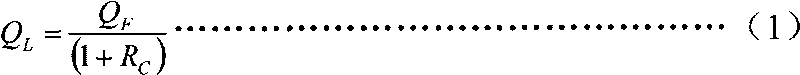Patents
Literature
529 results about "Ultra-high vacuum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
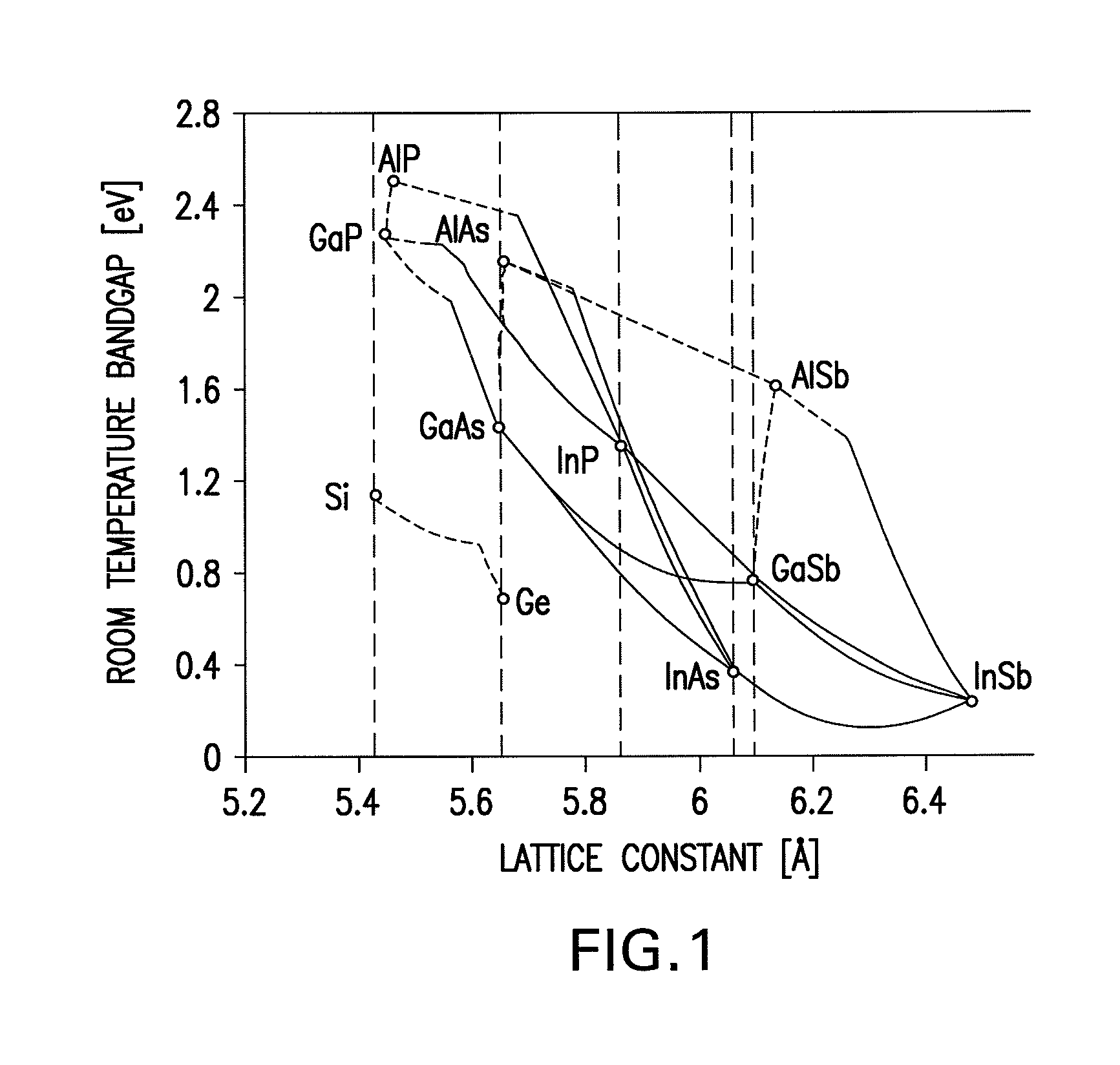
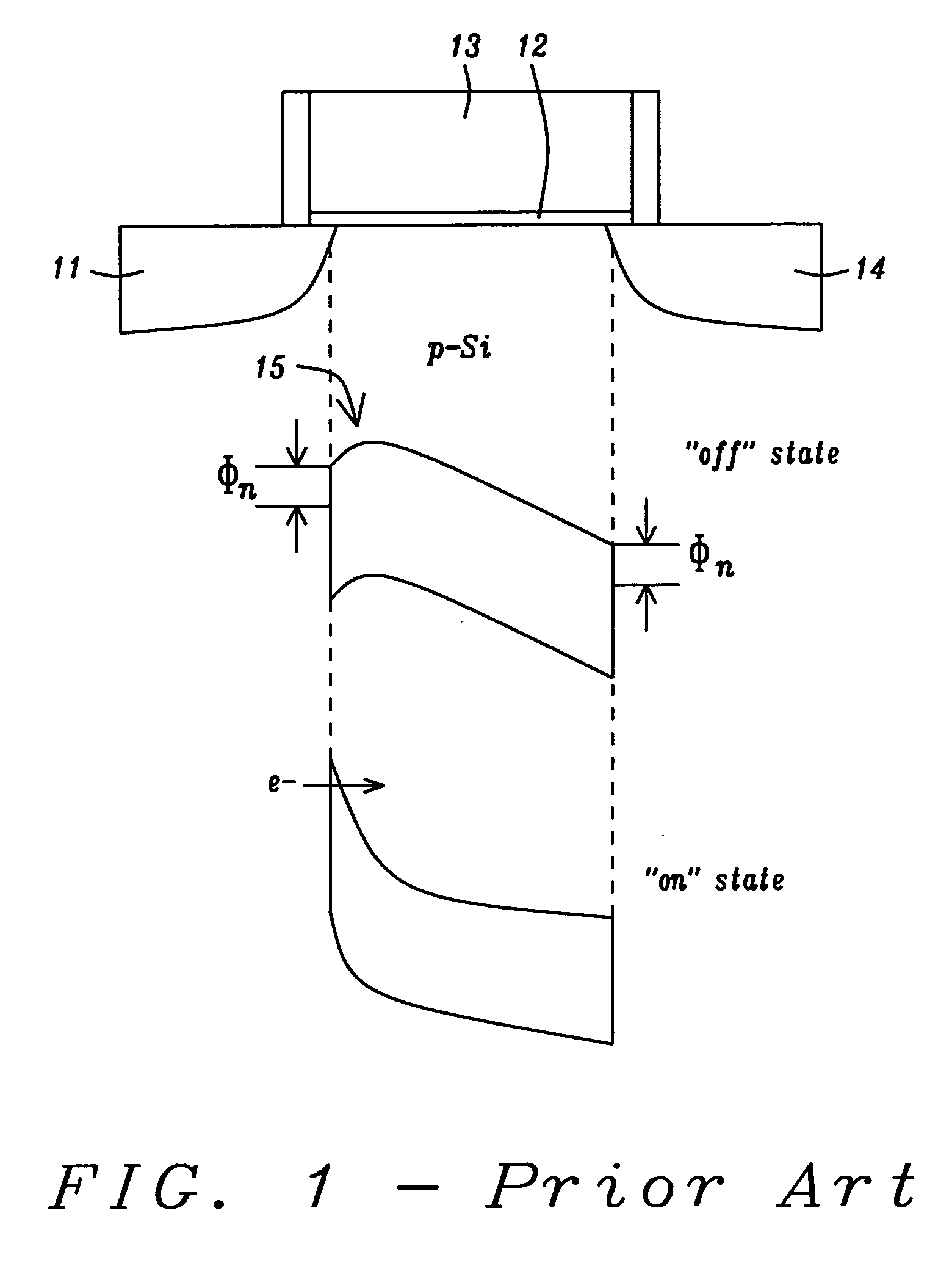
Ultra-high vacuum (UHV) is the vacuum regime characterised by pressures lower than about 10⁻⁷ pascal or 100 nanopascals (10⁻⁹ mbar, ~10⁻⁹ torr). UHV conditions are created by pumping the gas out of a UHV chamber. At these low pressures the mean free path of a gas molecule is greater than approximately 40 km, so the gas is in free molecular flow, and gas molecules will collide with the chamber walls many times before colliding with each other. Almost all molecular interactions therefore take place on various surfaces in the chamber.
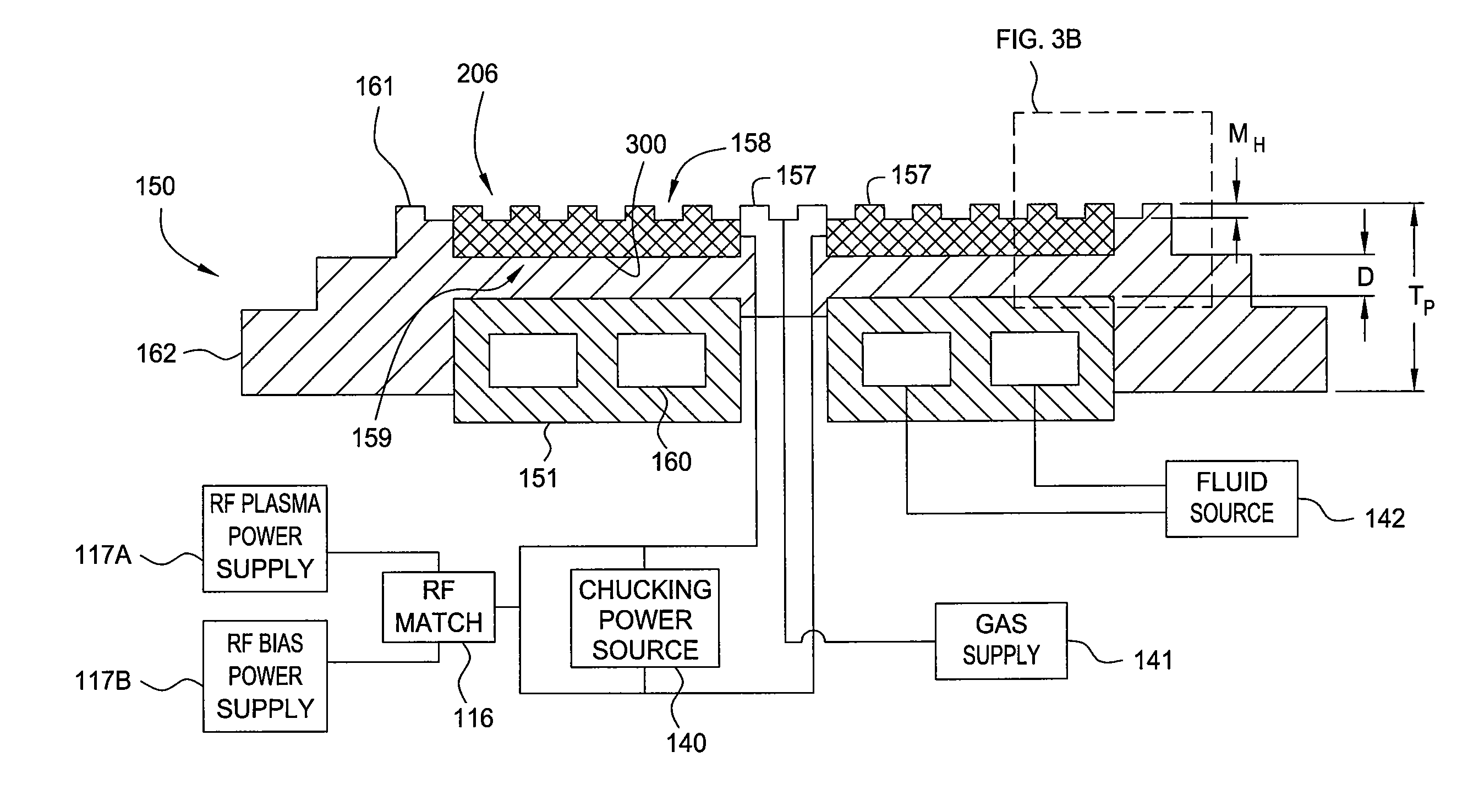
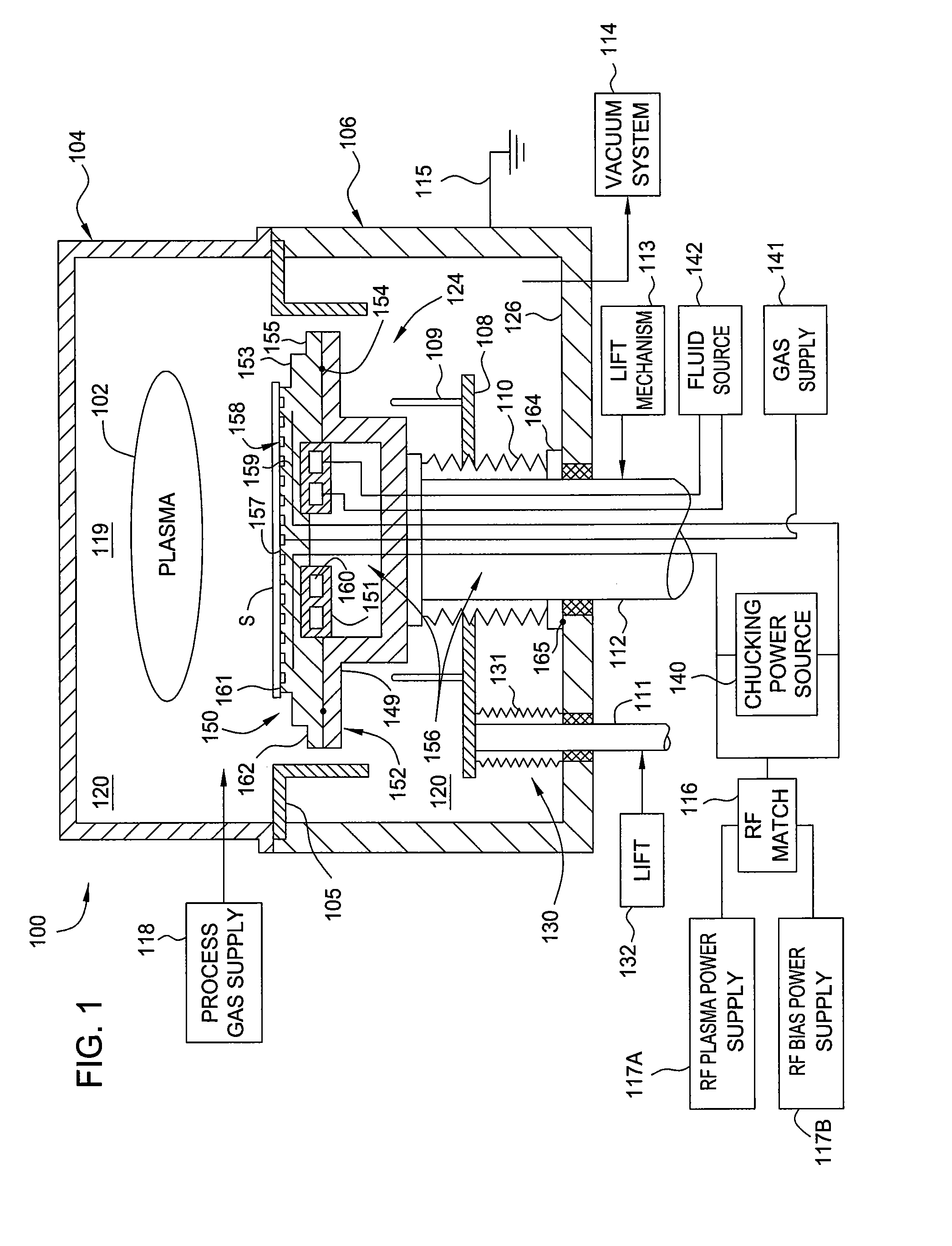
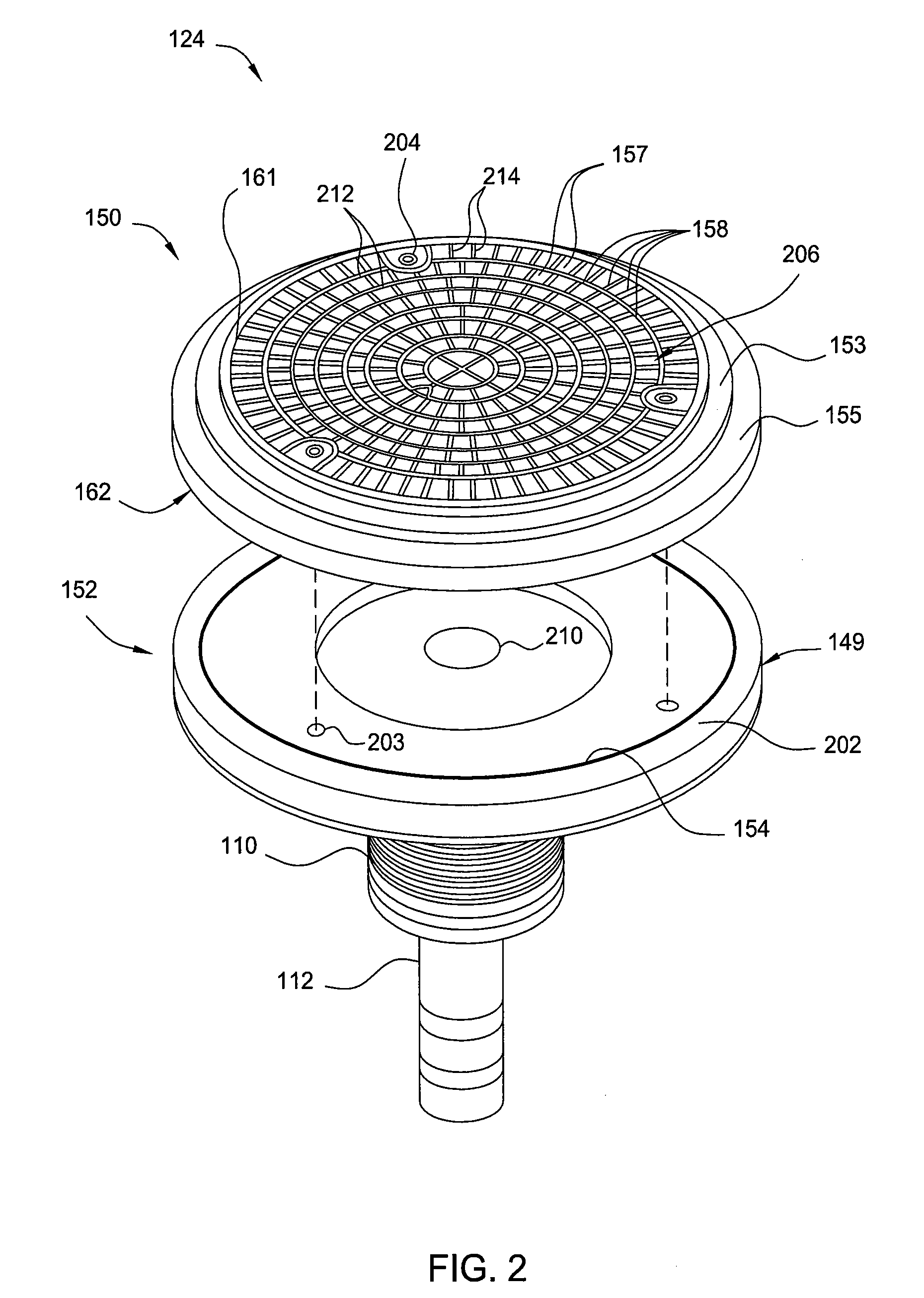
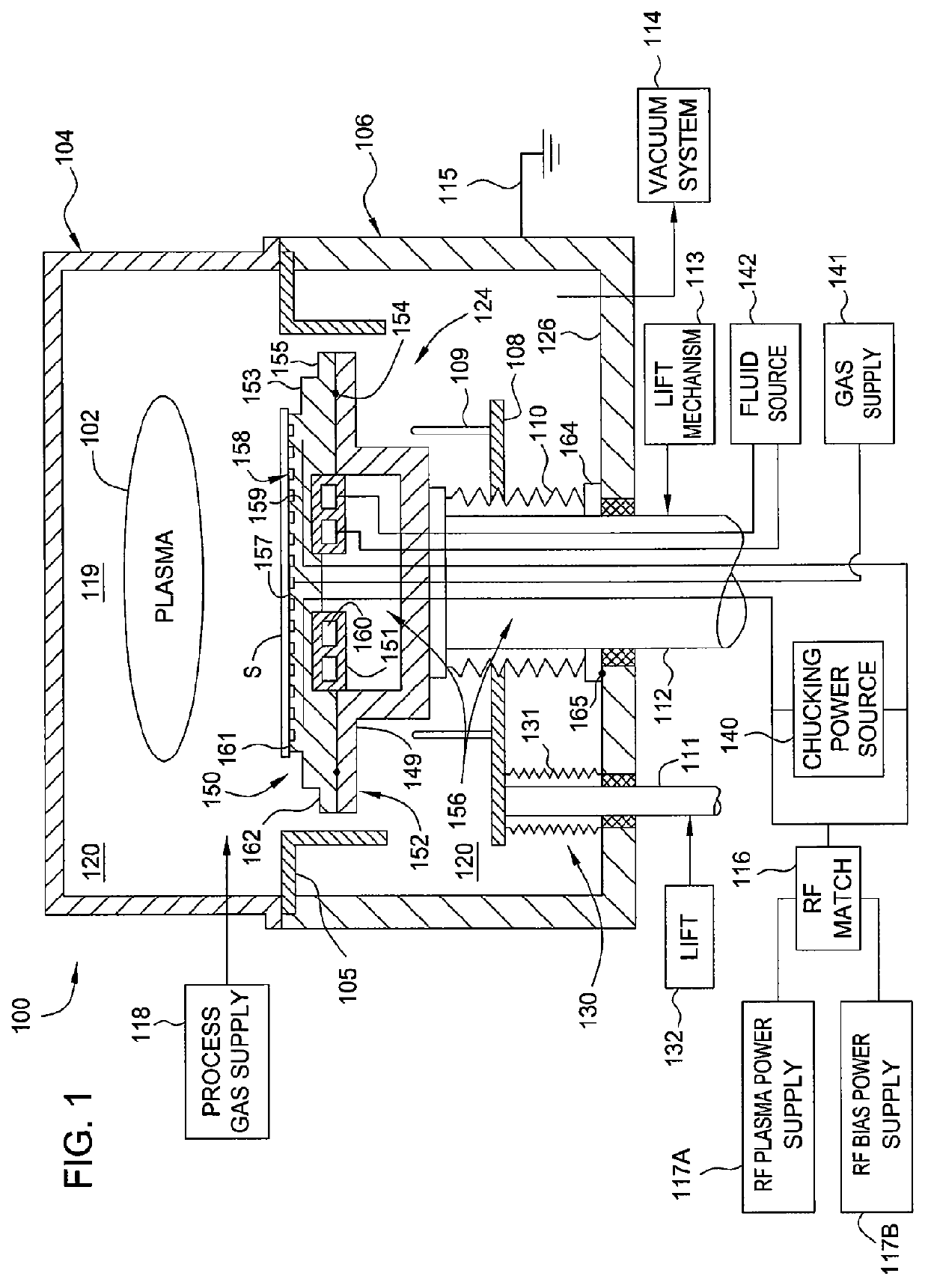
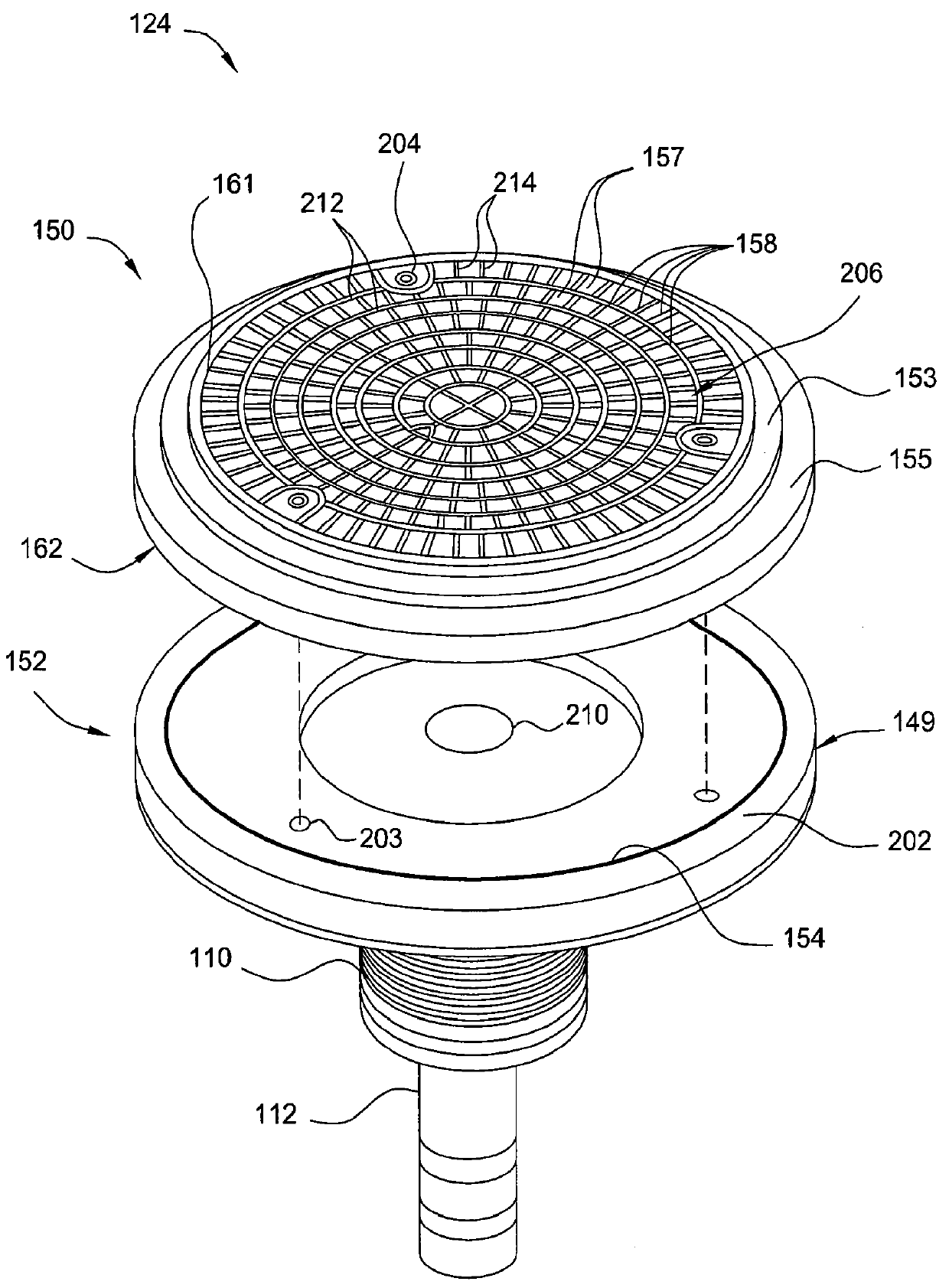
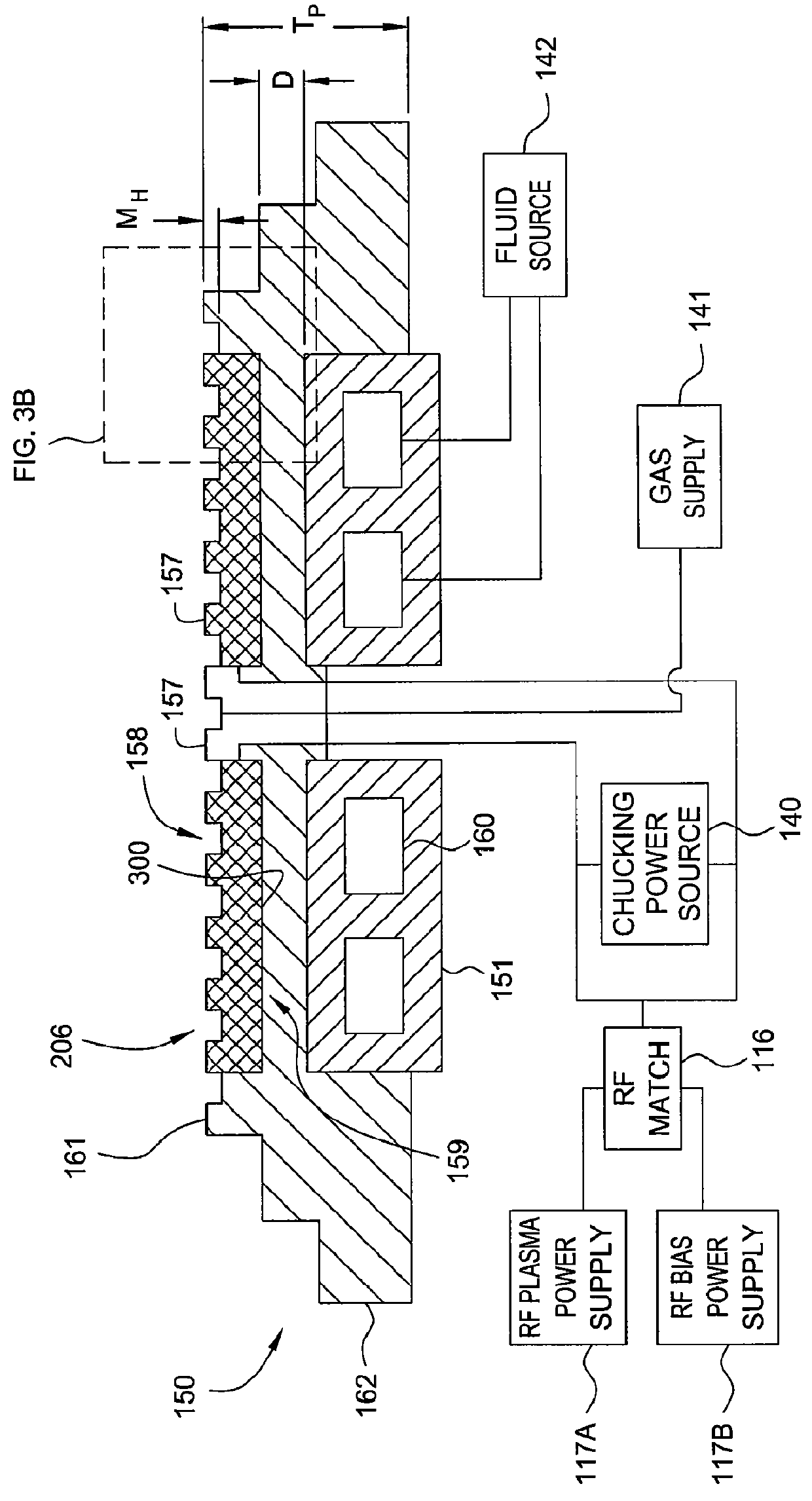
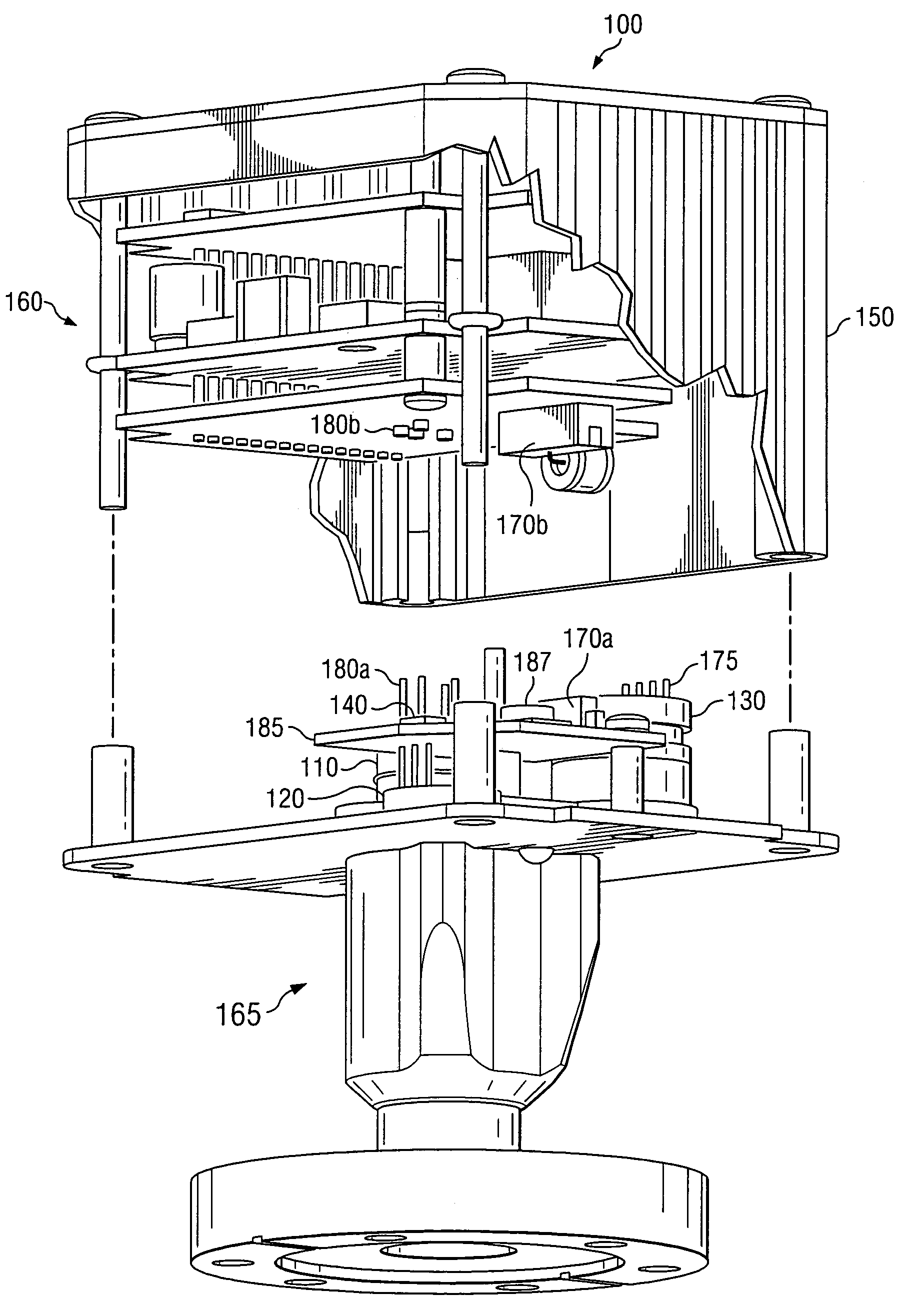
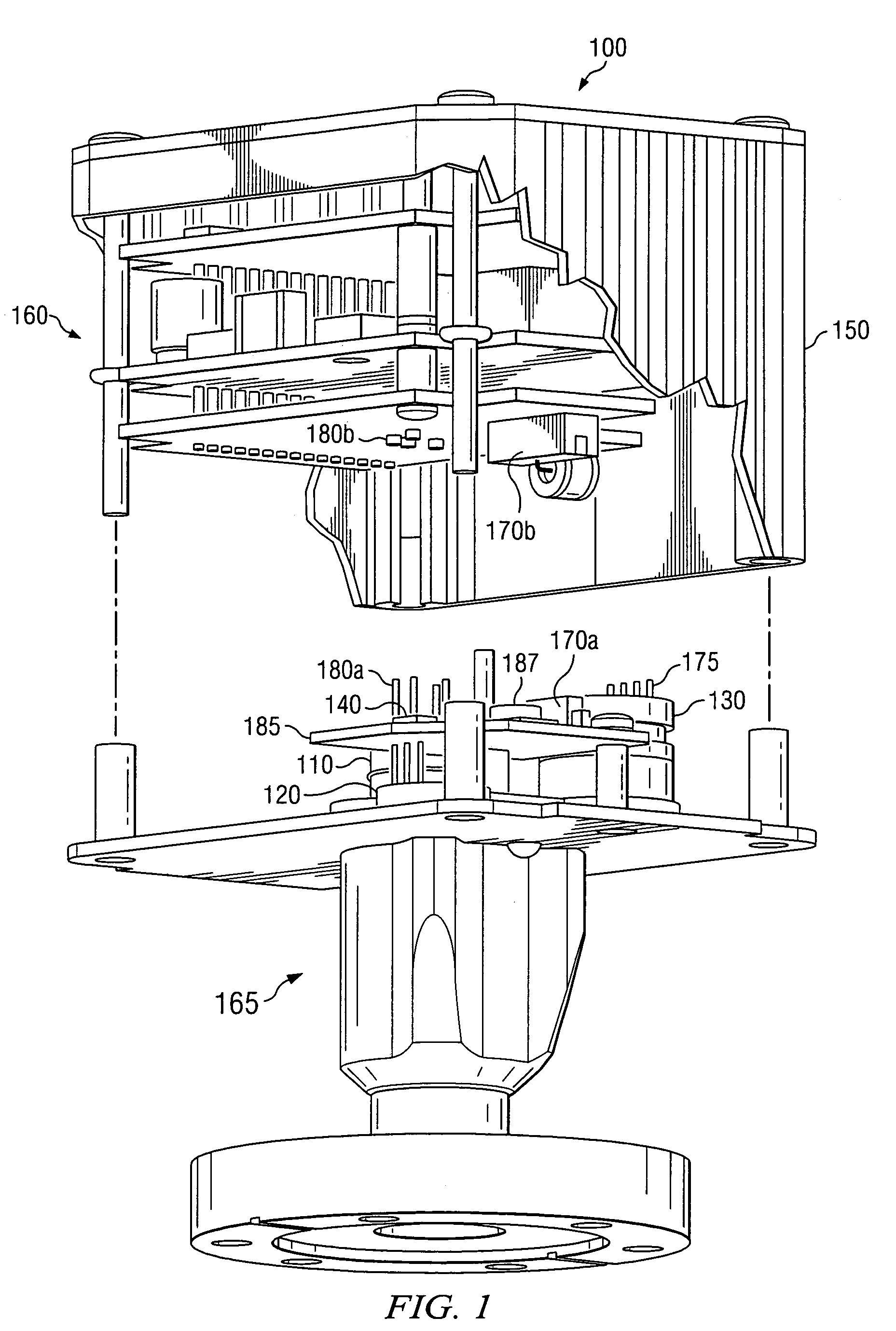
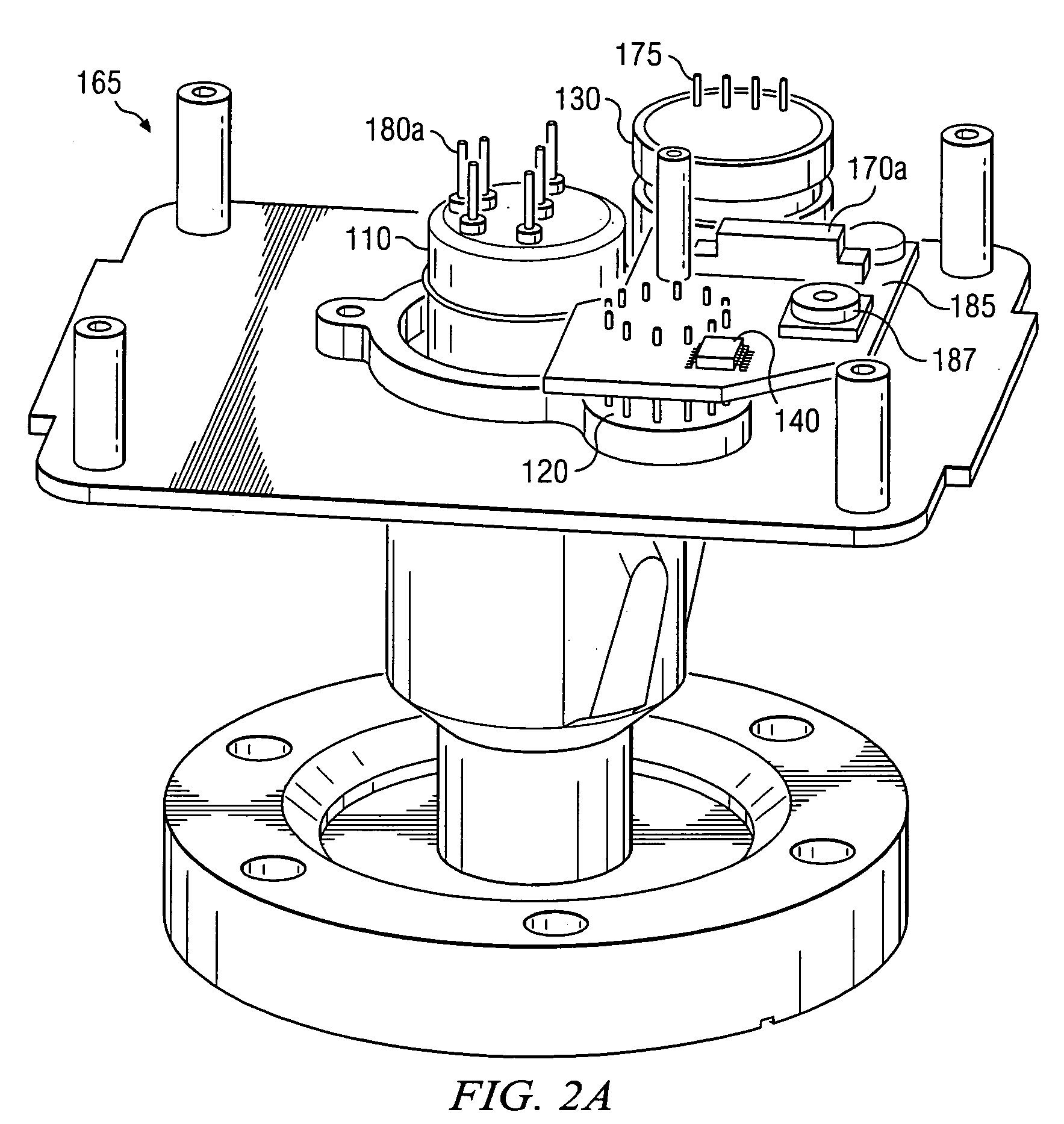
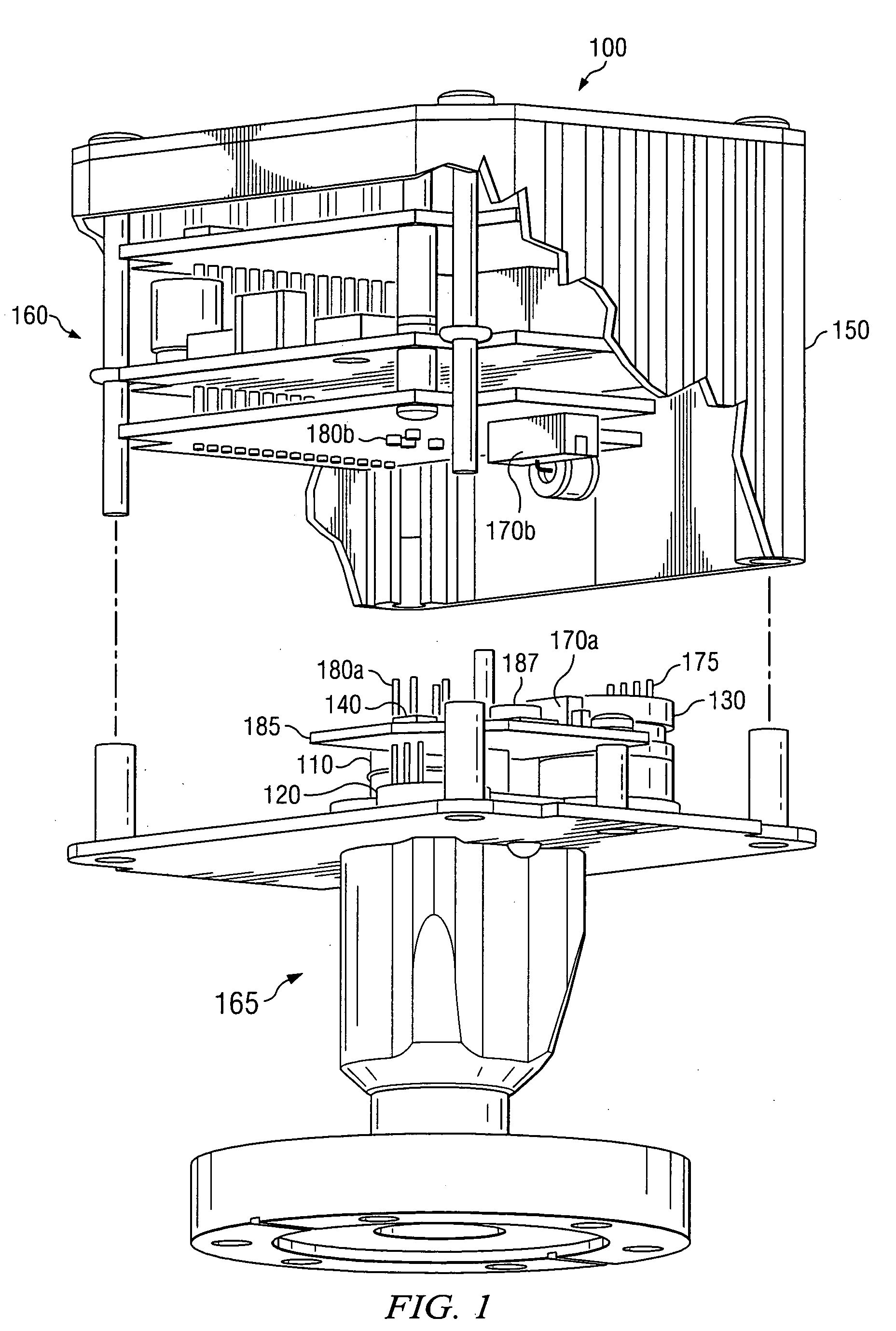
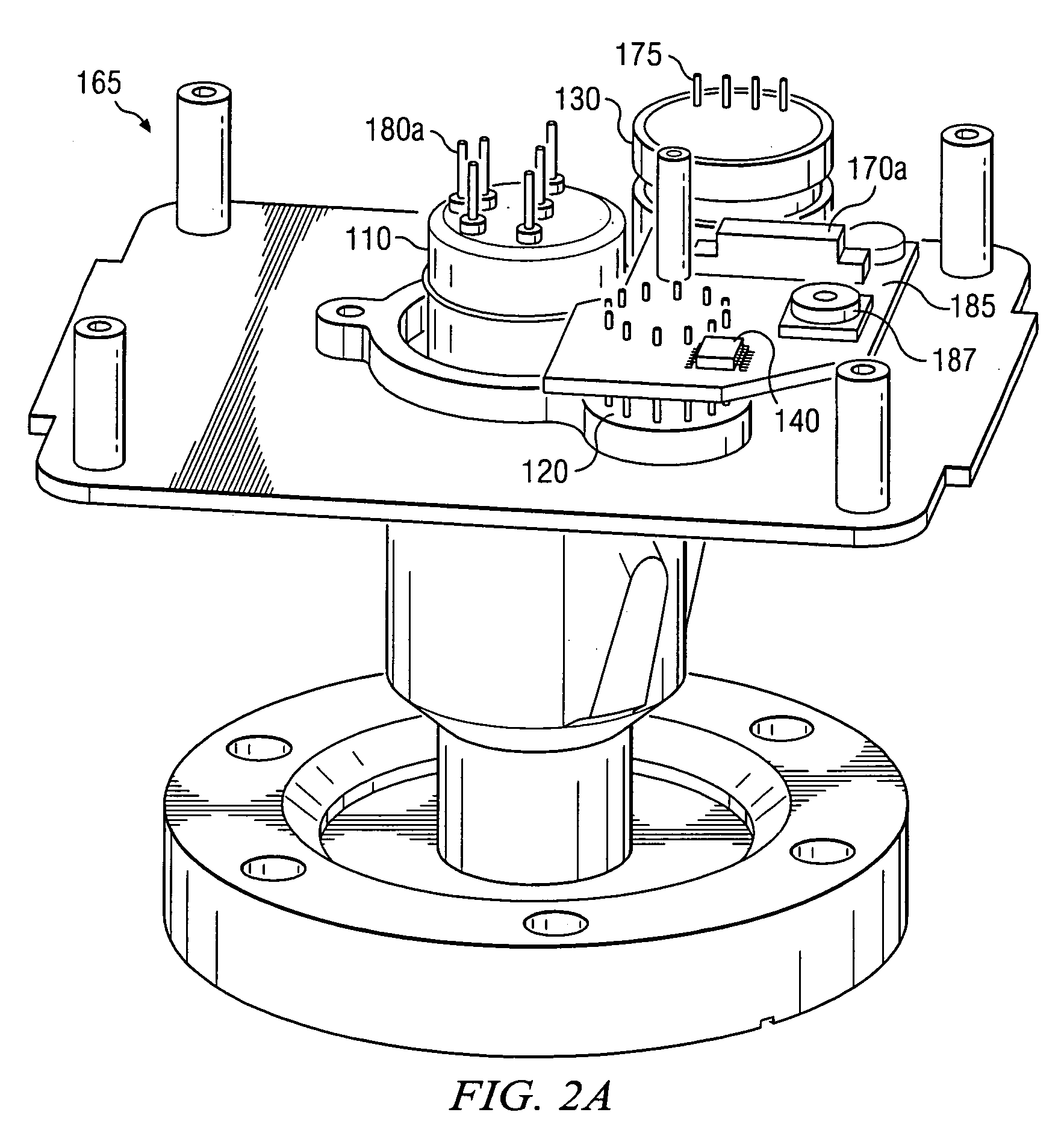
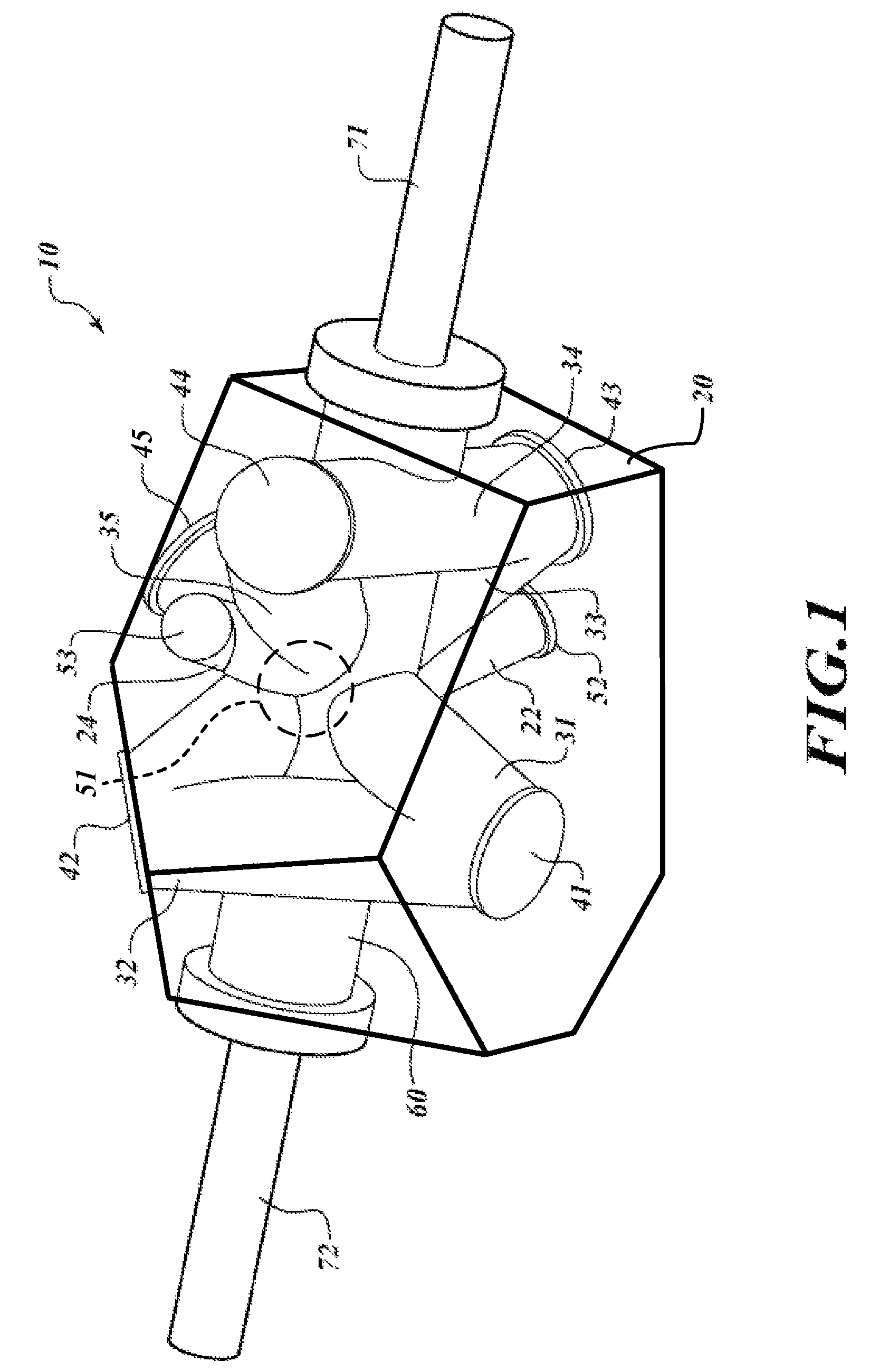
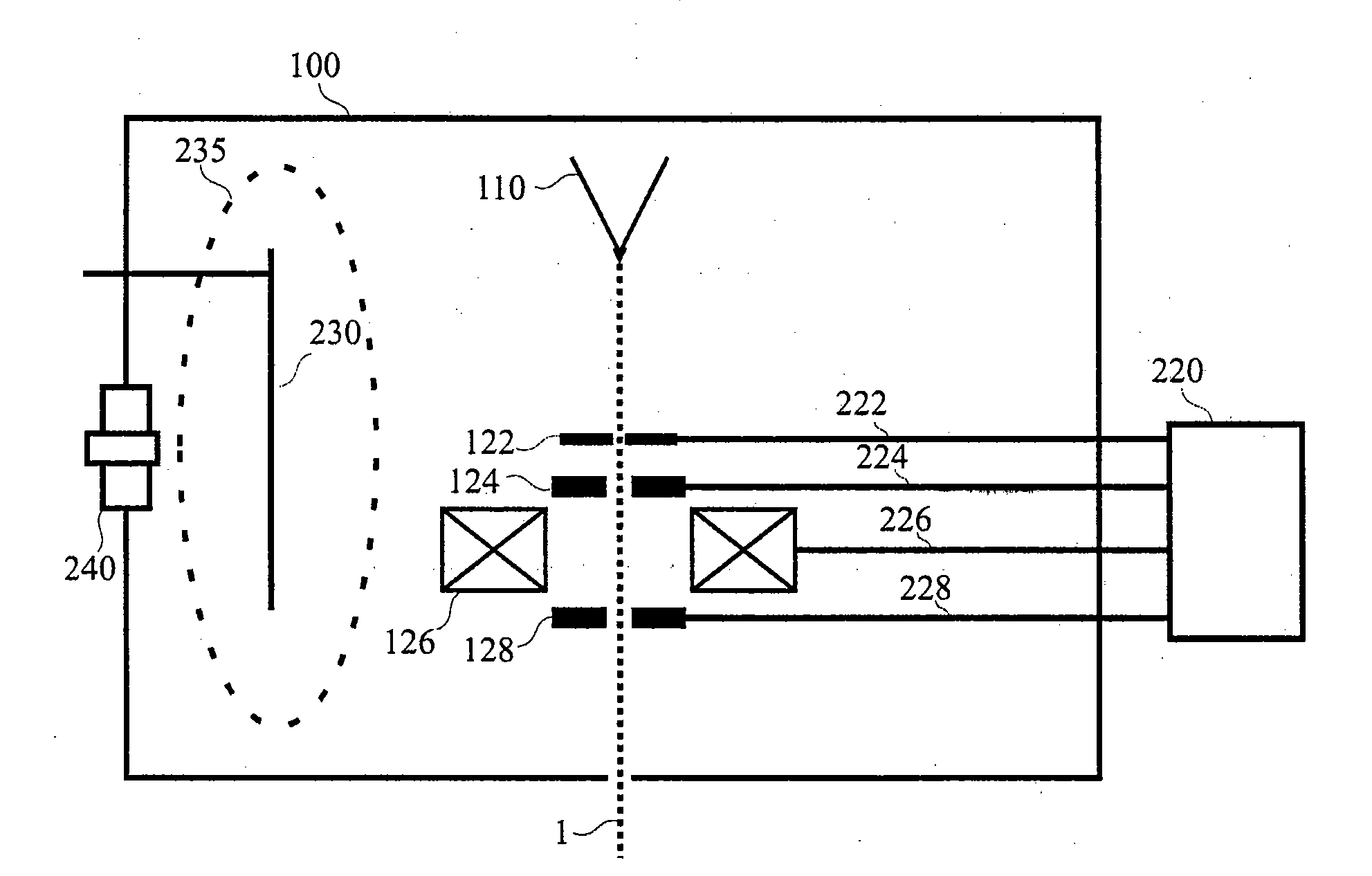
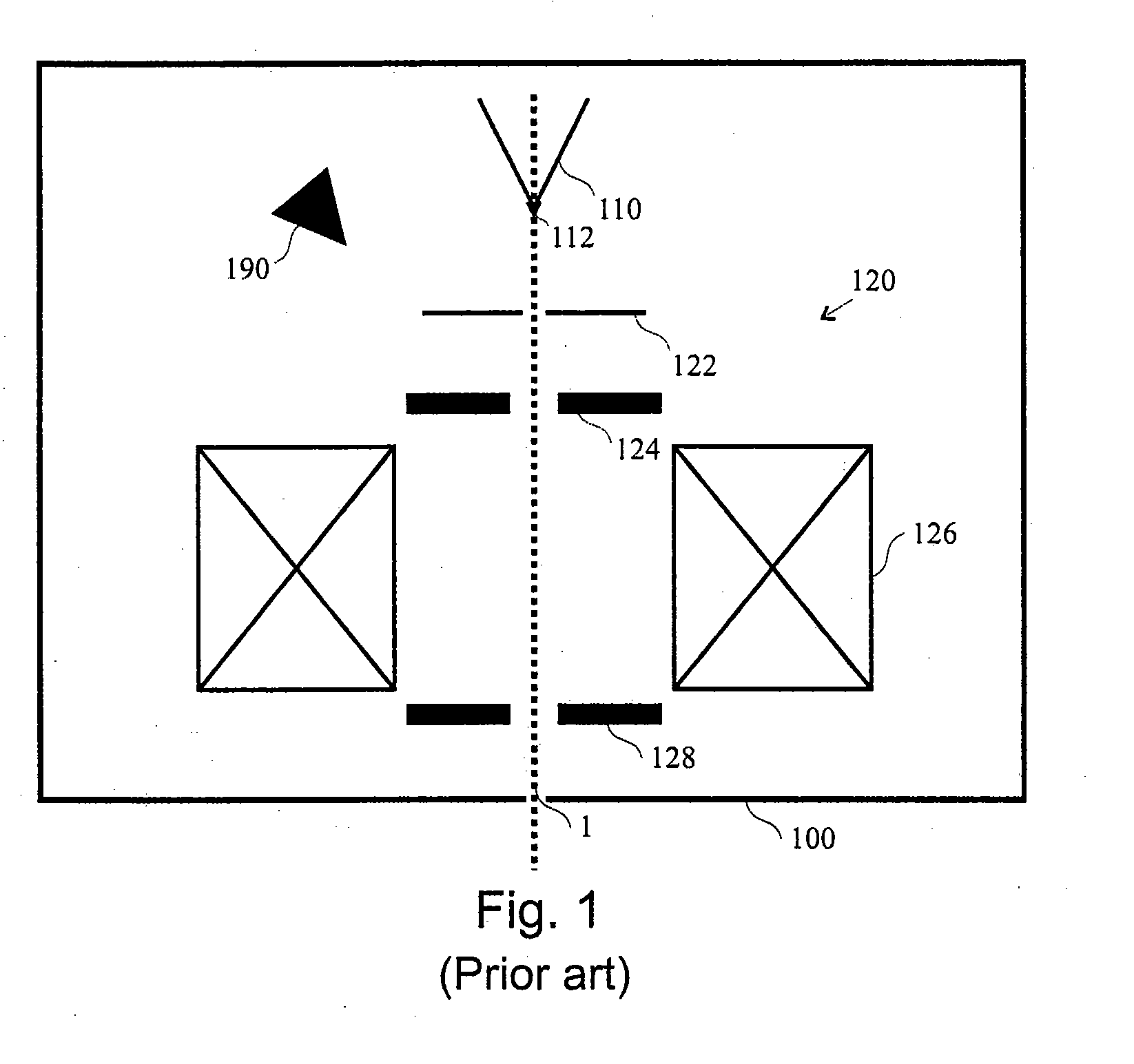
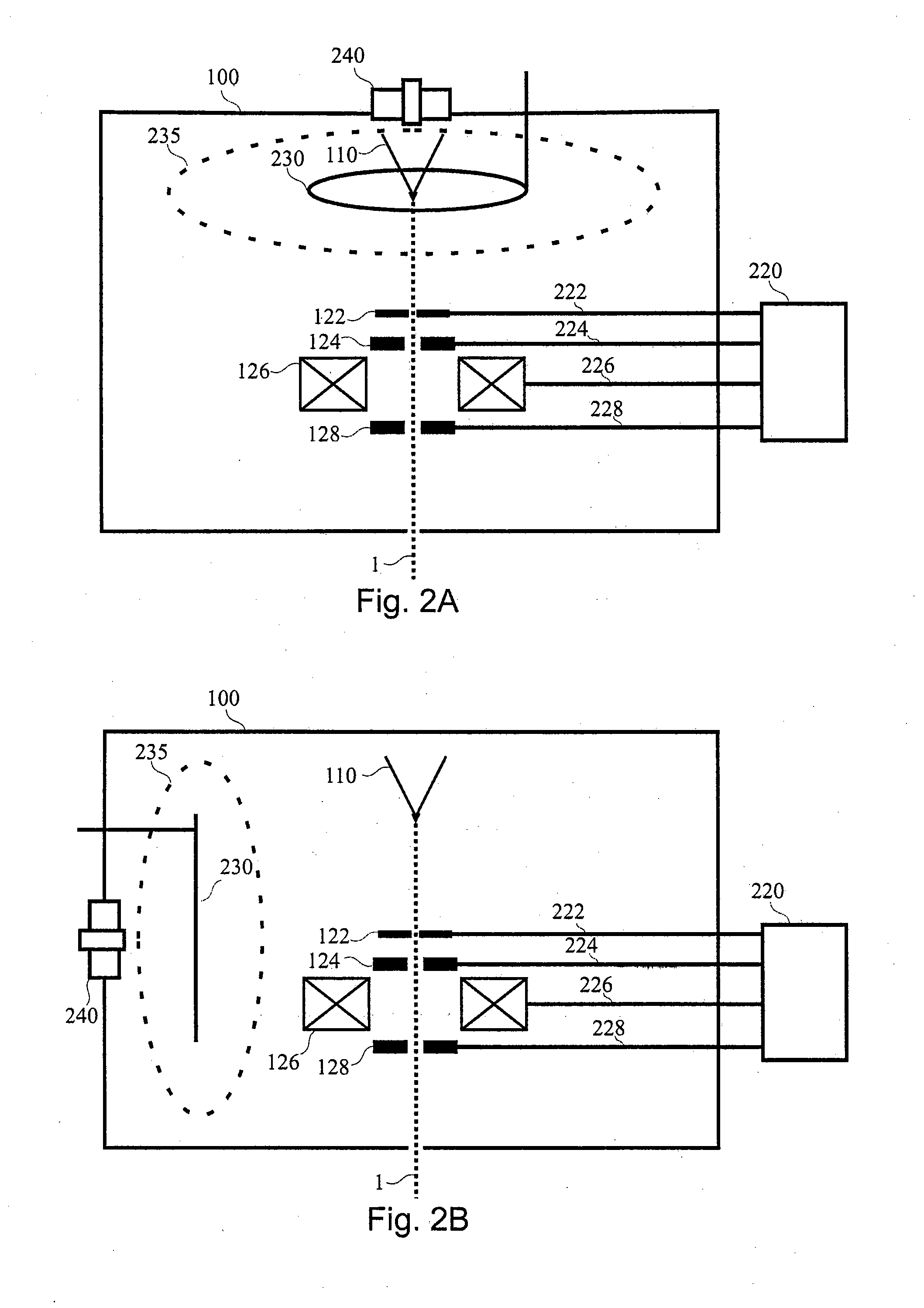
Electrostatic chuck assembly
ActiveUS20100039747A1Efficient couplingCost effectiveElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesUltra-high vacuumThermal expansion
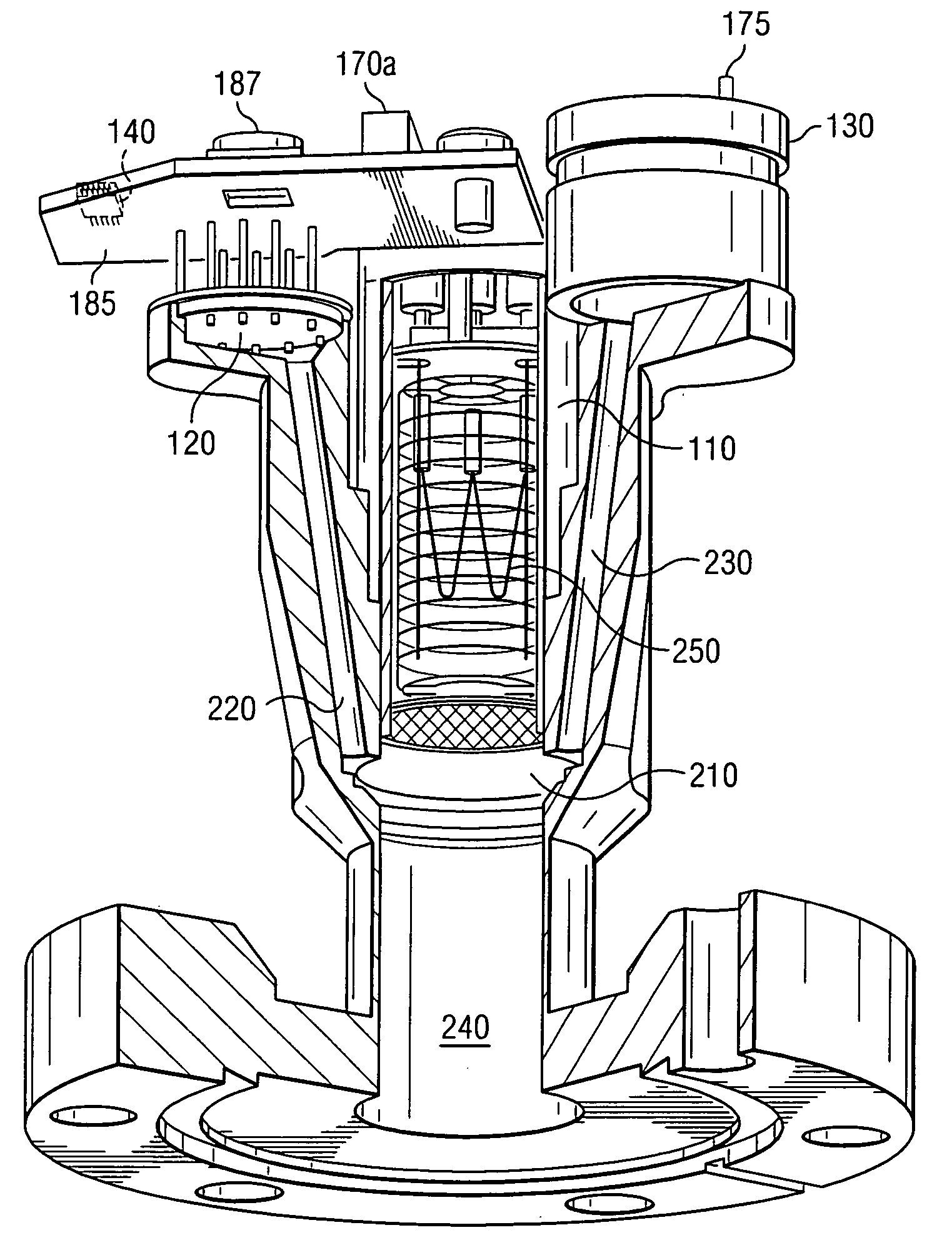
