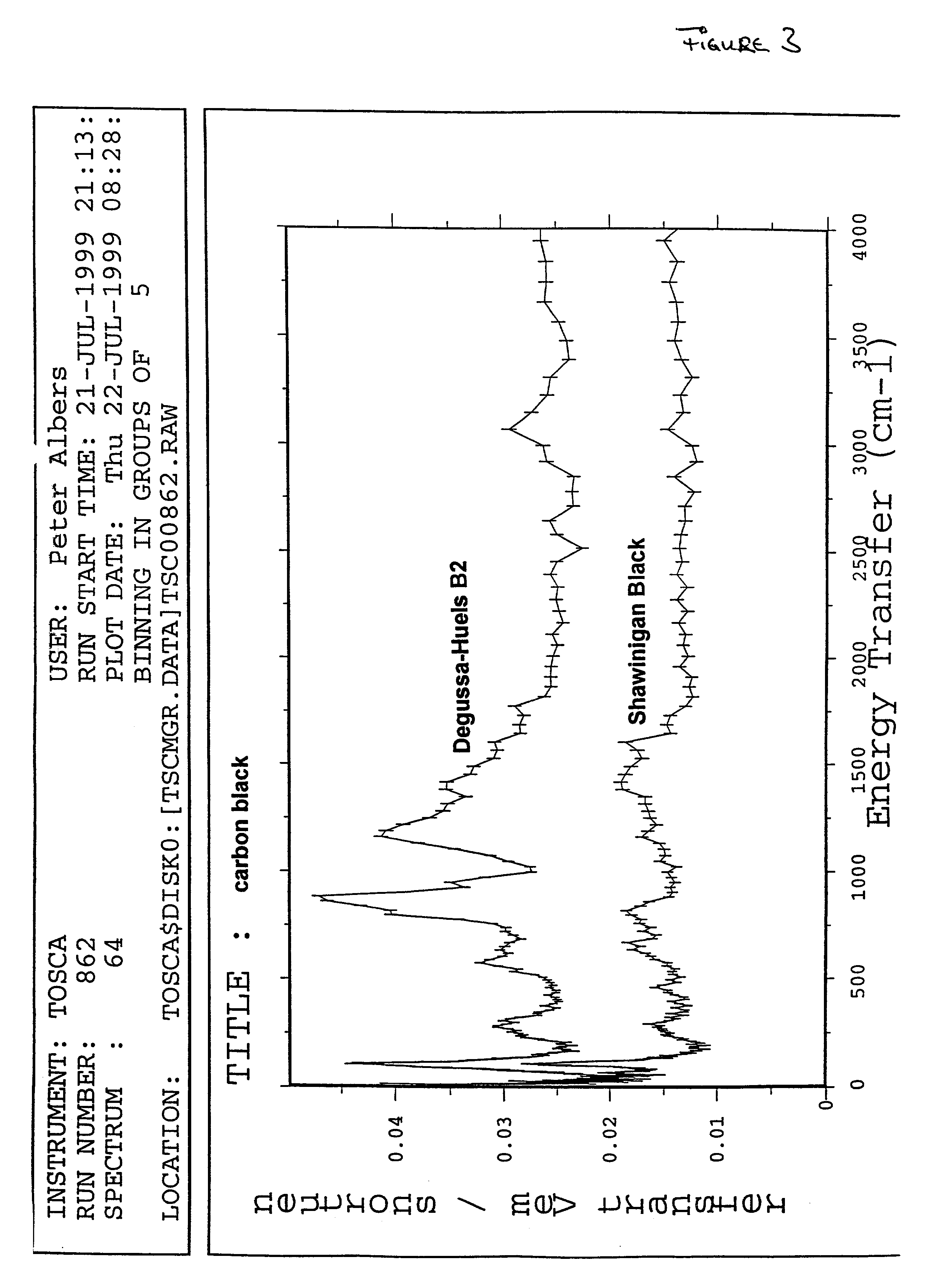
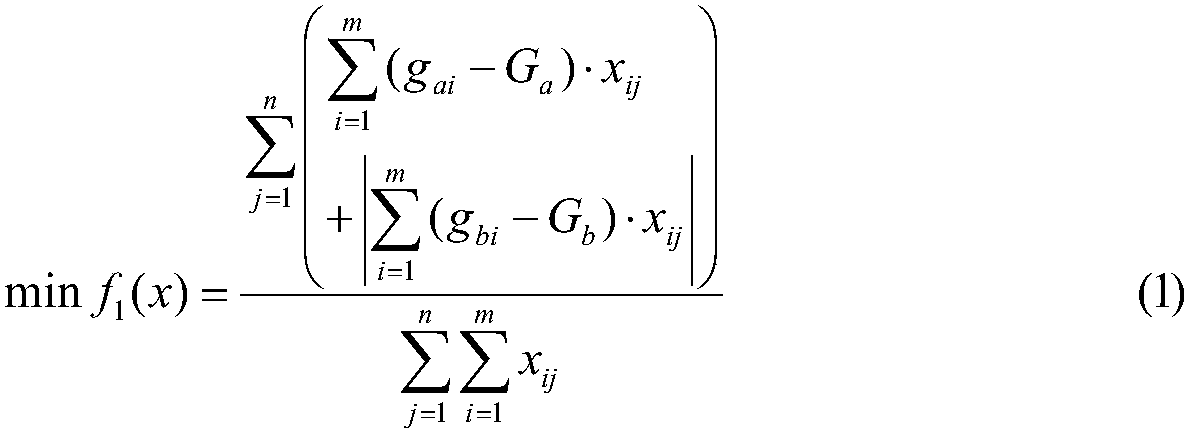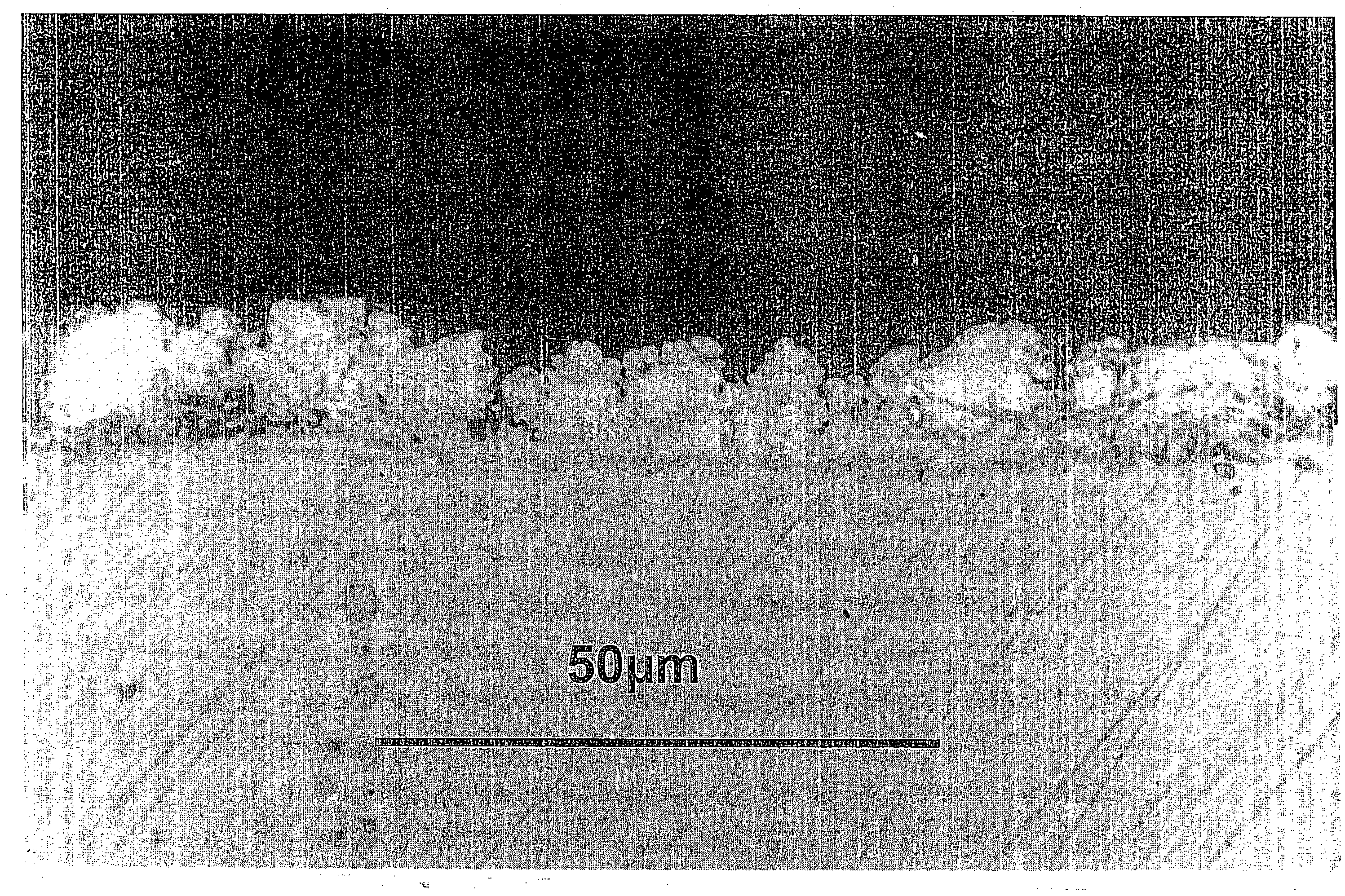Patents
Literature
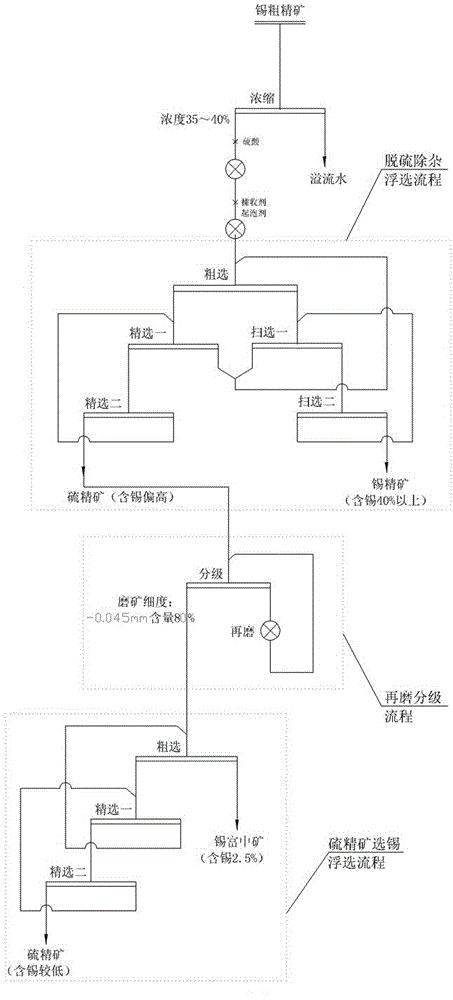
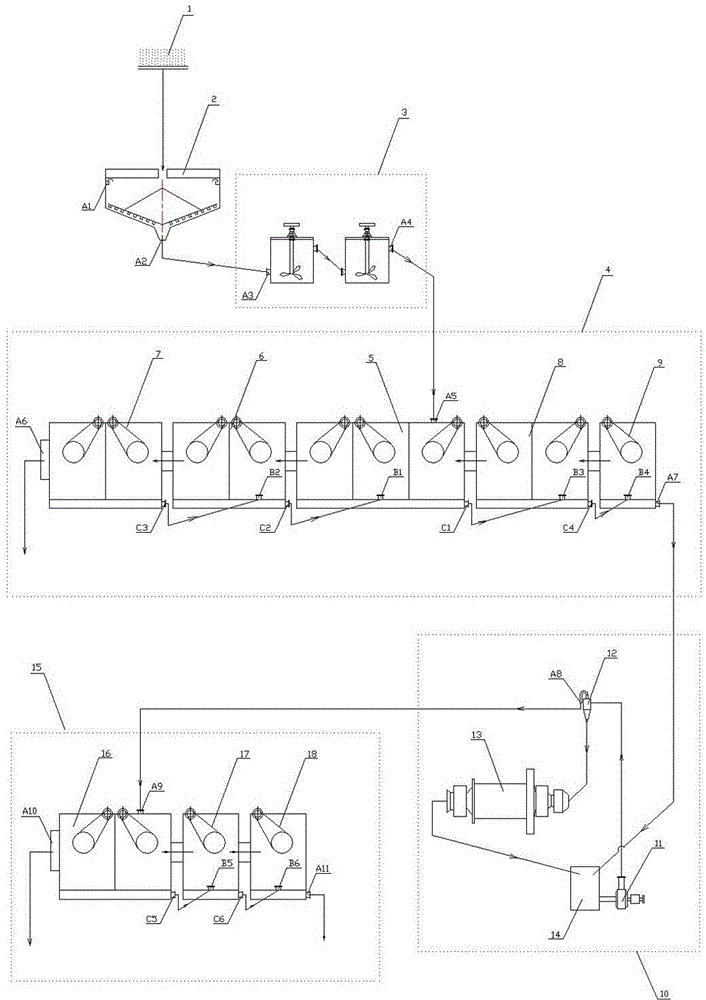
302 results about "Polymetal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry or mining, polymetal or polymetallic is a substance composed of a combination of different metals. When the substance contains only two metals the term bimetal (bimetallic) is sometimes preferred. A polymetallic ore (or polymetal ore) is an ore that is the source of more than one metal suitable for recovery. A mine containing polymetallic ore is a polymetallic mine. Polymetallic nodules are concretions of manganese and iron (and other metals) found on the ocean floor. They are sometimes called manganese nodules, after their principal component.
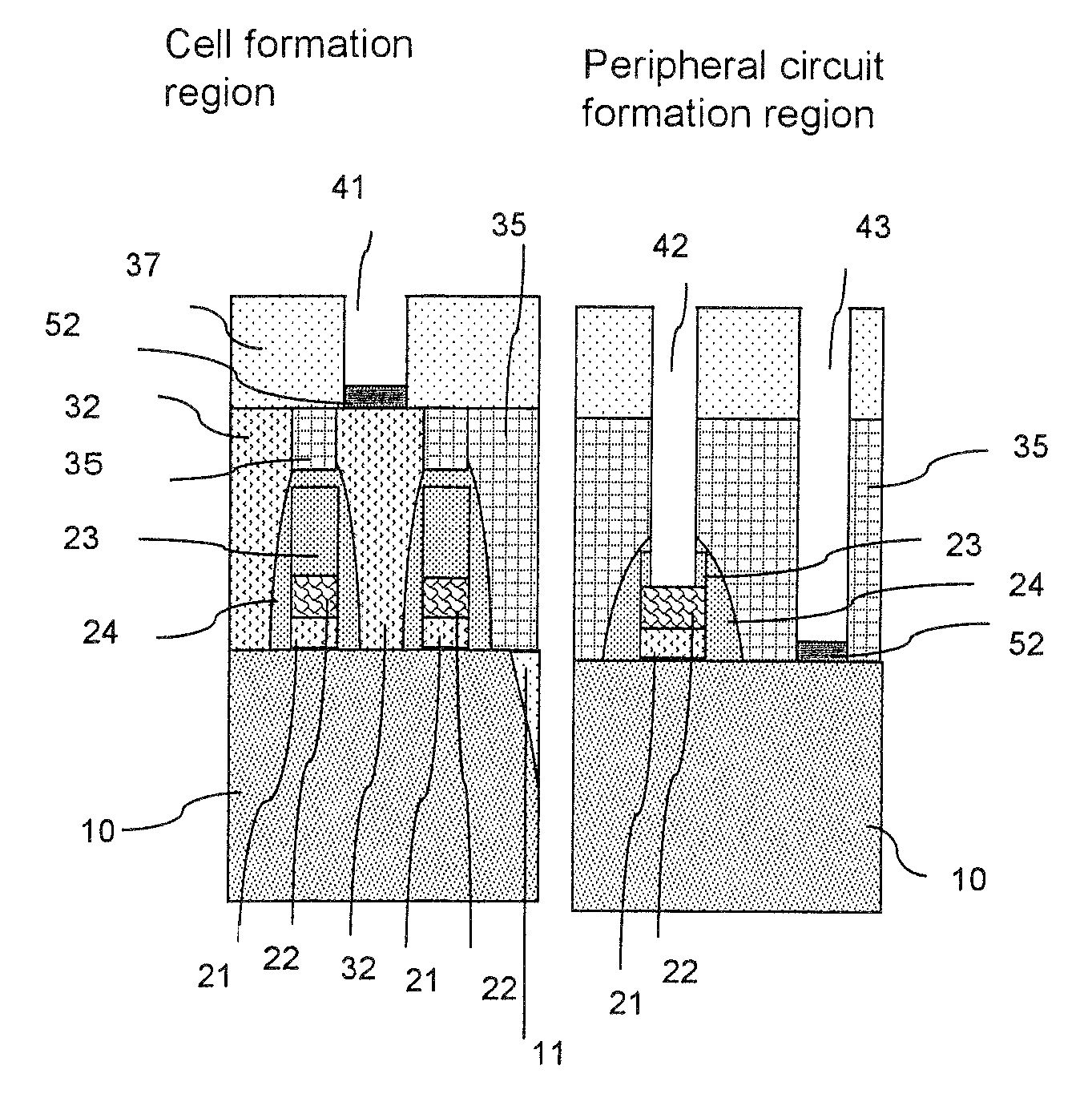
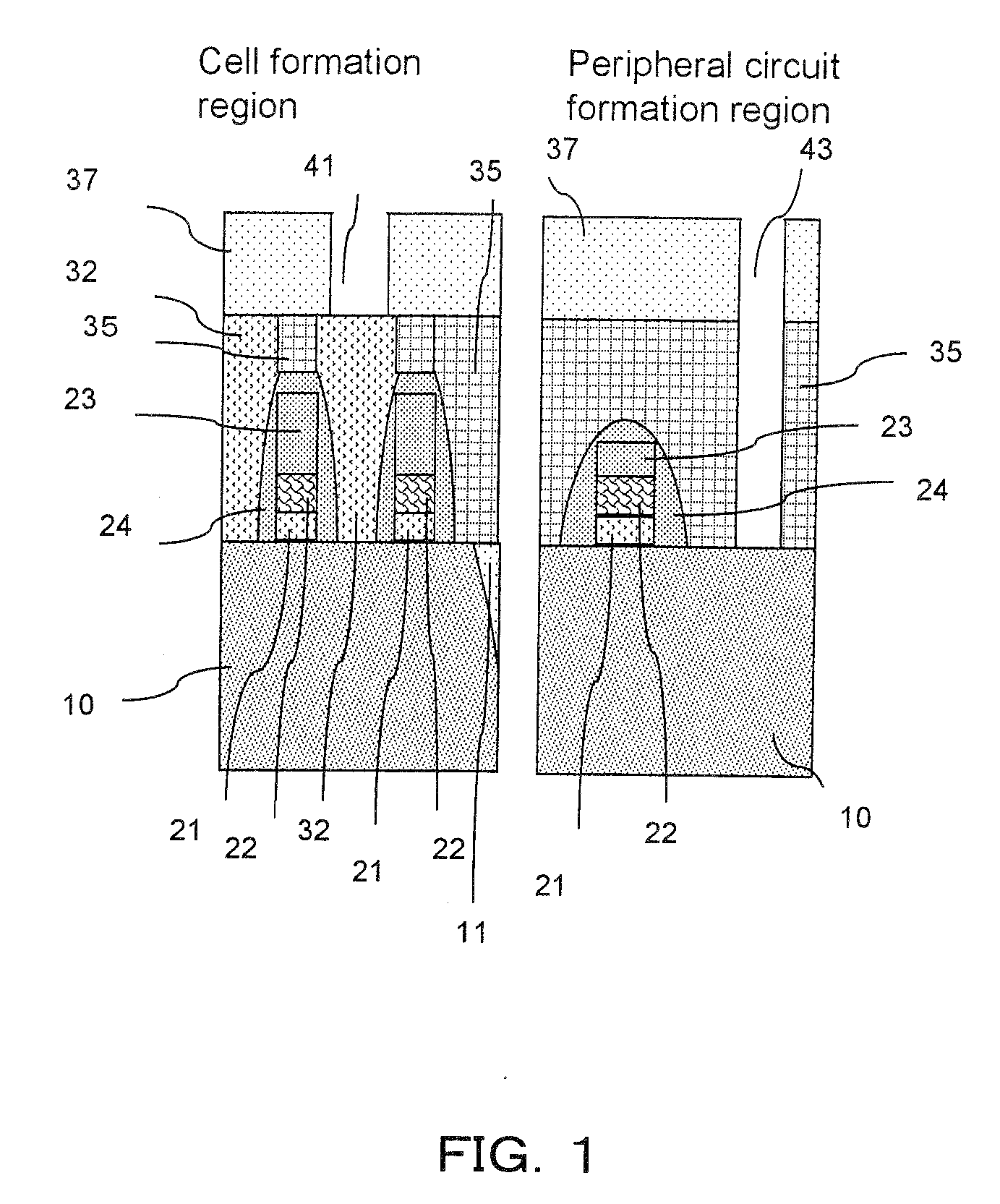
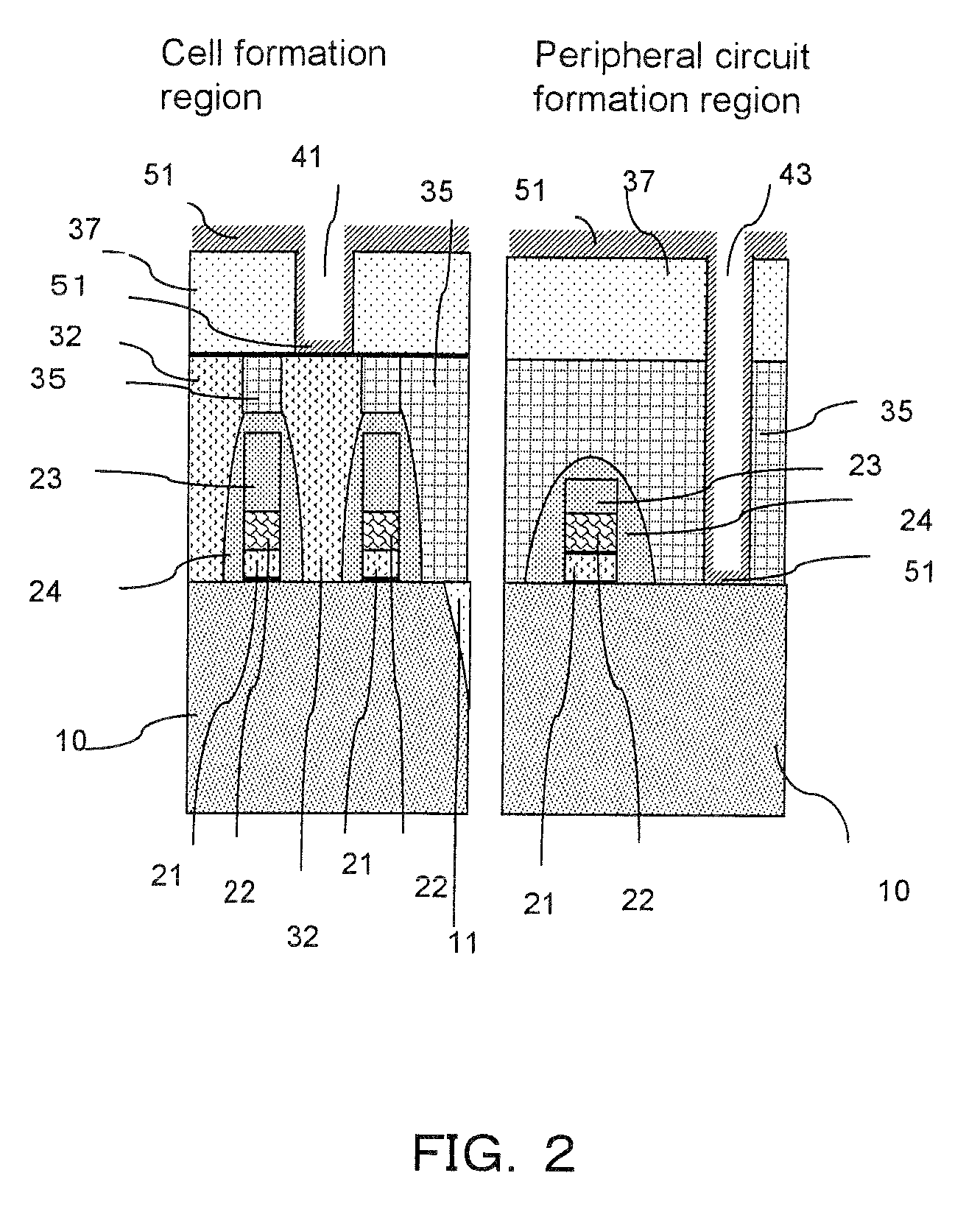
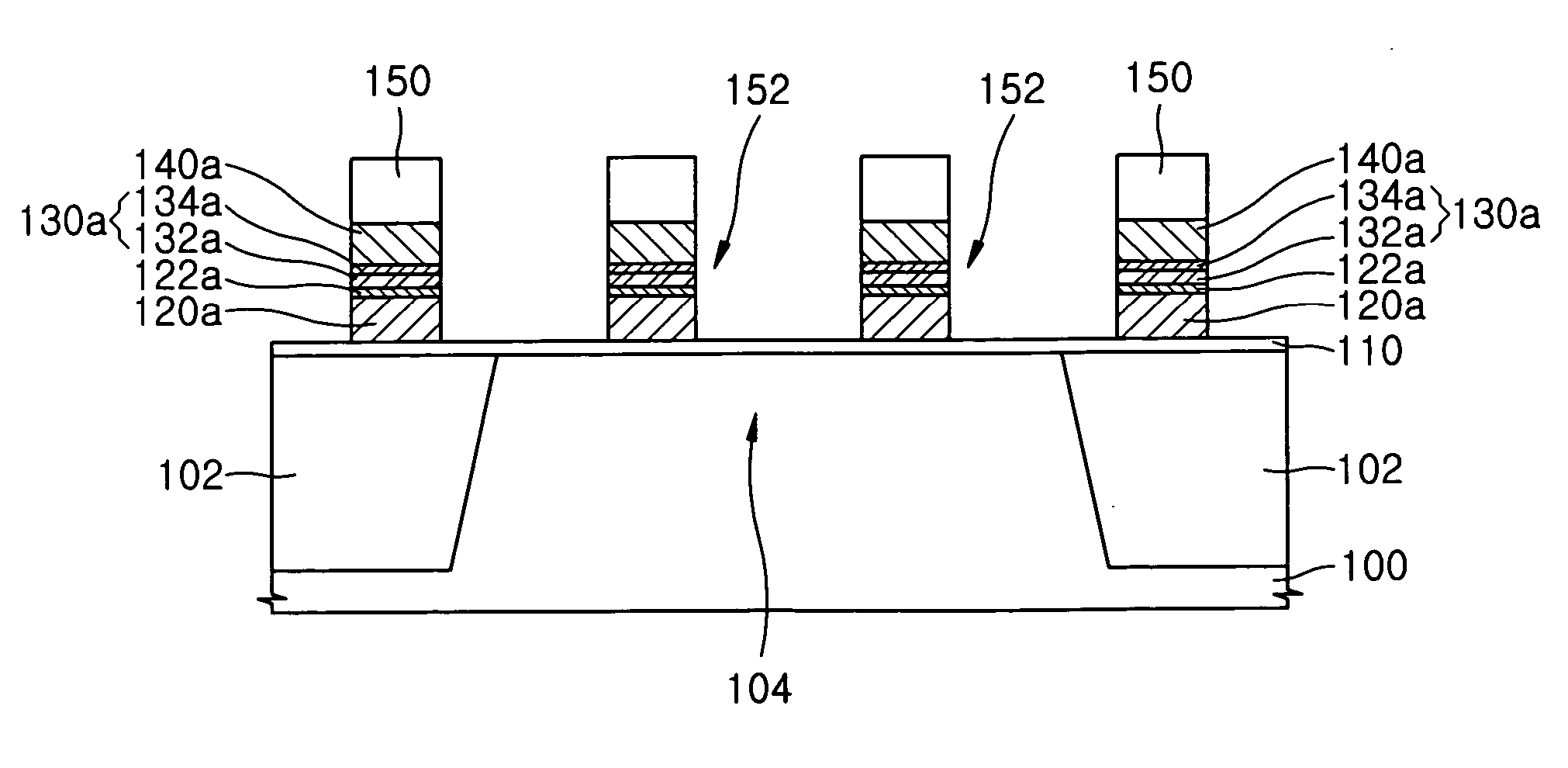
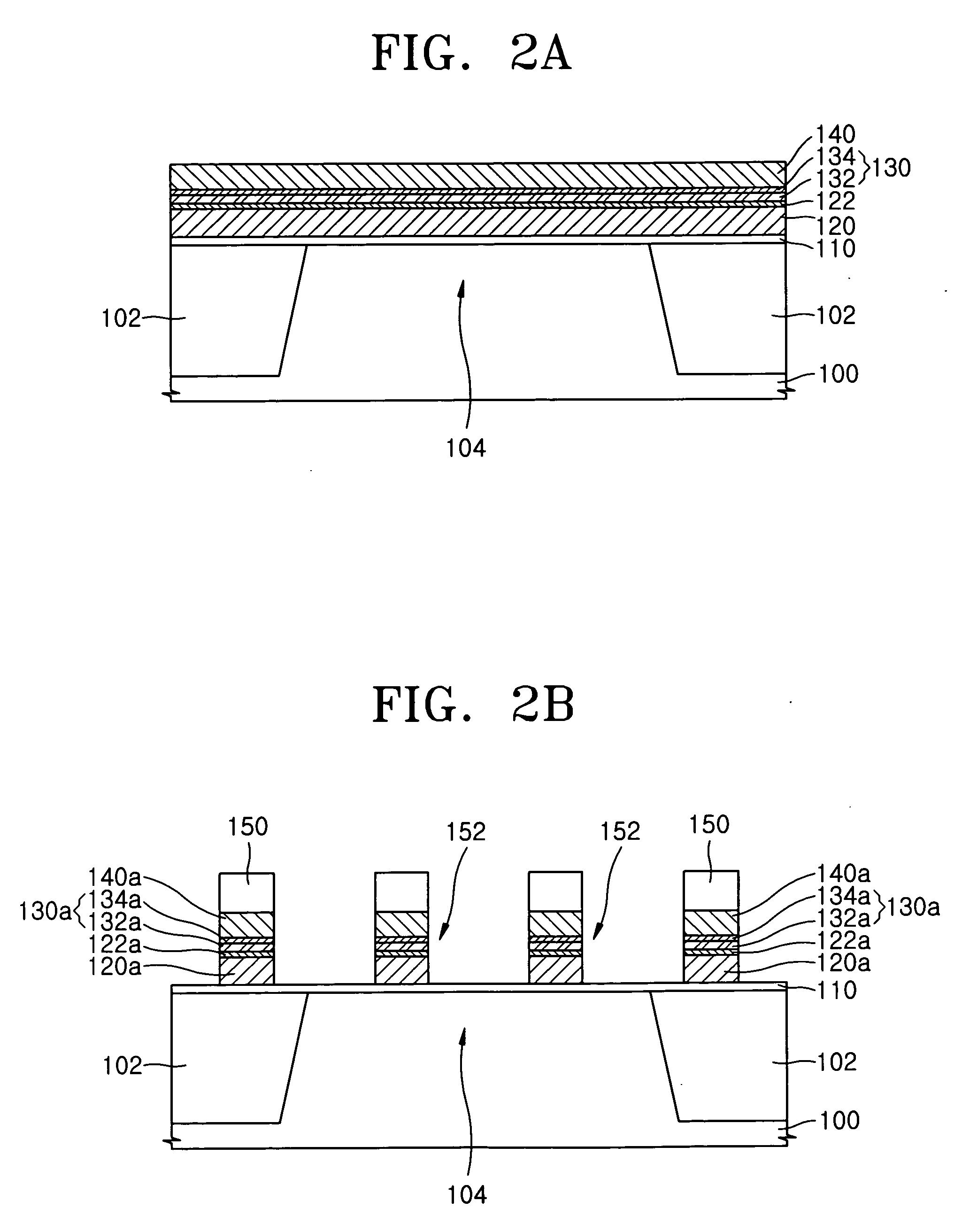
