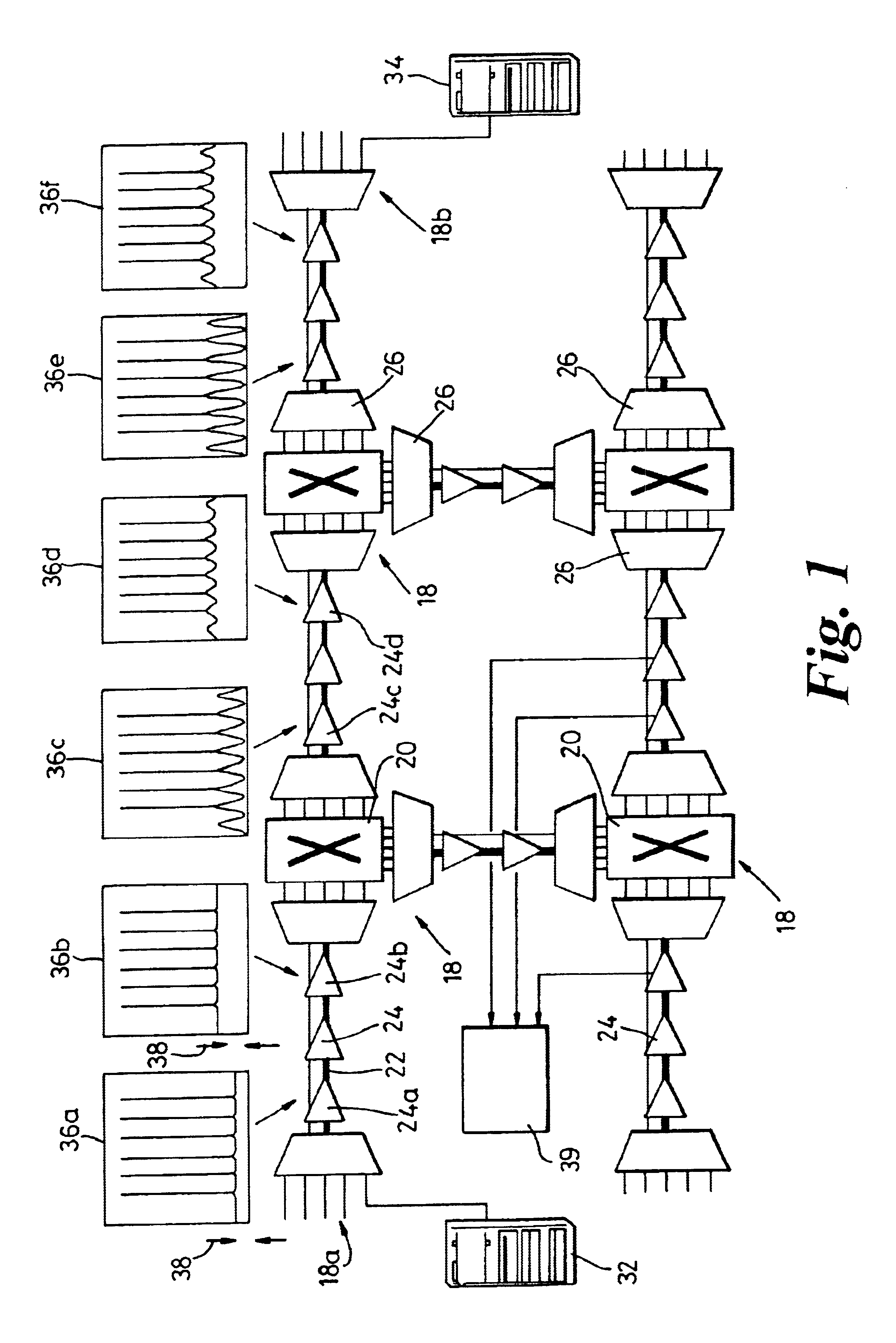
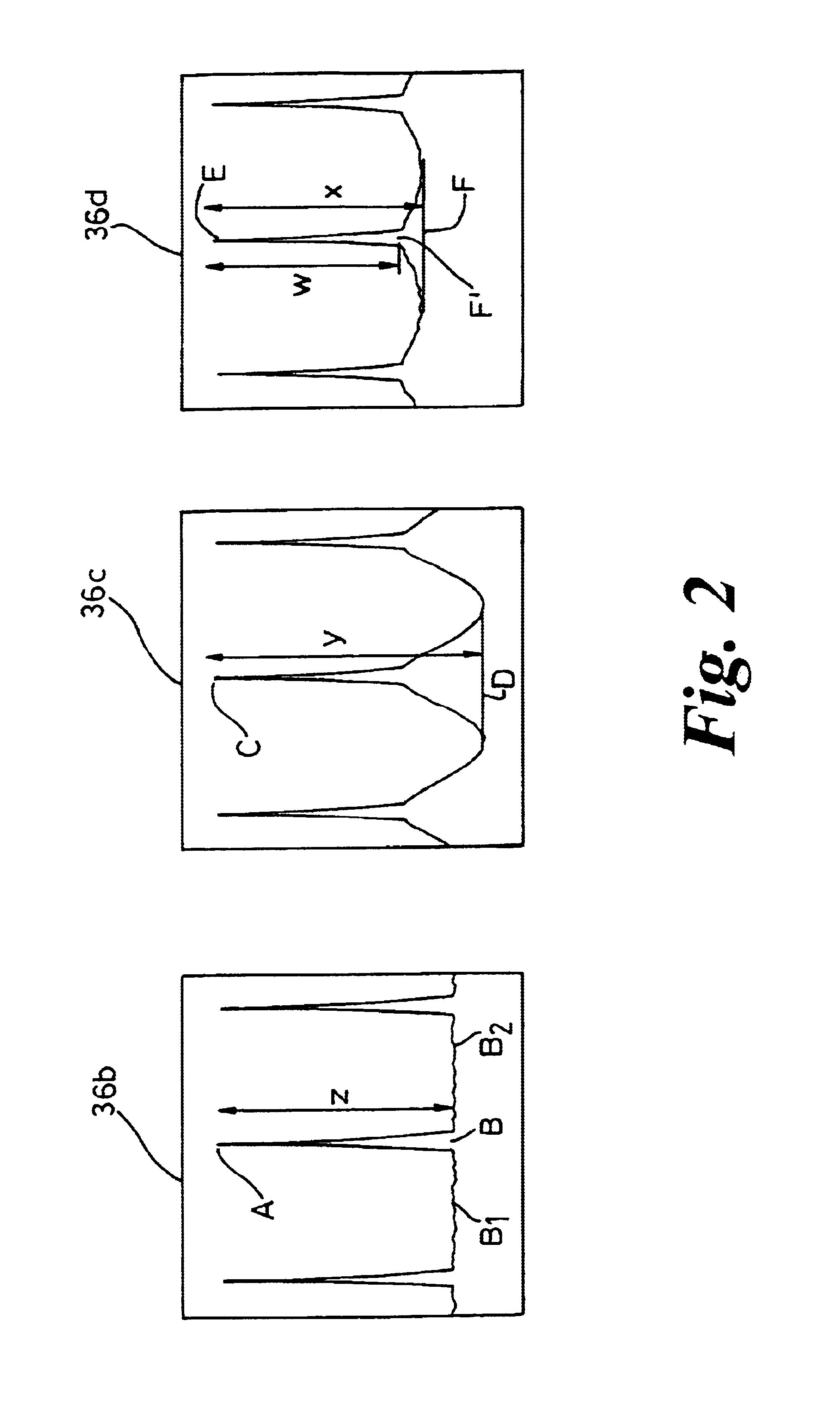
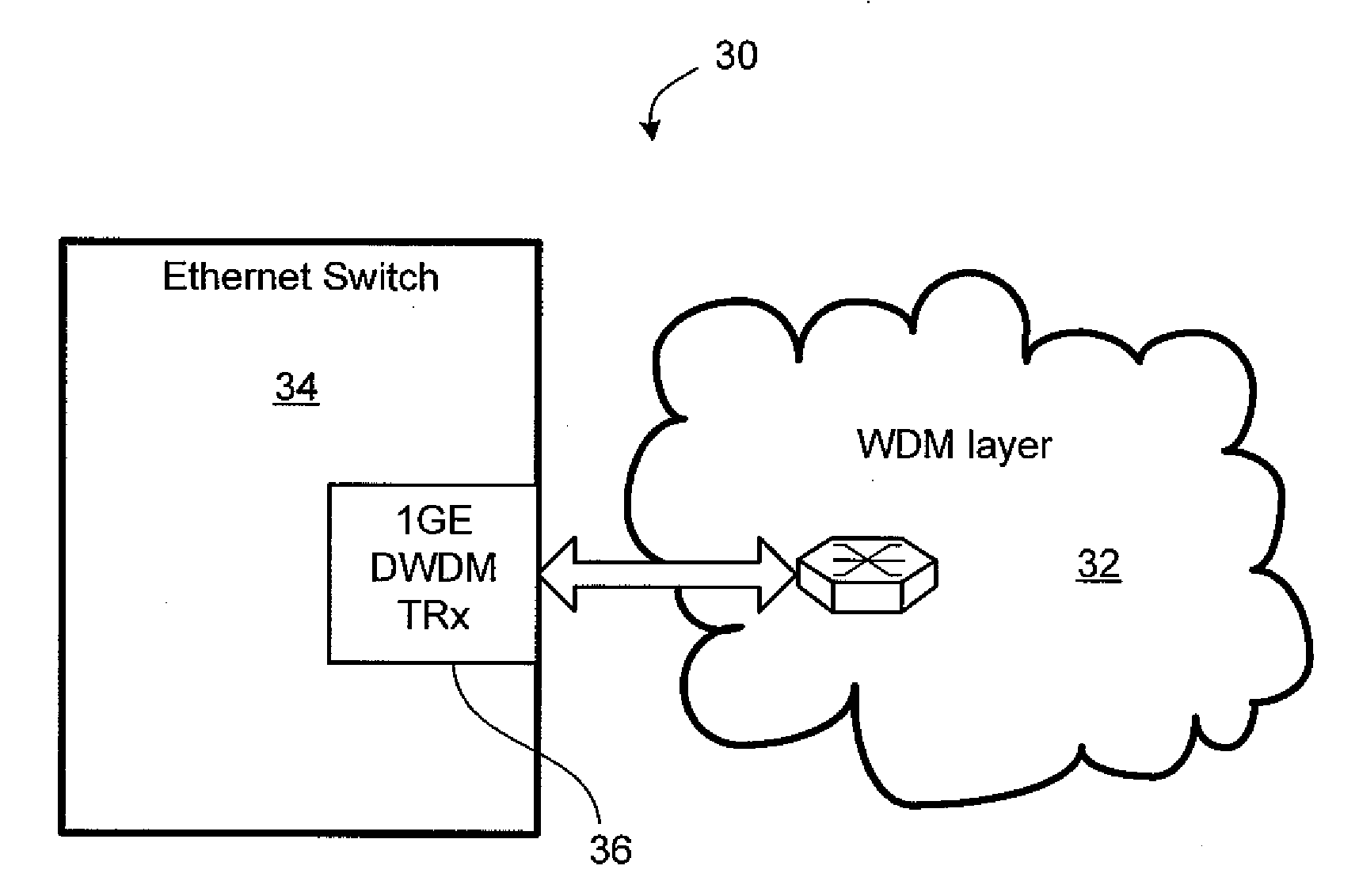
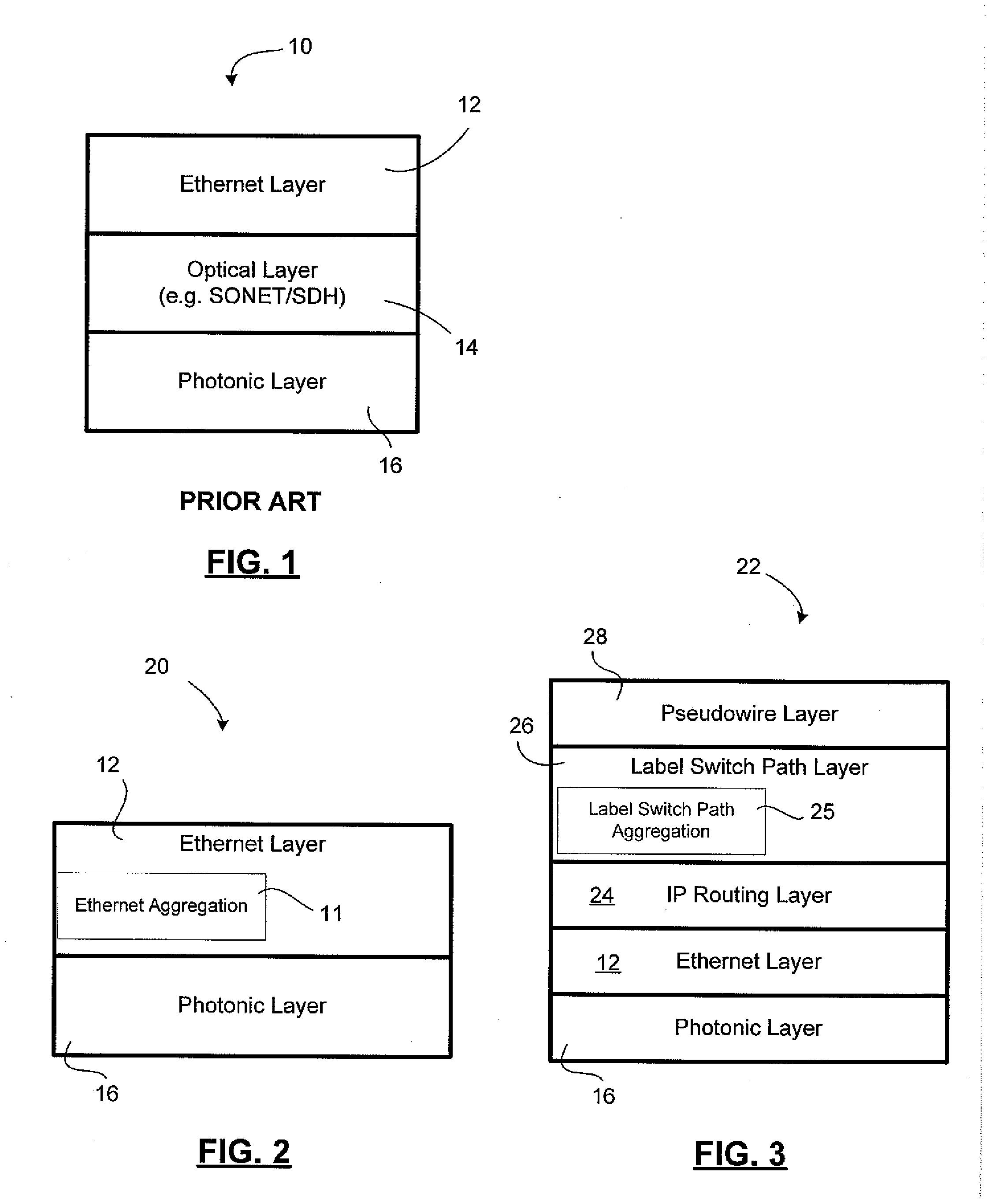
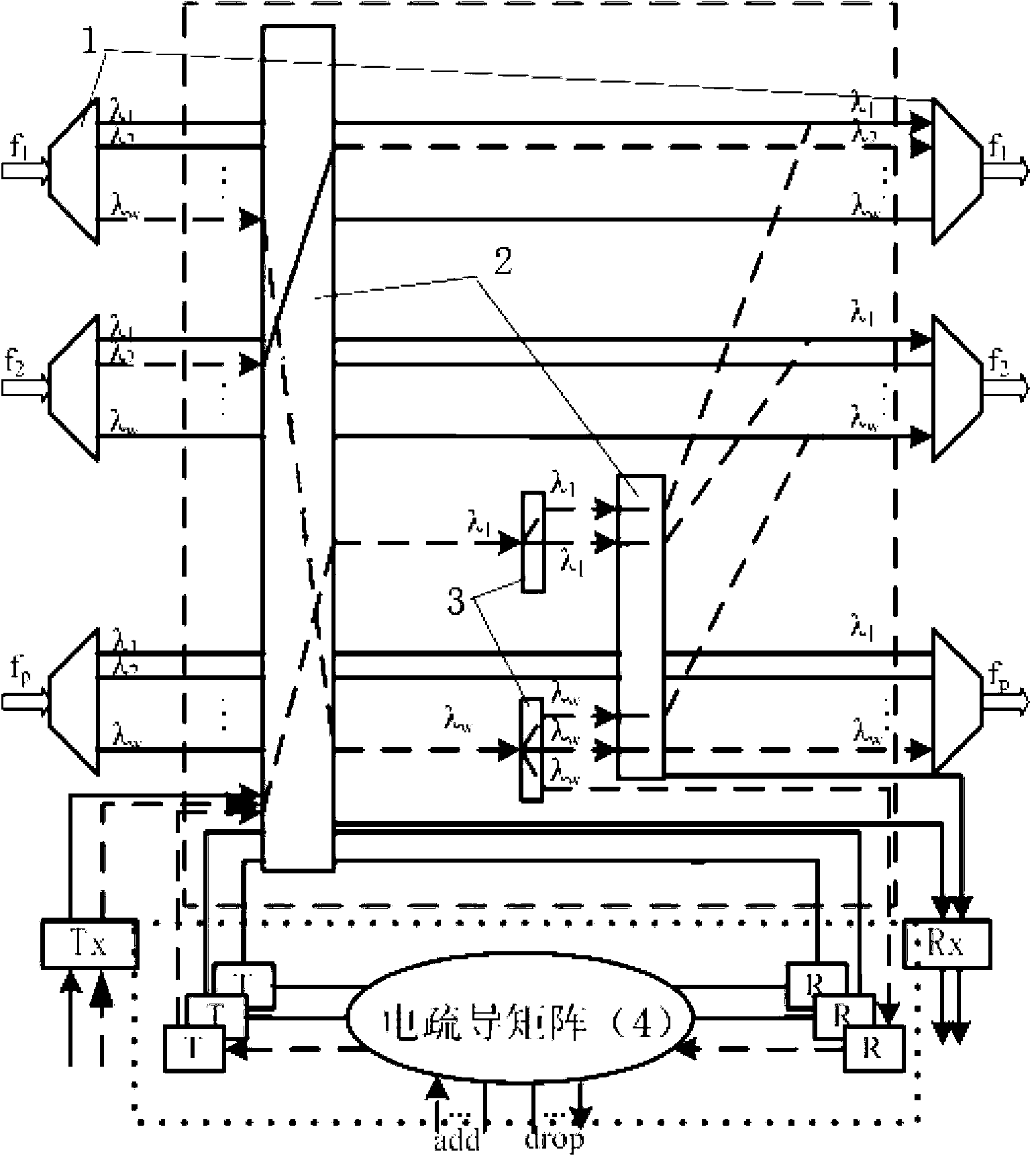
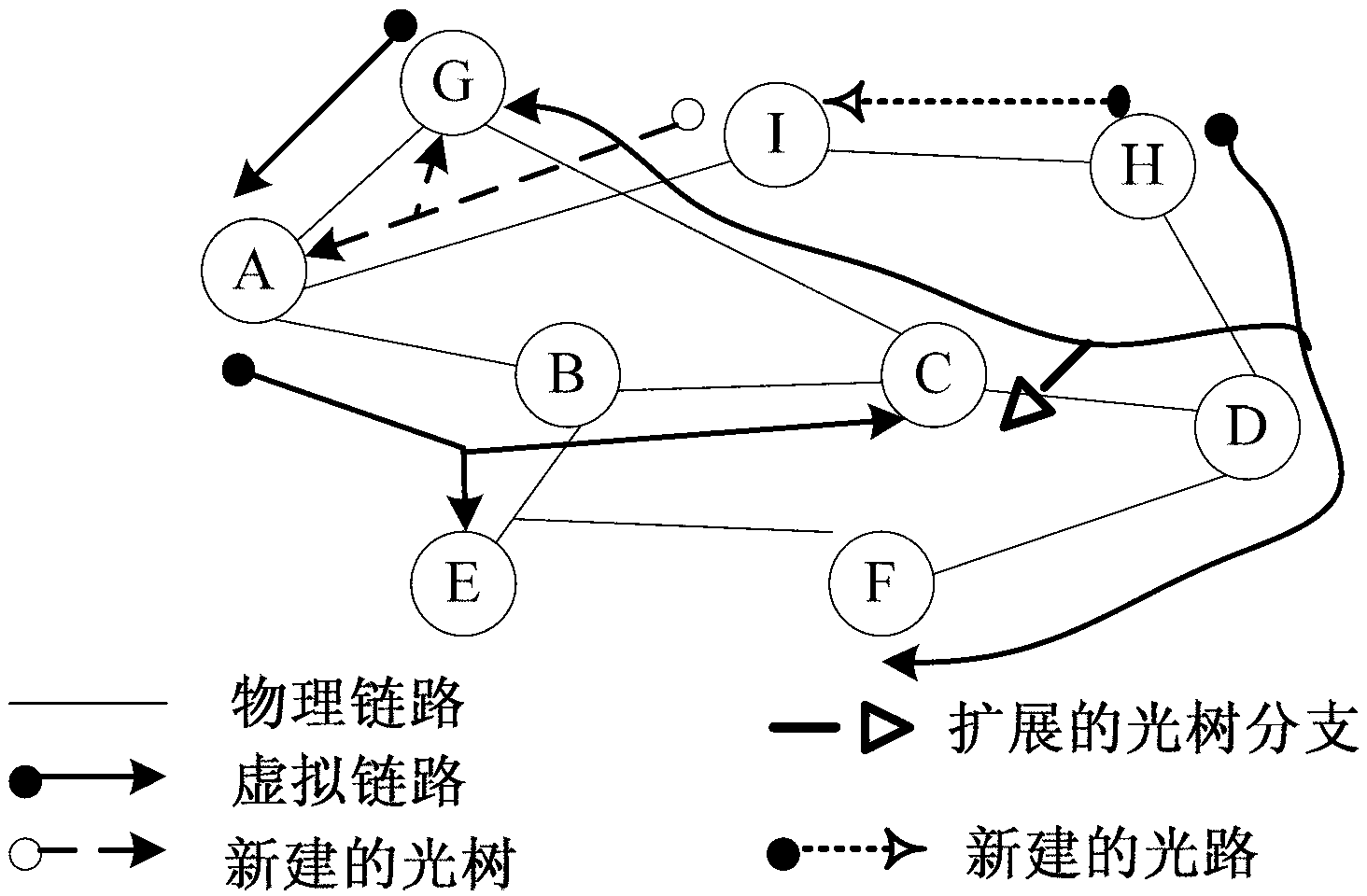
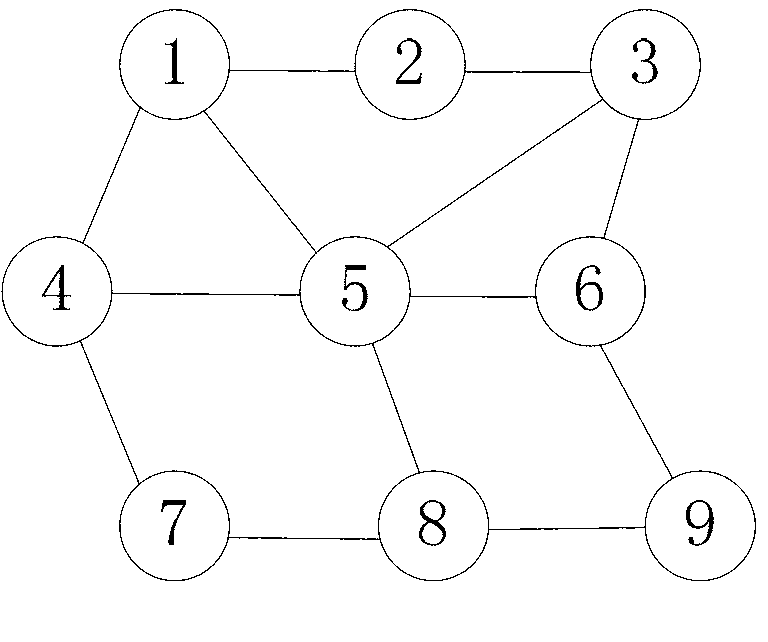
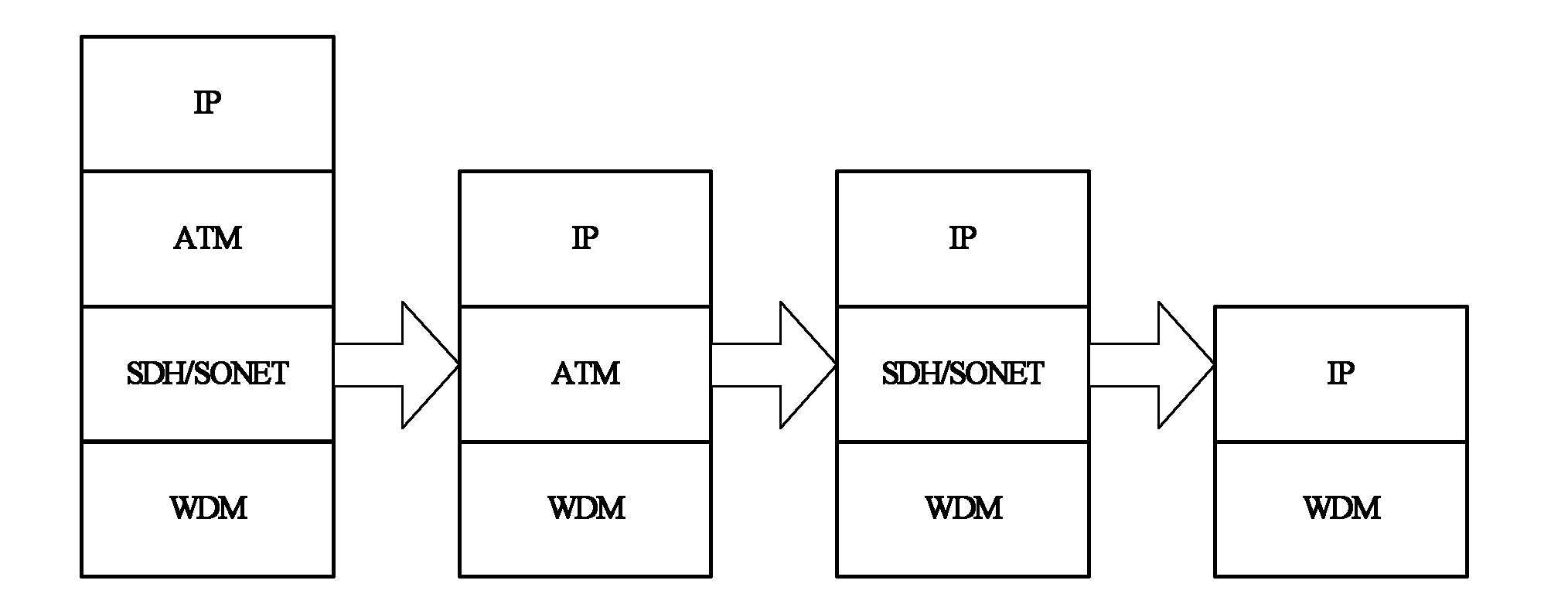
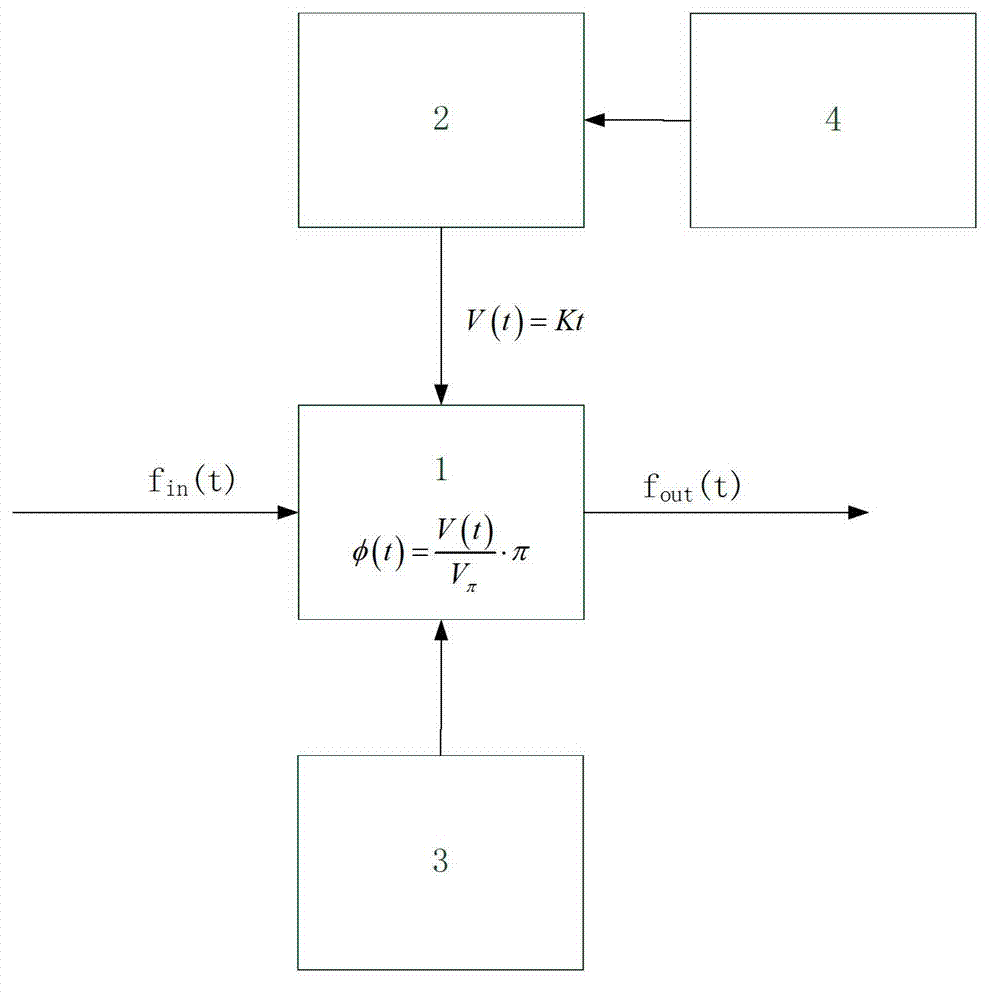Patents
Literature
97 results about "Wdm optical networks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical WDM Networks is a textbook for graduate level courses. Its focus is on the networking aspects of optical networking, but it also includes coverage of physical layers in optical networks. The author introduces WDM and its enabling technologies and discusses WDM local, access, metro, and long-haul network architectures.
