Patents
Literature
103results about How to "Wide band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
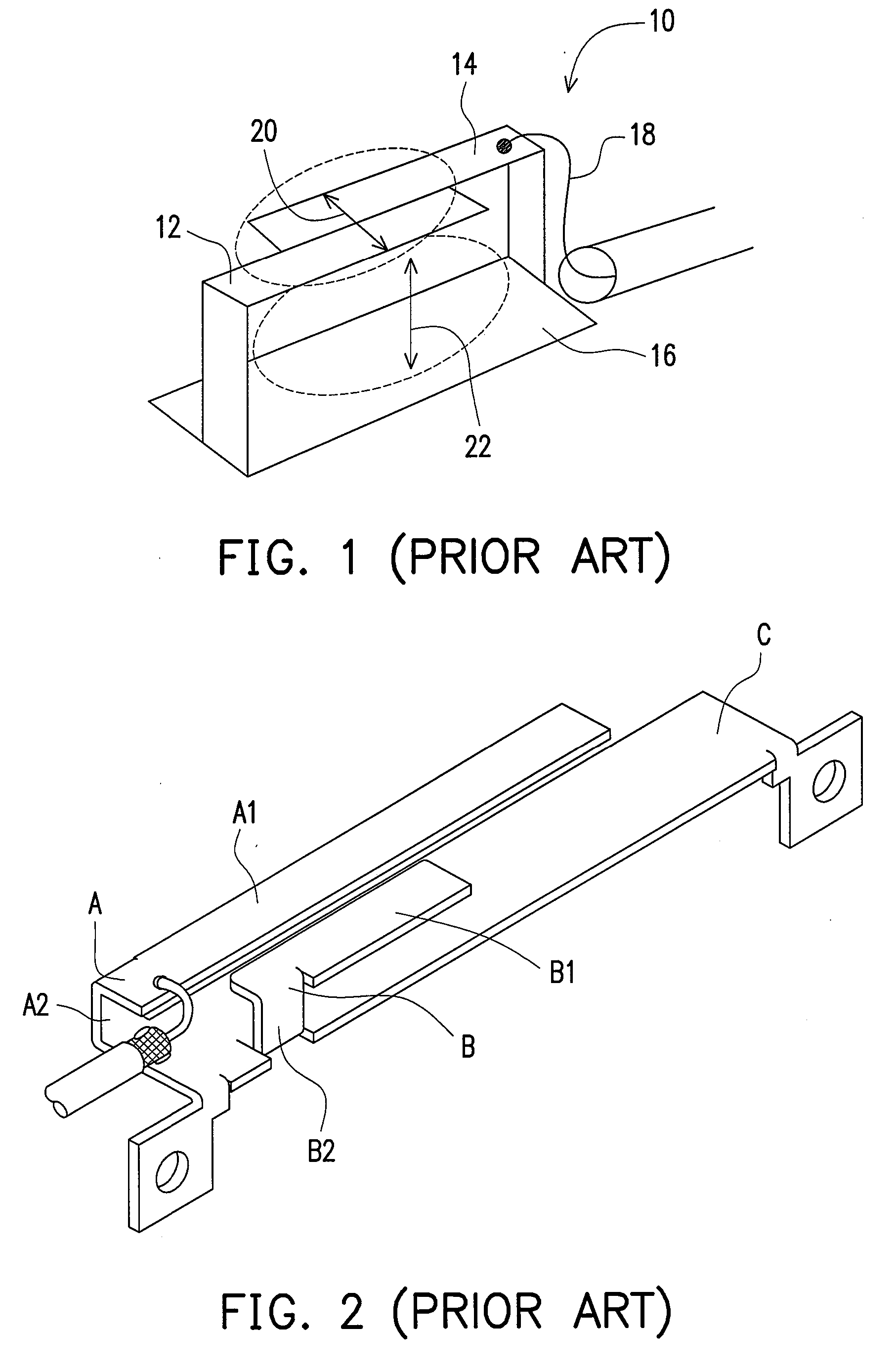
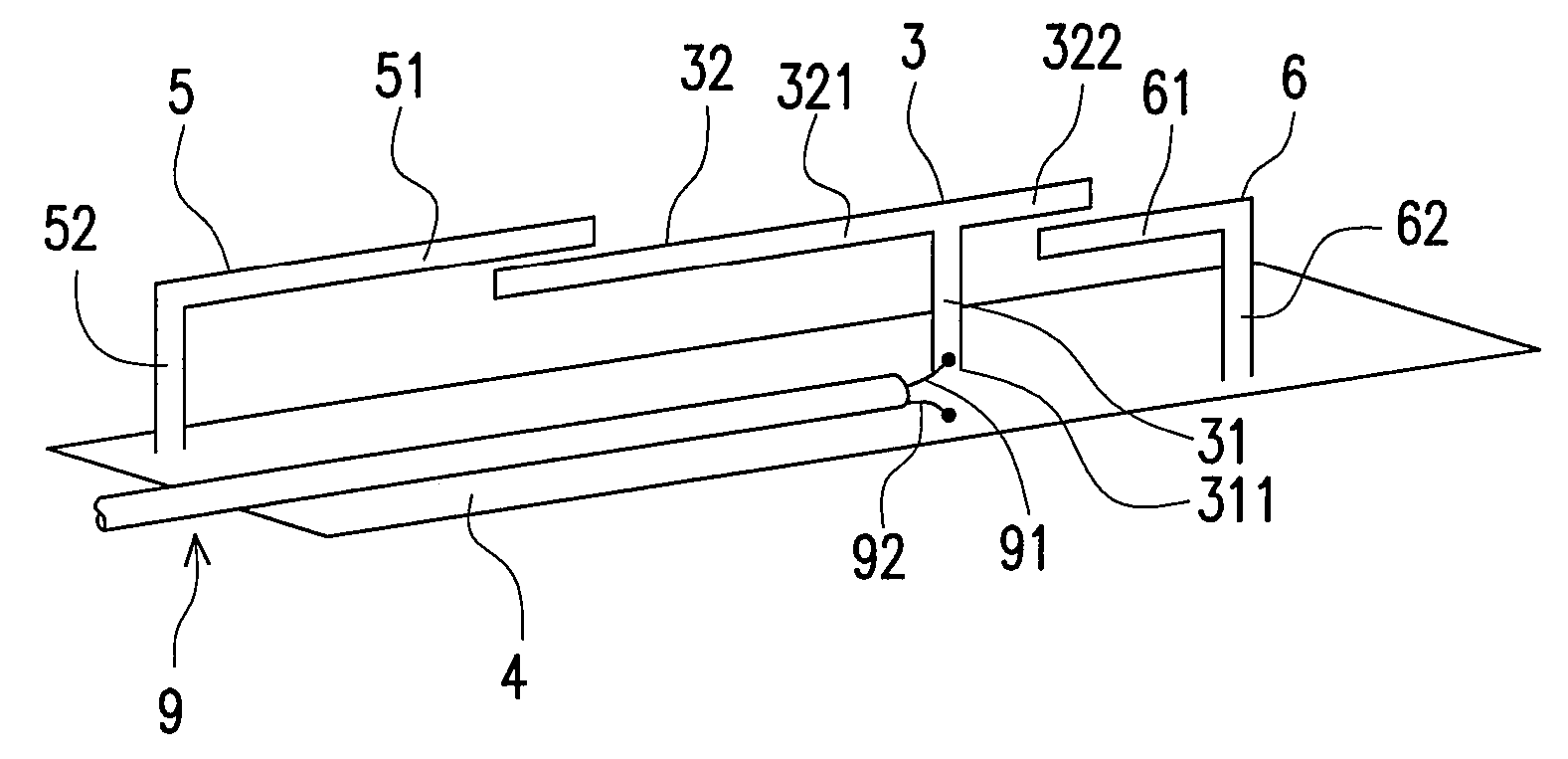
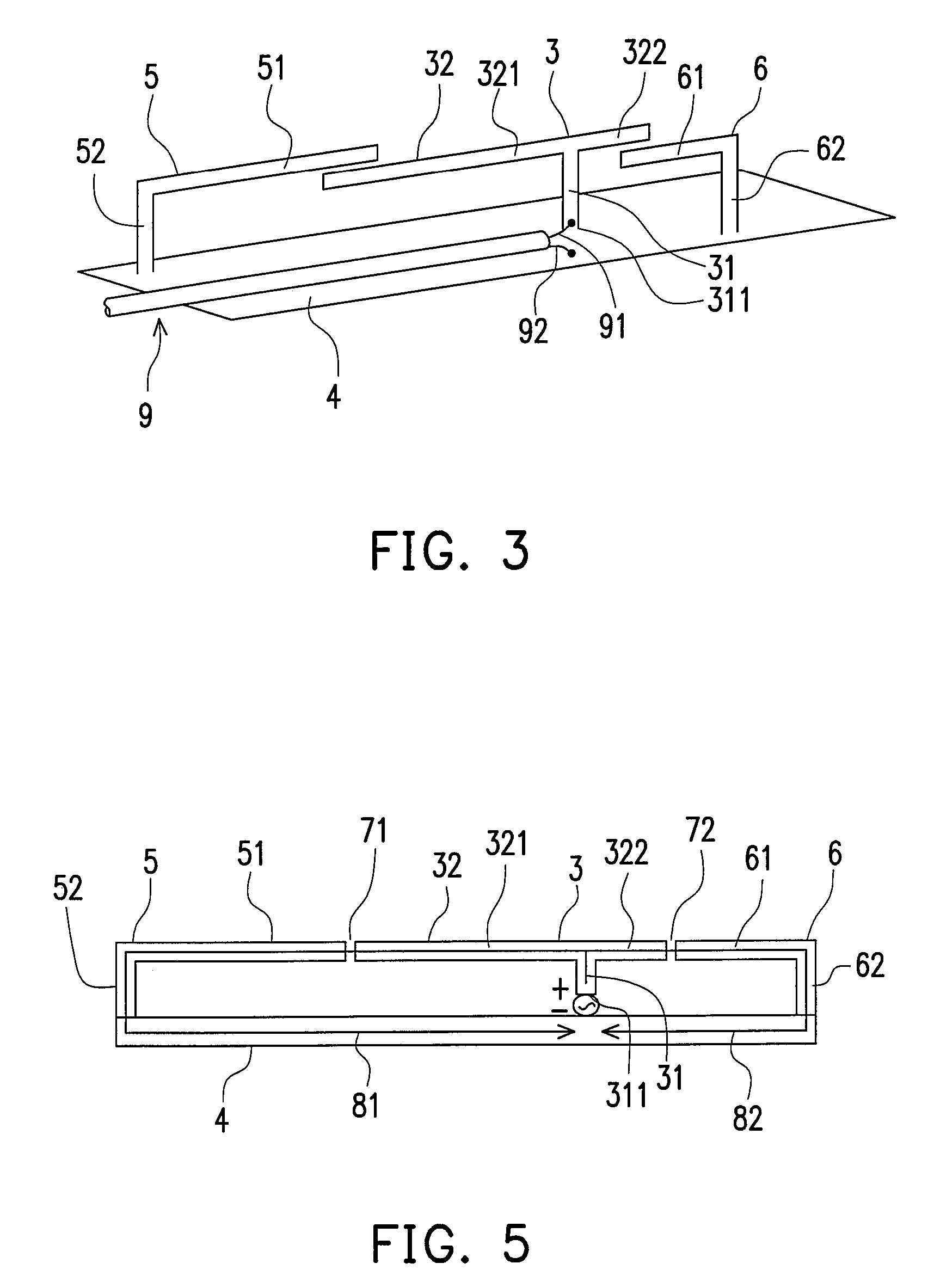
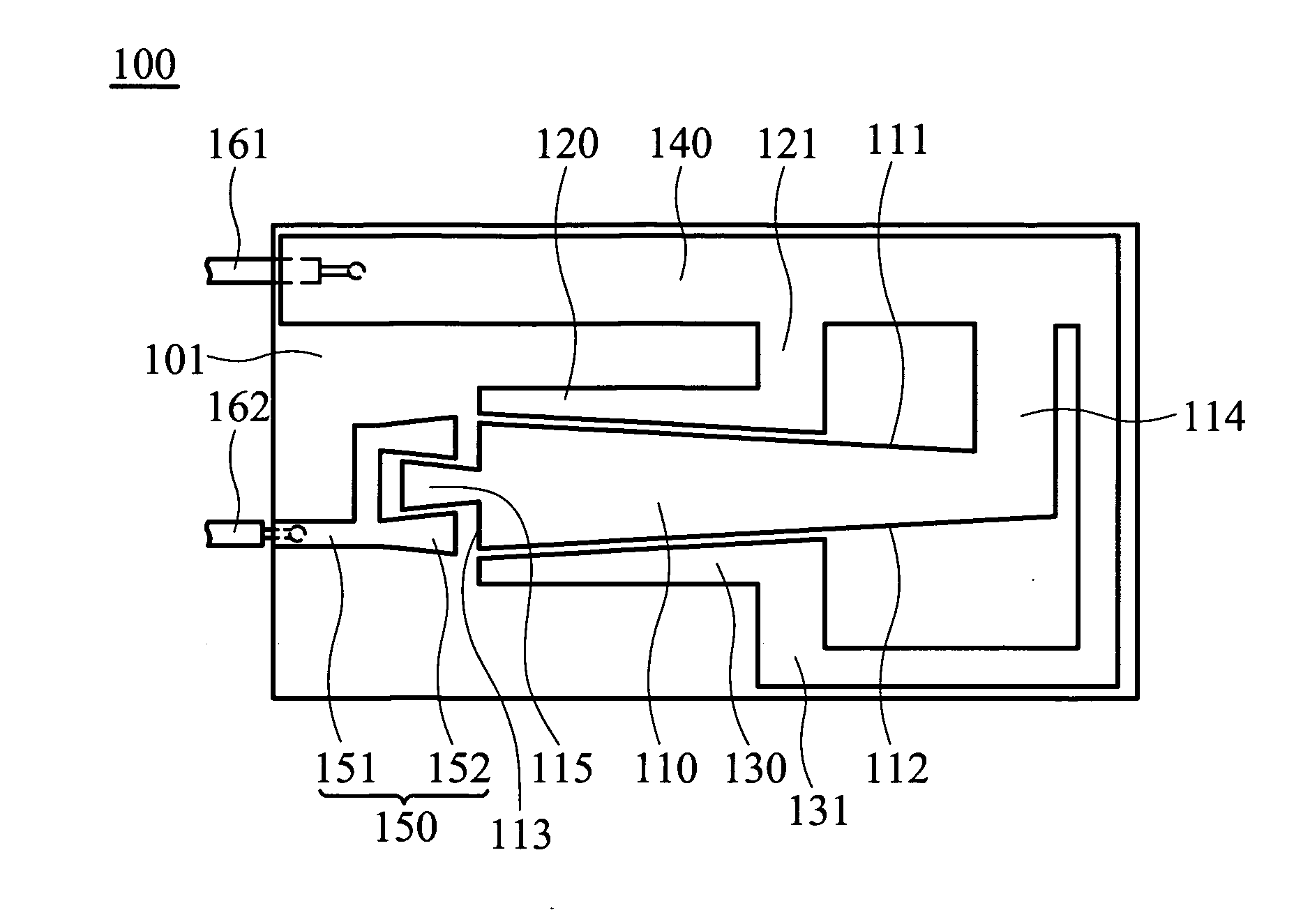
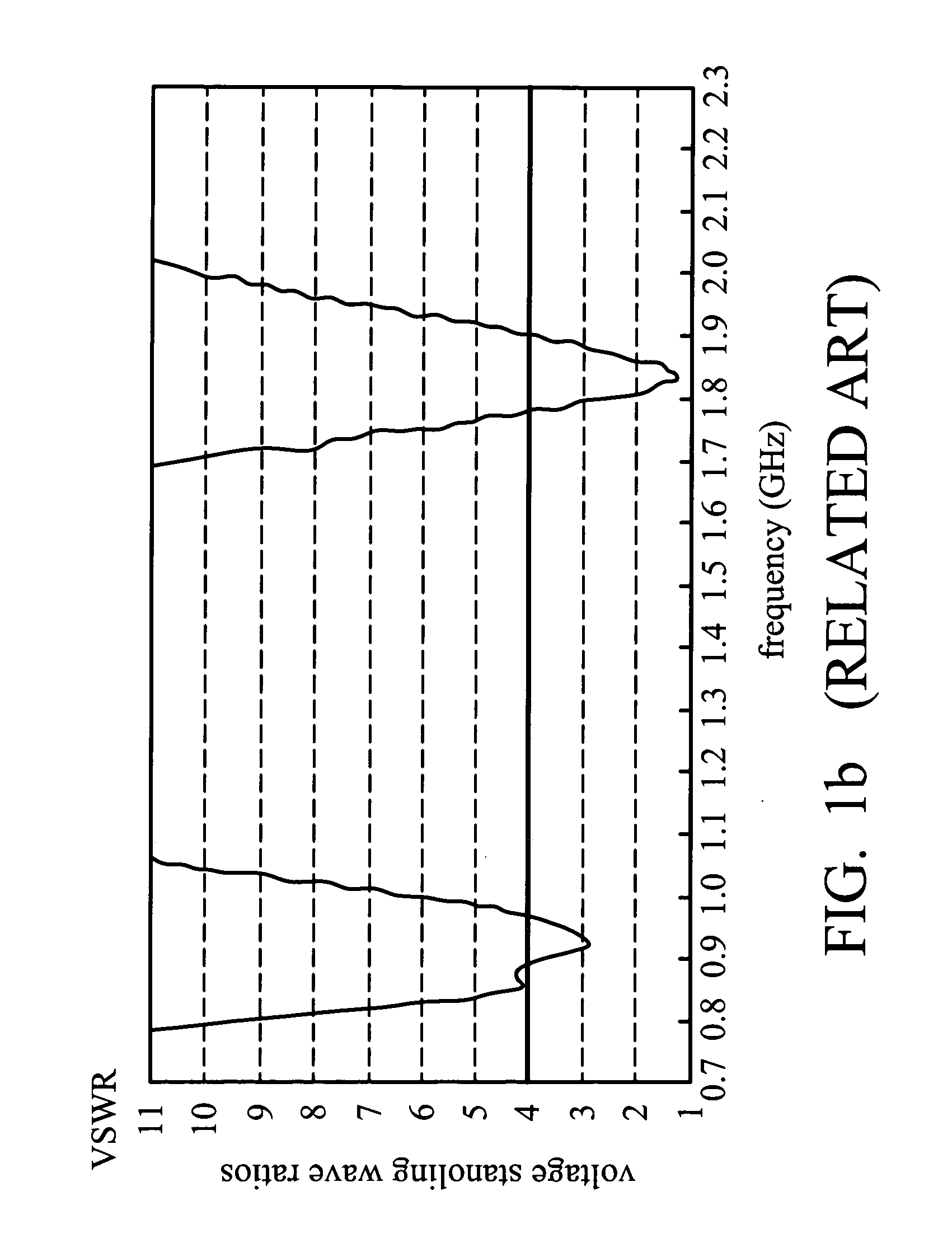
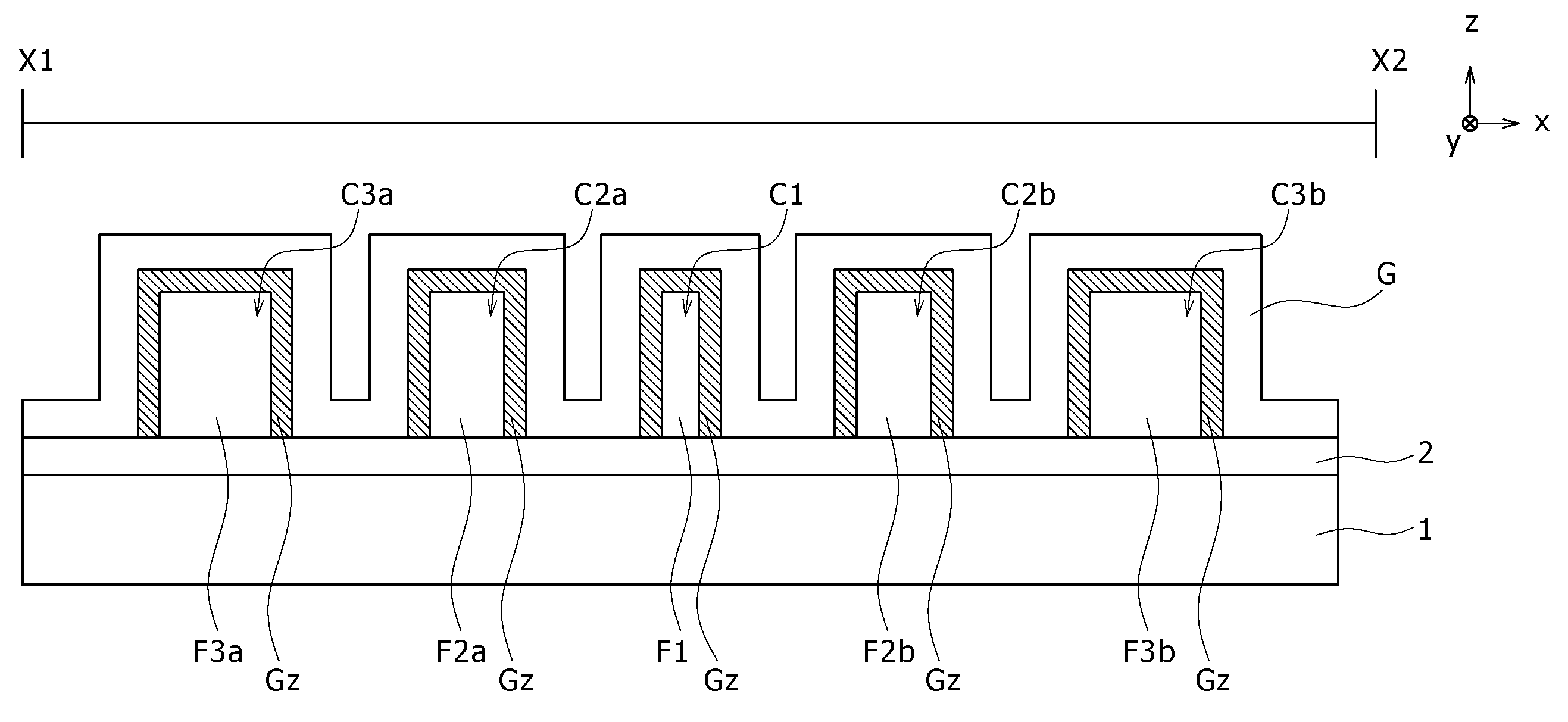
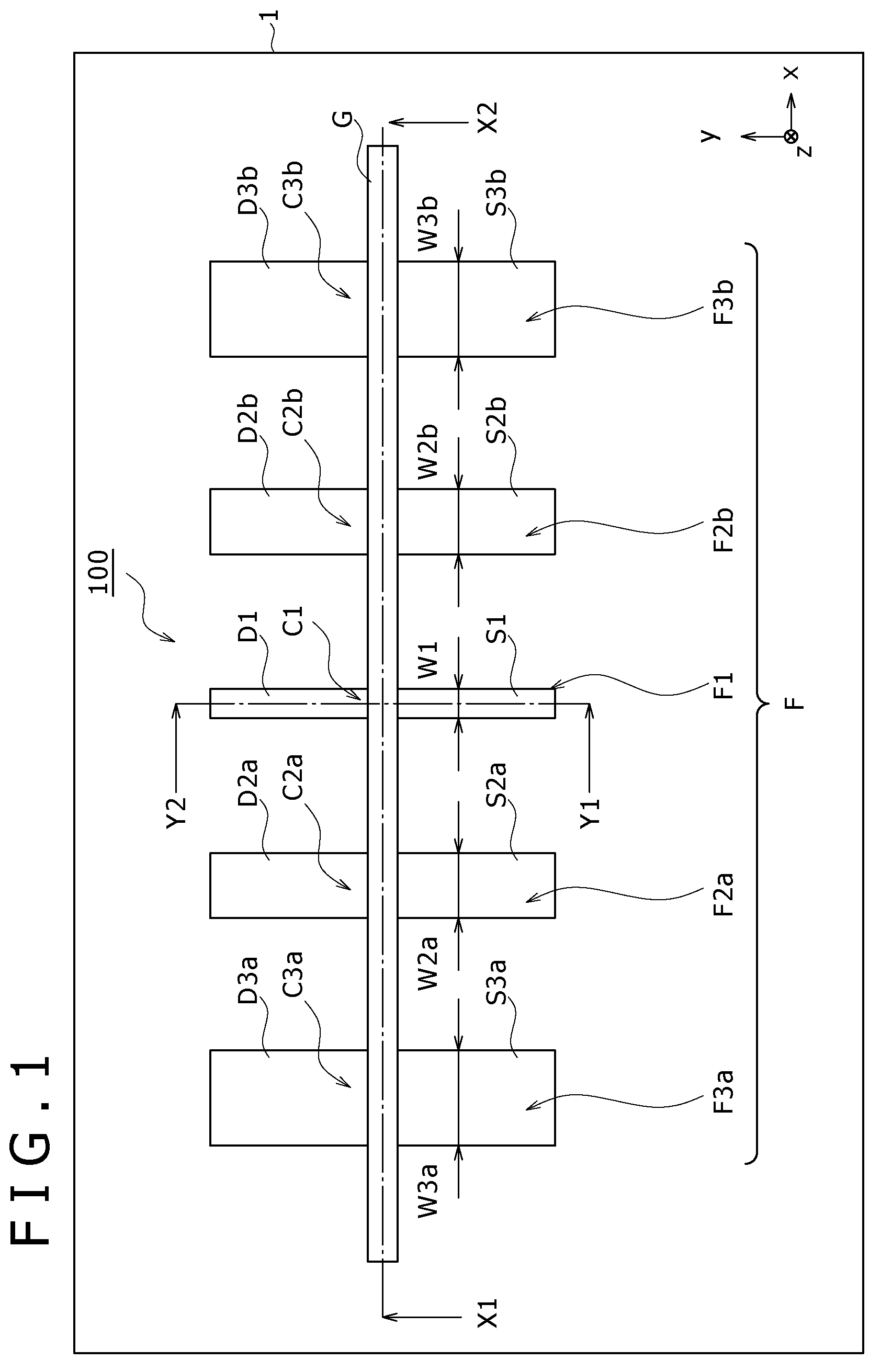
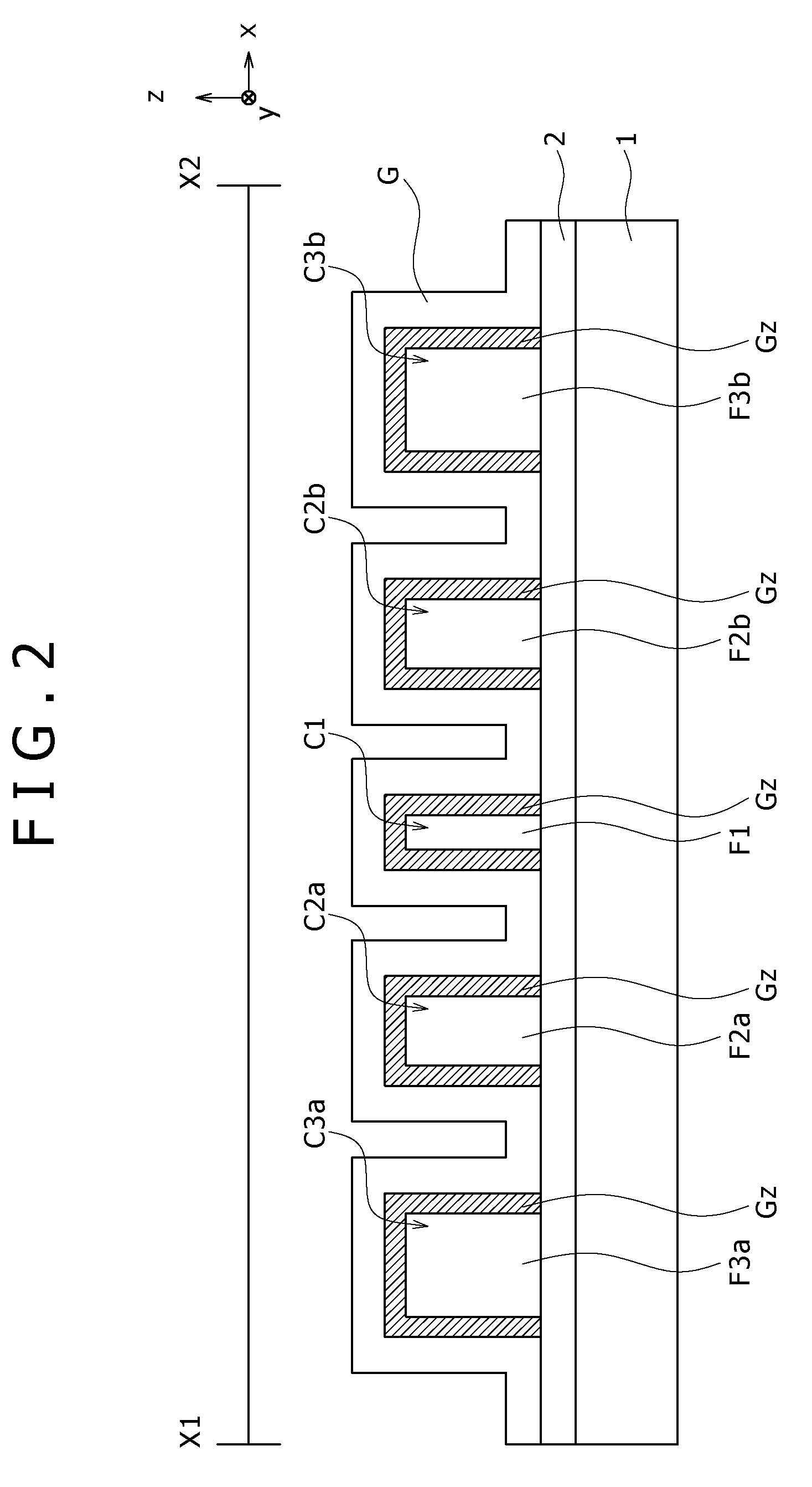
Circularly-polarized-wave patch antenna which can be used in a wide frequency band
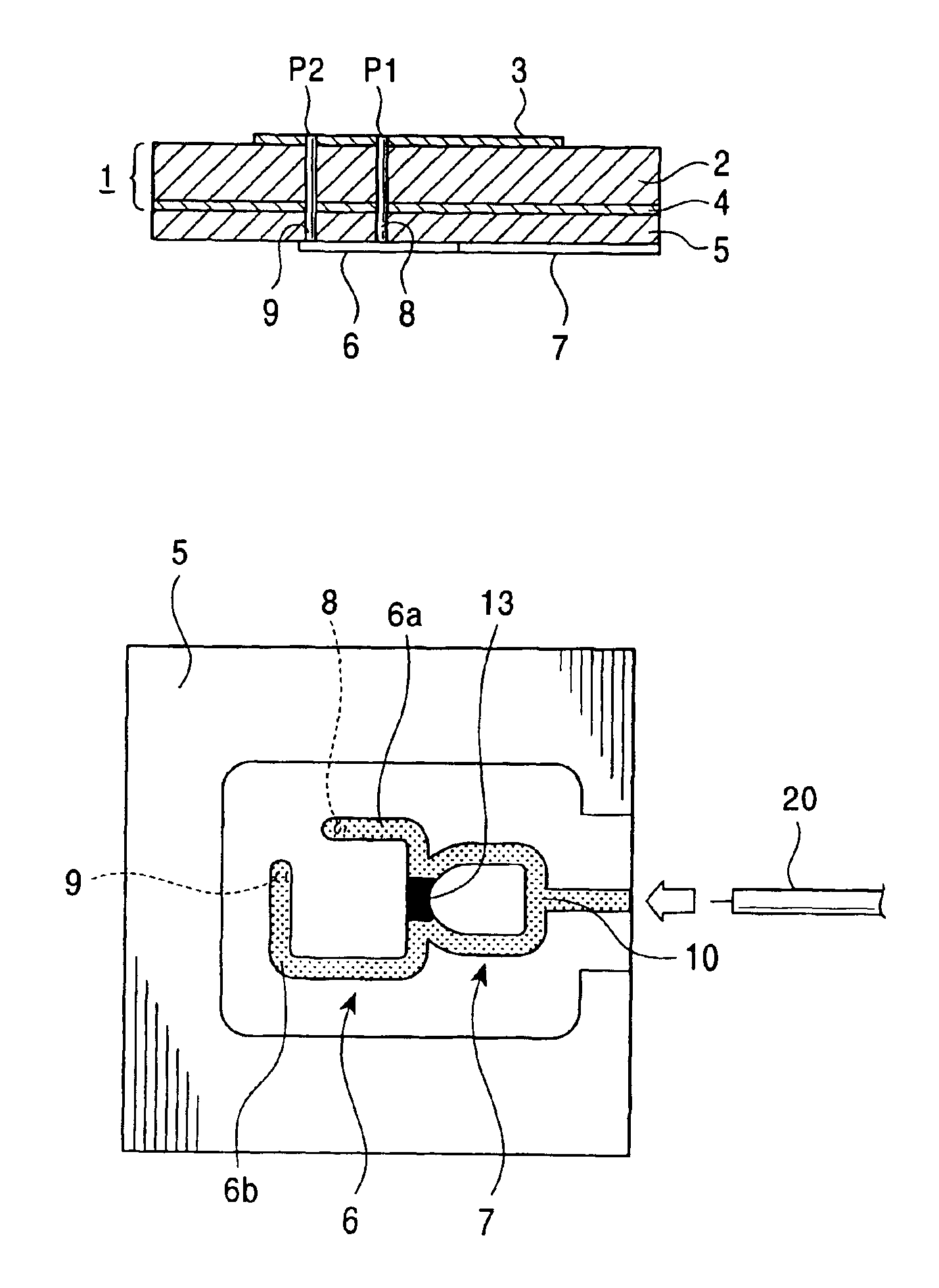
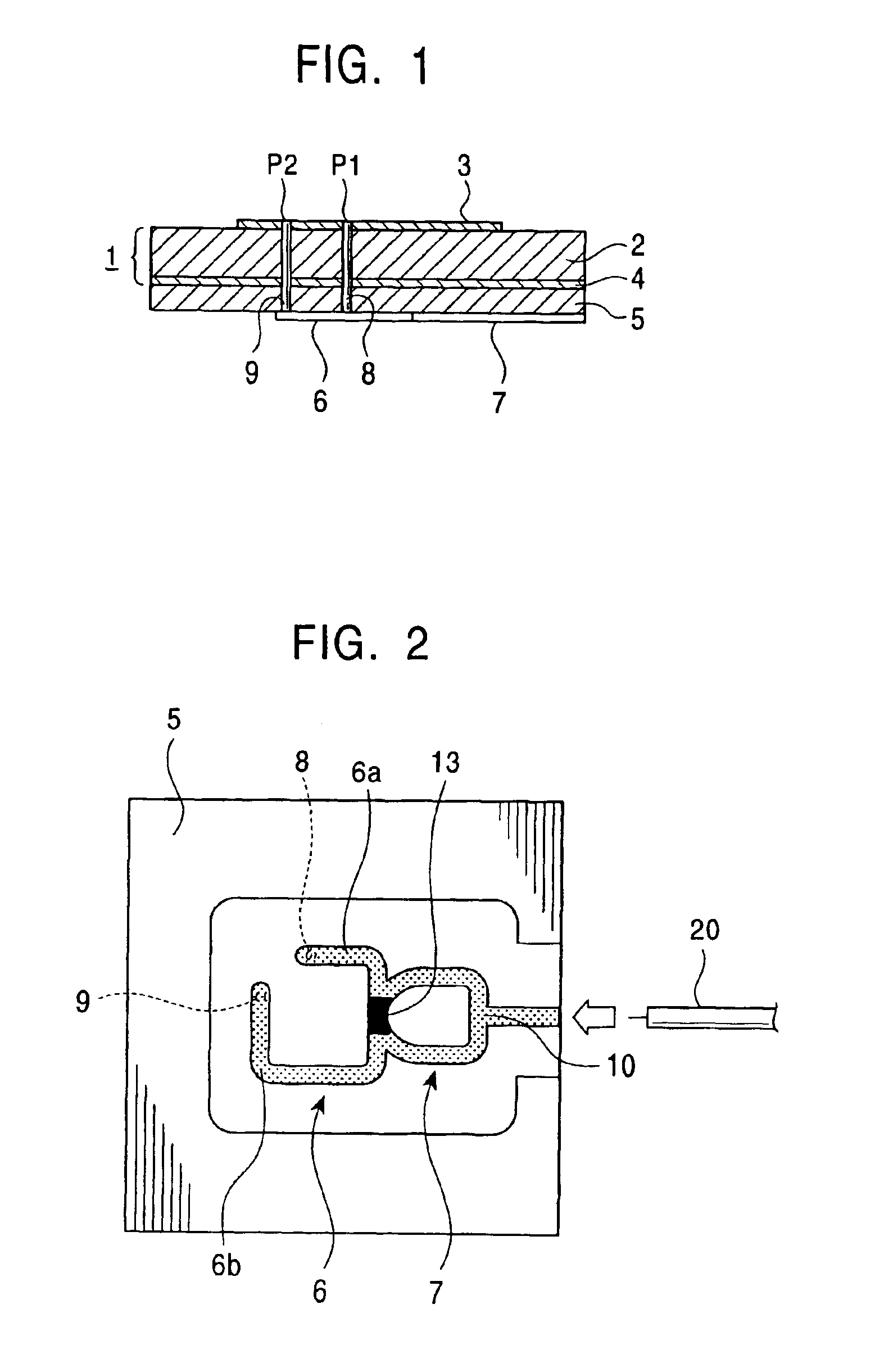
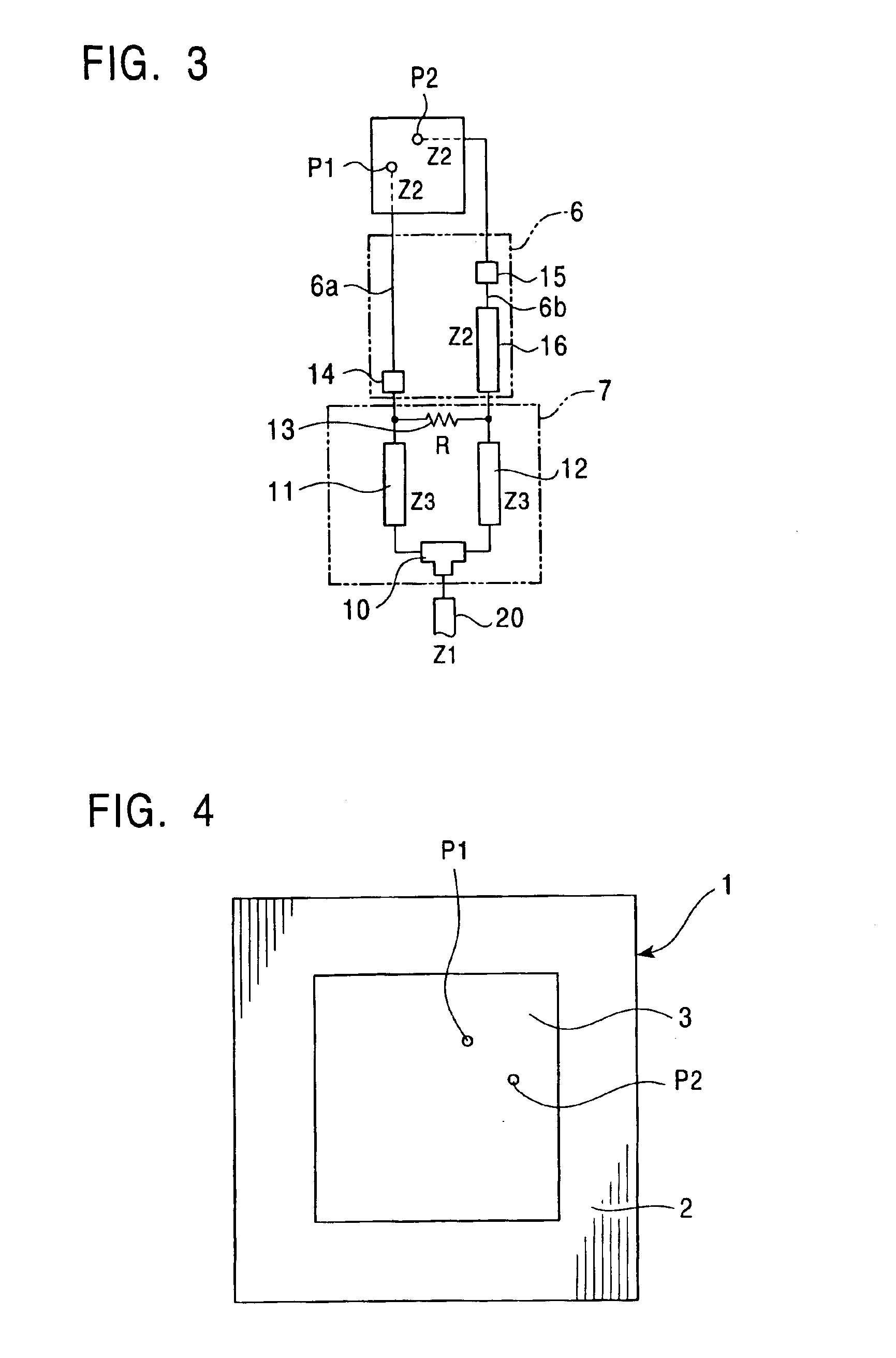
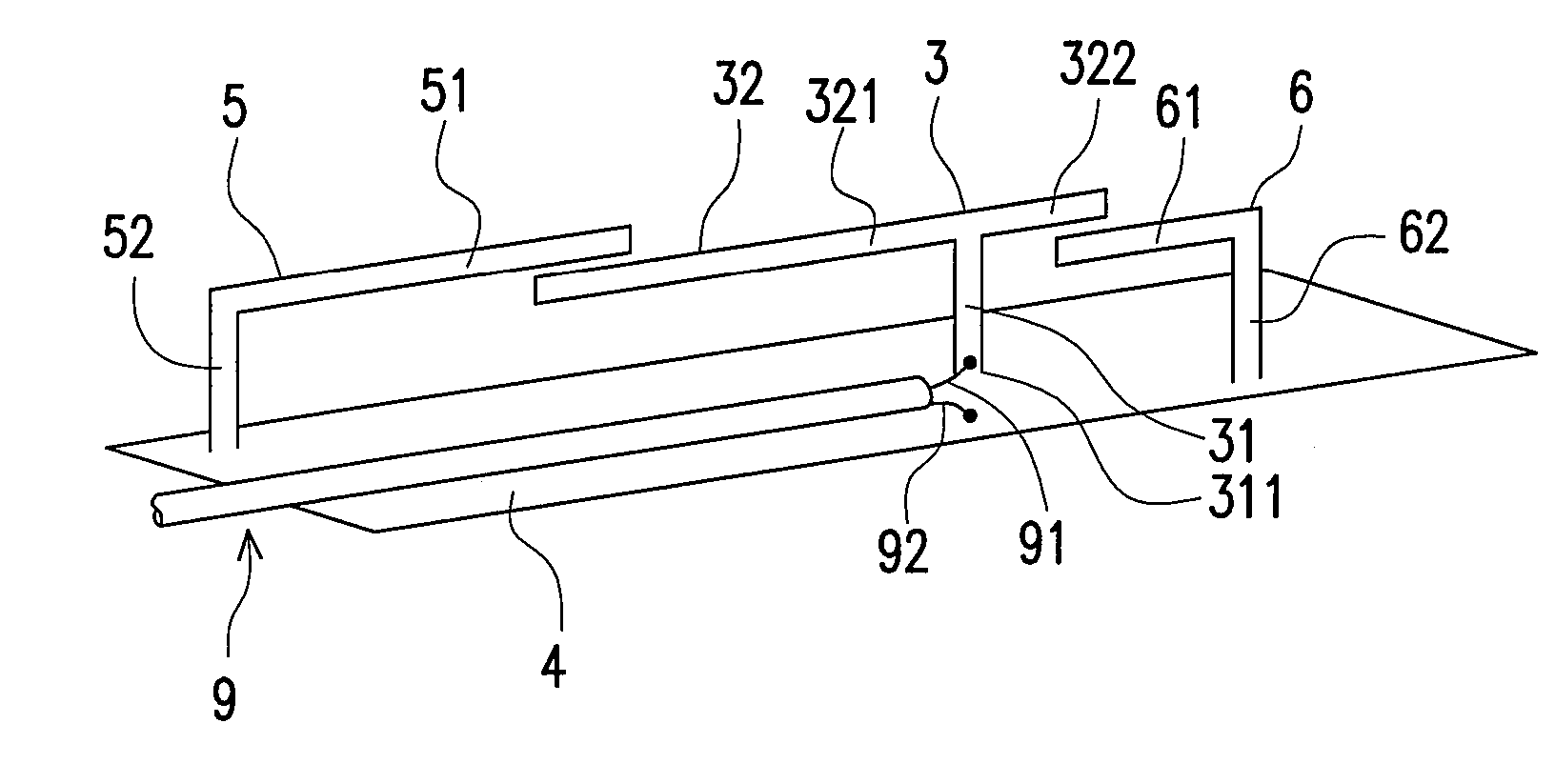
InactiveUS6952183B2Wide bandImprove axle ratioSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsAxial ratioCoaxial cable
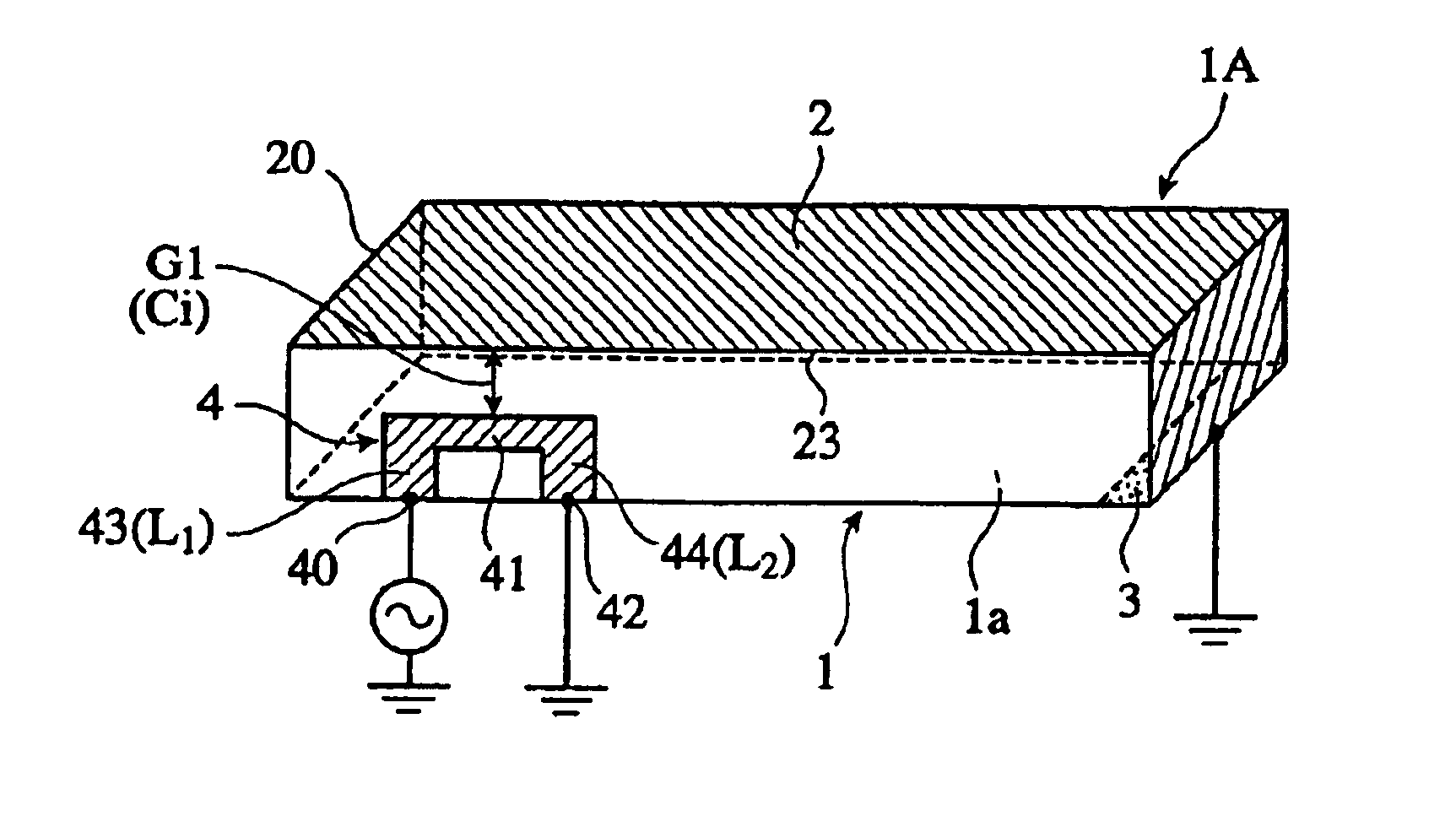
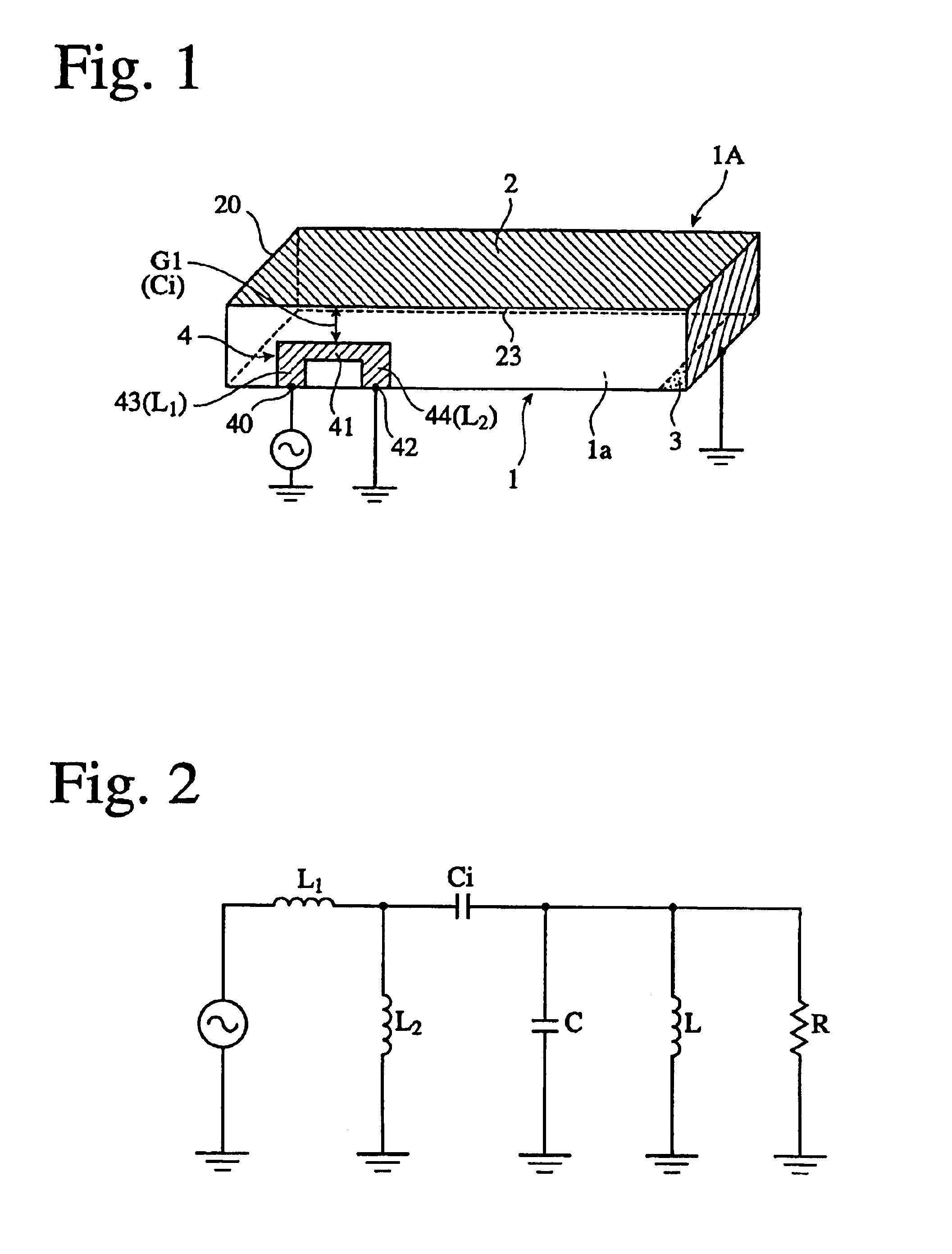
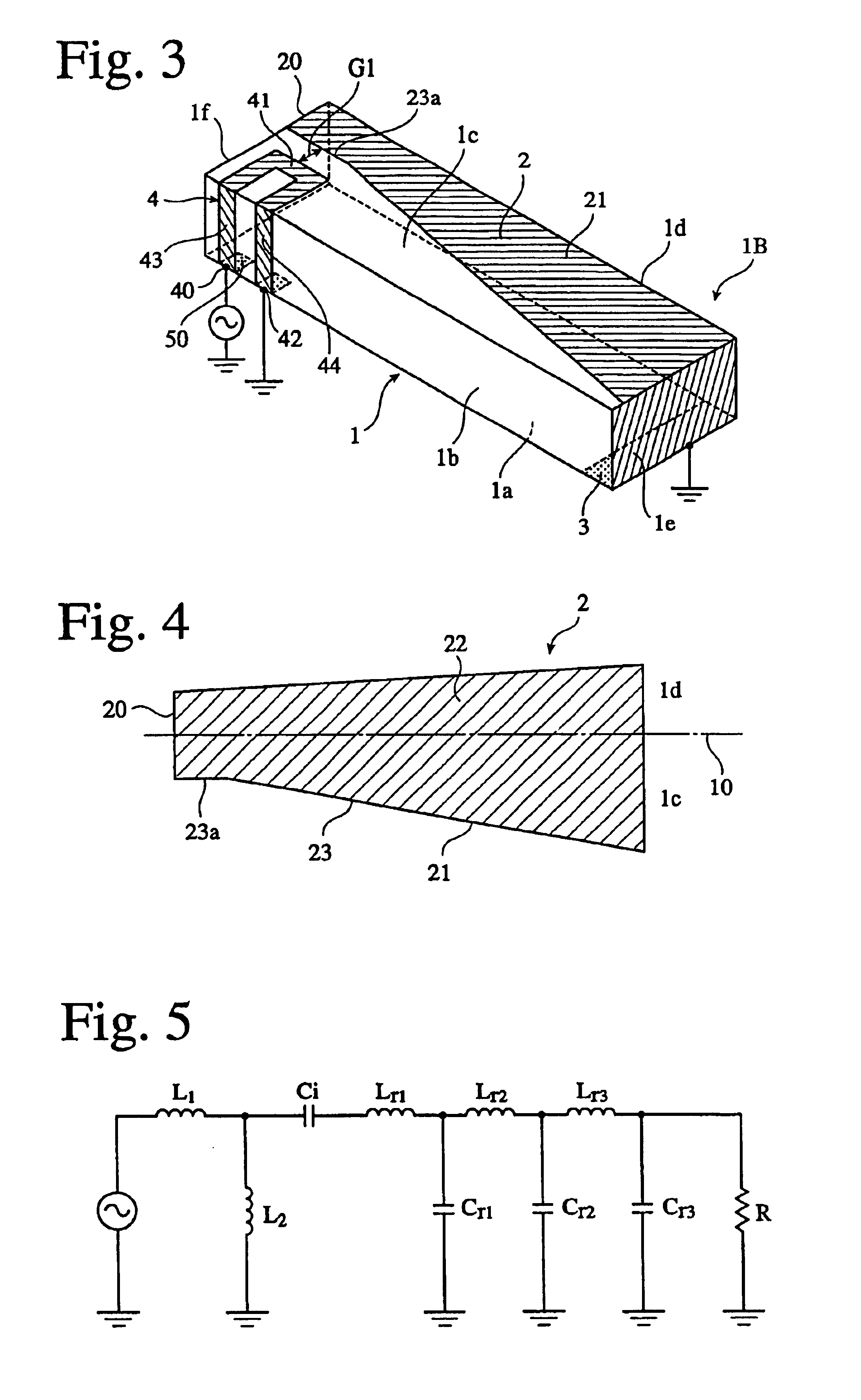
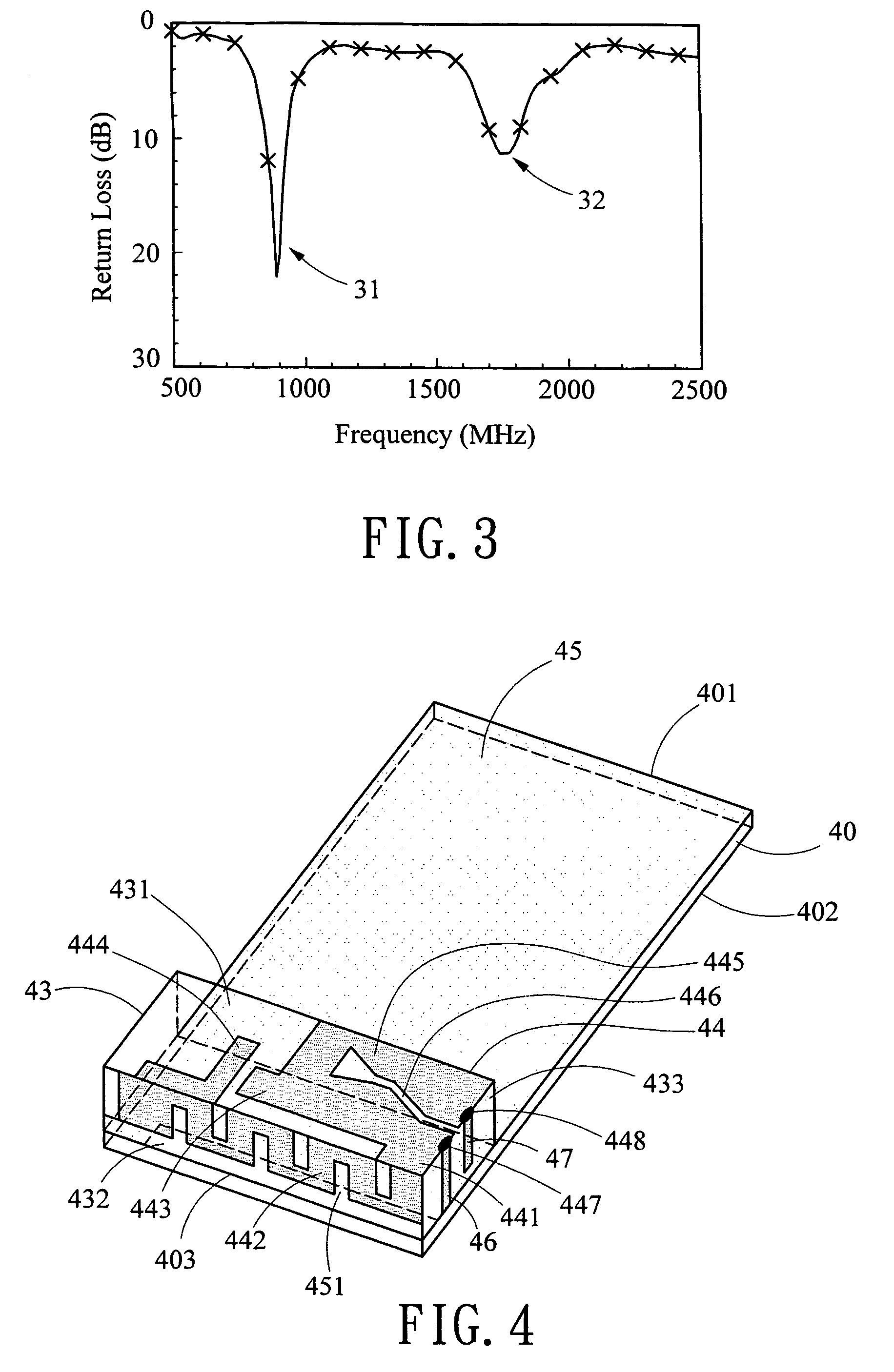
A circularly-polarized-wave patch antenna includes a main body having a patch electrode provided with two feeding points and a circuit for generating a phase difference of 90° between signals supplied to the feeding points. A Wilkinson distribution circuit is provided between the 90°-phase-difference generating circuit and a coaxial cable (feeder line) so as to improve a reflection characteristic. The patch antenna includes two feeding points, and thus a favorable axial ratio characteristic can be obtained in a wide band. Also, a favorable reflection characteristic can be obtained in a wide band because of the Wilkinson distribution circuit. Accordingly, the patch antenna can be used in a wider frequency band.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Multi-frequency antenna with dual loops
ActiveUS20070285321A1Increase capacityWide bandSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsDual loopEngineering
A multi-frequency antenna with dual loops is provided. The antenna includes a T-shaped radiator having a first arm and a second arm of unequal lengths as a main body, and two grounded L-shaped radiators, so as to form dual loops. Thus, the antenna can operate in a high-frequency operation mode and a low-frequency operation mode. With the dual loops, the antenna obtains enough bandwidths at high frequency, and also meets the requirements of low frequency. More specific, the antenna meets the requirements of high-frequency systems, such as DCS / PCS / UMTS and those of low-frequency systems, such as AMPS / GSM.