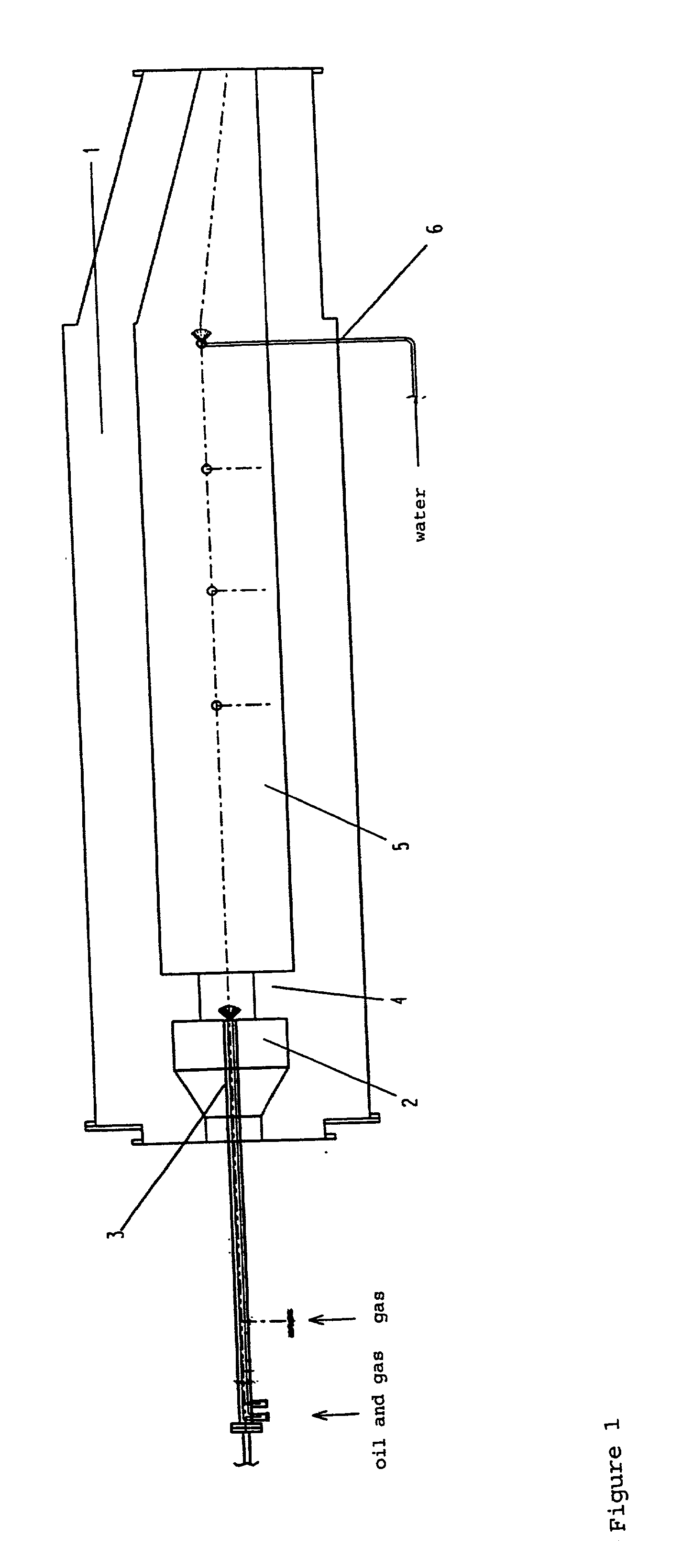
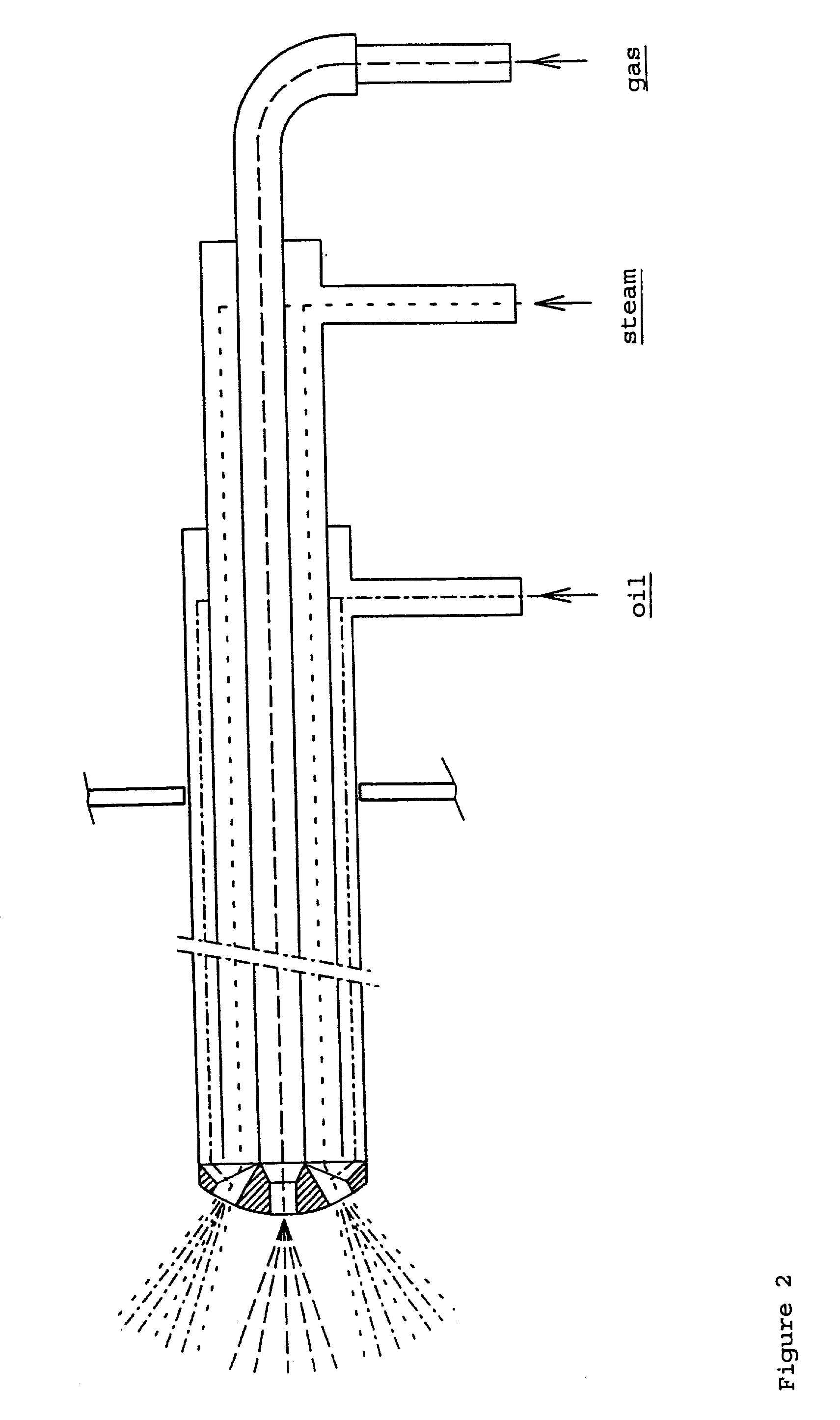
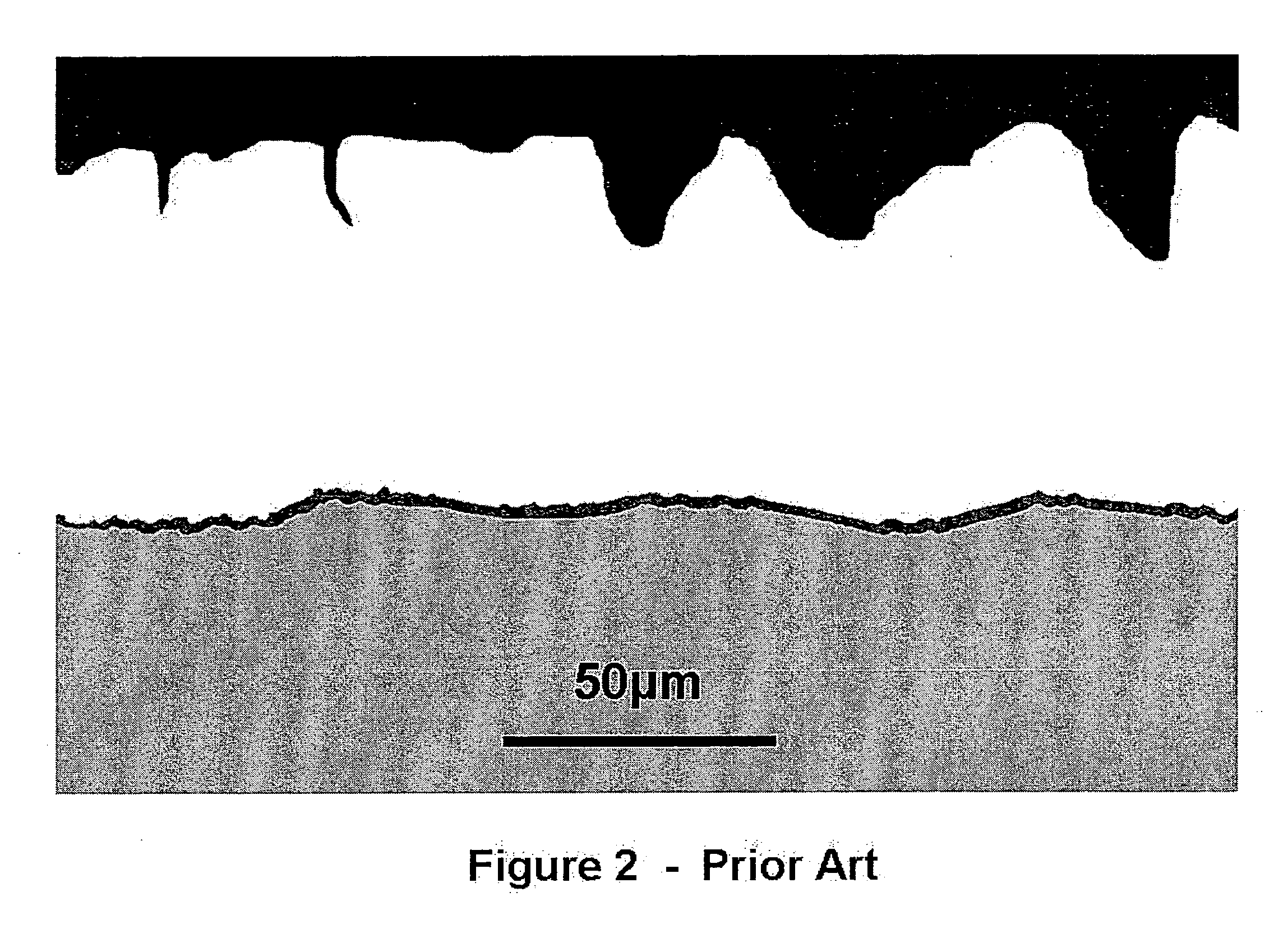
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080081472A1Reduce processing stepsIncrease the number ofSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesChemical solutionDevice material
A first structure is formed, having a contact plug formed on the bottom of a first opening in an interlayer insulating film, a second opening formed through the interlayer insulating film to reach a semiconductor substrate, and a third opening formed through the interlayer insulating film to reach a polymetal gate electrode. A cobalt layer is deposited on the surface of the structure, and thermally treated to form a cobalt silicide layer on the surface of the contact plug and on the bottom face of the second opening. The structure is then treated to remove the cobalt, in the state in which the cobalt silicide layer is formed, with the use of a chemical solution capable of dissolving cobalt but not the polymetal.