Passive optical network with asymmetric modulation scheme
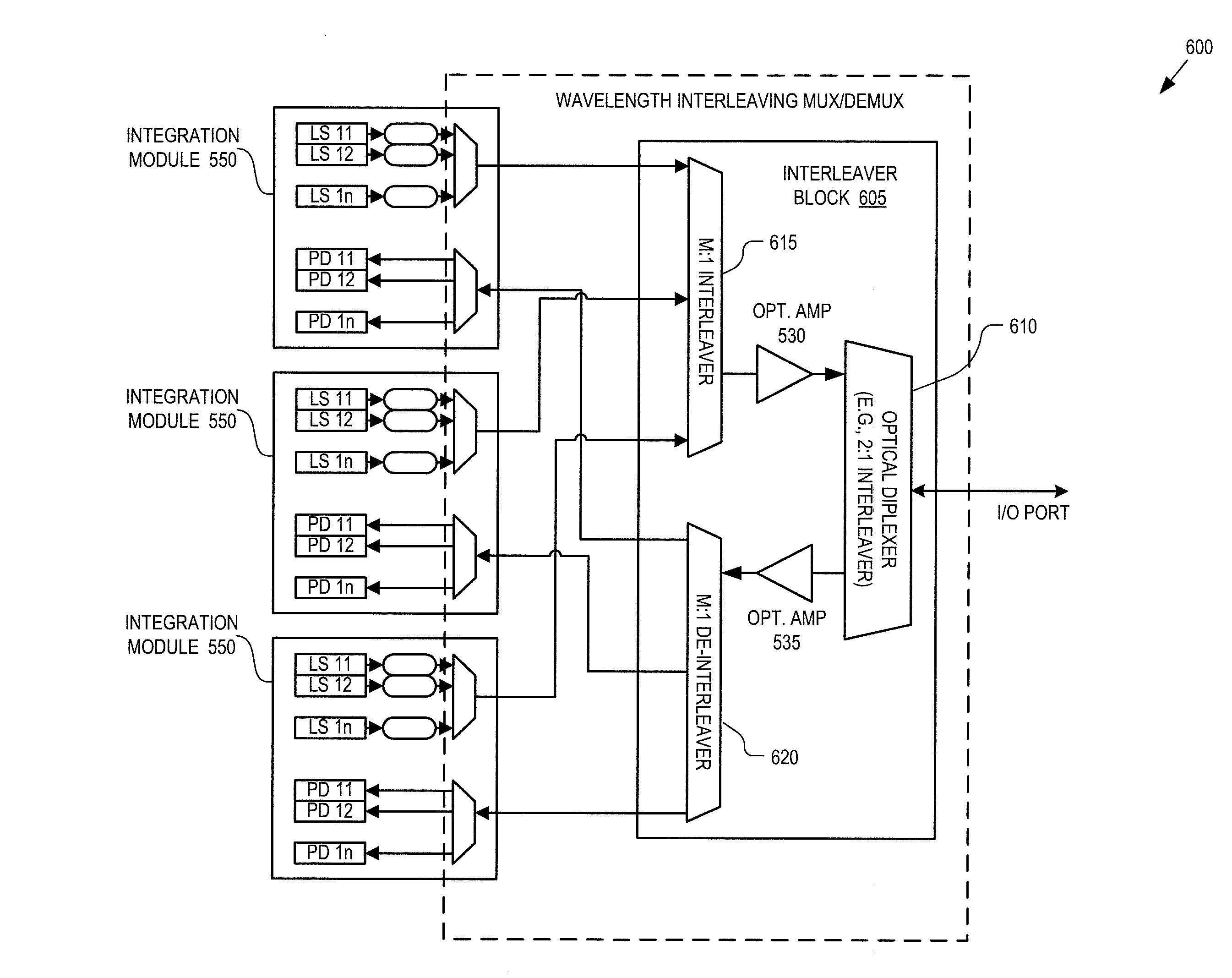
A passive optical network couples a WDM optical line terminal (“OLT”) to WDM optical network units (“ONUs”). The WDM OLT includes an optical transmitter array with coherent transmitters to generate downstream WDM signals encoded using phase modulation, an optical receiver array with direct detection photo-detectors to receive upstream WDM signals encoded with amplitude modulation, and an optical diplexer optically coupled to the optical transmitter array and the optical receiver array. The WDM ONU includes a tunable optical transmitter having a first tunable laser source coupled to generate a selectable upstream carrier wavelength and direct amplitude modulation circuitry coupled to amplitude modulate the first tunable laser source and a tunable optical receiver having coherent detection circuitry to demodulate phase information from the downstream WDM signals and a second tunable laser source operated as a local oscillator and coupled to tune to a selectable downstream carrier wavelength.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
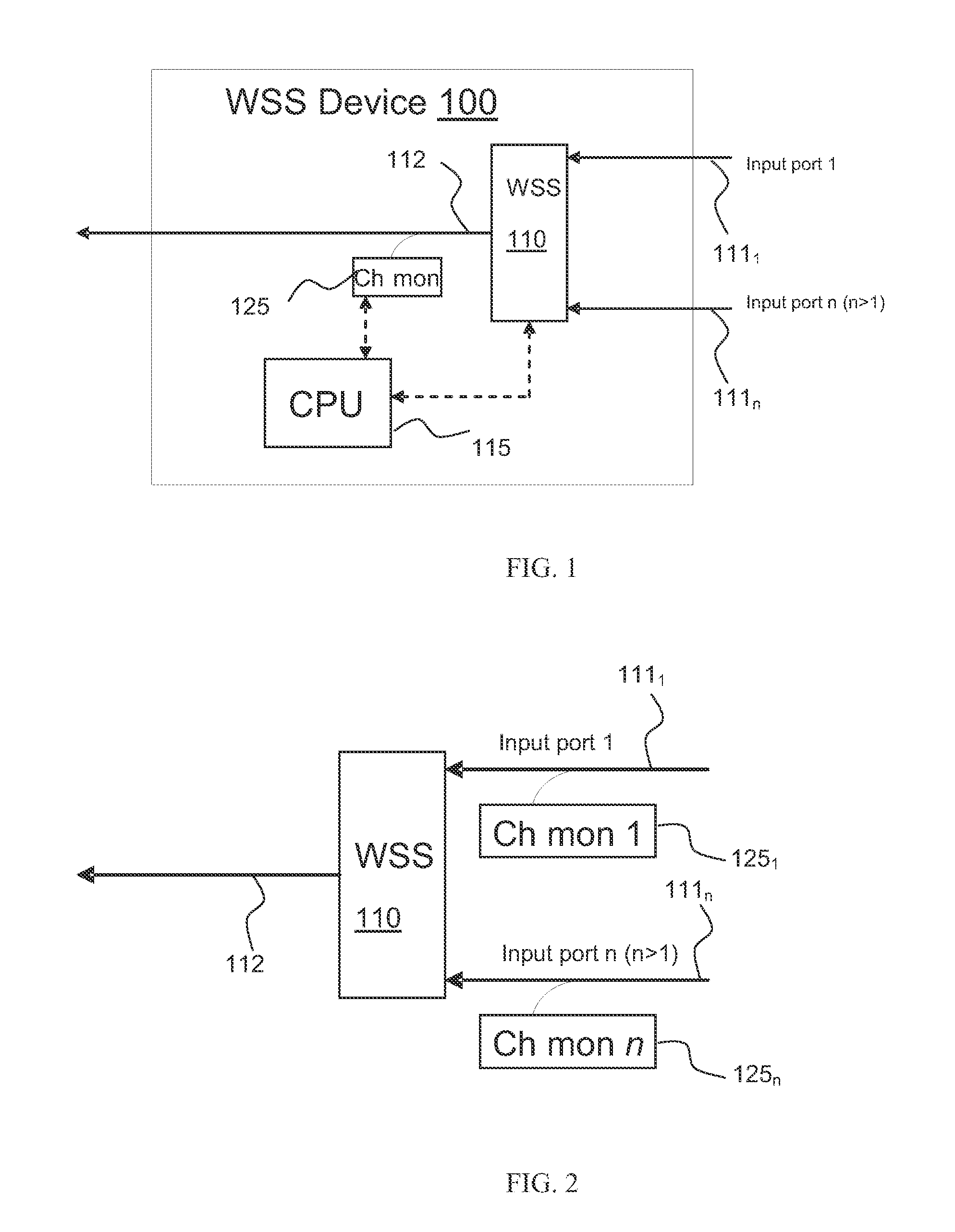
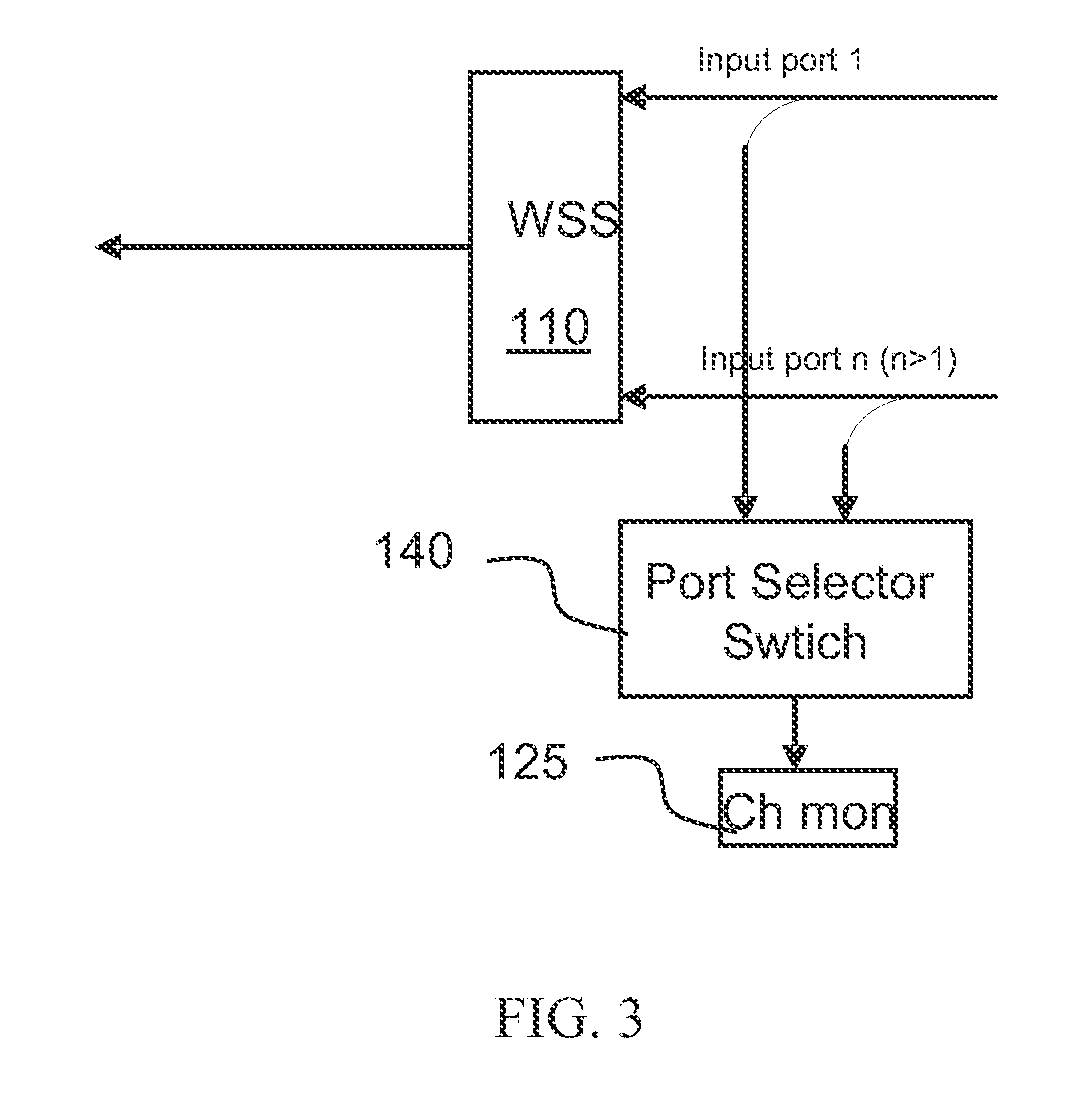
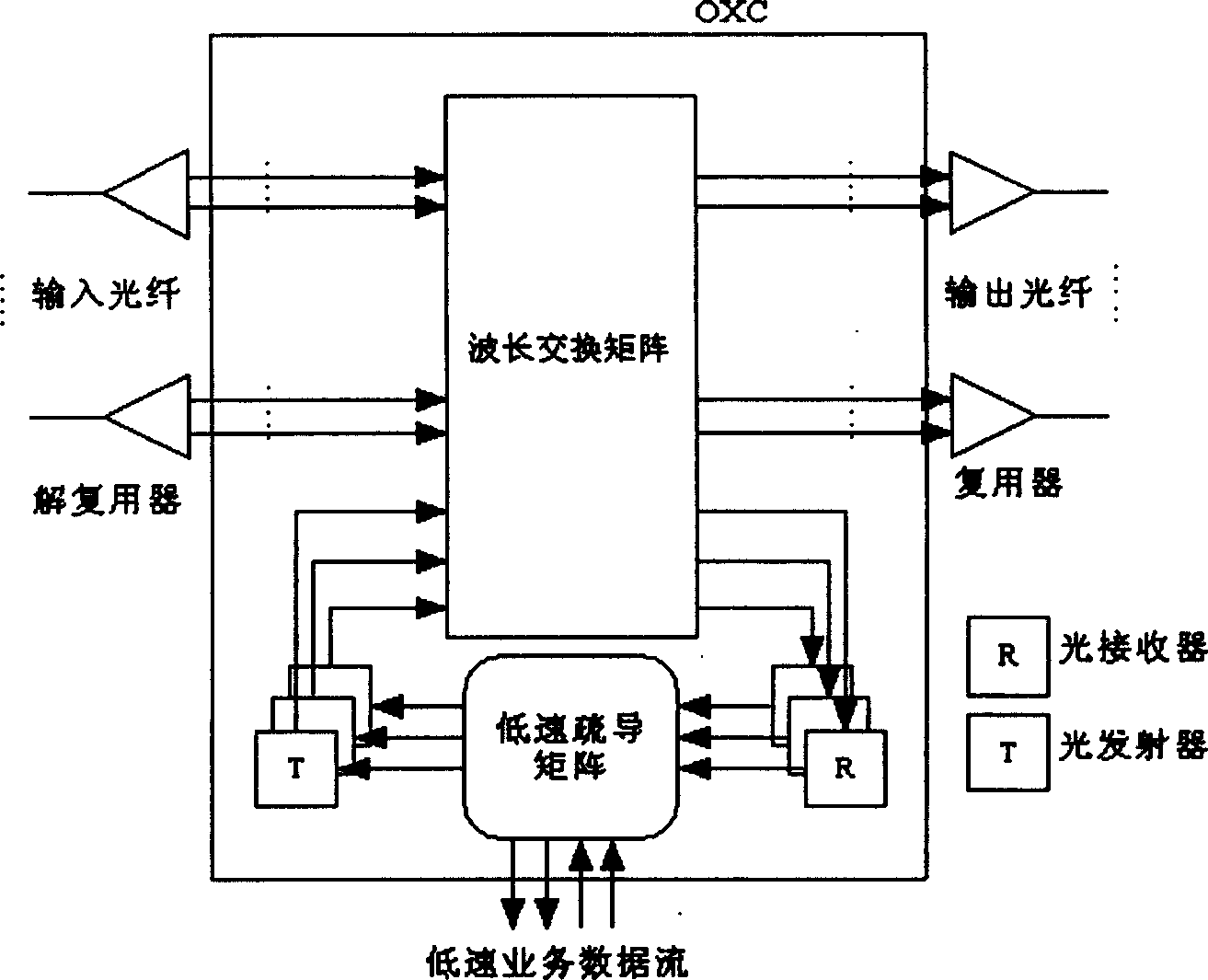
Method for auto-configuration of a wavelength selective switch in an optical network
ActiveUS20100221004A1Raise priorityMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexAuto-configurationWdm optical networks
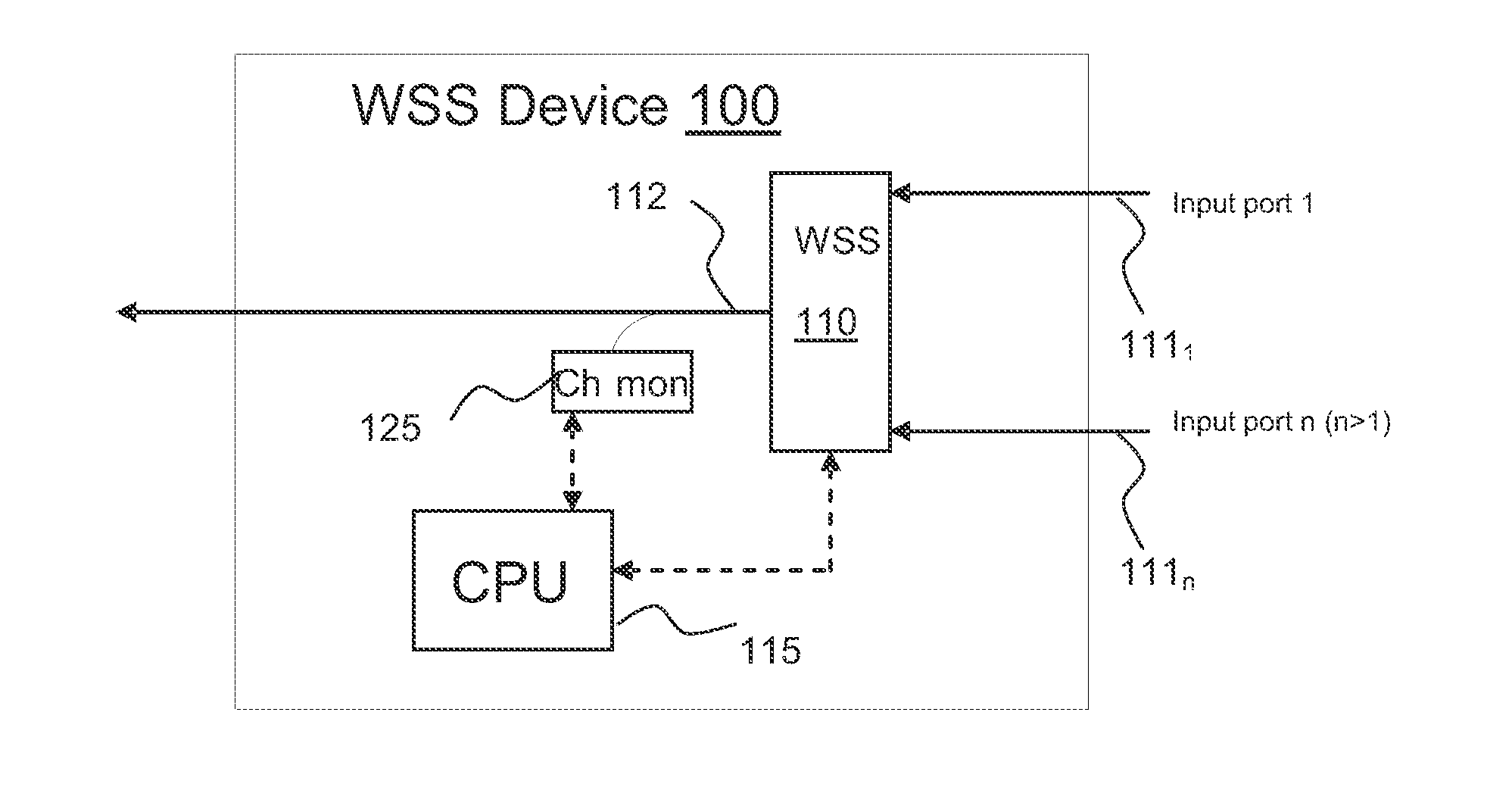
The invention relates to a method for auto-configuring a wavelength selective switch (WSS) device having an output port and a plurality of input ports and coupled to a WSS controller. When connected to a WDM optical network, the WSS controller is programmed to utilize one or more optical channel monitors (OCM) coupled to the input and / or output ports to detect which of the wavelengths are present at the input ports. Wavelengths that are not detected on any input port are blocked by the WSS. Any wavelength detected as present at one and only one input port is switched by the WSS to the output port. If a wavelength is detected at two or more input ports, it is either blocked by the WSS at each of the input ports until user intervention, or is blocked at all but one of the input ports as defined by assigned port priorities.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Integrated service leading method for WDM optical network
InactiveCN1791000ASave resourcesLow costWavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching networksLink weightTransceiver
The invention provides a synthesis persuasion business method WDM OTN. Wherein, building a persuasion chart model combined with virtual topological design, rout and wavelength allocation problem, calculating on the chart to find out proper persuasion path. For business request, using built optical link for persuasion. This invention uses dynamic regulation link weight to regulate dynamically whole network link weight at any moment to balance load, and saves optical transceiver resources to reduce cost.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
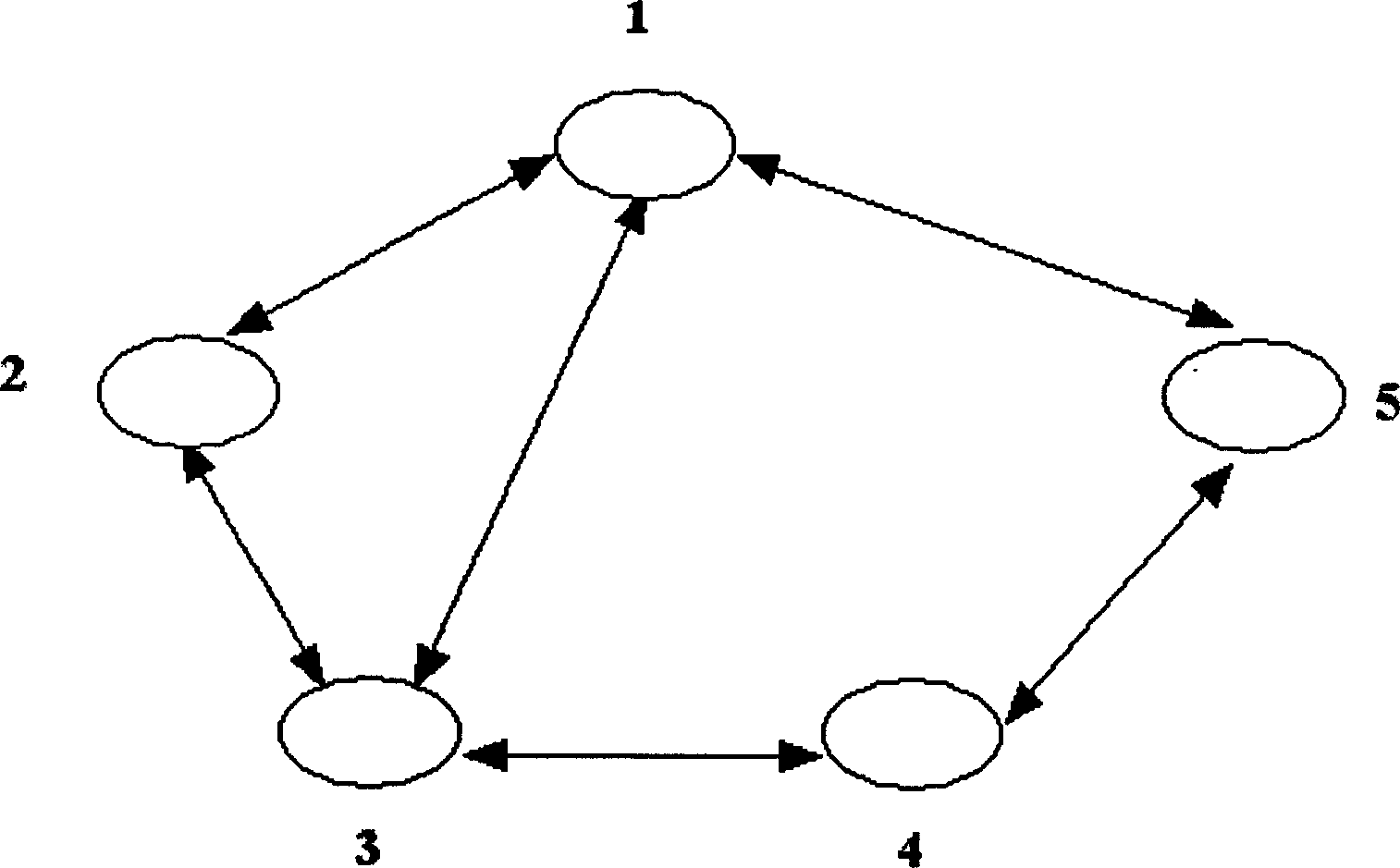
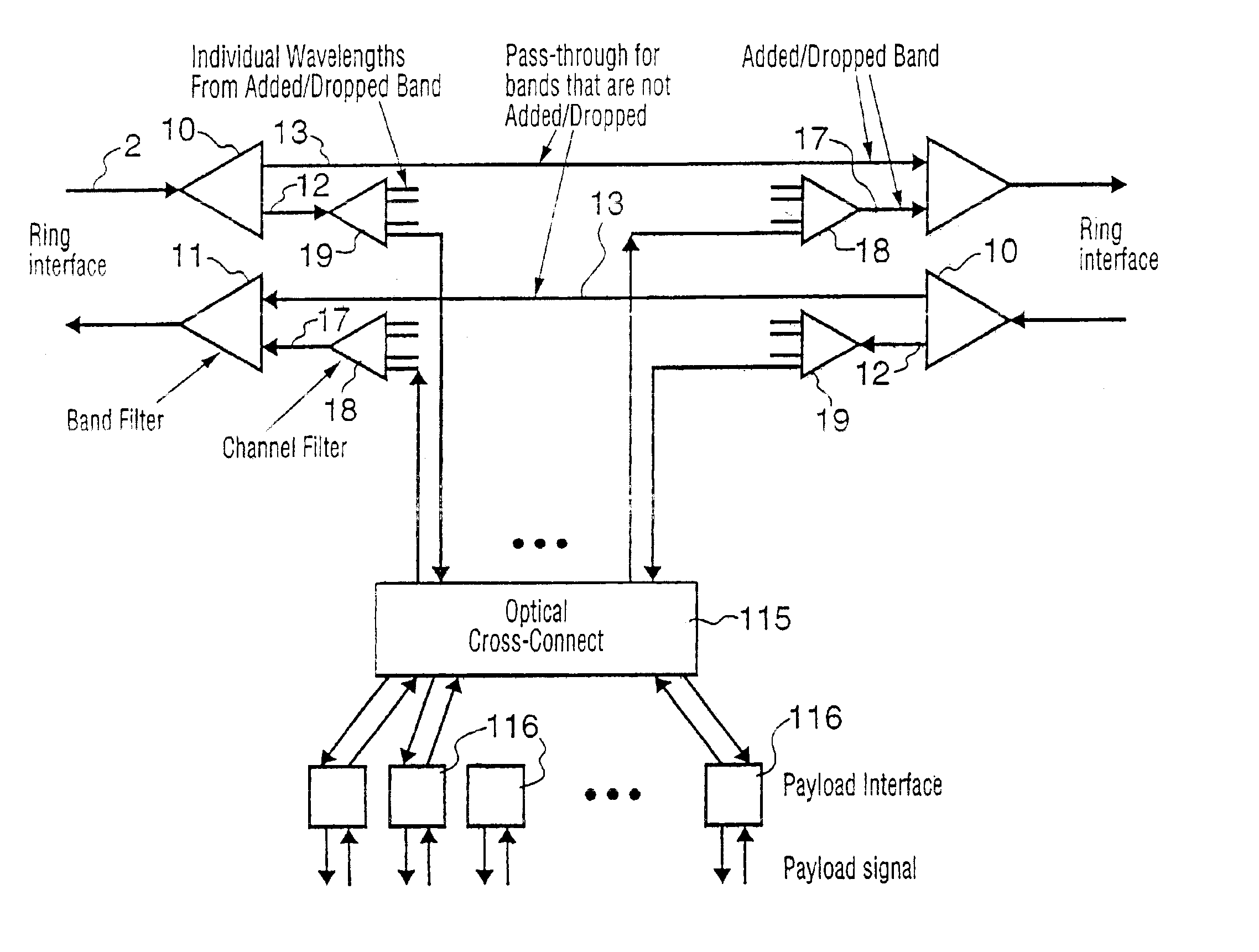
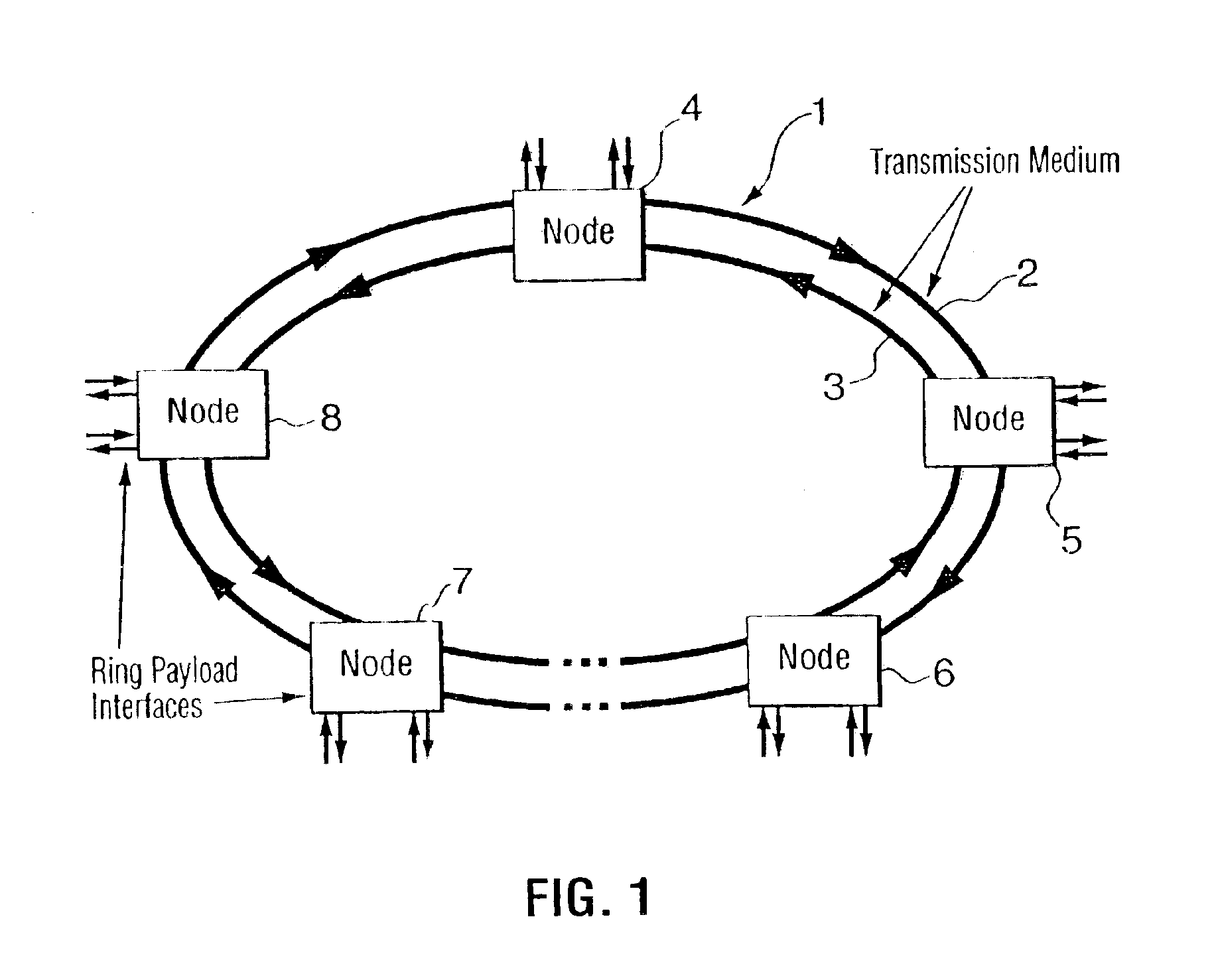
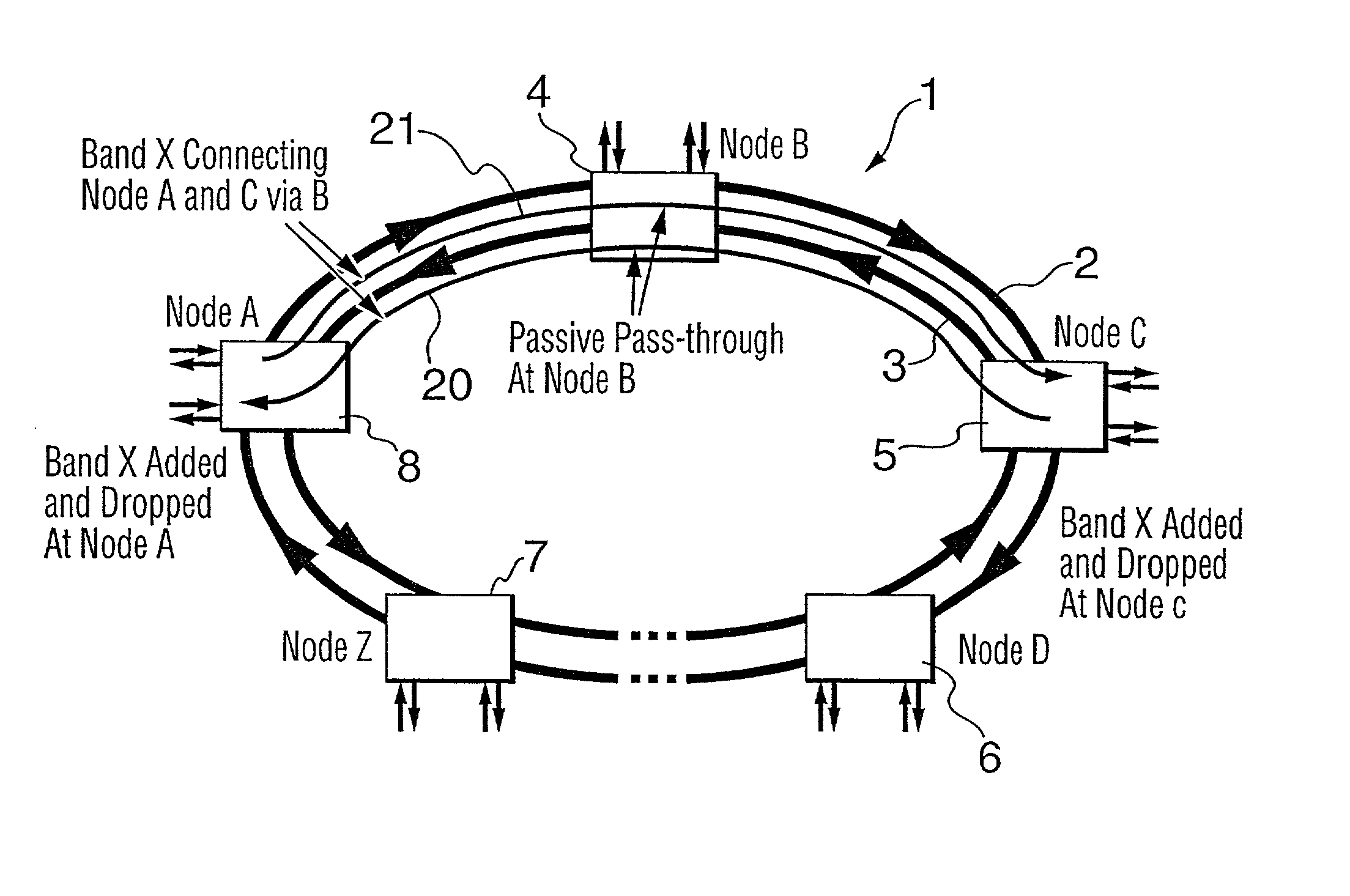
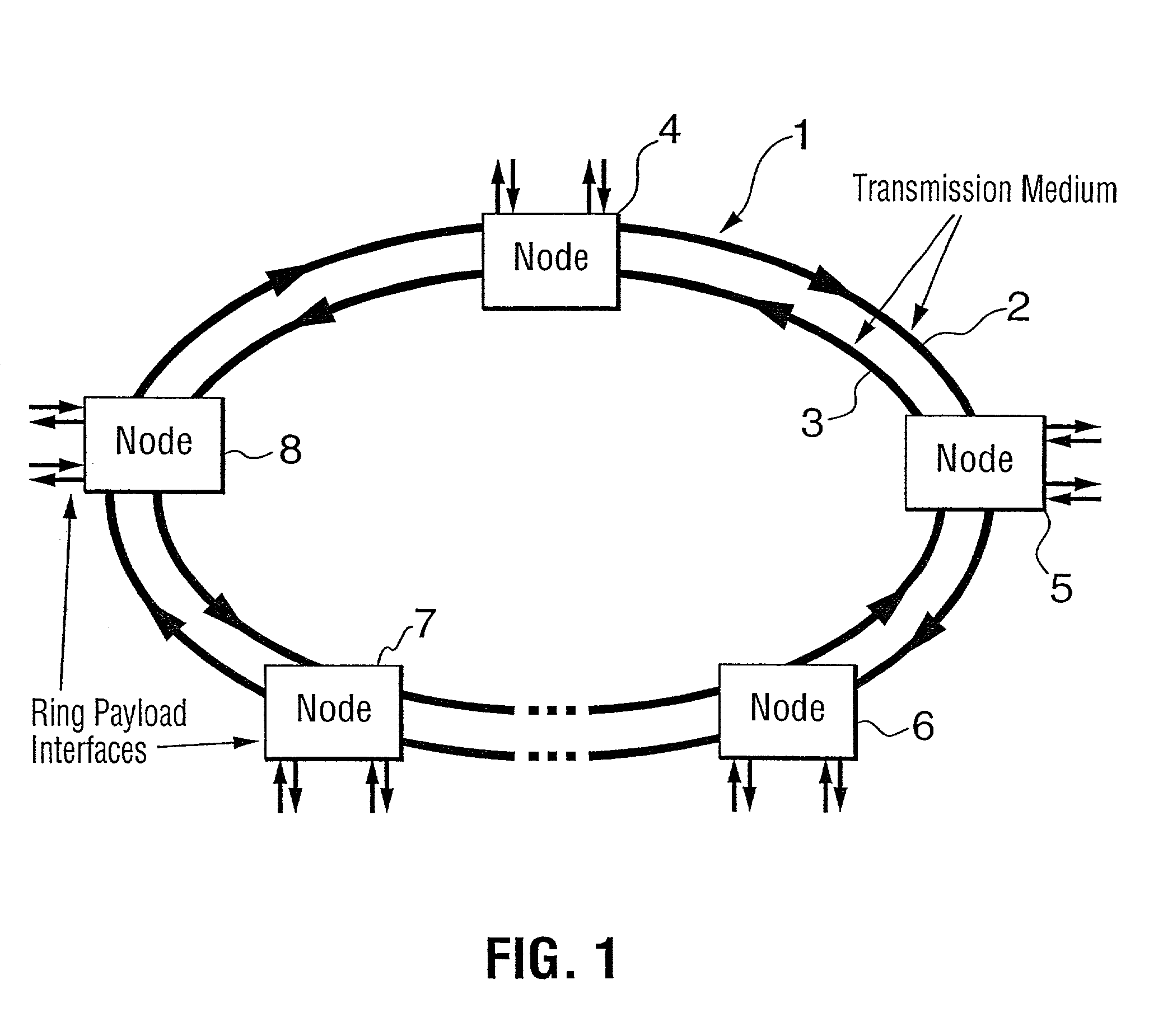
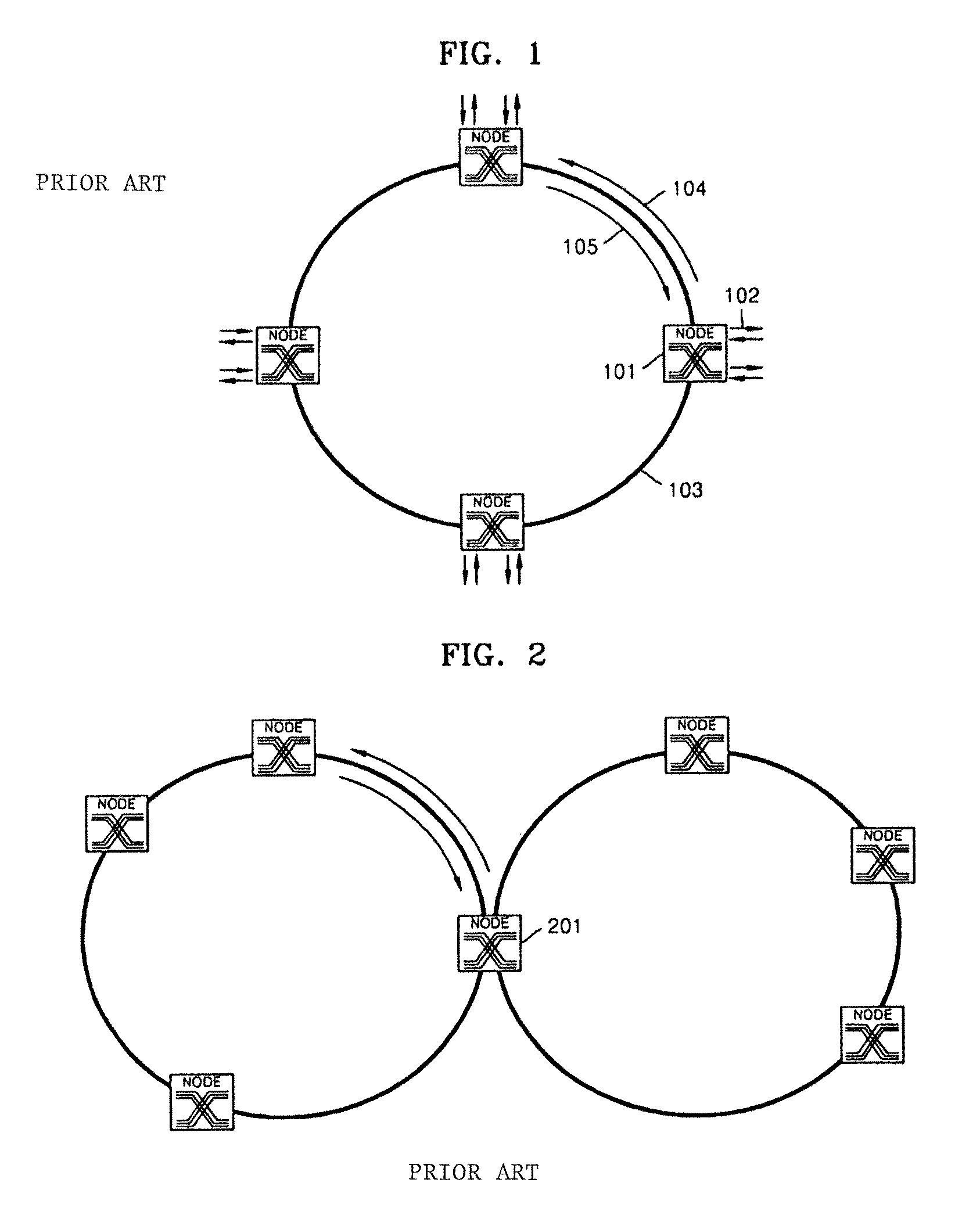
WDM optical network with passive pass-through at each node
