Patents
Literature
347 results about "Radar beam" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
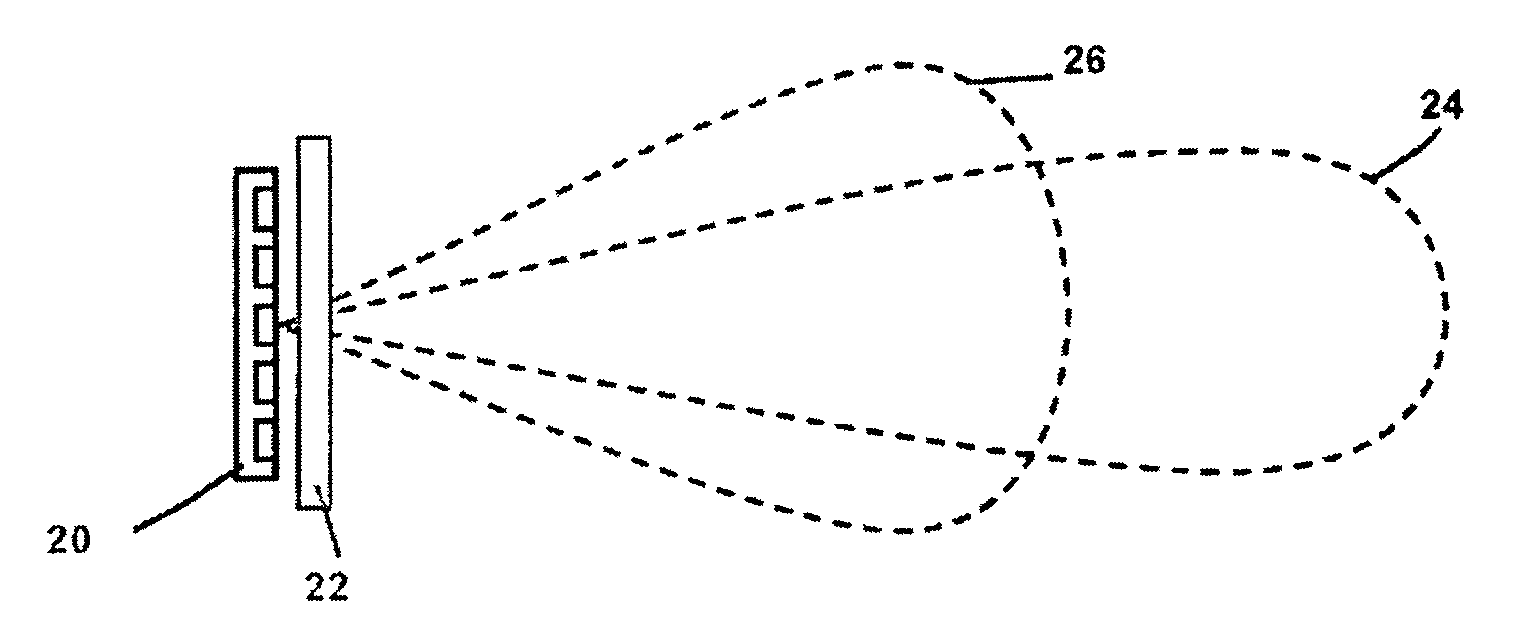
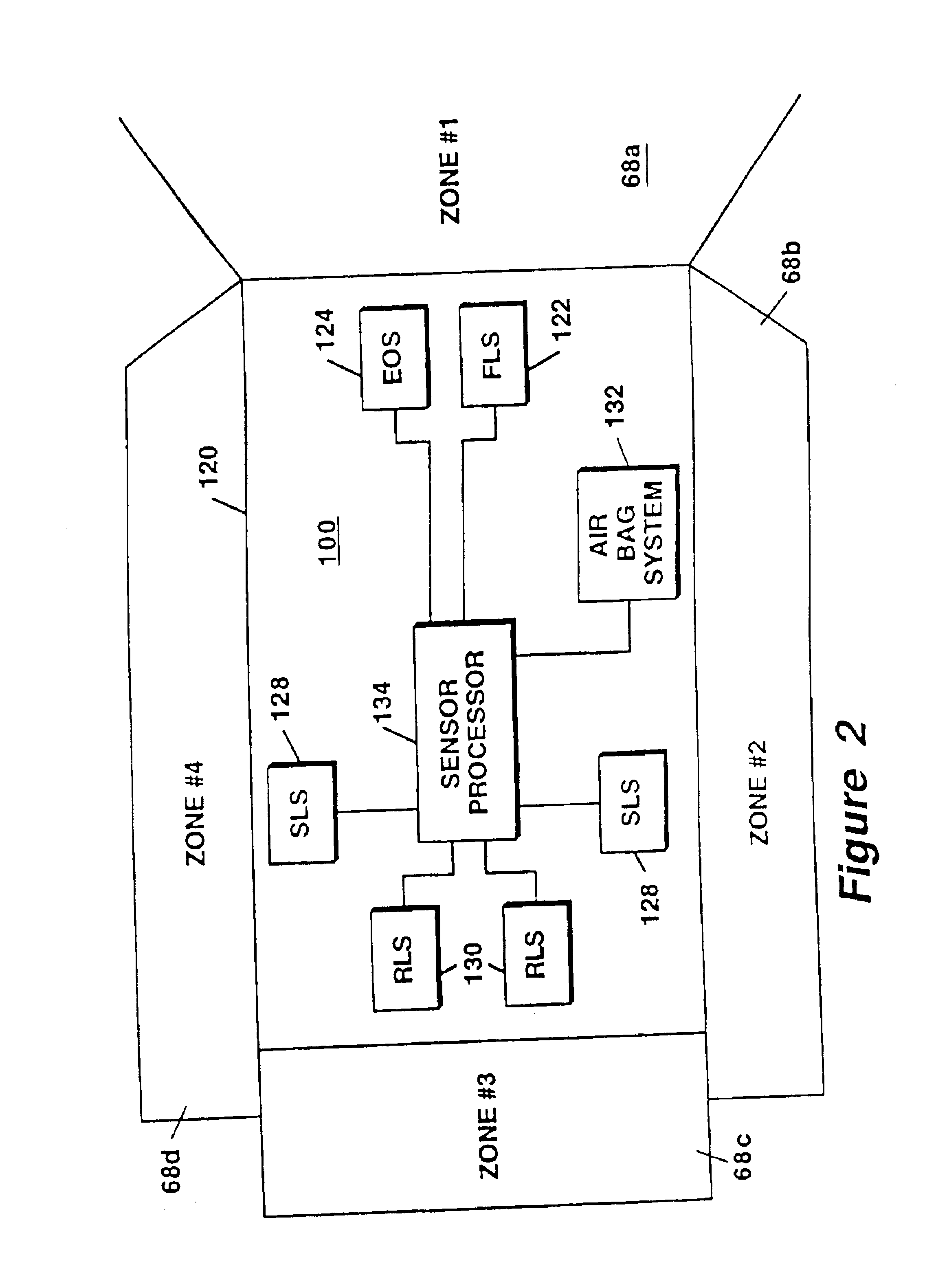
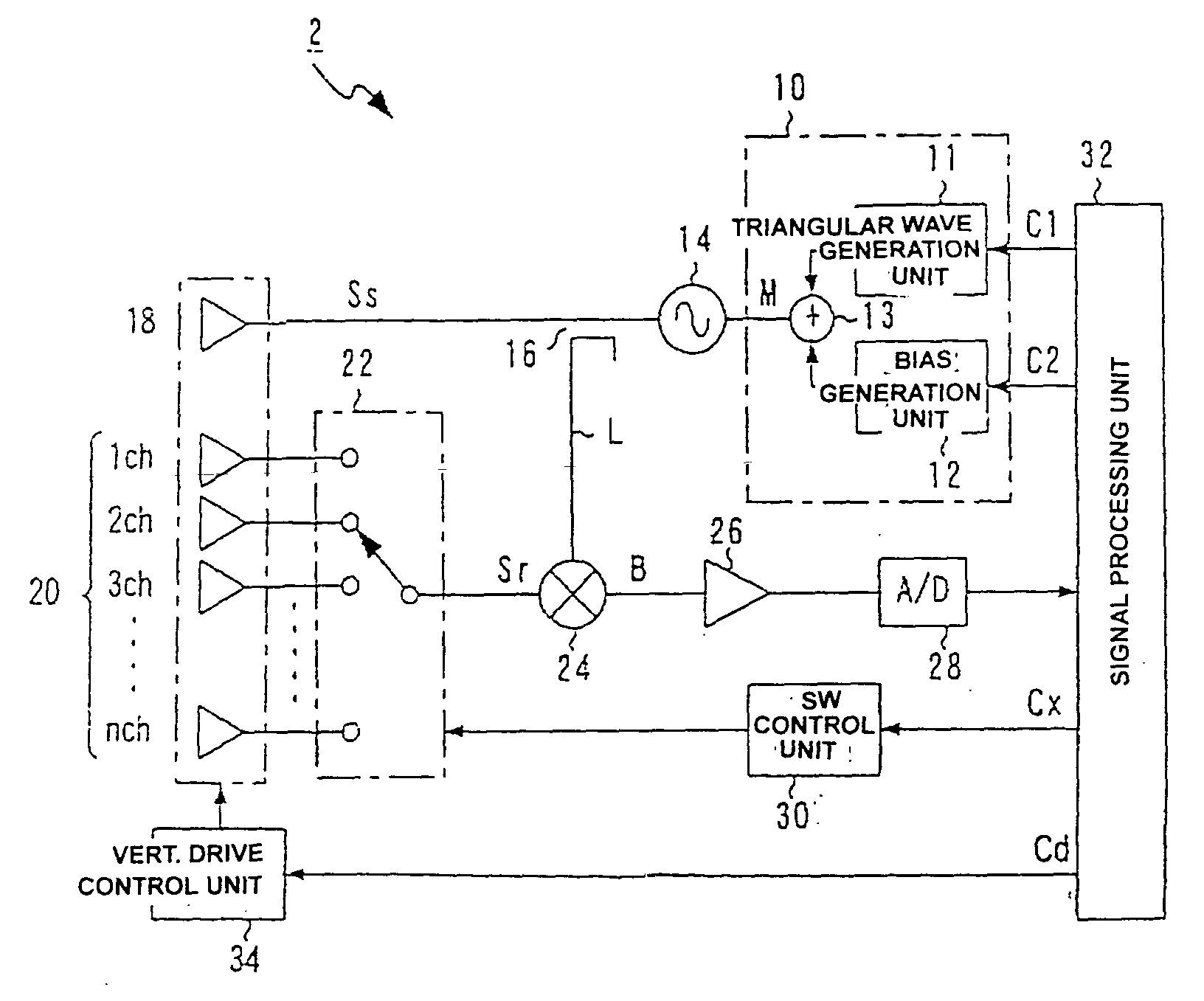
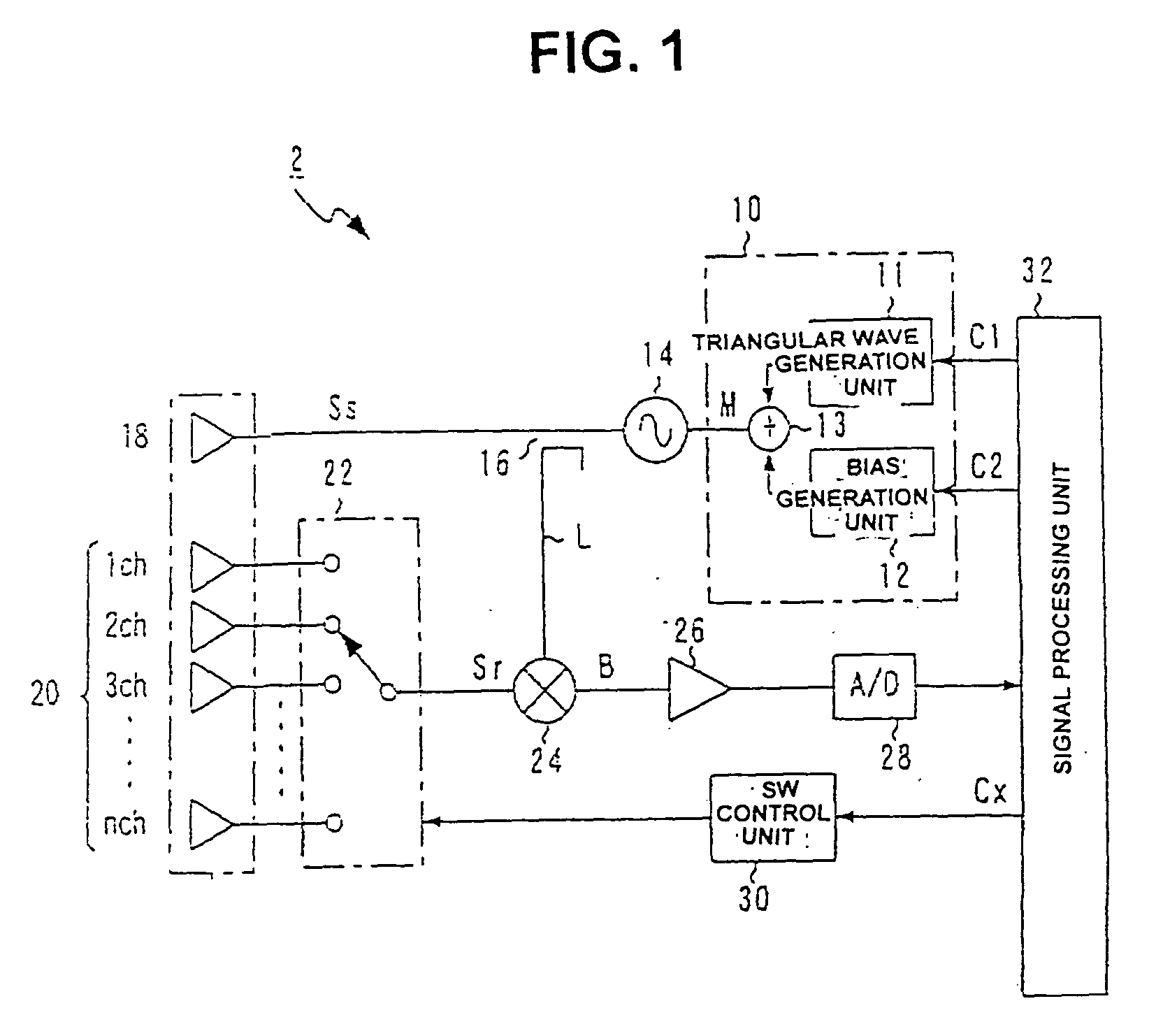
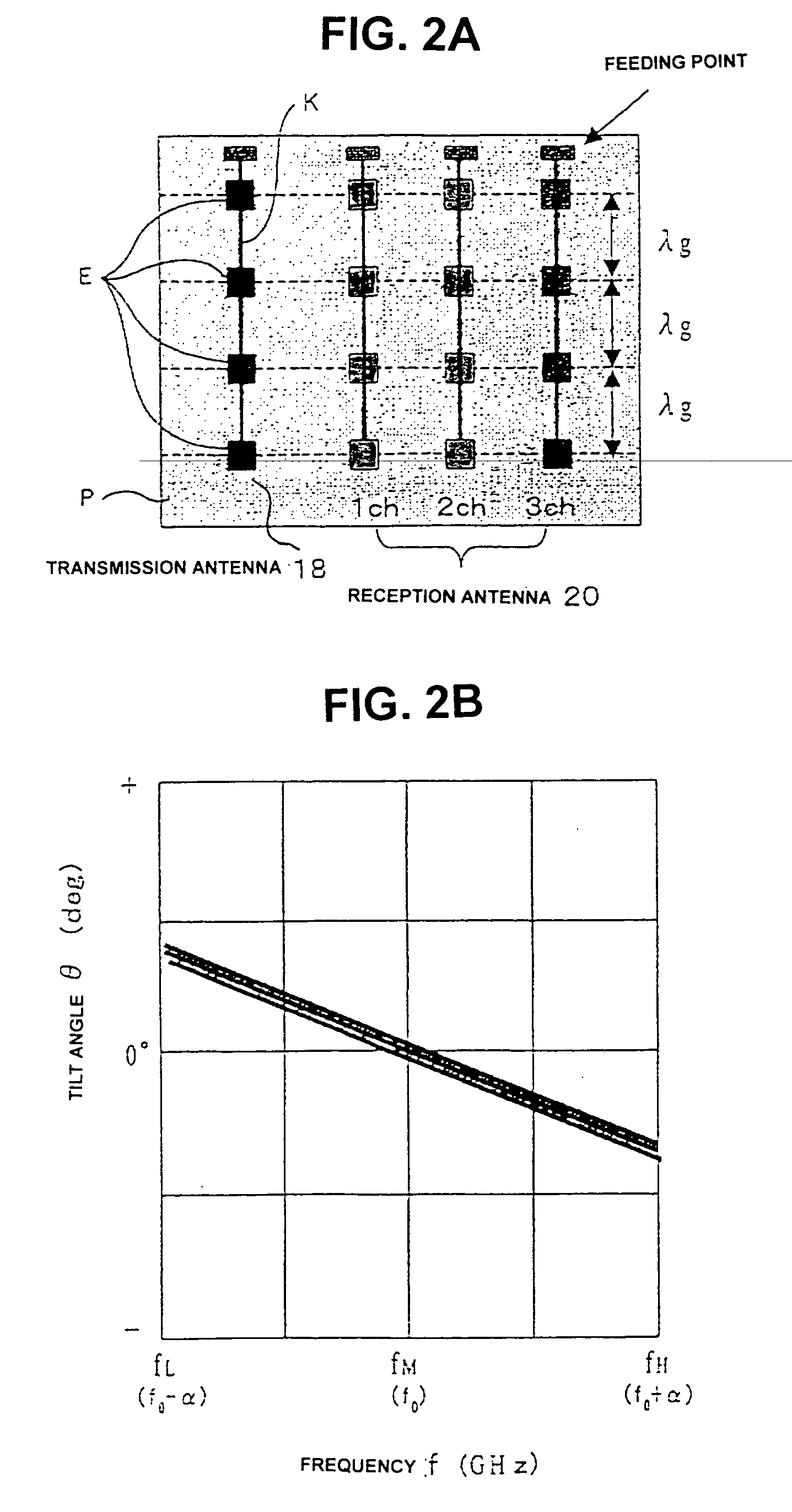
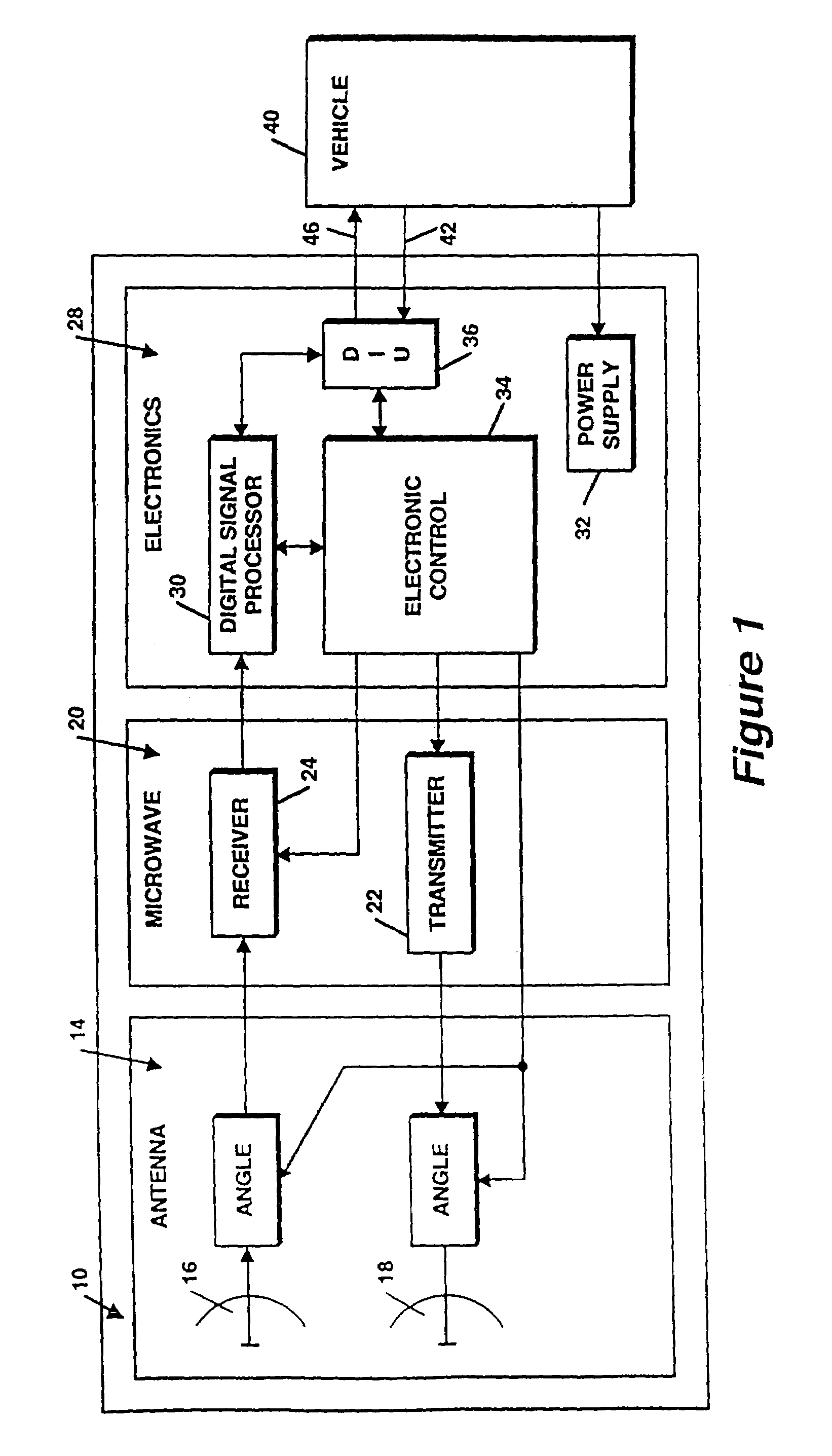
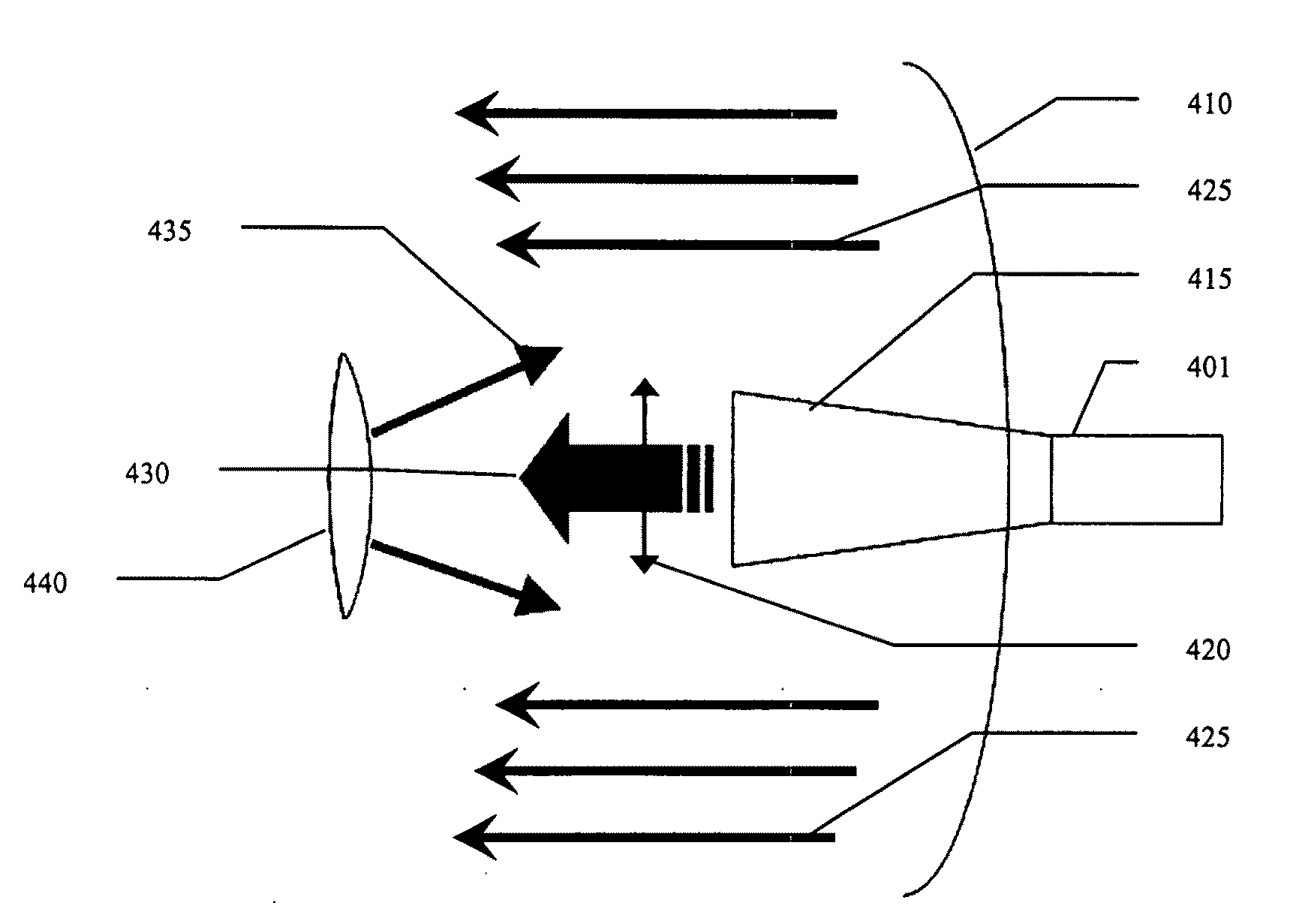
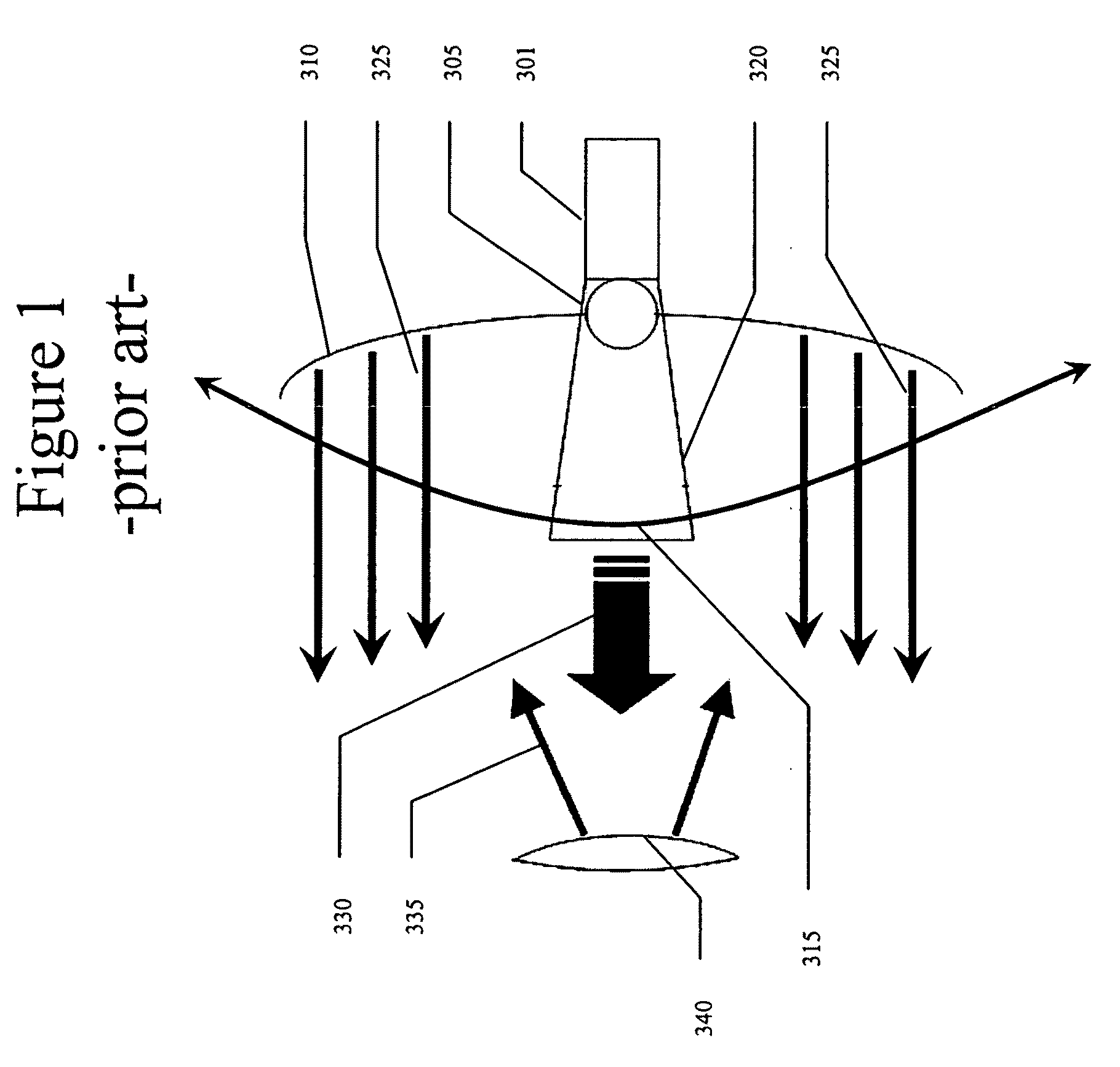
Active radar system
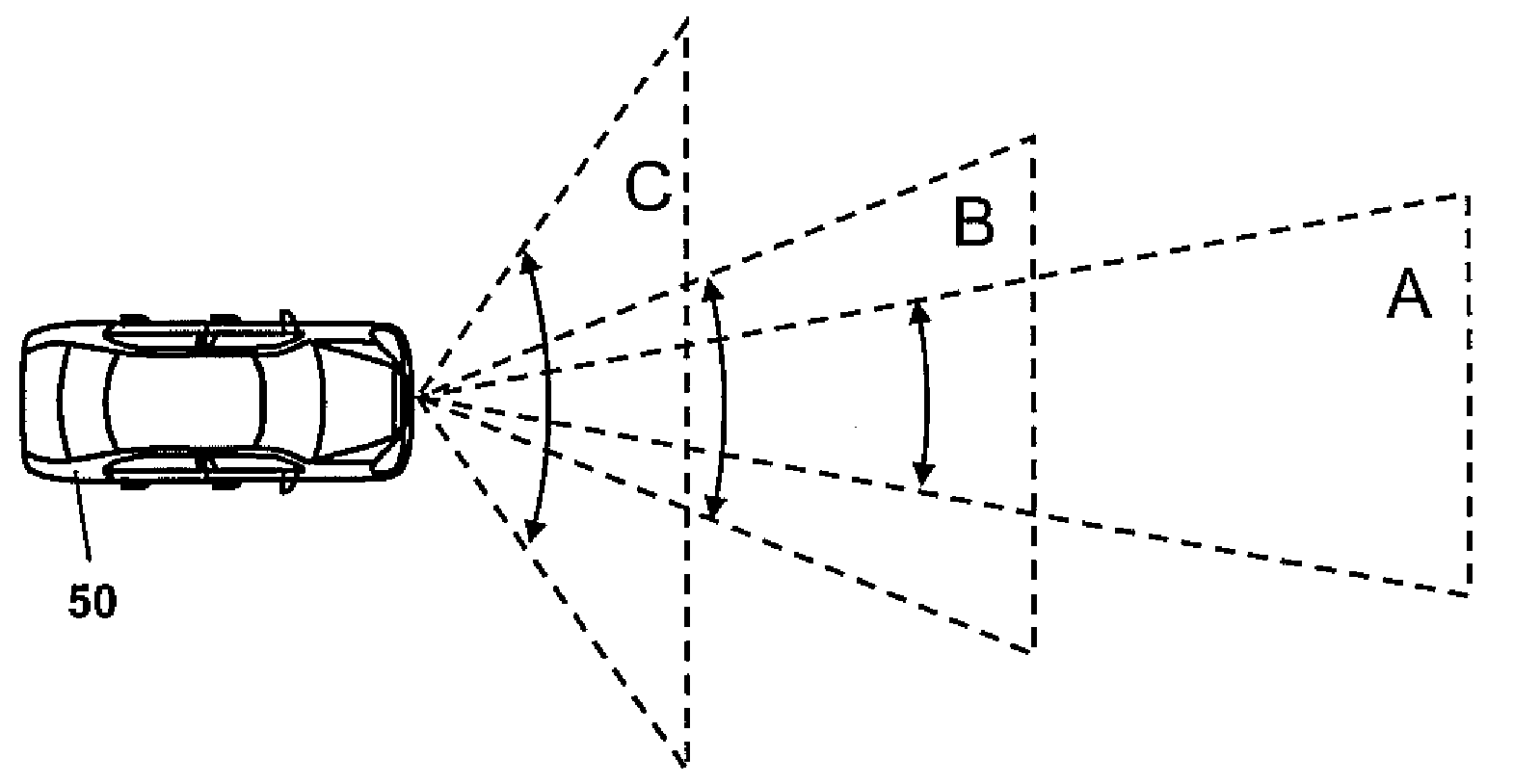
An example radar system for a vehicle comprises a radar antenna, operable to produce a radar beam, and a lens assembly including at least one active lens, the radar beam passing through the lens assembly. The radar beam has a field of view that is adjustable using the active lens. In some examples, the active lens comprises a metamaterial, the metamaterial having an adjustable property such as an adjustable negative index, the field of view being adjustable using the adjustable property of the metamaterial.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
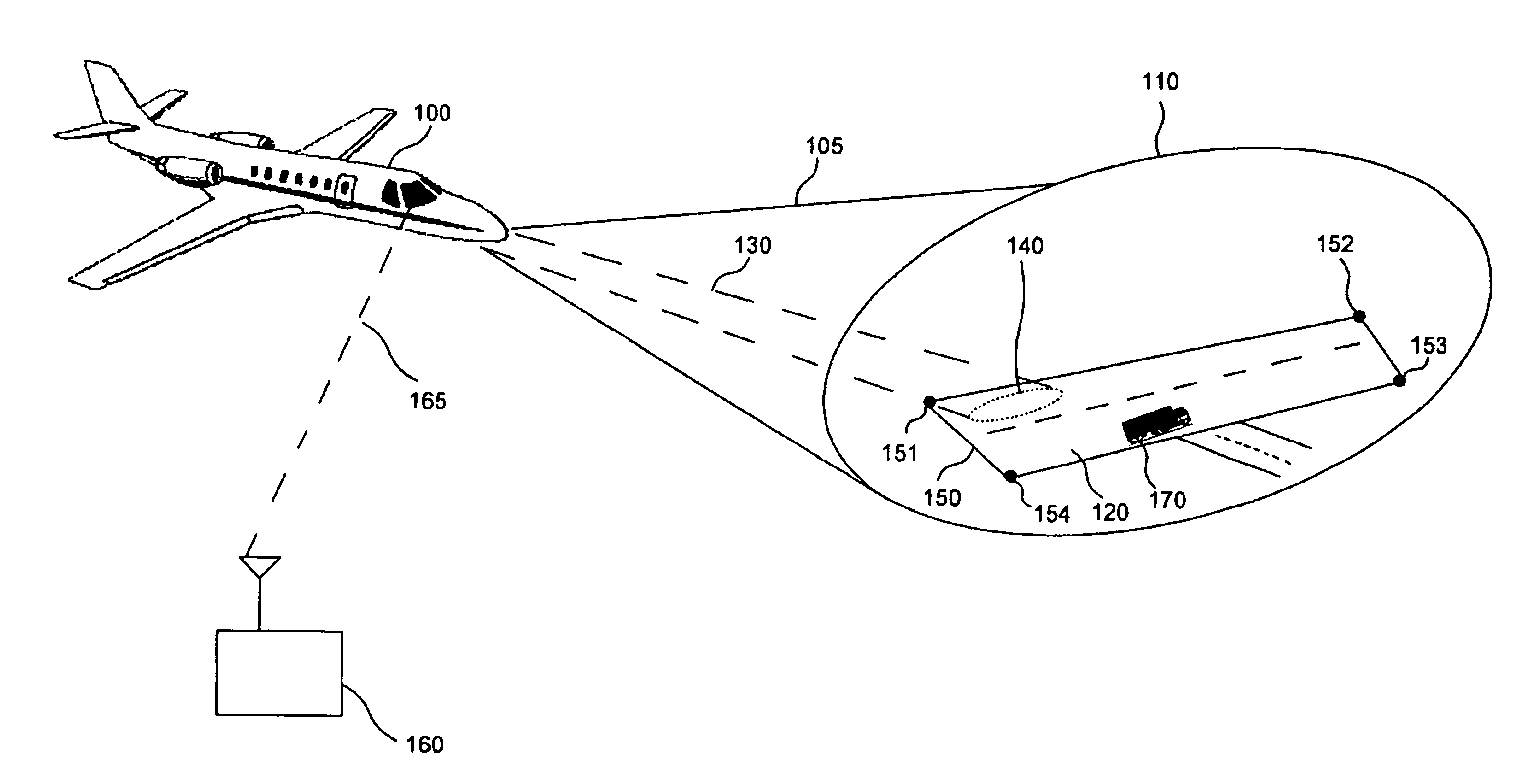
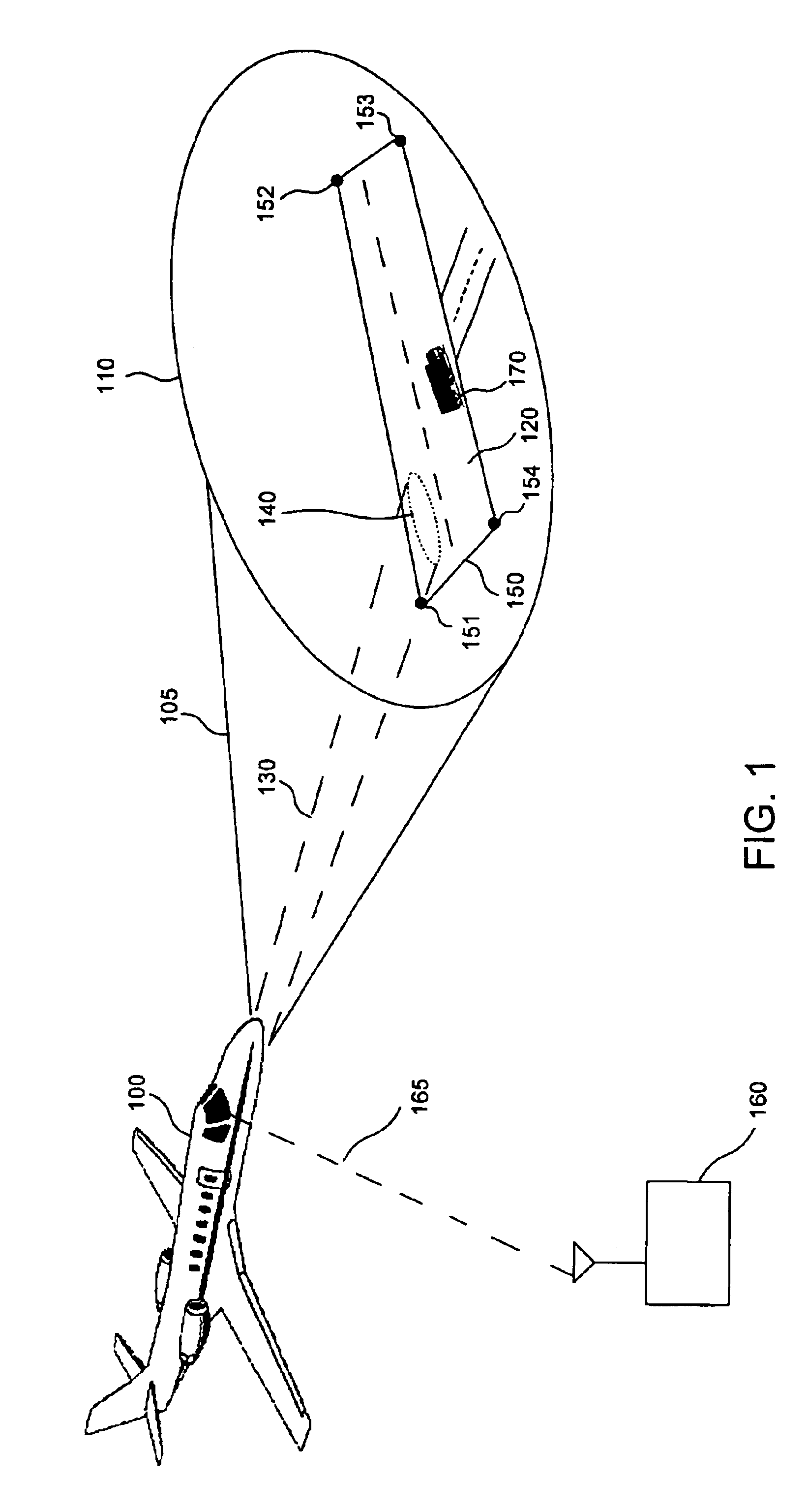
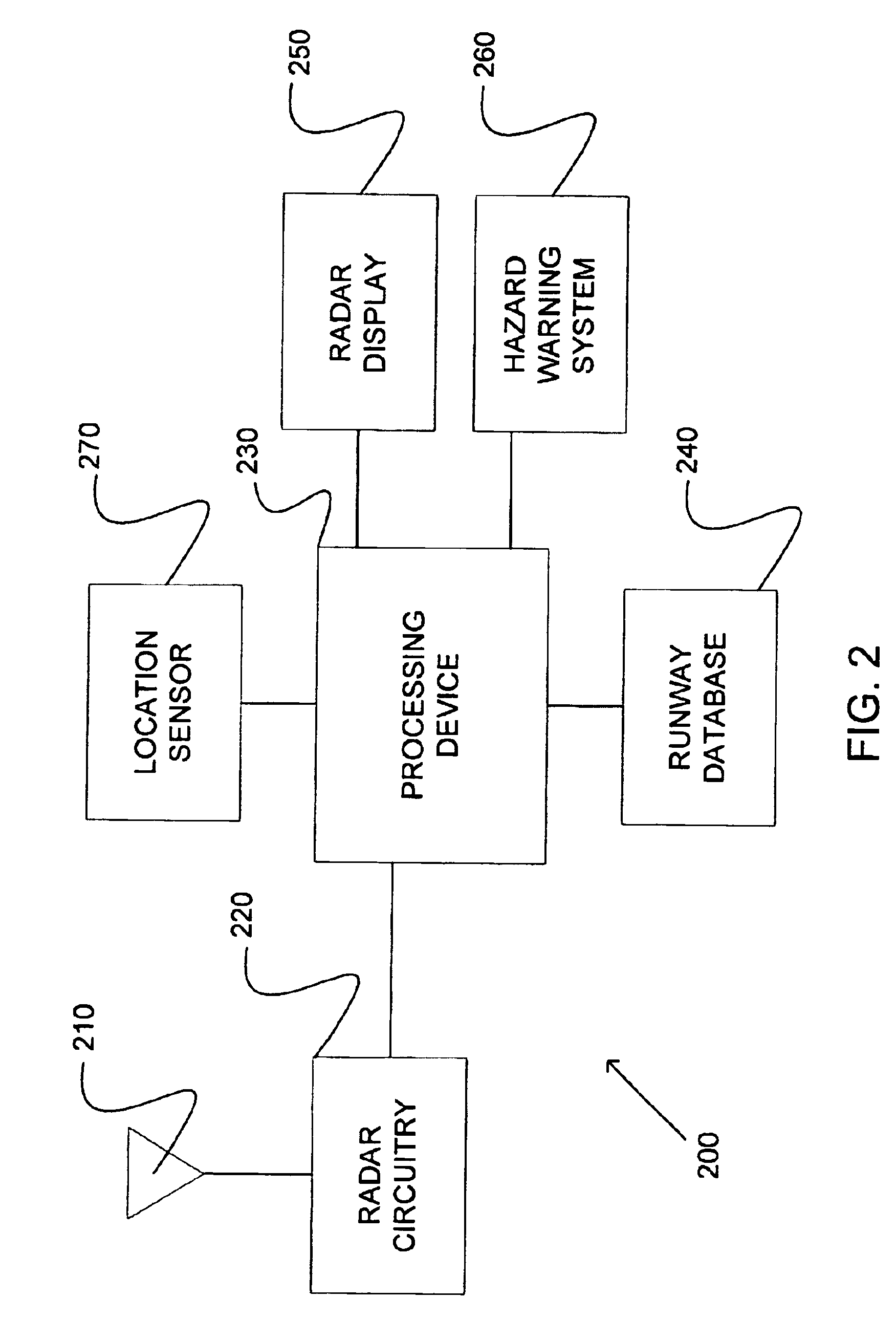
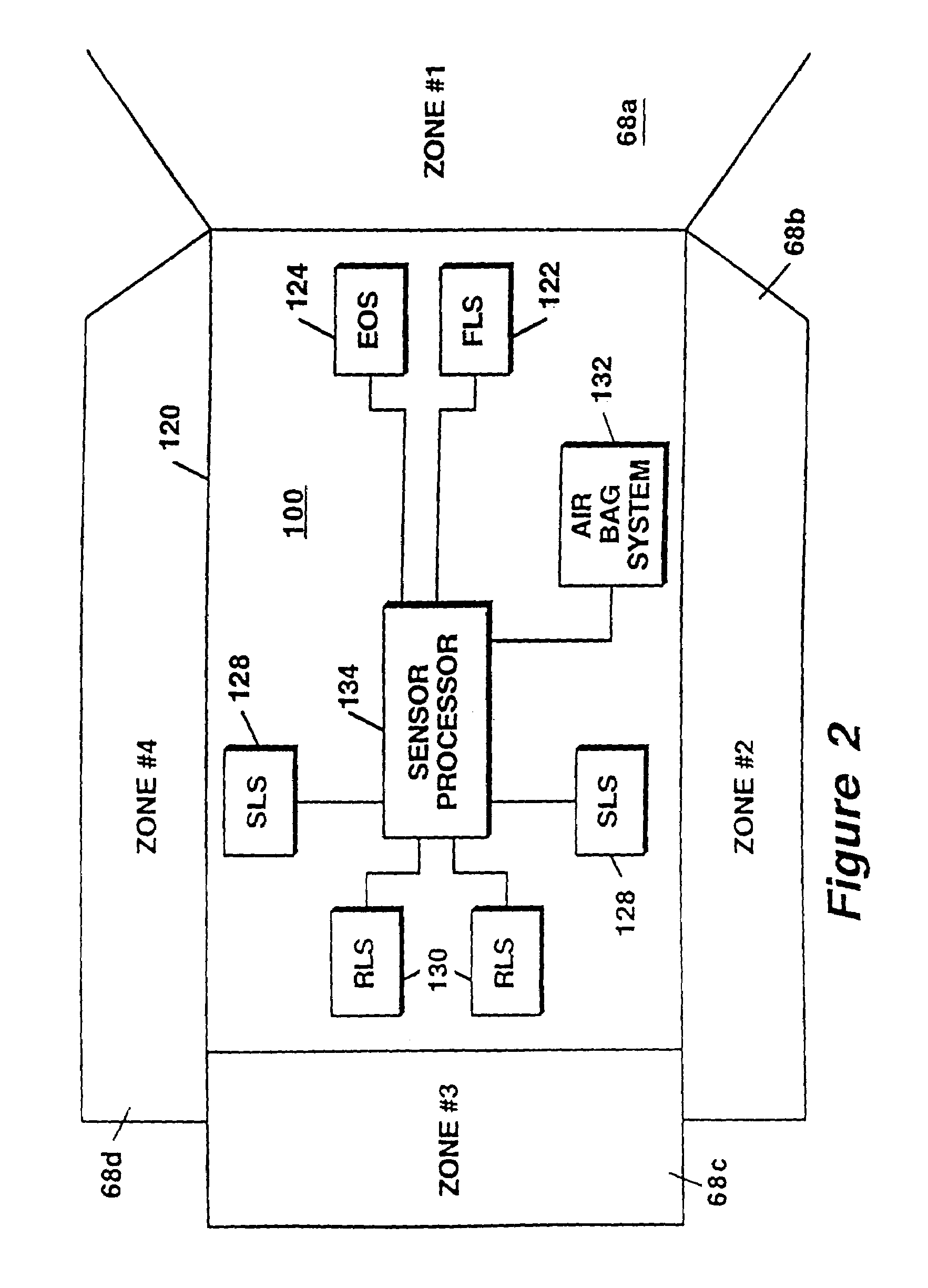
Runway obstacle detection system and method
InactiveUS6850185B1Satellite radio beaconingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar antennasRadar systems