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
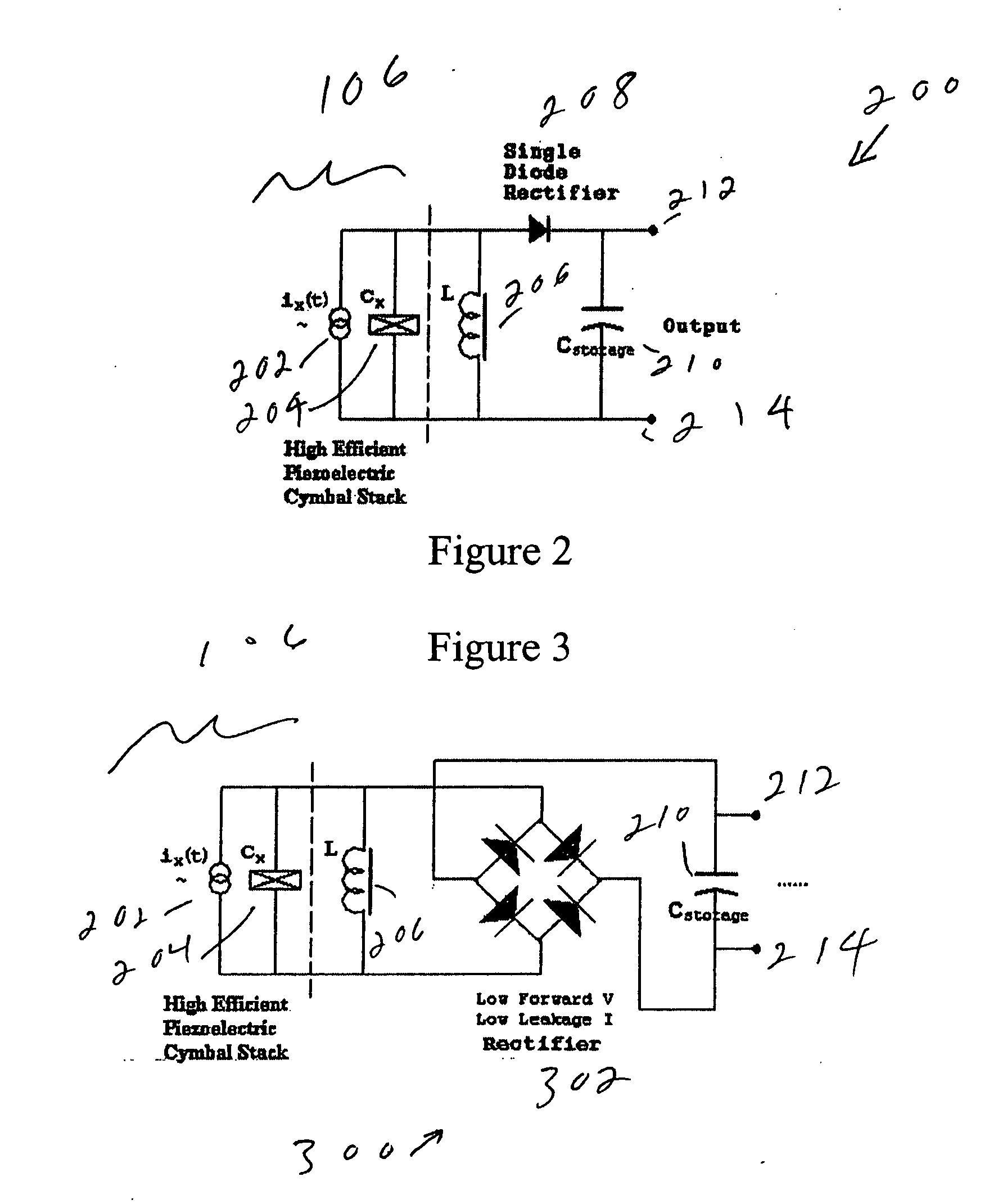
Piezoelectric vibration energy harvesting device
InactiveUS20050134149A1Efficient HarvestingSmall sizePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringVibration energy harvesting
A piezoelectric vibration energy harvesting device which is made up of a first mass, a second, a first spring coupled to the first mass, and a second spring coupled to the second mass. A piezoelectric element is bonded between the first mass and the second spring, so that a stress applied to the second spring is applied to the piezoelectric element
Owner:WILCOXON RES
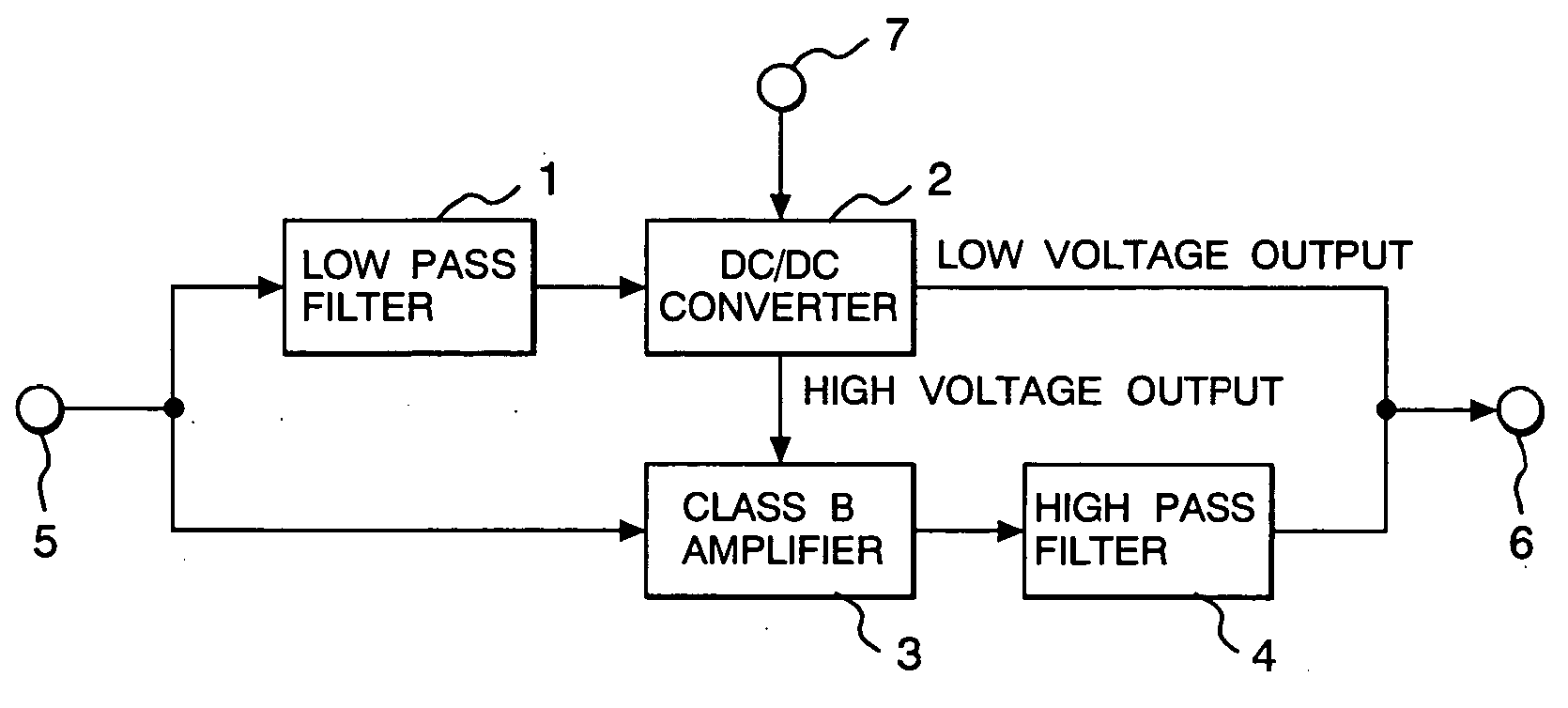
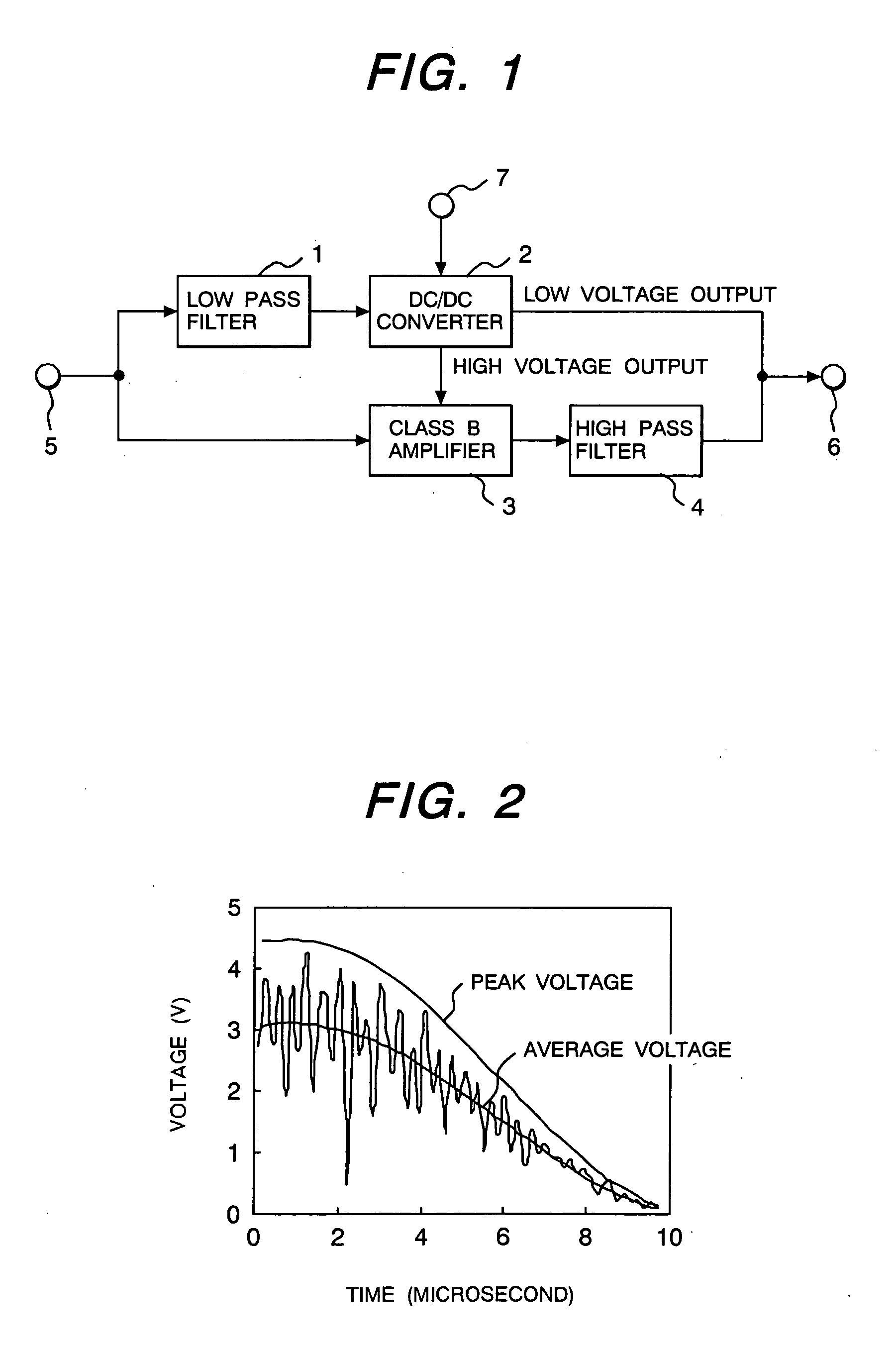
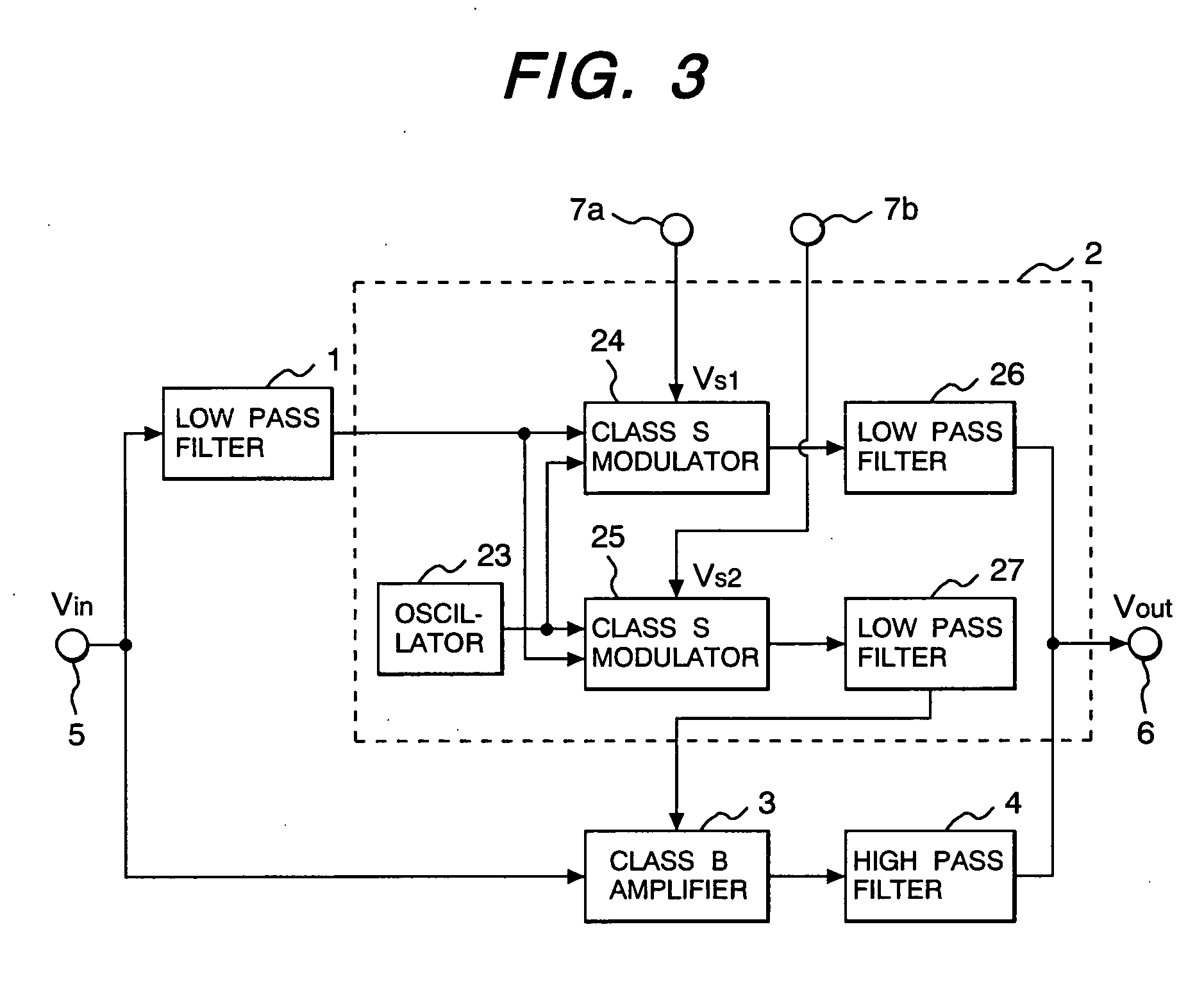
Amplifier and radio frequency power amplifier using the same
InactiveUS20050046474A1Wide bandImprove efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersLow distortionEngineering
An amplifier using a wide band, high efficiency, and low distortion amplifier free from clipping distortion, and a high efficiency and low distortion radio frequency power amplifier, using that amplifier, which can be applied to wide band wireless communication systems are provided. The amplifier has a DC-DC converter 2, augmented with a low pass filter 4, for amplifying the low frequency components of an input signal from a terminal 5, and a class B amplifier, augmented with a high pass filter, for amplifying the input signal and supplying its high frequency components after amplification. The DC-DC converter and the class B amplifier are connected in parallel, and the power supply voltage of the class B amplifier is controlled with the low frequency components of the input signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Surface-mounted antenna and communications apparatus comprising same
InactiveUS6873291B2High gainEasy impedance matchingSimultaneous aerial operationsMotorised scootersCapacitanceBand shape
A surface-mounted antenna comprising a substrate made of a high-dielectric constant material having a dielectric constant ∈r of 6 or more, a ribbon-shaped radiation electrode having one end which is grounded and the other end which is open, a grounding electrode connected or capacitance-coupled to one end of the radiation electrode, and a current-feeding electrode in a portal shape formed on a side surface separate from the radiation electrode with a gap; the current-feeding electrode having a current-feeding portion at one end, a grounding portion at the other end, and a portion substantially in alignment with the radiation electrode between them; and the length of the aligning portion, a gap width or a portal shape being able to be properly set such that capacitance owned by the current-feeding electrode and inductance can be adjusted for easily achieving impedance matching.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Resource mapping method and apparatus in wireless communication system
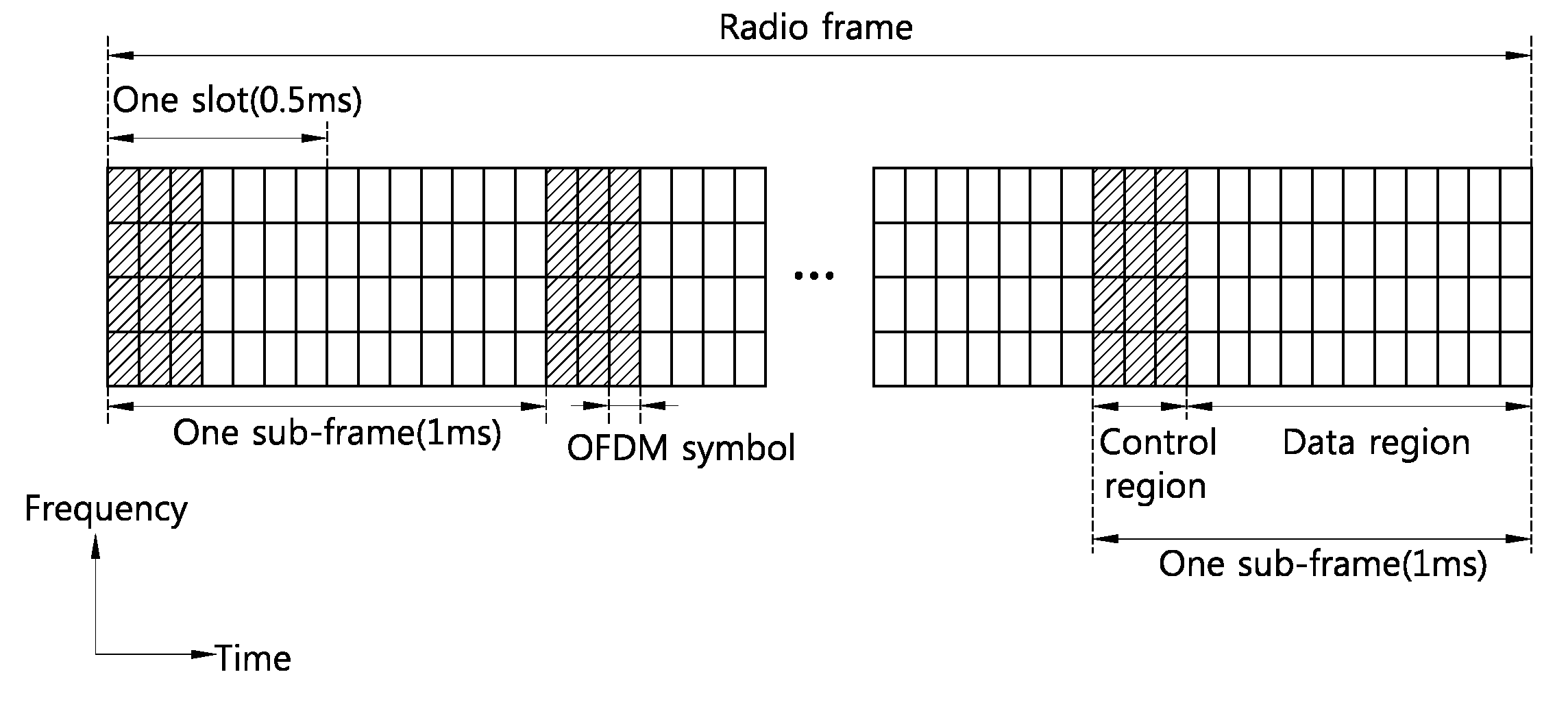
InactiveUS20120087331A1Wide bandEfficient implementationNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionCommunications systemResource block
The present invention provided a method and an apparatus for mapping radio resources in a wireless communication system. A terminal determines the size of an RBG (resource block group of a f basic band according to the number of RBs (resource blocks) within the basic band in the overall bands which include the fundamental band and an aggregated segment band. The size of an RBG of the aggregated segment band is determined on the basis of the size of the RBG of the basic band.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
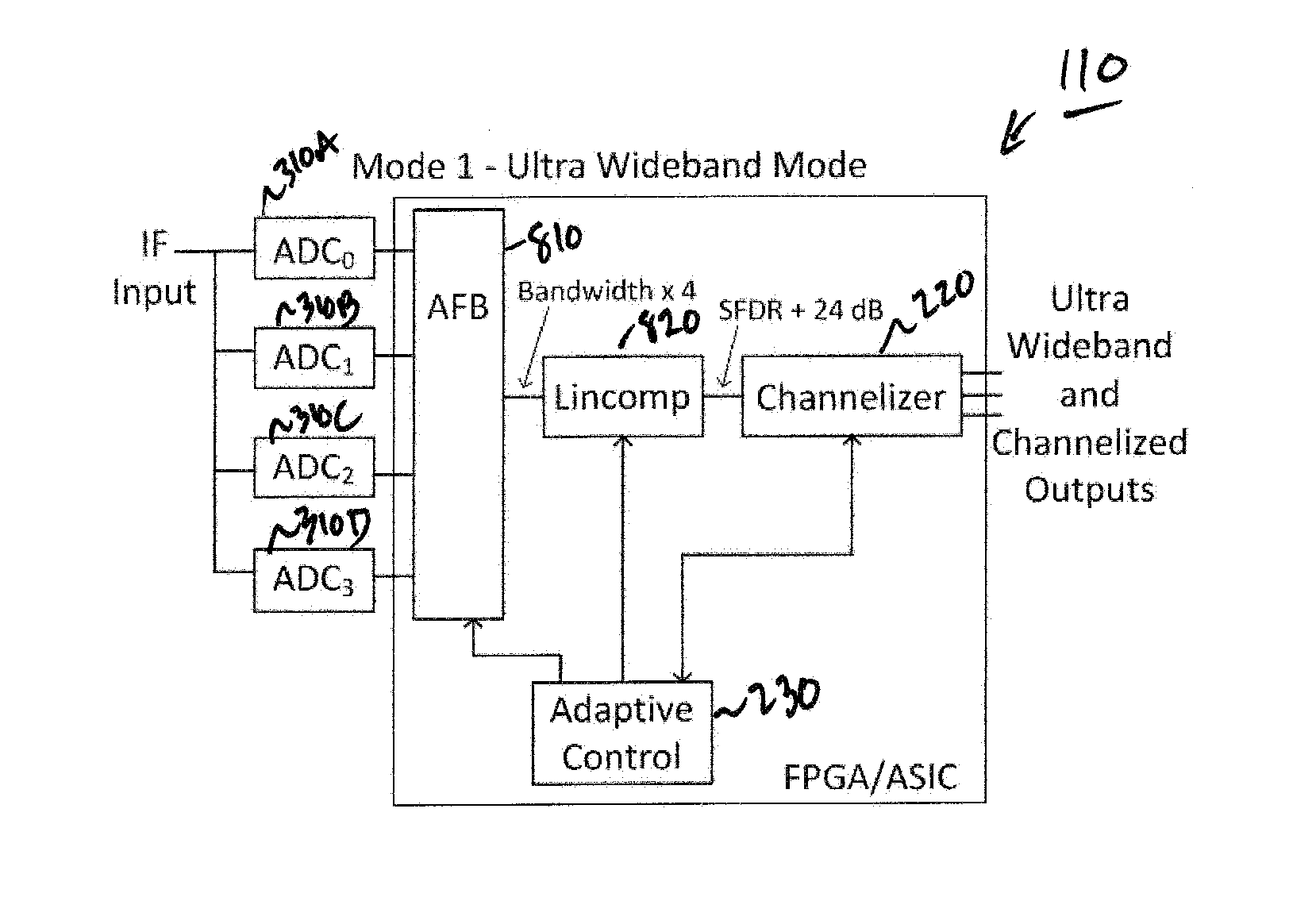
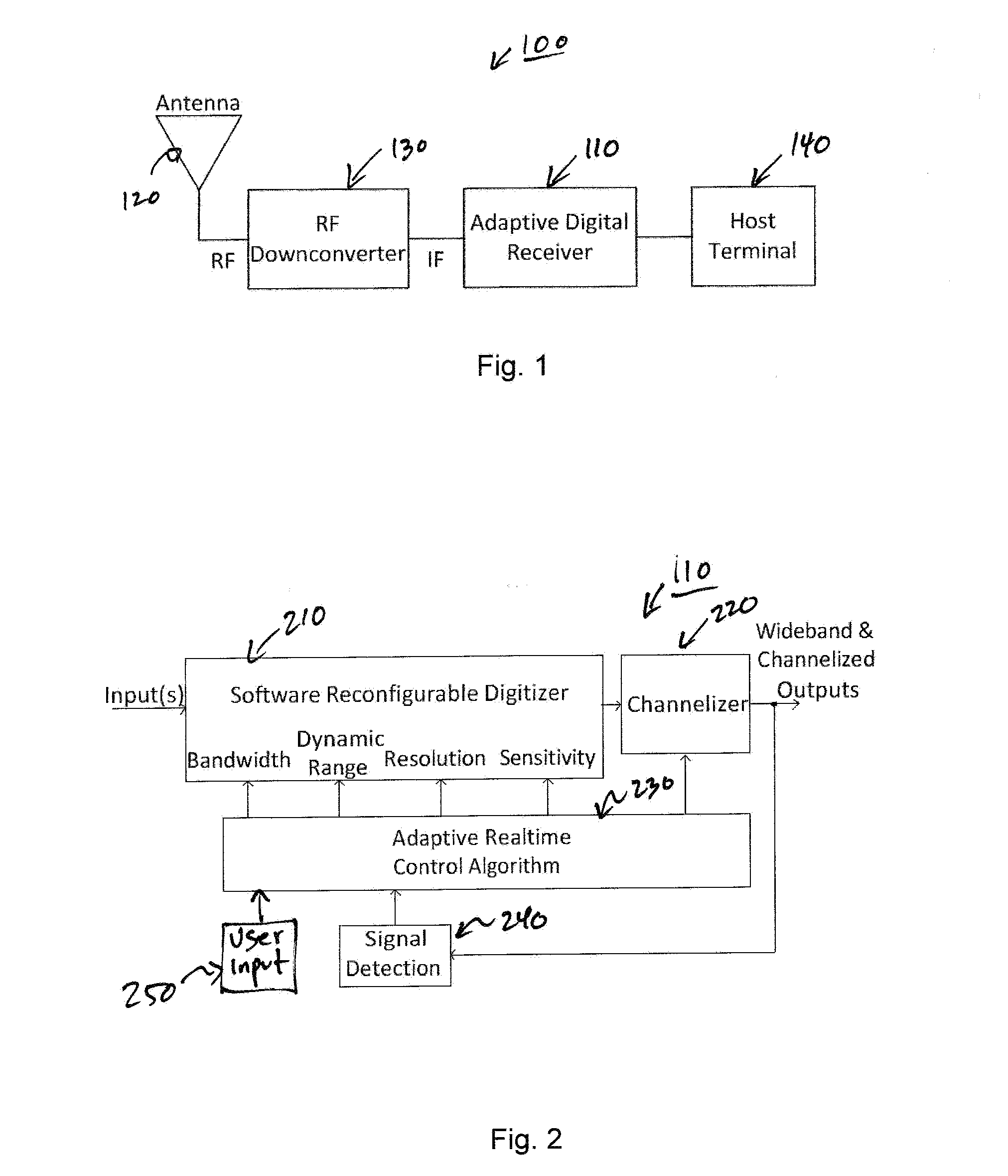
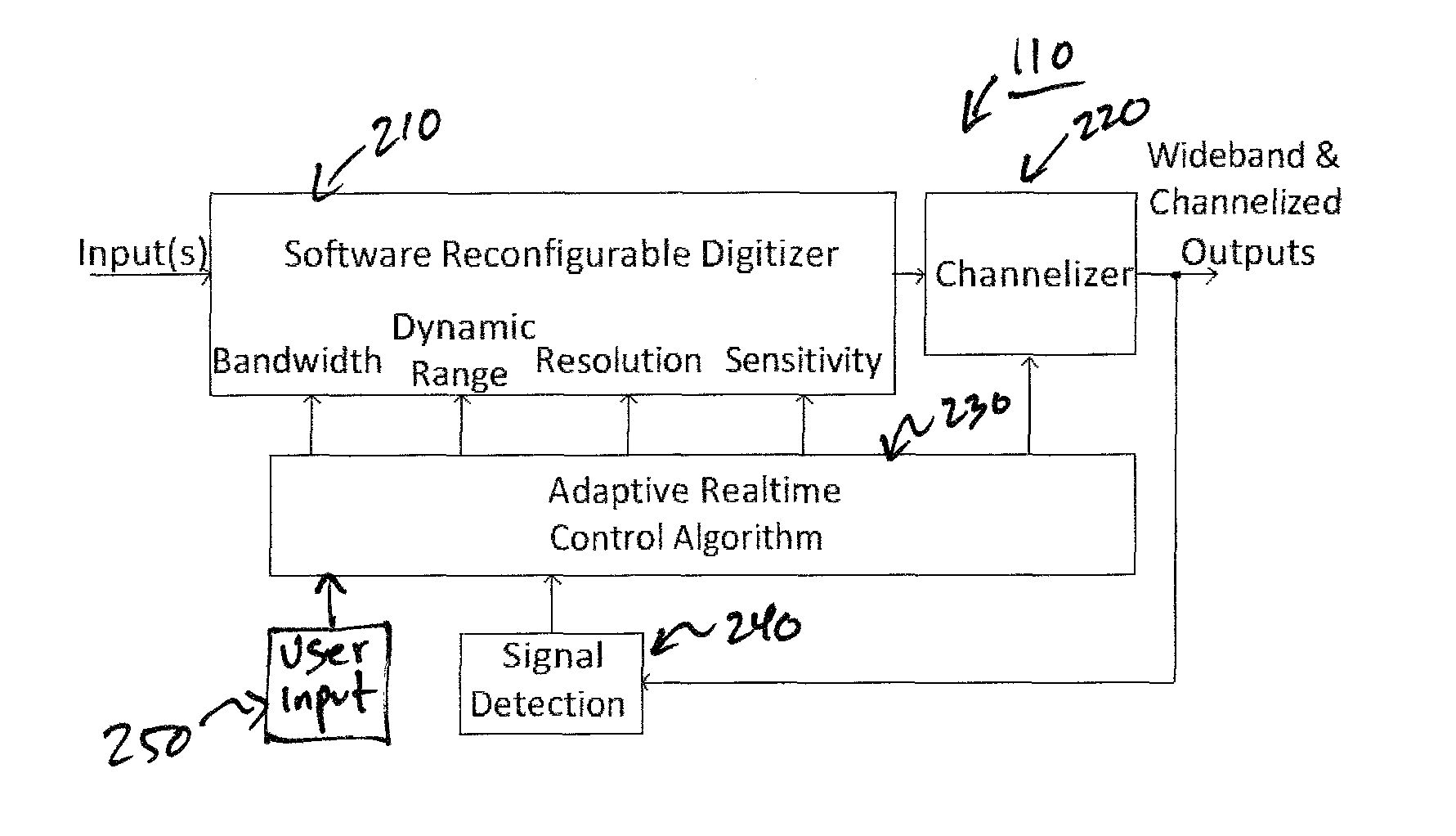
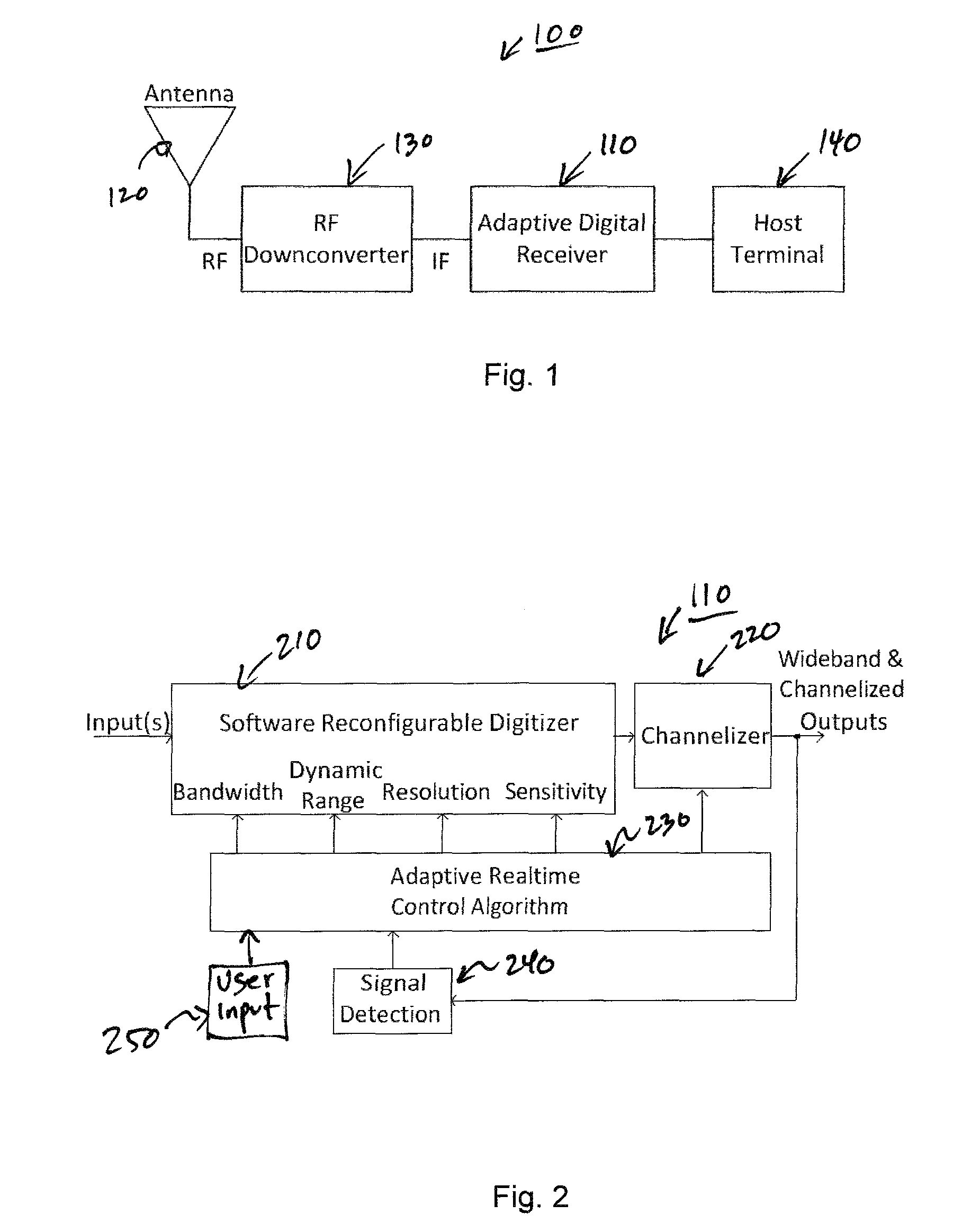
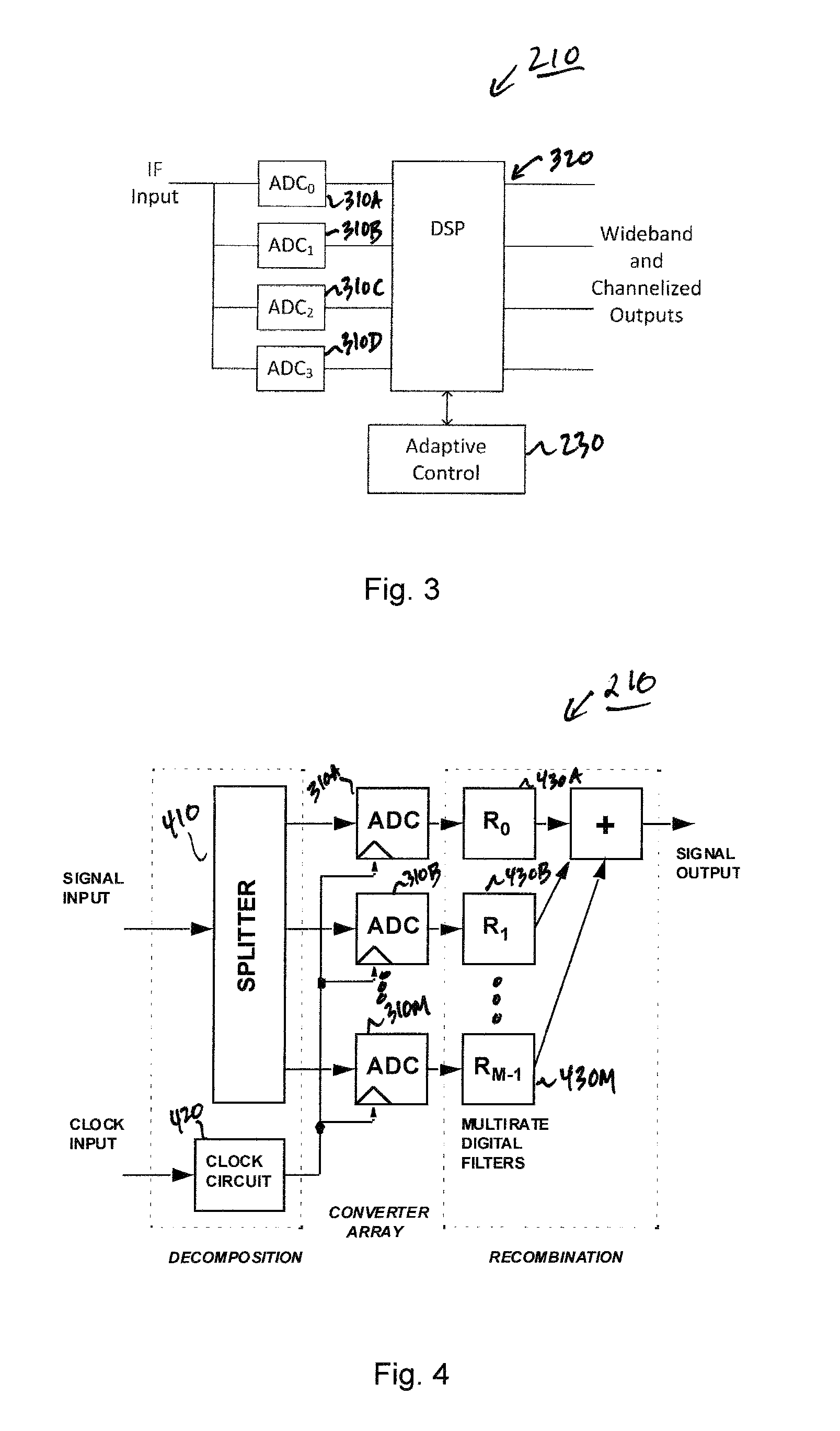
Adaptive digital receiver
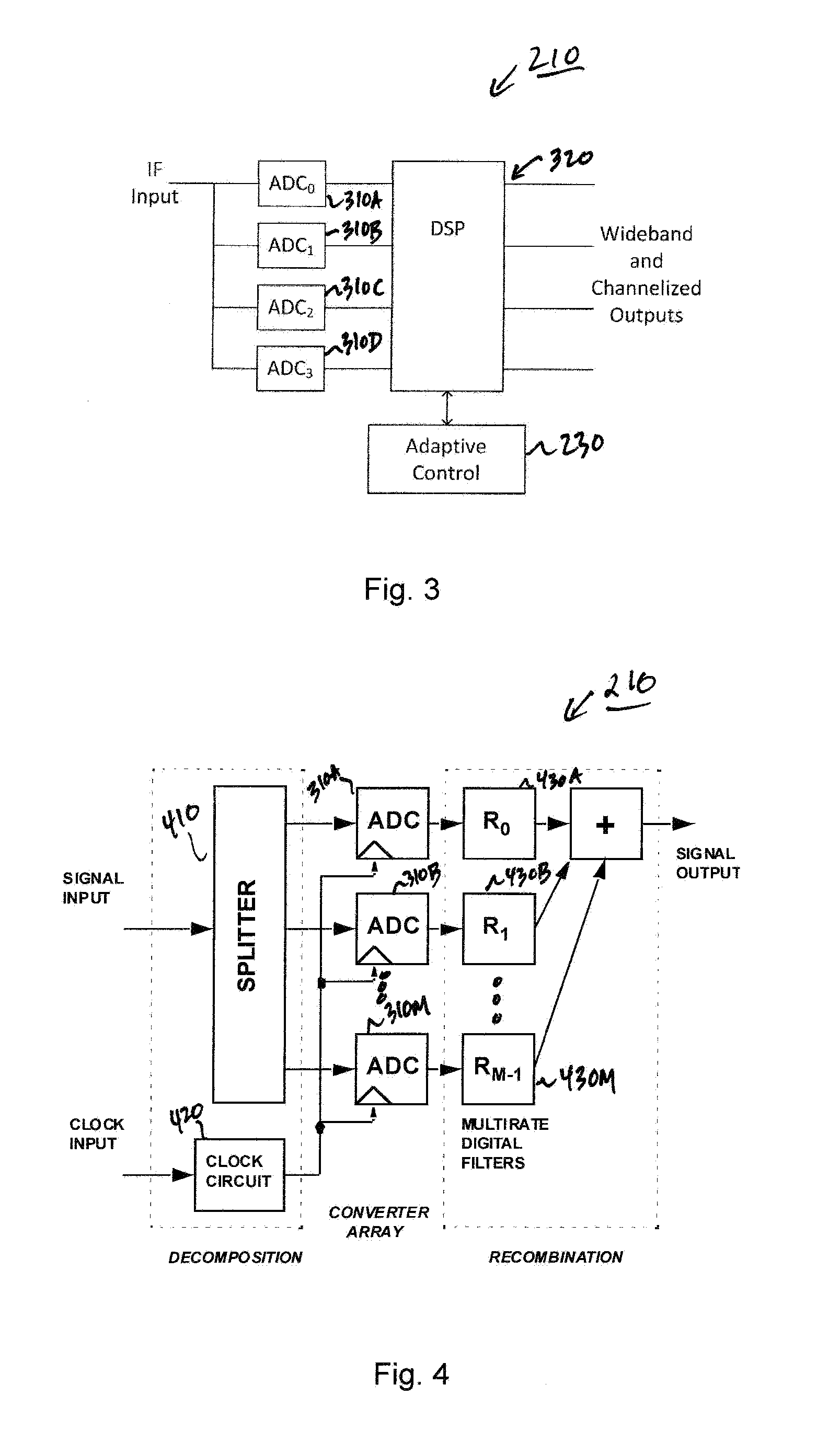
ActiveUS20130016798A1Wide bandwidthHigh resolutionElectric signal transmission systemsChannel dividing arrangementsAdaptive optimizationEngineering
The present invention provides a high-performance adaptive digital receiver with adaptive background control that optimizes the performance in rapidly changing signal environments and provides 3.6 GH; instantaneous bandwidth, SFDR>90 dB, SNR=66 dB, with dynamic digital channelization. The receiver takes advantage of several levels of adaptivity that conventional approaches do not offer. In addition to a dynamic digital channelizer that is adaptively tuned based on detected signals, the present invention employs a powerful software reconfigurable digitizer that is adaptively optimized for the current signal environment to control important receiver parameters such as bandwidth, dynamic range, resolution, and sensitivity.
