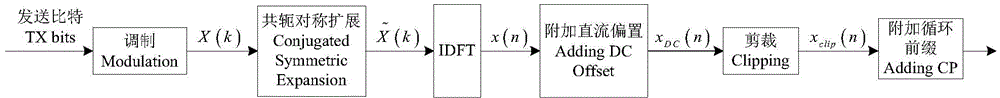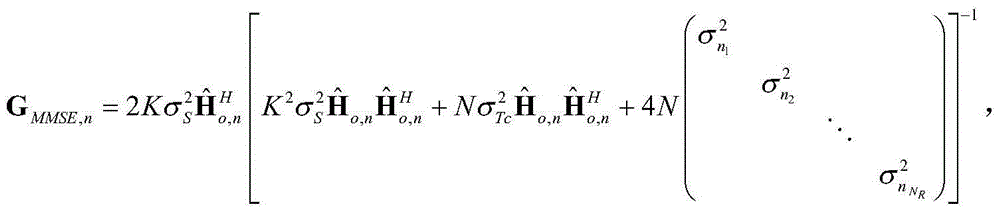Patents
Literature
64 results about "Clipping noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
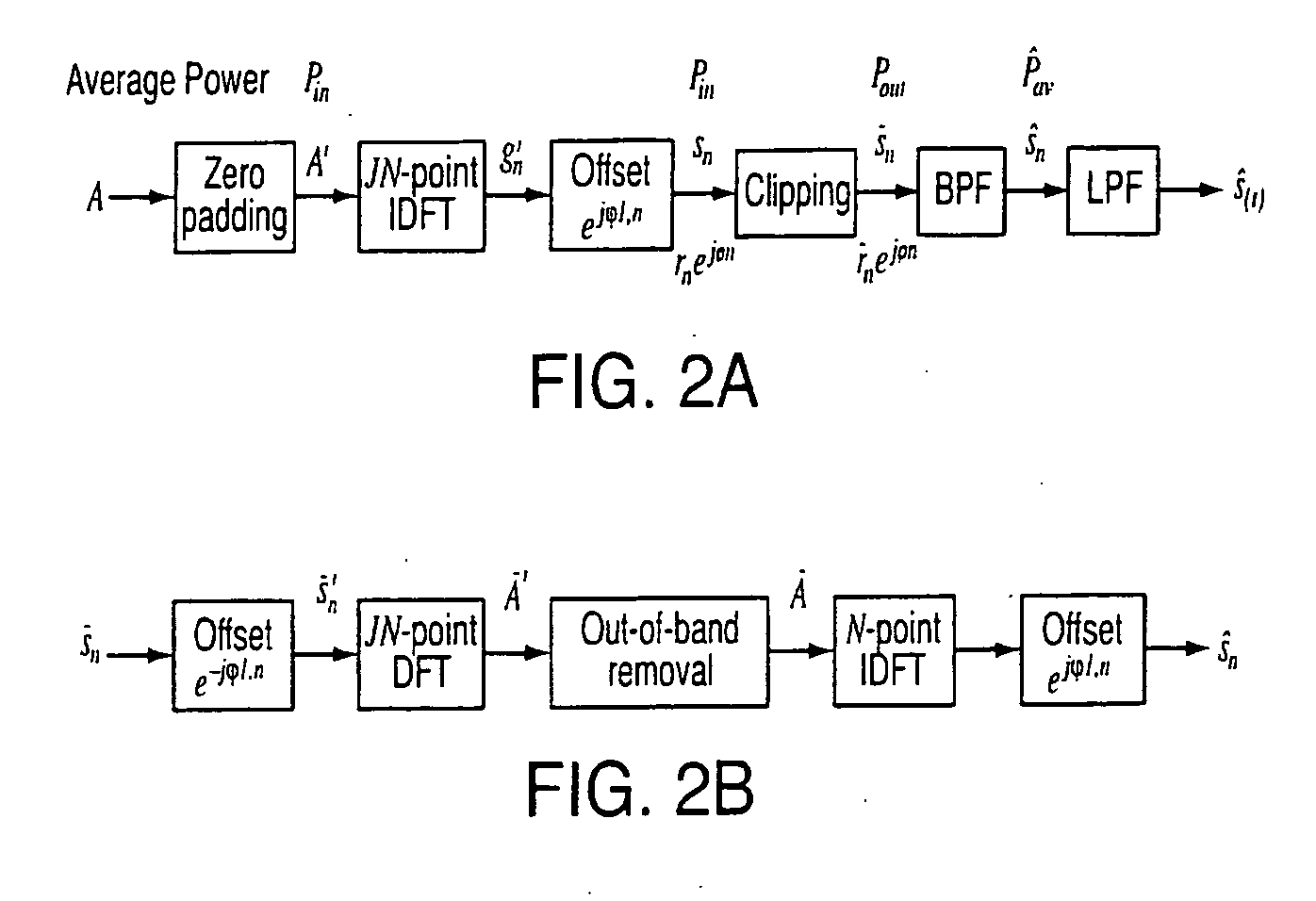
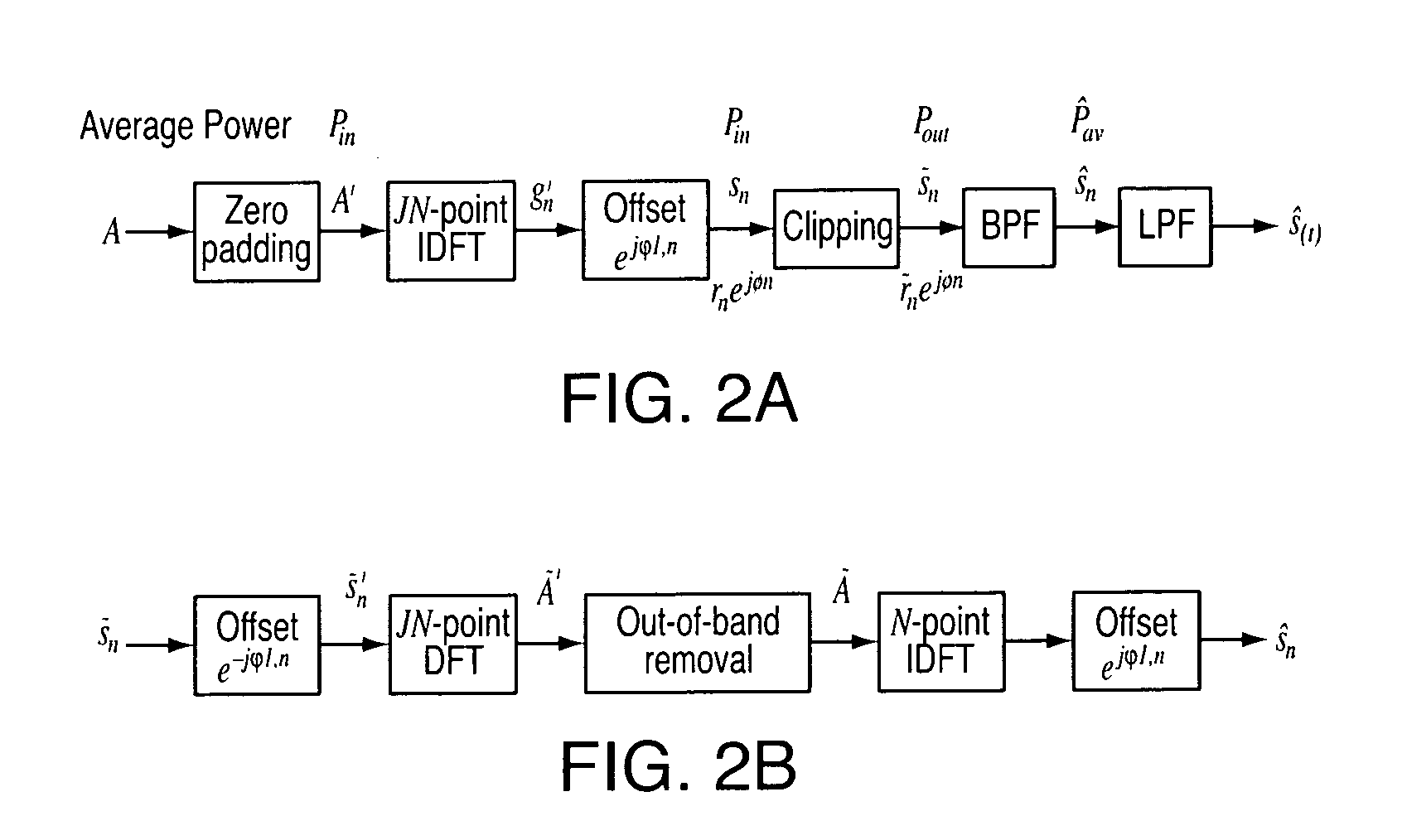
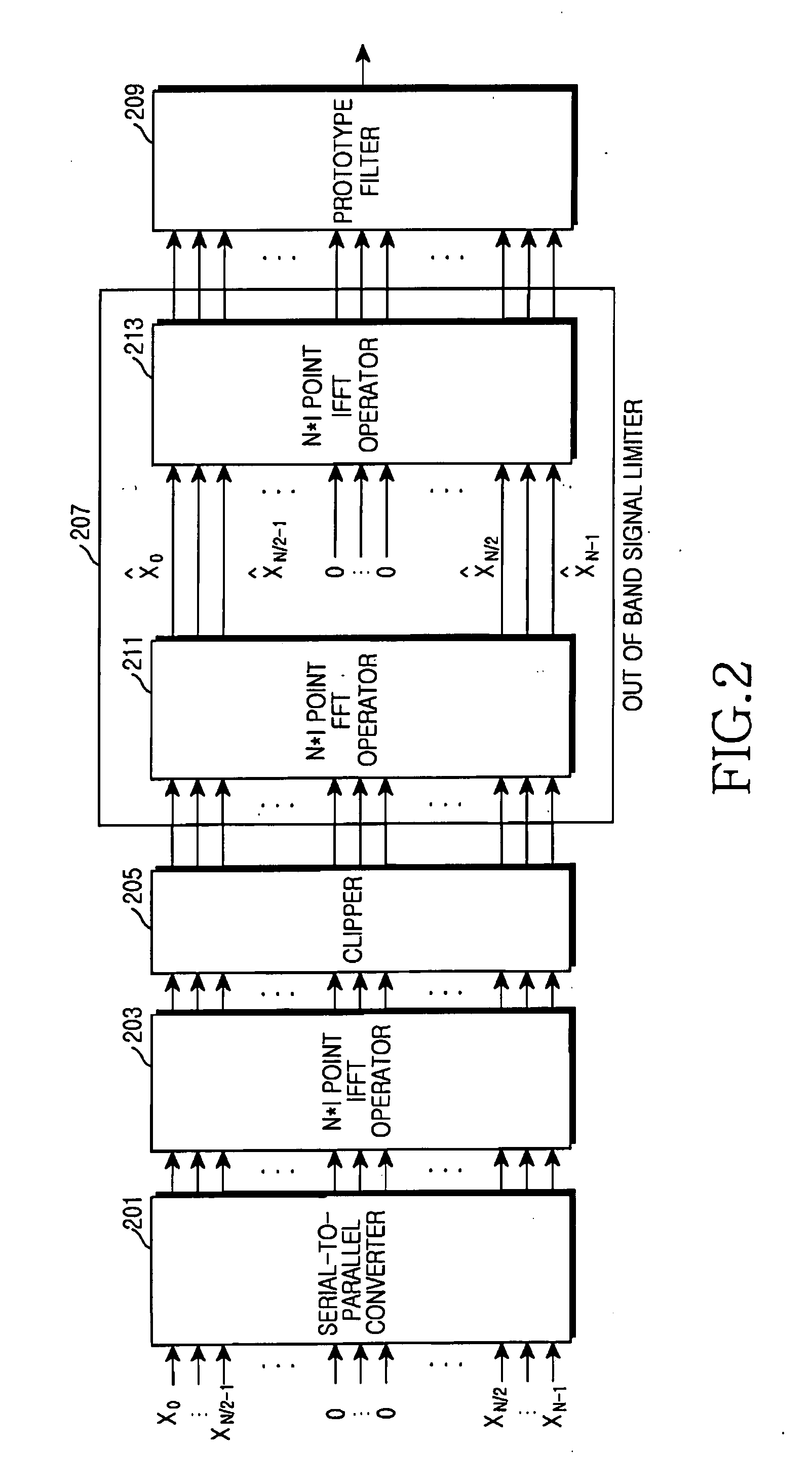
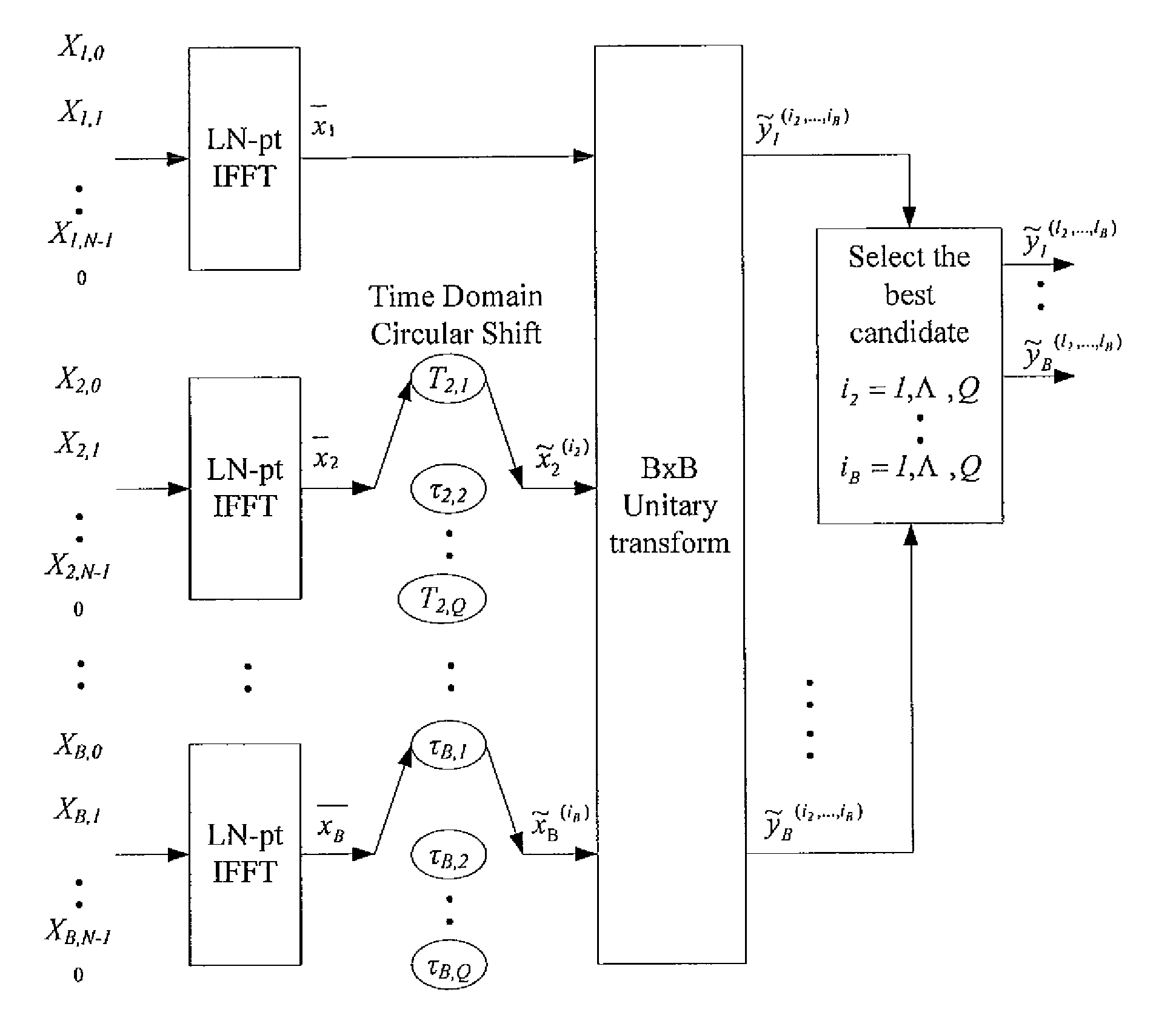
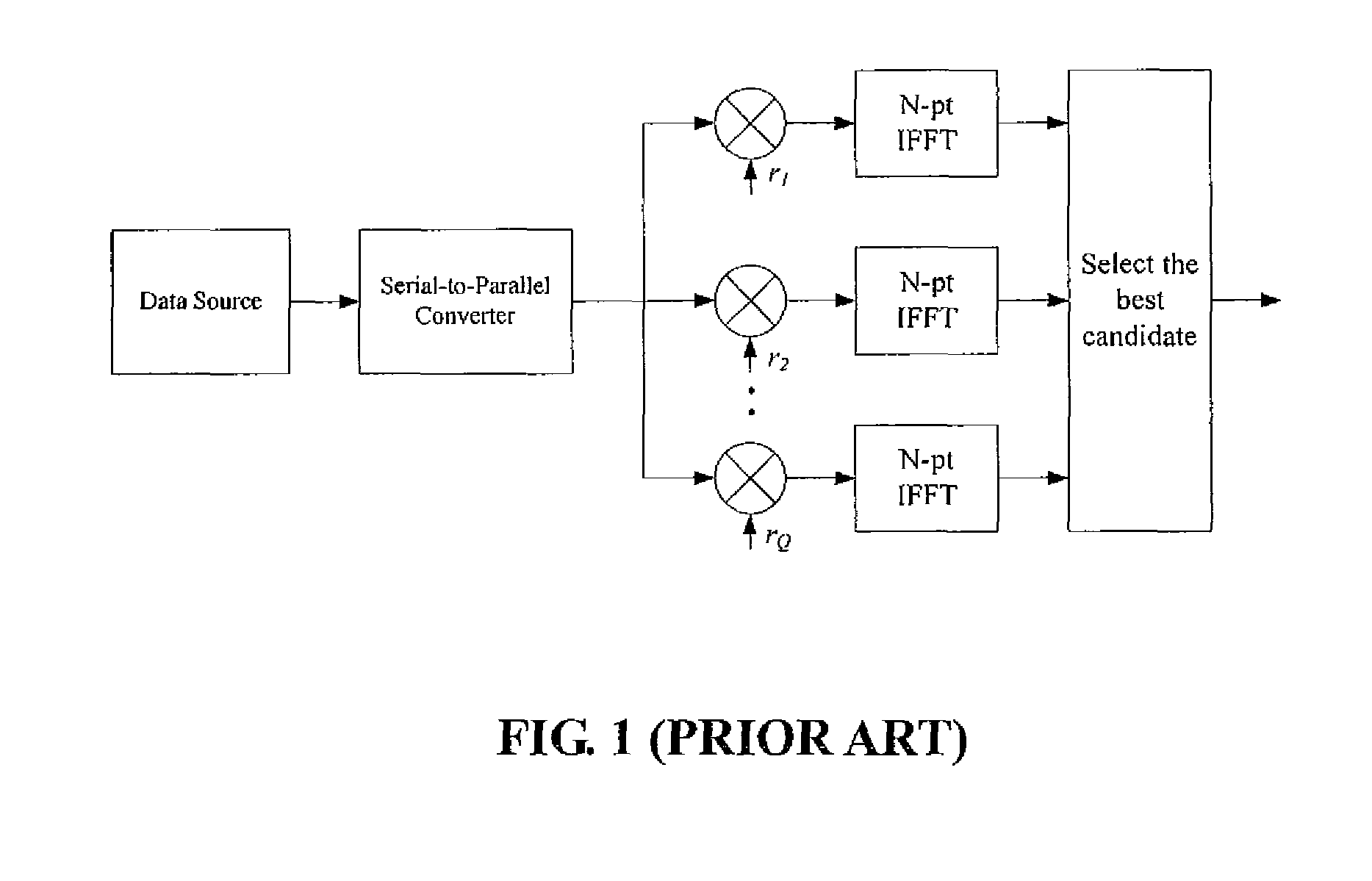
Method for solving high papr problem of mcm communication system using unitary transform
ActiveUS20090147870A1Sacrificing error rateLess complexSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainCommunications system
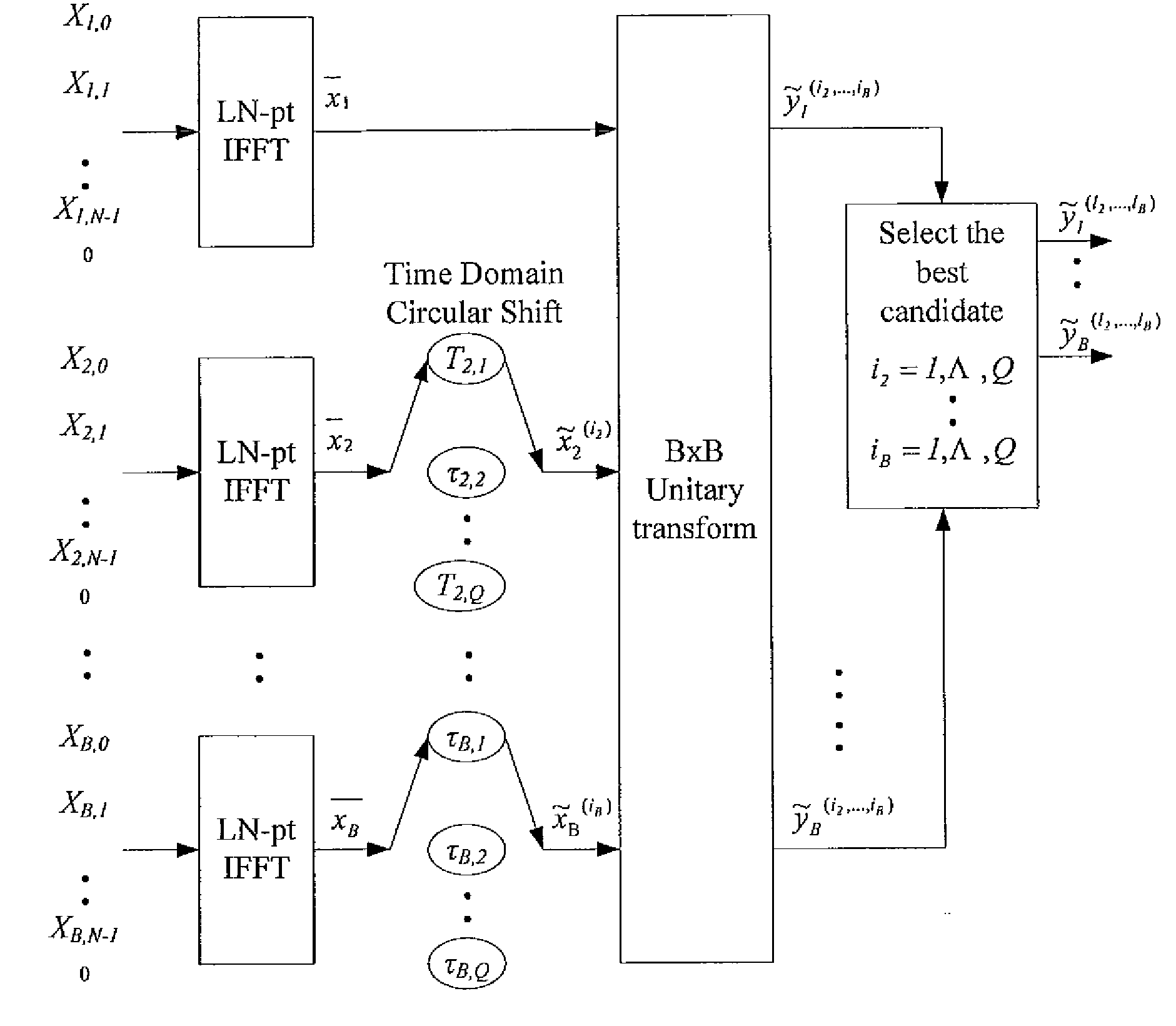
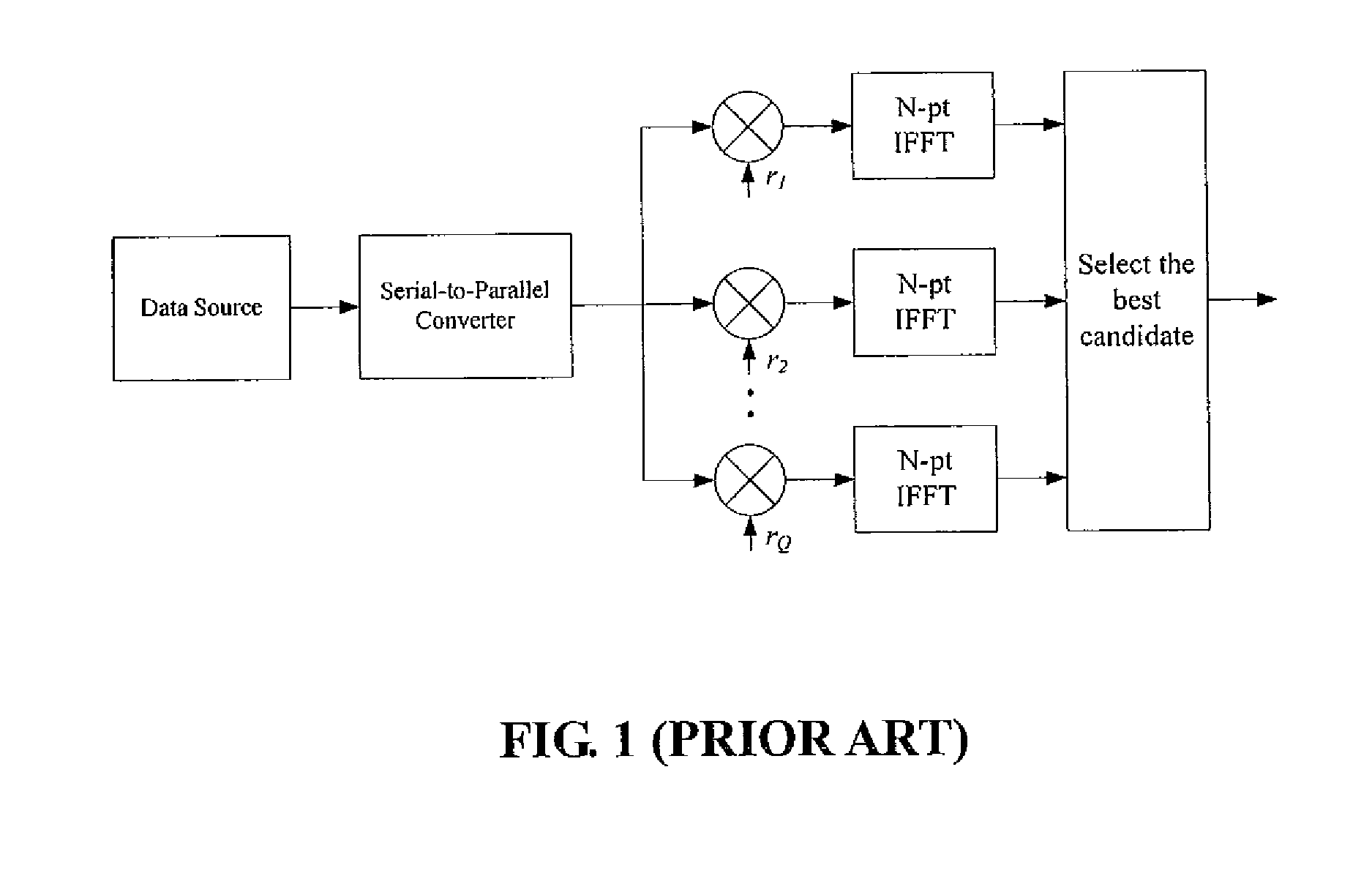
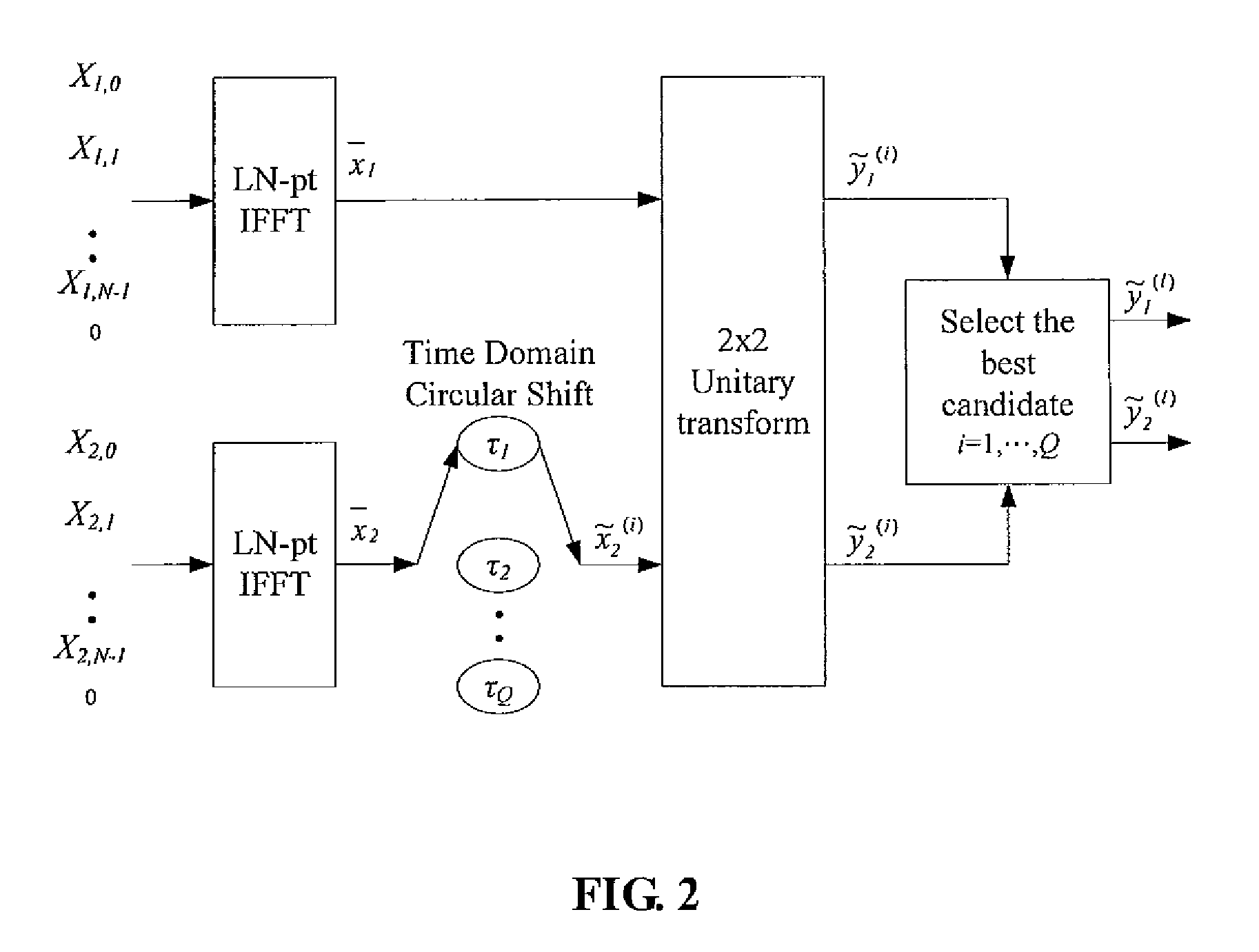
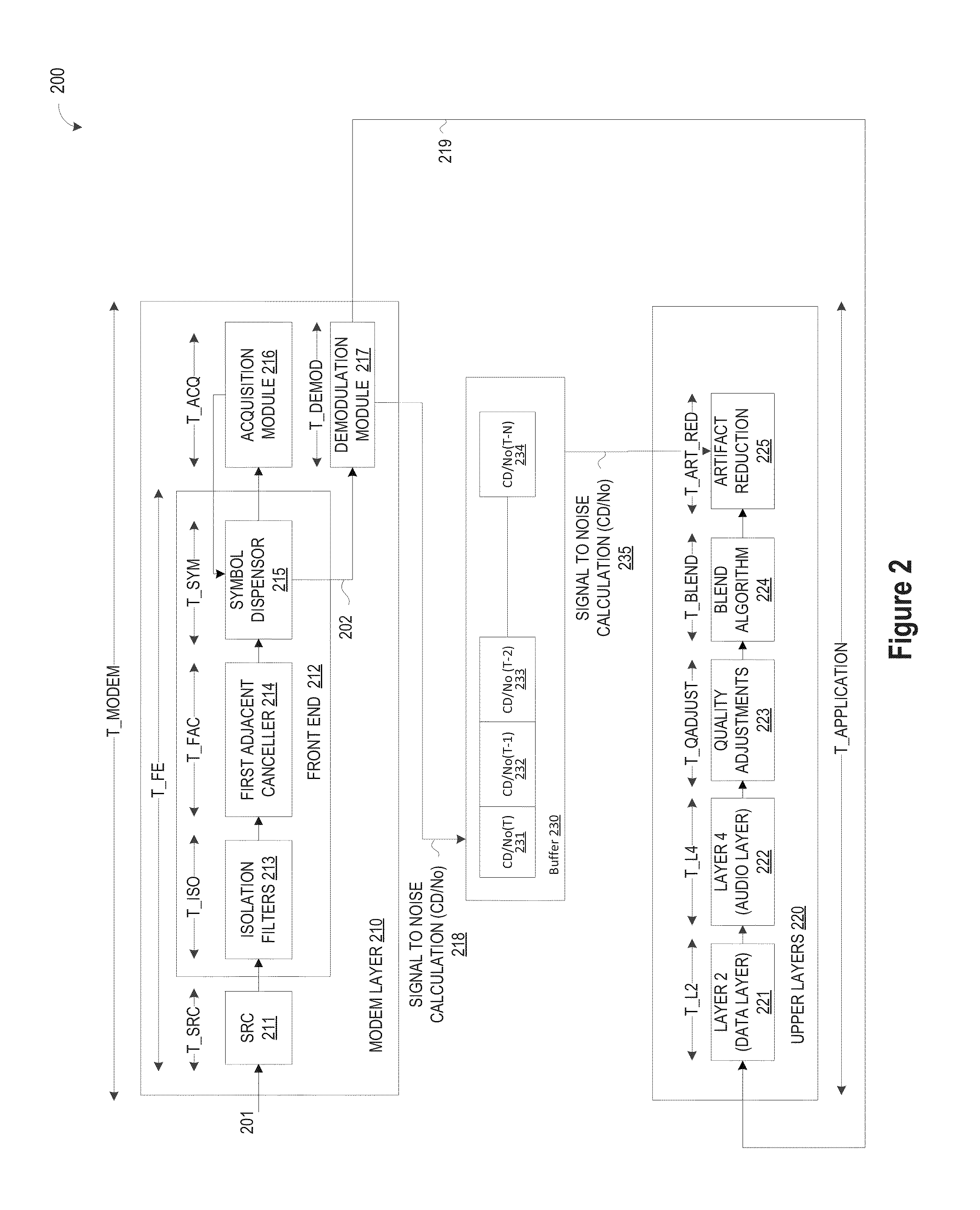
The method contains the following steps. First, in a MCM system with N sub-carriers, the baseband signal blocks Xj, j=1, 2, . . . ,B are supplemented with zeros and processed with LN-point IFFT, respectively, to obtain L-time oversampled time-domain signal blocks xj, j=1,2, . . . ,B. Then, xj undergoes Q Time Domain Circular Shifts or Frequency Domain Circular Shifts to obtain Q signal blocks {tilde over (x)}j(i<sub2>j< / sub2>), ij=1,Λ,Q. Subsequently, a B×B unitary transform is performed against ( x1,{tilde over (x)}2(i<sub2>2< / sub2>), . . . ,{tilde over (x)}B(i<sub2>B< / sub2>)). After the unitary transform, for each (i2, . . . ,iB) a combination having B time-domain signal blocks is obtained as follows: ({tilde over (y)}1(i<sub2>2< / sub2>, . . . ,i<sub2>B< / sub2>),{tilde over (y)}2(i<sub2>2< / sub2>, . . . ,i<sub2>B< / sub2>), . . . ,{tilde over (y)}B(i<sub2>2< / sub2>, . . . ,i<sub2>B< / sub2>)=( x1,{tilde over (x)}2(i<sub2>2< / sub2>), . . . ,{tilde over (x)}B(i<sub2>B< / sub2>)) cU where U is the B×B unitary matrix, and c is an arbitrary constant (c≠0). Finally, the total QB-1 combinations are compared against each other to select a best candidate for transmission that could produce the lowest peak value, or the smallest PAPR, or the lowest clipping noise power.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
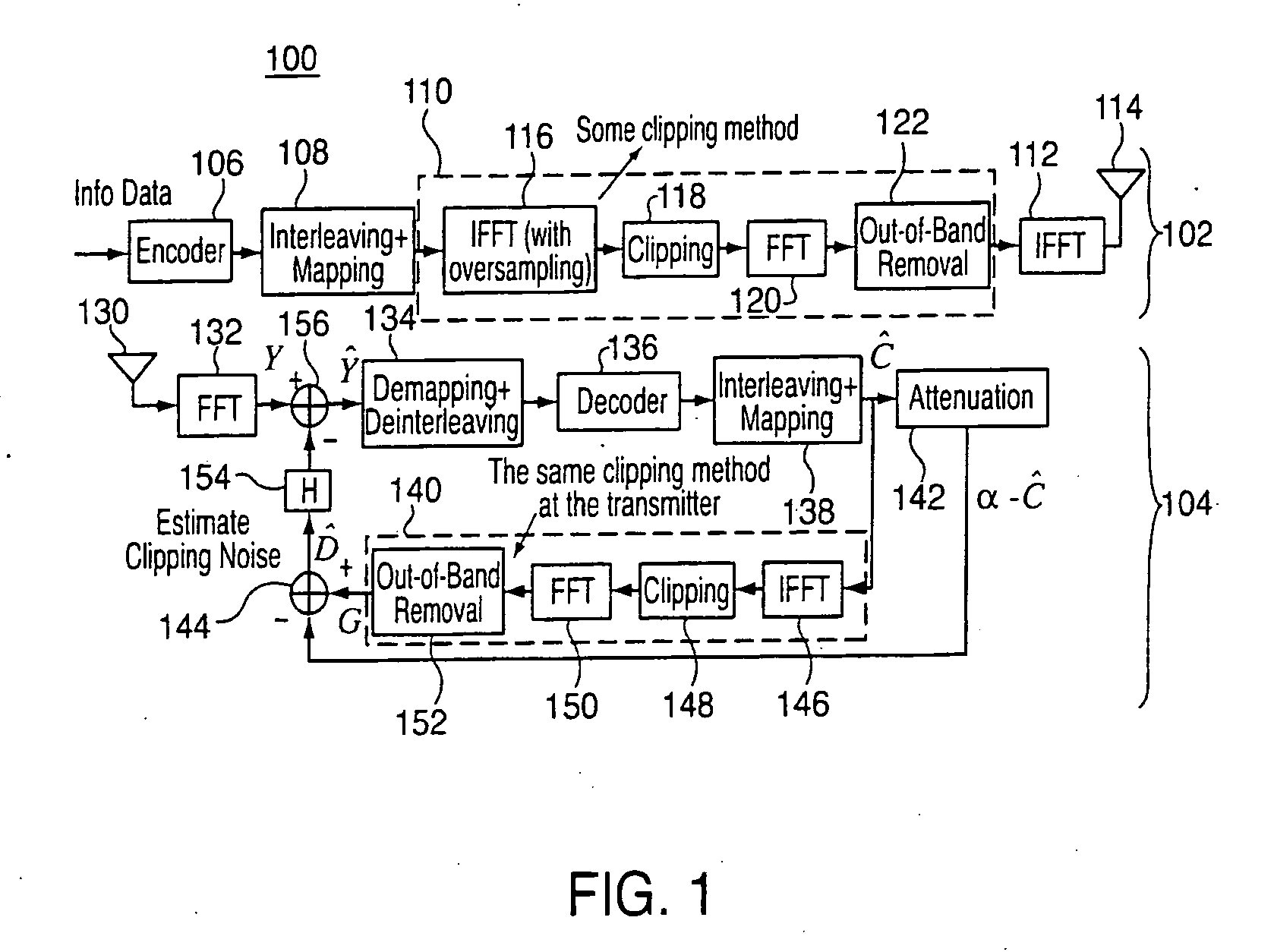
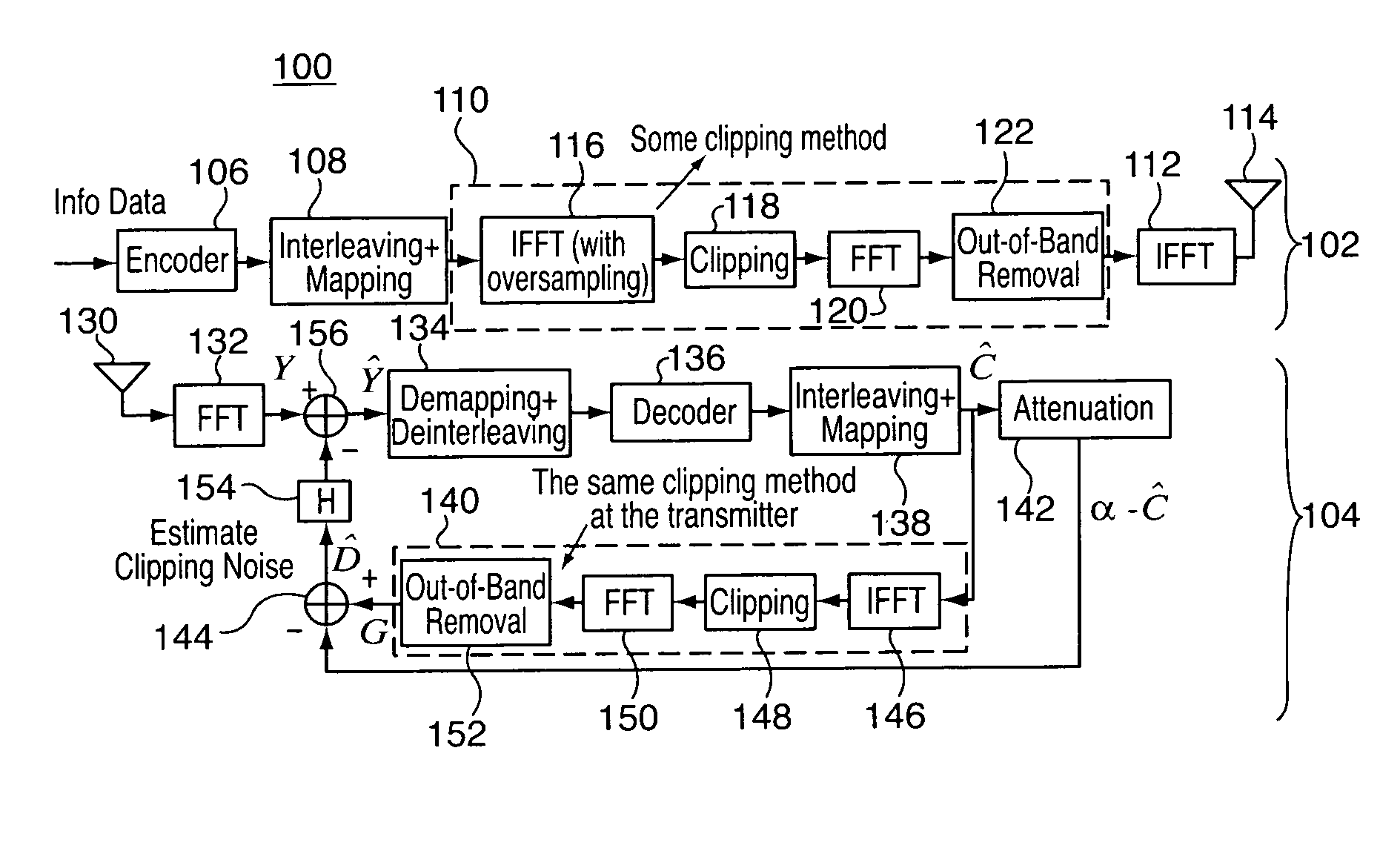
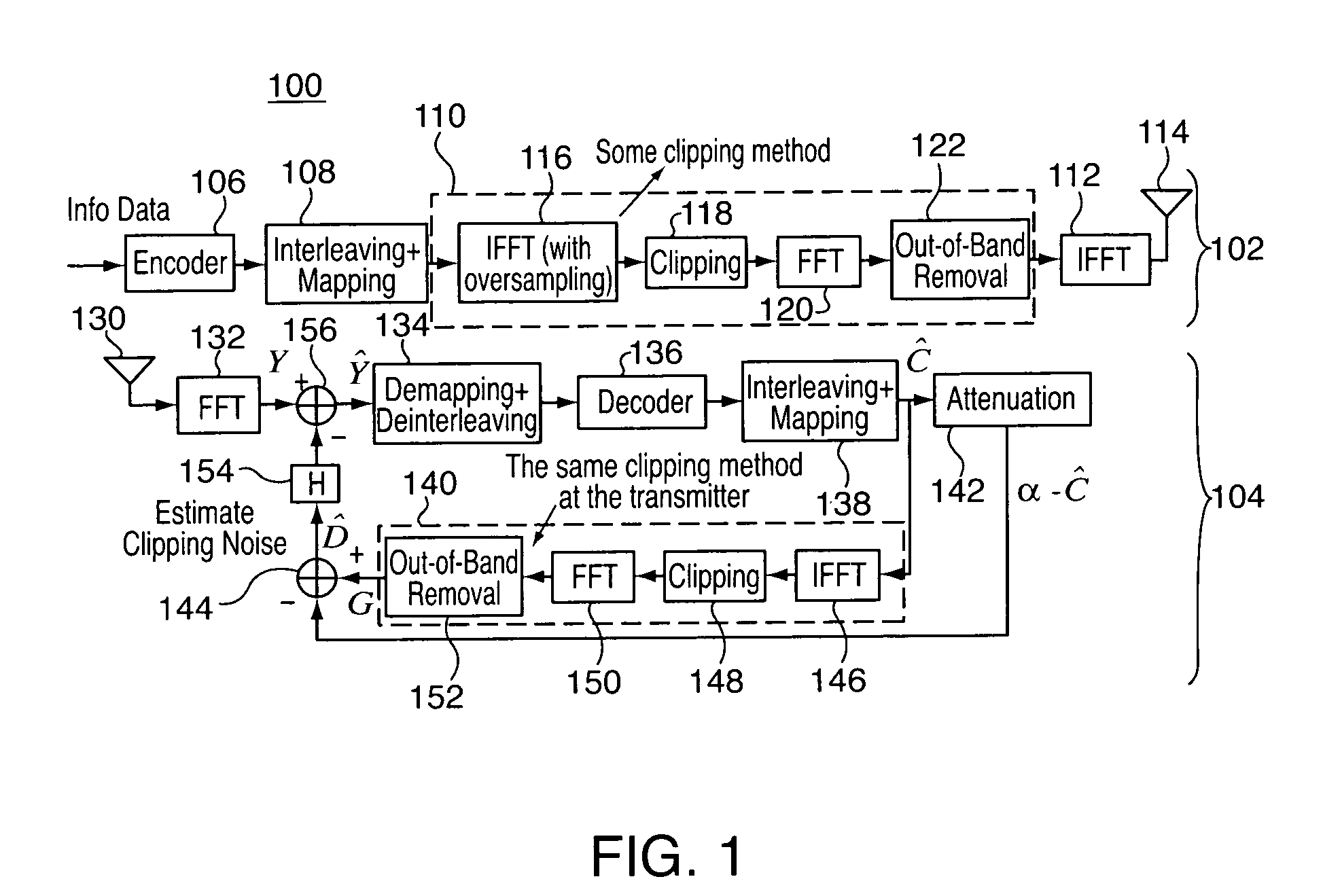
Clipping distortion canceller for OFDM signals
ActiveUS20060250936A1Multi-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexDistortionOrthogonal frequency code division multiplexing
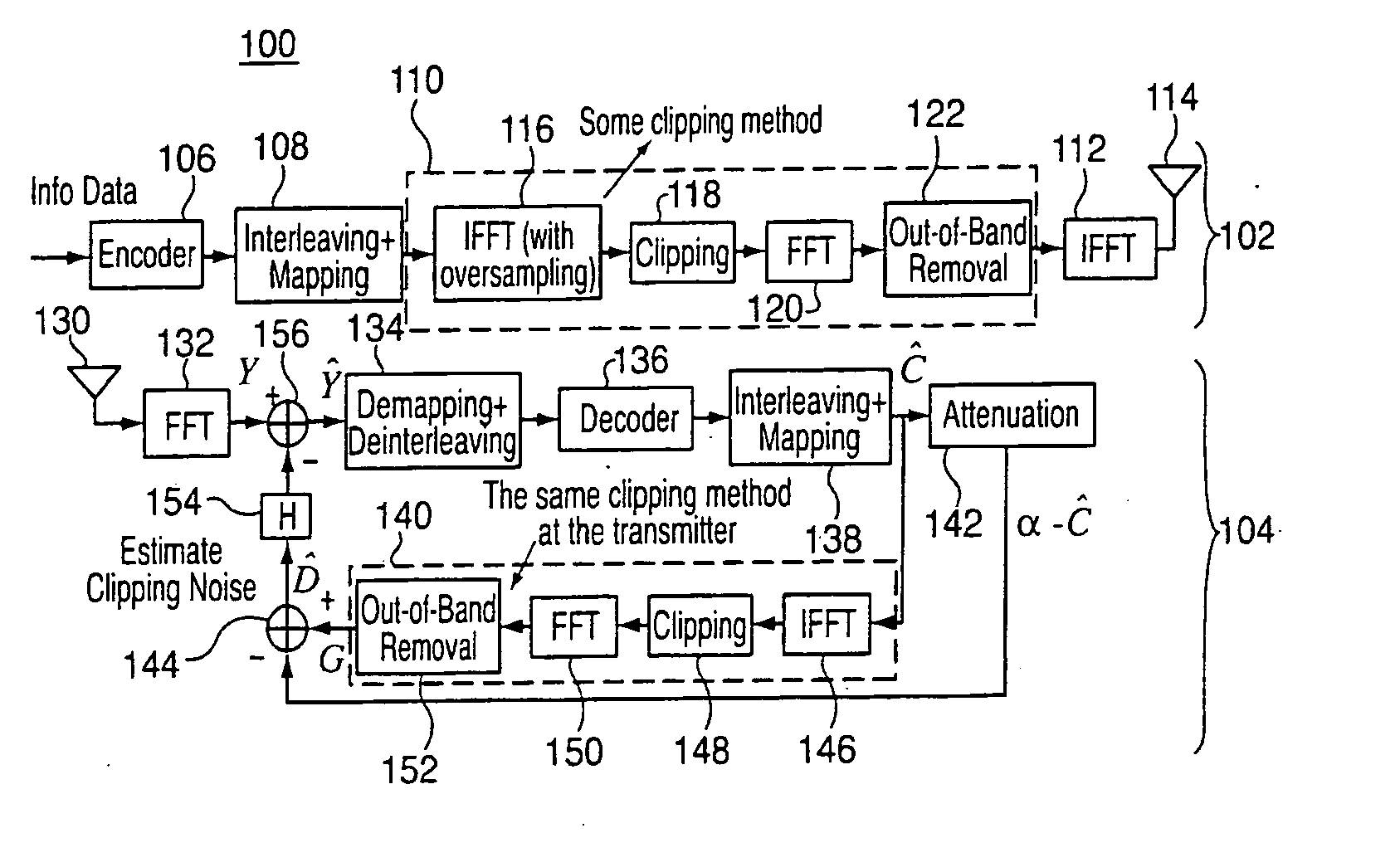
Methods and apparatus are provided for reducing clipping noise from an OFDM signal, the methods and apparatus are operable to carry out actions including: (a) transforming a received orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) signal from a transmission channel into the frequency domain, the OFDM signal having been subject to a clipping function prior to transmission in order to reduce the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR); (b) recovering data symbols from the transformed OFDM signal, which include clipping noise; (c) estimating the clipping noise in the frequency domain based on the data symbols; and (d) subtracting the estimated clipping noise from the transformed OFDM signal.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
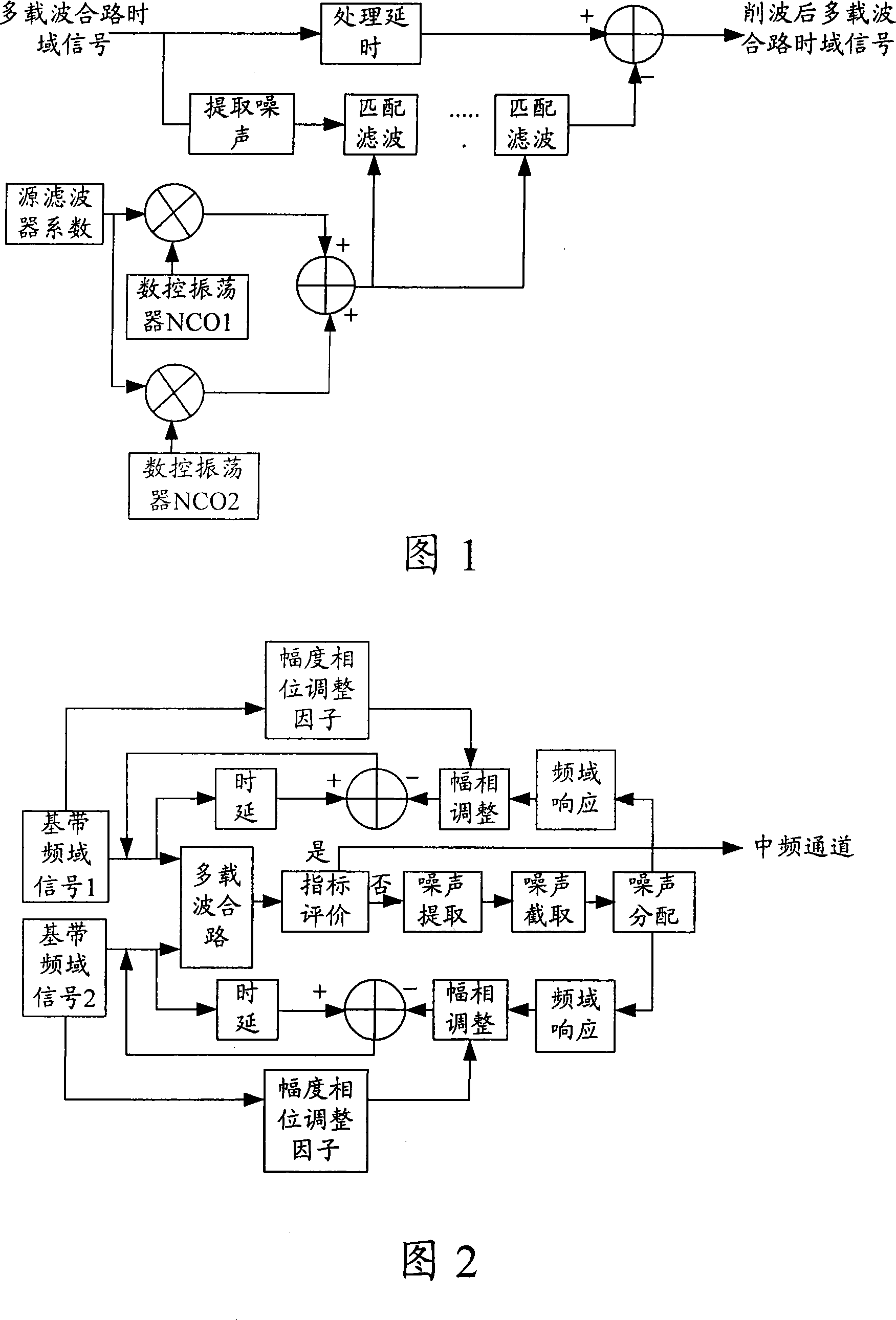