InactiveUS6892032B2Minimal lossReduce lossMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksPath lengthWdm optical networks
A communications network has a plurality of nodes interconnected by an optical transmission medium. The transmission medium is capable of a carrying a plurality of wavelengths organized into bands. A filter at each node for drops a band associated therewith and passively forwards other bands through the transmission medium. A device is provided at each node for adding a band to the transmission medium. Communication can be established directly between a pair of nodes in the network sharing a common band without the active intervention of any intervening node. This allows the network to be protocol independent. Also, the low losses incurred by the passive filters permit relatively long path lengths without optical amplification.
Owner:CIENA
Wavelength and path assignment in wavelength division multiplexed ring networks
ActiveUS7088920B2Ring-type electromagnetic networksWavelength-division multiplex systemsRing networkWdm optical networks
A method is provided for establishing a service connection between first and second network nodes in a WDM optical network for a plurality of network users. The method begins by receiving, from each network user, user-preferences prioritizing a plurality of decision criteria defining preferable characteristics of the service connection. Next, a prescribed algorithm is used to select a path and a channel wavelength at which information is to be conveyed over the path between the first and second nodes. The selection is based on the plurality of decision criteria as prioritized in accordance with the user-preferences. Finally, the first and second network nodes are interconnected over the selected path with the selected channel wavelength.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
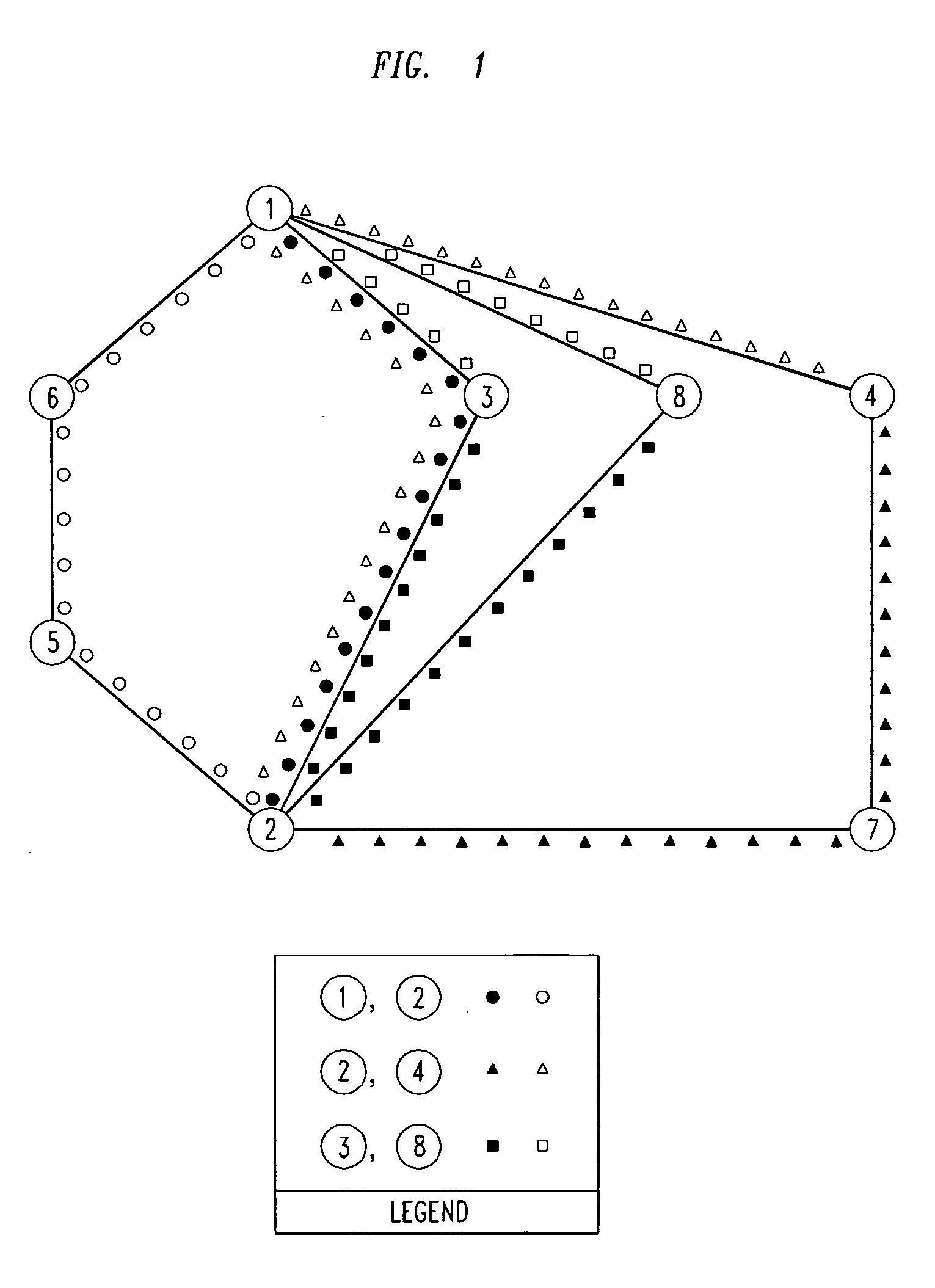
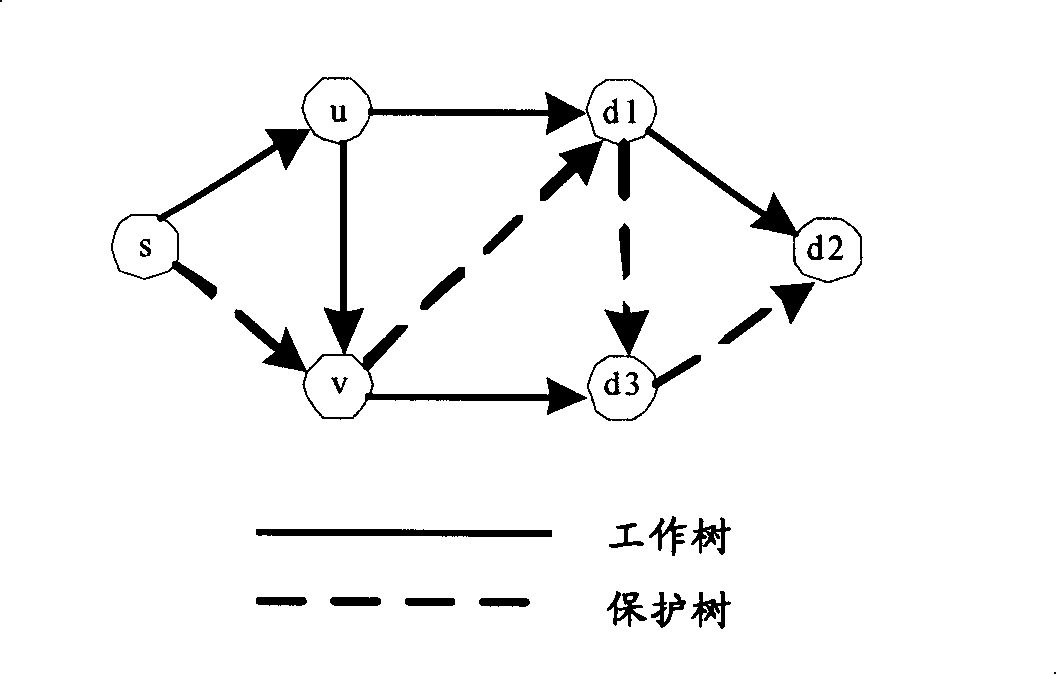
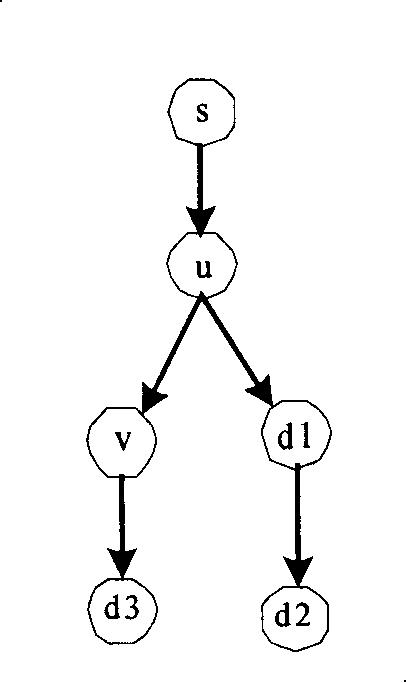
Design method for WDM optical networks including alternate routes for fault recovery
A procedure for designing WDM optical networks provides both working circuits and protection circuits for carrying traffic demands between node pairs. The protection circuits are activated for the purpose of network recovery in case of a fault on a working circuit. Each protection circuit is link-disjoint, and preferably node-disjoint, from its corresponding working circuit. The network is subdivided into logically defined rings, such that each working and protection circuit lies on one or more of the rings. In particular embodiments of the invention, the joint routing of circuits is carried out so as to minimize the total length of the working and protection circuits according to a length that includes a weight for each link. The weight is selected to promote the efficient packing of optical fibers with wavelength channels.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
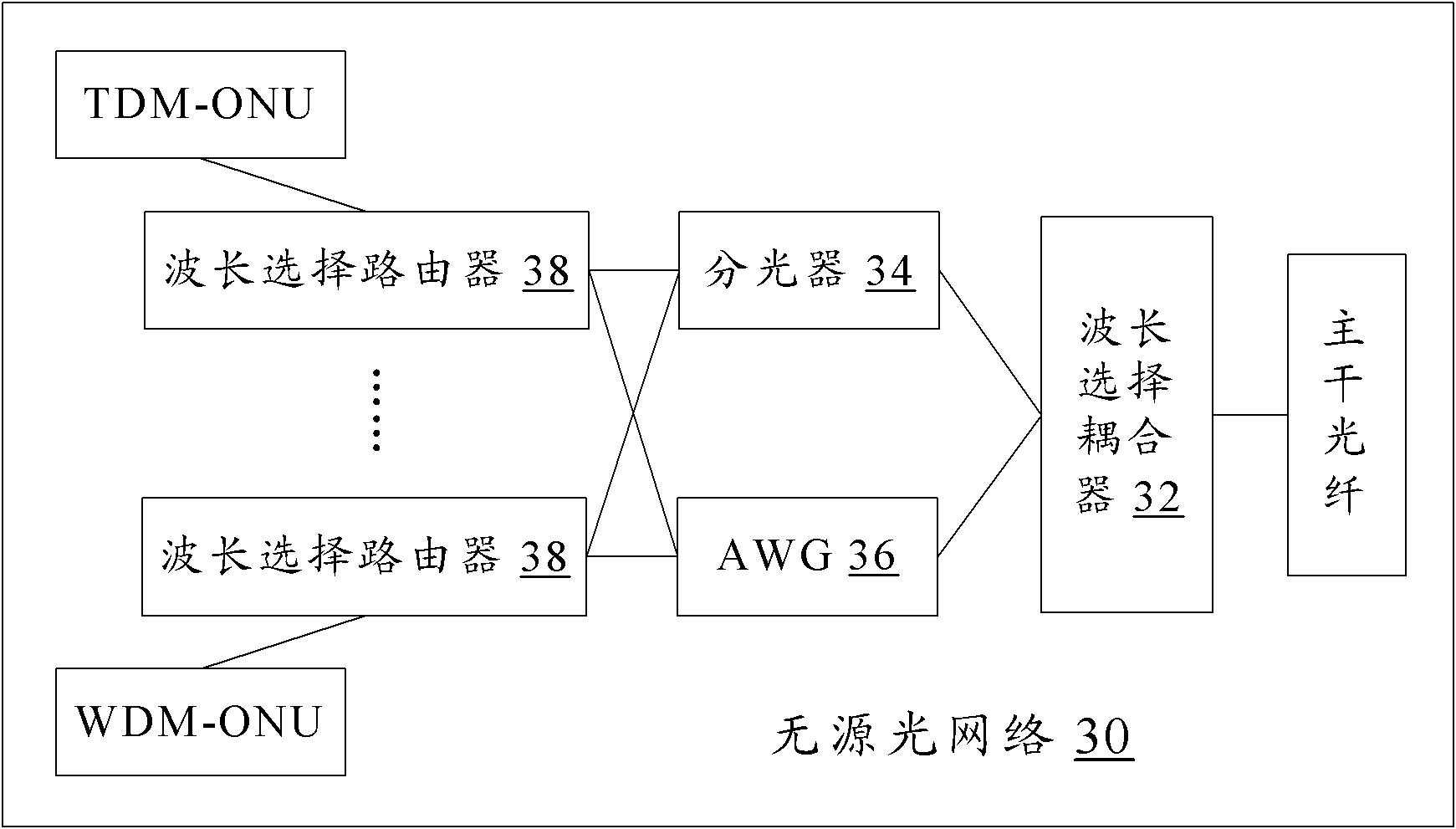
Passive optical network and signal transmission method thereof
ActiveCN101984673AResolve incompatibilitiesImprove compatibilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical line terminationWdm optical networks
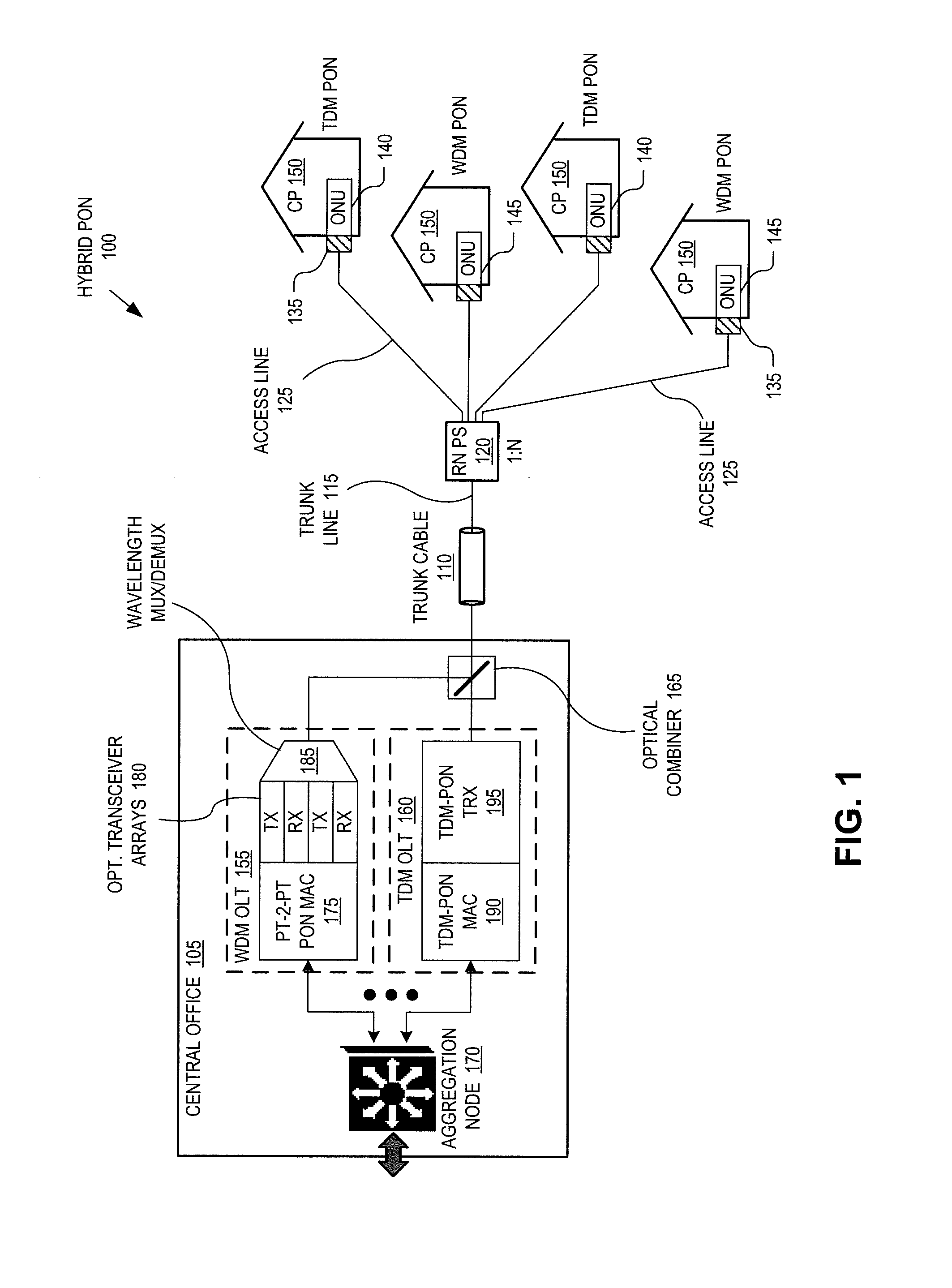
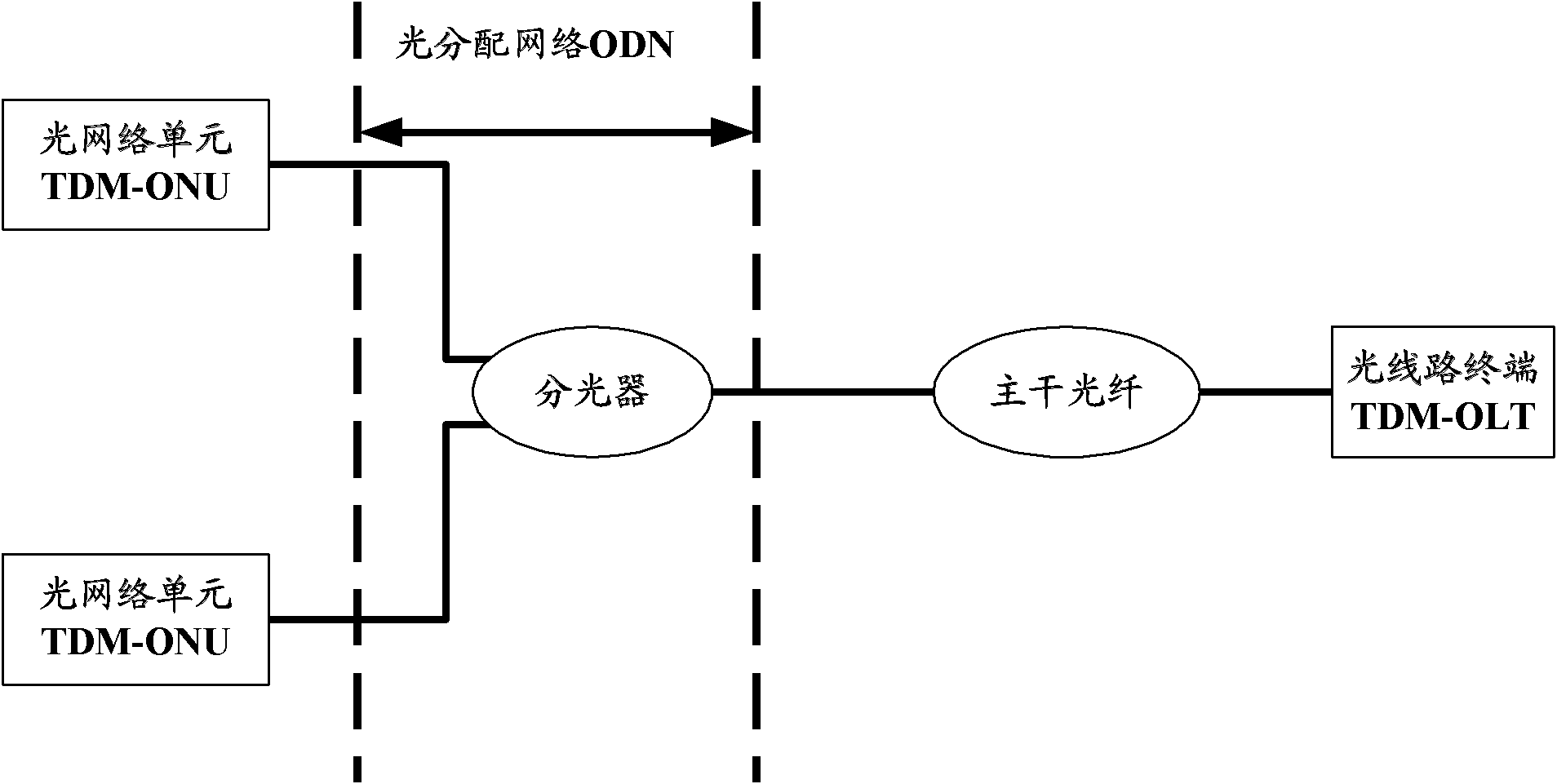
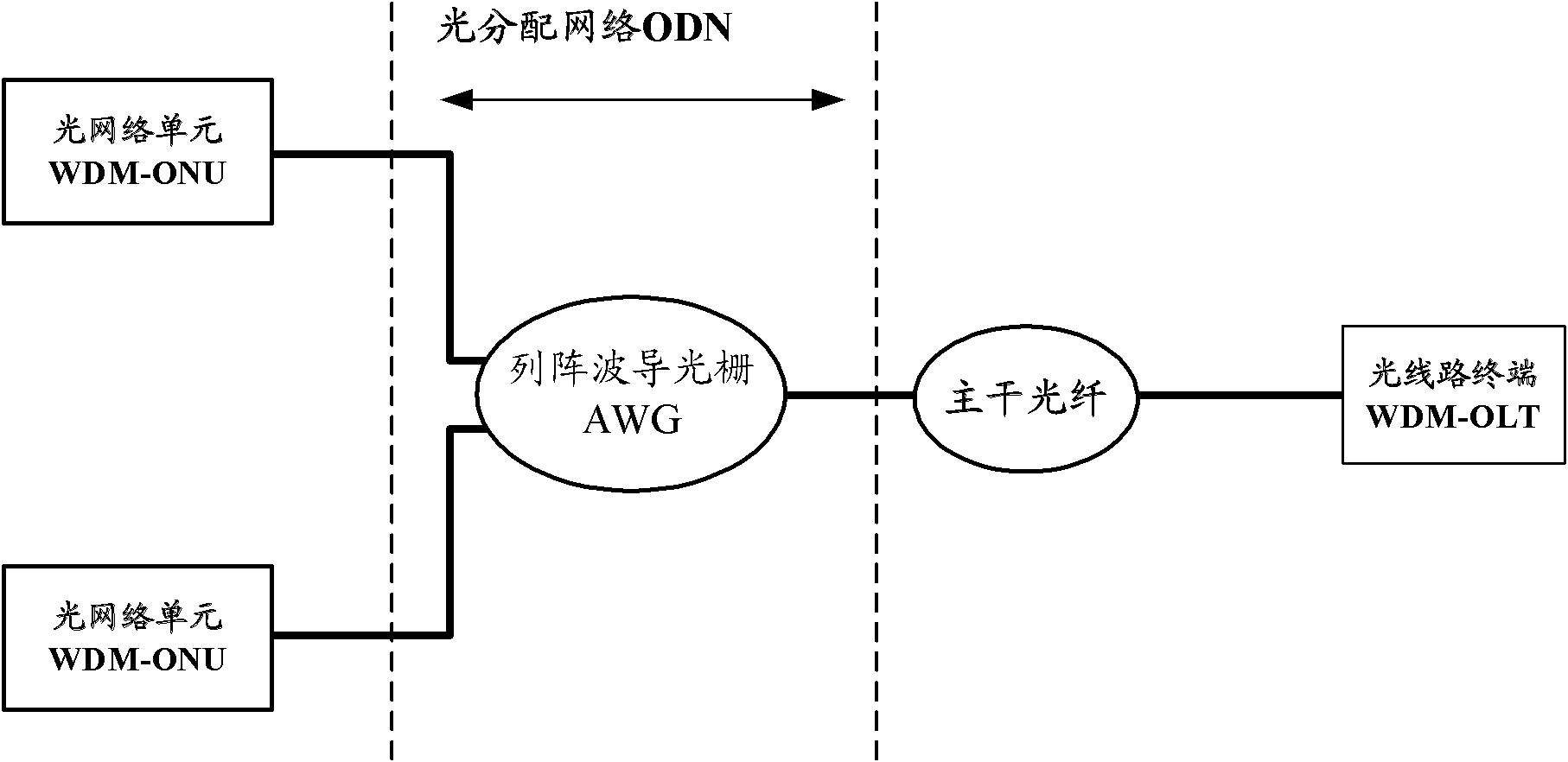
