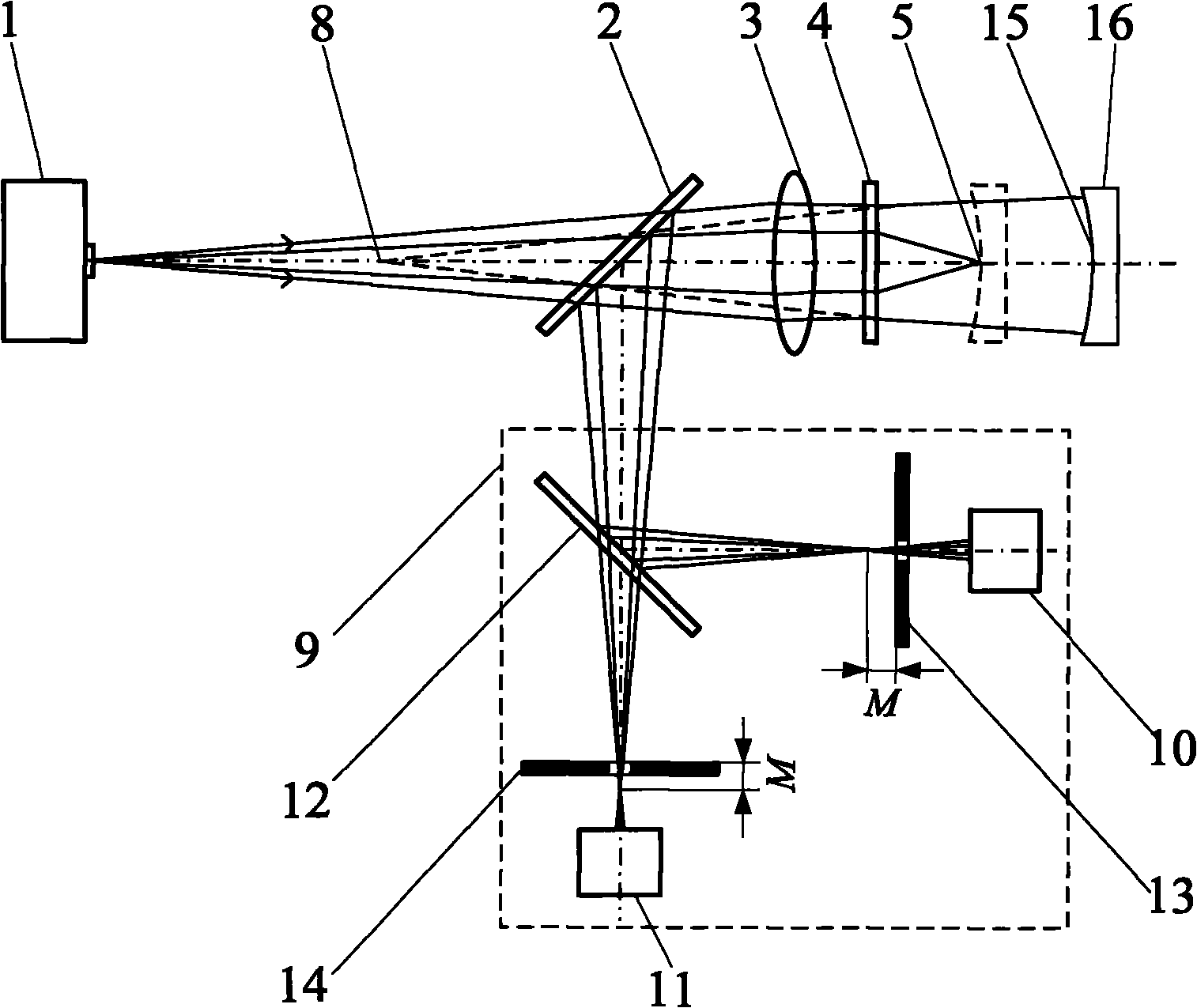
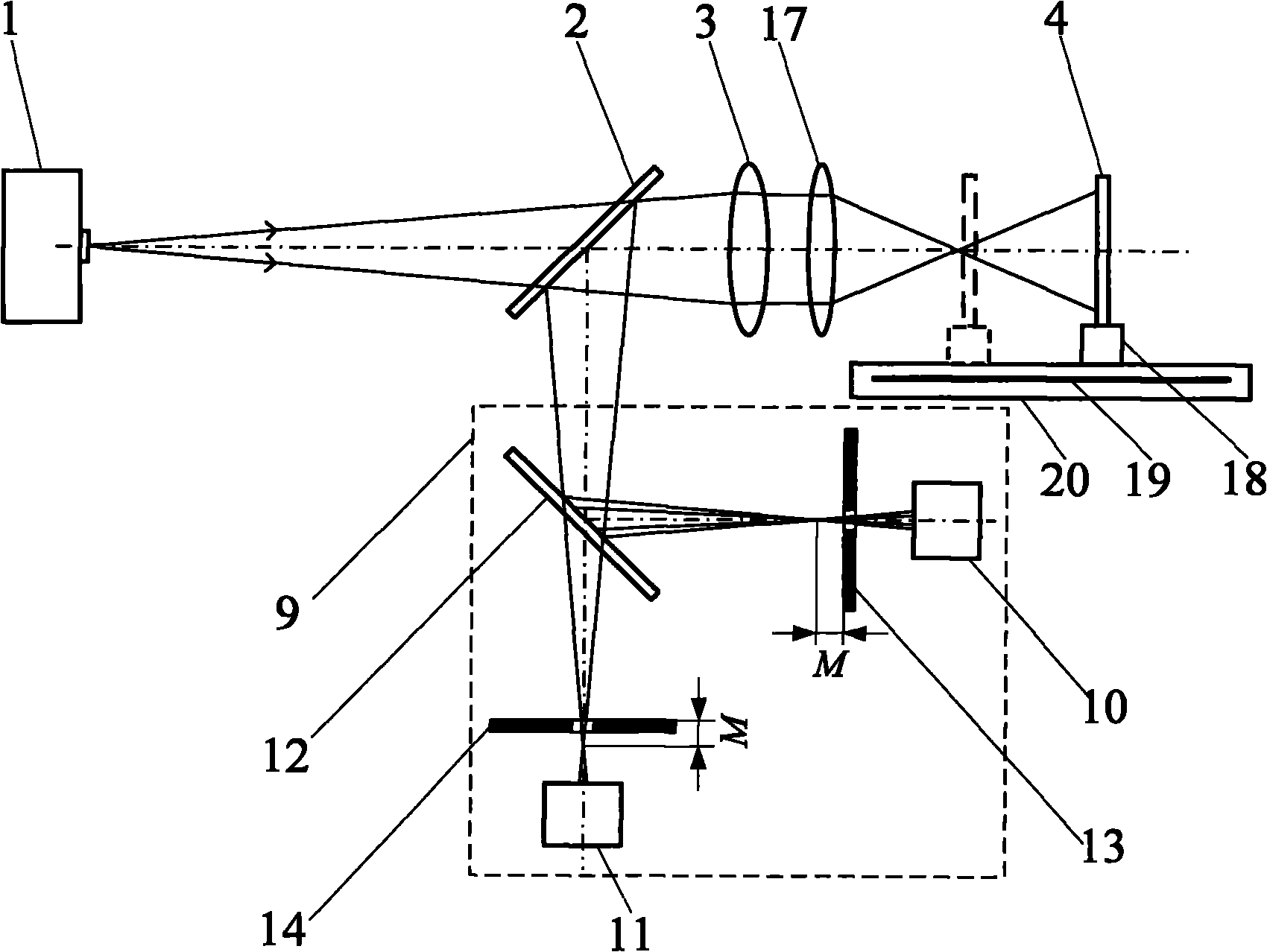
Multifocal holographic differential confocal super-large curvature radius measuring method and device
InactiveCN101858736AReduce mistakesReduce movement distanceUsing optical meansContact highInterference resistance
The invention relates to multifocal holographic differential confocal super-large curvature radius measuring method and device, belonging to the technical field of optical precision measurement. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, calibrating the long-focus value of a multifocal holographic lens by utilizing a differential confocal system so as to reduce the system error of measurement; realizing non-contact high-precision positioning at the cat eye position and the cofocal position of a measured piece by utilizing a differential confocal fixed-focus principle; and subsequently, realizing the high-precision measurement of a super-large curvature radius by utilizing a geometrical optics principle. The device comprises a point light source, a first spectroscope, a collimator objective, the multifocal holographic lens, the differential confocal system, an adjusting frame, a length measuring system and a moving track. The invention integrates the differential confocal high-precision fixed-focus principle and a multifocal holographic lens compression optical path principle for the first time, has the advantages of small displacement distance of the measured piece, high measurement precision, high measurement speed, strong ambient interference resistance, no damage to the measured surface and the like and can be used for the high-precision non-contact measurement of the super-large curvature radius.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
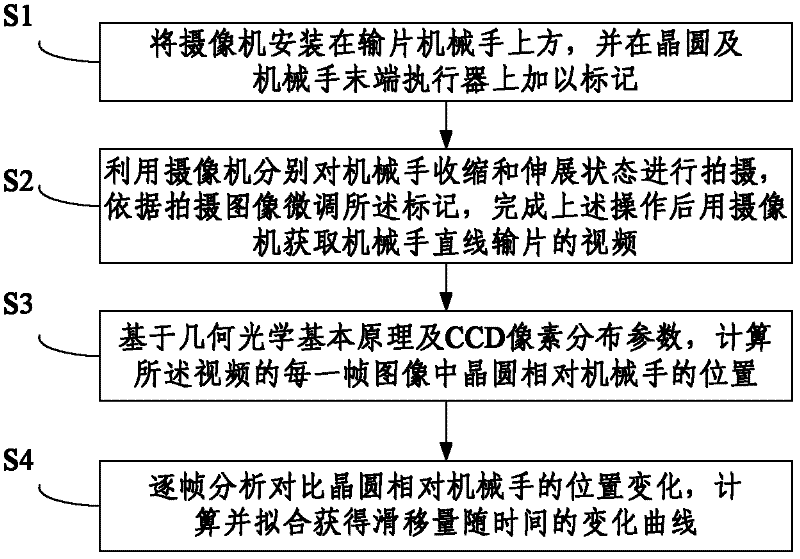
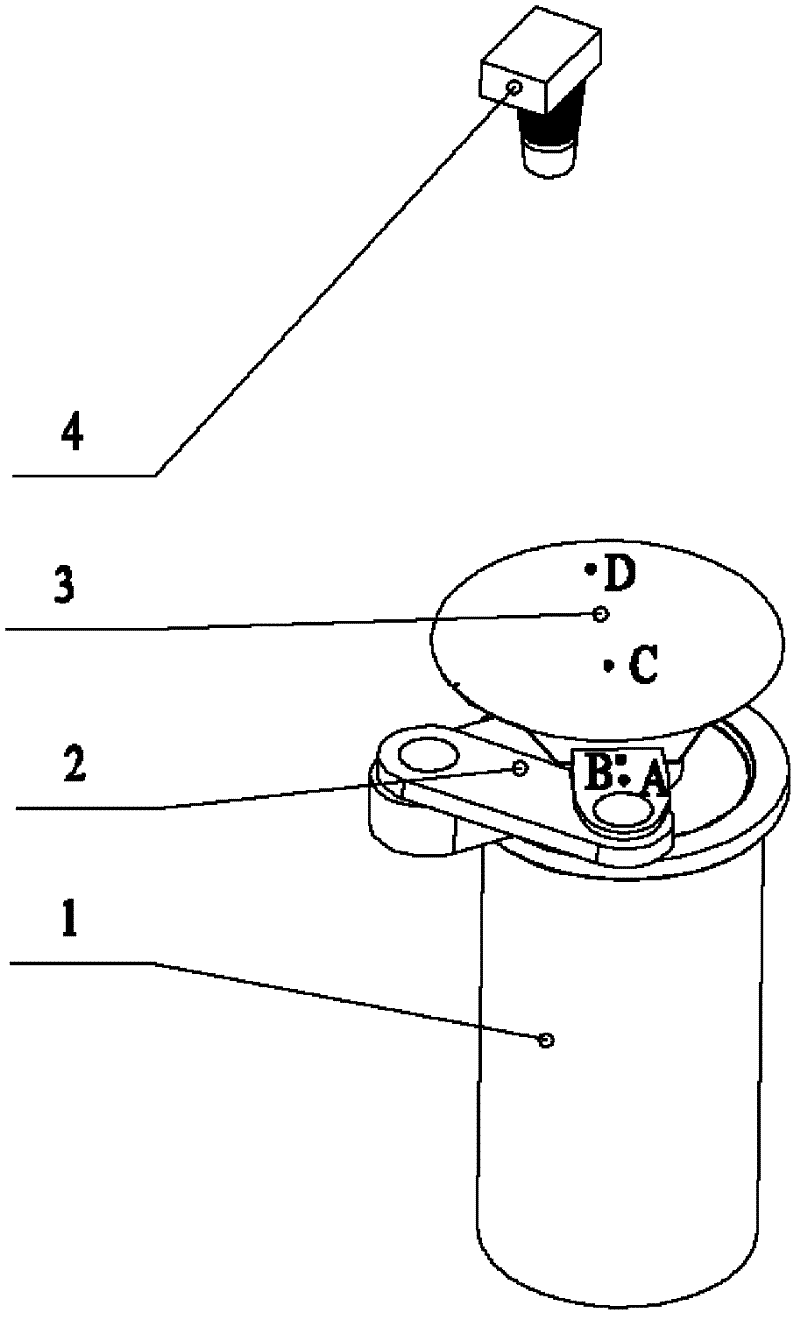
Method for detecting slip during linear delivery of wafer by using image processing technology
InactiveCN102564319AImprove delivery efficiencyMeet the requirements of slippage detection under different precision levelsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementUsing optical meansPattern recognitionActuator
The invention discloses a method for detecting slip during the linear delivery of a wafer by using an image processing technology. The method comprises the following steps: S1, mounting a video camera above a wafer delivering manipulator, and marking the wafer and the tail end actuator of the manipulator; S2, shooting the contraction and the extending states of the manipulator through the video camera, trimming the marks according to the shot images, and then obtaining a linear wafer delivering video of the manipulator through the video camera; S3, calculating the position of the wafer in each frame of the video on the basis of the geometrical optics fundamental principle and a CCD (charge-coupled device) pixel distribution parameter; and S4, analyzing and contrasting the change of the positions of the wafer relative to the manipulator frame by frame, and calculating and fitting to obtain a slip time history curve. The method can meet the requirements for detecting slip under different accuracy classes, and provide a theoretic and experimental reference for optimizing and controlling the speed and the acceleration of the wafer delivering manipulator, so as to achieve higher transmission efficiency under the premise that the delivering accuracy is met.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Reflective film with moth eye structure and preparation technology thereof
