Patents
Literature
100results about How to "Suppression ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solid state image pick-up device and image pick-up system
ActiveUS20050168618A1Suppress of ratio of output signalSuppression ratioTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCouplingEngineering
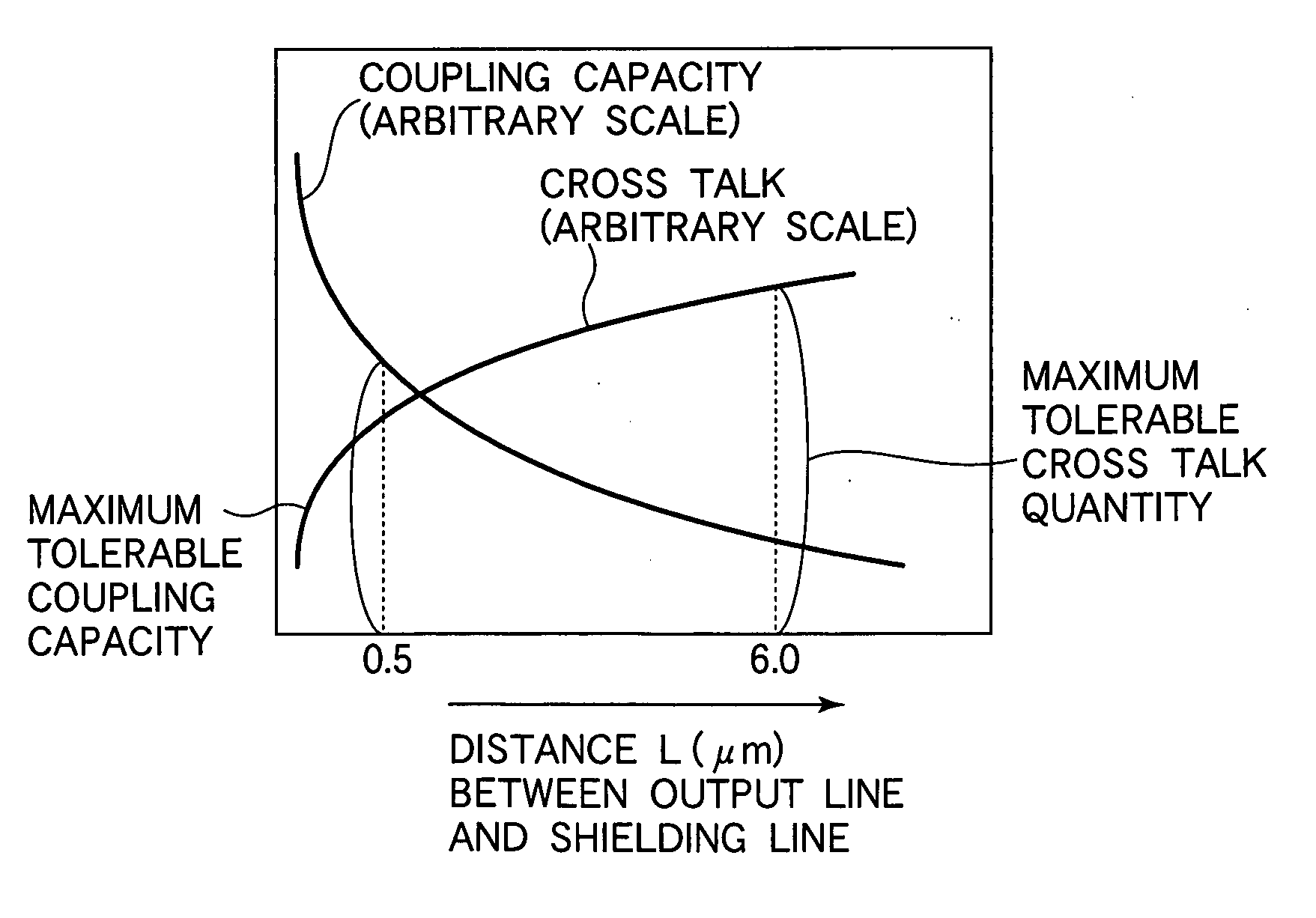
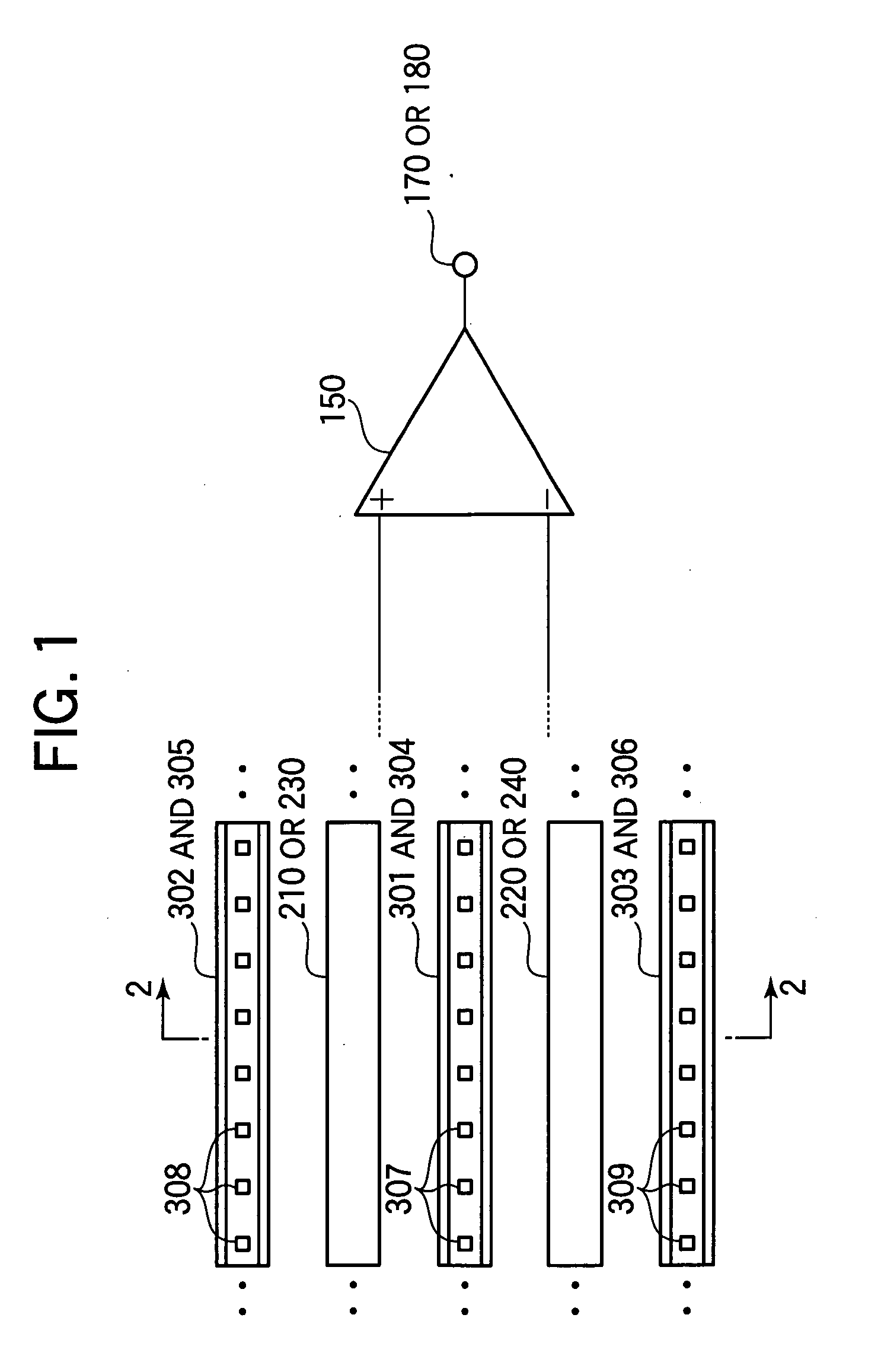
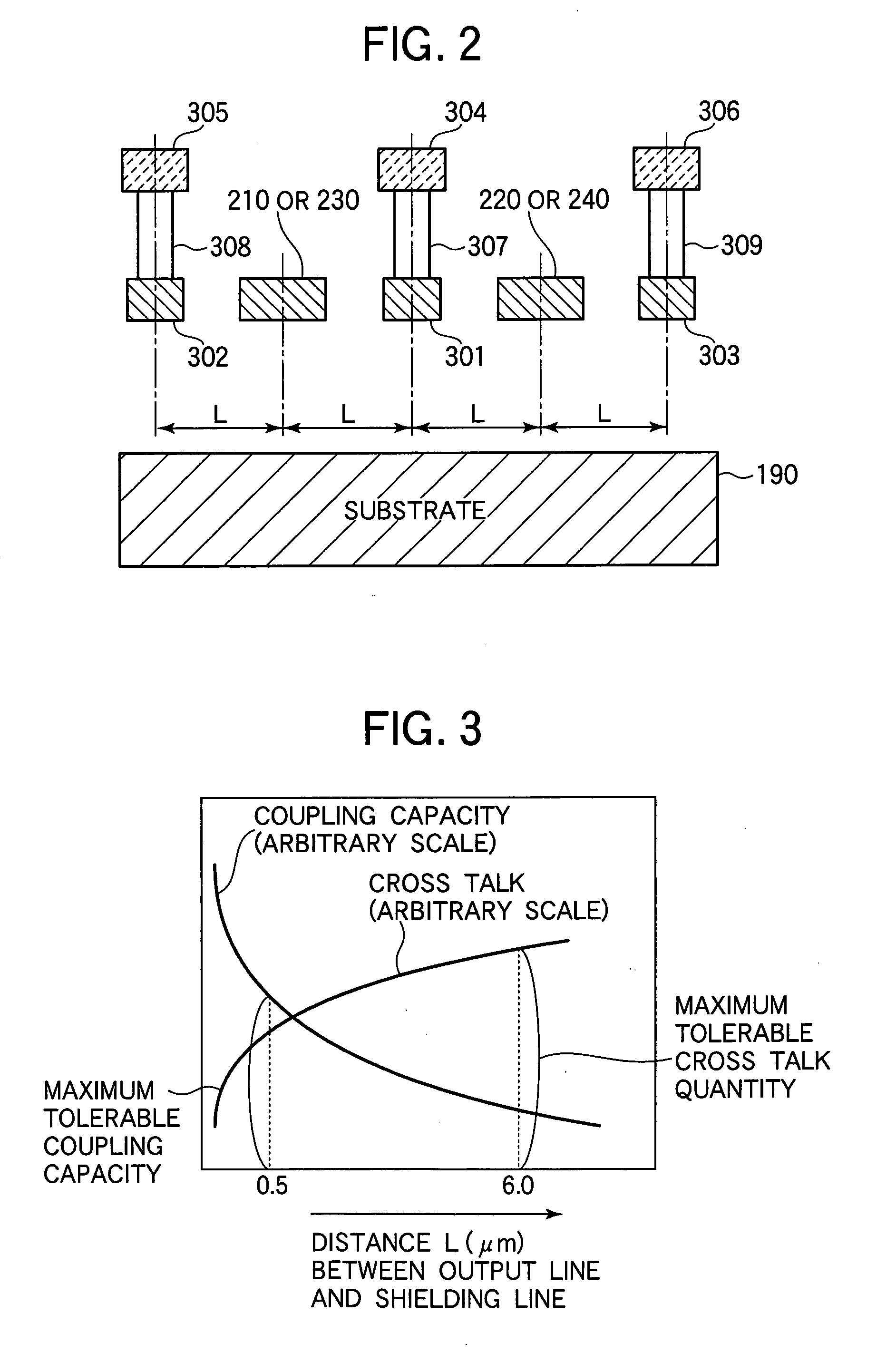
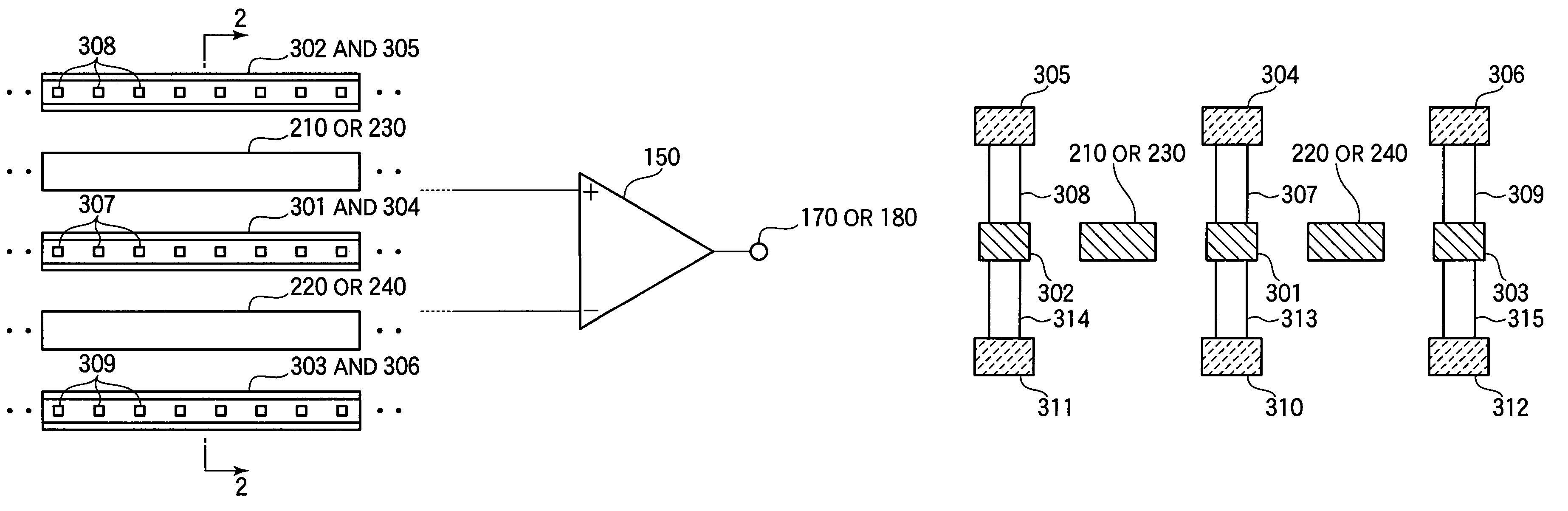
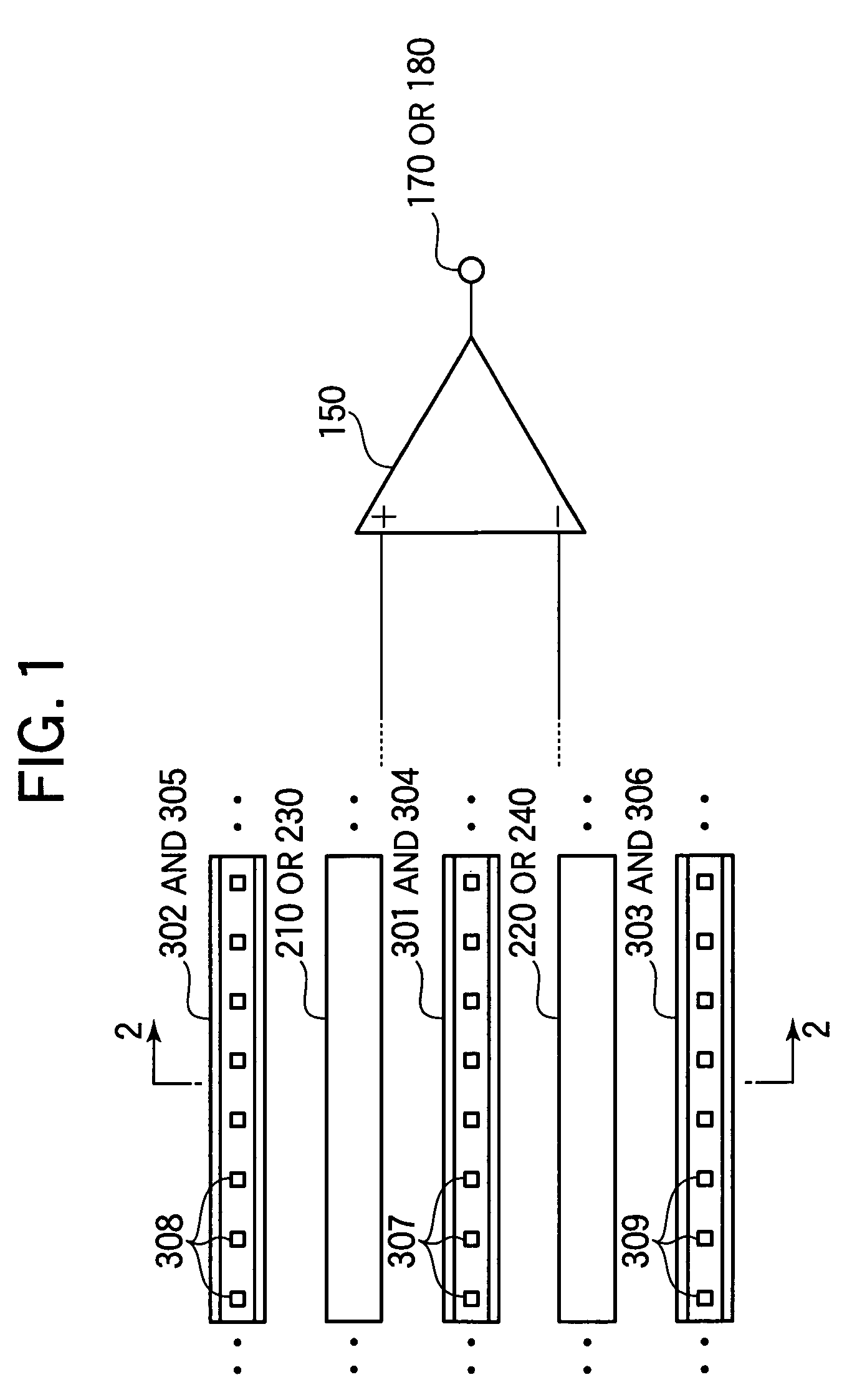
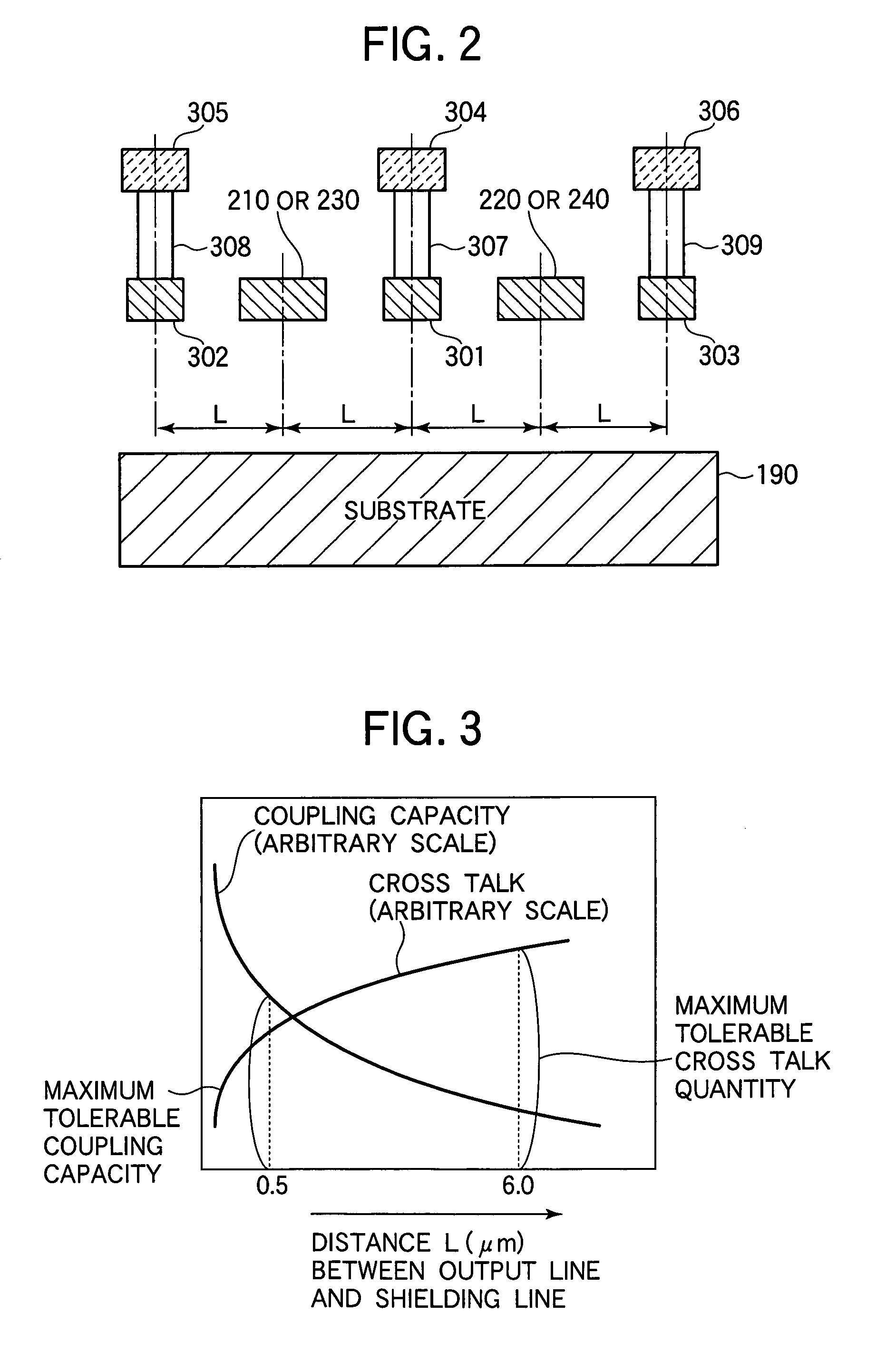
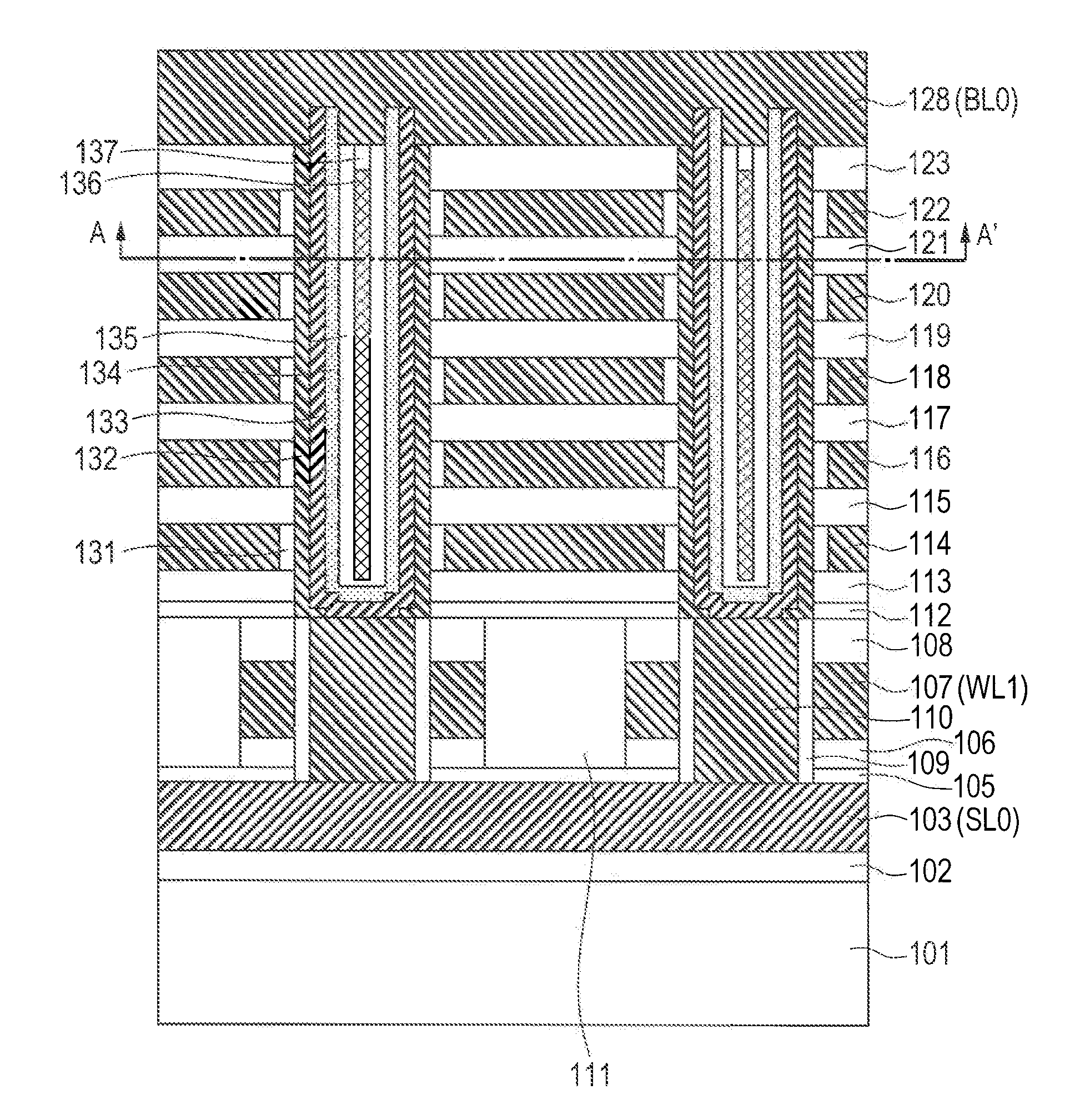
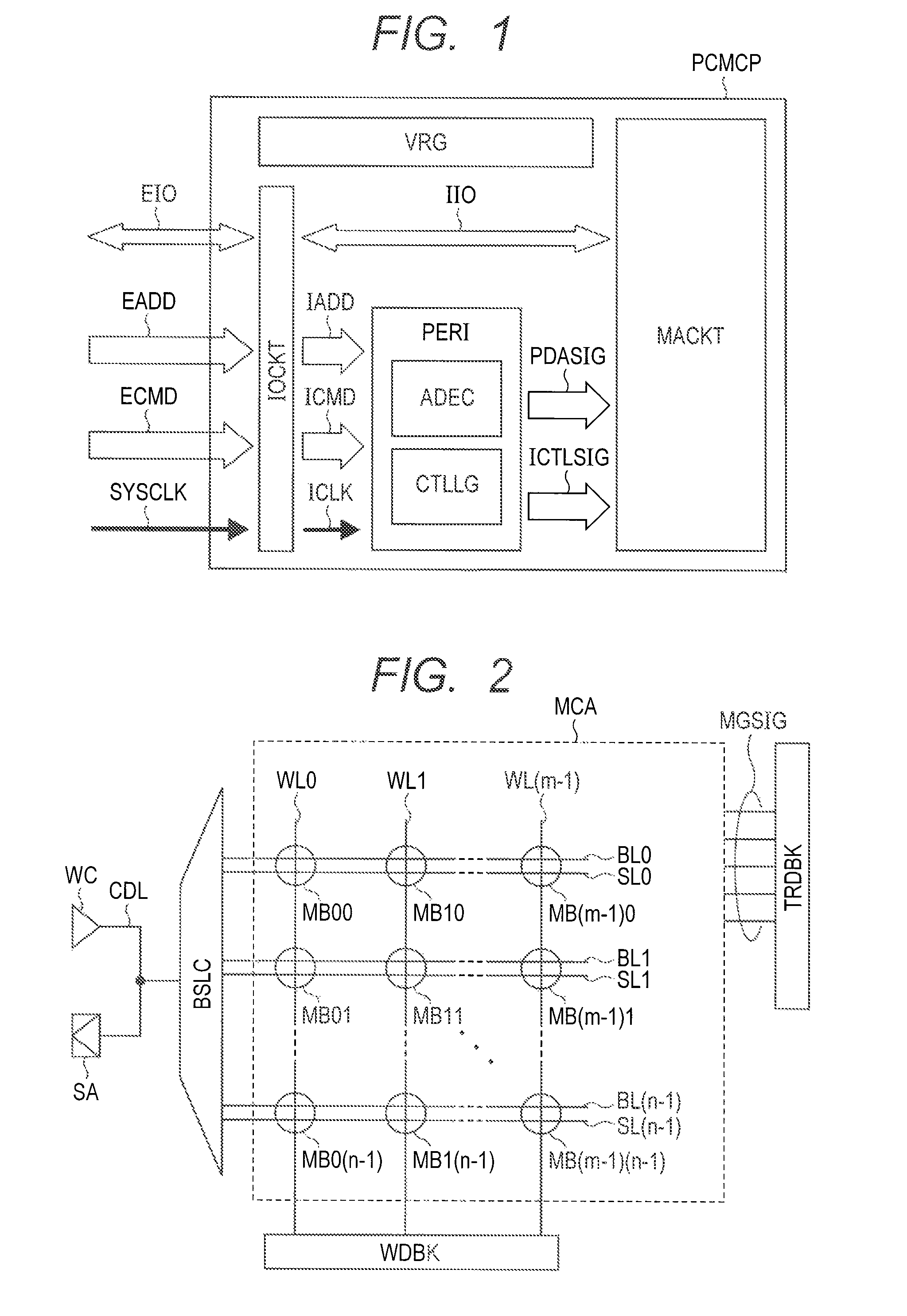
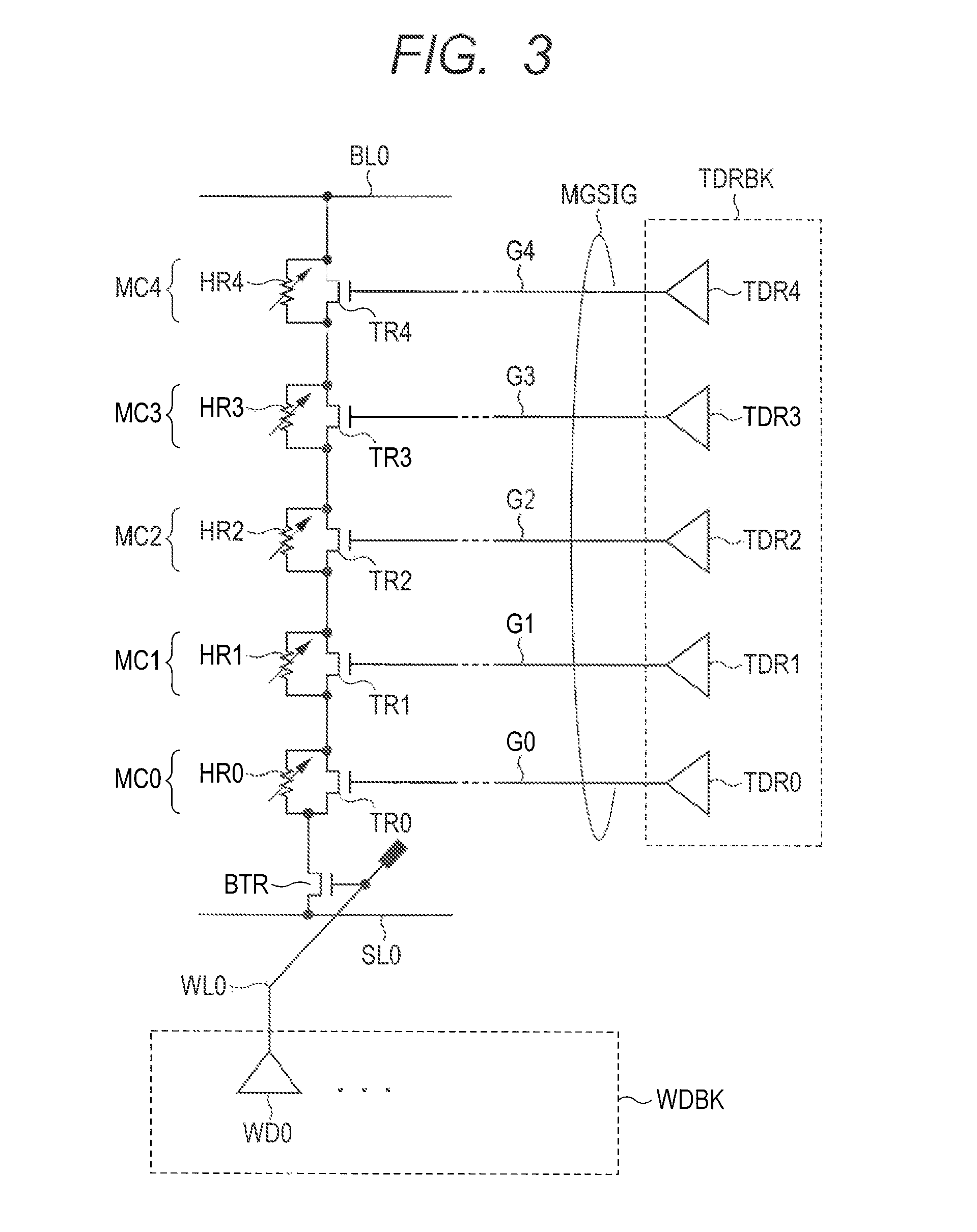
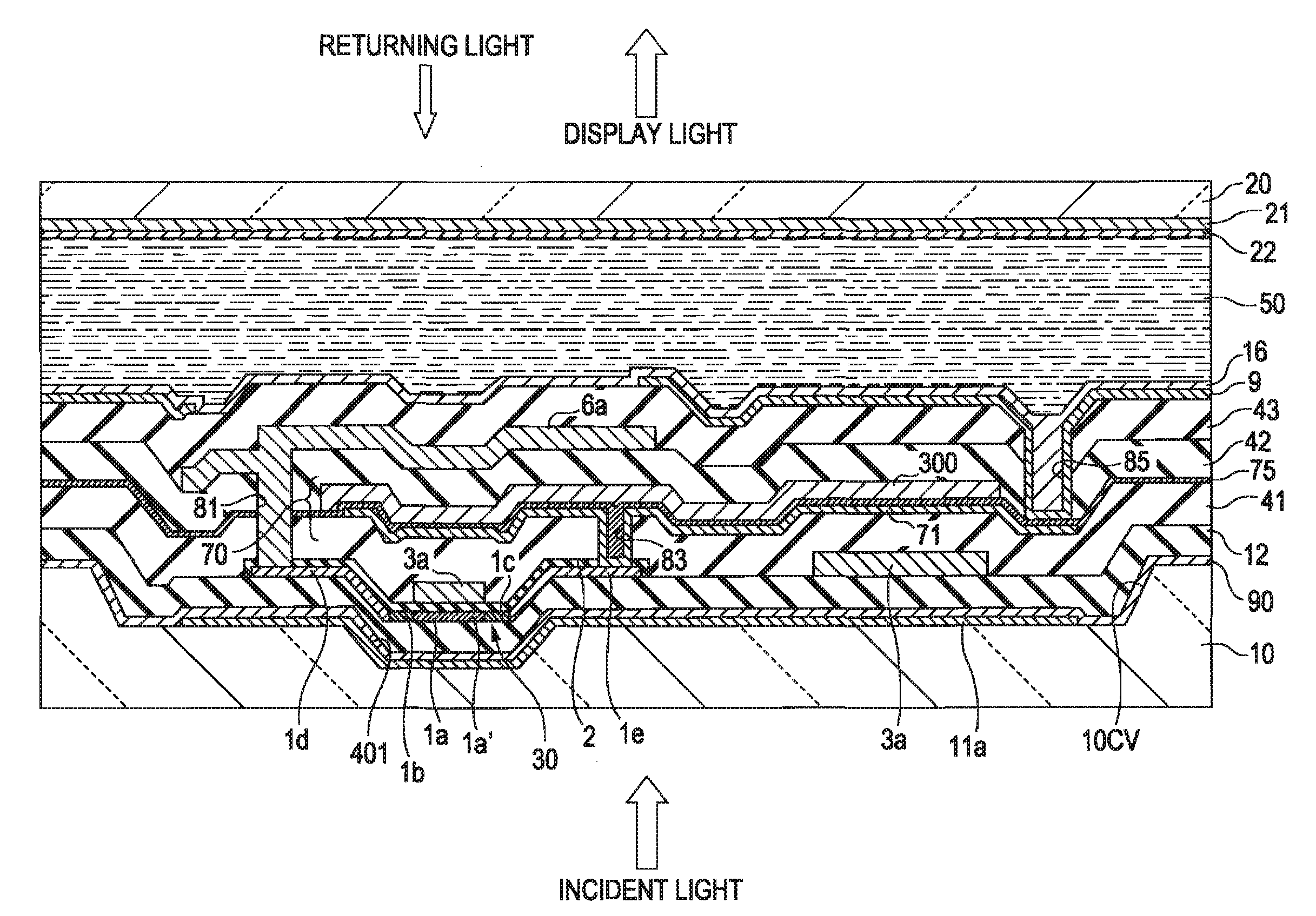
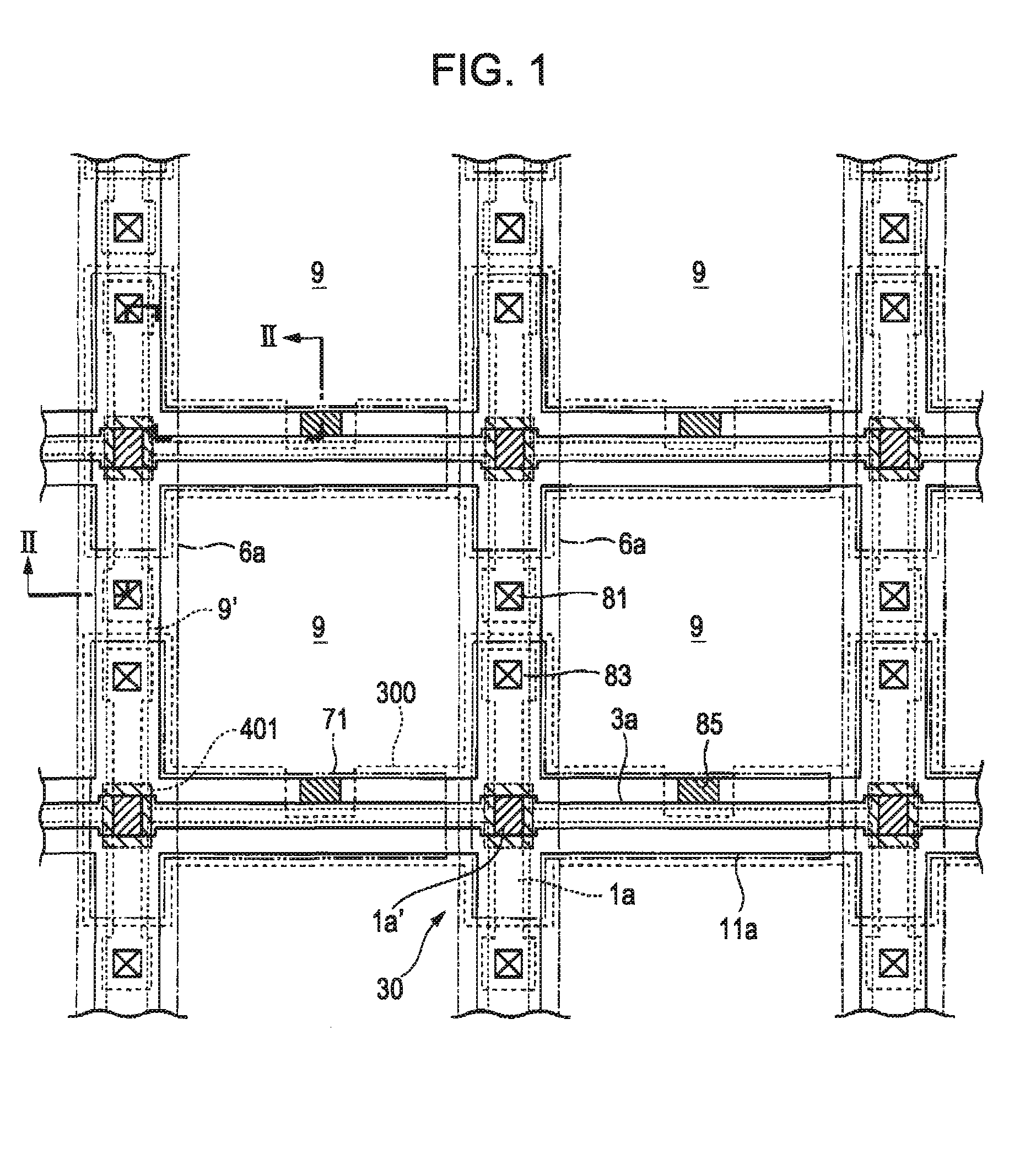
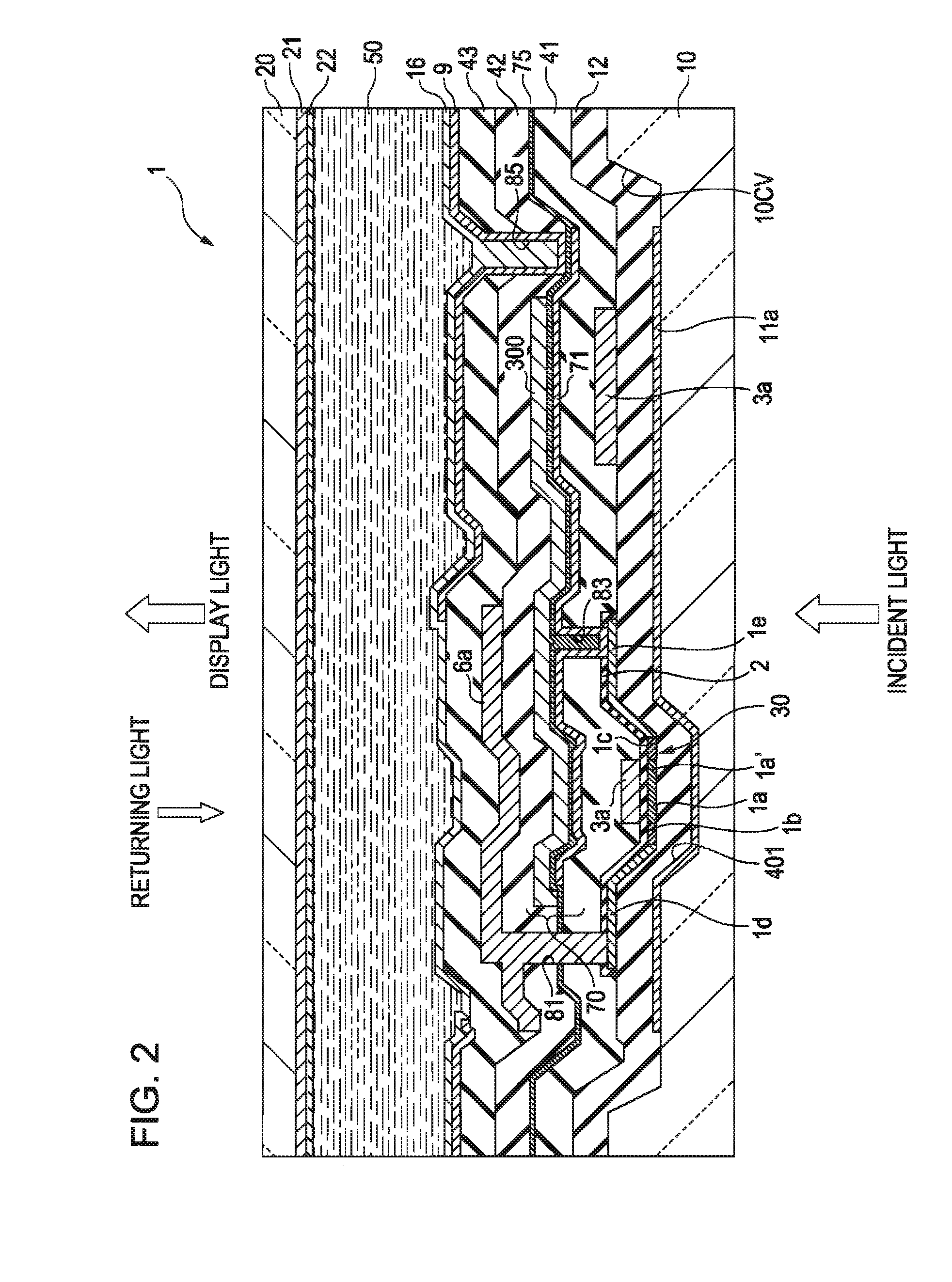
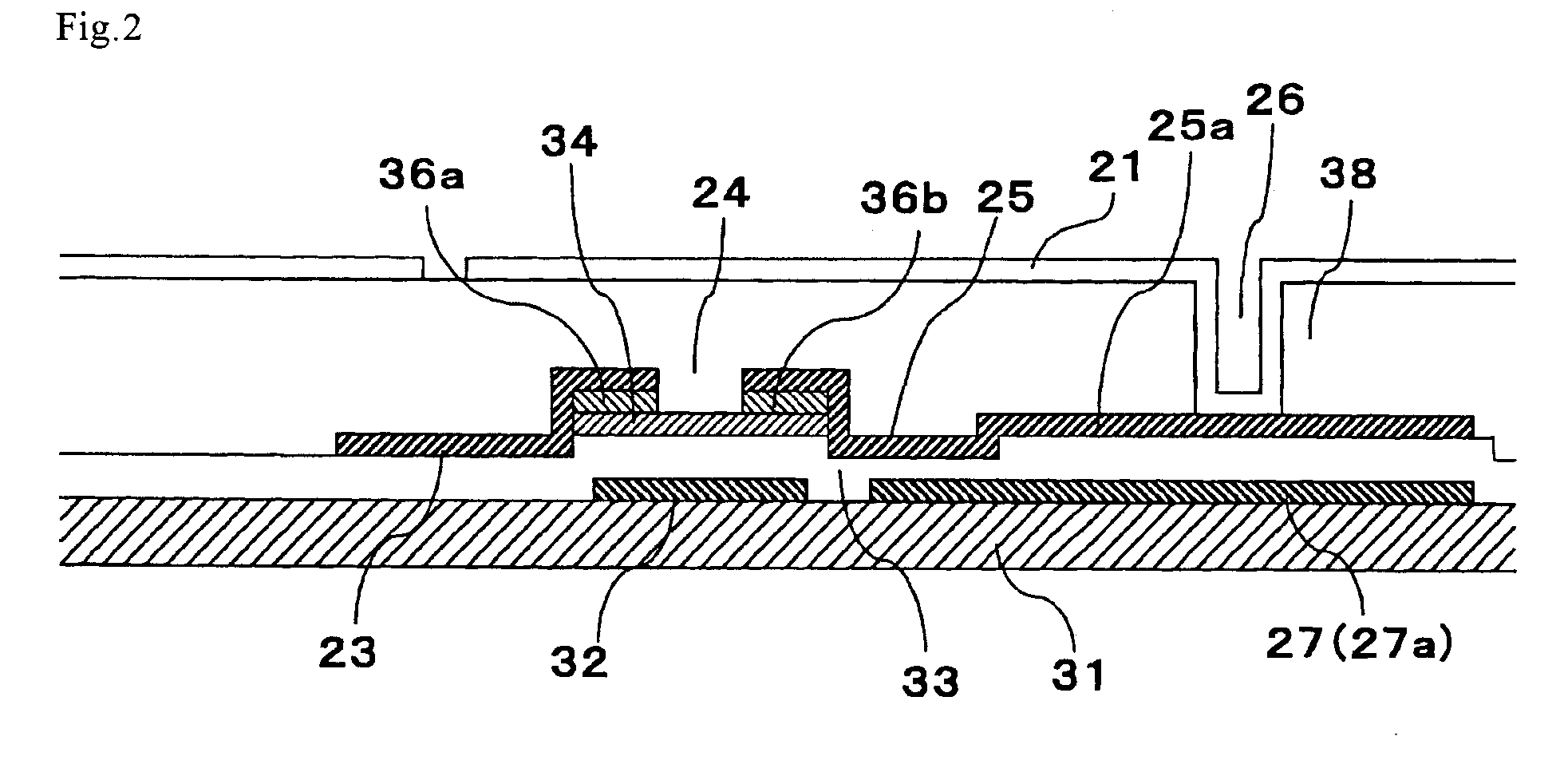
A solid state image pick-up device has shields for suppressing deterioration in a ratio of an output signal to output noises caused by crosstalks, suppressing deterioration in a ratio of the output signal to output noises caused by a coupling capacity, and suppressing deterioration in a ratio of the output signal to output noises caused by imbalance is provided. Shielding lines 301, 302, and 303 are arranged in a layer to which output lines 210 and 220 belong. Shielding lines 304, 305, and 306 are arranged over the shielding lines 301, 302, and 303, respectively. Further, shielding pins 307, 308, and 309 are arranged between the shielding lines 301 and 304, between the shielding lines 302 and 305, and between the shielding lines 303 and 306, respectively. No shielding line is arranged over output lines 210 and 220. A structure is made to be plane-symmetrical with respect to a plane including a center line of the shielding line 301 and a plane including a center line of the shielding line 304.
Owner:CANON KK
Solid state image pick-up device and image pick-up system
ActiveUS7538804B2Suppression ratioTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceCoupling
A solid state image pick-up device has shields for suppressing deterioration in a ratio of an output signal to output noises caused by crosstalks, suppressing deterioration in a ratio of the output signal to output noises caused by a coupling capacity, and suppressing deterioration in a ratio of the output signal to output noises caused by imbalance is provided. Shielding lines 301, 302, and 303 are arranged in a layer to which output lines 210 and 220 belong. Shielding lines 304, 305, and 306 are arranged over the shielding lines 301, 302, and 303, respectively. Further, shielding pins 307, 308, and 309 are arranged between the shielding lines 301 and 304, between the shielding lines 302 and 305, and between the shielding lines 303 and 306, respectively. No shielding line is arranged over output lines 210 and 220. A structure is made to be plane-symmetrical with respect to a plane including a center line of the shielding line 301 and a plane including a center line of the shielding line 304.