The invention discloses a passive optical network (PON) and a signal transmission method thereof. The PON comprises a wavelength selection coupler, an optical splitter, an array waveguide grating (AWG) and a plurality of wavelength selection routers, wherein, the wavelength selection routers couple a downlink signal from a time division multiplexing optical line terminal (TDM-OLT) of the optical splitter and a downlink signal from a wavelength division multiplexing optical line terminal (WDM-OLT) of the AWG and then transmit the coupled signals to branch optical fibers connected with the wavelength selection routers, and transmit an uplink signal in a branch optical fiber connected with a WDM optical network unit (WDM-ONU ) to the AWG and then transmit an uplink signal in a branch optical fiber connected with a TDM-ONU to the optical splitter. The invention enhances network compatibility and improves user experiences.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Optical spectral power monitors employing time-division-multiplexing detection schemes
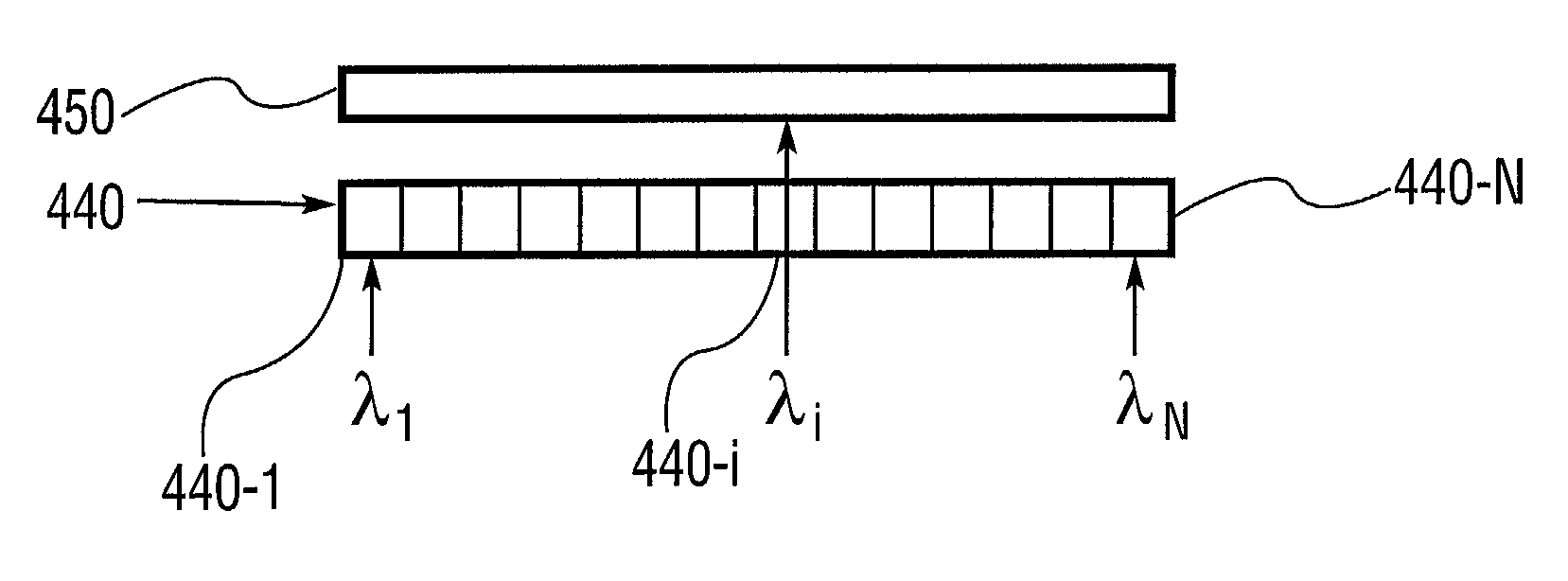
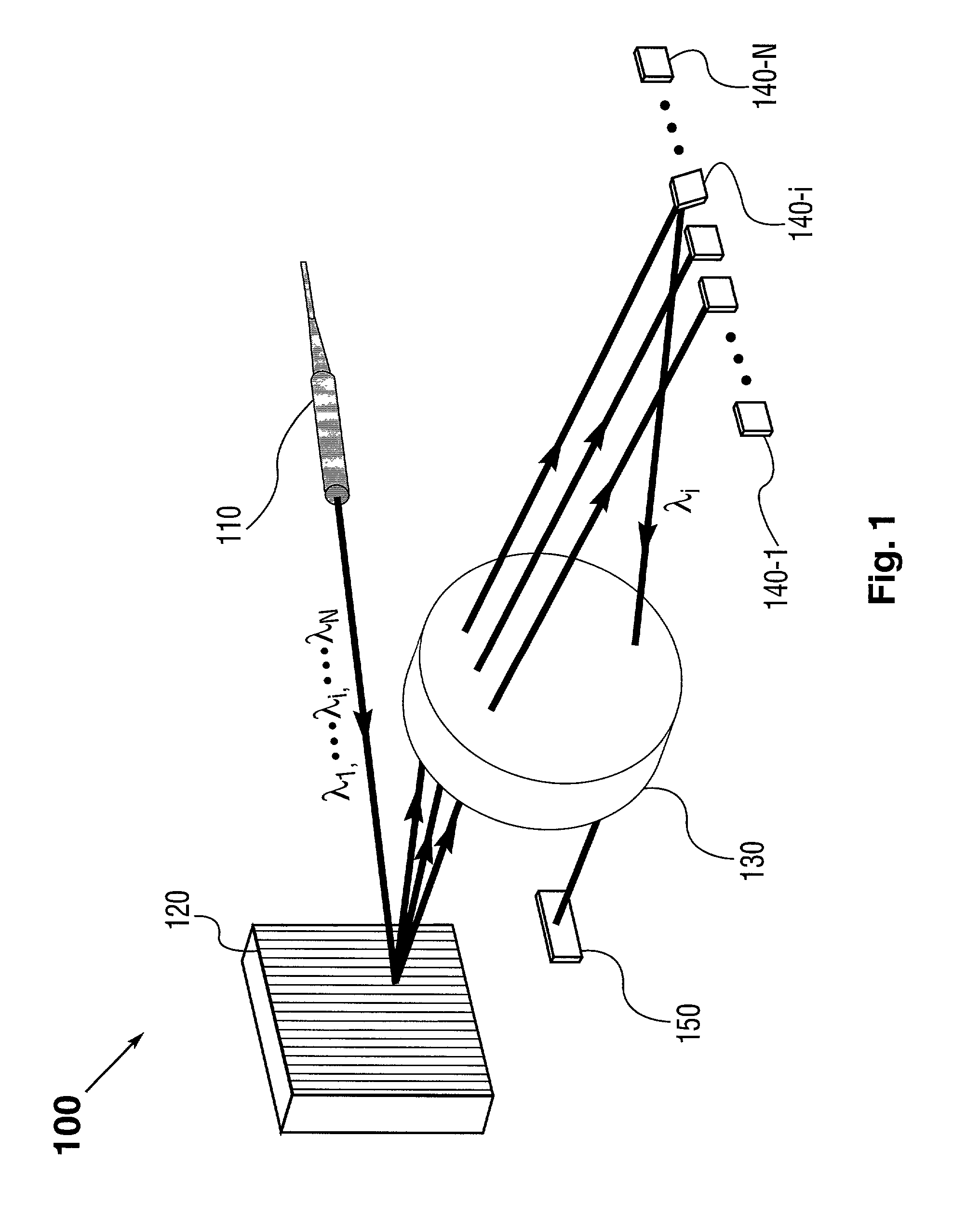
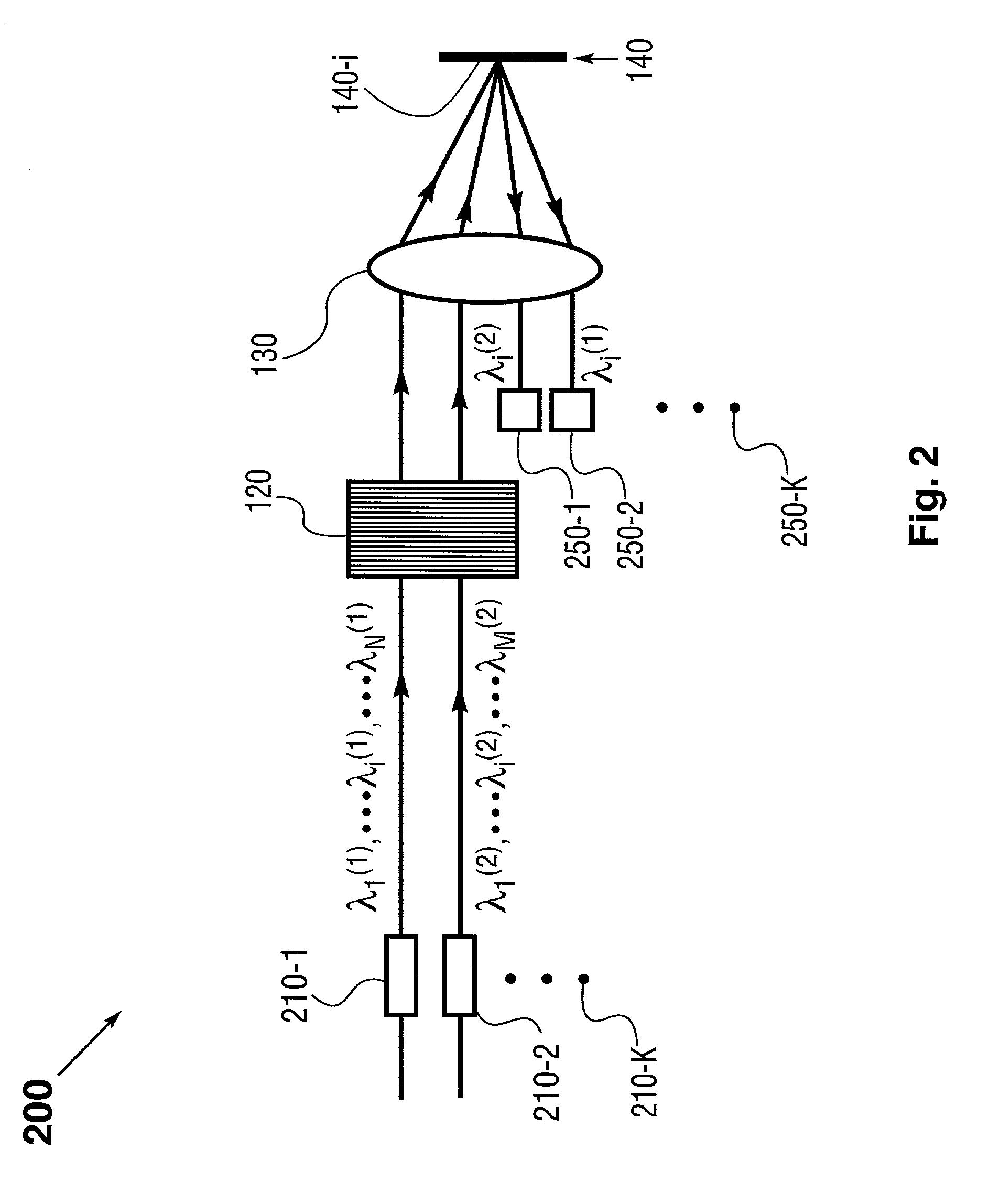
InactiveUS7177496B1Overcome effectImprove versatilitySpectrum investigationTime-division optical multiplex systemsPolarization diversityWdm optical networks
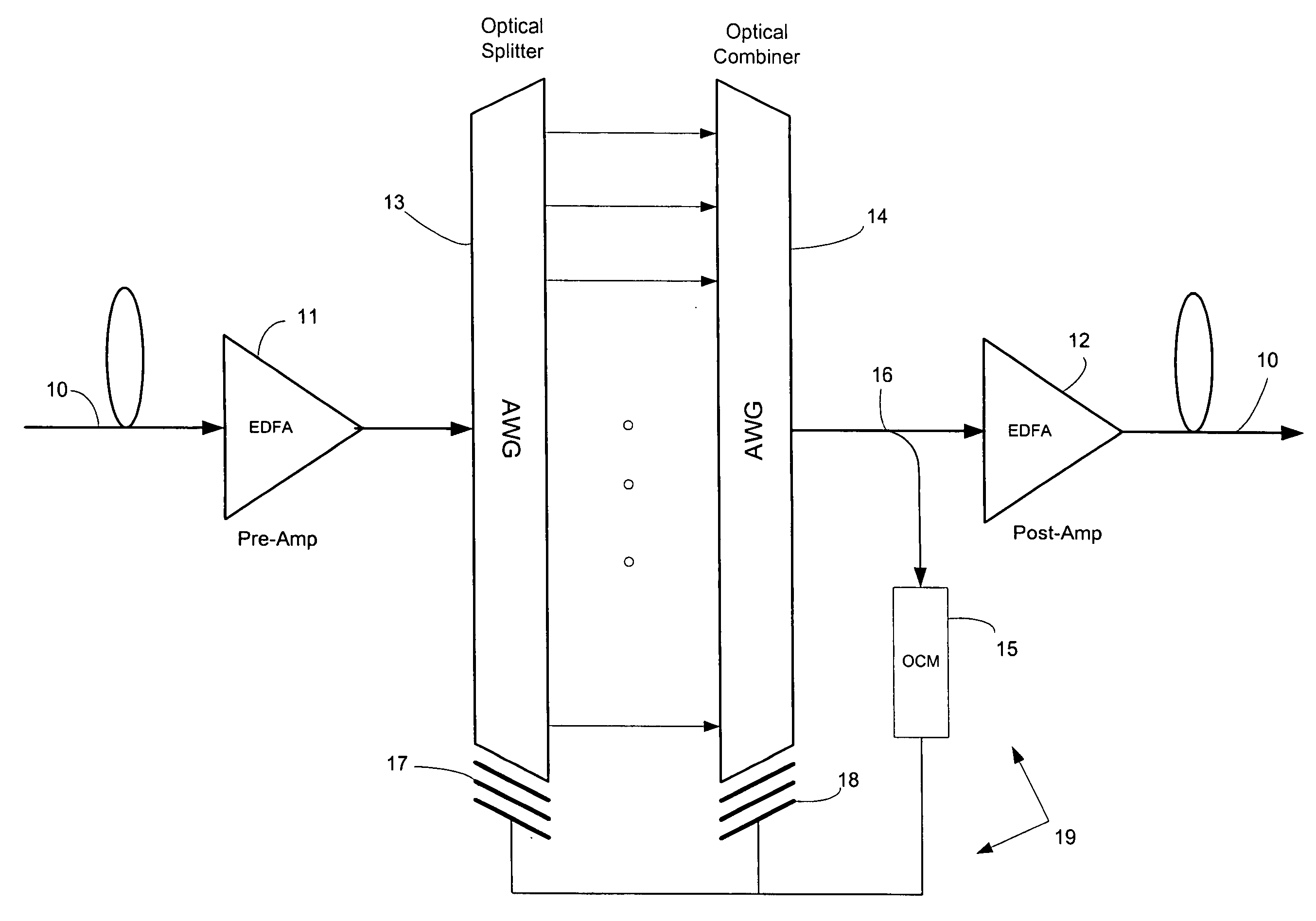
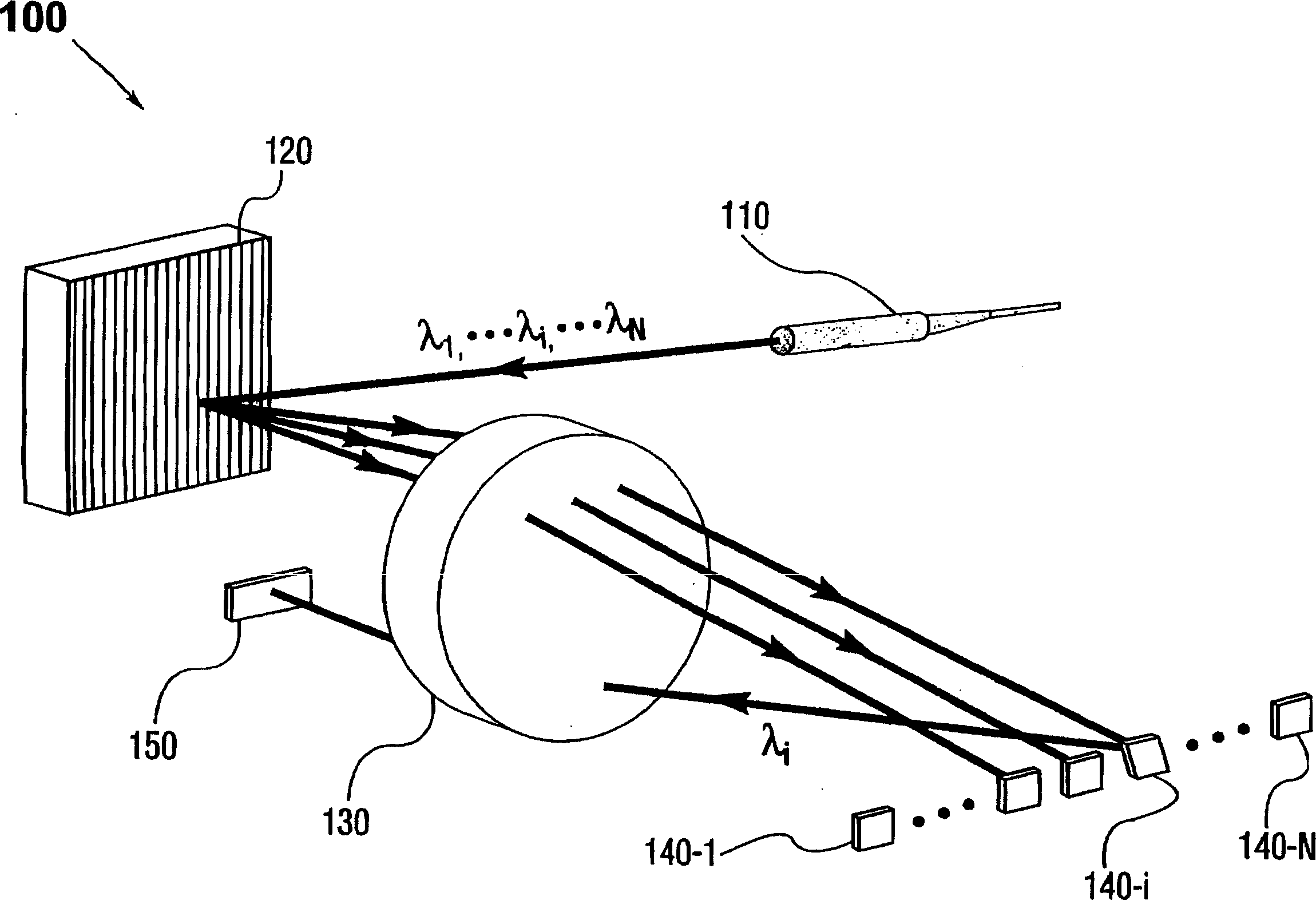
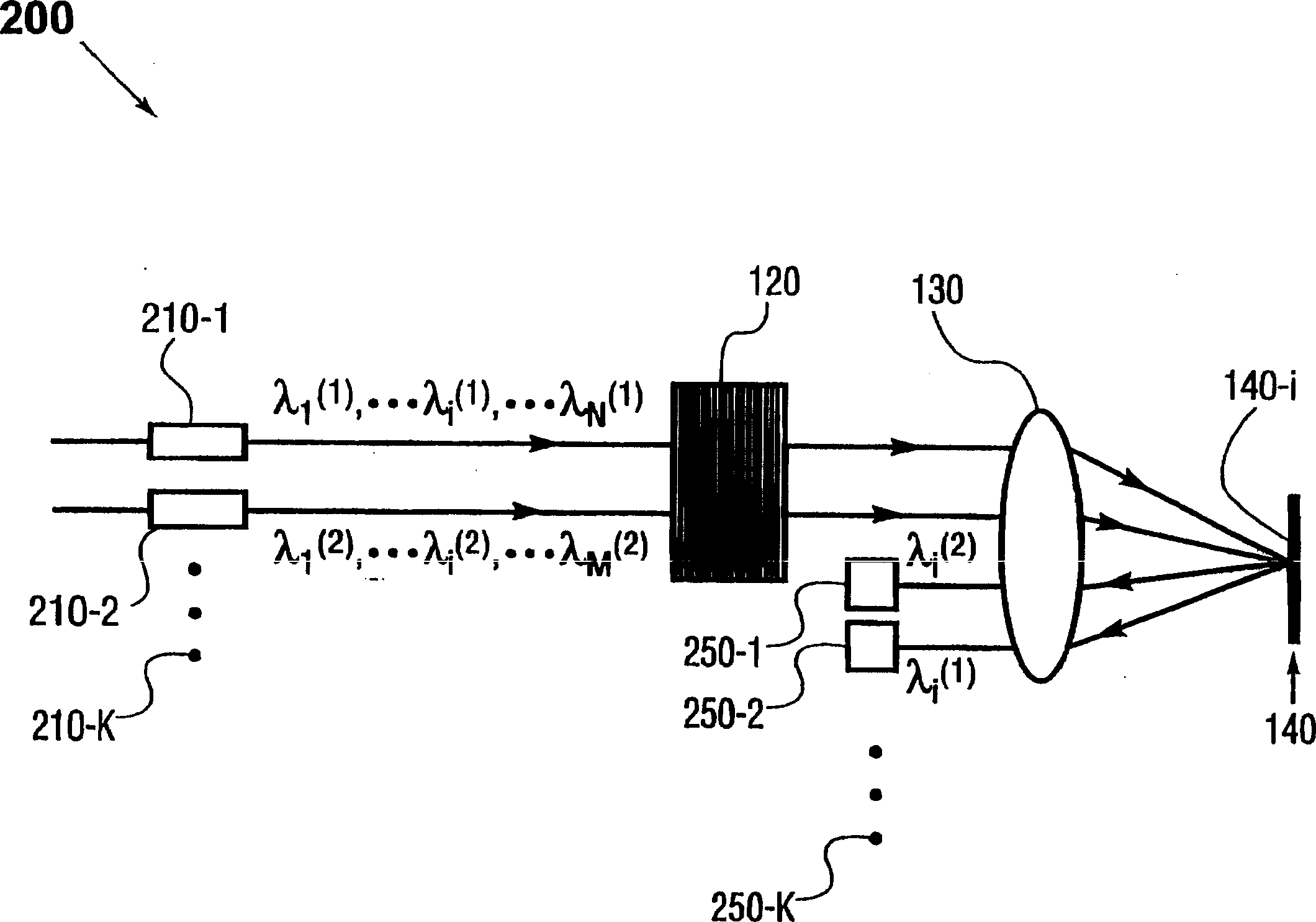
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for optical spectral power monitoring that employ a time-division-multiplexed detection scheme. The optical spectral power monitoring apparatus of the present invention uses a wavelength-dispersing means such as a diffraction grating to separate a multi-wavelength optical signal into multiple spectral channels and an array of beam-manipulating elements positioned to correspond with the spectral channels. The beam-manipulating elements are individually controllable so as to direct the spectral channels into an optical detector in a time-division-multiplexed sequence. The optical spectral power monitoring apparatus may further employ a polarization diversity scheme, thereby becoming polarization insensitive. This enables the apparatus of the present invention to enhance spectral resolution, while providing improved accuracy in optical spectral power detection. Accordingly, a variety of novel optical spectral power monitors can be constructed according to the present invention, that are well suitable for WDM optical networking applications.
Owner:CAPELLA PHOTONICS INC
WDM optical network and switching node with pilot tone communications
InactiveUS20020126334A1Minimal lossReduce lossMultiplex system selection arrangementsRing-type electromagnetic networksPath lengthWdm optical networks
A communications network has a plurality of nodes interconnected by an optical transmission medium. The transmission medium is capable of a carrying a plurality of wavelengths organized into bands. A filter at each node for drops a band associated therewith and passively forwards other bands through the transmission medium. A device is provided at each node for adding a band to the transmission medium. Communication can be established directly between a pair of nodes in the network sharing a common band without the active intervention of any intervening node. This allows the network to be protocol independent. Also, the low losses incurred by the passive filters permit relatively long path lengths without optical amplification.