The present invention provides a reflective film with a moth eye structure and a preparation technology thereof. The reflective film provided by the invention comprises a PET layer, a reflective structure layer and a moth eye anti-reflection structure layer. Through the geometric optics principle, the reflective structure layer is configured to take a pyramid structure with three vertical surfaces as a reflective structure. Through the bionics principle, the moth eye anti-reflection structure layer is configured to take a moth eye micro-nano structure as an anti-reflection layer. Compared with the traditional reflective film, the reflective film provided by the invention has a better reflective effect. Through adoption of reel-to-reel UV two-sided rolling technology (R2R UV-NIL), the preparation technology provided by the invention comprises adhesive dripping, filling, UV illumination and demolding. According to the invention, different structure layers may be printed on the surfaces at two sides of the PET layer; and moreover, the preparation technology is simple, and the fast and large-area commercialization requirement with high resolution and high throughput may be satisfied.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Device for forming quasi-double half-gauss hollow laser beam
The invention discloses a quasi-double semi-gaussian hollow laser beam forming apparatus which realizes the conversion from a gaussian solid laser beam to a quasi-double semi-gaussian hollow laser beam to a certain extent, and belongs to the laser technical field. The prior hollow laser beam forming apparatus adopting the geometrical optics method has the defects that the light intensity of the formed hollow laser beam still has double-gaussian distribution, and the formed laser beam is not a practical hollow laser beam. The quasi-double semi-gaussian hollow laser beam forming apparatus is sequentially composed of a concave spherical reflecting mirror, a normal conical surface reflecting mirror and a positive lens, the three of which are coaxial in optics; the conical surface of the normal conical surface reflecting mirror is opposite to the concave spherical surface of the concave spherical reflecting mirror; an incident hole is formed in the center of the concave spherical reflecting mirror; and the object focal point of the positive lens is coincident to the reflected light convergence dot of the concave spherical reflecting mirror. The light intensity distribution of the hollow laser beam formed by the apparatus is near the quasi-double semi-gaussian distribution state, and the formed laser beam is the quasi-double semi-gaussian hollow laser beam applied to the fields of laser processing, atom cooling, bioengineering and the like.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fiber tractography using entropy spectrum pathways
A method for fiber tractography processes multi-shell diffusion weighted MRI data to identify fiber tracts by calculating intravoxel diffusion characteristics from the MRI data. A transition probability is calculated for each possible path on the lattice, with the transition probability weighted according the intravoxel characteristics. Entropy is calculated for each path and the paths are ranked according to entropy. A geometrical optics algorithm is applied to the entropy data to define pathways, which are ranked according to their significance to generate a map of the pathways.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
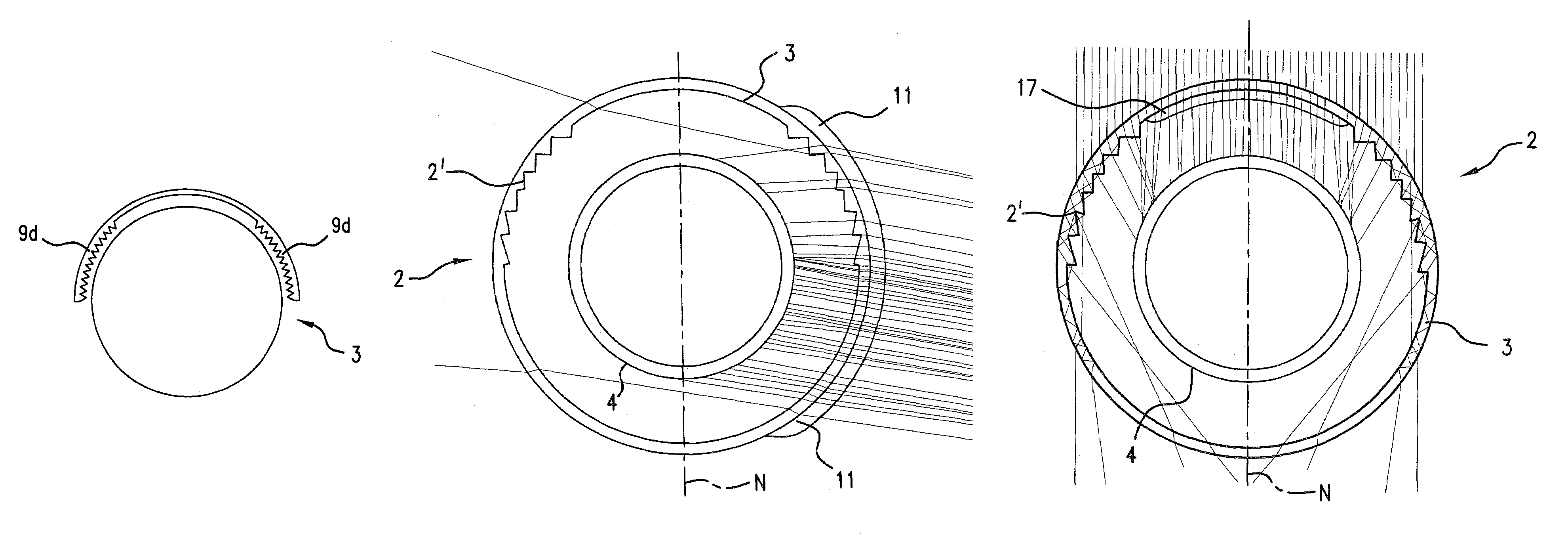
Receiver tube with receiver tubular jacket and parabolic trough collector containing same
InactiveUS7395820B2Small overall deformationPrevent bulk materialSolar heating energySolar heat devicesStructural elementEngineering
The parabolic trough collector includes a single-axis parabolic mirror (1) and a receiver tube (2) arranged at the focal point (F) of the parabolic mirror (1). The receiver tube (2) includes an absorber tube (4) and an outer tubular glass jacket (3) around it. To compensate for focusing errors in the parabolic collector and thus to reduce associated geometric optical losses, the tubular jacket (3) is provided with structural elements (9a, 9b, 9c, 9d), which focus sunlight reflected from the mirror as well as sunlight that falls directly on the receiver tube from the sun on the absorber tube. The receiver tube is preferably arranged relative to the parabolic mirror, so that its center is displaced from the focal point (F) by a distance equal to half the spacing between the tubular jacket (3) and the absorber tube (4).