Owner:LINEARITY LLC
Raman amplifier, optical repeater, and raman amplification method
InactiveUS20070247701A1Soften propertyWide bandLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsLong wavelengthLight source
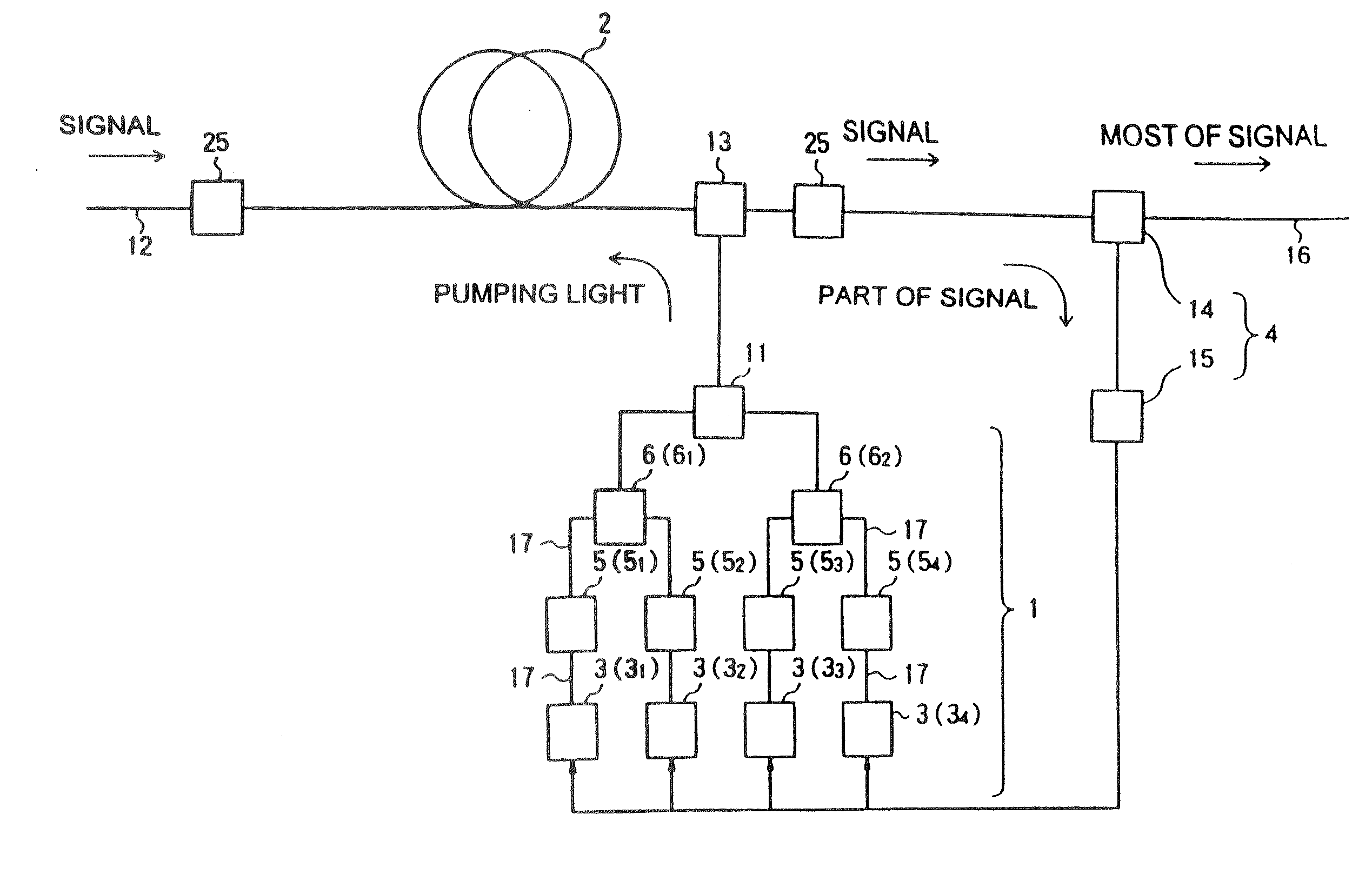
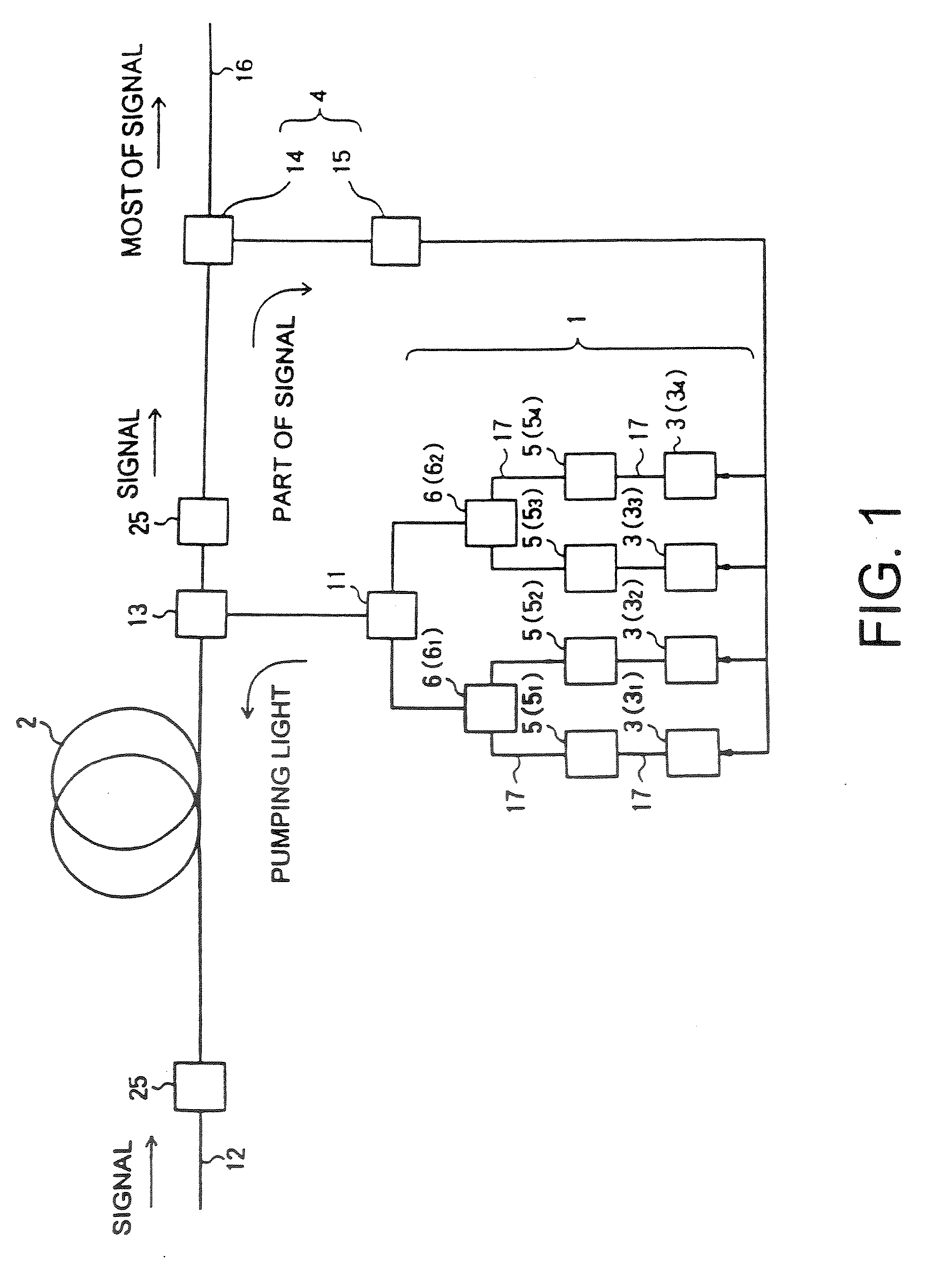
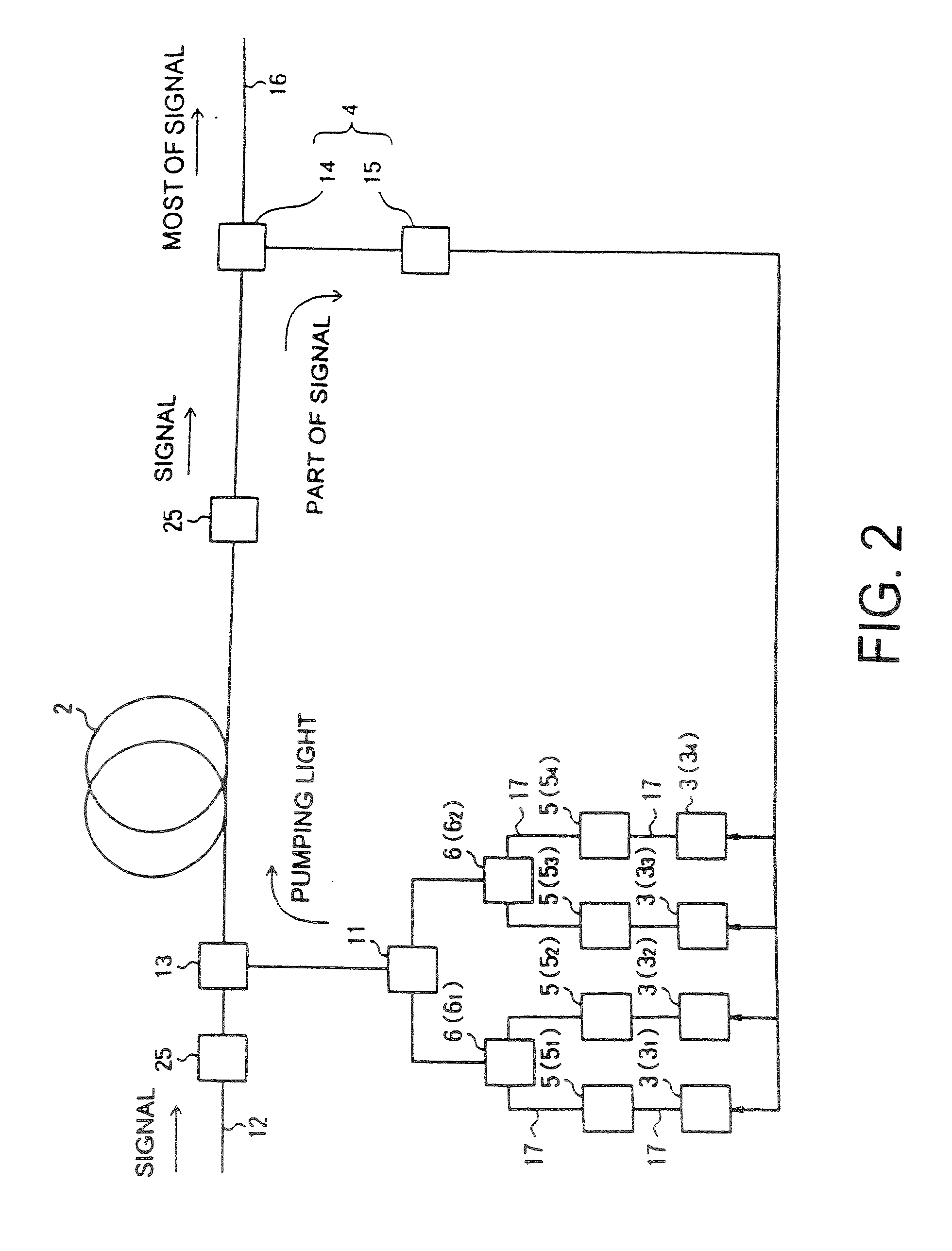
A Raman amplifier according to the present invention comprises a plurality of pumping means using semiconductor lasers of Fabry-Perot, DFB, or DBR type or MOPAs, and pumping lights outputted from the pumping means have different central wavelengths, and interval between the adjacent central wavelength is greater than 6 nm and smaller than 35 nm. An optical repeater according to the present invention comprises the above-mentioned Raman amplifier and adapted to compensate loss in an optical fiber transmission line by the Raman amplifier. In a Raman amplification method according to the present invention, the shorter the central wavelength of the pumping light the higher light power of said pumping light. In the Raman amplifier according to the present invention, when a certain pumping wavelength is defined as a first channel, and second to n-th channels are defined to be arranged with an interval of about 1 THz toward a longer wavelength side, the pumping lights having wavelengths corresponding to the first to n-th channels are multiplexed, and an pumping light having a wavelength spaced apart from the n-th channel by 2 THz or more toward the longer wavelength side is combined with the multiplexed light, thereby forming the pumping light source. The pumping lights having wavelengths corresponding to the channels other than (n-1)-th and (n-2)-th channels may be multiplexed, thereby forming the pumping light source. The pumping lights having wavelengths corresponding to the channels other than (n-2)-th and (n-3)-th channels may be multiplexed, thereby forming the pumping light source.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Multi-frequency antenna with dual loops
ActiveUS7425924B2Increase capacityWide bandSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsOperation modeGSM
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
Surface-mounted antenna and communications apparatus comprising same
InactiveUS20030006936A1MiniaturizationHigh bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsMotorised scootersCapacitanceBand shape
A surface-mounted antenna comprising a substrate made of a high-dielectric constant material having a dielectric constant is inr of 6 or more, a ribbon-shaped radiation electrode having one end which is grounded and the other end which is open, a grounding electrode connected or capacitance-coupled to one end of the radiation electrode, and a current-feeding electrode in a portal shape formed on a side surface separate from the radiation electrode with a gap; the current-feeding electrode having a current-feeding portion at one end, a grounding portion at the other end, and a portion substantially in alignment with the radiation electrode between them; and the length of the aligning portion, a gap width or a portal shape being able to be properly set such that capacitance owned by the current-feeding electrode and inductance can be adjusted for easily achieving impedance matching.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Inverted-F antenna
InactiveUS7183980B2Increase bandwidth and efficiencyLow capacitance rateSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMetal stripsMicrowave
An inverted-F antenna comprises a microwave plate, a dielectric substrate, a radiating metal sheet, a ground surface, a shorting metal strip, and a feeding metal strip. The radiating metal sheet comprises a connecting metal sheet, first, second, and third child radiating metal sheets, a matching metal sheet, a slot, a shorting point, and a feeding point. The first child radiating metal sheet is for forming a low frequency operating mode. The second child radiating metal sheet is for forming a high frequency operating mode. The third child radiating metal sheet is for adjusting operating frequency and bandwidth of the second operating mode. The slot, the shorting point, and the feeding point are for adjusting impedance matching. The grounding surface is for increasing the operating bandwidth of the low frequency operating mode. The shorting metal sheet and the feeding metal sheet are for grounding the antenna and signal transmission.