Owner:CANON KK
Multilayer porous film
ActiveUS20100203396A1Improve heat resistanceGood shutdown functionSynthetic resin layered productsCell component detailsPolyolefinHeat resistance
Provided is a multilayer porous film having a porous film comprised of a resin composition comprising a polypropylene and one or more polyolefins other than polypropylenes and an inorganic filler-containing porous layer stacked on at least on one side of the porous film. The multilayer porous film is capable of preventing short circuit between two electrodes even when a heat generation amount is large at the time of abnormal heat generation and therefore satisfying both excellent heat resistance and good shutdown function.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI E-MATERIALS CORPORATION
Modacrylic Shrinkable Fiber and Method for Manufacturing The Same
A modacrylic shrinkable fiber according to the present invention is containing a polymer composition obtained by mixing 50 to 99 parts by weight of a polymer (A) containing 40 wt % to 80 wt % of acrylonitrile, 20 wt % to 60 wt % of a halogen-ontaining monomer and 0 wt % to 5 wt % of a sulfonic-acid-containing monomer, and 1 to 50 parts by weight of a polymer (B) containing 5 wt % to 70 wt % of acrylonitrile, 20 wt % to 94 wt % of an acrylic ester and 1 wt % to 40 wt % of a sulfonic-acid-containing monomer containing a methallylsulfonic acid or metal salts thereof or amine salts thereof, in which a total amount of the polymer (A) and the polymer (B) is 100 parts by weight. In this way, a modacrylic shrinkable fiber that has a favorable color development property after dyeing and a high shrinkage ratio even after dyeing is obtained.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Semiconductor storage device
InactiveUS20120287697A1Reduce the bottom areaSuppression ratioSolid-state devicesDigital storageSemiconductor storage devicesEngineering physics
A semiconductor storage device crystallizes variable resistive element material layers arranged on side surfaces of multiple semiconductor layers in a stacked structure concurrently by applying a first current to any one of semiconductor layers in the stacked structure, and thereafter applies a second current to semiconductor layers other than a semiconductor layer to which the first current was applied.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Variable resistance non-volatile memory device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110006278A1Reliability of device deterioratesIncrease valueSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
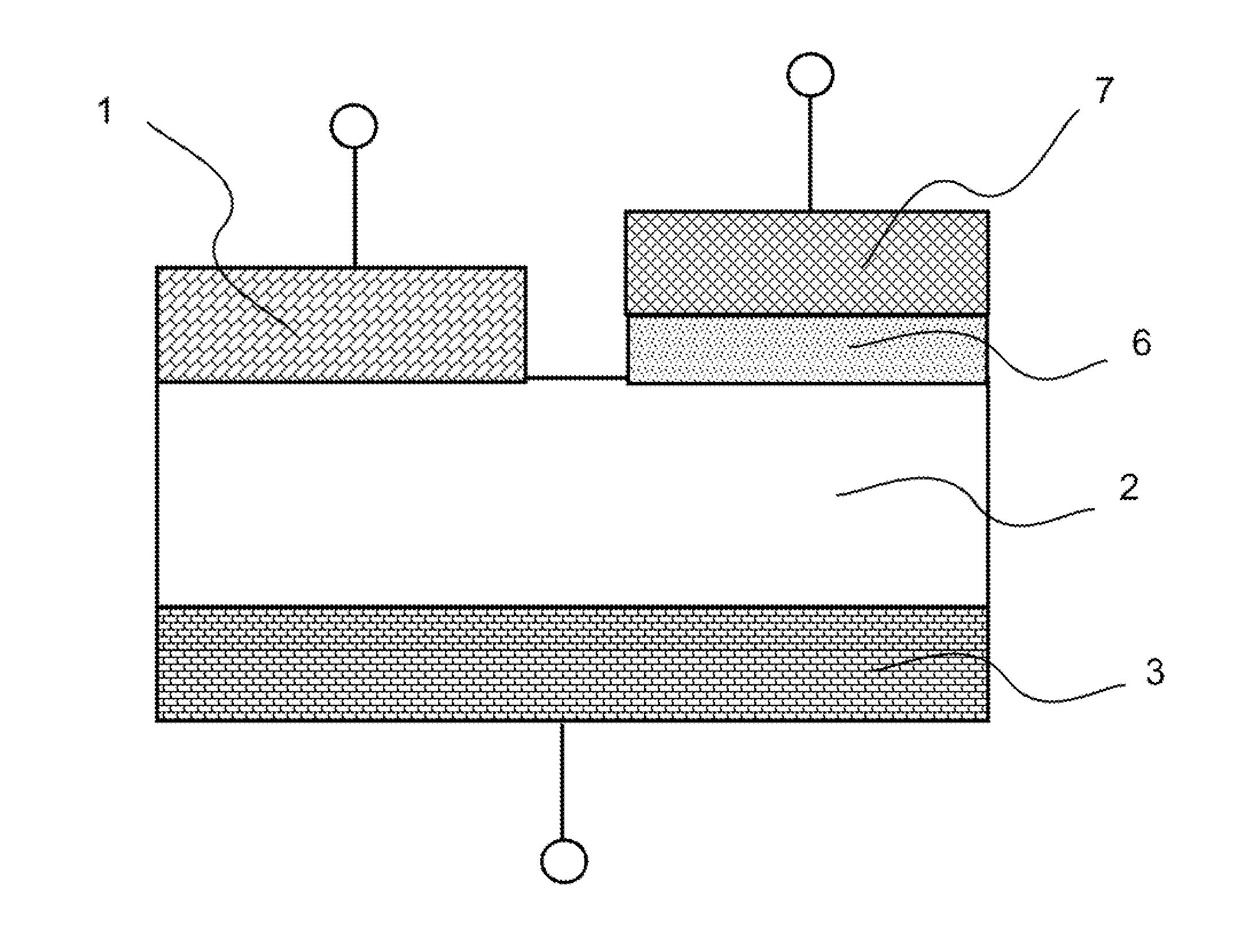
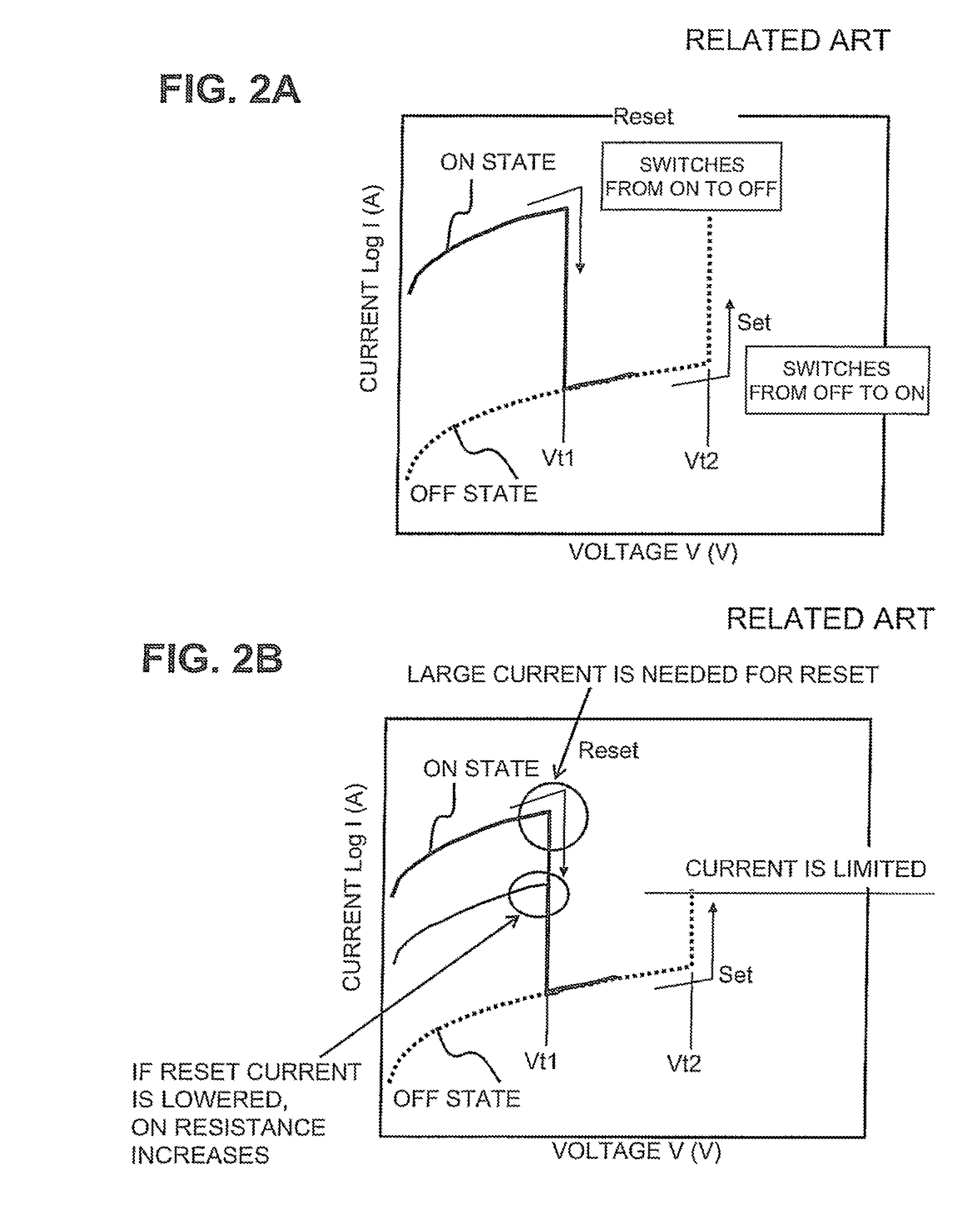
A variable resistance non-volatile memory device of the laminated structure of an upper electrode a variable resistance material a lower electrode includes an insulating film formed for being contacted with the variable resistance material and a reset electrode formed for being contacted with the insulating film without being contacted with the upper electrode or the lower electrode. The device is reset by applying a voltage to the reset electrode. A low resistance value for the set state and a high resistance value for the reset state may be obtained as the current during the reset operation of the device is reduced. A low reset current and a high resistance ratio between the resistance value for the set state and that for the reset state are simultaneously achieved.
Owner:NEC CORP
External cavity widely tunable laser using a silicon resonator and micromechanically adjustable coupling
InactiveUS20120195332A1Widely tunableEasy to manufactureOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersTunable laserMicrolens
A widely tunable laser is described where a compound semiconductor gain chip is coupled to a waveguide filter fabricated on silicon. The filter has two resonators with different free-spectral-ranges, such that Vernier tuning between the filters can be used to provide a single wavelength of light feedback into the gain chip, where the wavelength is adjustable over a wide range. The coupling between the gain chip and the filter is realized through a microlens whose position can be adjusted using micromechanics and locked in place.
Owner:T&S COMM
Apparatus and Method for Peak Suppression in Wireless Communication Systems
InactiveUS20090060070A1Suppressing peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR)Prevent degradationCriteria allocationSecret communicationCommunications systemPeak value
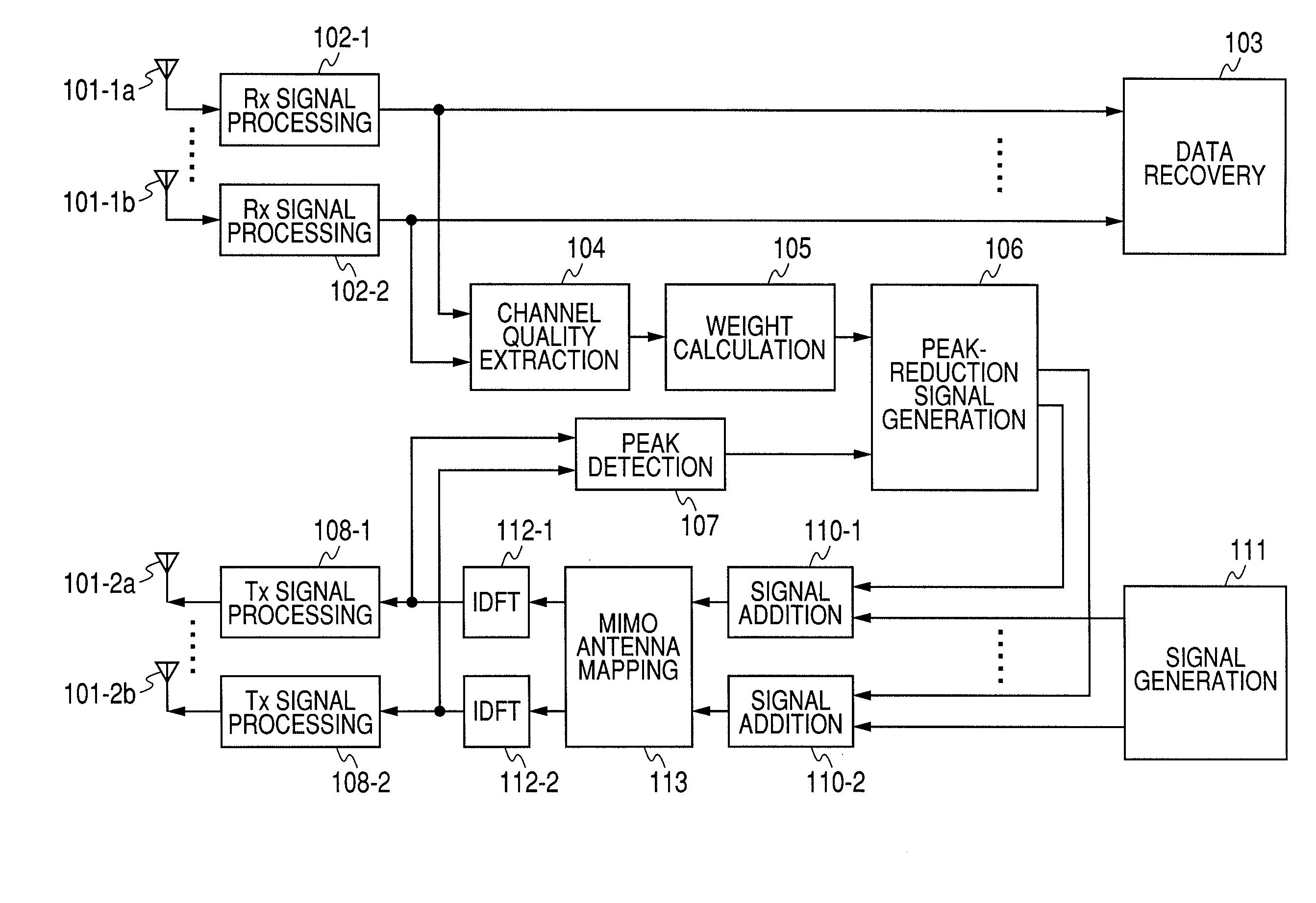
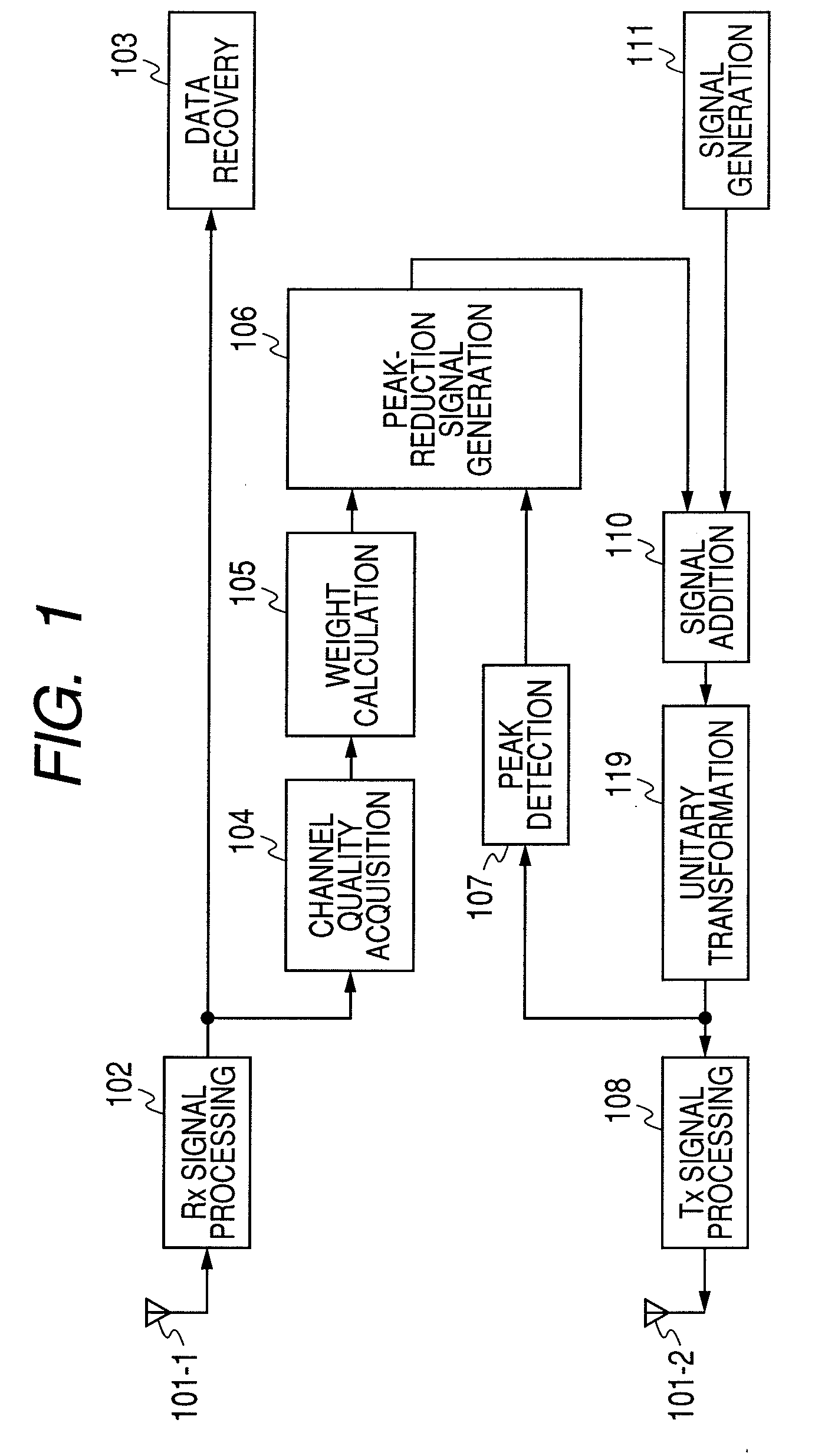