An airborne radar system is disclosed. The airborne radar system comprises a radar antenna, radar circuitry coupled to the radar antenna, and a runway database comprising runway location information. The airborne radar system also comprises a processing device retrieving from the runway database, runway location information for a runway being approached by an aircraft, based on the location of the aircraft, and directing a radar beam defined by a polygon which represents the runway and which is derived from the runway information, the processing device determining whether there are any obstacles on the runway.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
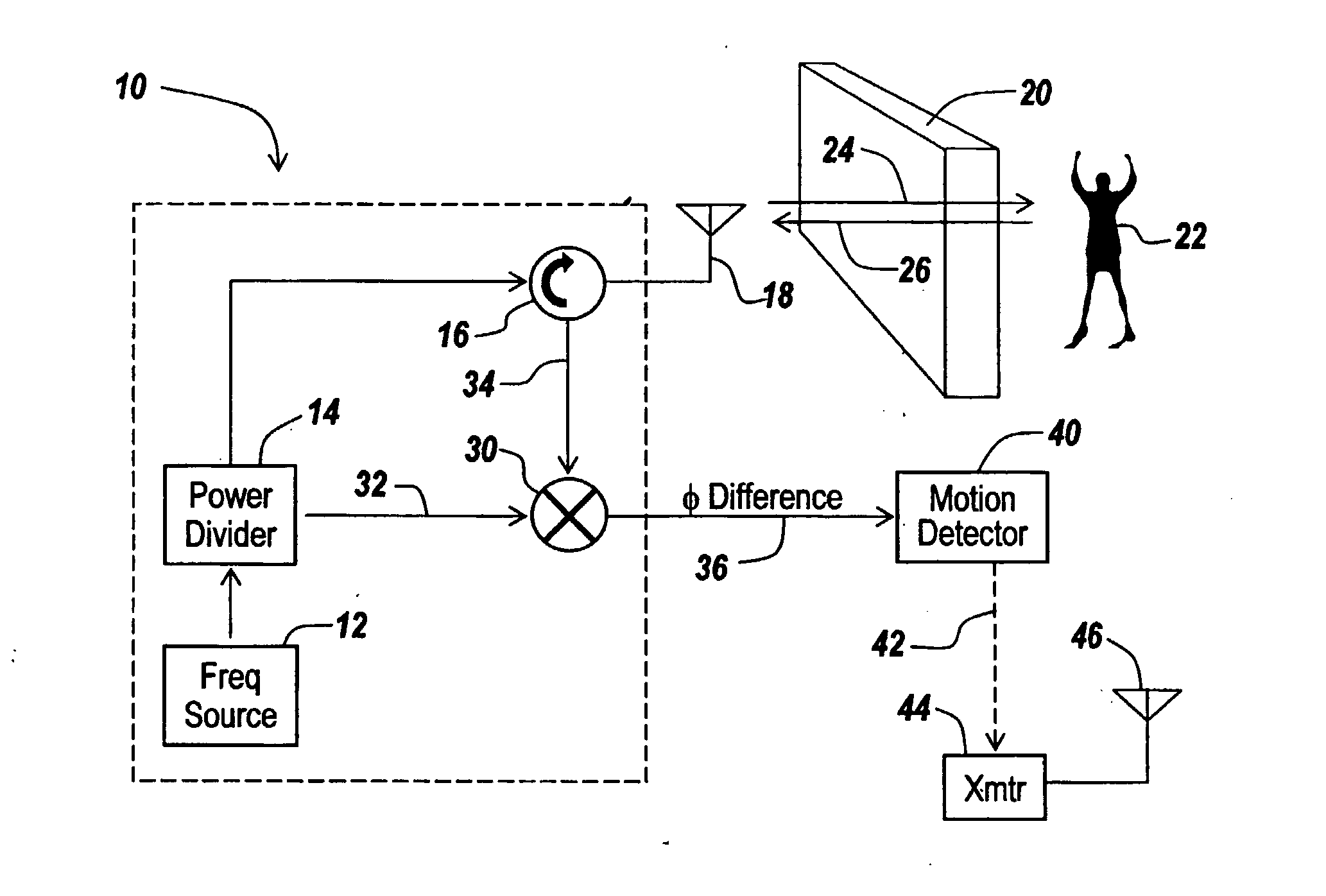
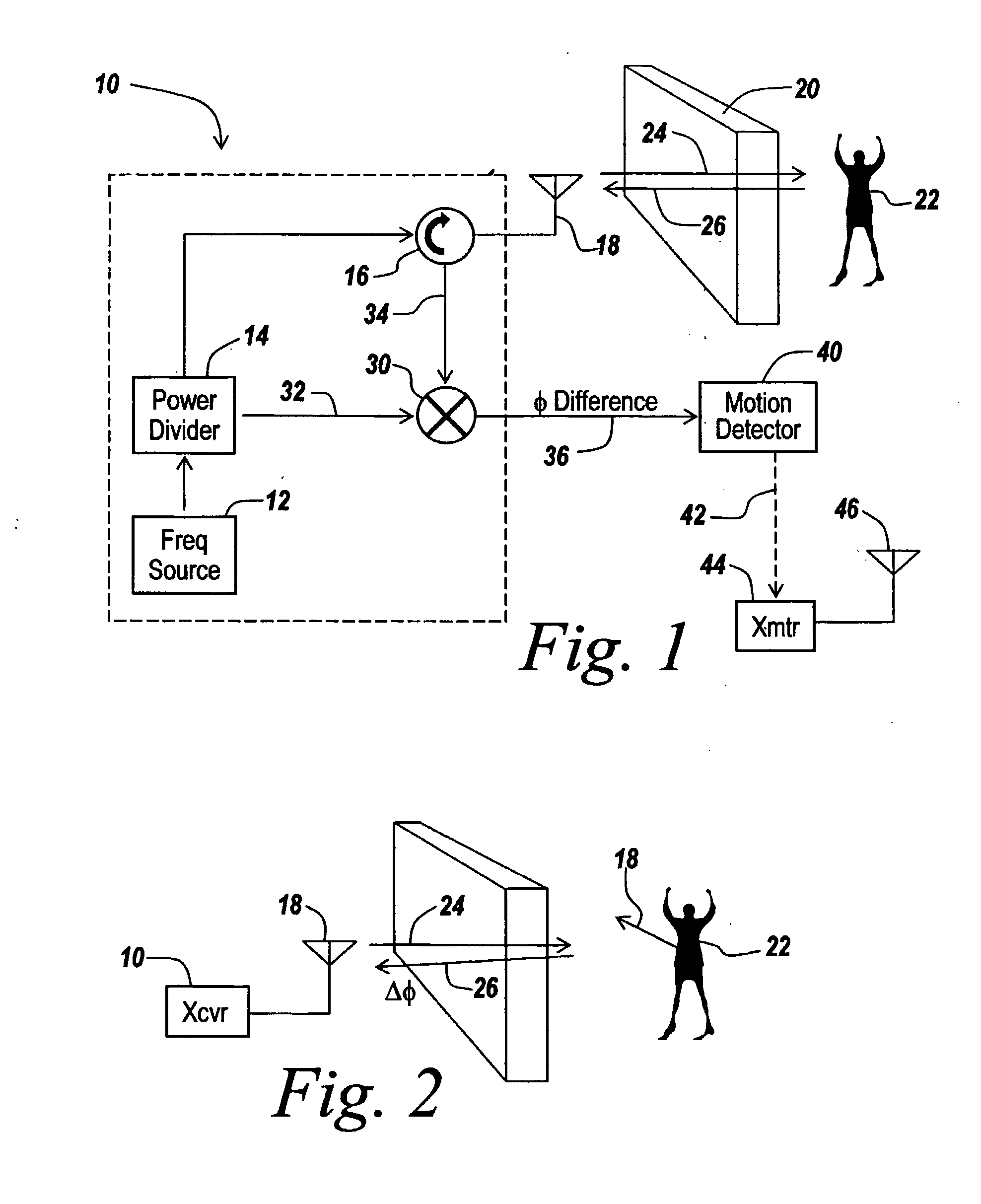
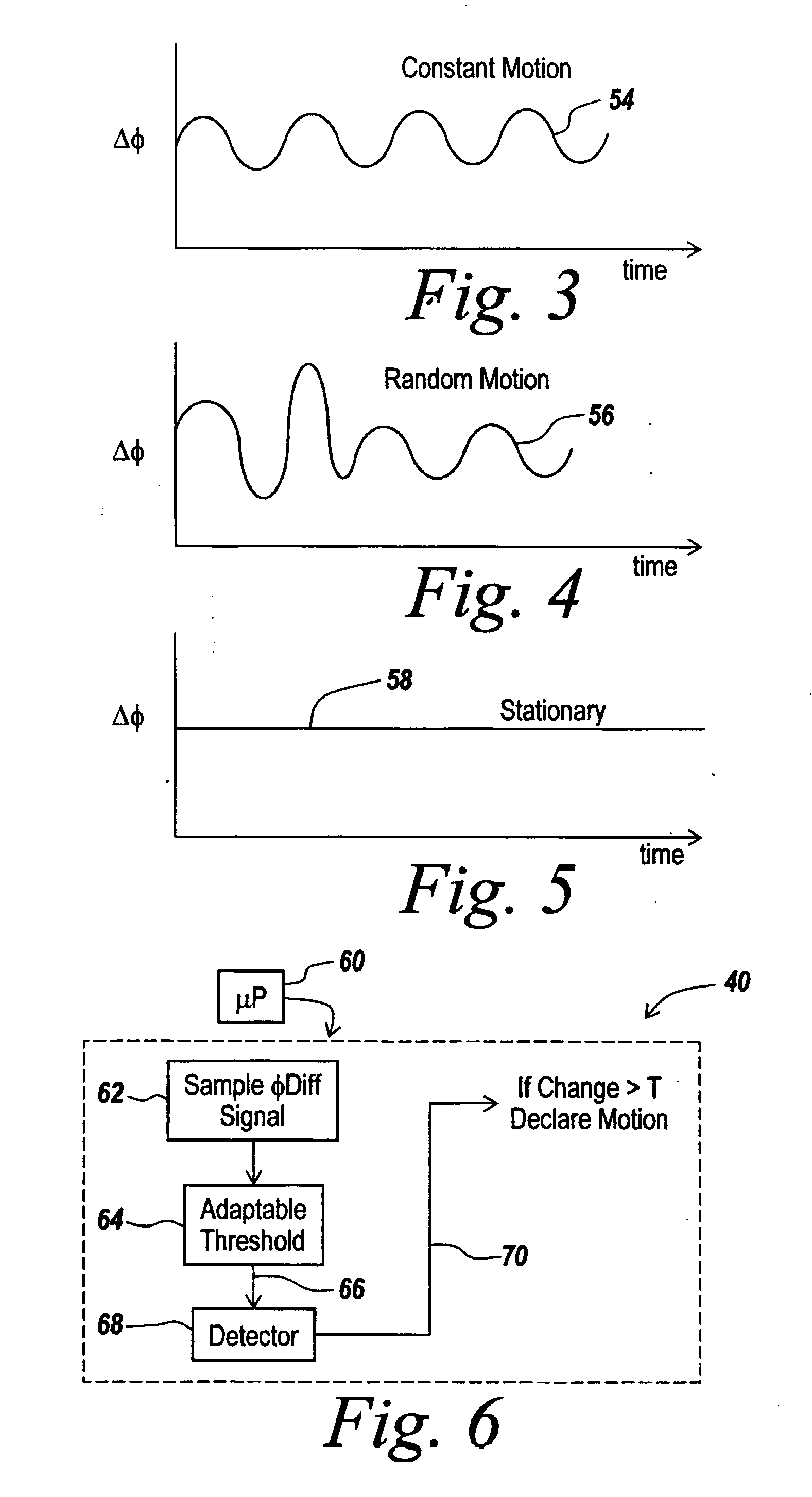
Method and apparatus for through-the-wall motion detection utilizing cw radar
InactiveUS20070024488A1Easy to detectReduce the required powerRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase differenceClassical mechanics
A CW radar (10) is used to detect motion of objects (22) behind a wall (20) by projecting a radar beam through the wall and by measuring the returns from the objects behind the wall, with a change in the phase difference between the transmitted and received CW signals providing an indication of motion behind the wall and thus the presence of an individual.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
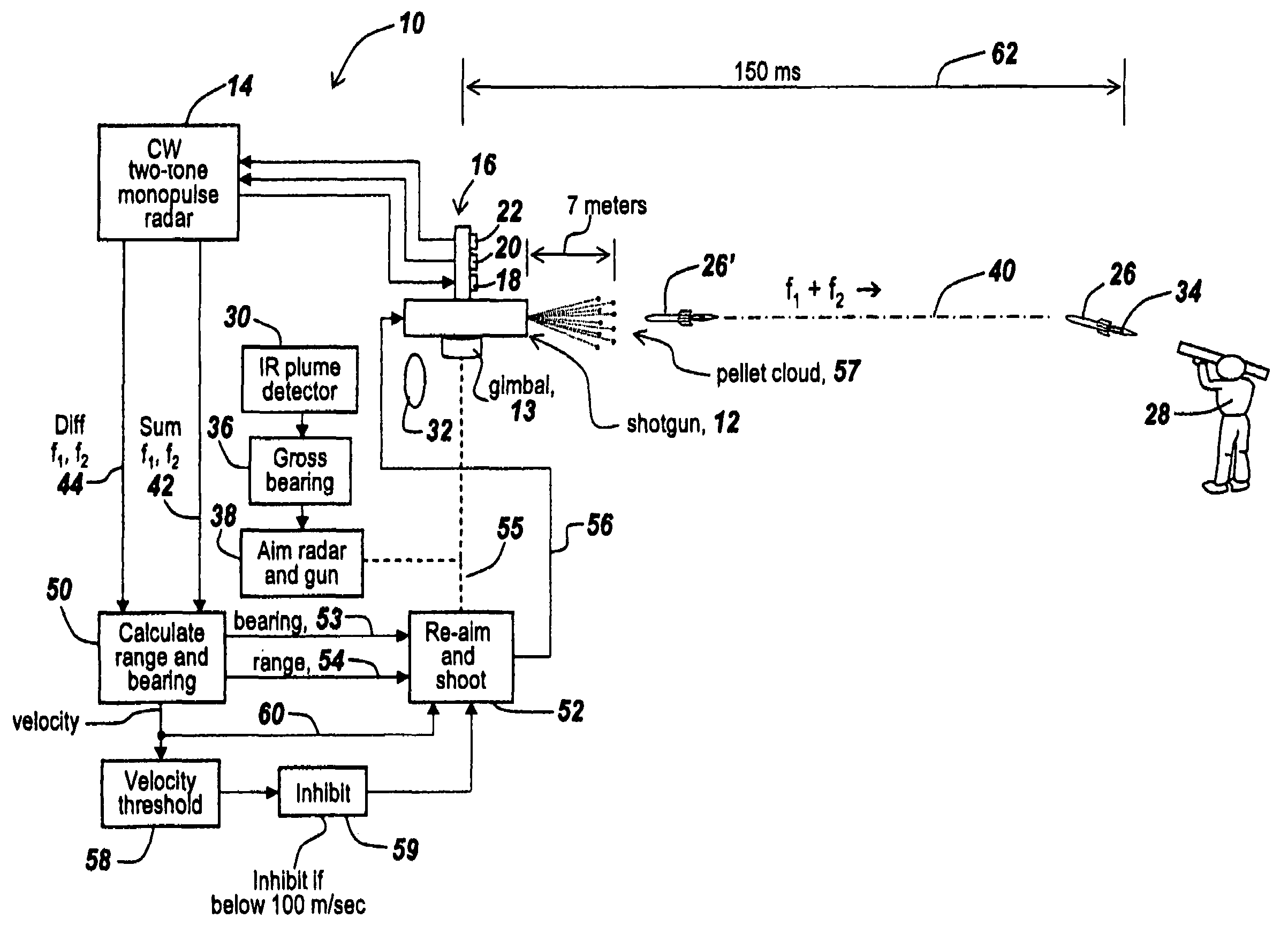
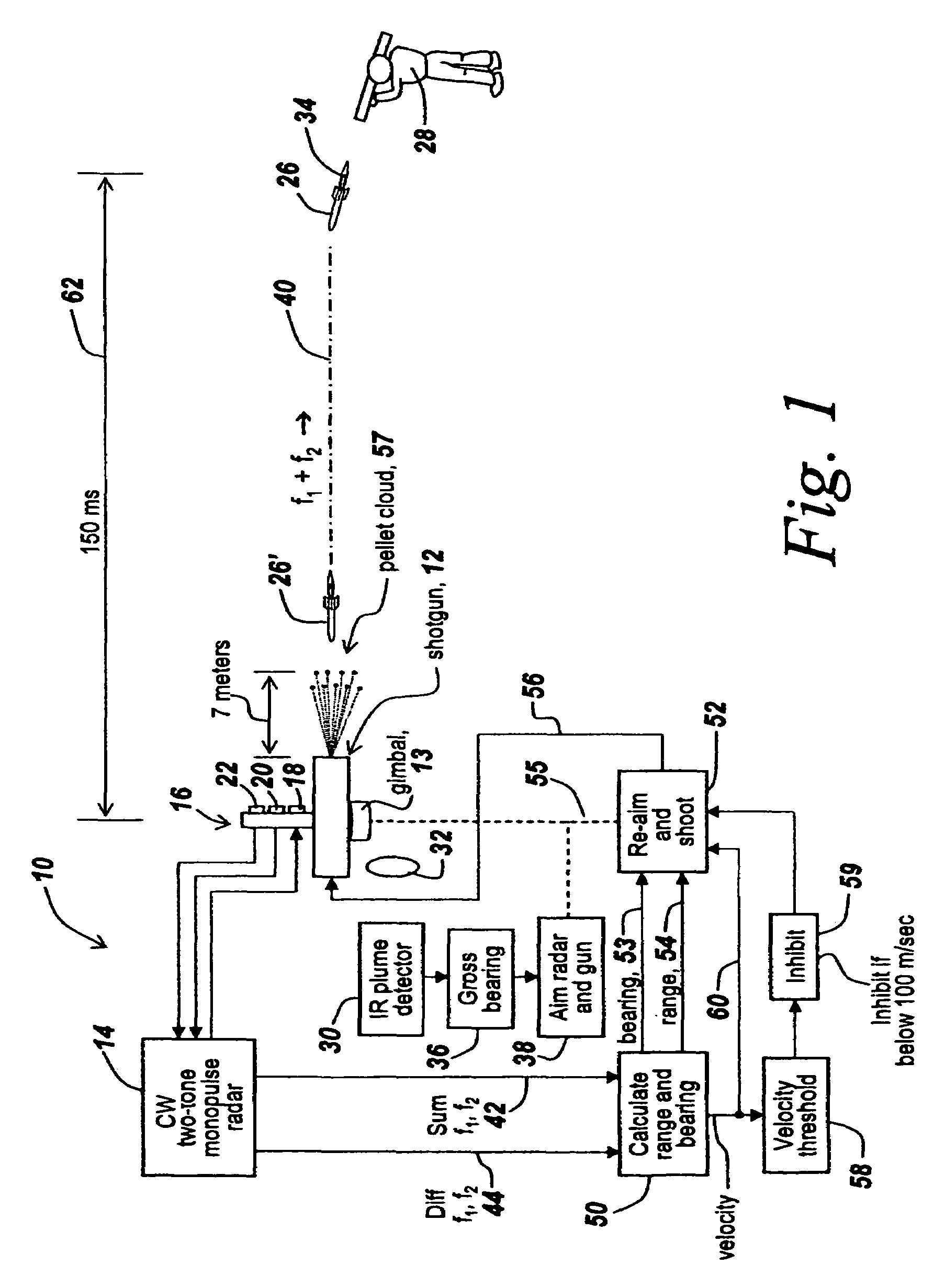
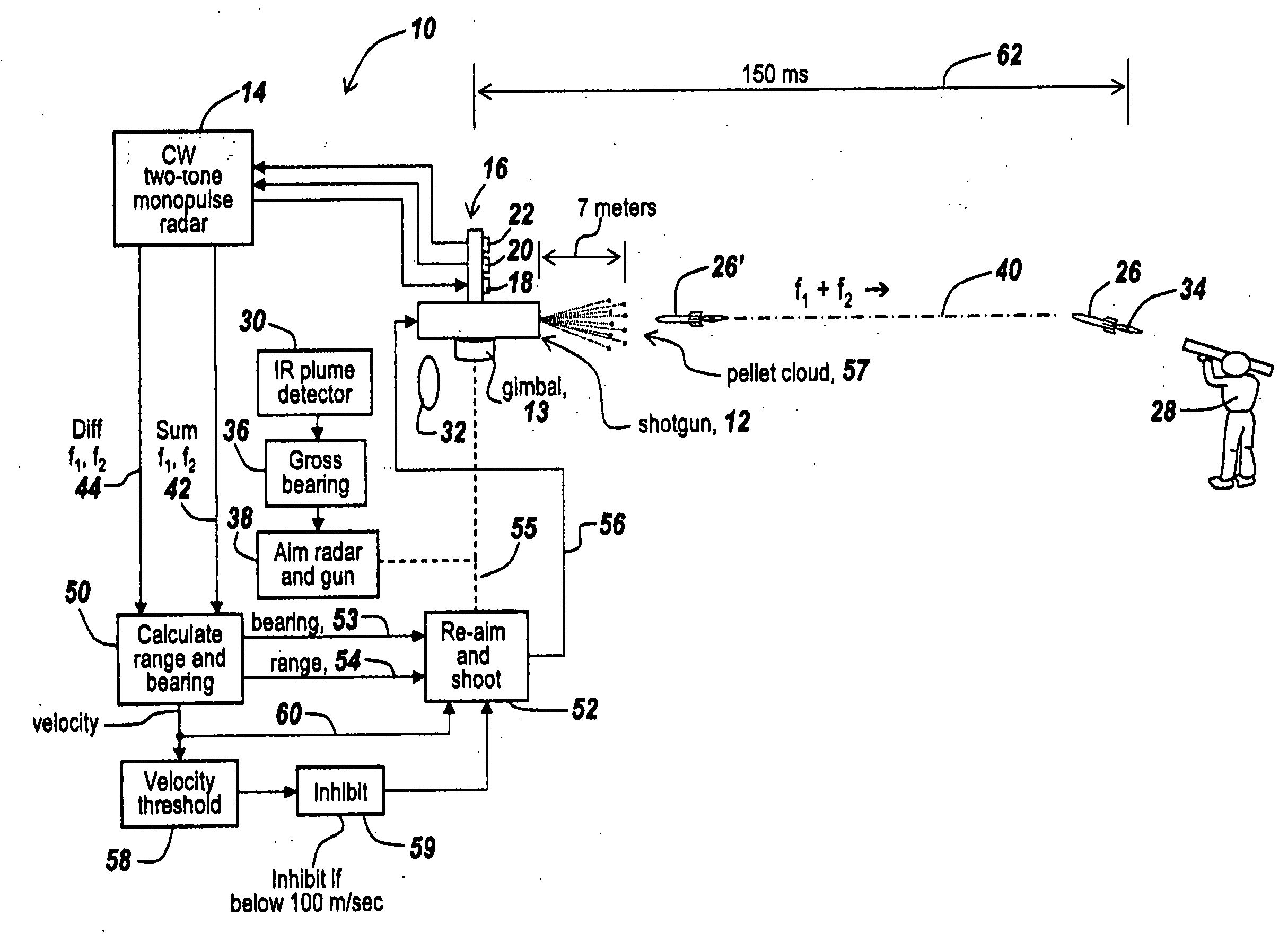
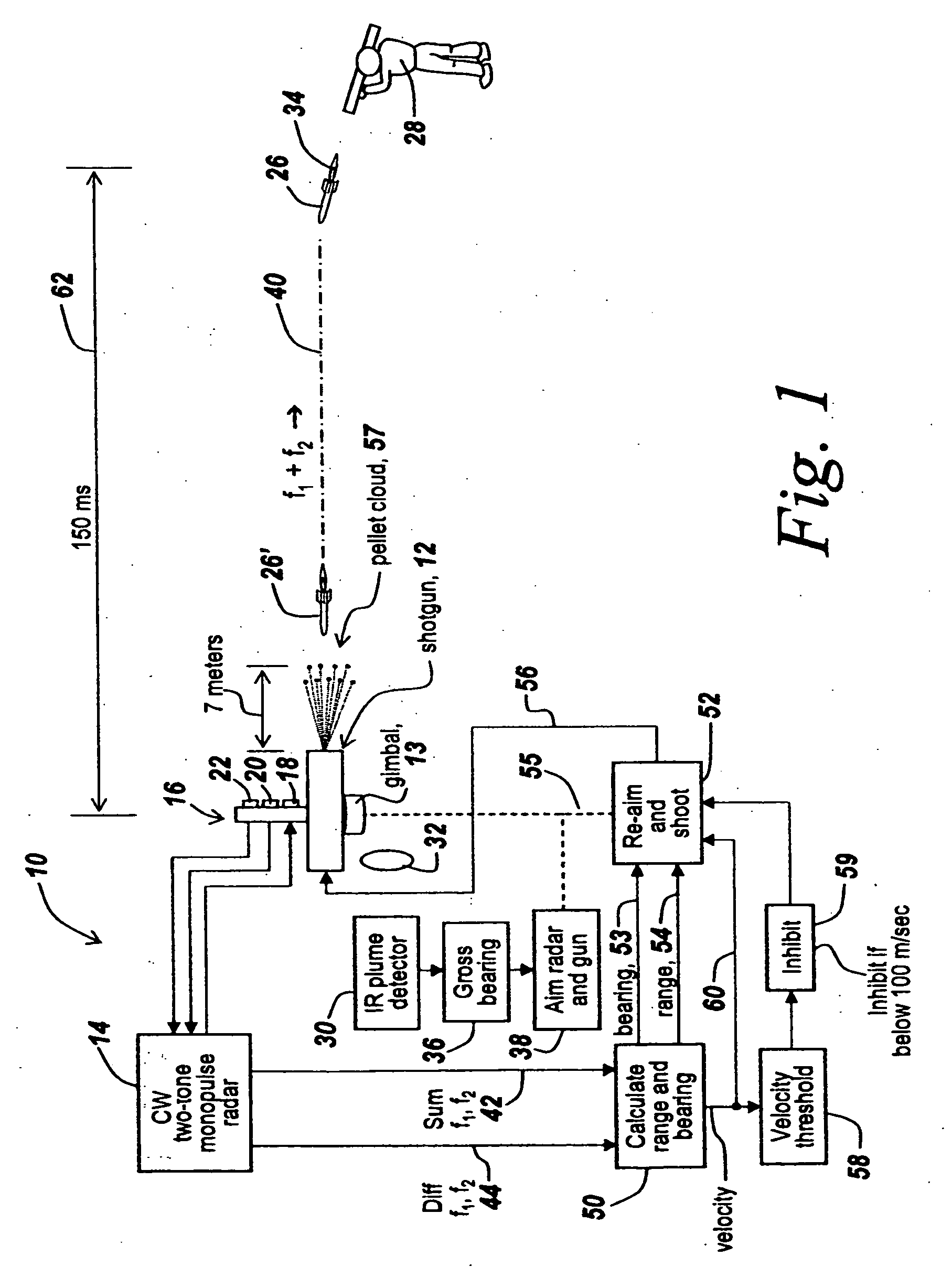
Method and apparatus for improved determination of range and angle of arrival utilizing a two tone CW radar