Owner:CIENA
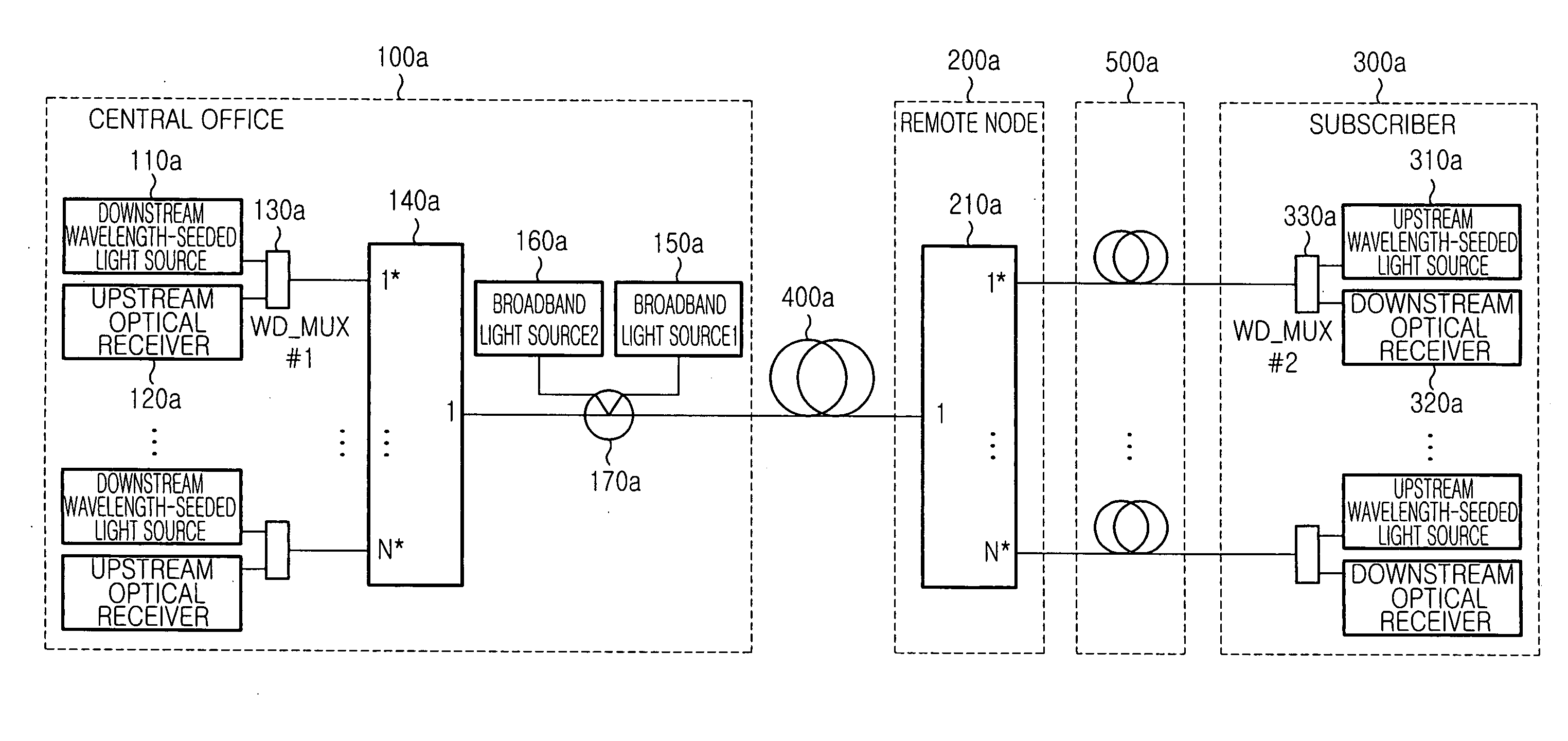
Wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network system using wavelength-seeded light source
InactiveUS20050074240A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionWdm optical networksSingle strand
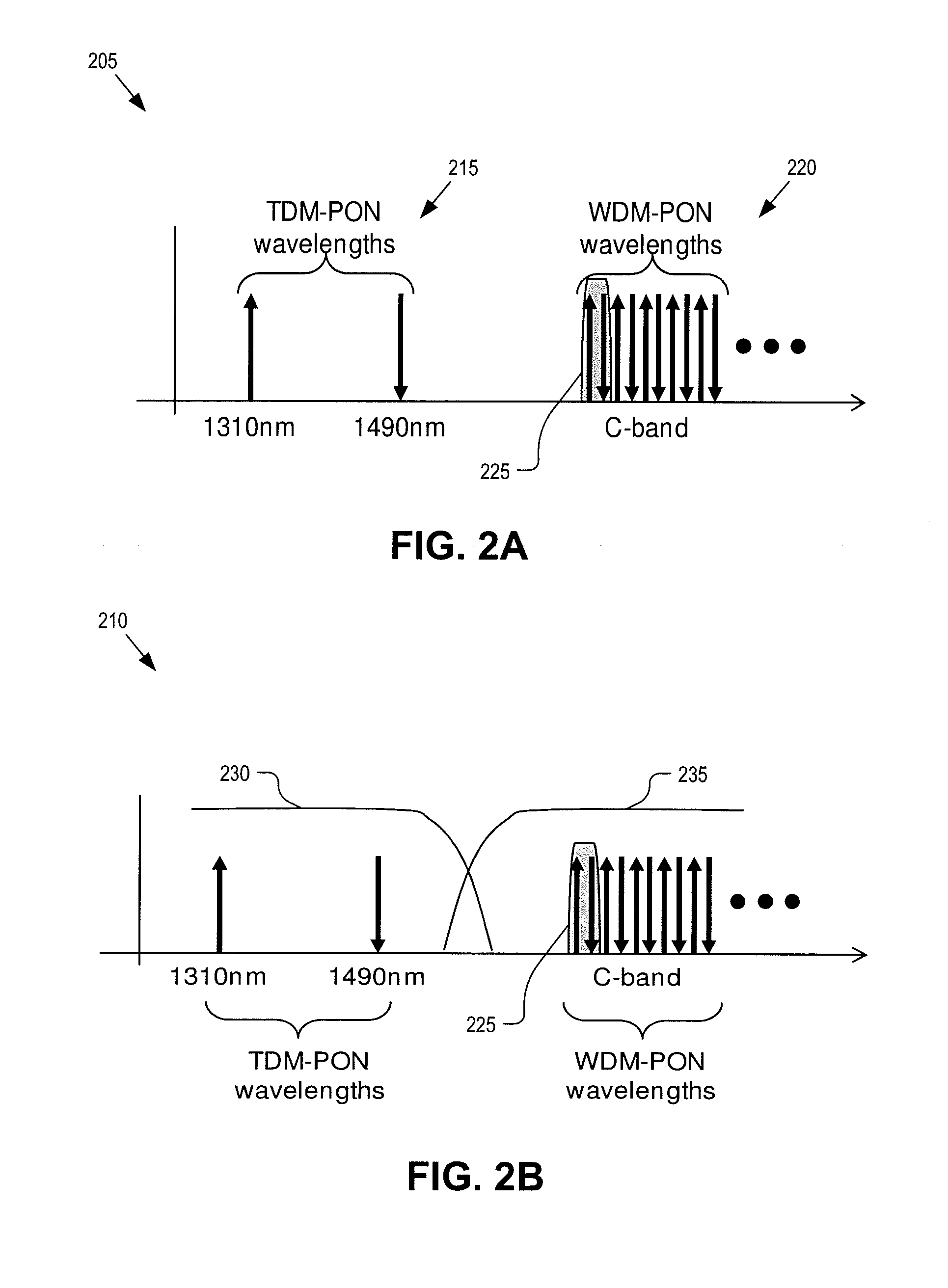
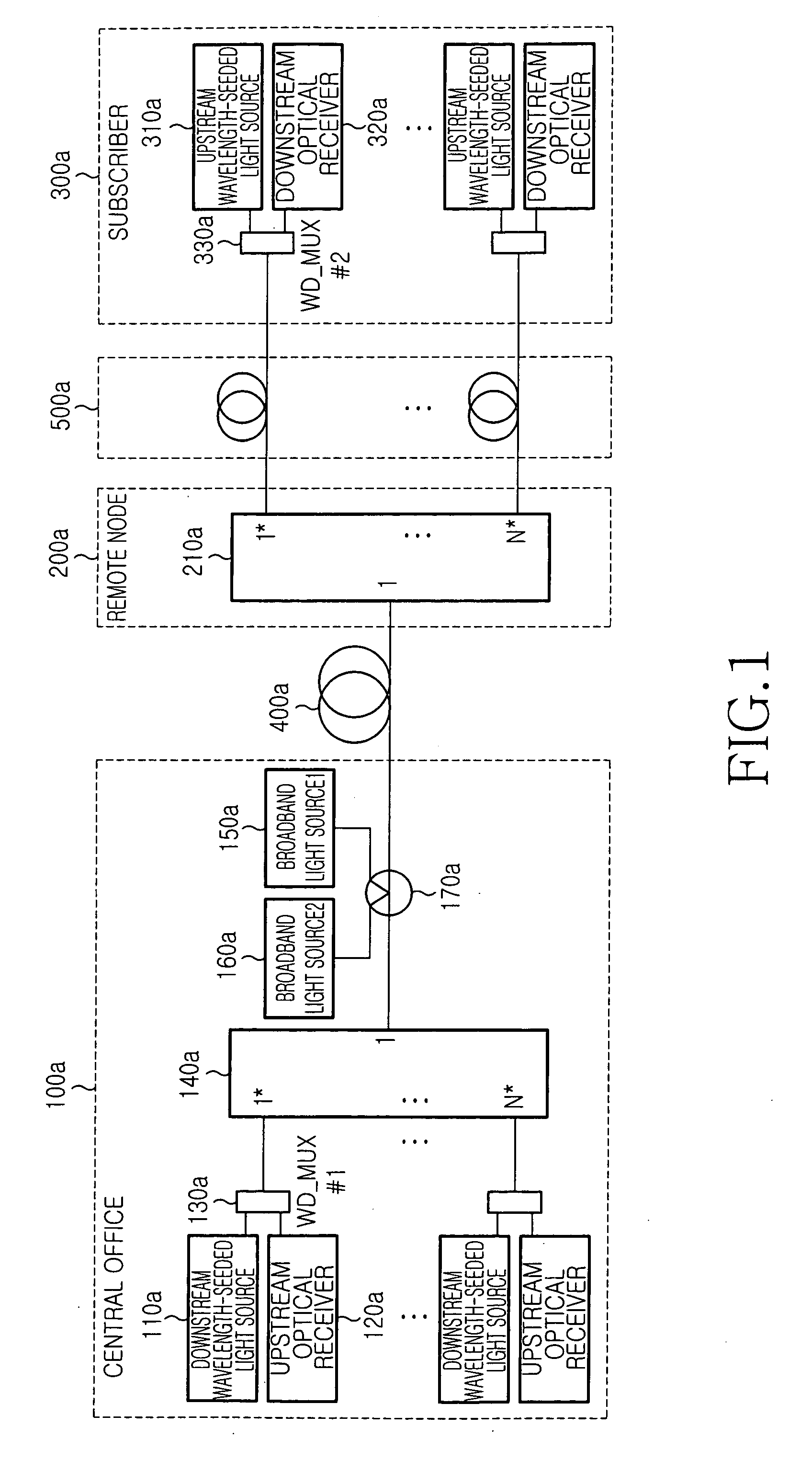
An economical wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network (WDM-PON) system is realized by directly modulating a wavelength-seeded light source to transmit upstream or downstream data, without using an expensive external modulator. A multiplexed signal having the same wavelength as the waveguide grating is generated and used to control the temperature of the waveguide grating and adjust the wavelength of a wavelength-division-multiplexed signal routed to a transfer link. The wavelength selectivity and stabilization of each light source are not required. Since upstream and downstream signals can be multiplexed and demultiplexed concurrently by each waveguide grating located in the central office and the remote node, it is possible to reduce the number of waveguide gratings used in a WDM optical network. In addition, upstream and downstream signals can be transmitted concurrently using a single-strand transfer optical fiber, thereby realizing an economical and efficient WDM-PON.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Sideband filtering of directly modulated lasers with feedback loops in optical networks
InactiveUS20060177225A1Minimizing chirpMonitor qualityWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTemperature controlPeak value
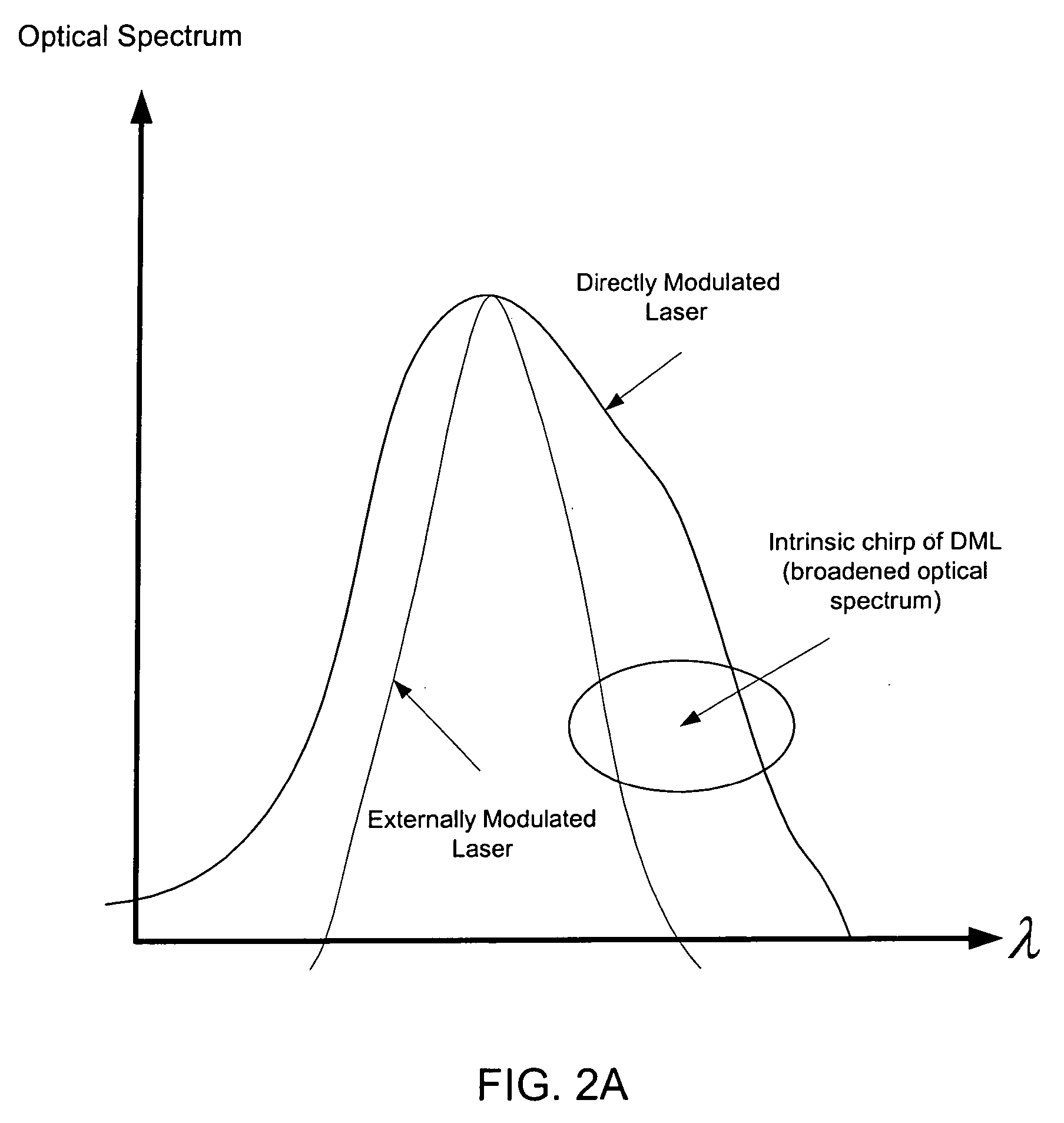
In a WDM optical network DML signals are sideband filtered to compensate for chirp with a feedback loop carrying signals from a monitor unit which helps maintain the sideband filter offset from a peak output of the DMLs. Network components with filtering characteristics, such as AWGs, can be used as the sideband filters. The monitor units monitor the Q-factors or BERs of the filtered signals and the sideband offset is maintained by temperature control of the sideband filters with respect to the DMLs.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
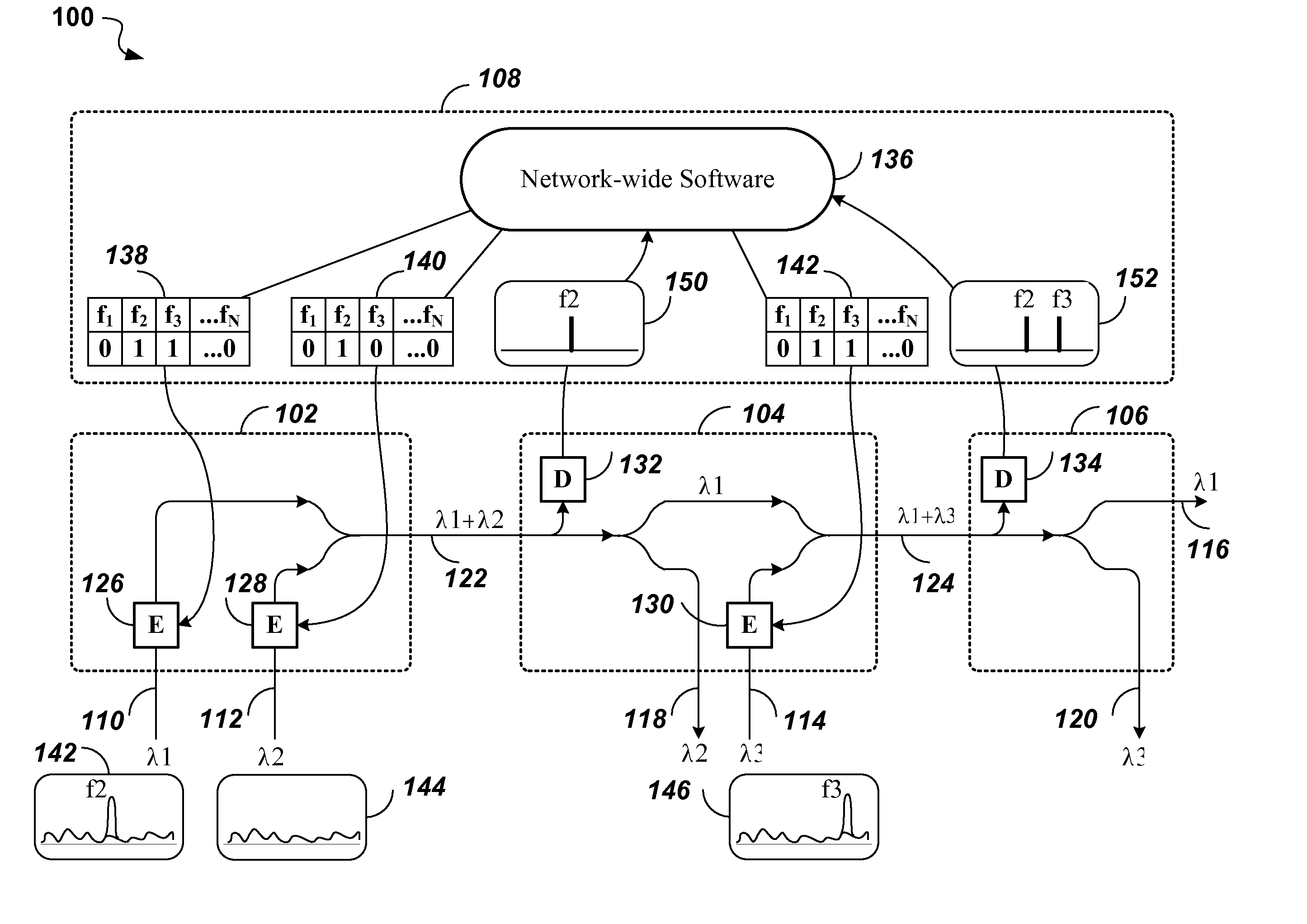
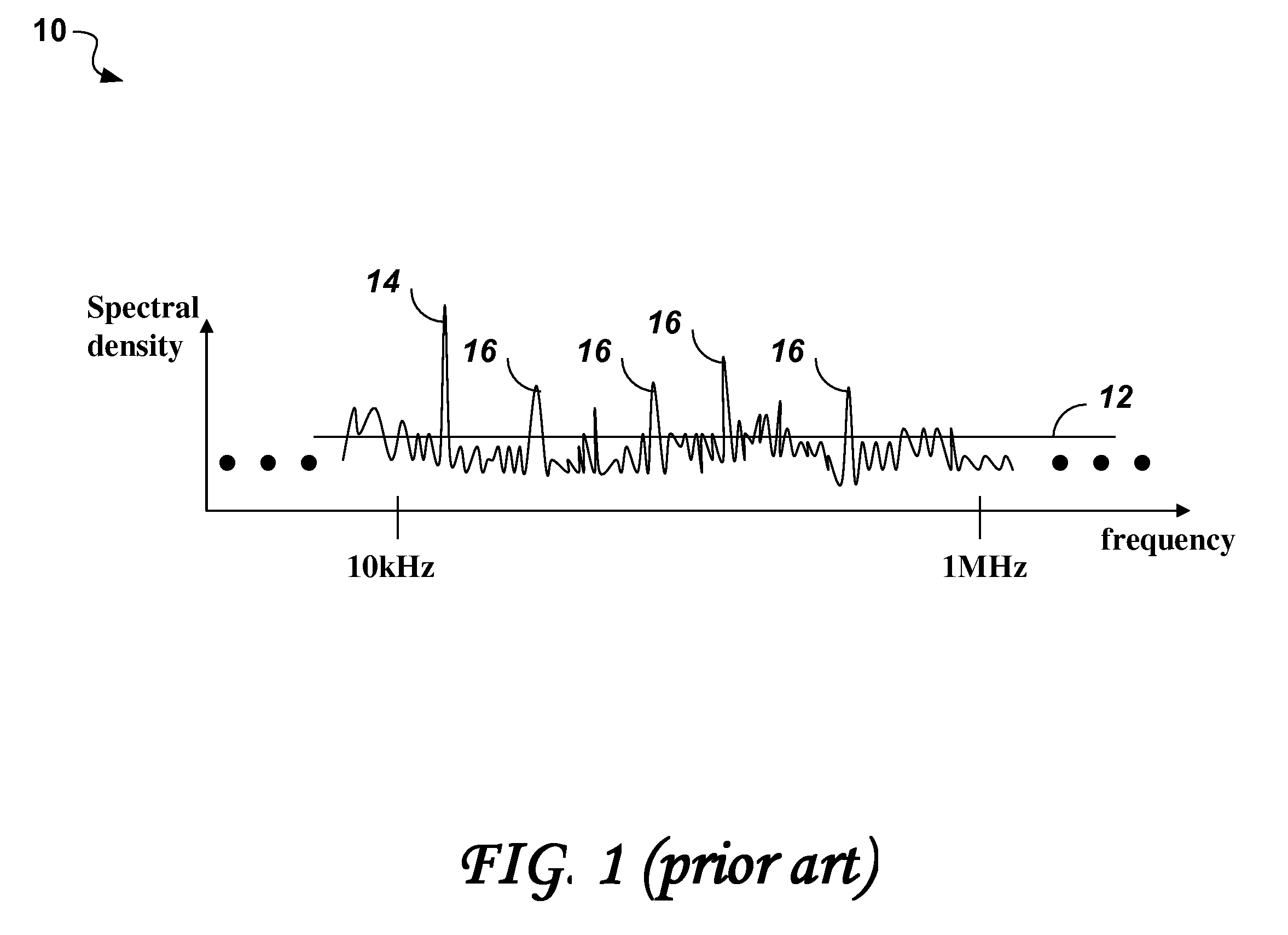
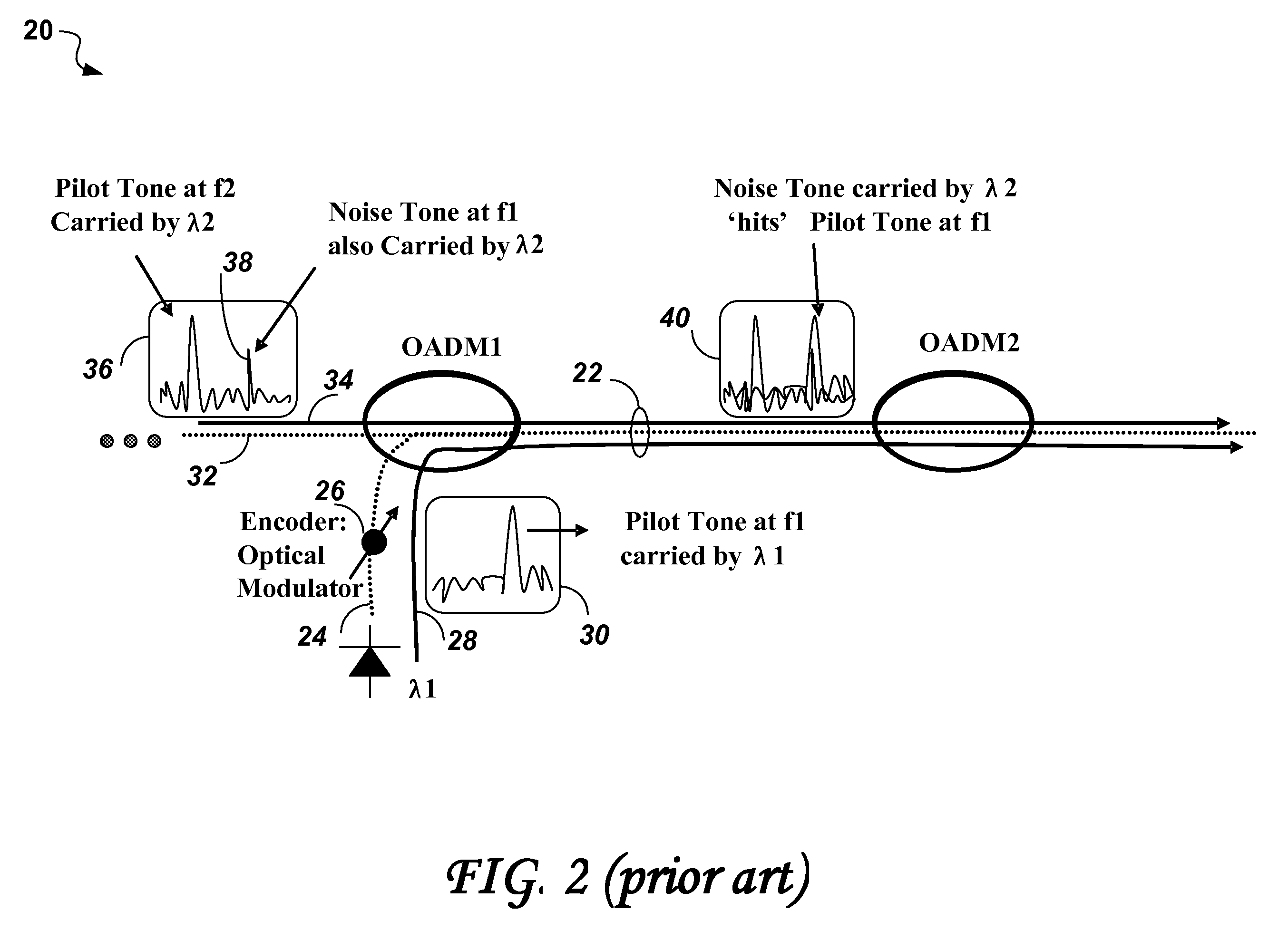
Noise tone avoidance in optical networks
Identification of optical channels in wavelength division multiplex (WDM) optical networks may be confounded by unwanted noise tones interfering with pilot / dither tones used for identifying optical channels. The invention describes a method of selecting pilot / dither tones that are selectively restricted to avoid allocating dither / pilot tone frequencies that appear as noise tones along the path of an optical channel in the optical network.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Subtree-based multicasting traffic grooming method in WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplex) optical network
ActiveCN102137313AReduced feature requirementsStrong dynamic configuration traffic grooming capabilitySpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTraffic groomingNetwork communication
The invention provides a subtree-based multicasting traffic grooming method in a WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplex) optical network, belonging to the technical field of network communication. The method comprises the steps of: initializing, searching an optimal subtree, grooming by using the optimal subtree, adding a subtree, newly building a subtree, allocating resources, and releasing corresponding resources. Under the condition of multiple restrains, the method is used for carrying out service grooming by using the existing optical tree and the optical path in the network, has wider applicable range, low requirement on functions of network nodes in the WDM optical network, and has strong dynamic configuration traffic grooming capability due to no need of the network nodes compared with the virtual topology based traffic grooming method, and a relatively simple structure of the needed node.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method and apparatus for measuring and estimating optical signal to noise ratio in photonic networks
InactiveUS6907197B2Accurate measurementWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringAudio power amplifierSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A WDM optical network comprising a plurality of nodes has a first apparatus for optical analysis at the site of a first optical amplifier upstream of the first node, a second apparatus for optical analysis at the site of a second optical amplifier at the downstream output of the first node, and a third apparatus for optical analysis at the site of a third optical amplifier further downstream of the first node, where knowledge of the optical sin to noise ratio (OSNR) is desired. The first, second and third apparatus are for measuring the signal level at frequencies both at and in-between the channel frequencies. The signal levels at the channel frequencies and between the channel frequencies at the first, second and third apparatus are used to derive the OSNR at the third apparatus. This enables the OSNR to be measured accurately at any site in the network, using calculations in which noise shaping of the nodes can be factored in to the calculation of OSNR.