Owner:SCHOTT AG
All-fiber Bessel light beam generator
InactiveCN104181637ASolve alignment difficultiesSmall structureOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberRefractive index
The invention provides an all-fiber Bessel light beam generator which is composed of a standard single-core fiber, an annular core fiber and a graded index fiber. When light wave is input to the single-core fiber, the transmission light wave can be coupled to the annular core fiber to form an annular light field, then the annular light field is formed into the Bessel light beam at a fiber end through the equivalent Fourier expansion optical transformation of the graded index fiber. Due to the light beam generator provided by the invention employing an all-fiber system, the graded index fiber is used for realizing a function of the lens, the whole generator is easy to align and is more stable compared with the traditional geometry optical system. In addition, the light beam generator has the characteristics of minimal structure, agile operation and strong anti-interference capability. The light beam generator can be applied to the fields of light beam generation, particle controlling and sensing and the like.
Owner:无锡万润光子技术有限公司
Optical sensor of novel high-output all-semiconductor dust particle counter
InactiveCN101793669AThe amplitude of the scattered signal increasesImprove counting efficiencyIndividual particle analysisPhotodetectorTrapping
The invention discloses an optical sensor of a novel high-output all-semiconductor dust particle counter. An aspherical mirror, an entrance lens screen, an exit lens screen and a light trapping are arranged in sequence in the heading direction of the light beam sent out by a semiconductor laser light source, a spherical reflector, a lens screen and a photodetector are arranged in the direction perpendicular to the light path, and the photosensitive area and the photosensitive surface of the photodetector are respectively positioned at the two sides of the center of the spherical reflector and satisfy the object-image relationship in the geometrical optics, wherein the light source is a high-power semiconductor laser light source, the photodetector is a photodiode, and a gain adjustable preamplification circuit is arranged on the shell behind the photodetector. The invention improves the counting efficiency, and raises the counting efficiency and the particle size resolution of the instruments. Besides, the invention has the advantages of long service life of the instruments, good exchangeability of the instruments, low power consumption and low cost; moreover, the optical sensor has small size, which is beneficial to the micromation of the complete device.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Image processing device and image field-depth processing method
InactiveCN105989574ANatural and Continuous Image EffectFades borderline imageImage analysisGeometric image transformationImaging processingDepth of field
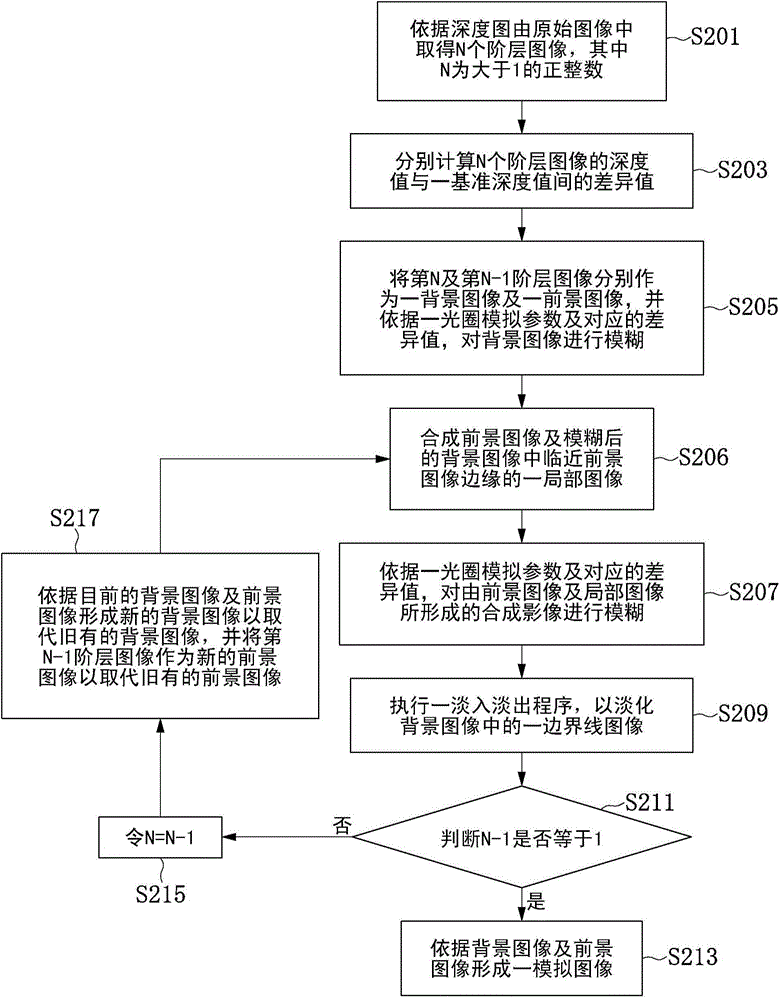