ActiveUS7205932B2Double accuracyImprove noiseRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSingular value decompositionFire-control system
An improved system is provided for aiming a shotgun-based or other countermeasure system so as to be able to countermeasure incoming rockets or projectiles. In one embodiment a shotgun aimed and controlled by the subject system projects a pattern of pellets to intercept a rocket-propelled grenade or incoming projectile. The fire control system uses a CW two-tone monopulse radar to derive range and angle of arrival within 150 milliseconds, with range and angle of arrival measurements having approximately twice the accuracy of prior CW two-tone monopulse radars. The improvement derives from using all of the information in the returned radar beams and is the result of the recognition that one can use the Sum and Difference signals to assemble a two-by-two Rank One matrix that permits using singular value decomposition techniques to generate range and angle of arrival matrices in which all available information is used and in which noise is eliminated.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
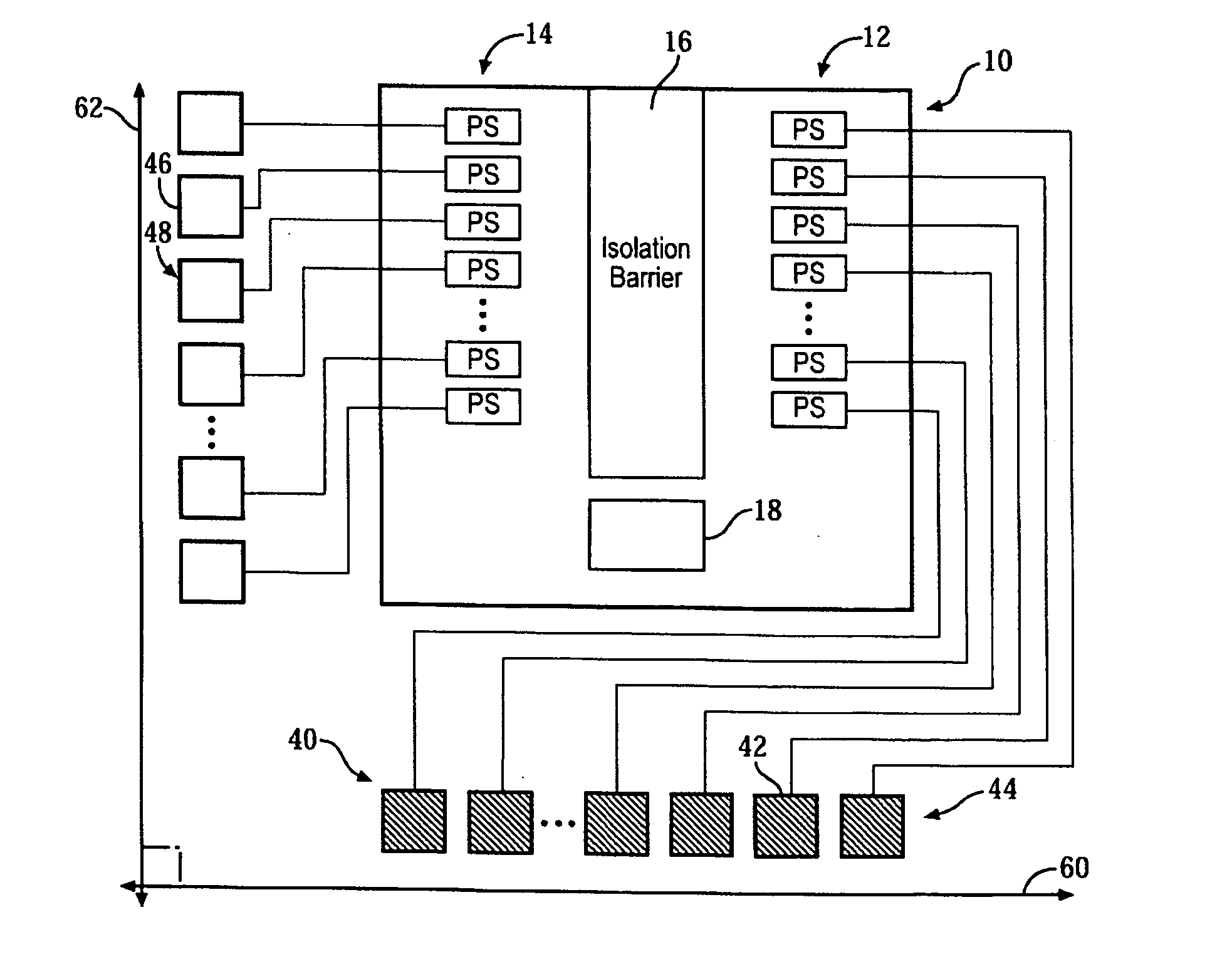
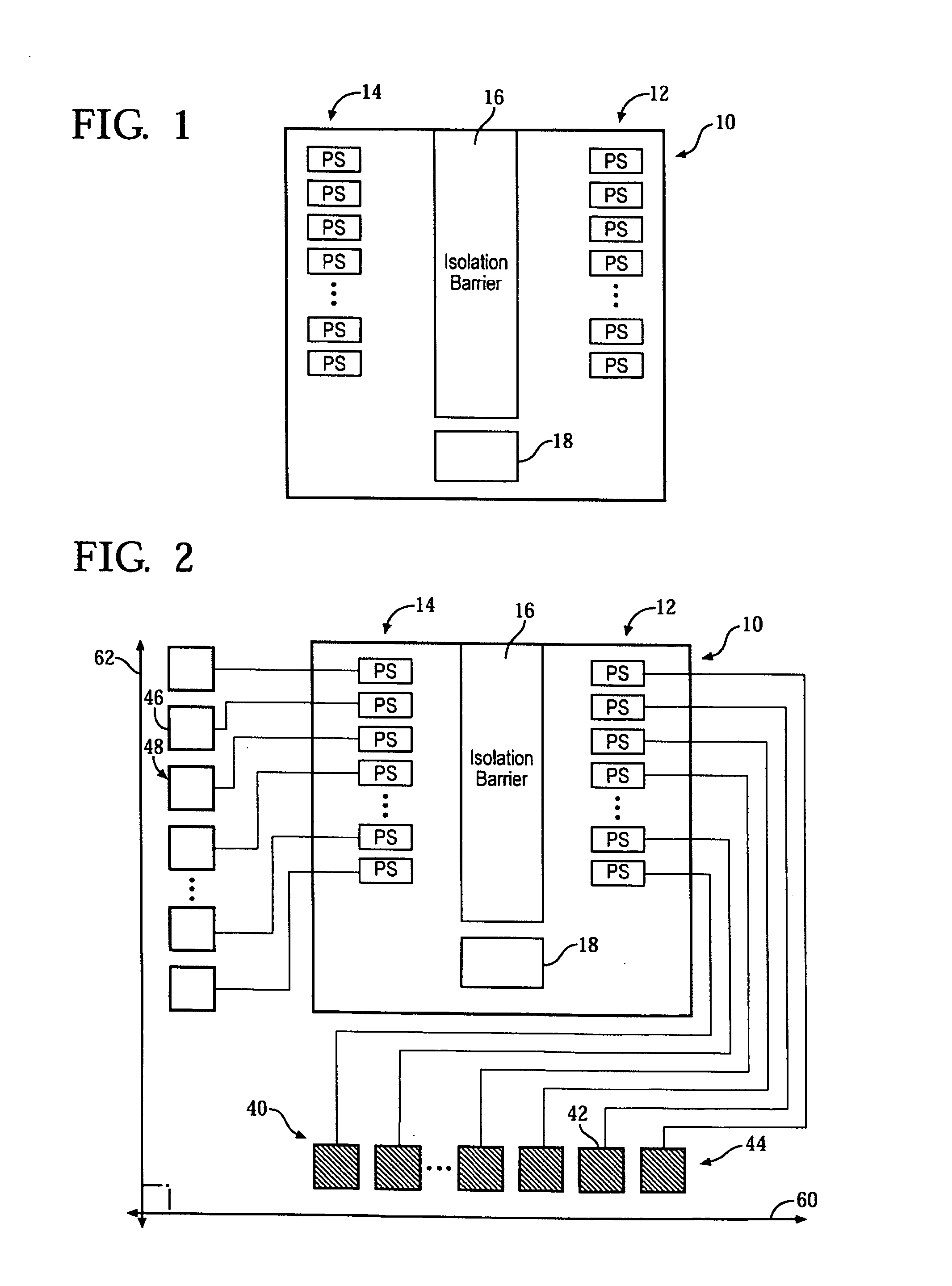
3D short range detection with phased array radar
InactiveUS20140070994A1Improve target classificationImprove classificationWave based measurement systemsAntenna detailsLight beamPhased array