A method for suppressing the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) while limiting deterioration in signal characteristics in wireless communication devices utilizing wireless communication methods (OFDM method, MIMO method) for multiplexing and sending multiple signals. A weight calculator unit sets a large weight for transmit signals whose channel quality is poor, relative to the weight of each base component based on the acquired channel quality. A peak detector unit detects the peak from the signal string after unitary conversion, and extracts a distortion component to apply for suppressing the peak. A peak suppression signal generation unit calculates the peak signal from the distortion component and weight of each base component, to add to each base component, and adds the peak suppression signal to each base component prior to unitary transformation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Coded OFDM system and method with improved PAPR reduction
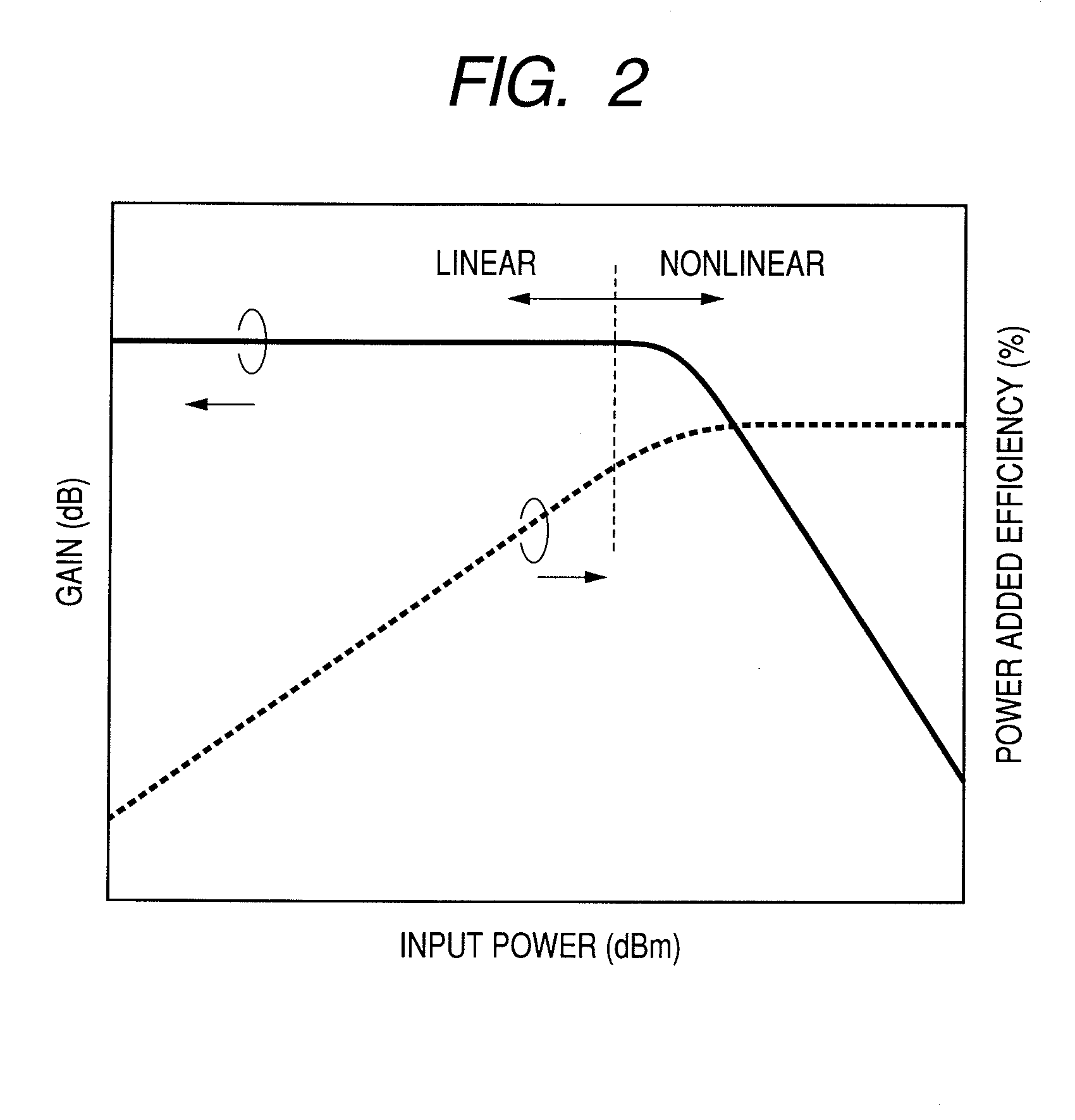
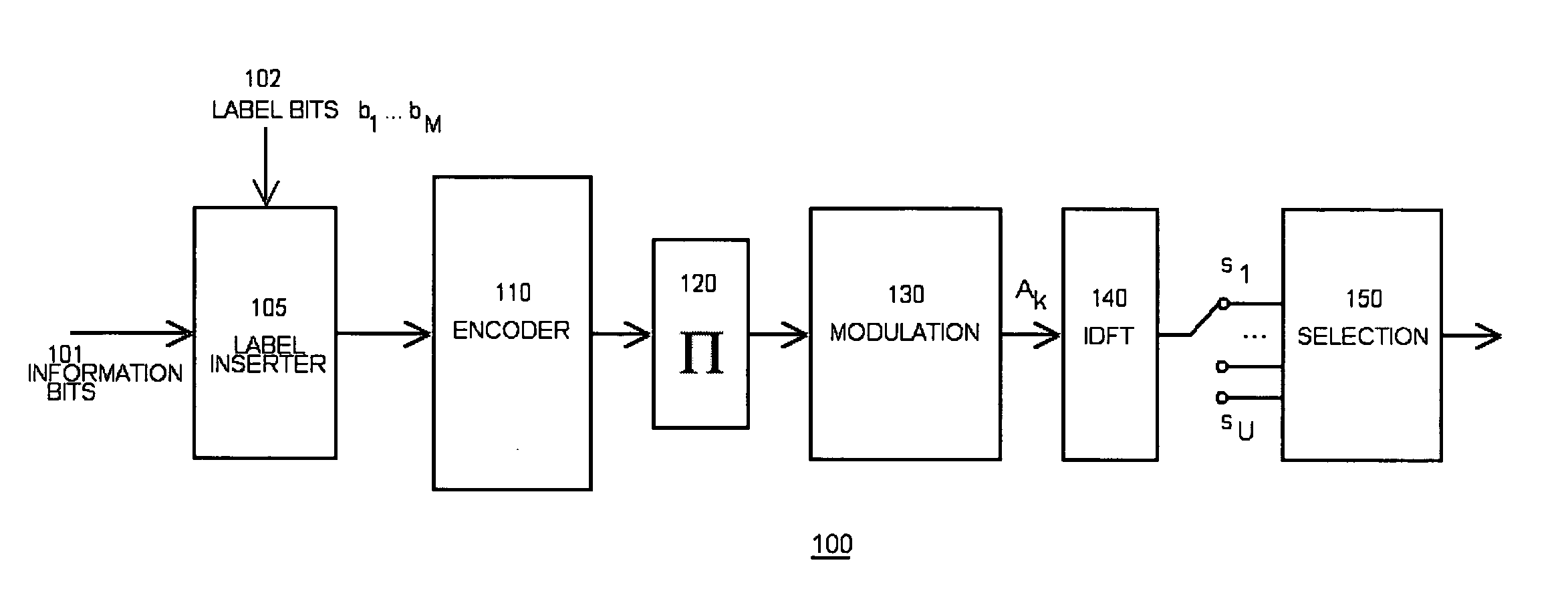
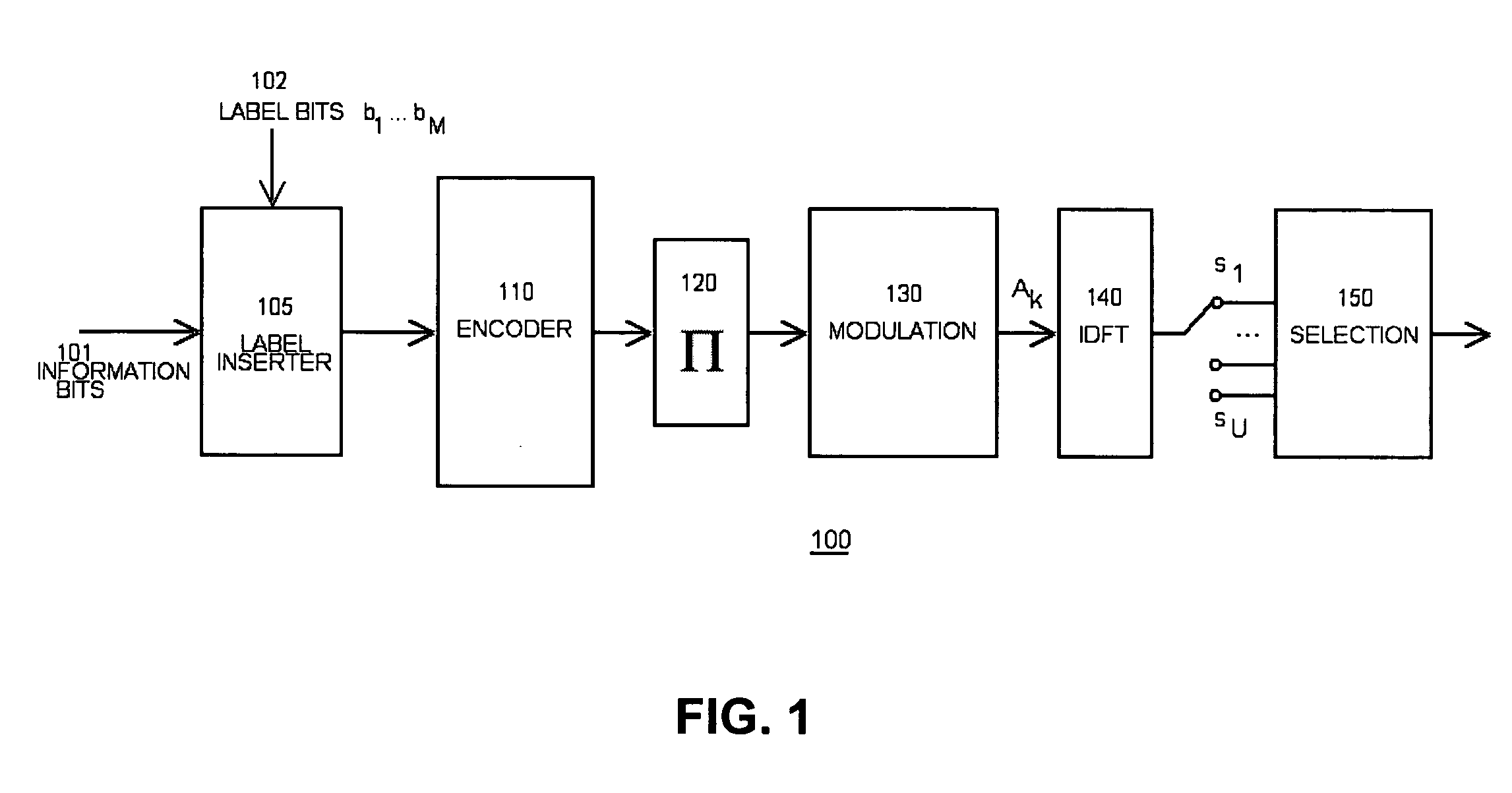
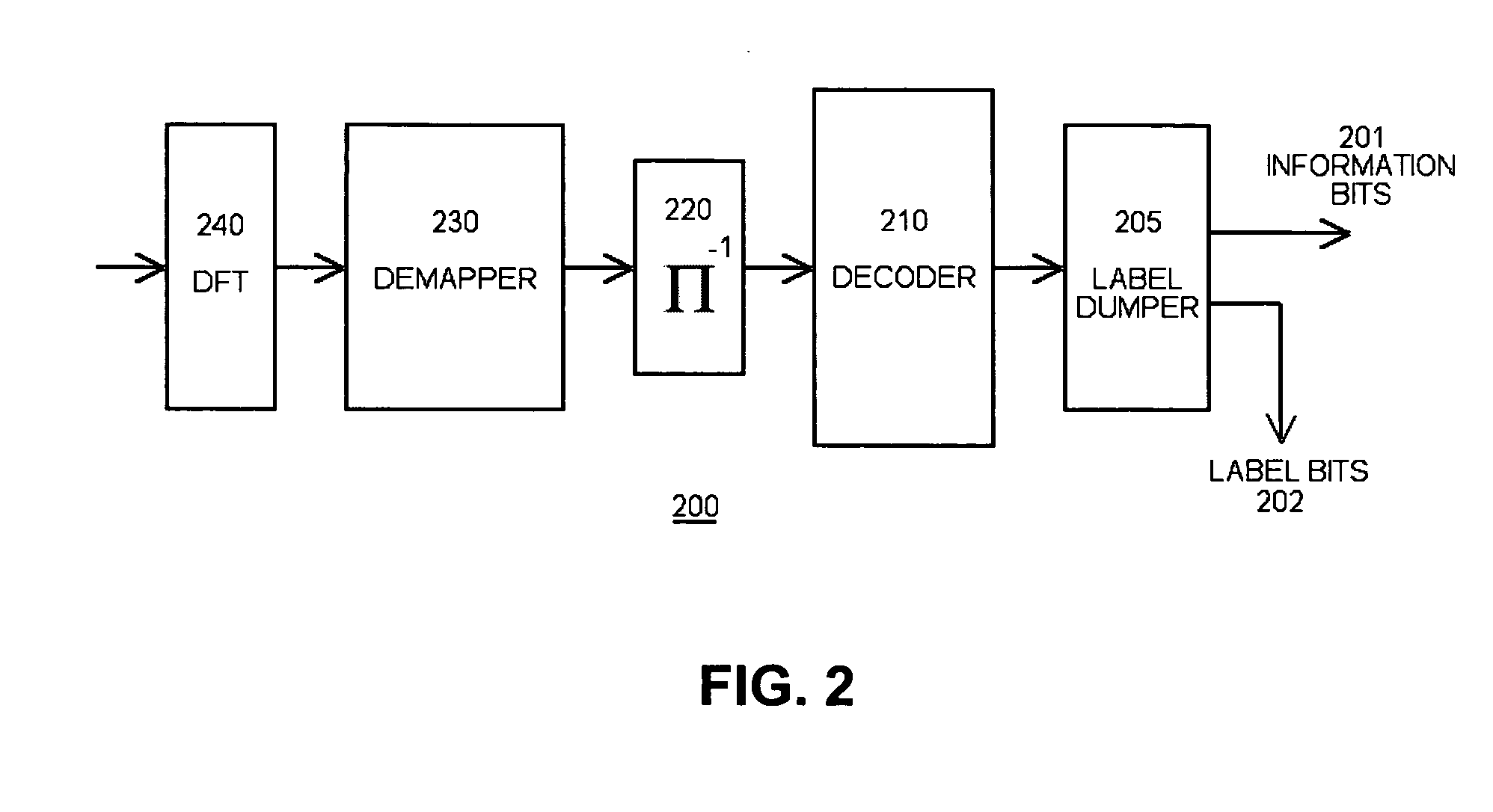
InactiveUS20060098747A1Reduce peak-to-averageSuppression ratioSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal frequency code division multiplexingElectrical and Electronics engineering
A system and method is herein disclosed for reducing peak-to-average power ratio in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system which utilizes label bits inserted at predetermined locations of an information stream prior to encoding.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Heat treatment apparatus and method for manufacturing toner
InactiveUS9075328B2Suppress coarseningLess fine powderDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsCoarse particleHeat treated
Owner:CANON KK
Semiconductor storage device with memory cell utilized as a set-dedicated memory cell
InactiveUS8634257B2Reduce the bottom areaSuppression ratioSolid-state devicesDigital storagePower flowSemiconductor storage devices
A semiconductor storage device crystallizes variable resistive element material layers arranged on side surfaces of multiple semiconductor layers in a stacked structure concurrently by applying a first current to any one of semiconductor layers in the stacked structure, and thereafter applies a second current to semiconductor layers other than a semiconductor layer to which the first current was applied.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Passive optical network system, optical line terminal, and optical network unit
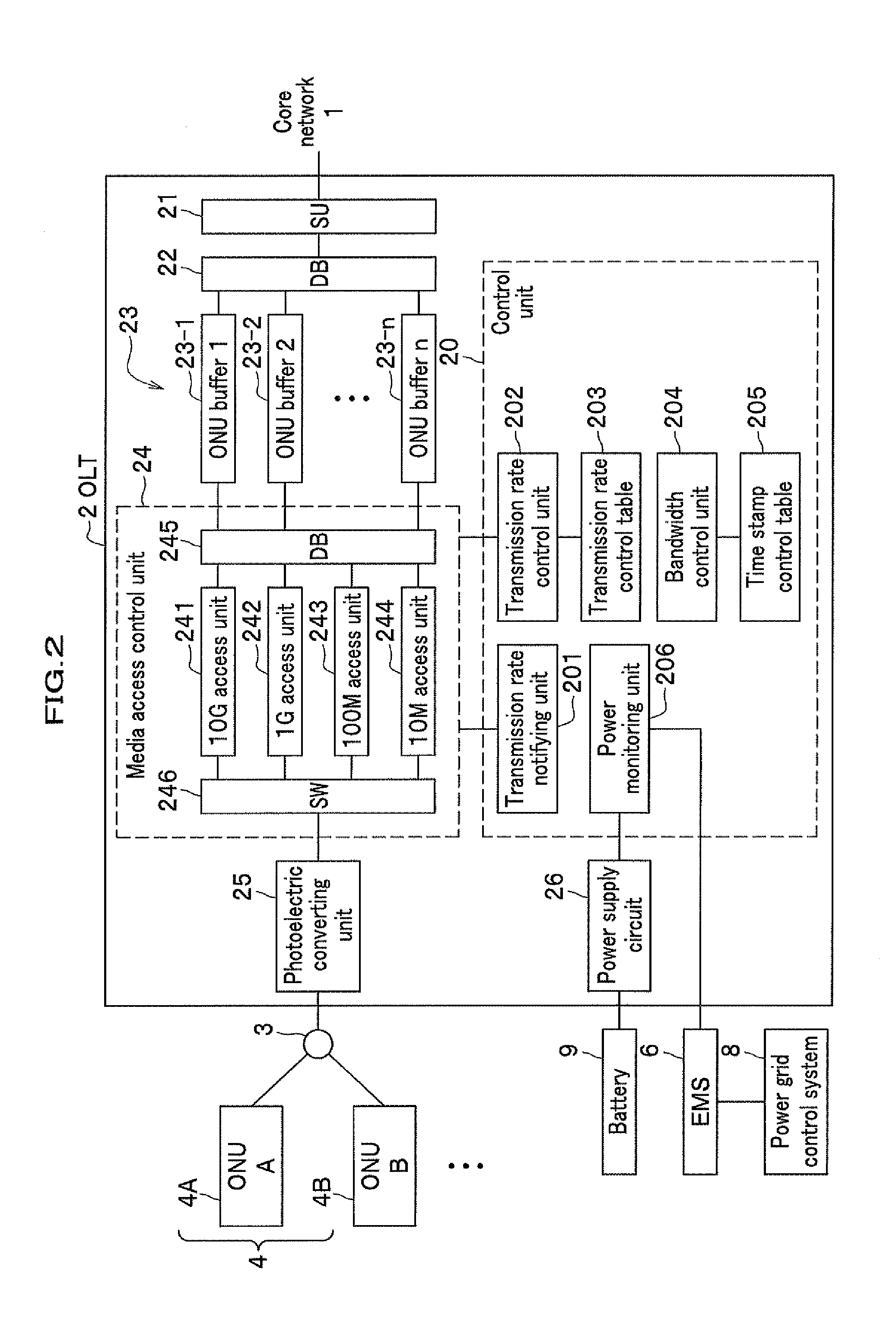
InactiveUS20130148972A1Minimal communicationLow transfer rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsClock rateOptical line termination
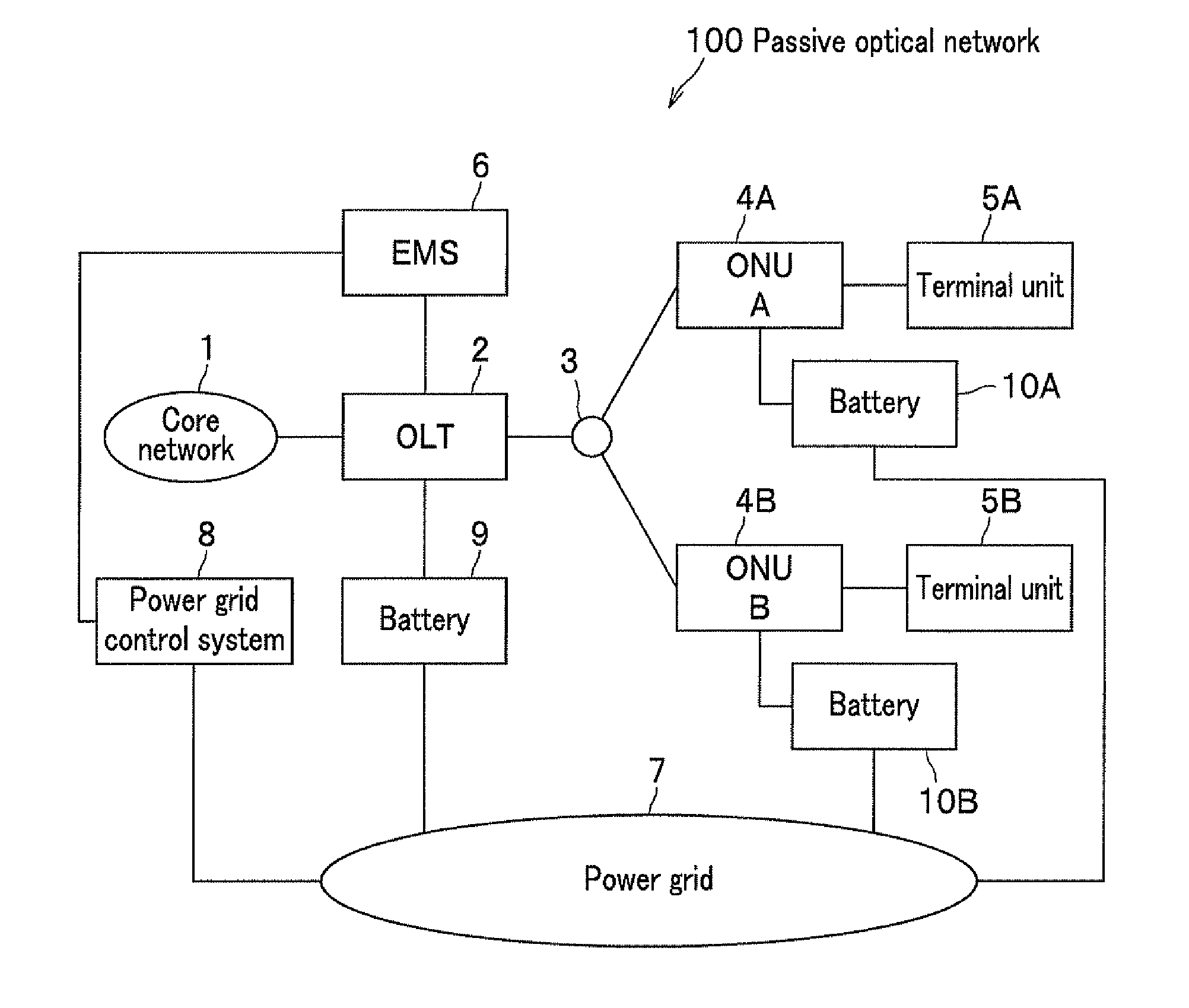
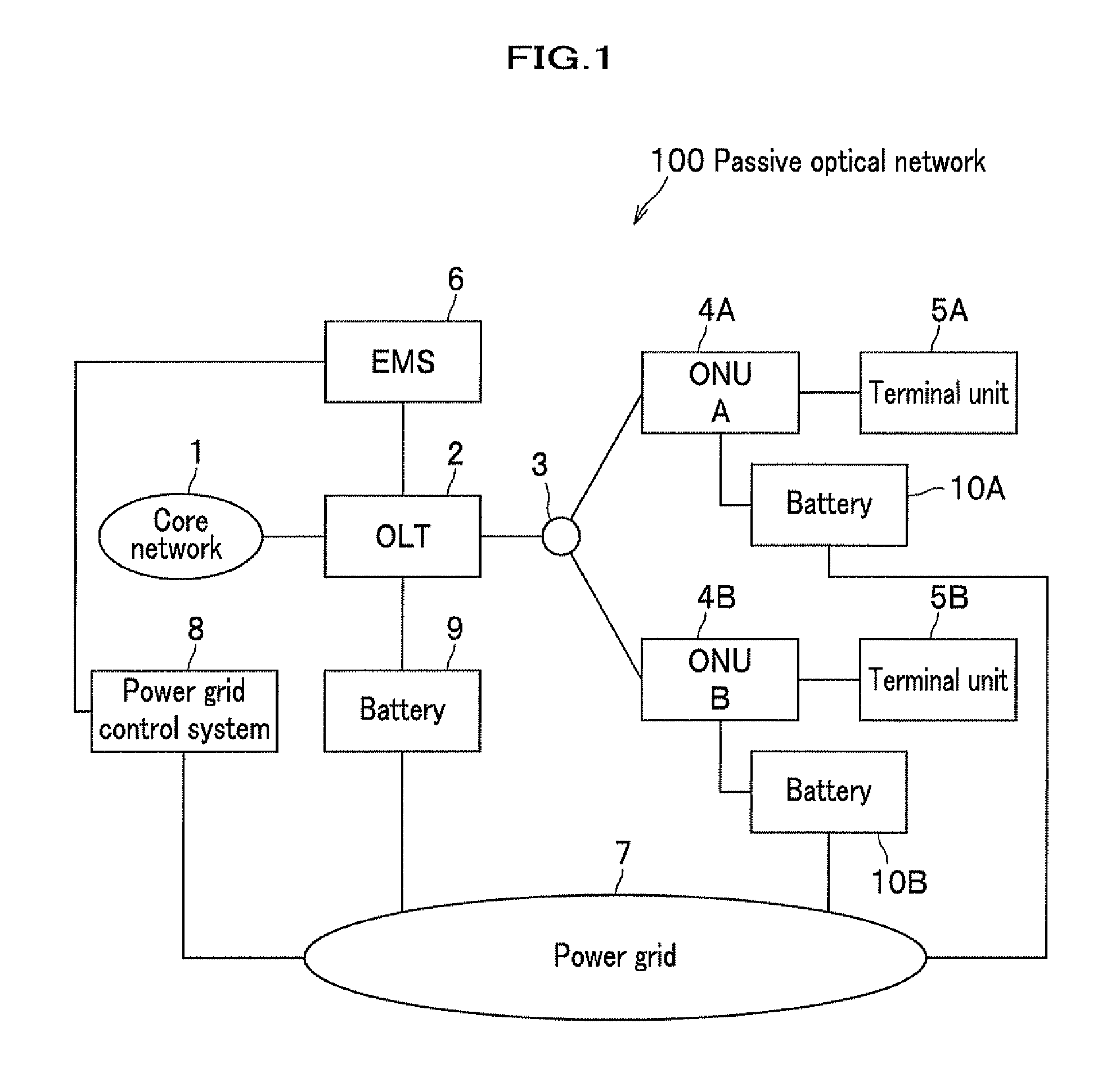
An optical line terminal includes the transmission rate control table for storing a minimum bandwidth for an emergency status for each of optical network units in addition to a maximum assigned bandwidth in a normal status. When a decrease in a supply power is detected, the optical line terminal calculates a transmission clock rate providing a minimum bandwidth required by each optical network unit with reference to the transmission rate control table. The optical line terminal determines change timing of downstream and upstream transmission clock rates, and change timing of upstream data for time-division multiplexing to instruct each of the optical network units. Both the optical line terminal and the optical network unit change the transmission clock rates with substantial synchronization therebetween.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
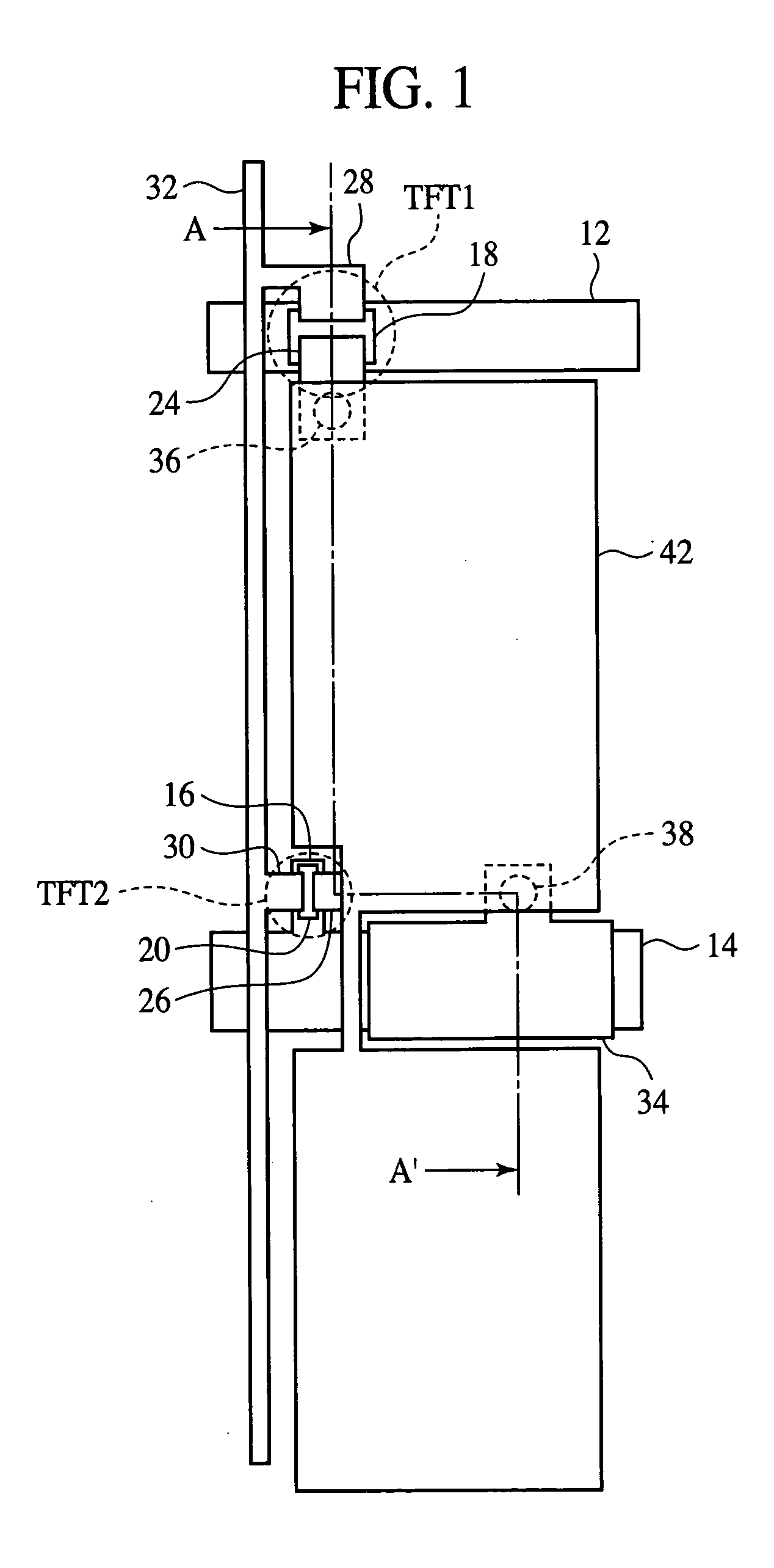
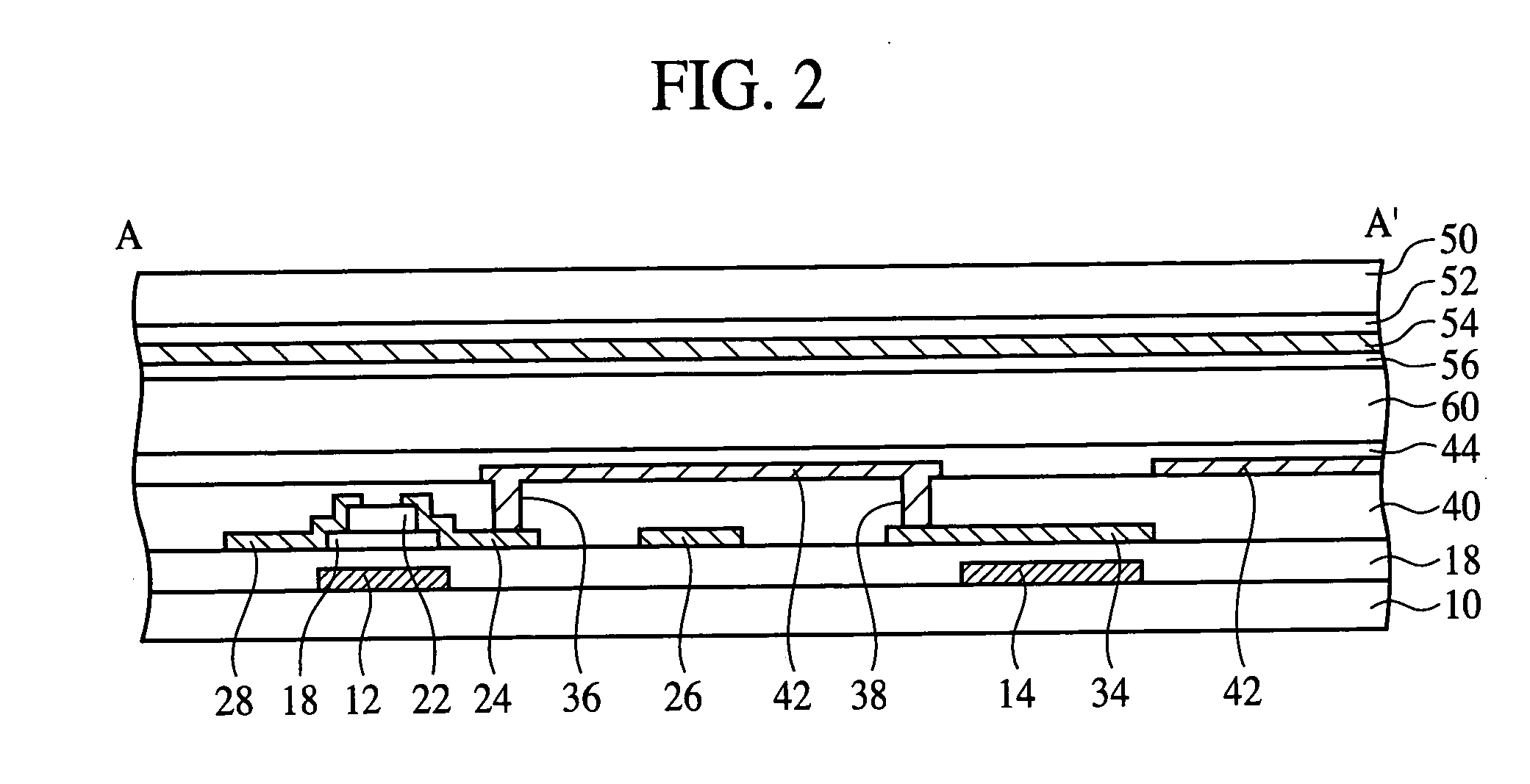
Active matrix substrate and display device
InactiveUS20090073335A1Solve insufficient storage capacityIncrease the aperture ratioNon-linear opticsSemiconductor devicesActive matrixDisplay device
An active matrix substrate suppresses reduction in production yield and increase in production steps and simultaneously permits both sufficient securing of a storage capacity and improvement of an aperture ratio of a pixel. The active matrix substrate is an active matrix substrate and includes a thin film transistor disposed at an intersection of a scanning signal line with a data signal line on a substrate, the thin film transistor including a gate electrode connected to the scanning signal line, a source electrode connected to the data signal line, and a drain electrode connected to a drain lead-out wiring; a storage capacitor upper electrode connected to the drain lead-out wiring and a pixel electrode; and a storage capacitor wiring overlapping with the storage capacitor upper electrode through an insulating film, wherein the storage capacitor wiring has an extending portion overlapping with the drain lead-out wiring through the insulating film.