The invention discloses an image field-depth processing method. The method comprises that a background image and a foreground image are obtained from an original image according to a depth map corresponding to the original image, and the depth value of background image is greater than that of the foreground image; the background image is made fuzzy; the foreground image and a local image in the fuzzy background image are made fuzzy; and then, an analog image is formed according to the foreground and background images. The foreground image and the local image in the background image are made fuzzy according to the depth value of the foreground image, so that transition between the foreground image and the background image satisfies physical principles of geometrical optics more, natural and continuous image effects are achieved, further, a fade-in fade-out program is executed to fade a boundary image in the background image, and the analog image with large-aperture monocular field-depth shooting effect is generated.
Owner:LITE ON TECH CORP +1
Initiative light source type crop canopy reflection spectral measurement device and method
InactiveCN103293113AOptical path parameters are adjustableChange geometryColor/spectral properties measurementsMeasurement deviceSpectral response
The invention provides an initiative light source type crop canopy reflection spectral measurement device and method and belongs to the field of geometrical optics and agricultural information nondestructive testing. A driving light source is a double-channel narrow-band LED (Light Emitting Diode) light source and adopts a special structure with adjustable light path parameters; the change of initiative light source irradiation characteristic parameters is realized according to measurement requirements so that spectral reflectance measurement of canopies with different scales can be met; a light path structure of a measurement system can guarantee that a constant value proportion relation can be kept when the height change is measured by a double-channel reflection spectral response value, so that measurement values of specific value type spectral indexes including NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), RVI (Ratio Vegetation Index) and the like are theoretically not changed along with the measurement height.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
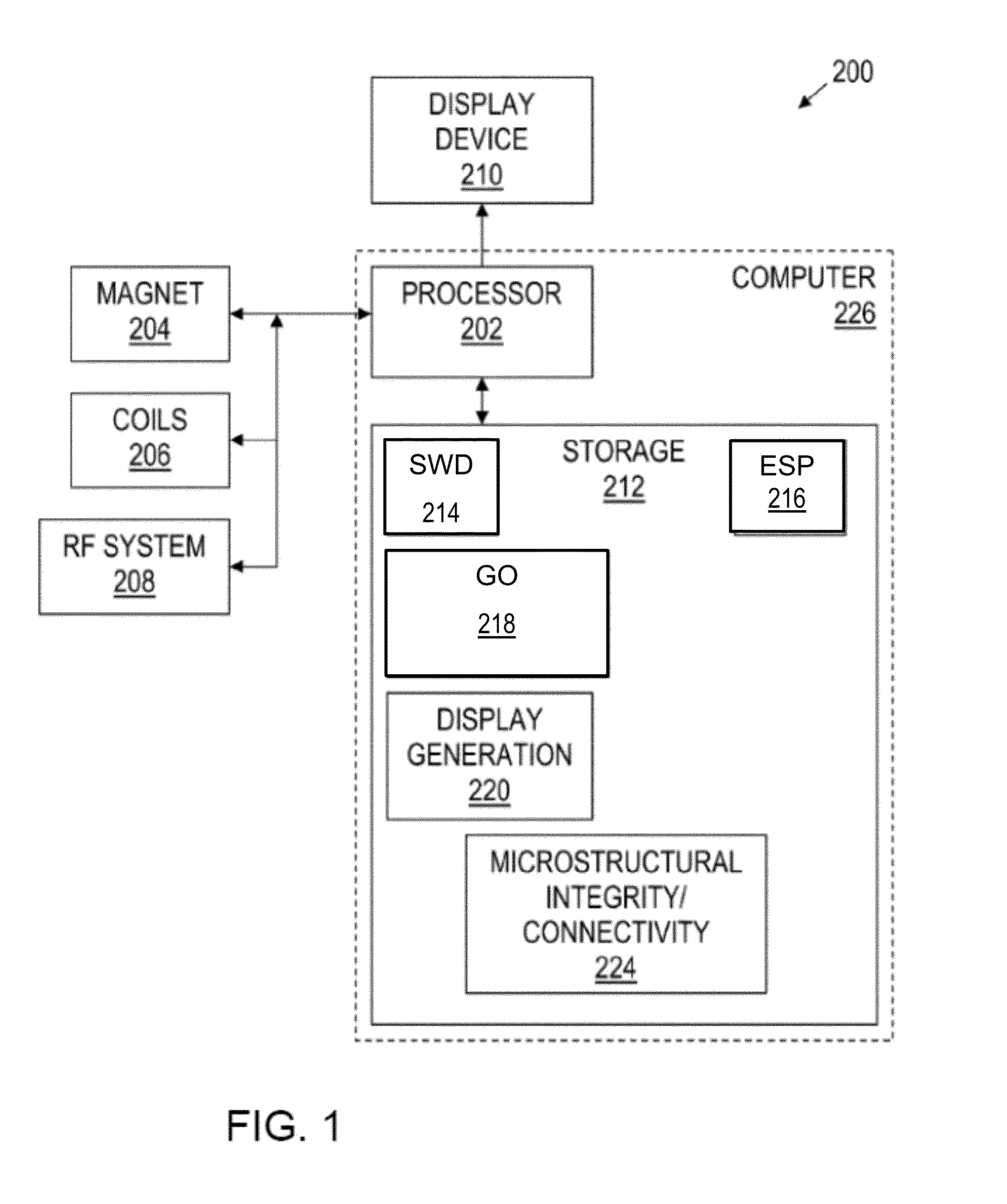
Display device
InactiveUS20100085511A1Evenly distributedIlluminated signsOptical light guidesLight guideDisplay device
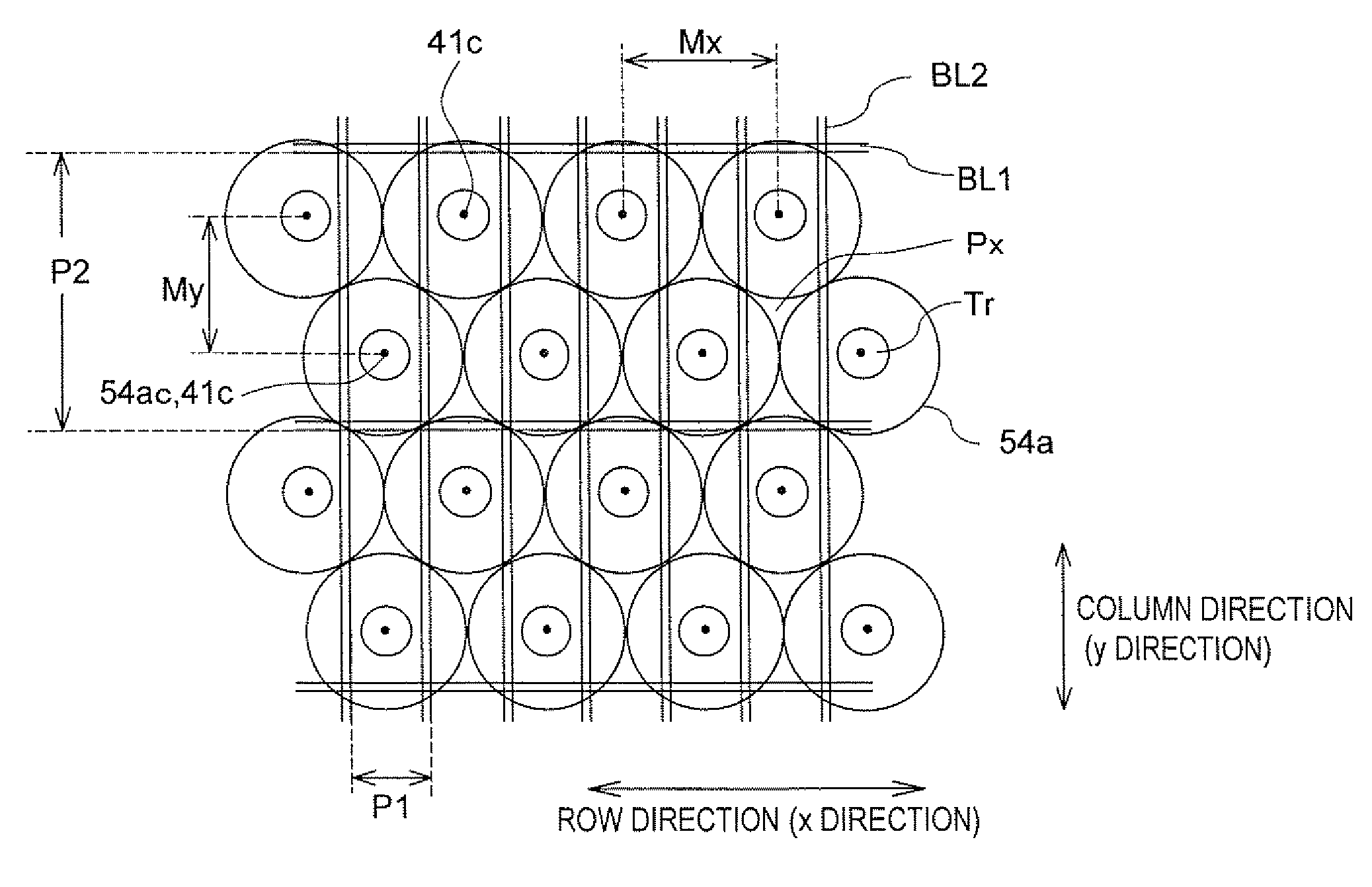
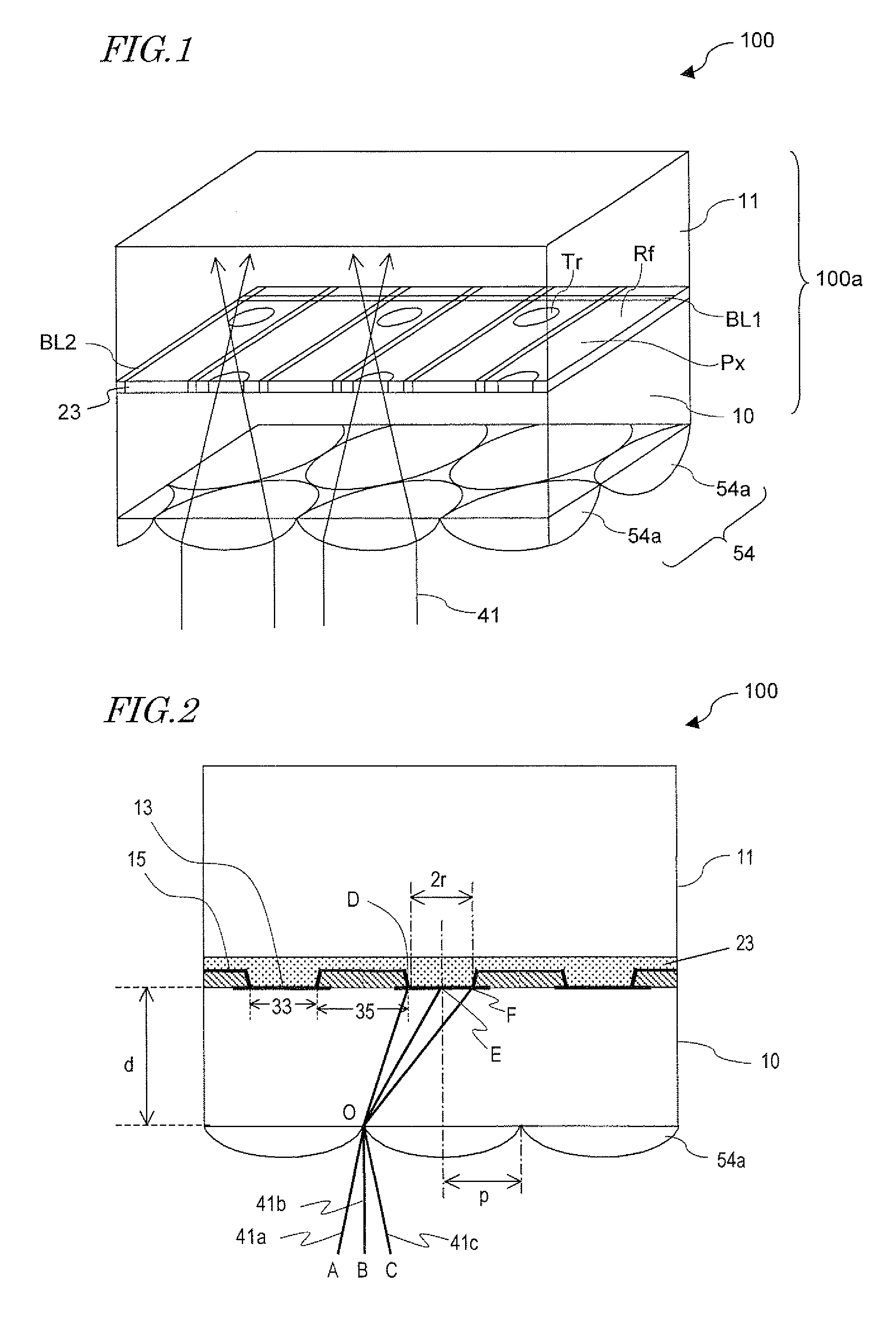
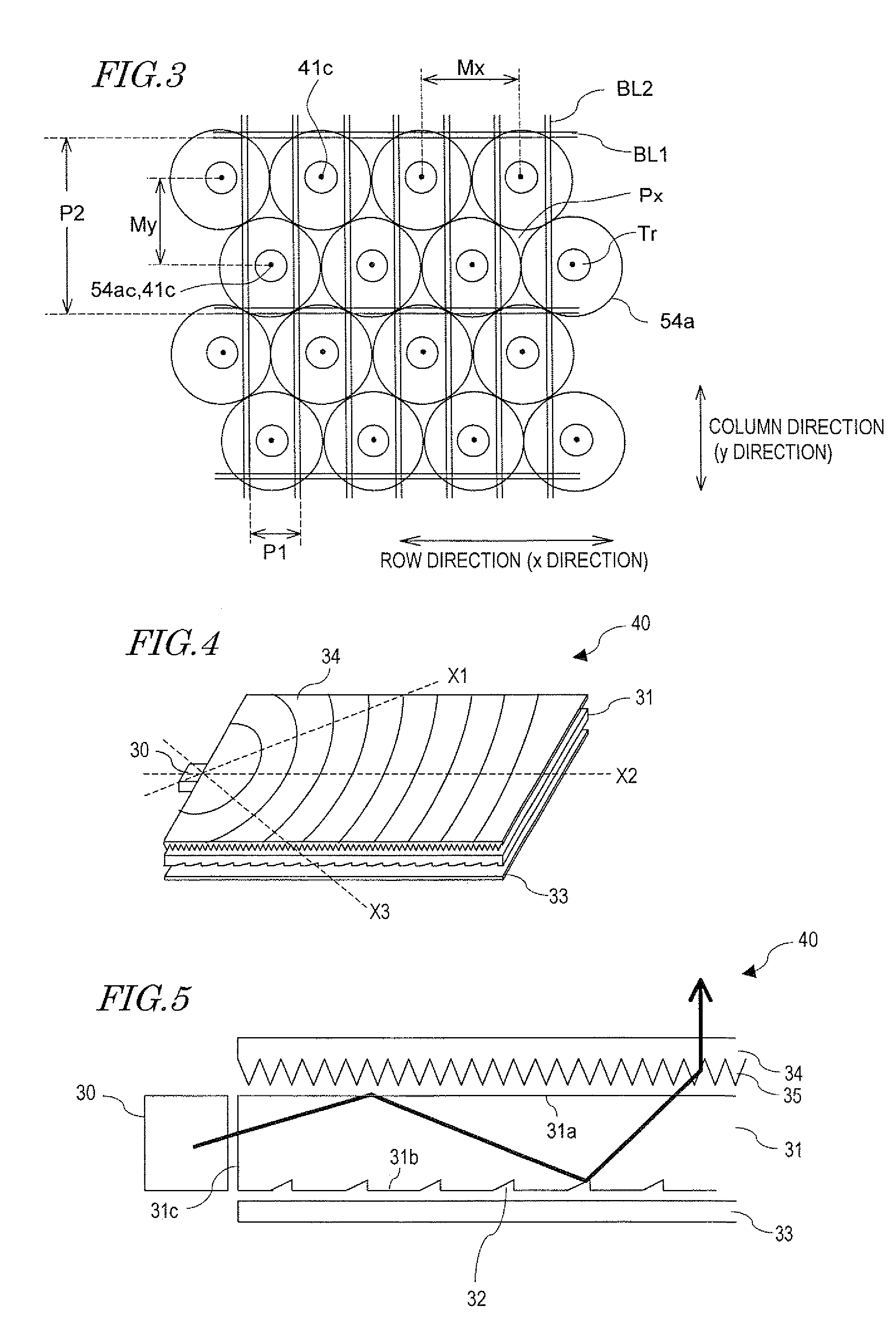
A display device of the present invention includes: a display panel 100a including a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix; a lighting device 50 including a light source 30 and a light guide plate 31 for outputting light toward the front; and a plurality of light condensing elements 54a placed between the display panel and the lighting device. The directivity of light emerging from the lighting device to be incident on the light condensing elements varies with the position in the display panel plane, and when the range of a polar angle of light, out of the light emerging from the lighting device to be incident on the light condensing elements, that is used for display after passing through the light condensing elements and then the display panel, with respect to the normal to the display panel plane determined based on geometrical optics is ±ω or less and the luminous flux within the range of the polar angle ±ω (within ∠AOC) is Φω, the minimum one of values of luminous flux Φω at the centers of nine regions, obtained by dividing a region corresponding to the display region of the display panel plane into nine equal parts, is 70% or more of the maximum one of the values.