Embodiments of the present invention provide a cost effective electrostatic chuck assembly capable of operating over a wide temperature range in an ultra-high vacuum environment while minimizing thermo-mechanical stresses within the electrostatic chuck assembly. In one embodiment, the electrostatic chuck assembly includes a dielectric body having chucking electrodes which comprise a metal matrix composite material with a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that is matched to the CTE of the dielectric body.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrostatic chuck assembly
ActiveUS8390980B2Efficient couplingCost effectiveElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesUltra-high vacuumThermal expansion
Embodiments of the present invention provide a cost effective electrostatic chuck assembly capable of operating over a wide temperature range in an ultra-high vacuum environment while minimizing thermo-mechanical stresses within the electrostatic chuck assembly. In one embodiment, the electrostatic chuck assembly includes a dielectric body having chucking electrodes which comprise a metal matrix composite material with a coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that is matched to the CTE of the dielectric body.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
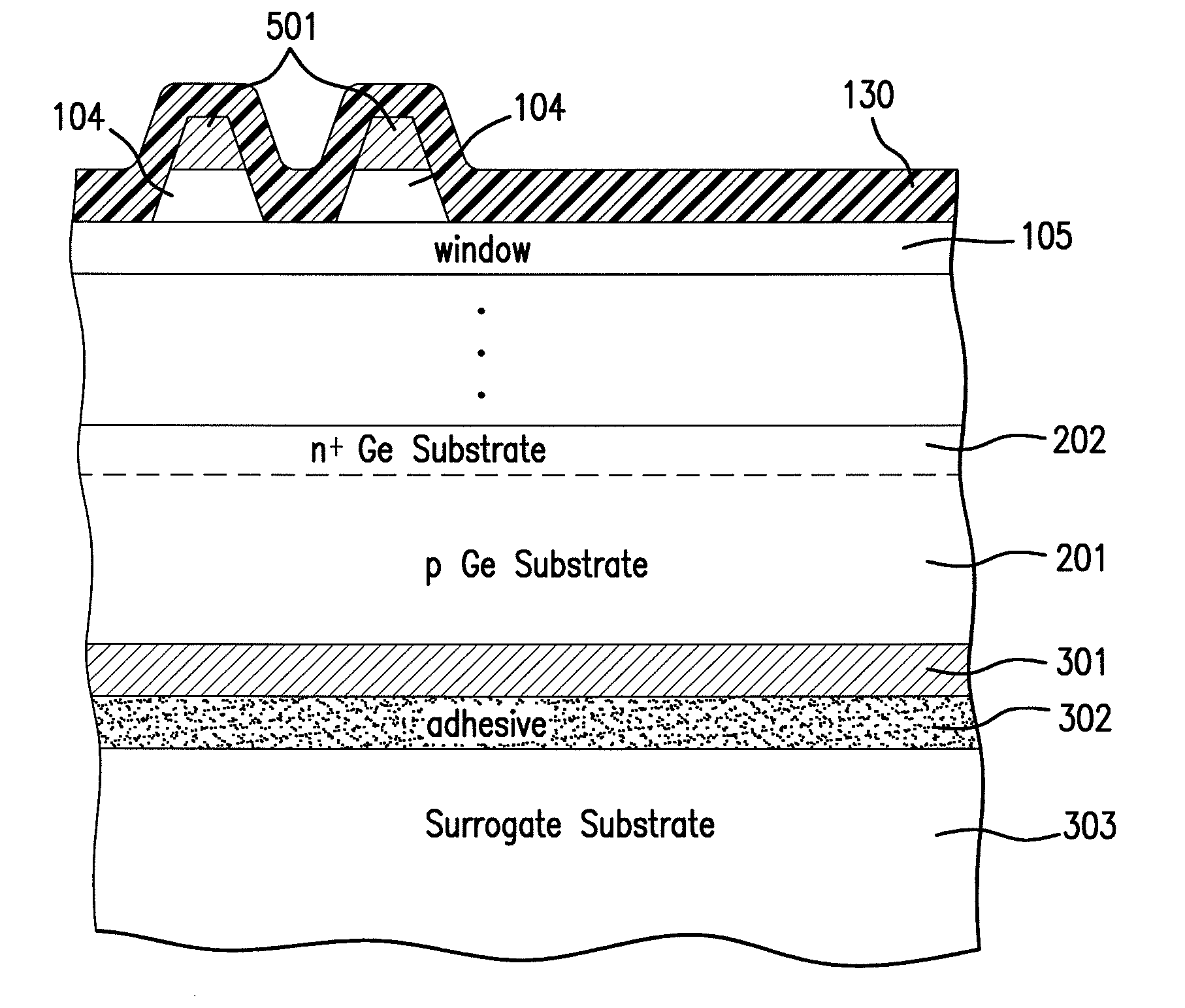
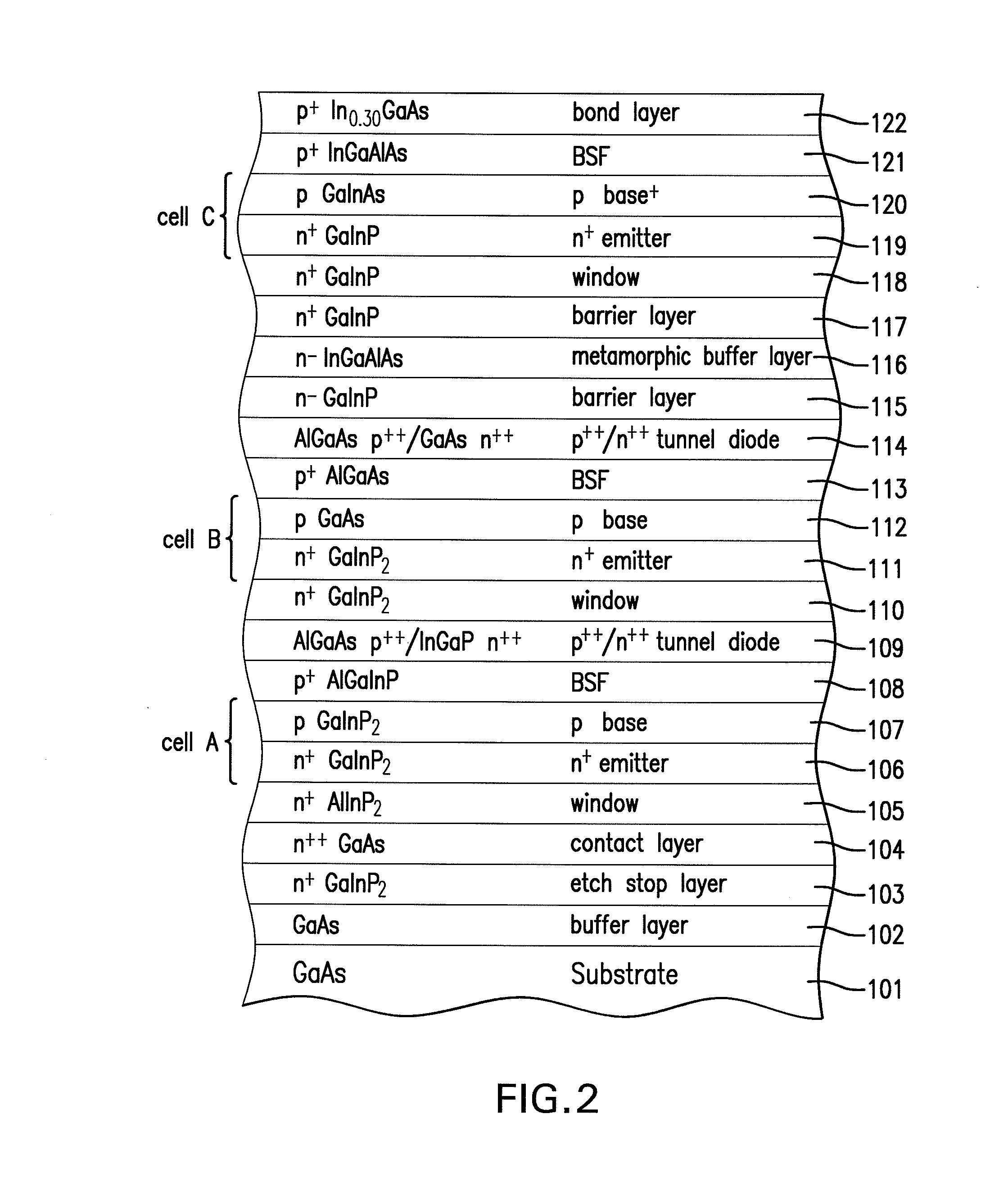
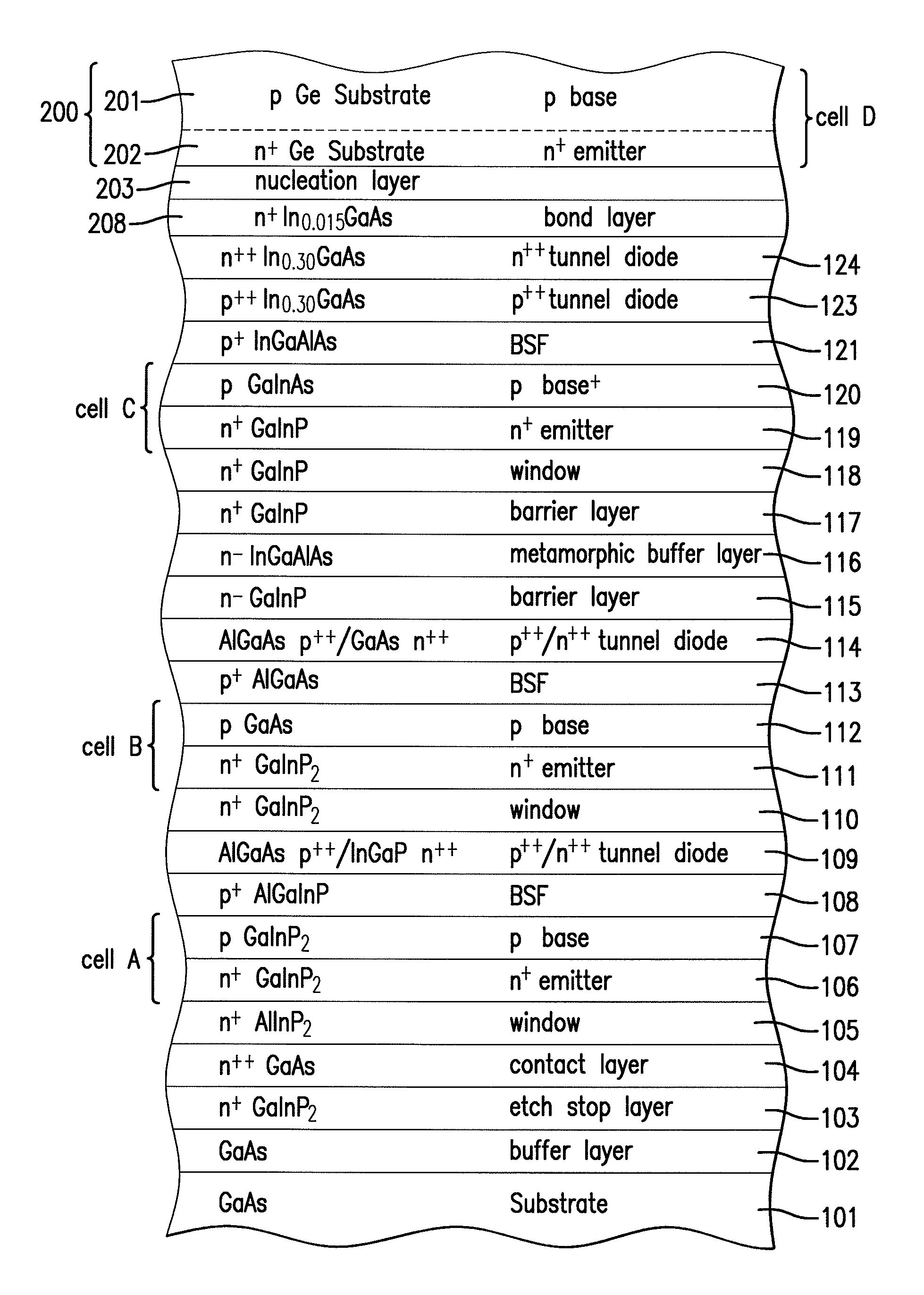
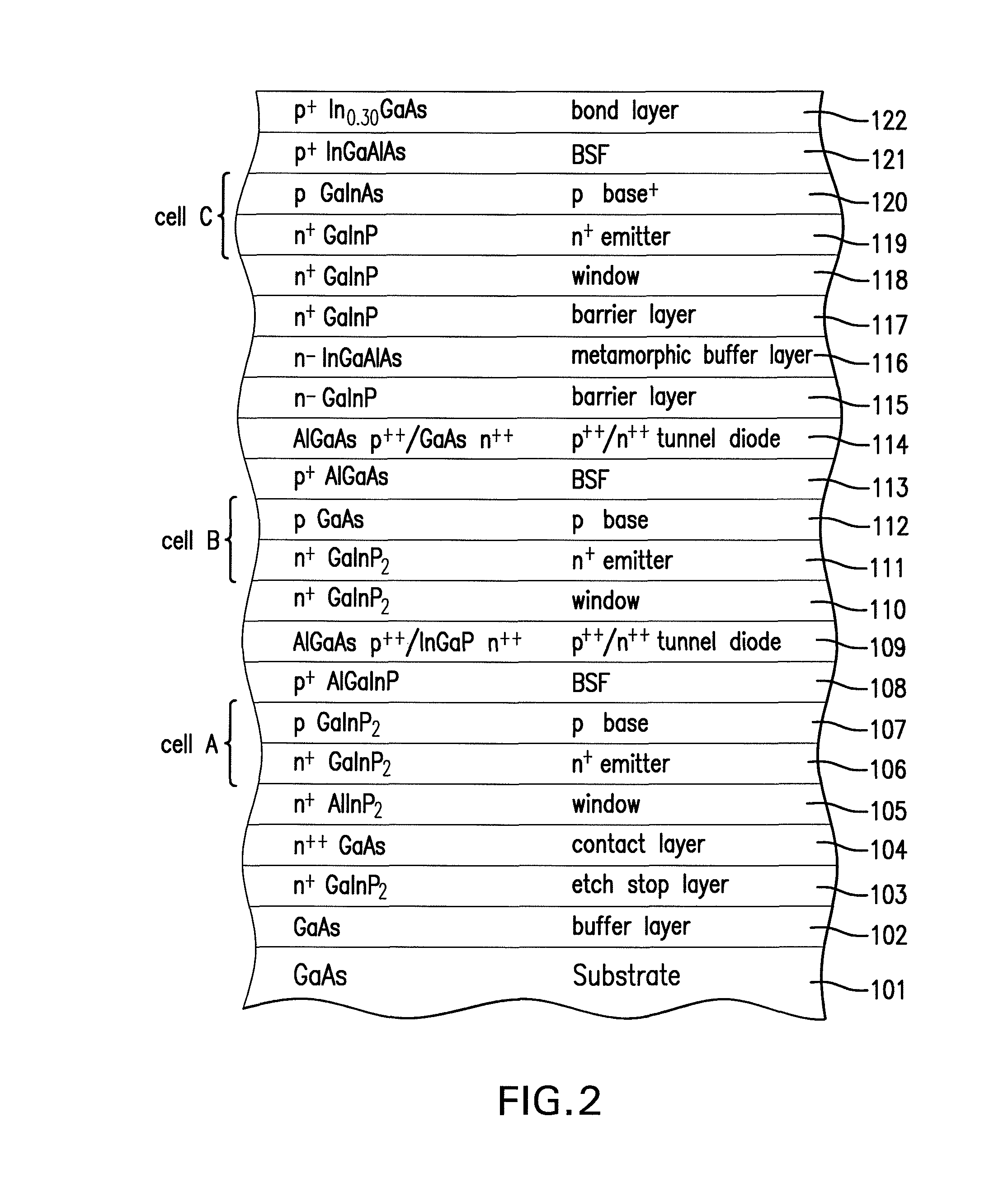
Four junction inverted metamorphic multijunction solar cell
ActiveUS20100116327A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsUltra-high vacuum