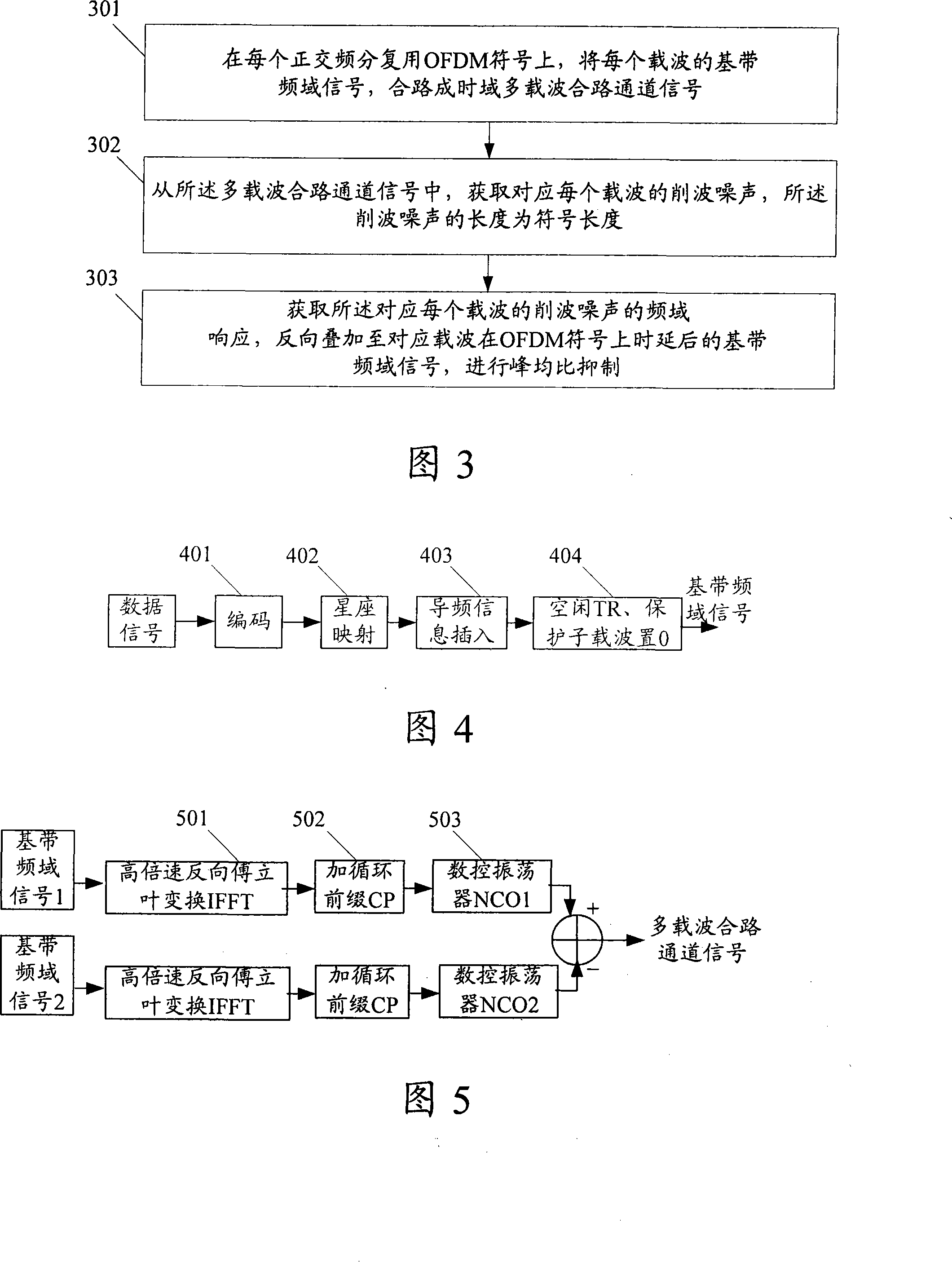
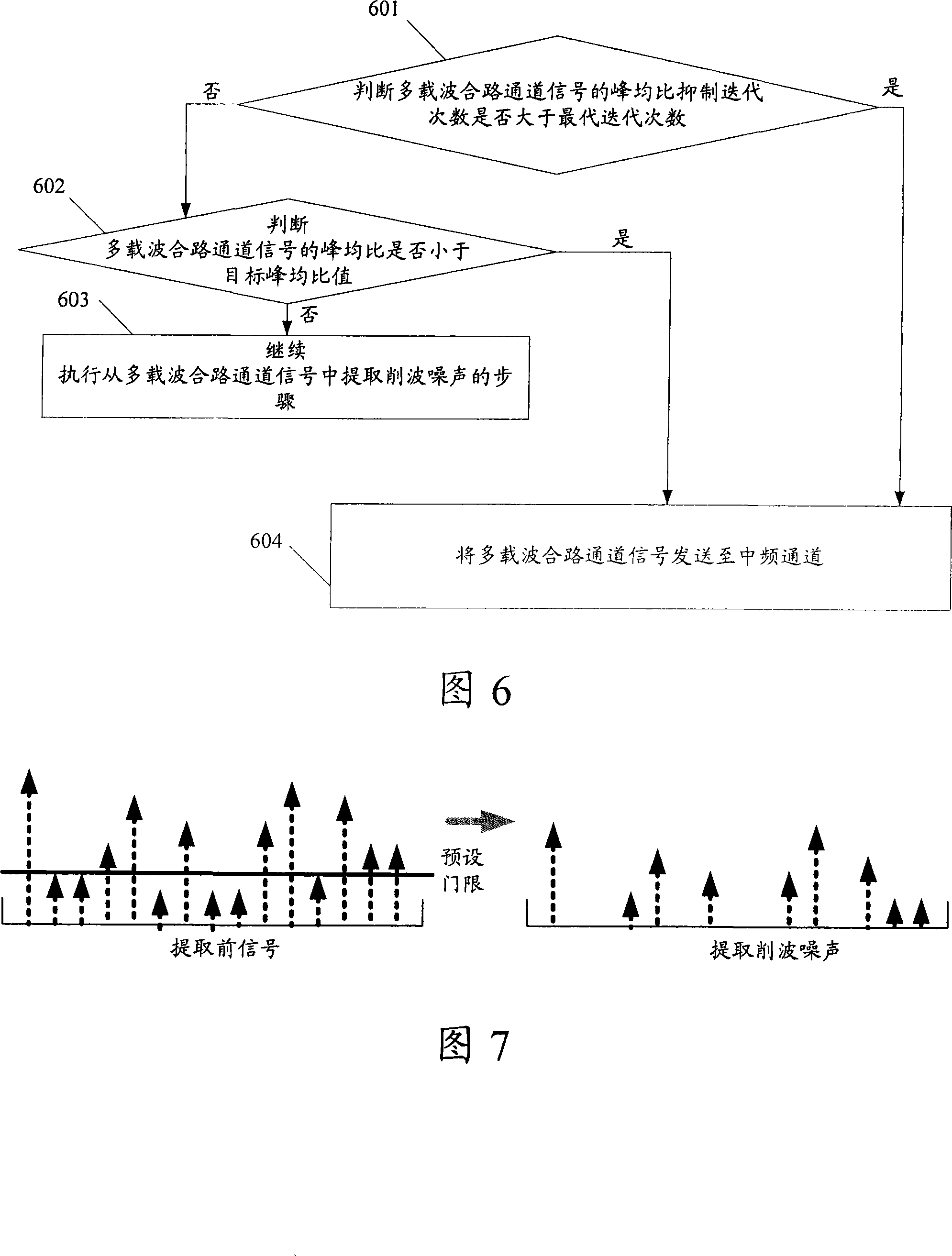
Peak-to-average ratio restraining method and device in multi-carrier orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
ActiveCN101222468APeak-to-average suppression ratioMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainTime delays
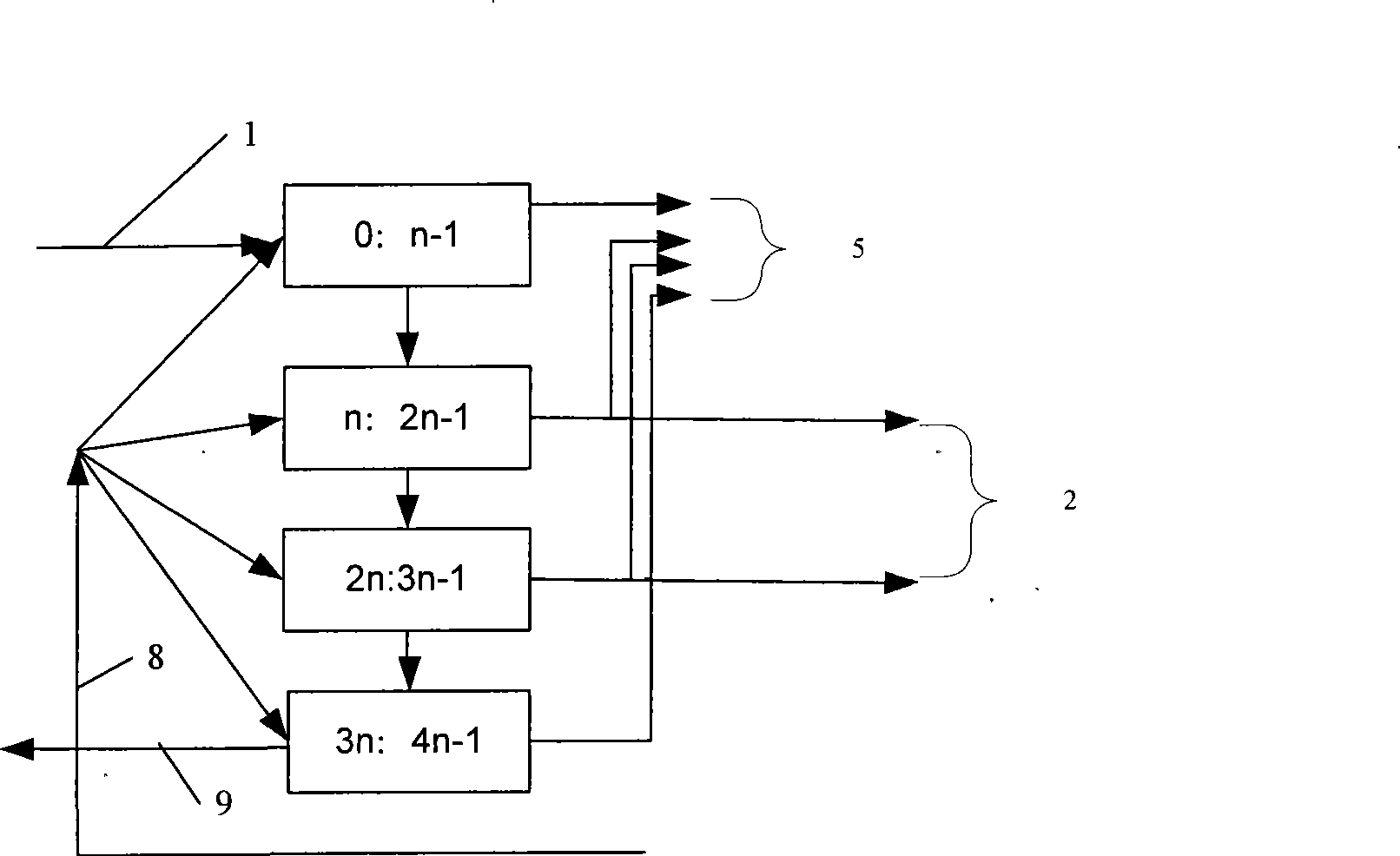
The invention discloses a method for peak-to-average ratio suppression in a multi-carrier orthogonal frequency division multiplexing OFDM system. The system comprises that: baseband frequency-domain signals of each carrier are combined into a time-domain multi-carrier combination channel signal on each OFDM symbol; clipping noise corresponding to each carrier is obtained from the multi-carrier combination channel signal, the length of the clipping noise is a symbol length; a frequency-domain response of the clipping noise corresponding to each carrier and symbol length is obtained, is reversely superposed to a baseband frequency-domain signal after the corresponding carrier has a time delay on an OFDM symbol to make a peak-to-average ratio suppression. The invention also discloses a device for peak-to-average ratio suppression in a multi-carrier OFDM system. The invention can make an effective suppression to the peak-to-average ratio in the multi-carrier OFDM system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Clipping distortion canceller for OFDM signals
Methods and apparatus are provided for reducing clipping noise from an OFDM signal, the methods and apparatus are operable to carry out actions including: (a) transforming a received orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (OFDM) signal from a transmission channel into the frequency domain, the OFDM signal having been subject to a clipping function prior to transmission in order to reduce the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR); (b) recovering data symbols from the transformed OFDM signal, which include clipping noise; (c) estimating the clipping noise in the frequency domain based on the data symbols; and (d) subtracting the estimated clipping noise from the transformed OFDM signal.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
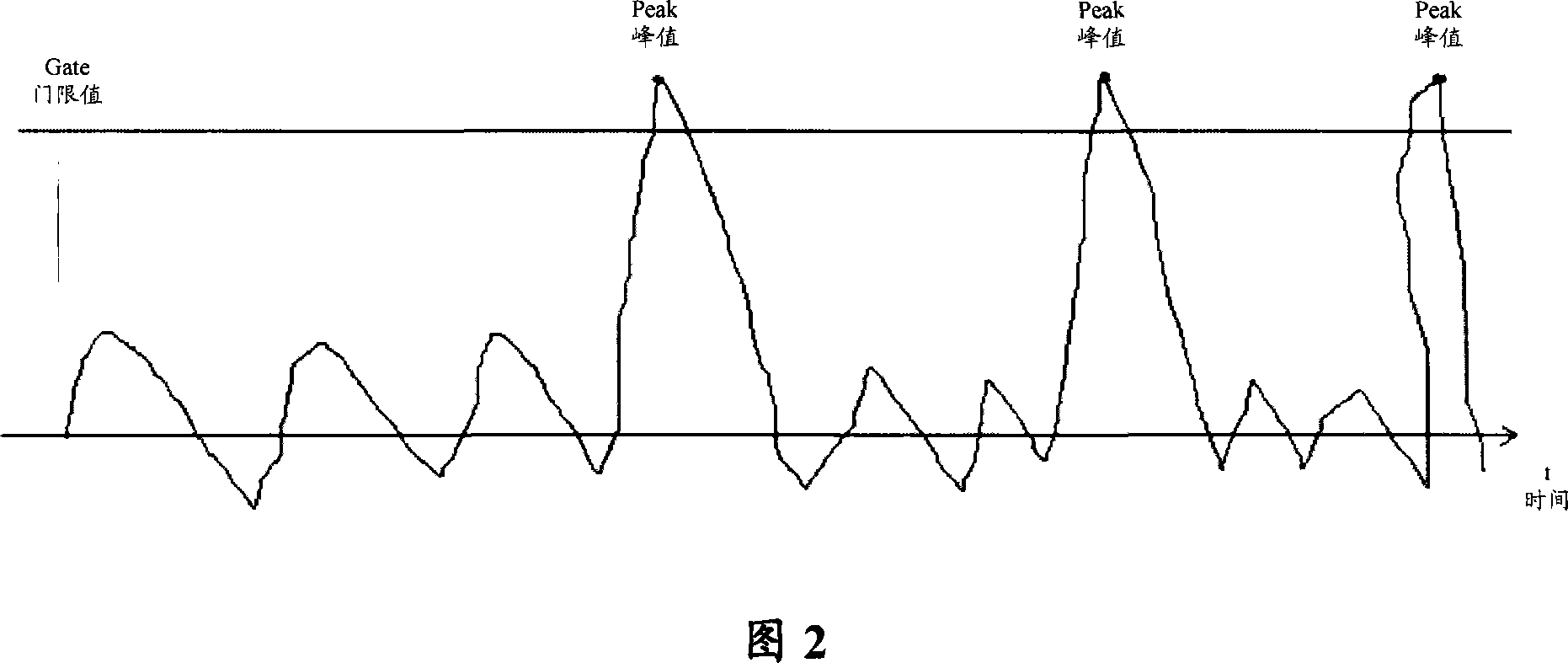
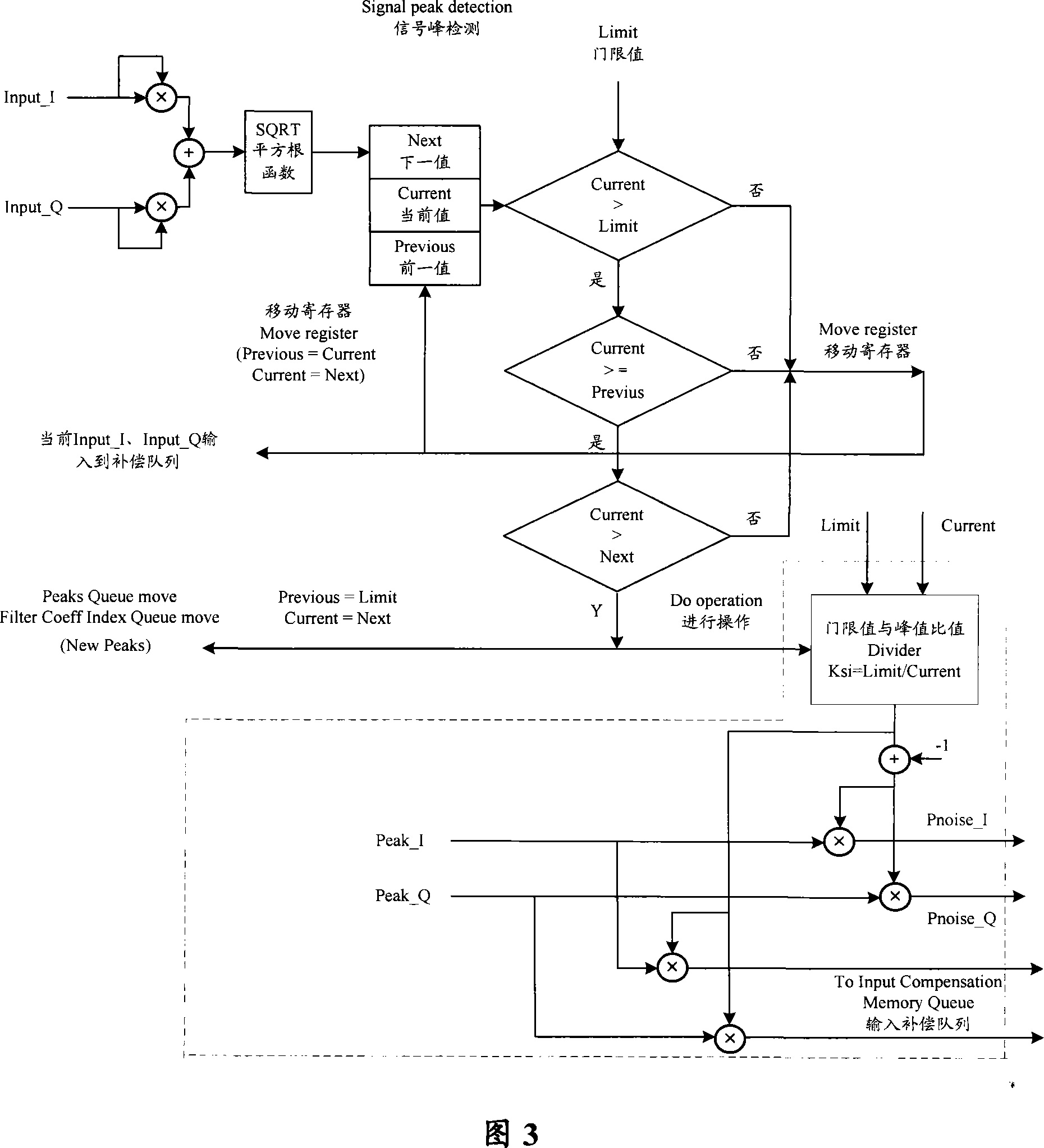
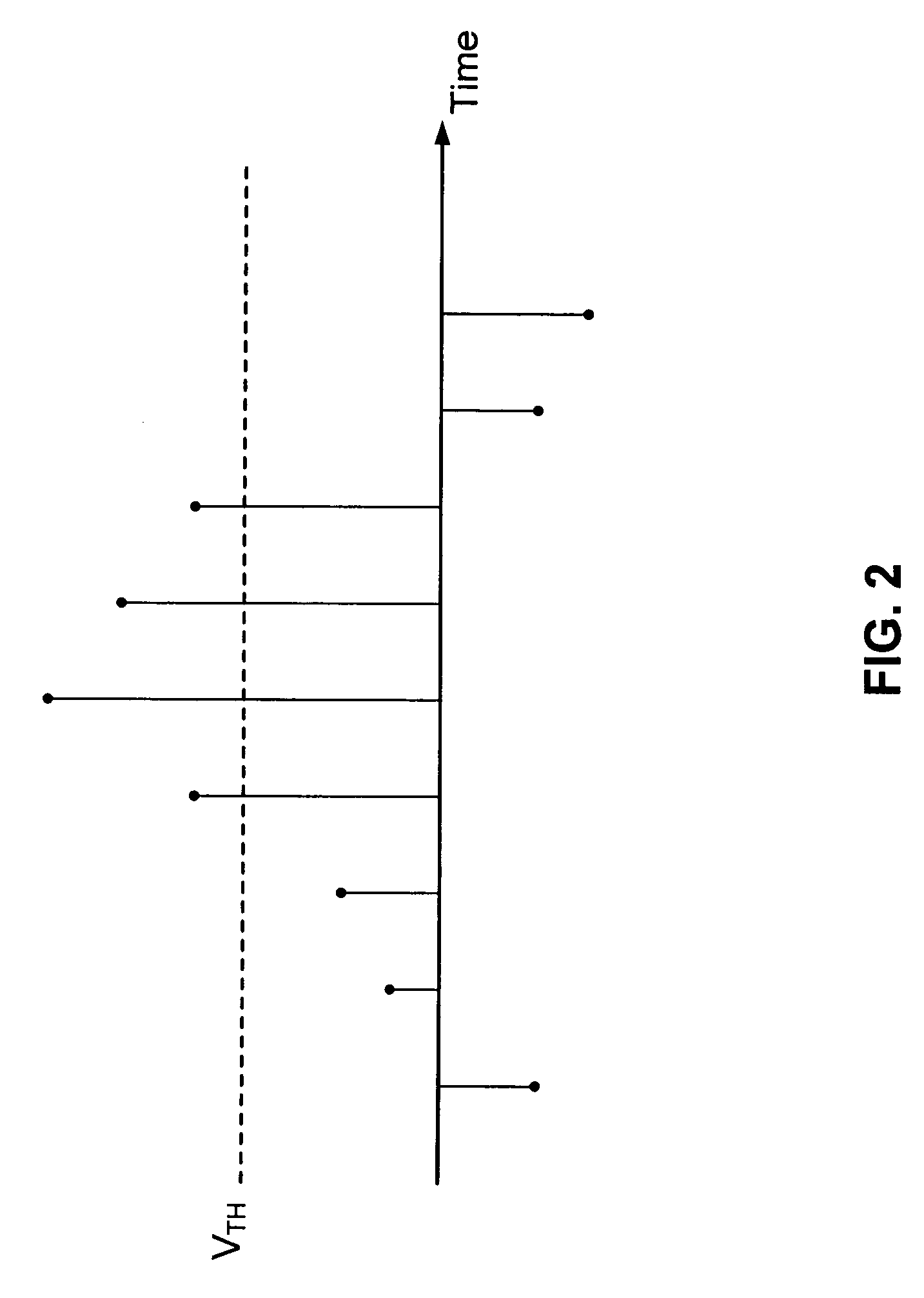
Method and apparatus for processing clipped wave
ActiveCN101076008AReduce peak-to-average ratioIncrease output powerMulti-frequency code systemsPeak valuePeak detection
The method comprises: detecting the s peak point signal which is over the preset threshold; according to said peak point signal over the preset threshold and the threshold, generating a clipping noise; according to the clipping noise, making clipping process. The invention also reveals a signal clipping treatment apparatus comprising a peak point detecting module and a clipping treatment module.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
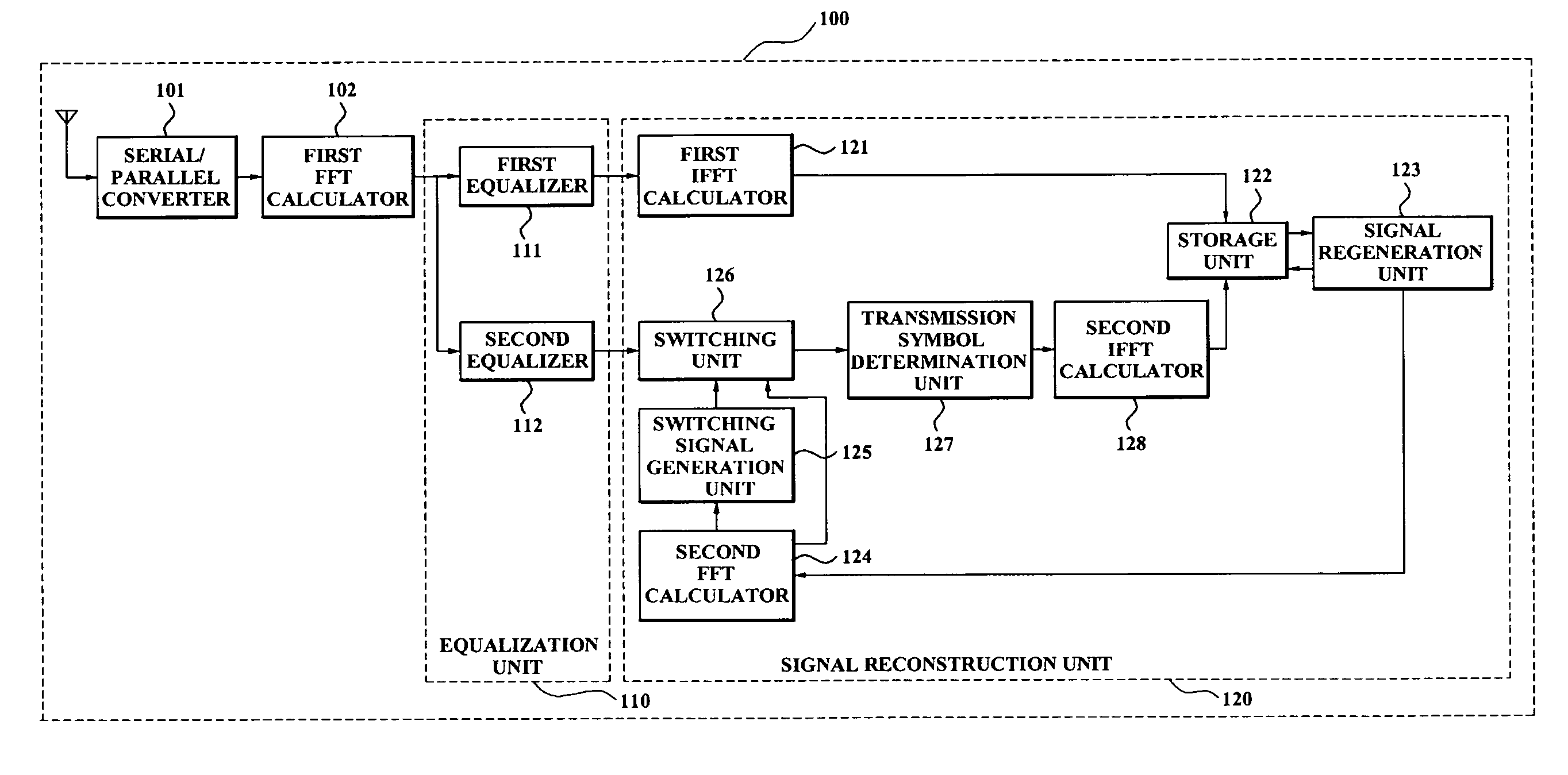
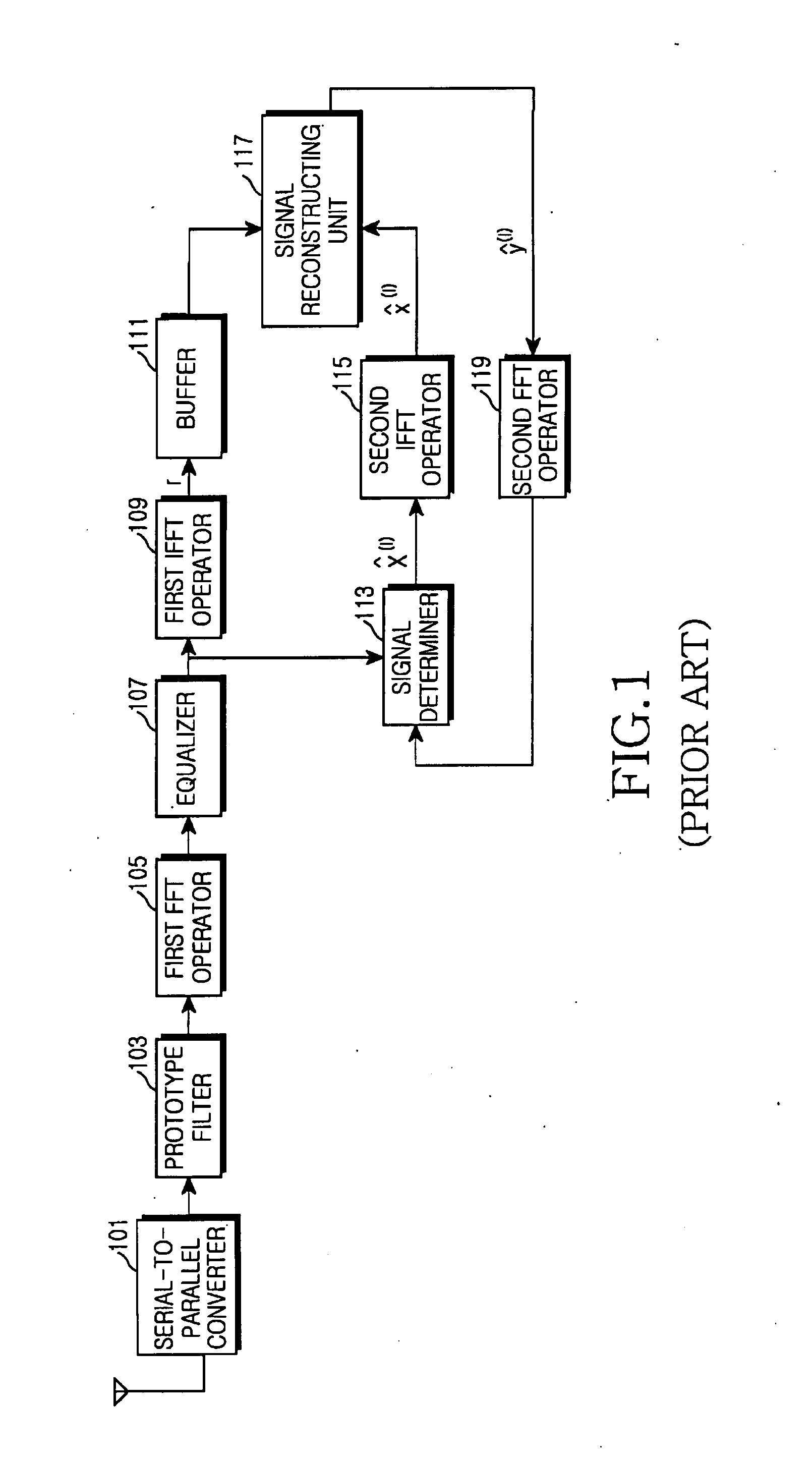
Apparatus for equalizing clipping noise signals of receiver systems and method thereof
ActiveUS7787557B2Reduce in quantityImprove reliabilityError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionBlind equalizationEqualization
