Patents
Literature
30 results about "Ultra low expansion glass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
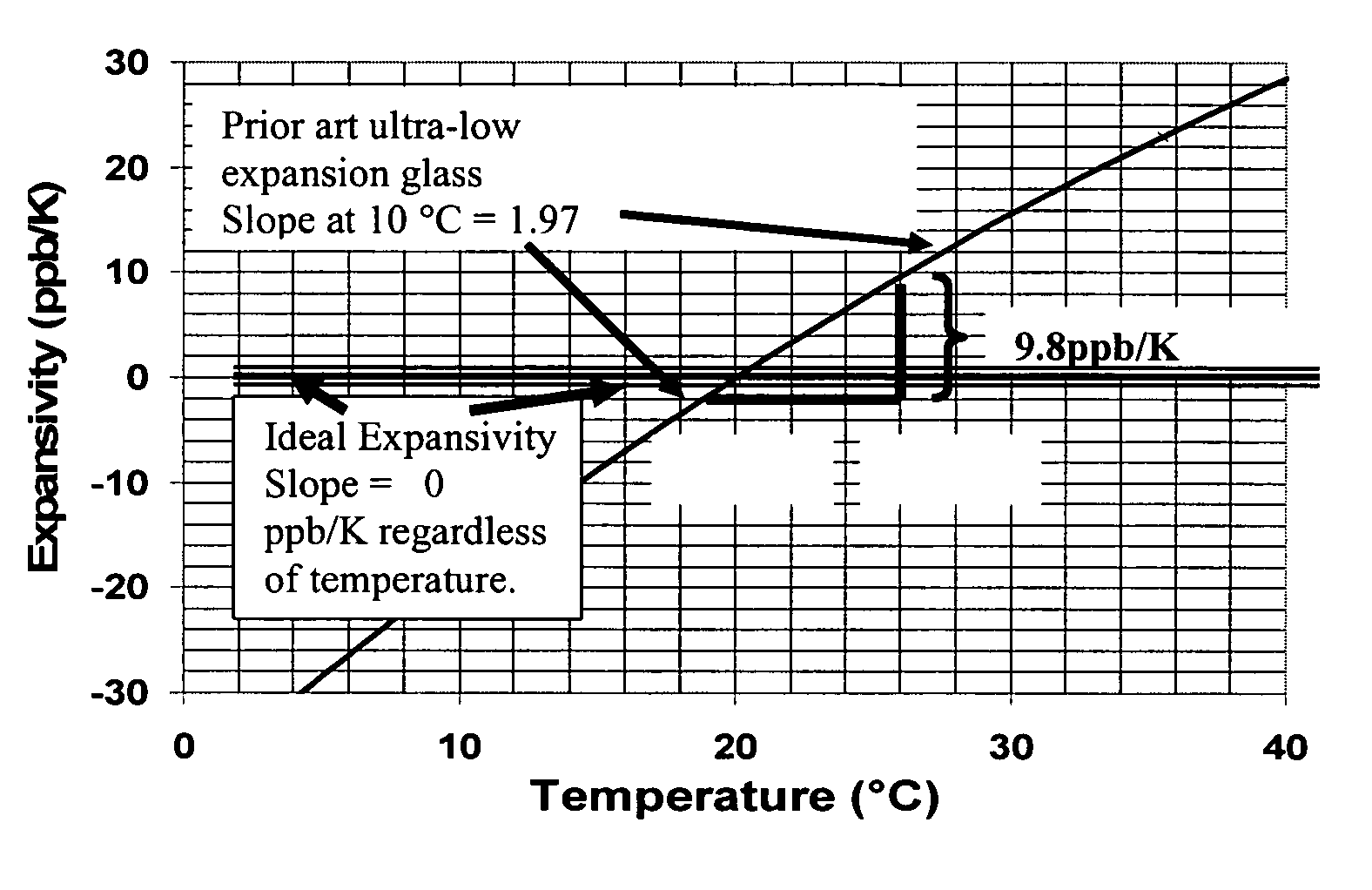
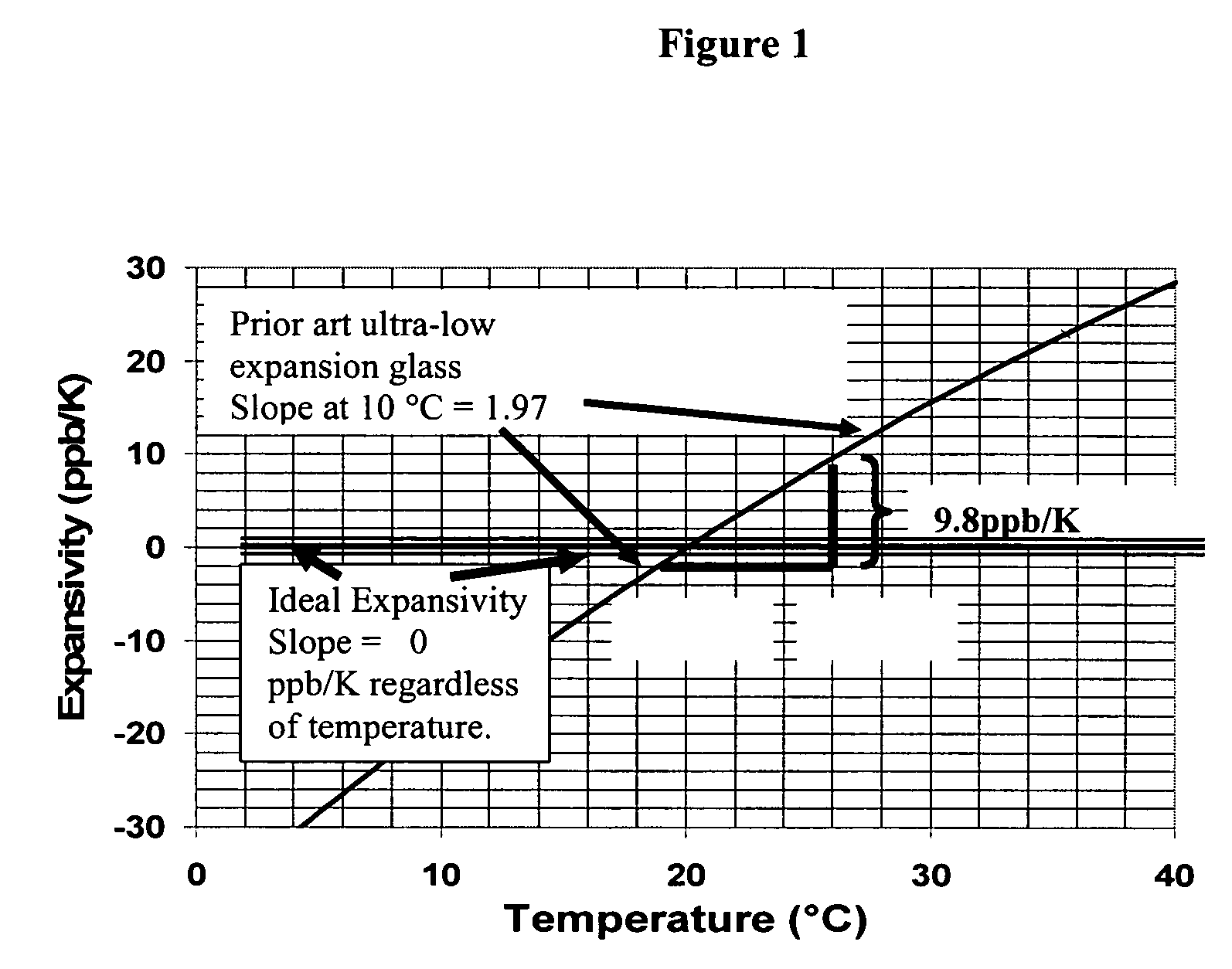
Ultra low expansion glass (ULE) is a registered trademark of Corning Incorporated. ULE has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion and contains as components silica and less than 10% titanium dioxide. Such high resistance to thermal expansion makes it very resistant to high temperature thermal shock. ULE has been made by Corning since the 1960s, but is still very important to current applications.
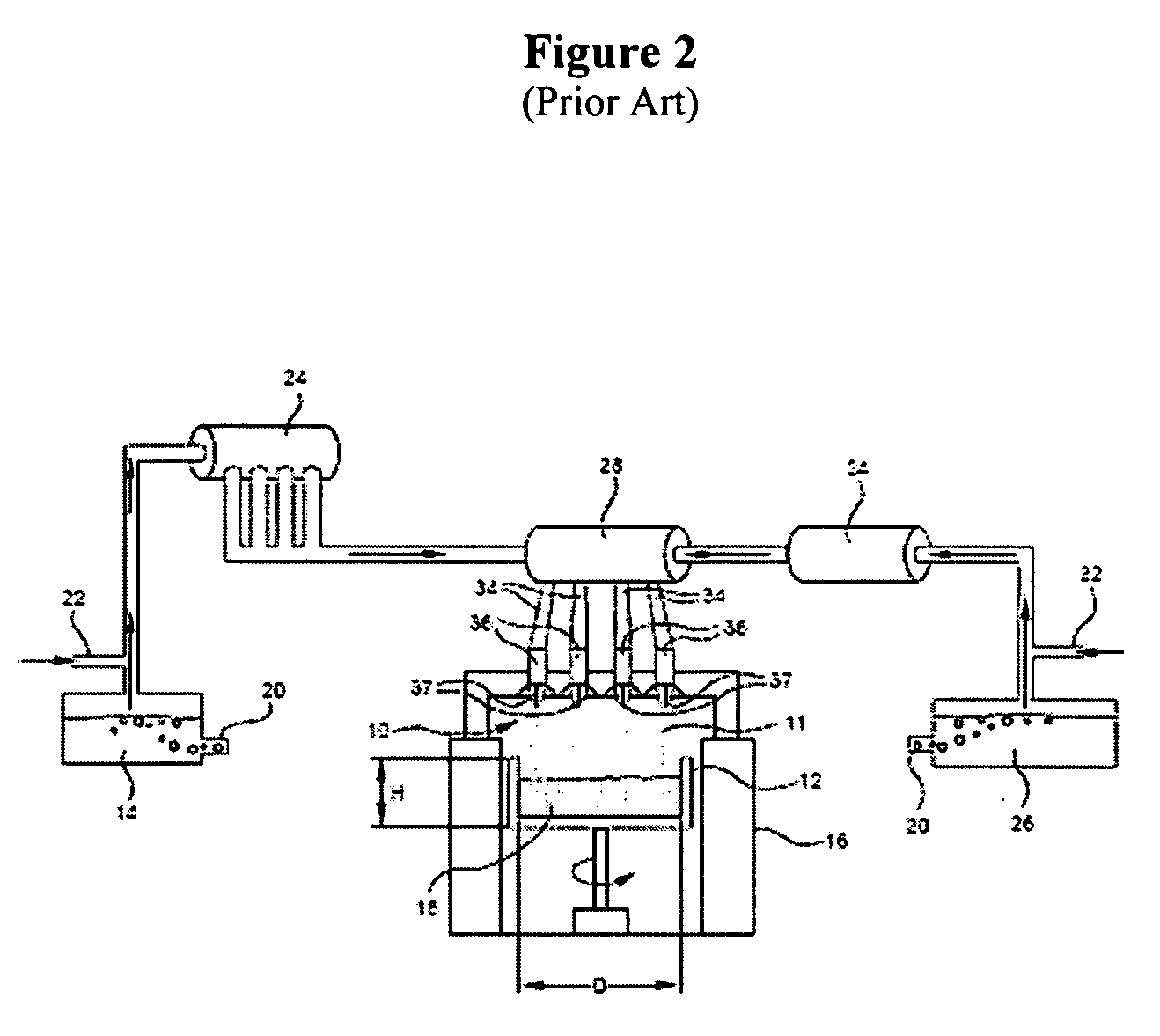
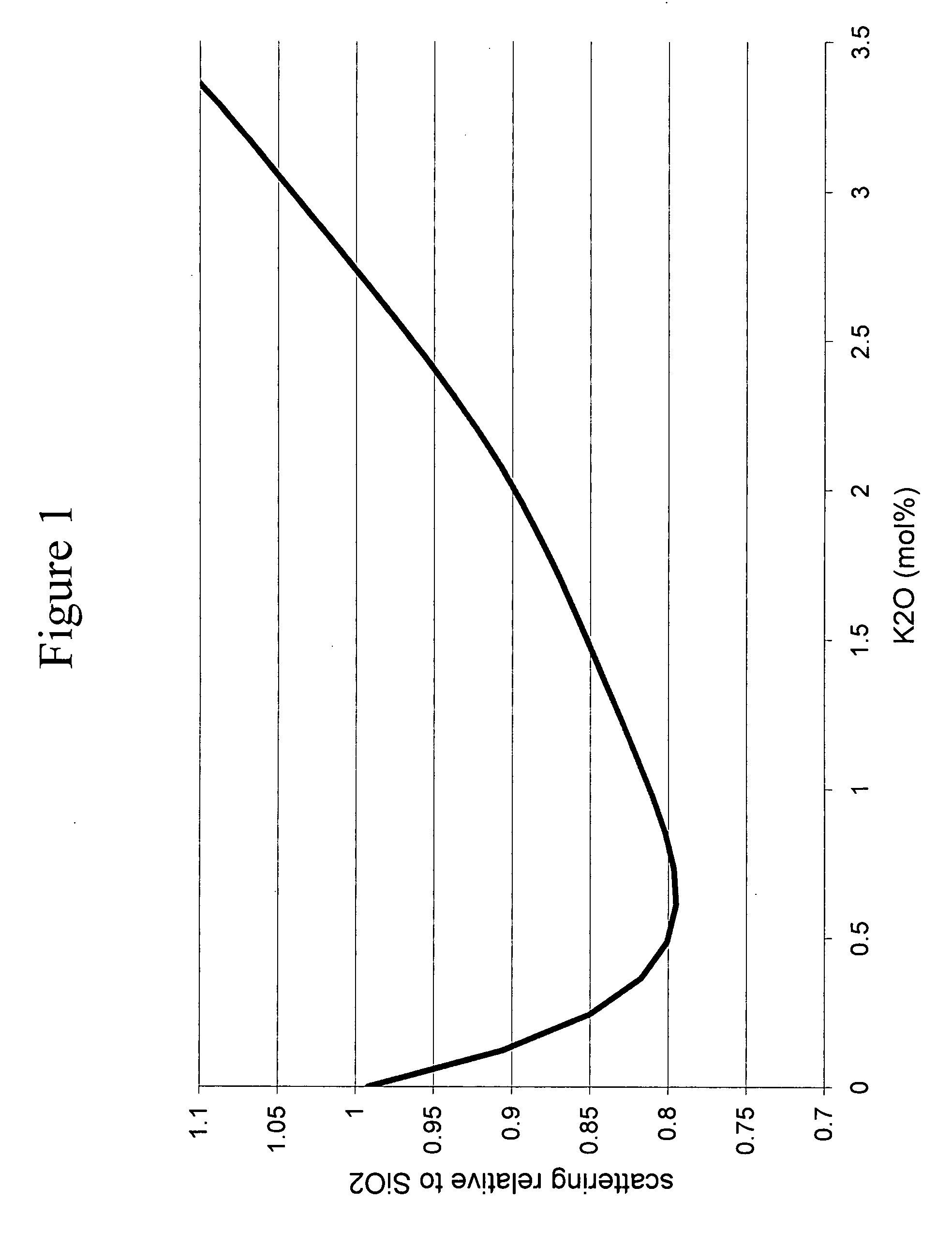
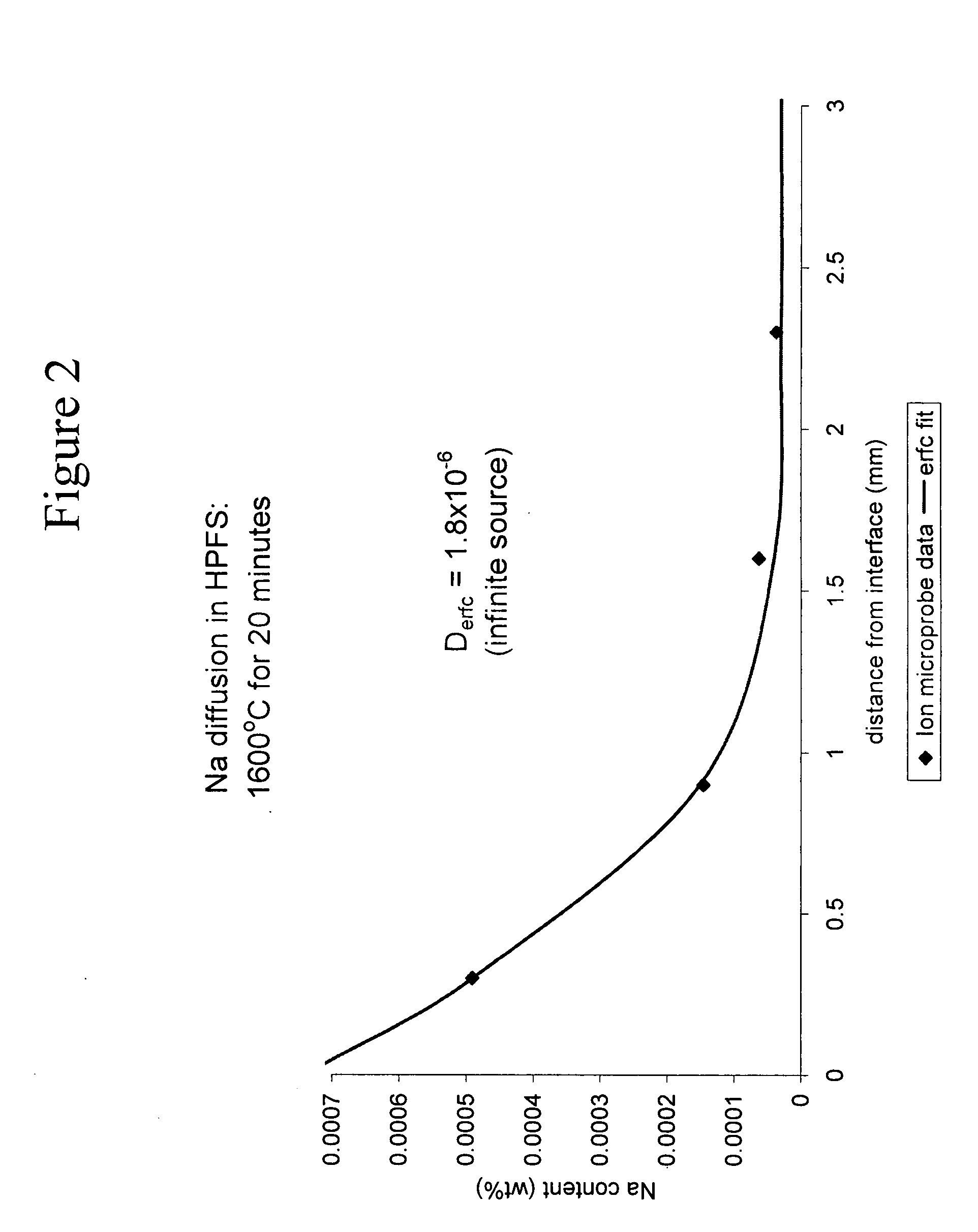
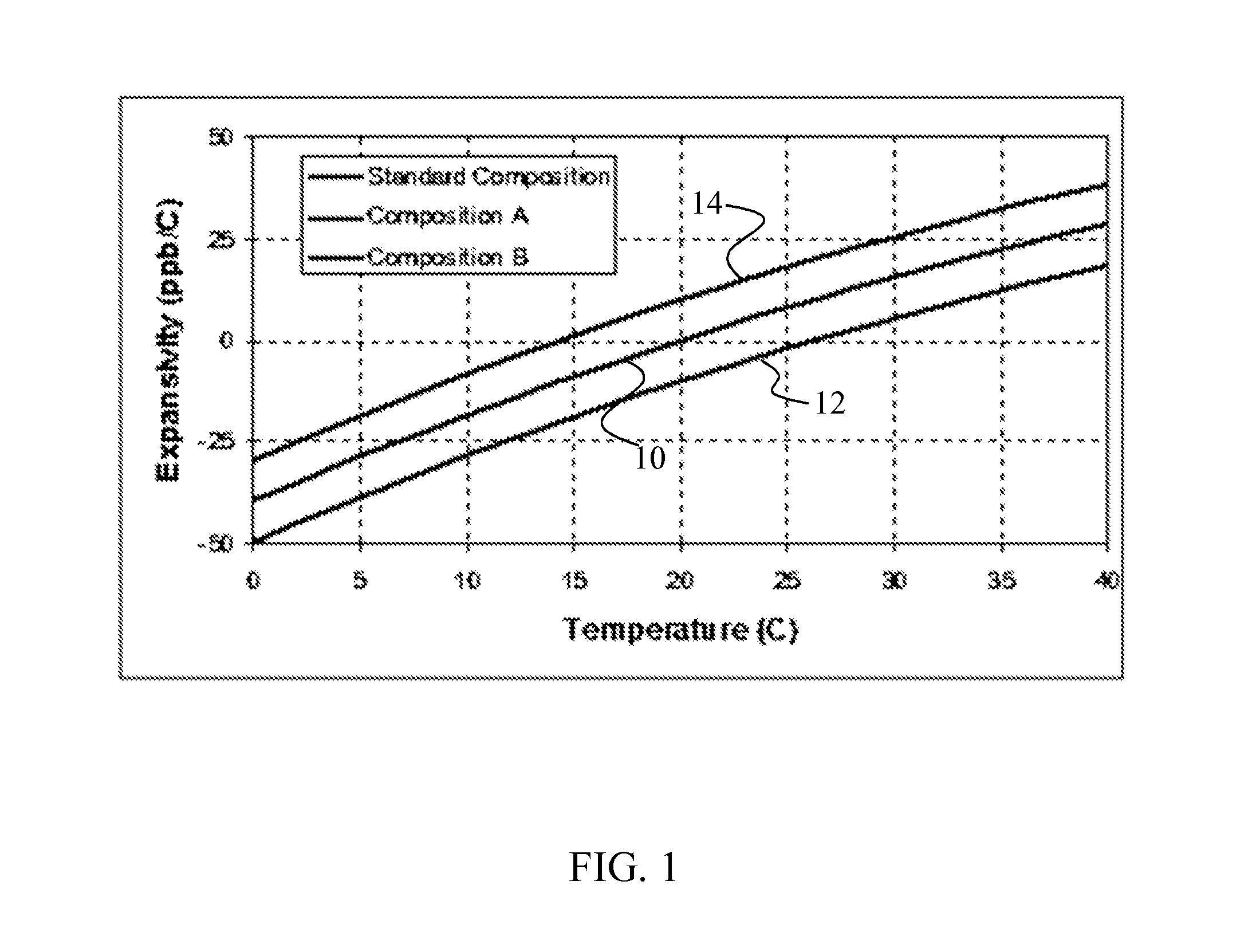
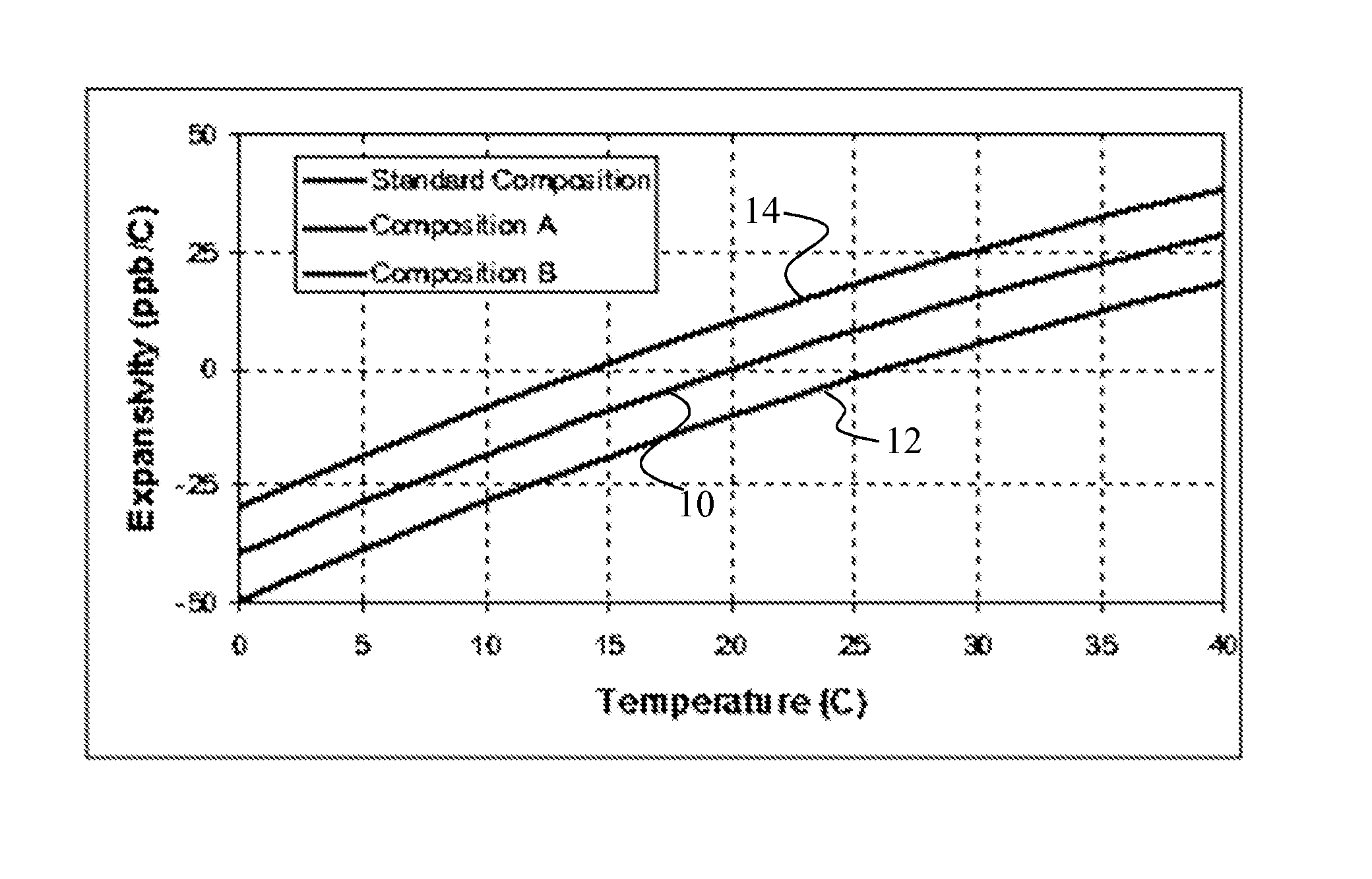
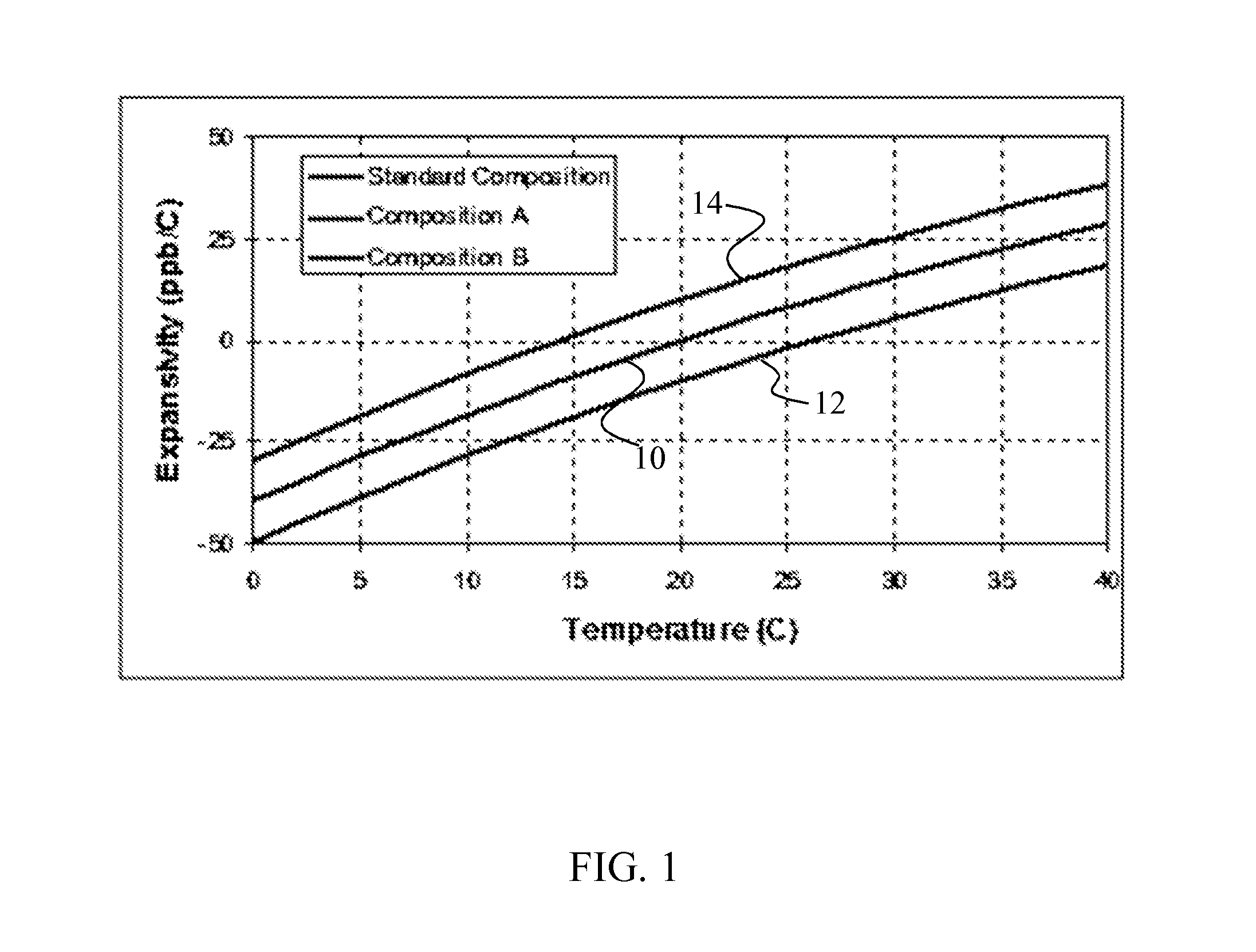
Adjusting expansivity in doped silica glasses
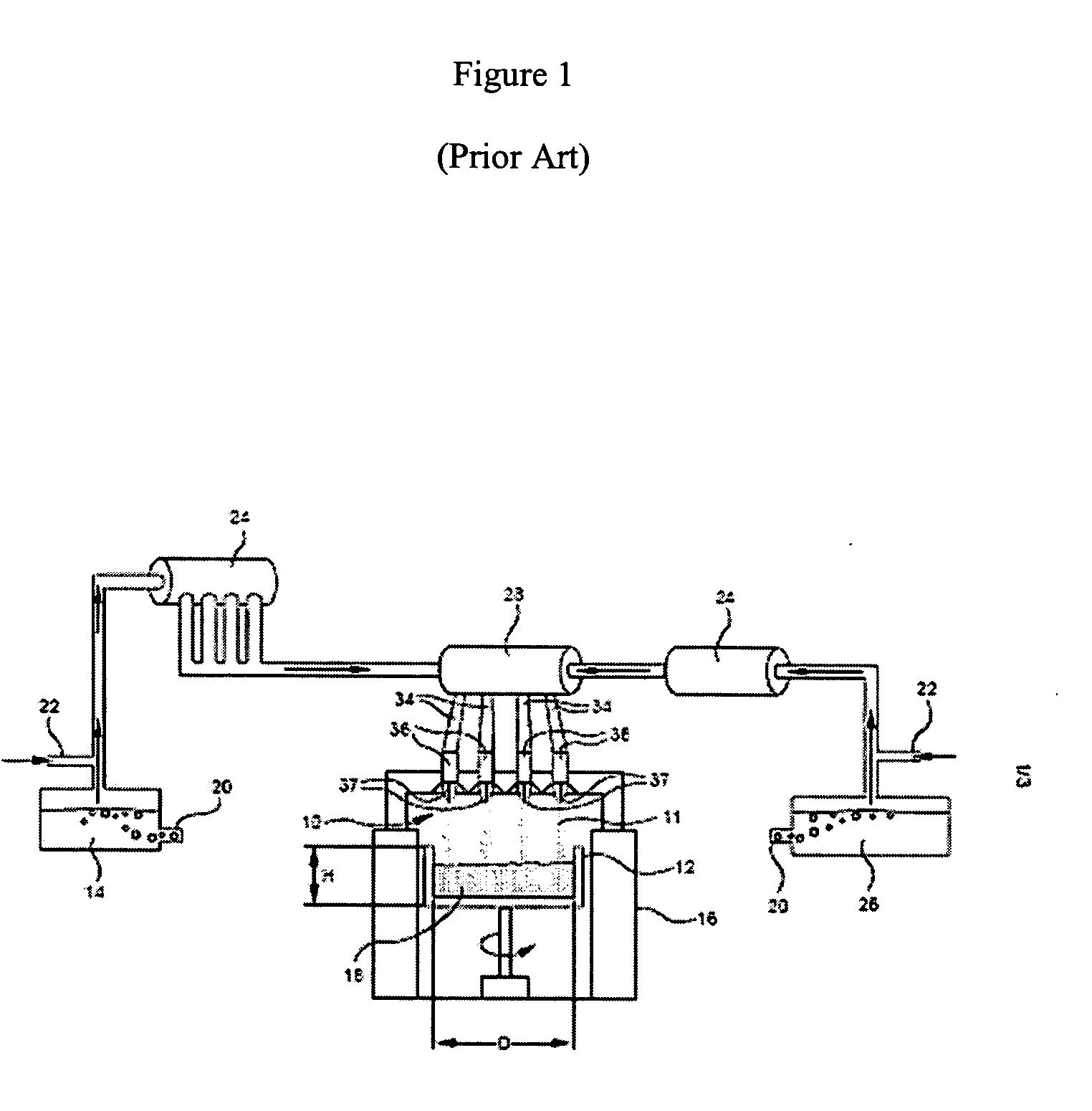
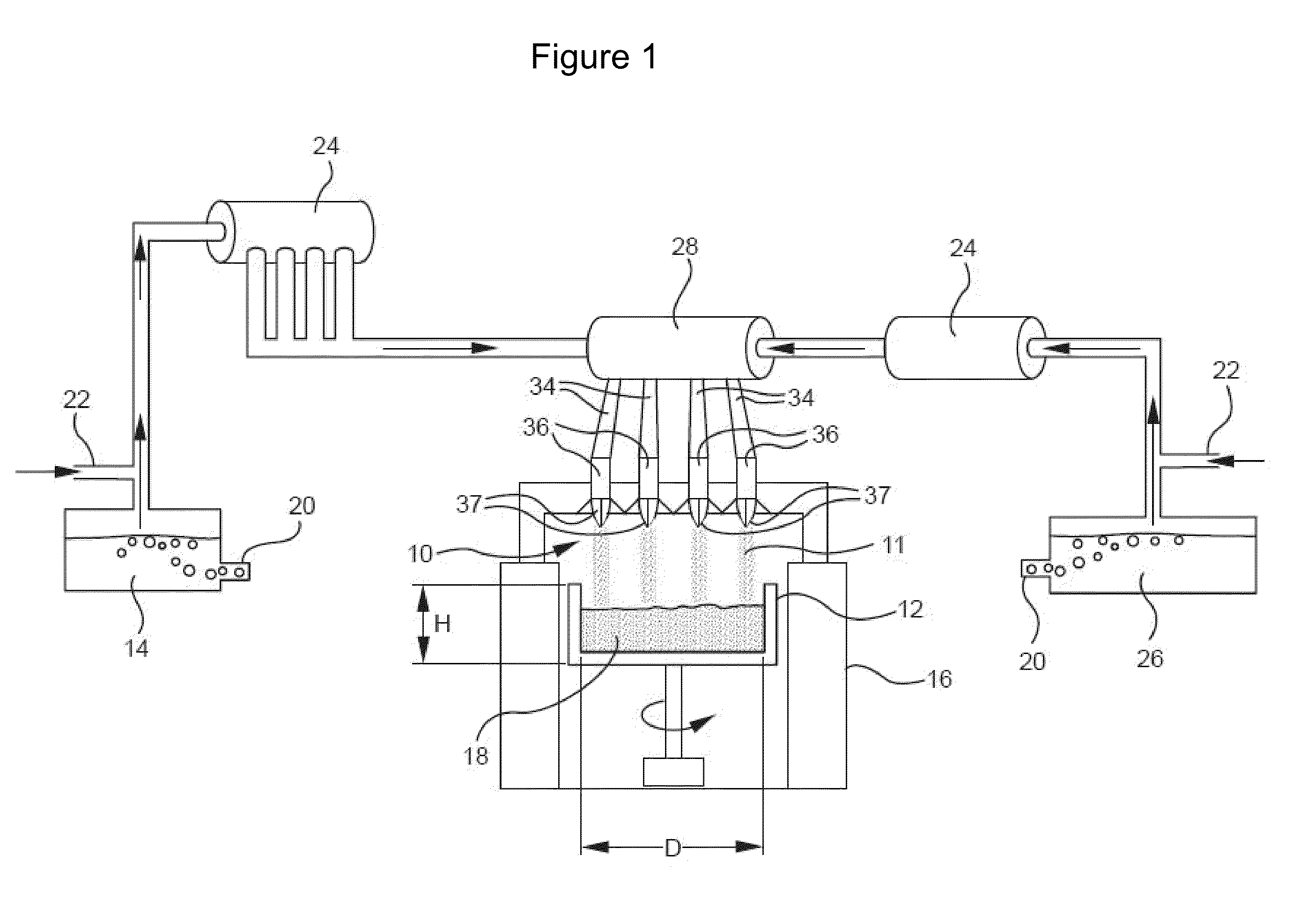
InactiveUS20060179879A1Low viscosityGlass shaping apparatusGlass deposition burnersDopantUltra low expansion glass
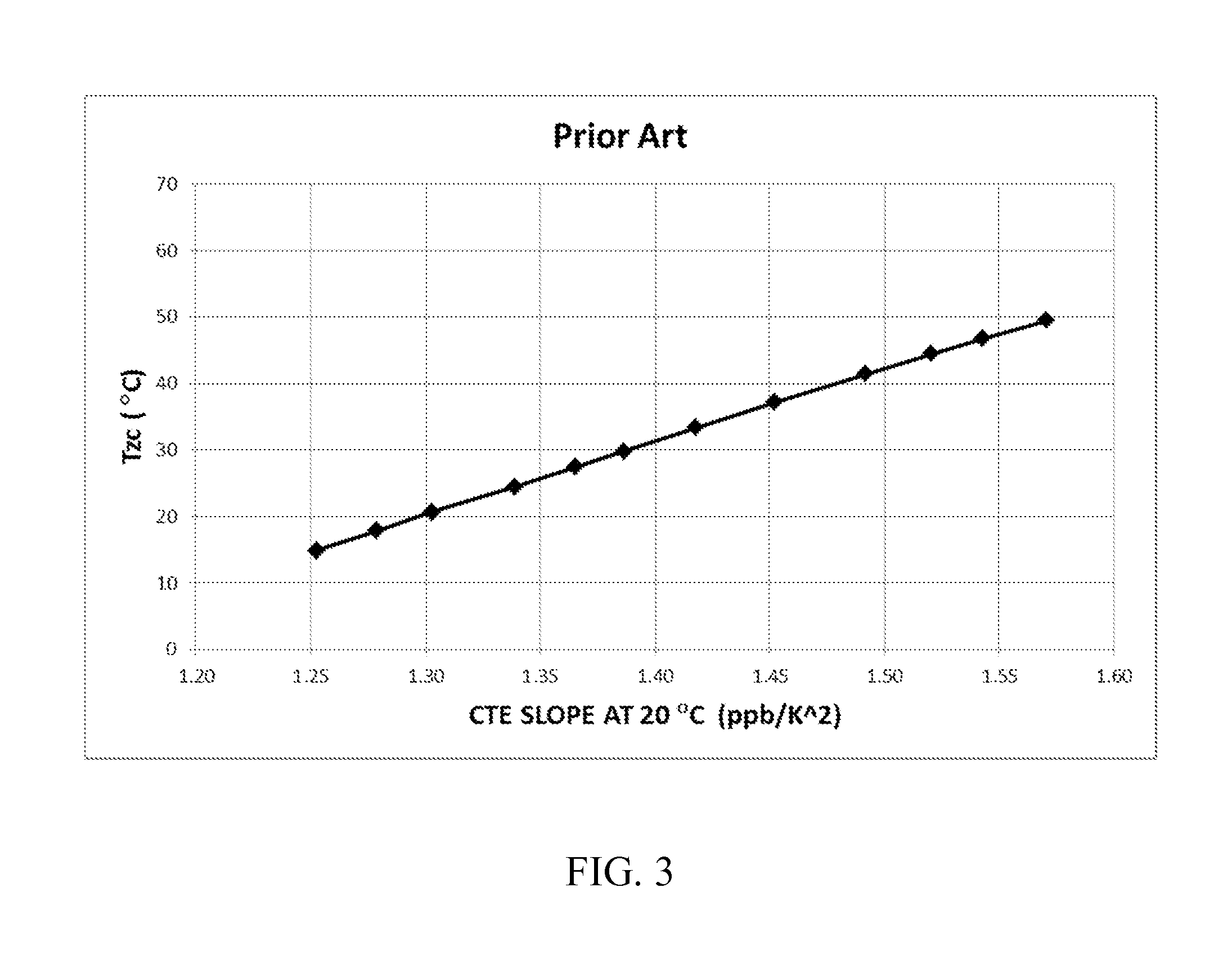
The invention is directed to ultra-low expansion glasses to which adjustments have been made to selected variables in order to improve the properties of the glasses, and particularly to lower the expansivity of the glasses. The glasses are titania-doped silica glasses. The variables being adjusted include an adjustment in β-OH level; an adjustment to the cooling rate of the molten glass material through the setting point; and the addition of selected dopants to impact the CTE behavior.
Owner:CORNING INC
Ultra-low-expansion glass ceramic for laser gyro and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101538118ANo sheddingImprove bindingSagnac effect gyrometersAdditive ingredientTransmittance