A method of manufacturing a solar cell by providing a first semiconductor substrate and depositing a first sequence of layers of semiconductor material to form a first solar subcell, including a first bond layer disposed on the top of the first sequence of layers. A second semiconductor substrate is provided, and on the top surface of the second substrate a second sequence of layers of semiconductor material is deposited forming at least a second solar subcell. A second bond layer is disposed on the top of said second sequence of layers. The first solar subcell is mounted on top of the second solar subcell by joining the first bond layer to the second bond layer in an ultra high vacuum chamber, and the first semiconductor substrate is removed.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
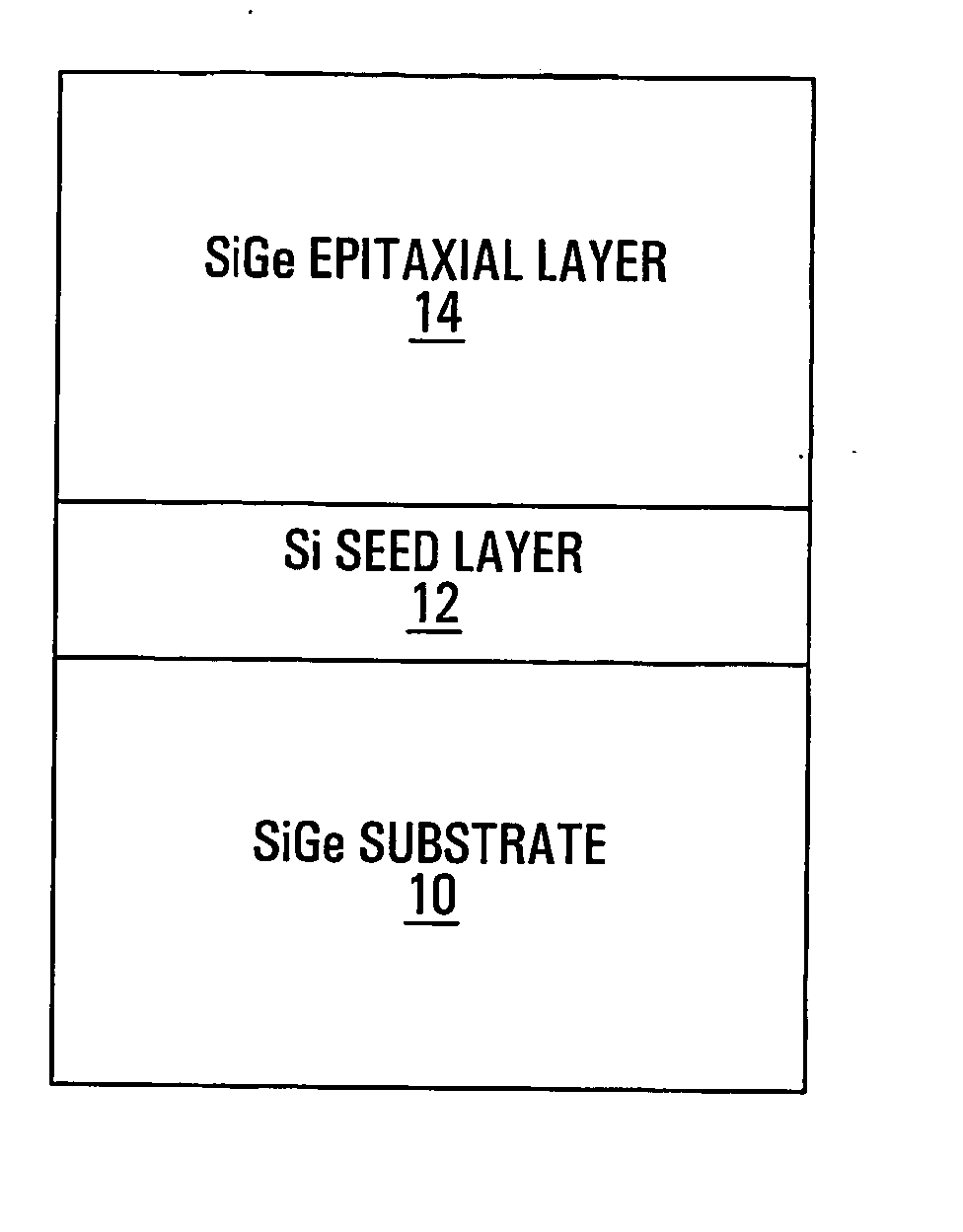
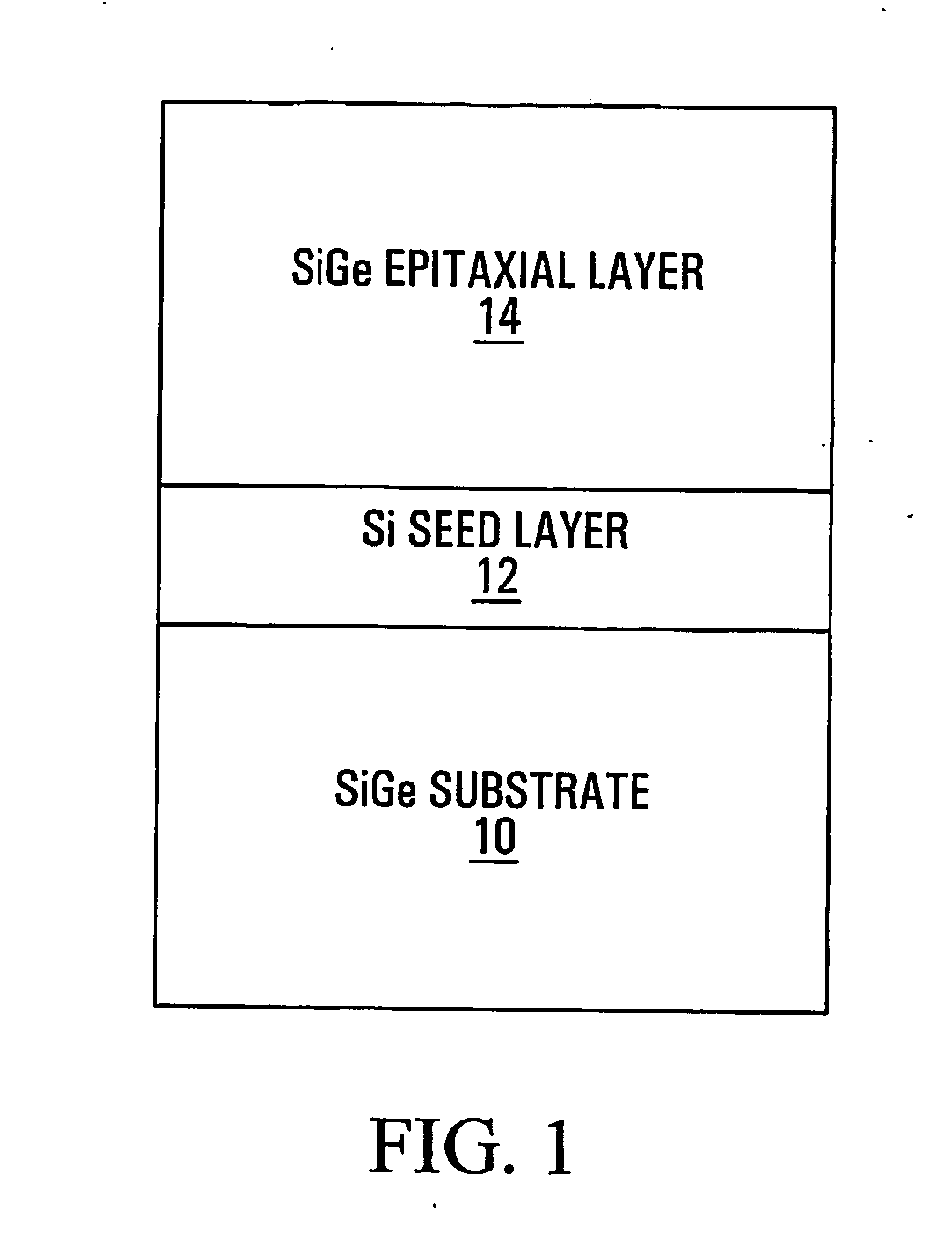
Method of depositing high-quality sige on sige substrates
InactiveUS20050070076A1Polycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateAtomic force microscopyGas phase
This invention provides a method of depositing high-quality Si or SiGe epitaxial layers on SiGe substrates. By first depositing a thin Si seed layer on the SiGe substrate, the quality of the seed layer and of the subsequently deposited layers is greatly improved over what is obtained from depositing SiGe directly onto the SiGe substrate. Indeed, whereas the RMS surface roughness of the deposition of SiGe directly on SiGe, as measured by atomic-force microscopy (AFM), was 3-4 nm, it was more than an order of magnitude better when a thin Si seed layer was employed. This work was performed on an ultra-high-vacuum chemical vapor deposition (UHV / CVD) system; however, the same method would apply to other deposition systems such as atmospheric-pressure, low-pressure and rapid-thermal CVD.