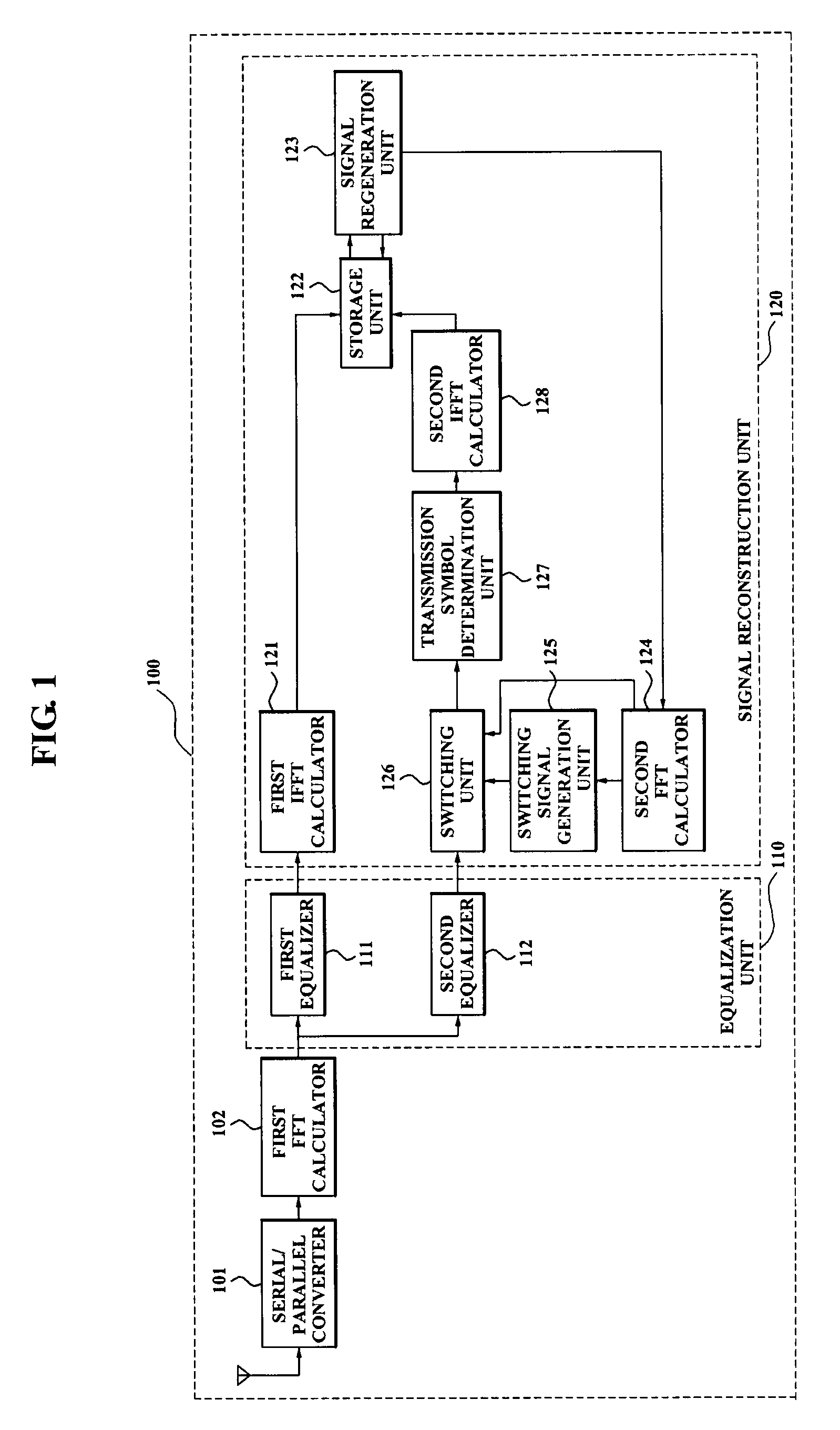
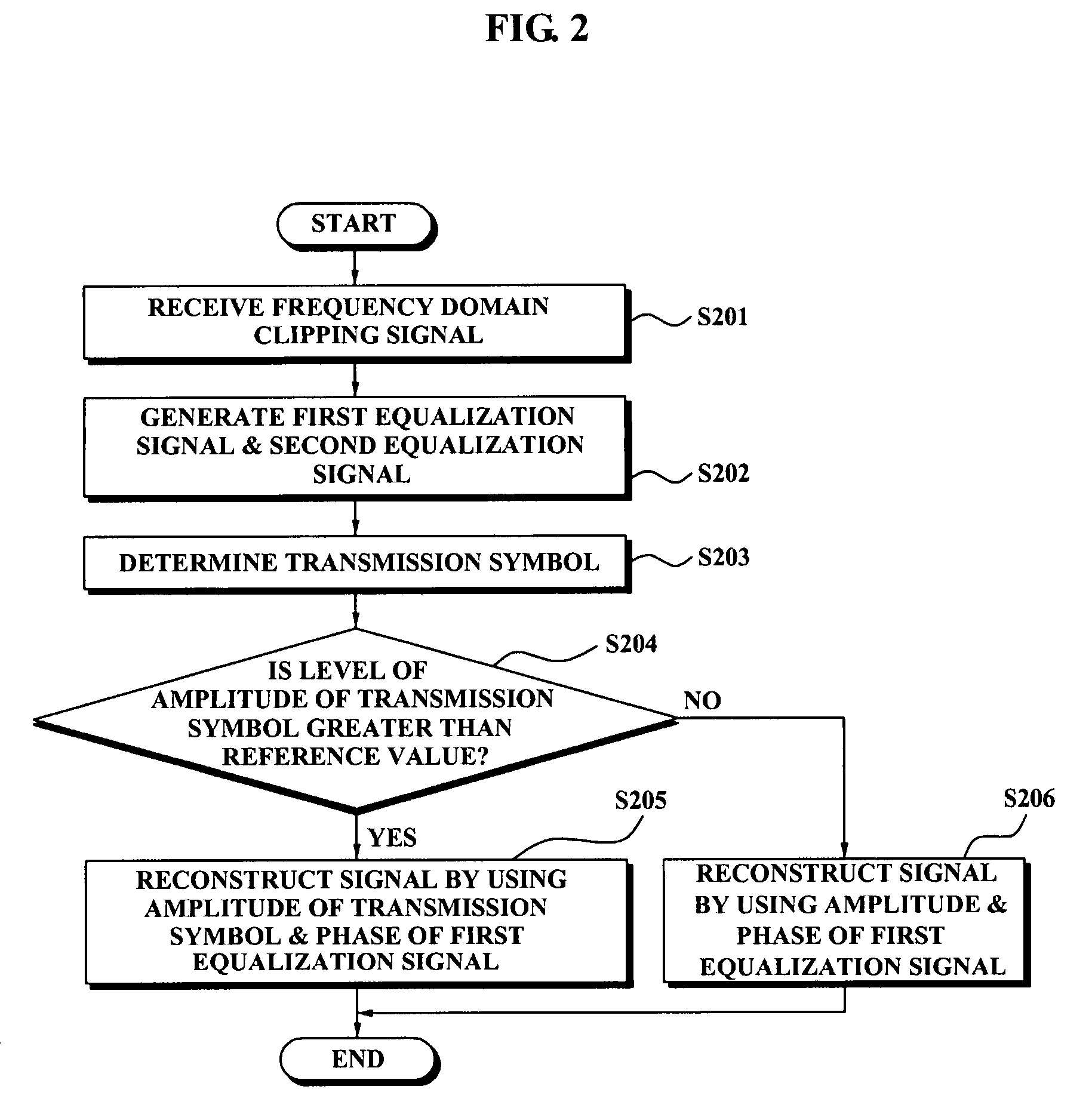
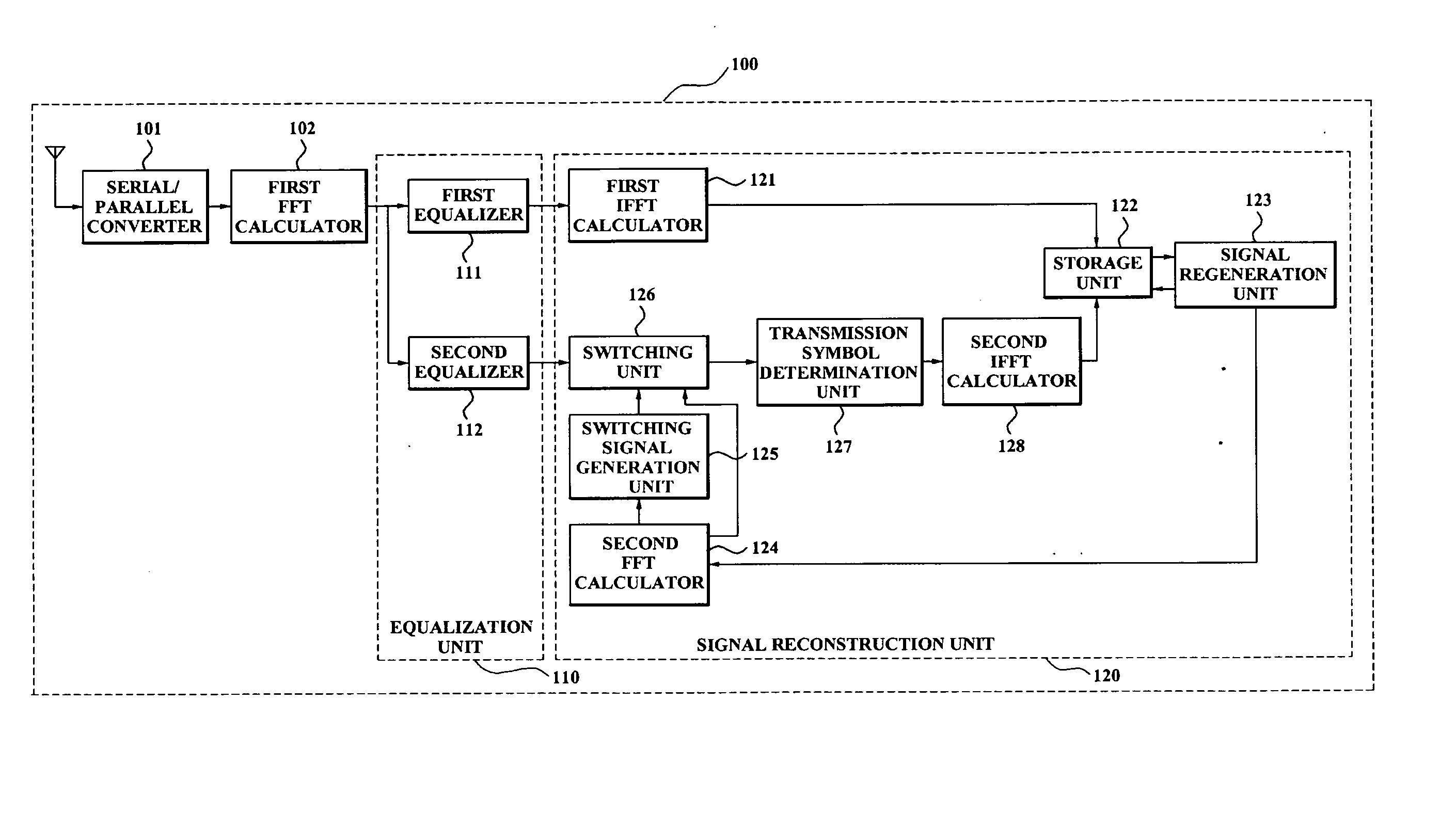
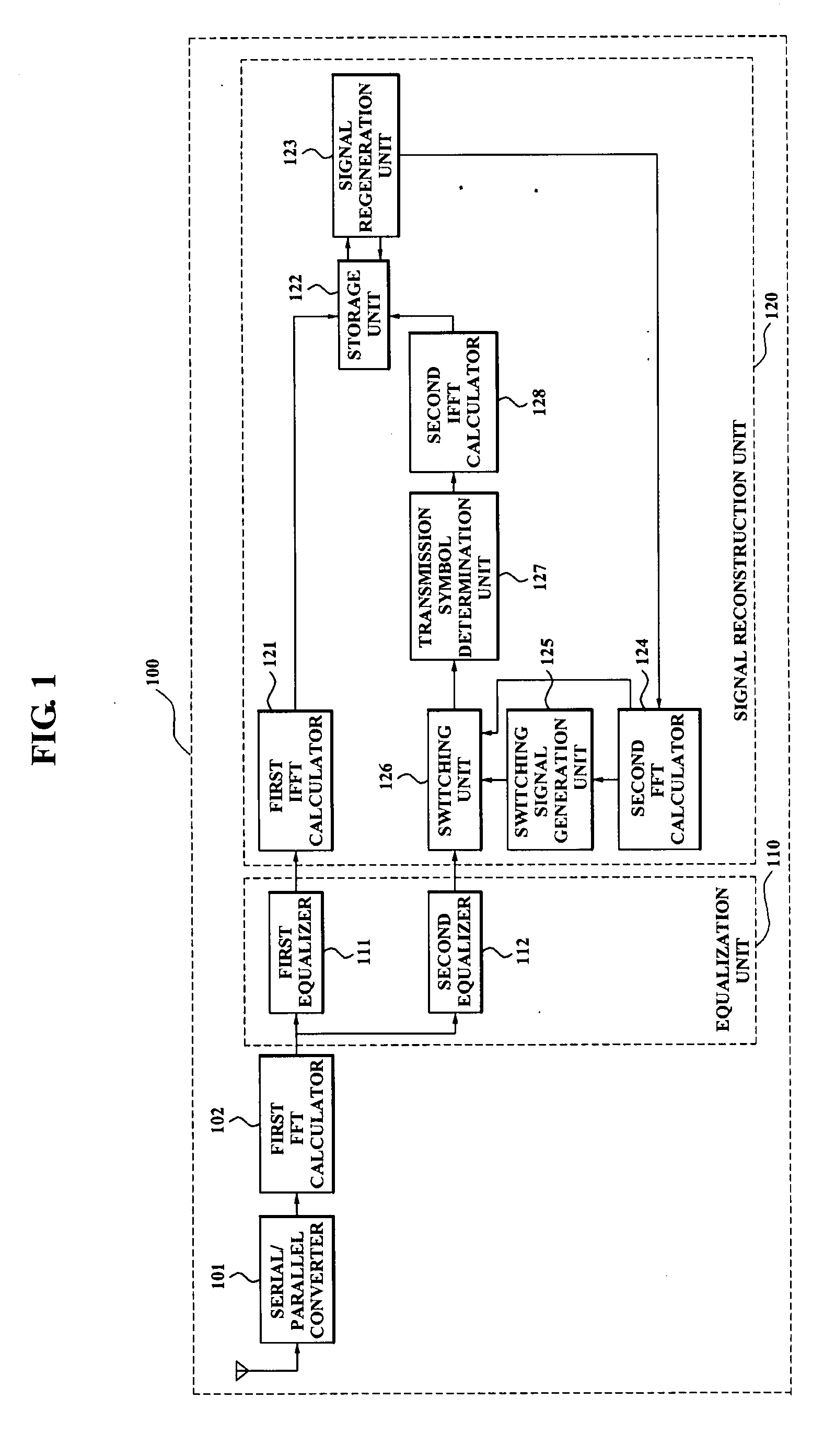
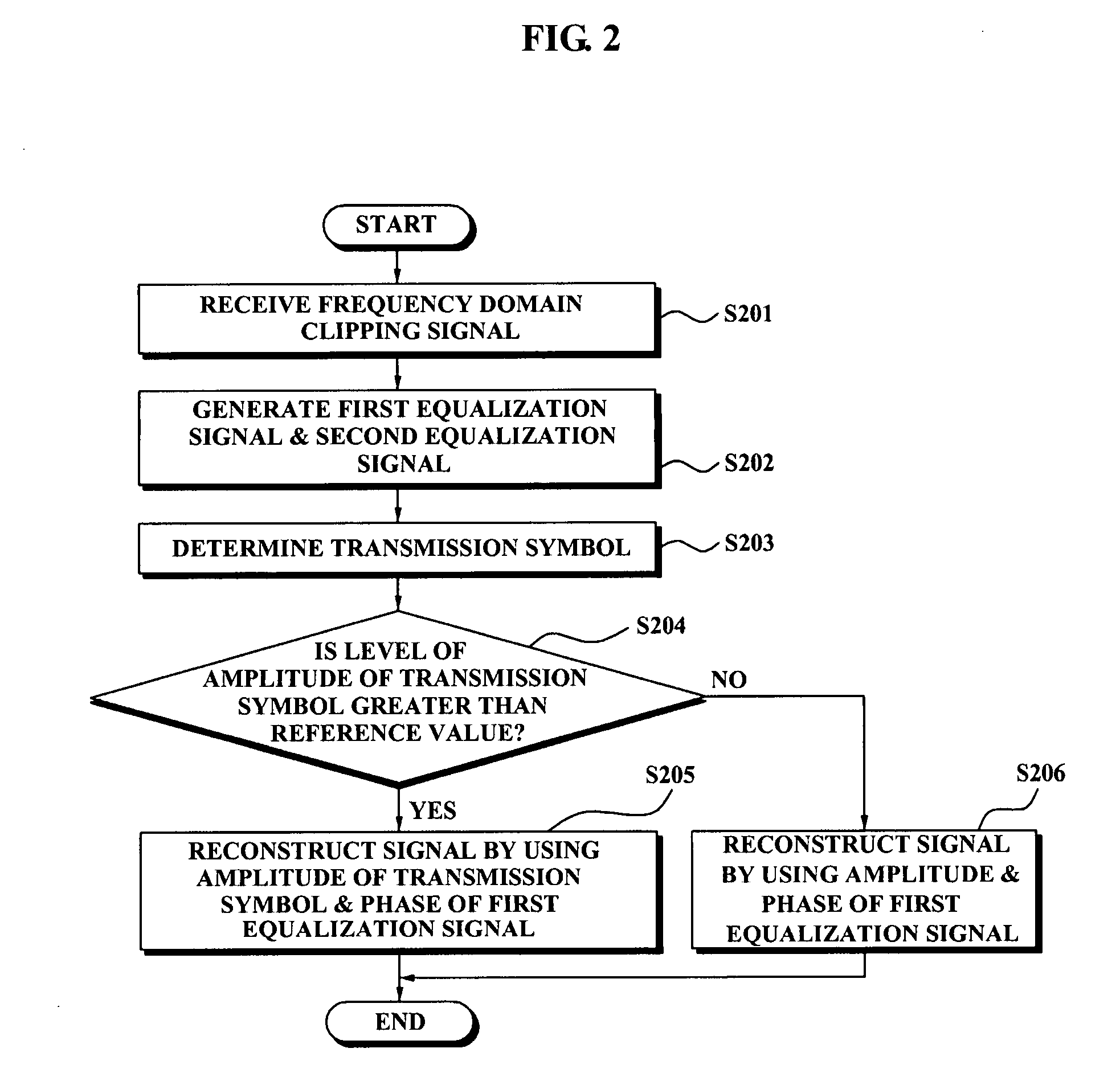
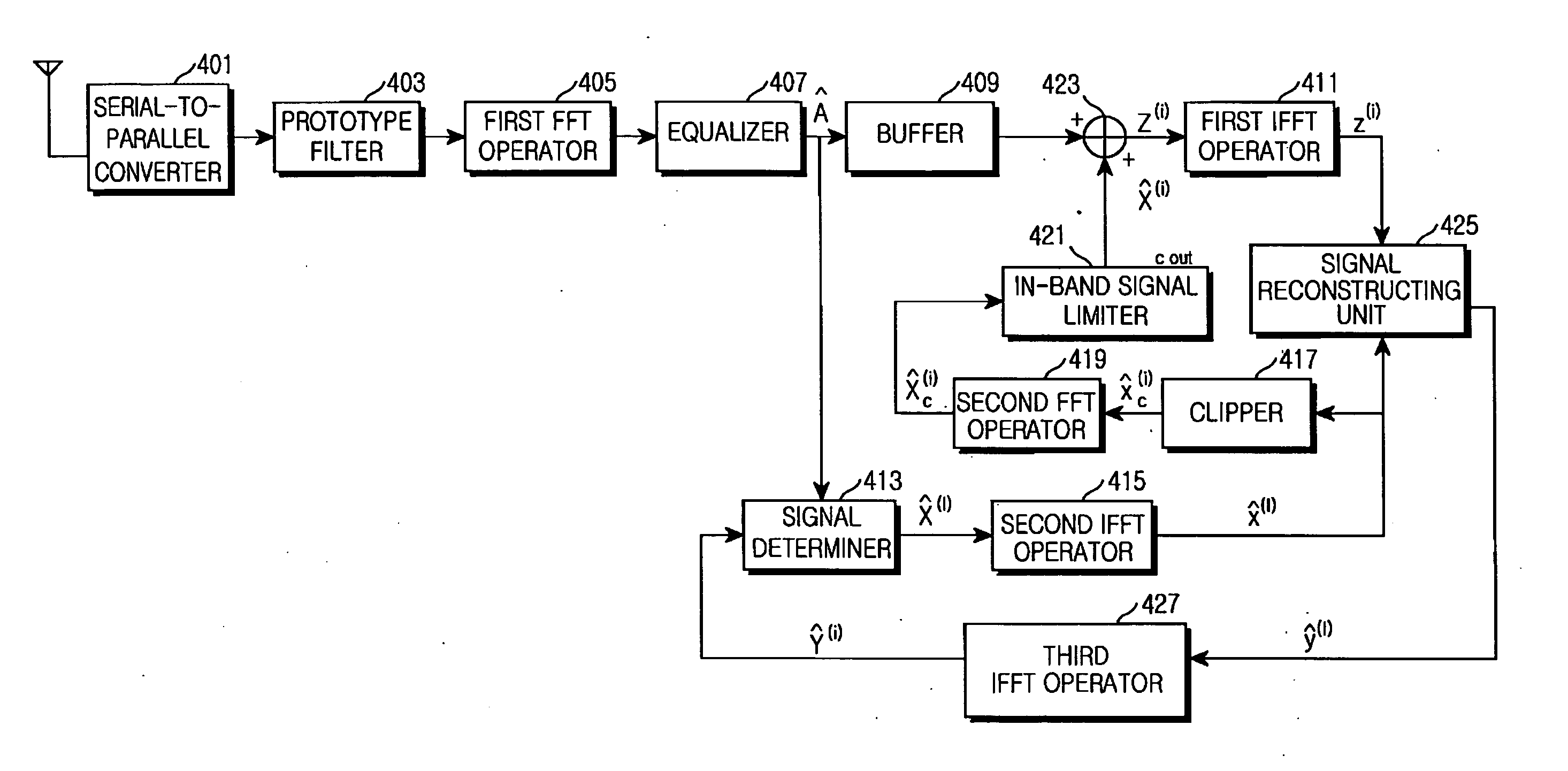
An apparatus for correcting clipping distortion of a receiver system includes: an equalizer which generates a first equalization signal by equalizing a frequency domain clipping signal via a first equalization coefficient correcting a channel distortion, and generates a second equalization signal by equalizing the frequency domain clipping signal via a second equalization coefficient correcting the clipping distortion and the channel distortion; and a signal reconstruction unit which receives the first equalization signal and the second equalization signal from the equalizer, determines a transmission symbol by performing a hard decision with respect to the second equalization, and reconstructs a signal by using an amplitude of the transmission symbol and a phase of the first equalization signal when a level of the amplitude of the transmission symbol is greater than or equal to a reference value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Apparatus for equalizing clipping noise signals of receiver systems and method thereof
ActiveUS20080089224A1Reduce system complexityReduce in quantityError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringEqualization
An apparatus for correcting clipping distortion of a receiver system includes: an equalizer which generates a first equalization signal by equalizing a frequency domain clipping signal via a first equalization coefficient correcting a channel distortion, and generates a second equalization signal by equalizing the frequency domain clipping signal via a second equalization coefficient correcting the clipping distortion and the channel distortion; and a signal reconstruction unit which receives the first equalization signal and the second equalization signal from the equalizer, determines a transmission symbol by performing a hard decision with respect to the second equalization, and reconstructs a signal by using an amplitude of the transmission symbol and a phase of the first equalization signal when a level of the amplitude of the transmission symbol is greater than or equal to a reference value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
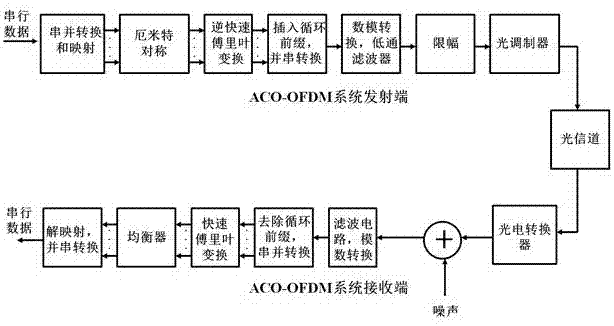
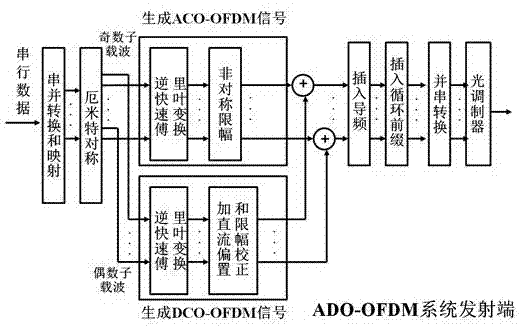
ADO-OFDM visible light communication system based on improved algorithm
InactiveCN107395276AReduce bit error rateImprove reliabilityClose-range type systemsMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformSignal on
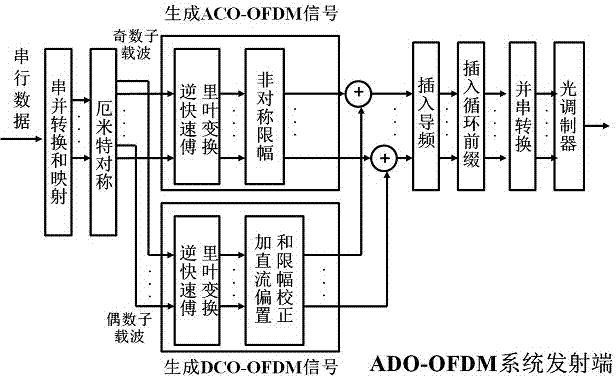
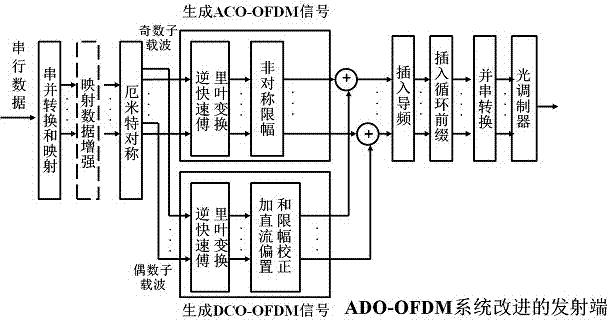
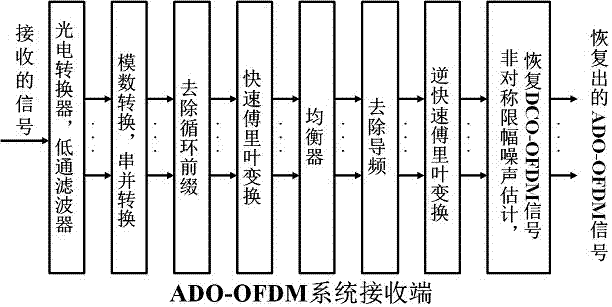