Owner:SHARP KK
Impedance conversion circuit, drive circuit, and control method of impedance conversion circuit
InactiveUS20060050037A1Reduce in quantityVoltage is accurateStatic indicating devicesAudio power amplifierElectrical current
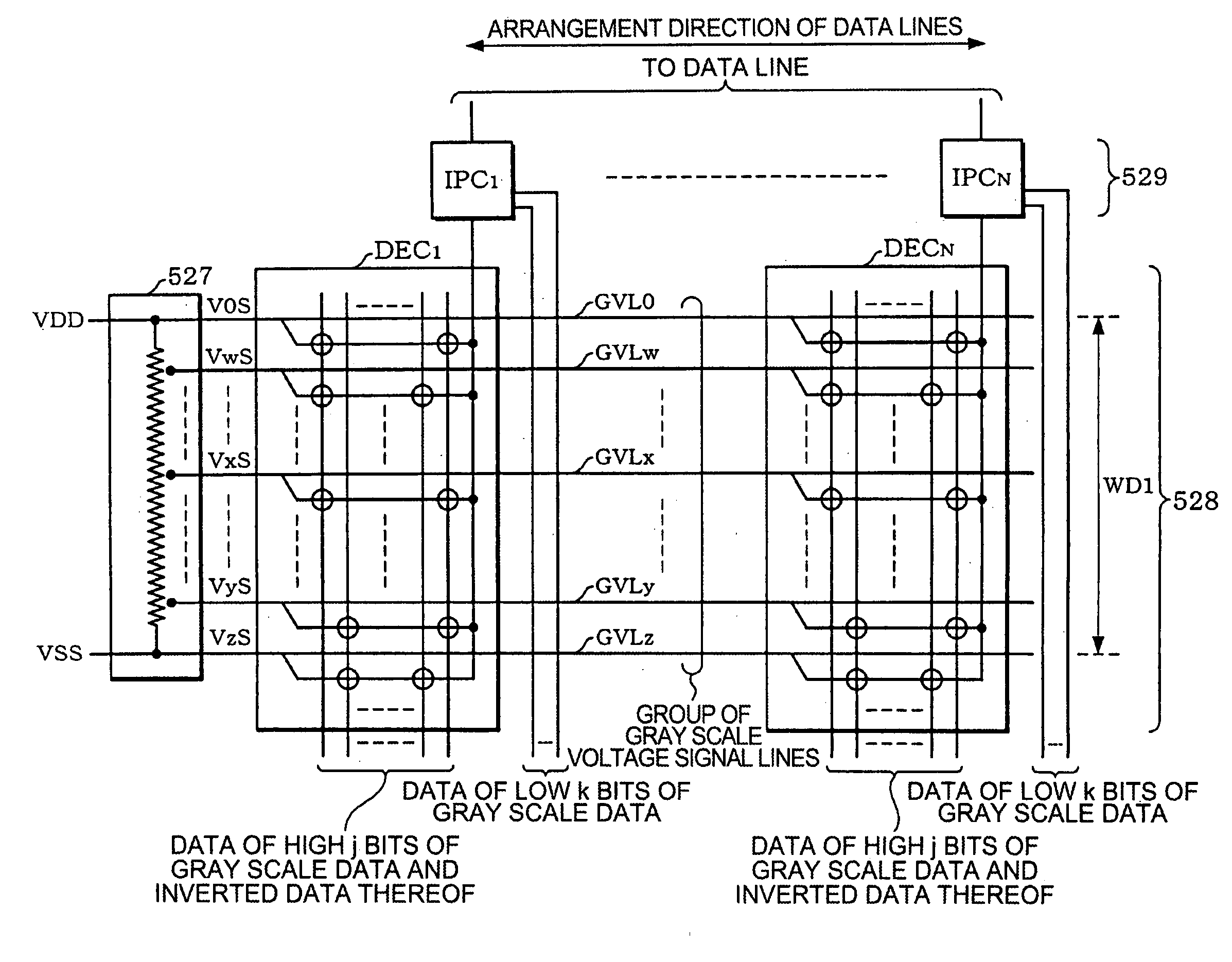
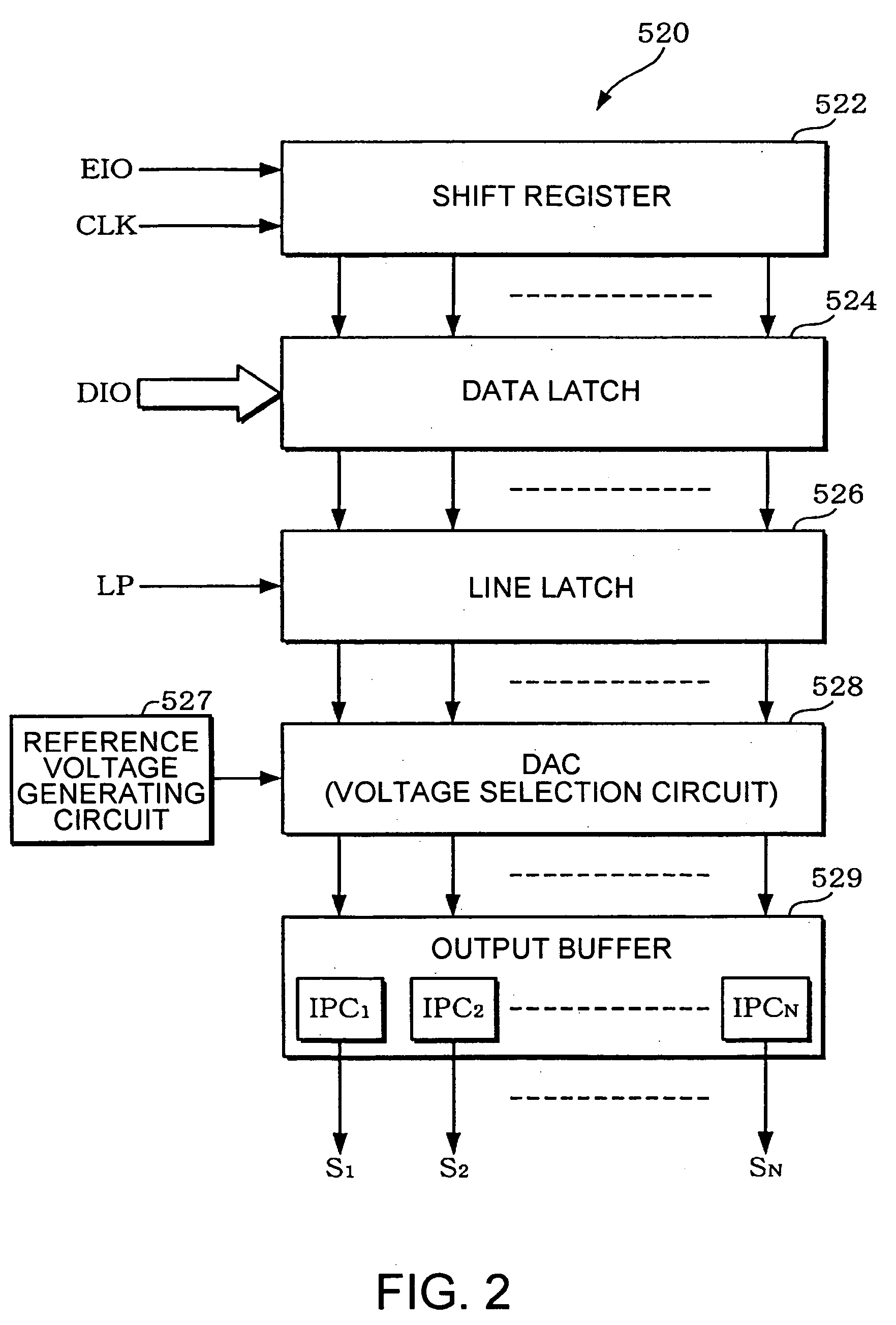
An impedance conversion circuit IPC1 including: an operational amplifier OP1 connected as a voltage follower and supplied with, as an input voltage Vin, a voltage selected from 2j levels of voltages (j is a positive integer) based on data of high j bits of the gray scale data; and an output voltage setting circuit OVS1 for precharging or discharging an output of the operational amplifier OP1 based on data of a most significant bit of low k bits (k is an integer more than 1) of the gray scale data. The operational amplifier OP1 outputs, as an output voltage, a voltage having a difference from the input voltage by a dead zone width after the output voltage setting circuit OVS1 precharges or discharges the output of the operational amplifier OP1. The dead zone width is determined by an operating current of the operational amplifier OP1. The operating current is varied based on data of low k bits of the gray scale data.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Liquid crystal display device, method for repairing liquid crystal display device, and method for driving liquid crystal display device
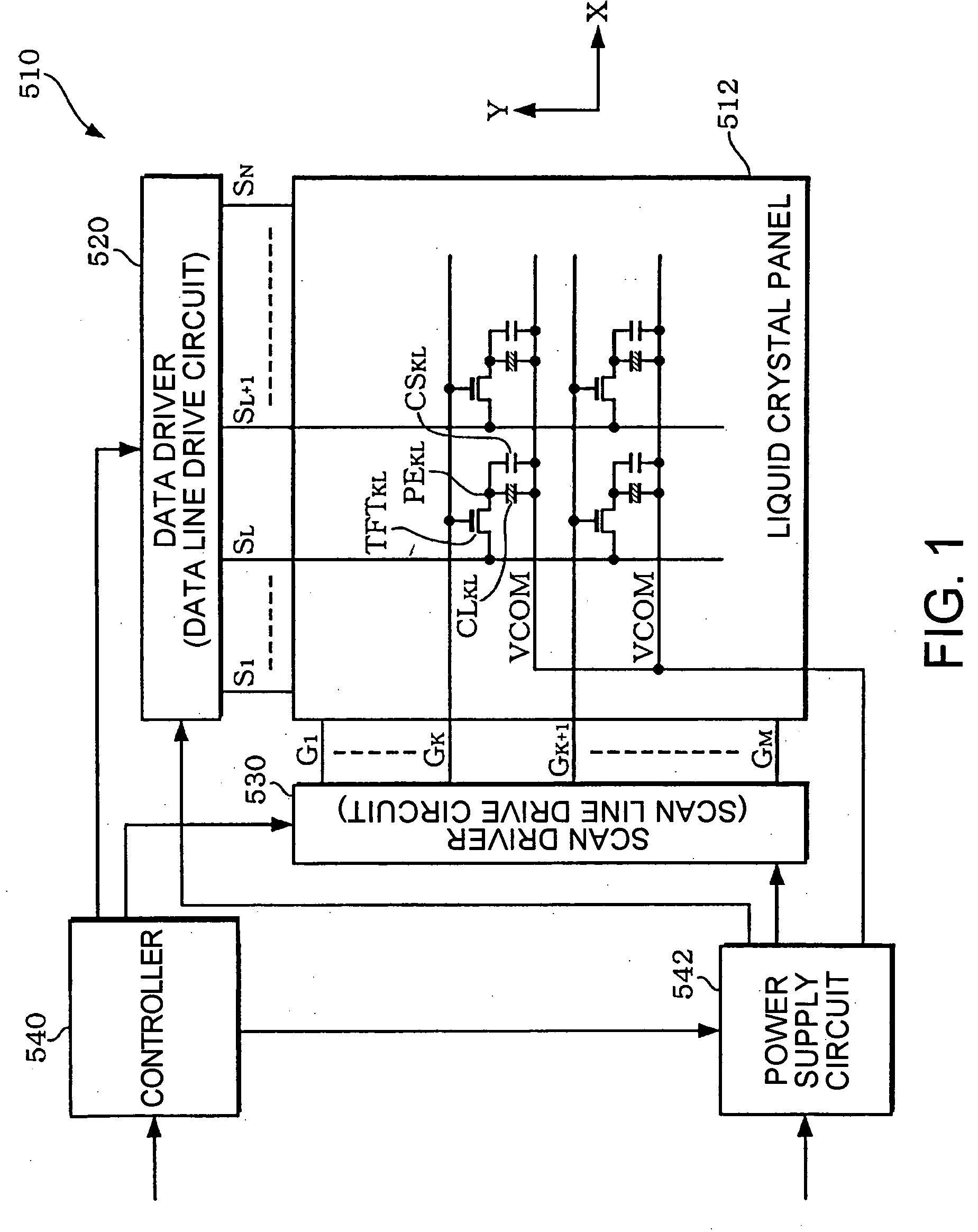
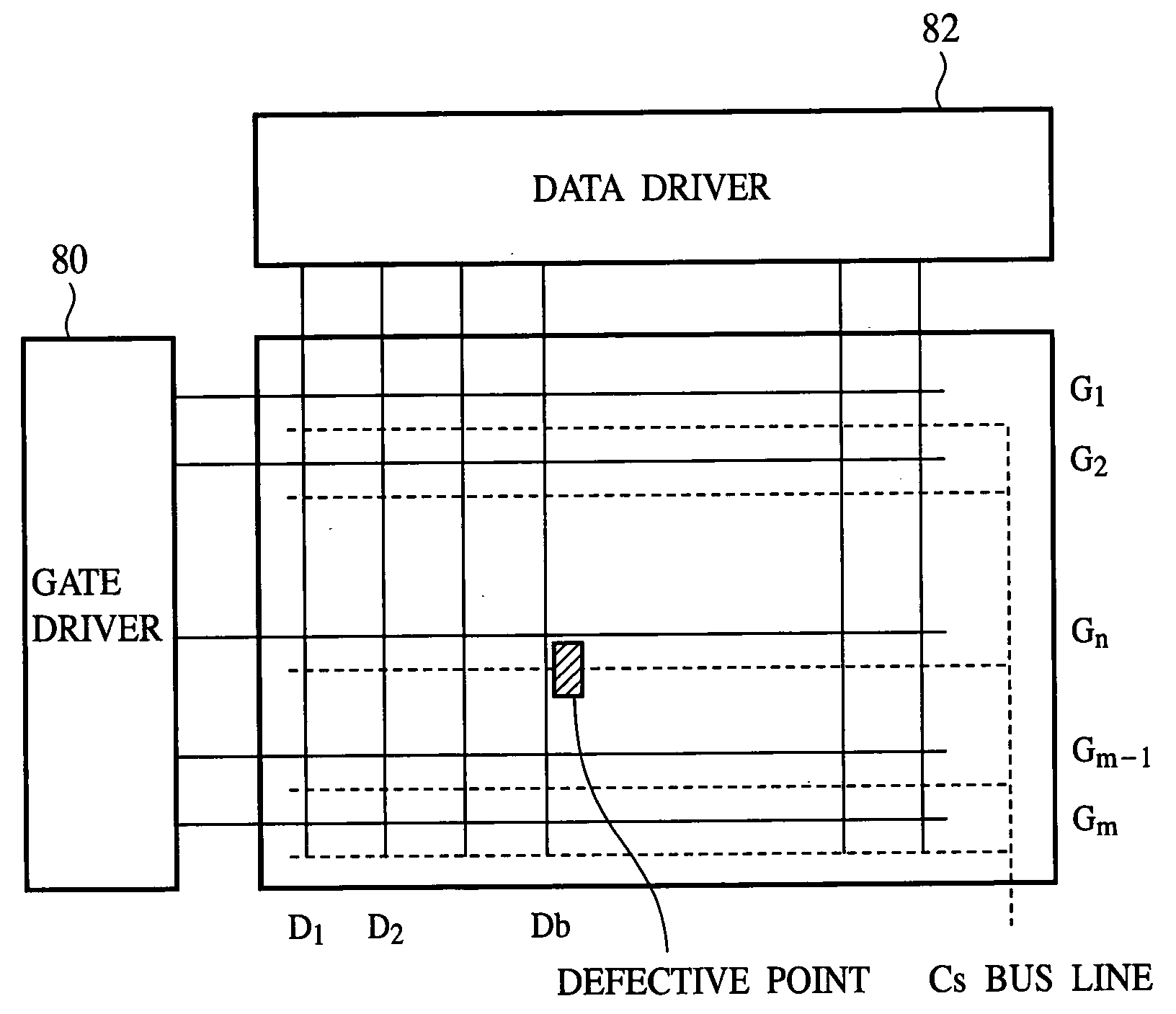
ActiveUS20060017674A1Aperture ratio suppressedImprove yieldStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The liquid crystal display device comprises: a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix, adjacent to each other row-wise and column-wise; a plurality of first bus lines extended row-wise and connected to the pixels arranged row-wise; a plurality of second bus lines extended column-wise and connected to the pixels arranged column-wise; and a plurality of third bus lines extended row-wise, connected to the pixels arranged row-wise, and being capable of applying a voltage which independently changes with time. Said plurality of the pixels each includes: a pixel electrode; a first switching element connected to the pixel electrode and the second bus line, for controlling the connection between the pixel electrode and the second bus line by the first bus line; and a second switching element having one electrode connected to the second bus line and the other electrode arranged, overlapping the pixel electrode with an insulating film formed therebetween, for controlling the connection between said one electrode and said the other electrode by the third bus line.
Owner:SHARP KK
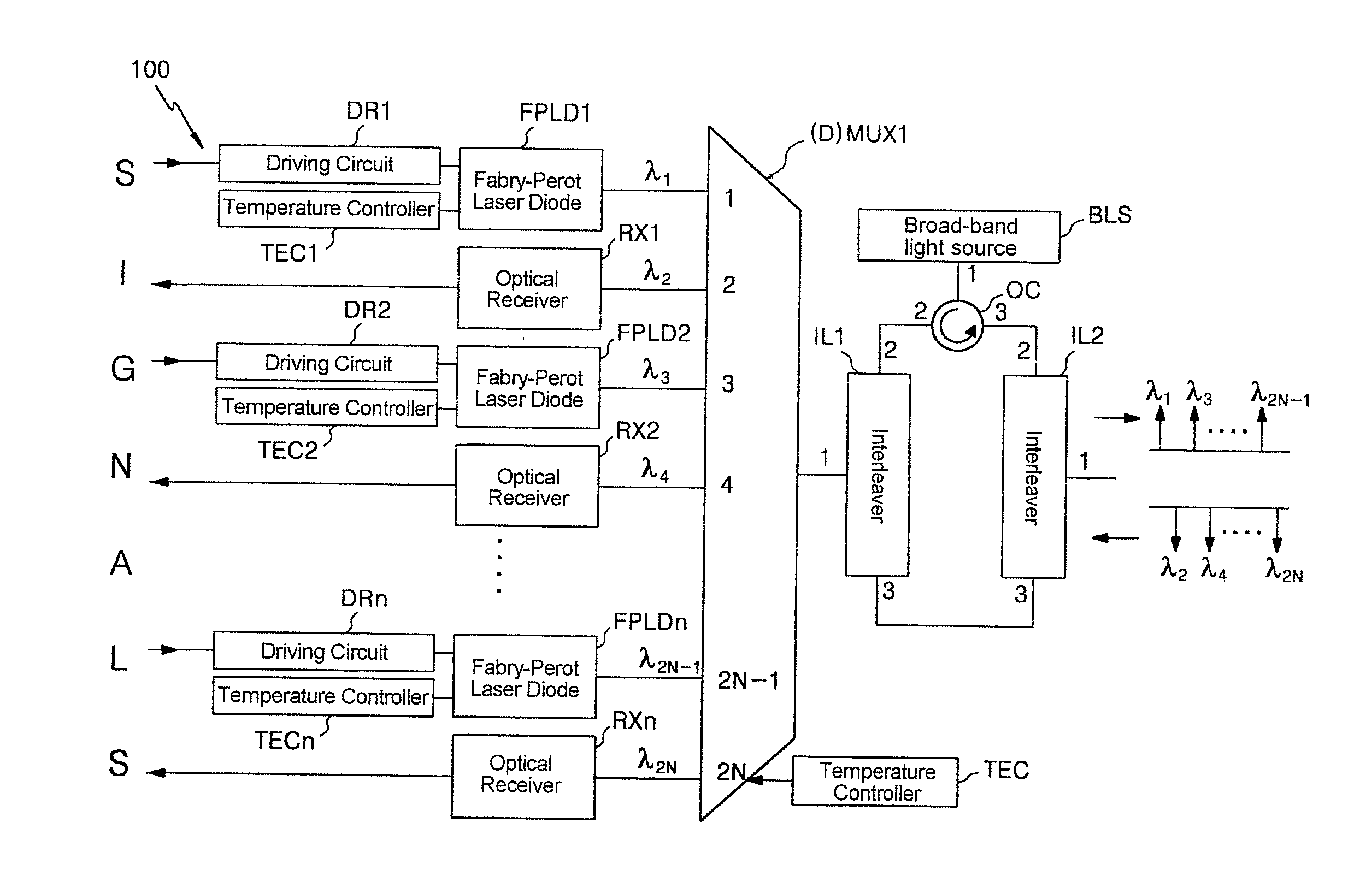
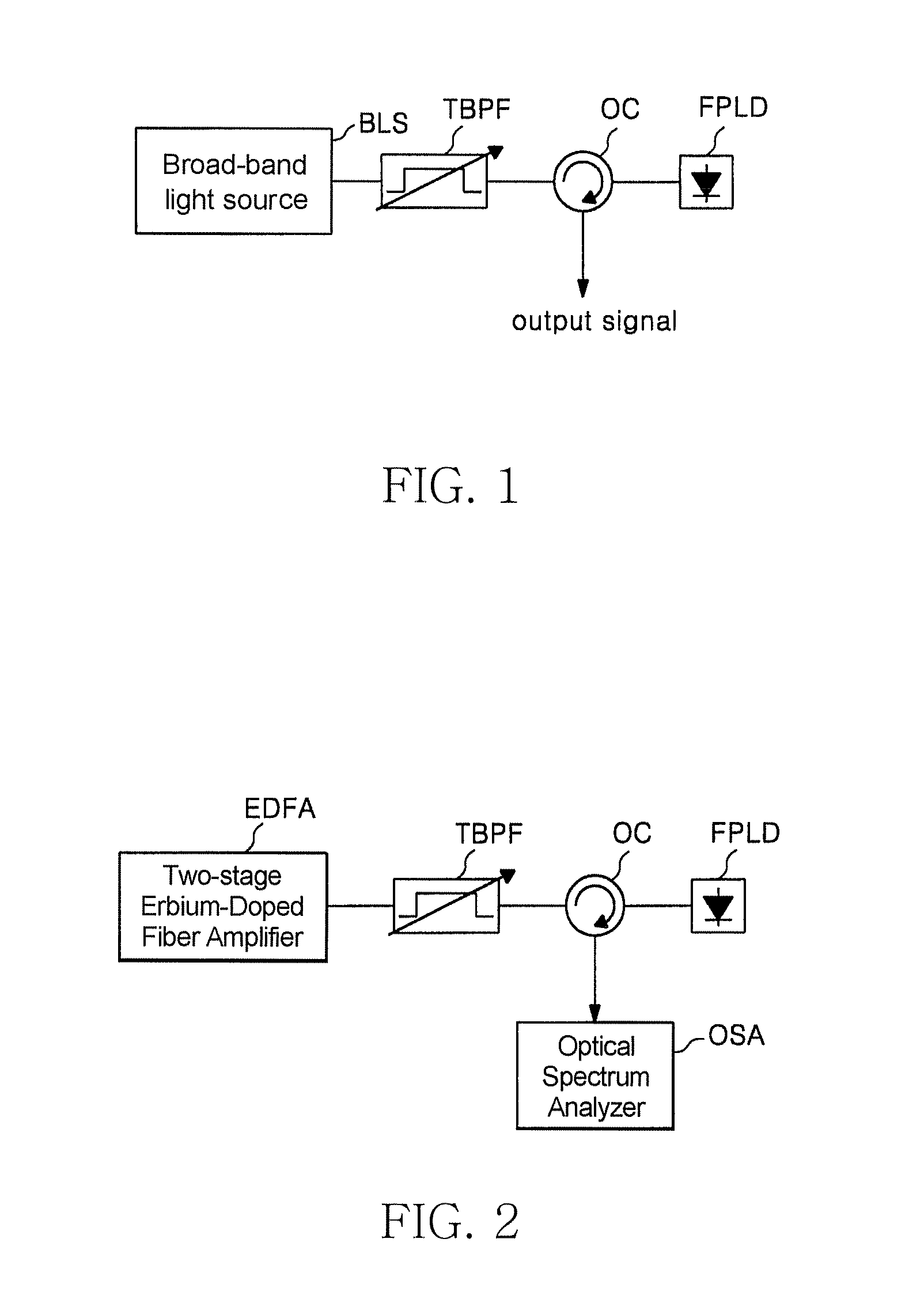
Wavelength-tunable light source and wavelength-division multiplexed transmission system using the source
InactiveUS20070081823A1Increase output powerEasy to manufactureWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersLength waveTransmission system
The present invention relates to a wavelength-tunable light source whose output wavelength can be externally controlled and a wavelength-division multiplexed transmission system using the source. A wavelength-tunable light source in accordance with the present invention is constituted to be able to vary the output wavelength of a Fabry-Perot laser diode, that is wavelength-locked to an injected light, by controlling the wavelength of the injected light. A wavelength-tunable light source in accordance with the present invention provides comparatively large output power and excellent economic features. The present invention also presents a wavelength-division multiplexed transmission system using the wavelength-tunable light source.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Optical transmission apparatus
InactiveUS20070230968A1Increase speedImprove stabilityWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsSpectrum analyzerOptical power
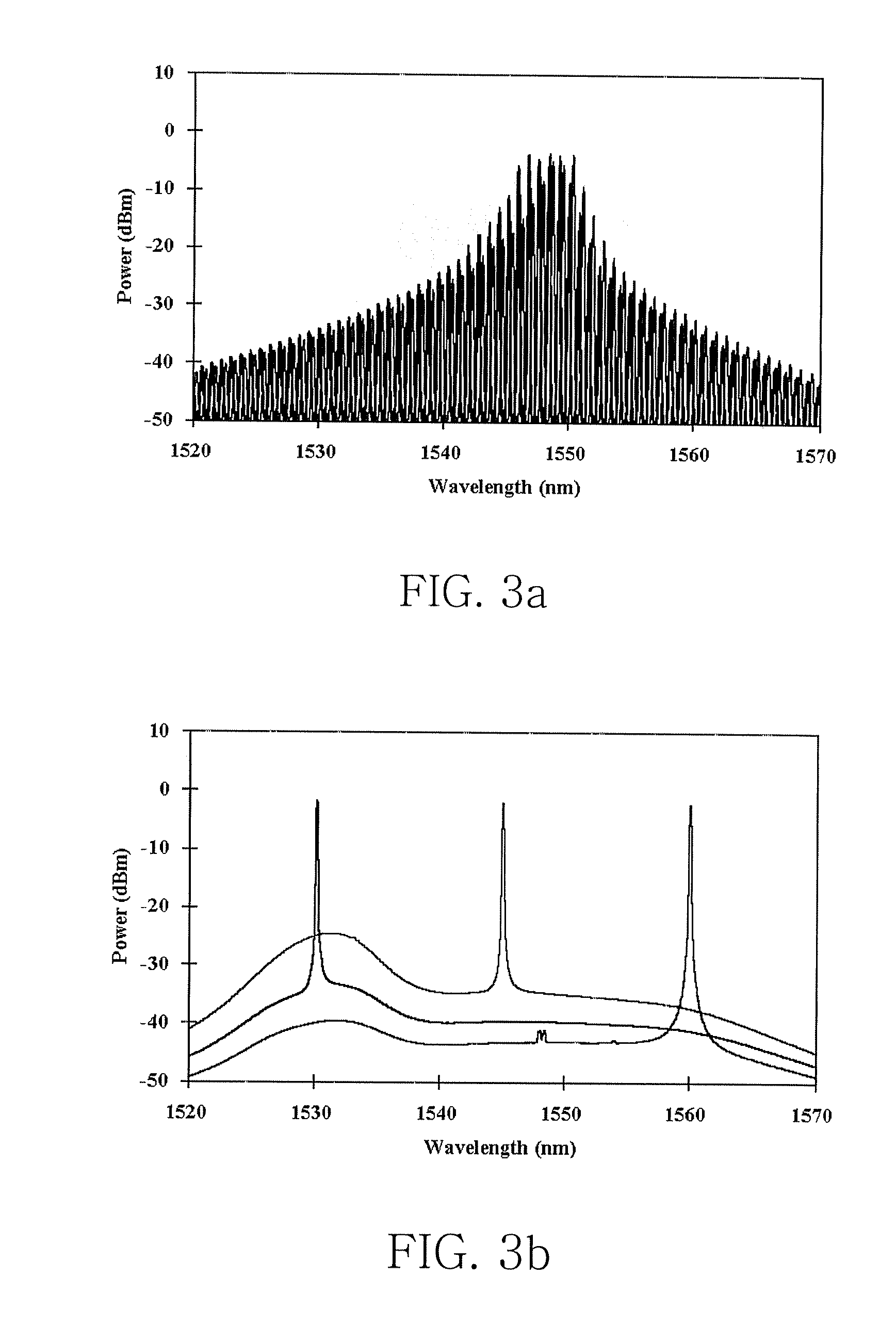
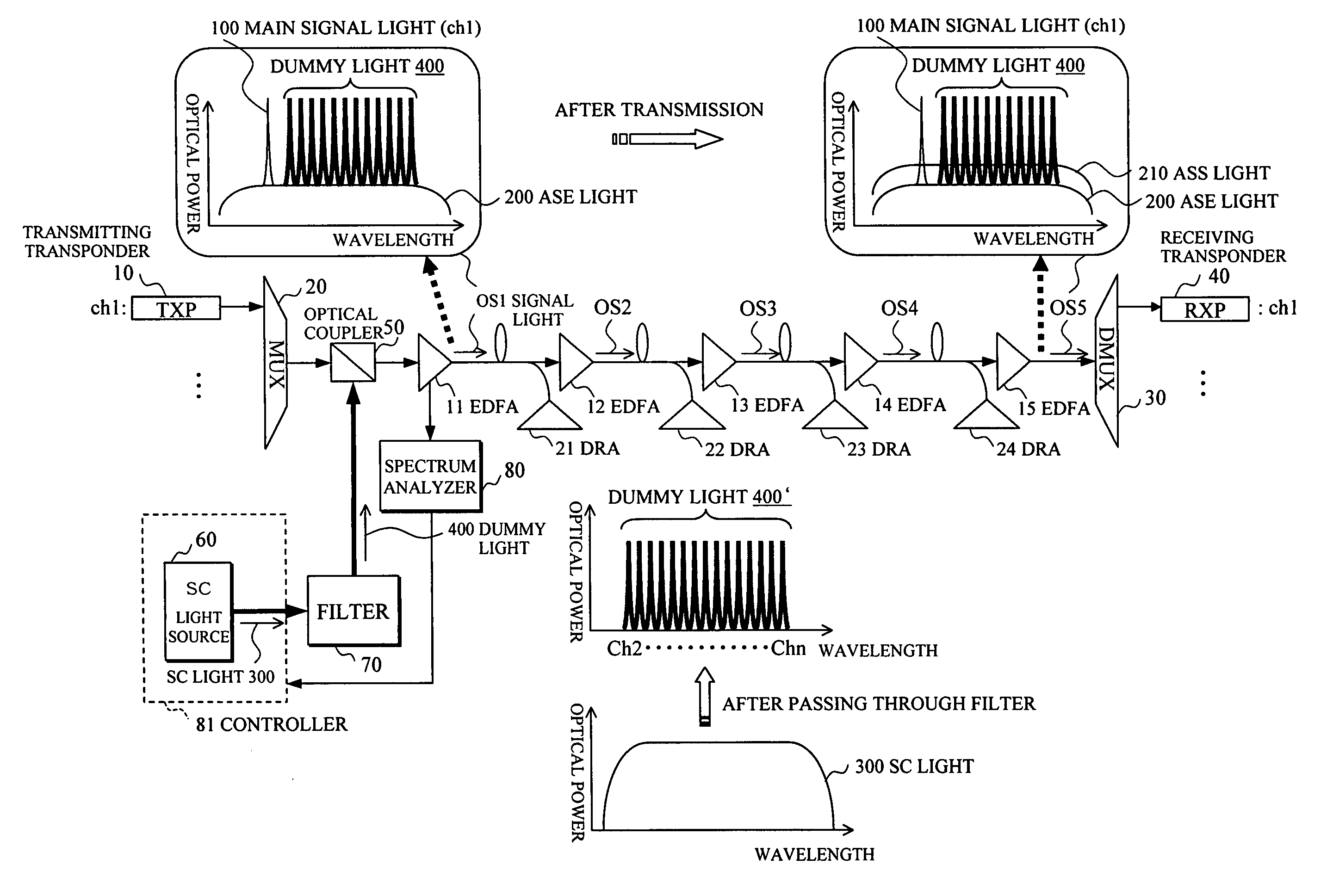
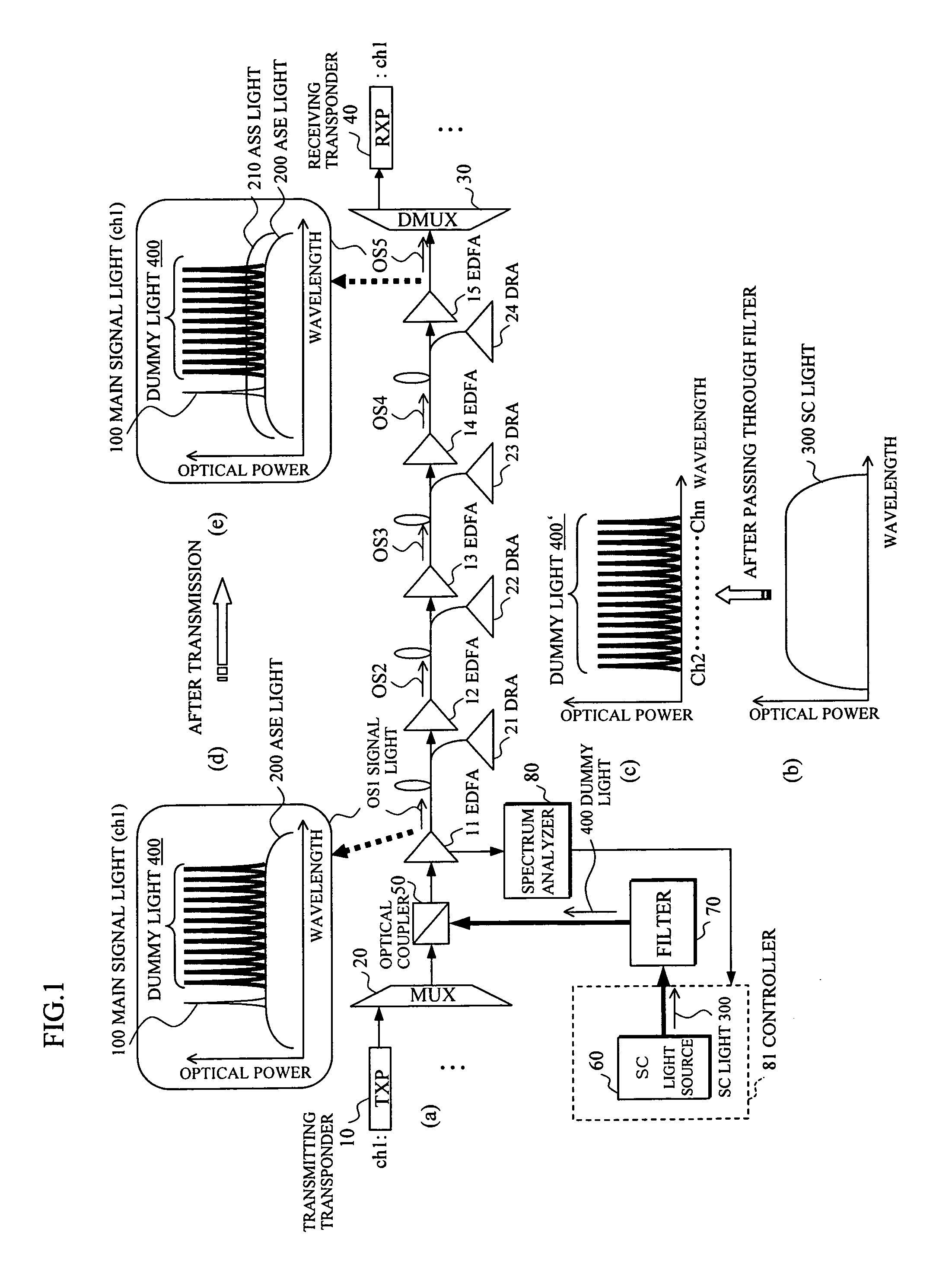
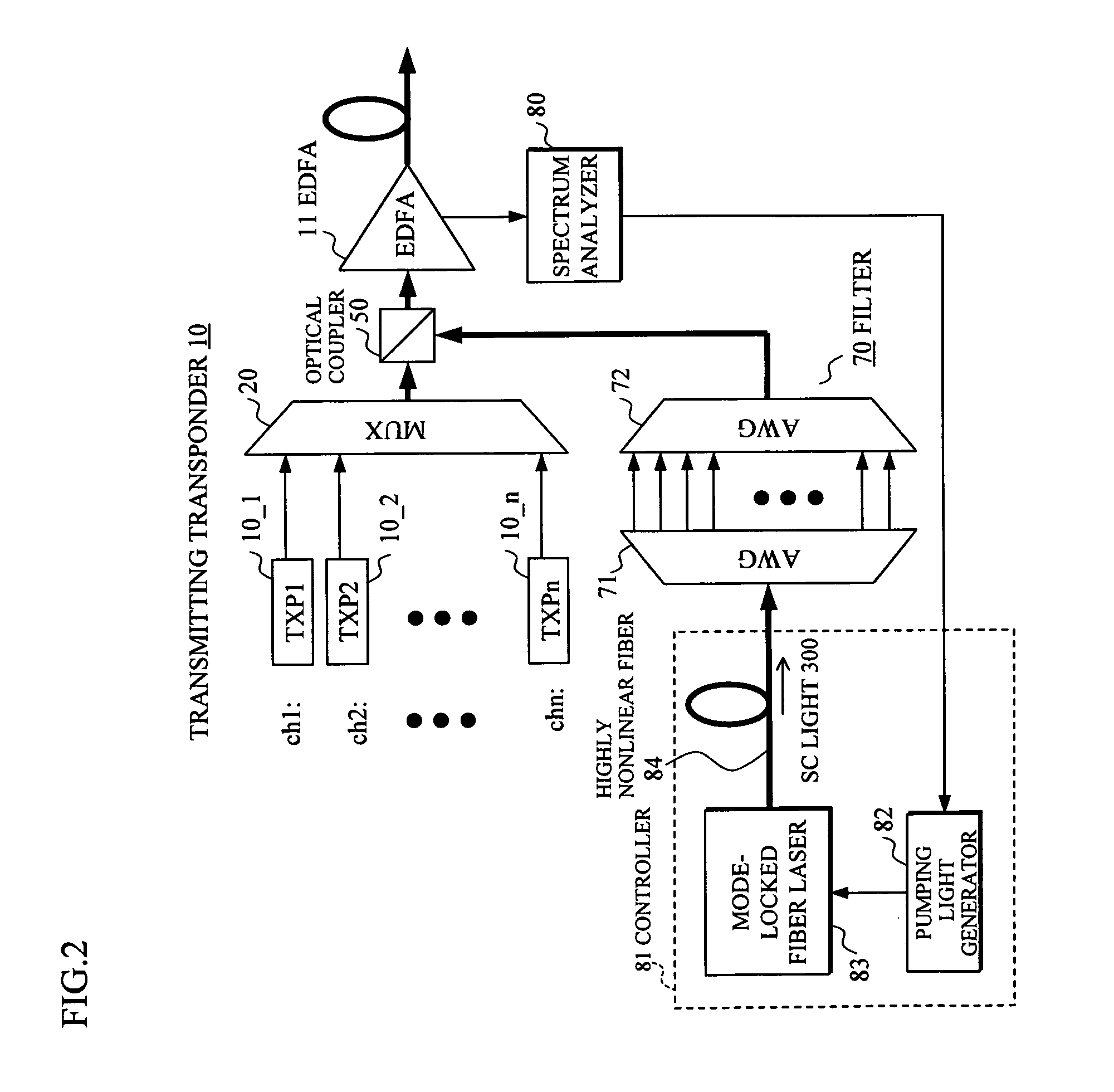
In an optical transmission apparatus, a number of wavelengths of an output light to an optical transmission line and an optical power of each of the wavelengths are detected by a spectrum analyzer, and a power of a super continuum light outputted to a highly nonlinear fiber is controlled by a controller so as to confine the number of wavelengths and the optical power within predetermined ranges. A wavelength component corresponding to a signal light is removed by a filter from the output light from the highly nonlinear fiber, and an output light of the filter and the signal light is coupled by an optical coupler.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Liquid crystal device and projector
ActiveUS20070182874A1Improve display qualitySuppression ratioStatic indicating devicesColor television detailsComputer scienceTransmitted light