Owner:SIGE SEMICON
Cold atom micro primary standard
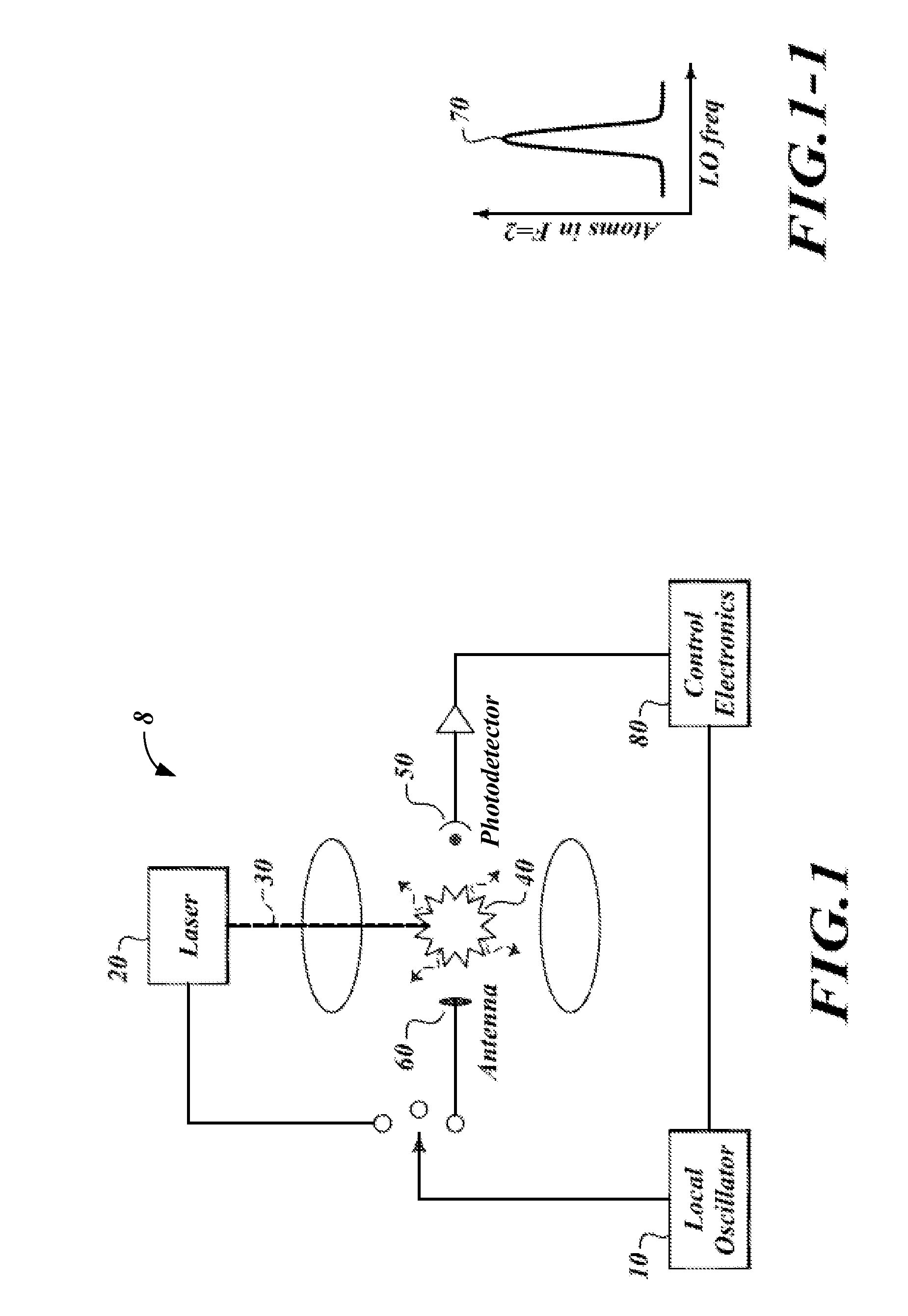
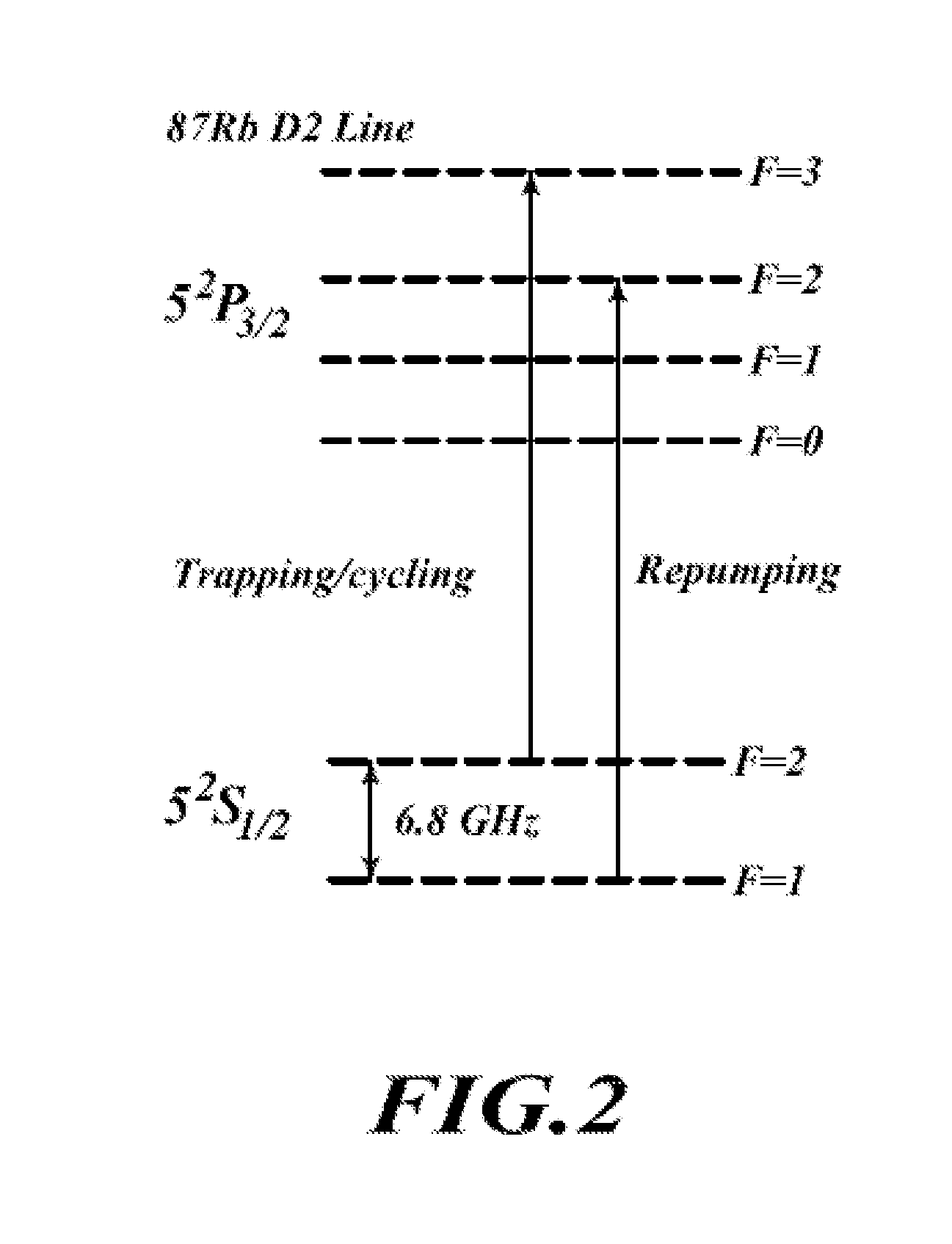
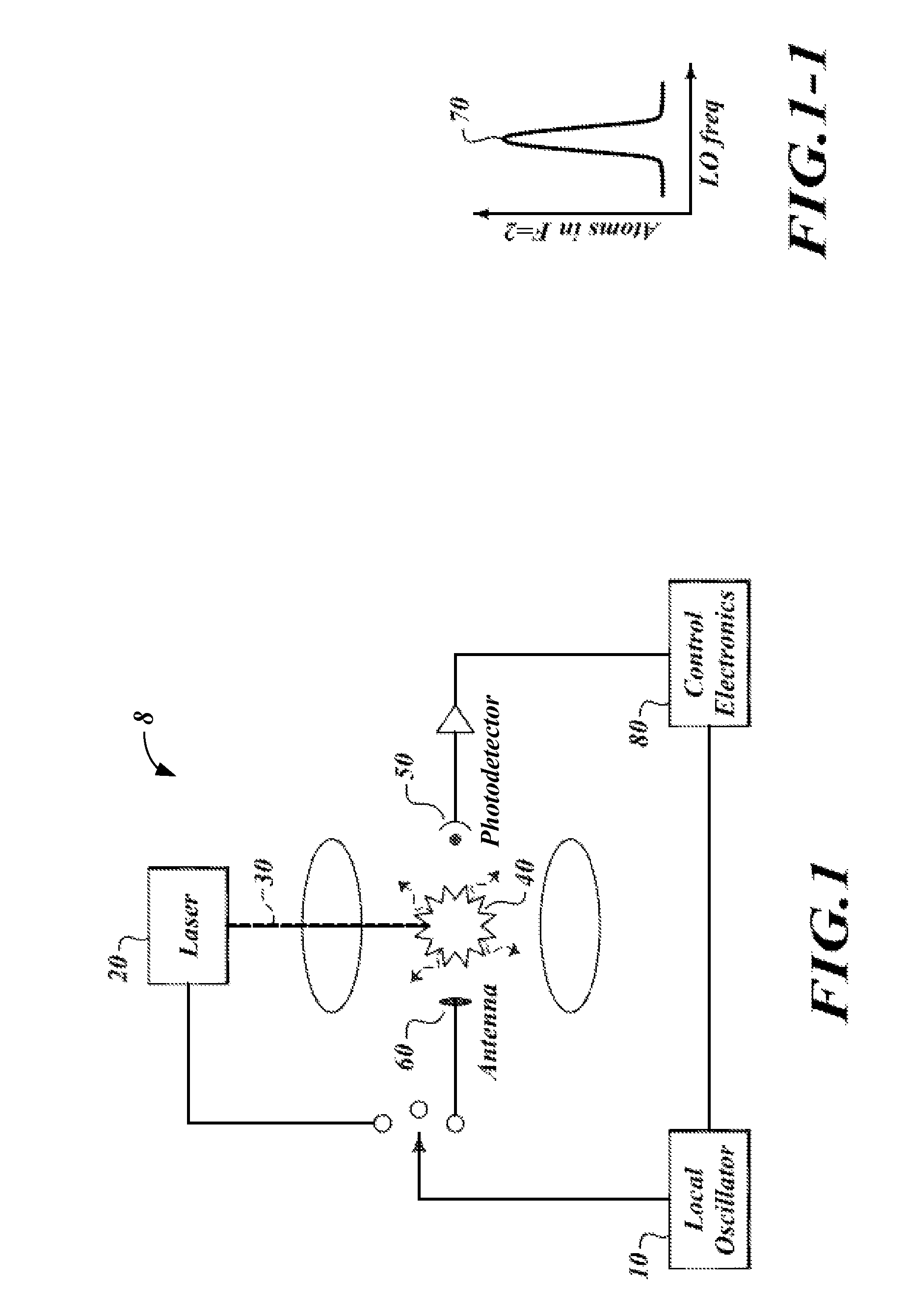
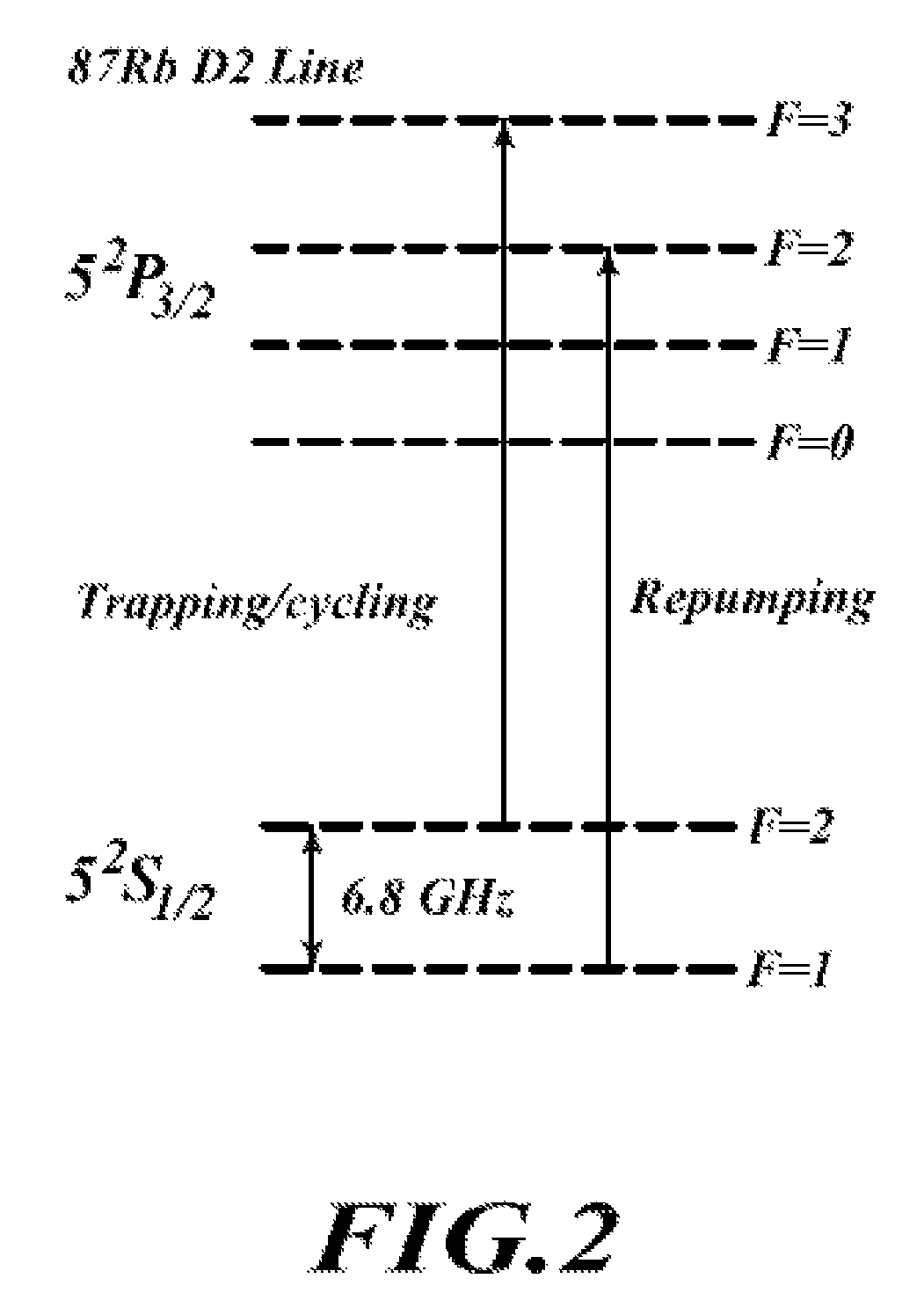
InactiveUS20100033256A1Maximizing numberLong life-timeLaser detailsApparatus using atomic clocksUltra-high vacuumTrapping
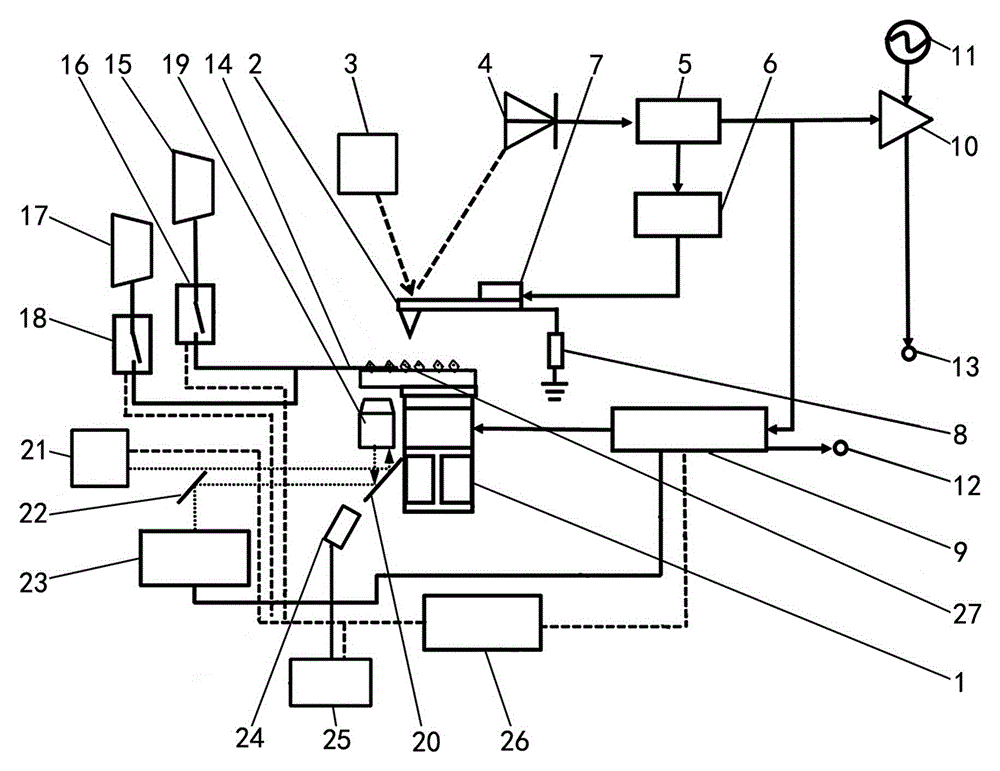
An atomic clock having a physics package that includes a vacuum chamber cavity that holds atoms of Rb-87 under high vacuum conditions, an optical bench having a single laser light source, a local oscillator, a plurality of magnetic field coils, an antenna, at least one photo-detector and integrated control electronics. The single laser light source has a fold-retro-reflected design to create three retro-reflected optical beams that cross at 90° angles relative to one another in the vacuum chamber cavity. This design allows the single laser light source to make the required six trapping beams needed to trap and cool the atoms of Rb-87. The foregoing design makes possible atomic clocks having reduced size and power consumption and capable of maintaining an ultra-high vacuum without active pumping.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Device and method for measuring air permeability of isolation material
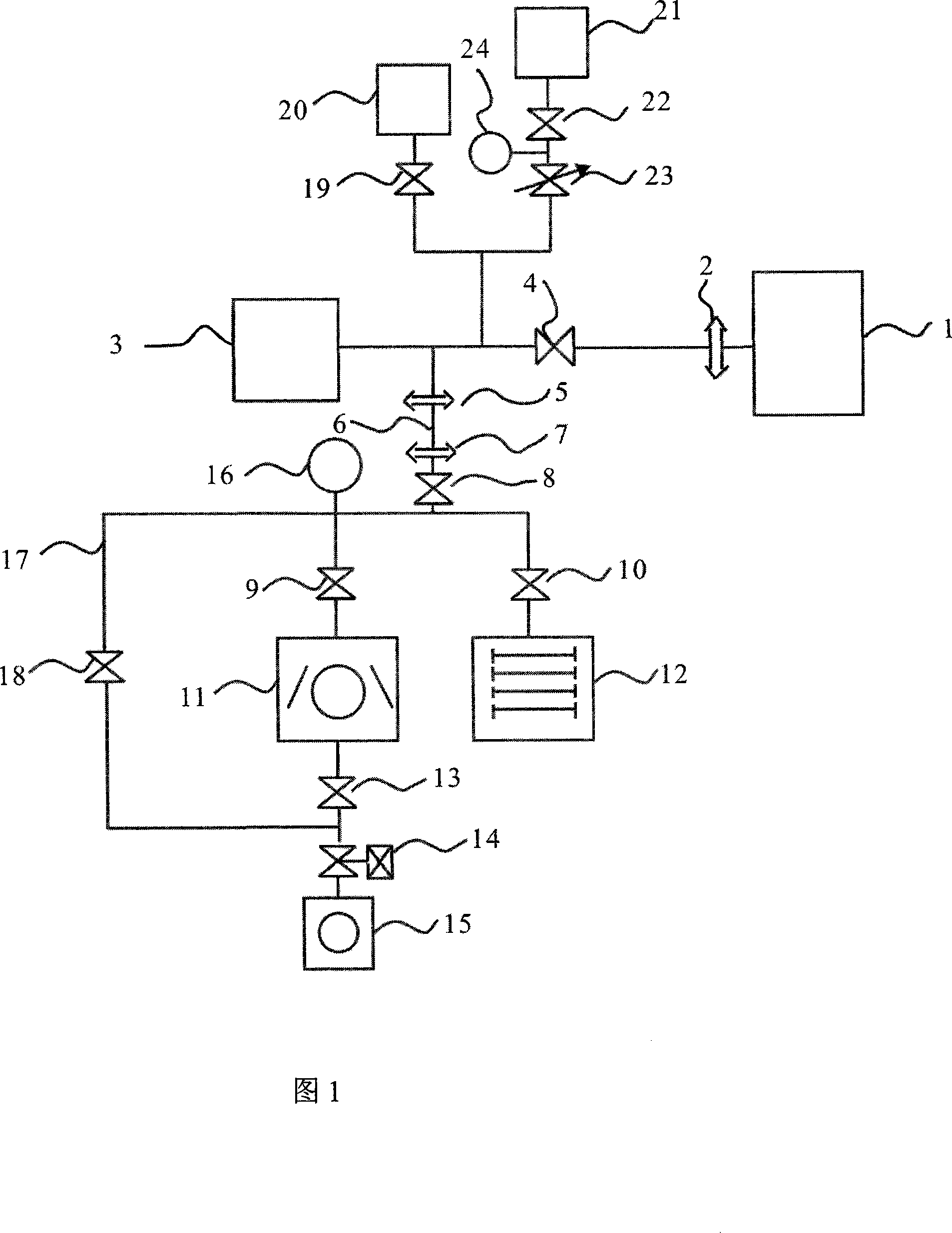
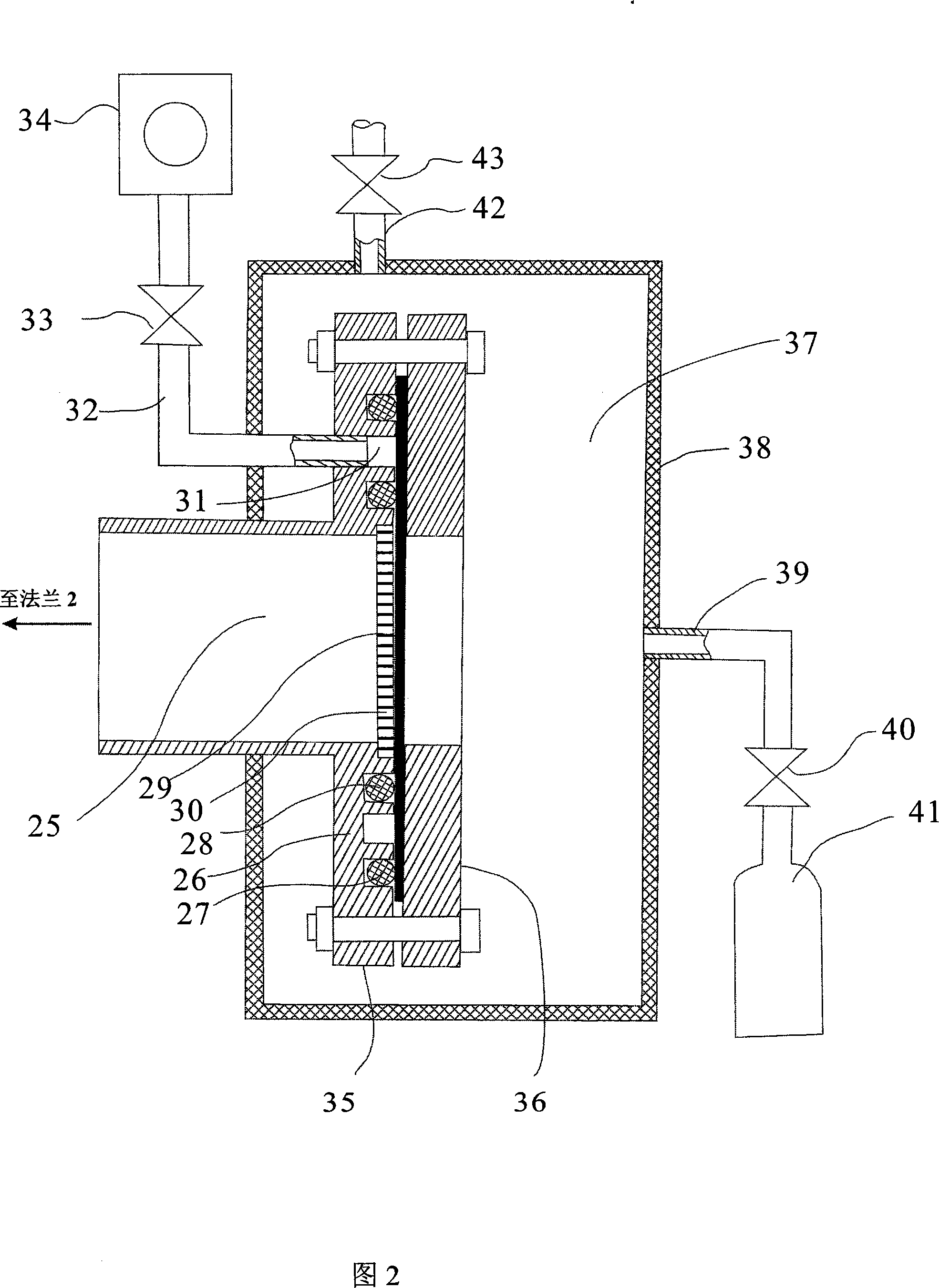
InactiveCN101246095AReduced leak rate into vacuum chamberReduce the pressure valueWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMeasurement deviceCurrent limiting
The present invention discloses an isolating material air permeability measuring device which comprises a double vacuum sealing structure permeating gas sampling device and an isolation material air permeability measuring device of the current limiting air extraction pipeline, the device comprises a permeation gas sampling device with double vacuum sealing structure, an ultrahigh vacuum system, a mass spectrograph and a calibrating device, wherein the permeation gas sampling device is connected to the mass spectrograph 3, the current limiting air extraction pipeline 6 and the calibrating device 19-24 through the flange 2 and the vacuum valve 4. The device can overcome the defects of low signal-to-noise ratio when the mass spectrum signal of the permeation air is measured and difficulty for measuring the isolation material with low air permeability existing in the existing technique, and has the characters of quick measuring speed, being able to measure the permeability rate of all gases to the isolation material.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
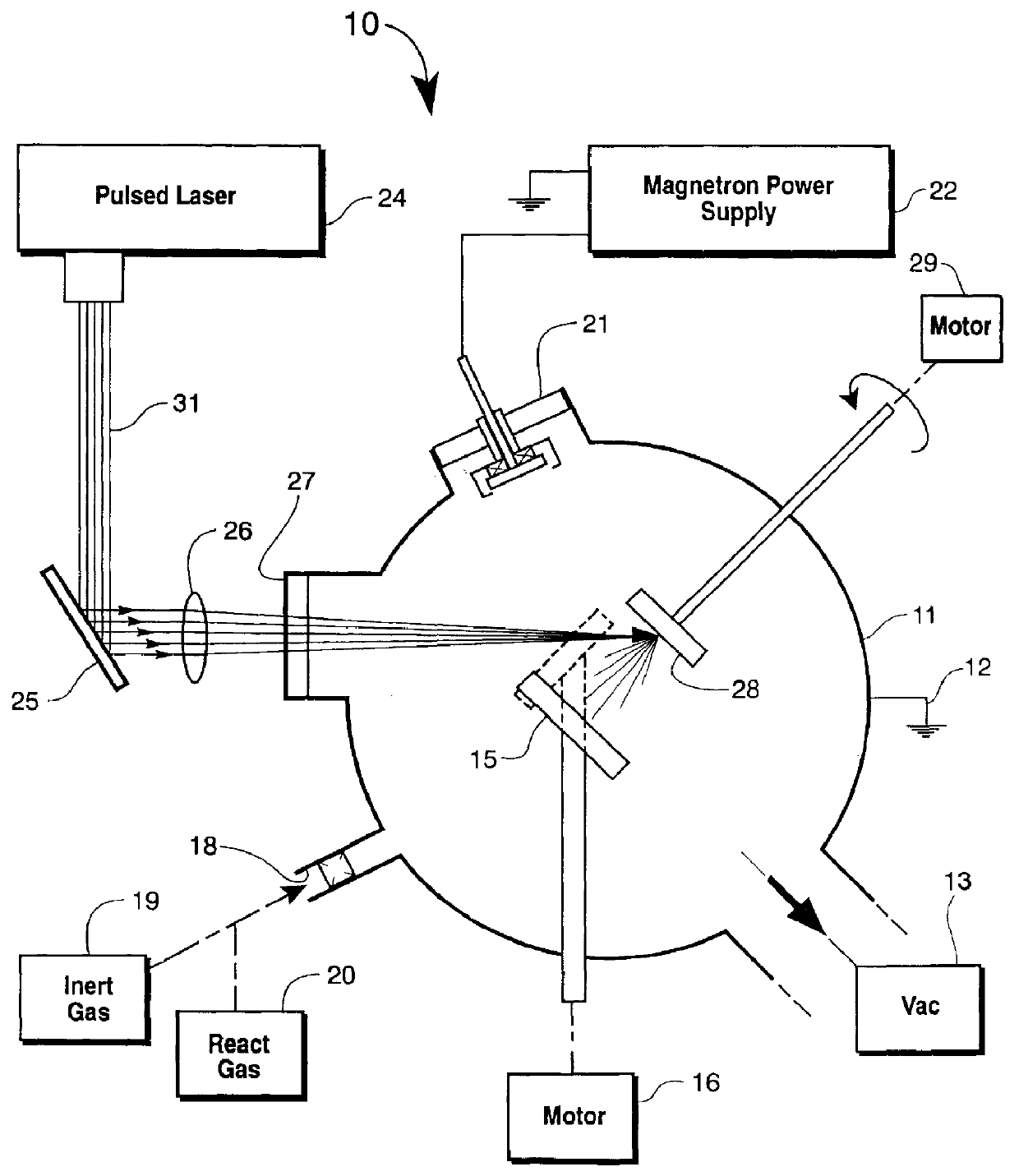
Magnetron sputter-pulsed laser deposition system and method
InactiveUSH1933H1Increase deposition rateImprove performanceCellsVacuum evaporation coatingSputteringDiamond-like carbon
System and method for high vacuum sputtering combining magnetron sputtering and pulsed laser plasma deposition are described wherein simultaneous or sequential magnetron sputtering and pulsed laser deposition operations in a single ultra-high vacuum system provides high deposition rates with precise control of film morphology, stoichiometry, microstructure, composition gradient, and uniformity, in the deposition of high performance coatings of various metal, ceramic and diamond-like carbon materials.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE +1