The invention discloses an ADO-OFDM (asymmetrical-clipping and DC bias orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) visible light communication system based on an improved algorithm. The system comprises a transmitter end and a receiver end. An ACO-OFDM signal of the transmitter end is transmitted on odd subcarriers, while a DCO-OFDM signal is transmitted on even subcarriers; after IFFT (inverse fast Fourier transform), asymmetrically clipping is carried out on the odd subcarriers, while the signal on the even subcarriers is subjected to DC bias to generate a single-polarity signal; and then, the odd subcarriers and the even subcarriers are merged to form an ADO-OFDM signal. By increasing the power of the ACO-OFDM input signal in data mapping, error rate of the system is reduced, and reliability can be improved. At the receiver end, the ACO-OFDM signal is subjected to estimation and optimization based on the newly-recovered DCO-OFDM signal, and furthermore, influence of the clipping noise on the DCO-OFDM signal is eliminated through the optimized and regenerated ACO-OFDM signal, thereby improving the received signal and improving system reliability.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
ADO-OFDM-based visible light communication system
InactiveCN107395277AImprove spectrum utilizationImprove power utilizationClose-range type systemsMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumSignal on
The invention discloses a visible light communication system based on ADO-OFDM (asymmetrically clipped and direct-current-biased optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing). The visible light communication system comprises a transmitter end and a receiver end. An ACO-OFDM signal of the transmitter end is transmitted on odd subcarriers, while a DCO-OFDM signal is transmitted on even subcarriers; after IFFT (inverse fast Fourier transform), asymmetrically clipping is carried out on the odd subcarriers, while the signal on the even subcarriers is subjected to DC bias to generate a single-polarity signal; and then, the odd subcarriers and the even subcarriers are merged to form an ADO-OFDM signal. At the receiver end, when the asymmetrically clipping is carried out, the clipping noise of the odd subcarriers exerts an influence on the even subcarriers, so that when the DCO-OFDM signal is recovered, influence of the clipping noise needs to be removed. The ADO-OFDM-based visible light communication system has higher spectrum utilization ratio compared with an ACO-OFDM system, and has higher power utilization rate compared with a DCO-OFDM system.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
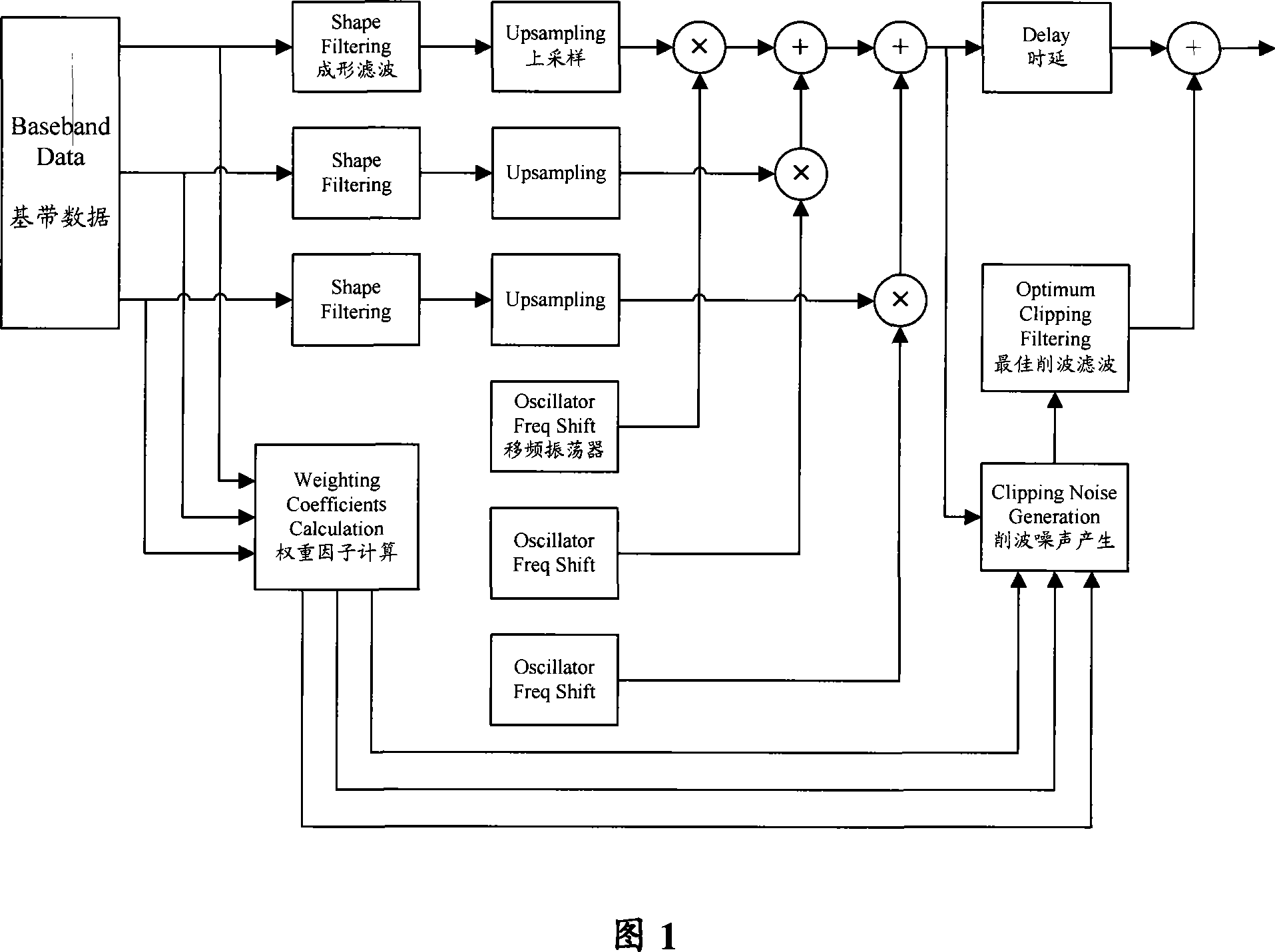
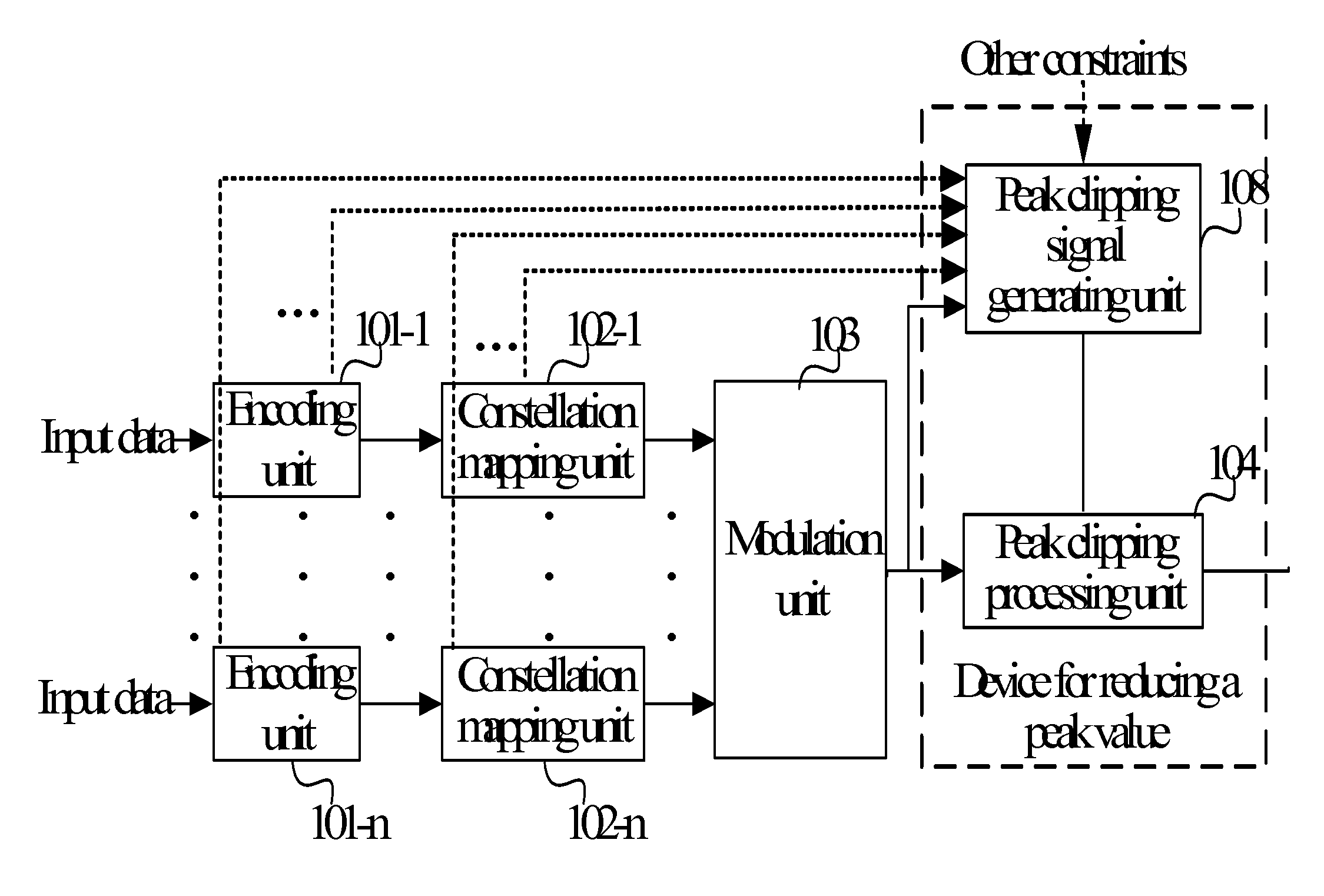
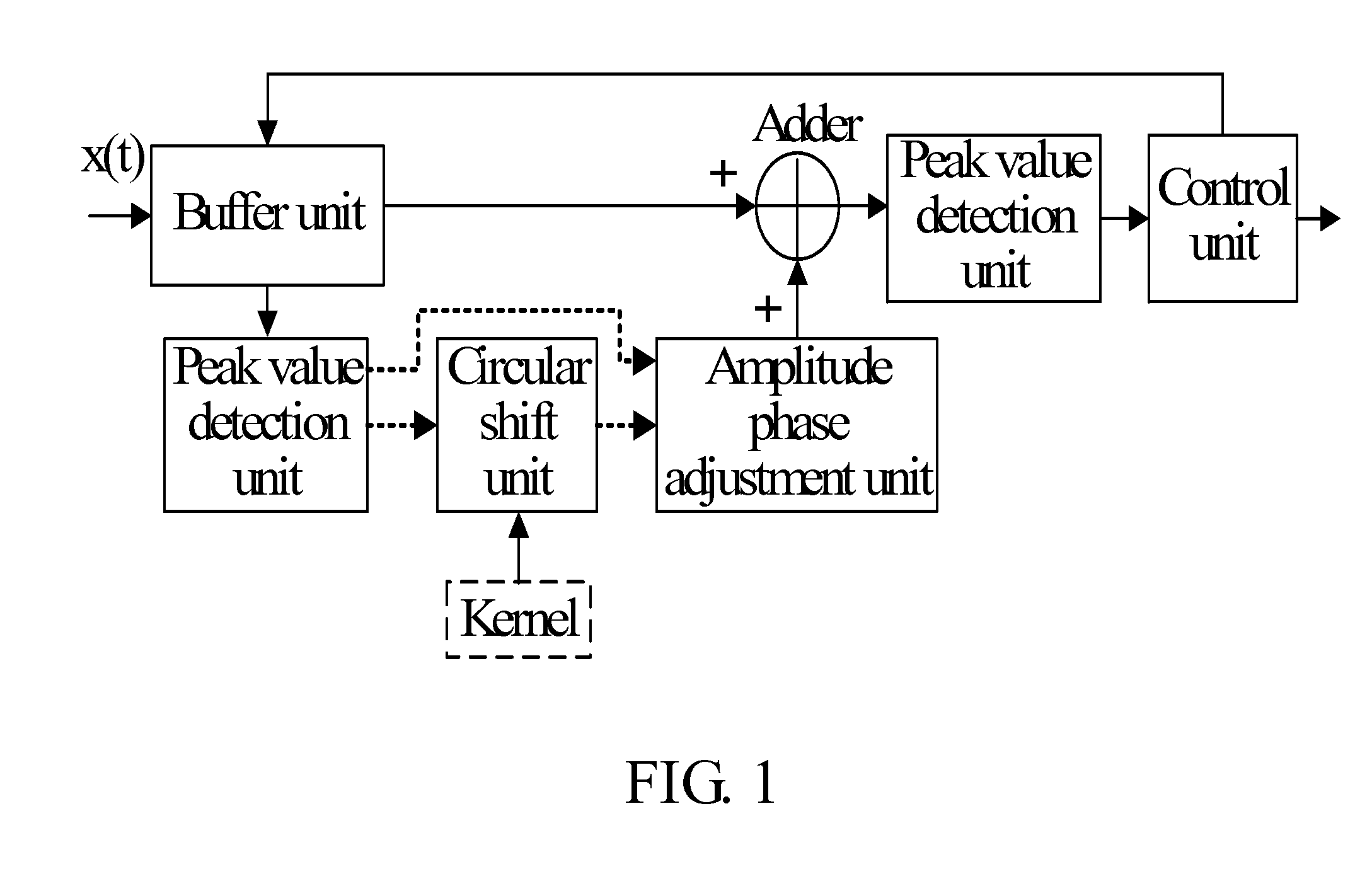
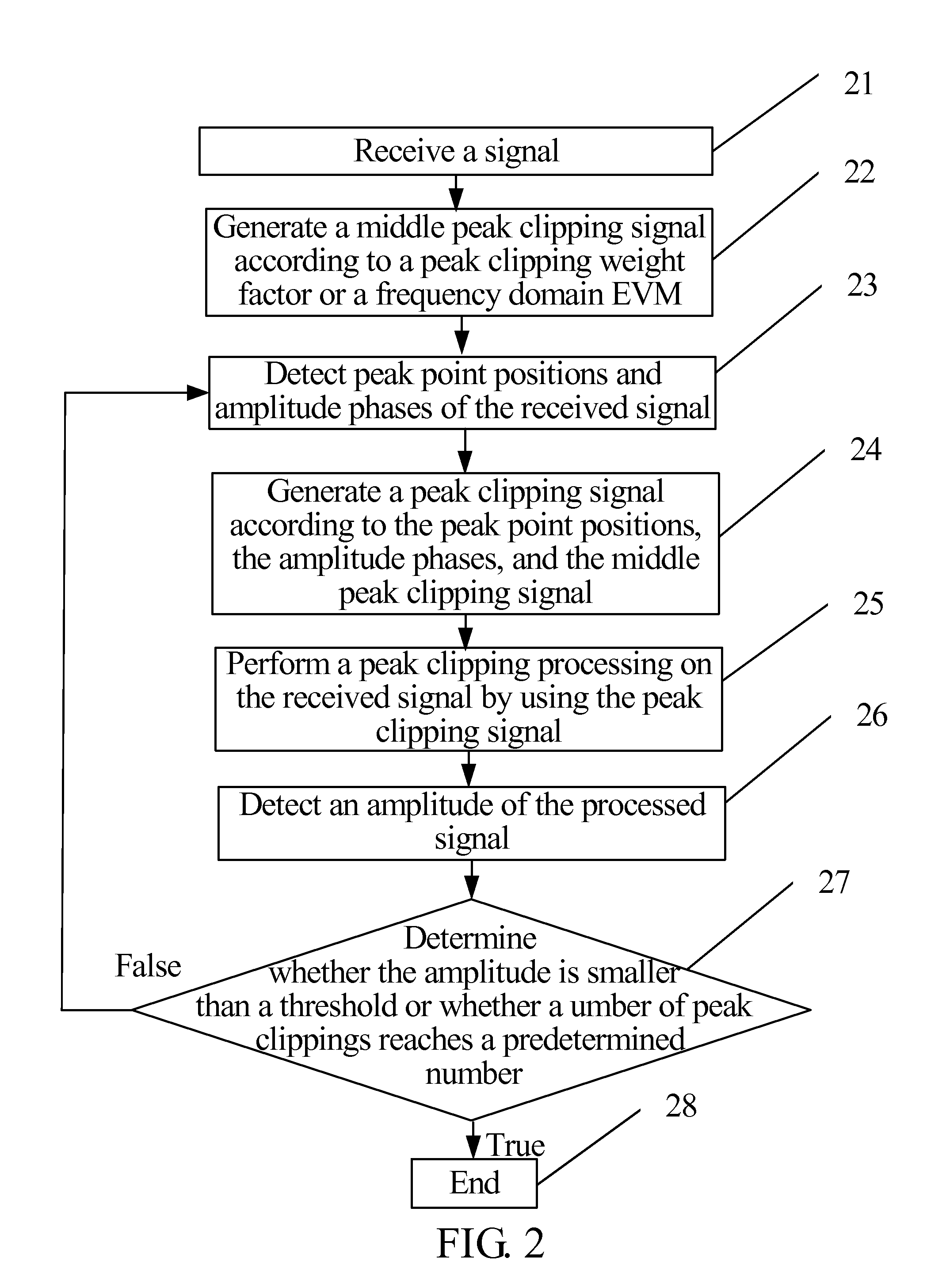
Method and device for reducing signal peak value and transmitting device
InactiveUS20100020895A1Improve system performanceImprove anti-interference abilityModulated-carrier systemsPulse demodulatorCarrier signalError vector magnitude
A method and a device for reducing a signal peak value are adapted to solve a problem that overall performance of a system is significantly degraded caused by allocating a same weight to each sub-carrier so as to averagely distribute a peak clipping noise to each sub-carrier. The method includes: receiving a signal (21); and performing a peak clipping processing on the received signal by using a peak clipping signal (25). The peak clipping signal is formed according to a peak clipping weight factor and the received signal, or according to a frequency domain error vector magnitude (EVM) and the received signal. In the method, a weight of each sub-carrier is set according to the peak clipping weight factor or the frequency domain EVM during the peak clipping processing, thereby improving the overall performance of the system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