Owner:SHARP KK
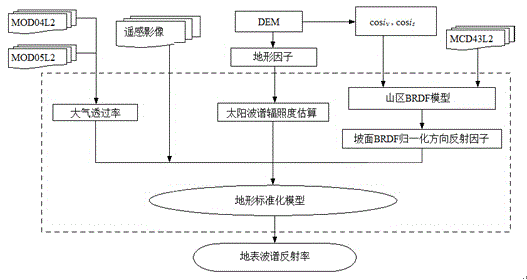
Remote sensing image terrain standardization method
The invention discloses a remote sensing image terrain standardization method. In a Ross Thick-Li Sparse linear kernel driver model, slope and orientation are introduced into a Ross volume scattering kernel function and a Li geometrical optical kernel function to establish a mountain BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function) model; on the basis of a conventional remote sensing image terrain standardization result, an assumption of the earth surface about a Lambertian reflectance characteristic is changed, and the mountain BRDF model is introduced to maximally reduce the influence of a change in the BRDF shape of a complicated topographical region; atmospheric parameters at the border crossing moment of a satellite image are obtained by taking MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) water vapor and aerosol atmosphere products as terrain standardization model parameters, so that the influence of optical factors of the atmosphere is eliminated. According to the method, radiometric distortion of a remote sensing image caused by optical properties of the atmosphere is eliminated, and in addition, radiometric distortion caused by factors such as terrain shielding and BRDF properties of the earth surface is effectively eliminated, so that the real reflectivity of the earth surface is obtained.
Owner:HANGZHOU DADI TECH CO LTD
Method for improving business nuclear drive bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) model hot spot
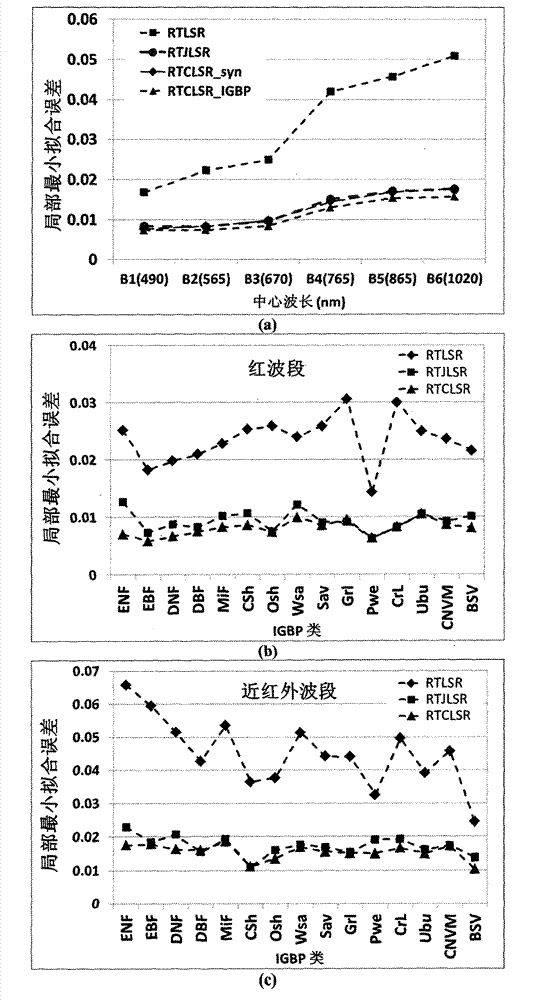
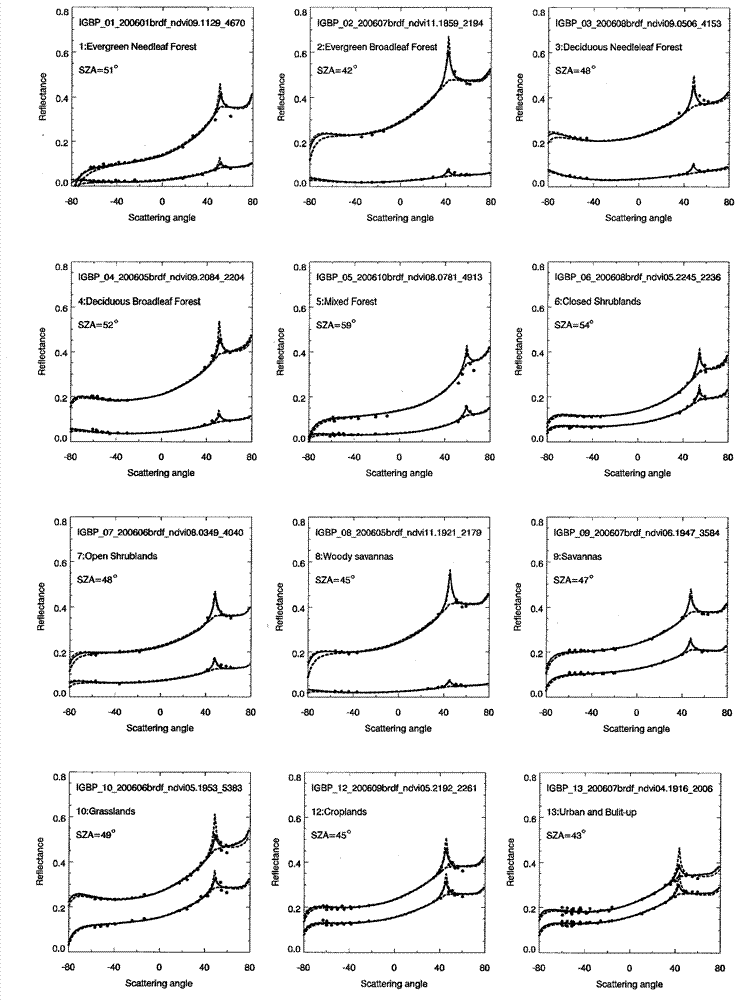
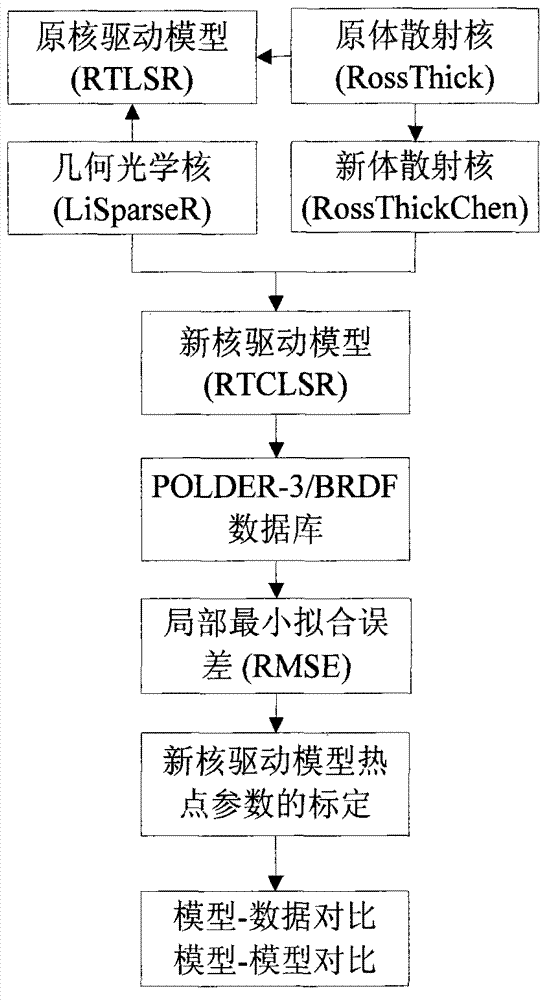
InactiveCN103324827AImprove inversion accuracyImprove reflectivitySpecial data processing applicationsAlbedoBidirectional reflectance distribution function
The invention relates to a method for improving a business nuclear drive bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) model hot spot. The method comprises the following steps: a new volume scattering nucleus considering the hot spot change is put forward through carrying out the hot spot calibration on the volume scattering nucleus of a conventional MODIS business nucleus drive BRDF model RTLSR, an RTCLSR model generated by the linear combination of the nucleus with an original geometrical optics nucleus has preferable fitting capability to the hot spot, but the fitting precision in the other observation directions is not influenced, a POLDER-3 / BRDF database and onboard CAR data are used to carry out calibration and verification on the hot spot parameters of the RTCLSR model, the new RTCLSR model is available to study the change of the hot spot effect with earth surface category, NDVI and a solar zenith angle, meanwhile, the new model maintains the linear form of an original model very well, and the complexity of model calculation is not greatly increased, so that a new algorithmic base and a solution provided for the MODIS BRDF / albedo business product up-gradation is made into possible. The method for improving the business nuclear drive bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) model hot spot has significant application value in the technical field of spatial information, in particular to the aspect of quantitative remote sensing.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Nonlinear absorption measuring method based on lens geometric optical imaging
InactiveCN101477047ARealize measurementLow sensitivity to random fluctuationsTransmissivity measurementsImaging lensCcd camera