Owner:HEFEI RELIANCE MEMORY LTD
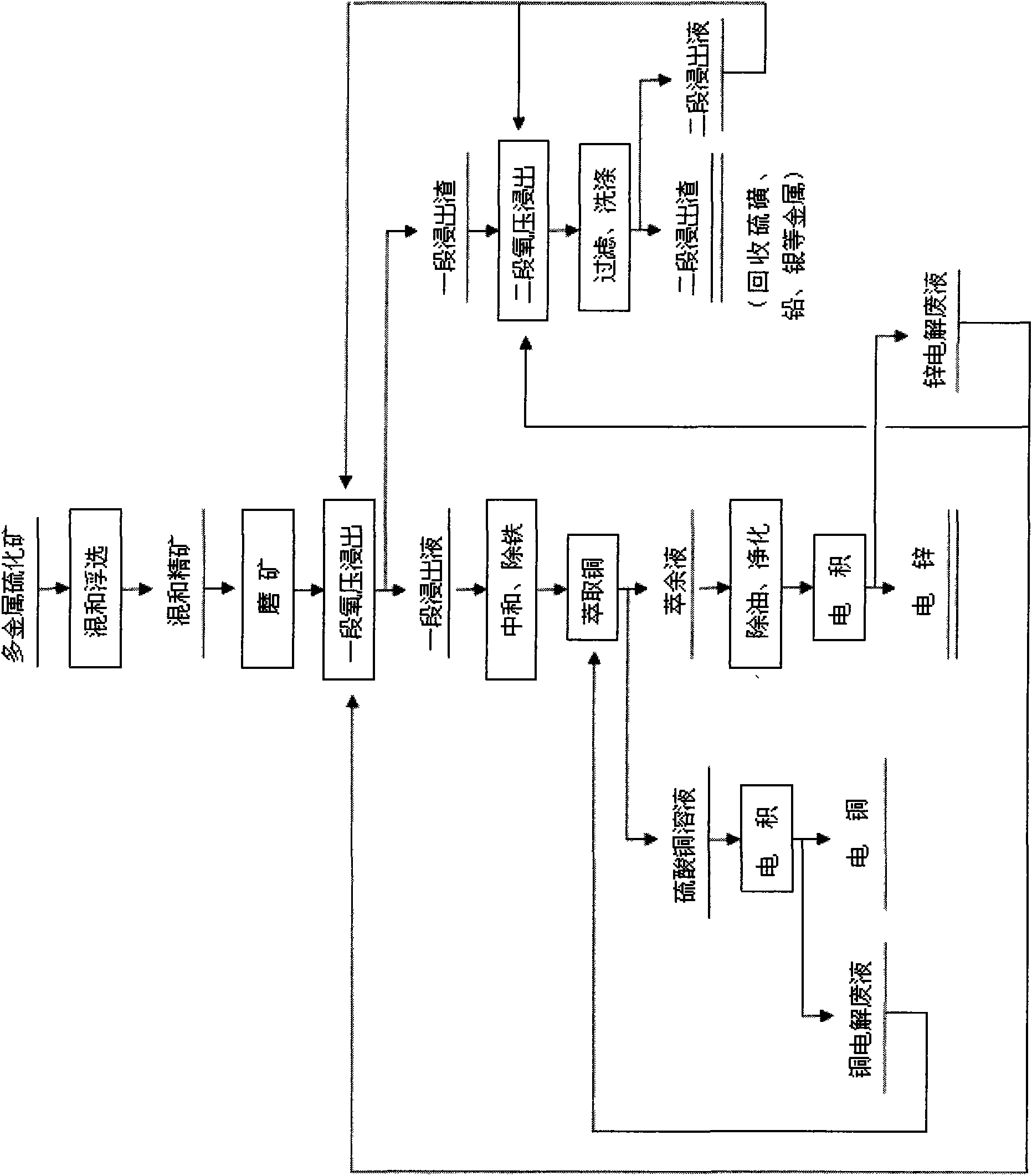
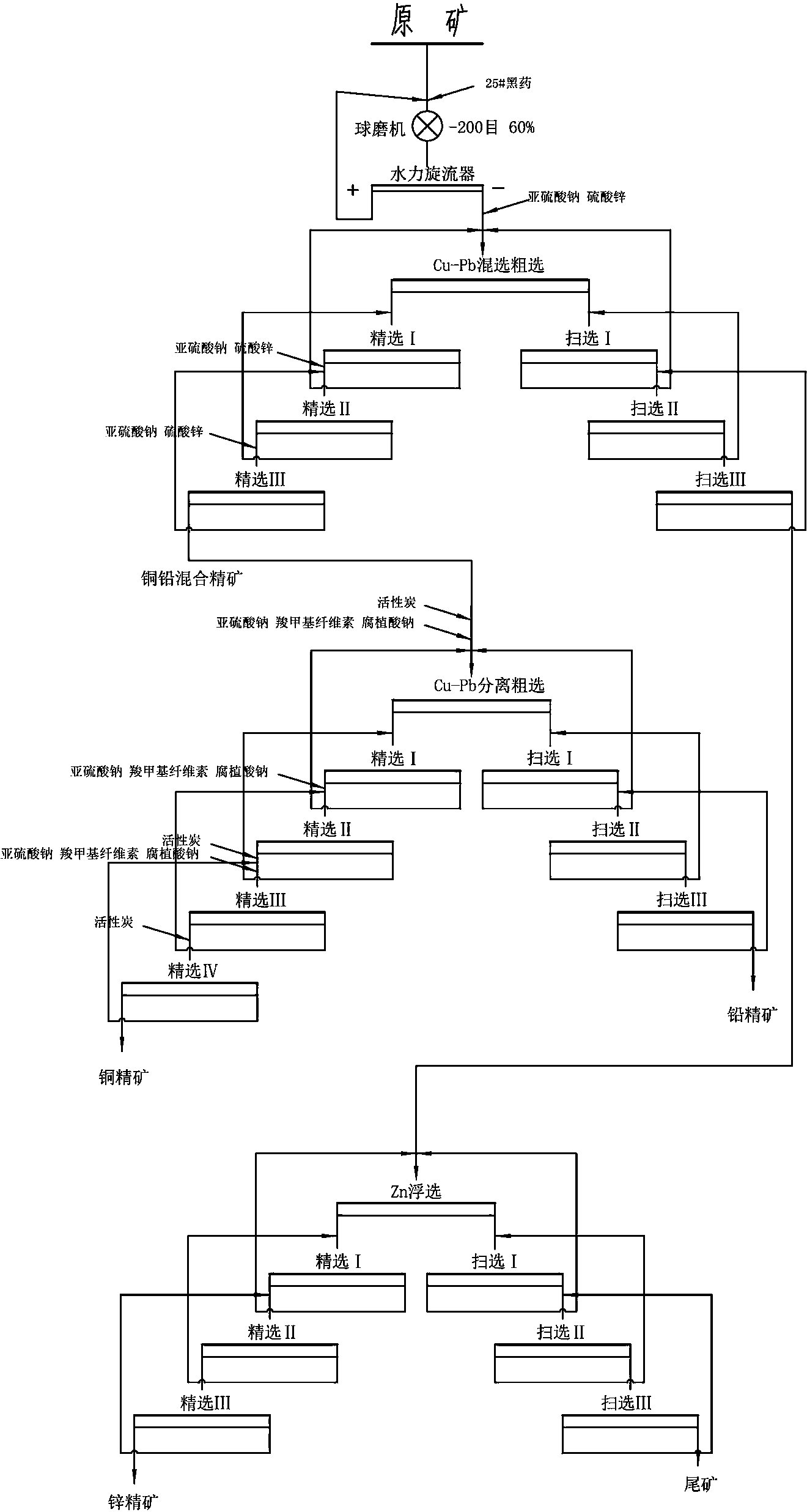
Comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc
InactiveCN101643857AHigh recovery rateSimple processSulfur preparation/purificationFlotationRecovery methodLead smelting
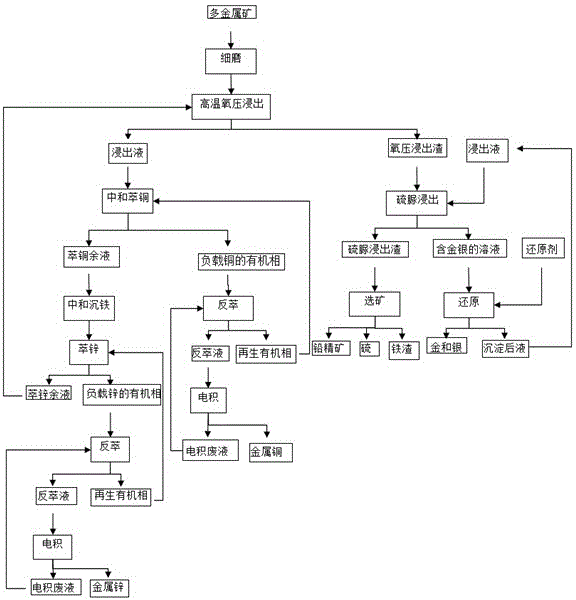
The invention discloses a comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc and adopts dressing-metallurgy combination method and hydrometallurgy-pyrometallurgy combination method to recover metals. The recovery method comprises the following steps: first performing bulk flotation to the complex polymetal sulphide ore, fine grinding the obtained concentrate, leaching by using two-step counter flow oxygen pressure leaching process, extracting and separating copper and zinc from the obtained leachate, electrodepositing the strip liquor of copper-loaded organic phase to obtain cathode copper, cleaning the obtained raffinate and electrodepositing to obtain cathode zinc; pressurizing leaching residue to perform flotation separation and obtain sulfur concentrate and lead silver residue, distilling sulfur concentrate to obtain sulfur; performing lead smelting process to lead silver residue to obtain electrolytic lead product and lead anodic slime; and comprehensively recovering noble metals such as gold, silver and the like from lead anodic slime. The method can greatly improve the metal recovery rate, resource utilization and the economic efficiency of mines and generate a lot of sulfur so as to obviously reduce the sulfur dioxide pollution to the atmosphere.
Owner:WESTERN MINING CO LTD
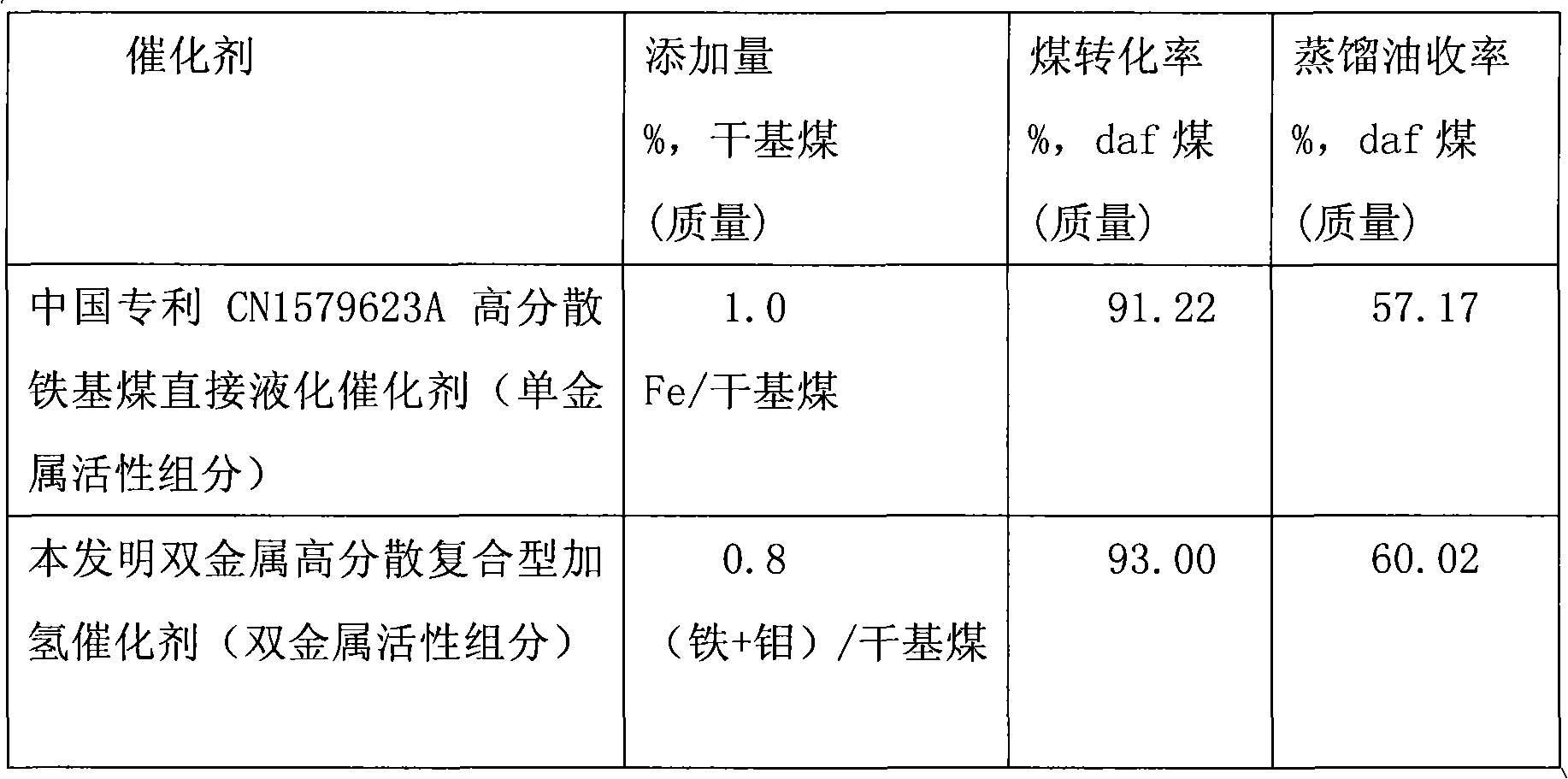
Bimetal or multi-metal high-dispersion composite coal tar hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102380396AHigh activityReduce manufacturing costLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionTreatment with hydrotreatment processesSolubilityCobalt
The invention relates to a bimetal or multi-metal high-dispersion composite coal tar hydrogenation catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst comprises molecular high-activity components of one or a plurality of mixtures of water-solubility salt compounds of metal from molybdenum, nickel, tungsten or cobalt, nanometer low-activity components gamma-FeOOH grains and micro or sub nanometer carrier pulverized coal, the activity components are uniformly and highly dispersed on the surfaces of the carrier pulverized coal, the catalyst is micro or sub nanometer fine powder and is high in activity, particles of the activity components are small and are highly uniformly dispersed on the surface of a carrier, the utilization quantity of the catalyst is low, cost is reduced, and the bimetal or multi-metal high-dispersion composite coal tar hydrogenation catalyst can be widely applied to coal tar hydrogenation or coal liquefaction.
Owner:CCTEG CHINA COAL RES INST
Method for separating and recycling valuable metals in powder rich in multiple metals of waste circuit board
ActiveCN102747229AShort processImprove efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSlag
The invention discloses a method for separating and recycling valuable metals in powder rich in multiple metals of a waste circuit board. The method comprises the following steps: (1) oxidizing and smelting at low temperature; (2) carrying out water leaching; and (3) leaching with Na2S to obtain leaching slag and two leachates finally, wherein copper and all noble metals are rich in the slag, the first leachate is alkali solution of Na2SnO3, Na2PbO2 and Na2ZnO2, and the second leachate is Na3SbS4 solution; and respectively recycling according to the prior art, wherein recovery rates of tin, antimony and zinc are more than 95%, the recovery rate of lead is more than 90%, the enrichment rates of the copper and the noble metals are high, and the metal loss is small. The method has the advantages of short process flow, reliable technology, environmental protection and low cost, and is an effective method for separating and recycling valuable metals from the waste circuit board.
Owner:广西自贸区西江资源循环科技产业股份有限公司
Beneficiation method for separating fluorite and tungsten through flotation
ActiveCN104084315AAvoid the problem of poor floatability and difficult flotation recoveryAvoid lostFlotationSulfidationTungsten
The invention discloses a beneficiation method for separating fluorite, white tungsten (black tungsten) and gangue minerals in complex polymetallic ore through flotation. Non-magnetic products of tailings subjected to sulphide ore flotation or tailings subjected to sulphide ore flotation and then subjected to strong magnetic separation for recycling black tungsten serve as two kinds of samples. The pH value is controlled by adding regulators, white tungsten, black tungsten, other gangue combined inhibitors and collectors are added, fluorite is subjected to differential flotation, then, tungsten minerals are subjected to flotation, and therefore fluorite and tungsten can be efficiently recycled. Loss of fluorite in tungsten flotation concentrate is avoided when tungsten minerals are subjected to differential flotation, and the defect that when tungsten flotation is performed, fluorite is difficult to recycle through flotation because the inhibitors have strong inhibition on fluorite, and beneficiation efficiency is low is avoided. Compared with a current beneficiation situation, the fluorite recycling rates of tests on the two different samples are increased by 39% to 48 % and 9% respectively, and the tungsten recycling efficiency is improved by 3%.