A radar microchip for short range detection with phased array radar uses phase shifters along with an antenna array to steer the transmitted and received radar beams along orthogonal axes to achieve a 3D scan. Individual phase shifters connected to antenna cells that transmit and receive the radar beams steer the radar along two orthogonal axes by controlling the phase of the radar. The radar then detects where the two beams overlap. The antenna cells are further aligned along these orthogonal axes. An isolation barrier between the phase shifters of the transmitted and received signals reduces cross coupling on the radar microchip.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR ENGINEERING & MANUFACTURING NORTH AMERICA
Radar system with an active lens for adjustable field of view
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
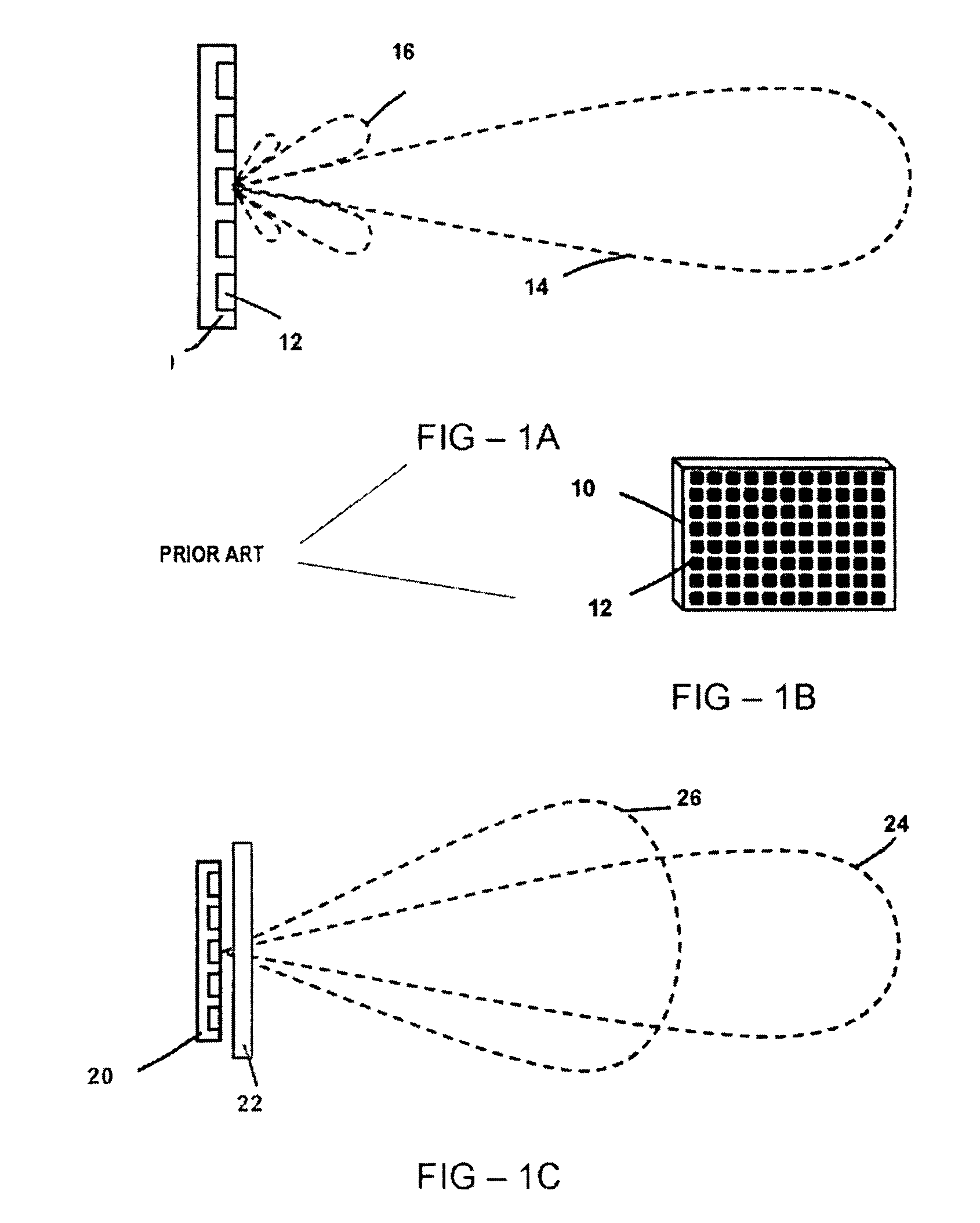
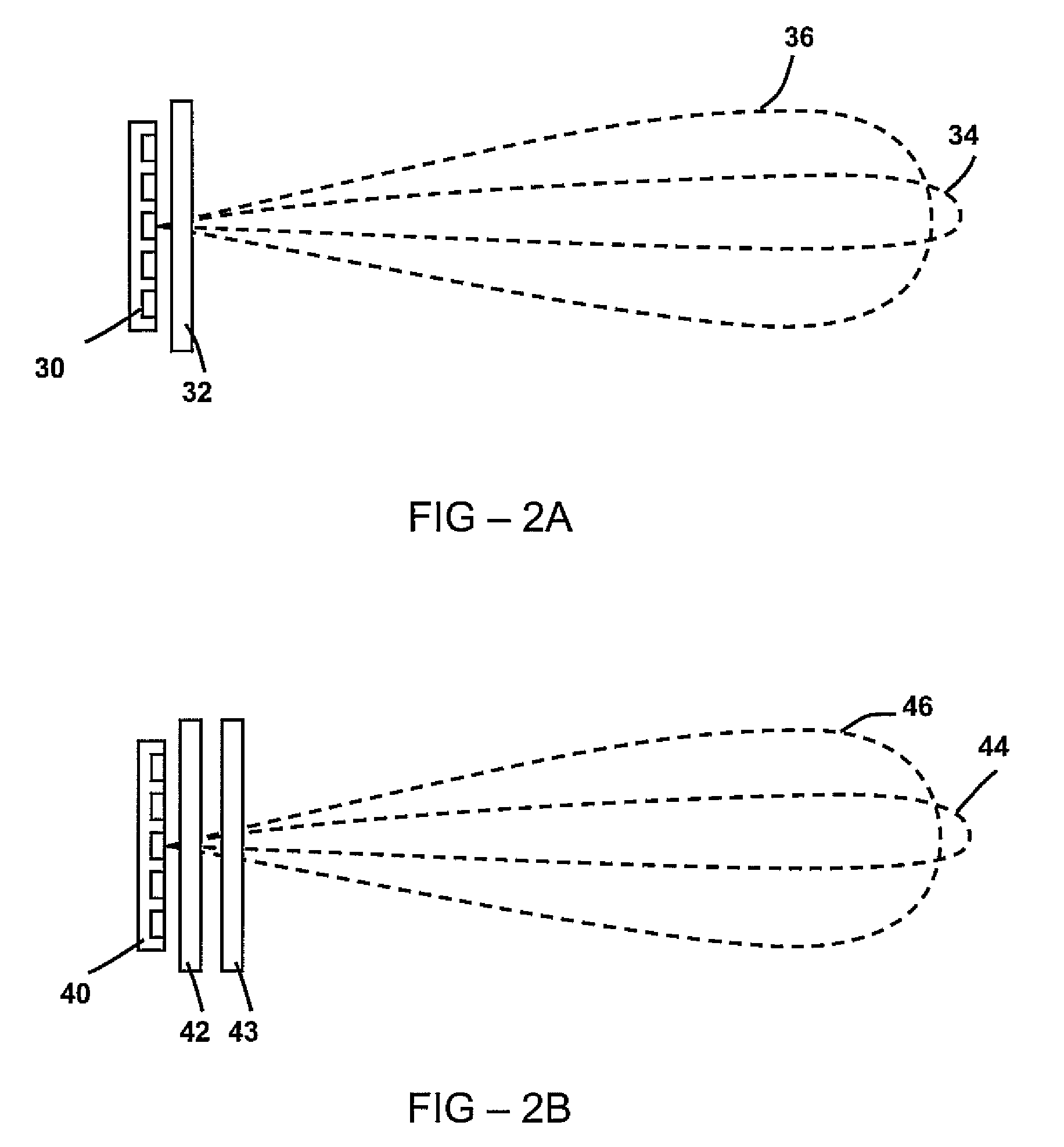
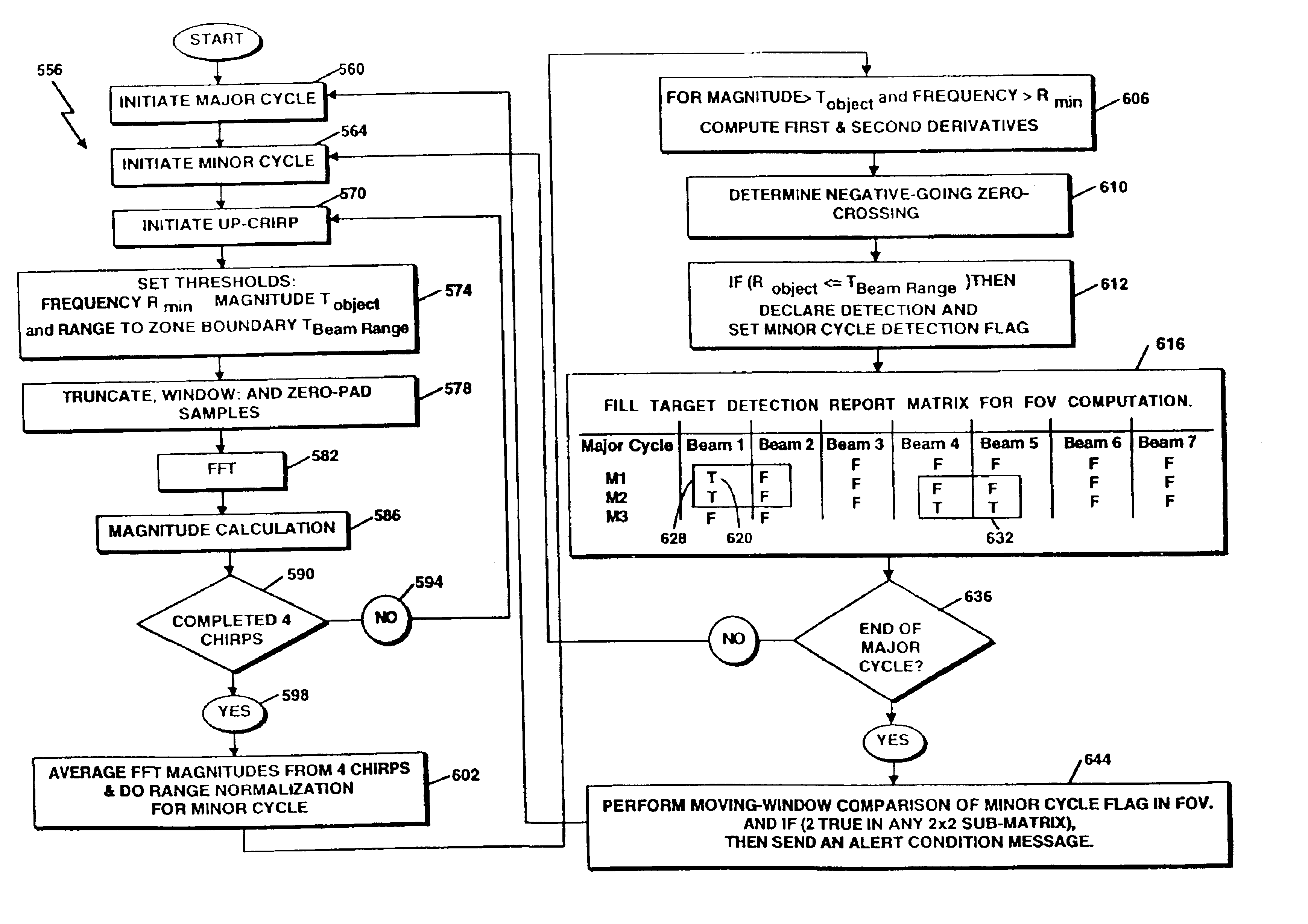
Radar detection method and apparatus
InactiveUS6864831B2Increase probabilityImprove accuracyMultiple-port networksVehicle fittingsRadar detectionRadar beam
A radar detection process includes computing a derivative of an FFT output signal to detect an object within a specified detection zone. In one embodiment, a zero crossing in the second derivative of the FFT output signal indicates the presence of an object. The range of the object is determined as a function of the frequency at which the zero crossing occurs. Also described is a detection table containing indicators of the presence or absence of an object within a respective radar beam and processing cycle. At least two such indicators are combined in order to detect the presence of an object within the detection zone.