The invention provides an ultra-low-expansion glass ceramic for a laser gyro and a preparation method thereof, wherein, the ultra-low-expansion glass ceramic includes the following ingredients according to mass percentages: 56-68% of SiO2, 21-27% of Al2O3, 2-4% of Li2, 0-1% of Na2, 0-1% of K2, 0-3% of MgO, 0-1.5% of ZnO, 4.5-6.8% of P2O5, 1-2.5% of TiO2, 1-2.5% of ZrO2 and 0.5-1.5% of Sb2O3 / As2O3; the principal crystalline phase is beta quartz solid solution; the crystalline phase content is 70-85%; the grain size is lower than 50nm; and the magnitude order of coefficient of heat expansion is 10<-8>. The preparation method comprises the steps of dosing, mixing, melting, evening, clarifying, glass moulding, annealing and sitallization heat treatment, wherein, the steps of melting, evening and clarifying are carried out at 1570-1590 DEG C; the sitallization heat treatment comprises the steps as follows: the materials are crystallized after 6-10 hours of warm keeping at nucleating temperature of 650-750 DEG C with crystallizing rate of 1 DEG C / min; the crystallizing temperature is 750-850 DEG C; and the warm-keeping time is 6-10 hours. The buckling strength of the ultra-low expansion glass ceramic is higher than 170MPa; the process roughness is higher than 2-star; and the spectrum transmittance is more than 90% within the waveband of 0.6-2mum. In addition, the ultra-low-expansion glass ceramic has excellent hardness and abrasion resistance.
Owner:SINOMA SYNTHETIC CRYSTALS CO LTD +1
Ultra low expansion glass and methods for making
InactiveUS20080004169A1Decreasing viscosity of glassReduce the amplitudeOptical elementsDopantSilica gel
A low expansion silica-titania glass suitable for making extreme ultraviolet lithographic element, with the titania-containing silica glass having a titania content in the range of 5-10 wt. % and a including a further constituent of a viscosity reducing dopant having a content in the range of 0.001 to 1 wt %.