Owner:CIENA
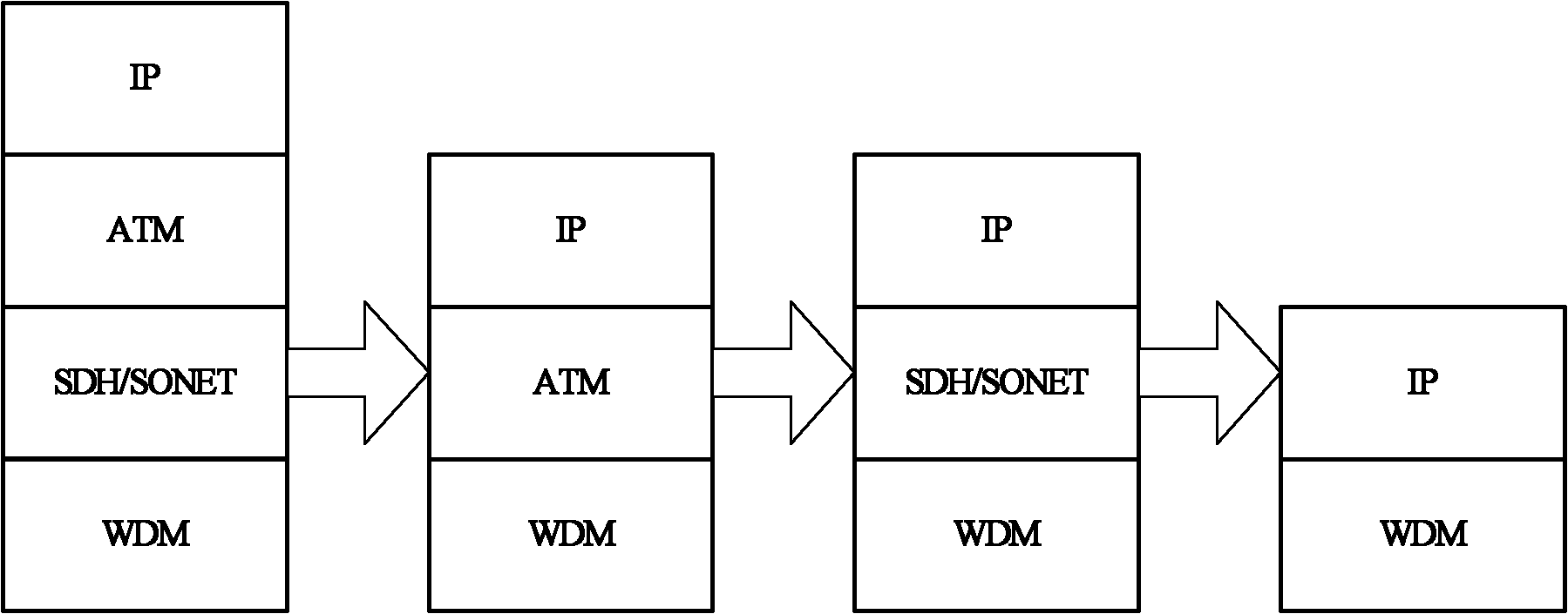
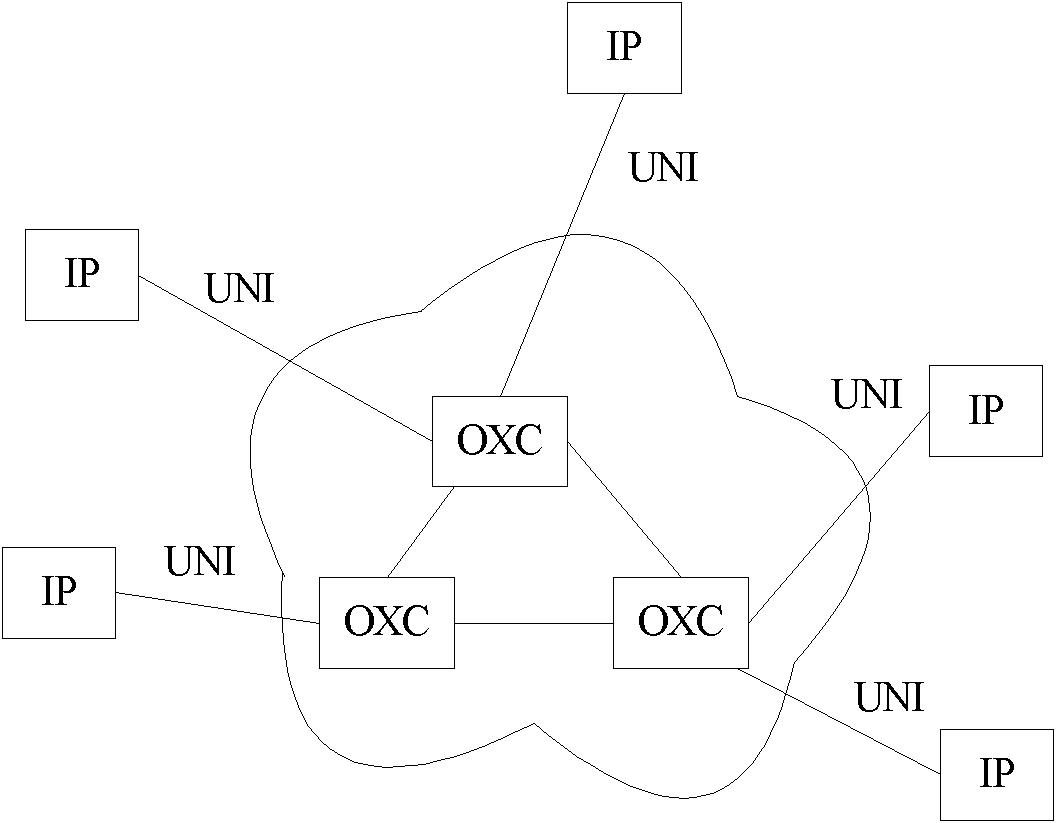
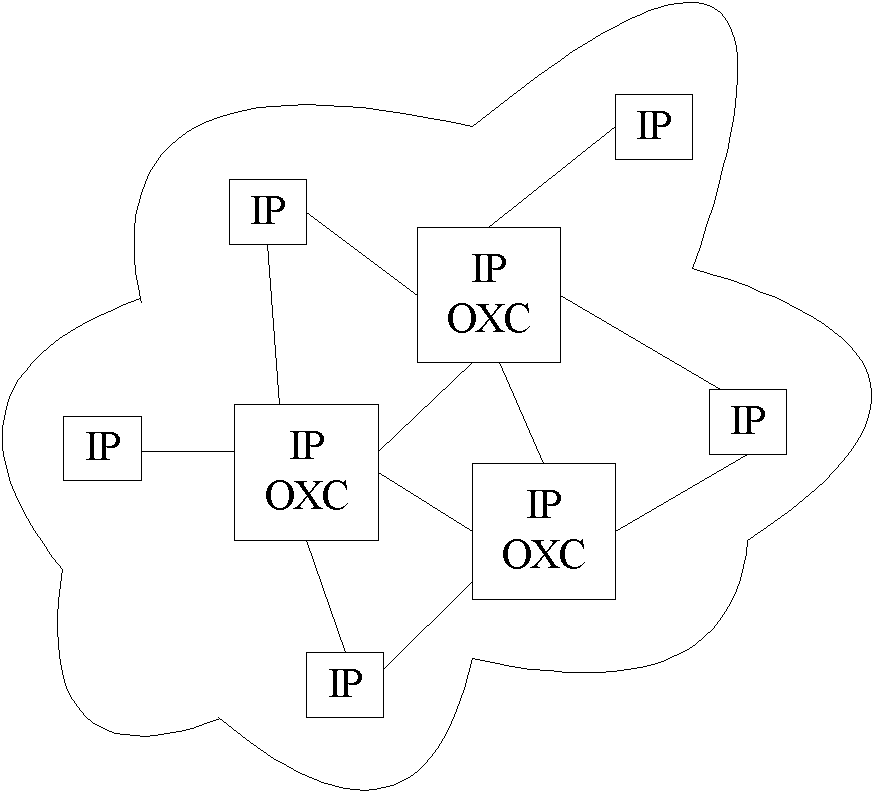
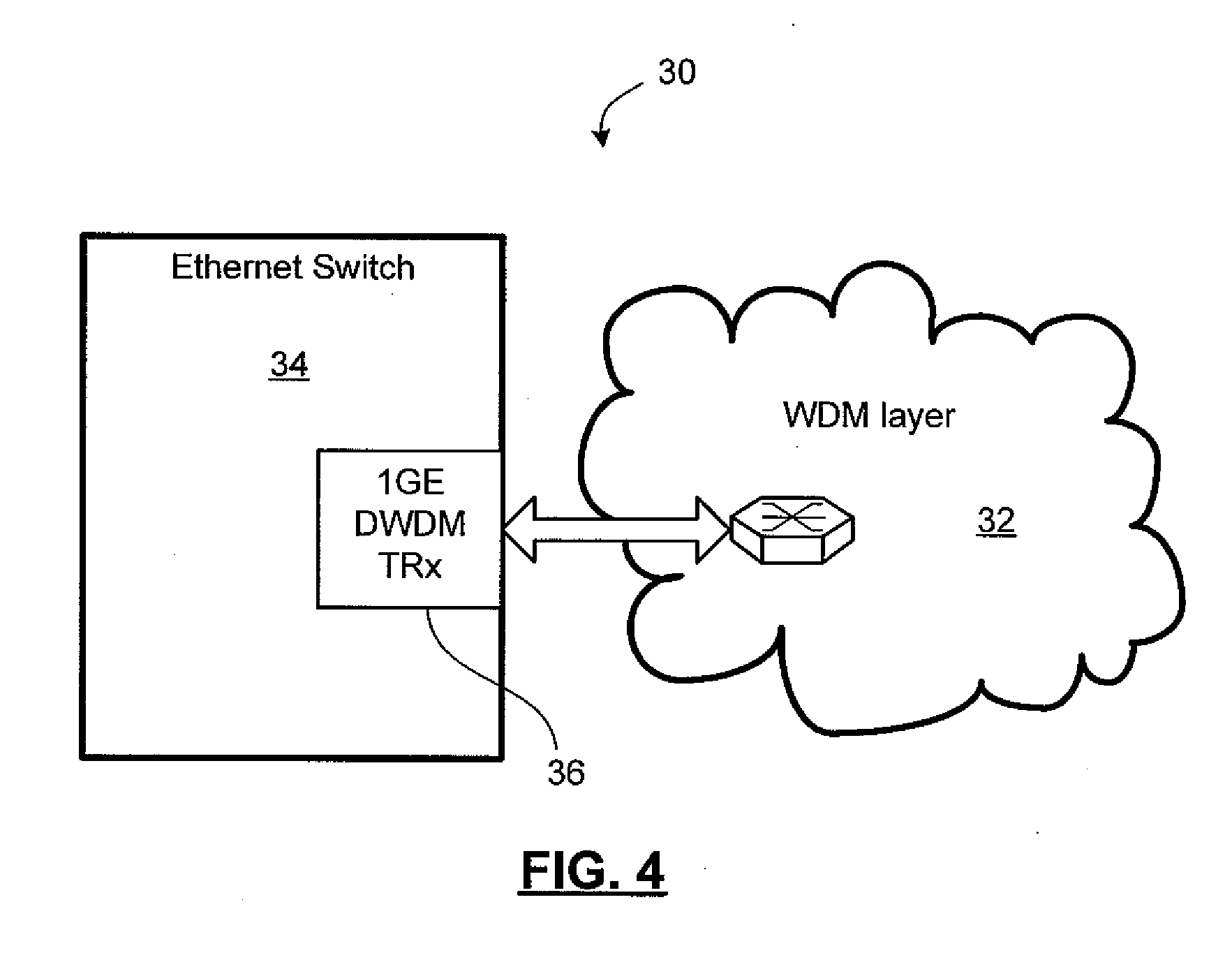
Method and system for configuring a connection-oriented packet network over a wavelength division multiplexed optical network
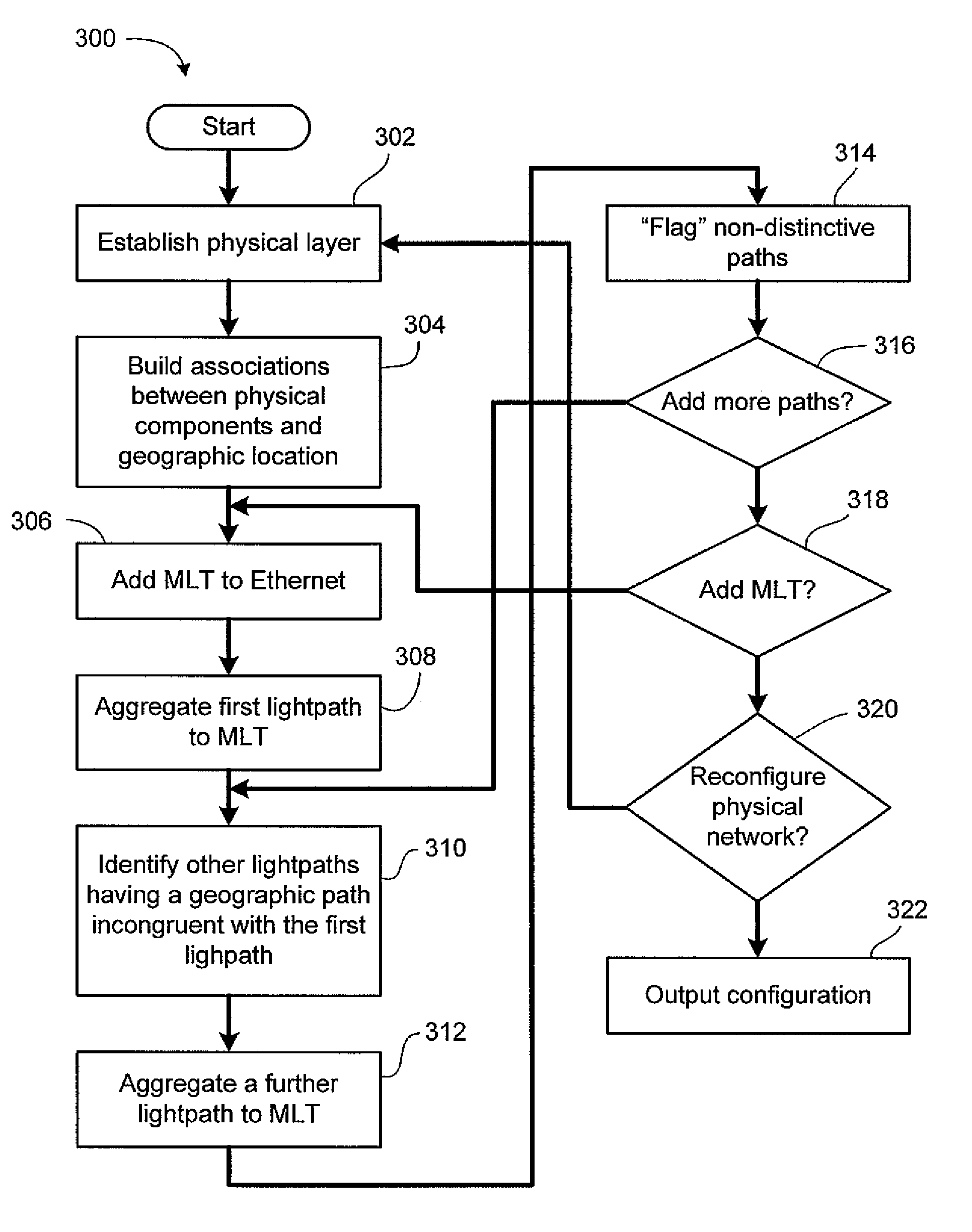
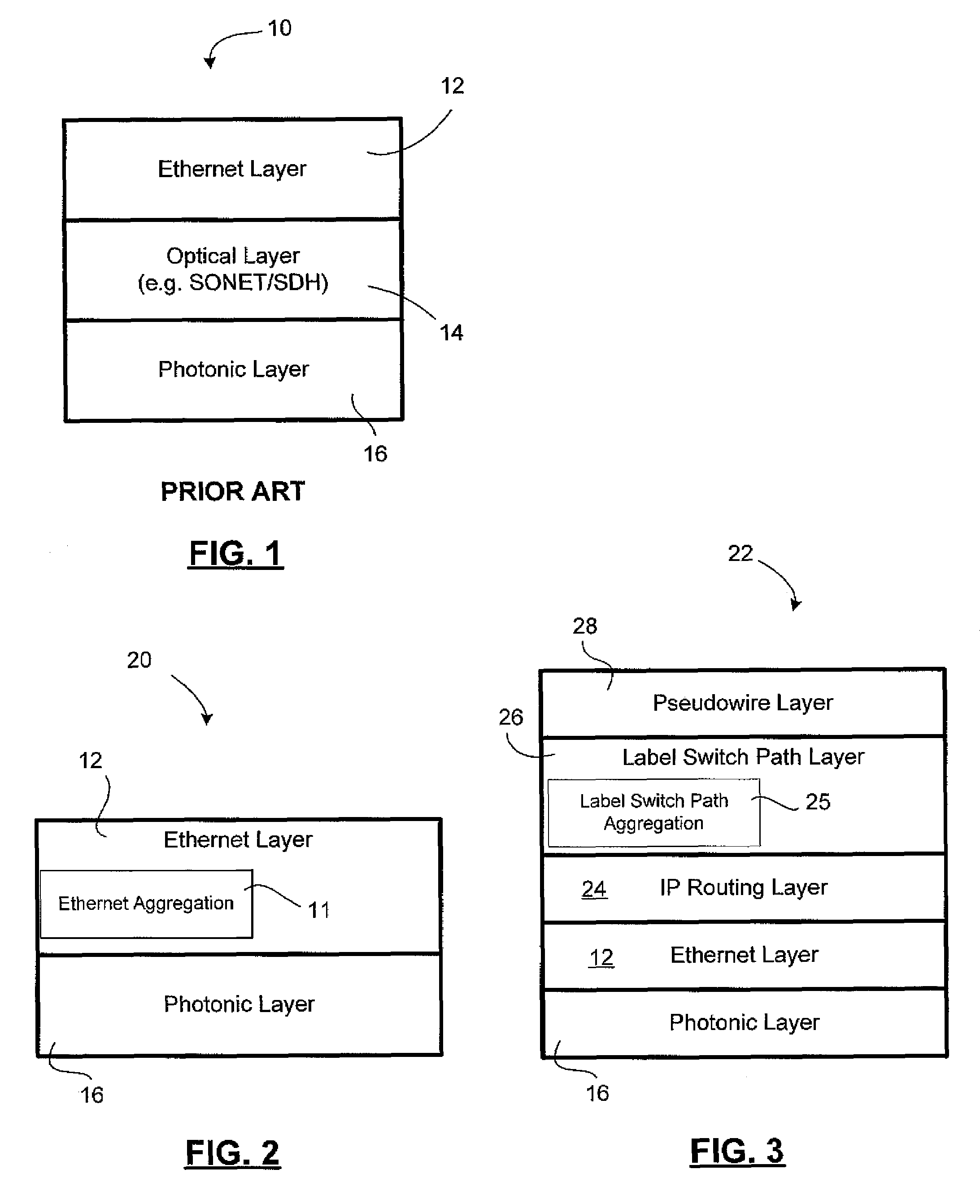
InactiveUS20080002975A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexOptical pathWdm optical networks
A network planning tool and method for configuring a connection-oriented packet network over a WDM optical network without an optical control layer, such as a SONET / SDH layer. The optical network includes a plurality of optical fibers interconnected through nodes and the connection-oriented packet network, such an Ethernet network, MPLS network, or pseudowire network, includes two or more terminal devices. The method and tool function by building an association between the components of the physical layer, such as the optical fiber, and their geographic location or path. The connection-oriented packet network is configured by building multi-link trunks (MLTs) between terminal devices, where the MLTs are built by aggregating lightpaths that traverse distinctive geographic paths. The MLTs are planned and configured through aggregating lightpaths that traverse incongruent sets of photonic elements. A predetermined target for resiliency to physical failure events may determine the degree of congruence allowed between the sets of photonic elements associated with lightpaths in the same MLT.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Utility-based interlayer coordination method in WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) optical network
ActiveCN102186124AReduce failure recovery timeIncreased protection resource usageMultiplex system selection arrangementsFault recovery arrangementsOptical pathWdm optical networks
The invention provides a utility-based interlayer coordination method in a WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) optical network, which comprises the following steps of: calculating the utilization rate of resources protected by a WDM layer; calculating the failure recovery utility of a light path of an IP (Internet Protocol) layer; and comparing the failure recovery utility of the WDM layer with the failure recovery utility of the IP layer. When the method is adopted, a failure recovery sequence of determining respective layers can be realized in case of a failure, and a utility-based interlayer coordination mechanism used for balancing the failure recovery time and the utilization rate of the protected resources is designed to be used for dynamically assessing and deciding the failure recovery in comprehensive consideration of the failure recovery time and the utilization rate of the protected resources; thus, the advantages of the recovery of the WDM layer and the recovery of the IP layer can be better utilized, the failure recovery time is reduced, and the utilization rate of the protected resources is increased.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Subchannel Photonic Routing, Switching and Protection with Simplified Upgrades of WDM Optical Networks
ActiveUS20110158641A1Easy to switchIncrease the number ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsNetwork architecturePhotonics
The present invention includes novel techniques, apparatus, and systems for optical WDM communications. Tunable lasers are employed to generate respective subcarrier frequencies which represent subchannels of an ITU channel to which client signals can be mapped. In one embodiment, subchannels are polarization interleaved to reduce crosstalk. In another embodiment, polarization multiplexing is used to increase the spectral density. Client circuits can be divided and combined with one another before being mapped, independent of one another, to individual subchannels within and across ITU channels. A crosspoint switch can be used to control the client to subchannel mapping, thereby enabling subchannel protection switching and hitless wavelength switching. Network architectures and subchannel transponders, muxponders and crossponders are disclosed, and techniques are employed (at the subchannel level / layer), to facilitate the desired optical routing, switching, concatenation and protection of the client circuits mapped to these subchannels across the nodes of a WDM network.
Owner:VELLO SYST +1
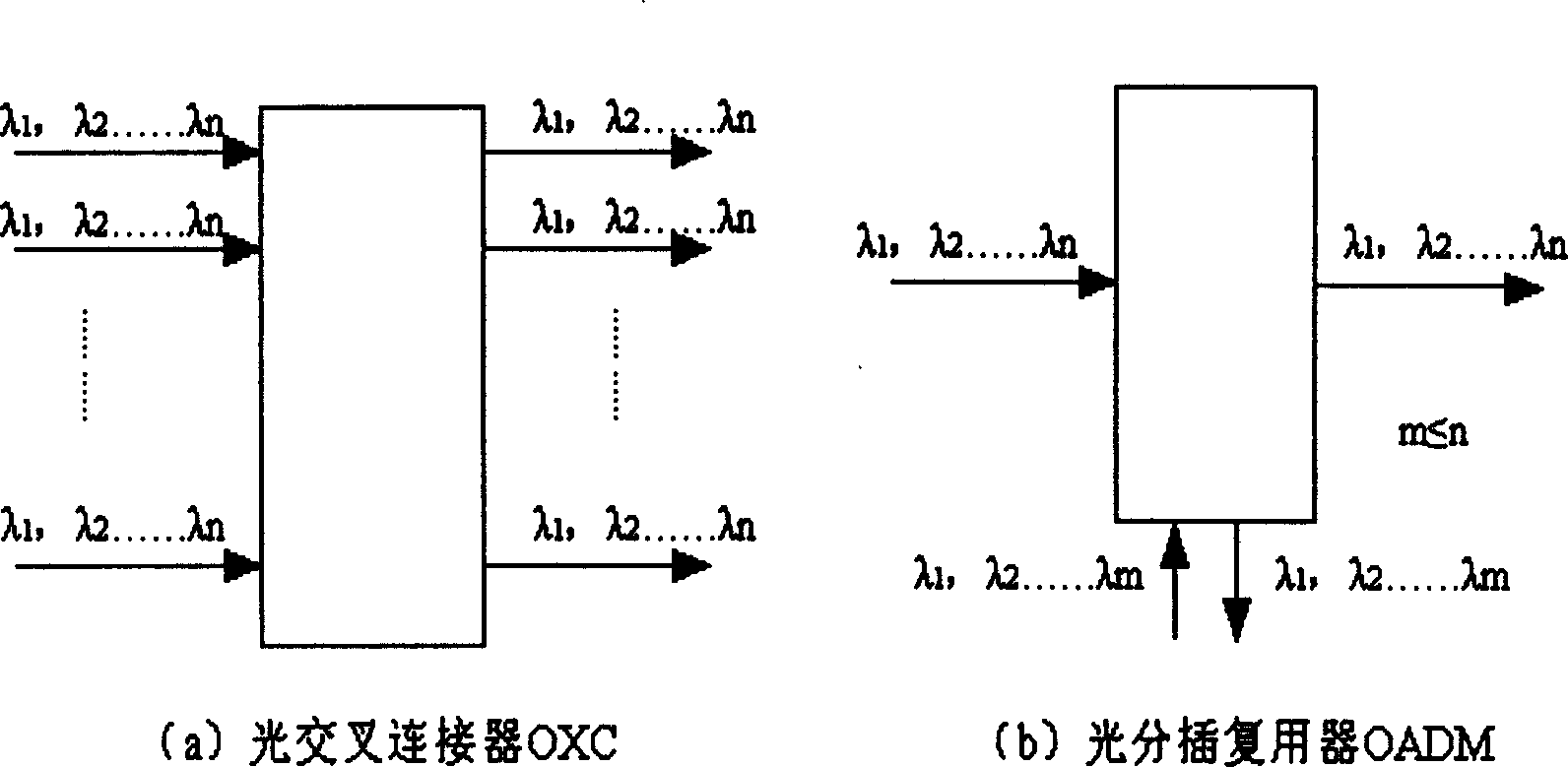
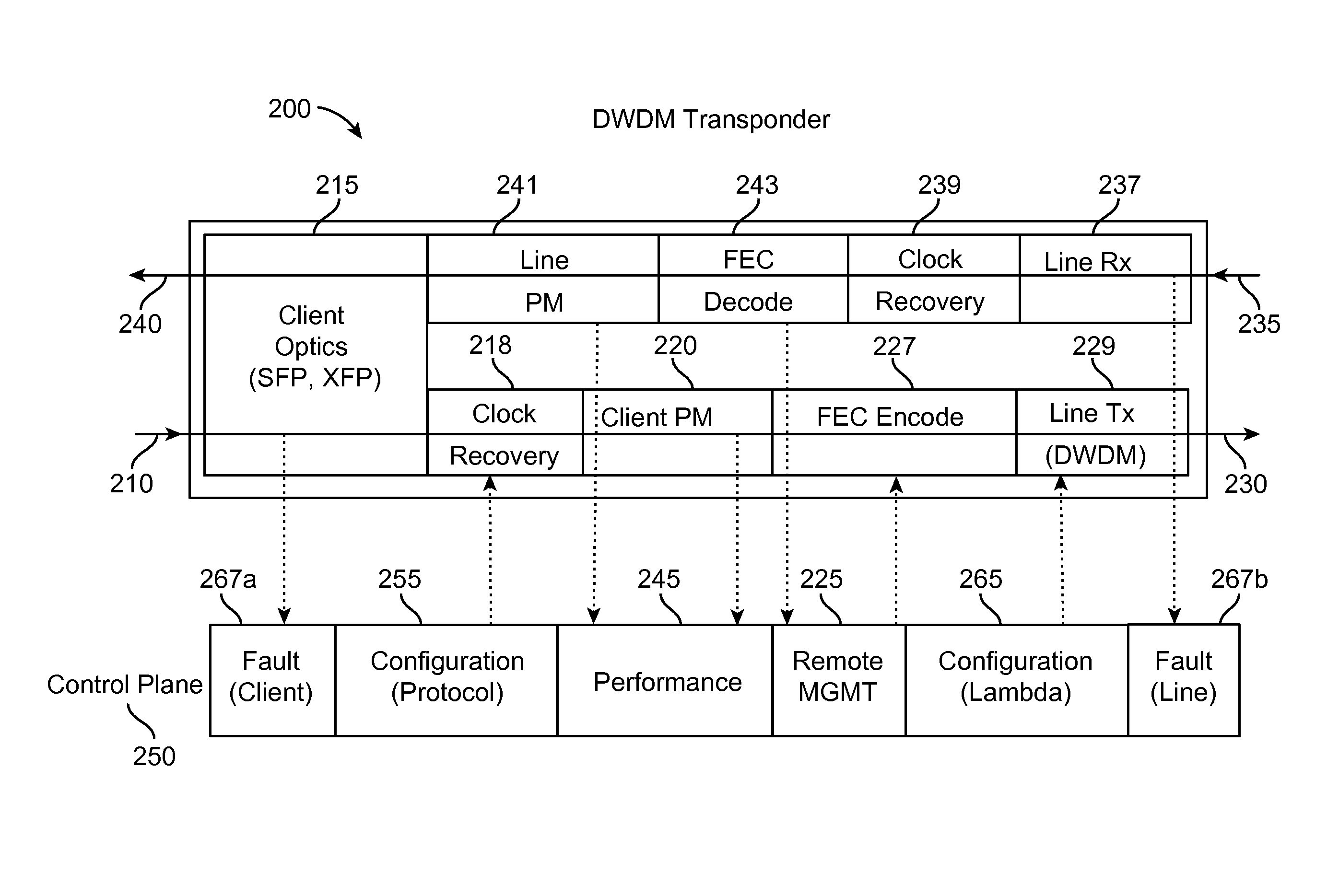
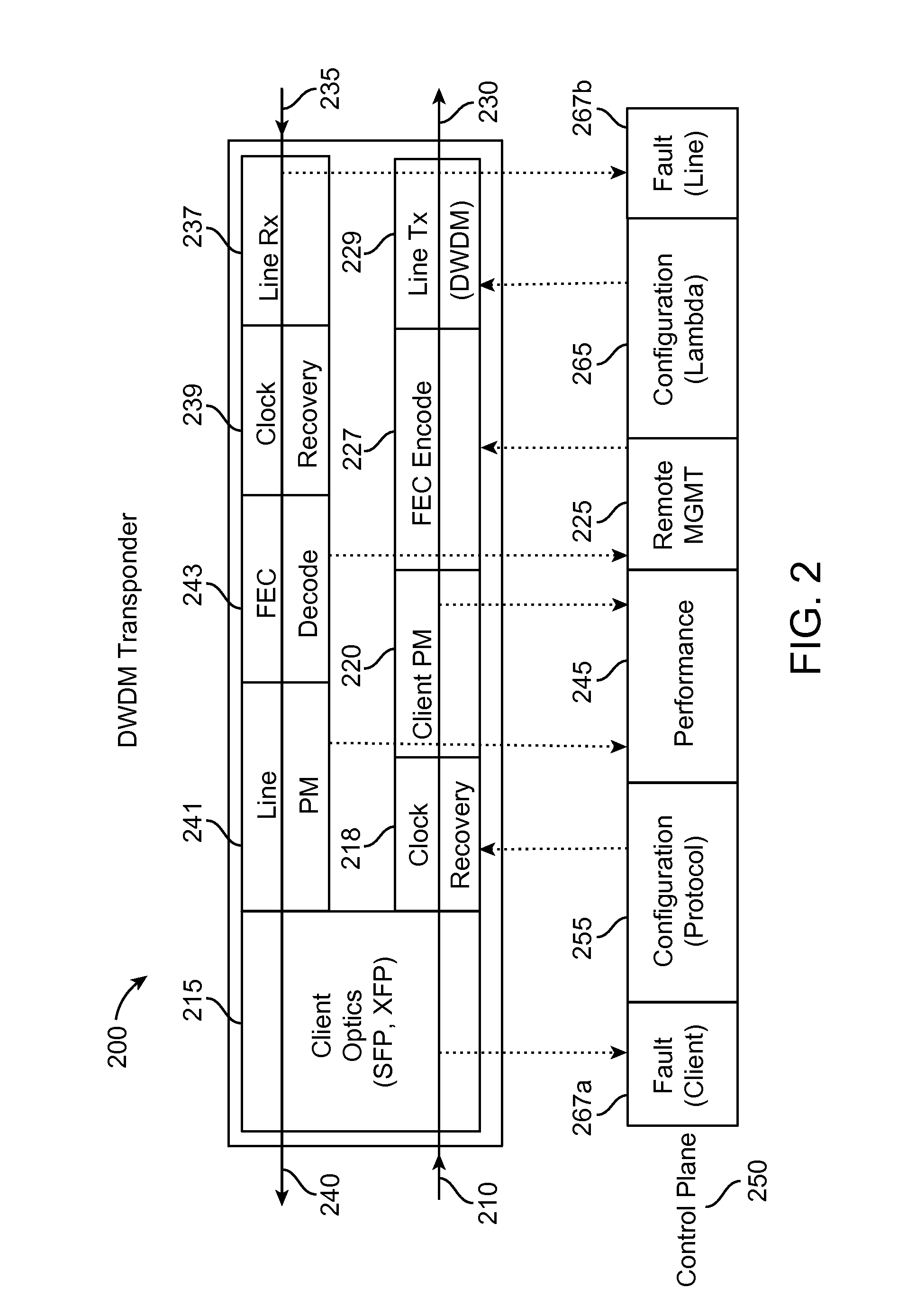
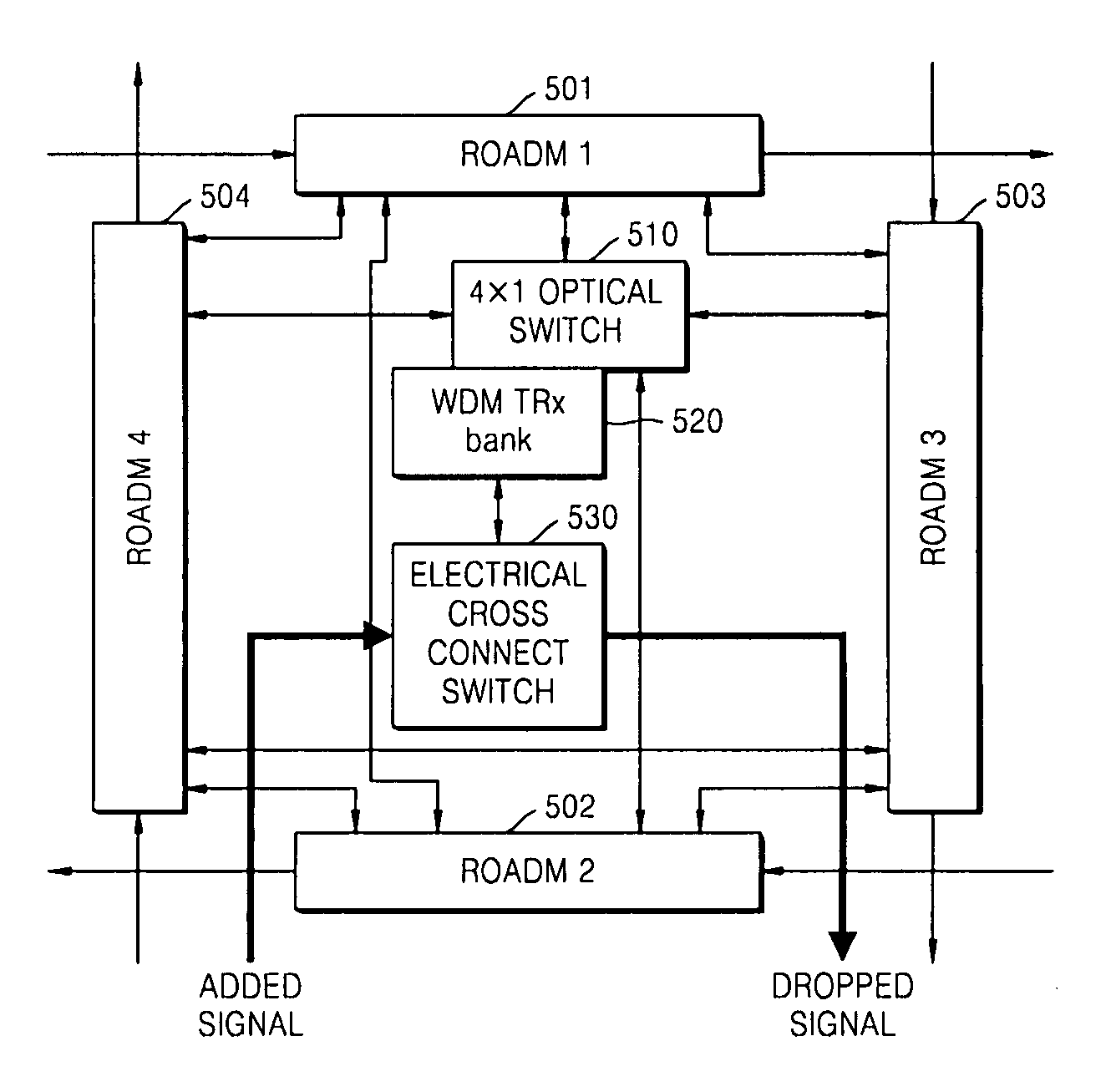
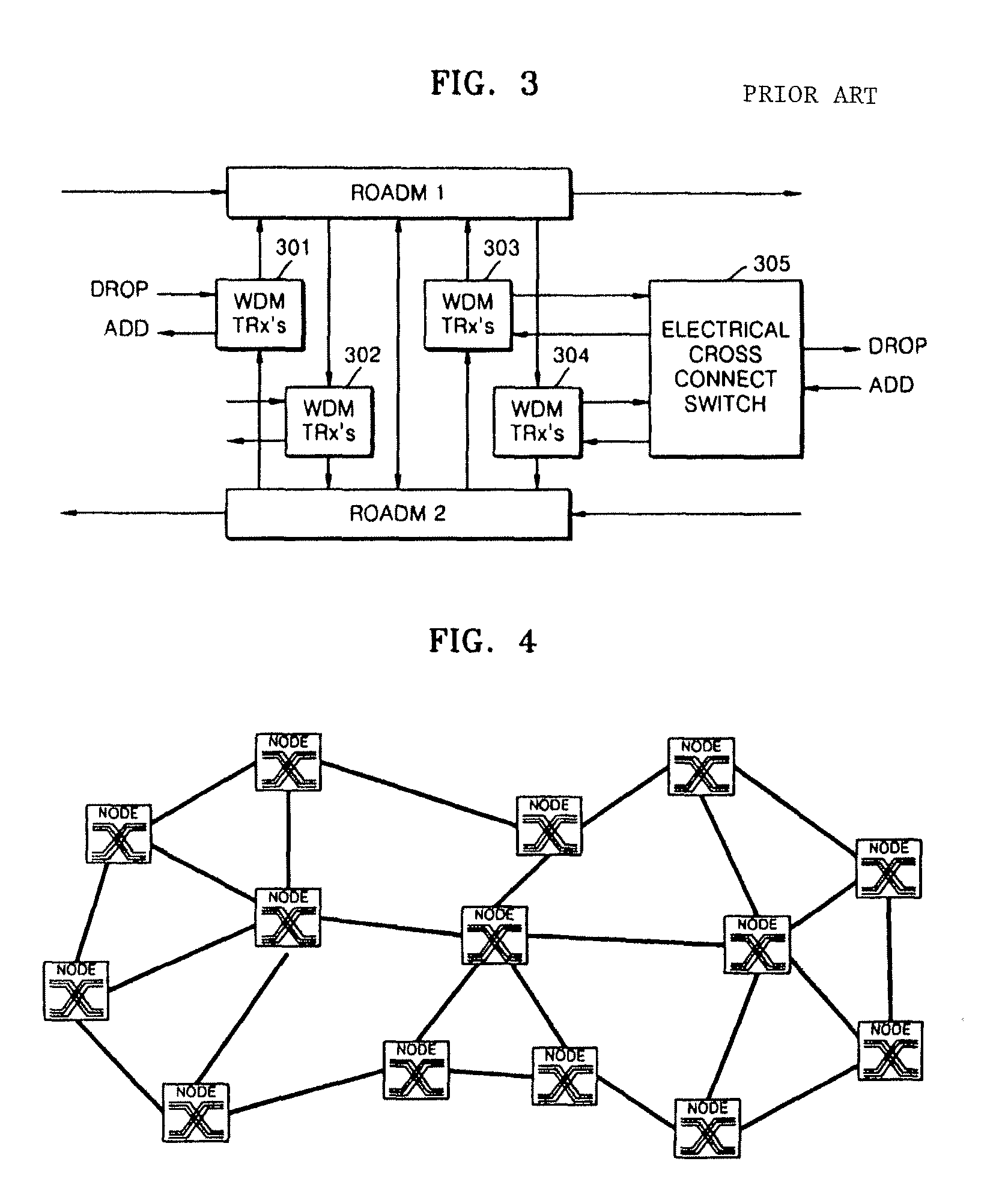
Optical node for mesh-type WDM optical network
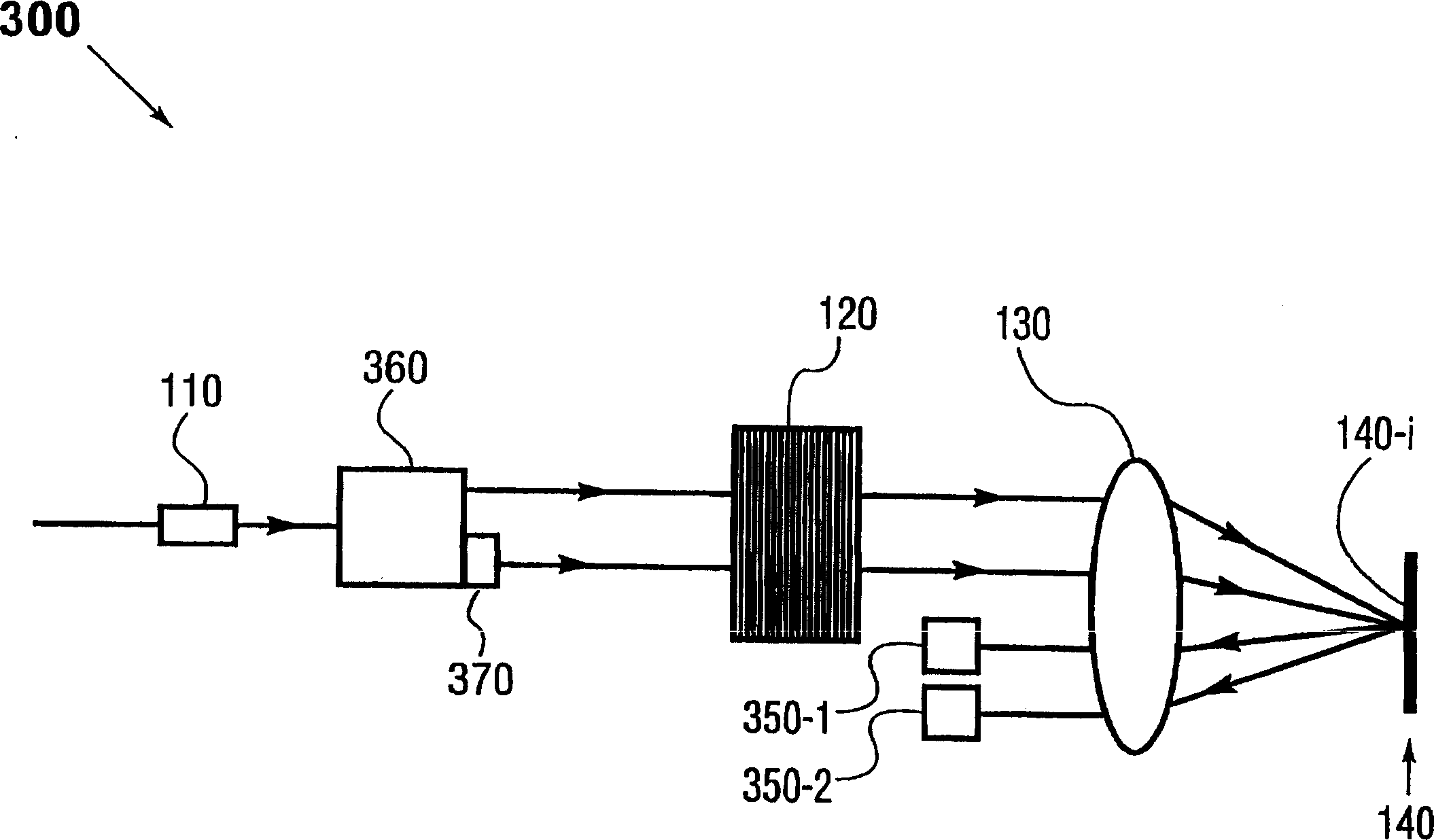
InactiveUS8009986B2Reduce in quantityWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic network arrangementsElectricityTransceiver
An optical node capable of supporting a mesh-type optical network is provided. The node includes: N ROADMs, which separate specific wavelength channels from a multiple wavelength channel optical signal that is input from any node constituting the optical network, allows the rest of the wavelength channels to be passed, and combine another added wavelength channel with the passed wavelength channel to allow the combined wavelength channel to be passed; an N×1 optical switch which selects the specific wavelength channel separated from one of the N ROADMs and inputs the specific wavelength channel into an optical transceiver and selects one of the N ROADMs and connects a wavelength channel that is output from the optical transceiver to the selected ROADM; and an electrical cross connect switch which drops a part of electrical signal bandwidth of the specific wavelength channels separated by the ROADM, which is converted into the electrical signals in the optical transceiver, toward an external client and combines the rest of the electrical signal bandwidth with a electrical signal added by the external client to form an electrical signal bandwidth of a wavelength channel and output the electrical signal to the optical transceiver. Accordingly, optical fiber inputs and outputs in various directions can be supported, and the number of WDM transceivers used for each node is remarkably reduced, thereby improving efficiency and economical efficiency of a network.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Multicast protection method in WDM optical network
InactiveCN101192883AReduce blocking rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWdm optical networksDistributed computing
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Multi-failure protection method for multiple service levels in WDM network
InactiveCN101262298AAddressing the need for protectionMultiple fault protection satisfiesWavelength-division multiplex systemsFault recovery arrangementsGrade of serviceResource utilization