Owner:HUNAN SHIZHUYUAN NON FERROUS METAL +1
Inorganic composite material for absorbent refining multiple metal ion industrial sewage and application method thereof
ActiveCN102658082AGood adsorption propertiesImprove purification effectOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionCelluloseIndustrial waste water
The invention provides an inorganic composite material for absorbent refining multiple metal ion industrial sewage. The inorganic composite material is prepared by mixing, by percentage by weight, 5-15% of intercalation expandable graphite, 10-25% of hydroxyapatite, 5-15% of zeolite, 5-10% of rectorite, 5-10% of chalk, 5-25% of bentonite and 15-40% of kieselguhr, adding 5wt% of clear water of total mass of mixture and 5wt% of sodium carboxymethylcellulose, evenly mixing to prepare spheroidal particle with the grain size of 1-3mm, and roasting for 2h at the temperature of 200-800 DEG C after drying. The inorganic composite material is apt to obtain technique materials and simple in handling process, and is used for absorbent refining of the multiple metal ion industrial sewage.
Owner:陕西合兴硅砂有限公司
Semiconductor devices having polymetal gate electrodes and methods of manufacturing the same
Semiconductor devices and methods of fabricating the same are provided. A gate insulating film is provided on a semiconductor substrate. A polymetal gate electrode is provided on the gate insulating film. The polymetal gate electrode includes a conductive polysilicon film on the gate insulating film, a first metal silicide film on the conductive polysilicon film, a barrier film on the first metal silicide film, and a metal film on the barrier film. The barrier film includes a titanium nitride (TiN) film on the first metal silicide film and a buffer layer between the TiN film and the metal film.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
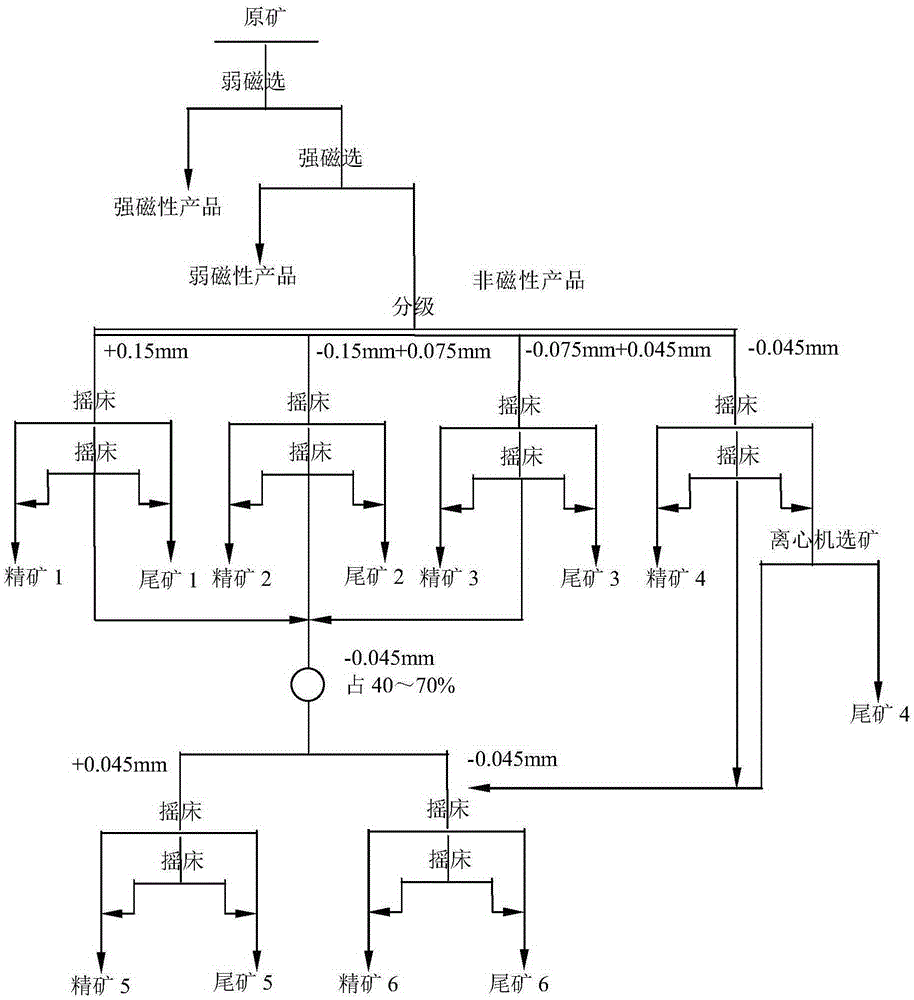
Mineral separation and enrichment method suitable for associated scheelite in molybdenite floatation tailings
InactiveCN105312148AReduce processingImprove sorting efficiencyMechanical material recoveryWet separationEnrichment methodsNon magnetic
The invention provides a mineral separation and enrichment method suitable for associated scheelite in molybdenite floatation tailings. The method includes the steps of low-intensity magnetic separation, high-intensity magnetic separation, non-magnetic ore pulp material size fraction grading, gravity separation, middling regrinding, regrading gravity separation and the like. A high-grade and high-recovery scheelite concentrate product is obtained, the associated low-grade scheelite resource in Cu-Mo polymetallic mixed associated ore is effectively and comprehensively recovered and used. The method can be widely applied to the field of recovering and using the associated low-grade scheelite resource.
Owner:INST OF MULTIPURPOSE UTILIZATION OF MINERAL RESOURCES CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
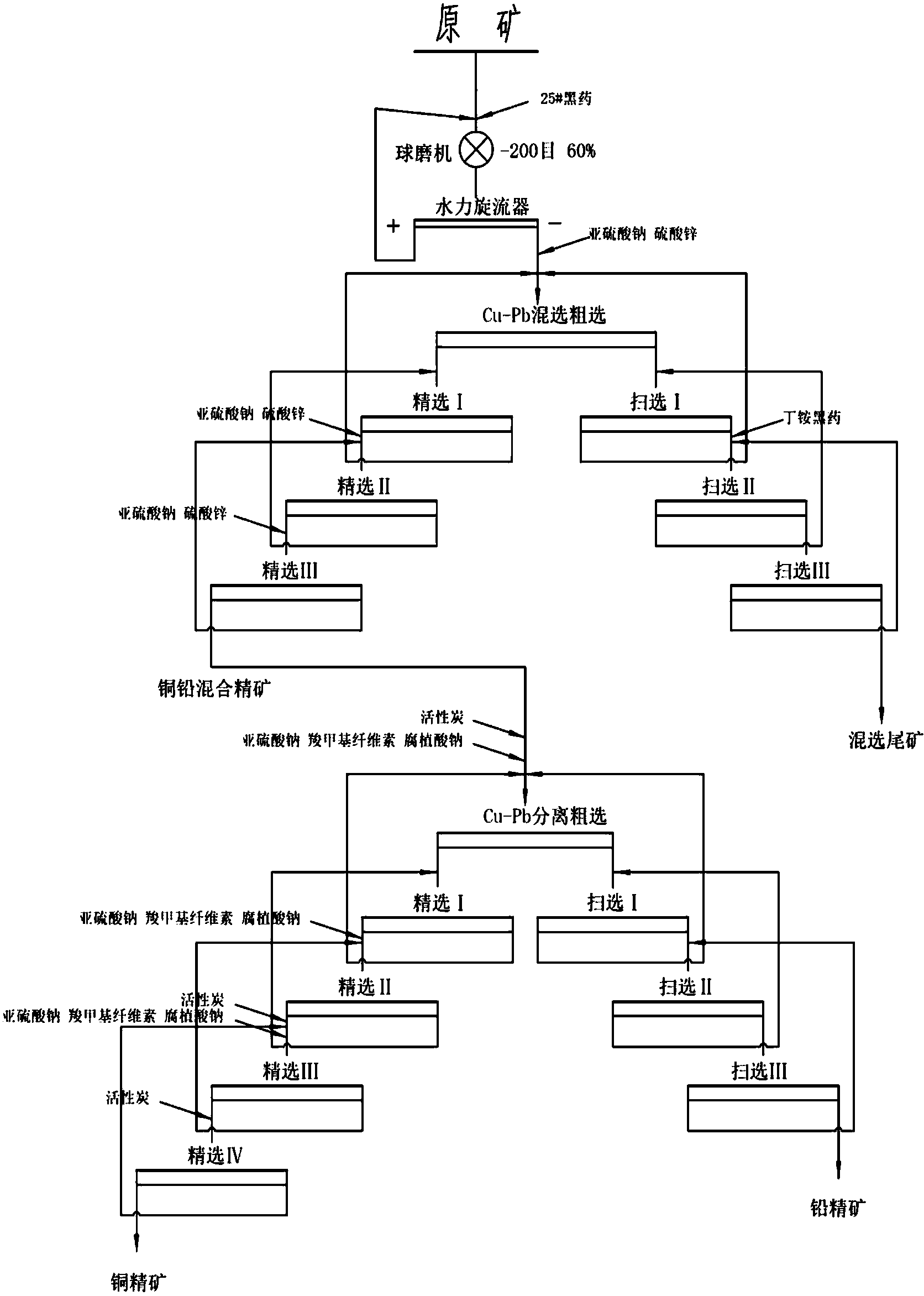
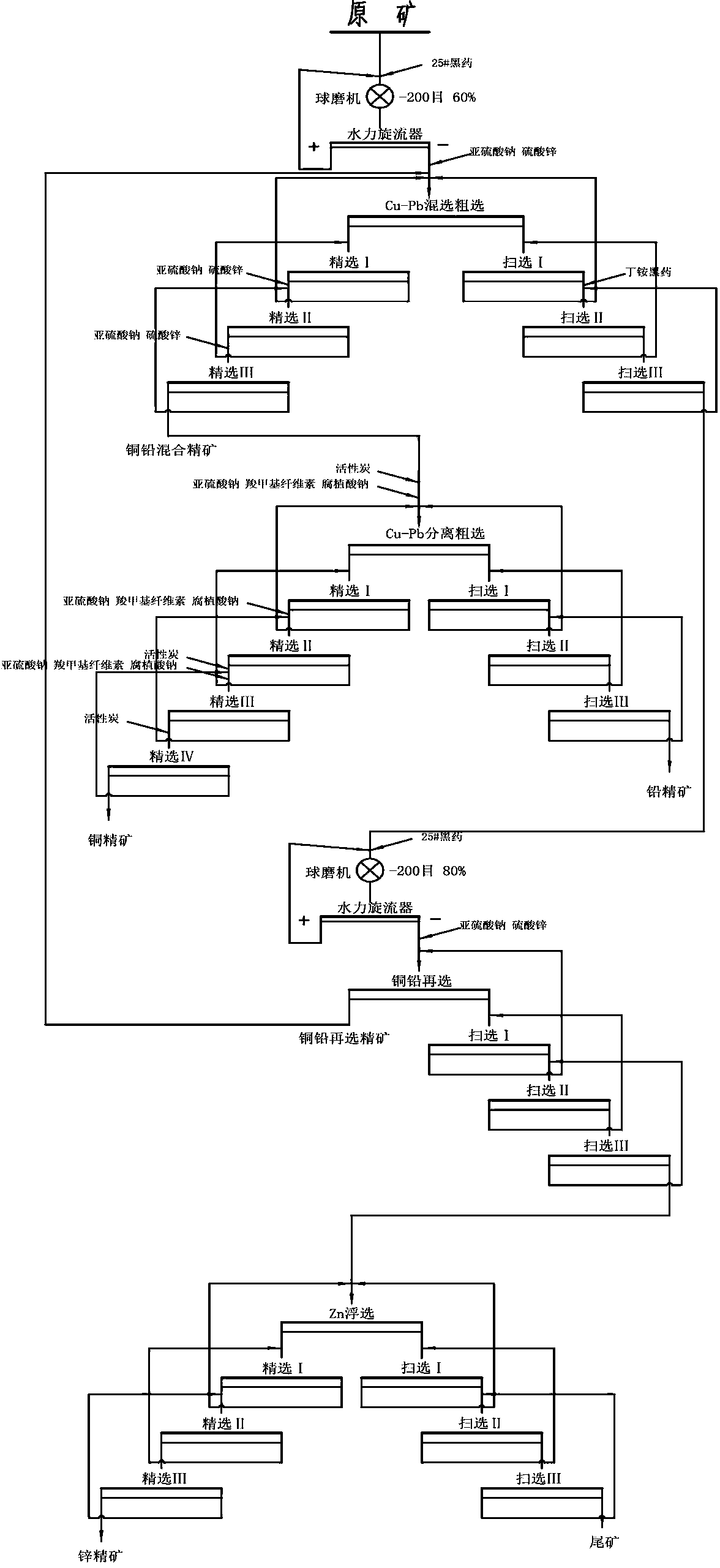
Copper and lead separating cyanide-chrome-free beneficiation method for low-grade multi-metal sulfide ore
The invention discloses a copper and lead separating cyanide-chrome-free beneficiation method for low-grade multi-metal sulfide ore. The beneficiation method is performed according to the following steps that (1) raw ore after ore grinding and grading enters the step of copper and lead bulk flotation to obtain copper and lead bulk concentrate and bulk flotation tailings, beneficiation reagents including 25# black powder and tetrabutyl ammonium black powder are adopted as collecting agents for copper and lead ore, and sodium sulfite and zinc sulfate are adopted as inhibitors of zinc ore; (2) copper and lead separating flotation is performed on the copper and lead bulk concentrate to obtain qualified copper concentrate and lead concentrate, in the copper and lead separating flotation process, activated carbon is adopted for reagent removal, and an inhibitor combined by sodium sulfite, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and sodium humate serves as the inhibitor of lead sulfide ore. The beneficiation method has the following advantages of being low in price and production and application cost, it is unnecessary to perform special treatment on ore pulp, the process is easy to control, and technological and economic indexes are stable. The great defect that a dichromate titration method, a cyanide method and a less-cyanide-chrome technology can cause pollution to the environment is overcome, and the usage amount of beneficiation new water is greatly reduced.
Owner:XINBARHU YOU BANNER RONG DA MINING LLC
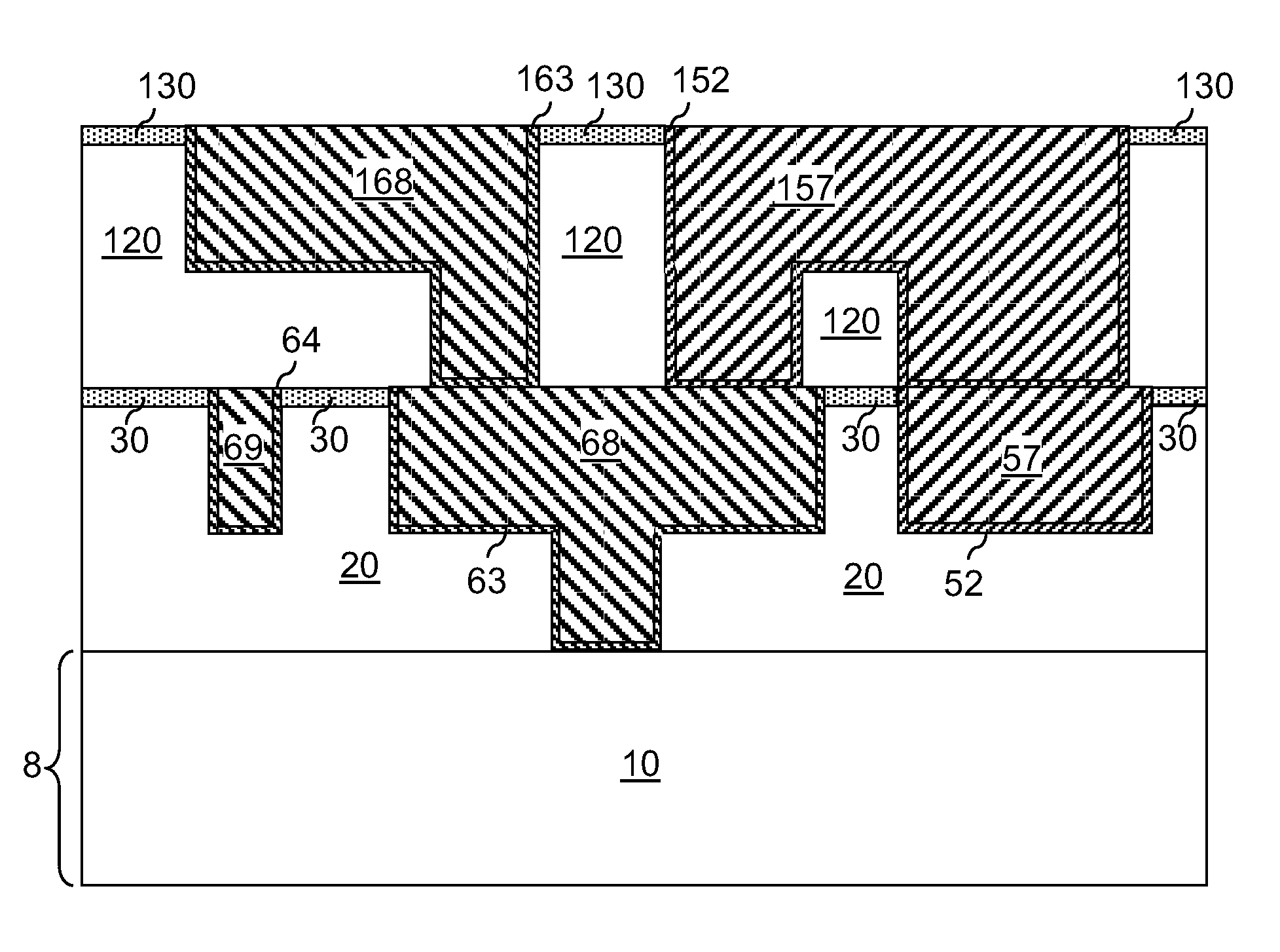
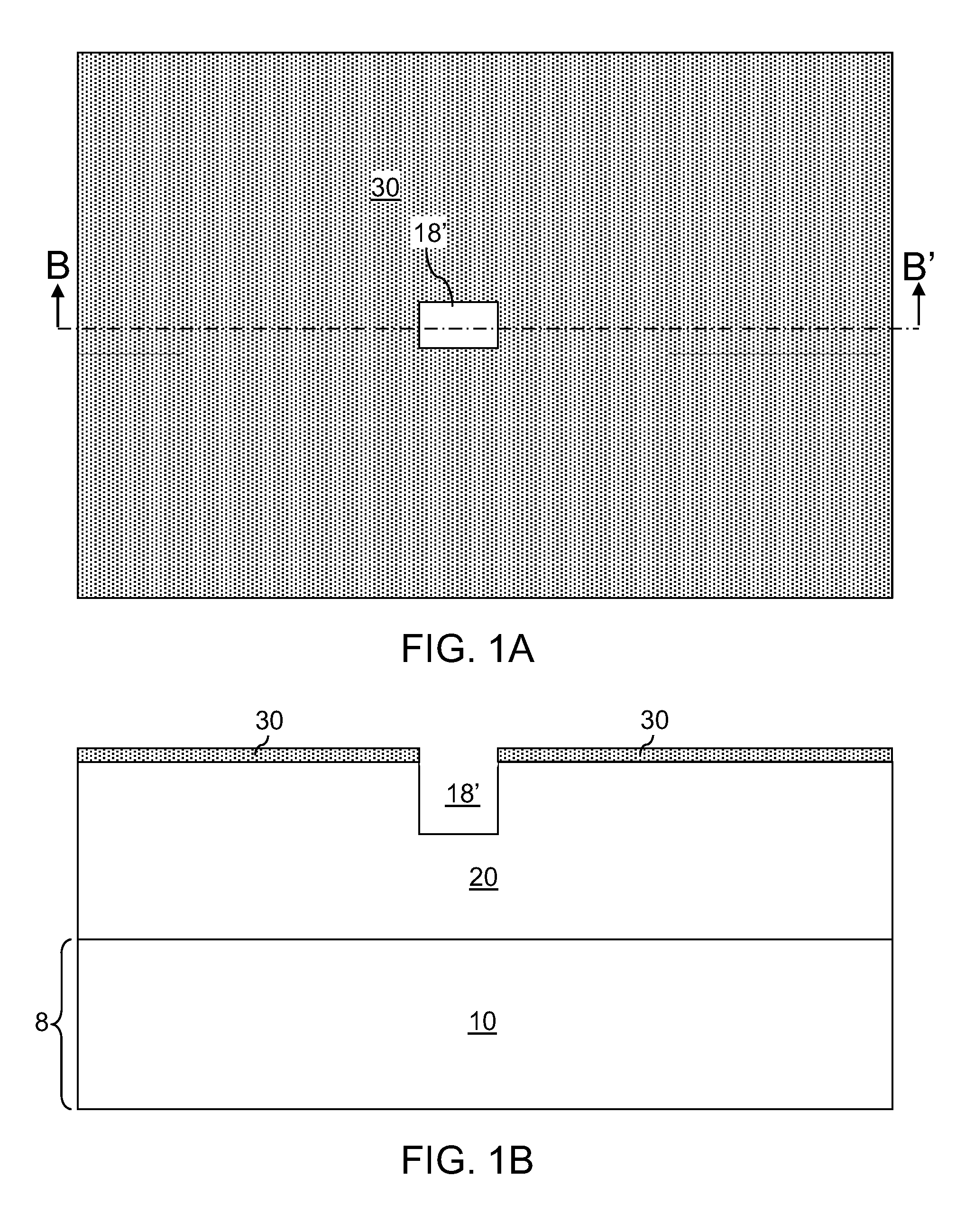
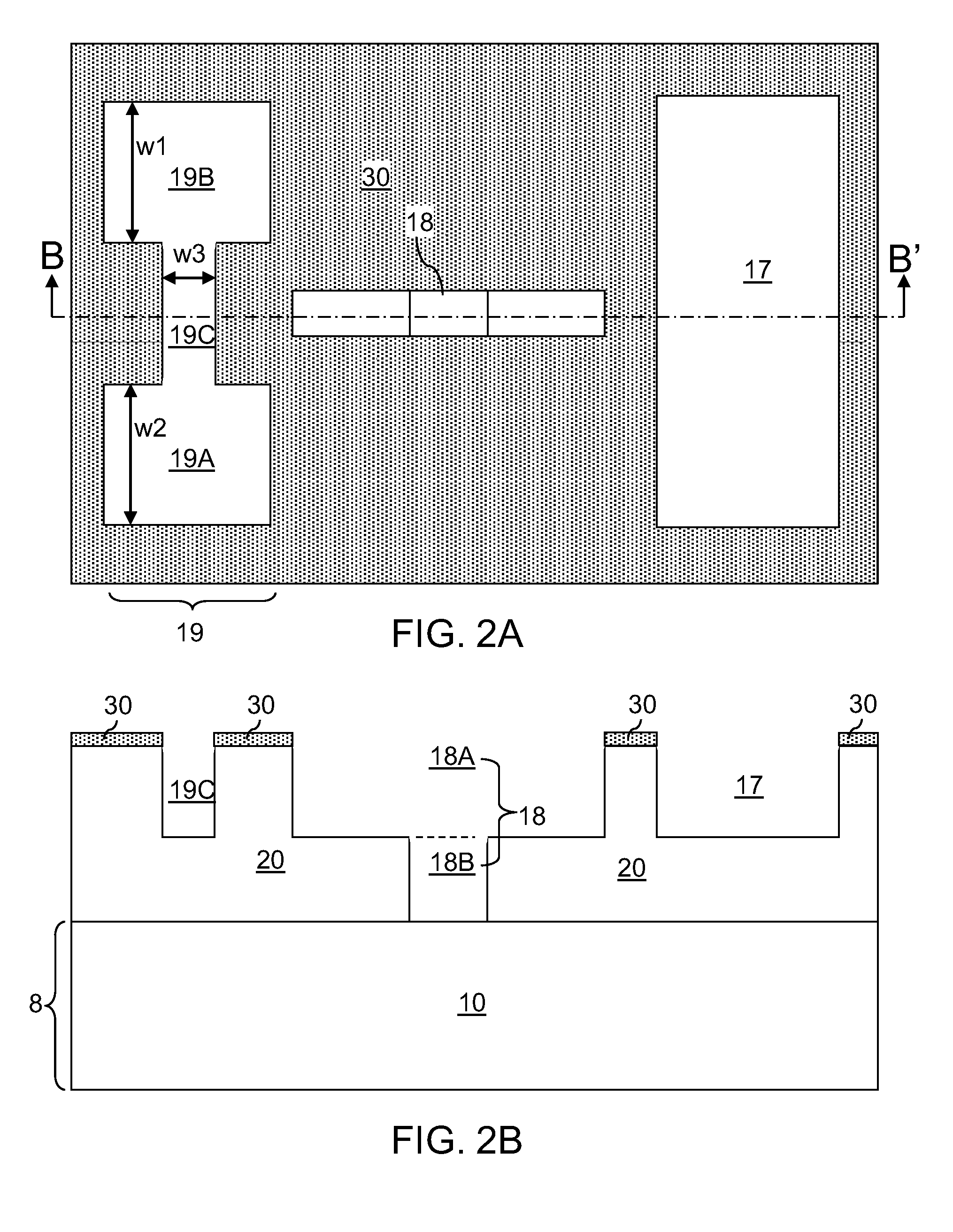
Size-filtered multimetal structures
InactiveUS20130043556A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetal interconnectMaterials science
A size-filtered metal interconnect structure allows formation of metal structures having different compositions. Trenches having different widths are formed in a dielectric material layer. A blocking material layer is conformally deposited to completely fill trenches having a width less than a threshold width. An isotropic etch is performed to remove the blocking material layer in wide trenches, i.e., trenches having a width greater than the threshold width, while narrow trenches, i.e., trenches having a width less than the threshold width, remain plugged with remaining portions of the blocking material layer. The wide trenches are filled and planarized with a first metal to form first metal structures having a width greater than the critical width. The remaining portions of the blocking material layer are removed to form cavities, which are filled with a second metal to form second metal structures having a width less than the critical width.