Owner:VALEO RADAR SYST
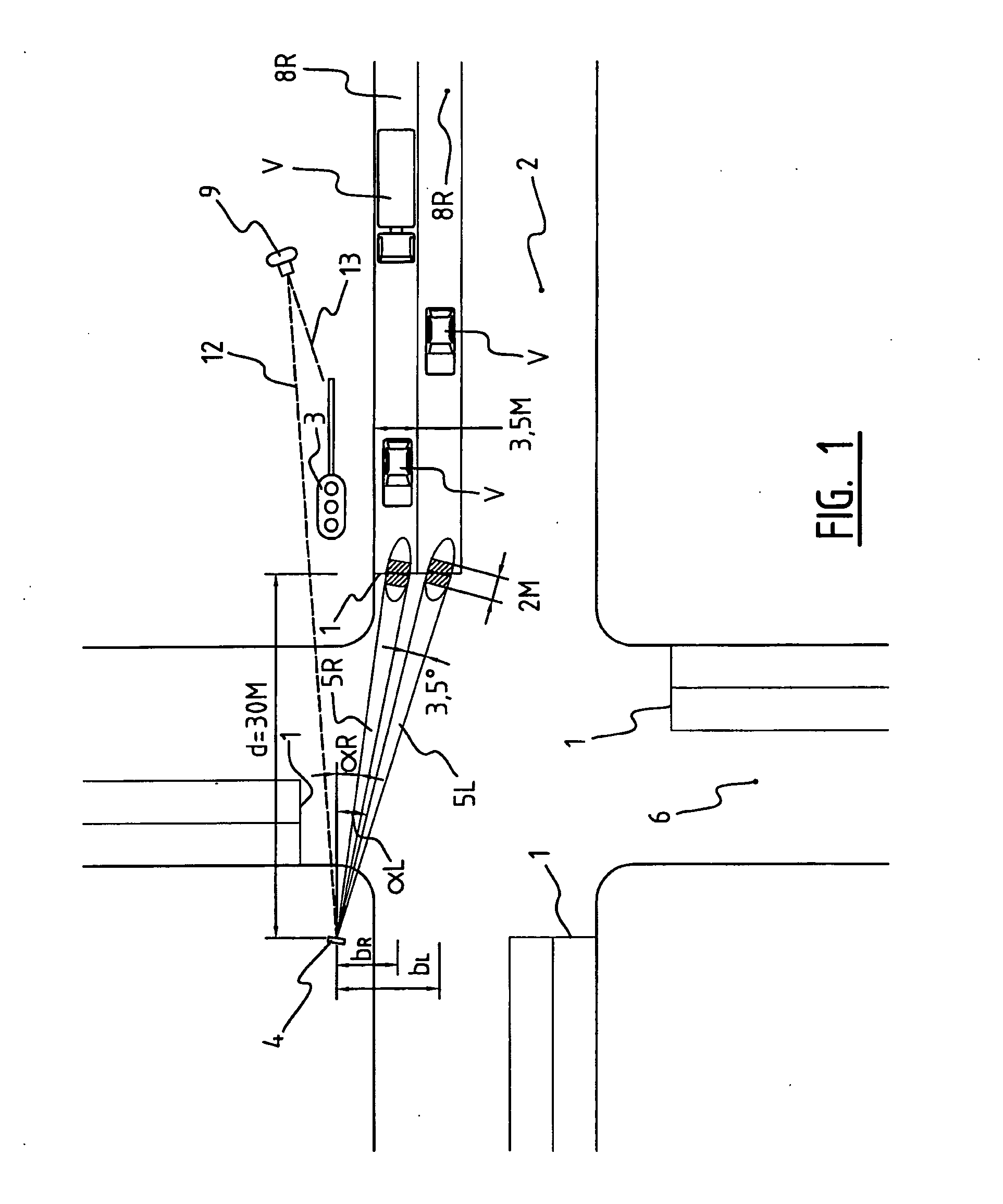
Method and system for detecting with radar the passage by a vehicle of a point for monitoring on a road
ActiveUS20060066472A1Plurality of obstructionConserve costArrangements for variable traffic instructionsDetection of traffic movementMonitoring siteEngineering
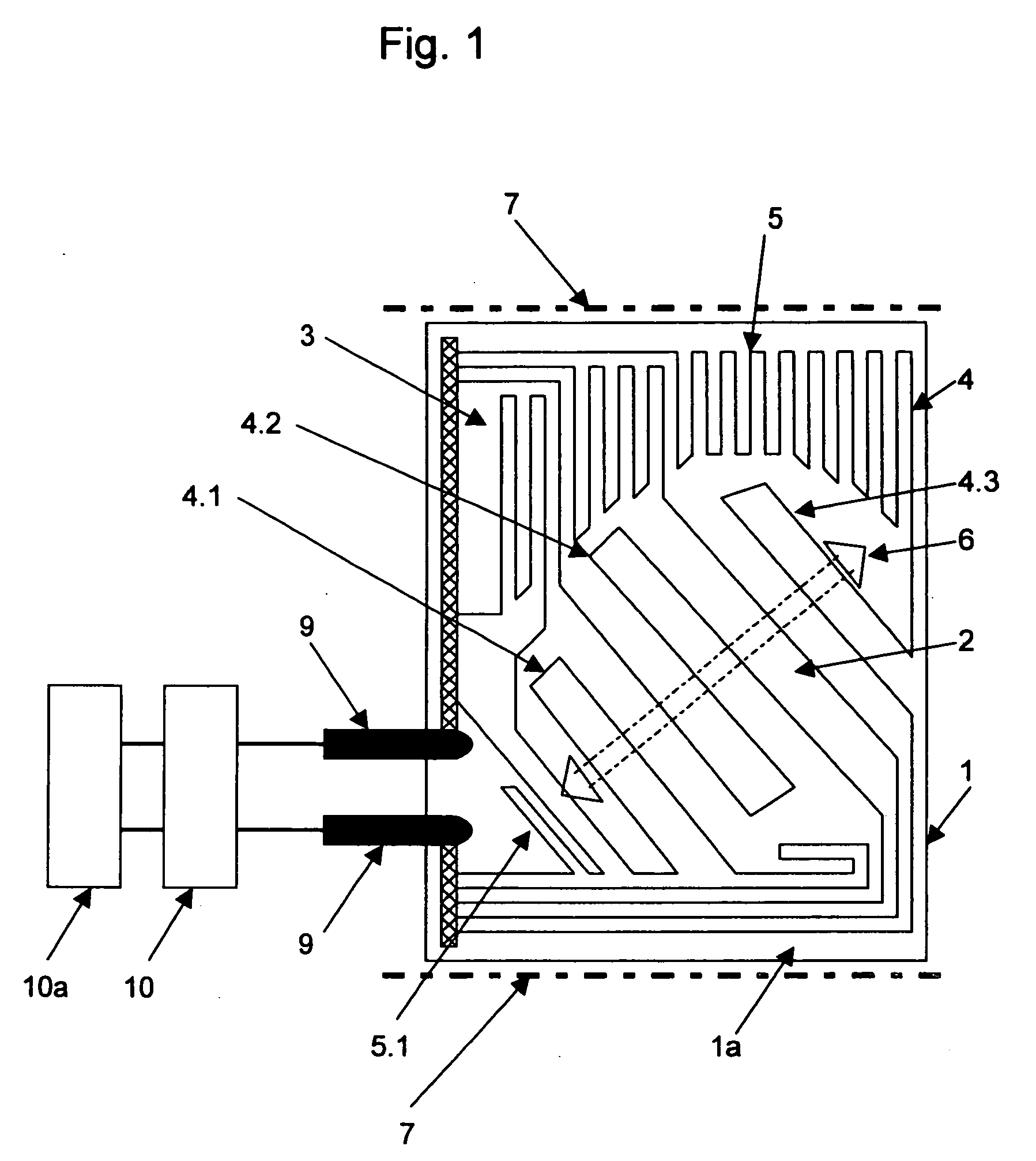
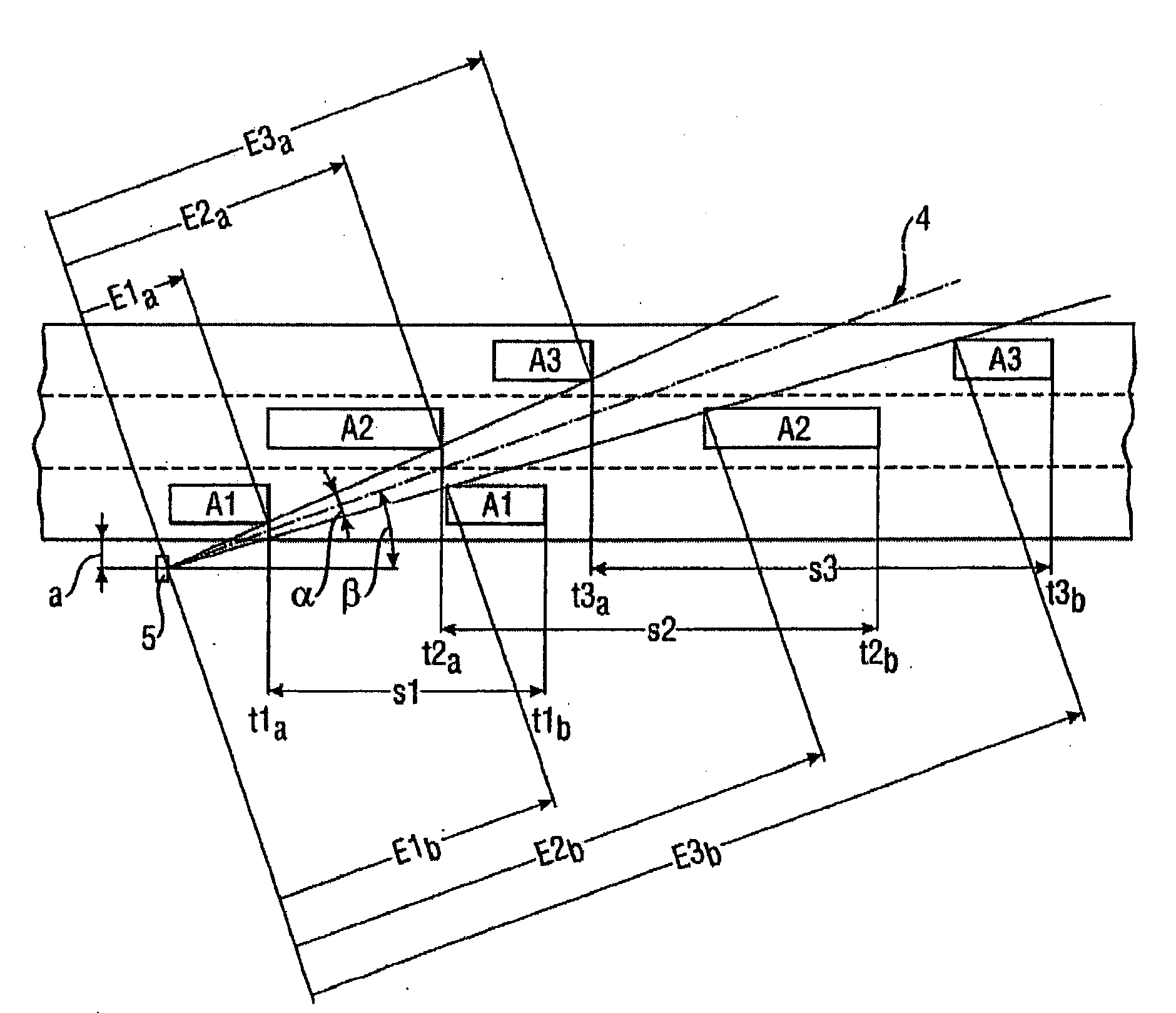
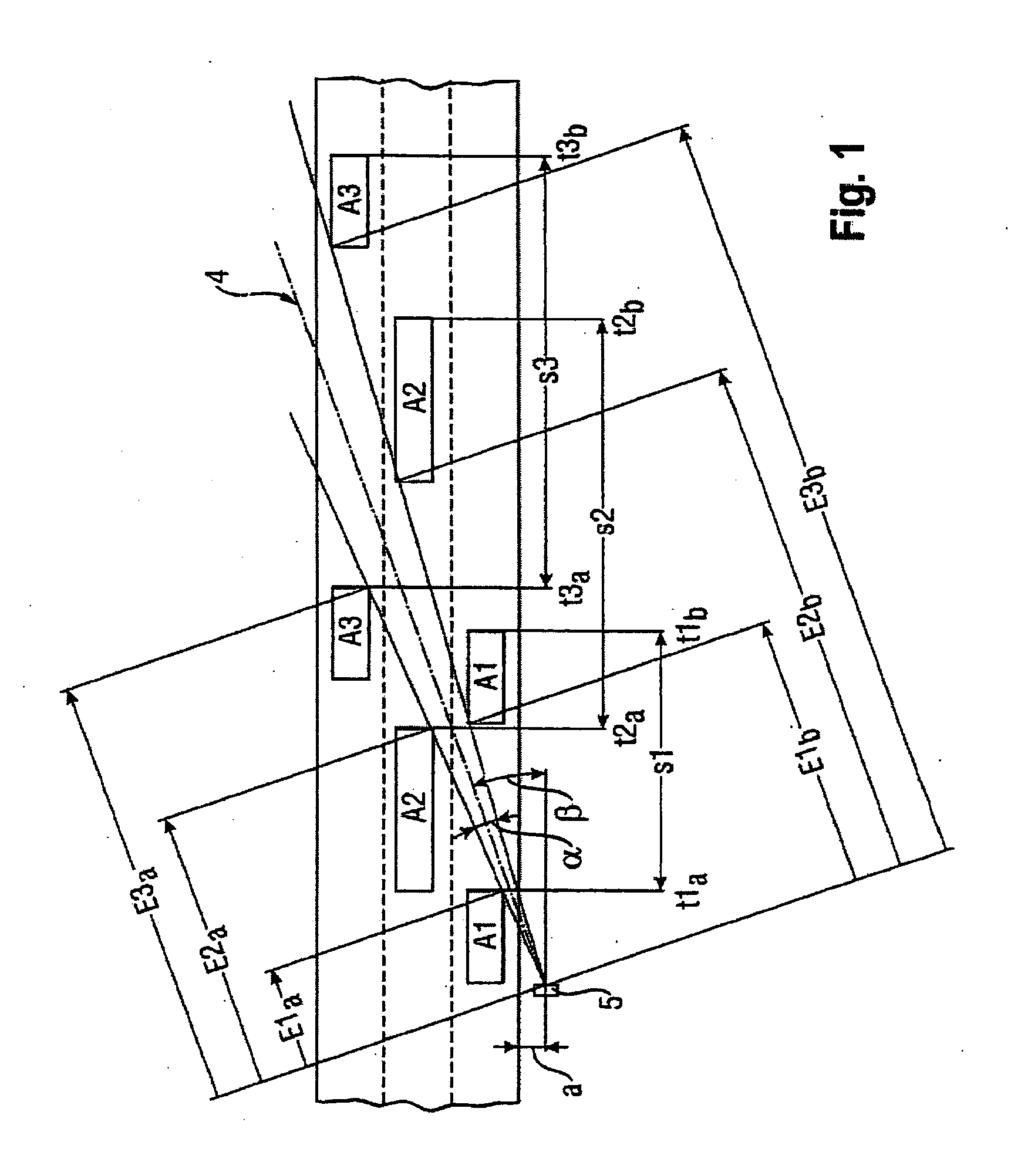
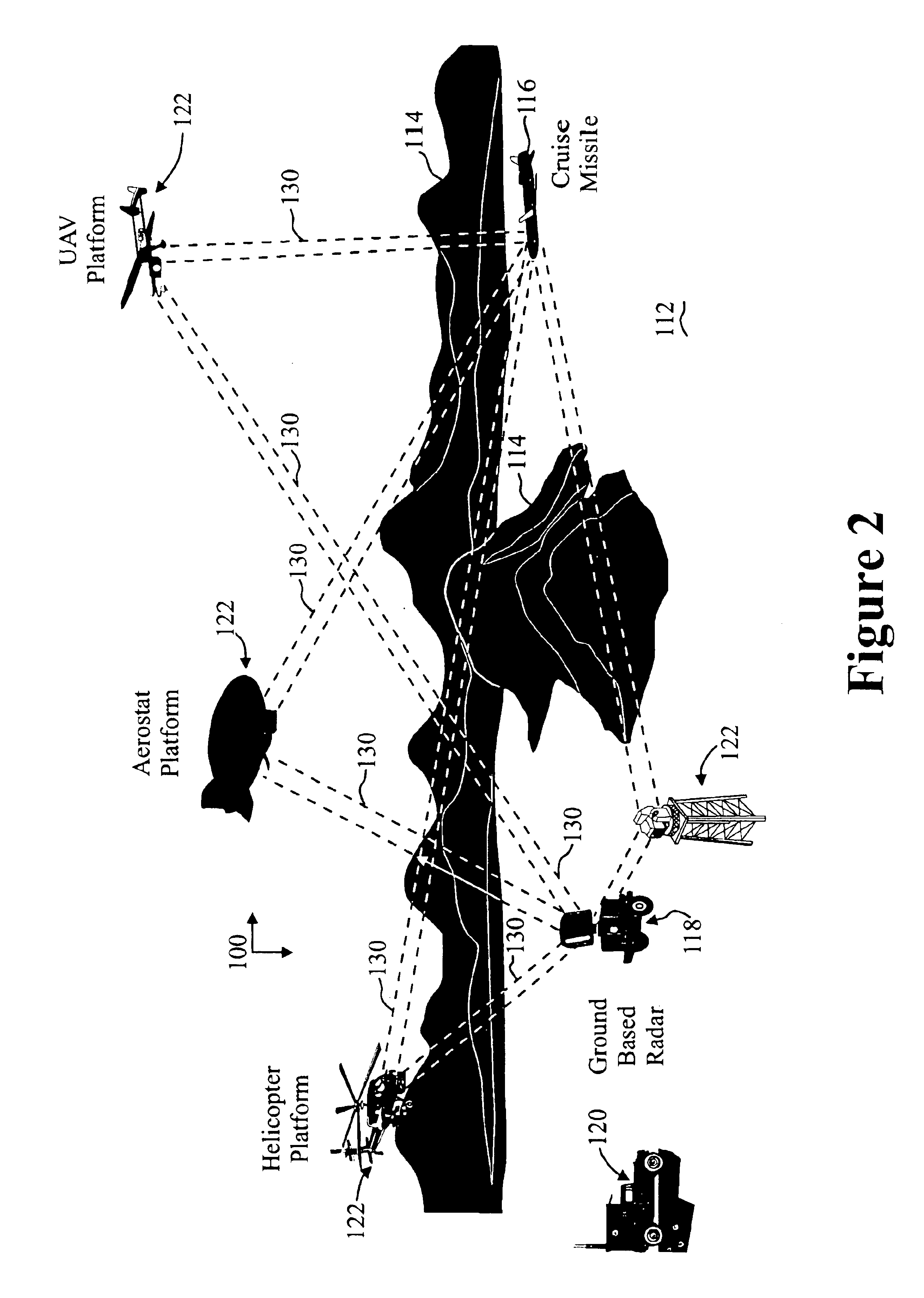
The invention relates to a method for detecting the passage by a vehicle of a determined point for monitoring on a road, wherein from a remotely situated location a radar beam is transmitted continuously to the point for monitoring, reflections from the transmitted radar beam are received at the remotely situated location, and it is determined from the received reflections that the vehicle is passing the point for monitoring. The radar beam can herein be transmitted at an acute angle to the travel direction of the passing vehicle. The detection can be used to activate a red-light camera, to measure the speed of the vehicle or measure the traffic intensity, without sensors, for instance induction loops, having to be arranged in the road for this purpose. The invention further relates to a system for performing this method.