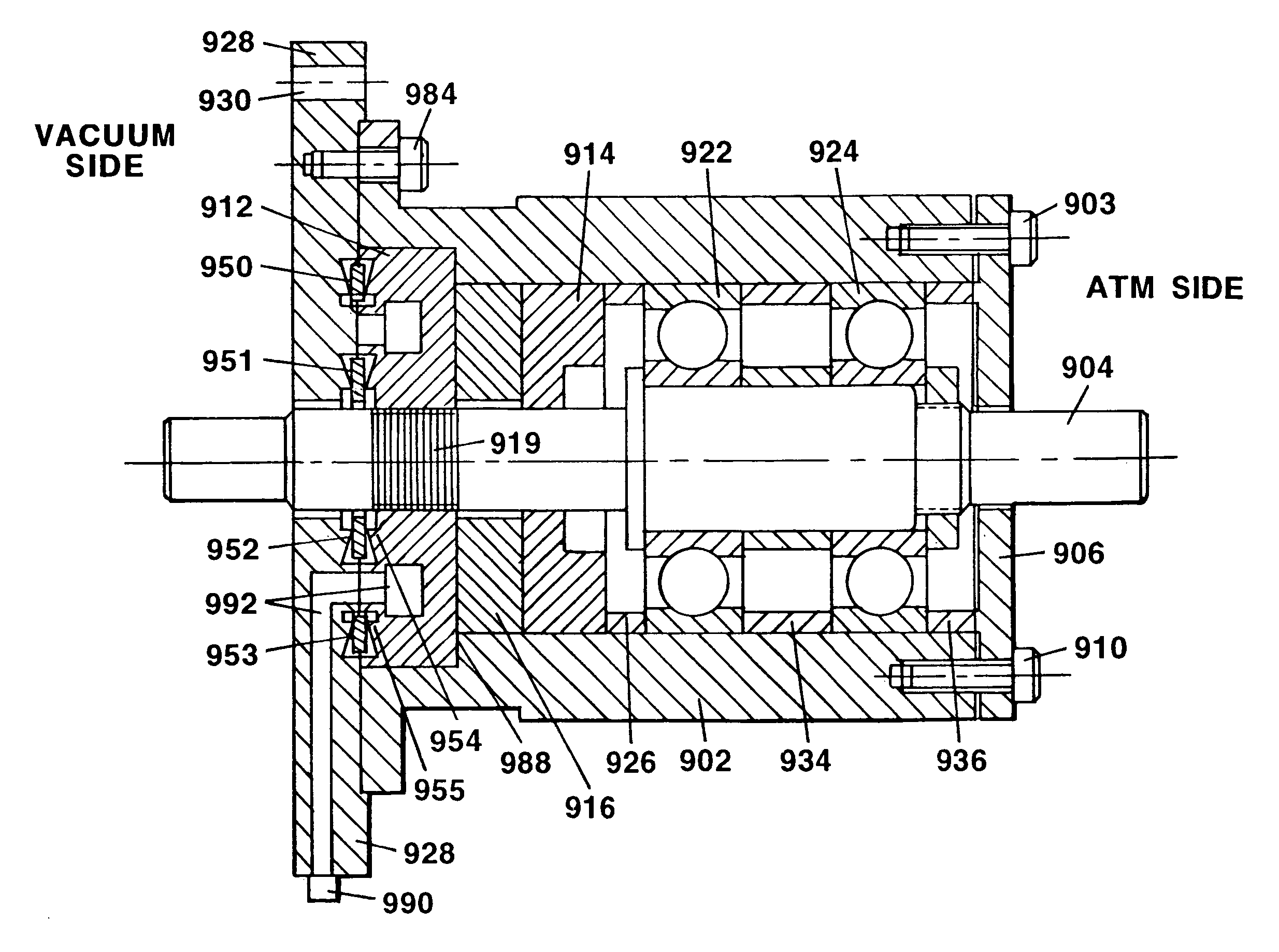
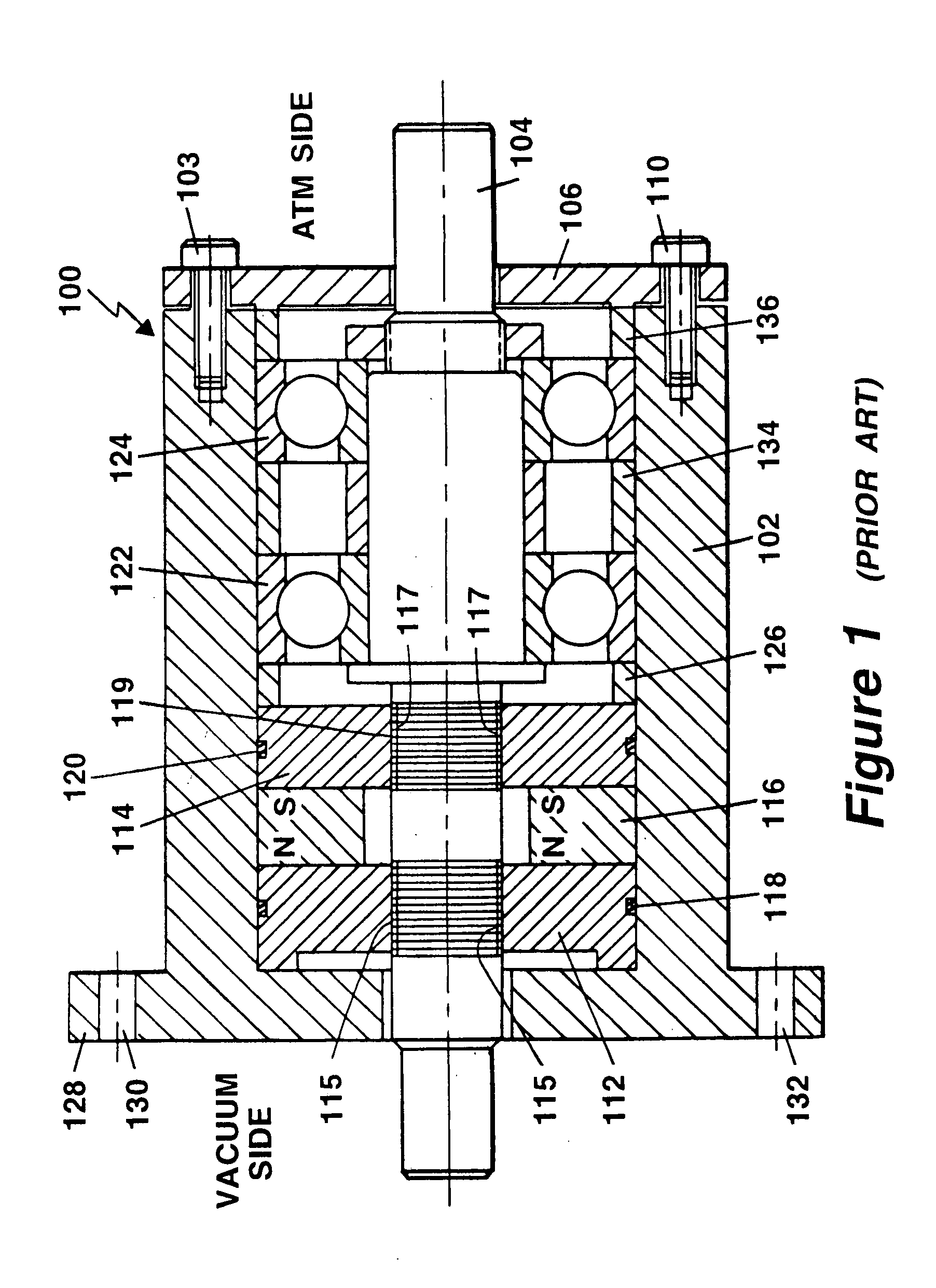
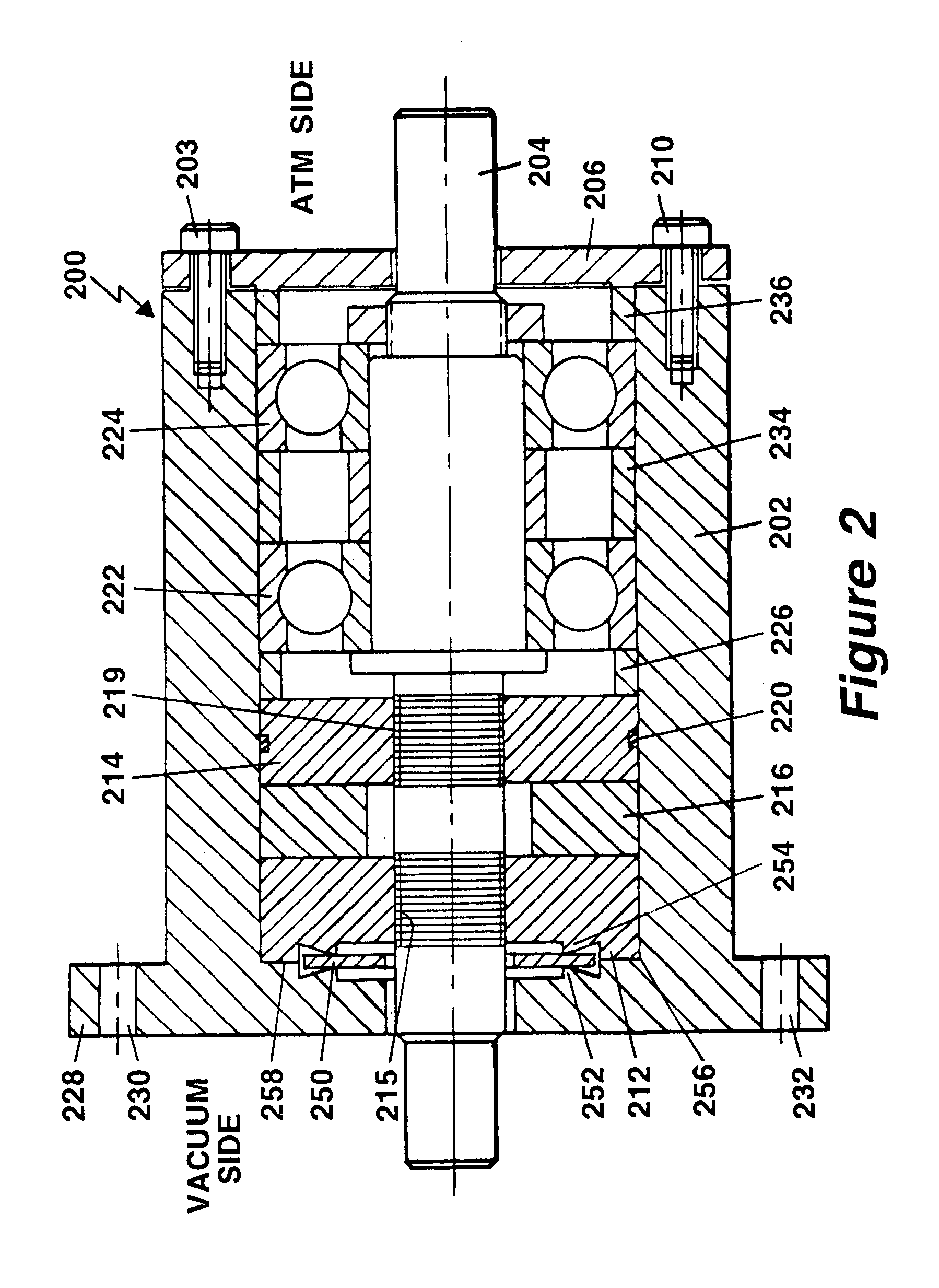
Ultra high vacuum ferrofluidic seals and method of manufacture
A ferrofluid seal incorporates a metal seal comprised of two knife-edges and a flat metal washer is formed between a pole piece and the housing at the axial interface between the parts. One knife edge is machined into the inner face of the housing flange and the other knife edge is machined into the opposing pole piece face. This metal seal effectively seals the pole piece to the housing with a seal suitable for ultra high vacuum applications.
Owner:FEEROTEC USA
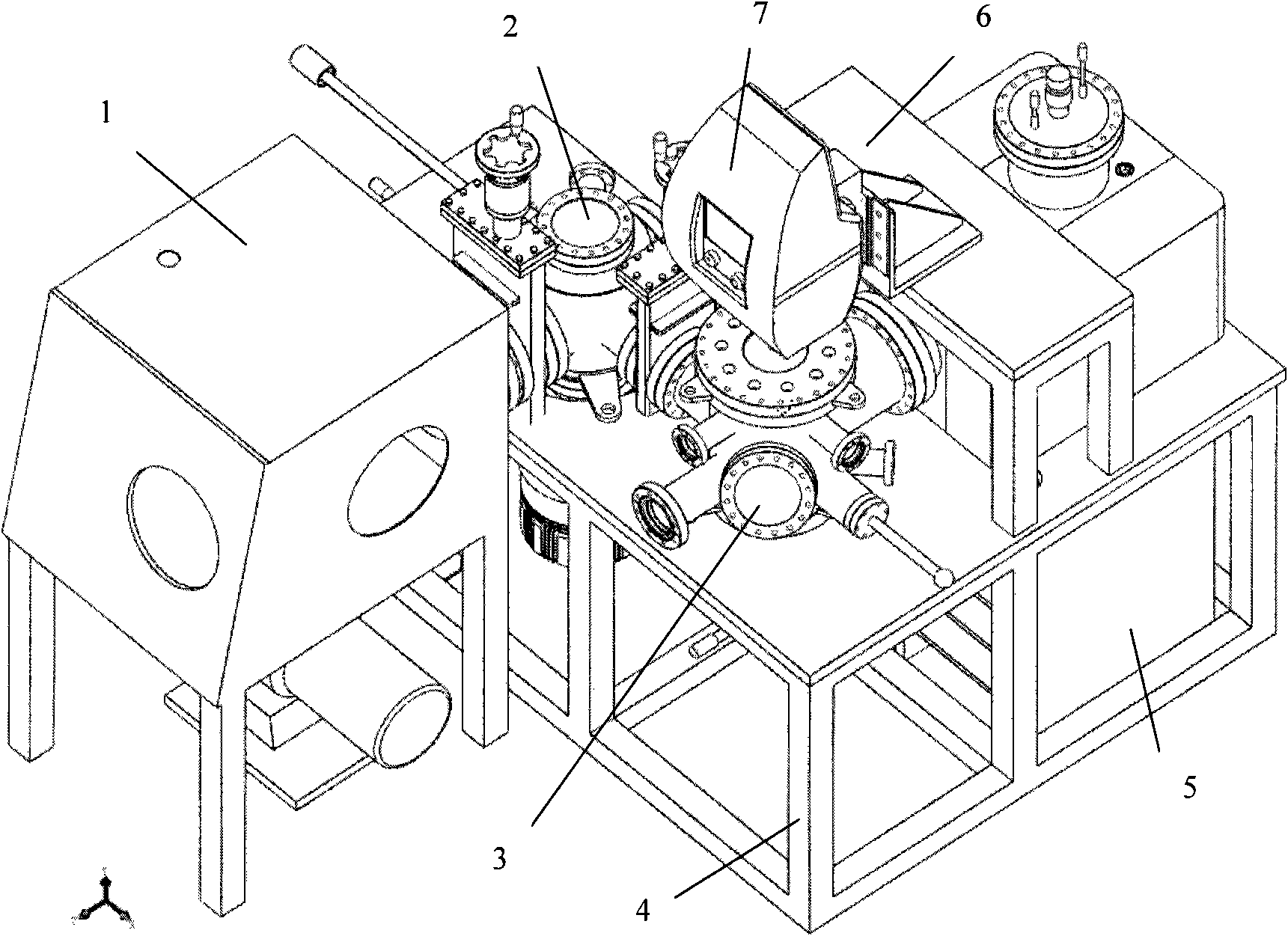
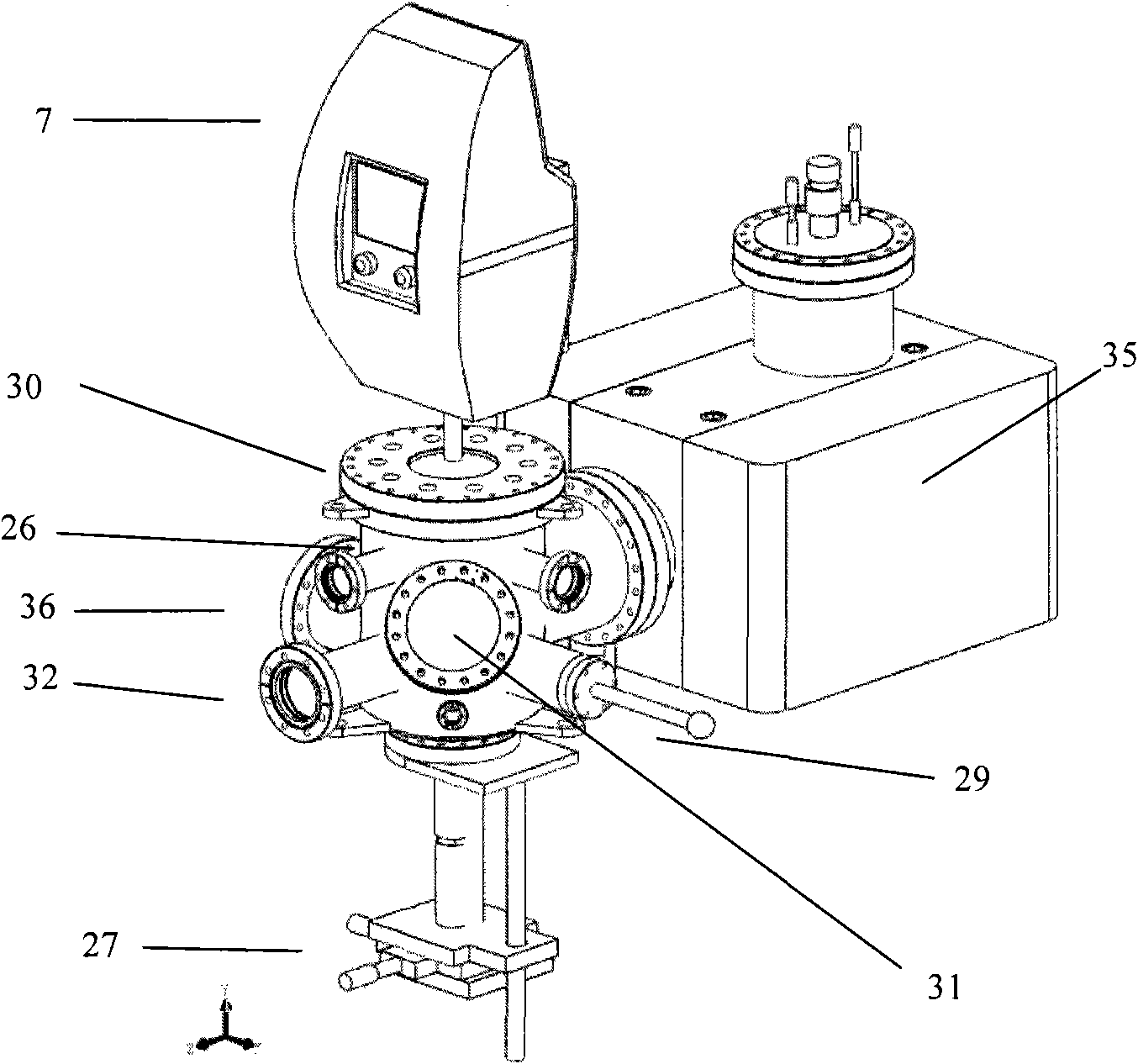
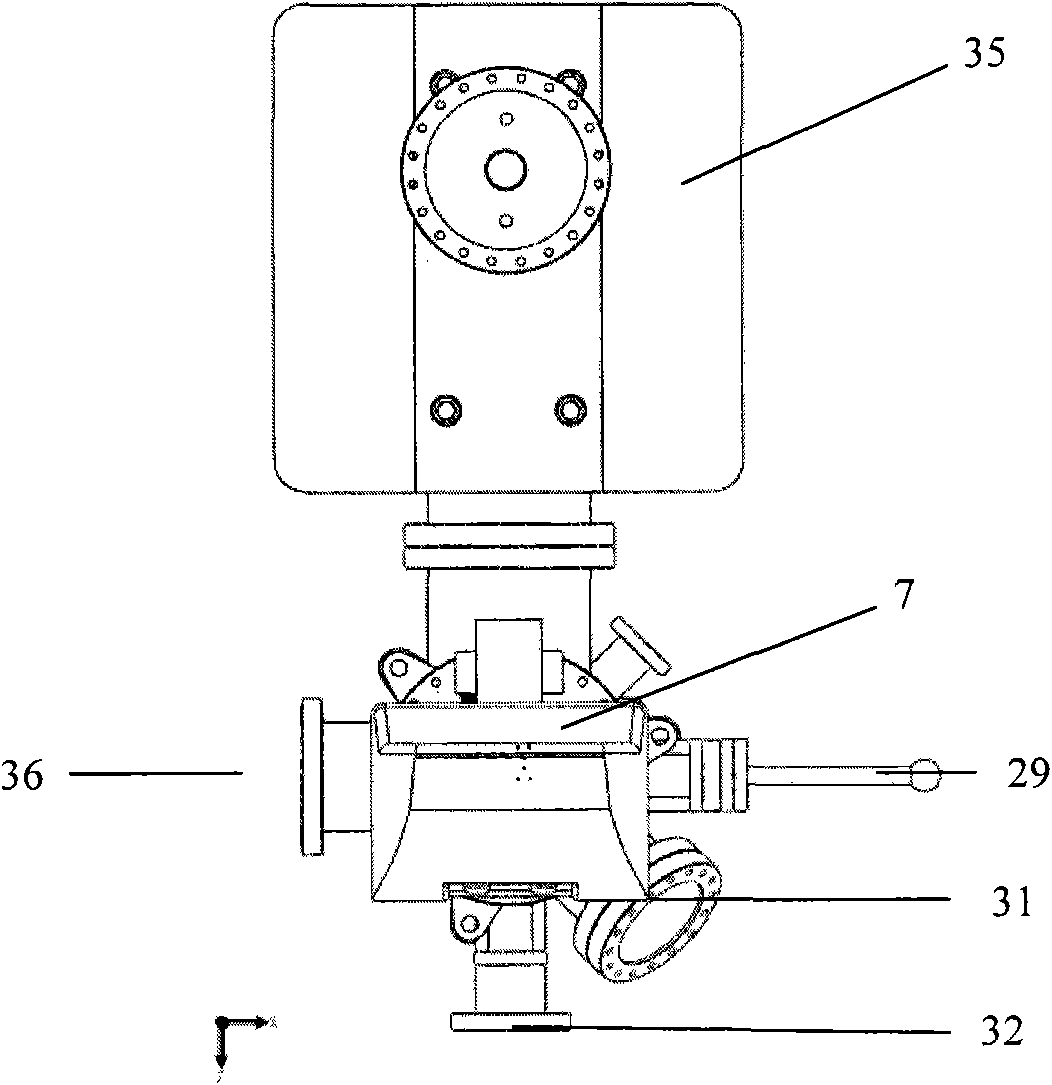
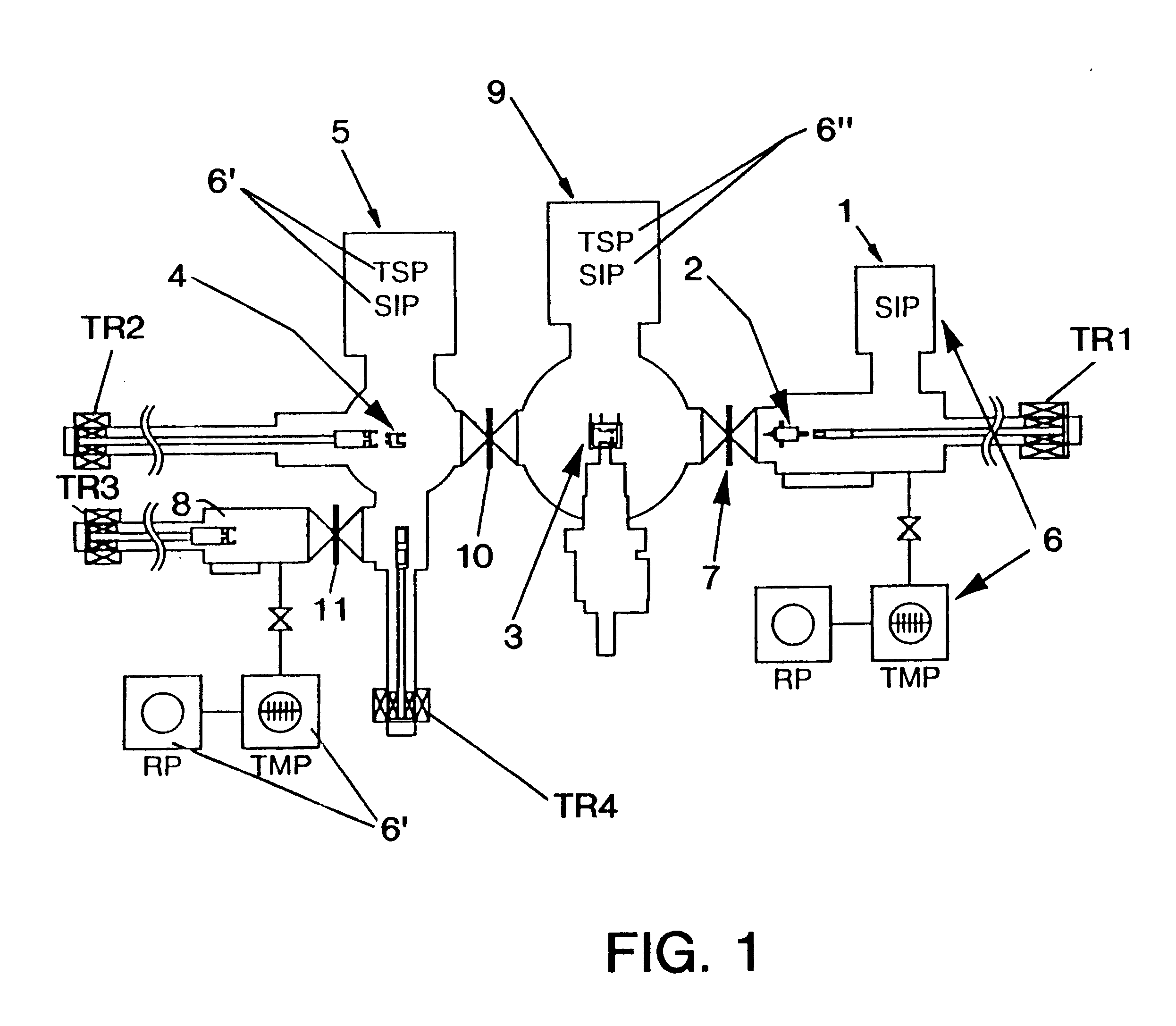
Ultra-high vacuum multifunctional integrated test system
ActiveCN101846635AAvoid serious deviationsGuaranteed mechanical propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical testingMicro nanoUltra-high vacuum
The invention discloses an ultra-high vacuum multifunctional integrated test system which is used for surface treatment, surface modification and in-situ characterization of micro-nano devices. The invention comprises a first ultra-high vacuum chamber, a second ultra-high vacuum chamber, a constant pressure chamber and a system frame, wherein the first ultra-high vacuum chamber and the second ultra-high vacuum chamber are connected in a sealing way, the constant pressure chamber is connected with the second ultra-high vacuum chamber in a sealing way, the system frame is of a rectangular frame, and the first ultra-high vacuum chamber, the second ultra-high vacuum chamber and the constant pressure chamber are fixed on the system frame to form the ultra-high vacuum test system. The invention realizes the integration of functions of surface treatment, surface modification and in-situ mechanical characterization, electrical performance test and the like of the micro-nano devices, avoids the serious deviation of test results, which is caused because the surface of a processed stamp is re-polluted during the process of the delivering and testing, and provides the guarantee for clearly and accurately studying the influence of surface damage on the mechanical and electrical properties of the devices.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Joining method for preparing an inverted metamorphic multijunction solar cell
ActiveUS8236600B2Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsUltra-high vacuum
A method of manufacturing a solar cell by providing a first semiconductor substrate and depositing a first sequence of layers of semiconductor material to form a first solar subcell, including a first bond layer disposed on the top of the first sequence of layers. A second semiconductor substrate is provided, and on the top surface of the second substrate a second sequence of layers of semiconductor material is deposited forming at least a second solar subcell. A second bond layer is disposed on the top of said second sequence of layers. The first solar subcell is mounted on top of the second solar subcell by joining the first bond layer to the second bond layer in an ultra high vacuum chamber, and the first semiconductor substrate is removed.