Owner:IBM CORP
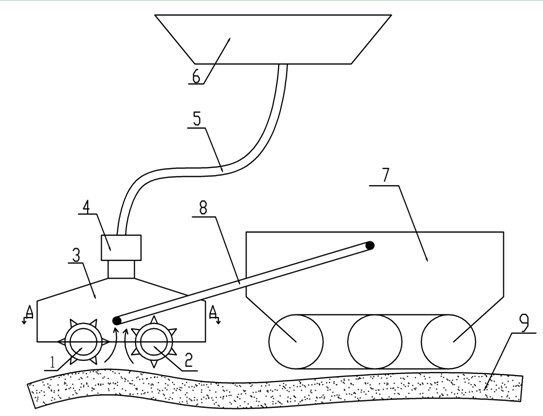
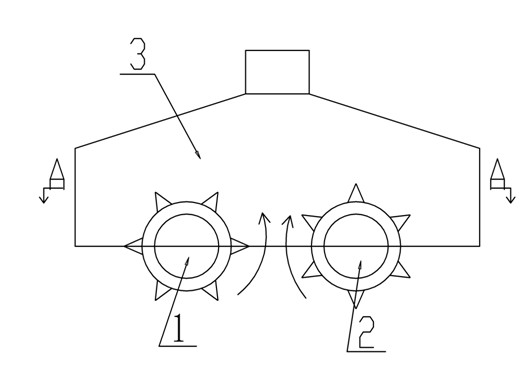
Marine polymetallic sulfide cutting device
InactiveCN102434164AAvoid pollutionPrevent proliferationMineral miningHydraulic pumpMetallic sulfide
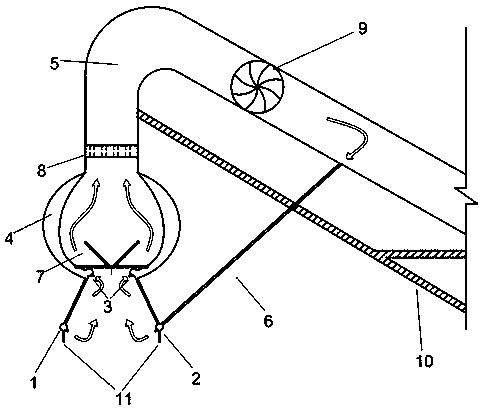
The invention discloses a marine polymetallic sulfide cutting device, which comprises a left cutting head, a right cutting head, a collection cover, a lifting pump, a pipeline, a mining ship, a mining machine, a rocker arm, a left hydraulic pump and a right hydraulic pump, and is characterized in that: the left cutting head is arranged on the left side of the collection cover; the right cutting head is arranged on the right side of the collection cover; the left cutting head and the right cutting head are arranged at the same horizontal height and have the completely same structural shape; cutting teeth of the left cutting head and the right cutting head are arranged in a staggered mode; the lifting pump is arranged at an input end of the left cutting head; the lifting pump is communicated with the mining ship through the pipeline; the collection cover is connected with the mining machine through the rocker arm; and a polymetallic sulfide ore deposit is positioned below the mining machine. By the device, the stripped marine polymetallic sulfides are prevented from polluting a marine environment.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
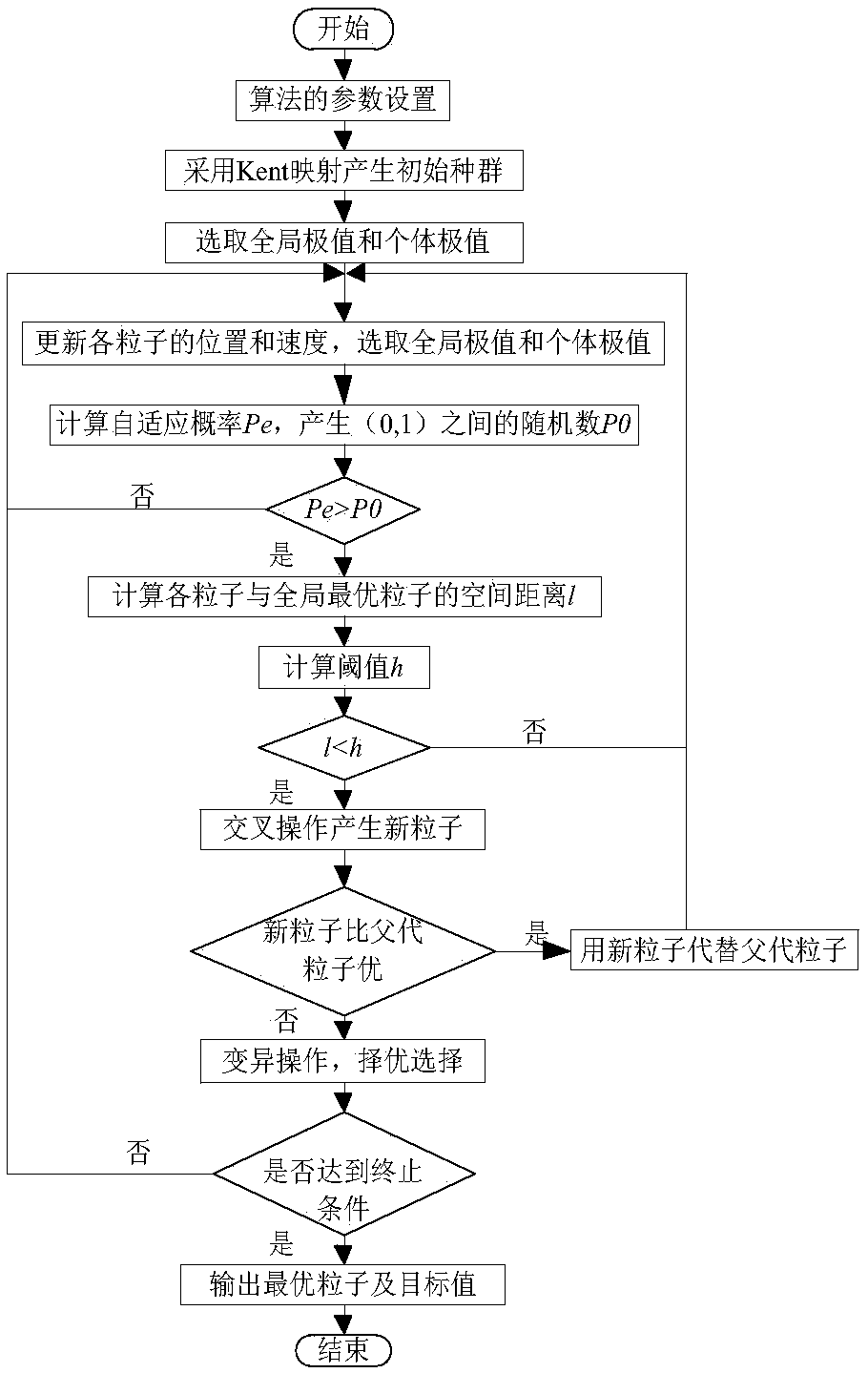
Multi-metal multi-objective ore blending method based on adaptive particle swarm algorithm
InactiveCN107609681AThe principle is simpleIn line with the results of ore blendingForecastingBiological modelsEconomic benefitsMulti objective model
The present invention discloses a multi-metal multi-objective ore blending method based on an adaptive particle swarm algorithm. The method comprises: determining actual production requirements and indexes of ore blending of metal opencast mines; minimizing the transportation work and the grade deviation as the objective, and constructing a multi-metal multi-objective ore blending model; carryingout improvement on the basic particle swarm algorithm to obtain an adaptive multi-objective particle swarm algorithm; and using the adaptive multi-objective particle swarm algorithm to solve the multi-metal multi-objective ore blending model. The present invention provides an effective ore blending method for the production management of the multi-metal multi-objective ore blending, realizes complete description of the actual ore blending process of the multi-metal multi-objective opencast mines, and adopts an adaptive multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm to solve the problem,so that the solution of the multi-metal multi-objective model is more scientific, reasonable and practical; and the ore blending method can effectively achieve the equilibrium of the ore blending grade, reduce the transportation cost of the enterprise, and significantly improve the comprehensive utilization rate and economic benefit of the ore.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Catalyst for the hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds
Hydrogenation catalyst containing, as the carbon support, a carbon black with an H content of >4000 ppm and, as the catalytically active component, palladium and / or platinum or bi- or multi-metallically doped or alloyed palladium and / or platinum is prepared by addition of metal salt solutions to a suspension of the carbon black with an H content of >4000 ppm, hydrolyzing the metal salt solutions by using a basic compound and carrying out complete deposition of the metal by reduction with a reducing agent. The hydrogenation catalyst can be employed for the hydrogenation of nitroaromatics.
Owner:DEGUSSA AG
Electroplating sludge resource utilization method
ActiveCN106007423ASolve pollutionPromote the development of circular economySpecific water treatment objectivesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesHeavy metalsPolymetal
An electroplating sludge resource utilization method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment: separating heavy metal elements from electroplating sludge by a wet process, and neutralizing the electroplating sludge with lime or limestone, to obtain an electroplating sludge waste residue with calcium sulphate dihydrate as a main component; (2) preparation of raw material: replacing all gypsum and all iron raw materials in raw material ingredients with the electroplating sludge waste residue, or replacing a part of gypsum and a part of iron raw materials with the electroplating sludge waste residue, then blending with gypsum and vanadine, and powder-grinding to prepare the raw material for producing a calcium sulphoaluminate or calcium sulphoferrate clinker; and (3) baking for 0.5-1 h at the temperature of 1250-1400 DEG C. The electroplating sludge is used as the raw material containing polymetal and is subjected to resource utilization to produce two kinds of materials, namely a corresponding metal and / or metal salt material and a gypsum-based building material, so the problem of pollution in electroplating industry is facilitated to be solved, and the implementation of circular economy development is facilitated.