Owner:CORNING INC
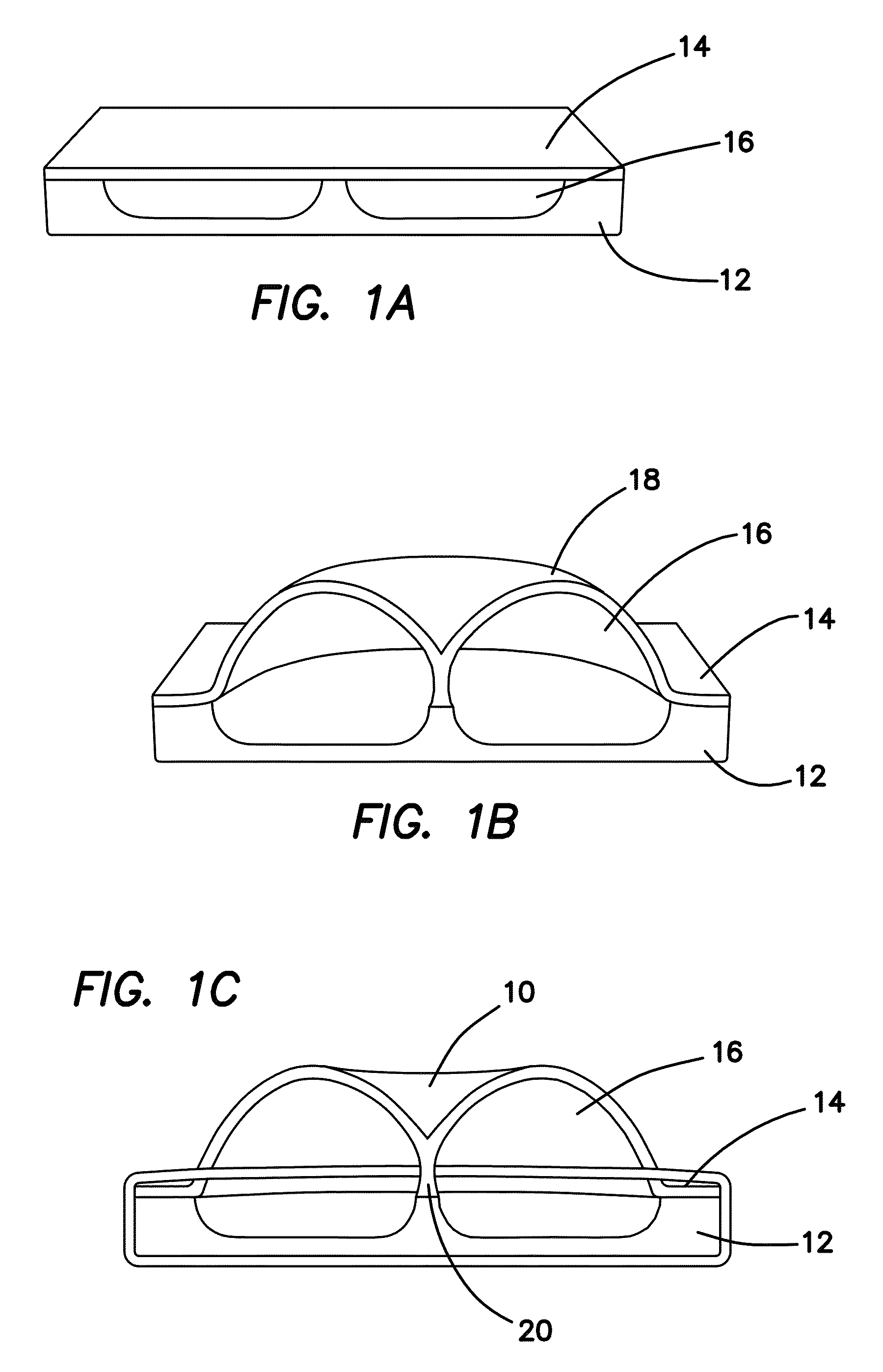
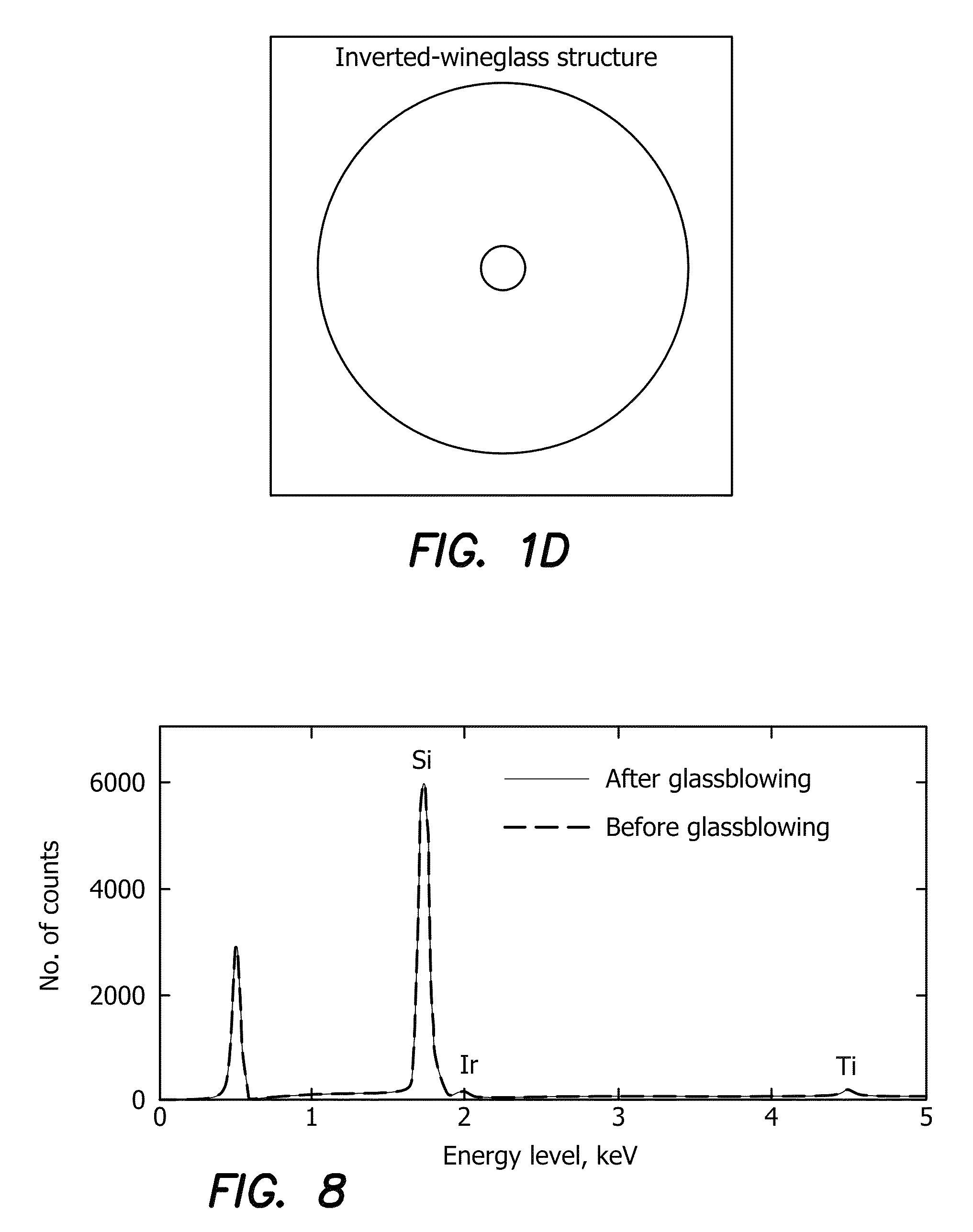
Microfabrication of High Quality Three Dimensional Structures Using Wafer-Level Glassblowing of Fused Quartz and Ultra Low Expansion Glasses
ActiveUS20140021561A1Improve performanceHigh symmetryDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingMicrofabrication
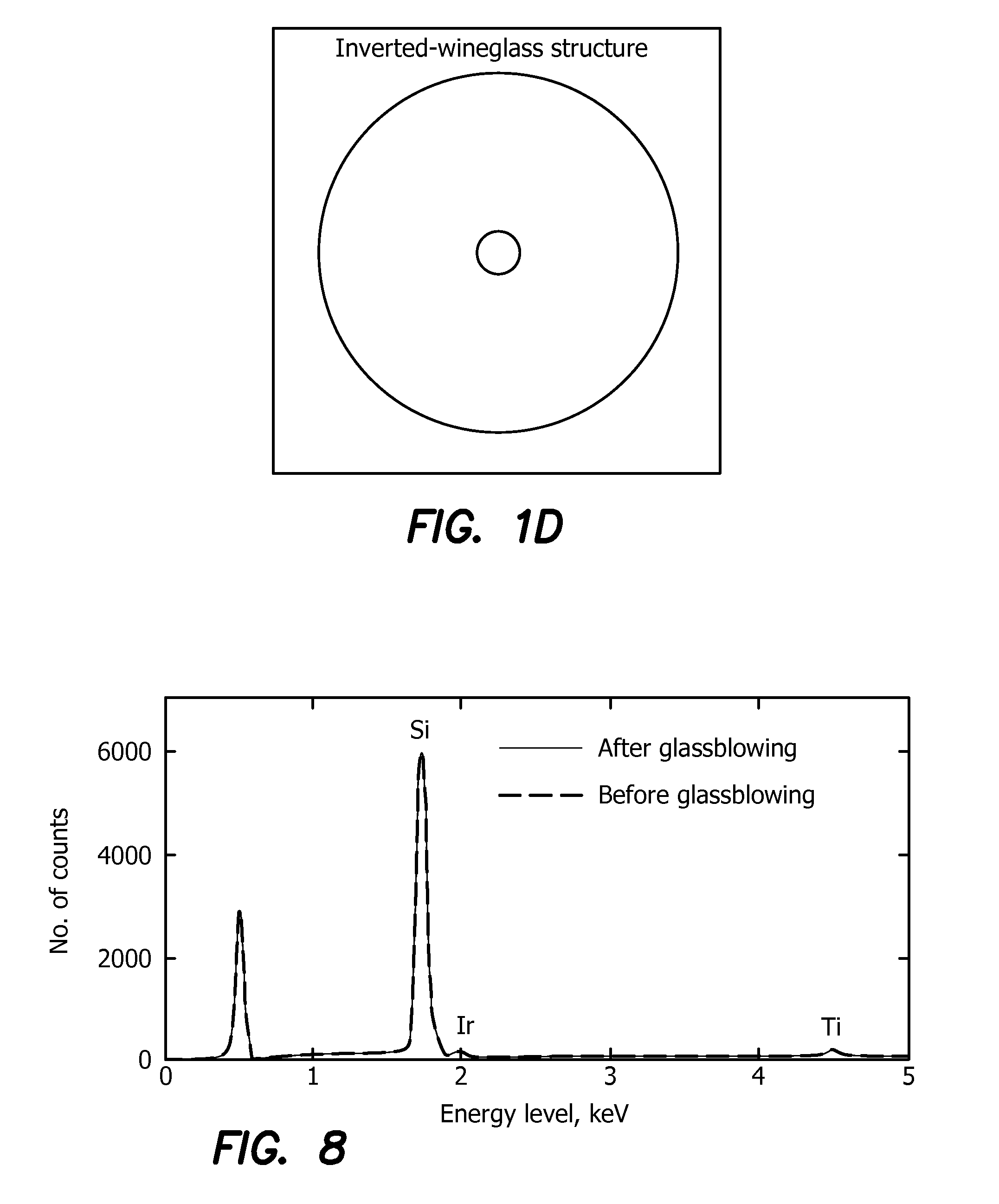
A high temperature micro-glassblowing process and a novel inverted-wineglass architecture that provides self-aligned stem structures. The fabrication process involves the etching of a fused quartz substrate wafer. A TSG or fused quartz device layer is then bonded onto the fused quartz substrate, creating a trapped air pocket or cavity between the substrate and the TSG device layer. The substrate and TSG device layer 14 are then heated at an extremely high temperature of approximately 1700° C., forming an inverted wineglass structure. Finally, the glassblown structure is cut or etched from the substrate to create a three dimensional wineglass resonator micro-device. The inverted wineglass structure may be used as a high performance resonator for use as a key element in precision clock resonators, dynamic MEMS sensors, and MEMS inertial sensors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
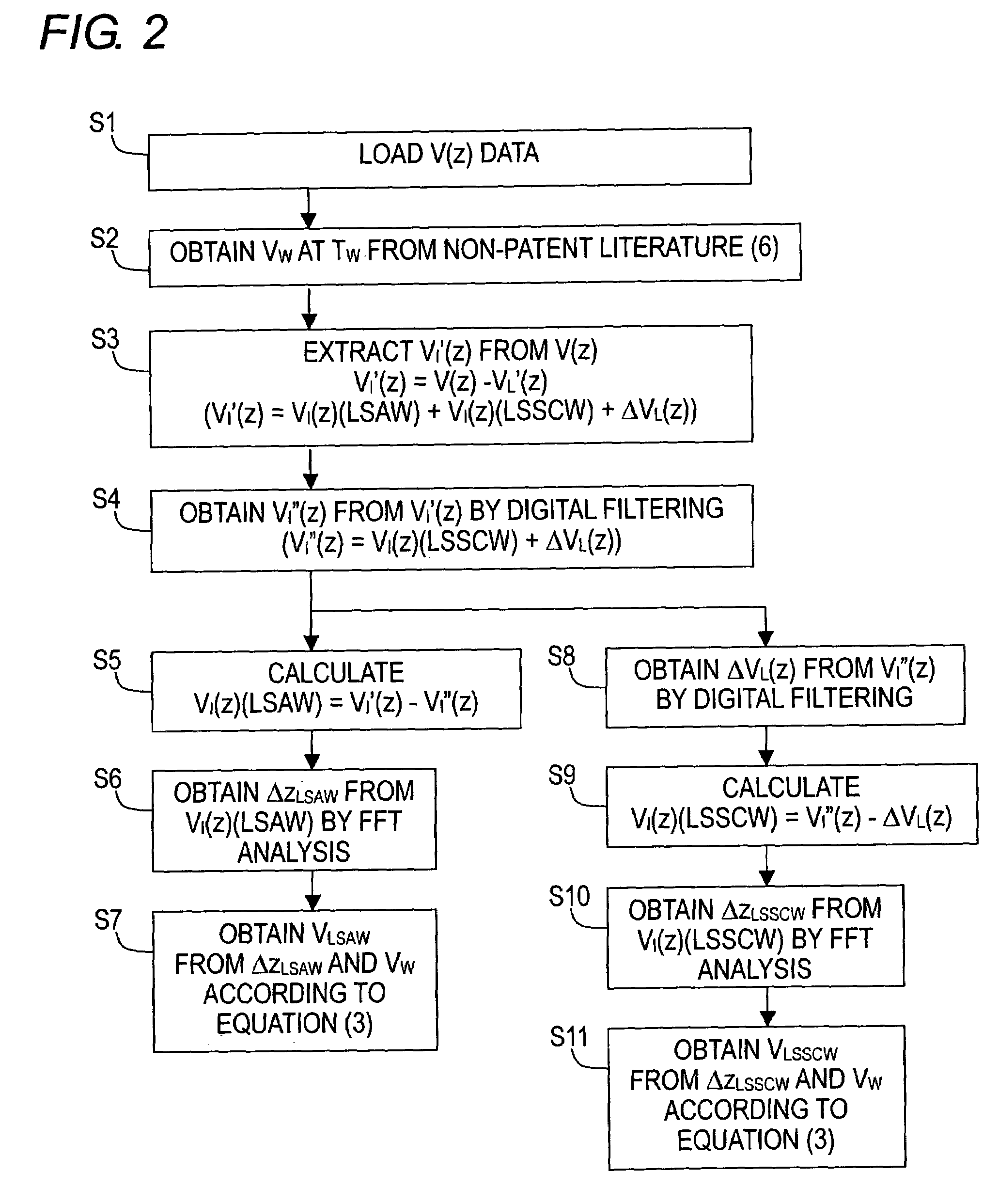
Evaluation method for coefficient of thermal expansion of ultra-low-expansion glass material
InactiveUS20060028096A1Material thermal coefficient of expansionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