Provided is a liquid crystal device including: a plurality of data Lines and a plurality of scanning lines which cross each other; switching elements which are provided in correspondence with intersections between the data lines and the scanning lines; pixel electrodes connected to the switching elements; pixels configured in correspondence with the pixel electrodes; an image display region configured by the plurality of pixels; a first substrate having at least the switching elements; a second substrate which faces the first substrate; and liquid crystal interposed between the first substrate and the second substrate, wherein light incident from the first substrate is modulated by the liquid crystal, a light-shielding film is provided on a light incident side of at least the switching elements of the first substrate, and at least a portion corresponding to the image display region of the second substrate includes only a transparent layer which transmits light incident to the liquid crystal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
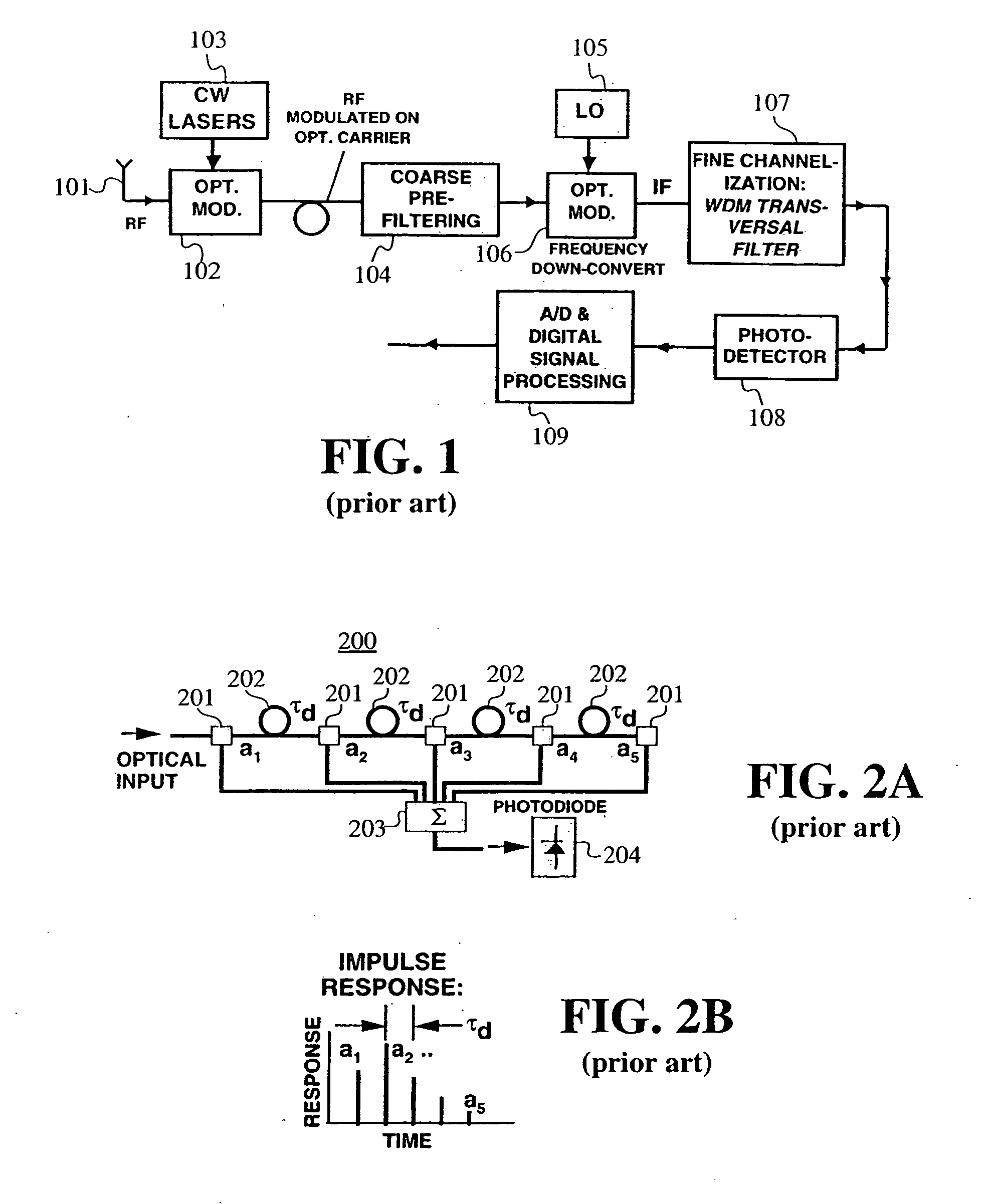
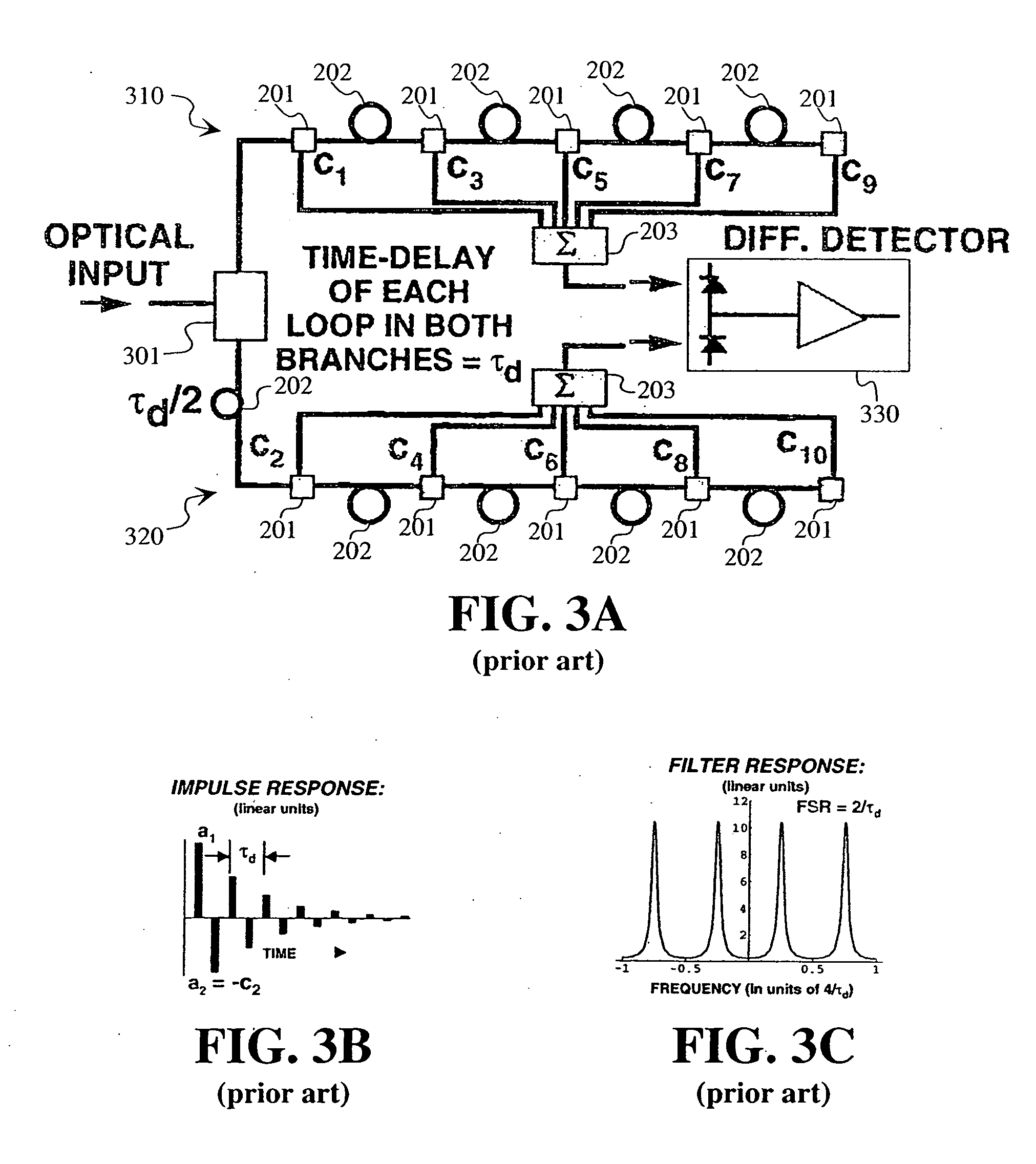
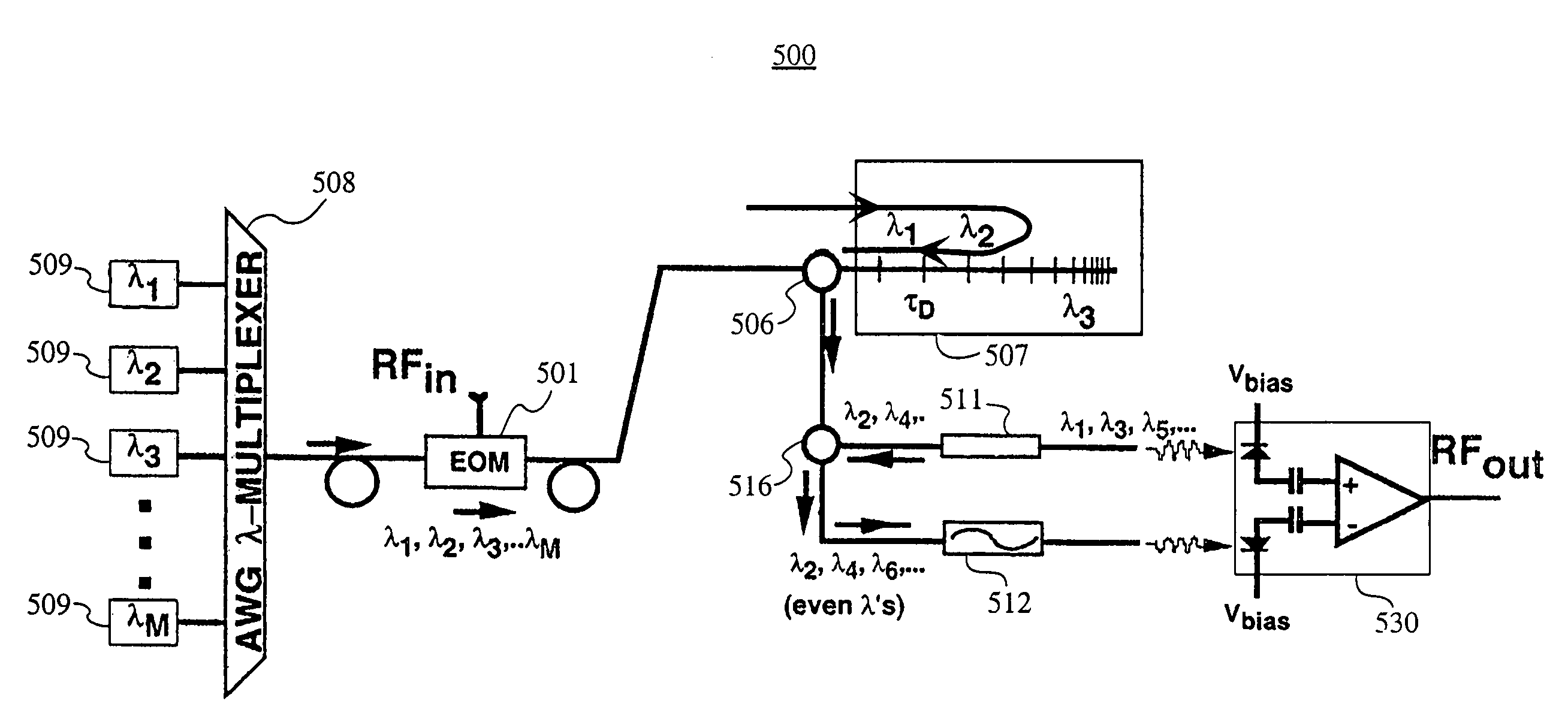
Bipolar RF-photonic transversal filter with dynamically reconfigurable passbands
ActiveUS20050094928A1Suppression ratioAgile bandpass synthesis and reconfigurabilityCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionGratingIntermediate frequency
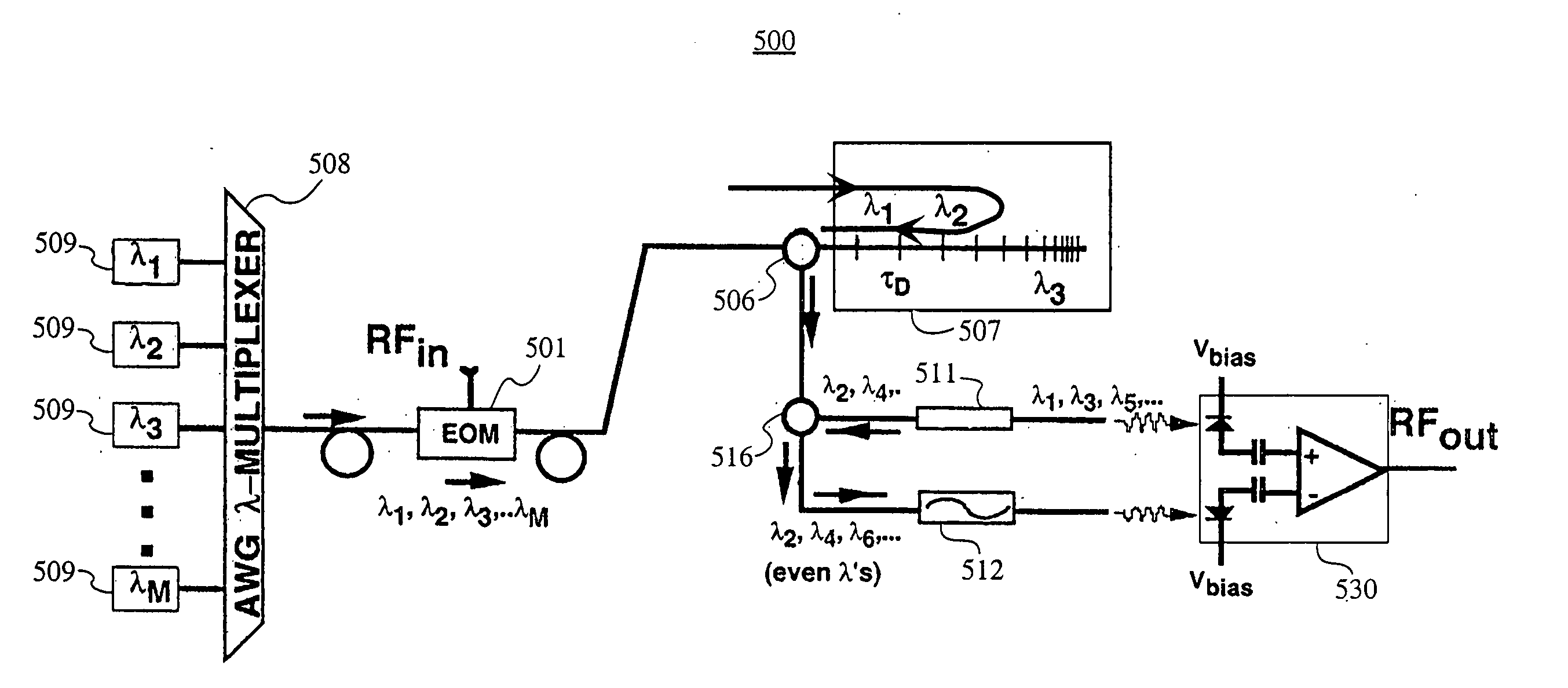
An architecture that enables one to realize a FIR transversal filter with apodized, interlaced bipolar tap coefficients (an). The tap coefficients, an, are varied via the control of the optical powers emitted by an array of WDM laser sources. Also, a filter architecture where tap coefficients can be agilely reconfigured in both polarity and magnitude. One chirped fiber-grating may be used to implement a series of wavelength-dependent tap-weights. The filter designs can be utilized to eliminate the low-pass response centered at DC, allowing one to place the center frequency (fc)1 of the first passband at a targeted intermediate frequency (IF).
Owner:HRL LAB
Methods and materials for stabilizing analyte sensors
ActiveUS20080027287A1Reduce noiseImprove sensor performanceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringChemical reactionAnalyte
The disclosure provides a sensor including a sensor having an external surface and a cannula. The cannula comprises a substantially cylindrical wall encircling a lumen, at least one aperture and a distal end. The sensor is positioned within the lumen and the distal end of the cannula extends beyond the sensor. This configuration functions for example to stabilize chemical reactions associated with the sensor by creating a buffer zone between the sensor and the surrounding tissues at the site of implantation. In certain embodiments, the sensor can further comprise an accessory material in proximity to the external surface, wherein the accessory material modifies the biological response of a tissue that is in contact with the sensor. The sensor can also comprise anchors that keeps the sensor in contact with subcutaneous tissue of a subject upon insertion of the sensor into the body of the subject.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Magnetoresistive effect element and magnetic memory device
ActiveUS7034348B2Heat-resisting temperature can be improvedImproved heat resistance propertyTransistorNanomagnetismMagnetoresistanceNuclear magnetic resonance
A magnetoresistive effect element may be given satisfactory magnetic characteristics because a deterioration of a magnetoresistive changing rate by annealing can be suppressed and a magnetic memory device includes this magnetoresistive effect element to provide excellent write characteristics. A magnetoresistive effect element has a pair of ferromagnetic layers (magnetization fixed layer 5 and magnetization free layer 7) opposed to each other through an intermediate layer 6 to cause an electric current to flow in the direction perpendicular to the layer surface to obtain a magnetoresistive change. A magnetic memory device comprises the magnetoresistive effect element 1 in which at least one of the pair of ferromagnetic layers 5, 7 contains an amorphous ferromagnetic material whose crystallization temperature is higher than 623 K and bit lines and word lines sandwiching this magnetoresistive effect element and the magnetoresistive effect element in the thickness direction.
Owner:SONY CORP
External cavity widely tunable laser using a silicon resonator and micromechanically adjustable coupling
InactiveUS8908723B2Widely tunableEasy to manufactureLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionCouplingLength wave
A widely tunable laser is described where a compound semiconductor gain chip is coupled to a waveguide filter fabricated on silicon. The filter has two resonators with different free-spectral-ranges, such that Vernier tuning between the filters can be used to provide a single wavelength of light feedback into the gain chip, where the wavelength is adjustable over a wide range. The coupling between the gain chip and the filter is realized through a microlens whose position can be adjusted using micromechanics and locked in place.