Owner:GATSOMETER
Radar beam scanning method, on-vehicle radar apparatus and radar scanning computer program
InactiveUS20040145513A1Efficient receptionImprove signal-to-noise ratioAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDistance detectionScan angle
In the on-vehicle radar apparatus of the present invention, the vertical scanning width of the radar beam is narrowed, before the horizontal scanning, thereby avoiding unnecessary data processing and improving the data processing efficiently. Further, the SIN ratio of the target detection signal is increased, thereby stabilizing the distance detection and its accuracy. The vertical scanning antenna is a single travelling wave excitation antenna (TWEA) constructed by a plurality of antenna elements. At the same time, the horizontal scanning antenna is a multi-channel antenna wherein a plurality of TWEAs is assigned to a plurality of horizontal directions. The horizontal scanning angle is arbitrarily widened by increasing the number of TWEAs.
Owner:DENSO CORP
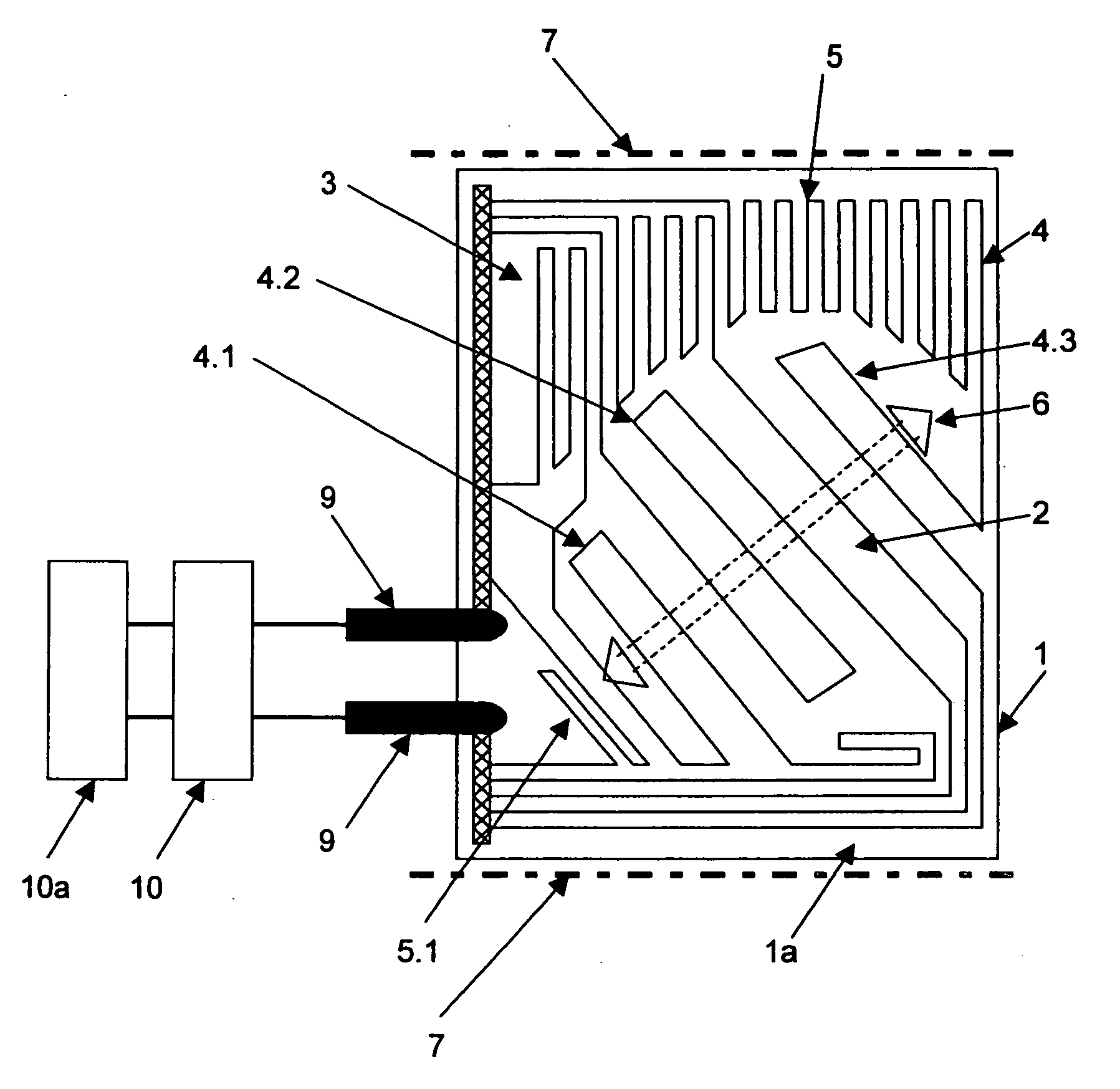
Heating element on the polymer inside surface of a motor vehicle front-end module/bumper in an operative connection to a radar transmitter/receiver unit
InactiveUS20060086710A1Excellent radar transmittingExcellent receiving characteristicVehicle seatsDielectric heating circuitsMobile vehicleElectrical conductor
A heating element for an inside surface of a front-end module / bumper for a motor vehicle. The heating element is operatively connected to a radar transmitting / receiving unit. The heating element comprises a heating film formed of a polymer, an array of conductor strips integrated into the heating film, and an electronic control element that controls the conductor strips. The array of conductor strips is divided into an inner region through which a radar beam from the radar transmitting / receiving unit is transmitted, and an outer region through which the radar beam is not transmitted. The conductor strips in the inner region are inclined by angles of about 45° to about 90° relative to a polarization plane of the radar beam. The conductor strips in the outer region are arranged in a meandering pattern.
Owner:REHAU AG & CO
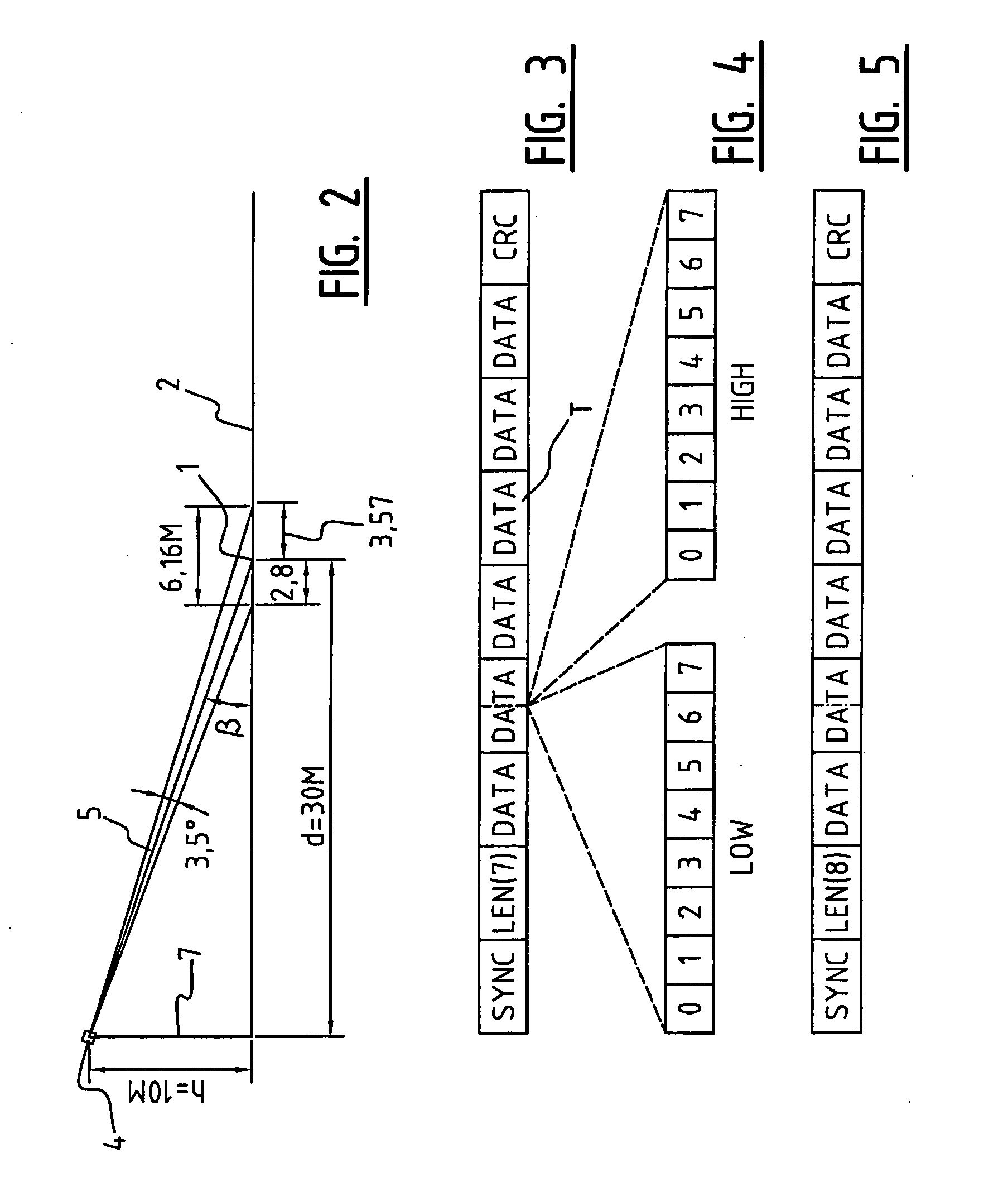
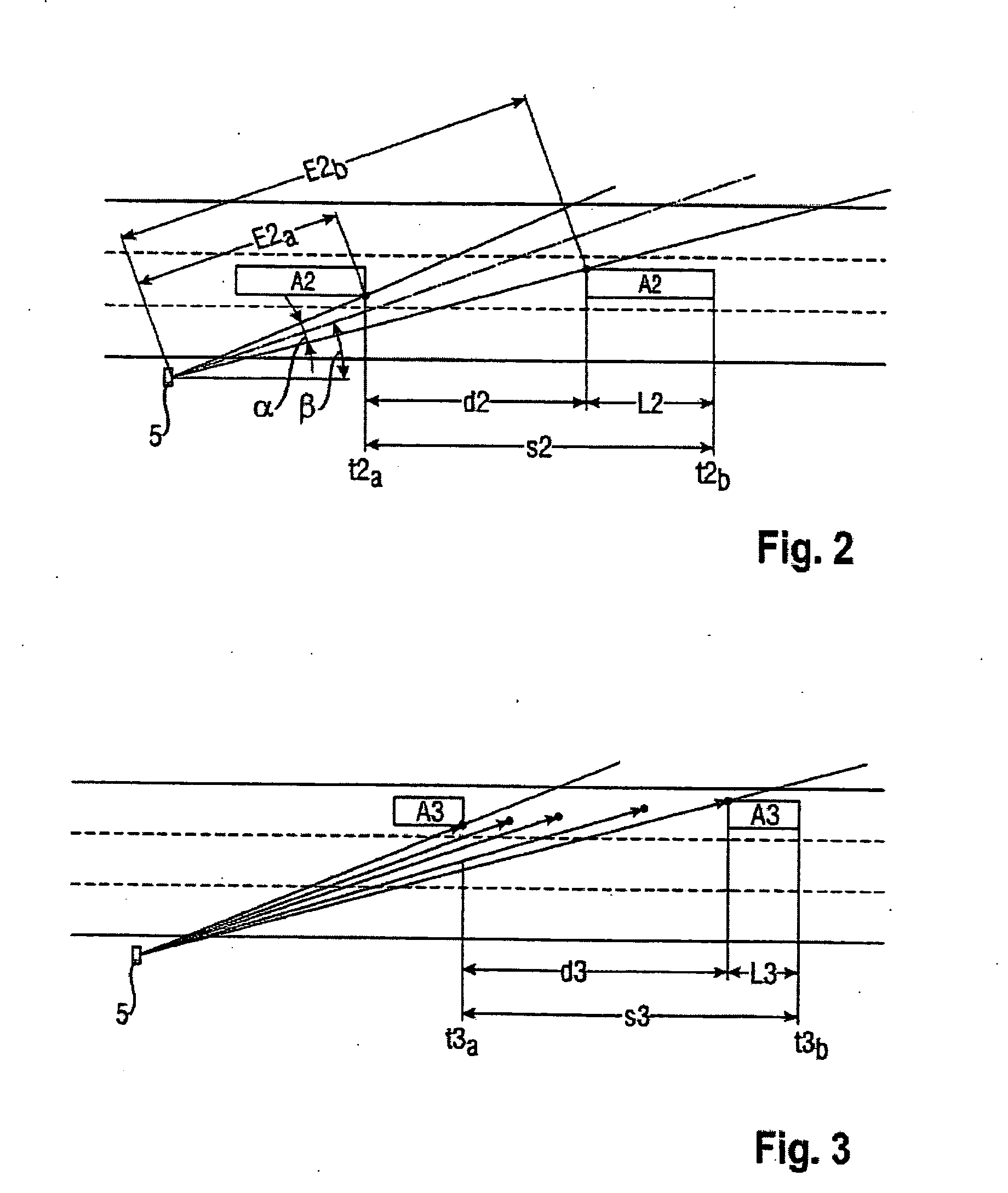
Method and Device for Determining the Vehicle Class of Vehicles
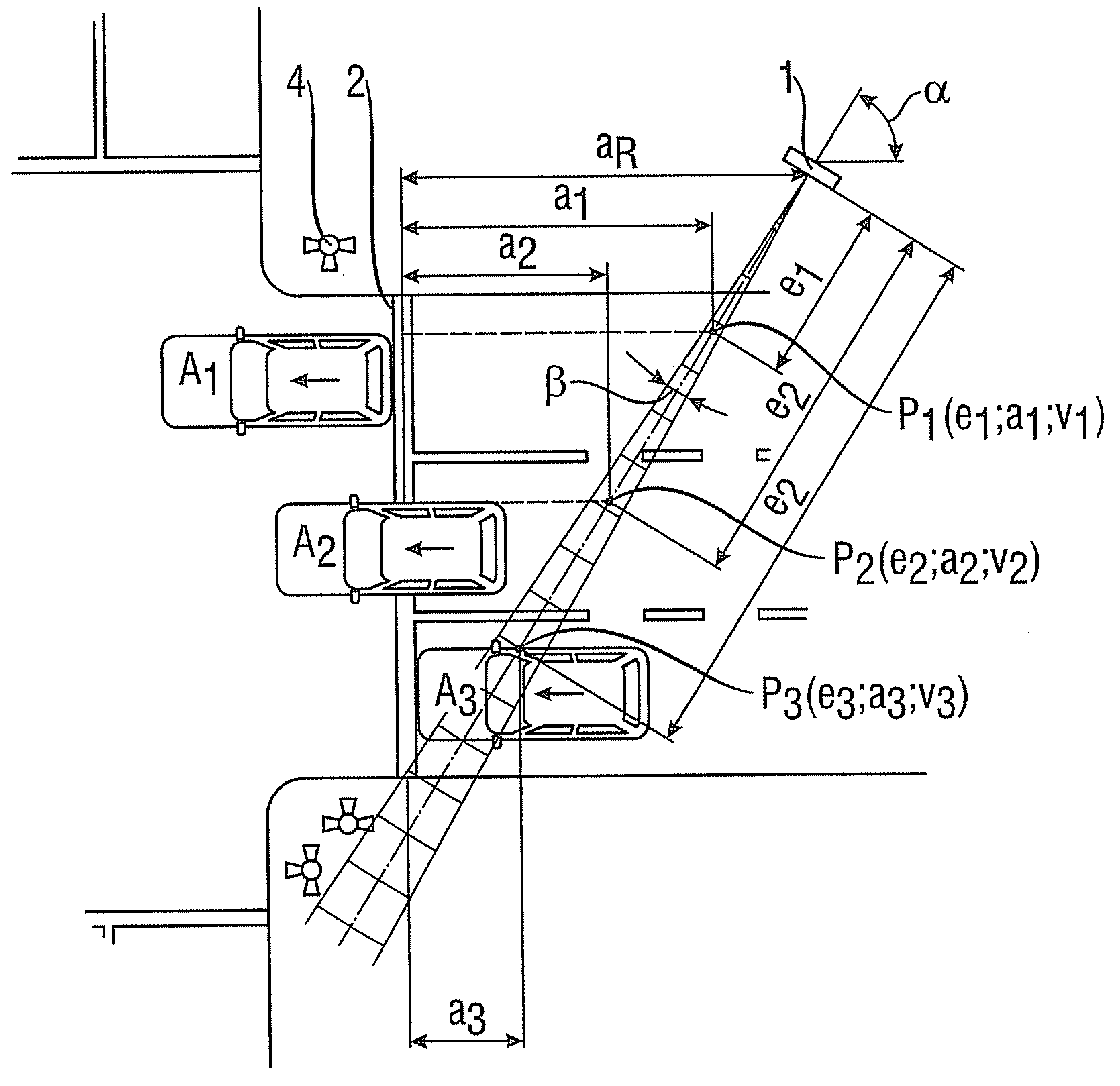
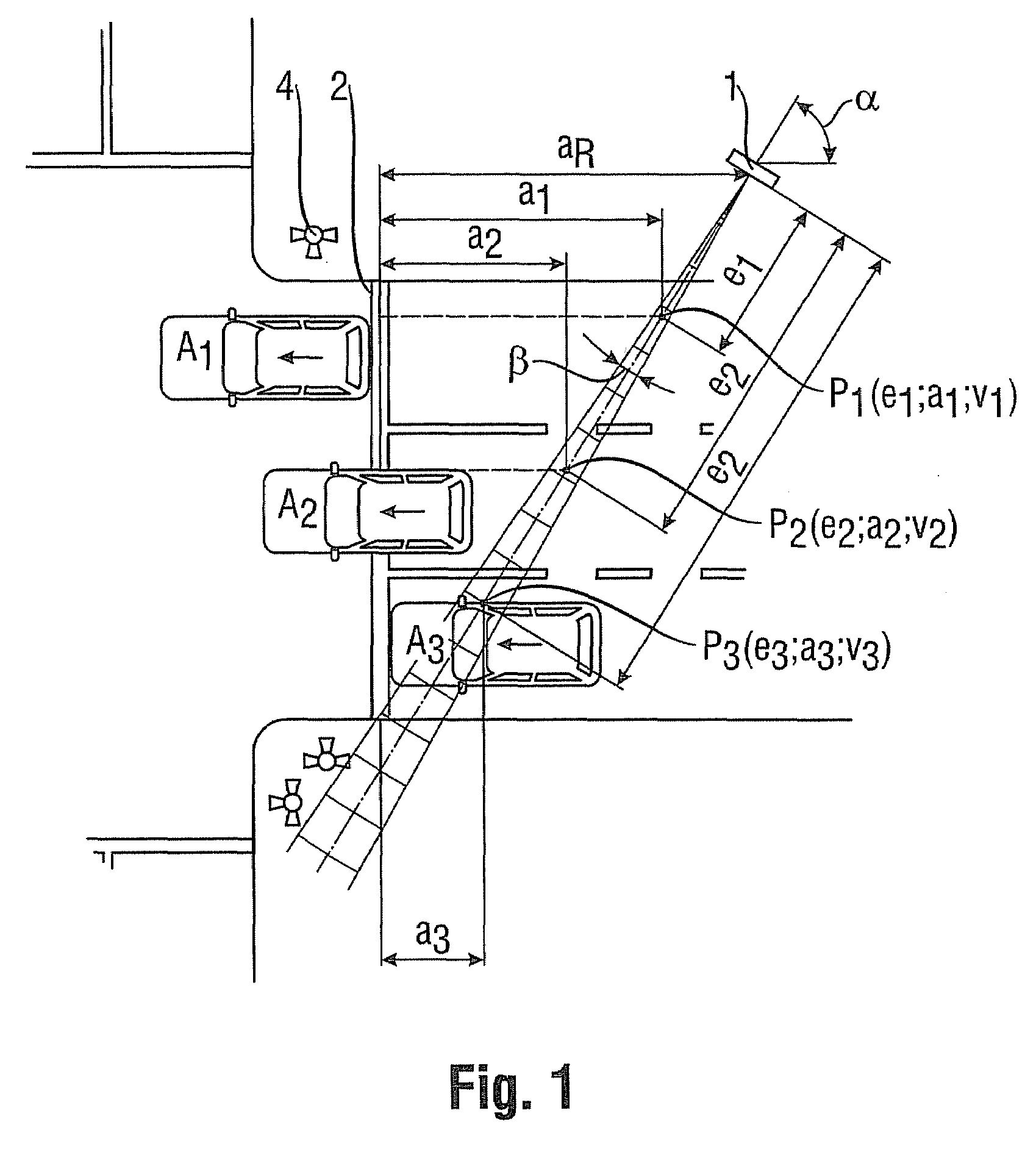
InactiveUS20080278366A1Criterion be improvedAccurately derivedRoad vehicles traffic controlRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLength measurementRadar beam
The invention relates to a method and device with which a vehicle traveling through a radar cone is classified by means of length criteria. The length criteria are formed by the difference of the driven distance that the vehicle covers, during which it reflects the radar beam, and the passage distance of the vehicle through the radar cone, which gives a more or less precise measurement for the vehicle length according to the accuracy of the determined passage distance. For determining the passage distance, range values are derived from the radar signals.