The invention discloses a method for measuring nonlinear absorption based on geometric optical imaging of a lens. Light output by a laser is divided into monitoring light and detection light; the monitoring light is received by an energy meter probe and is used for monitoring the energy transmitted on a sample to be tested in a real-time mode; the detection light is focused by a focusing lens and then irradiates on the sample to be tested positioned at a focus or the nearby position of the focusing lens; the non-linearity leads the space distribution of the detection light which passes through the sample to change; and the change is recorded by a CCD camera through an imaging lens arranged at the rear position. A theoretical model of a measurement system which works according to the method is simple; and the method has the advantages that the method has easy data processing and quick measurement speed, reduces optical accumulation effect by single pulse measurement, has low sensitivity to the random fluctuation of laser beams, and has accurate measurement results as well as intuitive and clear experimental results, the measurement of non-linear absorption is not affected by non-linear refraction, and so on.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
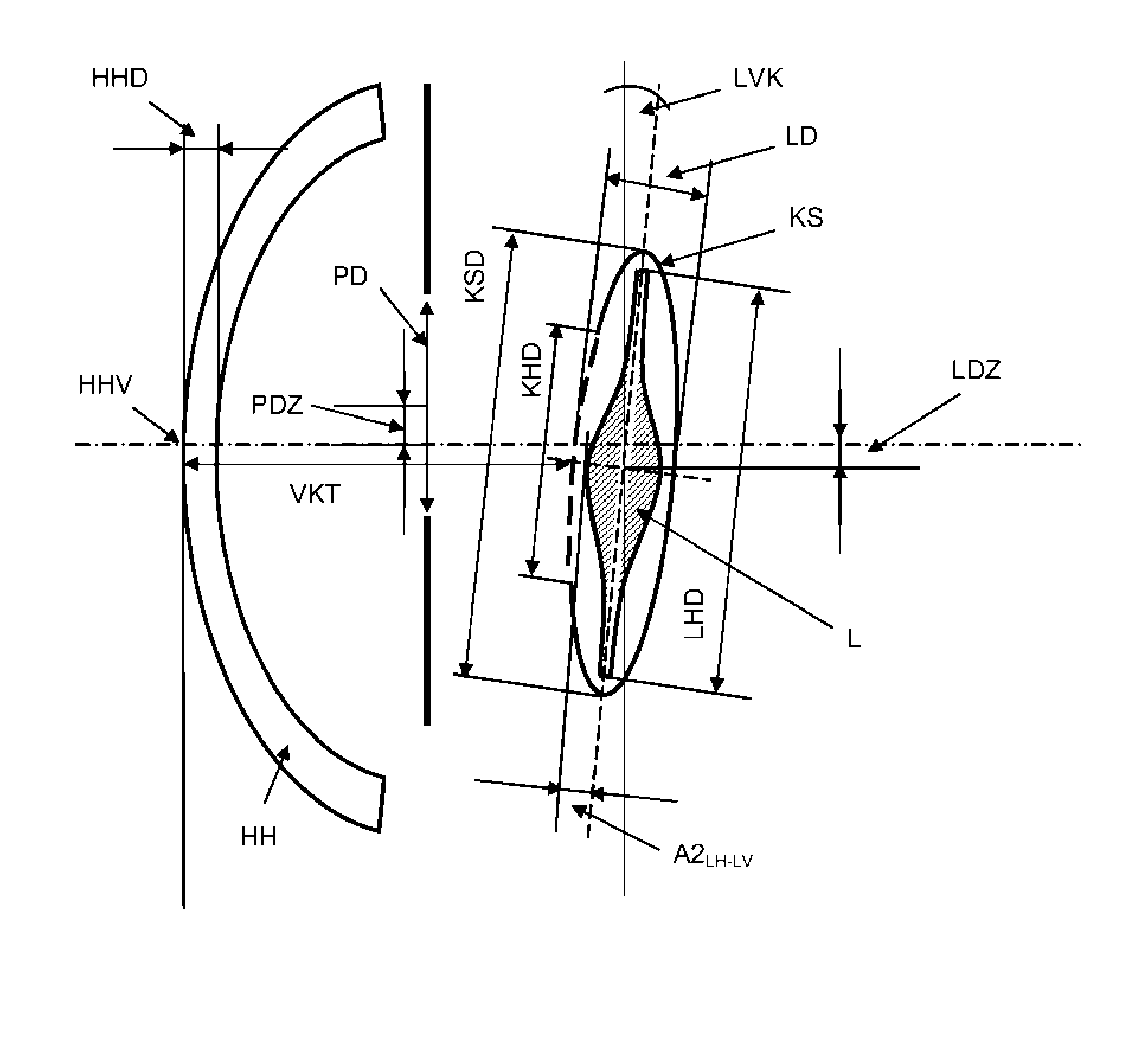
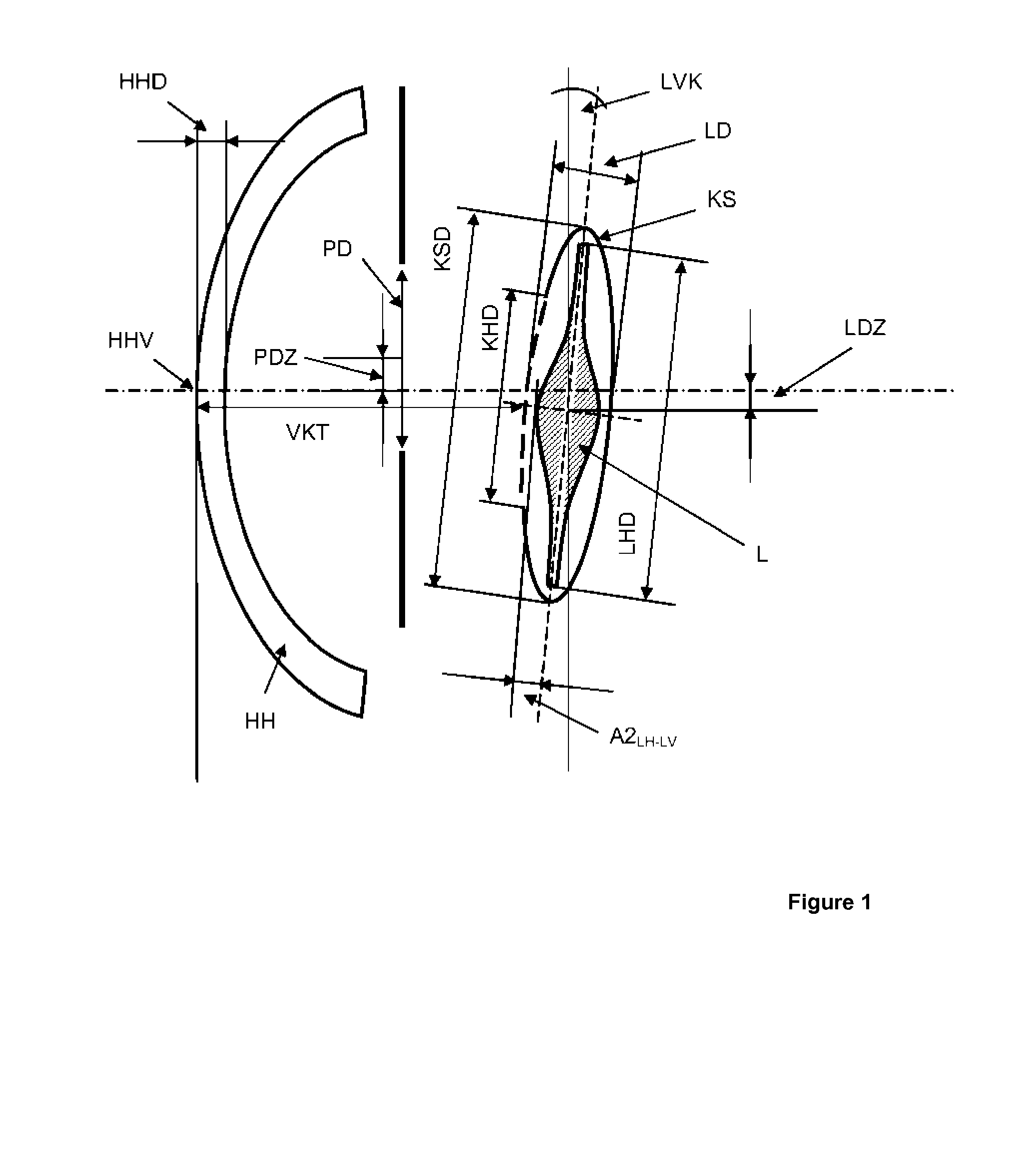
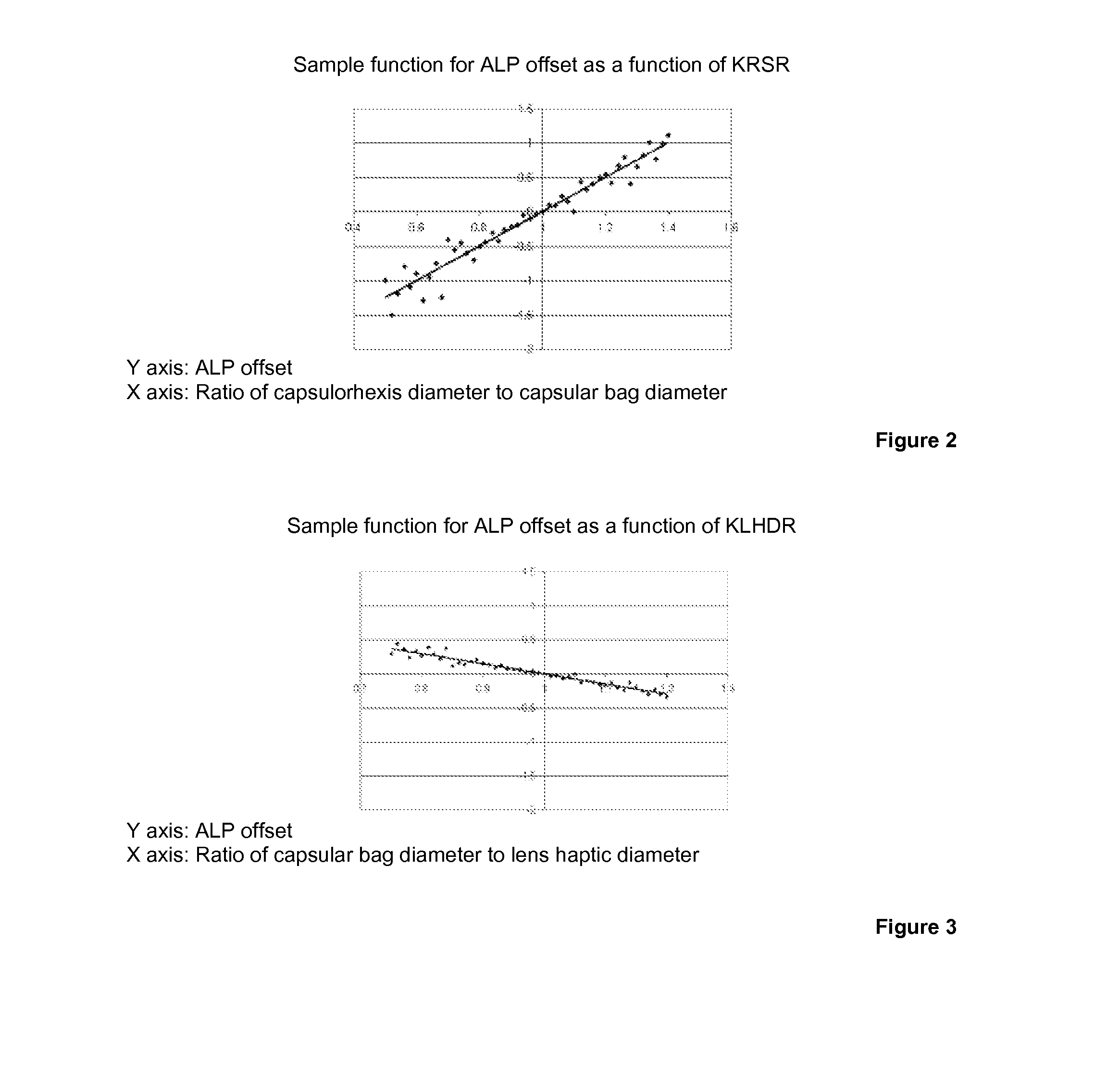
Method for optimized prediction of the postoperative anatomical position of an intraocular lens implanted in a pseudopakic eye
ActiveUS20140125955A1Easy to predictEliminate disadvantagesEye surgeryIntraocular lensPosterior lensLens plate
Postoperative lens position is predicted on the basis of known measured values, such as the corneal thickness, the depth of the anterior chamber, the eye length, and the distances of the capsular bag equator and / or of the lens haptic from the anterior surface of the lens. In addition, the calculation also takes into account the attitude of the intraocular lens, for which purpose additional parameters of the pseudophakic eye are used that have not previously been taken into consideration.; The proposed method is suitable for a more exact prediction of the strength and nature of an intraocular lens to be implanted in a pseudophakic eye in the context of cataract surgery or of a refractive intervention. The method is based on the use of suitable calculation methods, e.g. geometric optical formulae, or of ray tracing.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Method for performing online measurement on fatigue crack propagation of organic glass
InactiveCN105699218AReliable Extended Test Measurement AccuracyReduce storageMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesStress strengthCcd camera
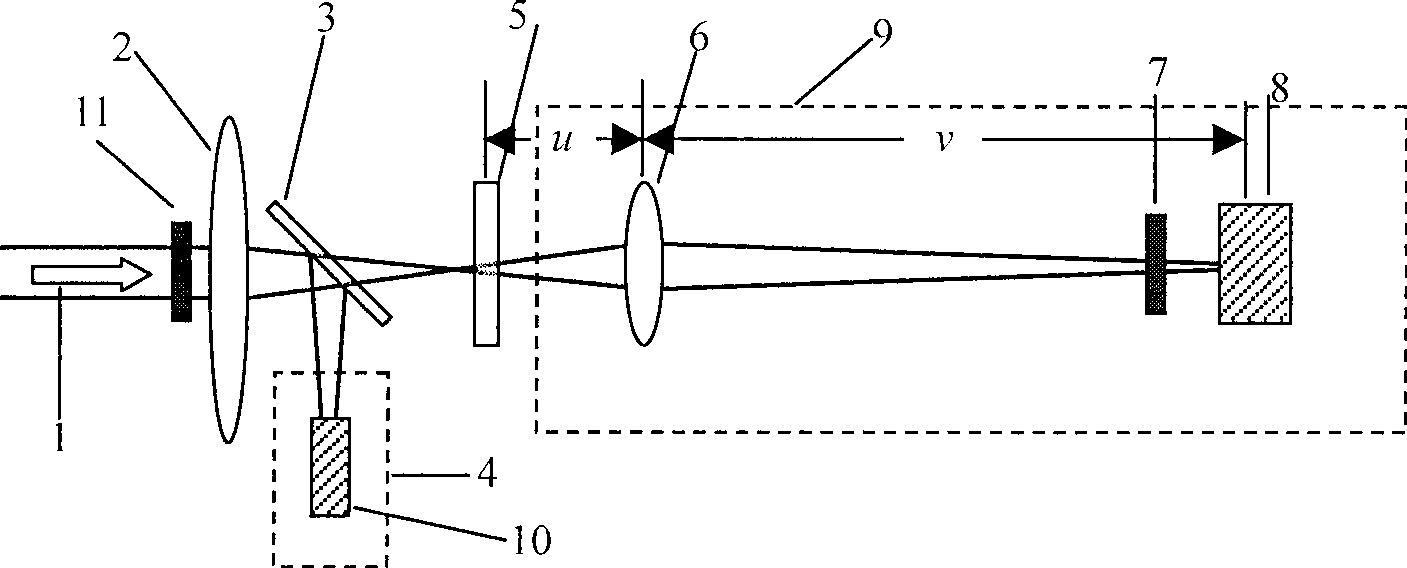
The invention provides a method for performing online measurement on fatigue crack propagation of organic glass and belongs to the fields of fatigue fracture mechanics test technologies and digital image technologies. According to the method, a transmission-type caustic optical technology is adopted, a CCD camera is utilized to online and continuously collect propagation processes of shadow spot images and cracks nearby crack tips of an organic glass testpiece containing cracks under different fatigue circle periods, image processing and condition selection are performed on shadow spot images in a cache region of a computer in real time, and the crack length and the crack tip stress strength