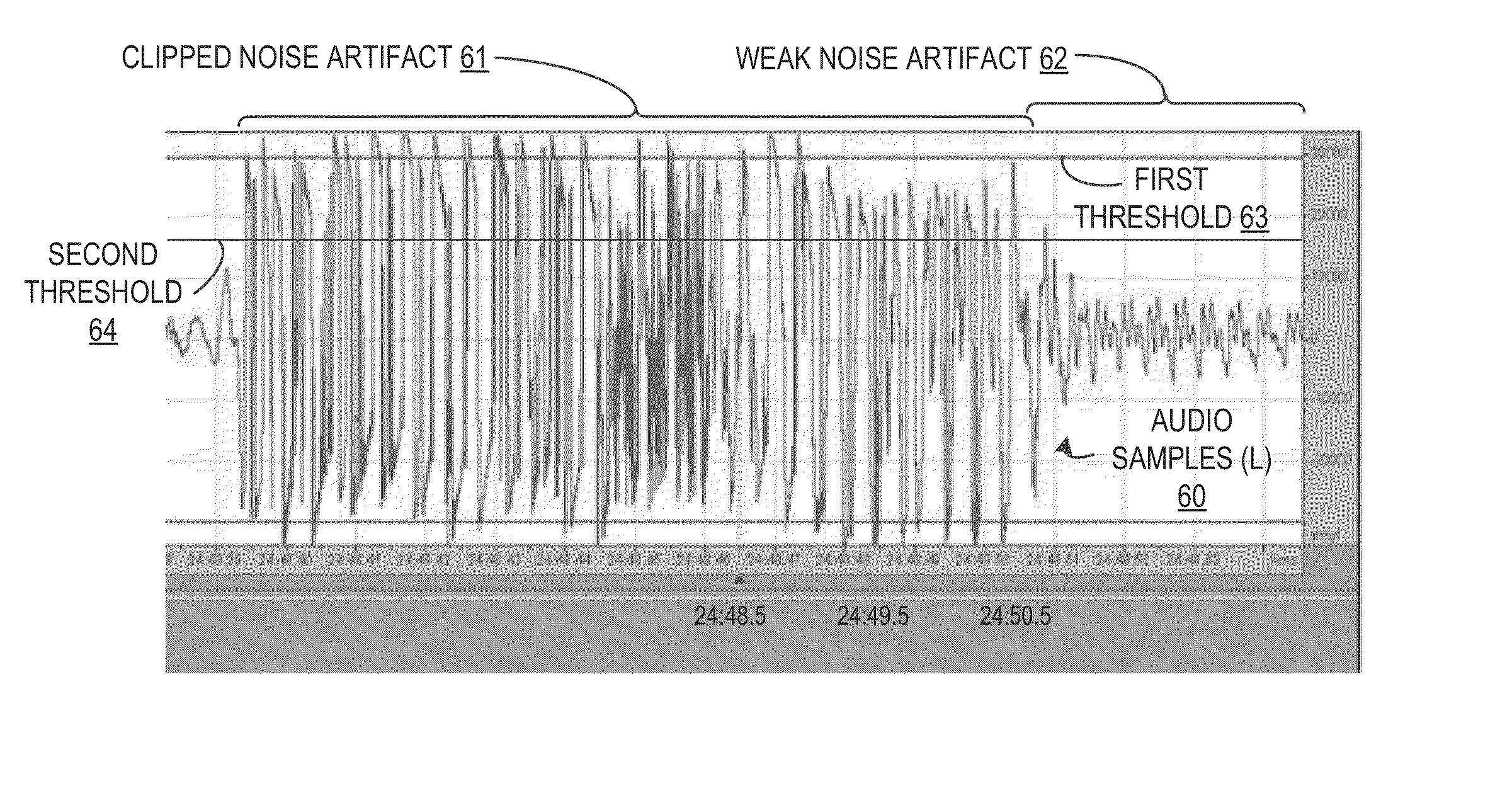
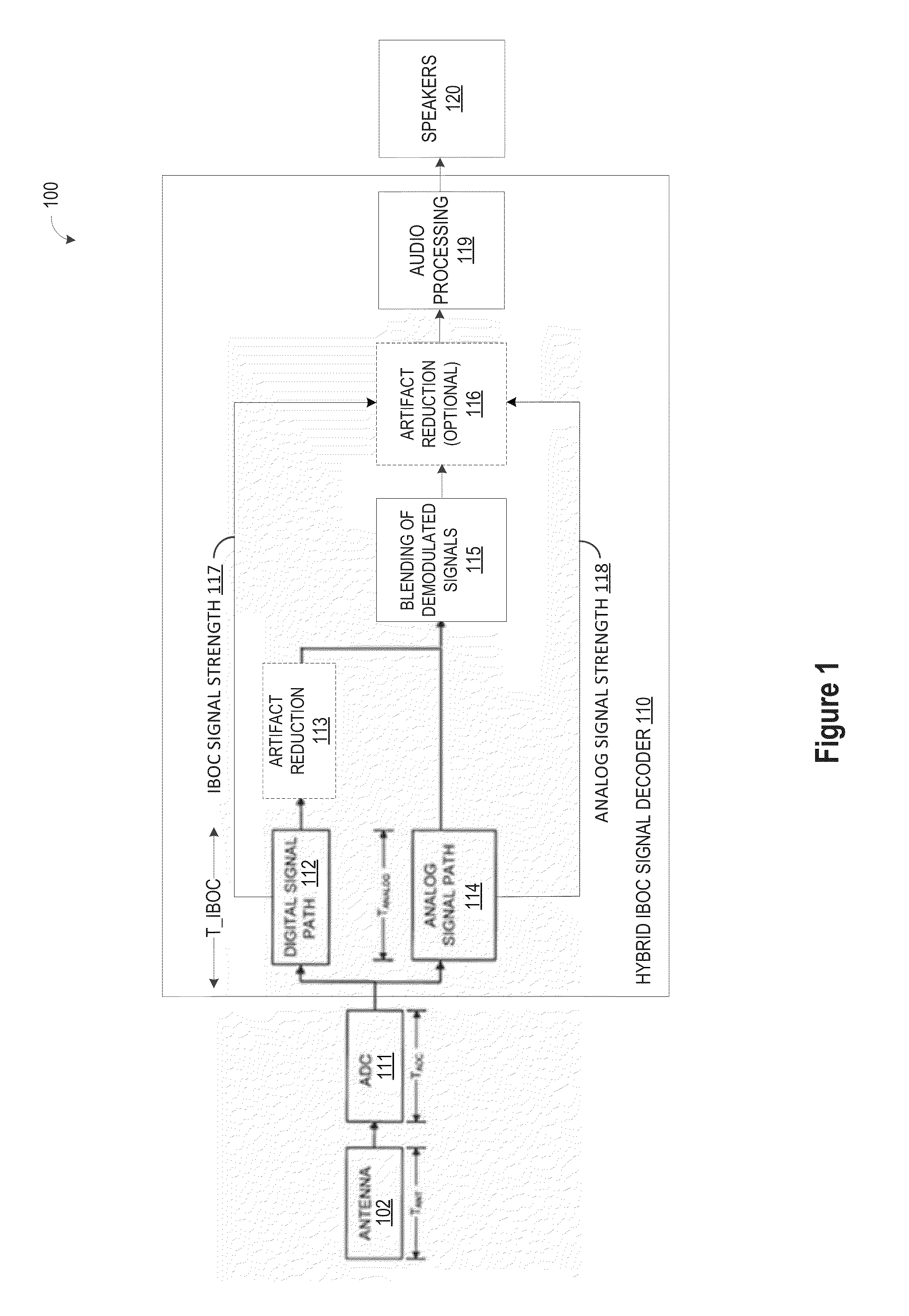
Signal Artifact Detection and Elimination for Audio Output
A method and apparatus are provided for processing a received digital radio broadcast signal to efficiently remove signal interference artifacts from digital and / or analog signals by using signal quality information extracted from audio samples in one or more buffered audio frames to detect audio frames containing clipped noise artifacts and weaker noise artifacts and to selectively apply anti-interference processing to remove the signal interference artifacts.
Owner:IBIQUITY DIGITAL CORP
Method, apparatus, system for clipping signal and signal radiation system
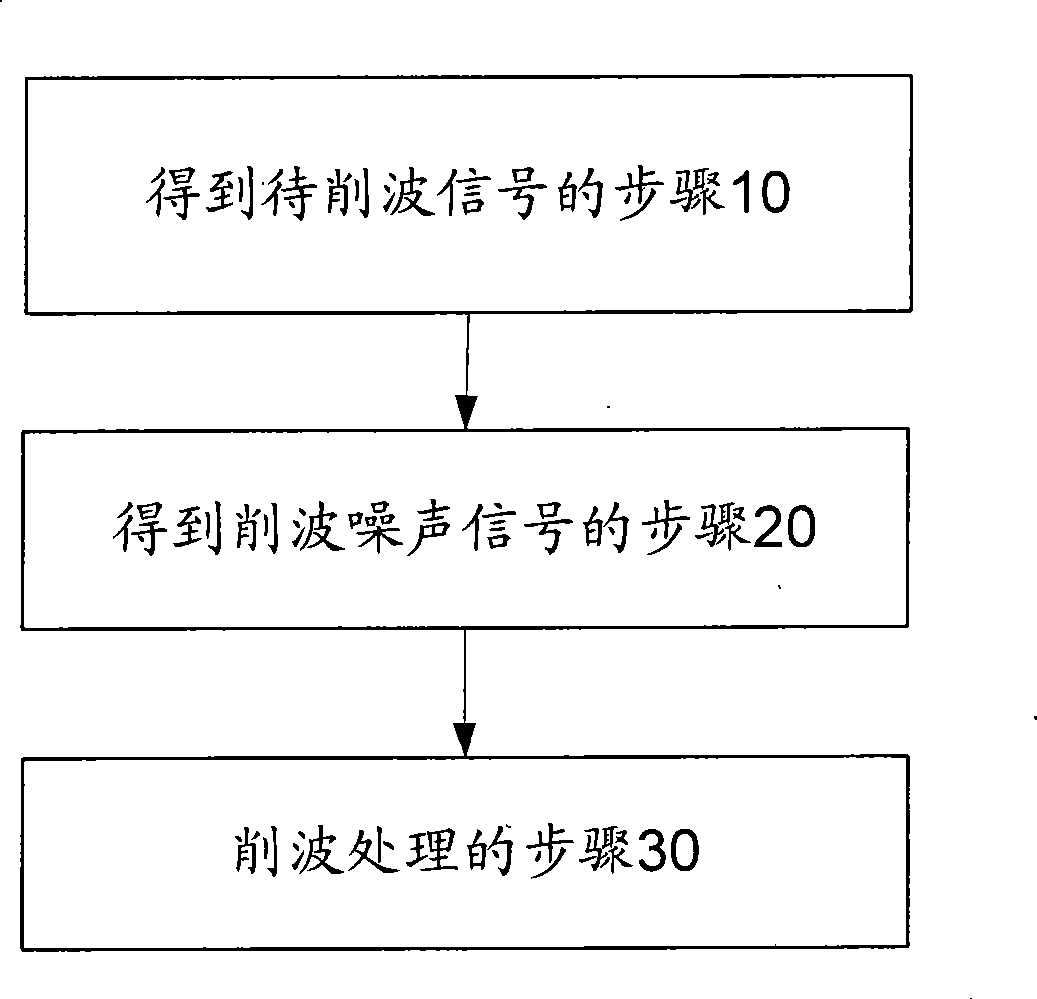
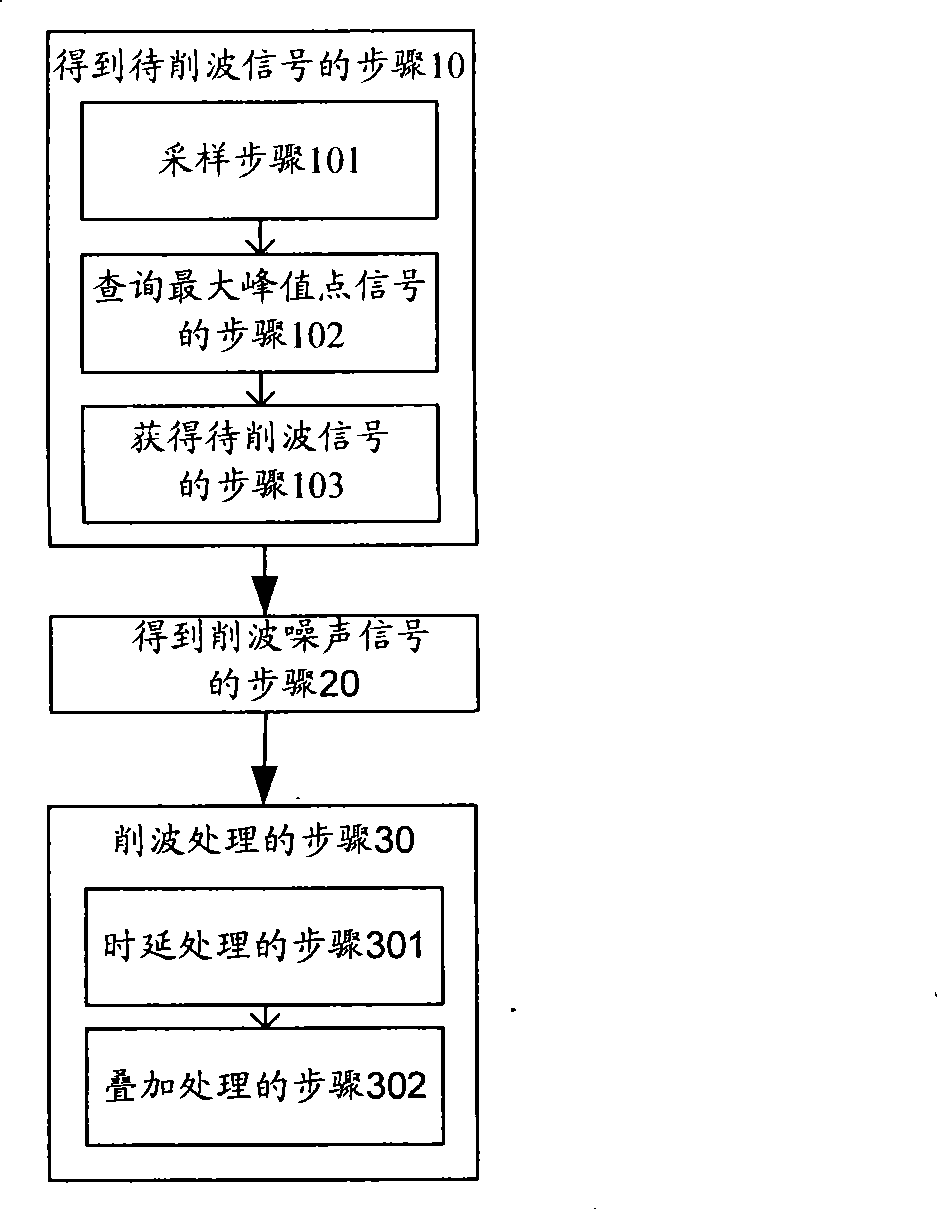
ActiveCN101442348ARelieve pressureSimplify Logic DesignPower managementModulated-carrier systemsPeak valueComputer science
The invention discloses a signal clipping method, which comprises the following steps: sampling input signals, detecting out a maximal peak point signal over a preset threshold from the input signals, and making the sampling point signals using the maximal peak point signal as a center be the signals to be clipped; multiplying the maximal peak point signal with a preset clipping coefficient to obtain a clipping noise signal; and reversely stacking the clipping noise signal to the signals to be clipped to finish clipping treatment. The invention also discloses a signal clipping device, a system and a signal emitting system. The signal clipping method, the device, the system and the signal emitting system adopt once clipping treatment to achieve removal of the maximal peak point signal of the input signals, are simple in logical design, can achieve inhibit of peak-to-mean ratio signals under the condition of optimizing hardware resources, and further reduce pressure of a power amplifieron output power and efficiency.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method of transmitting calls in a cellular type telecommunications system using adjacent carrier frequency bands
InactiveUS20030096630A1Increase radiusLarge capacityFrequency-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsAudio power amplifierPeak value
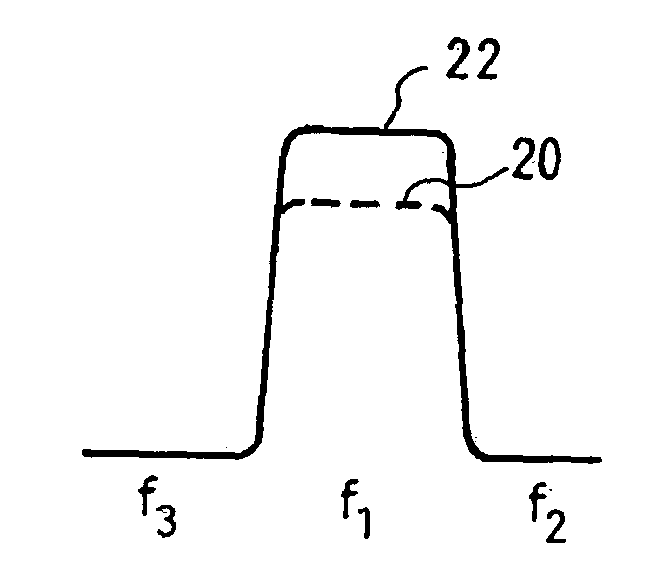
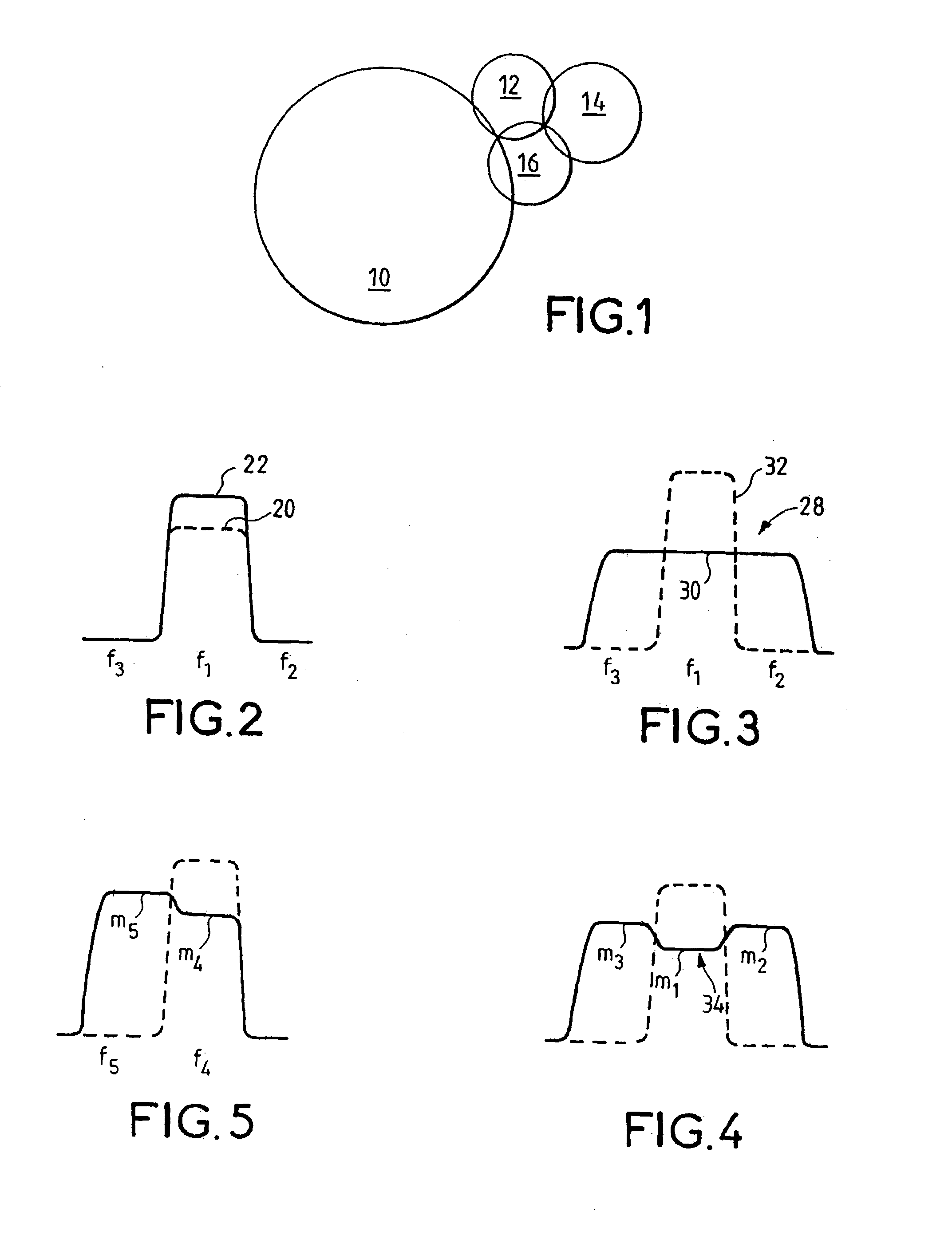
The invention relates to a method of transmitting calls in a cellular type telecommunications system using a plurality adjacent carrier frequency bands and in which a first cell or a first site uses only a fraction of said frequency bands, the transmitted signals being subjected to peak clipping prior to application to an amplifier of a transmitter system in order to optimize the efficiency of the amplifier. Prior to being applied to the input of the amplifier, the signals (32) to be transmitted for the first cell (or first site) are subjected to filtering (28) so that the power density of the peak-clipping noise is not eliminated in adjacent frequency bands (f2, f3) that are unused by said first cell.