Owner:ROBOT VISUAL SYST
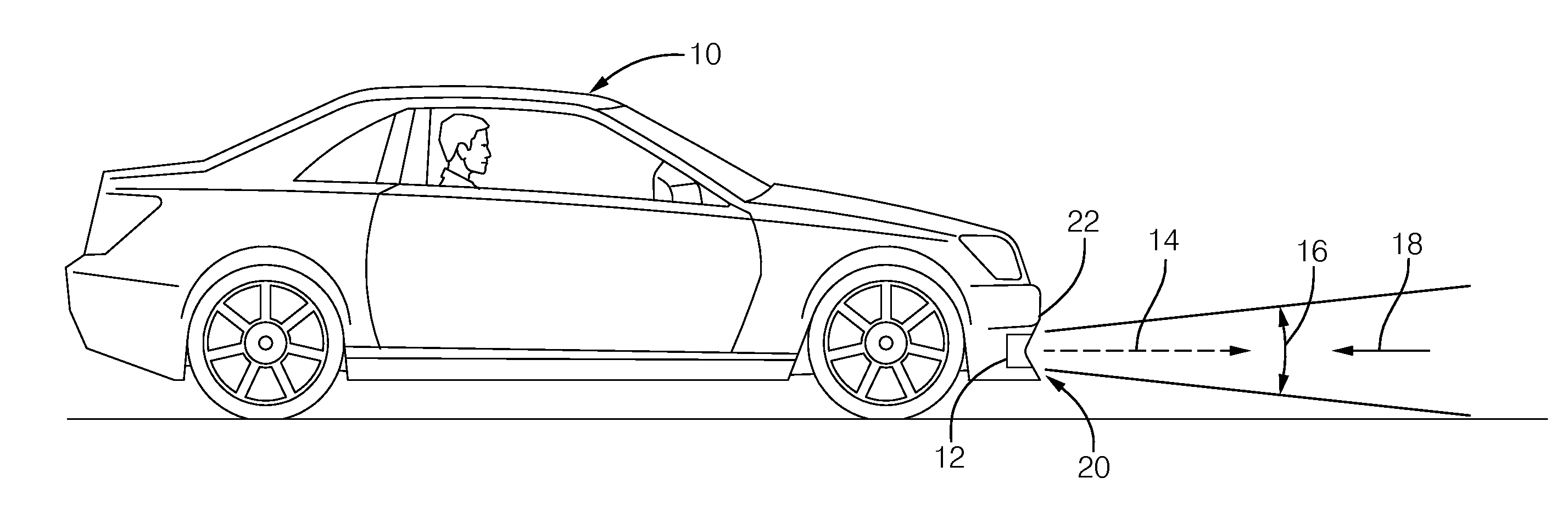
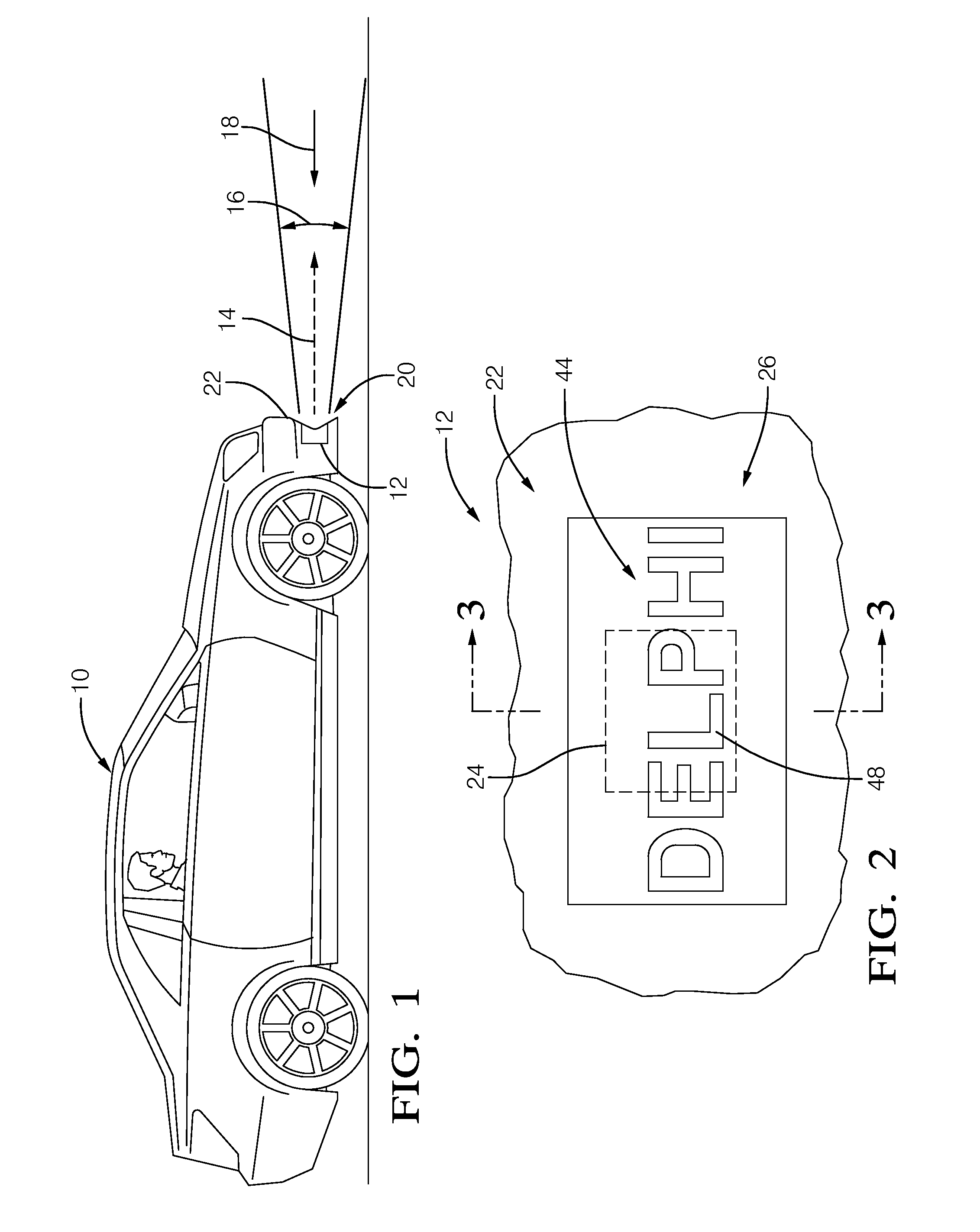
Radome for a radar sensor assembly
InactiveUS20140091969A1Minimize distortionAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating element housingsWavelengthRadome
A radome for a radar sensor that includes a first and second section. Each section is formed of layers that have an electrical thickness substantially equal to an integer multiple of a guided half-wavelengths of the radar beam. Each of the sections are configured such that, at a location spaced apart from the radome, a first phase angle of the first portion of the radar beam differs from a second phase angle of the second portion of the radar beam by an amount substantially corresponding to an integer number of three hundred sixty degrees (360°) of phase angle shift.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
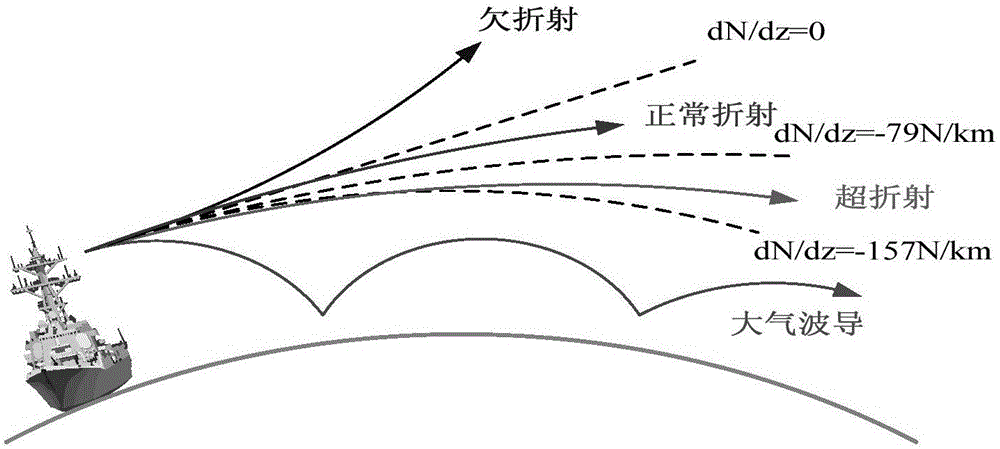
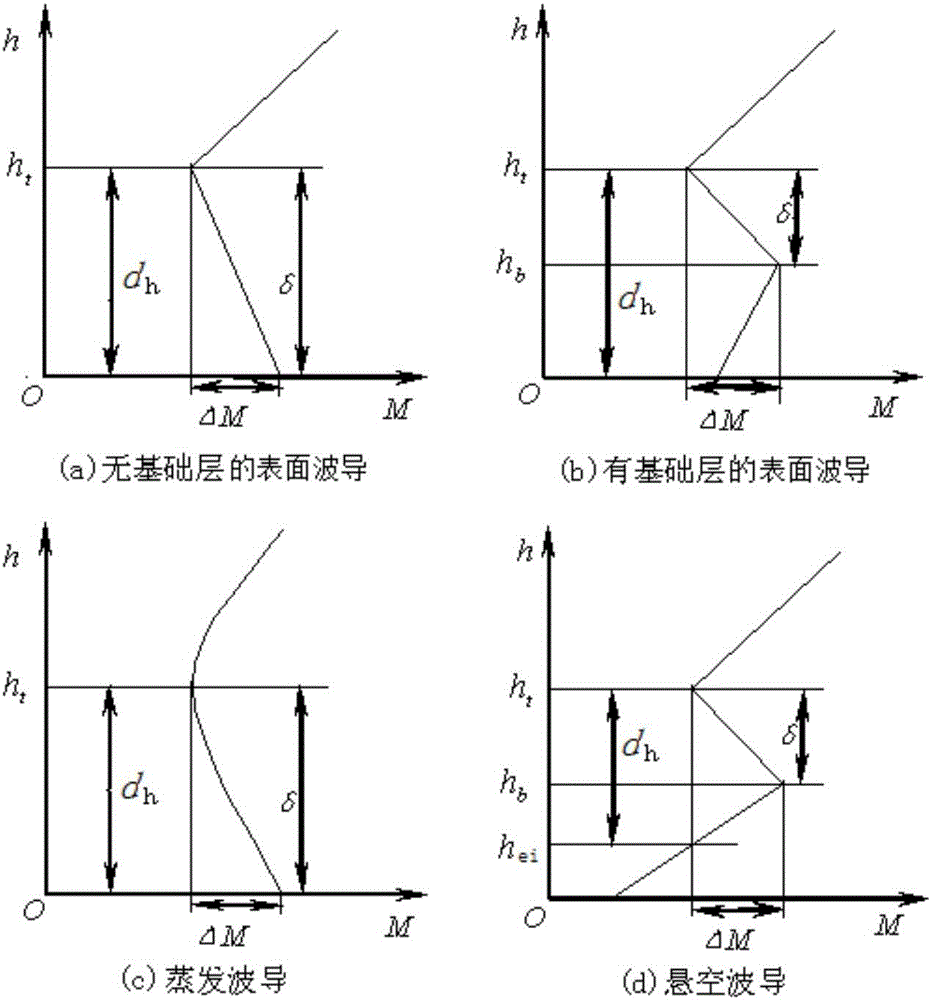
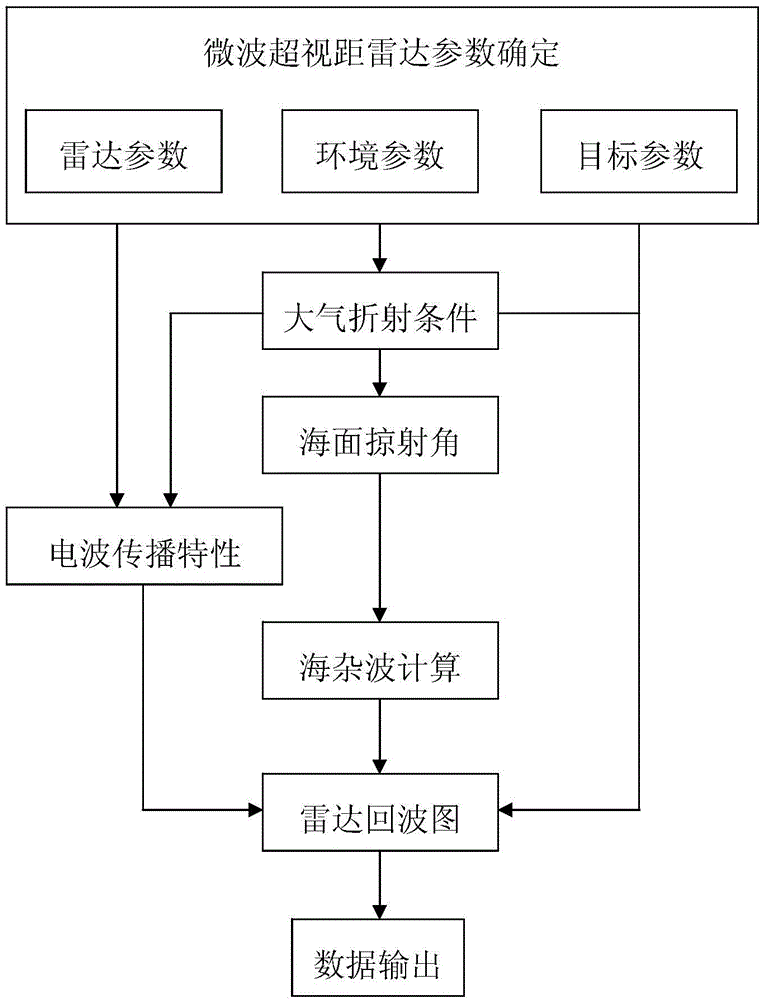
Microwave over-the-horizon radar echo chart calculating method
ActiveCN106772300AFully consider the echoFully consider the impact of the target echoWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsEvaporation
The invention discloses a microwave over-the-horizon radar echo chart calculating method, which comprises the following steps: 1) determination of relevant parameters, target parameters and environment parameters of a microwave over-the-horizon radar; 2) prediction of characteristic parameters of an evaporation waveguide and measurement of characteristic parameters of a surface waveguide; 3) calculation of an atmosphere waveguide or atmosphere refraction propagation sea surface glancing angle; 4) calculation of an atmosphere waveguide or atmosphere refraction propagation factor; 5) calculation of a sea clutter and target echo power diagram; and 6) simulation of a dynamic radar echo chart. The disclosed microwave over-the-horizon radar echo chart calculating method takes influence, formed under ocean hydrological conditions, of atmospheric duct propagation on sea surface echoes and target echoes into full consideration under the actual microwave over-the-horizon radar working environment, provides an actual radar beam sea surface grazing angle calculating method under the atmospheric refraction or atmospheric duct condition on the basis of radar system parameters and marine hydrometeorological parameters, and with relevant sea clutter models being combined, can effectively predicate and estimate the sea surface echo power.