Owner:湖南省小尹无忌环境能源科技开发有限公司 +1
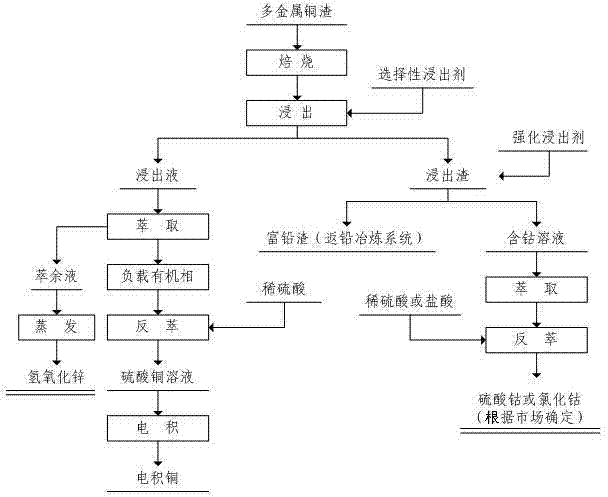
Method for producing electrodeposited copper from polymetallic copper slag
ActiveCN104846202AImprove leaching efficiencyHigh recovery ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementZinc hydroxideLead smelting
The invention discloses a method for producing electrodeposited copper from polymetallic copper slag, which includes the following steps: the polymetallic copper slag is roasted to oxidize, so that the complex states of valuable metals in the polymetallic copper slag are transformed into oxides, changed into a state which can be selectively leached; leaching first adopts selective leaching agent to leach copper and zinc, the leachate is extracted, reextracted and electrodeposited, so that electrodeposited copper is obtained, and raffinate is vaporized and crystallized, so that zinc hydroxide is obtained; mechanical intensified leaching agent is then used for intensely leaching leaching residue, so that cobalt, nickel and the like in the leaching residue are leached, lead, iron and the like are enriched into the slag, the lead-rich slag is adopted as material for lead smelting, the leachate is extracted and reextracted, so that cobaltous sulfate or cobalt chloride is obtained, and if the nickel content in the leachate is overhigh, multi-stage extraction can be carried out to separate cobalt and nickel, so that nickel sulfate or nickel chloride is produced. The method can comprehensively recover a variety of metals, the leaching efficiency is high, the recovery rate is high, the method is environment-friendly, and is easy to implement, the method ensures that all the valuable metals in the polymetallic copper slag can be effectively separated and recycled, and the solid waste utilization rate can reach more than 99 percent.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
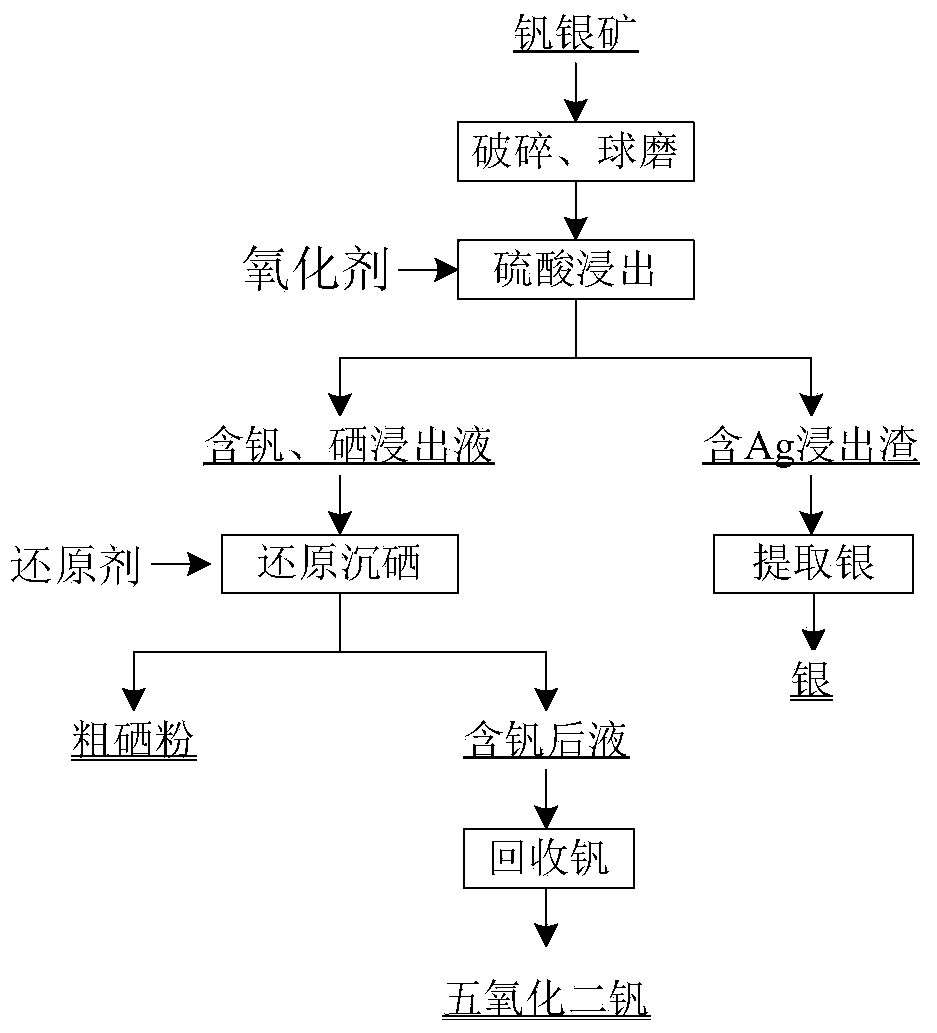
Method for comprehensively recovering selenium, vanadium and silver from vanadium silver polymetallic ore containing selenium employing wet process
ActiveCN103555962AHigh recovery rateFriendly Comprehensive RecyclingProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumIonIon exchange
The invention provides a method for comprehensively recovering selenium, vanadium and silver from a vanadium silver polymetallic ore containing selenium by adopting a total-wet process aiming at a vanadium silver polymetallic shale mine containing selenium. The method concretely comprises the following steps: crushing and grinding the vanadium silver polymetallic ore containing selenium, then carrying out sulfuric acid leaching under an oxidation condition; leaching selenium in an oxidation manner and entering inside a solution together with vanadium, leaving silver in leaching residue, precipitating crude selenium from lixivium in a reduction manner; continuing to recover vanadium from by a selenium-precipitating solution by extraction or ion exchange, wherein the lixivium containing silver adopts a common process to recover silver. The technology has the advantages of being short in flow, simple to operate, low in energy consumption, high in metal recovery rate, low in production cost and the like; the target of clean and energy-saving and environment-friendly comprehensive recovery from the vanadium silver polymetallic ore is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
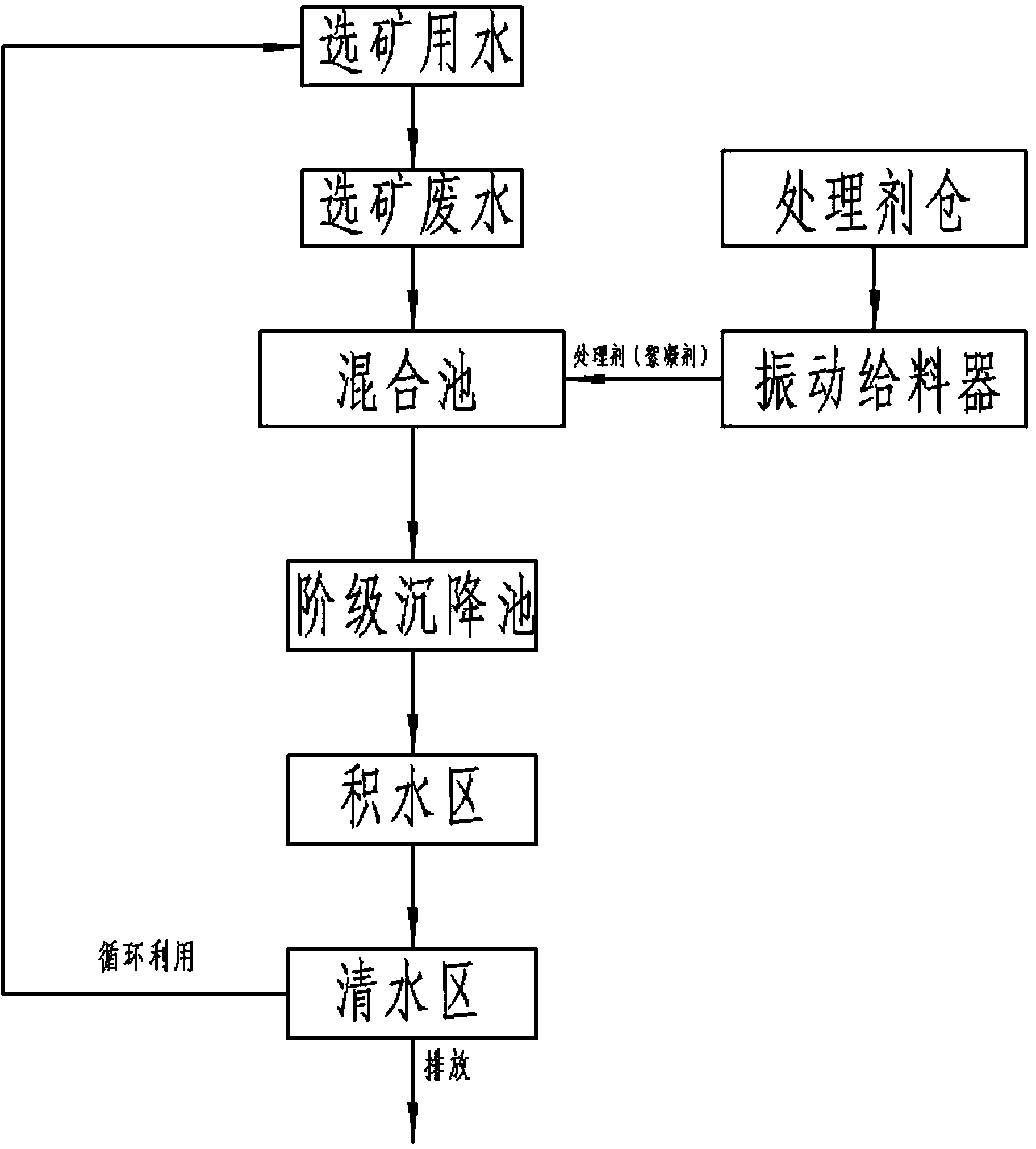
Polymetallic ore beneficiation wastewater recycling method
InactiveCN103708591AReduce productionIncrease the amount of purificationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSlagWater circulation
The invention provides a polymetallic ore beneficiation wastewater recycling method. The polymetallic ore beneficiation wastewater recycling method is characterized by comprising two steps of physical treatment and biological treatment. According to the polymetallic ore beneficiation wastewater recycling method, the existing beneficiation wastewater output equipment and tailings ponds of aluminium and zinc beneficiation industries are used, wastewater treating agents such as calcium hydroxide, saponification slag and calcium carbide are added to wastewater in a mixing tank so as to ensure that suspended matters in the wastewater settle, the wastewater is purified so as to meet the technical requirements that obtained clear water is continuously used for beneficiation, the content of suspended matters in the treated water is less than 100mg / L, the pH value of the treated water is 8, and the cyclic utilization of the beneficiation wastewater is realized. The polymetallic ore beneficiation wastewater recycling method has the characteristics of low investment, low running cost, energy conservation, emission reduction and cyclic economy and is suitable for the cyclic utilization of the polymetallic ore beneficiation wastewater.
Owner:GUANGXI KESHENGDA MACHINERY MFG
Process for improving quality and reducing impurities of tin stone multi-metal sulfide ore tin ore concentrate and combined equipment
The invention relates to the field of metallurgy and particularly relates to a process for improving quality and reducing impurities of a tin stone multi-metal sulfide ore tin ore concentrate and combined equipment. The process comprises the following three procedures of: adjusting the grade of a shaking bed cut ore; increasing a procedure of sulfur removal and impurity removal for a tin rough ore concentrate; and increasing a procedure of tin selection of the ore concentrate subjected to the sulfur removal and impurity removal, so as to ensure the quality of the tin ore concentrate. The grade of the tin ore concentrate and the sulfur and arsenic content can easily reach to the quality standard of the ore concentrate; the requirements on the grade of the shaking bed cut ore are reduced and the cutting amount of the tin ore concentrated is obviously increased; the tin recycling rate is obviously improved; and a tine stone which is difficult to recycle and is tightly grown with a pyrite ore is sufficiently recycled on a shaking bed, and is produced in a manner of an enriched ore, so that the recycling rate of tin is improved.
Owner:YUNNAN HUALIAN ZINC & INDIUM
Methods of preparing thin polymetal diffusion coatings
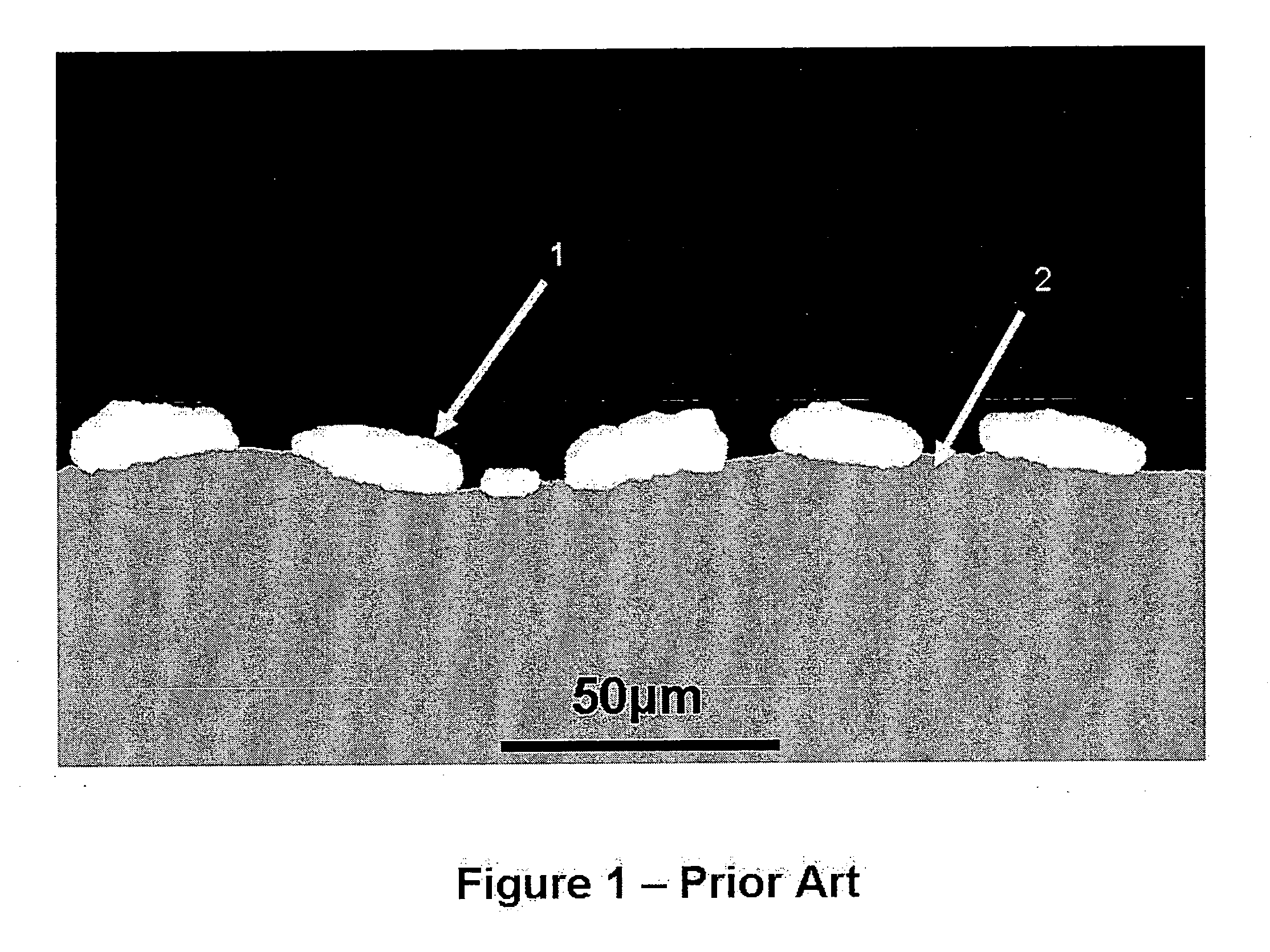
ActiveUS20100215980A1Increased formationHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesMetalMaterials science
A thin zinc diffusion coating, the diffusion coating including: (a) an iron-based substrate, and (b) a zinc-iron intermetallic layer coating the iron-based substrate, the intermetallic layer having a first average thickness of less than 15 μm, as measured by a magnetic thickness gage, the intermetallic layer having a second average thickness as measured by an X-Ray fluorescence thickness measurement, and wherein a difference between the first average thickness and the second average is less than 4 μm.
Owner:GREENKOTE (ISRAEL) LTD
Horizontal submarine polymetallic sulfide deposit area chimney sampling drill