Owner:EVOLIUM +1
Method for suppressing signal peak-to-average ratio based on ACE algorithm
ActiveCN108512796AOvercoming the disadvantage of insufficient gainOvercome the disadvantage of time-domain expansion requiring multiple iterationsMulti-frequency code systemsCommunications systemComputer science
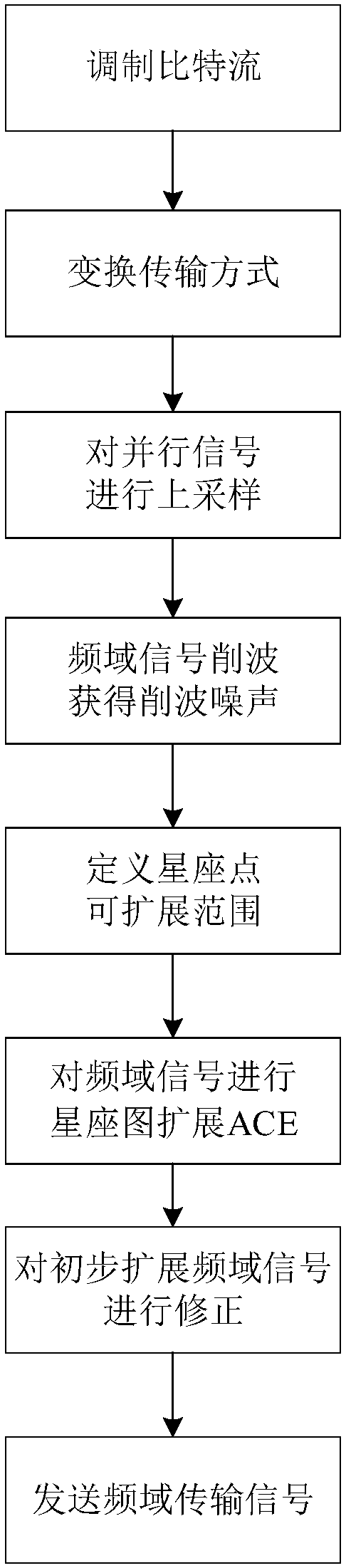
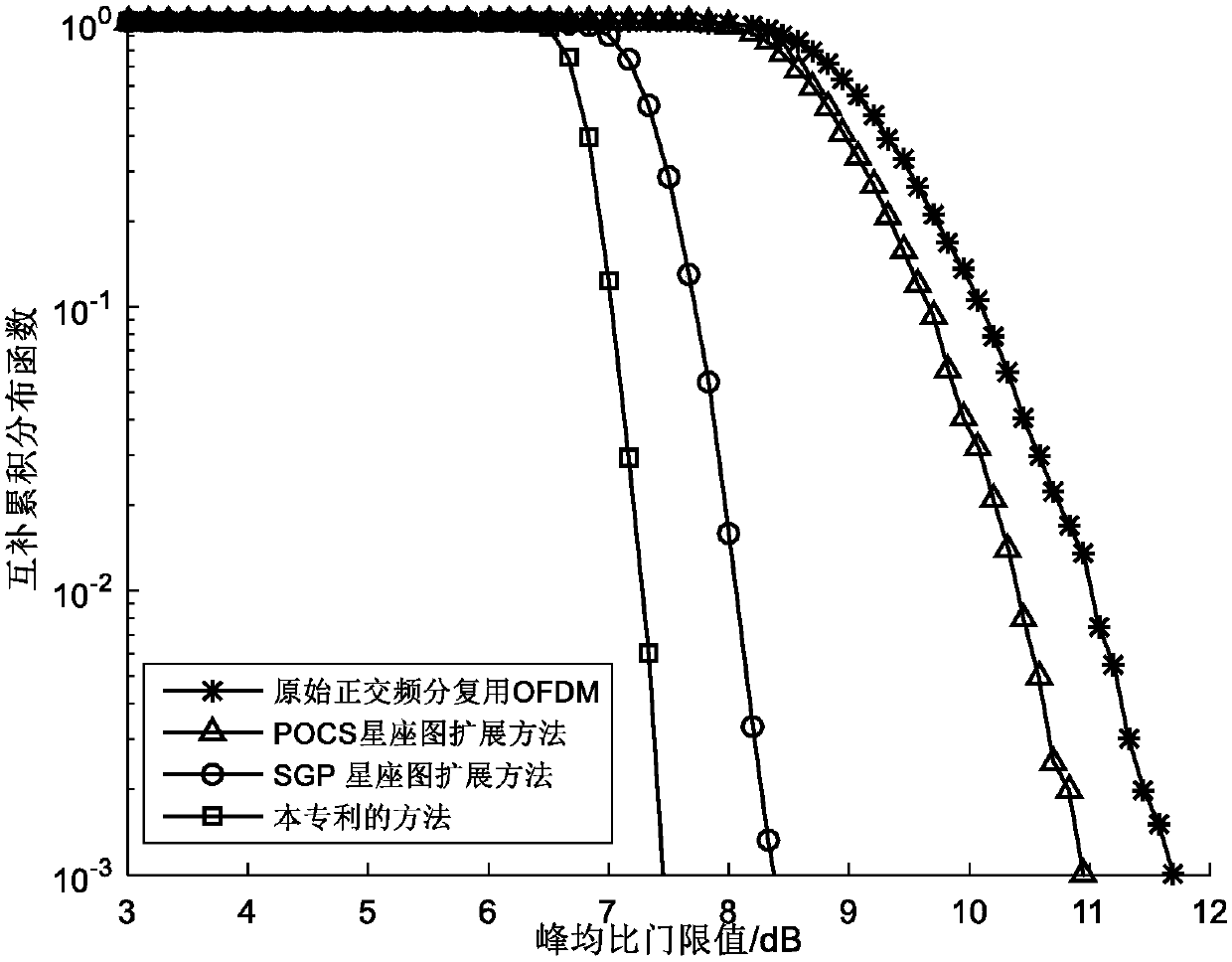
The invention discloses a method for suppressing a signal peak-to-average ratio based on an active constellation extension ACE algorithm in an OFDM system for mainly solving the problem that the signal peak-to-average ratio in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing OFDM system in the prior art is too high. The specific steps comprise: (1) modulating a bit stream; (2) transforming a transmission mode; (3) performing upsampling on a parallel signal; (4) clipping a frequency domain signal to obtain clipping noise; (5) defining a scalable range of a constellation point (6) performing activeconstellation extension ACE on the frequency domain signal; (7) correcting the preliminarily extended frequency domain signal; and (8) sending a frequency domain transmission signal. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being suitable for the OFDM system of a high-order orthogonal amplitude modulation and having low implementation complexity, and the power utilization rateof a communication system transmitter is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
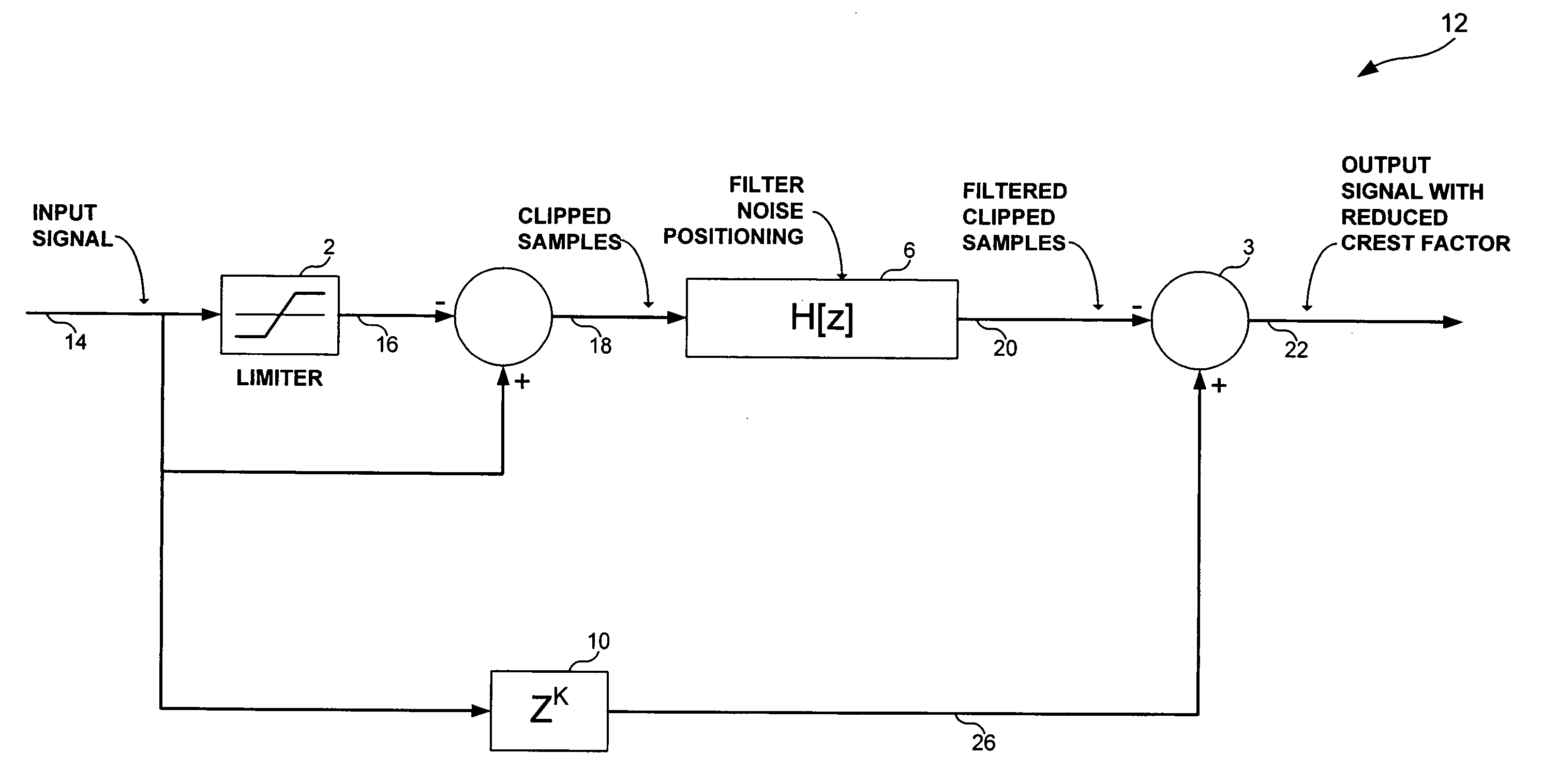
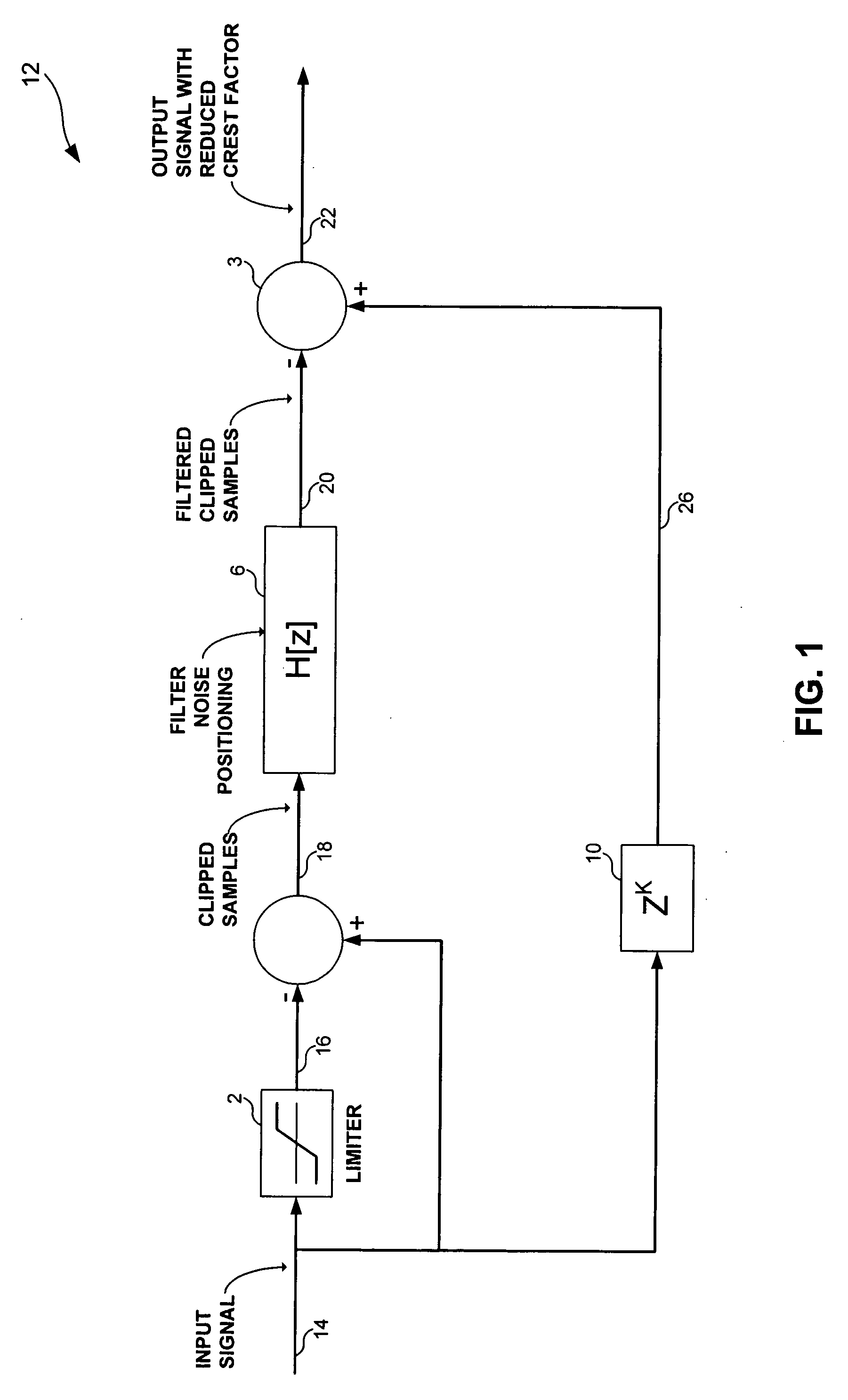
Power reduction
InactiveUS6931079B1Reduce signalingReduce the amplitudeAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationPeak valueEngineering
There is disclosed a technique in which any peaks above a threshold level are reduced, but not clipped, such that the effects of such peaks is reduced. Although the implementation of the technique preferably includes a clipping step, it is performed on the front-end rather than as the last step in the technique, such that the output signal is not a clipped signal. Any noise introduced by the clipping step, so-called clipping noise, is preferably filtered out of the useful frequency band of the signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
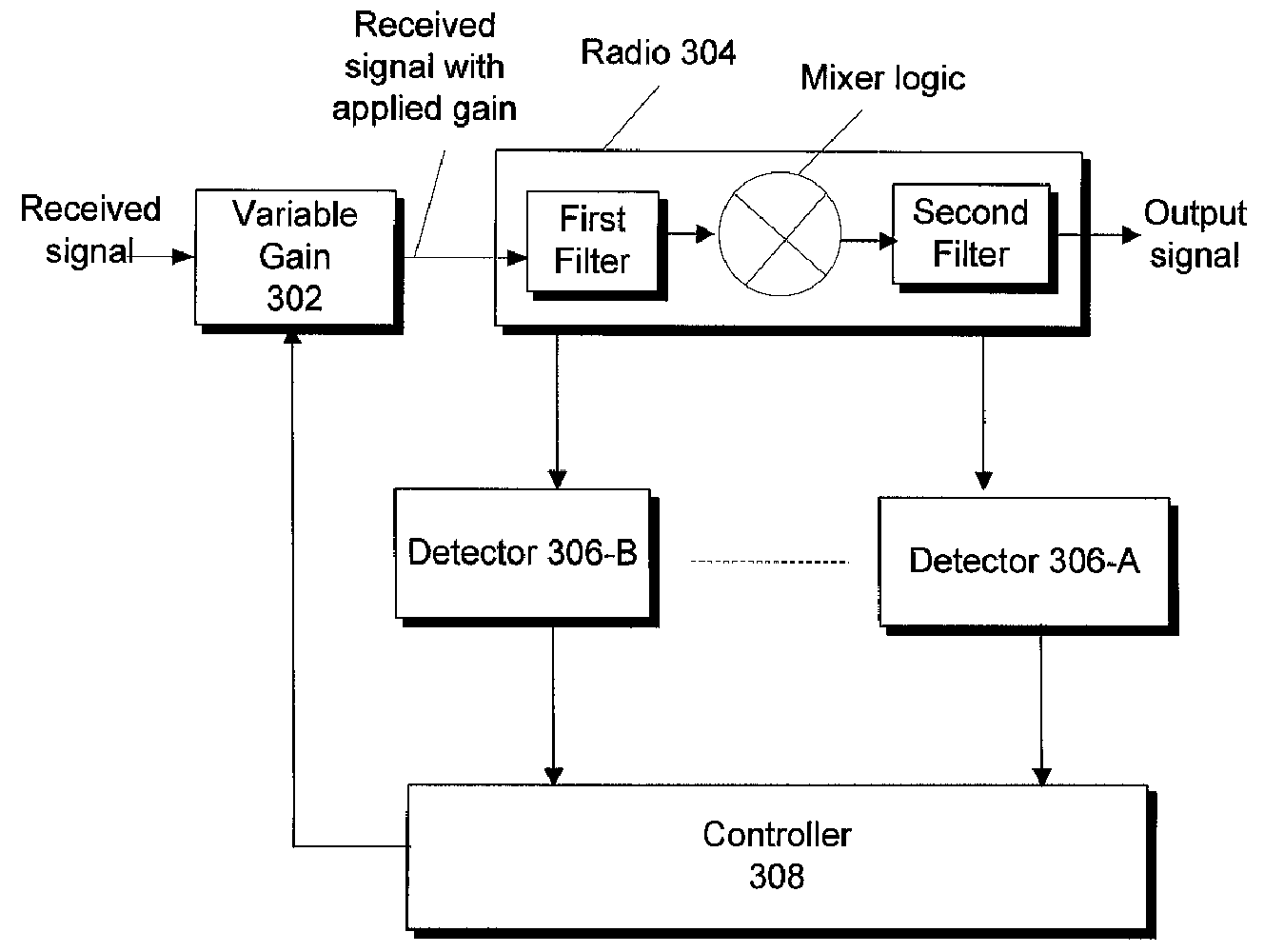
Techniques to deterministically reduce signal interference
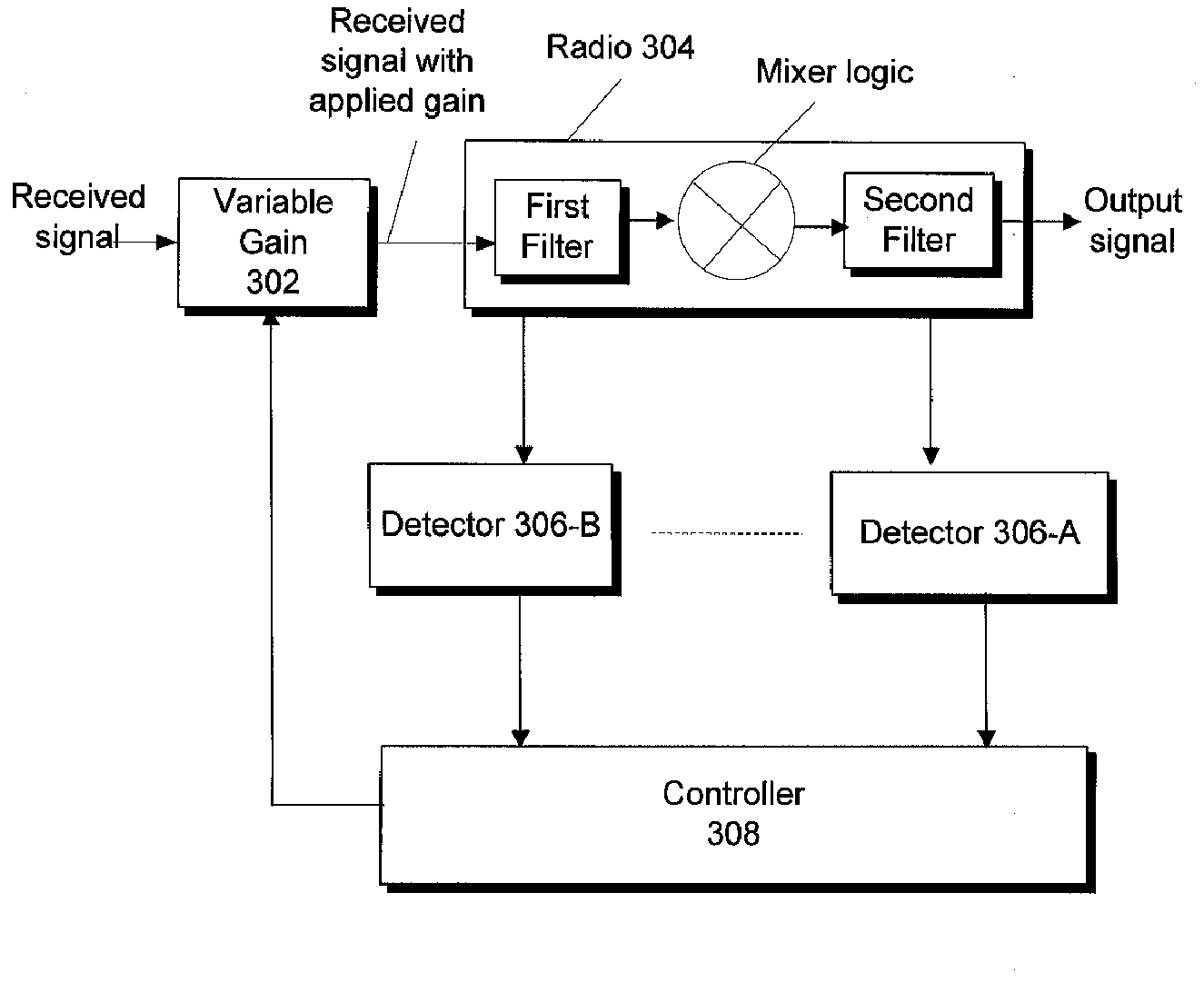
Techniques are described that can be used to reduce interference in a desired channel by one or more other channels. A radio includes a level detect logic that is responsive to both the frequency offset and amplitude of undesired signals and sets the gain applied to received signals based on the offset frequency and determined amplitude of undesired signals. For example, detection of a signal amplitude in an interfering signal in a channel adjacent to the desired channel may be made. Detection of a signal amplitude in an interfering signal in a channel other than the adjacent channel and desired channel may also be made. Based on detection of one or more interfering channel, a gain of an input signal may be adjusted. Interference arising from at least spectral re-growth of noise and clipping noise may be reduced.
Owner:APPLE INC
Apparatus for reducing clipping noise in a broadband wireless communication system and method thereof
InactiveUS20070258528A1Reducing clipping noiseError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionBroadbandClipping noise
Provided are an apparatus for reducing clipping noise in a broadband wireless communication system in which a clipping method is used and a method thereof. The method includes, when clipped signals are received, decoding and equalizing the received signals to determine transmitted symbols, comparing the magnitudes of the amplitudes of the determined transmitted symbols with a predetermined reference value, and reconstructing signals using the amplitudes of the transmitted symbols and the phases of the received signals when it is determined that the magnitudes of the amplitudes of the transmitted symbols are greater than the reference value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Power reduction
InactiveUS20050232373A1Reduce signalingReduce the amplitudeSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsPeak valueClipping noise
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
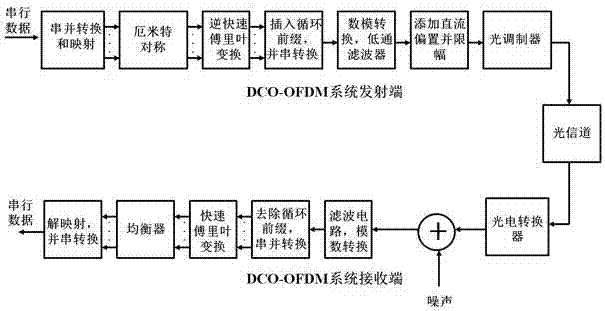
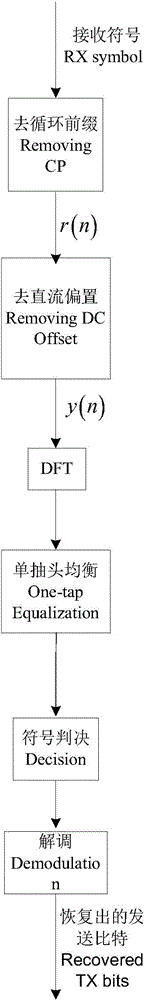
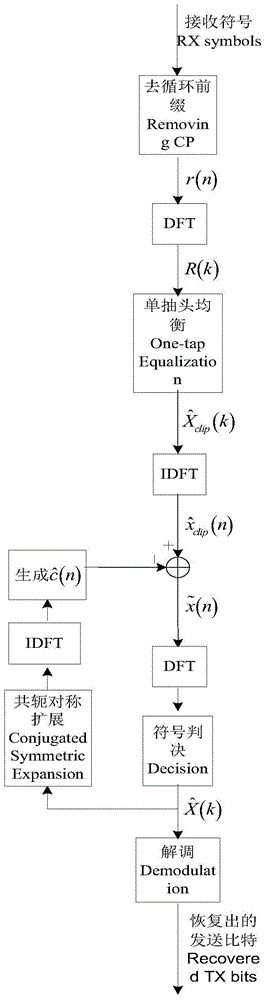
Symbol detection method of DCO-OFDM (Direct Current Offset-Orthogonal frequency Division Multiplexing) system
ActiveCN104158784ASmall amount of calculationImprove the effective signal-to-noise ratioMulti-frequency code systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Inverse discrete fourier transform
The invention discloses a symbol detection method of a DCO-OFDM (Direct Current Offset-Orthogonal frequency Division Multiplexing) system, belonging to the field of visible light wireless communication. The method is carried out according to the following steps of firstly, preprocessing a received symbol r(n) to obtain an estimated value x(clip)n of a clipped sending signal; secondly, reconstructing clipping noise c(n) and subtracting the clipping noise from the signal x(clip)n to obtain an estimated value x(clip)n of an unclipped sending signal; thirdly, carrying out frequency domain conversion and symbol judgment operation on the x(n), and reconstructing the clipping noise c(n) by utilizing a judged symbol; fourthly, repeating the steps to reach a preset number of iterations; and lastly, demodulating the judged symbol to restore transmitted bits. According to the symbol detection method provided by the invention, the negative effect of the clipping noise on the detection performance can be reduced, an effective signal to noise ratio of a receiving signal is increased, in comparison with the conventional symbol detection method, the better detection performance can be obtained. Meanwhile, the method provided by the invention only needs simple symbol taking operation and DFT / IDFT (Discrete Fourier Transform / Inverse Discrete Fourier Transform) operation and has the advantages of small calculated amount and easiness in implementation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
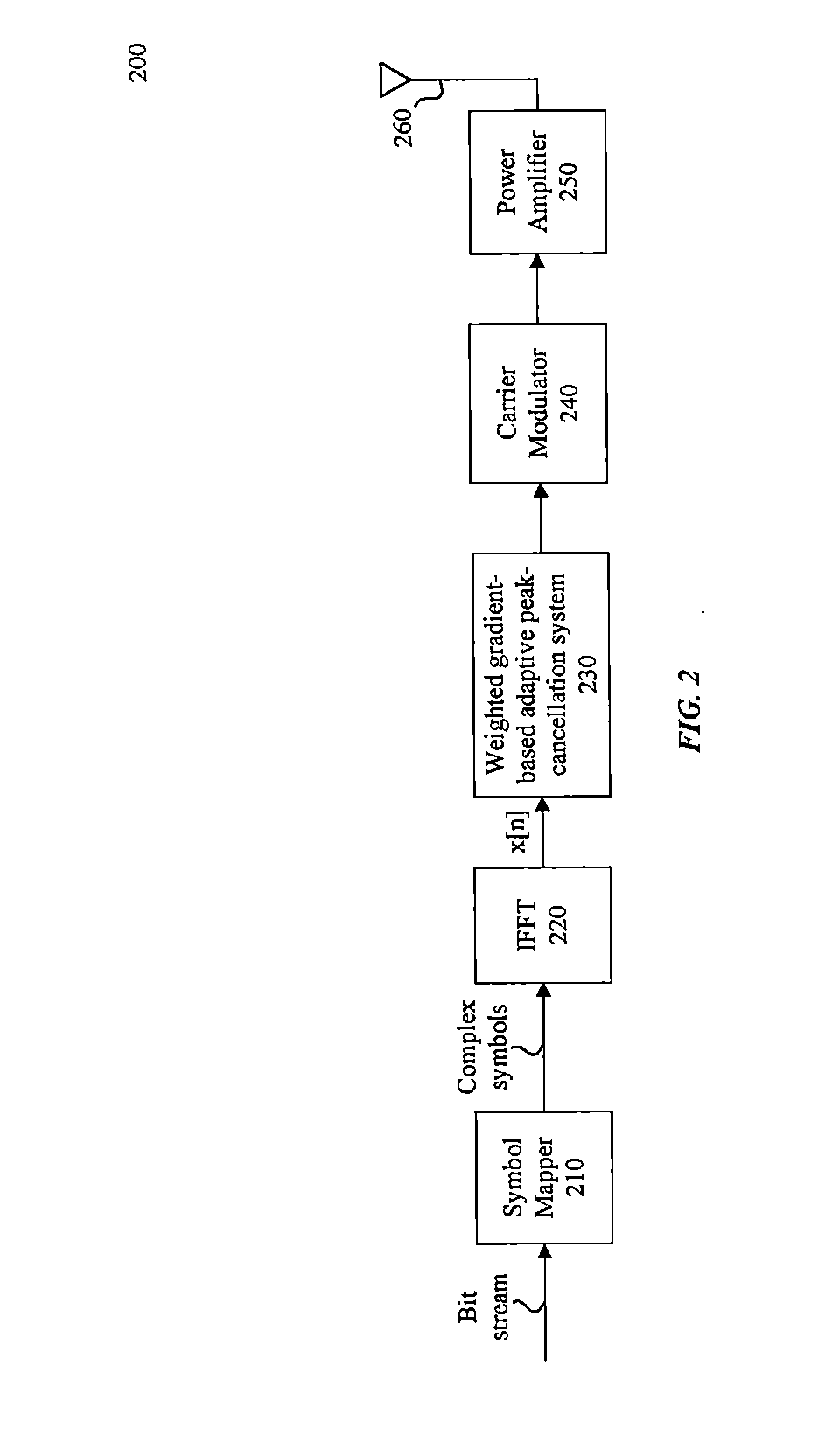
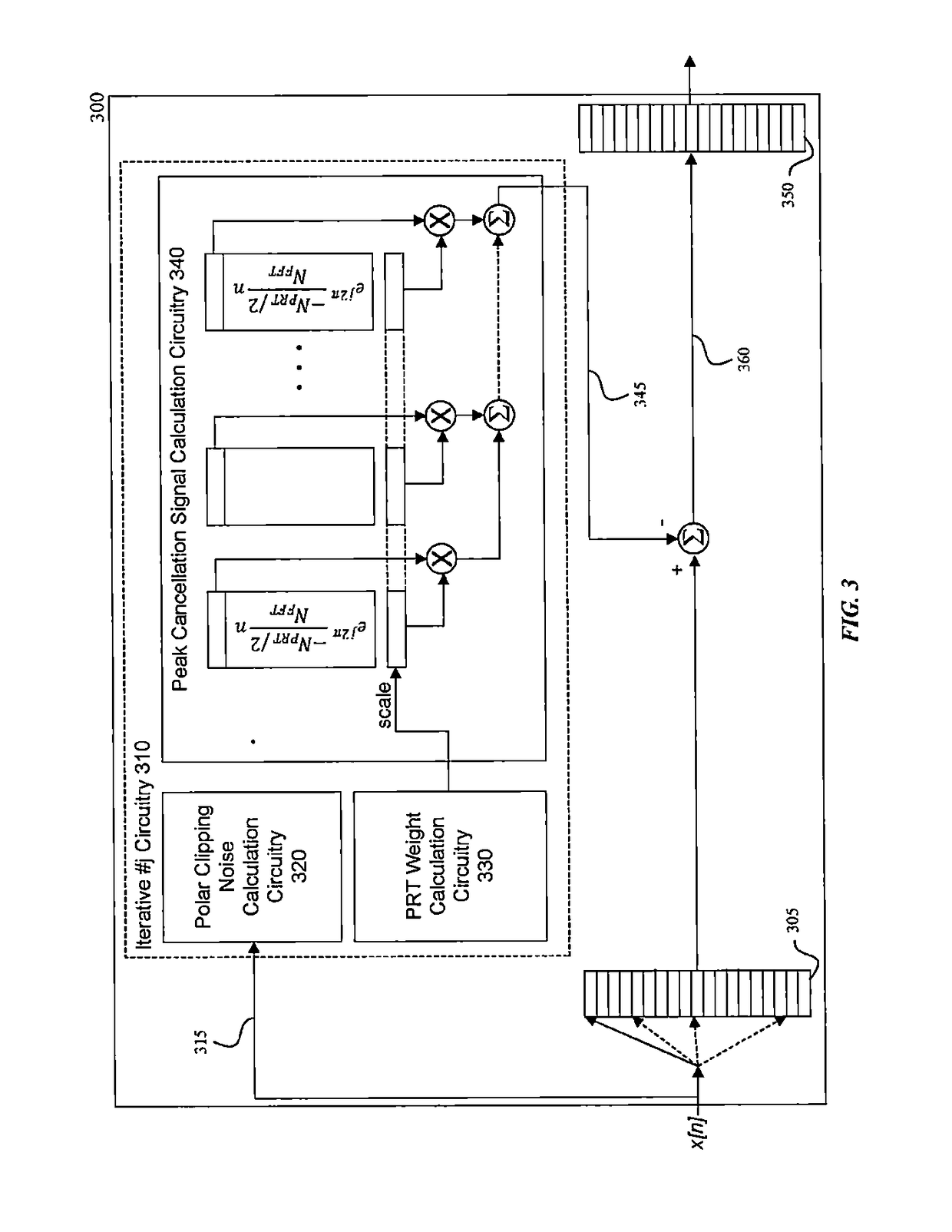
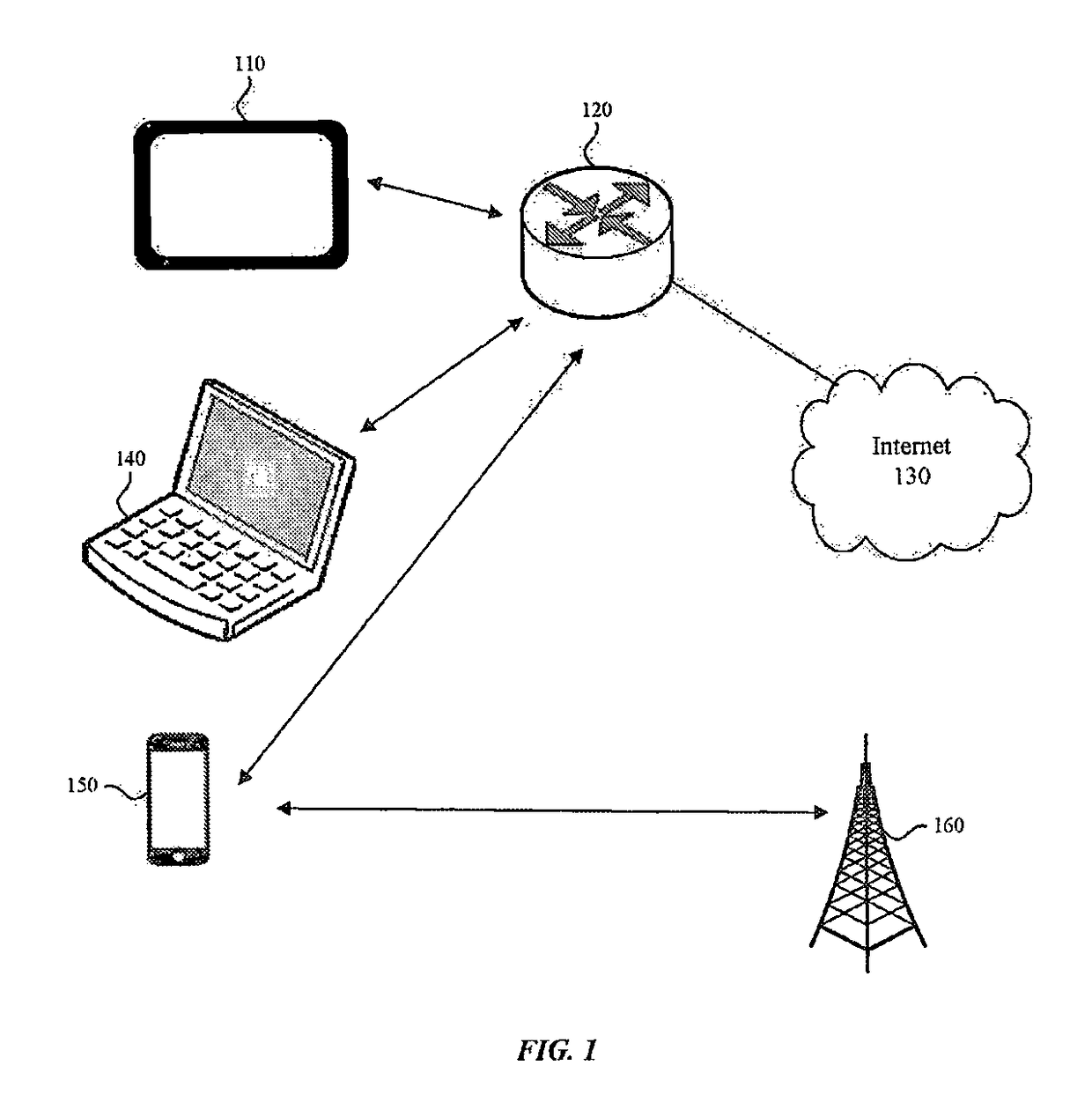
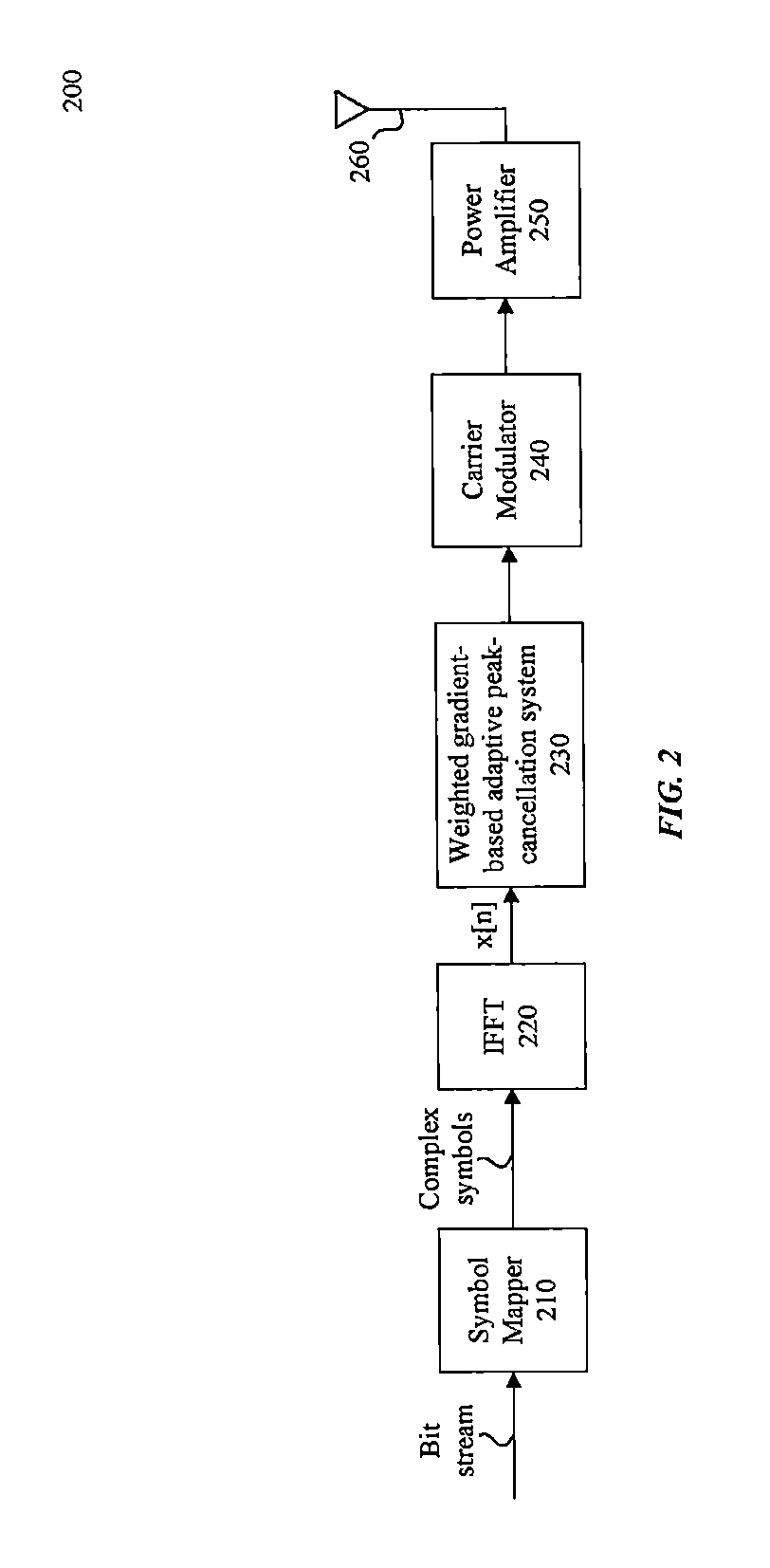
System and method for peak-to-average power ratio reduction of OFDM signals via weighted gradient-based adaptive peak cancellation
ActiveUS20180083820A1Reduce ratio of average powerMulti-frequency code systemsData switching networksEngineeringPeak value
Embodiments include a system, method, and computer program product that receives an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbol, and utilizes a weighted gradient-based adaptive peak cancellation convergence algorithm to create a peak cancellation signal to reduce a peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) as well as induced error rates of the OFDM symbol. Iterations of the weighted gradient-based adaptive peak cancellation convergence algorithm produce a peak cancellation signal that converges to a desired peak cancellation signal that satisfies a targeted PAPR. Some embodiments utilize a priori knowledge of a power spectral density of clipping noise and pre-defined transmission constraints in the frequency domain to create a peak cancellation signal with specific and desired spectral density properties. For example, some peak reduction tones (PRTs) may be scaled to take advantage of available power resources associated with the pre-defined transmission constraints, where the scaling is specific to each PRT.