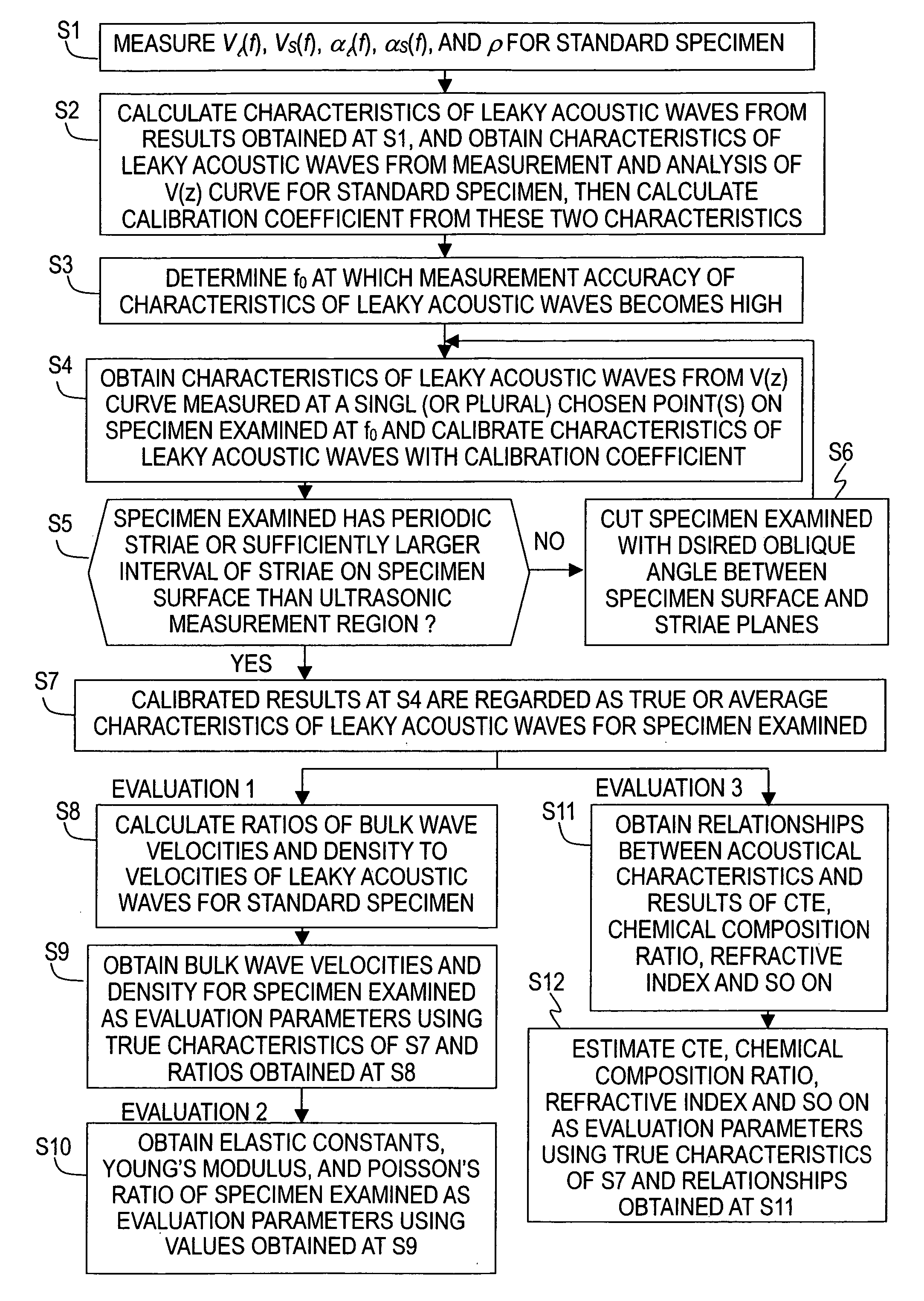
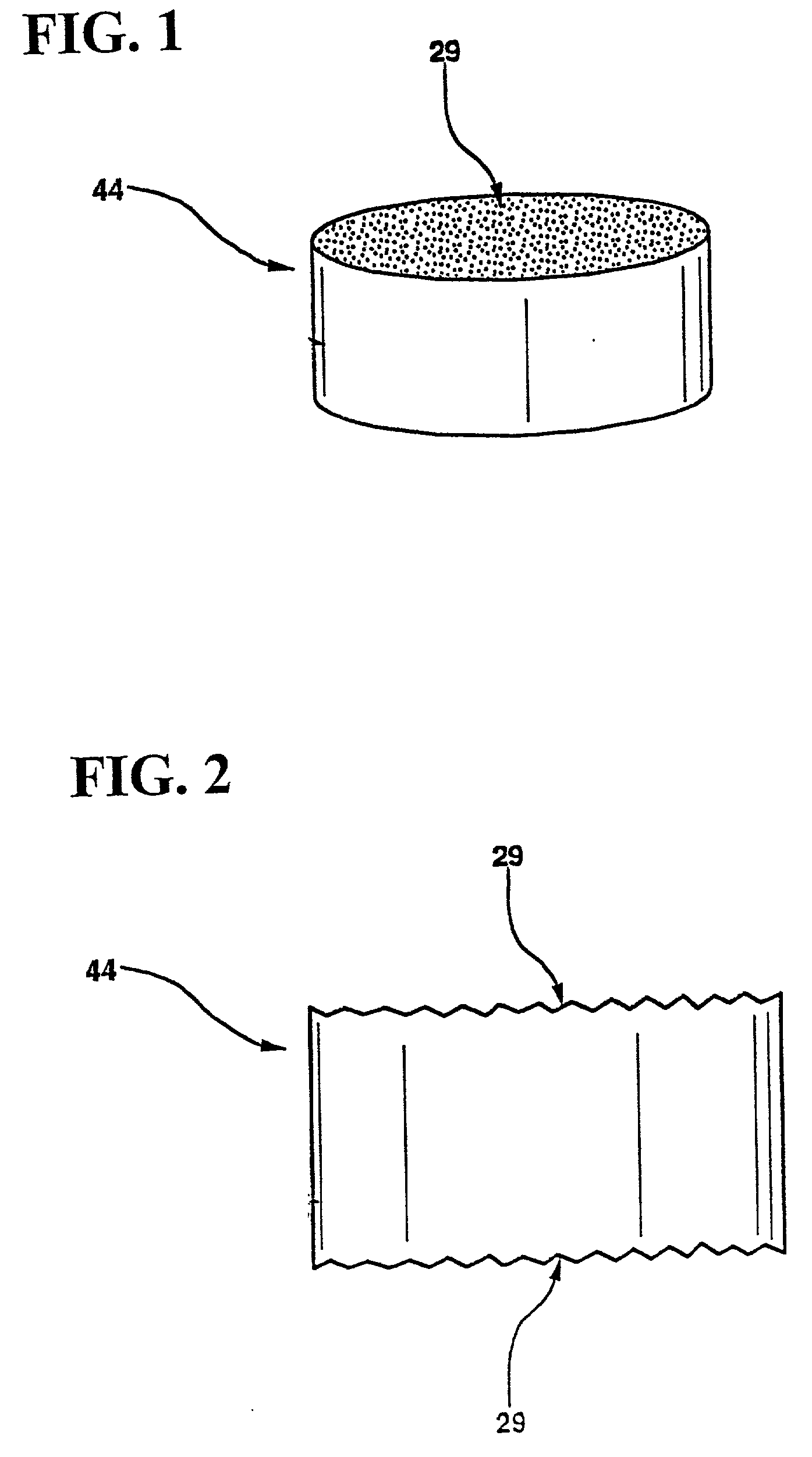
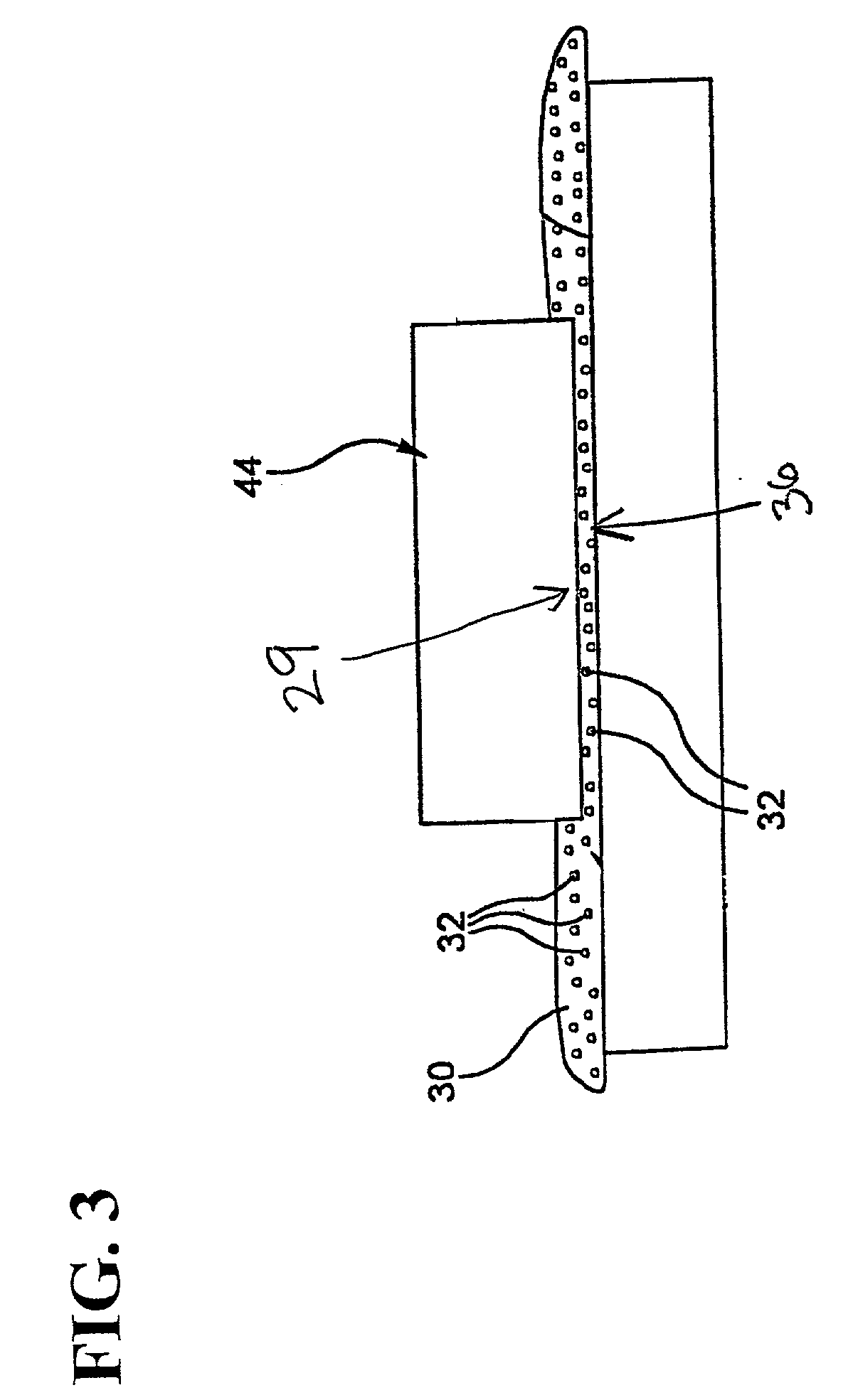
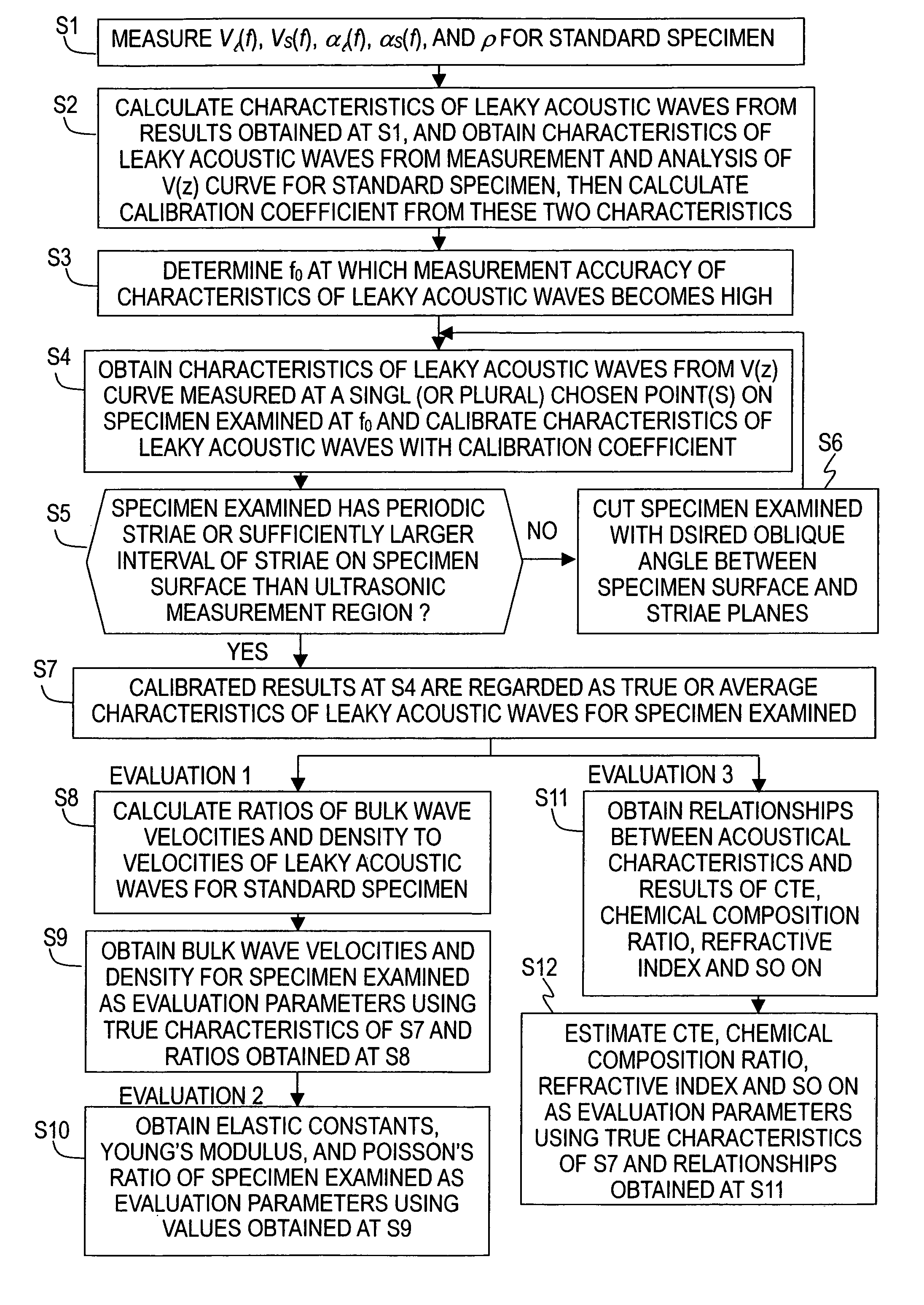
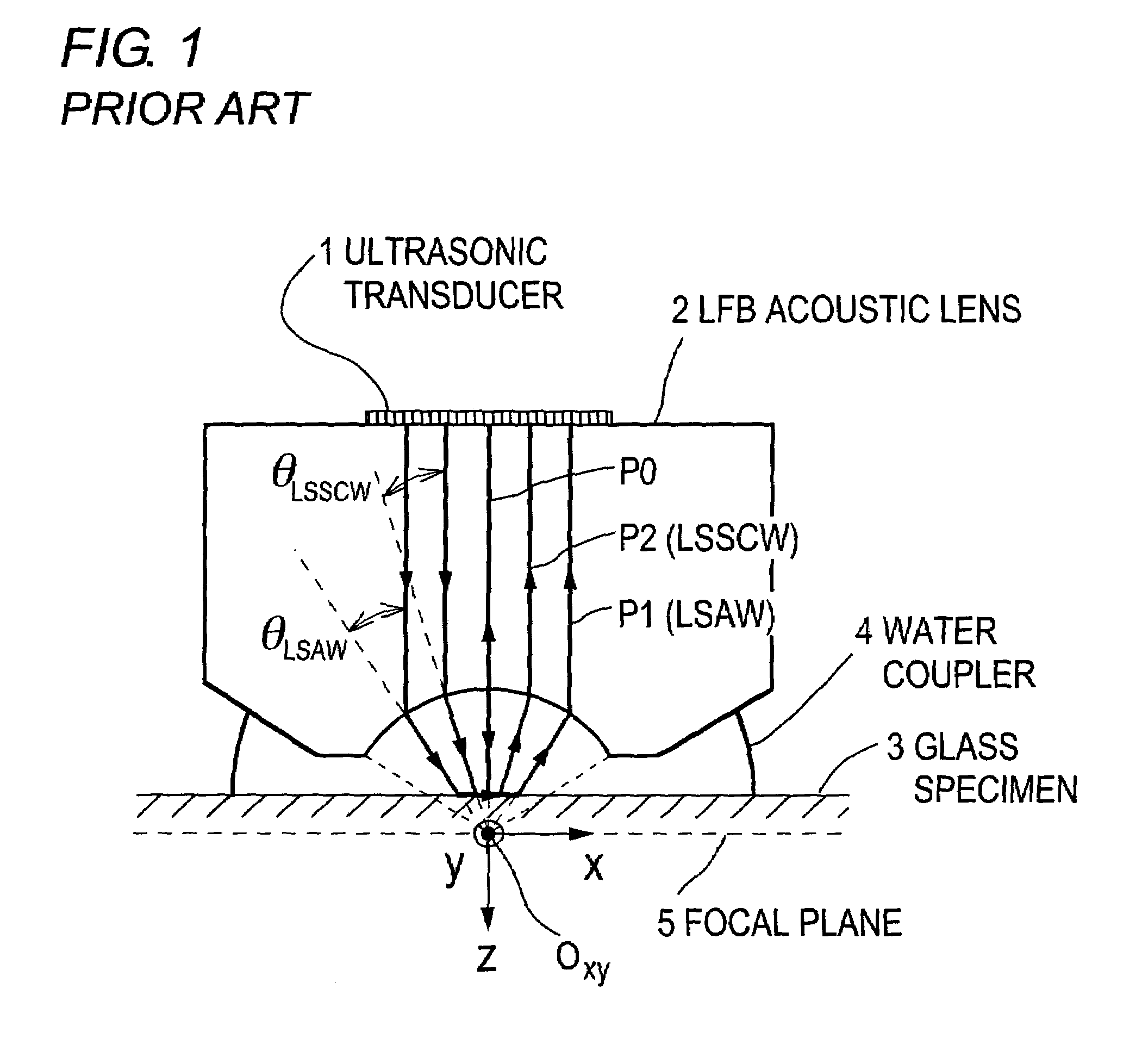
By measuring, for an ultra-low-expansion glass material, the frequency dependence of acoustic velocities and attenuation coefficients of bulk waves (longitudinal waves and shear waves), and the density, its fundamental acoustic properties are revealed, and a standard specimen for use in system calibration is prepared. By an absolute calibration method using the standard specimen, absolute values for both the LSAW and LSSCW velocities are obtained. Moreover, there are obtained relationships for the acoustic properties and the coefficient of thermal expansion to evaluate the coefficient of thermal expansion from the acoustic properties. In case there is a distribution of characteristics due to periodic striae, an accurate acoustic property distribution in the substrate can be ascertained and an evaluation performed, by selecting for the substrate a cutting angle with respect to the striae plane.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV +1
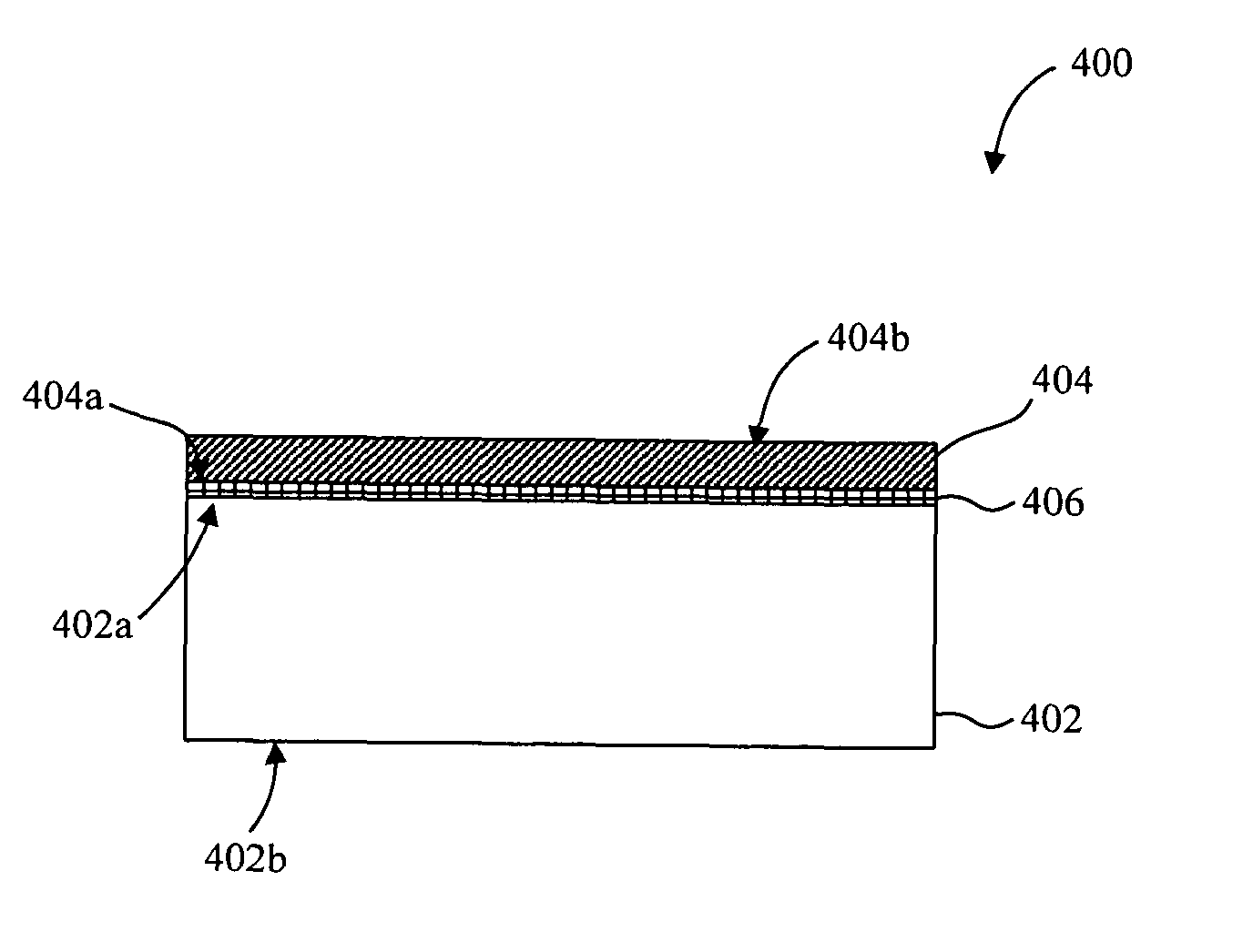
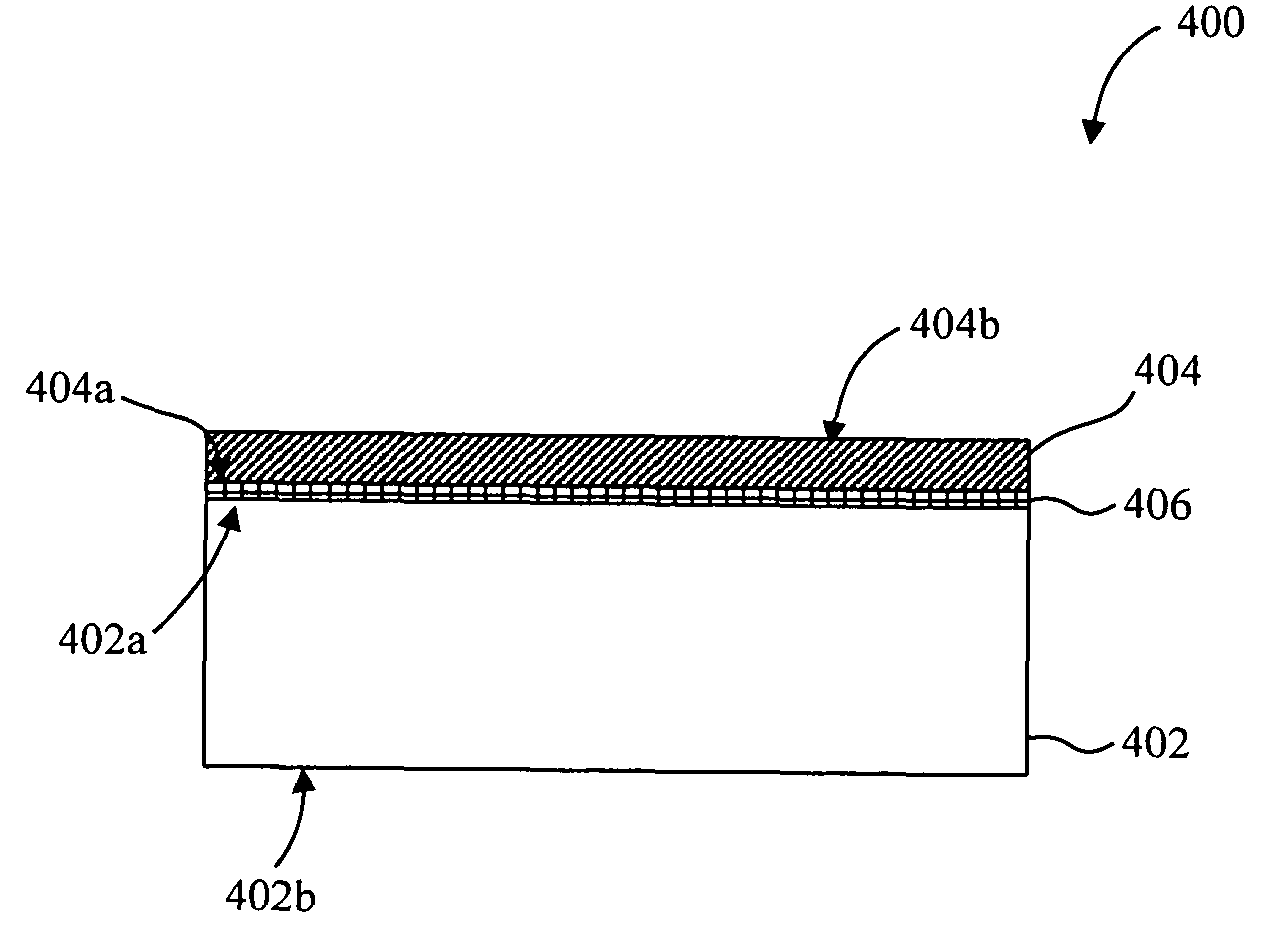
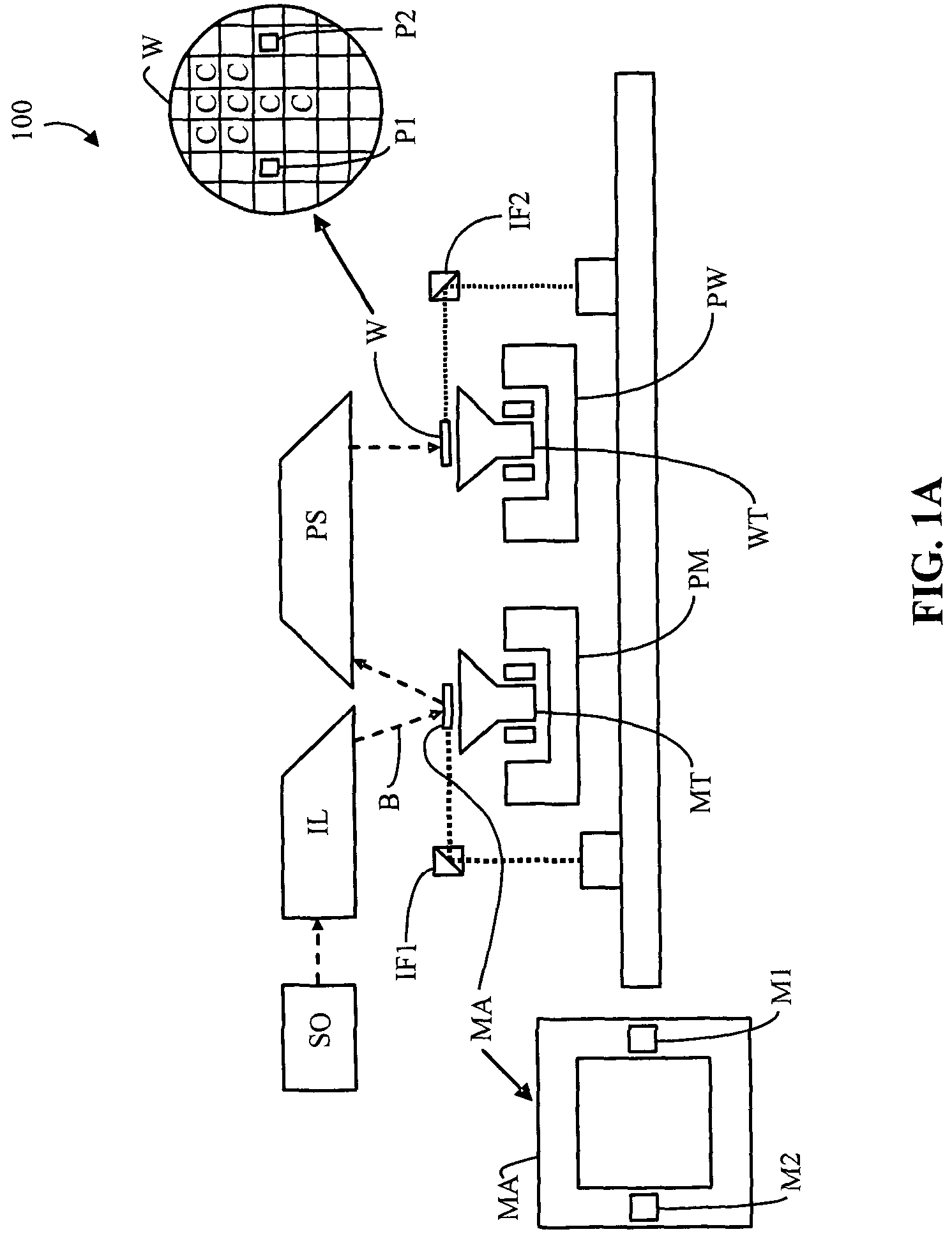
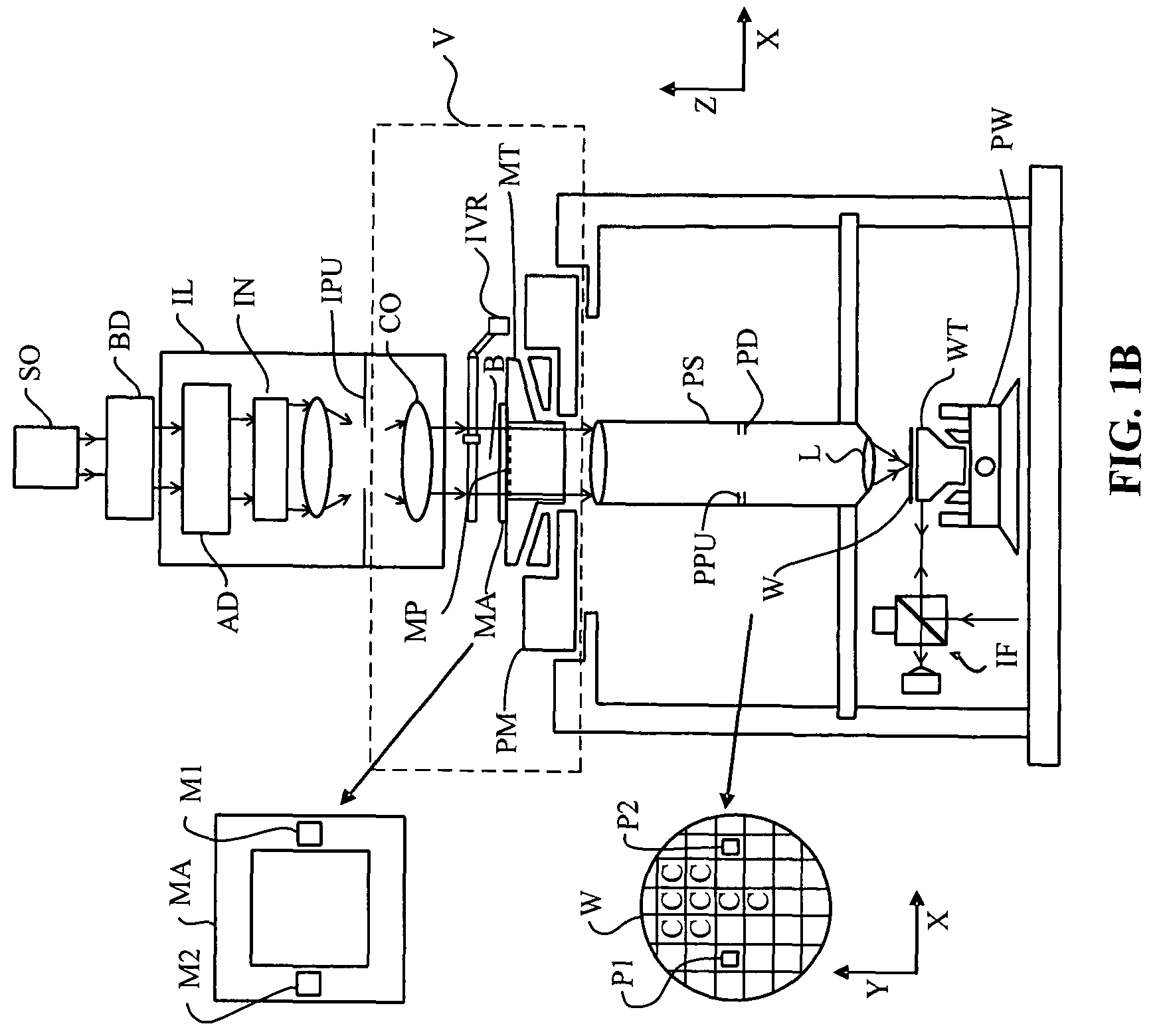
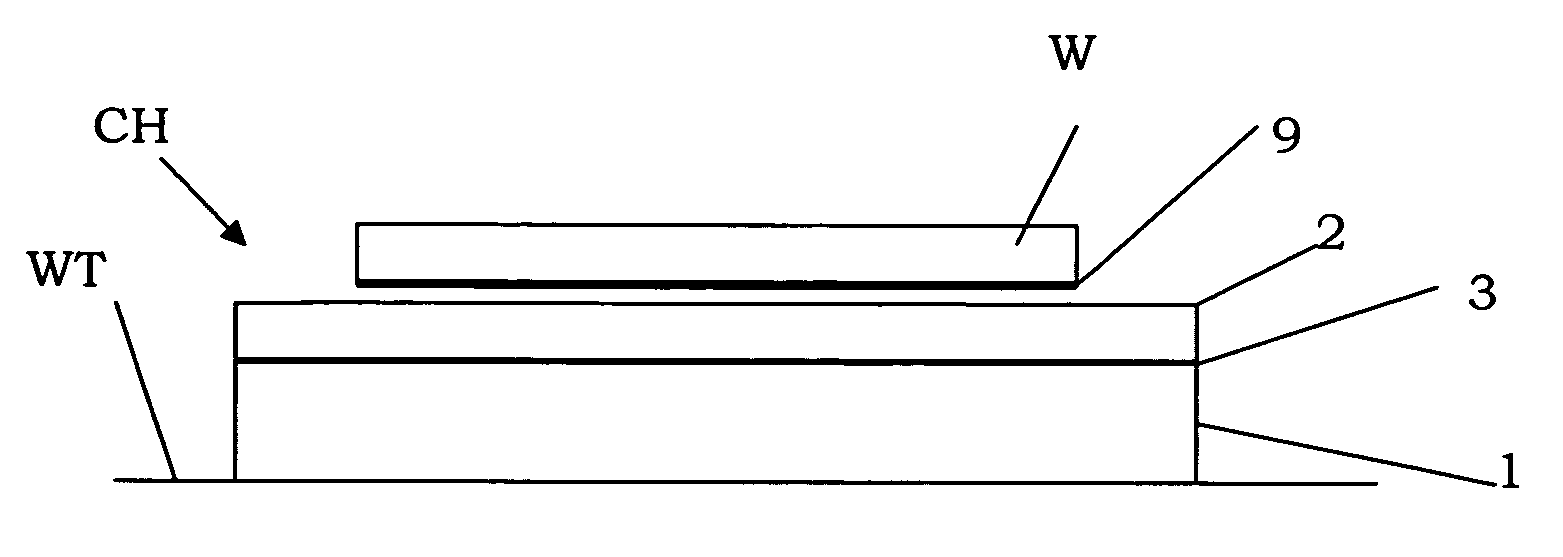
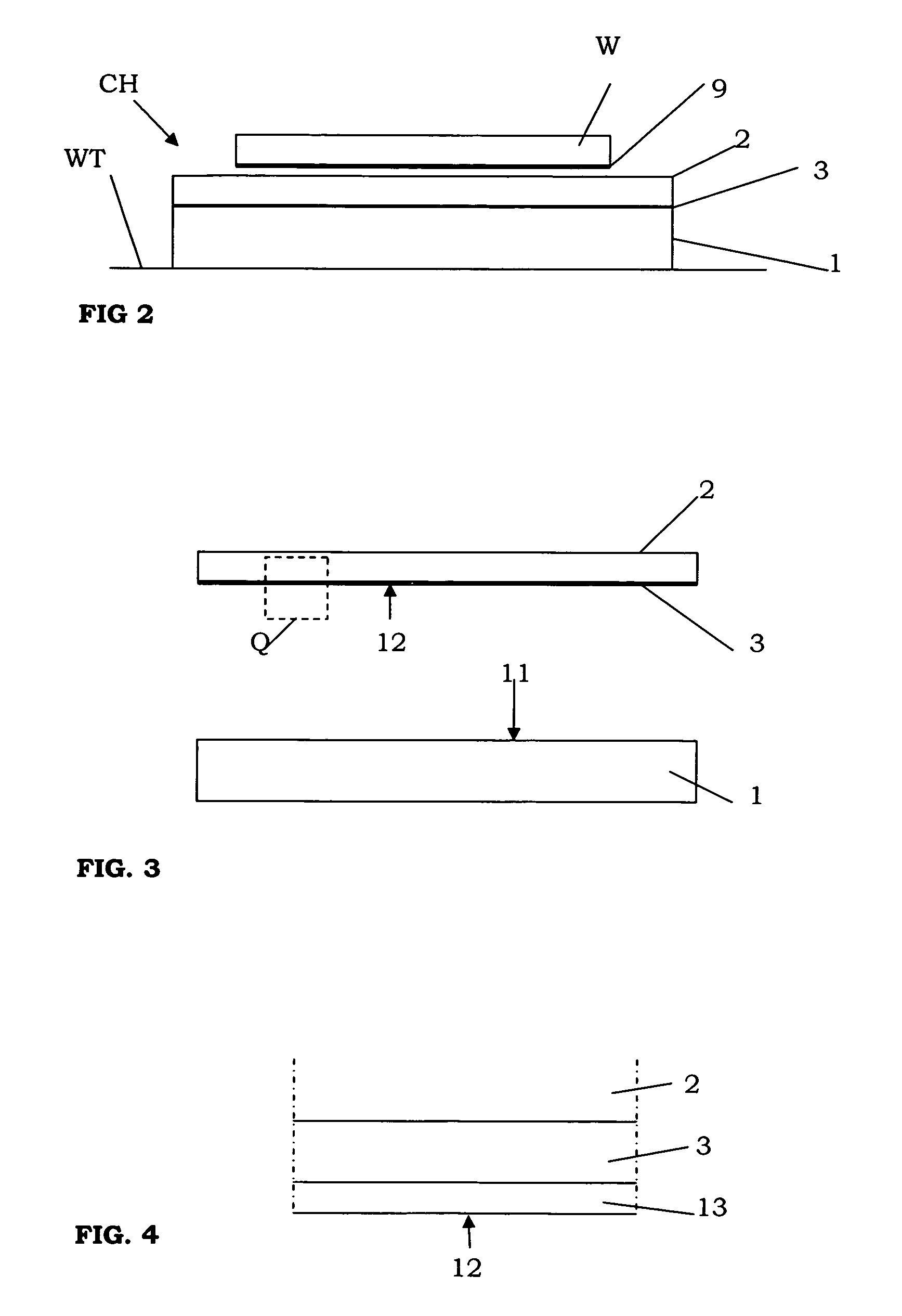
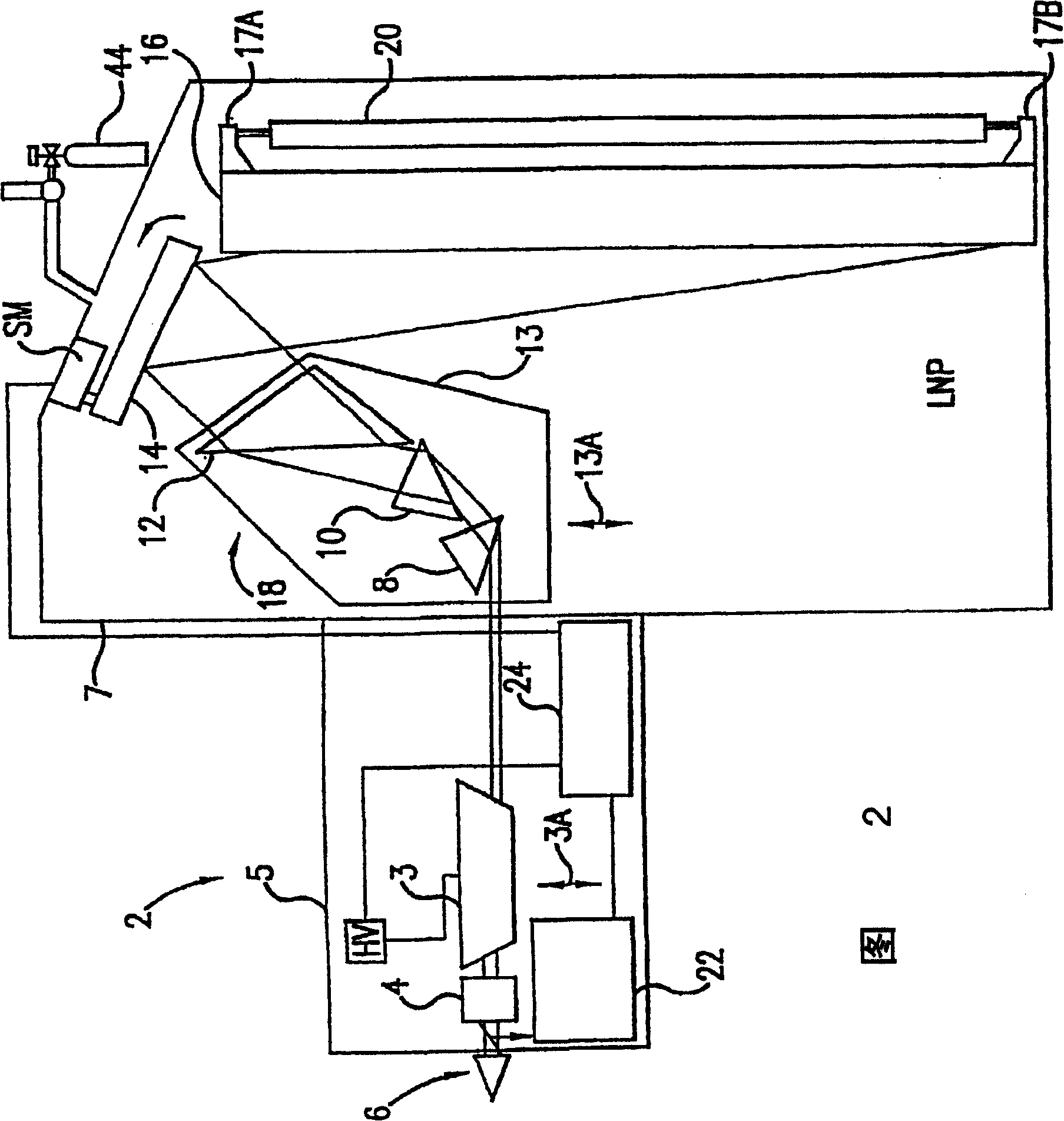
Method for joining at least a first member and a second member, lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method, as well as a device manufactured thereby