Owner:SOLAERO TECH CORP
Shallow pn junction formed by in situ doping during selective growth of an embedded semiconductor alloy by a cyclic growth/etch deposition process
ActiveUS20100025779A1Increase strainImprove device performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn situ dopingUltra-high vacuum
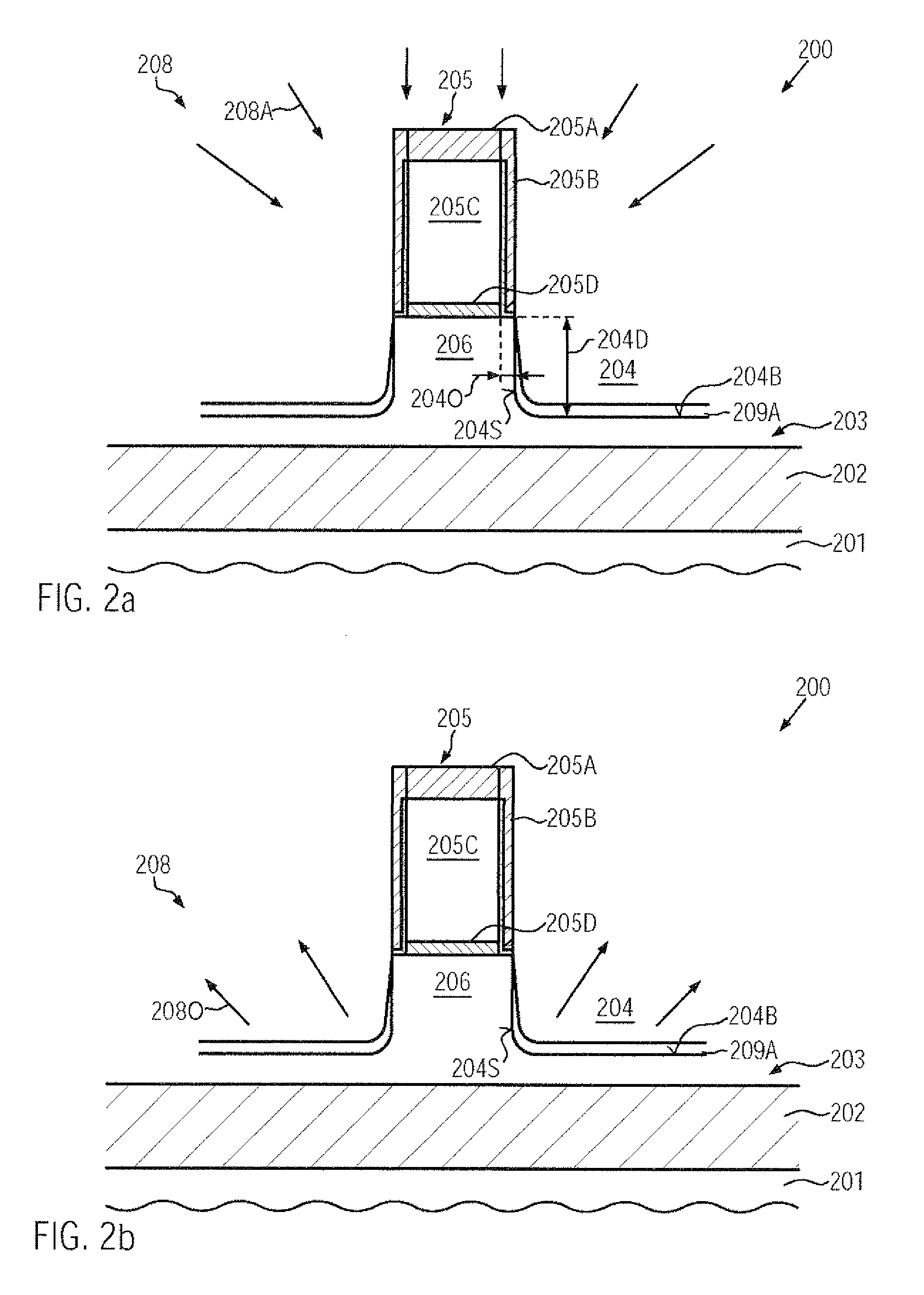
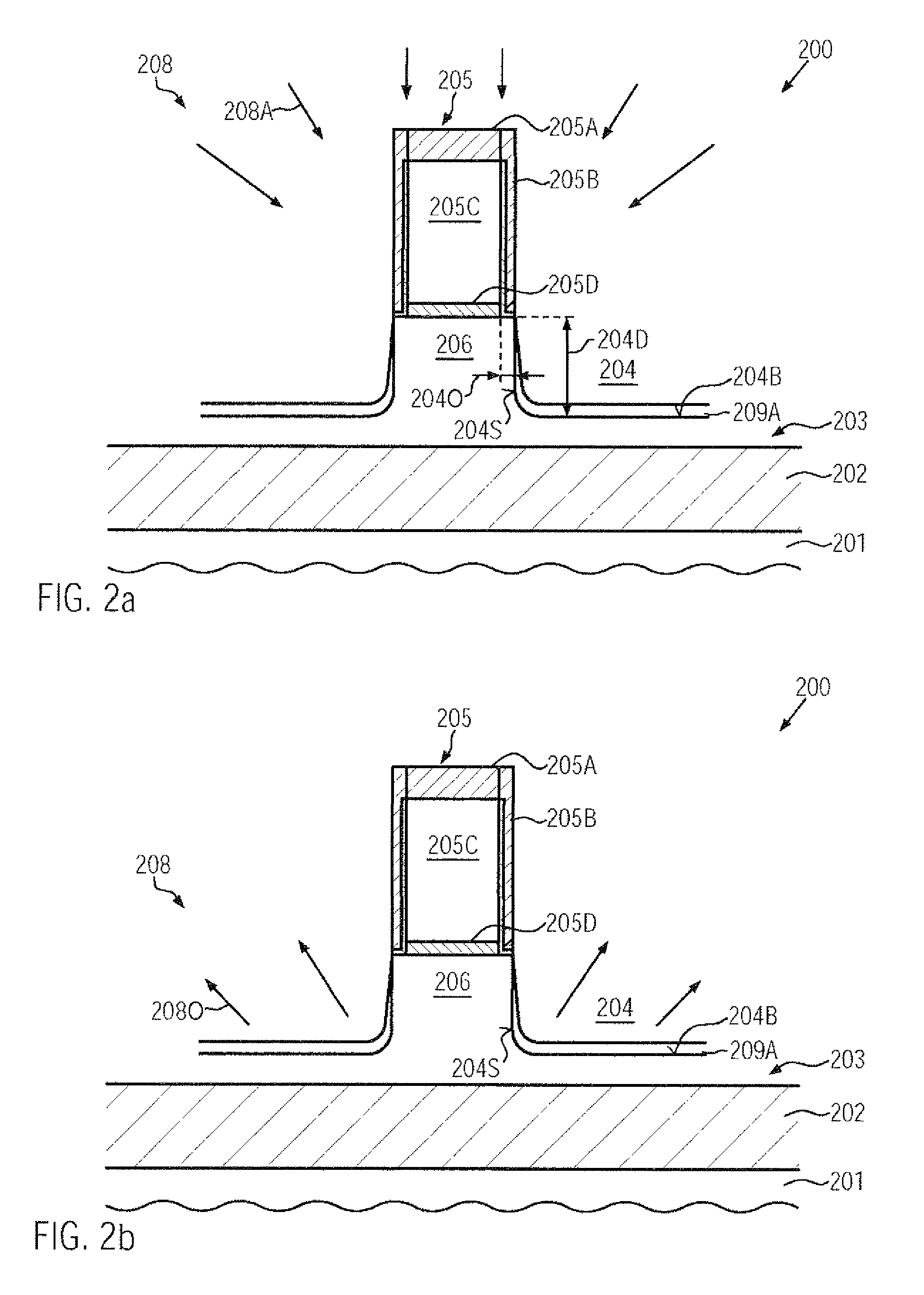
A silicon / carbon alloy may be formed in drain and source regions, wherein another portion may be provided as an in situ doped material with a reduced offset with respect to the gate electrode material. For this purpose, in one illustrative embodiment, a cyclic epitaxial growth process including a plurality of growth / etch cycles may be used at low temperatures in an ultra-high vacuum ambient, thereby obtaining a substantially bottom to top fill behavior.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Ultrahigh vacuum magnetic fluid seal transmission device
InactiveCN104948744AIncrease ultimate vacuumSolve the problem of easy contaminationEngine sealsUltra-high vacuumMagnetic poles
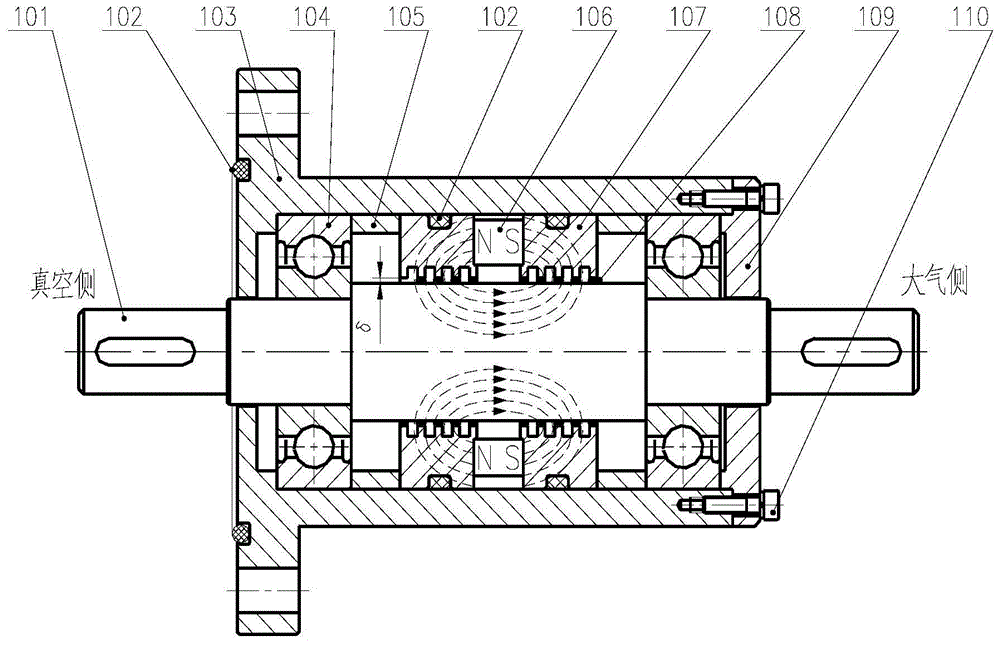
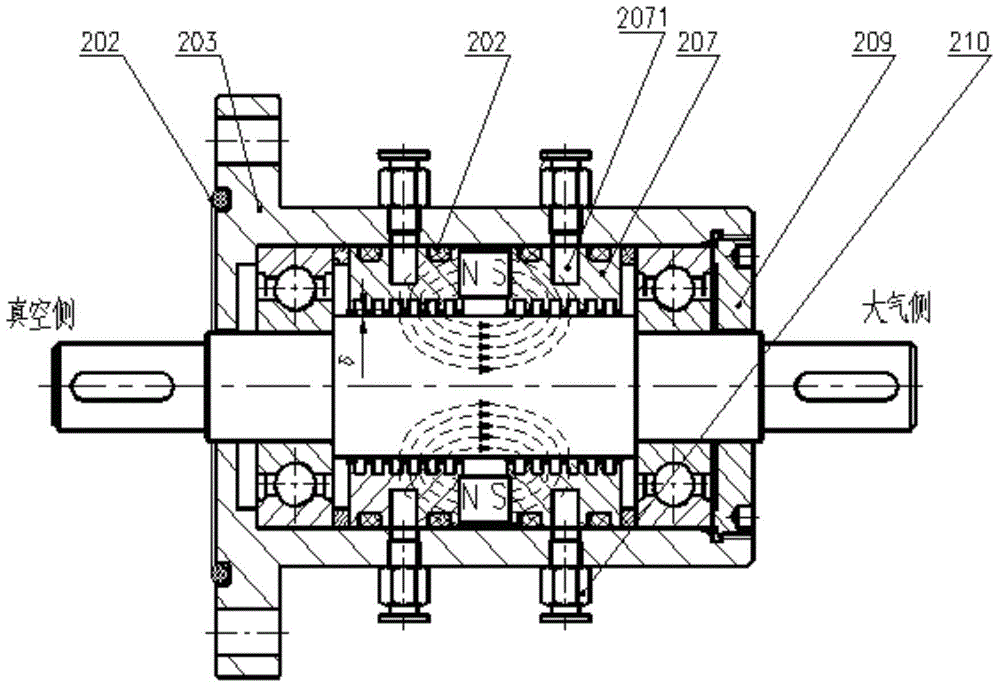
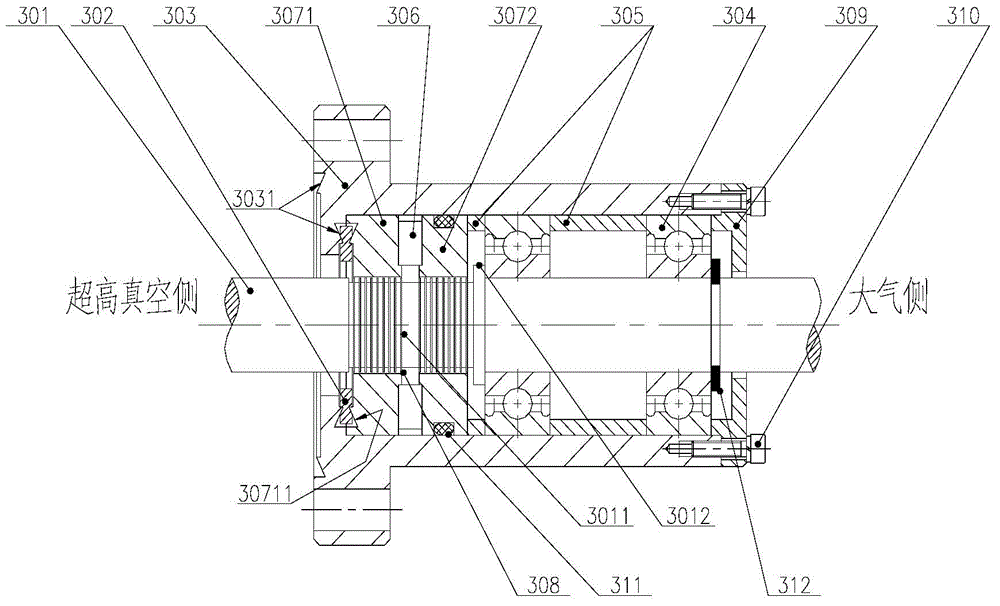
The invention discloses an ultrahigh vacuum magnetic fluid seal transmission device. The ultrahigh vacuum magnetic fluid seal transmission device comprises a shell, a seal assembly and bearings; the seal assembly comprises a main shaft, a permanent magnet, a first magnetic pole, a second magnetic pole and magnetic fluid, wherein the first magnetic pole and the second magnetic pole are arranged at the two sides of the permanent magnet, the magnetic fluid is arranged between the main shaft and the first magnetic pole and / or the second magnetic pole, and the seal assembly is arranged between the ultrahigh vacuum side and all the bearings; a first seal type cavity is arranged on the contact surface between the first magnetic pole and a flange of the shell, a first metal sealing gasket is arranged in the first seal type cavity, and after the first metal sealing gasket is compressed to be deformed by the axial force between the flange and the first magnetic pole, the flange and the first magnetic pole are sealed. The ultrahigh vacuum magnetic fluid seal transmission device has the advantages of being stable in seal, high in limiting vacuum, low in leak rate, low in gas permeability, large in pumping rate and free of vacuum pollution.
Owner:VIC FERROFLUIDICS
Wide-range combination vacuum gauge
InactiveUS7207224B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDifferential pressureUltra-high vacuum
A combination vacuum gauge provides simultaneous absolute and differential pressure measurements over a wide range of pressures ranging from atmospheric pressures to ultrahigh vacuum by processing the readings from an absolute high vacuum gauge (e.g., an ionization gauge and / or a heat-loss sensor), a differential low vacuum gauge providing a differential relative to ambient pressure (e.g., a diaphragm sensor), and a barometric absolute pressure sensor exposed to the ambient atmosphere outside the measurement region. The barometric absolute pressure sensor reading is used to convert the differential vacuum gauge reading from uncalibrated differential pressure to calibrated absolute pressure.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Cold atom micro primary standard
An atomic clock having a physics package that includes a vacuum chamber cavity that holds atoms of Rb-87 under high vacuum conditions, an optical bench having a single laser light source, a local oscillator, a plurality of magnetic field coils, an antenna, at least one photo-detector and integrated control electronics. The single laser light source has a fold-retro-reflected design to create three retro-reflected optical beams that cross at 90° angles relative to one another in the vacuum chamber cavity. This design allows the single laser light source to make the required six trapping beams needed to trap and cool the atoms of Rb-87. The foregoing design makes possible atomic clocks having reduced size and power consumption and capable of maintaining an ultra-high vacuum without active pumping.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Shallow PN junction formed by in situ doping during selective growth of an embedded semiconductor alloy by a cyclic growth/etch deposition process
ActiveUS8053273B2Increase strainImprove device performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn situ dopingUltra-high vacuum
A silicon / carbon alloy may be formed in drain and source regions, wherein another portion may be provided as an in situ doped material with a reduced offset with respect to the gate electrode material. For this purpose, in one illustrative embodiment, a cyclic epitaxial growth process including a plurality of growth / etch cycles may be used at low temperatures in an ultra-high vacuum ambient, thereby obtaining a substantially bottom to top fill behavior.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer
ActiveCN105137126ARemove restrictionsHigh measurement sensitivityScanning probe microscopyUltra-high vacuumFeedback control
The invention relates to a weak magnetic field measurement technique, in particular, a novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer. With the novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer adopted, the problems of low sensitivity and limited application range of existing weak magnetic field information measuring tools can be solved. The novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer of the nitrogen-vacancy center diamond includes an atomic force microscope system and an optical detection magnetic information system; and the atomic force microscope system includes an ultra-high vacuum chamber, a scanning tube, a nitrogen-vacancy center diamond probe, a 670nm-wavelength laser, a four-quadrant photodiode detector, a phase-locked loop, an automatic gain control loop, piezoelectric ceramic, a 50-ohm resistor, a feedback control loop, a lock-in amplifier, a carrier, a surface topography information output port and a magnetic information output port. The novel nitrogen-vacancy center diamond scanning magnetometer of the invention is suitable for weak magnetic field information measurement.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Measuring device and measuring method for measuring gas permeability of material
InactiveCN103115858AHigh measurement sensitivityIncreased permeability measurement sensitivityPermeability/surface area analysisMass spectrometry measurementThermodynamics
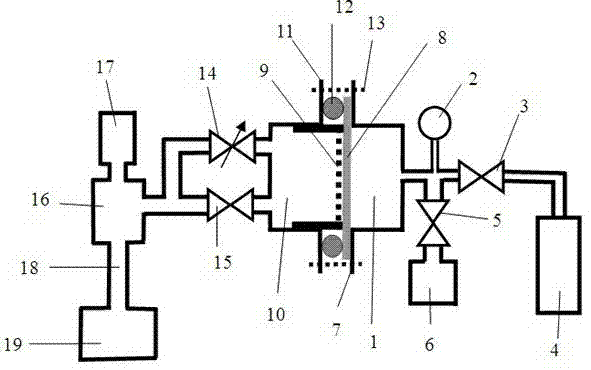
The invention discloses a measuring device and a measuring method for measuring gas permeability of a material. The measuring device comprises a gas chamber, a gas accumulation chamber and a high-vacuum chamber, wherein a film of the material to be measured or a thin sheet is installed between the gas chamber and the gas accumulation chamber; the gas chamber is connected with a gas source to be measured and a low-vacuum pump; the accumulation chamber is connected with the high-vacuum chamber through a needle valve; and the high-vacuum chamber is connected with a mass spectra gauge and a super-high-vacuum sucking system. By utilizing the device and the method, after a measured gas which permeates through the measured material is accumulated in the gas accumulation chamber to a relatively large gas quantity, part of the gas is sampled into the high-vacuum chamber to be subjected to mass-spectrometer measurement, so that the sensitivity in permeability measurement is improved; and the longer the accumulation time is, the higher the measurement sensitivity is, for example, the sensitivity in steam permeability measurement can reach the level of 10-7g / m<2>day grade.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Wide-range combination vacuum gauge
InactiveUS20060278004A1Accurate differential pressureAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDifferential pressureUltra-high vacuum