Owner:APPLE INC
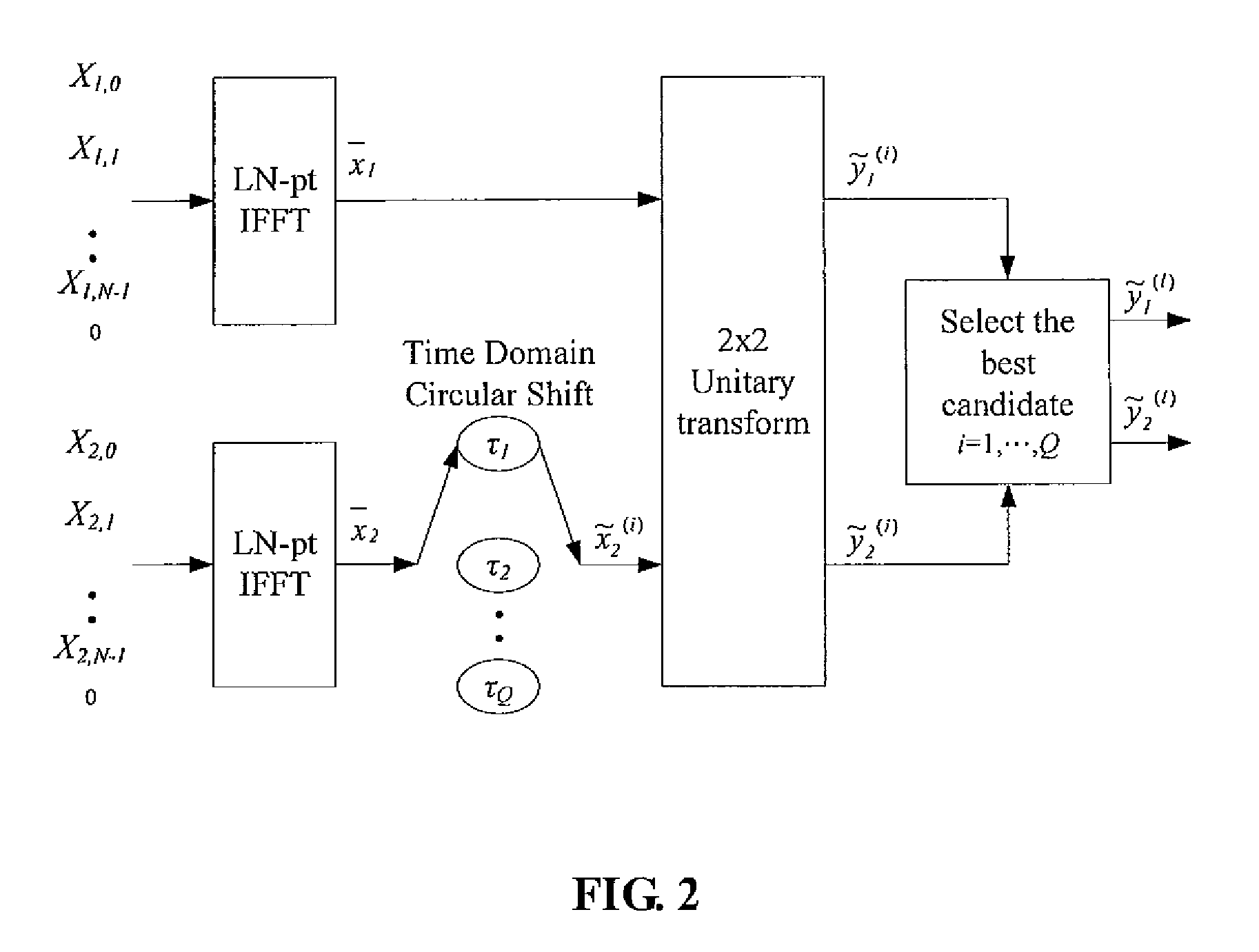
Method for solving high PAPR problem of MCM communication system using unitary transform
ActiveUS8027398B2Sacrificing error rateLess complexSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainCommunications system
The method contains the following steps. First, in a MCM system with N sub-carriers, the baseband signal blocks Xj, j=1, 2, . . . ,B are supplemented with zeros and processed with LN-point IFFT, respectively, to obtain L-time oversampled time-domain signal blocks xj, j=1,2, . . . ,B. Then, xj undergoes Q Time Domain Circular Shifts or Frequency Domain Circular Shifts to obtain Q signal blocks {tilde over (x)}j(i<sub2>j< / sub2>), ij=1, Λ, Q. Subsequently, a B×B unitary transform is performed against ( x1, {tilde over (x)}2(i<sub2>2< / sub2>), . . . , {tilde over (x)}B(i<sub2>B< / sub2>)). After the unitary transform, for each (i2, . . . , iB) a combination having B time-domain signal blocks is obtained as follows: ({tilde over (y)}1(i<sub2>2< / sub2>, . . . , i<sub2>B< / sub2>), {tilde over (y)}2(i<sub2>2< / sub2>, . . . , i<sub2>B< / sub2>), . . . , {tilde over (y)}B(i<sub2>2< / sub2>, . . . ,i<sub2>B< / sub2>))=( x1, {tilde over (x)}2(i<sub2>2< / sub2>), . . . , {tilde over (x)}B(i<sub2>B< / sub2>)) cU where U is the B×B unitary matrix, and c is an arbitrary constant (c≠0). Finally, the total QB−1 combinations are compared against each other to select a best candidate for transmission that could produce the lowest peak value, or the smallest PAPR, or the lowest clipping noise power.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
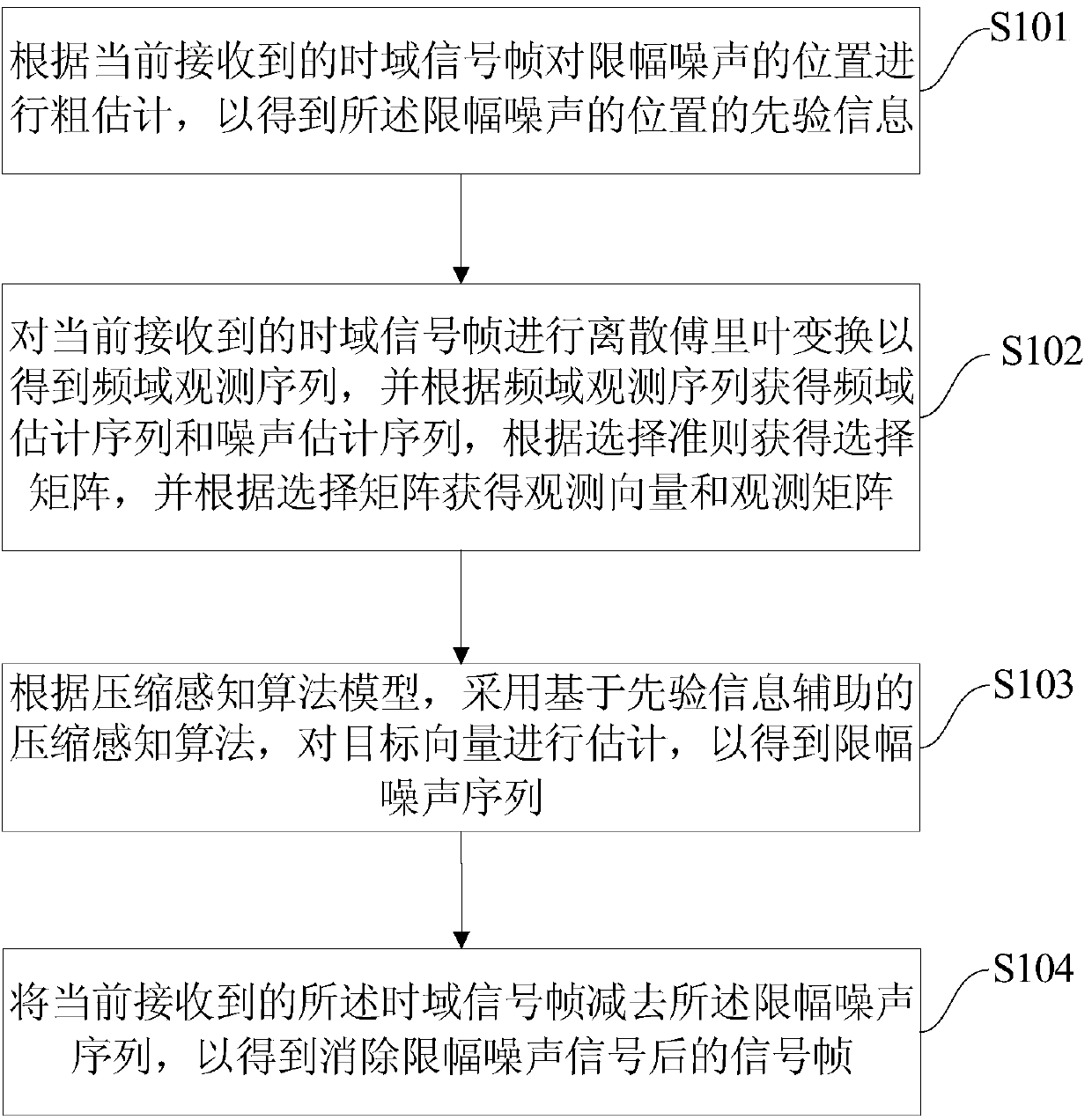
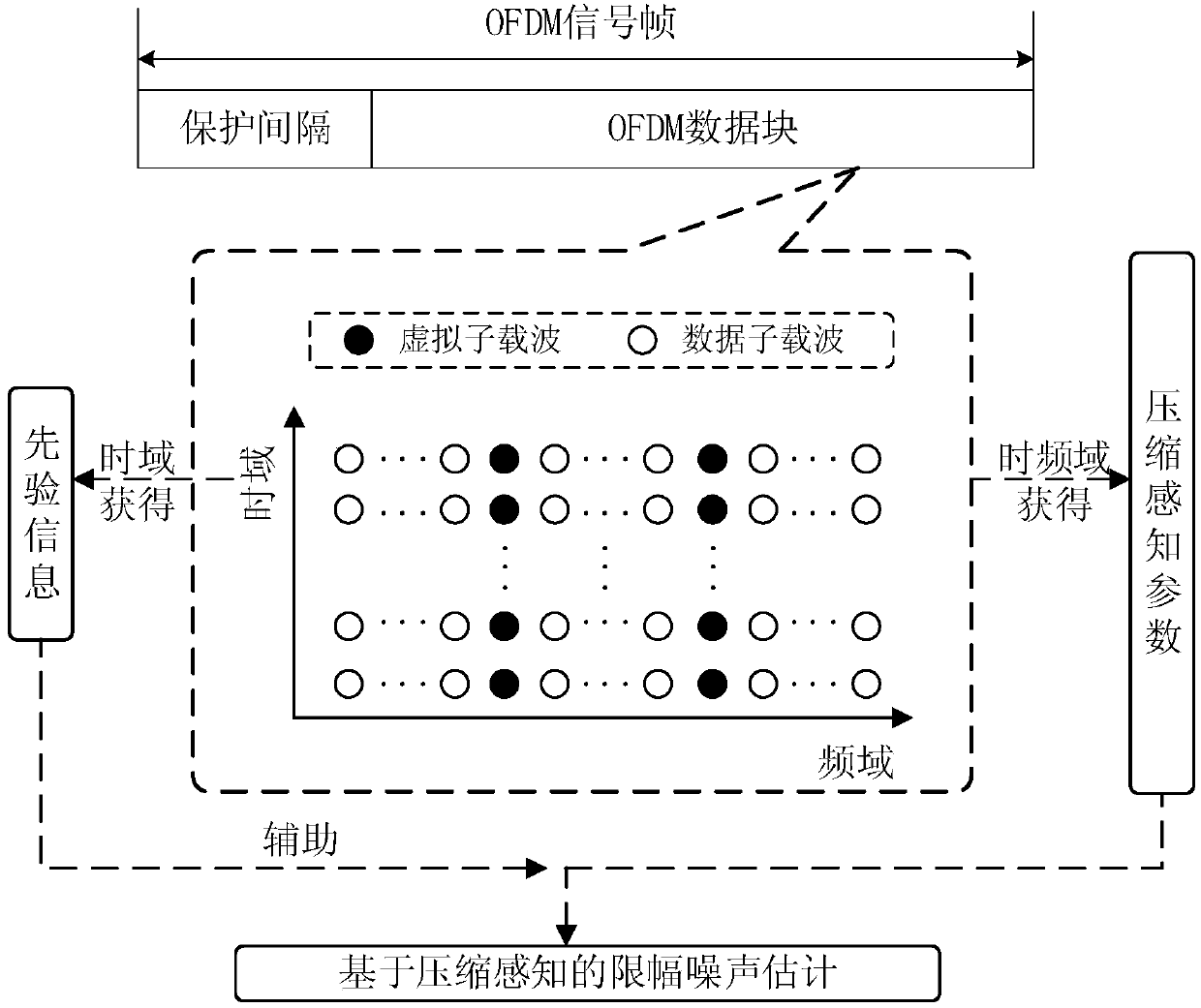
Clipping noise estimation and elimination method based on compressive sensing and device thereof
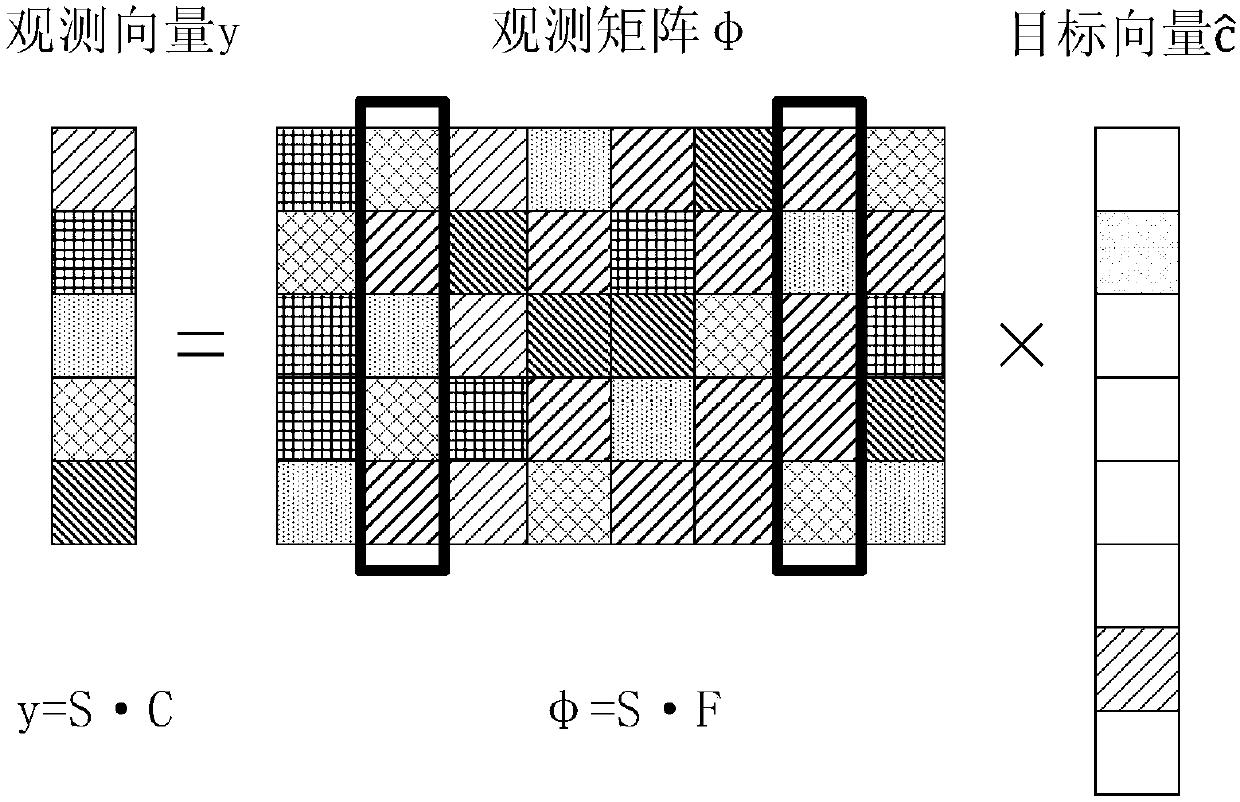
ActiveCN104935532ALarge dynamic rangeImprove received signal qualityLine-faulsts/interference reductionMulti-frequency code systemsSignal qualityObservation matrix
The invention provides a clipping noise estimation and elimination method based on compressive sensing and a device thereof. The method comprises the steps that coarse estimation is performed on the position of clipping noise according to time domain signal frames so that prior information of the position of clipping noise is obtained; discrete Fourier transform is performed on the time domain signal frames and a frequency domain observation sequence is obtained, a frequency domain estimation sequence and a noise estimation sequence are obtained according to the frequency domain observation sequence, a selection matrix is obtained according to choice criteria and an observation vector and an observation matrix are obtained according to the selection matrix; a target vector is estimated by adopting a compressive sensing algorithm based on prior information auxiliary so that a clipping noise sequence is obtained; and the clipping noise sequence is subtracted from the currently received time domain signal frames so that the signal frames after elimination of clipping noise signals can be obtained. According to the clipping noise estimation and elimination method based on compressive sensing, clipping noise in an OFDM system can be accurately estimated through relatively low complexity under a peak limited channel so that dynamic range of the signals can be effectively expanded, receiving signal quality can be enhanced and system robustness can be enhanced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for suppressing clipping noise of nonlinear distortion of LED in visible light communication
InactiveCN111327359AReduce the number of decompositionsImprove bit error rate performanceClose-range type systemsMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformNonlinear distortion
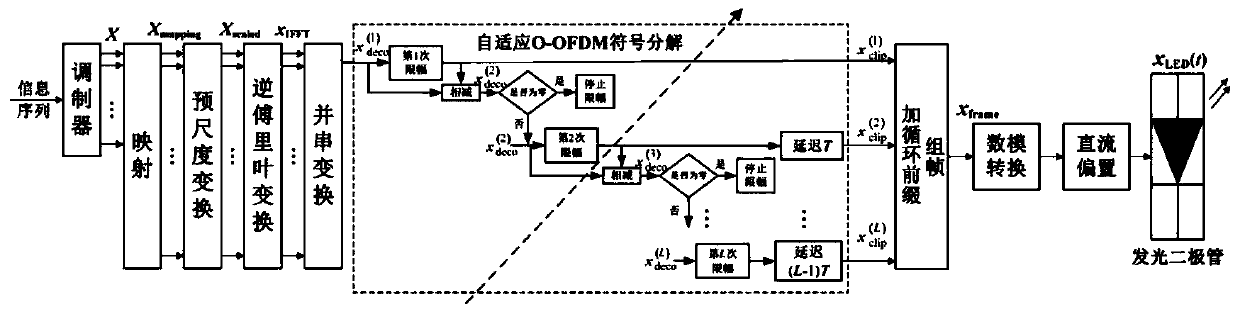
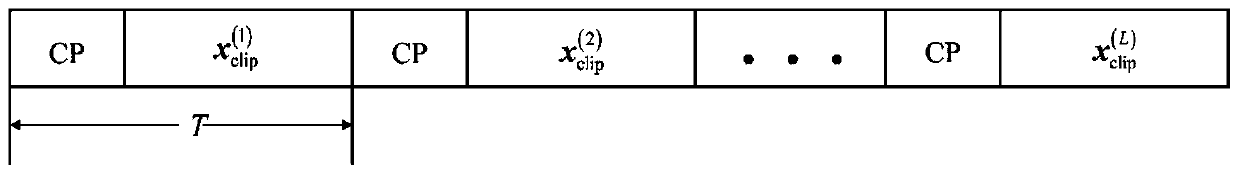
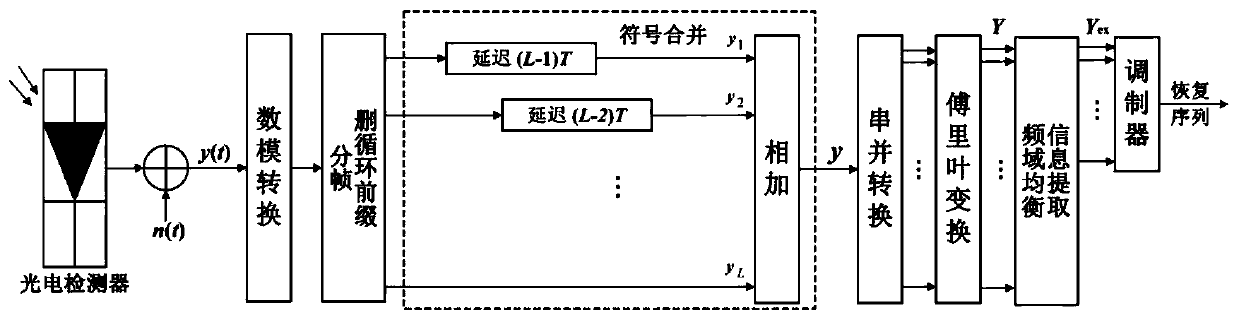
The invention discloses a method for suppressing clipping noise of nonlinear distortion of LED in visible light communication. The method comprises the following main steps: (1) mapping a modulation symbol into a vector signal meeting Hermitian symmetry; (2) performing pre-scale transformation to regulate and control an O-OFDM symbol variance; (3) carrying out adaptive O-OFDM symbol decompositionafter IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform); repeatedly clipping the amplitude of the symbol according to the clipping threshold and the maximum symbol decomposition frequency; and calculating a decision symbol after each clipping, and judging whether symbol decomposition is required or not; (4) sequentially performing serial framing on the decomposed symbols; (5) splitting a frame after photoelectric conversion, deleting CP, adding all decomposed symbols in one frame bit by bit, and combining the decomposed symbols into an O-OFDM symbol; and (6) extracting information after FFT, and demodulating and recovering original information.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
MIMO ACO-OFDM iteration receiving method in wireless optical communication system
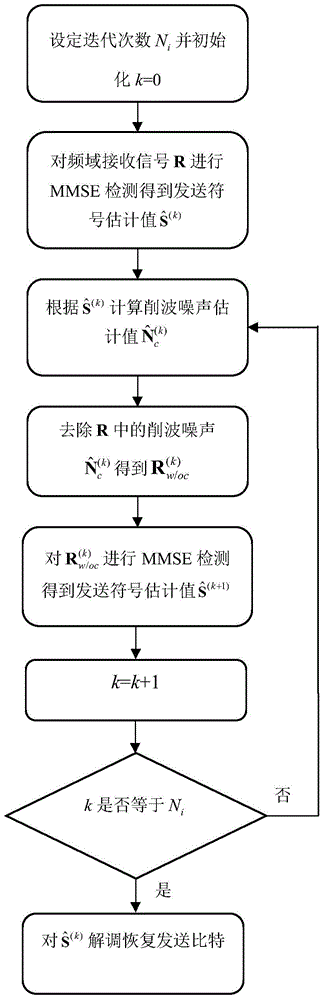
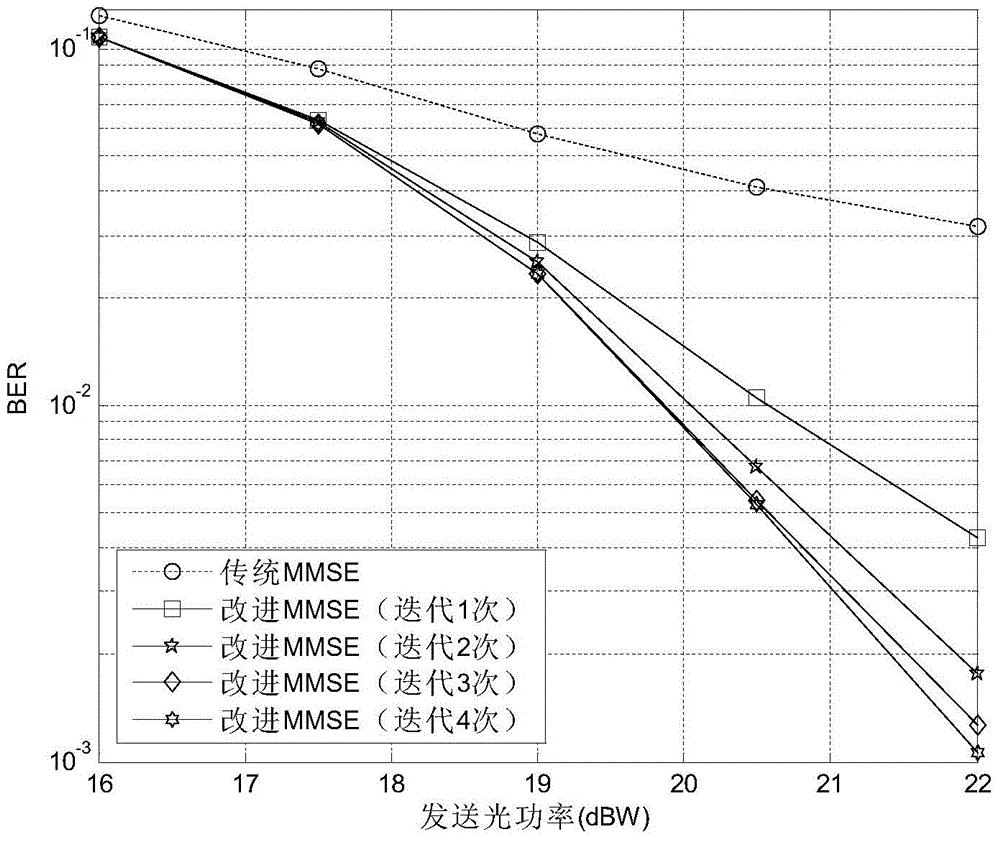
ActiveCN104836758ASignificant BER performance gainReduce complexityMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComputation complexityCommunications system
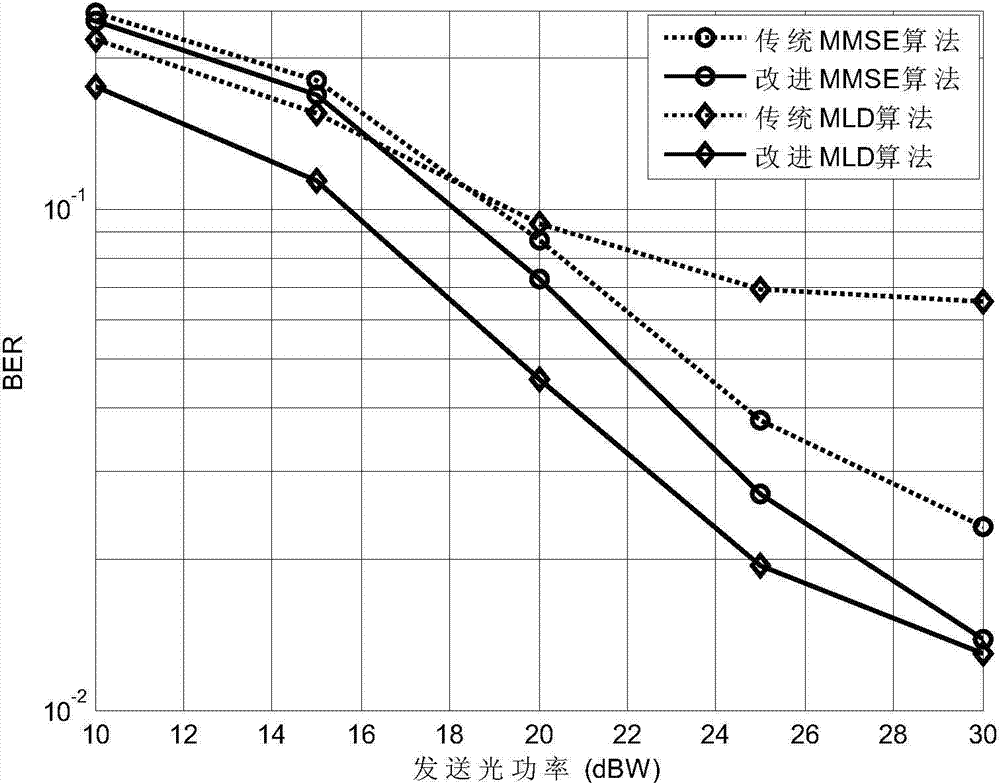
The invention discloses a multiple-input-multiple-output asymmetric clipping optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing modulation (MIMO ACO-OFDM) iteration receiving method in a wireless optical communication system, wherein the method is characterized by detecting a minimum mean square error (MMSE) of a receiving signal by using a linear approximation model of clipping operation at a receiving end and statistical property of clipping noise on the basis of a traditional MIMO ACO-OFDM receiving algorithm, and eliminating the clipping noise in an iterative manner. The improved receiving method provided by the invention can effectively reduce performance loss of the system caused by the clipping noise and greatly reduce the bit error rate in comparison with a traditional MIMO ACO-OFDM receiver. Simultaneously, the method of the invention reduces the complexity of each iterative computation and the number of needed iterations, and therefore the method of the invention is easy for engineering realization.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
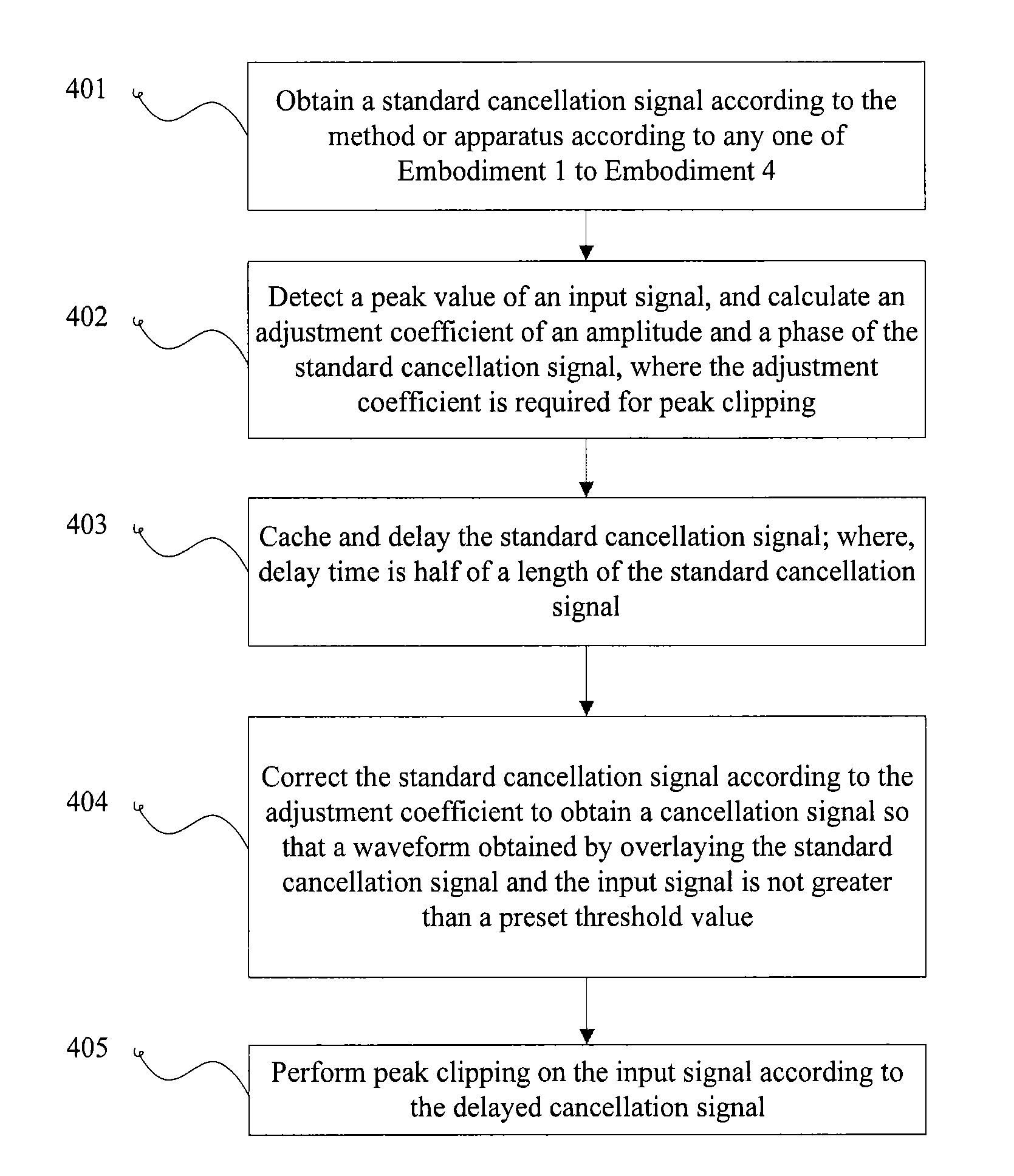
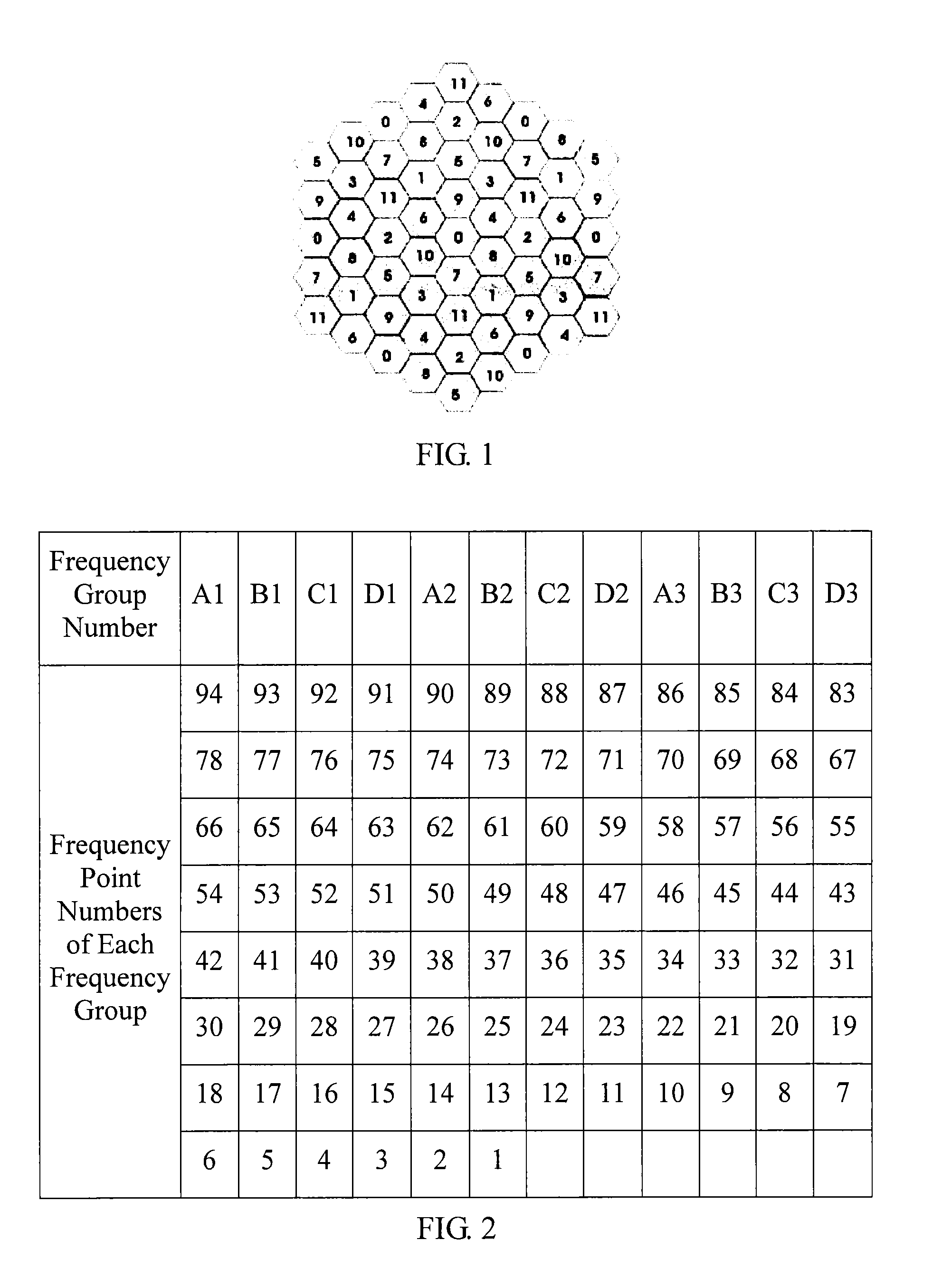
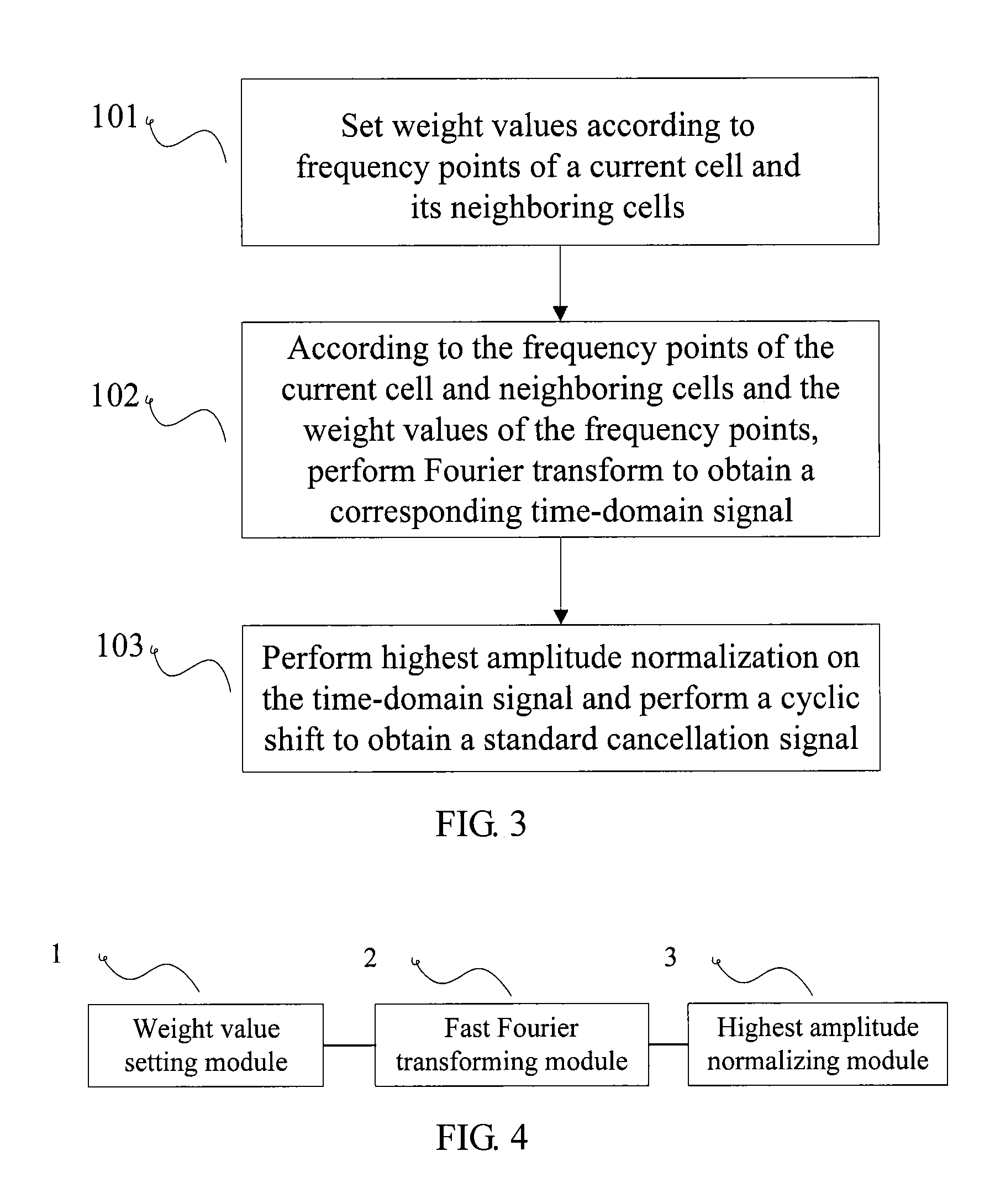