The invention relates to a protection method with a plurality of service grades for multiple faults in WDM networks, pertaining to the technical field of optical network communication. The method comprises the steps as follows: step one: connections of different grades are established for service requests arrived, that is, working accesses and accesses for protection are established; step two: for service connections conveying data in the networks, when failed links occur, the service grade is judged, different protection methods are executed to services of different grades, and enhanced recovery is executed to the service of the highest grade. The method of the invention meets the requirements for different protections raised by users in case of multilink faults in the WDM optical networks. EDSP takes into consideration of an enhanced recovery mechanism for load balancing, protection of resource sharing and resource recycling, so as to improve resource utilization rate and reduce blocking probability; effective multiple faults protection is also provided, and the requirement for services of diamond grade (highly reliable protection for multiple faults (three faults and more)), platinum grade (single fault being 100 percent protected) and economic grade (no protection) are met.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
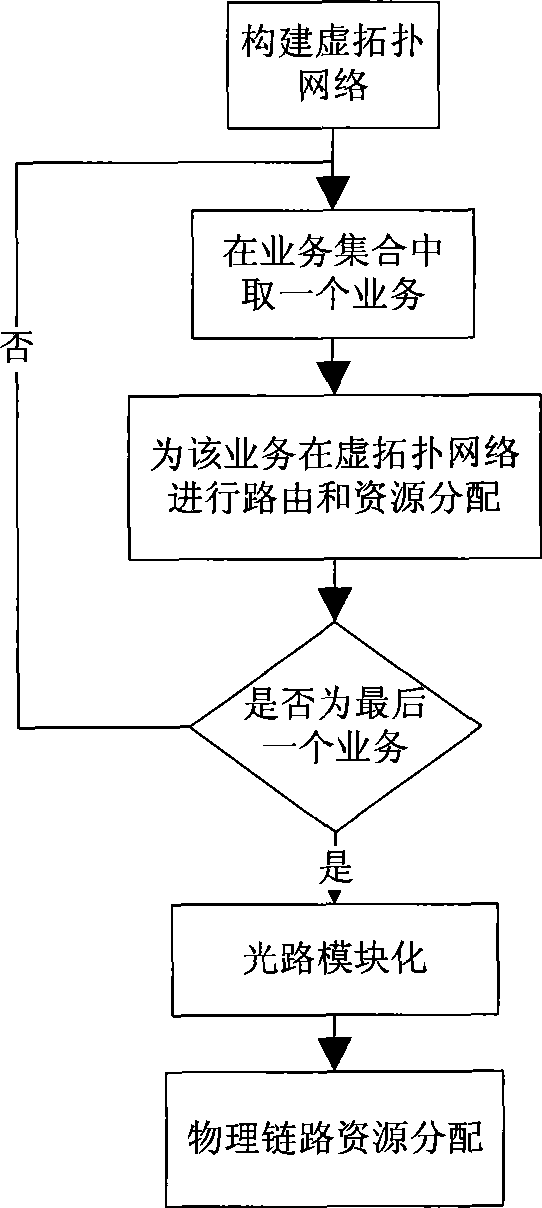
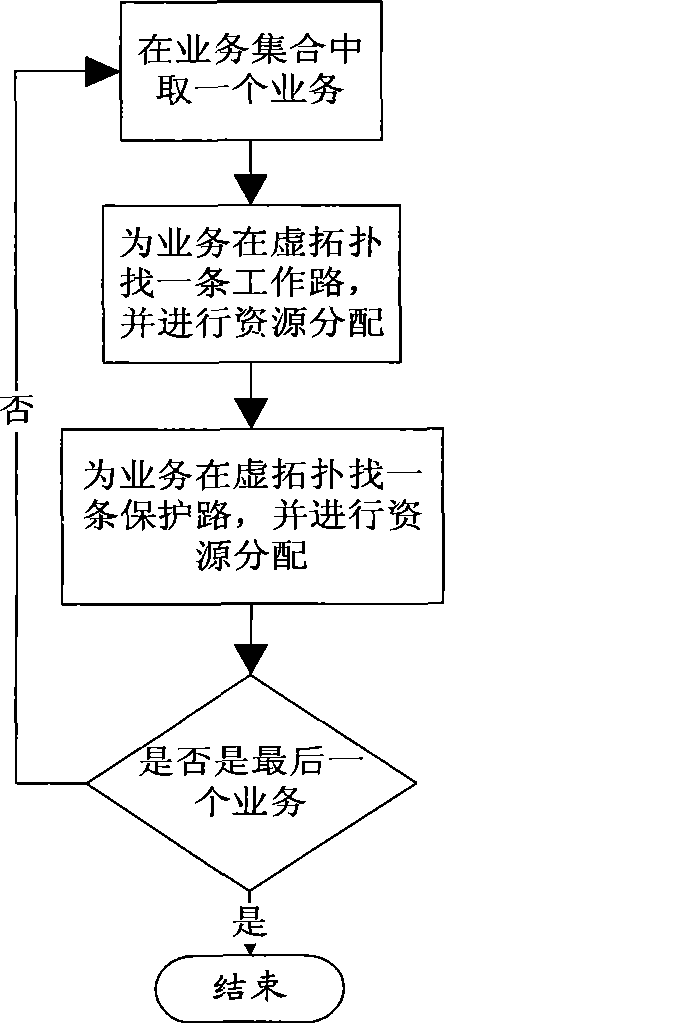
Survivable service flow conducting method based on interlayer message routing
InactiveCN101478705ATake up less resourcesRealize business needsMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsService flowSurvivability
A survivability business dredging method based on interlayer message routing belongs to the technical field of communication network, and relates to an optical network business dredging technique and resource allocation method. The survivability business dredging method comprises the following steps: step1: constructing a virtual topological network according to a physical topological network structure; step 2: executing routing and resource allocation to each service in service aggregate in the virtual topological network; step 3: modularizing optical path; and step 4: allocating resource for physical chain in the physical topological network according to the optical path modularization result obtained in the step 3. According to the invention, at the state the connection state and service aggregate between the network node and the node is known, the routing is searched for service and resource is collocated based on the interlayer information. The usage of total resource in the physical network is reduced as possible. Furthermore the resource collocation speed is greatly increased. The invention is suitable for WDM optical network and is also suitable for two-layer and multi-layer network with different service granularities of the upper layer and the lower layer, for example: IP / MPLS over WDM network, two-layer SDH network, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
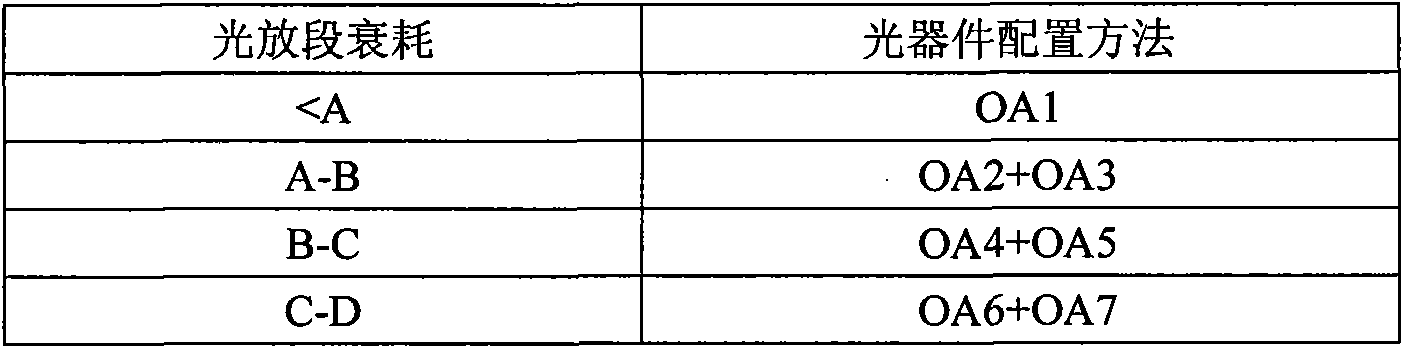
Automatic configuration method of physical device in WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) optical-fiber network
InactiveCN101834740AQuick Check ValidityAvoid configuration gapsWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmissionWdm optical networksOptical signal to noise ratio
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Optical spectral power monitors employing time-division-multiplexing detection schemes
InactiveCN1623082AImprove versatilityCost effectiveSpectrum investigationTime-division optical multiplex systemsBeam splitterNetwork connection
A method and apparatus for spectral power monitoring using a time division multiplexing detection scheme. The device uses a wavelength disperser (120), such as a diffraction grating, to split an optical signal into a plurality of spectral channels, and an array (140) of beam manipulation elements is positioned to correspond to the spectral channels. The beam steering elements are individually controllable to direct the spectral channels into an optical detector (150) in a time-division multiplexed sequence. The device further employs a polarization diversity scheme for polarization insensitive operation. This enhances the spectral resolution of the device while providing increased accuracy in spectral power detection. Spectral power monitors constructed in accordance with the present disclosure are well suited for WDM optical network connection applications.
Owner:CAPELLA PHOTONICS INC
Reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM) node, optical wavelength correction frequency shifter and implementation method
ActiveCN102970099AReduce lossOptical signal wavelength correctionWavelength-division multiplex systemsWdm optical networksFrequency shift
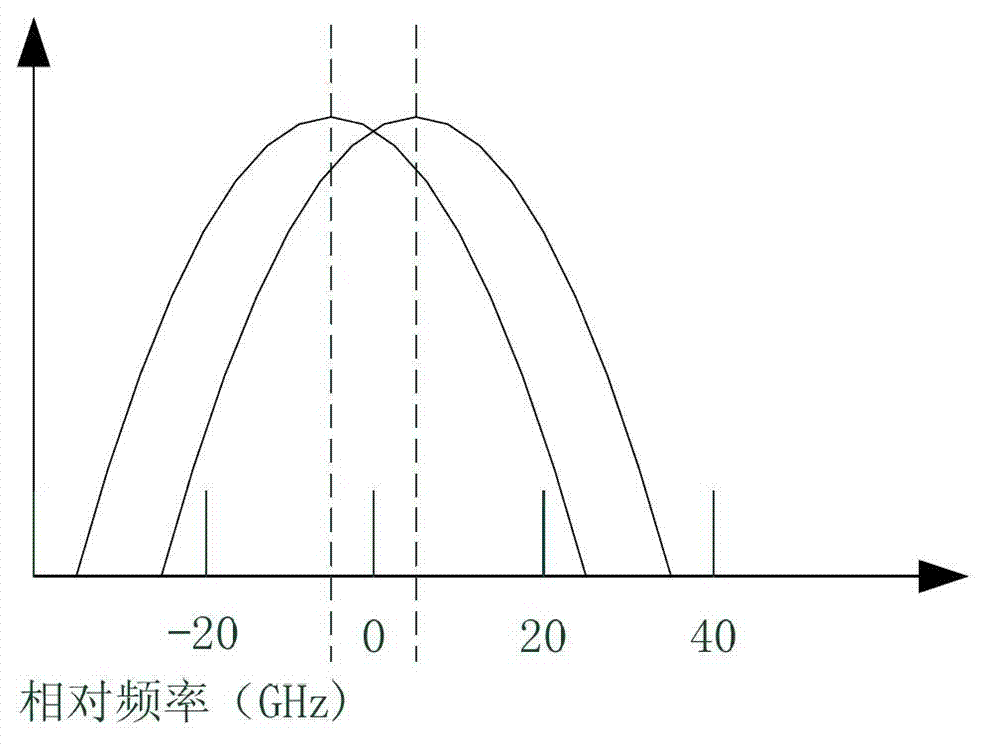
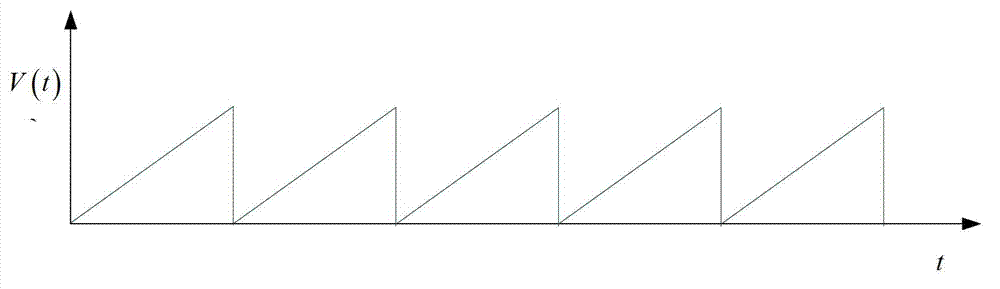
The invention discloses an ROADM node, an optical wavelength correction frequency shifter and an implementation method. The wavelength correction frequency shifter comprises a sawtooth wave electric signal generator and an electro-optic phase modulator, wherein the sawtooth wave electric signal generator produces continuous sawtooth wave electric signals with the repetition frequency of F, which serve as driving electric signals, and the electro-optic phase modulator loads driving electric signals to conduct frequency shift delta fi on the central wavelength of input optical signals, so that the central wavelength lambada i of input optical signals is close to the expected central wavelength lambada i-1, and c represents the velocity of light. According to the ROADM node, the optical wavelength correction frequency shifter and the implementation method, the central wavelength of input optical signals is close to the designed central wavelength of an ROADM through correction of the central wavelength of input optical signals, so that the effective bandwidth loss of the ROADM, which is caused by the multistage filtering cascaded filtering function, is reduced, an all-optical method is used for correcting the wavelength of optical signals, and the implementation method is applicable to ROADM nodes of any wavelength multiplexing wavelength division multiplex (WDM) optical networks of various transmission rates.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Persuasion method of self-adaptive dynamic multicast service and node system provided with the same
ActiveCN103067289AReduce blocking rateImprove throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksTransceiverWdm optical networks
The invention provides a persuasion method of a self-adaptive dynamic multicast service and a node system provided with the persuasion method of the self-adaptive dynamic multicast service, and belongs to the technical field of network communication. The node system comprises an optical layer and an electric domain layer. The persuasion method of the node system includes that a plurality of methods for a transmission service in a wavelength division multiplex (WDM) optical network are firstly analyzed, and two multicast service persuasion strategies including a node transceiver number minimum use strategy and a node persuasion port number minimum use strategy are proposed according to different optimization objectives. Due to the fact that network resource changes at different moments, a threshold value parameter is set to judge which resource is rare resource at the moment, and therefore the transmission of a new service is accomplished through a suitable selection of a persuasion strategy. The self-adaptive dynamic service persuasion method is capable of effectively solving the problem of dynamic multicast service persuasion in the WDM optical network, substantially improving the service persuasion performance of the WDM optical network, reducing service blocking rate, and increasing network throughput.