Owner:T&S COMM
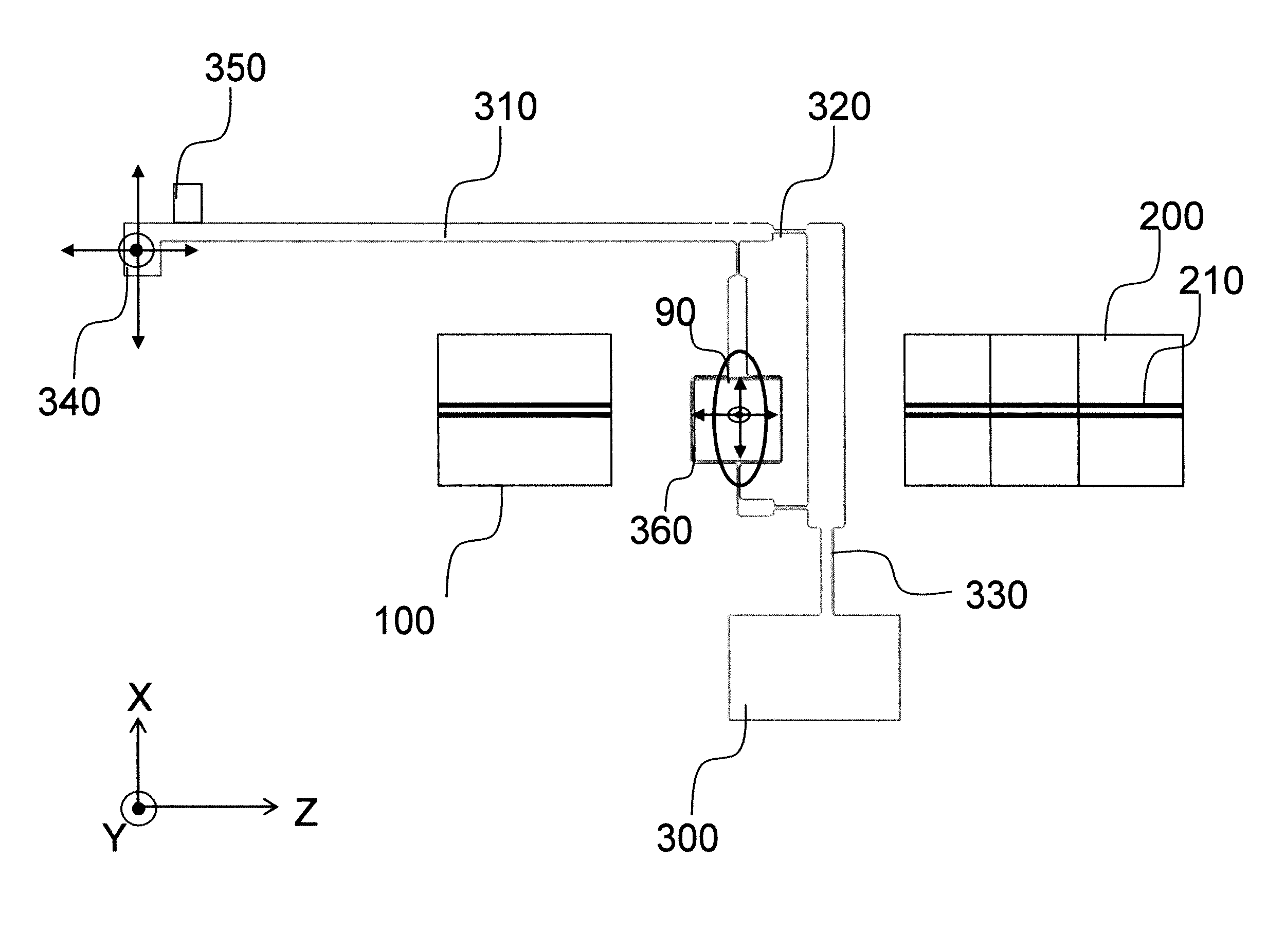
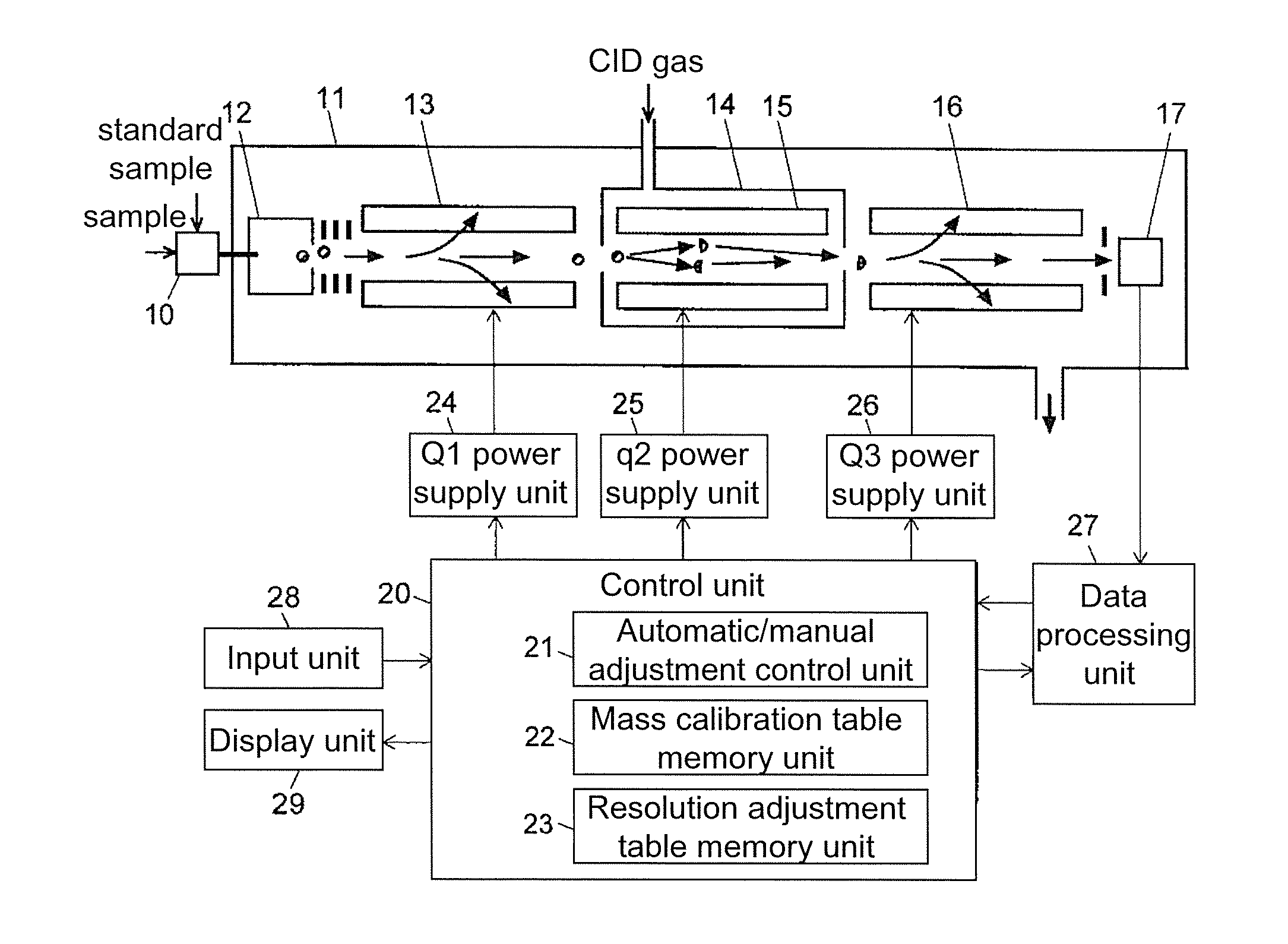
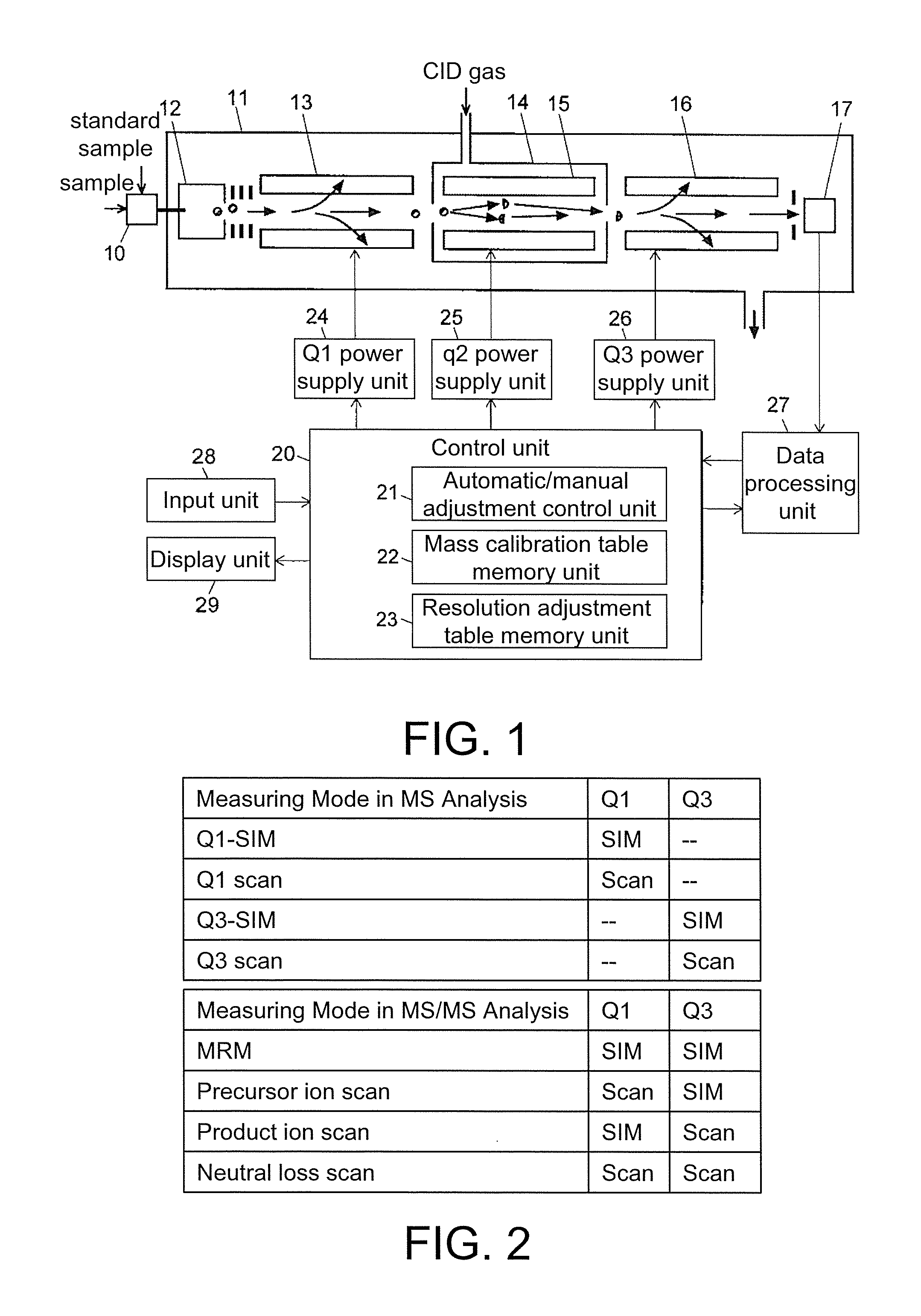
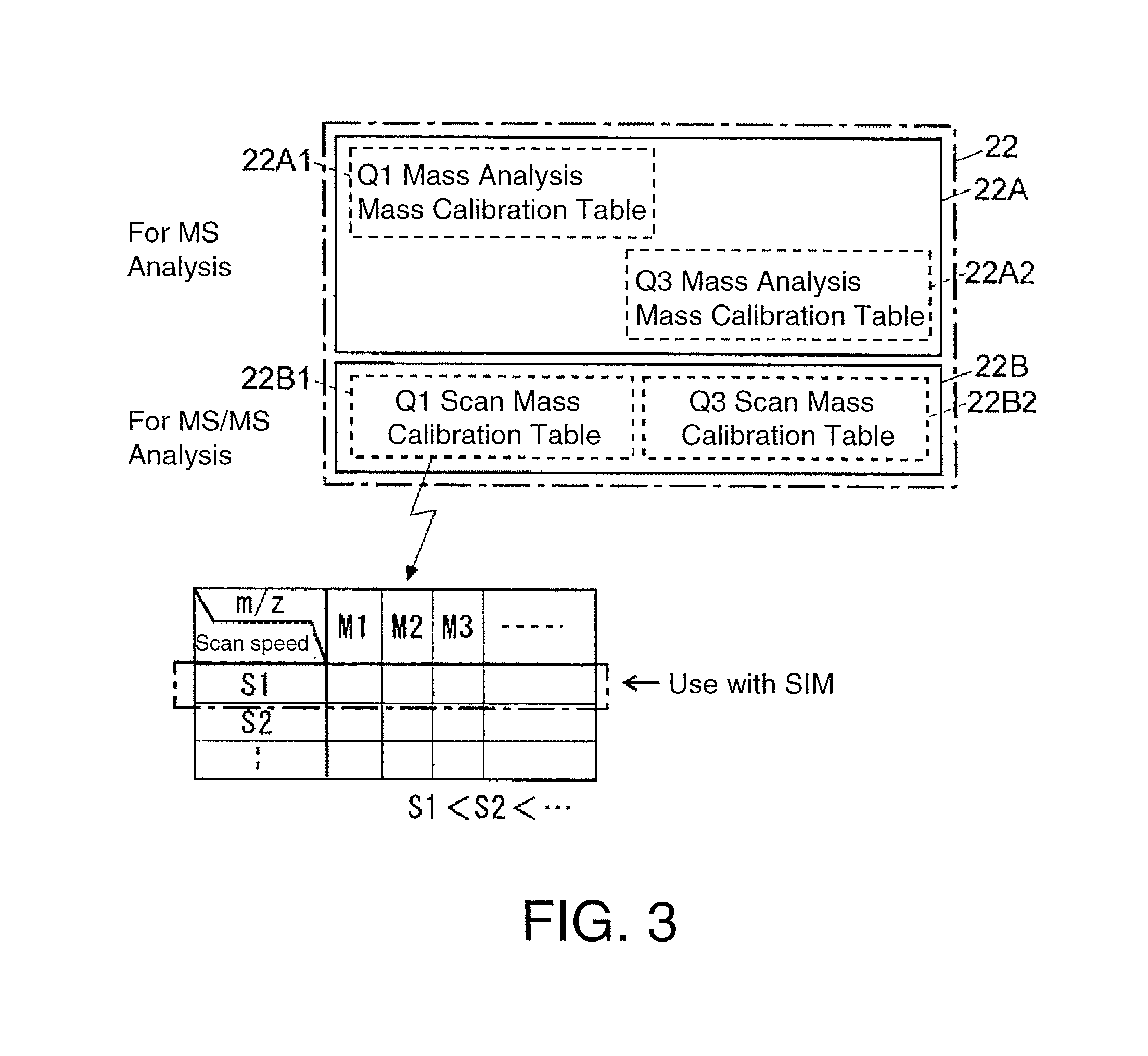
Triple quadrupole mass spectrometer
ActiveUS20130334415A1High quality and precisionHigh precisionStability-of-path spectrometersIsotope separationAtomic physics
A high-quality mass spectrum is provided with alleviated mass / charge axis deviation in a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer even when executing a high-speed mass scan with MS / MS analysis. Mass calibration tables which denote relations between m / z and a mass deviation value which scan speed is a parameter are prepared separately for use in MS analyses without involving dissociation operations and MS / MS analyses with involving dissociation operations. According to a measuring mode, such as a product ion scan measurement or a neutral loss scan measurement, when performing MS / MS analysis, a mass deviation value for the minimum scan speed in a table is used for a quadrupole where the selected m / z is fixed, and a mass deviation value for a designated scan speed in a table is used for a quadrupole where the mass scan is performed, thus controlling the operations of each of a pre-stage and a post-stage quadrupoles.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
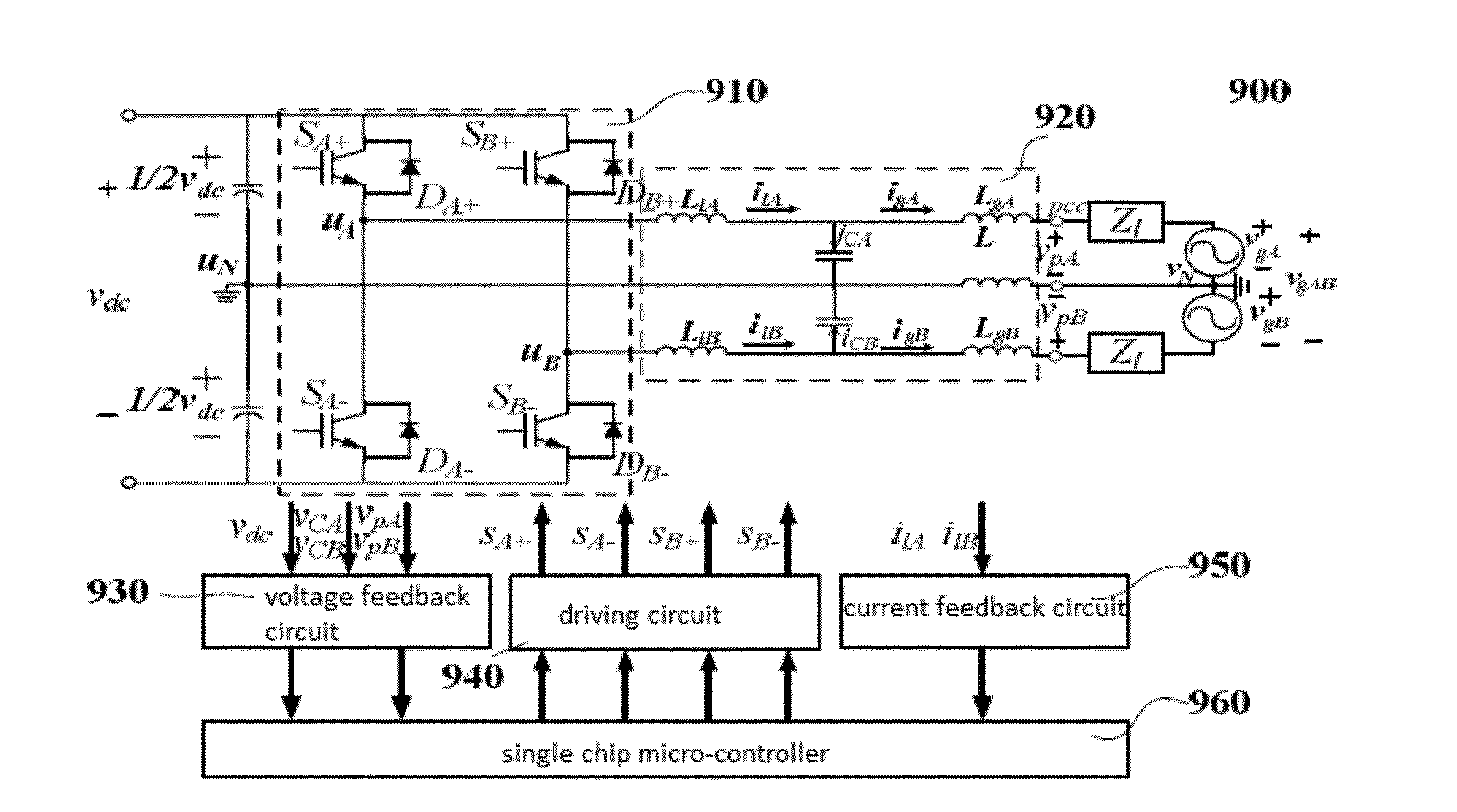
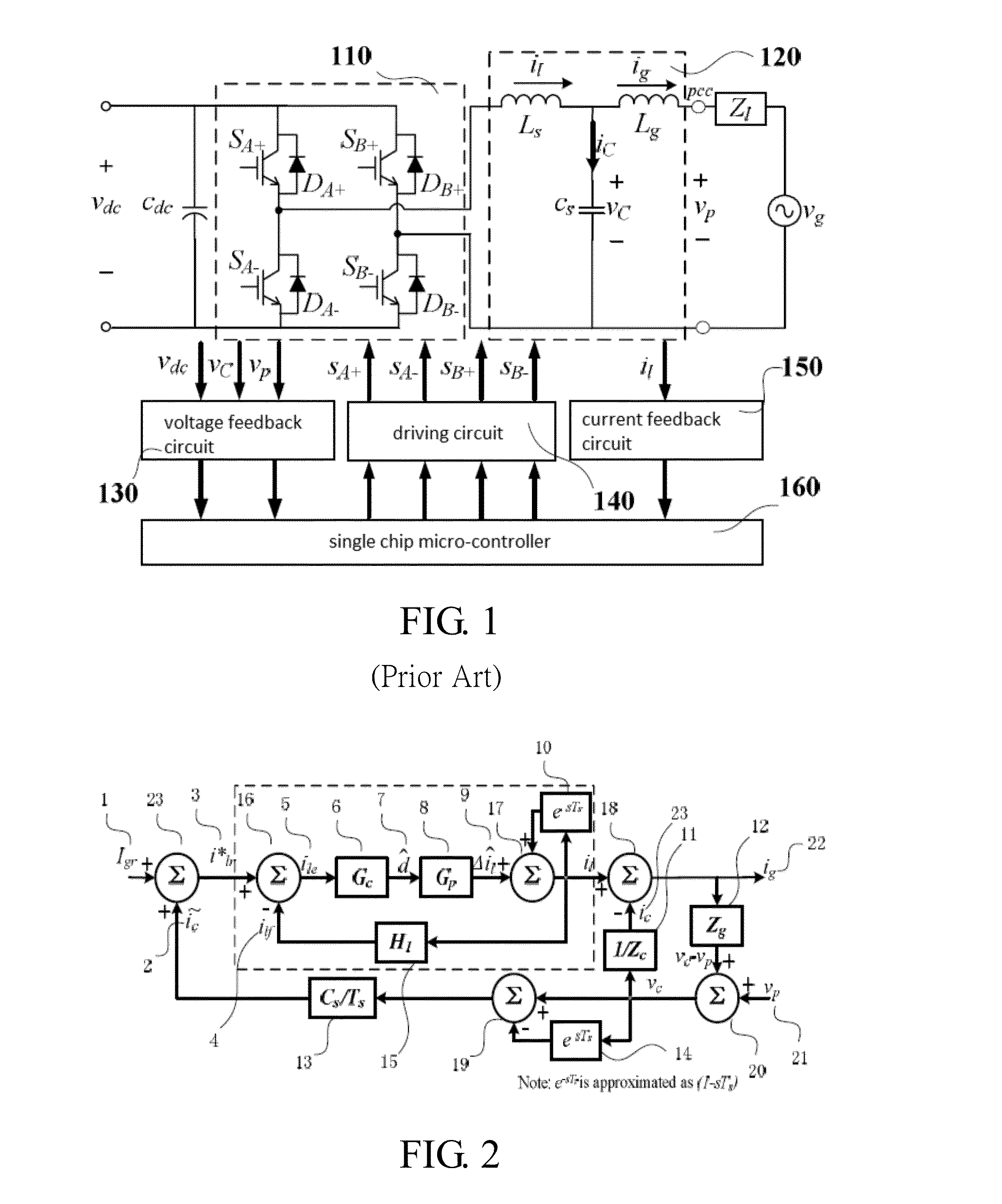
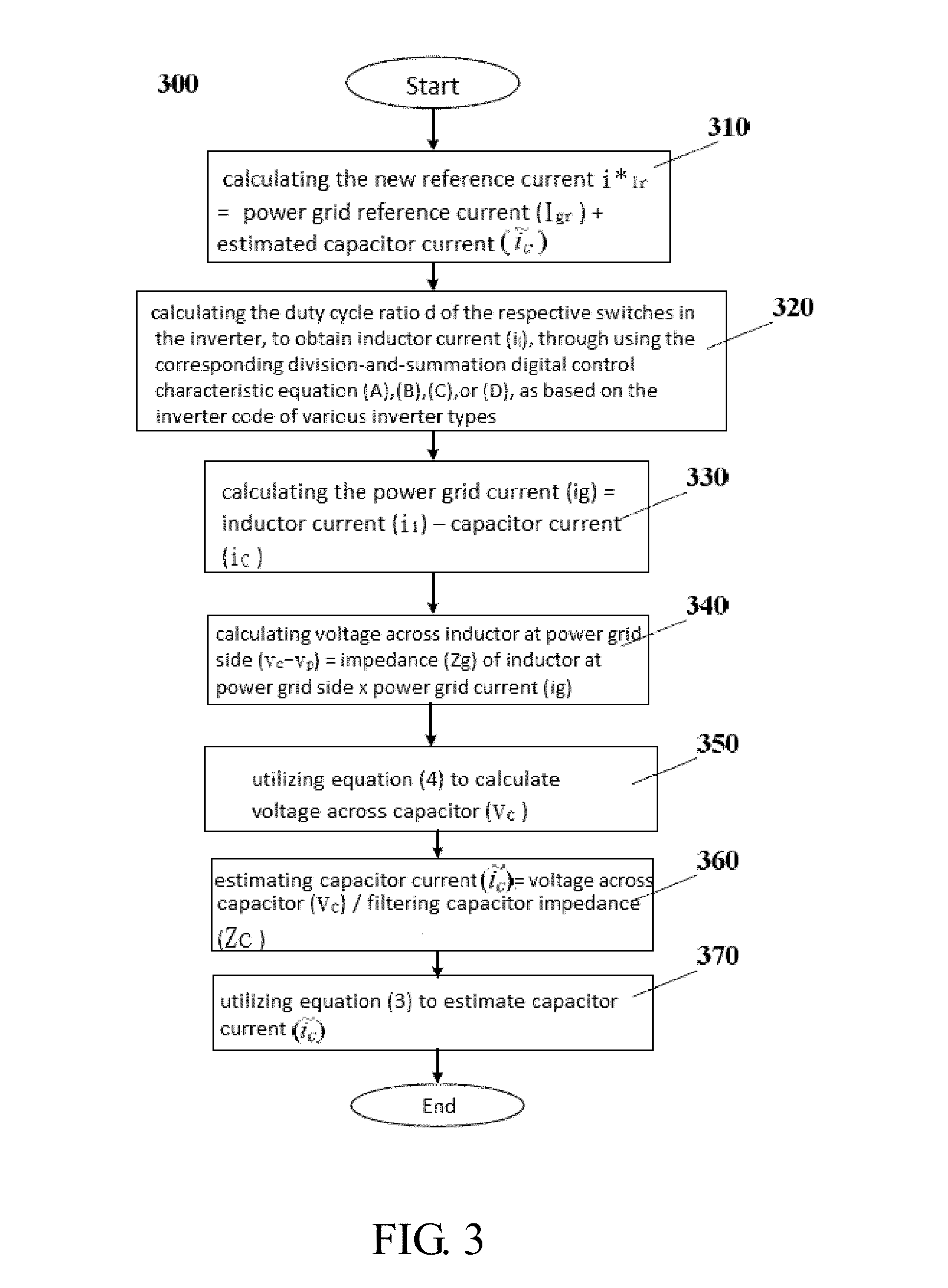
Lcl capacitor current compensation and control method based on division and summation technique
InactiveUS20160065049A1Suppress and eliminate harmonicHarmonic suppressionResistance/reactance/impedenceAc-dc conversionCapacitanceReference current
An LCL capacitor current compensation and control method based on division and summation technique, comprising following steps: calculating new reference current i*lr=power grid reference current (Igr)+estimated capacitor current (); calculating duty cycle ratio d of respective switches in inverter to obtain inductor current (il), through using corresponding division-and-summation digital control characteristic equation (A), (B), (C), or (D), as based on inverter code of various inverter types; calculating power grid current (ig)=inductor current (il)−capacitor current (ic); calculating voltage across inductor at power grid side (vc−vp)=impedance (Zg) of said inductor at power grid side x power grid current (ig); utilizing equation (4) to calculate voltage across capacitor (vc); estimating capacitor current ()=voltage across said capacitor (vc) / filtering capacitor impedance (Zc); and utilizing equation (3) to estimate capacitor current ().