Method and apparatus for generating standard cancellation signalstandard cancellation signal
ActiveUS20130040652A1Improve performanceSuppression ratioModulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexCurrent cellTime domain
A method and an apparatus for generating a standard cancellation signal includes: setting weight values according to frequency points of a current cell and its neighboring cells; according to the frequency points of the current cell and neighboring cells and the weight values of the frequency points, performing Fourier transform to obtain a corresponding time-domain signal; and performing highest amplitude normalization on the time-domain signal and performing a cyclic shift to obtain a standard cancellation signal. The embodiments generate a standard cancellation signal according to frequency points of the current cell and its neighboring cells, so that the current cell and its neighboring cells share the peak clipping noise, and therefore helping improve the peak clipping performance of the current cell or reduce the EVM distortion.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System and method for peak-to-average power ratio reduction of OFDM signals via weighted gradient-based adaptive peak cancellation
Embodiments include a system, method, and computer program product that receives an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbol, and utilizes a weighted gradient-based adaptive peak cancellation convergence algorithm to create a peak cancellation signal to reduce a peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) as well as induced error rates of the OFDM symbol. Iterations of the weighted gradient-based adaptive peak cancellation convergence algorithm produce a peak cancellation signal that converges to a desired peak cancellation signal that satisfies a targeted PAPR. Some embodiments utilize a priori knowledge of a power spectral density of clipping noise and pre-defined transmission constraints in the frequency domain to create a peak cancellation signal with specific and desired spectral density properties. For example, some peak reduction tones (PRTs) may be scaled to take advantage of available power resources associated with the pre-defined transmission constraints, where the scaling is specific to each PRT.
Owner:APPLE INC
Techniques to deterministically reduce signal interference
Techniques are described that can be used to reduce interference in a desired channel by one or more other channels. A radio includes a level detect logic that is responsive to both the frequency offset and amplitude of undesired signals and sets the gain applied to received signals based on the offset frequency and determined amplitude of undesired signals. For example, detection of a signal amplitude in an interfering signal in a channel adjacent to the desired channel may be made. Detection of a signal amplitude in an interfering signal in a channel other than the adjacent channel and desired channel may also be made. Based on detection of one or more interfering channel, a gain of an input signal may be adjusted. Interference arising from at least spectral re-growth of noise and clipping noise may be reduced.
Owner:APPLE INC
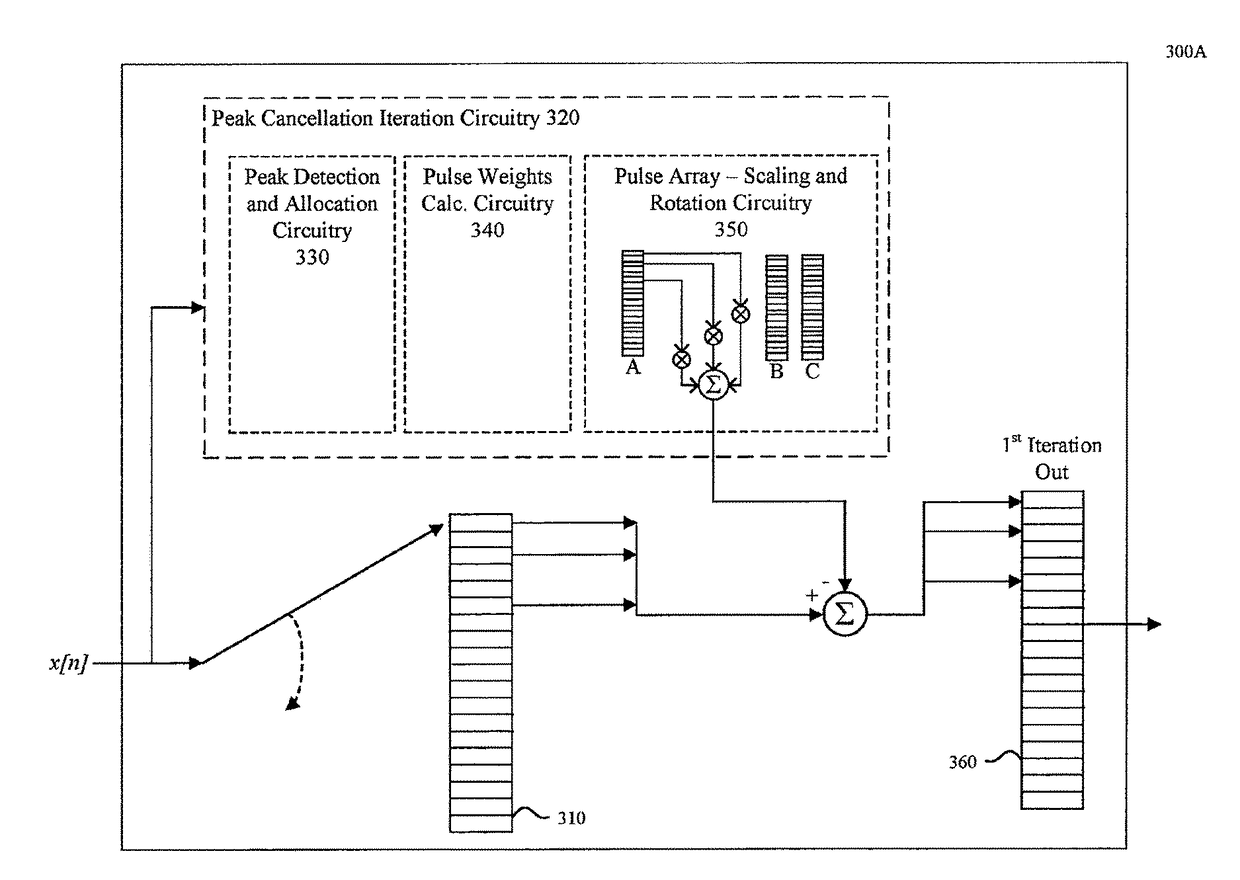
System and method for constrained peak cancellation
ActiveUS20180091348A1Reduce ratio of average powerReduce PAPRMulti-frequency code systemsTransmission path multiple useTime domainPeak value
Embodiments include a method, computer program product, and system for utilizing a system for peak cancellation for a received Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbol to reduce the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR). The system detects M sets of clipping noise samples of the symbol where each set includes one of the M highest clipping noise peaks of the symbol, determines cancellation pulses that correspond to the highest clipping noise peaks of the M sets in the time domain, and subtracts the cancellation pulses from the corresponding highest clipping noise peak samples to reduce the PAPR. The cancellation pulses are determined at least in part from the center-of-mass of each set of the clipping noise samples, the phase of some samples of each set, and the in-band energy limitation associated with the OFDM symbol.
Owner:APPLE INC
Bit allocation method and apparatus for multicarrier modulation signal, and system
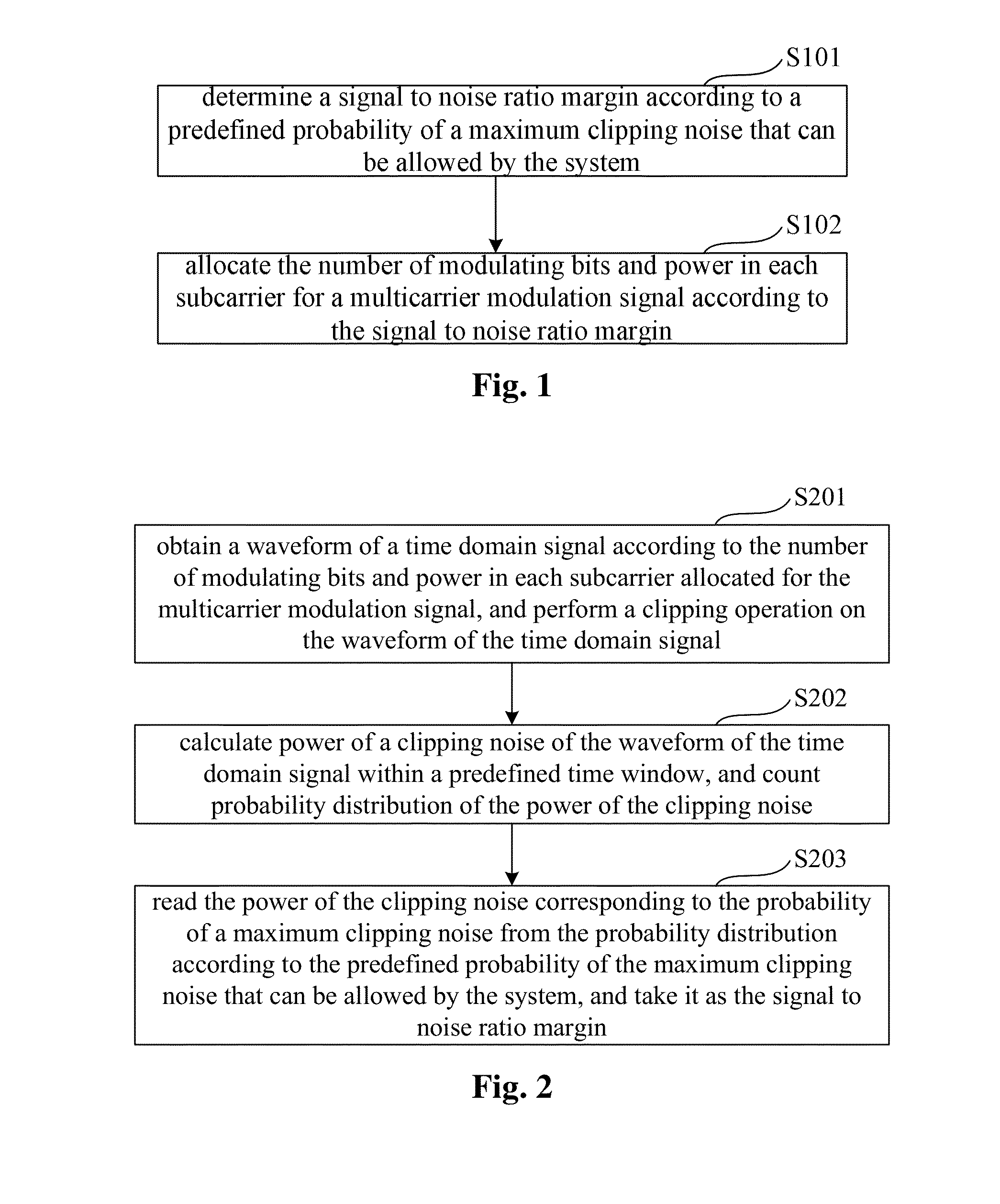
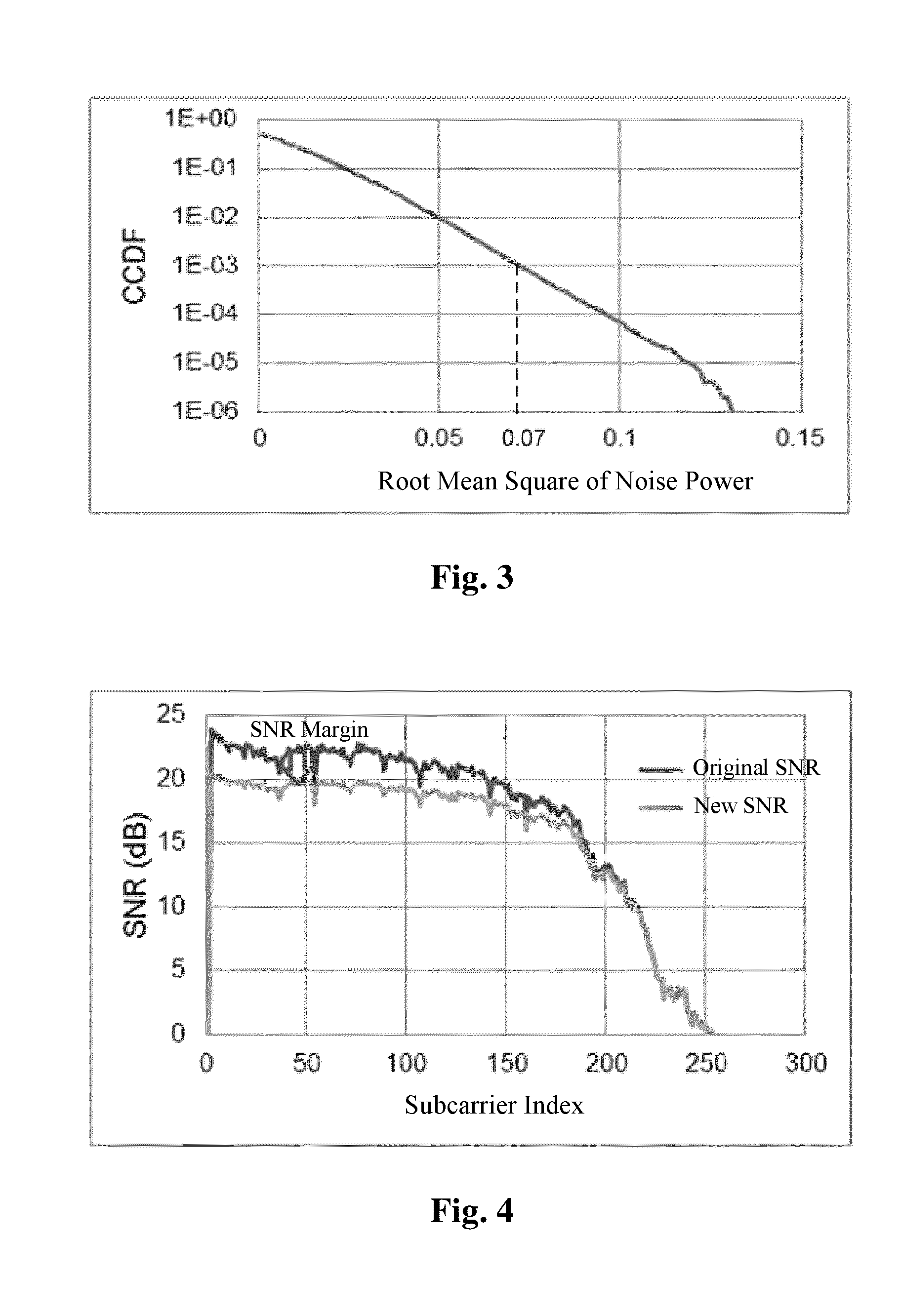
ActiveUS20160226613A1Reduce burst errorEnhanced signalPower managementMulti-frequency code systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Bit allocation
A bit allocation method and apparatus for a multicarrier modulation signal and a system where the method includes: determining a signal to noise ratio margin according to a predefined probability of a maximum clipping noise that can be allowed by the system; and allocating the number of modulating bits and power in each subcarrier for a multicarrier modulation signal according to the signal to noise ratio margin. By presetting a signal to noise ratio margin for a clipping noise, tolerance of the signal for the clipping noise is increased, and bit error rate is efficiently lowered.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
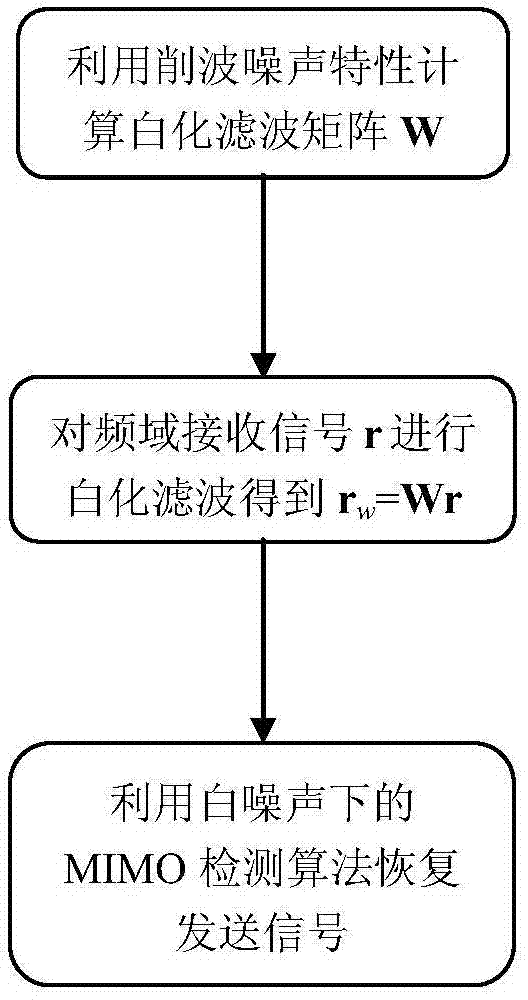
MIMO DCO-OFDM communication method, signal receiving device and system
ActiveCN104753849AReduce adverse effectsSignificant BER performance gainMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSignal onCarrier signal
The invention discloses an MIMO DCO-OFDM (multiple-input multiple-output direct-current-biased optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) communication method. The method includes: aiming at clipping noise generated by clipping operation of a sending end, creating a whitening filter at a receiving end according to a linearization model of the clipping operation of the sending end and statistical characteristics of the clipping noise, and utilizing the whitening filter to filter receiving signals on each sub-carrier and an equivalent wireless light MIMO channel matrix acquired by estimation respectively; utilizing the equivalent wireless light MIMO channel matrix after being filtered to restore the receiving signals after being filtered. The invention further discloses an MIMO DCO-OFDM signal receiving device and an MIMO DCO-OFDM communication system. Compared with the prior art, the MIMO DCO-OFDM communication method has the advantages that remarkable bit error rate performance gain can be acquired, and easiness in engineering realization is realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com