factor are calculated. A caustic optical testing technology adopted in the method refers to non-contact real-time measurement, is high in intuition, simple in geometrical optics model, easy in stress strength factor calculation, convenient in data processing and accurate and reliable in test result; compared with a traditional fatigue crack propagation measurement method, the method provided by he invention is capable of omitting tedious processes of manually measuring the crack length and solving out the stress strength fact range, and avoiding the influence of crack length halt measurement on the test result.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
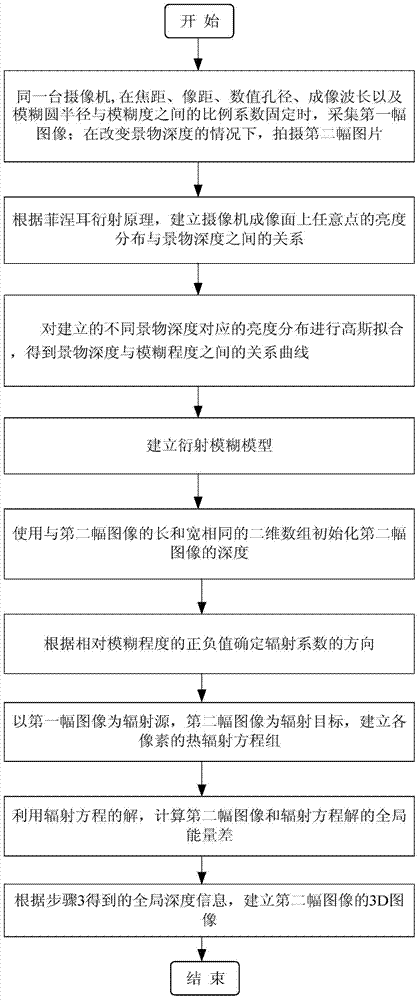
Single-vision overall depth information acquisition method based on diffraction blurring
The invention discloses a single-vision overall depth information acquisition method based on diffraction blurring and belongs to the technical field of image processing. A first image is collected when the focal length, the image distance, the numerical aperture, the imaging wave length and the proportionality coefficient between the blur circle radius and the ambiguity of the same camera are fixed; under the condition that the aspects are not changed, the distance between the camera and an object is changed, and then a second image is collected, wherein the change magnitude of the distance is delta s; a diffraction blurring model is established and used for describing the relation between the depth of the object and the image blurring degree; the diffraction blurring model and the two blurred images are used for determining the overall depth information of the second image; a 3D image of the second image is formed according to the obtained overall depth information. According to the single-vision overall depth information acquisition method based on diffraction blurring, the diffraction mechanism is fused into traditional geometrical optical convex lens blurring imaging, a mathematical model of the relation between diffraction blurring and the 3D depth of the object is established, and the accuracy of an out-of-focus object depth acquisition method based on traditional geometrical optics is improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
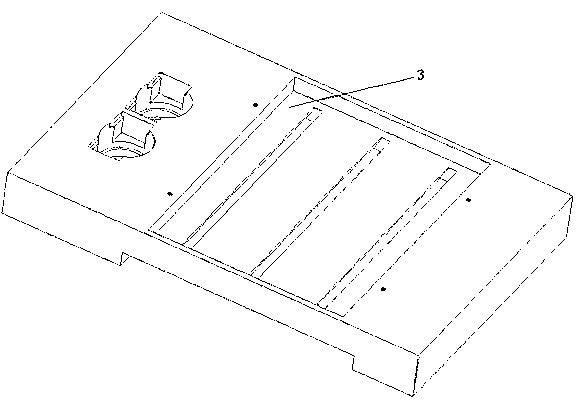
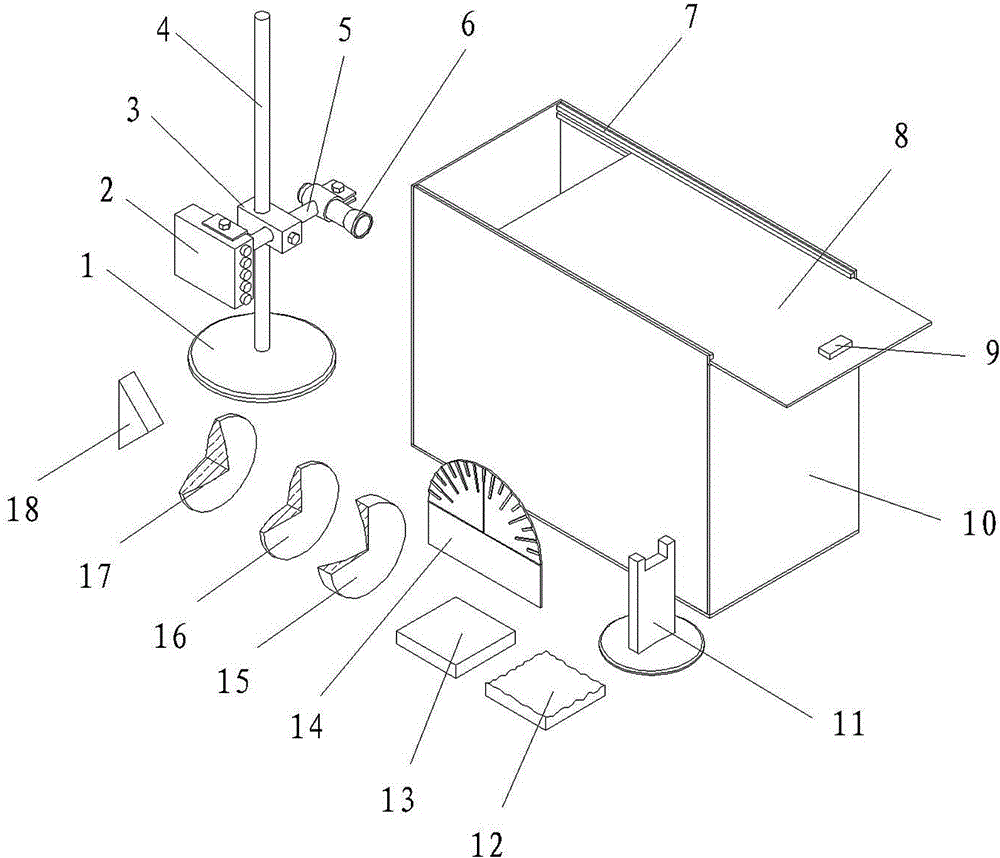
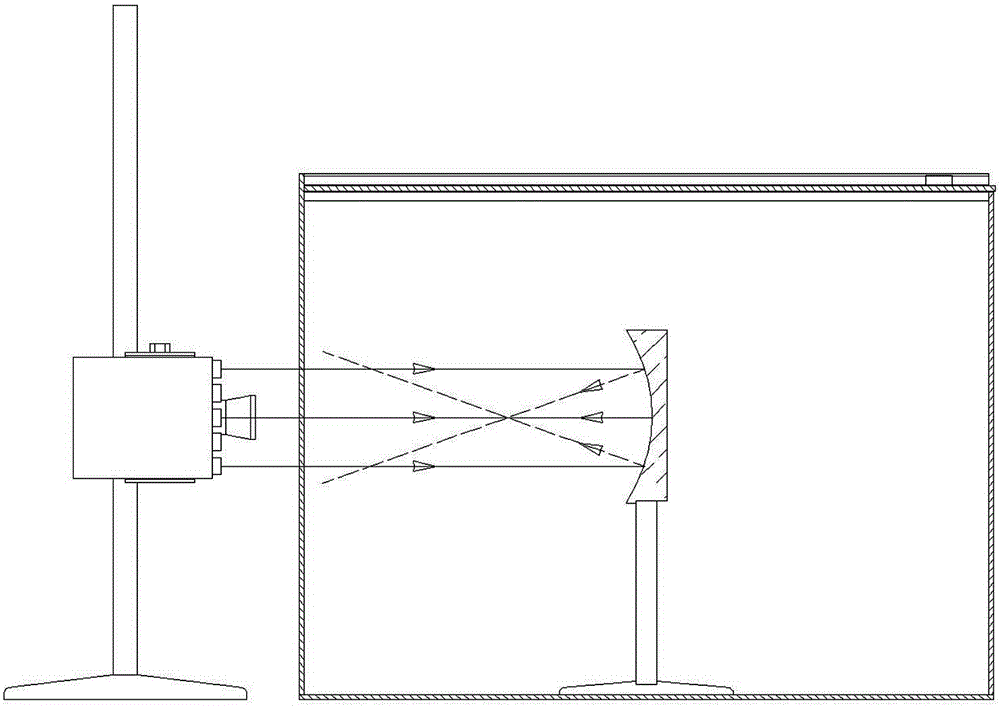
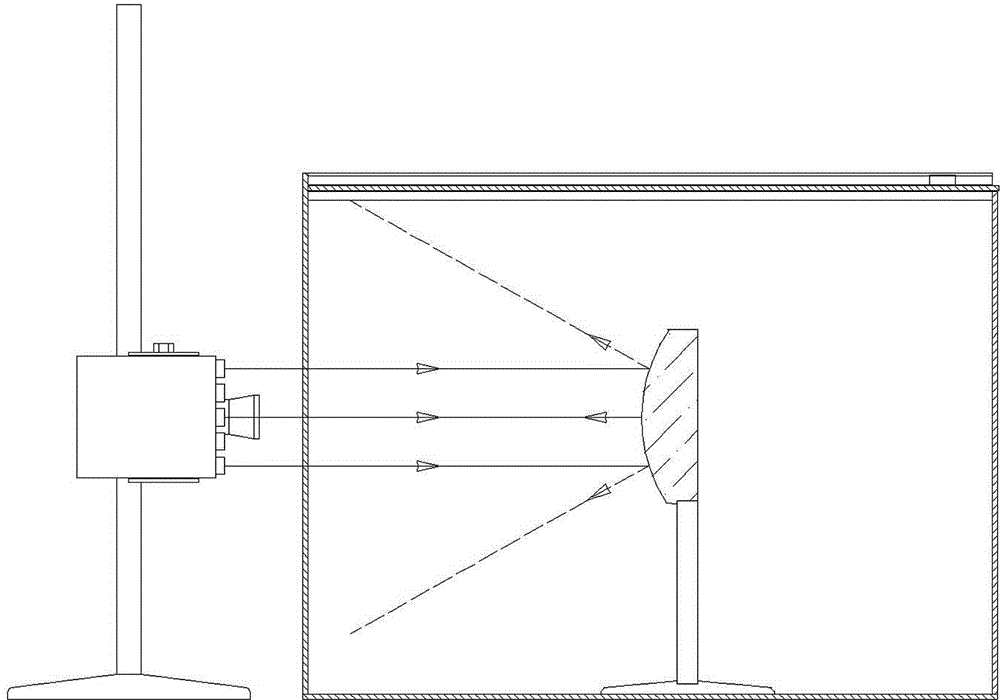
Geometric-optical comprehensive demonstration instrument
InactiveCN103150955AStrong three-dimensional observation in all directionsEasy to operateEducational modelsPlane mirrorEngineering
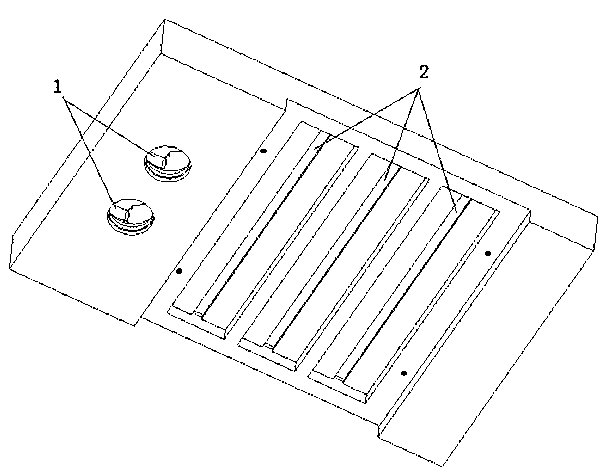
The invention relates to a geometric-optical comprehensive demonstration instrument comprising a box body (10) of an optical path display box, a chassis (1) of a laser source and an element group, wherein the upper ends of a front plate and a back plate of the box body (10) are provided with slide rails (7) and an upper cover (8); the chassis (1) is provided with a vertical rod (4), a regulating seat (3) capable of moving along the vertical rod up and down is arranged on the vertical rod (4) and is provided with a laser source fixing seat (5), a laser pen (6) is fixedly arranged on one end of the fixing seat (5), and a laser box (2) is arranged on the other end of the fixing seat (5); and the element group comprises a lens support (11), a convex and concave mirror (12), a plane mirror (13), an angle board (14), a concave mirror (15), a convex mirror (16), a convex lens (17) and a triangular prism (18). According to the technical scheme of the invention, the geometric-optical comprehensive demonstration instrument can carry out demonstration of different kinds according to different teaching contents and has the advantages of clear and bright demonstration light path, strong third dimension comprehensive observation, convenience in operation and the like.