Owner:ADVANCED CONNECTEK INC
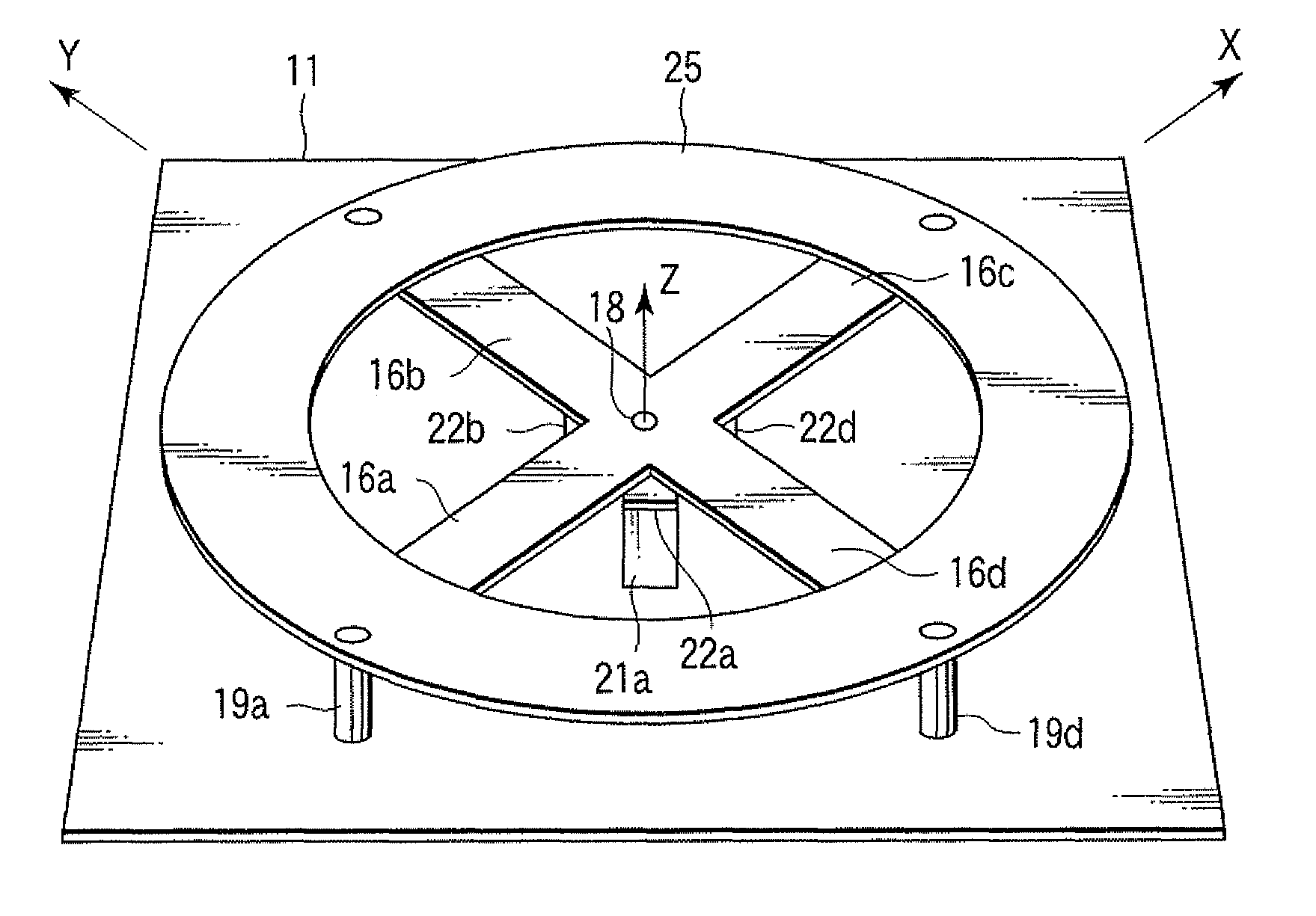
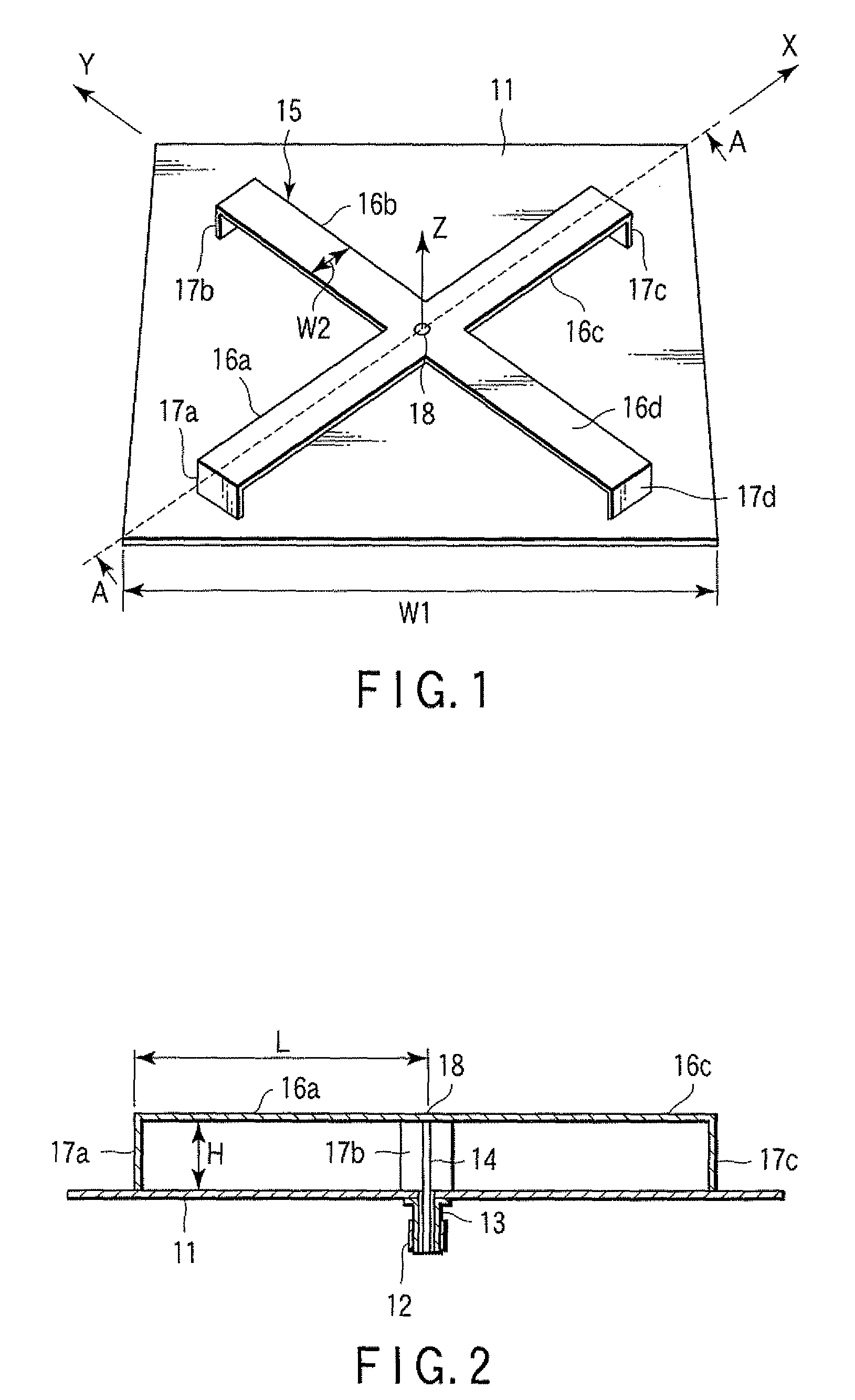
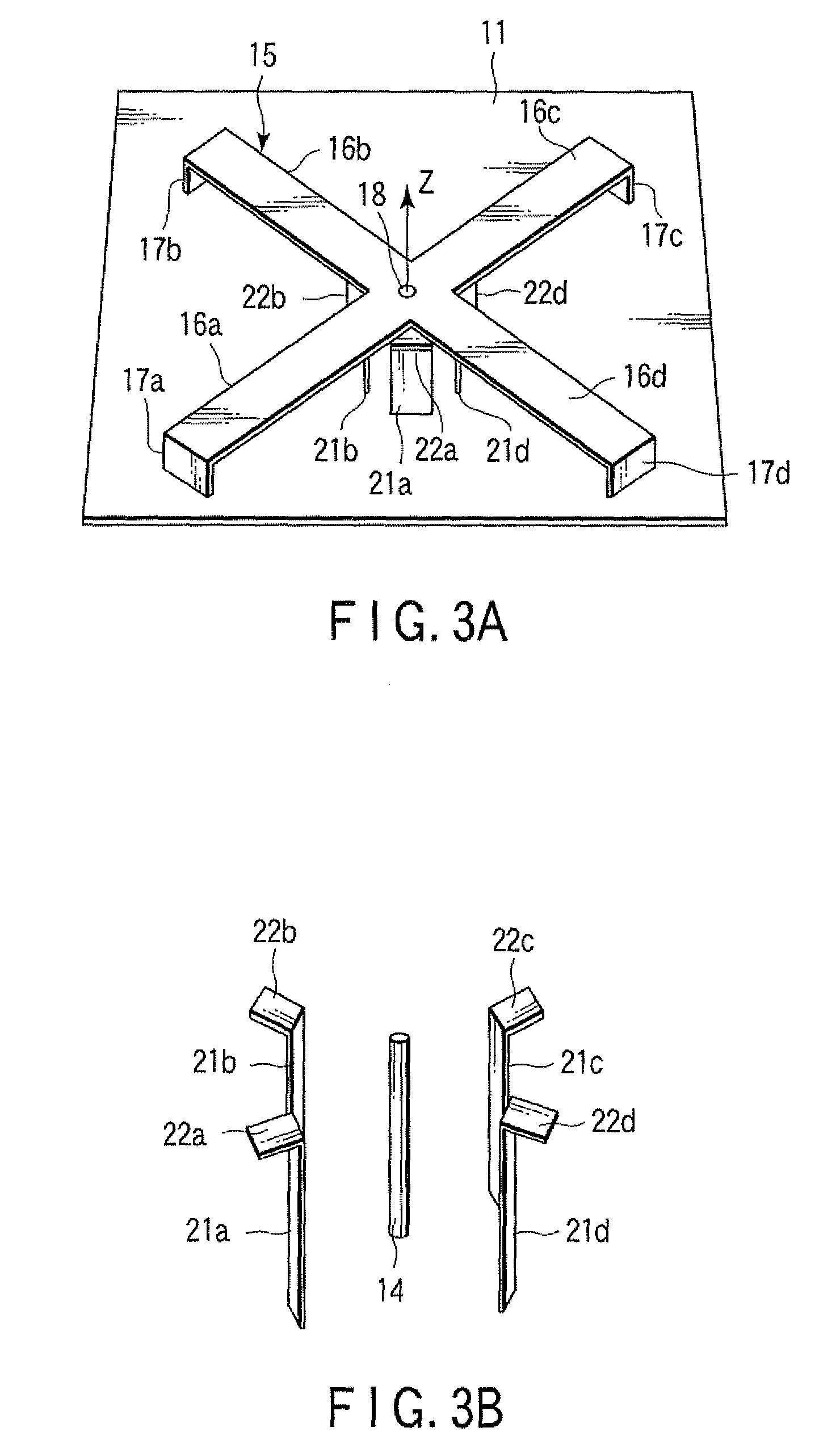
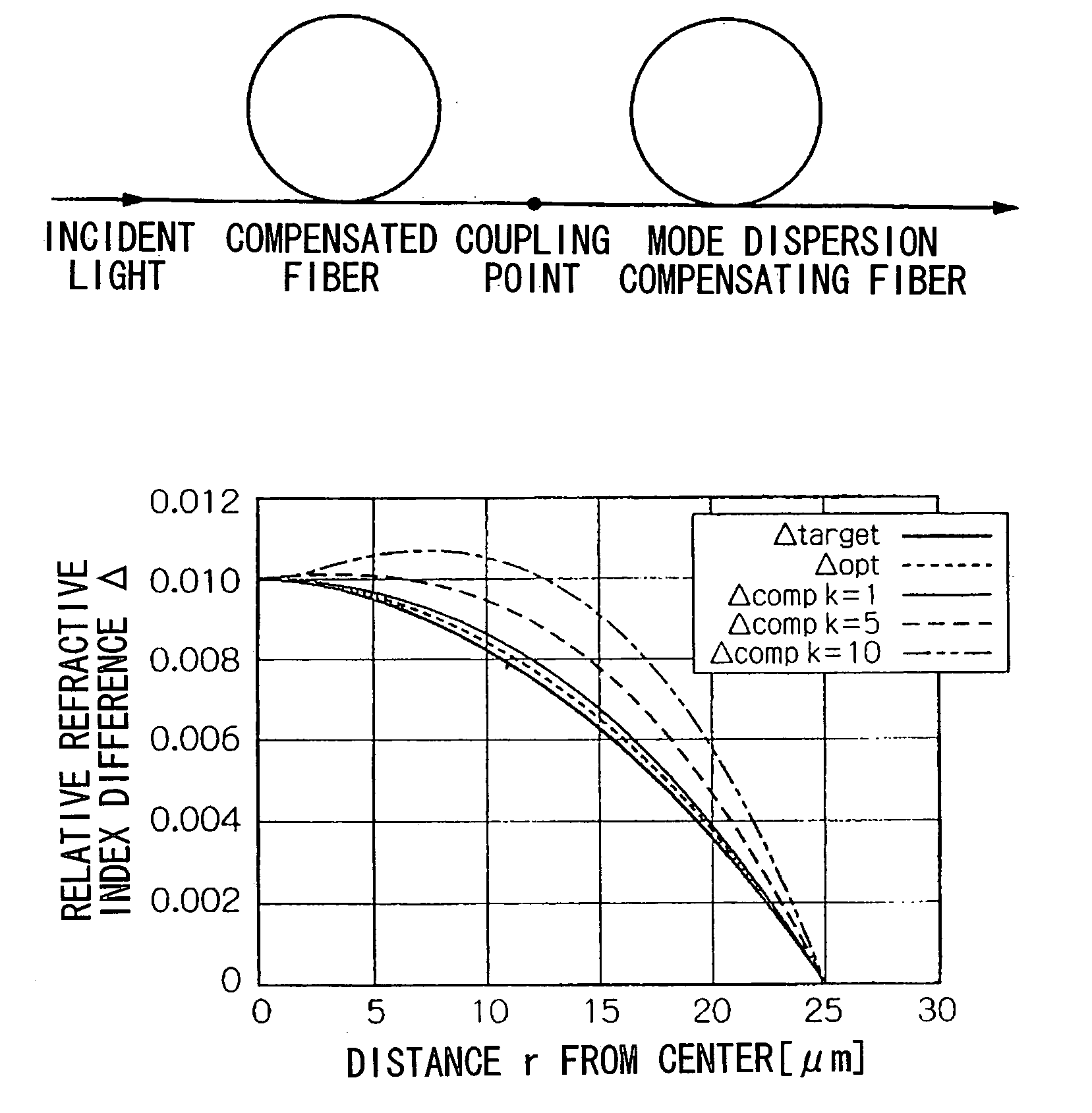
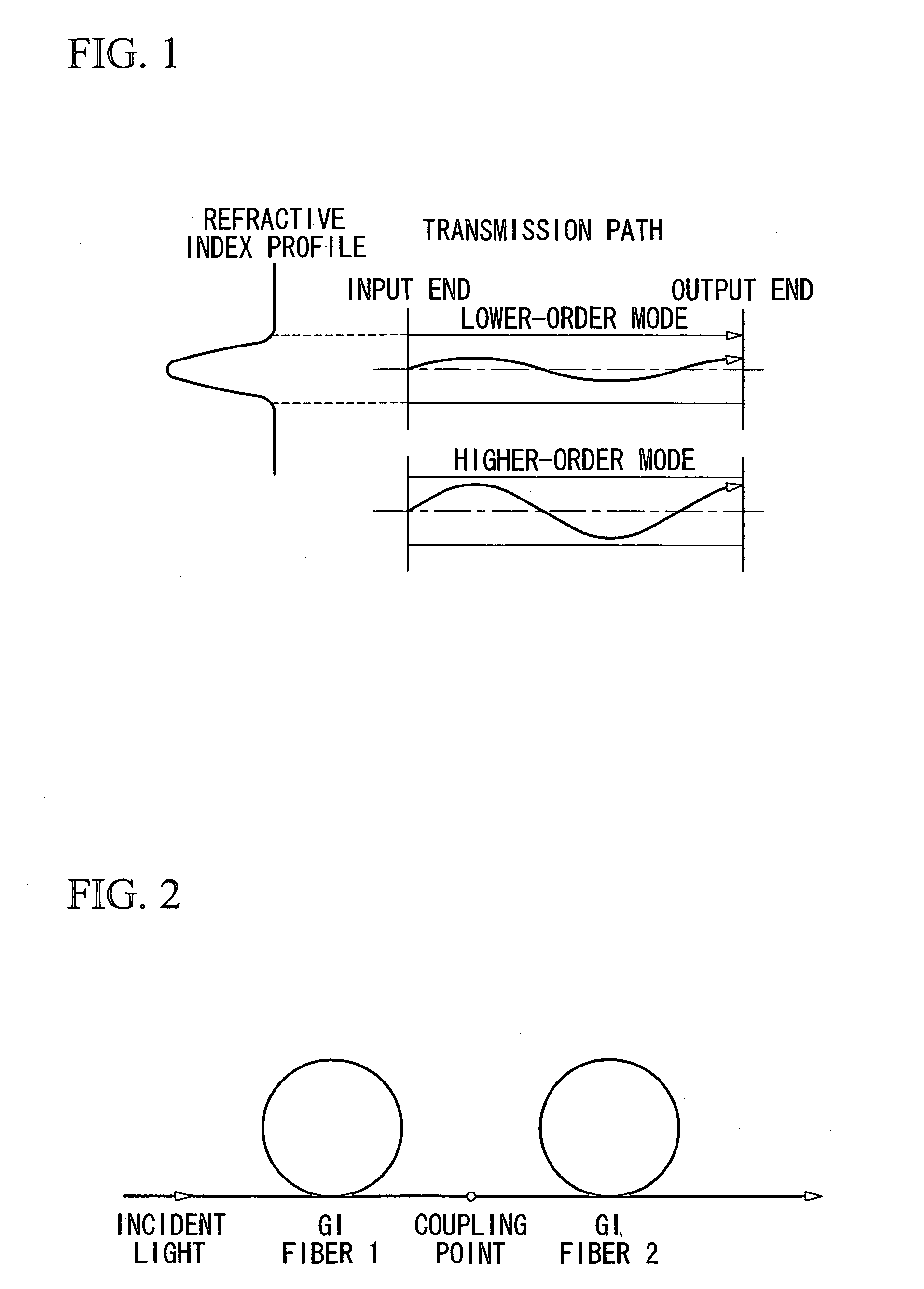
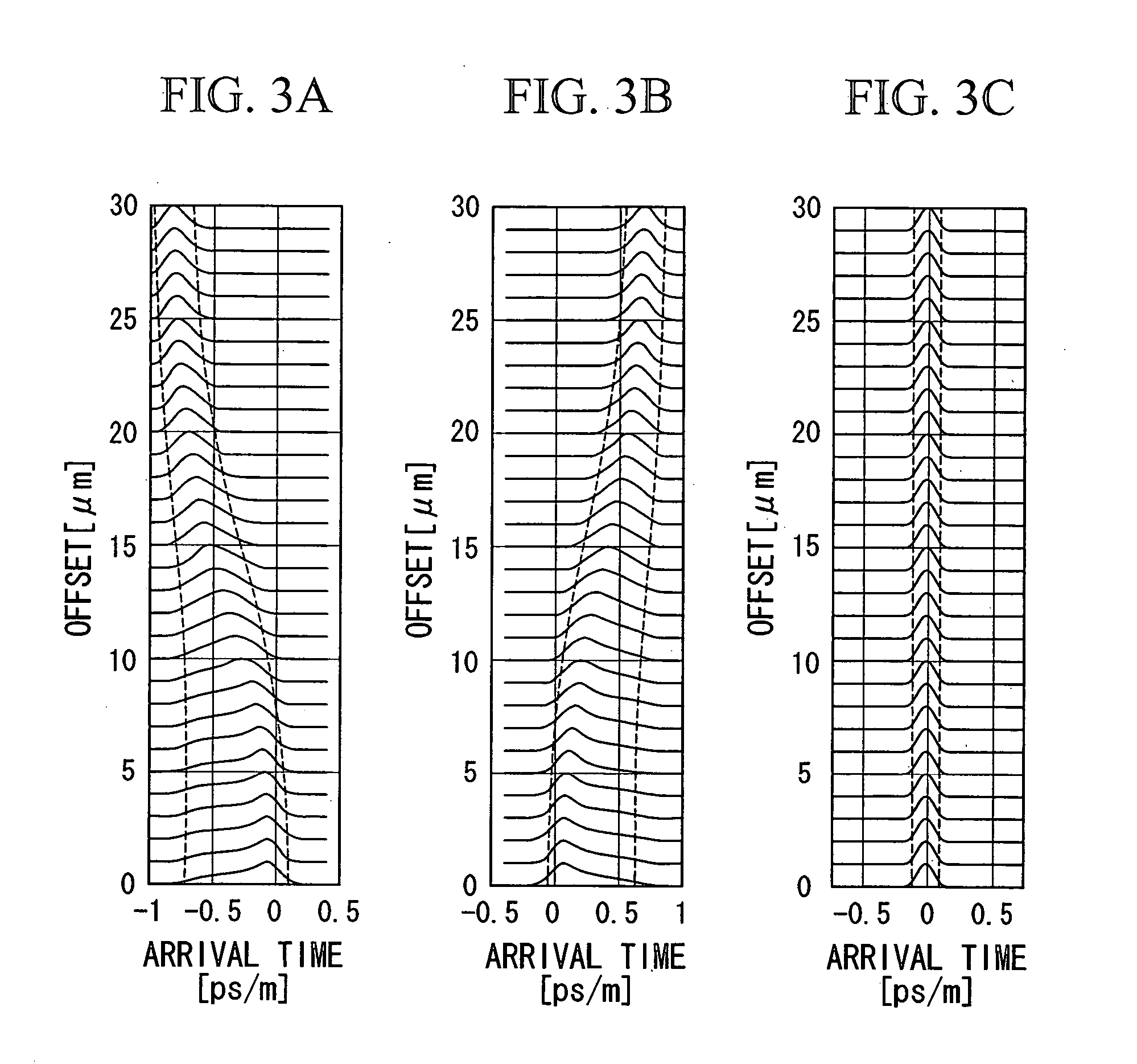
Method for compensating modal dispersion in multimode optical fiber transmission path
ActiveUS20060034573A1Well formedFormed over a long distance easily and at low-costCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesModal dispersionEngineering
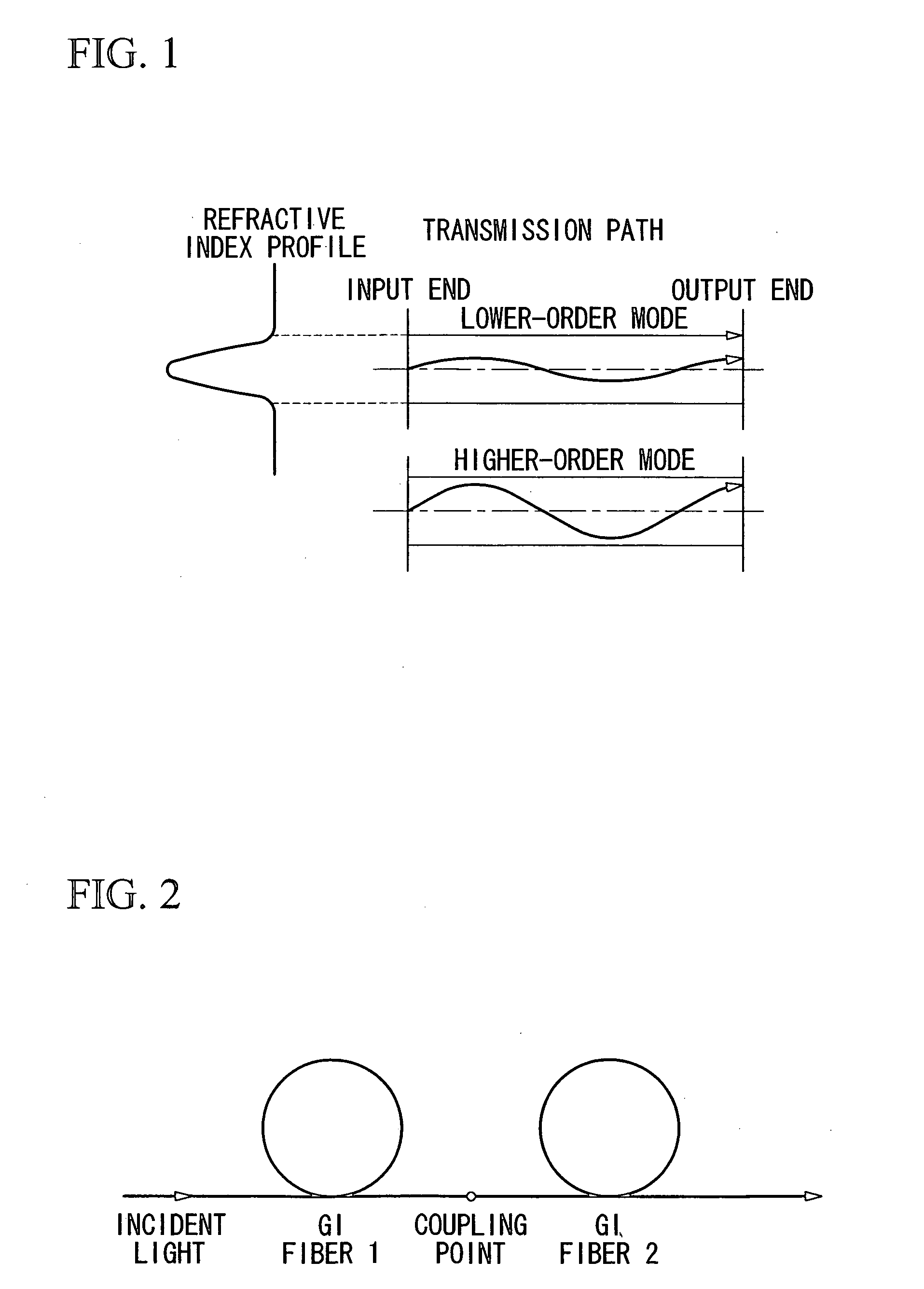
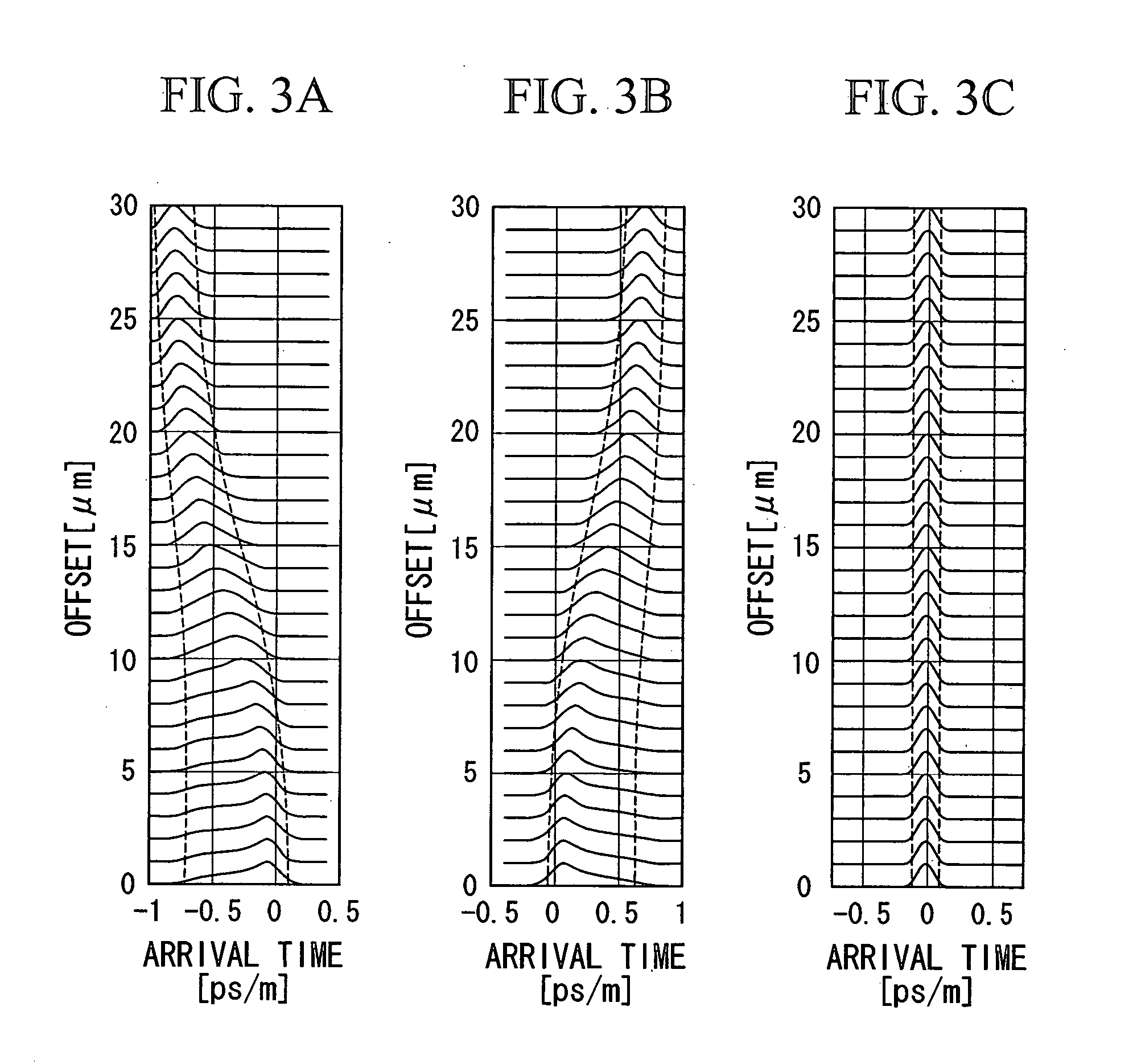
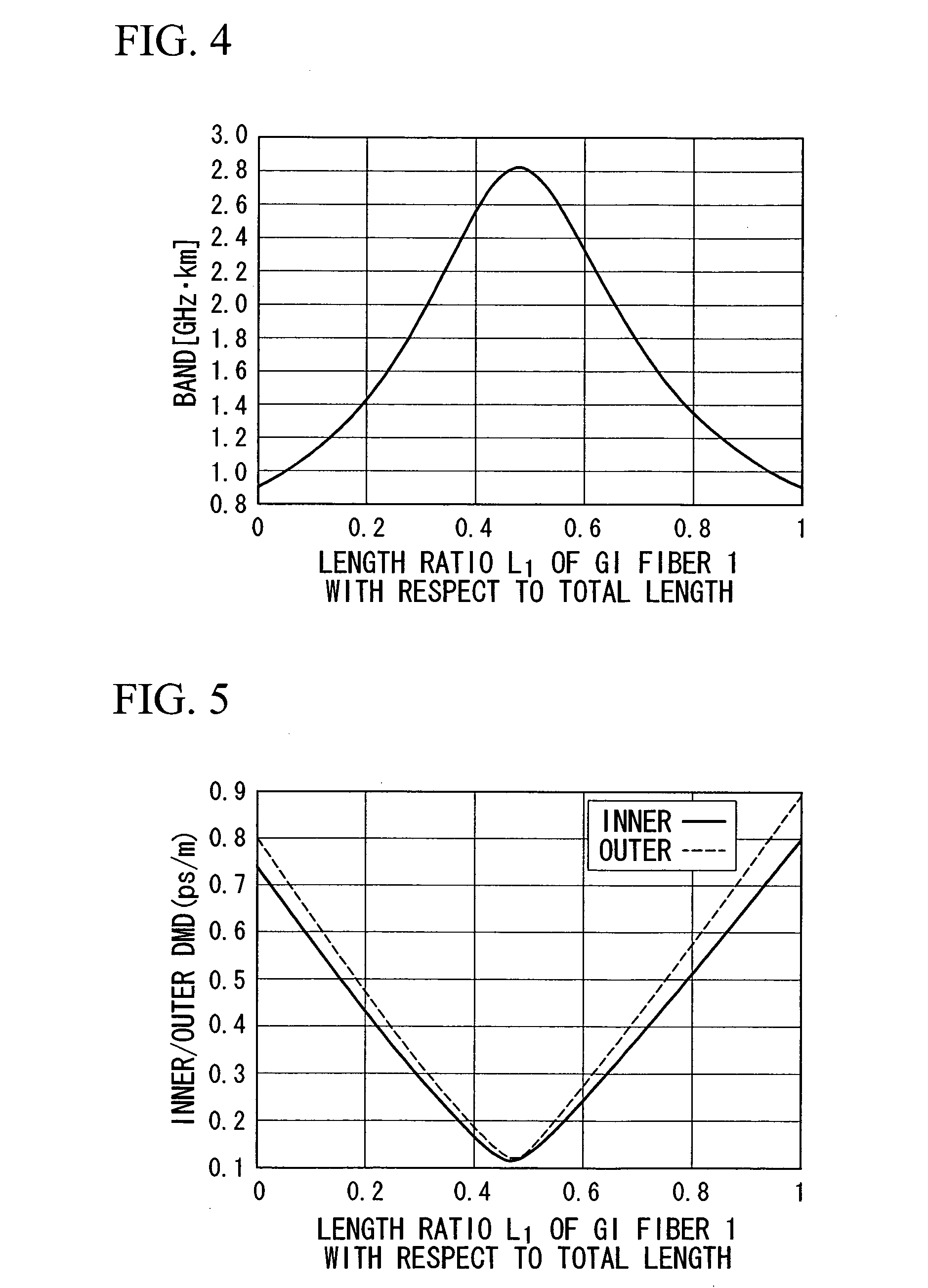
In an optical transmission path including multimode optical fibers, modal dispersion is reduced so that signal light can be transmitted at high speed and across a broad band, at low-cost and over a long distance. To reduce modal dispersion, when the transmission path is constructed by coupling a plurality of multimode optical fibers, a length ratio for the multimode optical fibers that obtains the maximum band of the optical transmission path is determined, and the multimode optical fibers are coupled according to this length ratio. The multimode optical fibers that are used have specific refractive index profiles as mode dispersion-compensating fibers. The compensated fiber and the mode dispersion-compensating fiber are coupled with specific lengths.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
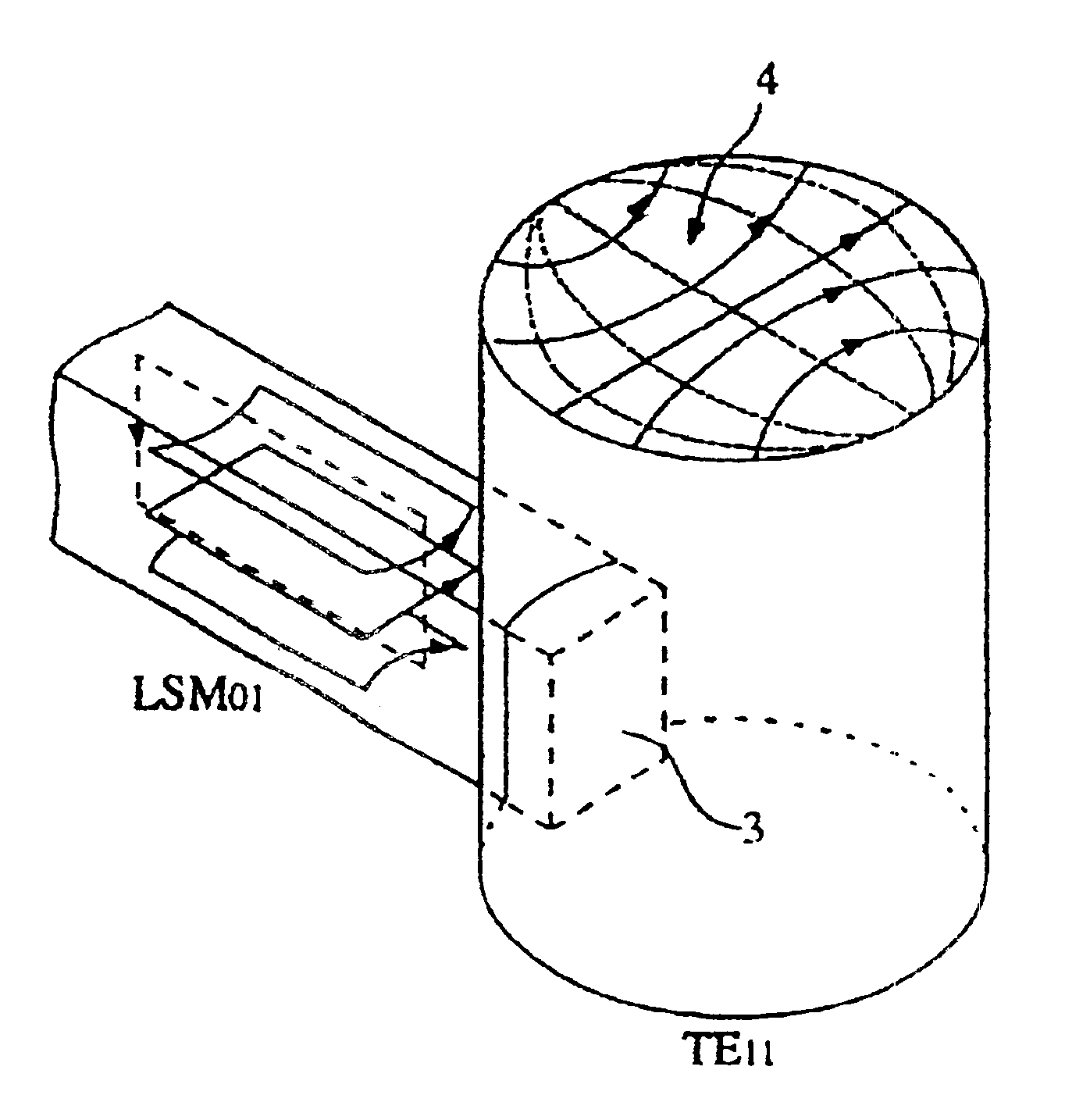
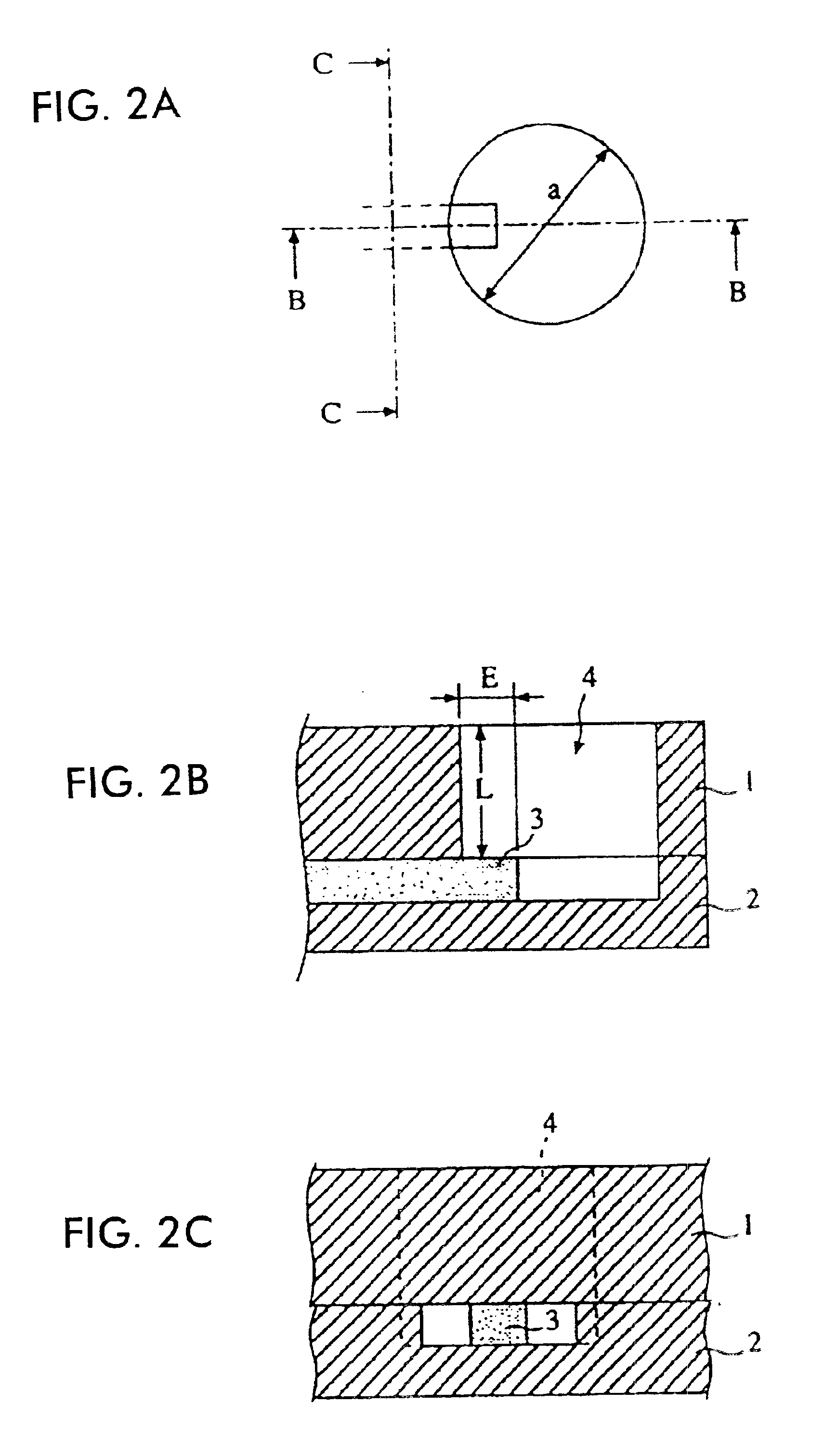
Line transition device between dielectric waveguide and waveguide, and oscillator, and transmitter using the same
InactiveUS6489855B1Avoid radiationReduce lossResonatorsWaveguidesElectrical conductorHollow waveguide
A line transition device which intervenes between a non radiative dielectric waveguide and a hollow waveguide for example, includes a dielectric waveguide having a dielectric strip held by a pair of conductors which face each other, and a waveguide, wherein a part of the dielectric strip of the dielectric waveguide is adjacent to or inserted in the hollow waveguide.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Optical fiber tape core
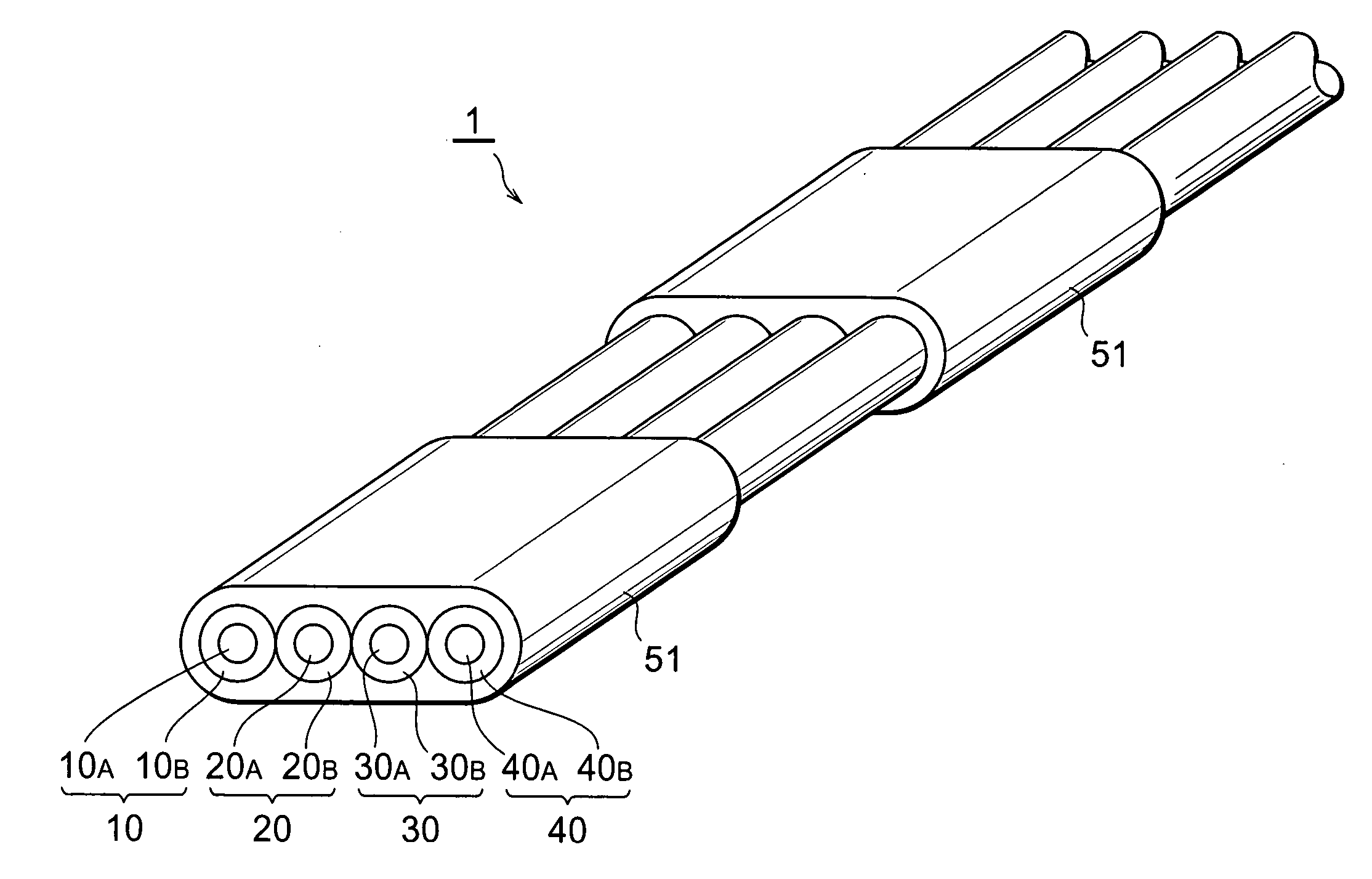
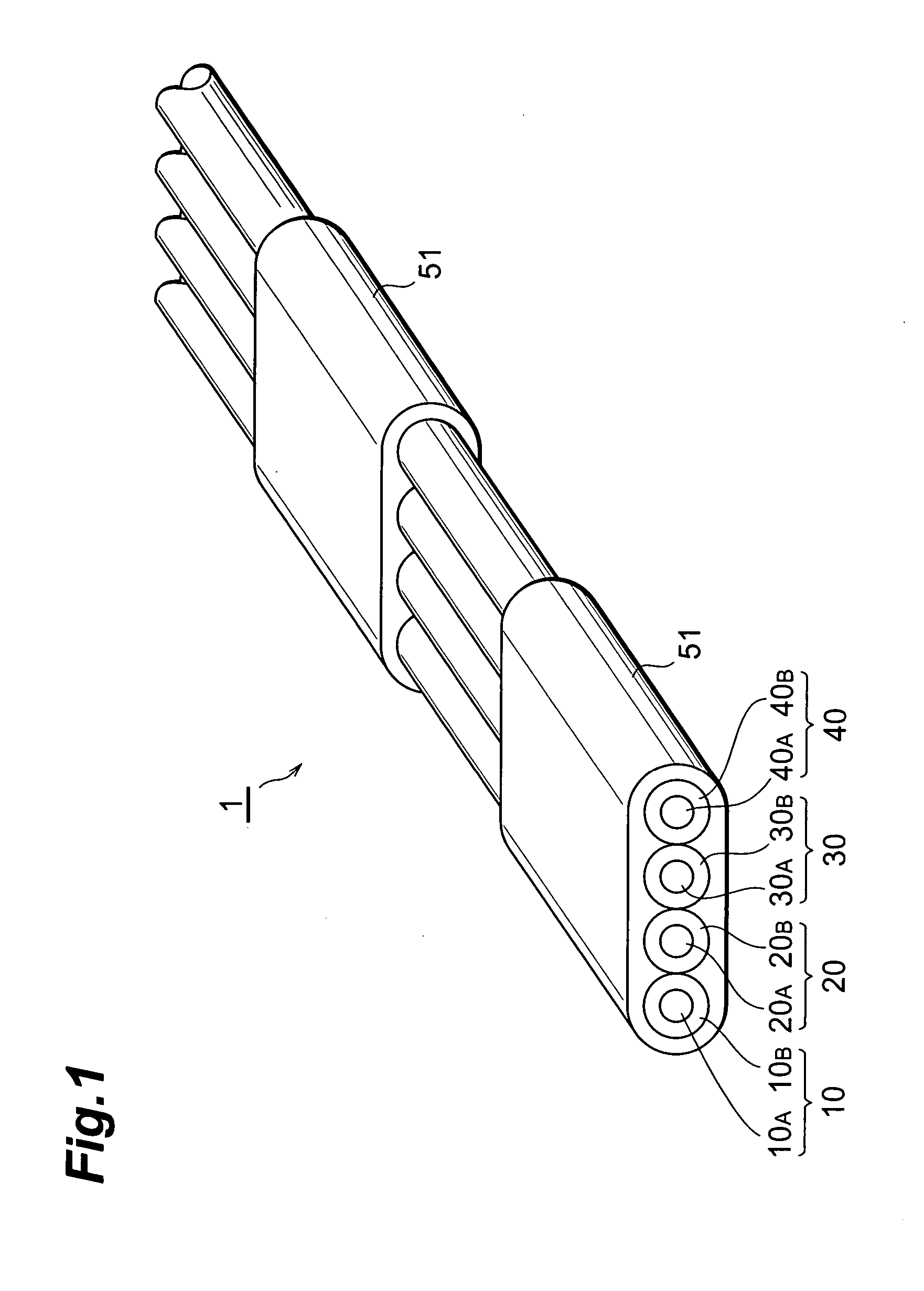
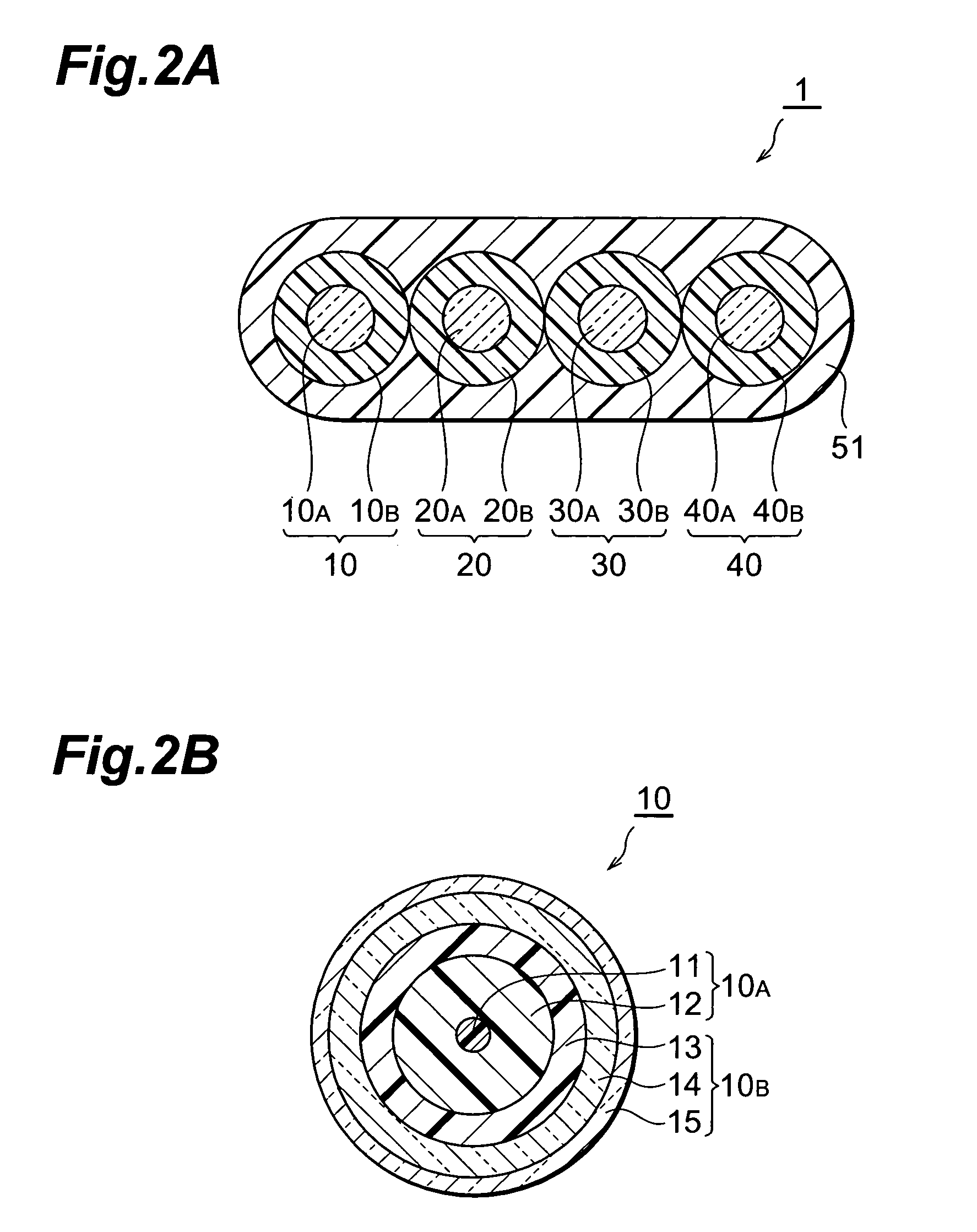
InactiveUS20050226573A1Quality improvementWide bandGlass optical fibreCoupling light guidesBand shapeEngineering
In an optical fiber ribbon 1 according to the present invention, four optical fibers 10, 20, 30 and 40 are arranged in parallel to each other in a plane, a part of the periphery of these four optical fibers is covered with a ribbon matrix 51, but no rest thereof is covered with the ribbon matrix. First areas covered with the ribbon matrix 51 and second areas uncovered with the ribbon matrix alternate with each other along the longitudinal direction thereof. Alternatively, the optical fiber ribbon 1 is covered with the ribbon matrix over its entire length. In the glass section of each optical fibers, the mode field diameter defined by the definition of Petermann-I at a wavelength of 1.55 μm is 8 μm or less, and the cable cutoff wavelength is 1.26 μm or less.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Apparatus and method for finding the direction of signal source
InactiveUS20130271323A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove accuracyPosition fixationDirection findersPhase differenceControl signal
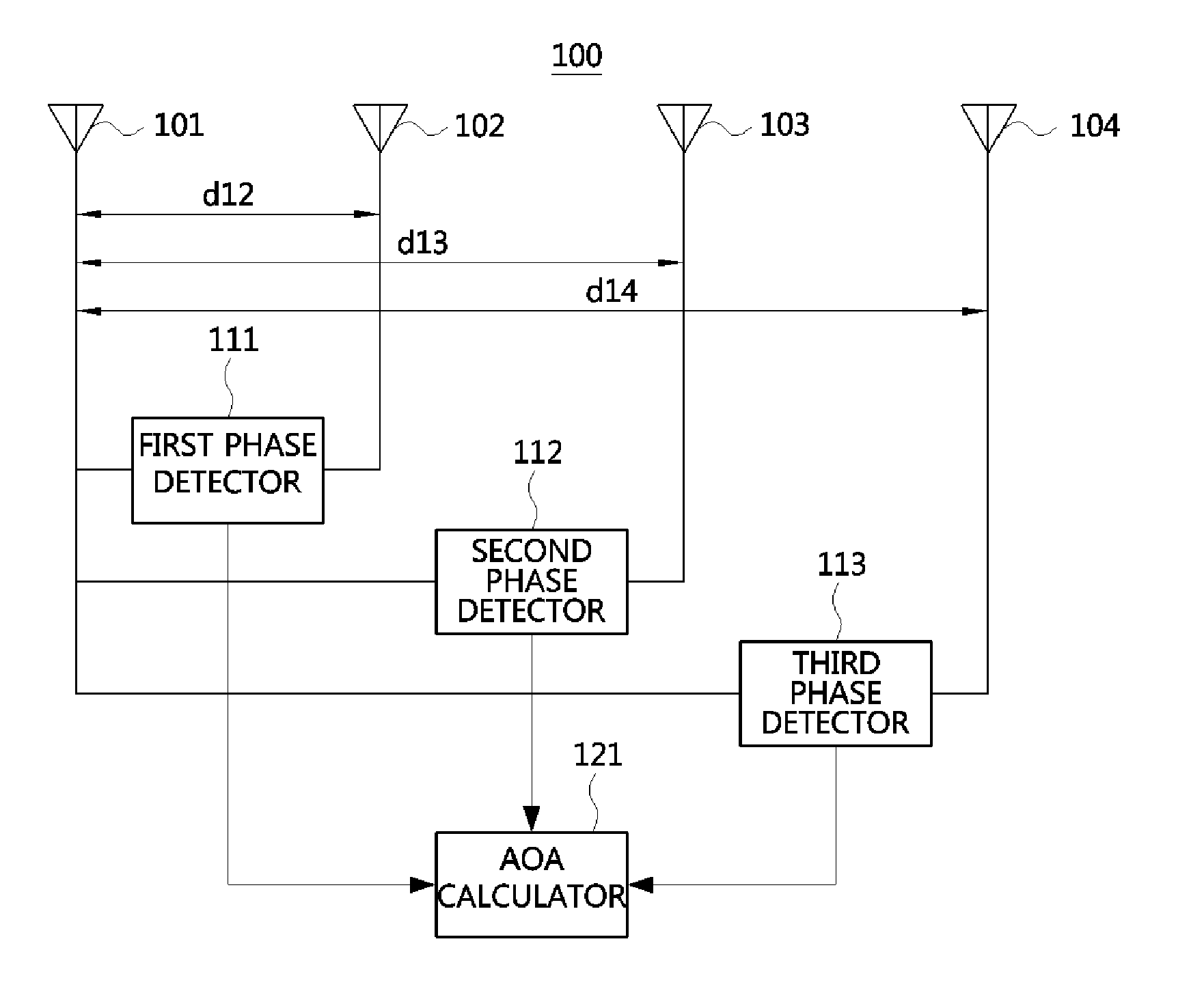
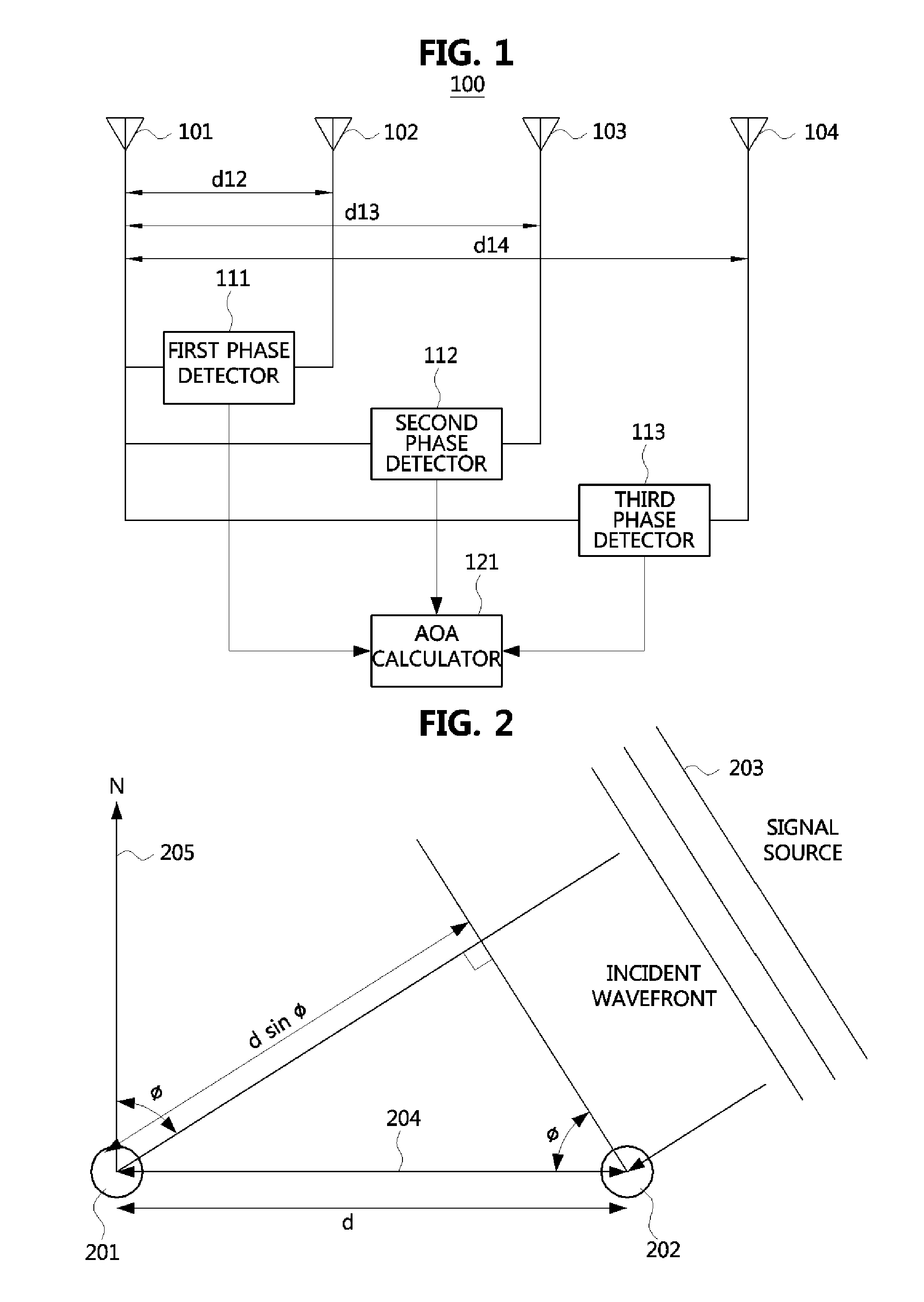
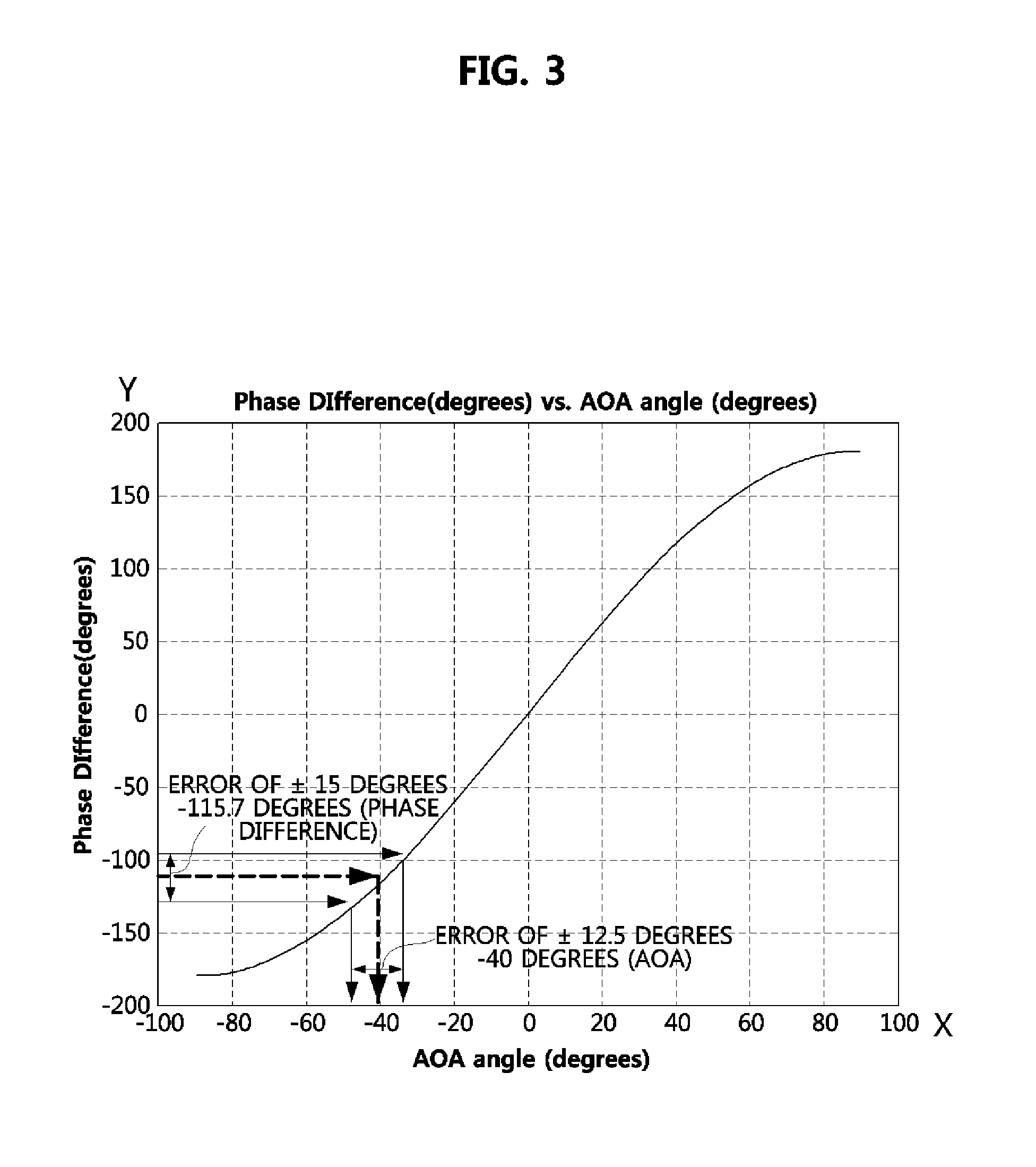