InactiveCN102628337AAchieving Drilling and SamplingDerricks/mastsBorehole drivesMining engineeringTransformer
A horizontal submarine polymetallic sulfide deposit area chimney sampling drill comprises a housing, a hydraulic system is arranged on the right end of the bottom of the housing, a front support, a lifting oil cylinder support and a rear support are sequentially arranged at the middle of the bottom of the housing, a lifting oil cylinder is arranged on the lifting oil cylinder support, a drilling mechanism is arranged on the rear support, an electronic cabin-fixing base, a front valve box, a valve box pressure compensation mechanism, a rear valve box, an underwater transformer and a transformer pressure compensation mechanism are sequentially arranged on the left end of the bottom of the housing, an electronic cabin is fixed on the electronic cabin-fixing base, and is respectively connected with the underwater transformer, the hydraulic system, the front valve box and the rear valve box, the front valve box is respectively connected with the hydraulic system, the lifting oil cylinder and the drilling mechanism, the rear valve box is respectively connected with the front valve box, the lifting oil cylinder and the drilling mechanism, the transformer pressure compensation mechanism is connected with the underwater transformer, and levelling oil cylinders are respectively arranged on the four corners of the housing. The horizontal submarine polymetallic sulfide deposit area chimney sampling drill can drill and sample submarine polymetallic sulfide deposit area chimney bases at fixed points.
Owner:CHINA MINMETALS CHANGSHA MINING RES INST
Recovery process of complex multi-metal ores difficult to treat
ActiveCN104531988AReduce pollutionAchieve pre-oxidationSulfur compoundsProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionThiourea
The invention discloses a recovery process of complex multi-metal ores difficult to treat and belongs to the technical field of ore dressing. According to the process, the complex multi-metal ores difficult to treat are taken as the raw materials, products such as gold, silver, copper, zinc, sulfur, lead concentrate and iron slag are extracted by virtue of the steps of ore fine grinding, high-temperature oxidative pressure leaching, copper and zinc recovery by extraction, gold and silver recovery by virtue of thiourea leaching, and lead, iron and sulfur separation by ore separation, and comprehensive recovery of the multi-metal gold ores is realized. The recovery process of the complex multi-metal ores difficult to treat is mainly characterized in that the high-temperature oxidative pressure leaching is performed on the complex multi-metal ores difficult to treat after fine grinding, copper and zinc in the leachate are recovered by use of an extraction-electrodeposition technique, and the extraction residual liquid is returned to oxidative pressure leaching, gold and silver are extracted from the oxidative pressure leaching slag by use of a thiourea leaching-reduction process, and sulfur, lead concentrate and iron slag are obtained from the thiourea leaching slag by use of an ore separation process, respectively. The recovery process is used for comprehensively recovering gold, silver, copper, zinc and the like, has the characteristics of high valuable metal recovery rate, low energy consumption, low cost, closed-loop solution circulation and the like, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
Nontoxic process for extraction gold from gold-bearing tailing
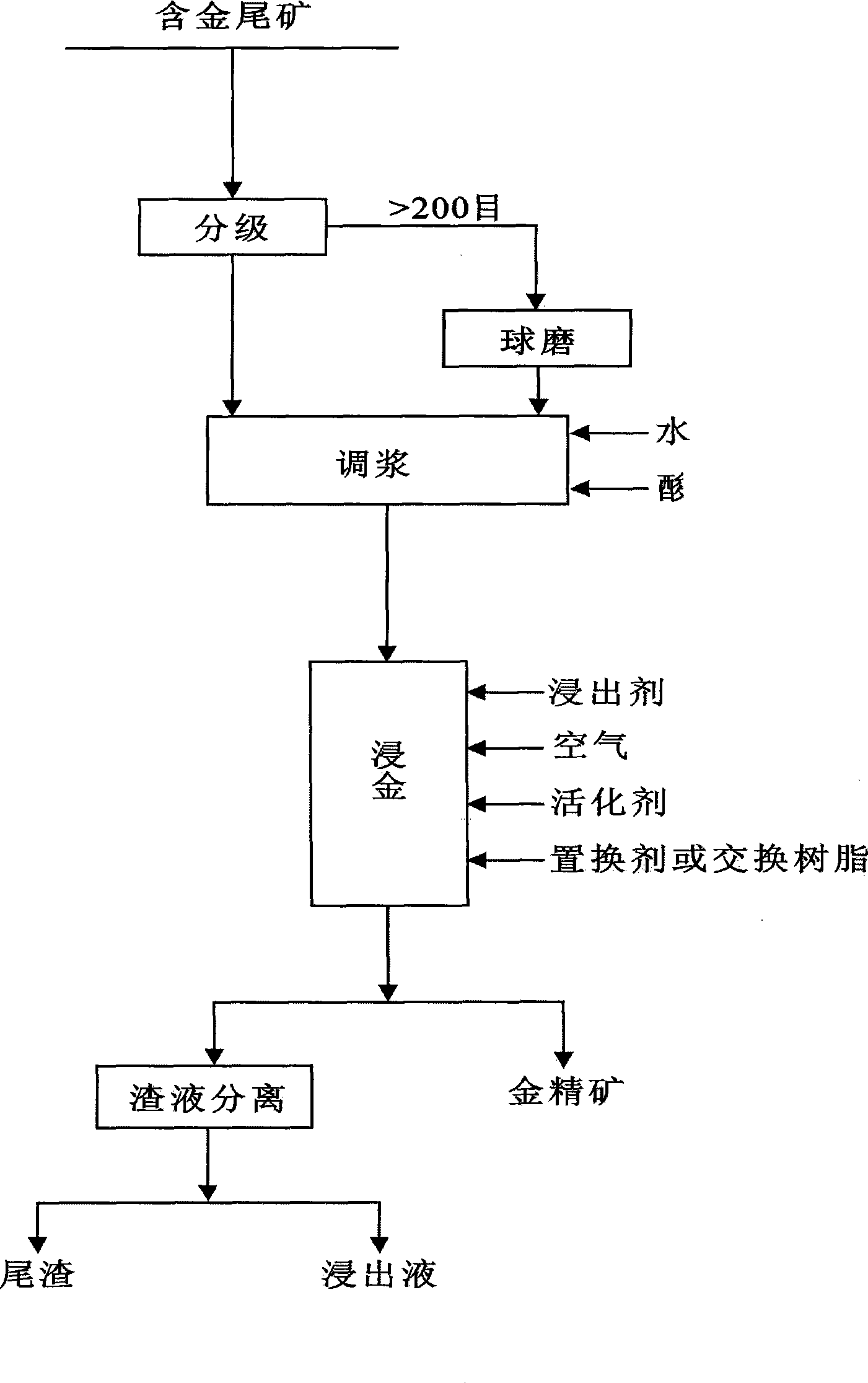
InactiveCN101363081ANon-toxicNo industrial pollutionProcess efficiency improvementSorbentMaterials science
The invention related to a beneficiation method, in particular to a beneficiation method of high bismuth and poly-metal intergrowth gold ores or accompanying gold ores, specifically, a non-toxic extraction method of gold from gold-containing tailings is referred. An organic chemical reagent is taken as a leaching agent, metal oxide and air are taken as activators, acid or alkali is taken as a regulator, cation exchange resin is taken as an adsorbent, and nonferrous metal is taken as a displacer. The gold is separated out by the displacer or is adsorbed by the cation exchange resin to obtain gold concentrate, the immersion fluid is pressed and filtered for separating the residue and the liquid, the immersion fluid without the residue can be recovered and reused. The agents used in the method are non-toxic and has no harm to human body. The method does not produce industrial pollution and has low recovery cost and high recovery rate.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
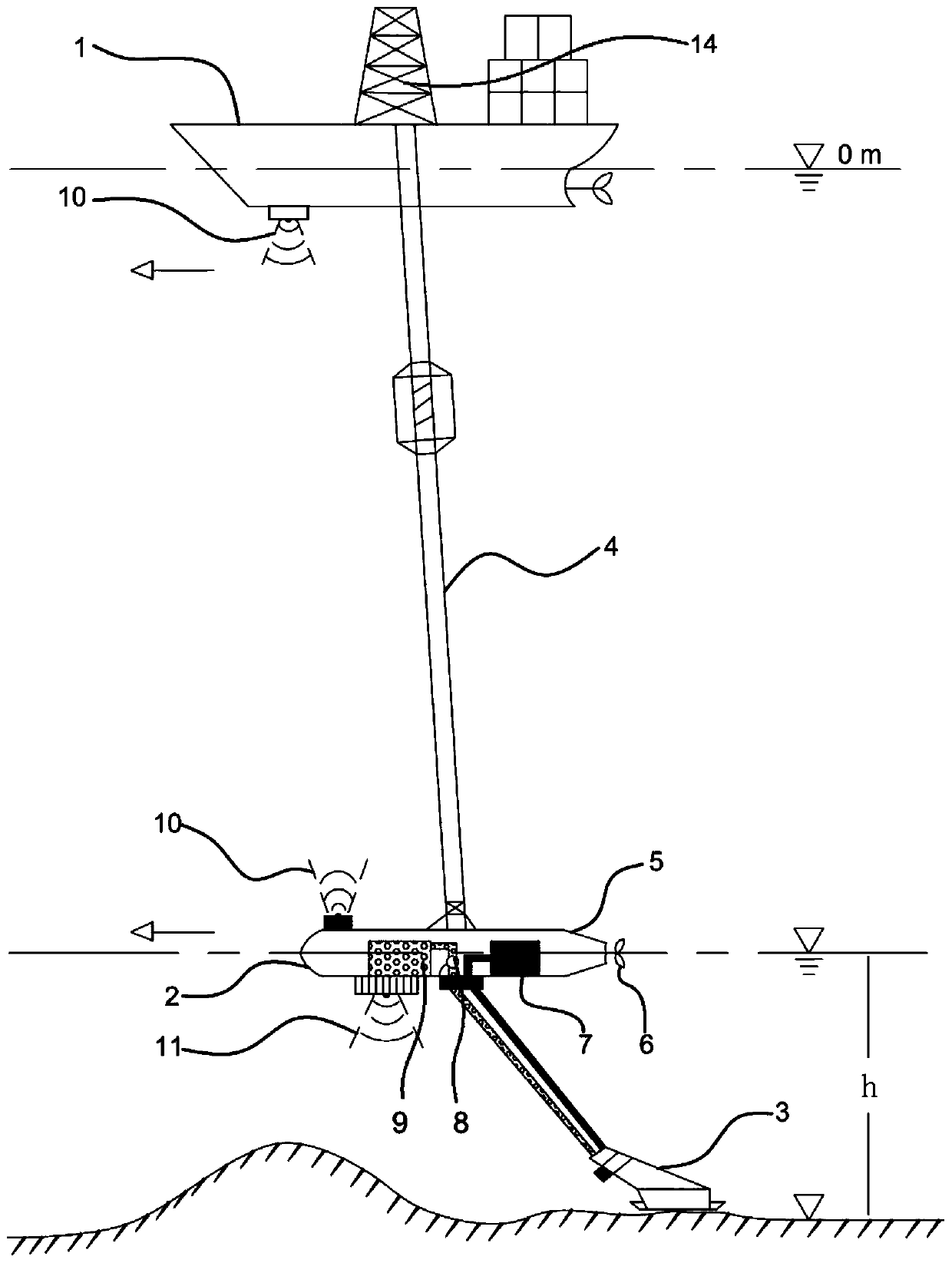
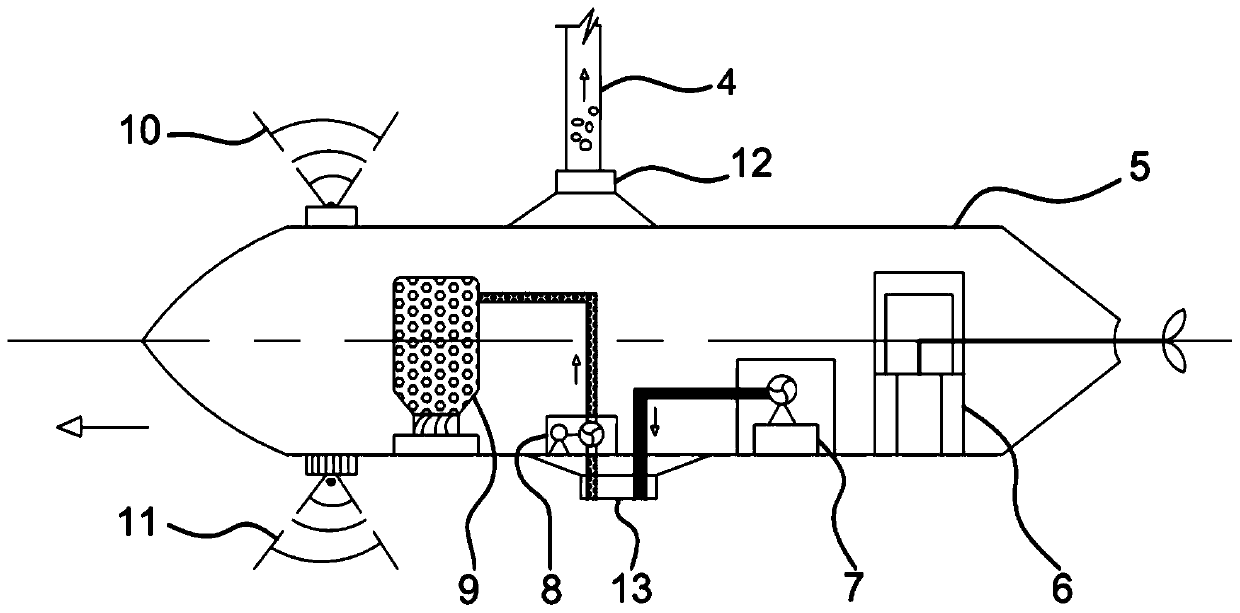
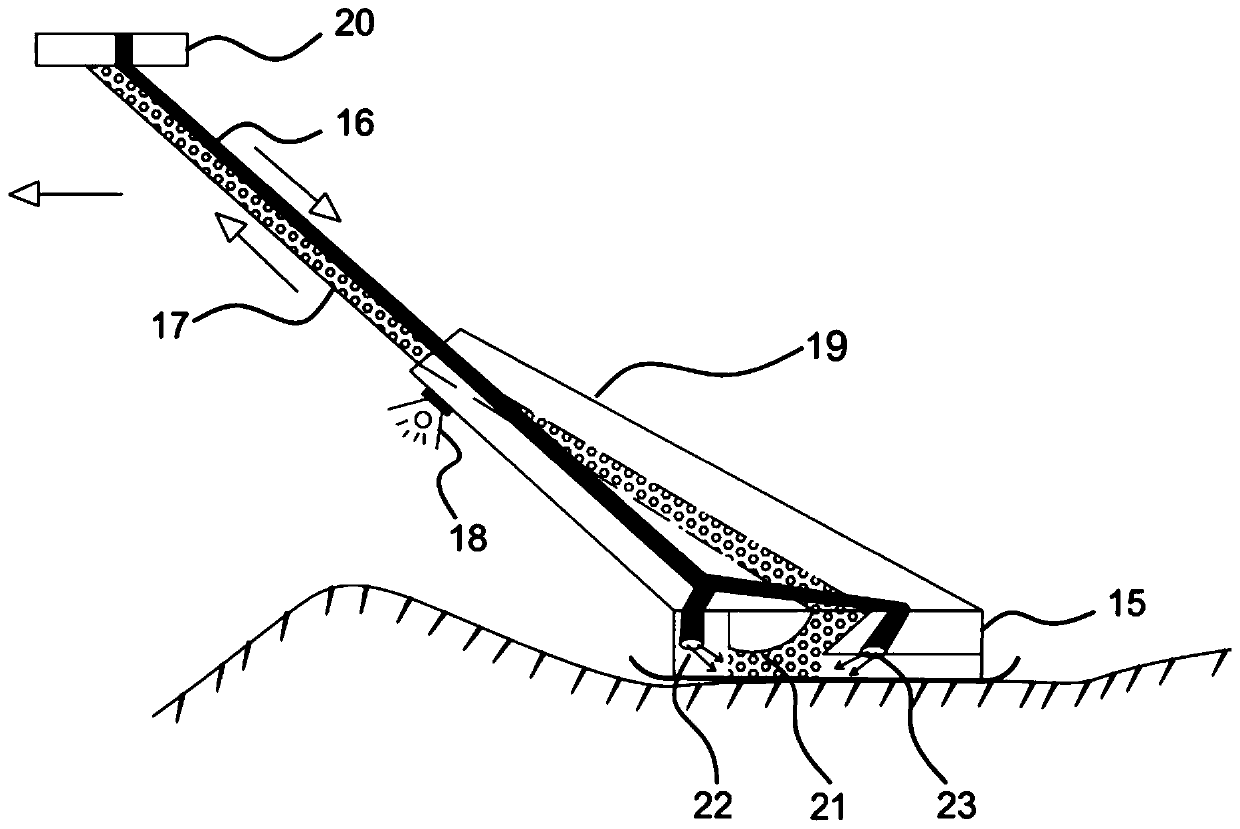
Hydraulic jet type seabed polymetallic nodule collecting device and method
ActiveCN111022055AAvoid buoyancy effectsReduce lossesMineral miningHydraulic miningMining engineeringHydraulic circuit
The invention discloses a hydraulic jet type seabed polymetallic nodule collecting device which comprises a collecting unit and an ore transferring and storing device which are installed at the two ends of the upper portion of seabed driving equipment, and the collecting unit can rotate on the seabed driving equipment and can work in cooperation with the ore transferring and storing device. The invention also discloses a collecting method using the device. Two hydraulic circuits are constructed to create an upward flow field environment for the polymetallic nodule ore by utilizing a seabed saturated water-rich environment through ingenious structural design, the polymetallic nodule ore is collected into the stock bin in a continuous hydraulic lifting mode, and the collecting device has small disturbance to the seabed environment and high collecting efficiency on the polymetallic nodule ore. The flow field is a circulating loop so that water is used up and the environmental friendlinessof the whole device is fully reflected under the condition of ensuring high efficiency and reliability of the whole device.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
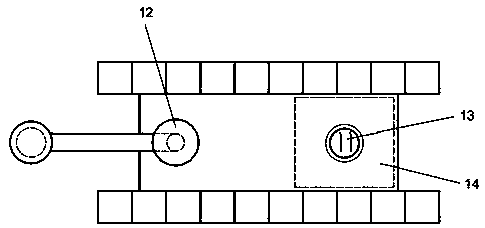
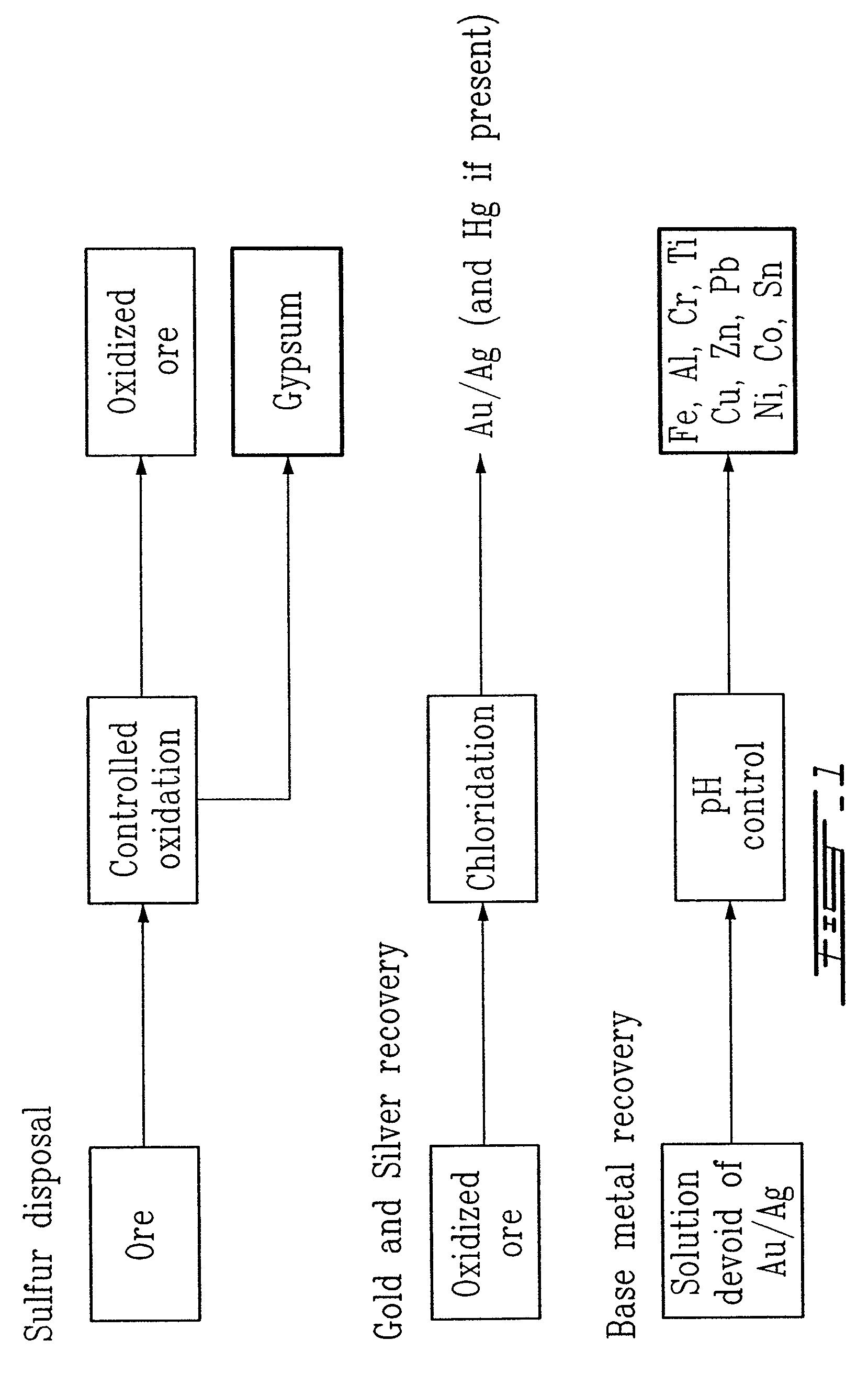
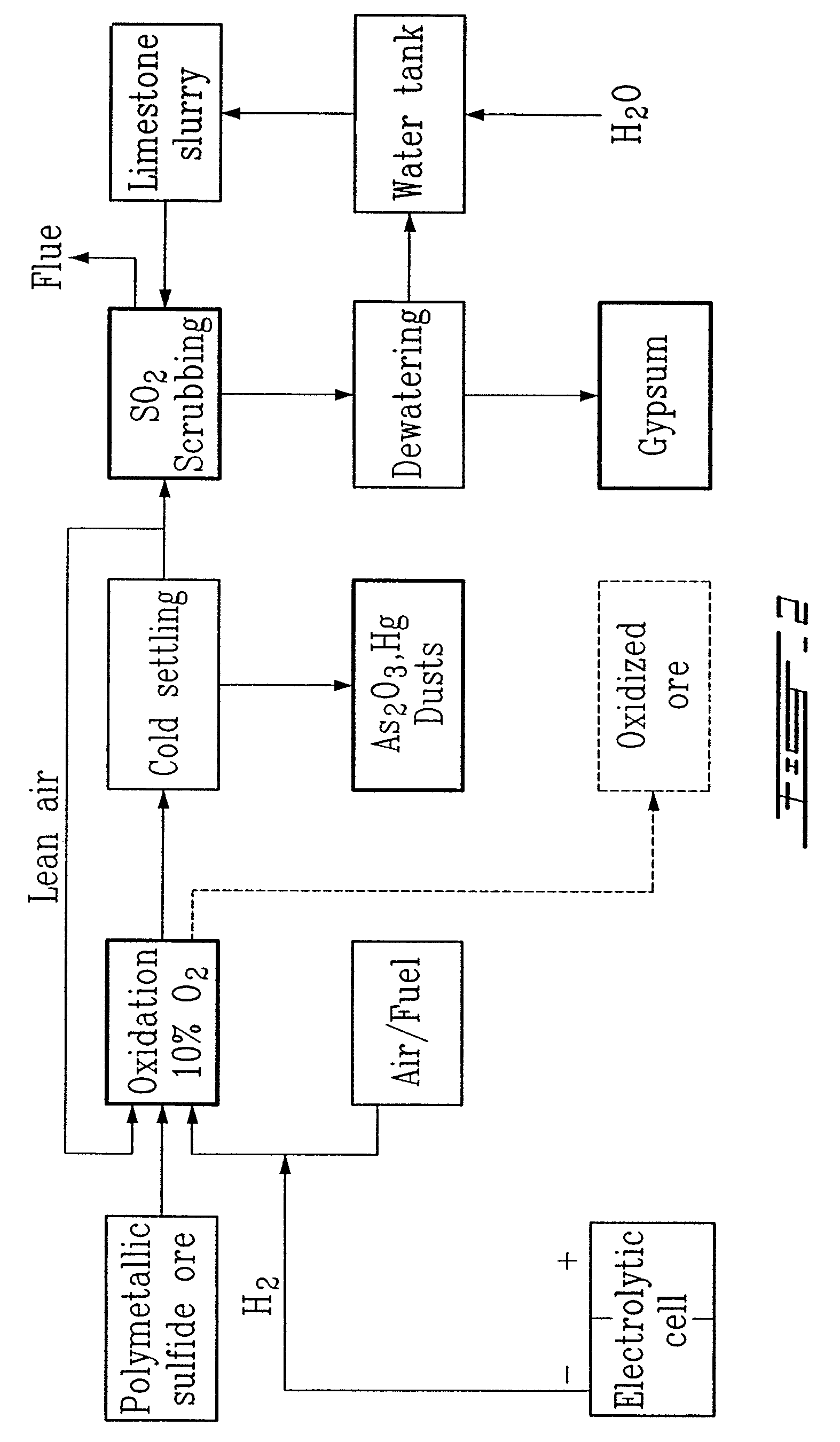
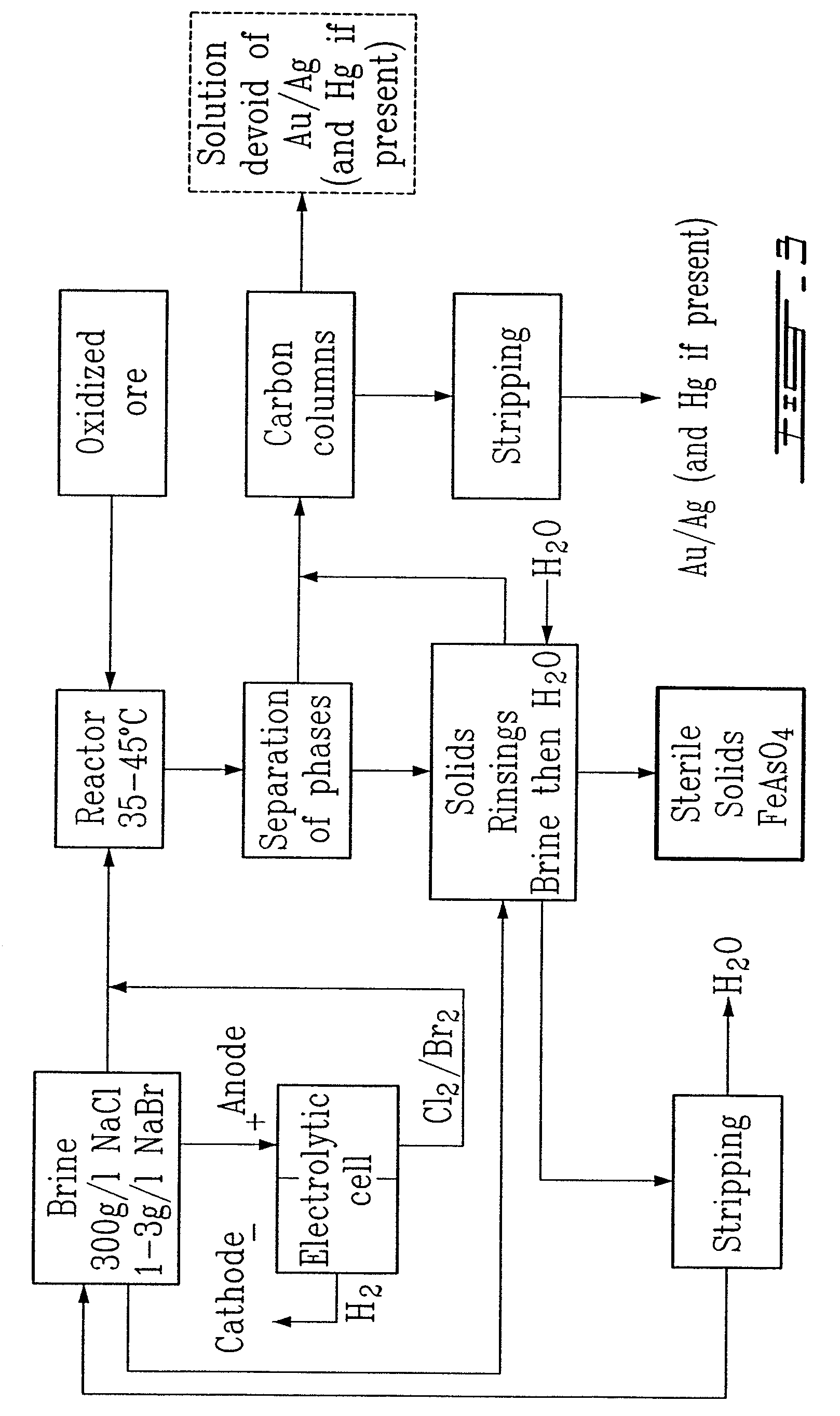
Gold and silver recovery from polymetallic sulfides by treatment with halogens
InactiveUS7537741B2Reduce cost investmentHigh treatment rateAluminium compoundsSolvent extractionMetallic sulfideTitanium
A method for treating a polymetallic sulfide ore containing gold and / or silver, and further containing base metals selected from the group consisting of iron, aluminum, chromium, titanium, copper, zinc, lead, nickel, cobalt, mercury, tin, and mixtures thereof, is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of grinding the polymetallic sulfide ore to produce granules, oxidizing the granules to produce oxidized granules, and chloride leaching the granules using a brine solution including dissolved halogens, as well as chloride and bromide salts.