Owner:重庆信科设计有限公司
Multicast-sharing and multilayer protection method based on subtrees in WDM (wavelength division multiplexer) optical network,
ActiveCN102186123AMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksMultiplexerNetwork communication
The invention provides a multicast-sharing and multilayer protection method based on subtrees in a WDM (wavelength division multiplexer) optical network, belonging to the technical field of network communications. The method comprises the steps of: establishing a working multicast forest, establishing a protection multicast forest, protecting a WDM layer and leaving services. In the method, under the premise of considering single-link faults, a multicast-sharing protection method is constructed on the basis of the subtrees, a subtree-protecting resource sharing strategy, a light-path resource sharing strategy and a wavelength link protecting resource sharing strategy are adopted according to differences of shared grain sizes, so that the quantity of damaged services when a physical link generates faults is reduced, the application range of the traditional multicast-sharing and multilayer protection method can be expanded, multiple constraining conditions are considered when multilayer protection is carried out, and the multicast-sharing and multilayer protection method is provided under multiple strategies.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for simulating WDM optical network
InactiveCN1369983AImprove performanceLow costWavelength-division multiplex systemsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationParallel computingNetwork on
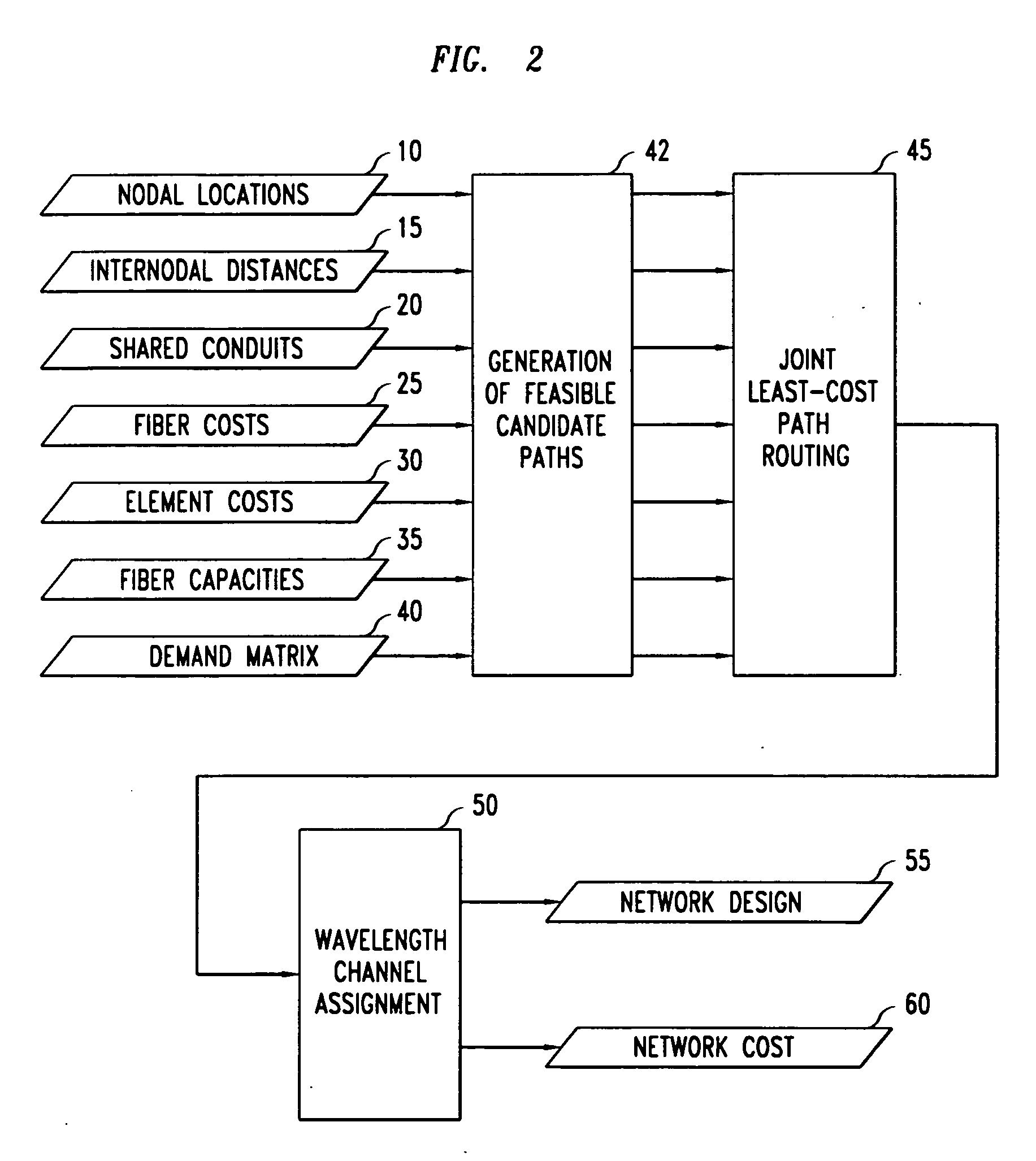
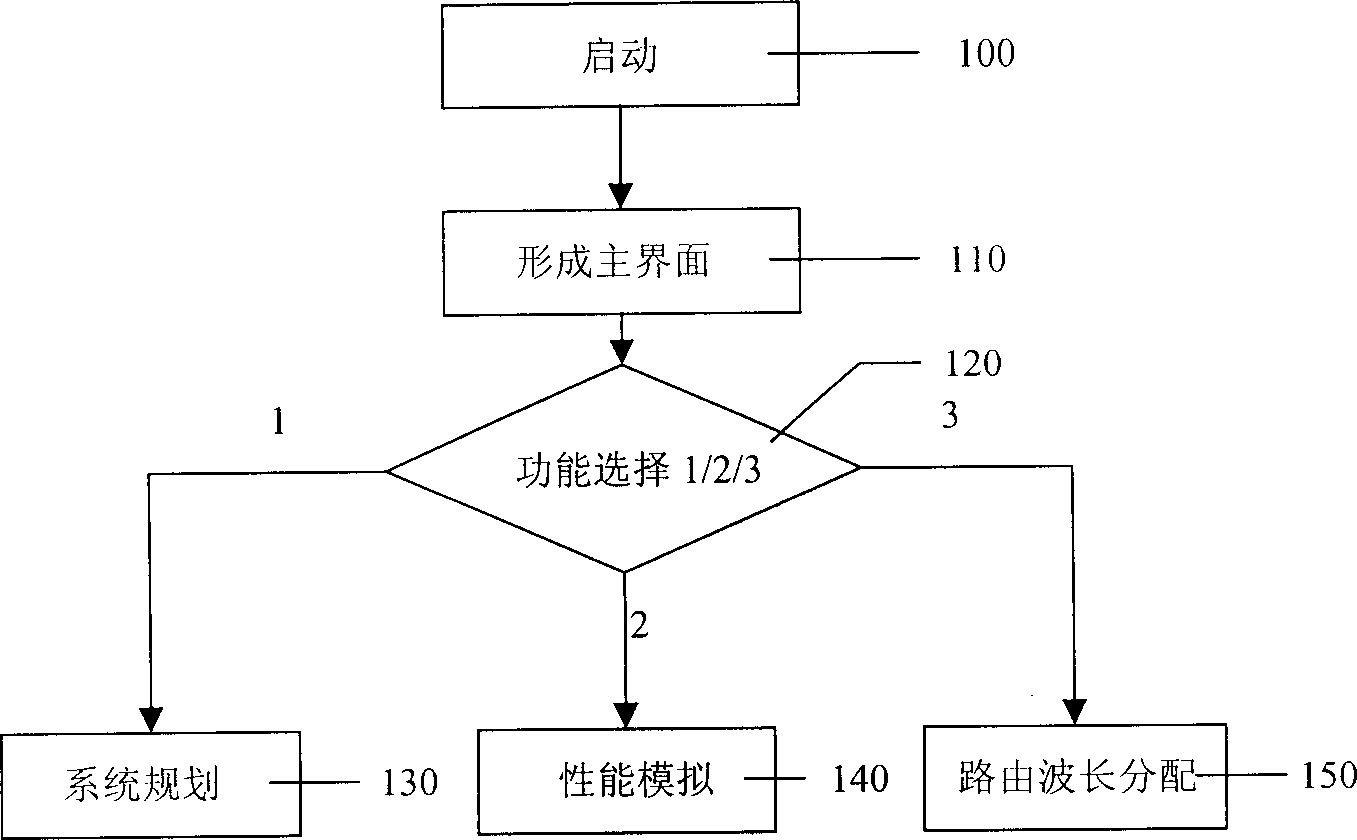
The invention discloses a method for simulating optical network of wave division multiplex (WDM) by computer. The computer executes following steps. The computer provides at least one main interface that includes a section for drawing layout of optical network, a toolbar section. The toolbar section provides selectable operations; system planning, performance simulation, simulaing algorithm of allocating route or wave length. Said function of system planning is that based on user's planning target, the system planning generates a topological graph of optical network on the said drawing section. The optical network on the drawing section is carried out a simulation by function of performance simulating. Based on physical toplogy and logical topology, the algorithm of allocating route or wavelength selects suitable route and allocates optimized wavelength and evaluates the algorithm for dynamic business.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
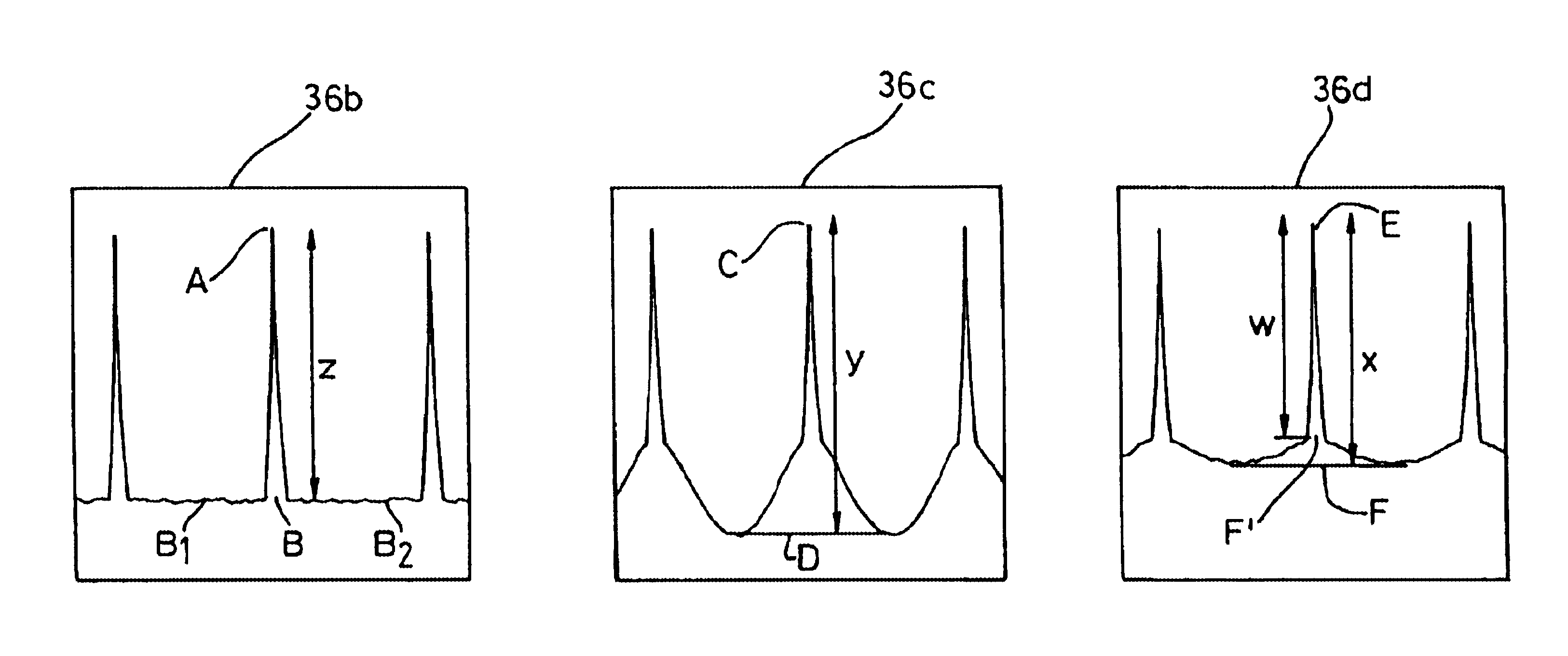
Apparatus for monitoring optical signal-to-noise ratio
InactiveUS7257324B2Guaranteed uptimeEffective maintenanceTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Wdm optical networks
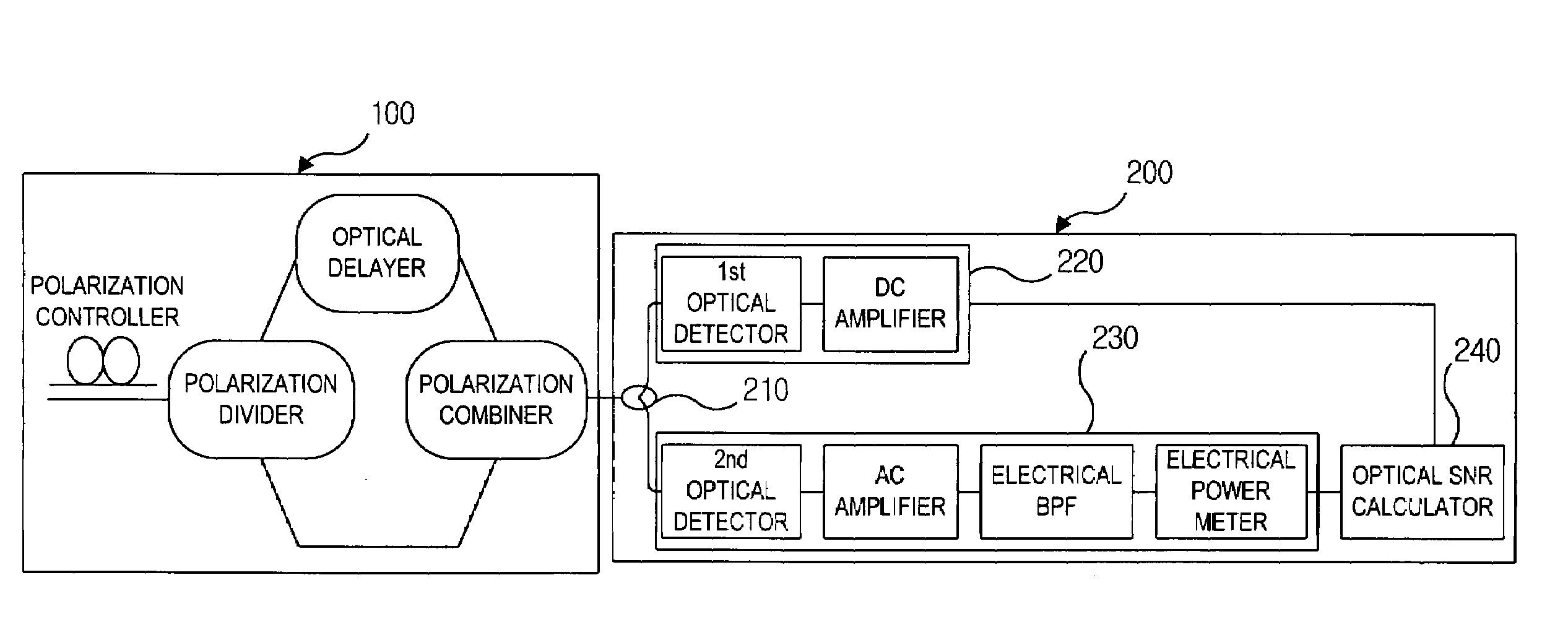
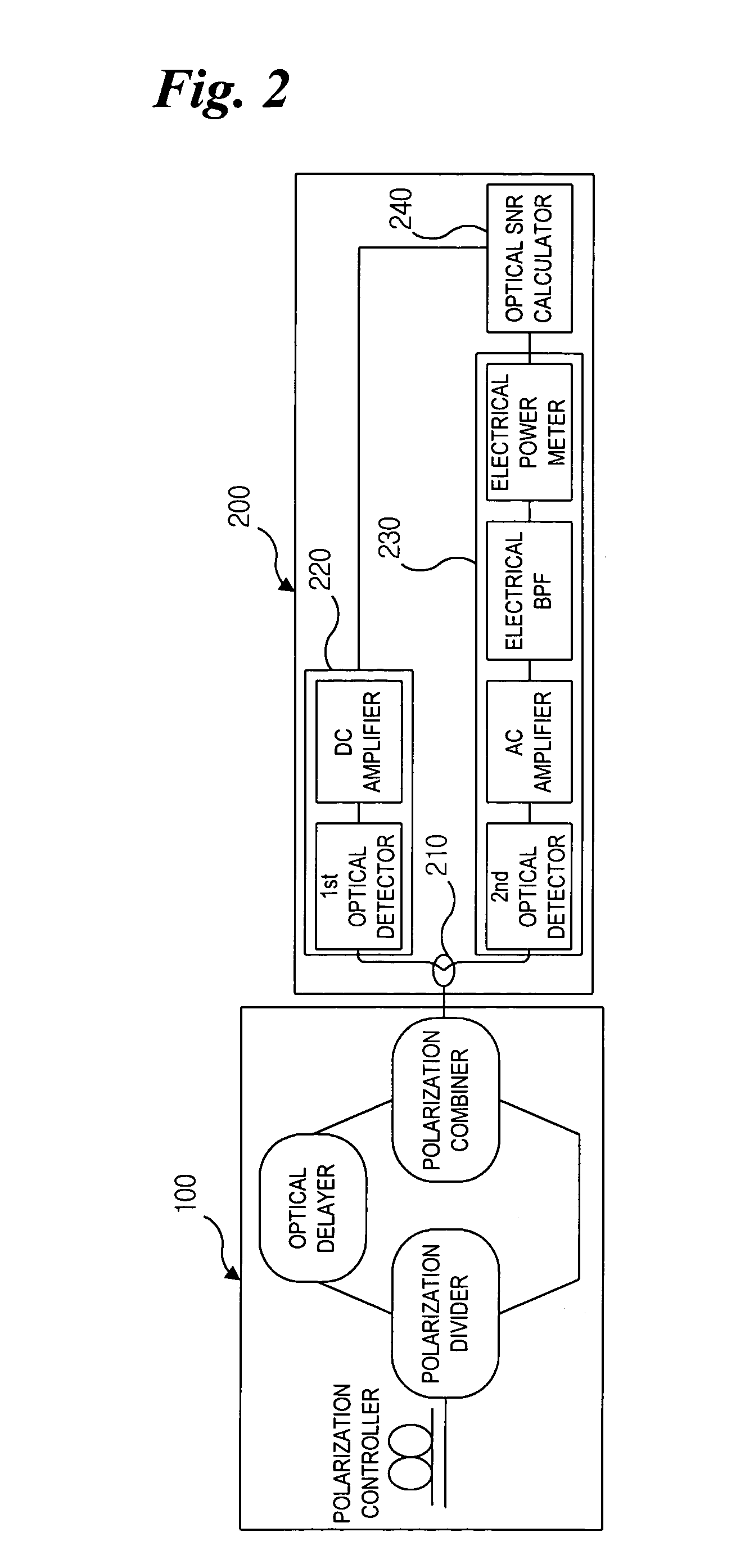
Disclosed is an apparatus for monitoring an optical signal-to-noise ratio in a WDM optical network. The apparatus includes an orthogonal polarization component module for receiving an optical signal and outputting it after removing a signal component thereof at a specific frequency band; and calculation means for measuring both average signal and noise component intensity of the optical signal outputted from the orthogonal polarization component module. By removing a signal component at a specific frequency bandwidth and passing only a noise component through, it is possible to easily measure the noise intensity within a signal bandwidth that cannot be measured in general. A frequency band is set within a signal bandwidth, and the signal intensity is minimized at the set frequency band, so that it is possible to measure the optical signal-to-noise ratio even for a signal whose amplified spontaneous emission noise spectrum is not flat, irrespective of the signal pattern length.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method and system for configuring a connection-oriented packet network over a wavelength division multiplexed optical network
A network planning tool and method for configuring a connection-oriented packet network over a WDM optical network without an optical control layer, such as a SONET / SDH layer. The optical network includes a plurality of optical fibers interconnected through nodes and the connection-oriented packet network, such an Ethernet network, MPLS network, or pseudowire network, includes two or more terminal devices. The method and tool function by building an association between the components of the physical layer, such as the optical fiber, and their geographic location or path. The connection-oriented packet network is configured by building multi-link trunks (MLTs) between terminal devices, where the MLTs are built by aggregating lightpaths that traverse distinctive geographic paths. The MLTs are planned and configured through aggregating lightpaths that traverse incongruent sets of photonic elements. A predetermined target for resiliency to physical failure events may determine the degree of congruence allowed between the sets of photonic elements associated with lightpaths in the same MLT.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
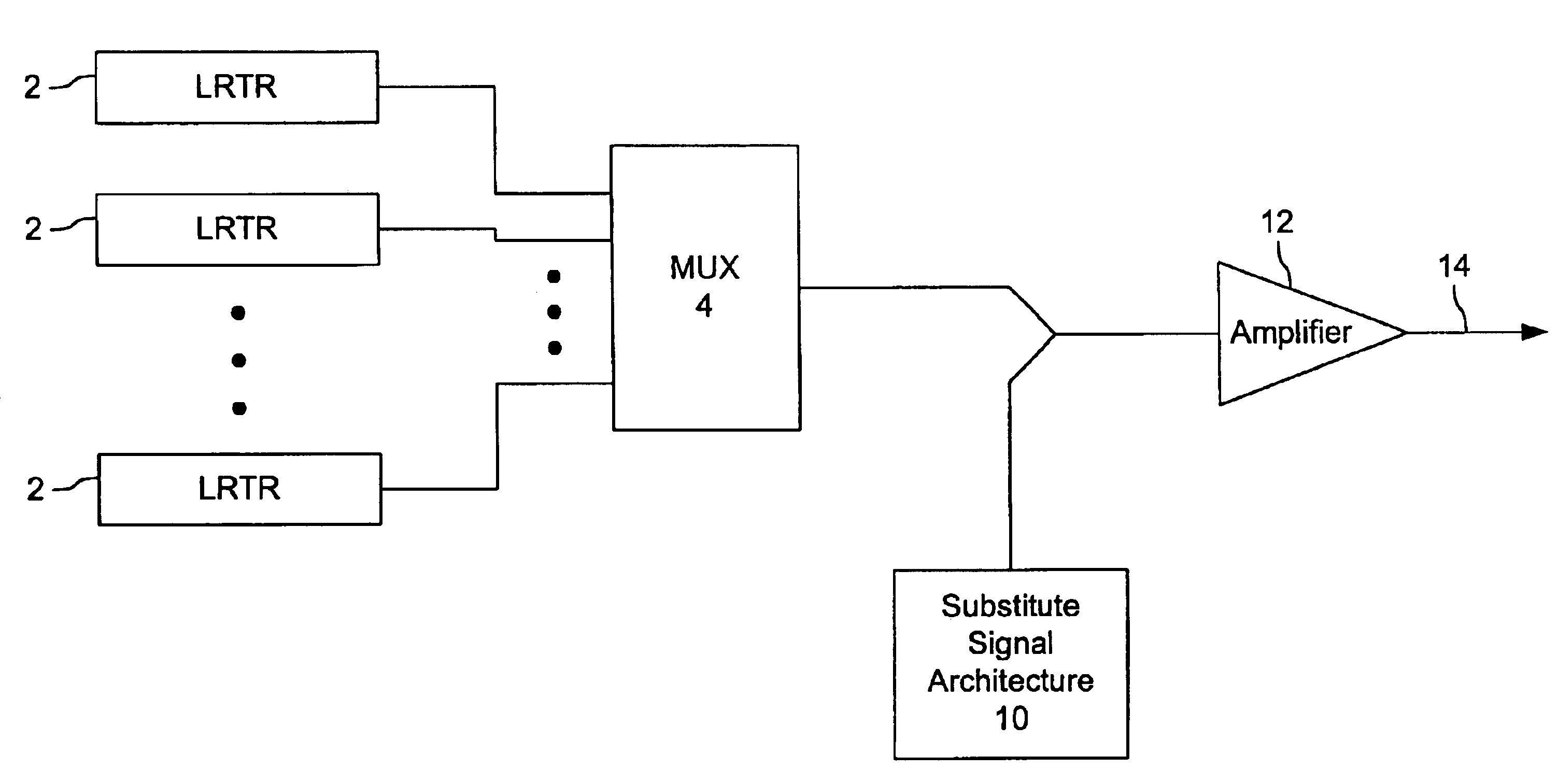
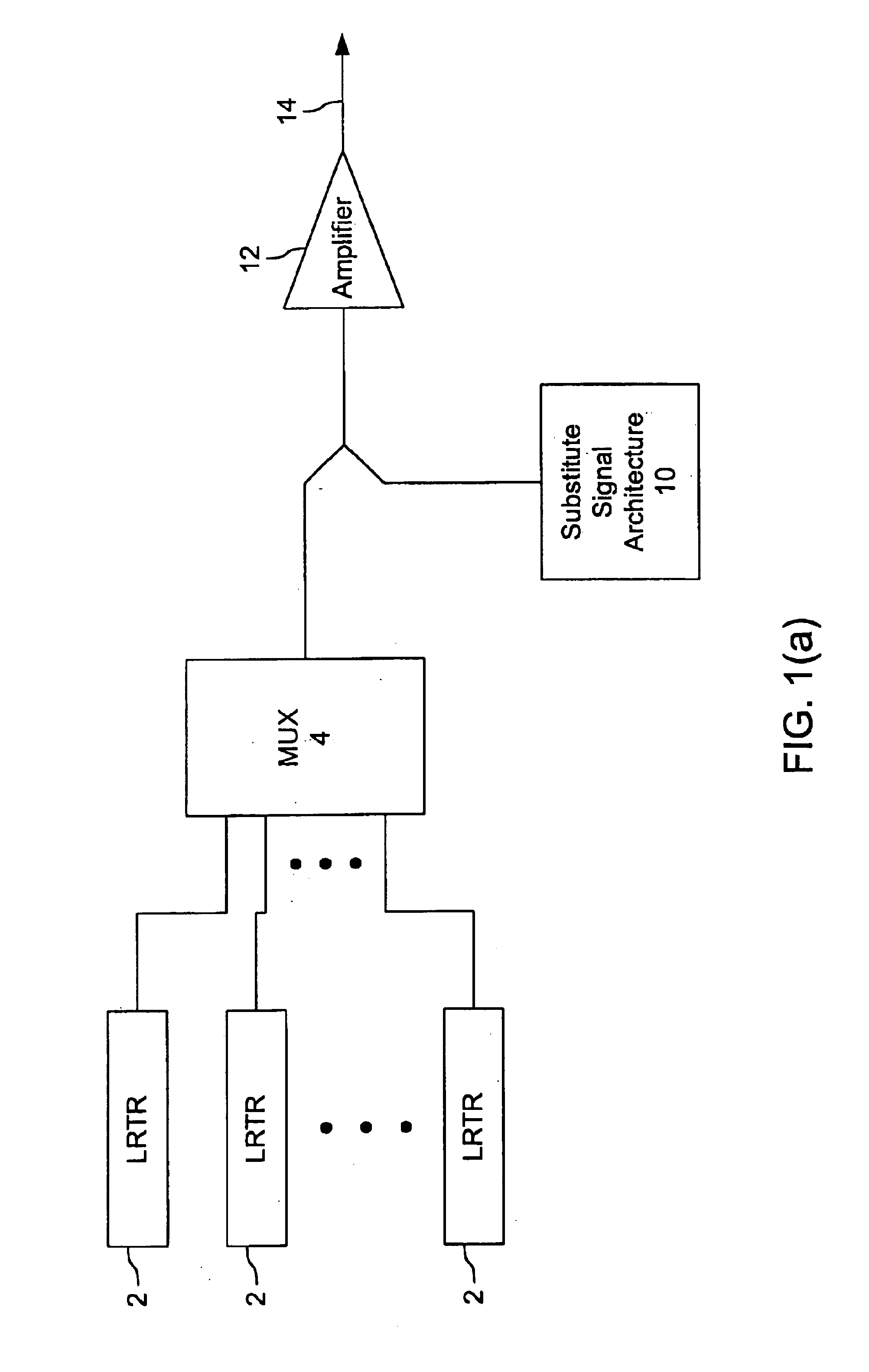
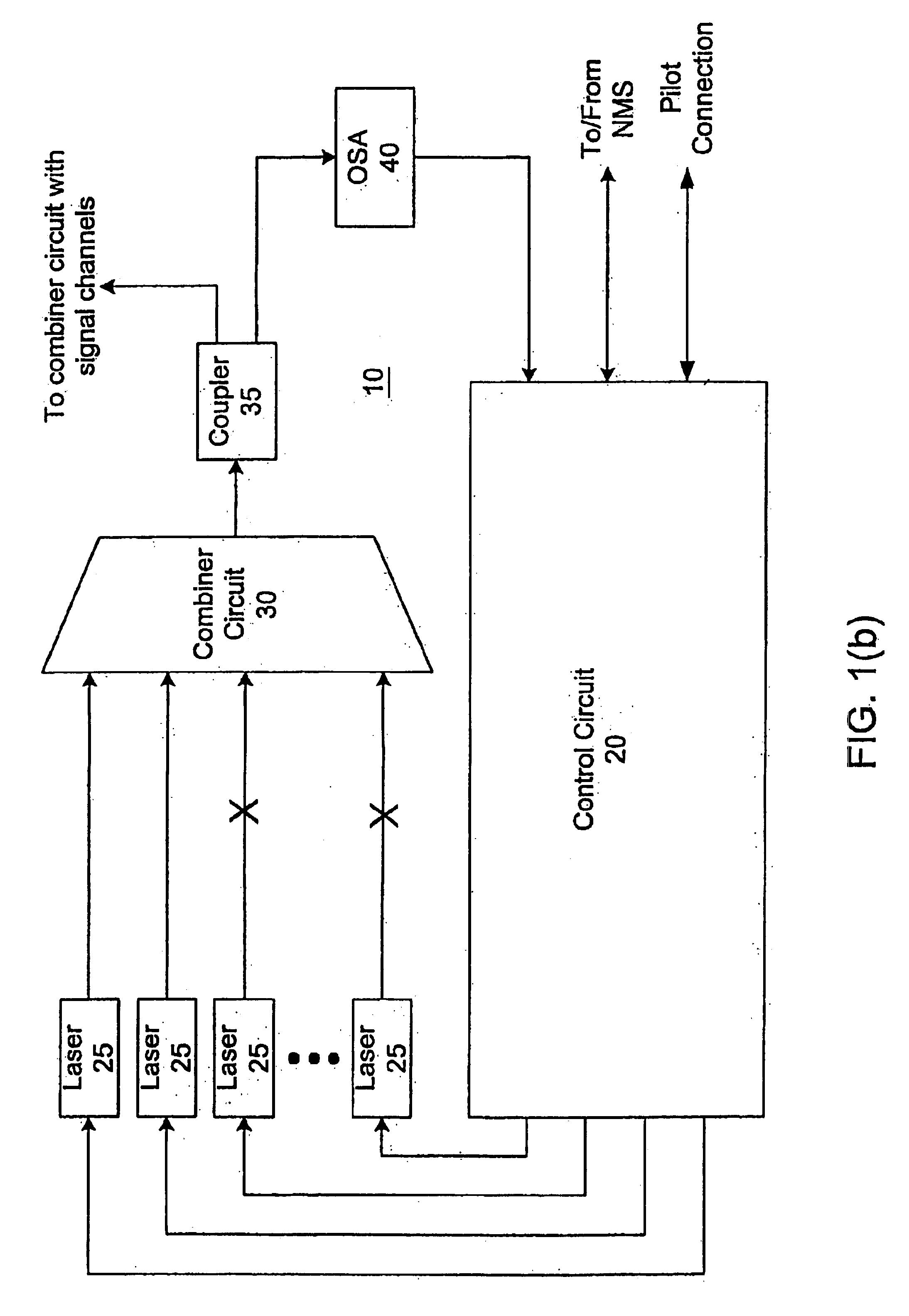
Terminals having sub-band substitute signal control in optical communication systems
A wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) optical network includes a plurality of optical transmitters, each optical transmitter generating a data signal sent over a respective one of a plurality of signal channels, the plurality of signal channels being divided into a number of sub-bands where each sub-band includes at least two signal channels, and a plurality of substitute signal transmitters, the number of substitute signal transmitters being equal to the number of sub-bands, each substitute signal transmitter generating a substitute signal which provides loading in a corresponding sub-band. The WDM optical network also includes a combining circuit which combines the data signals output from the plurality of optical transmitters and the substitute signals output from the plurality of substitute signal transmitters into a WDM signal, and an optical transmission fiber which receives the WDM signal from the combining circuit.
Owner:OPTIC153 LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com