A combination vacuum gauge provides simultaneous absolute and differential pressure measurements over a wide range of pressures ranging from atmospheric pressures to ultrahigh vacuum by processing the readings from an absolute high vacuum gauge (e.g., an ionization gauge and / or a heat-loss sensor), a differential low vacuum gauge providing a differential relative to ambient pressure (e.g., a diaphragm sensor), and a barometric absolute pressure sensor exposed to the ambient atmosphere outside the measurement region. The barometric absolute pressure sensor reading is used to convert the differential vacuum gauge reading from uncalibrated differential pressure to calibrated absolute pressure.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
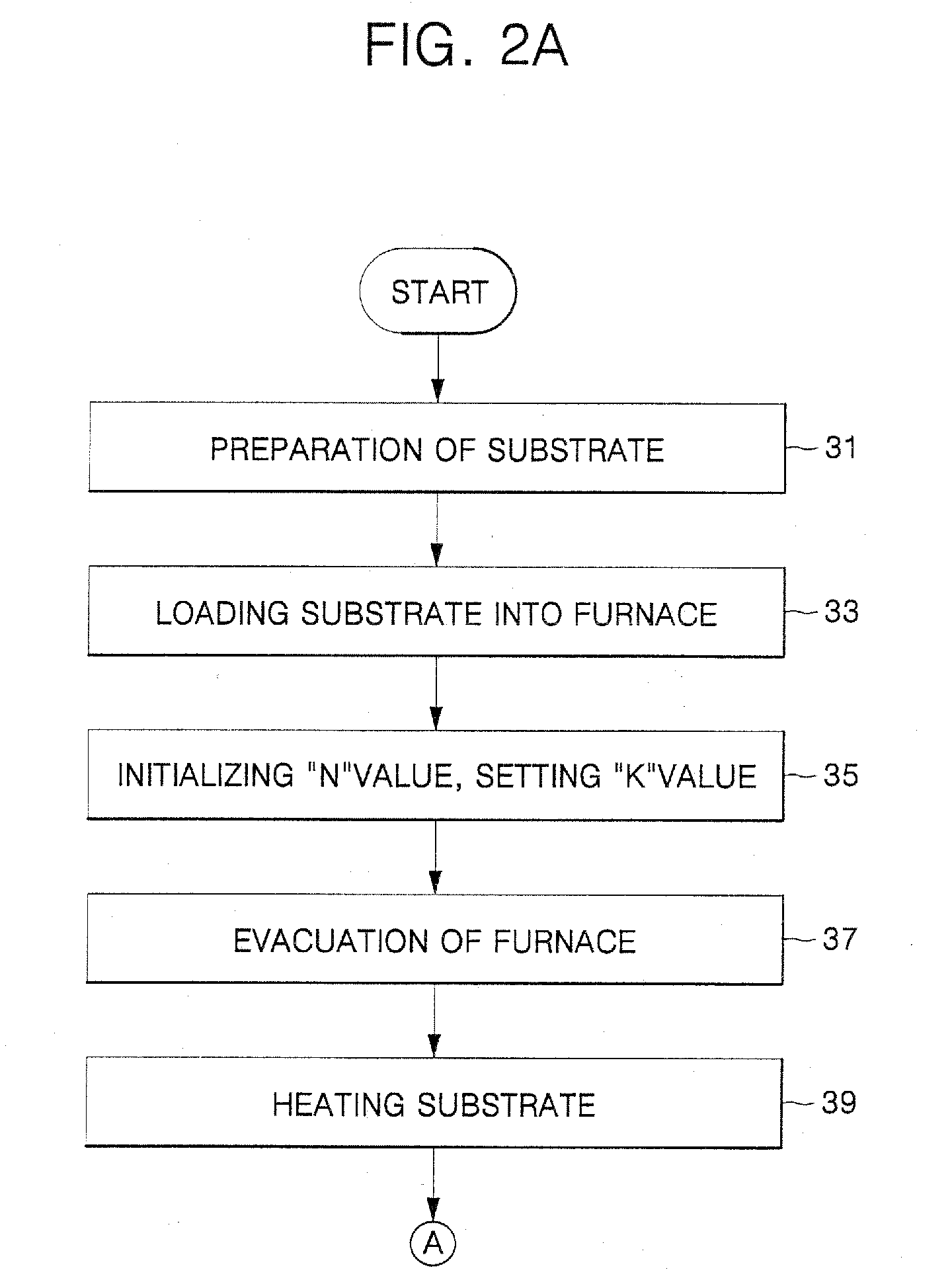
Methods of selectively forming an epitaxial semiconductor layer using ultra high vacuum chemical vapor deposition technique and batch-type ultra high vacuum chemical vapor deposition apparatus used therein
InactiveUS20070006800A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallurgyGas phase
Provided are methods of selectively forming an epitaxial semiconductor layer using an ultra high vacuum chemical vapor deposition (UHVCVD) technique. One embodiment is directed to a method that includes loading a substrate having an insulating layer pattern into a reaction furnace. The reaction furnace is evacuated, and the substrate in the reaction furnace is heated to a temperature of about 550 to about 700° C. A semiconductor source gas is injected into the reaction furnace for a first duration to selectively form an epitaxial semiconductor layer on a region of the heated substrate. The semiconductor source gas remaining in the reaction furnace is then purged for a second duration. A selective etching gas is injected into the reaction furnace for a third duration to selectively remove semiconductor atoms adsorbed on surfaces of the insulating layer pattern. The selective etching gas remaining in the reaction furnace is then purged for a fourth duration. A carrier gas may be injected into the reaction furnace during at least the second to fourth durations.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
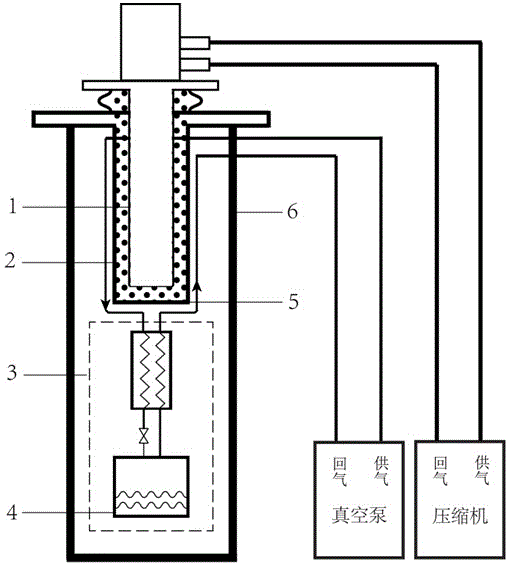
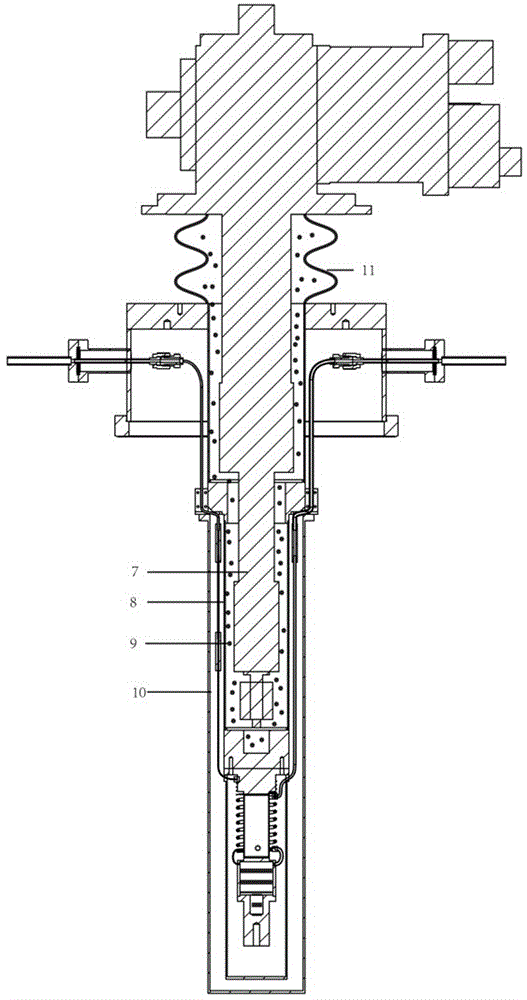
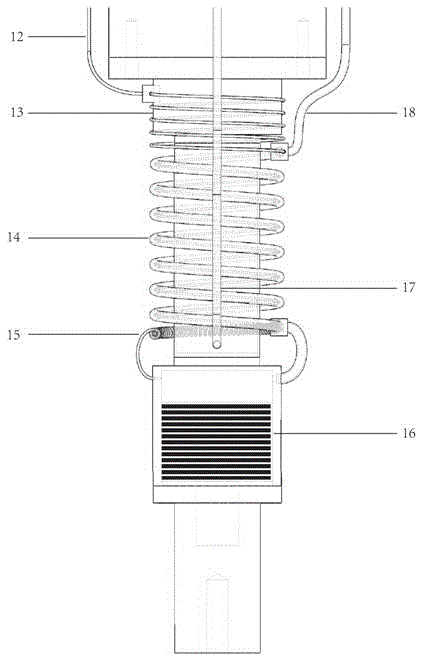
Mechanical vibration isolation liquid-helium-consumption-free extremely-low-temperature refrigerating system
ActiveCN105571190ASolve the problem of not being able to obtain extremely low temperatureIsolation of low frequency mechanical vibrationCompression machinesRefrigeration safety arrangementTemperature controlUltra-high vacuum
The invention belongs to the technical field of extremely-low-temperature refrigerating equipment, and particularly relates to a mechanical vibration isolation liquid-helium-consumption-free extremely-low-temperature refrigerating system. The system comprises a closed-cycle refrigerator system, a helium heat exchange air cooling vibration isolation system, an extremely-low-temperature throttle valve refrigerating system and a temperature feedback control system. According to the refrigerating manner provided by the system, the extremely-low temperature lowering to 1.4 K (based on helium-4 media) or 0.2 K (based on helium-3 media) can be achieved under the condition without consuming liquid helium, and meanwhile, the inherent mechanical vibration of the closed-cycle refrigerator system can be quite effectively isolated; and through the temperature feedback control system, variable temperature control can be achieved. The system is further suitable for an ultrahigh-vacuum environment needing to be subject to high-temperature baking.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Making method for IV-VI semiconductor single crystal film and the heterogeneous structure
InactiveCN101106092AQuality improvementPrecise and controllable thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFrom condensed vaporsBeam sourceUltra-high vacuum
The invention discloses a method to produce IV-VI semiconductor single-crystal thin film and the hetero-structure thereof. Under the condition of accurately controlled ultra-high vacuum, IV-VI atom and molecular beams vaporized from a beam source furnace encounter a clean single-crystal liner surface with good crystal surface orientation, and atom and molecular reaching the surface of the liner form high-quality single-crystal thin film after processes such as attachment, transition, and crystallization on the surface of liner. Through the accurate control of growth conditions, such as beam runoff and linear temperature, extended IV-VI compounds grow on the surface of linear by a molecular layer and a molecular layer. The method can grow IV-VI semiconductor hetero-structures, including quantum-well and super-lattice. The production cost is low, and the quality is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
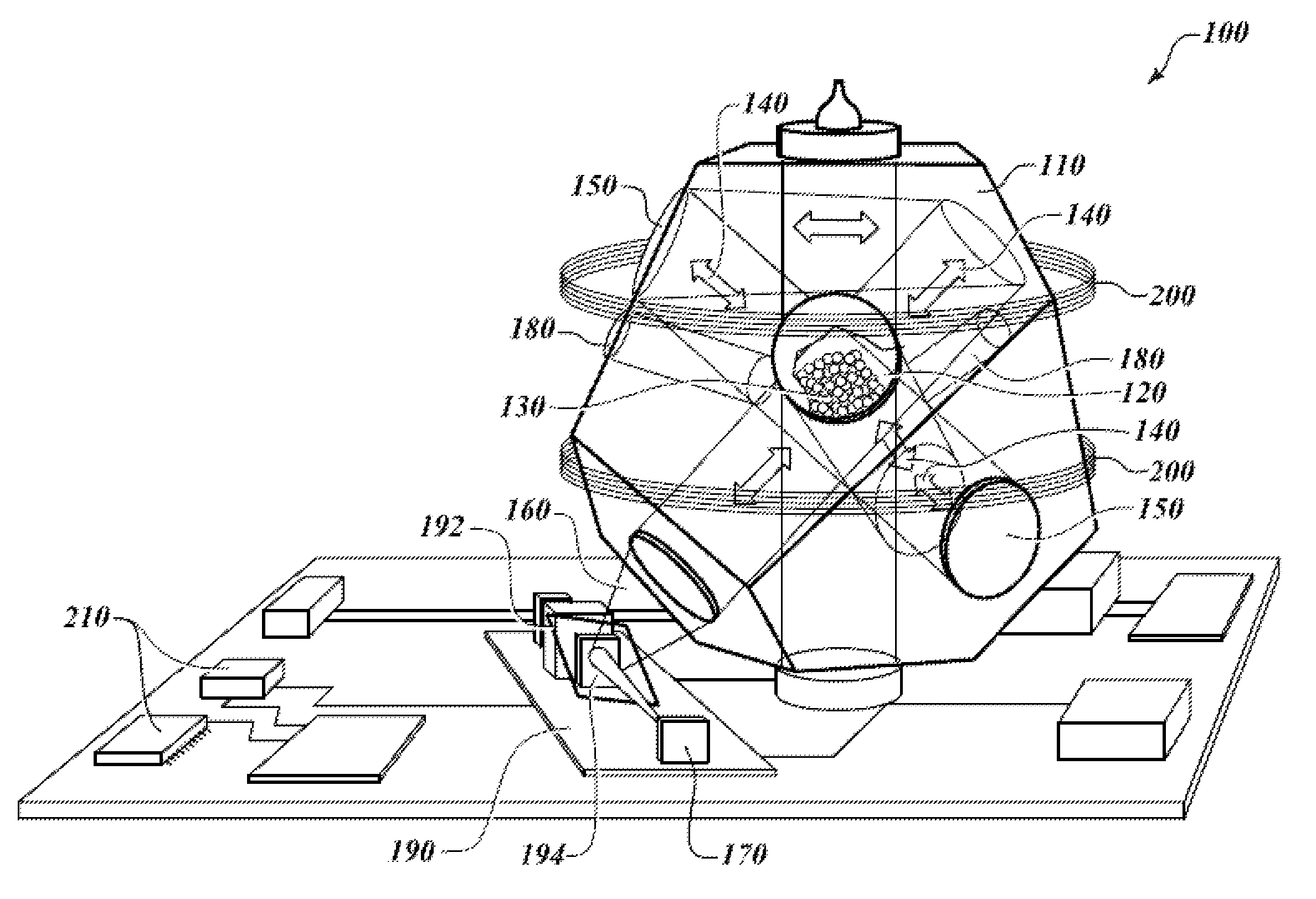
Physics package design for a cold atom primary frequency standard
InactiveUS20100033255A1Keep vacuumingLaser detailsPulse automatic controlPackage designUltra-high vacuum
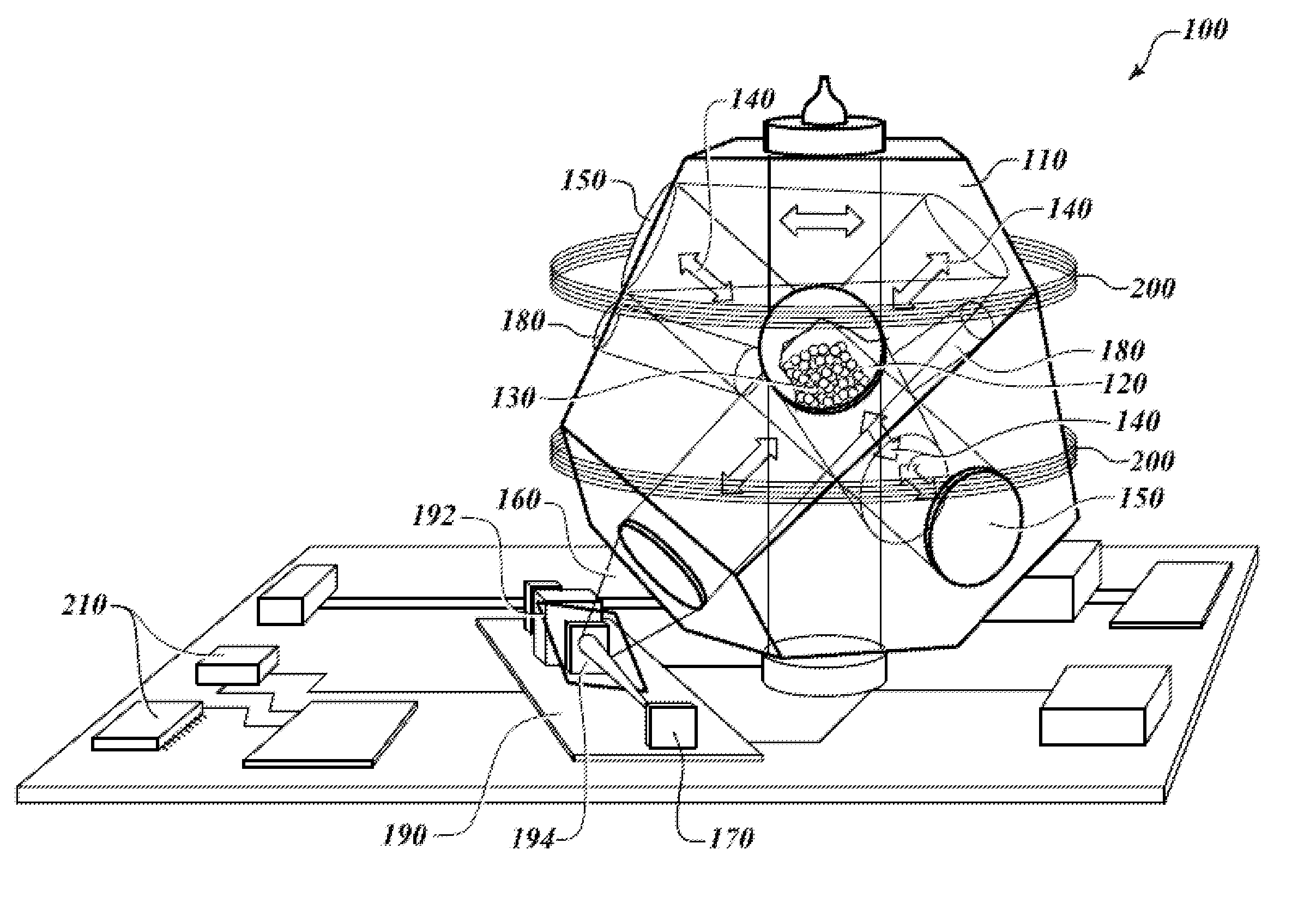
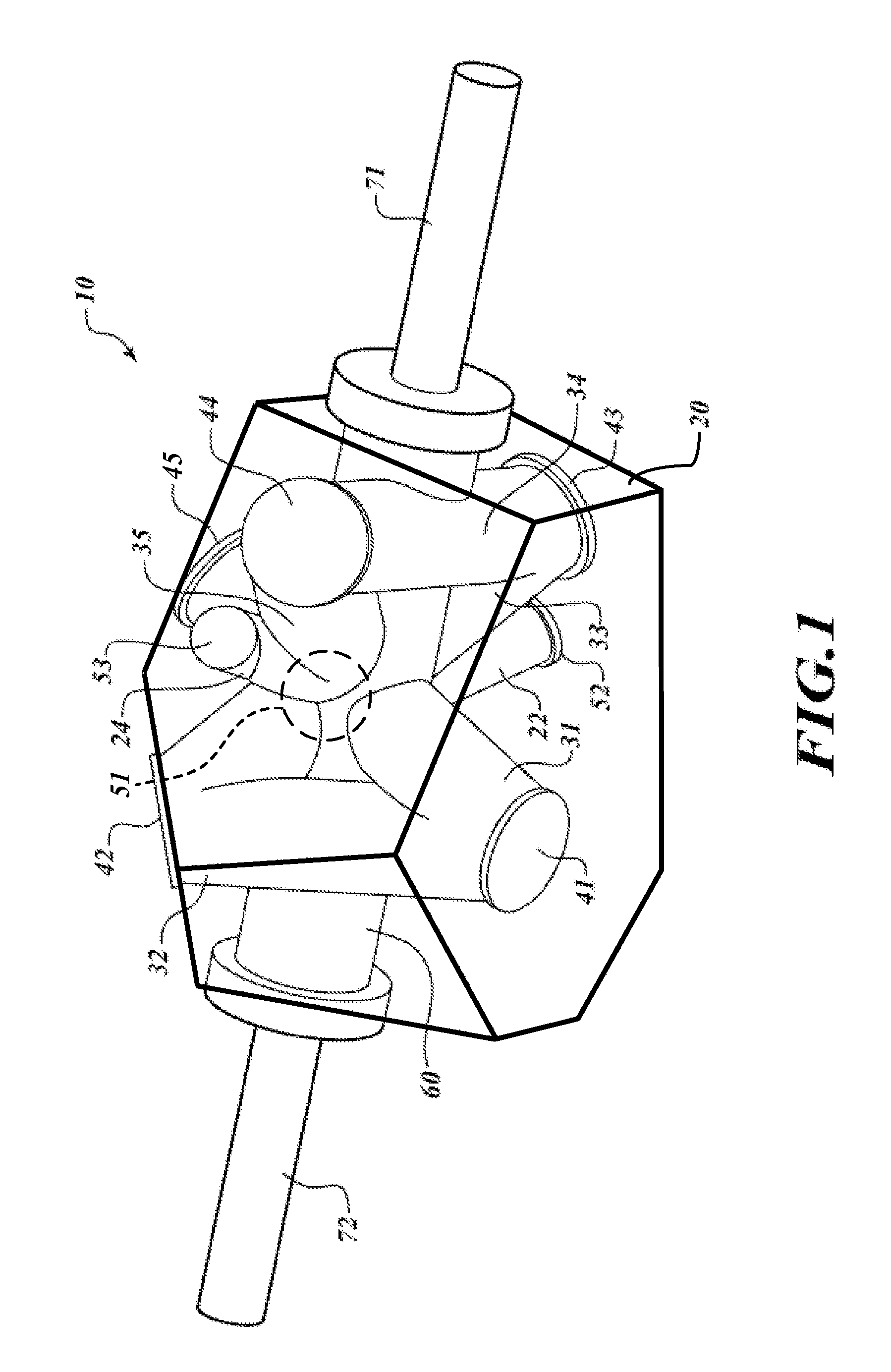
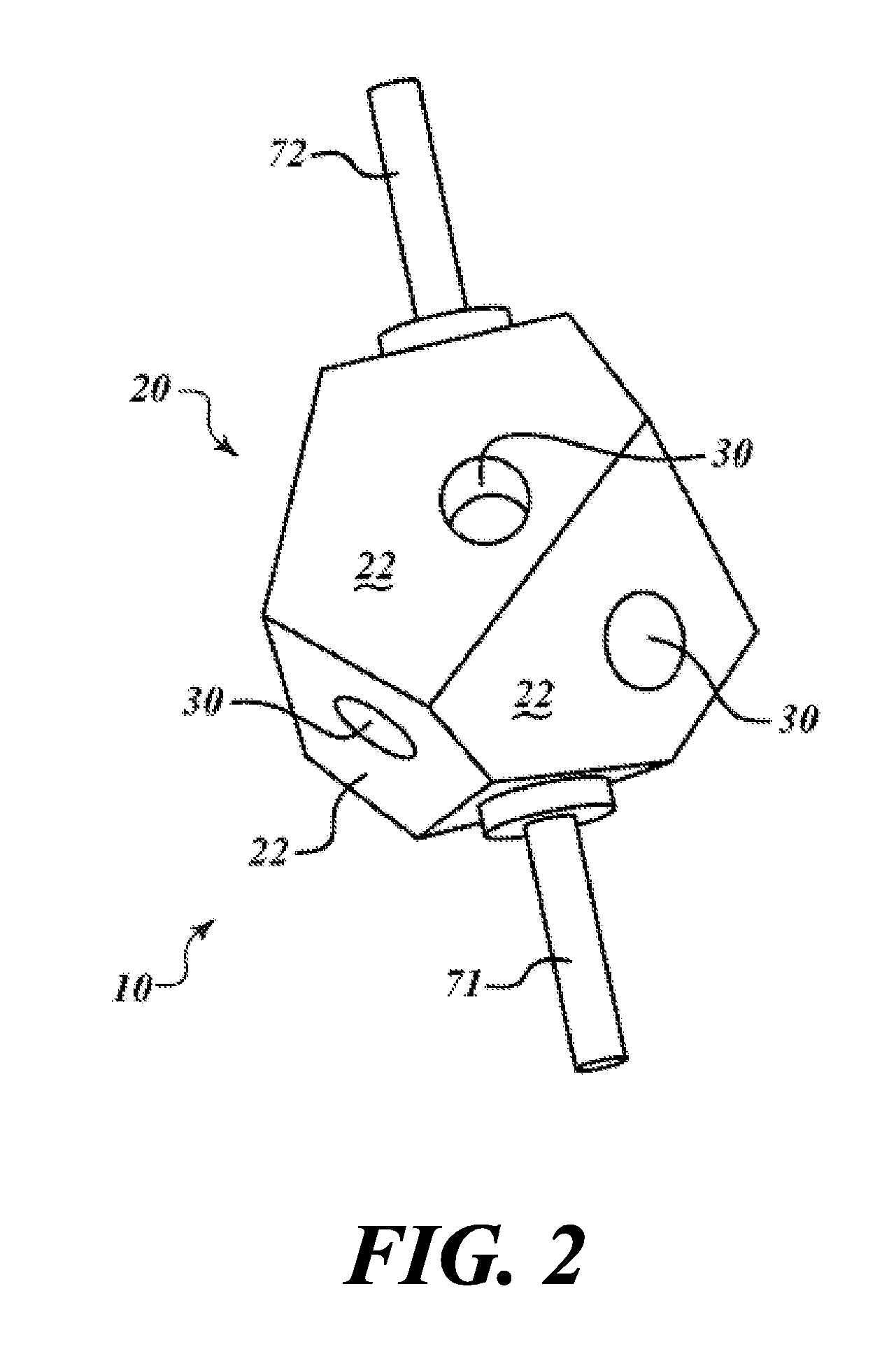
A physic package for an atomic clock comprising: a block made of optical glass, a glass ceramic material or another suitable material that includes a plurality of faces on its exterior and a plurality of angled borings that serve as a vacuum chamber cavity, light paths and measurement bores; mirrors fixedly attached using a vacuum tight seal to the exterior of the block at certain locations where two light paths intersect; optically clear windows fixedly attached using a vacuum tight seal to the block's exterior over openings of the measurement bores and at one location where two light paths intersect; and fill tubes fixedly attached using a vacuum tight seal to the exterior of the block over the ends of the vacuum chamber cavity. This physics package design makes possible atomic clocks having reduced size and power consumption and capable of maintaining an ultra-high vacuum without active pumping.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
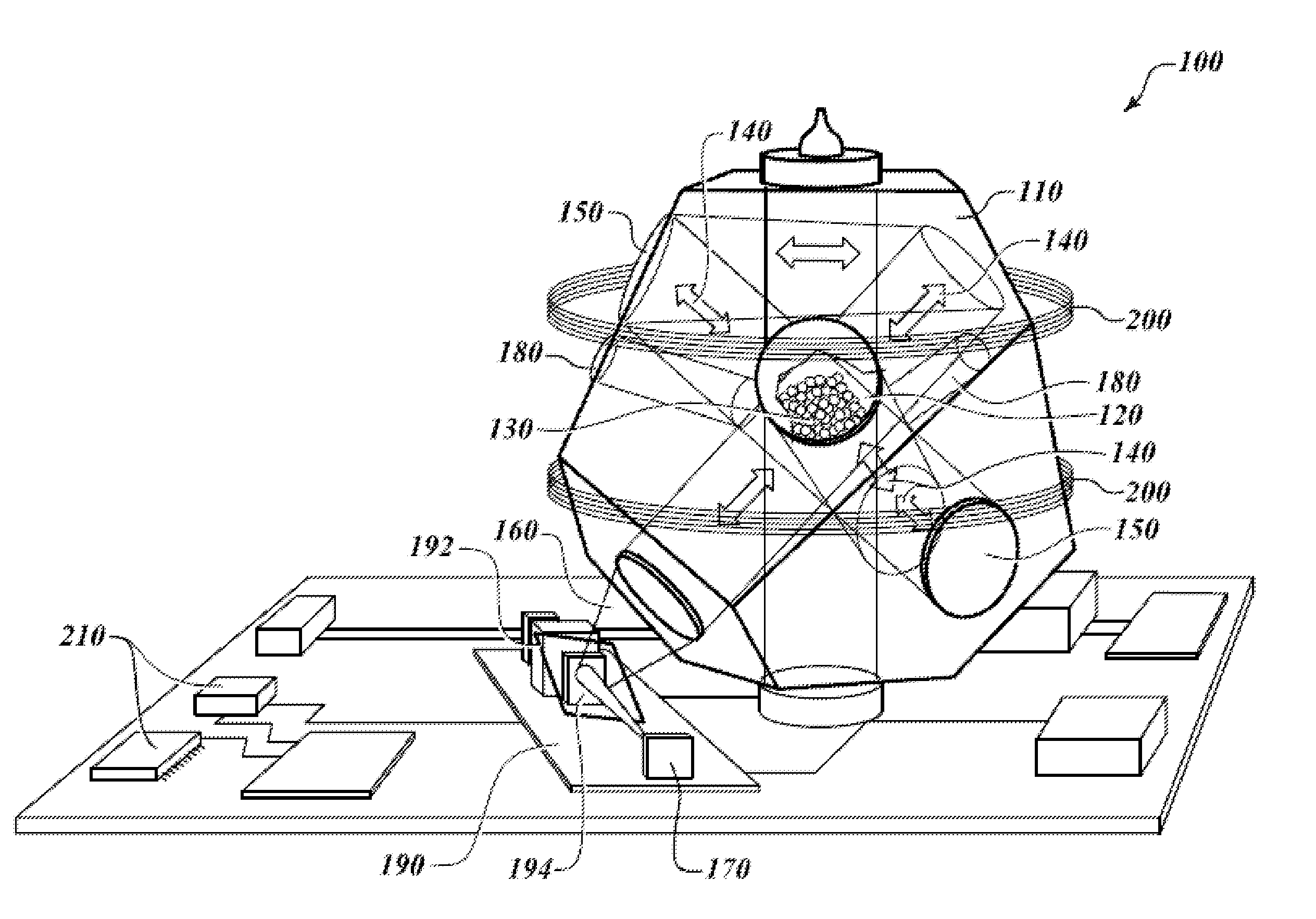
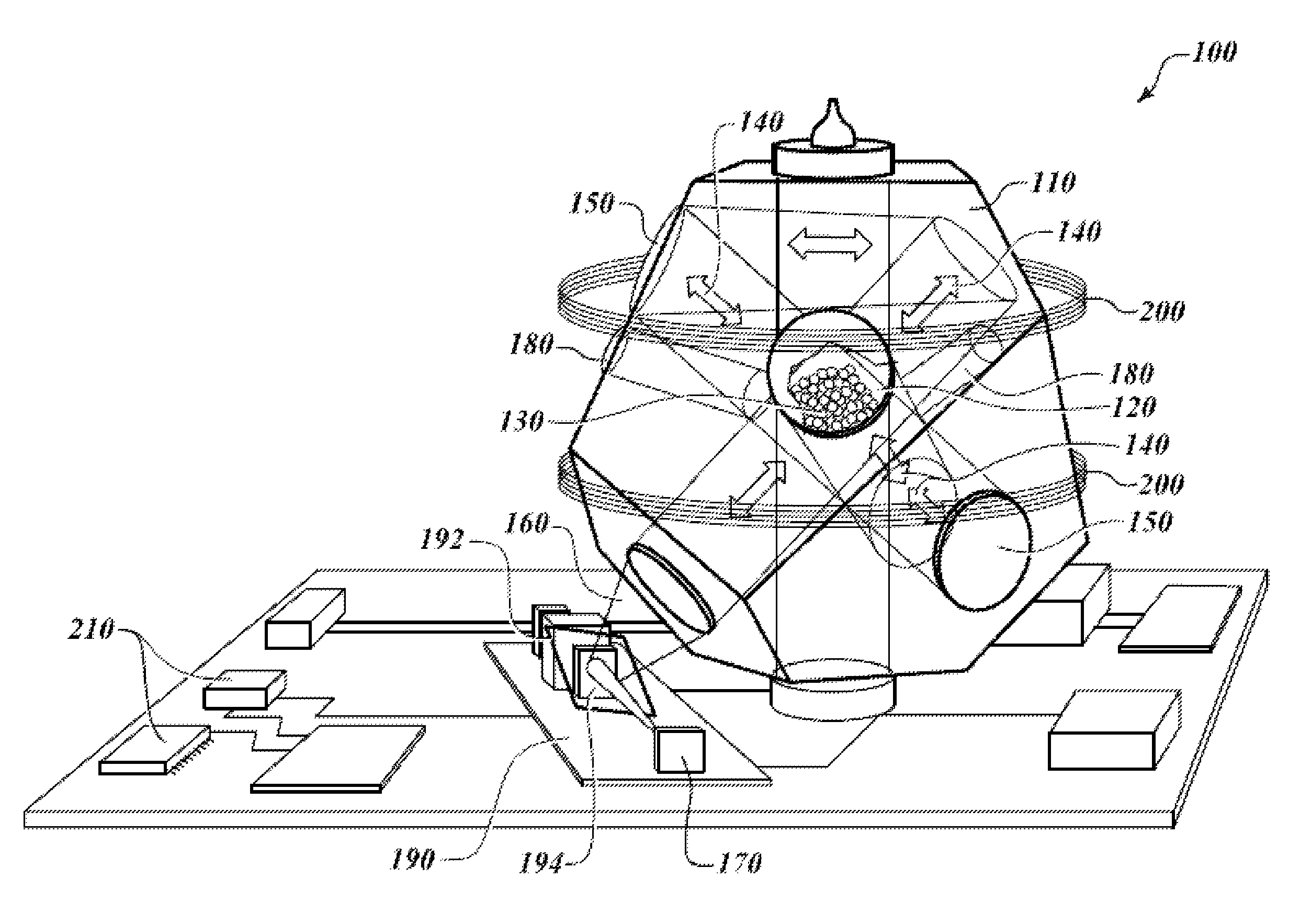
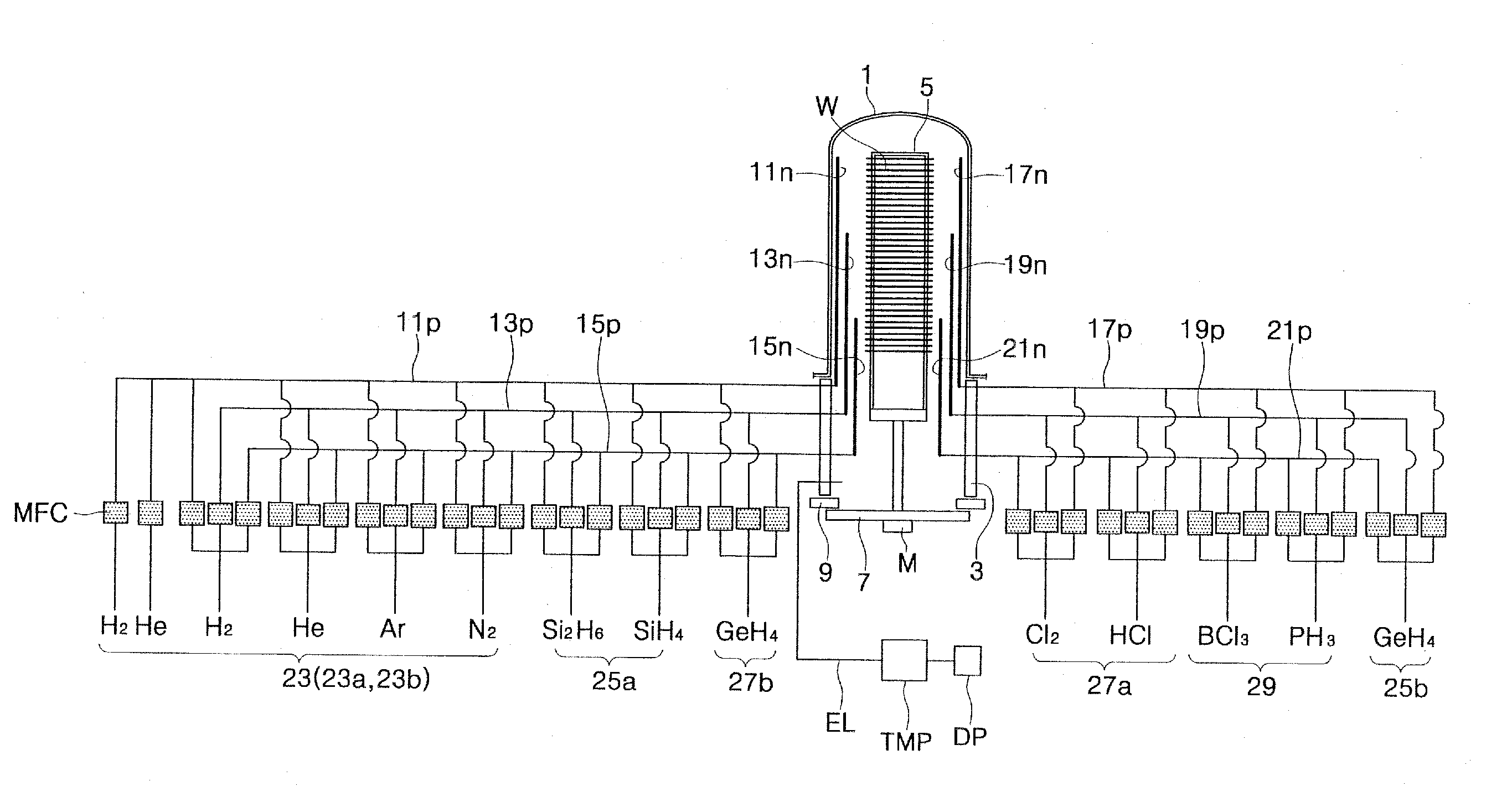
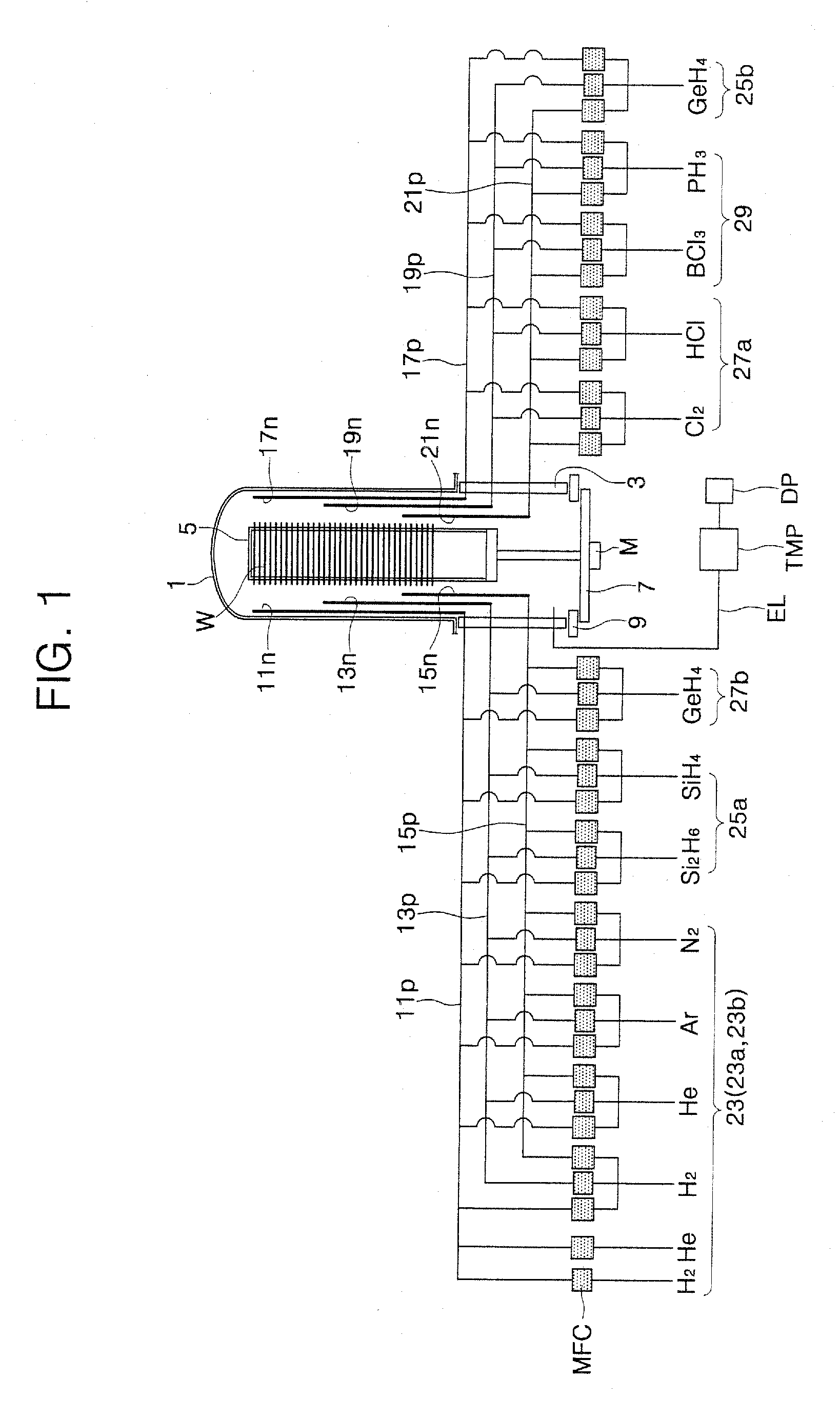
Microscopic system equipt with an electron microscope and a scanning probe microscope
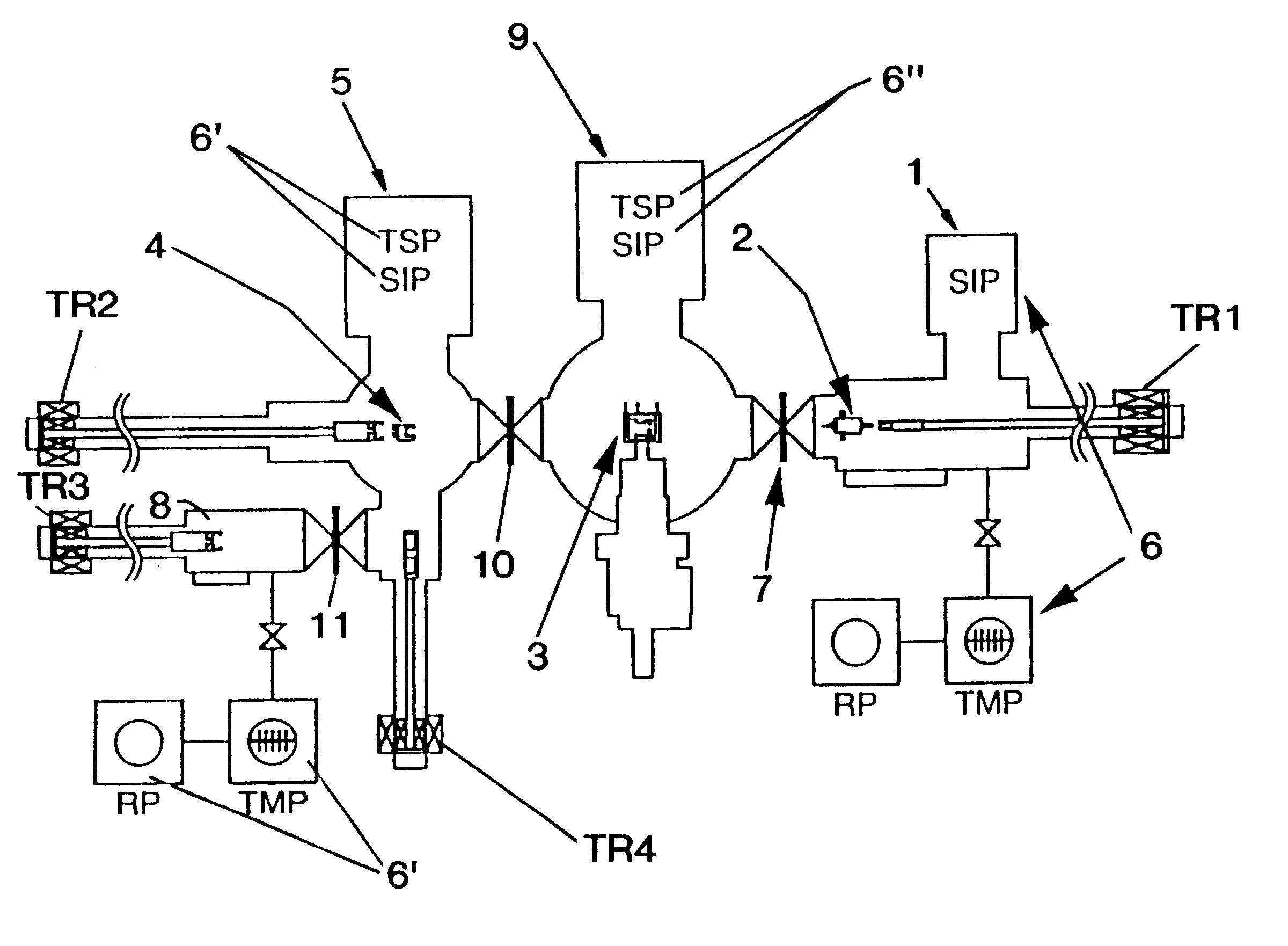
The present invention is to provide a microscopic system by which a simultaneous observation at an ultra high vacuum condition by an electron microscope and by a scanning probe microscope is possible in an ultra high vacuum electron microscope chamber 9 equipped with an observation stage 3, to which an ultra high vacuum chamber 1 for a scanning probe microscope equipping with a scanning probe microscope holder 2 in which scanning probe microscope is contained and a specimen treatment chamber 5 possessing a specimen holder 4 on which a specimen is held are connected. Said each chamber of microscopic system can be separately exhausted to the ultra high vacuum level and the specimen holder and the scanning probe microscope holder can voluntarily be fixed to said observation stage and be removed from said observation stage.
Owner:JEOL LTD +2
Physics package design for a cold atom primary frequency standard
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and device for accurately measuring the incident flux of ambient particles in a high or ultra-high vacuum environment
ActiveUS20110290991A1Quality improvementAccurately determineLaser detailsParticle separator tubesUltra-high vacuumOptical field
An apparatus and method that can measure flux density in-situ under high vacuum conditions includes a means for confining a collection of identical, elemental sensor particles to a volume of space by initial cooling by laser or another method, then confinement in a sensor volume using externally applied magnetic and / or optical fields.