Owner:孟钧
Method for simulating light scattering property of ice crystal particle
ActiveCN110455689AImprove inversion accuracyScattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisRefractive indexCloud particle
The invention discloses a method for simulating light scattering property of ice crystal particle. By the method, the problem that bubbles and impurity in the ice crystal particle in the prior art arenot considered to cause insufficient inversion accuracy. The method comprises the steps of building an ice crystal particle model; randomly adding a bubble and / or impurity model in the model, and adjusting conductivity and refractive index of the bubble and impurity model; calculating a scattering function and a scattering matrix by an approximate optical approximation method scattering program;calculating radiation values of an absorption channel and a non-absorption channel of a satellite sensor, cloud optical thickness and ice cloud particle effective radius by a RSTAR radiation transmission mode; building a lookup table according to the radiation values of the absorption channel and the non-absorption channel, the cloud optical thickness, the ice cloud particle effective radius and the ice cloud particle effective radius; and calculating the cloud optical thickness and cloud particle effective radius according to the radiation values observed by satellite and according to the lookup table. By the method, the inversion accuracy of the cloud particle effective particle and the cloud optical thickness is remarkably improved.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Inspector for surface deficiency of silicon sheet with scattered light intensity doubling system
InactiveCN1712945AAvoid interferenceEasy to collectMaterial analysis by optical meansIn planeOptical axis
A detector of detect on silicon wafer surface is featured as forming multiplier system of scattering light intensity by the first and the second spherical mirrors with a light trap and on a light axis regulating frame, presenting light axis of defect scattering light collection system in included angle beta to normal of silicon wafer to be detected and moving detected silicon wafer in plane and in rotation by operation table to let two spherical mirrors, trap and planar reflector satisfy to object - image relation of geometrical optics.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Practical leaf area index remote sensing inversion method
The invention discloses a practical leaf area index remote sensing inversion method. According to the method, a lookup table is built in a simulation manner on the base of a geometrical optics model, then, an LAI inversion model is built, a variable end element spectral mixing model is used in cooperation, and finally, the LAI inversion result is obtained. The practical leaf area index remote sensing inversion method is completely based on remote sensing images, no field measured LAI data are needed, and therefore, the LAI inversion cost is reduced; calculation is easy and convenient, and the method is a practical LAI remote sensing inversion method.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com