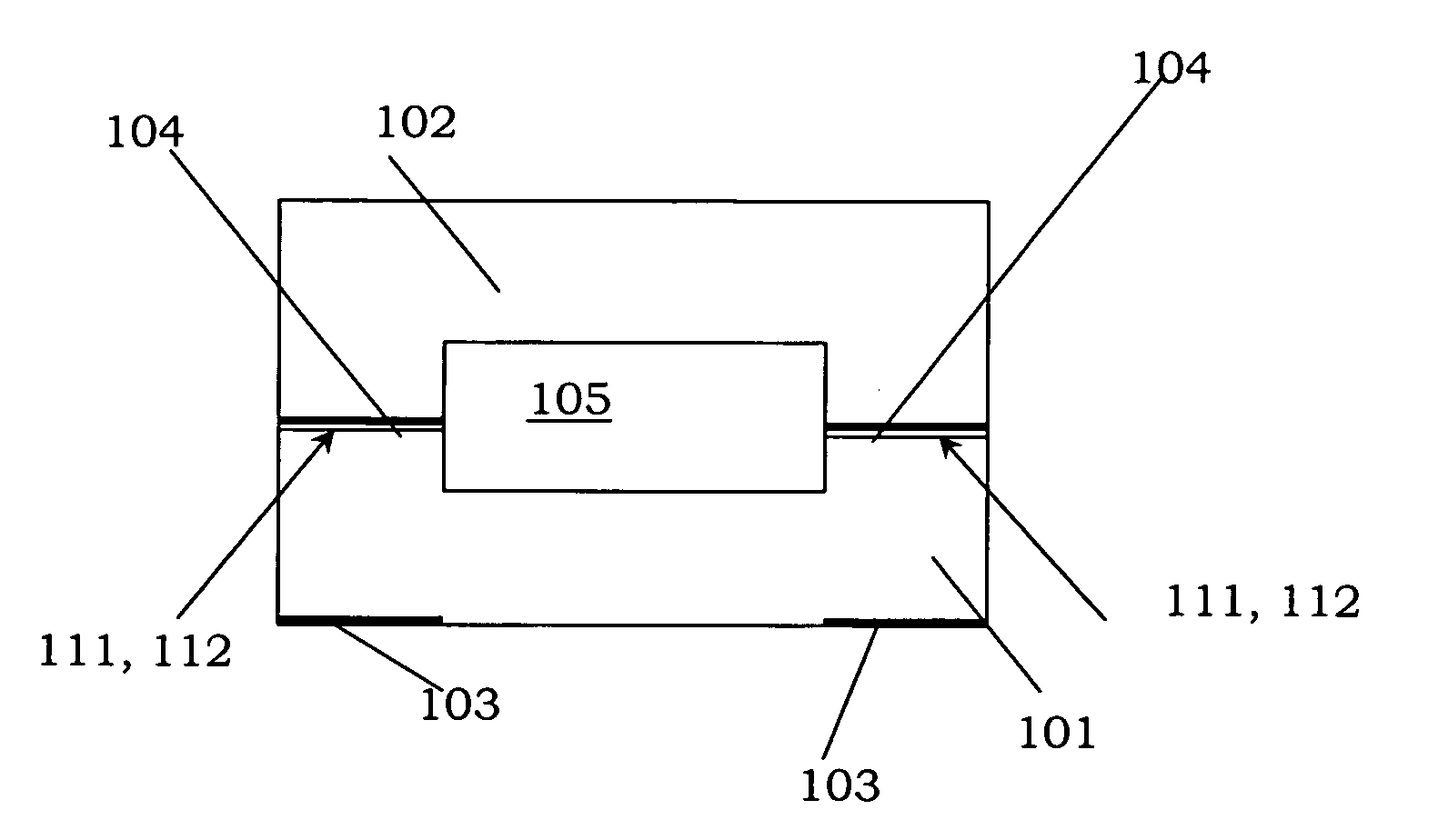
ActiveUS20050132750A1Easily brokenGood adhesionLamination ancillary operationsDuplicating/marking methodsEngineeringUltra low expansion glass
A method for joining at least two members of a lithographic apparatus is disclosed. The method includes providing a first member, providing a second member, direct-bonding the first member and the second member to form a direct-bond, and anodically bonding the first member and the second member. At least one of the members includes ultra low expansion glass and / or ultra low expansion glass ceramics.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
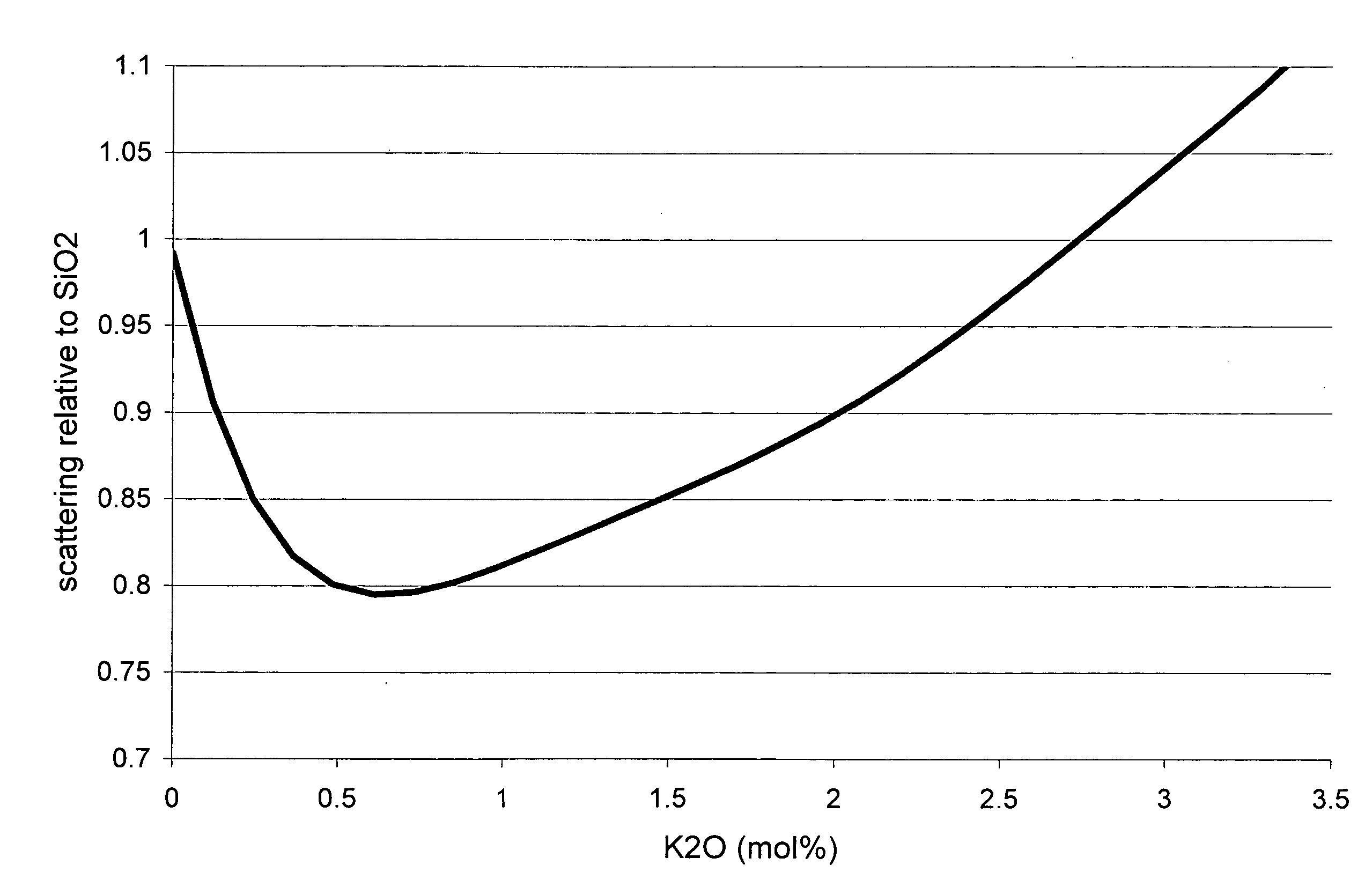
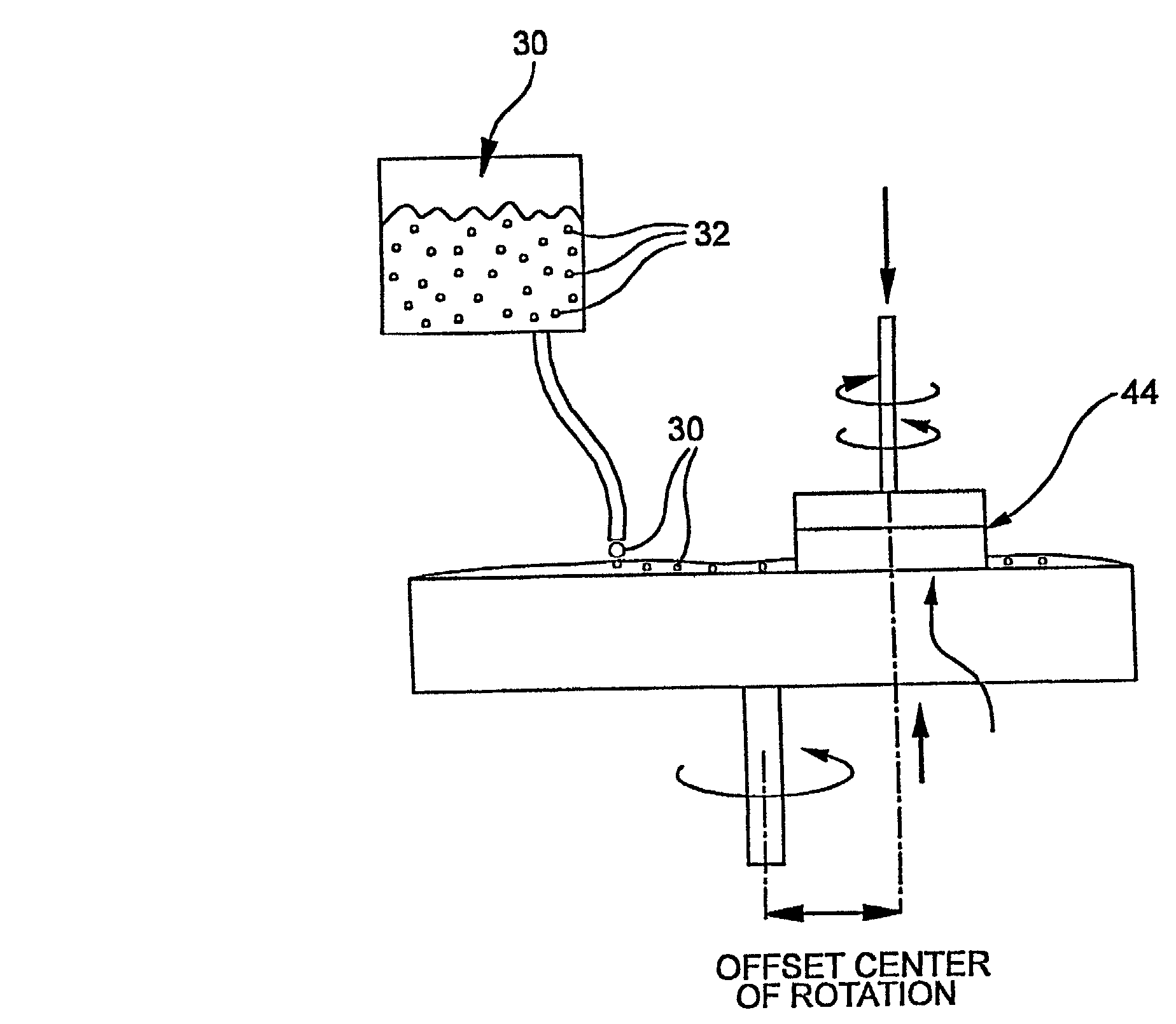
Colloidal silica polishing abrasive
InactiveUS6159077ALarge particle sizeSmall sizeDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingColloidal silicaGas phase
This colloidal silica soot is a byproduct of chemical vapor deposition processing of fused silica or ultra low expansion glasses in the finishing industry. The colloidal silica by product is referred to as "soot". Retaining the same physical properties as the parent glass and having a spherical morphology, the colloidal silica soot is an ideal candidate for polishing applications. The soot has a large particle size when compared to conventional colloidal or fumed silica. As a result, the large size produces less surface damage and allows for a higher (faster) removal rate. The large particle size also results in super polished surfaces.