The direction finding apparatus includes: a first and second antennas configured to receive radio signals respectively; a travel guide unit mechanically coupled with the first and second antennas and configured to provide a travel path along which the first and second antennas are linearly movable; a driver configured to provide a driving force for linearly moving at least one antenna of the first and second antennas in response to a driving control signal; a driving controller configured to provide the driving control signal, wherein the driving control signal is used to separate the first and second antennas from each other by a predetermined distance; and a direction finding unit configured to calculate an angle of arrival (AOA) of radio signals respectively received through the first and second antennas, based on the phase difference between the radio signals, and the predetermined distance.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Antenna device
InactiveUS7176837B2Increase freedomHigh gainSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorBand shape
Owner:AGC INC
Line transition device between dielectric waveguide and waveguide, and oscillator, and transmitter using the same
InactiveUS6867660B2Avoid radiationReduce lossResonatorsWaveguidesElectrical conductorHollow waveguide
A line transition device which intervenes between a non radiative dielectric waveguide and a hollow waveguide for example, includes a dielectric waveguide having a dielectric strip held by a pair of conductors which face each other, and a waveguide, wherein a part of the dielectric strip of the dielectric waveguide is adjacent to or inserted in the hollow waveguide.
Owner:KITURAMI BOILER
Microstrip patch antenna having high gain and wideband
ActiveUS7099686B2High gainHigh widebandSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectromagnetic couplingMicrostrip patch antenna
A microstrip patch antenna having high gain and wide band is disclosed. The microstrip patch antenna includes: a first patch antenna layer for radiating a energy supplied from transmitting / receiving feeding circuit and a first radiation patch electrically coupled to the first dielectric layer and supplying the energy to a receiving feeding circuit electrically coupled with the first radiation patch, wherein the energy is supplied by electromagnetic coupling of a first parasitic patch and second parasitic patch; a second patch antenna layer for improving impedance bandwidth of energy received through the first parasitic patch arranged in between the second dielectric layer and the third dielectric layer and radiating the improved impedance bandwidth; and a third patch antenna layer for improving a gain of the energy received through the second parasitic patch arraigned in between the fourth dielectric layer and the fifth dielectric layer.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Antenna, antenna apparatus, and communication device
InactiveUS20080316111A1Wide bandLow VSWRSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorAntenna element
An antenna is provided which includes a first antenna element having at least one base and a conductor penetrating through the base and a second antenna element having a conductor portion having a shape of a plate or a line and a connecting conductor, wherein a first end of the conductor of the first antenna element is connected to the connecting conductor of the second antenna element, and the connecting conductor of the second antenna element is connected to a partway on the conductor portion of the second antenna element.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Waveguide slotted array antenna
ActiveUS20180358709A1Reduce size of antennaLower complexityRadiating elements structural formsIndividually energised antenna arraysRadiationWideband