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
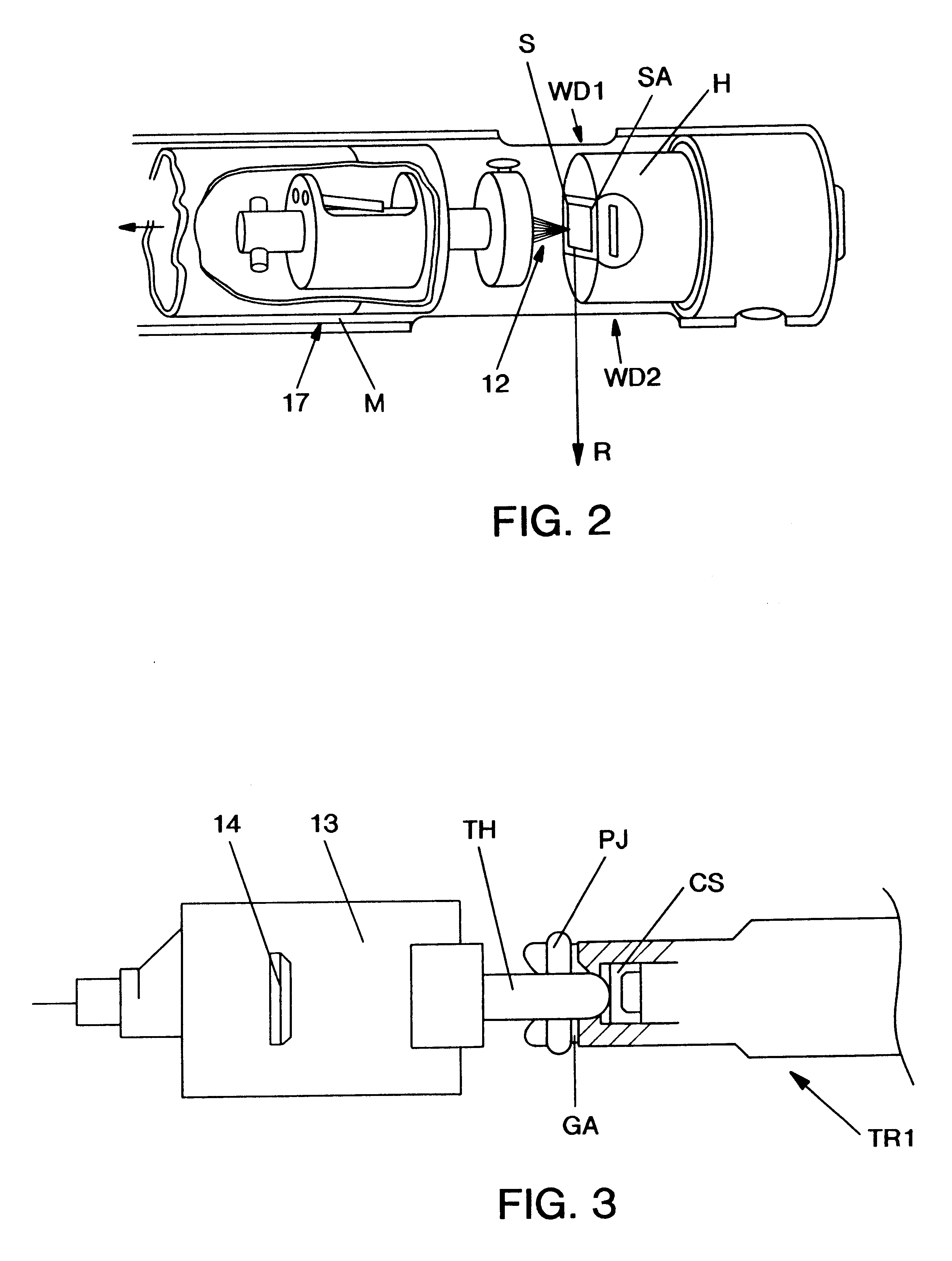
Method and apparatus of pretreatment of an electron gun chamber
A method of pre-treating an ultra high vacuum charged particle gun chamber by ion stimulated desorption is provided. The method includes generating a plasma for providing a plasma ion source, and applying a negative potential to at least one surface in the gun chamber, wherein the negative potential is adapted for extracting an ion flux from the plasma ion source to the at least one surface for desorbing contamination particles from the at least one surface by the ion flux impinging on the at least one surface.
Owner:ICT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TESTING GESELLSCHAFT FUER HALBLEITERPRUEFTECHNIK GMBH
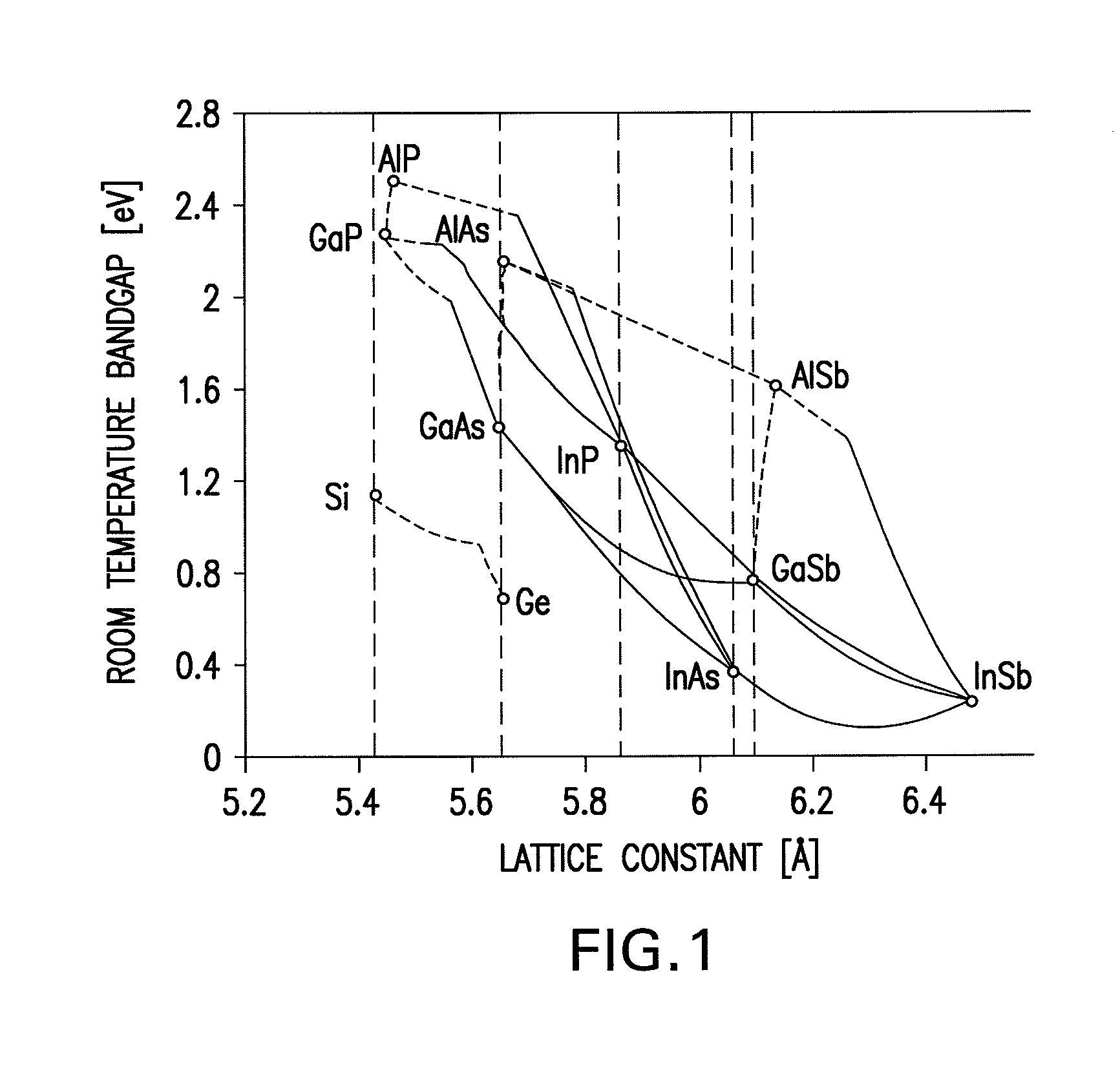
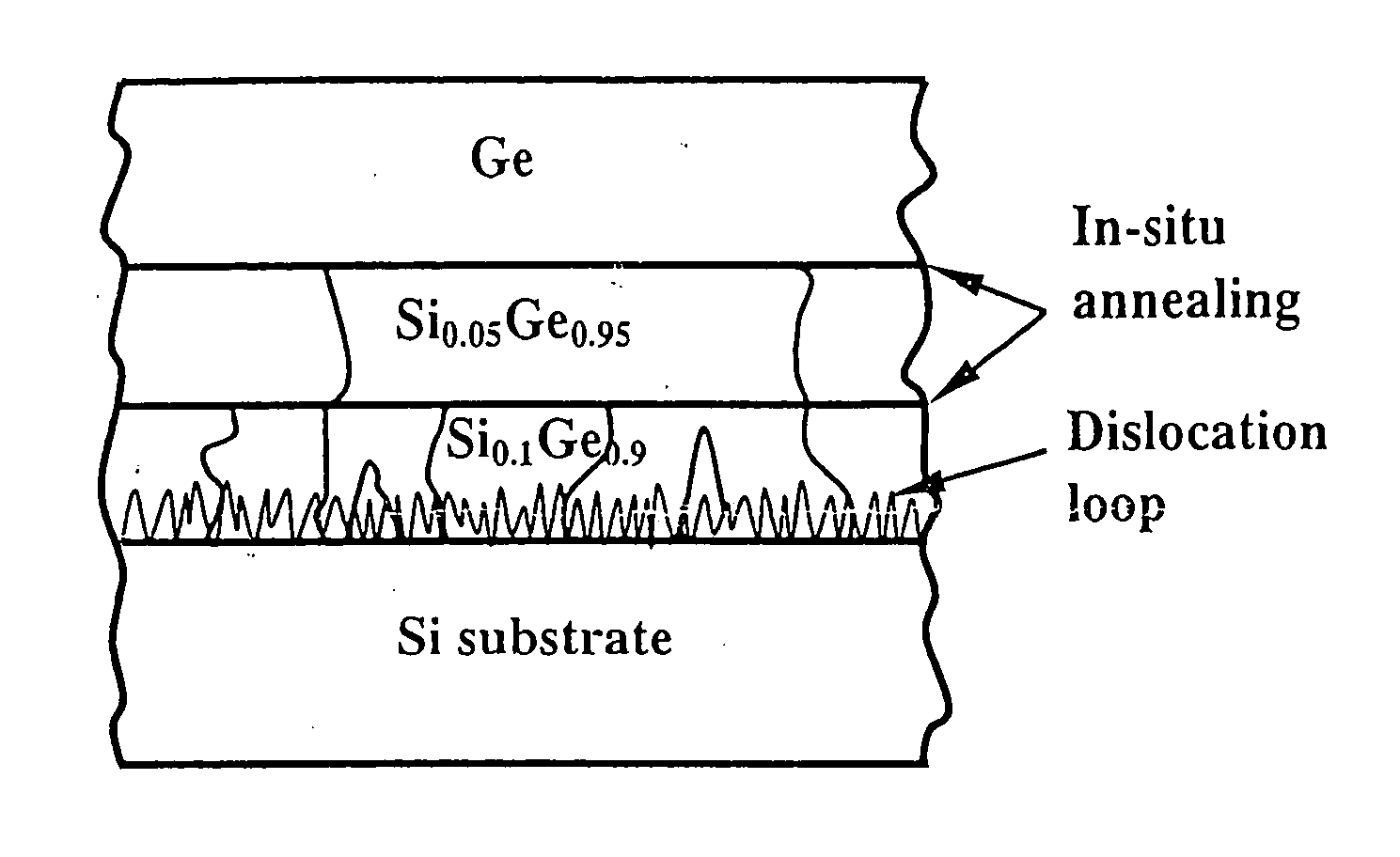
Growth of GaAs epitaixial layers on Si substrate by using a novel GeSi buffer layer
InactiveUS20050023552A1Reduce thicknessFlatten surface roughnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesUltra-high vacuumGas phase
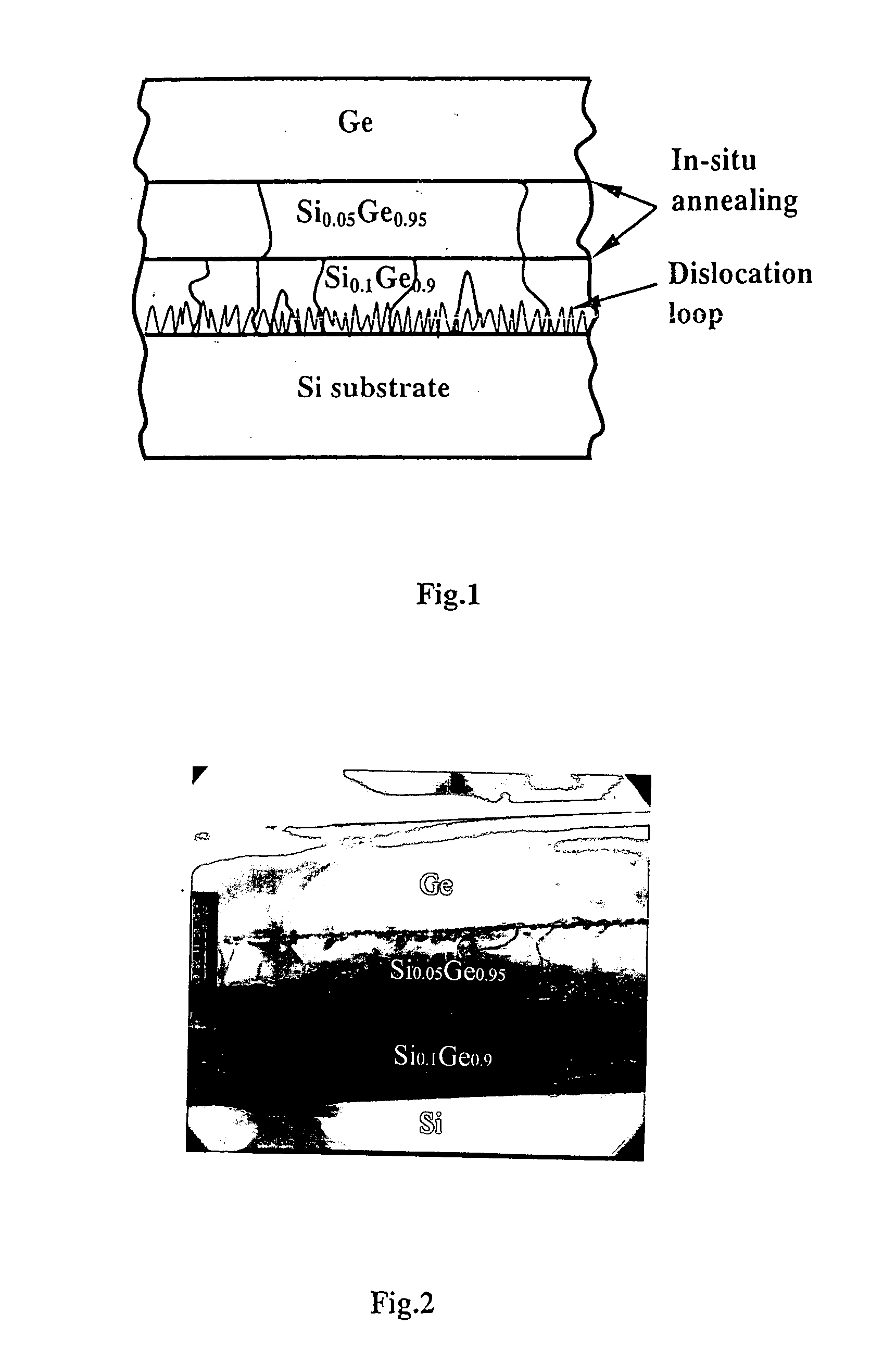
This invention provides a process for growing Ge epitaixial layers on Si substrate by using ultra-high vacuum chemical vapor deposition (UHVCVD), and subsequently growing a GaAs layer on Ge film of the surface of said Ge epitaixial layers by using metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). The process comprises steps of, firstly, pre-cleaning a silicon wafer in a standard cleaning procedure, dipping it with HF solution and prebaking to remove its native oxide layer. Then, growing a high Ge-composition epitaixial layer, such as Si0.1Ge0.9 in a thickness of 0.8 μm on said Si substrate by using ultra-high vacuum chemical vapor deposition under certain conditions. Thus, many dislocations are generated and located near the interface and in the low of part of Si0.1Ge0.9 due to the large mismatch between this layer and Si substrate. Furthermore, a subsequent 0.8 μm Si0.05Ge0.95 layer, and / or optionally a further 0.8 μm Si0.02Ge0.98 layer, are grown. They form strained interfaces of said layers can bend and terminate the propagated upward dislocation very effectively. Therefore, a film of pure Ge is grown on the surface of said epitaixial layers. Finally, a GaAs epitaixial layer is grown on said Ge film by using MOCVD.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Novel method to achieve increased trench depth, independent of CD as defined by lithography
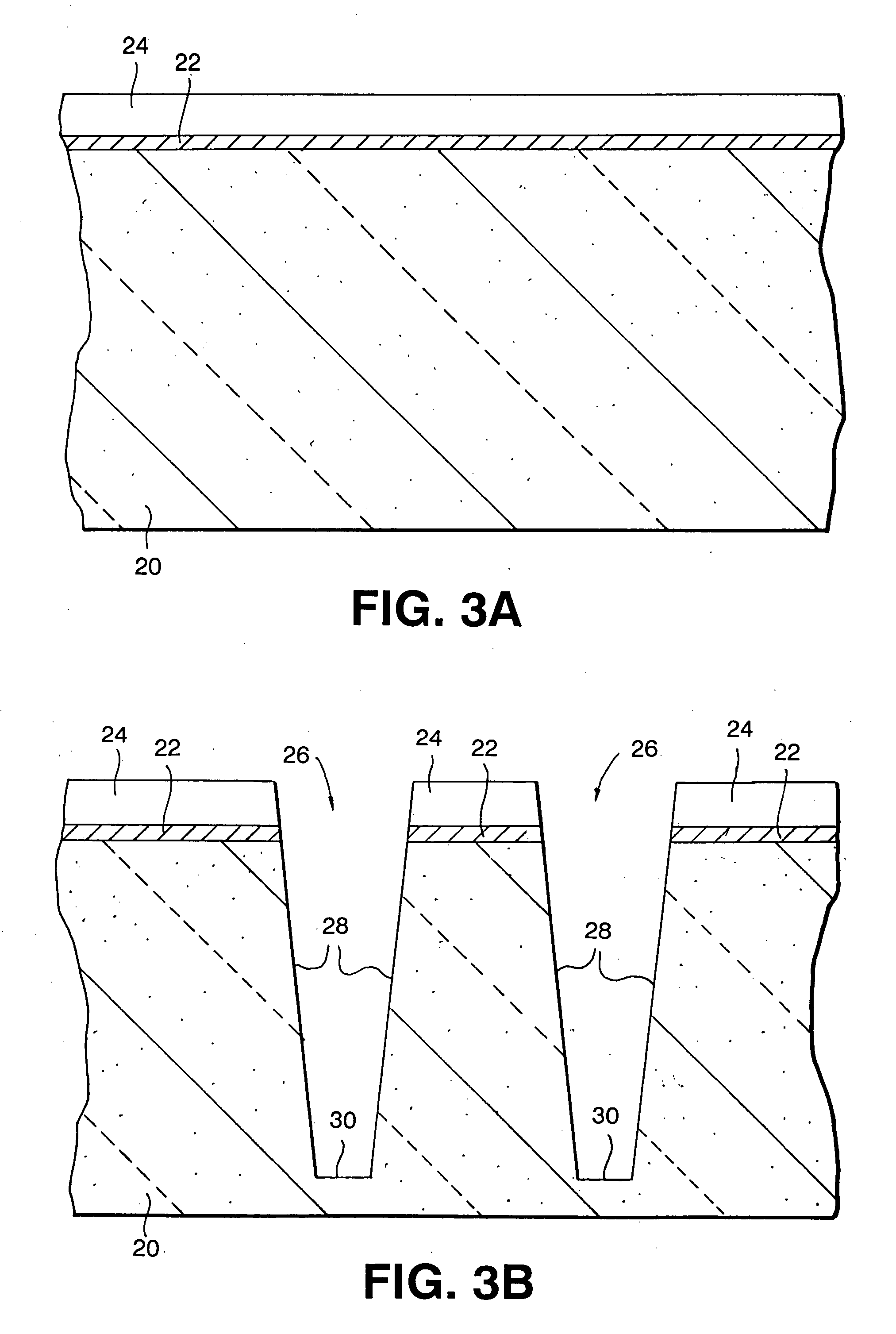
InactiveUS20050009295A1Reduced dimensionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithographic artistUltra-high vacuum
A method of forming at least one deep trench structure having an increased trench depth is provided. The method includes providing at least one deep trench having sidewalls that extend to a common bottom wall in a surface of a substrate. Each deep trench has initial dimensions that are wider than targeted dimensions for the deep trenches. To reduce the initial dimensions to that of the targeted dimensions, an epitaxial silicon film is formed selectively or non-selectively on at least some portions of the sidewalls using a low-temperature ultra-high vacuum epitaxial silicon growth tehnique.
Owner:IBM CORP
Device and method for calibrating flow-dividing vacuum leaking hole
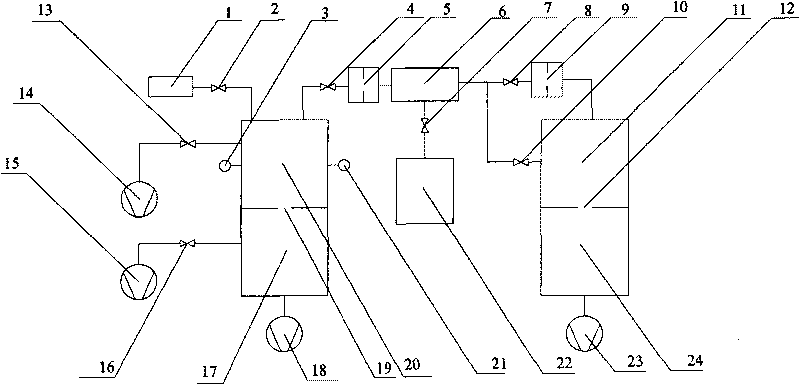
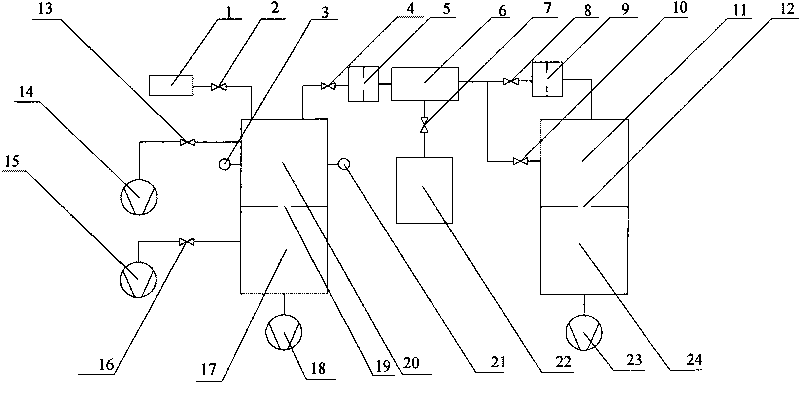
ActiveCN101713696AWide measurement rangeReduce measurement uncertaintyDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateUltra-high vacuumEngineering
The invention relates to a device and a method for calibrating a flow-dividing vacuum leaking hole, in particular to the device and the method for calibrating the vacuum leaking hole, the leakage value of which is less than 1*10-8 Pa.m3 / s by adopting flow-dividing technology, and belongs to the field of measuring technology. The device consists of the calibrated leaking hole, a valve, an ionization gauge, a small hole, a flow-dividing chamber, a non-evaporable getter pump, an ultrahigh vacuum calibrating chamber, a metering hole, a very high vacuum pumping chamber, an oil-free bi-turbo molecular pump air exhauster set, a quadrupole mass spectrometer, a flow meter, a super-high vacuum calibrating chamber, the metering hole, a super-high vacuum pumping chamber and a common molecular pump air exhauster set. The method adopts a fixed flow method gas micro-flow meter to provide a known gas flow rate, so the measuring range of the flow rate is wide and uncertainty of the measurement is low; and by adopting a flow-dividing method to calibrate the vacuum leaking hole, the method of the invention completely avoids a nonlinear error of the quadrupole mass spectrometer and can precisely calibrate the vacuum leaking hole the leakage value of which is less than 1*10-8 Pa.m3 / s.
Owner:NO 510 INST THE FIFTH RES INST OFCHINA AEROSPAE SCI & TECH
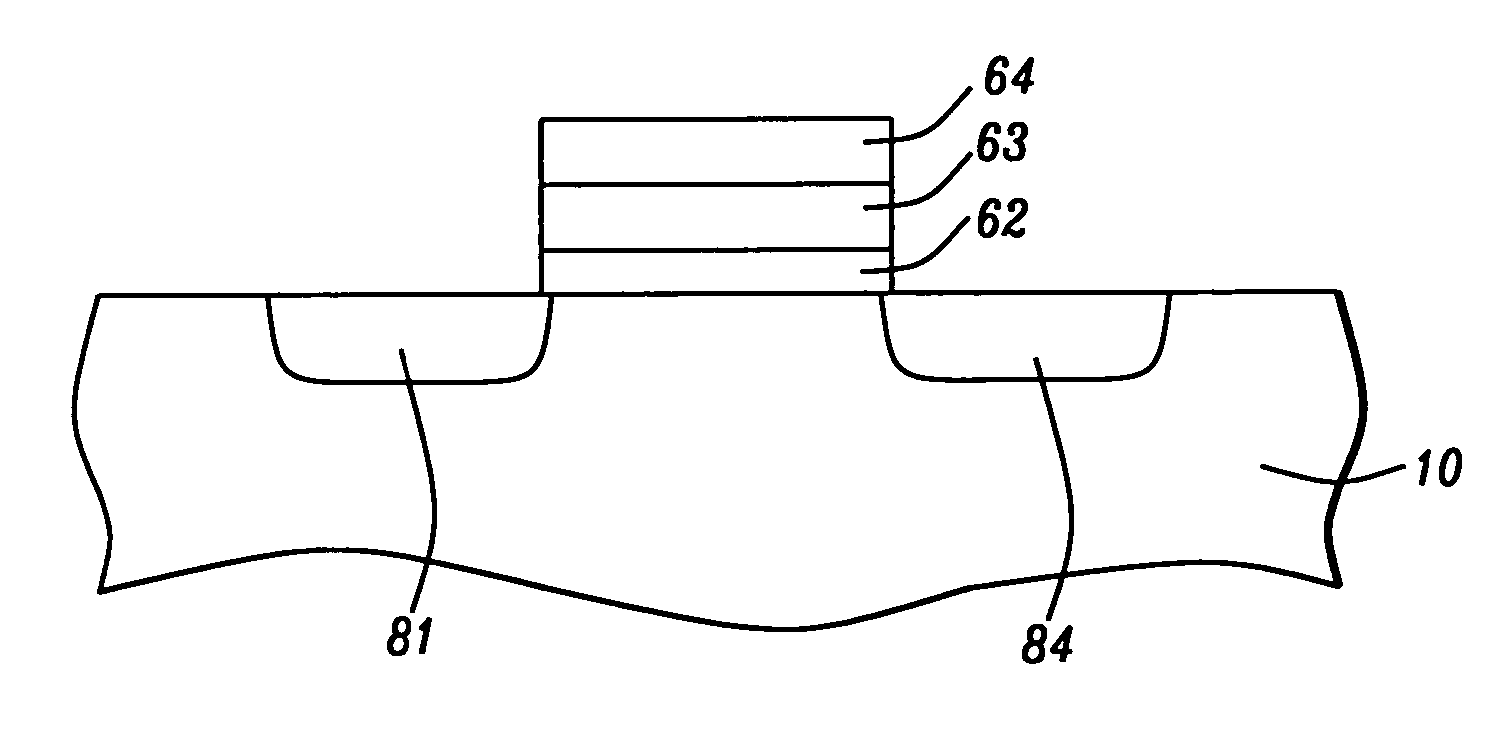
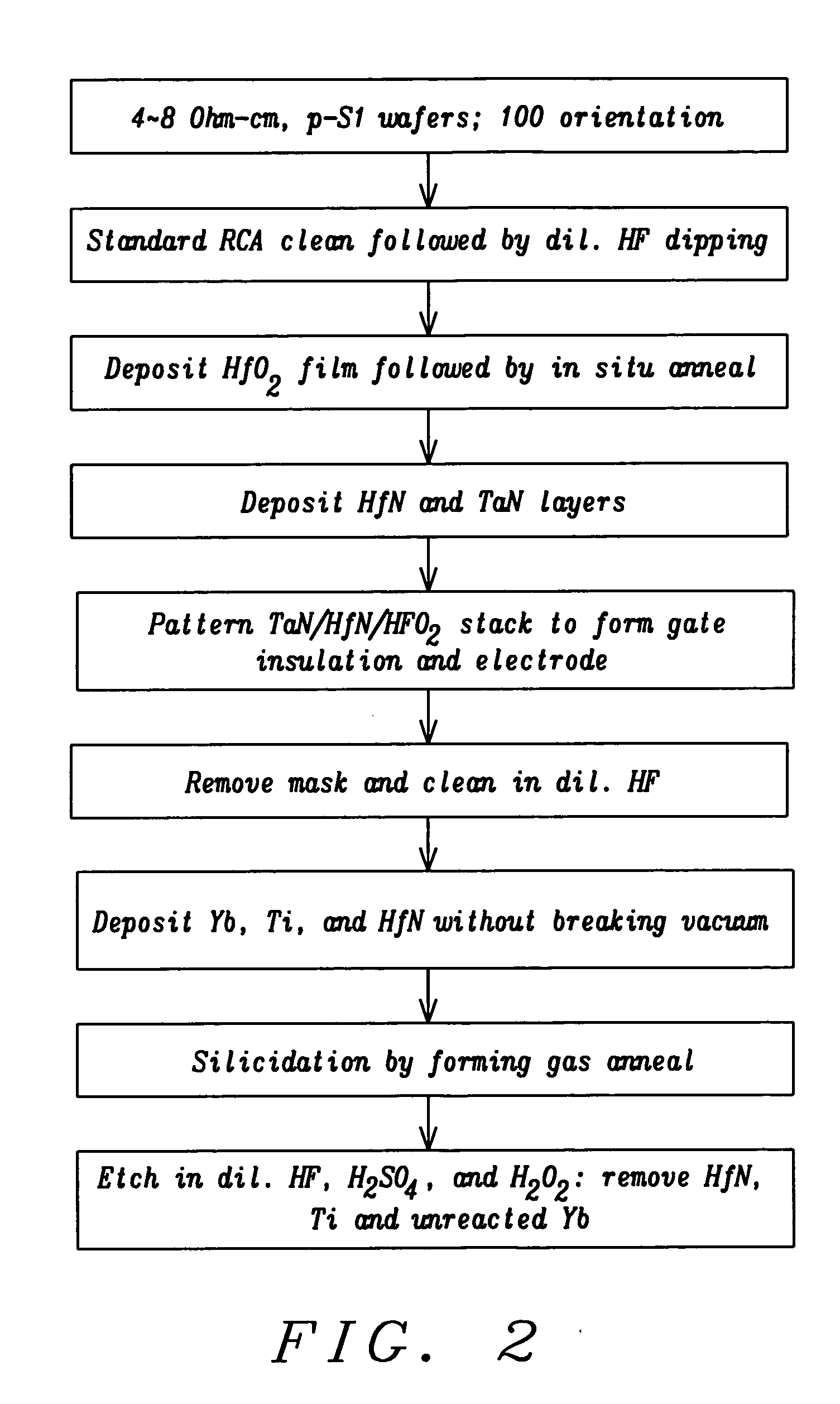
Schottky barrier source/drain N-MOSFET using ytterbium silicide
InactiveUS20050275033A1Improve electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETSchottky barrier
A method of fabricating an N-type Schottky barrier Source / Drain Transistor (N-SSDT) with ytterbium silicide (YbSi2-x) for source and drain is presented. The fabrication of YbSi2-x is compatible with the normal CMOS process but ultra-high vacuum, which is required for ErSi2-x fabrication, is not needed here. To prevent oxidation of ytterbium during ex situ annealing and to improve the film quality, a suitable capping layer stack has been developed.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com