Owner:CORNING INC
Ultralow expansion glass
ActiveUS20150080206A1Fast solutionEasy to adjustGlass productionTemperature controlUltra low expansion glass
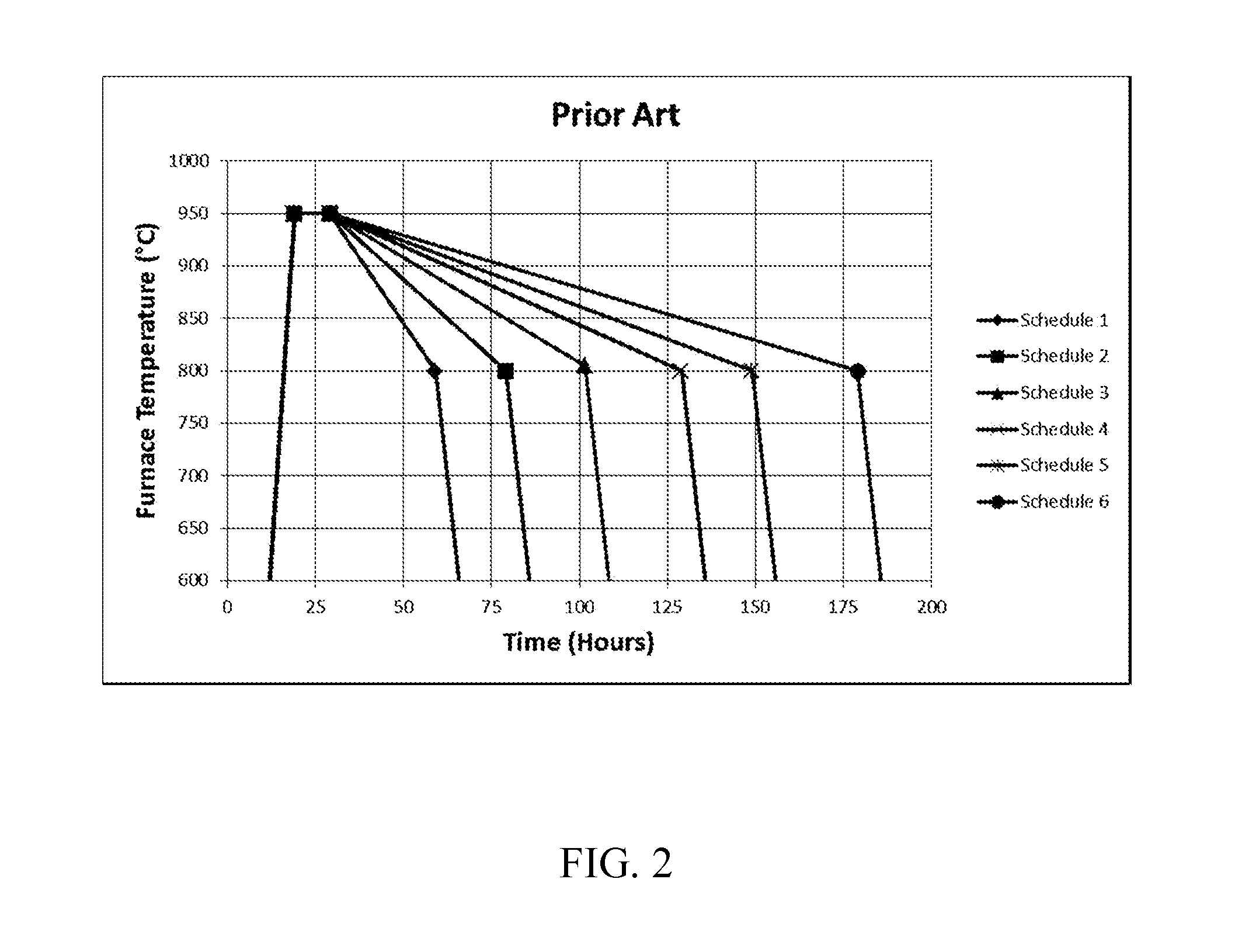
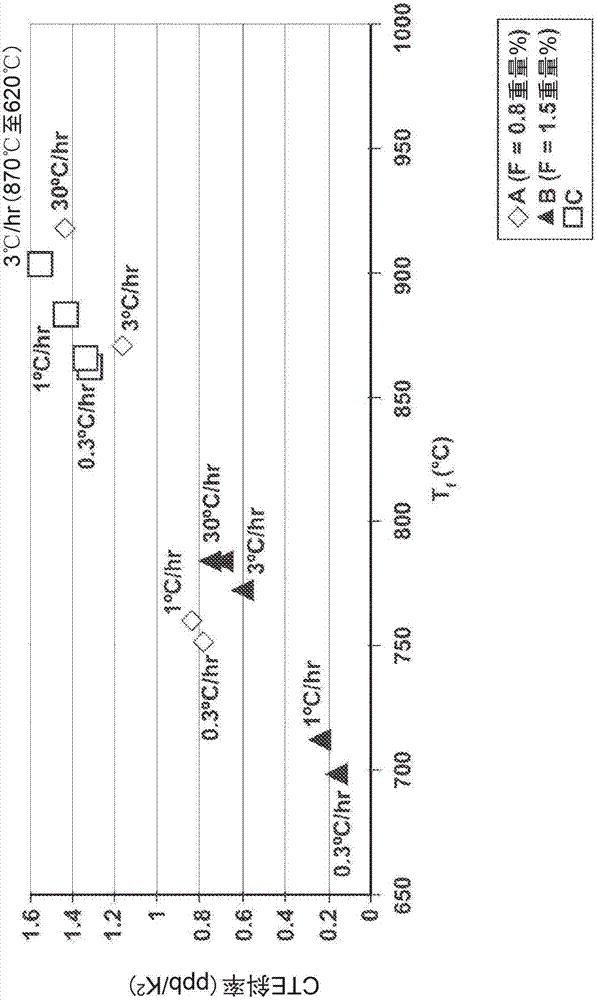
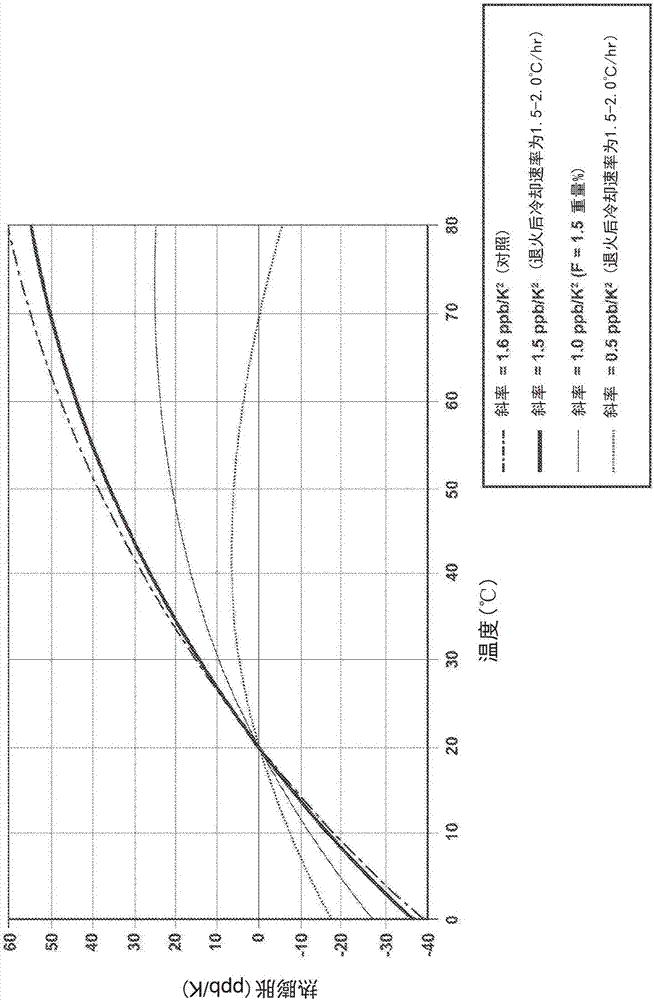
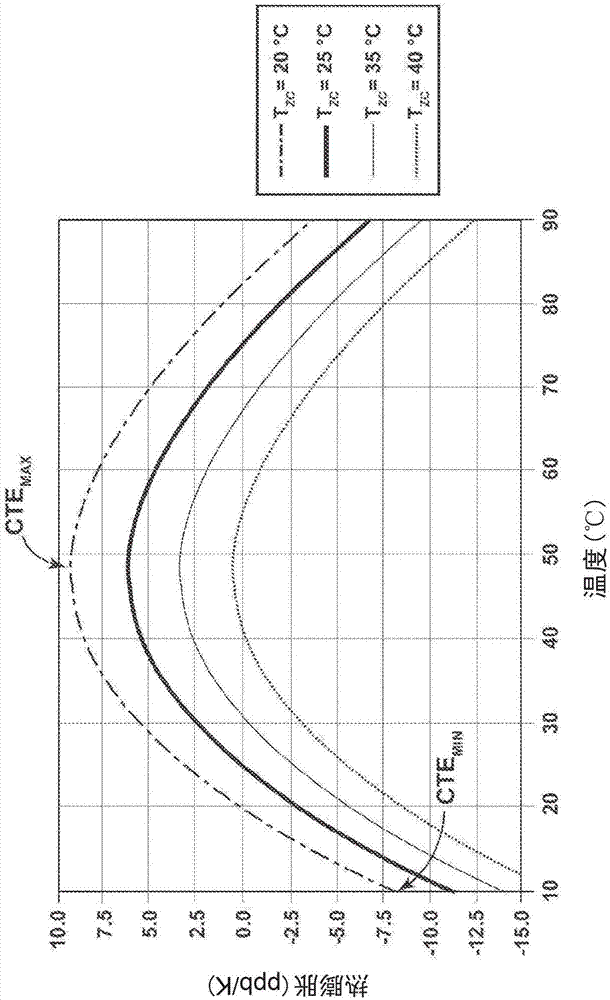
Silica-titania glasses with small temperature variations in coefficient of thermal expansion over a wide range of zero-crossover temperatures and methods for making the glasses. The method includes a cooling protocol with controlled anneals over two different temperature regimes. A higher temperature controlled anneal may occur over a temperature interval from 750° C.-950° C. or a sub-interval thereof. A lower temperature controlled anneal may occur over a temperature interval from 650° C.-875° C. or a sub-interval thereof. The controlled anneals permit independent control over CTE slope and Tzc of silica-titania glasses. The independent control provides CTE slope and Tzc values for silica-titania glasses of fixed composition over ranges heretofore possible only through variations in composition.
Owner:CORNING INC
Reduced striae low expansion glass and elements, and a method for making same
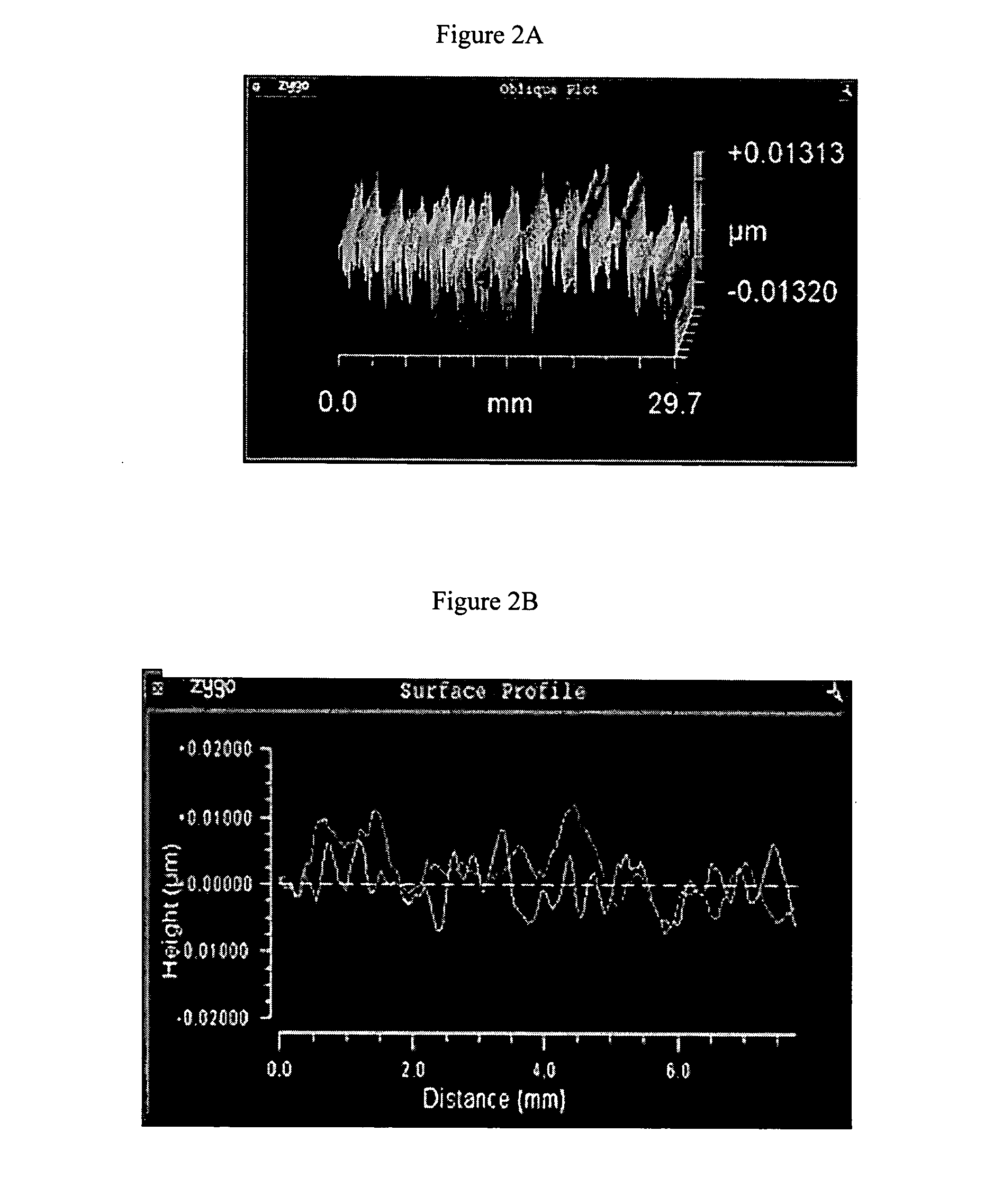
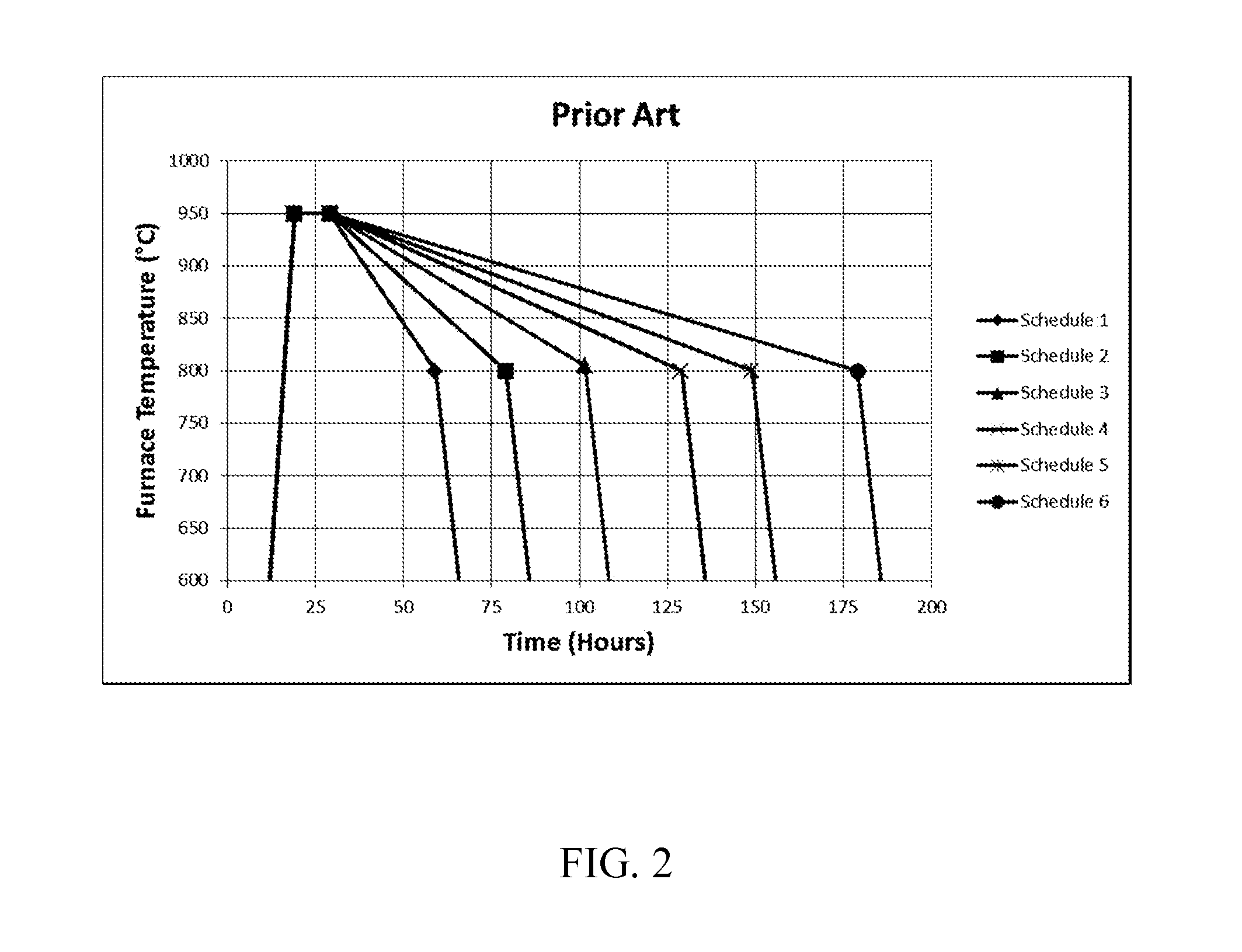
The invention is directed to a method for reducing striae in ultra-low expansion glass by heat-treating the glass at temperatures above 1600° C. for a time in the range of 72-288 hours. In one embodiment of the invention the glass is heat treated without forcing the glass to flow or “move”. The invention was found to reduce the magnitude of striae in an ultra-low expansion glass by 500%, and particularly reduces most of the “higher frequency” striae.
Owner:CORNING INC
EUV Reticle Substrates With High Thermal Conductivity
InactiveUS20110116068A1Reduces and eliminates pattern distortionReduce and eliminate distortionNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusCordieriteUltra low expansion glass
A reflective reticle substantially reduces or eliminates pattern distortion that results from the absorption of EUV radiation while maintaining a reticle thickness consistent with industry standards. The reflective reticle includes a layer of ultra-low expansion (ULE) glass and a substrate of Cordierite having a thermal conductivity substantially larger than that of ULE glass. An aluminum layer is disposed onto a first surface of the ULE glass and a second surface of the ULE glass is polished to be substantially flat and defect-free. The Cordierite substrate can be directly bonded to the aluminum layer using anodic bonding to form the reflective reticle. Alternatively, a first surface of an intermediate Zerodur layer can be bonded to the aluminum layer, and a second aluminum layer can be used to anodically bond the Cordierite substrate to a second surface of the Zerodur layer, thereby forming the reflective reticle.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
EUV reticle substrates with high thermal conductivity
InactiveUS8736810B2Reduce and eliminate distortionNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical apparatusCordieriteUltra low expansion glass
A reflective reticle substantially reduces or eliminates pattern distortion that results from the absorption of EUV radiation while maintaining a reticle thickness consistent with industry standards. The reflective reticle includes a layer of ultra-low expansion (ULE) glass and a substrate of Cordierite having a thermal conductivity substantially larger than that of ULE glass. An aluminum layer is disposed onto a first surface of the ULE glass and a second surface of the ULE glass is polished to be substantially flat and defect-free. The Cordierite substrate can be directly bonded to the aluminum layer using anodic bonding to form the reflective reticle. Alternatively, a first surface of an intermediate Zerodur layer can be bonded to the aluminum layer, and a second aluminum layer can be used to anodically bond the Cordierite substrate to a second surface of the Zerodur layer, thereby forming the reflective reticle.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Reduced striae low expansion glass and elements, and a method for making same
The invention is directed to a method for reducing striae in ultra-low expansion glass, for example, silica-titania glass, by heat-treating the glass at temperatures above 1600° C. for a time in the range of 72-288 hours. The silica-titania glass is formed by substantially simultaneously forming, collecting and consolidating a silica-titania soot formed in one or a plurality of burners using silicon-containing feedstock and a titanium-containing feedstock. In one embodiment of the invention the glass is heat treated without forcing the glass to flow or “move”. The invention was found to reduce the magnitude of striae in an ultra-low expansion glass by at least 50%, and particularly reduces most of the “higher frequency” striae.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for joining at least a first member and a second member, lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method, as well as a device manufactured thereby
ActiveUS8105457B2Easily brokenGood adhesionLamination ancillary operationsLaminationUltra low expansion glassCeramic
A method for joining at least two members of a lithographic apparatus is disclosed. The method includes providing a first member, providing a second member, direct-bonding the first member and the second member to form a direct-bond, and anodically bonding the first member and the second member. At least one of the members includes ultra low expansion glass and / or ultra low expansion glass ceramics.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
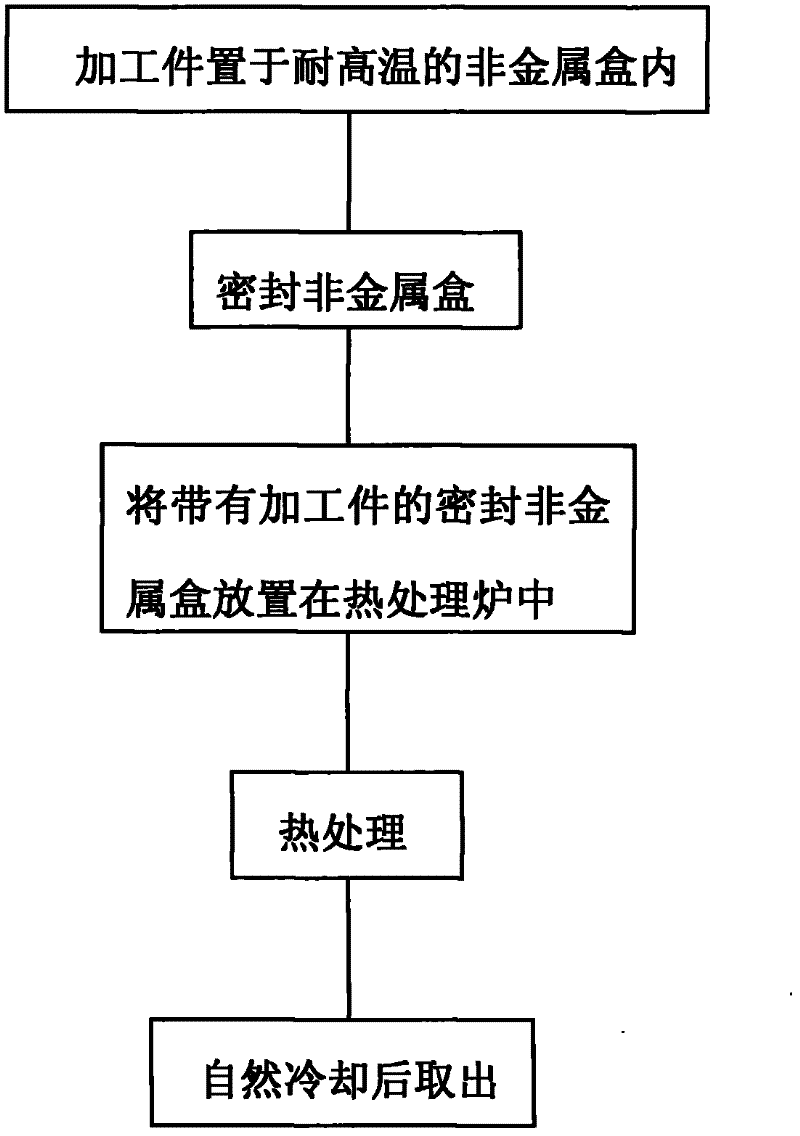
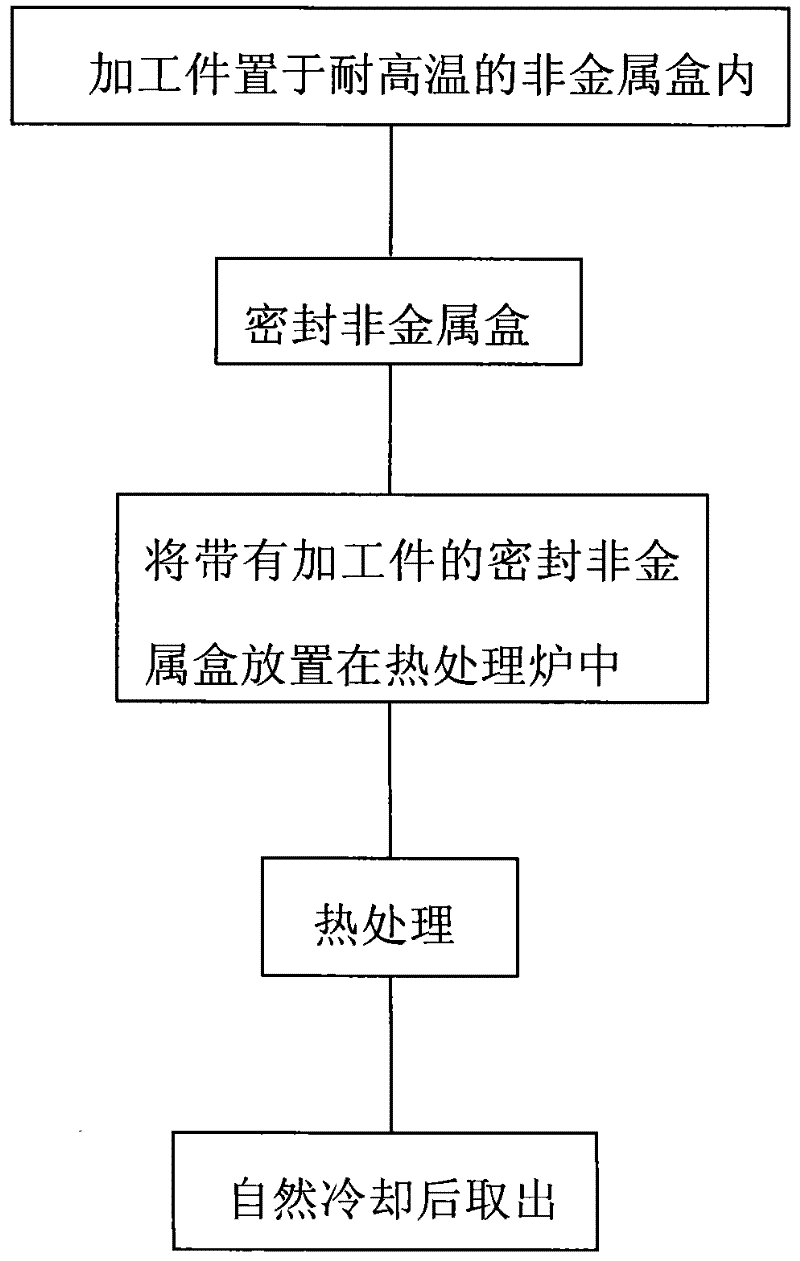
Ultra-low-expansion glass-ceramic super-stable treatment method
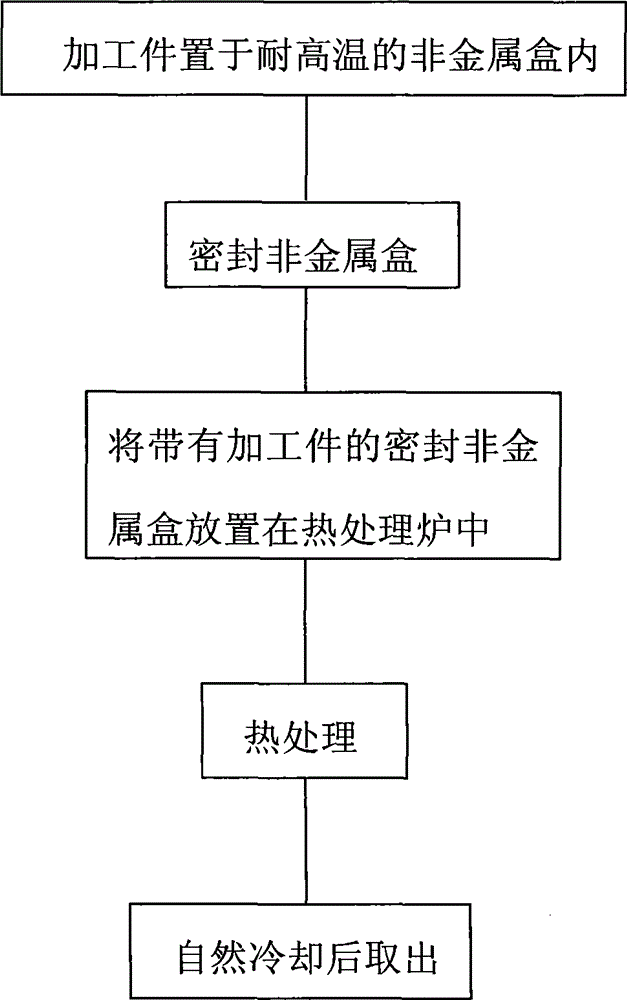
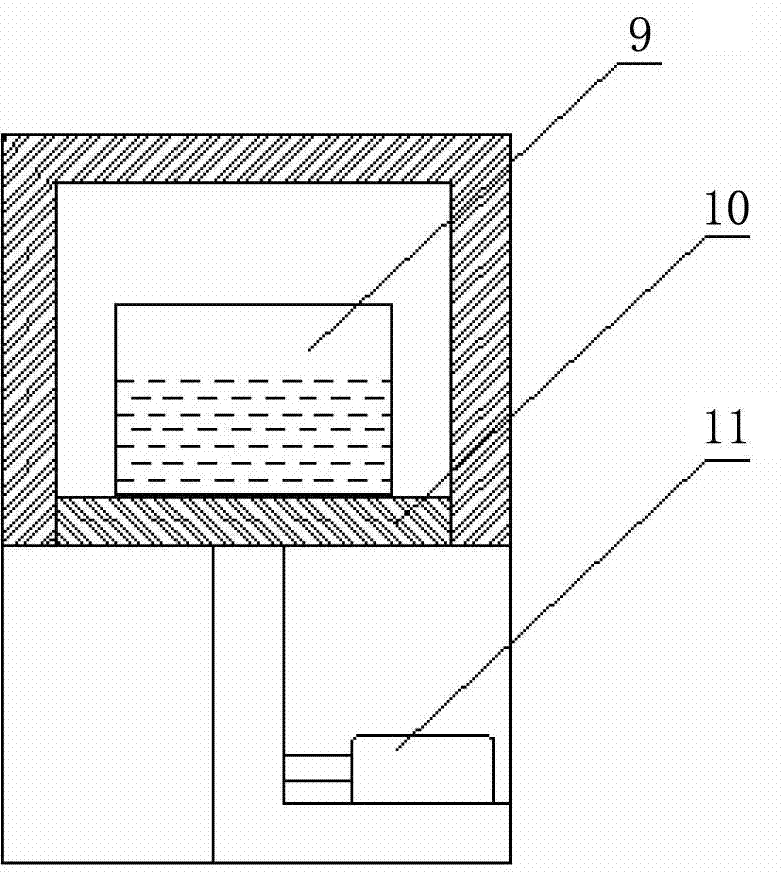
ActiveCN102503102AExcellent coefficient of linear expansionSmall thermal deformationSagnac effect gyrometersMachine partsControl system
The invention relates to an ultra-low-expansion glass-ceramic super-stable treatment method. The invention adopts an air-sealing low conductive high temperature dependent non-metallic box (1). The method comprises the following steps that: an ultra-low-expansion glass-ceramic machining part (2) to be treated is placed in a heat treatment furnace (3), the heat treatment furnace is heated from the room temperature to a temperature ranging from 360 DEG C to 420 DEG C at a rate of 3-5 DEG C / min according to the demand, the temperature is kept for 8-12 hours, then the temperature is reduced at a rate of 0.05-0.2DEG C / min; and when the temperature of the treatment furnace is reduced to 120+ / -20 DEG C, the treatment furnace control system is closed, and the treated machining part is placed in the furnace for 48 hours and then taken out. By adopting the ultra-low-expansion glass-ceramic super-stable treatment method, the internal stress existing in the machining part and the thermal deformation of the machining part can be effectively reduced so that the angle variation is less than 1 second of arc when the temperature changes from -50 DEG C to +100 DEG C; and the linear expansion coefficient of the glass-ceramic is ensured to be superior to 0.5*10<-7> / DEG C and the stabilization efficiency is increased.