A waveguide slotted array antenna comprises a feed layer and a radiation layer, wherein the feed layer is located below the radiation layer, and the radiation layer comprises a first radiation unit, a second radiation unit, a third radiation unit and a fourth radiation unit which are stacked from bottom to top; the first radiation unit comprises a first flat metal plate and a first radiation array arranged on the first flat metal plate, the second radiation unit comprises a second flat metal plate and a second radiation array arranged on the second flat metal plate, the third radiation unit comprises a third flat metal plate and a third radiation array arranged on the third flat metal plate, and the fourth radiation unit comprises a fourth flat metal plate and a fourth radiation array arranged on the fourth flat metal plate. The waveguide slotted array antenna has the advantages of low sidelobes and low cost while ensuring broad bands and high gains, and can be made small.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Antenna apparatus
ActiveUS8193989B2Low profileWide bandAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsEngineeringShort circuit
Owner:HITACHI KOKUSAI YAGI SOLUTIONS +1
Method for compensating modal dispersion in multimode optical fiber transmission path
ActiveUS7139457B2Well formedFormed over a long distance easily and at low-costCladded optical fibreCoupling light guidesFiberModal dispersion
In an optical transmission path including multimode optical fibers, modal dispersion is reduced so that signal light can be transmitted at high speed and across a broad band, at low-cost and over a long distance. To reduce modal dispersion, when the transmission path is constructed by coupling a plurality of multimode optical fibers, a length ratio for the multimode optical fibers that obtains the maximum band of the optical transmission path is determined, and the multimode optical fibers are coupled according to this length ratio. The multimode optical fibers that are used have specific refractive index profiles as mode dispersion-compensating fibers. The compensated fiber and the mode dispersion-compensating fiber are coupled with specific lengths.
Owner:FUJIKURA LTD
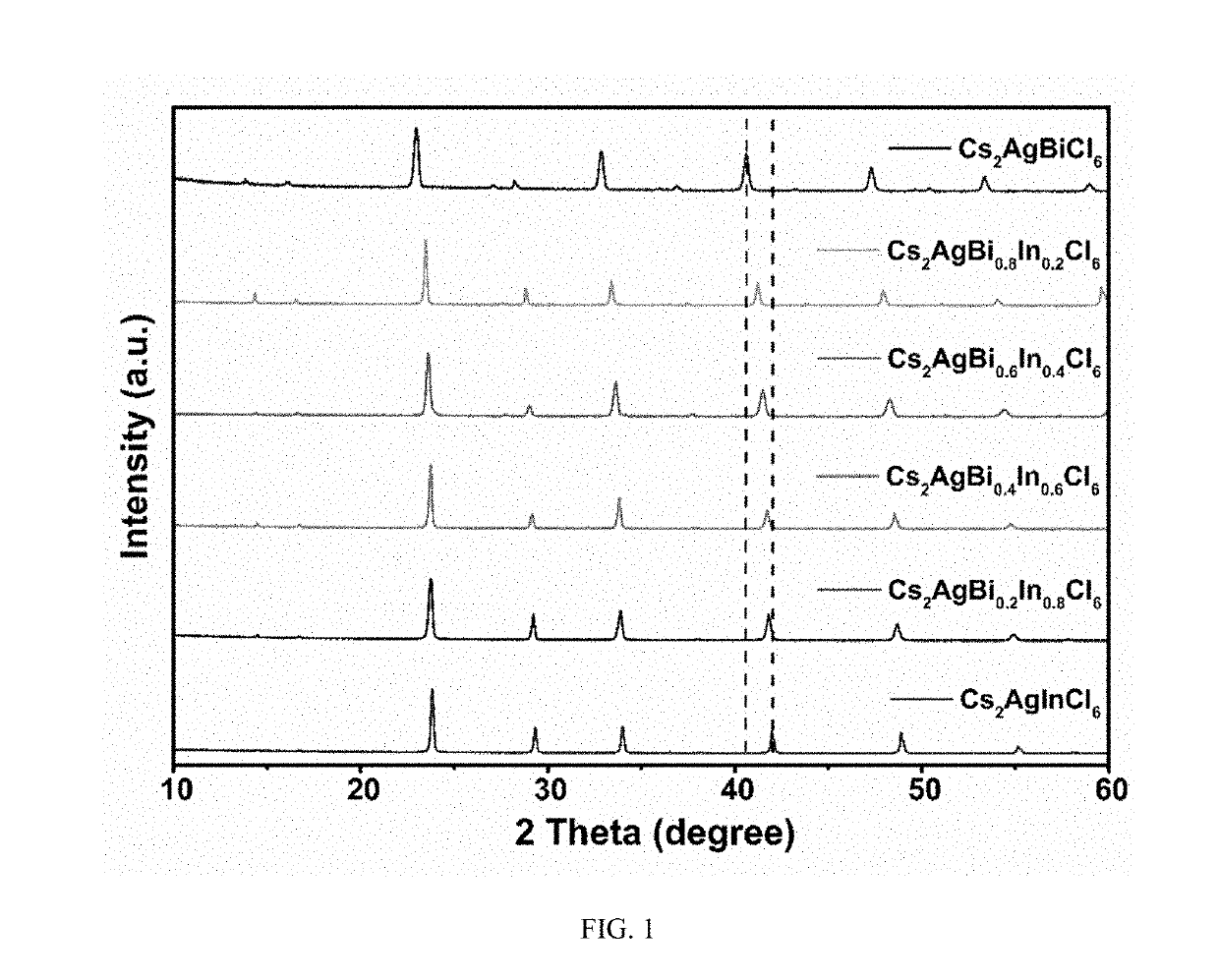
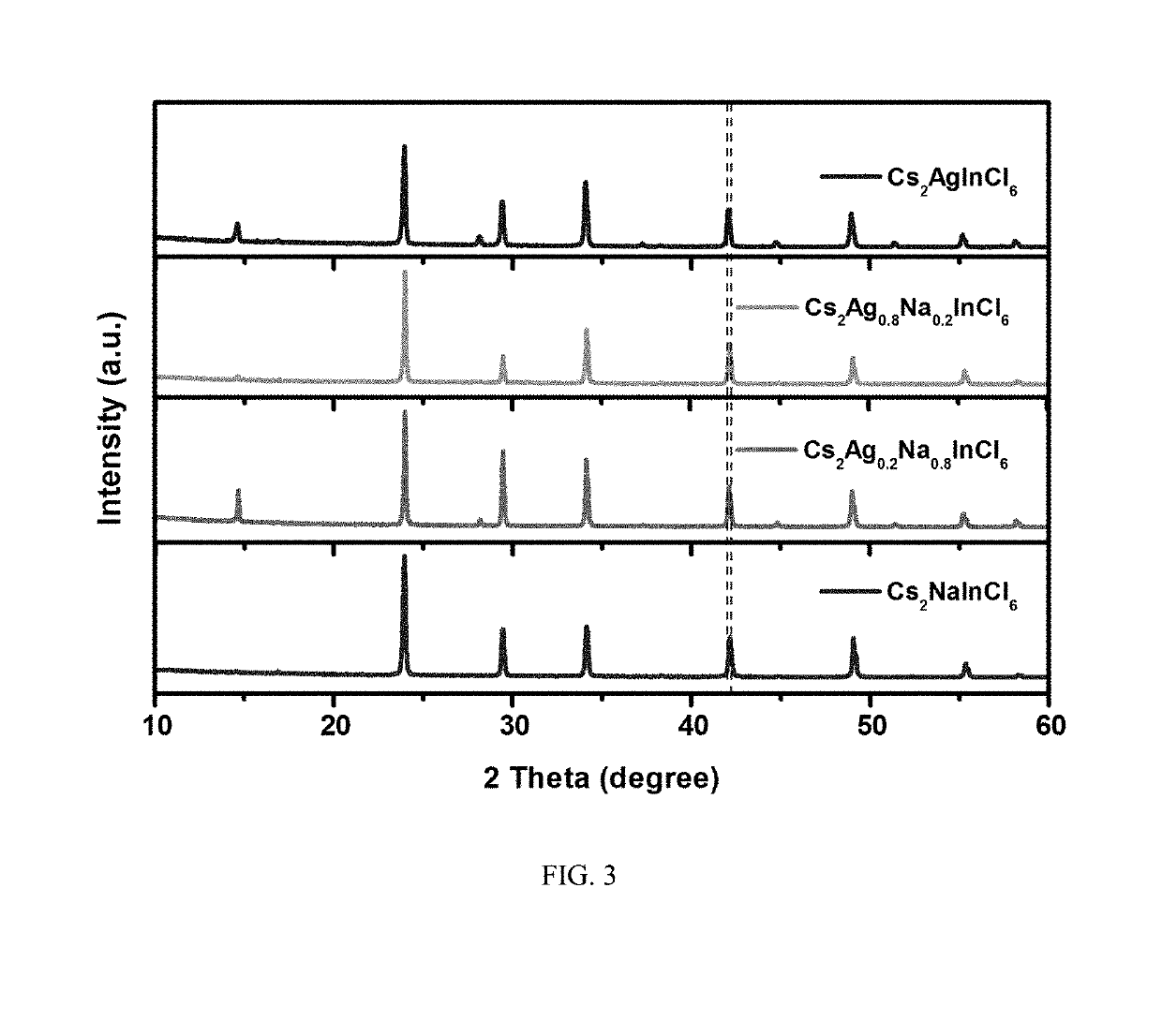
Multi-element perovskite material as well as preparation and luminescent application thereof
ActiveUS20190330074A1High fluorescence yieldImprove luminous performancePolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPhotoluminescenceSingle crystal
The present invention discloses a multi-element perovskite material, and a single crystal, powder and a film thereof, as well as the applications thereof in photoluminescence and electroluminescence, in which the multi-element perovskite material is a multi-element fully-inorganic salt of non-lead metal halide and has a perovskite structure; and the chemical formula of the multi-element perovskite material is Cs2NaxAg1-xInyBi1-yCl6, wherein 0≤x≤1, 0≤y≤1. Meanwhile, based on the very strong self-trapped excitors states of the double perovskite, the present invention proposes a high-efficiency single-phase broadband phosphor and an electroluminescent device.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Antenna array
ActiveUS20190058260A1Small arraying intervalWide bandIndividually energised antenna arraysModular arraysEngineeringAntenna array
An antenna array includes: an electrically conductive member having an electrically conductive surface in which a plurality of slots are open; a plurality of electrically-conductive ridge pairs on the electrically conductive surface, each pair protruding from edges of the central portion of a corresponding one of the plurality of slots. As viewed along a direction that the central portion of each slot extends, at least a portion of the first gap between the first ridge pair and at least a portion of the second gap between the second ridge pair overlap each other, with no other intervening electrically-conductive member therebetween; or at least a portion of the first ridge pair and at least a portion of the second ridge pair overlap each other, with no other intervening electrically-conductive member therebetween.