Owner:DUNDEE SUSTAINABLE TECH
Nanopolymetalic reducing agent filler
InactiveUS20120285899A1Reduce processingShort agglomerationWater contaminantsTreatment involving filtrationPyrolusiteIron powder
The present invention provides a nanopolymetallic reducing agent filler comprising 20%-70% iron powder, 10%-30% tourmaline power, 2%-15% copper power, 3%-10% bamboo charcoal powder, 2%-15% kaoline, 2%-15% magnesite powder, 2%-15% pyrolusite powder, and 10%-30% zeolite powder. All percentages described above are by weight. A process of forming the nanopolymetallic reducing agent filler is also provided, including grinding and ball milling raw materials of each component respectively into powder particles of 10 nm-100 μm, which are then mixed uniformly by weight percentage and granulated to form a granular mixture, and sintering the granular mixture at high temperature or cold pressing it into a granular filler.
Owner:T & H USA GROUP
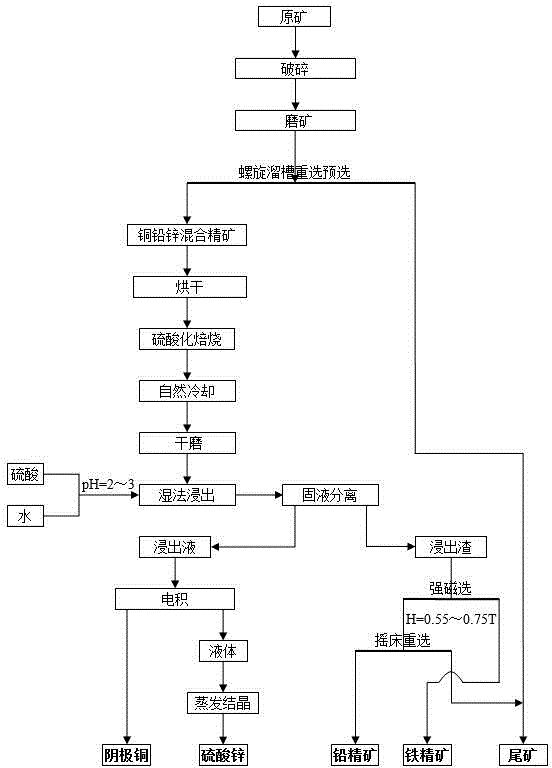
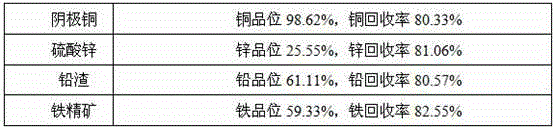
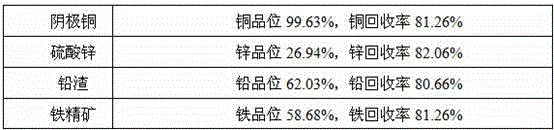
Method for treating low-grade copper-lead-zinc-iron multi-metal sulfide ores to extract valuable metals
InactiveCN104888940AExcellent process technical indicatorsRealize comprehensive utilizationWet separationSulfideMagnetic separation
The invention discloses a method for treating low-grade copper-lead-zinc-iron multi-metal sulfide ores to extract valuable metals. The method comprises the following steps: S1, a stage of crushing, and carrying out one-stage ore milling on ores; S2, a stage of reselecting and pre-selecting a spiral chute; S3, a stage of drying copper-lead-zinc-iron mixed concentrated ore; S4, a stage of carrying out sulfated roasting; S5, a stage of carrying out second-stage ore milling; S6, a stage of carrying out a wet-process leaching; S7, a stage of carrying out solid-liquid separation; S8, adopting an electro-deposition process to treat leaching liquor to obtain a cathode copper product, and evaporating and catalyzing the residual liquid to obtain a zinc sulfate product; S9, carrying out strong magnetic separation on leaching residue to obtain iron concentrated ore, wherein a non-magnetic product adopts a shaking bed to recycle lead to obtain lead concentrated ore. The method has the beneficial effects that: comprehensive utilization for valuable metals copper, lead, zinc and iron in the low-grade copper-lead-zinc-iron multi-metal sulfide ore source can be realized and various products are obtained; a physical mineral separation technical means is adopted to carry out pre-discarding for tailings, and additional medicament is not added in the mineral separation process.
Owner:四川有色金砂选矿药剂有限公司
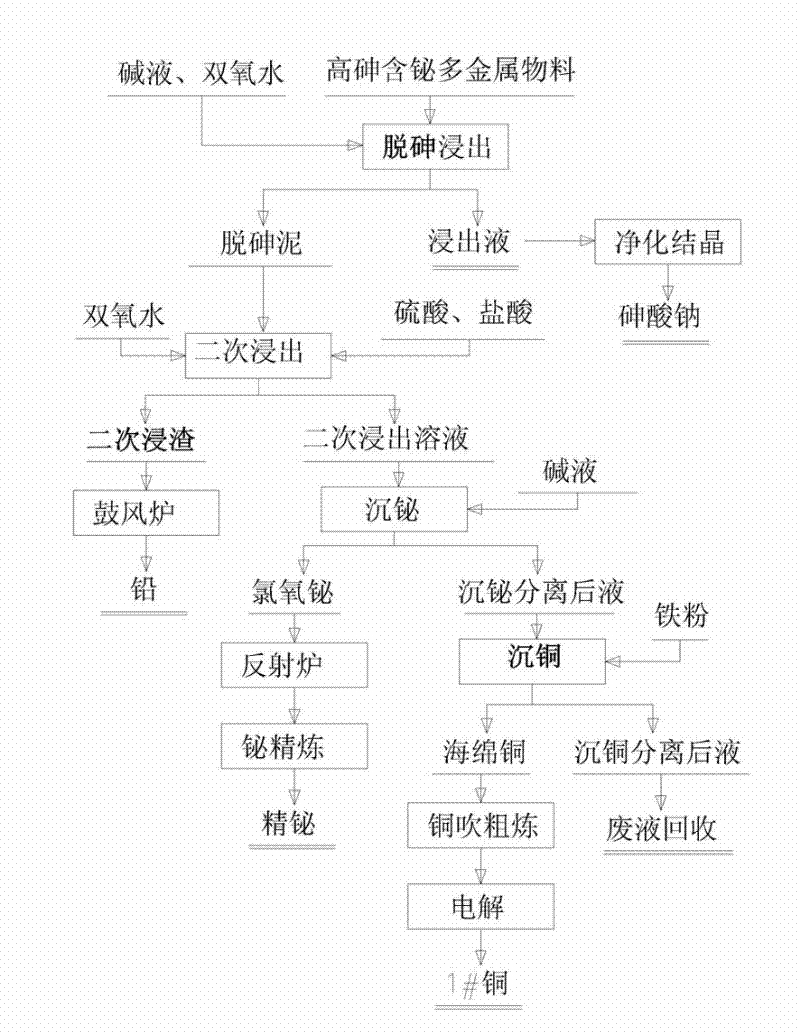
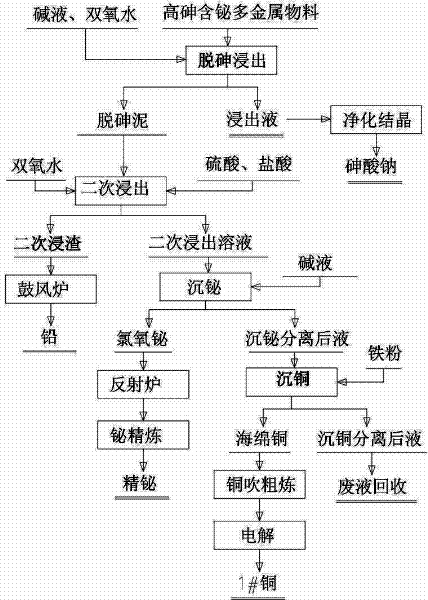
Process for comprehensively recovering high arsenic polymetallic material
ActiveCN102392136ALower requirementSimple operating conditionsProcess efficiency improvementArsenic pollutionPersulfate
The invention relates to a process for comprehensively recovering a high arsenic polymetallic material, which belongs to the non ferrous metal comprehensive recovery field. The process comprises the following steps: leaching arsenic in the polymetallic material from the polymetallic material by sodium hydroxide, hydrogen peroxide and water, routine purifying a leachate and removing impurities, crystallizing to obtain sodium arsenate; leaching the arsenic removal mud after removing arsenic by sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide twice, sending leaching residue to a blast furnace for refining lead; adding alkali loquor in a leaching solution for regulating pH value to 2.0-2.5, depositing bismuth by a bismuth chlorine oxygen form, separating and depositing bismuth chlorine oxygen and refining to obtain the refined bismuth; adding iron powder in a solution which is performed bismuth deposition and separation, electrolyzing to obtain 1#copper; sending solution which is performed copper deposition and separation to a waste liquid recovery pool for processing. The invention has the advantages of low production cost, simple operation condition and requirement, safe operation and no arsenic pollution. According to the invention, the arsenic recovery rate is greater than or equal to 96.5%, the lead recovery rate is greater than or equal to 98%, the bismuth recovery rate is greater than or equal to 95.8% and the copper recovery rate is greater than or equal to 96.5%.
Owner:郴州雄风环保科技有限公司
Deep-sea poly-metallic nodule near-bottom dragging mining system and method
PendingCN111577288AAvoid the problem of insufficient walking powerExcellent mechanical propertiesCargo handling apparatusMineral miningMining engineeringCollection system
The invention discloses a deep-sea poly-metallic nodule near-bottom dragging mining system and method. The deep-sea poly-metallic nodule near-bottom dragging mining system includes a surface support ship, an underwater near-bottom mining platform, and a seabed collection system; a tower crane on the surface support ship is equipped with a main ore lifting pipeline; the lower end of the main ore lifting pipeline is connected to the underwater near-bottom mining platform; the underwater near-bottom mining platform is connected to the seabed collection system through a dragging pipeline; the seabed collection system includes multiple sets of articulated hydraulic collection units; and the multiple sets of hydraulic collection units form a wide collection head. The deep-sea poly-metallic nodule near-bottom dragging mining method is as follows: the underwater near-bottom mining platform sends high-pressure water to the seabed collection system for high-pressure water jet collection of ore;and the underwater near-bottom mining platform sucks the ore back, and then sends the ore to the main ore lifting pipeline, so that the ore is lifted to the surface support ship on the surface of thesea. On the basis of solving the problem of insufficient power of the collection system and the adaptability of micro-terrain, the invention can greatly increase the width of the collection head and improve the mining efficiency.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
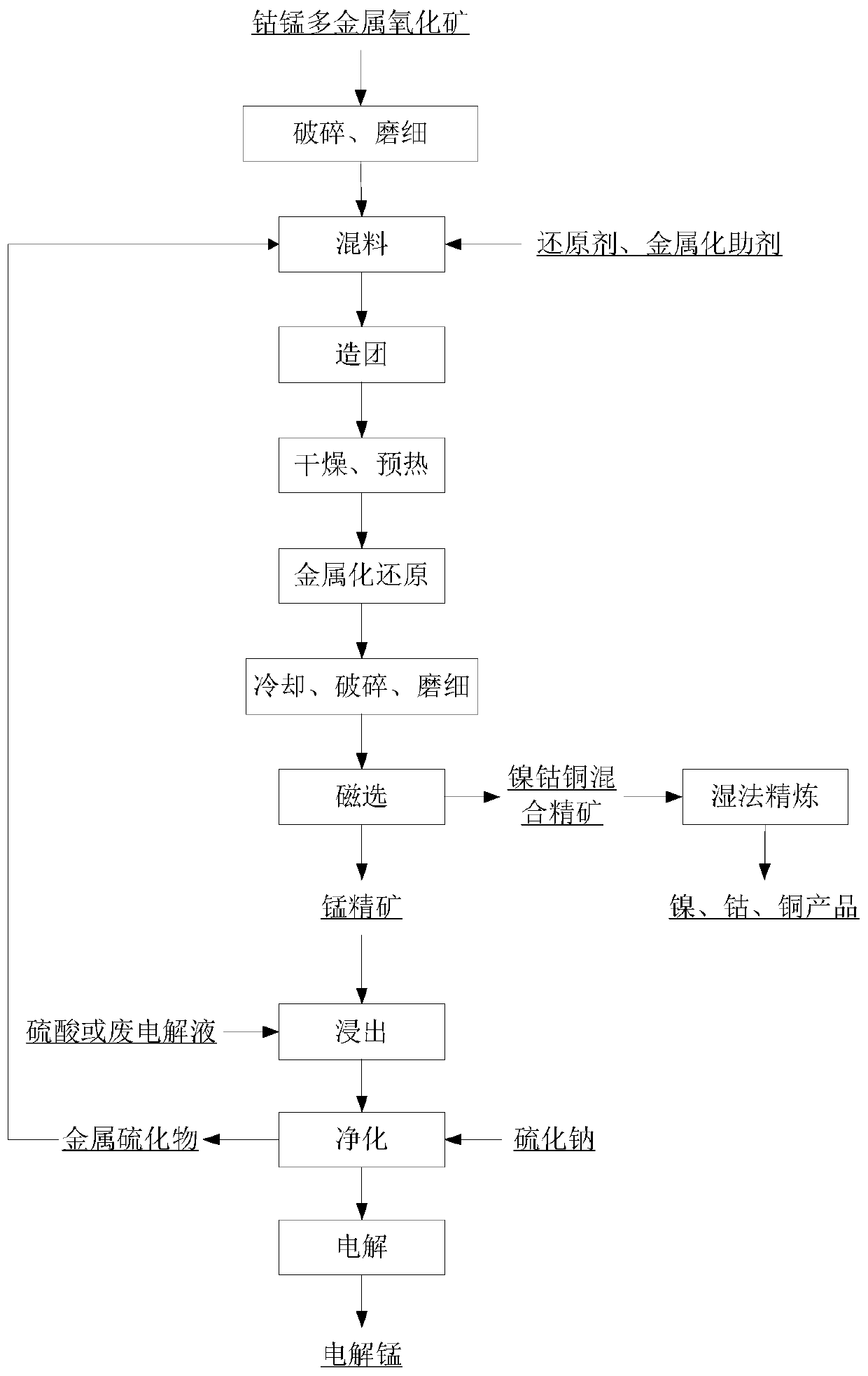
Method for dressing-smelting combination extracting manganese and comprehensively recovering nickel, cobalt and copper from cobalt-manganese polymetallic oxide ore
ActiveCN111172412ARealize the recycling effectSimple processProcess efficiency improvementMetallic sulfideManganese oxide
The invention discloses a method for dressing-smelting combination extracting manganese and comprehensively recovering nickel, cobalt and copper from a cobalt-manganese polymetallic oxide ore. The method includes the steps that the cobalt-manganese polymetallic oxide ore is crushed and ground to obtain fine ore with a particle size of less than 0.25mm; the fine ore, a reducing agent, a metallization aid and water are is mixed and pressed into pellets; the pellets are transferred to a reducing furnace for metallization reduction roasting at 1000-1300 DEG C after dried and pre-heated, and a material after reduction roasting is cooled; the cooled material is crushed, ground, and magnetically separated to obtain nickel cobalt copper mixed concentrate and manganese concentrate; the manganese concentrate is leached with a sulfuric acid solution or manganese electrolytic waste liquid, and manganese leachate and residue are obtained by solid-liquid separation; a vulcanized agent is added intothe manganese leachate for purification to obtain a manganese sulfate solution and metal sulfide; and the manganese sulfate solution is electrolyzed to produce electrolytic manganese or electrolytic manganese dioxide. The method is simple in process, less in post-processing amount, high in recovery rate, low in energy consumption and low in cost.
Owner:BEIJING MINING & METALLURGICAL TECH GRP CO LTD +1
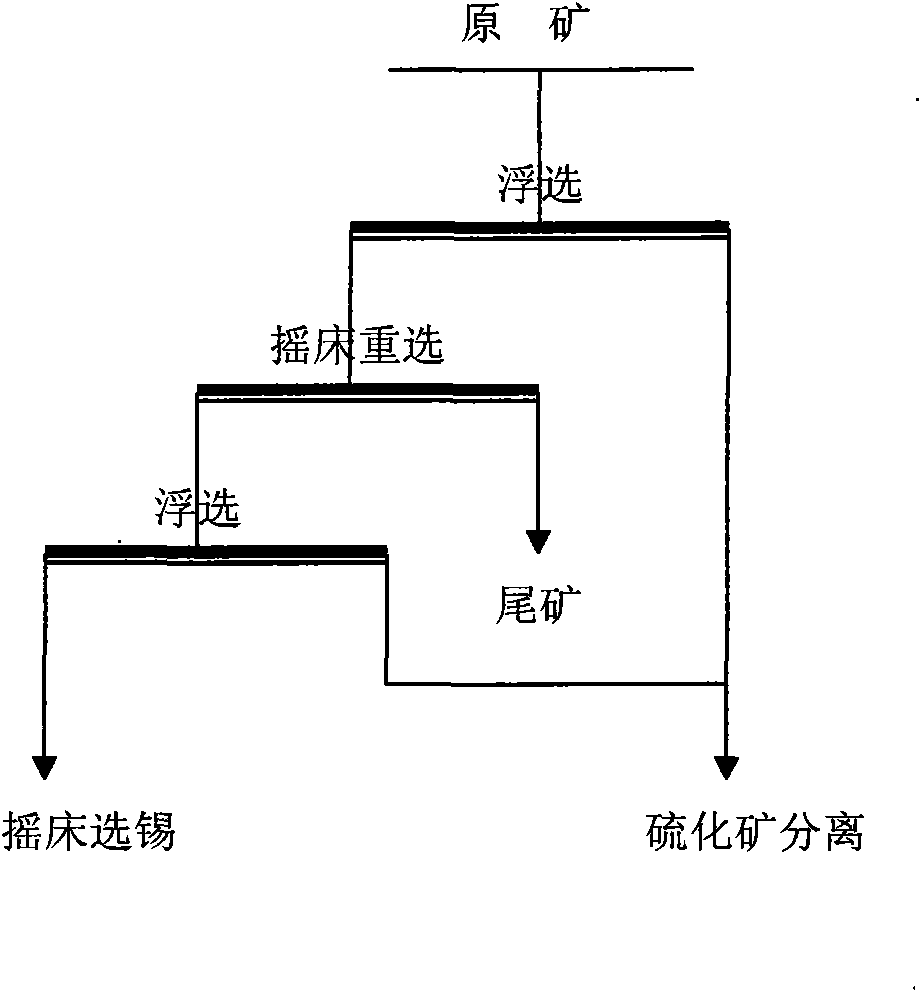
Method for desulphurizing cassiterite polymetallic sulphide ore tailing by flotation step by step
The invention relates to a method for desulphurizing cassiterite polymetallic sulphide ore tailing by flotation step by step. In the method, sulphide ore is removed step by step by using the flotability difference of sulphide ore. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing flotation on the sulphide ore with high flotability; secondly, upgrading the flotation tailing into a cassiterite sulphide ore mixed rough concentrate by using a table; and adding depressor sodium silicate, activator sodium sulfide and collecting agent yellow catching agent into the cassiterite sulphide ore mixed rough concentrate for strengthening the flotation. By using the method, the sulphide ore in the cassiterite can be removed effectively, beneficiation reagent cost is reduced and beneficiationeconomic benefit is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com