Owner:FLIGHT AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
Method of making optical fluoride laser crystal components
InactiveUS20030148711A1Reduce flatness requirementsLittle to no scratchingPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsColloidal silicaGas phase
The method of making optical fluoride crystal components provide optical components with beneficial final polished transmission surfaces for transmitting below 200 nm wavelengths of light, such as produced by excimer lasers and utilized in optical lithography. The invention utilizes colloidal silica soot in the polishing of optical fluoride crystal surfaces. This colloidal silica soot is a byproduct of chemical vapor deposition processing of fused silica or ultra low expansion glasses. The colloidal silica byproduct is referred to as "soot". Retaining the same physical properties as the parent glass and having a spherical morphology, the colloidal silica soot is an ideal for final polishing applications of optical fluoride crystals, and particularly for optical fluoride crystals such as calcium fluoride which have high transmission levels to below 300 nm light such as produced by excimer lasers. The soot has a large particle size and spherical shape when compared to conventional colloidal or fumed silica.
Owner:CORNING INC
Evaluation method for coefficient of thermal expansion of ultra-low-expansion glass material
InactiveUS7124635B2Material thermal coefficient of expansionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV +1
Method of making optical fluoride laser crystal components
InactiveUS6669536B2Reduction in flatnessEasy to polishPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsColloidal silicaGas phase
Owner:CORNING INC
Microfabrication of high quality three dimensional structures using wafer-level glassblowing of fused quartz and ultra low expansion glasses
ActiveUS9139417B2Reduce dissipationLow anchor lossesDecorative surface effectsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsEtchingMicrofabrication
A high temperature micro-glassblowing process and a novel inverted-wineglass architecture that provides self-aligned stem structures. The fabrication process involves the etching of a fused quartz substrate wafer. A TSG or fused quartz device layer is then bonded onto the fused quartz substrate, creating a trapped air pocket or cavity between the substrate and the TSG device layer. The substrate and TSG device layer 14 are then heated at an extremely high temperature of approximately 1700° C., forming an inverted wineglass structure. Finally, the glassblown structure is cut or etched from the substrate to create a three dimensional wineglass resonator micro-device. The inverted wineglass structure may be used as a high performance resonator for use as a key element in precision clock resonators, dynamic MEMS sensors, and MEMS inertial sensors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
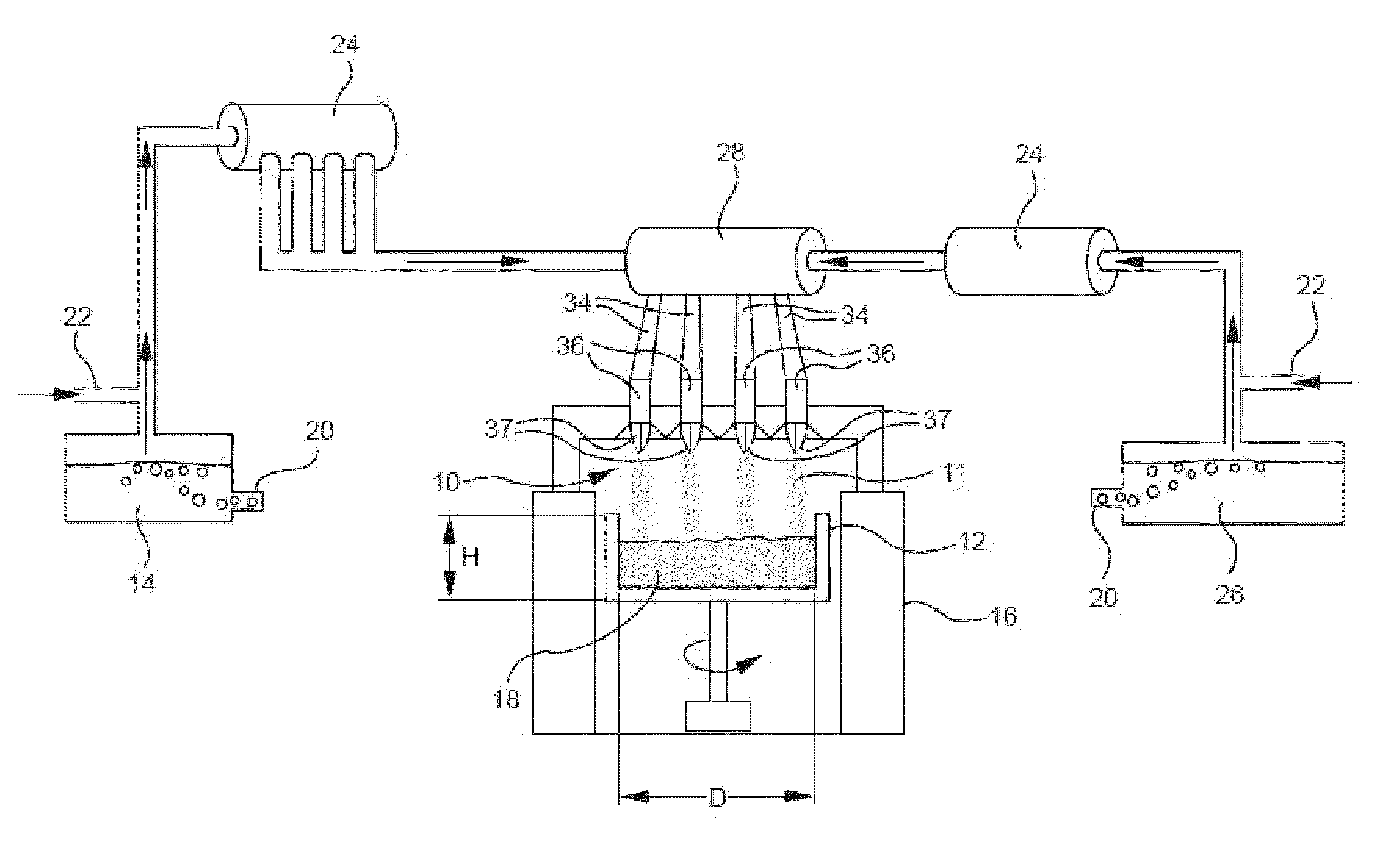
Ultralow-expansion glass ceramic continuous production line and method
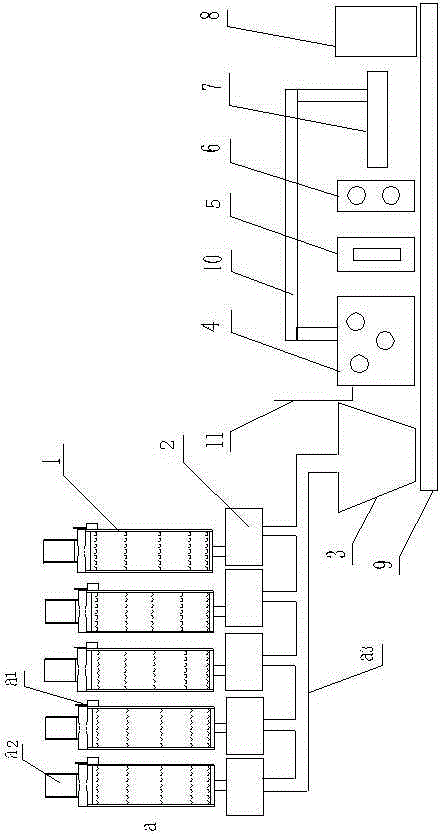
InactiveCN106082674AIncrease productivityReduce labor costsCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusUltra low expansion glassGlass-ceramic
An ultralow-expansion glass ceramic continuous production line comprises a material selection system including a plurality of material conveyers; the material conveyers are each composed of a material conveyer belt, an electric screen and a burdening weighing device, the material conveyer belt is connected with the electric screen, and the electric screen is connected with the burdening weighing device; after passing through the burdening weighing device, the materials enter a mixing conveyer belt connected with a mixing unit, and a discharge port of the mixing unit is connected with a conveying rail device; one side of the conveying rail device is sequentially provided with a melting furnace, a forming unit, an annealing furnace, a sorting device and a crystallizing furnace; a back-conveying belt is disposed between the sorting device and the melting furnace; the melting furnace is connected with a water pipe. The ultra-low-expansion glass ceramic continuous production line and method have greatly improved production efficiency, save labor cost and have controllable product quality.
Owner:NANTONG JINGXIN OPTICAL GLASS
Line narrowing unit with flexural grating mount
InactiveCN100416950CRelieve pressureEliminate the effects ofPrismsOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingHigh energy laser beam
A grating based line narrowing device for line narrowing lasers producing high energy laser beams. A flexure grating mount is provided which virtually eliminates stress on the grating caused by differential thermal expansion between the grating and the housing structure. The grating which is comprised of a very thin aluminum surface on a thick ultra low expansion glass substrate is attached to an aluminum housing structure using a flexure grating mount. At least one flexure joint is provided in the grating mount which permits thermal expansion and contraction of the substrate. In some embodiments the mount comprises a metal plate and the flexure joint is a H-Flex joint (124) with four legs (126) which is machined into the metal plate. In another embodiment two H-Flex joints are provided. In other embodiments, the flexure joint is a dovetail joint permitting one end of the mount to slip relative to the other.
Owner:西默有限公司
Ultralow expansion glass
Owner:CORNING INC
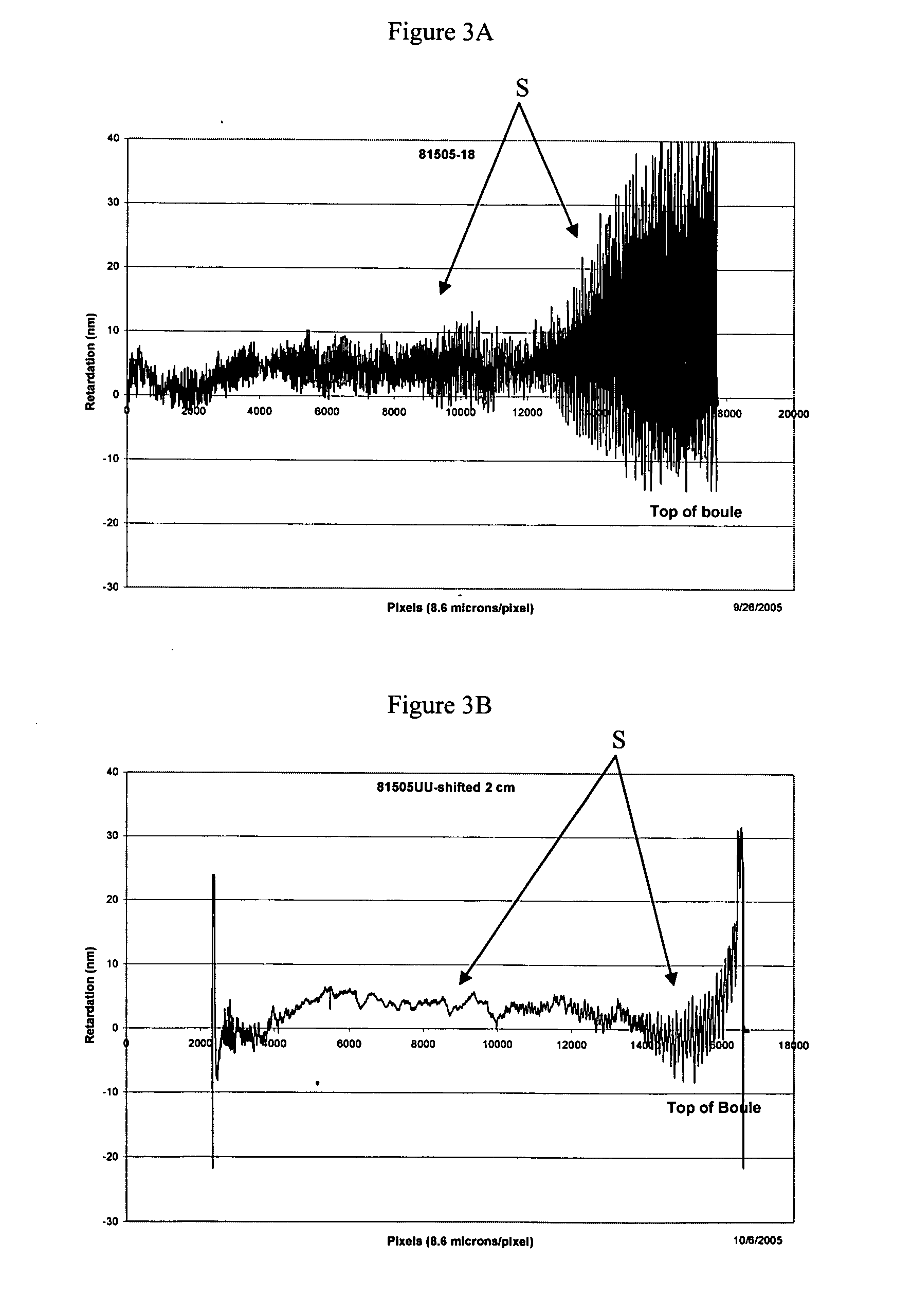
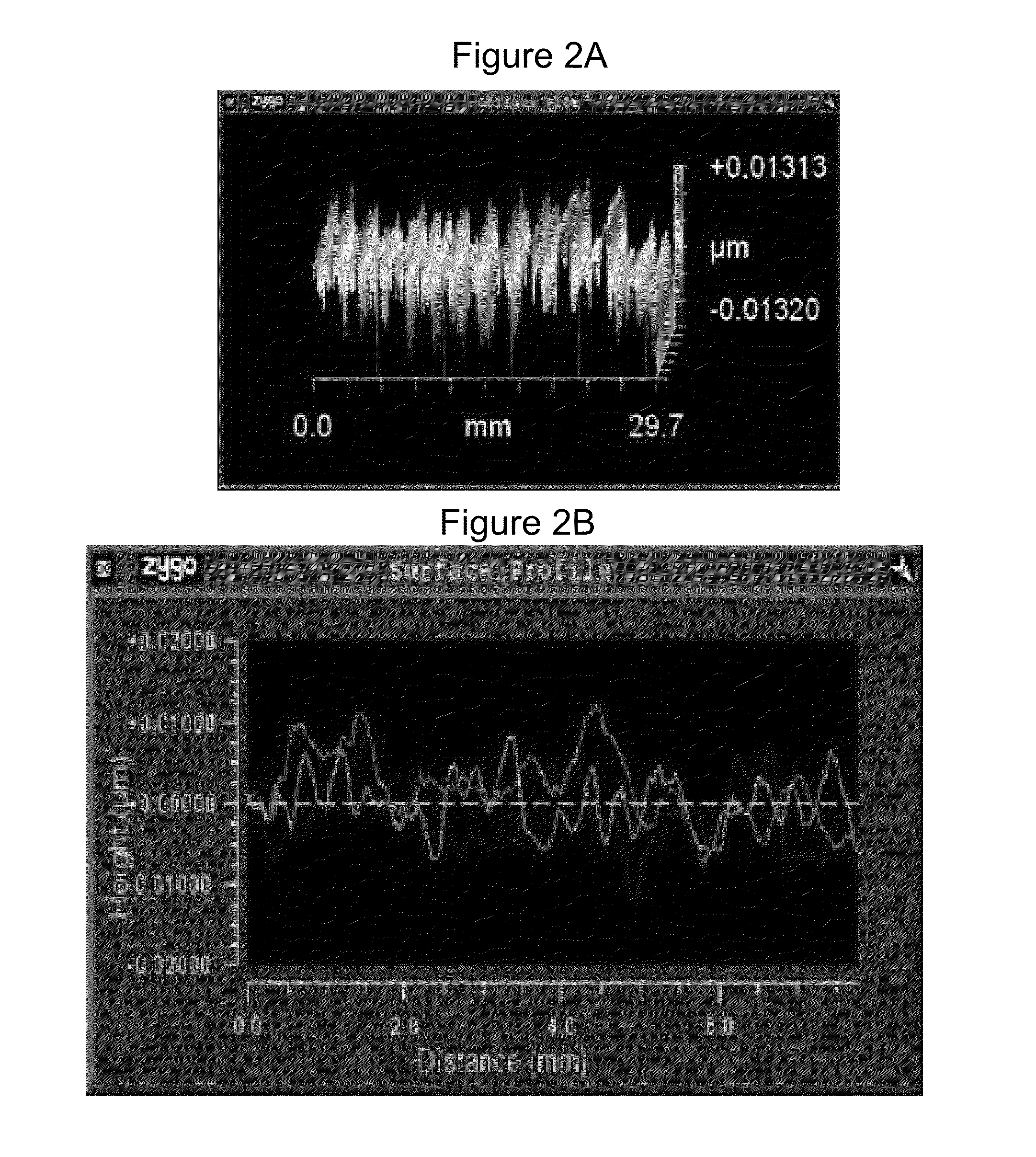
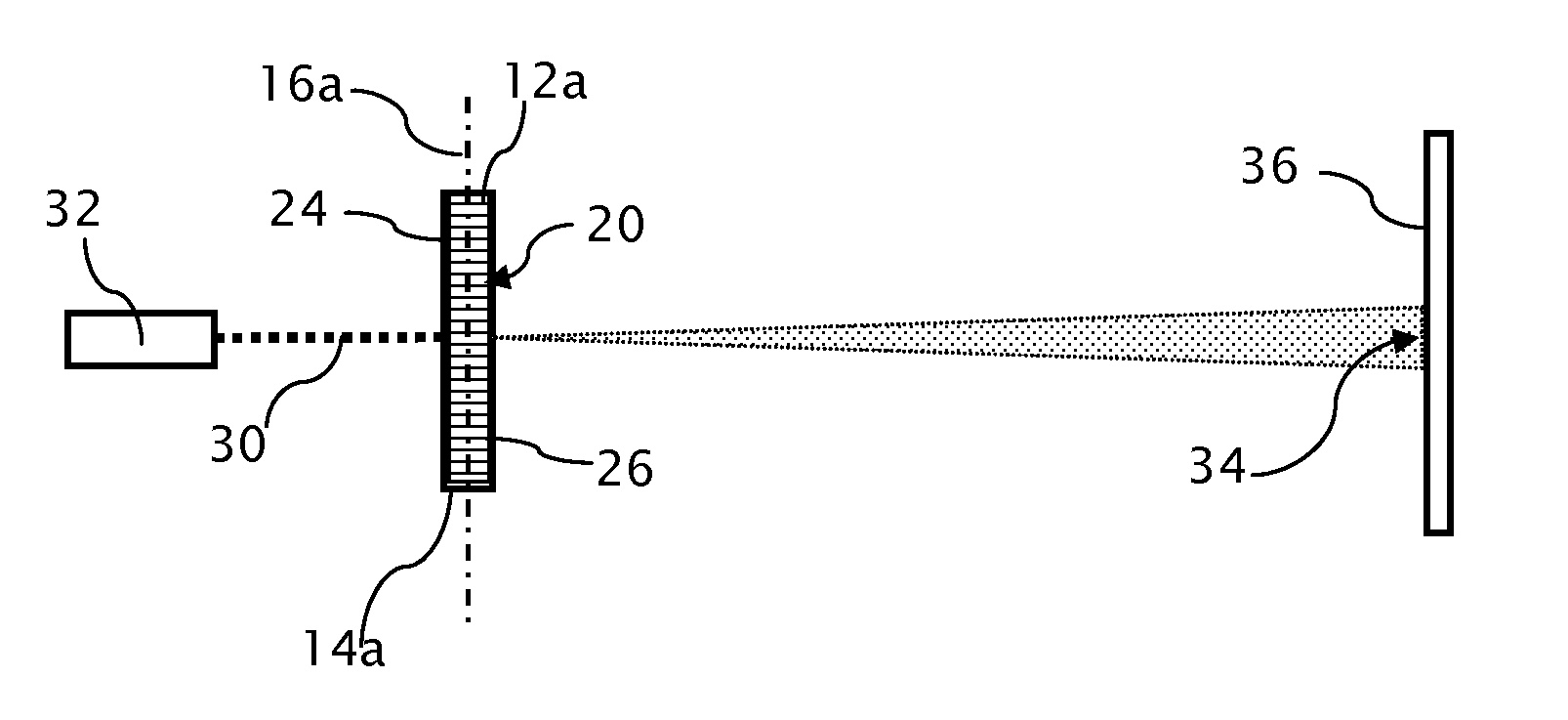
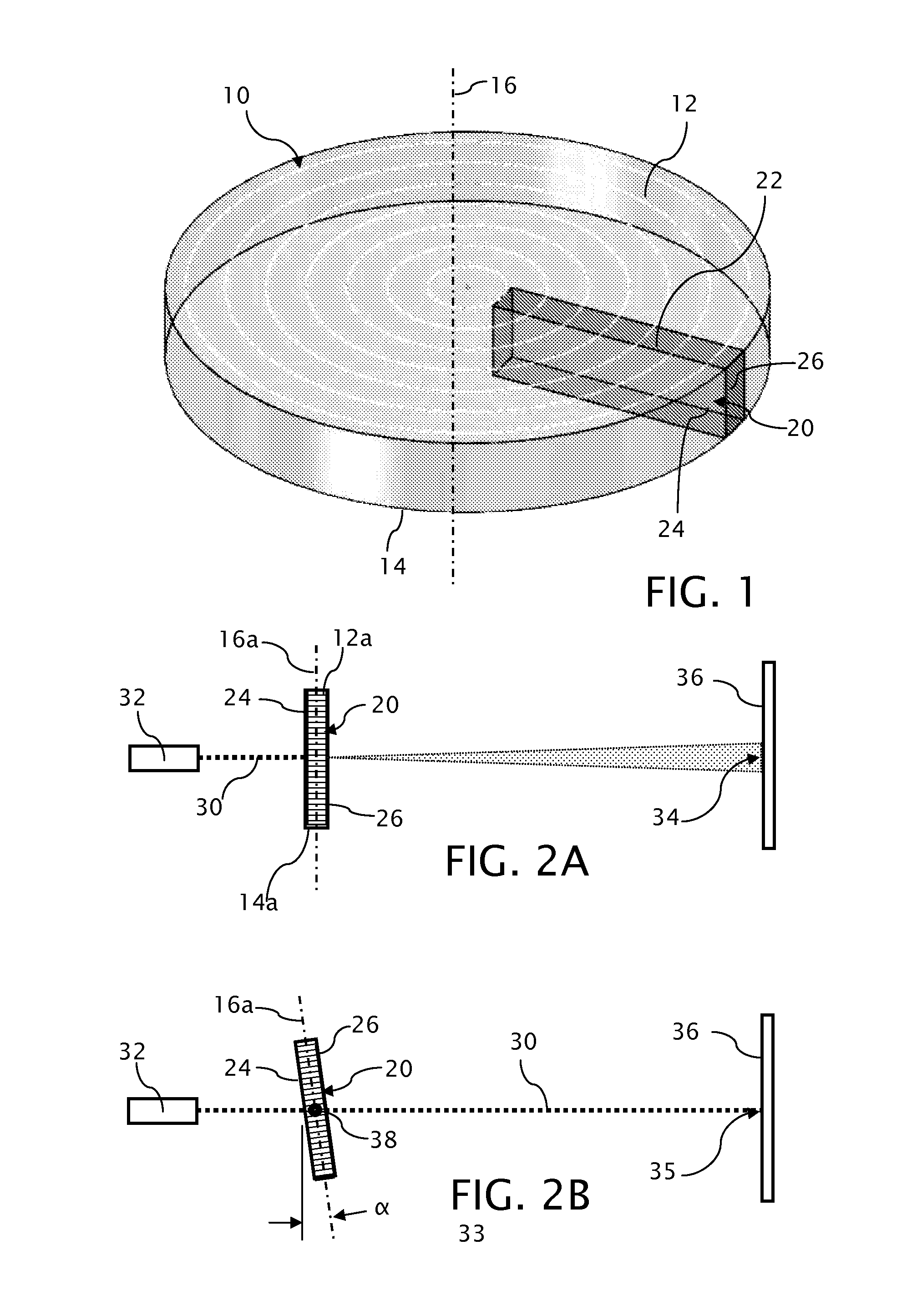
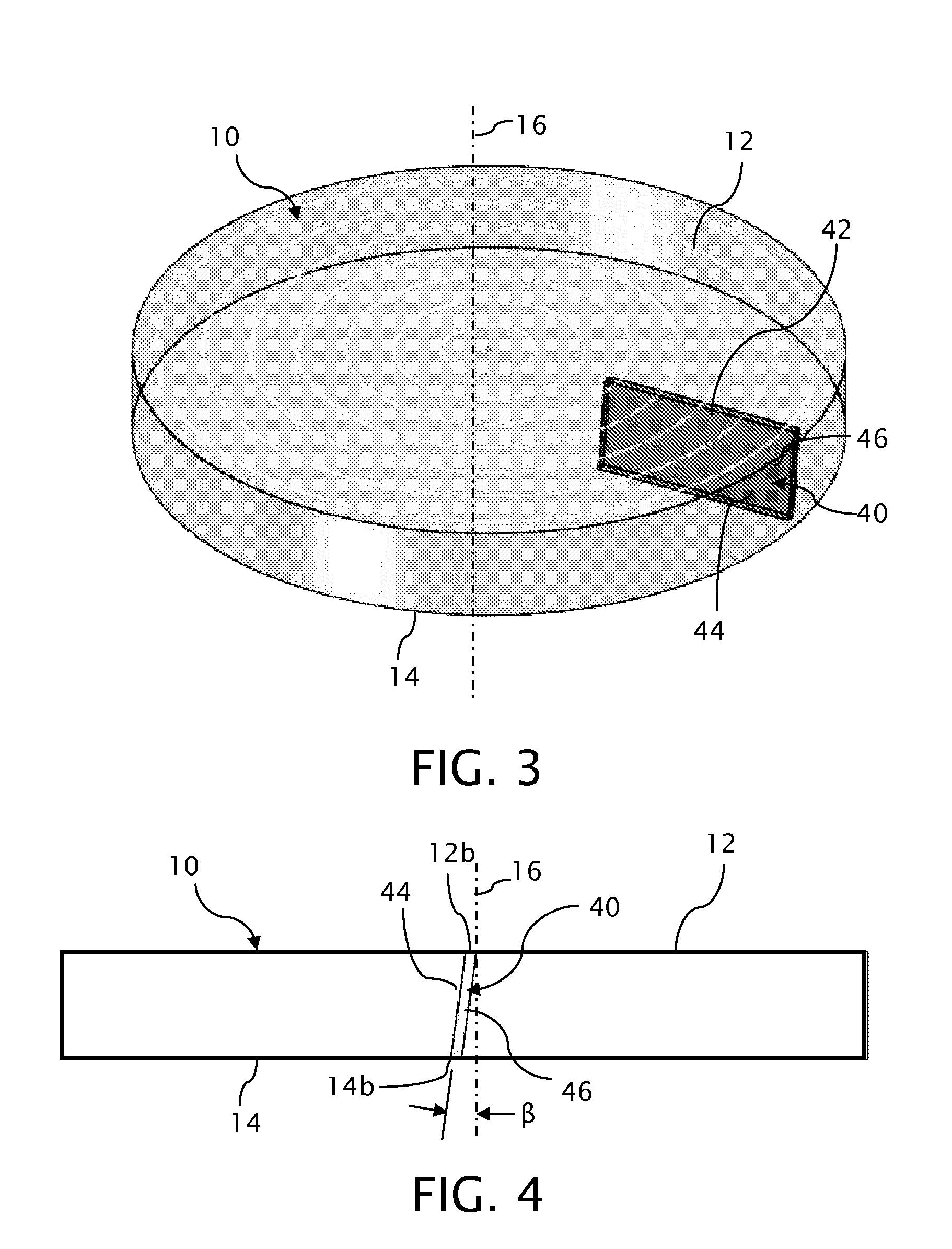
Skewed sectional measurement of striated glass
Thickness and group index variations in test strip samples of ultra-low expansion glass are made by extracting the strip samples with front and back faces oriented at an acute skew angle to the axis of the boule. The strip samples are positioned the within an interferometric measurement cavity so that a set of subcavities formed by pairings of each of two reference surfaces together with each of the front and back faces of the strip sample which each subcavity having a different optical path length spacing. The skew angle is sized to avoid diffusion effects of striae present in the boule.
Owner:CORNING INC
Ultra-low-expansion glass-ceramic super-stable treatment method
ActiveCN102503102BExcellent coefficient of linear expansionSmall thermal deformationSagnac effect gyrometersMachine partsControl system
The invention relates to an ultra-low-expansion glass-ceramic super-stable treatment method. The invention adopts an air-sealing low conductive high temperature dependent non-metallic box (1). The method comprises the following steps that: an ultra-low-expansion glass-ceramic machining part (2) to be treated is placed in a heat treatment furnace (3), the heat treatment furnace is heated from the room temperature to a temperature ranging from 360 DEG C to 420 DEG C at a rate of 3-5 DEG C / min according to the demand, the temperature is kept for 8-12 hours, then the temperature is reduced at a rate of 0.05-0.2DEG C / min; and when the temperature of the treatment furnace is reduced to 120+ / -20 DEG C, the treatment furnace control system is closed, and the treated machining part is placed in the furnace for 48 hours and then taken out. By adopting the ultra-low-expansion glass-ceramic super-stable treatment method, the internal stress existing in the machining part and the thermal deformation of the machining part can be effectively reduced so that the angle variation is less than 1 second of arc when the temperature changes from -50 DEG C to +100 DEG C; and the linear expansion coefficient of the glass-ceramic is ensured to be superior to 0.5*10<-7> / DEG C and the stabilization efficiency is increased.