Owner:NIDEC ELESYS +1
Antenna
ActiveUS20070159398A1WiderIncrease transfer speedAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsCouplingElectrical and Electronics engineering
An antenna comprises a ground element, a first transmission element, a feed element, a second transmission element and a third transmission element. The first transmission element is electrically connected to the ground element, wherein the first transmission element comprises at least one coupling portion, a first side and a second side. The feed element corresponds to the coupling portion. The second transmission element corresponds to the first side and is electrically connected to the ground element. The third transmission element corresponds to the second side and is electrically connected to the ground element. When a first wireless signal is transmitted, the feed element couples to the first transmission element to transmit the first wireless signal. When a second wireless signal is transmitted, the feed element couples to the first transmission element, and the second and third transmission elements couple to the first transmission element to transmit the second wireless signal.
Owner:WISTRON NEWEB
Multilayer capacitor and electronic device
ActiveUS7667950B2Increase the number ofLower impedanceFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricEngineeringDielectric layer
A multilayer capacitor has a laminate body in which a first internal electrode and a second internal electrode are alternately laminated with a dielectric layer in between, a first terminal electrode provided on one end side of the laminate body, and a second terminal electrode provided on the other end side of the laminate body. The first internal electrode has a first lead portion connected to the first terminal electrode. The second internal electrode has a second lead portion connected to the second terminal electrode. The first internal electrode consists of plural types of first internal electrodes and the plural types of first internal electrodes have their respective first lead portions at different positions. Distances between the first lead portions of the respective types of the first internal electrodes and the second lead portion are different from each other.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
90-degree hybrid
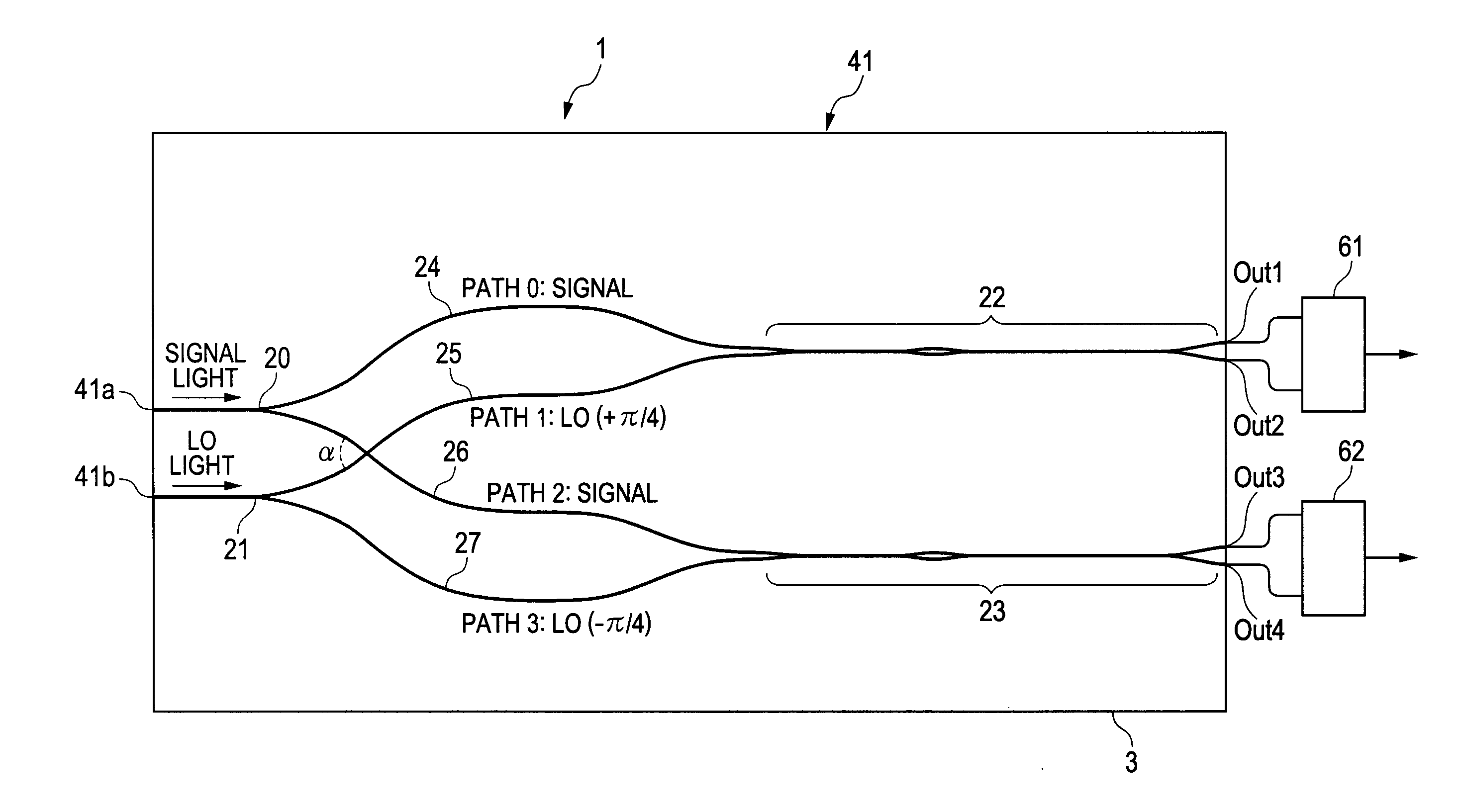
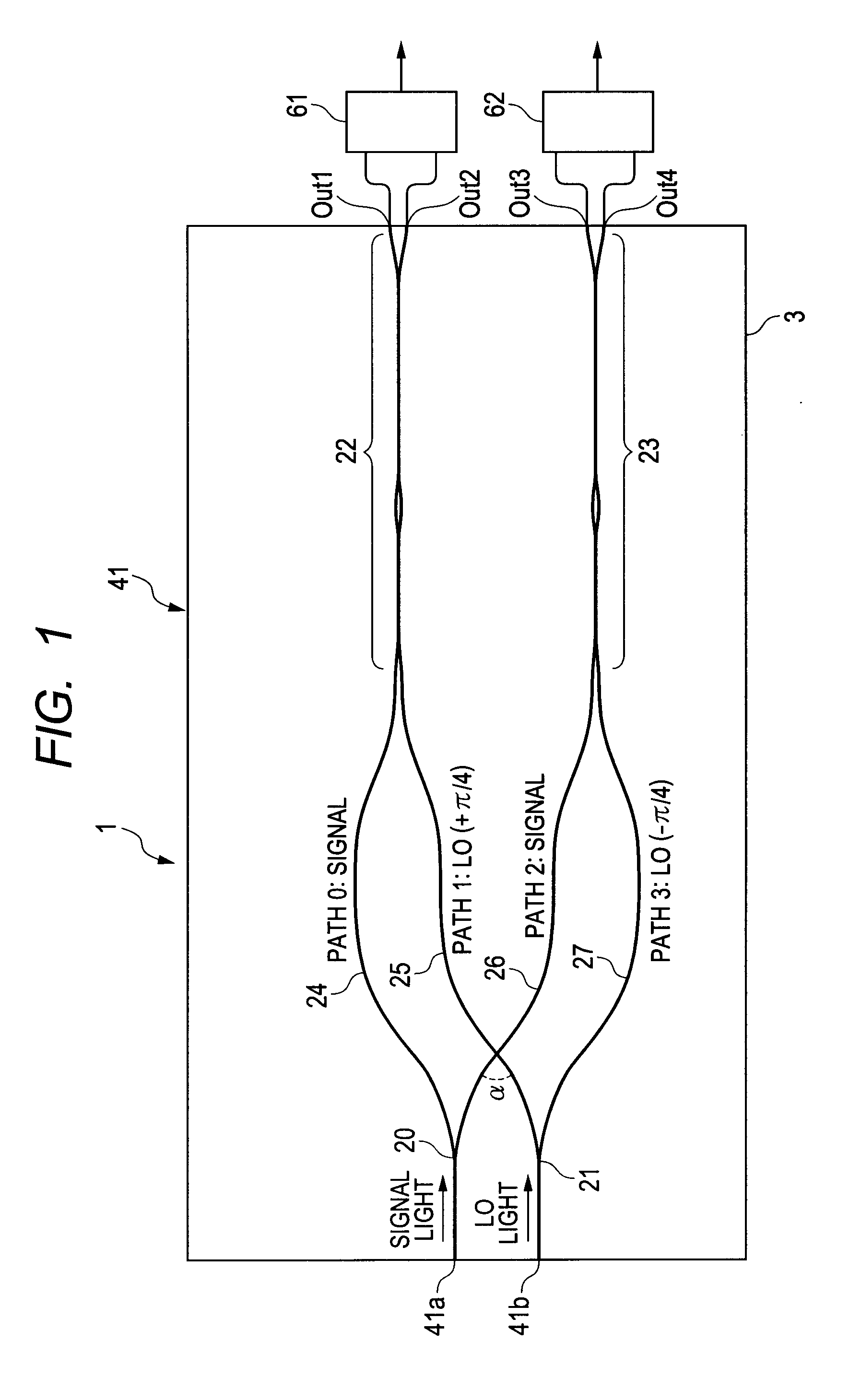
ActiveUS20120224812A1Guaranteed uptimeWide bandModulated-carrier systemsCoupling light guidesMiniaturizationSignal light
The present invention provides a 90-degree hybrid capable of miniaturization and also capable of a stable operation in a wide band. According to an embodiment of the present invention, a PLC-type 90-degree hybrid comprises: a PLC chip having a planar lightwave circuit formed therein; and a 90-degree hybrid circuit formed in the planar lightwave circuit, mixing a modulated signal light and an LO light to separate the signal light into quadrature components I and Q, and outputting the same. The 90-degree hybrid circuit includes: two Y-branch couplers each branching the signal light and the LO light; and two wavelength-independent directional couplers which cause LO lights passing through two paths and signal lights passing through two paths to interfere with each other, respectively. The above-described paths include waveguides having mutually inverted shapes and waveguides having an identical shape, and have a shape substantially symmetrical with respect to the signal light.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Surface acoustic wave resonator, surface acoustic wave device, and communications equipment
ActiveUS20070024397A1Reduced insertion lossLimit on characteristicImpedence networksAcoustic waveSurface acoustic wave resonators
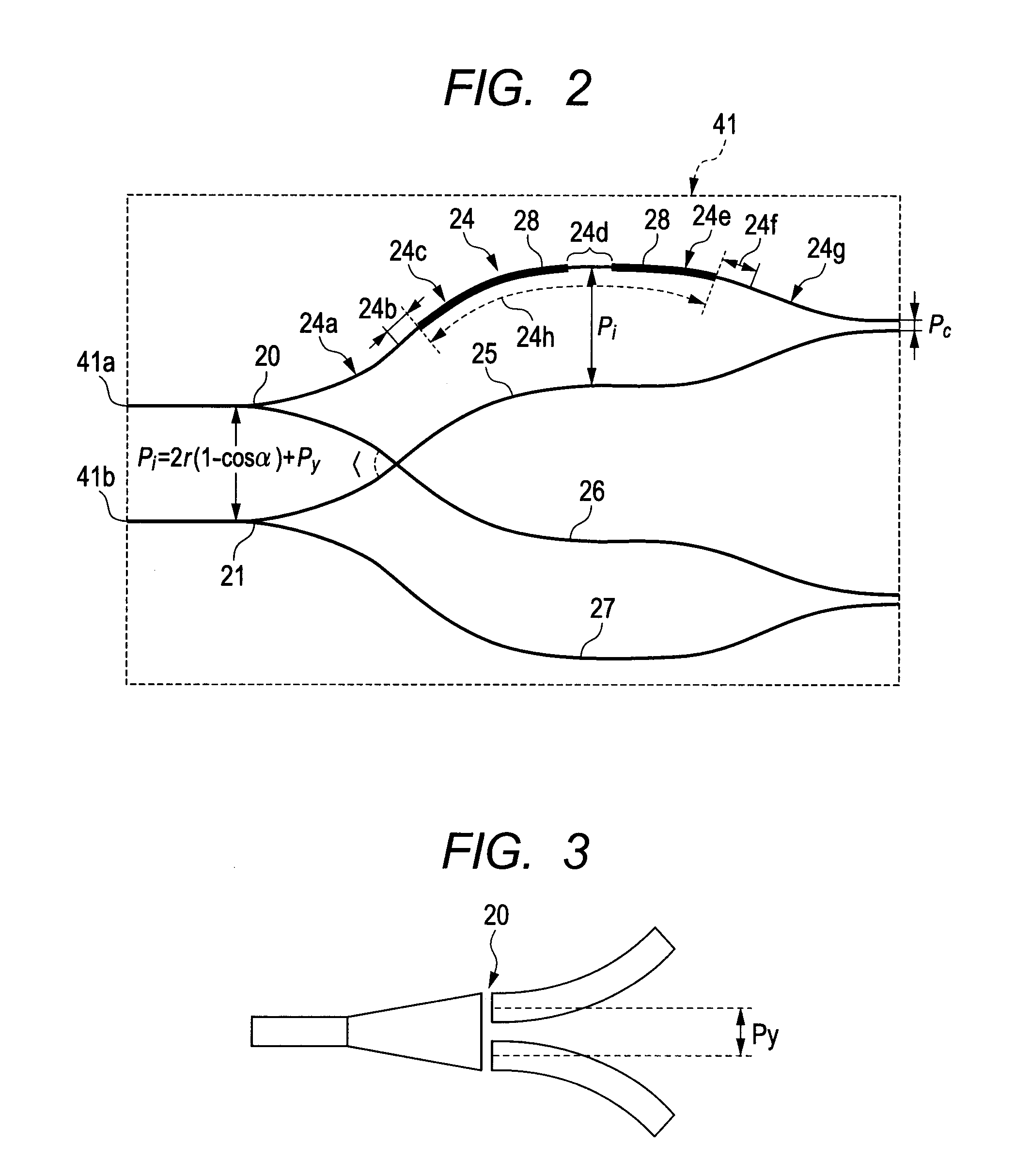
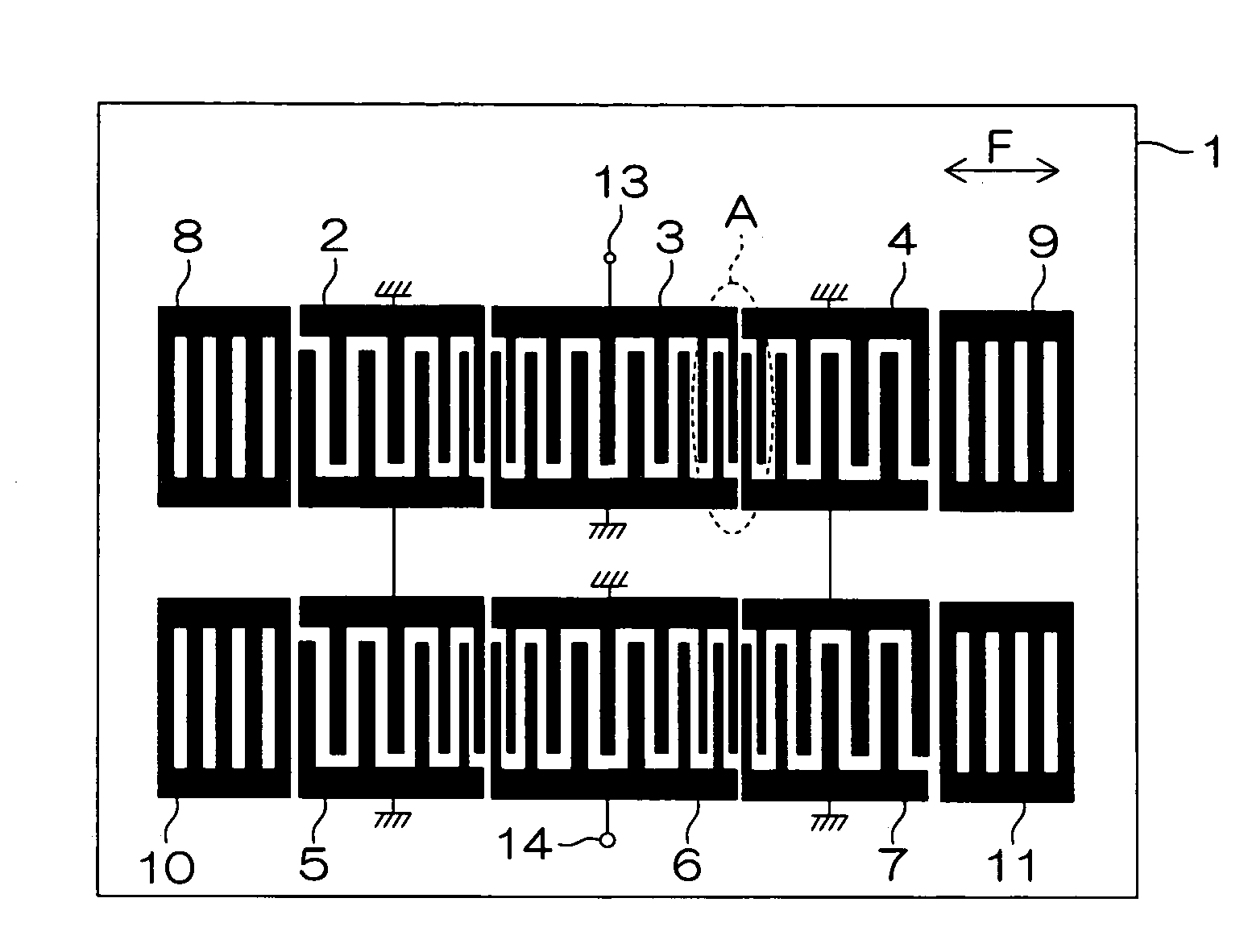
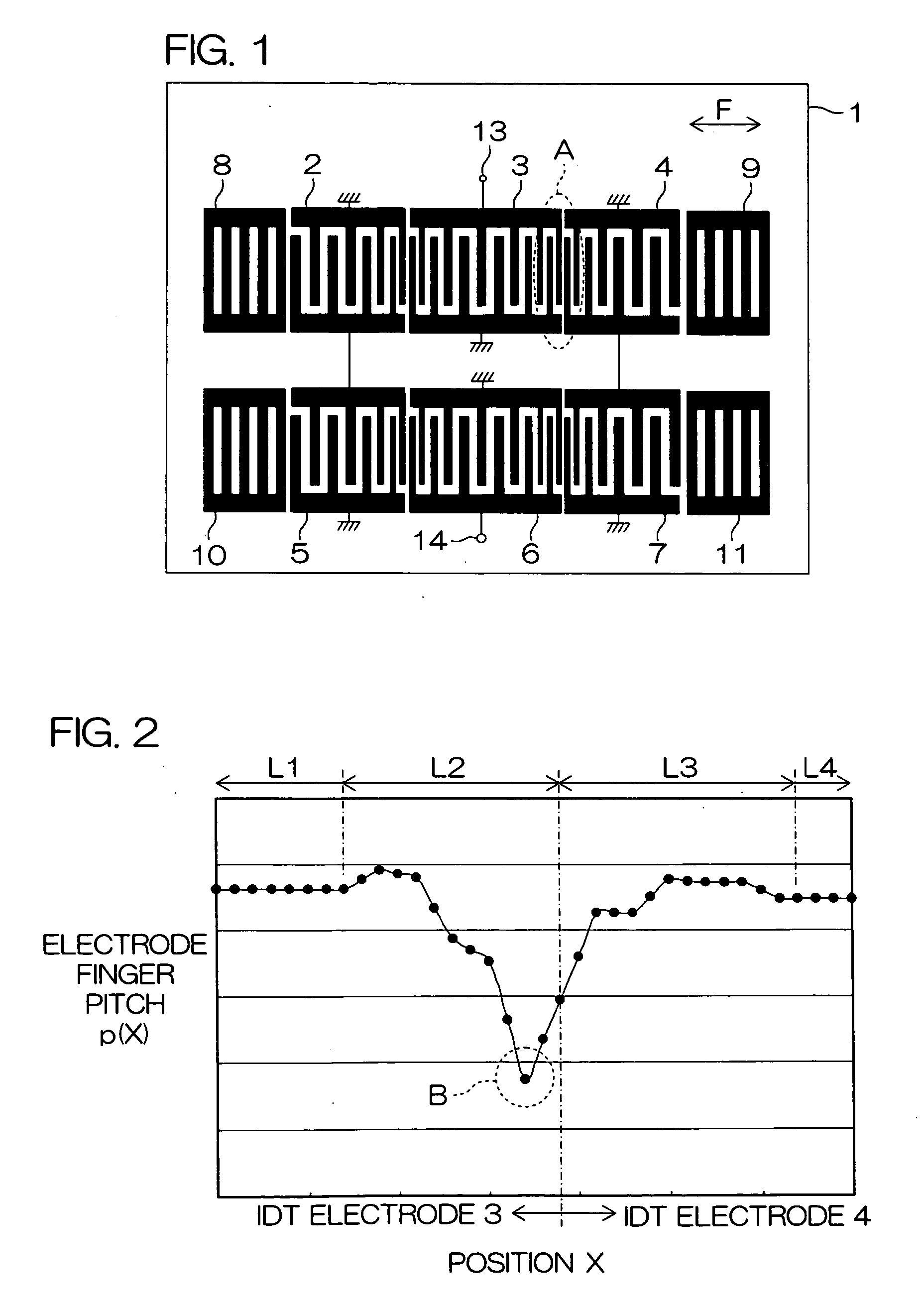
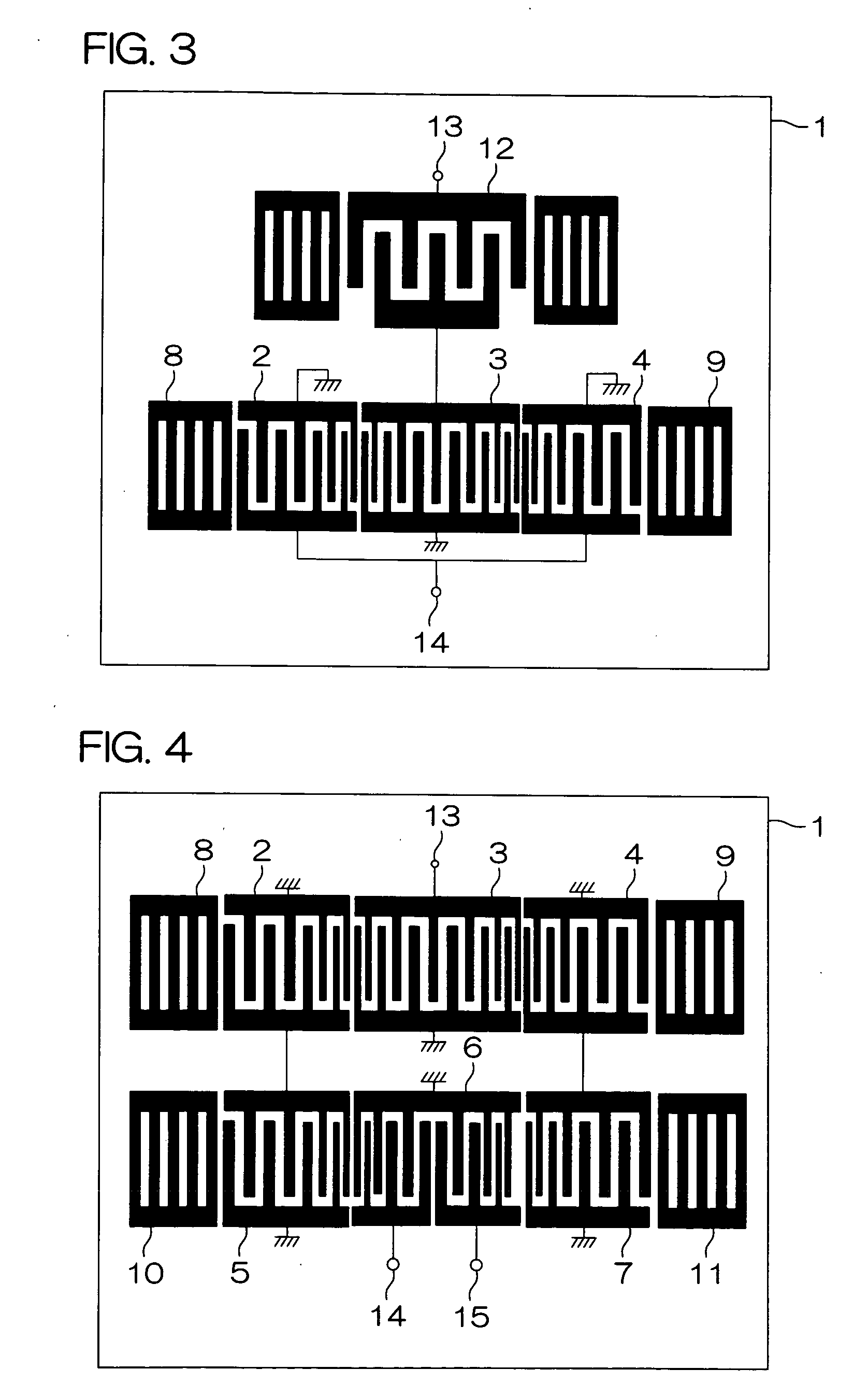
A plurality of IDT electrodes 2 to 7 each having a large number of electrode fingers extending in a direction perpendicular to a propagation direction of a surface acoustic wave propagating on a piezoelectric substrate 1 are arranged on the piezoelectric substrate 1 along the propagation direction, and each of the two adjacent IDT electrodes out of the plurality of IDT electrodes 2 to 7 comprises a variable pitch section and a fixed pitch section. The electrode finger pitch in the variable pitch section gradually decreases toward the boundary between the two adjacent IDT electrodes, and the minimum electrode finger pitch portion in the two variable pitch sections is on one side spaced apart from the boundary. There can be provided a surface acoustic wave apparatus having a large pass bandwidth, having a low insertion loss, and having improved flatness in a pass band.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Semiconductor device having a fin field effect transistor
ActiveUS7888751B2The implementation process is simpleLow distortion characteristicTransistorSolid-state devicesField-effect transistorSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes a fin field effect transistor configured to include at least a first fin and a second fin. Threshold voltage of the first fin and threshold voltage of the second fin are different from each other in the fin field effect transistor.
Owner:SONY CORP
Adaptive digital receiver
ActiveUS8582694B2High resolutionWide bandwidthElectric signal transmission systemsChannel dividing arrangementsImage resolutionAdaptive optimization
The present invention provides a high-performance adaptive digital receiver with adaptive background control that optimizes the performance in rapidly changing signal environments and provides 3.6 GH; instantaneous bandwidth, SFDR>90 dB, SNR=66 dB, with dynamic digital channelization. The receiver takes advantage of several levels of adaptivity that conventional approaches do not offer. In addition to a dynamic digital channelizer that is adaptively tuned based on detected signals, the present invention employs a powerful software reconfigurable digitizer that is adaptively optimized for the current signal environment to control important receiver parameters such as bandwidth, dynamic range, resolution, and sensitivity.
Owner:LINEARITY LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com