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
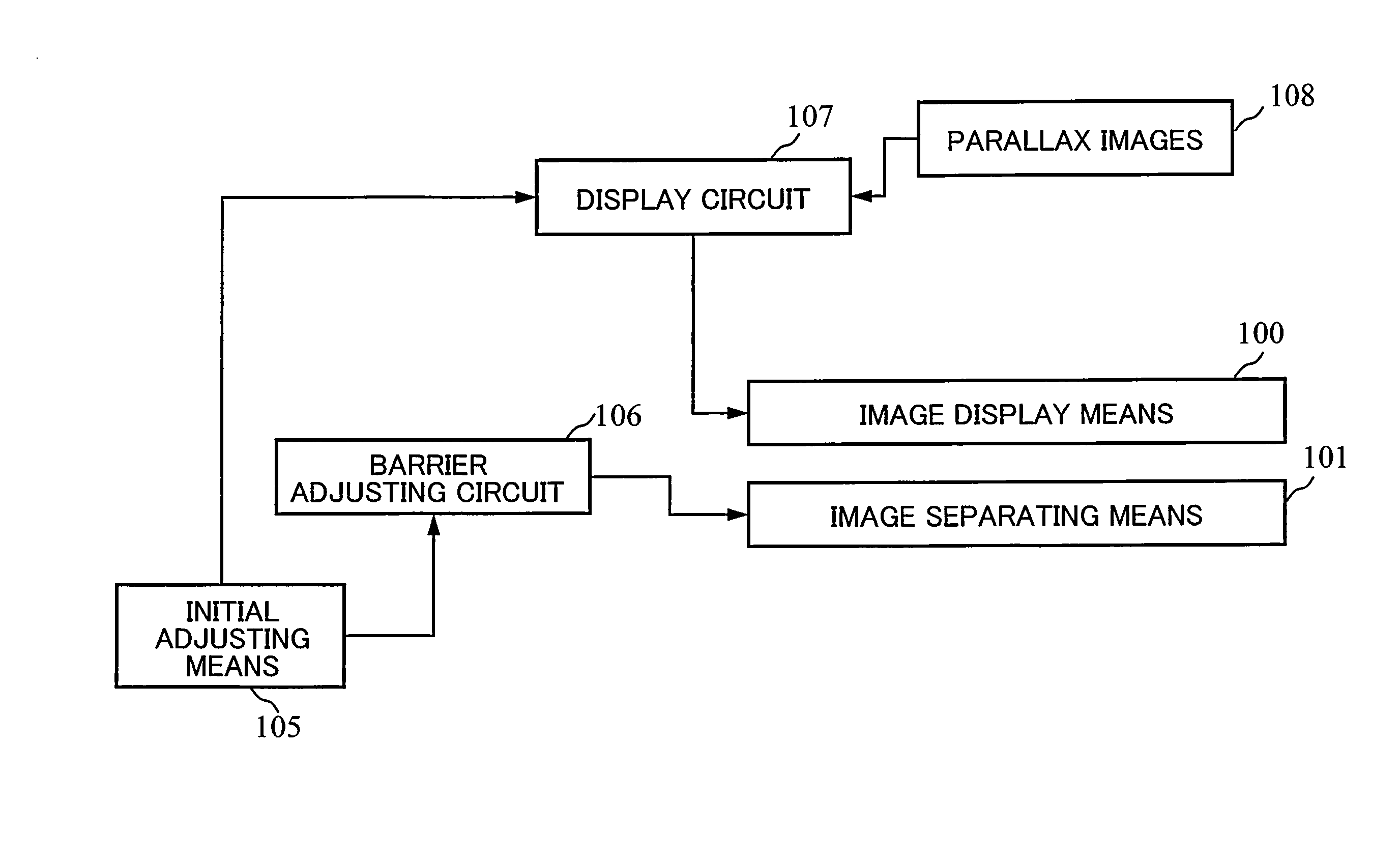
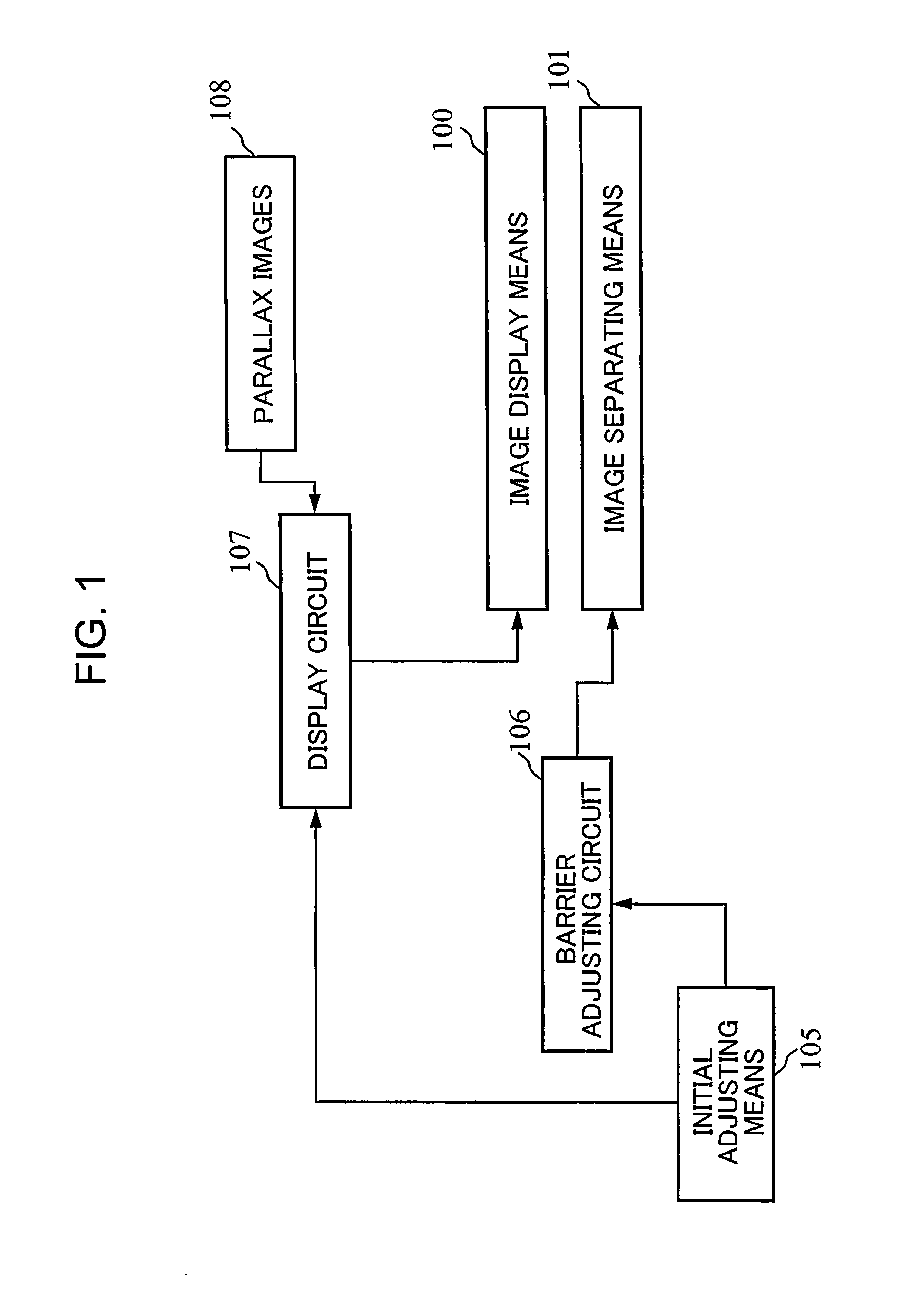
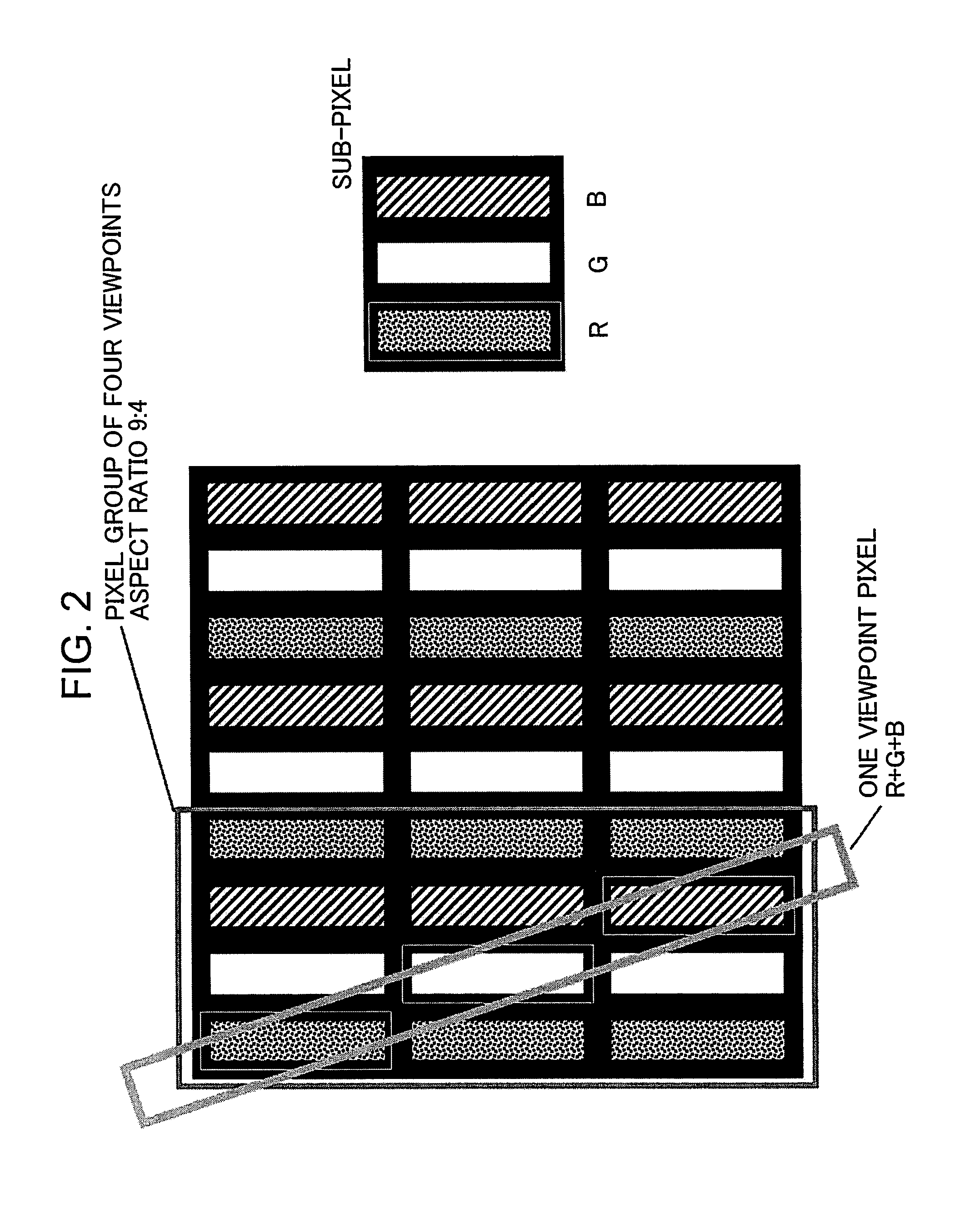
Image display device
InactiveUS20140009463A1Improve crosstalkReduced viewing distanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsParallaxDisplay device
A parallax composite image displayed by image display means is separated by image separating means so that parallax images are observed at a predetermined position. Parallax images are alternately arranged for each of image rows in the parallax composite image. If the separating means has an inclination angle between 10 and 15 degrees and if a center of the separating means and a center of a pixel exist at a predetermined interval, crosstalk may be suppressed and a proper viewing distance may be shortened. By providing the image separating means with a notched structure of which aperture width periodically varies, adding irregularities to an aperture edge, and controlling an amount of blur of pixels observed through the aperture or alike, moiré reduction may be achieved.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Semiconductor DBR Laser
ActiveUS20150288140A1Shorten the lengthReduce back reflectionLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingWaveguide
A semiconductor distributed Bragg reflector laser configured for single longitudinal mode operation, having an optical waveguide comprising an optical gain section, a first reflector being a first distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) section comprising a grating configured to produce a reflection spectrum having one or more first reflective peaks, and a second reflector, wherein the first DBR section is configured to compensate for thermal chirp that is induced inhomogeneously along the length of the DBR section, in use.
Owner:LUMENTUM TECH UK LTD
Liquid crystal device and projector
InactiveUS8031300B2Suppression ratioIncrease brightnessStatic indicating devicesColor television detailsComputer scienceTransmitted light
Provided is a liquid crystal device including: a plurality of data lines and a plurality of scanning lines which cross each other; switching elements which are provided in correspondence with intersections between the data lines and the scanning lines; pixel electrodes connected to the switching elements; pixels configured in correspondence with the pixel electrodes; an image display region configured by the plurality of pixels; a first substrate having at least the switching elements; a second substrate which faces the first substrate; and liquid crystal interposed between the first substrate and the second substrate, wherein light incident from the first substrate is modulated by the liquid crystal, a light-shielding film is provided on a light incident side of at least the switching elements of the first substrate, and at least a portion corresponding to the image display region of the second substrate includes only a transparent layer which transmits light incident to the liquid crystal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Active matrix substrate where a portion of the storage capacitor wiring or the scanning signal line overlaps with the drain lead-out wiring connected to the drain electrode of a thin film transistor and display device having such an active matrix substrate
InactiveUS7812893B2Improve yieldIncrease the aperture ratioNon-linear opticsSemiconductor devicesActive matrixDisplay device
An active matrix substrate suppresses reduction in production yield and increase in production steps and simultaneously permits both sufficient securing of a storage capacity and improvement of an aperture ratio of a pixel. The active matrix substrate is an active matrix substrate and includes a thin film transistor disposed at an intersection of a scanning signal line with a data signal line on a substrate, the thin film transistor including a gate electrode connected to the scanning signal line, a source electrode connected to the data signal line, and a drain electrode connected to a drain lead-out wiring; a storage capacitor upper electrode connected to the drain lead-out wiring and a pixel electrode; and a storage capacitor wiring overlapping with the storage capacitor upper electrode through an insulating film, wherein the storage capacitor wiring has an extending portion overlapping with the drain lead-out wiring through the insulating film.
Owner:SHARP KK
Light branching optical waveguide
InactiveUS7840108B2Reduced branch lossSmall wavelength dependenceCoupling light guidesLength waveWaveguide
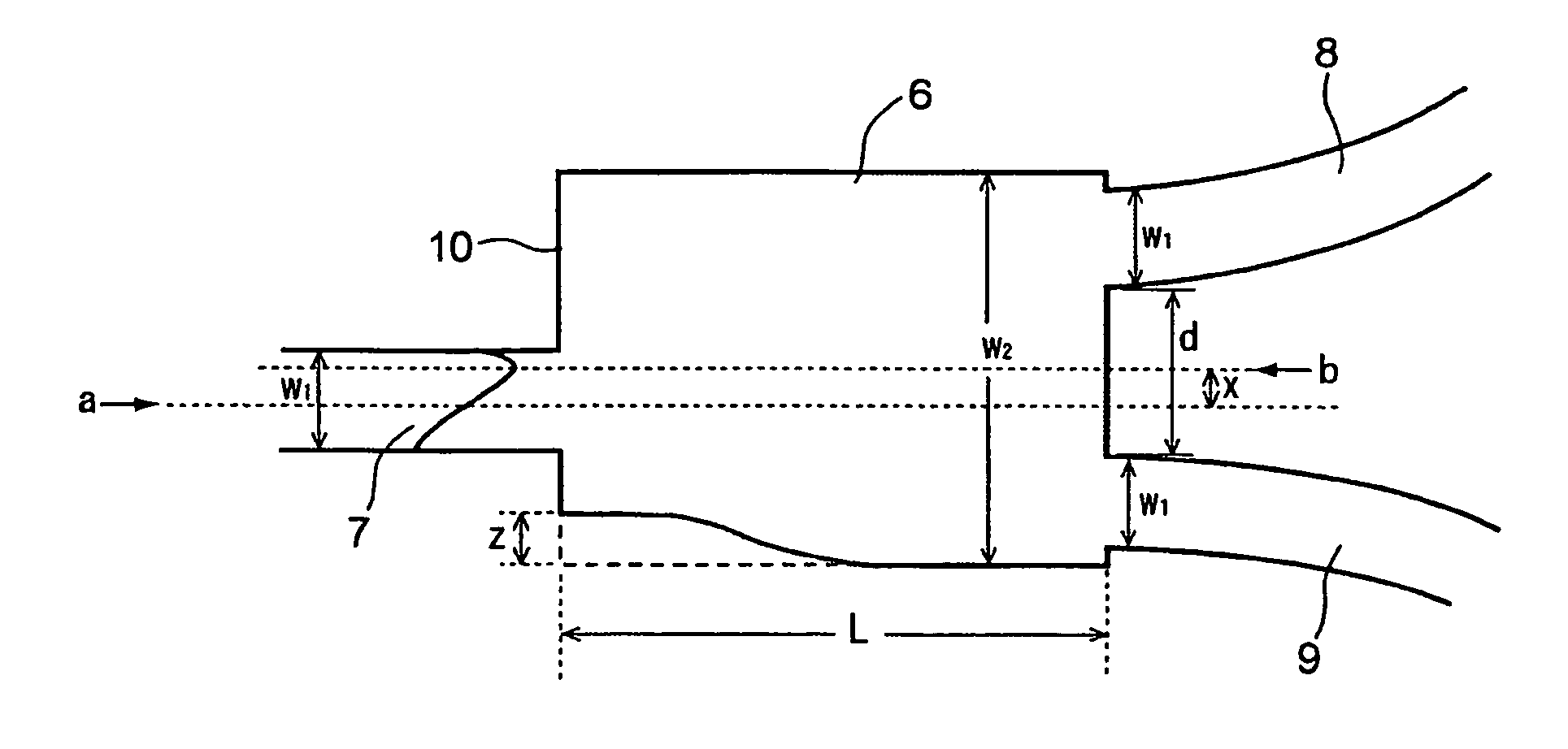
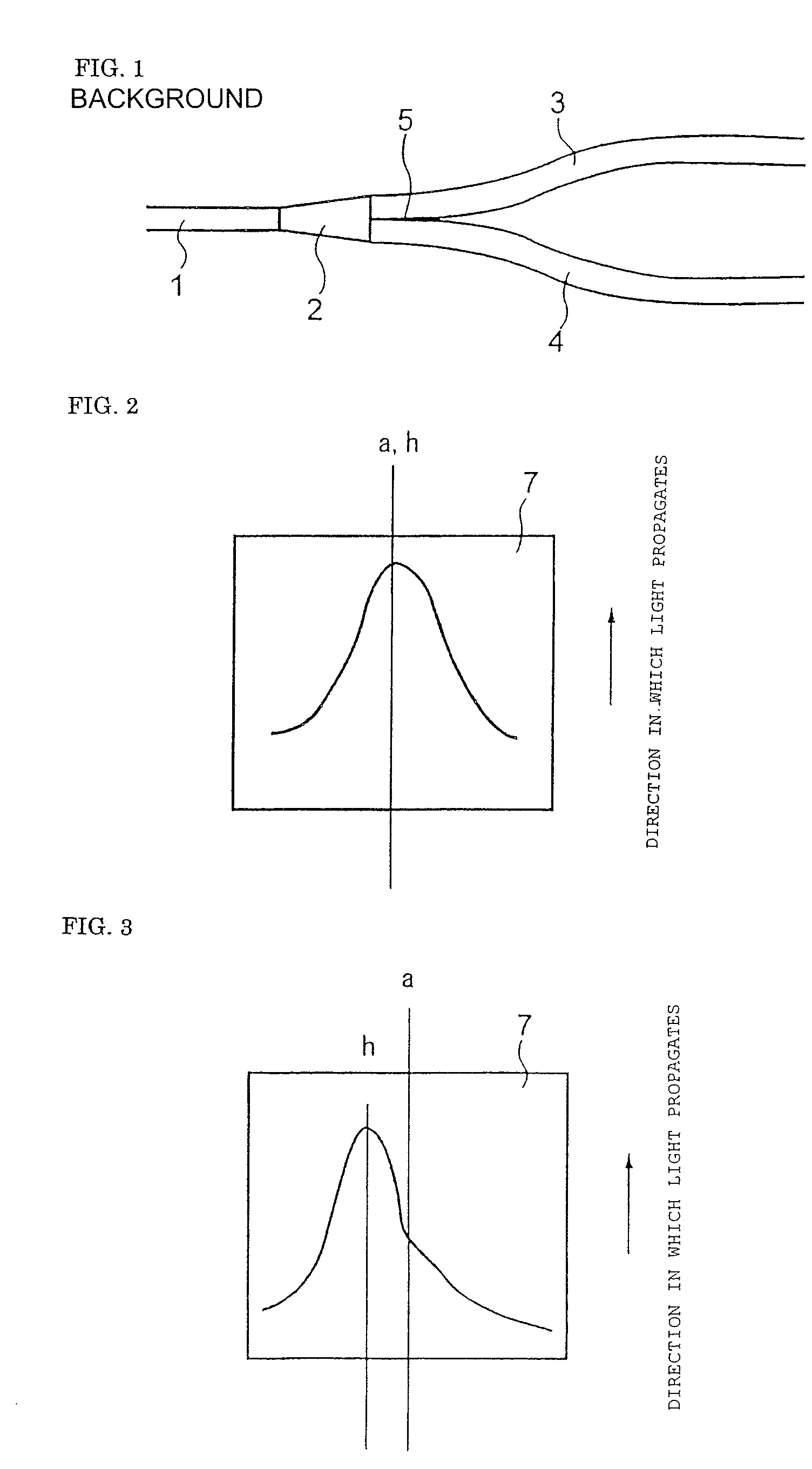
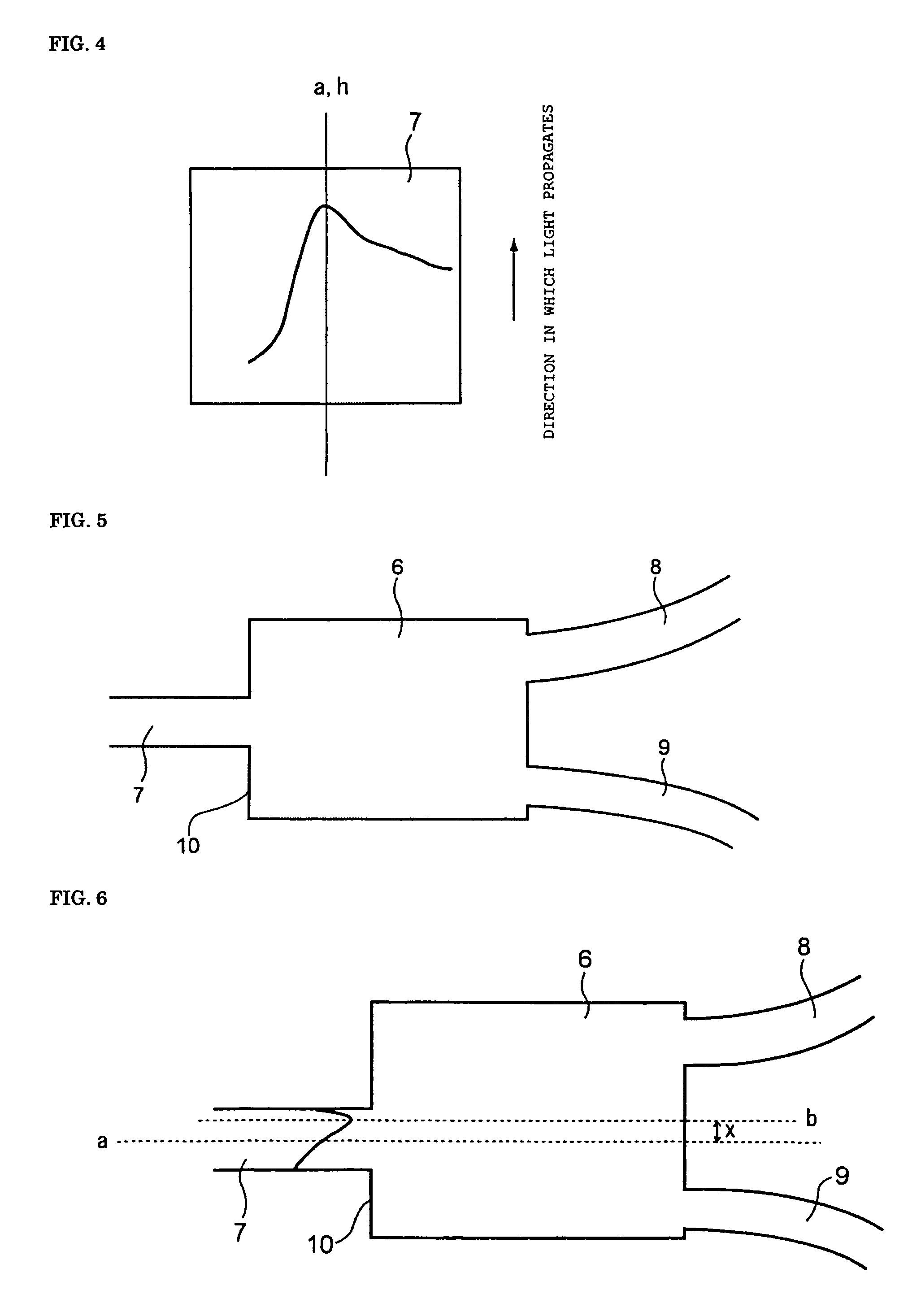
Provided is a light branching optical waveguide including: at least one incident light waveguide (A) optically connected to one end of a multi-mode optical waveguide; and output light waveguides (B) larger in number than the incident light waveguide (A) optically connected to the other end thereof, the light branching optical waveguide being characterized in that: an intensity distribution of light incident from at least one optical waveguide (a) out of the incident light waveguide (A) on the multi-mode optical waveguide at a connecting surface of the incident light waveguide (A) and the multi-mode optical waveguide is asymmetric with respect to a geometrical central axis of the optical waveguide (a); and an extended line of the geometrical center axis of the optical waveguide (a) does not coincide with a geometrical central axis of the multi-mode optical waveguide. Accordingly, it is possible to obtain a low-loss light branching optical waveguide having a reduced branch loss and a reduced variation in branching ratio, and further to obtain a light branching optical waveguide having small wavelength dependence as well as a reduced branch loss and a reduced variation in branching ratio.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Bipolar RF-photonic transversal filter with dynamically reconfigurable passbands
ActiveUS7269312B2Suppression ratioAgile bandpass synthesis and reconfigurabilityCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionGratingIntermediate frequency
An architecture that enables one to realize a FIR transversal filter with apodized, interlaced bipolar tap coefficients (an). The tap coefficients, an, are varied via the control of the optical powers emitted by an array of WDM laser sources. Also, a filter architecture where tap coefficients can be agilely reconfigured in both polarity and magnitude. One chirped fiber-grating may be used to implement a series of wavelength-dependent tap-weights. The filter designs can be utilized to eliminate the low-pass response centered at DC, allowing one to place the center frequency (fc)1 of the first passband at a targeted intermediate frequency (IF).
Owner:HRL LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com