Owner:FLIGHT AUTOMATIC CONTROL RES INST
Skewed sectional measurement of striated glass
Thickness and group index variations in test strip samples of ultra-low expansion glass are made by extracting the strip samples with front and back faces oriented at an acute skew angle to the axis of the boule. The strip samples are positioned the within an interferometric measurement cavity so that a set of subcavities formed by pairings of each of two reference surfaces together with each of the front and back faces of the strip sample which each subcavity having a different optical path length spacing. The skew angle is sized to avoid diffusion effects of striae present in the boule.
Owner:CORNING INC
Ultra-low expansion glass-ceramic for laser gyroscope and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101538118BNo sheddingImprove bindingSagnac effect gyrometersFlexural strengthSpectral transmittance
The invention provides an ultra-low expansion glass-ceramic for a laser gyroscope and a preparation method thereof, wherein the composition of the ultra-low-expansion glass-ceramic is: SiO2: 56-68%, Al2O3: 21-27%, Li2O: 2~4%, Na2O: 0~1%, K2O: 0~1%, MgO: 0~3%, ZnO: 0~1.5%, P2O5: 4.5~6.8%, TiO2: 1~2.5%, ZrO2: 1 ~2.5%, Sb2O3 / As2O3: 0.5~1.5%; its main crystal phase is β quartz solid solution, the crystal phase content is 70%~85%, the grain size is less than 50nm, and the order of magnitude of thermal expansion coefficient is 10-8. The preparation method includes batching, mixing, melting, homogenization, clarification, glass forming, annealing, and microcrystallization heat treatment; wherein the melting, homogenization, and clarification steps are all carried out at a temperature of 1570 ° C to 1590 ° C; the microcrystallization heat treatment process It is: under the condition that the nucleation rate is 1°C / min and the nucleation temperature is 650-750°C, keep warm for 6-10 hours and then heat up for crystallization, the crystallization rate is 1°C / min, and the crystallization temperature is 750-750°C 850°C, keep warm for 6-10 hours. The bending strength of this product is higher than 170MPa, and the processing roughness is better than that of the spectral transmittance in the 0.6-2μm band, reaching more than 90%; it has good hardness and anti-wear performance.
Owner:SINOMA SYNTHETIC CRYSTALS CO LTD +1
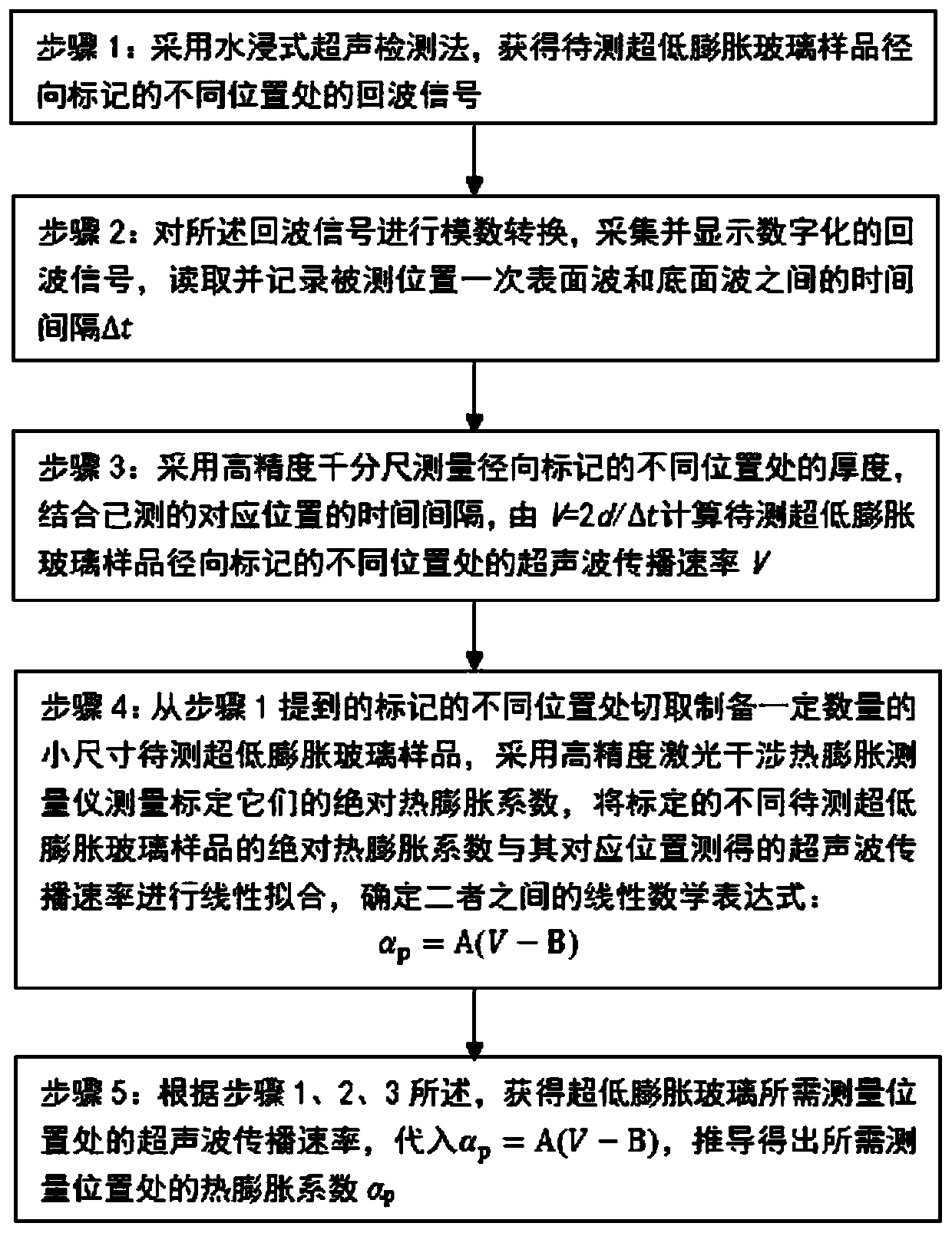
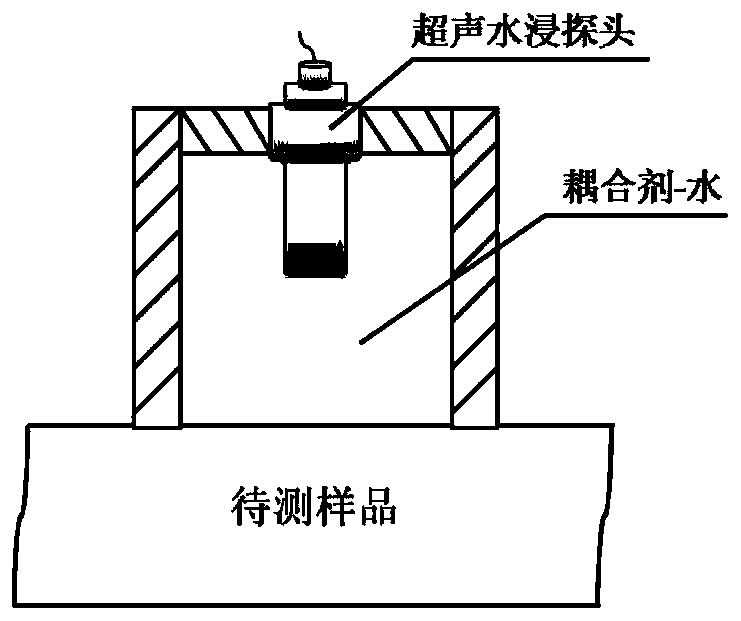
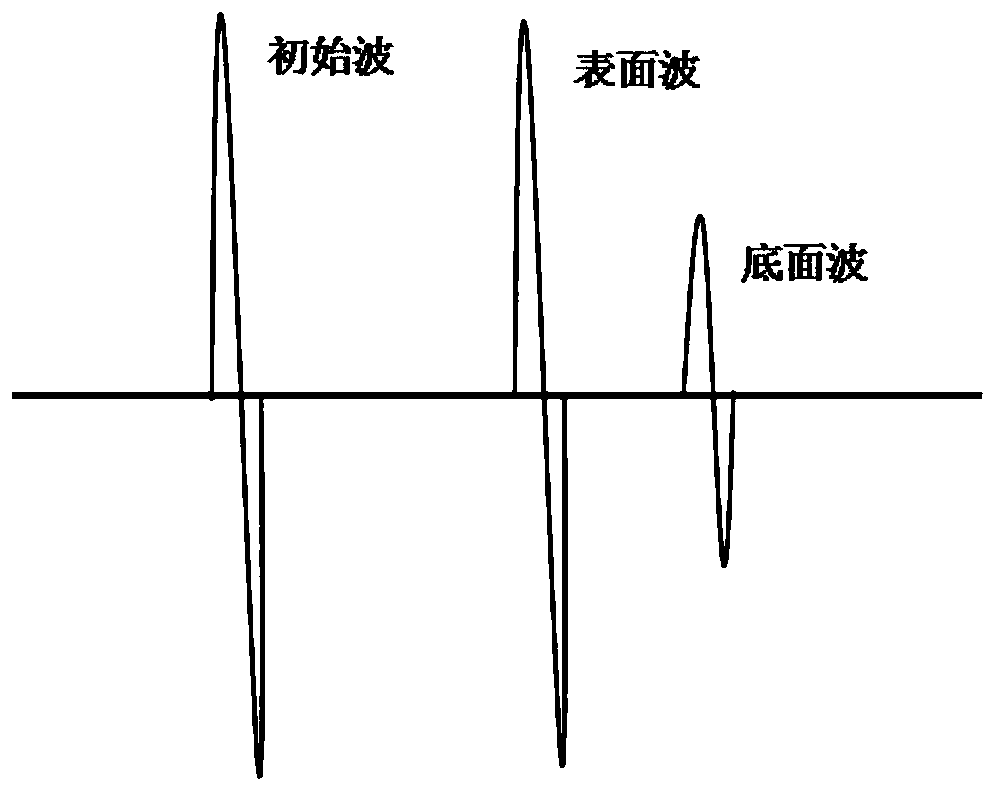
Method for measuring thermal expansion coefficient of ultralow-expansion glass
PendingCN111366640AImprove detection efficiencyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalThermal dilatationWater immersion
The invention relates to a method for measuring the thermal expansion coefficient of ultralow-expansion glass, and belongs to the technical field of ultrasonic detection. Ultrasonic propagation ratesat different positions of a radial mark of the ultralow-expansion glass are measured by using a water immersion type ultrasonic pulse echo method so as to achieve the measurement of the thermal expansion coefficient of the ultralow-expansion glass. The thermal expansion coefficient and the ultrasonic propagation rate of the ultralow-expansion glass are related to the TiO2 content in the glass, related researches show that the thermal expansion coefficient [alpha] of the ultralow-expansion glass and the ultrasonic propagation rate V are in a linear relationship, so that the thermal expansion coefficients at different positions can be deduced by measuring the ultrasonic propagation rates at different positions of the ultralow-expansion glass.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A production line for ultra-low expansion glass-ceramics
The invention provides a production line of an ultra-low-expansion microcrystalline glass. The production line of the ultra-low-expansion microcrystalline glass mainly comprises a melting furnace, a forming machine, an annealing furnace, a crystallizing furnace, a conveying device and a rail, wherein the melting furnace, the forming machine, the annealing furnace and the crystallizing furnace are sequentially distributed on one side of the rail; and the conveying device is arranged on the rail and can move among the melting furnace, the forming machine, the annealing furnace and the crystallizing furnace. By adopting the production line of the ultra-low-expansion microcrystalline glass, provided by the invention, high-quality and large-scale microcrystalline glass products can be produced; and the products are specifically suitable for being used for meeting the demand of laser navigation equipment.
Owner:NEW METALLURGY HI TECH GRP
Integral production line for ultra-low expansion glass-ceramics
InactiveCN106082675AReduce labor costsIncrease productivityCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusProduction lineButt joint
The invention relates to an integral production line for ultra-low expansion glass-ceramics. The integral production line comprises a raw material selecting and preparing system. The raw material selecting and preparing system comprises a plurality of raw material conveyors. Each raw material conveyor comprises a raw material conveying belt, an electric sieve and a material preparing and weighing device, wherein the raw material conveying belt is connected with the electric sieve, and the electric sieve is connected with the material preparing and weighing device. Raw materials pass the material preparing and weighing devices and enter a material mixing conveying belt connected with a material mixer. The raw materials fully mixed by the material mixer enters a conveying rail device. A melting furnace, a forming machine, an annealing furnace, a sorting device and a crystallization furnace are sequentially arranged on one side of the conveying rail device. A return belt is arranged between the sorting device and the melting furnace. The integral production line has the advantages that automatic production is achieved, various procedures of the production are in smooth butt joint, manpower cost is saved greatly, production efficiency is increased, and product quality is stable and controllable.
Owner:NANTONG JINGXIN OPTICAL GLASS
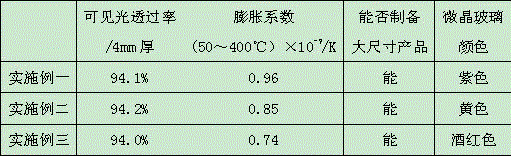
Colored glass-ceramic with ultra-low expansion coefficient and high transparency and preparation method thereof
A colored glass-ceramic with ultra-low expansion coefficient and high transparency. The basic components of the glass-ceramics are: 65-69% SiO2, 19-20% Al2O3, 3.1-4.2% Li2O, 3 ~4.5% B2O3, 0.1~0.4% Na2O, 0.1~0.4% K2O, 0.3~0.5% MgO, 0.6~1.4% BaO, 0.6~1.4% ZnO, 1.0~1.7% TiO2, 1.0~ 1.3% ZrO2, 0.4-0.8% P2O5, 0.3-0.8% F and 0.02-0.3% CeO2; when the weight of the basic components is 100%, add coloring not exceeding 4% of the total weight of the basic components agent. The colored glass-ceramic of the present invention has high transparency, ultra-low expansion coefficient and can produce products with large size or complex structure.
Owner:虎石新材料(宜兴)有限公司
Doped ultra-low expansion glass and methods for making the same
A doped silica-titania glass article is provided that includes a glass article having a glass composition comprising (i) a silica-titania base glass, (ii) a fluorine dopant, and (iii) a second dopant. The fluorine dopant has a concentration of fluorine of up to 5 wt. % and the second dopant comprises one or more oxides selected from the group consisting of Al, Nb, Ta, B, Na, K, Mg, Ca and Li oxides at a total oxide concentration from 50 ppm to 6 wt.%. Further, the glass article has an expansivity slope of less than 0.5 ppb / K2 at 20DEG C. The second dopant can be optional. The composition of the glass article may also contain an OH concentration of less than 100 ppm.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com