Owner:中国电波传播研究所 +1
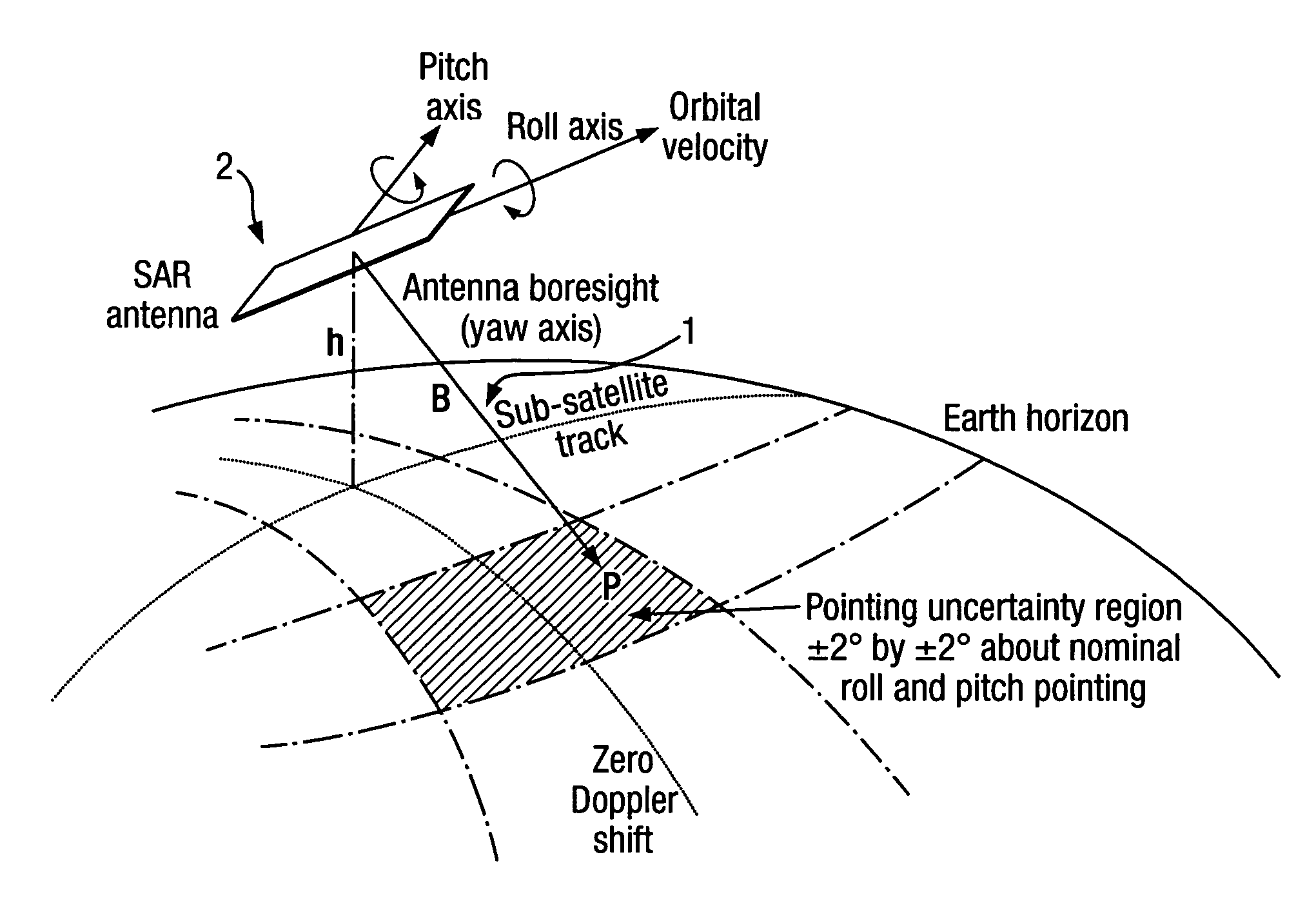
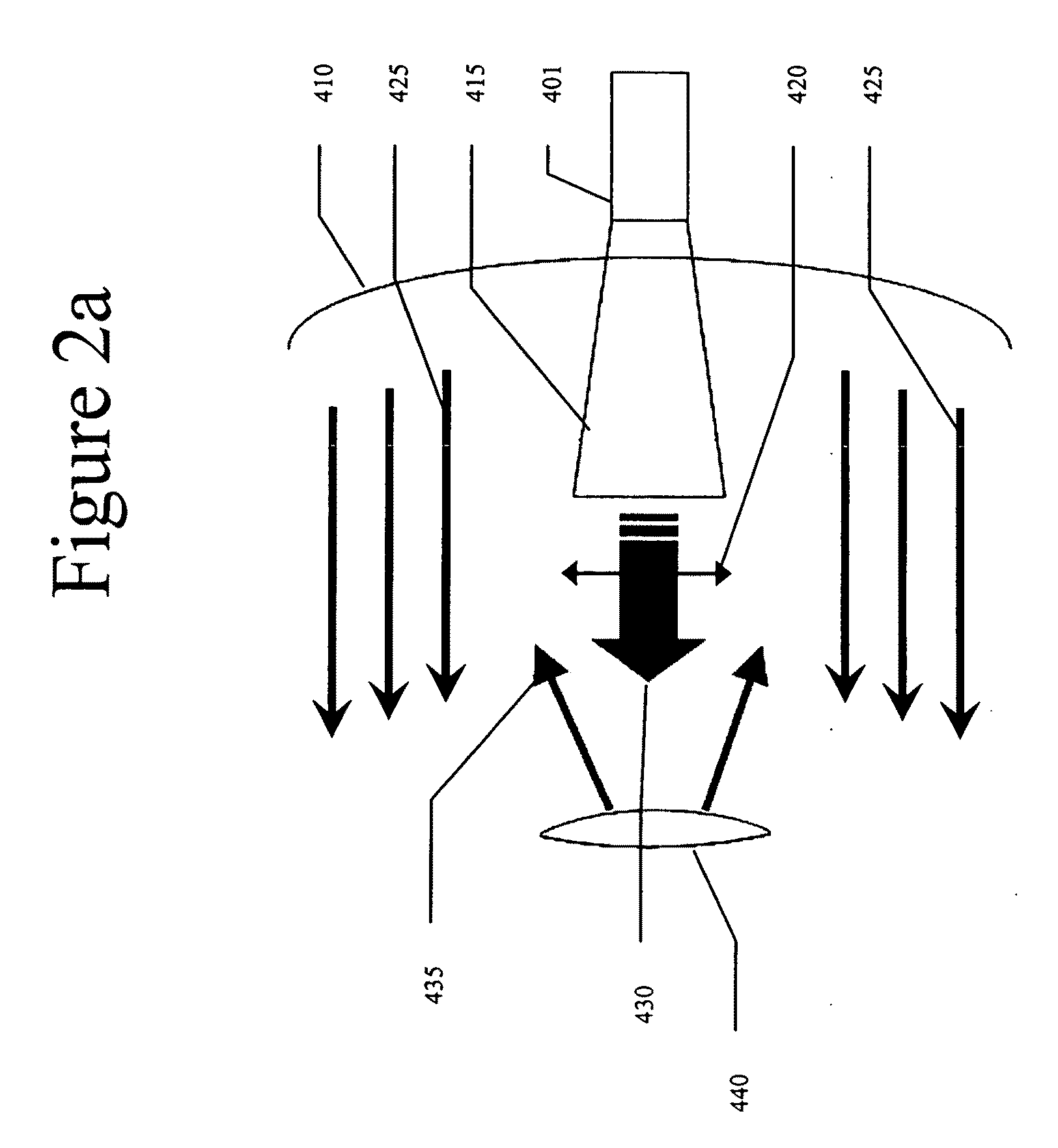
Imaging apparatus and method
InactiveUS7196653B2Low costFeasible effortRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar observationsImaging equipment
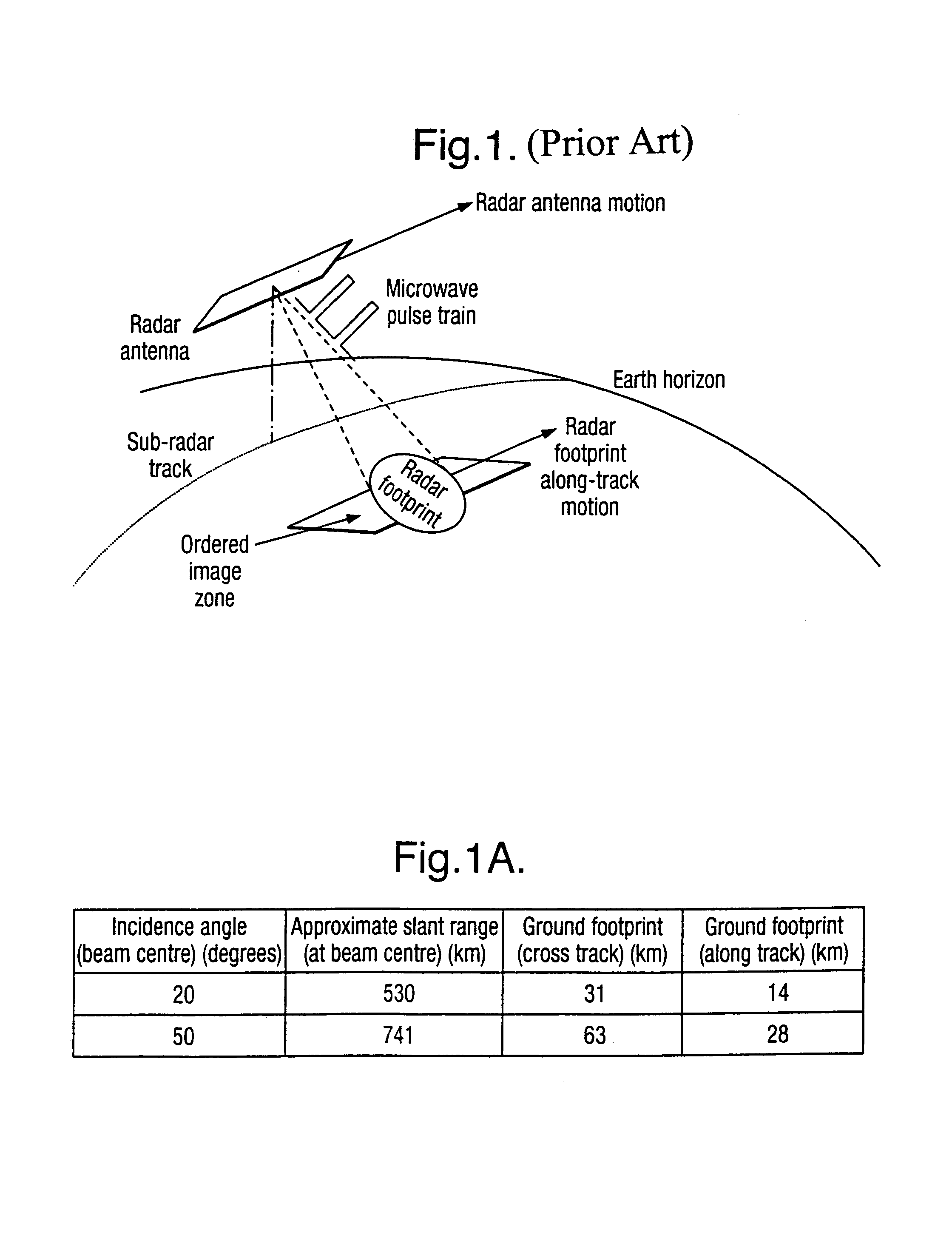
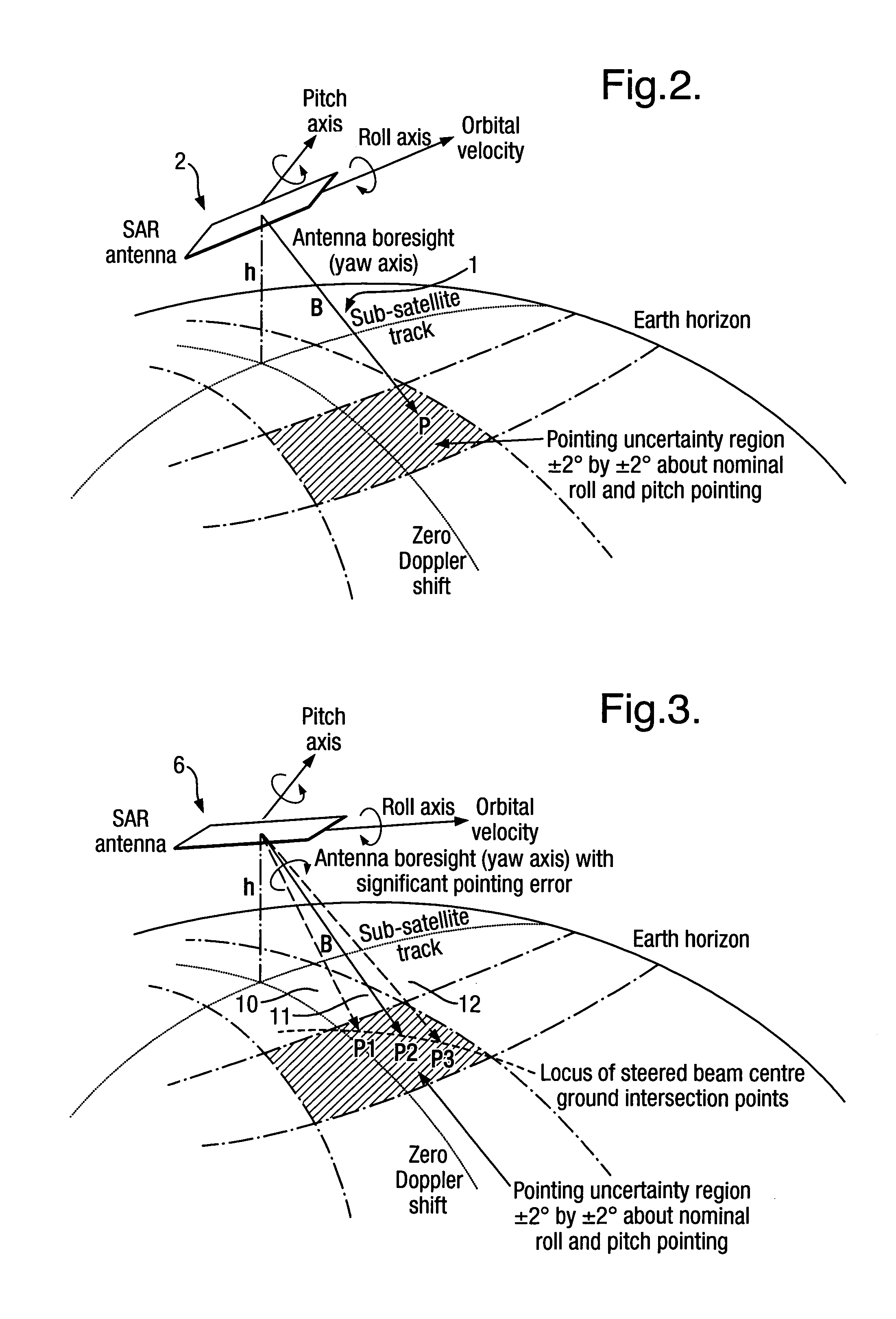
An imaging apparatus has transmitter illuminating a selected surface with a radar beam footprint, and processor for profiling / processing the radar returns so as to derive attitude information in real time about a number of predefined axes associated with the radar which depends upon the relative dispositions of the radar, the selected surface and upon the radar beam footprint characteristics.A plurality of transmit beams image the surface and the processing arrangement has the capability of determining roll, pitch and / or yaw pointing data associated with the radar, such pointing data being determined by derivation of the attitude information and by selective input of terrain elevation data so as to take account of variations in the radar viewing geometry with terrain elevation.This provides a low cost advantage over known radar designs, and retains utility for many applications, for example spaceborne and airborne applications.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
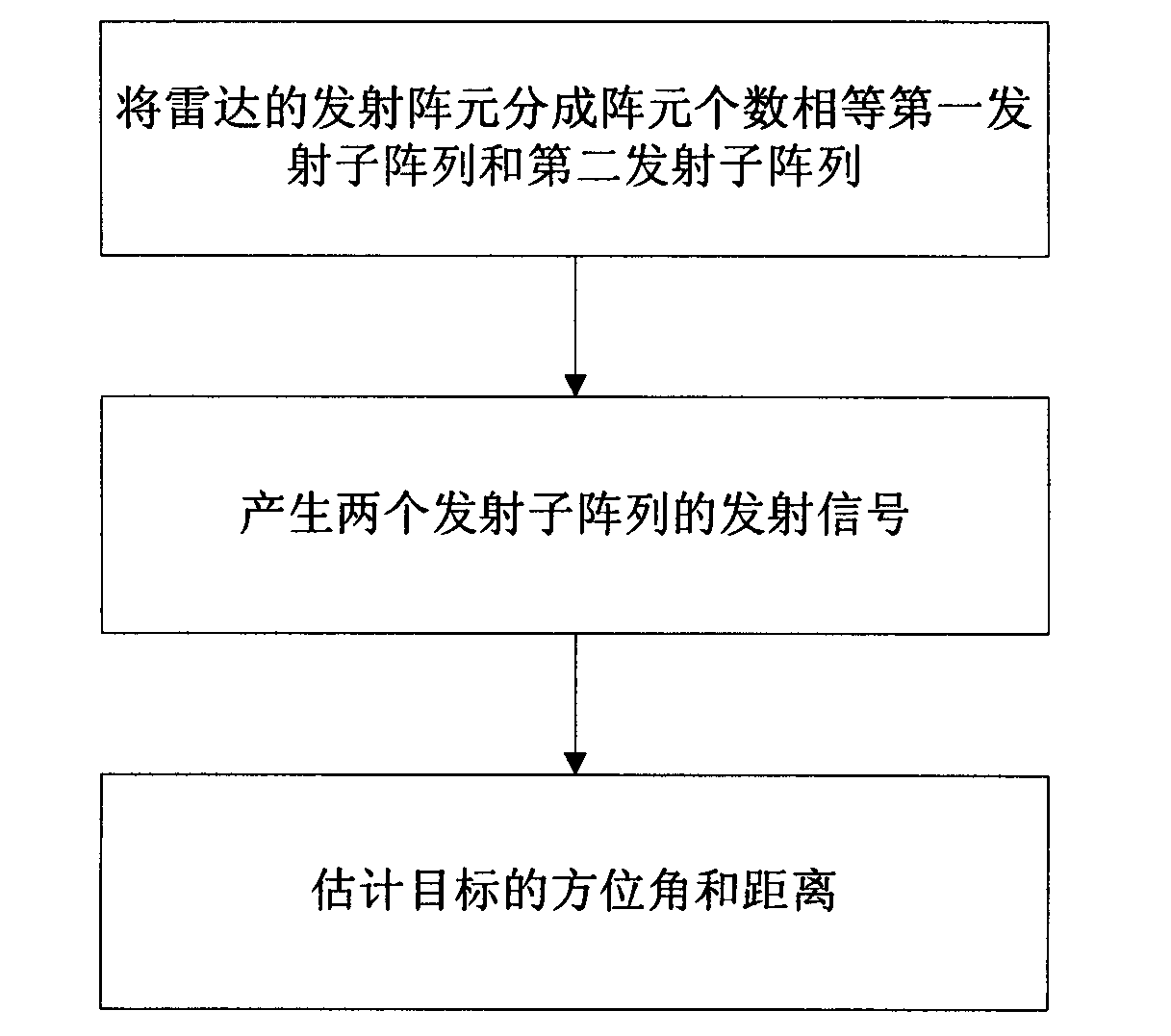
Method for utilizing frequency distribution array (FDA) radar to estimate object distance and azimuthal angle and FDA radar
InactiveCN103018737AEfficient joint estimationSolve the coupling problemRadio wave reradiation/reflectionArray elementRadar beam
The invention belongs to the technical field of frequency distribution array (FDA) radars and discloses a method for utilizing a frequency distribution array (FDA) radar to estimate an object distance and an azimuthal angle. The method comprises the steps of dividing transmitting array elements of the radar into a first transmitting subarray and a second transmitting subarray with equal array element numbers, generating transmitting signals of the two transmitting subarrays, and estimating the azimuthal angle of the distance of an object. According to the method, the distance dependence characteristics of FDA radar beam can be effectively utilized to perform joint estimation on the azimuthal angle of the distance of the object, and the coupled problem which occurs when the FDA radar is utilized to estimate the distance and the azimuthal angle of the object is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for improved determination of range and angle of arrival utilizing a two tone CW radar
ActiveUS20070052580A1Double accuracyImproved noise filteringRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSingular value decompositionFire-control system
An improved system is provided for aiming a shotgun-based or other countermeasure system so as to be able to countermeasure incoming rockets or projectiles. In one embodiment a shotgun aimed and controlled by the subject system projects a pattern of pellets to intercept a rocket-propelled grenade or incoming projectile. The fire control system uses a CW two-tone monopulse radar to derive range and angle of arrival within 150 milliseconds, with range and angle of arrival measurements having approximately twice the accuracy of prior CW two-tone monopulse radars. The improvement derives from using all of the information in the returned radar beams and is the result of the recognition that one can use the Sum and Difference signals to assemble a two-by-two Rank One matrix that permits using singular value decomposition techniques to generate range and angle of arrival matrices in which all available information is used and in which noise is eliminated.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
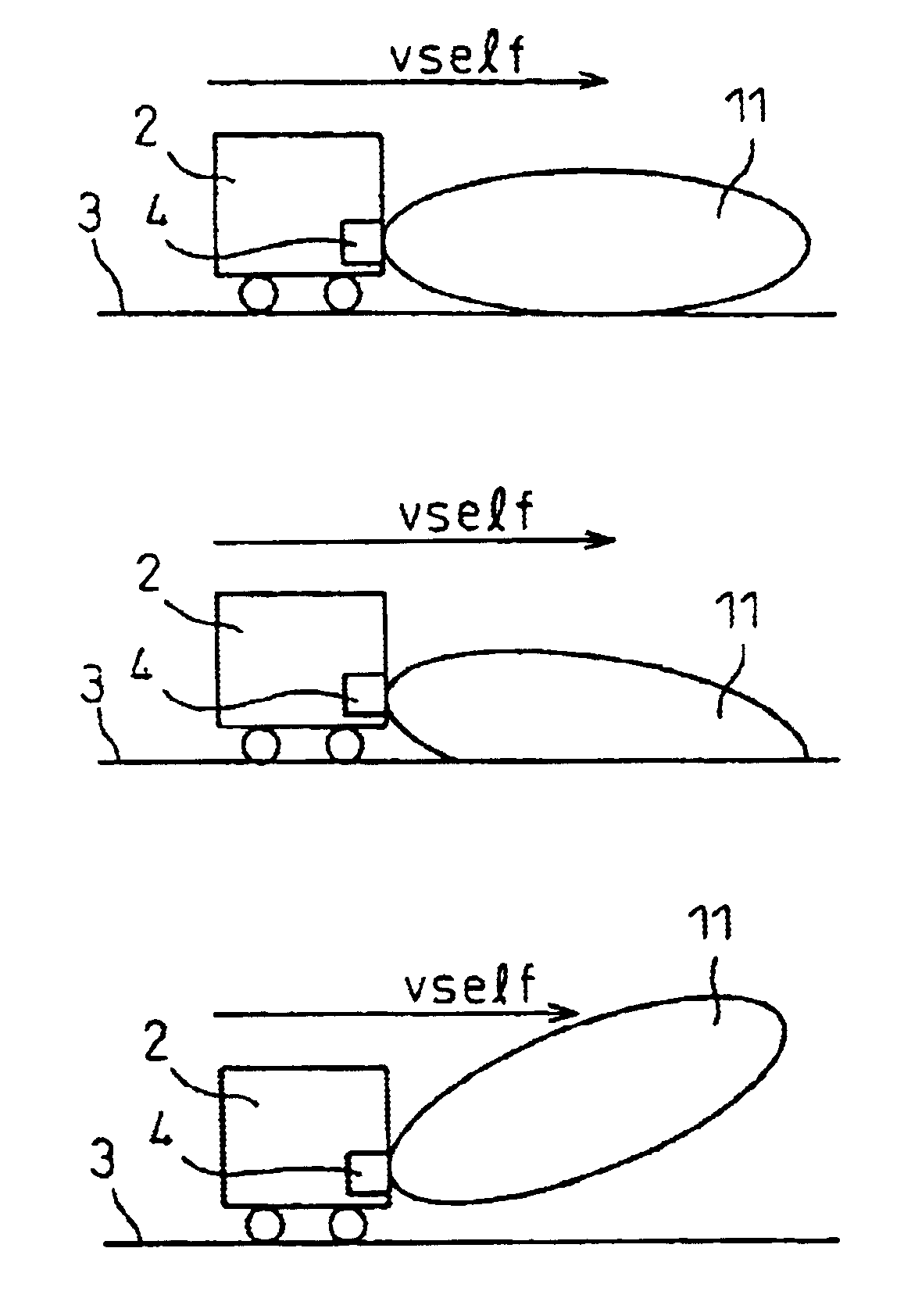
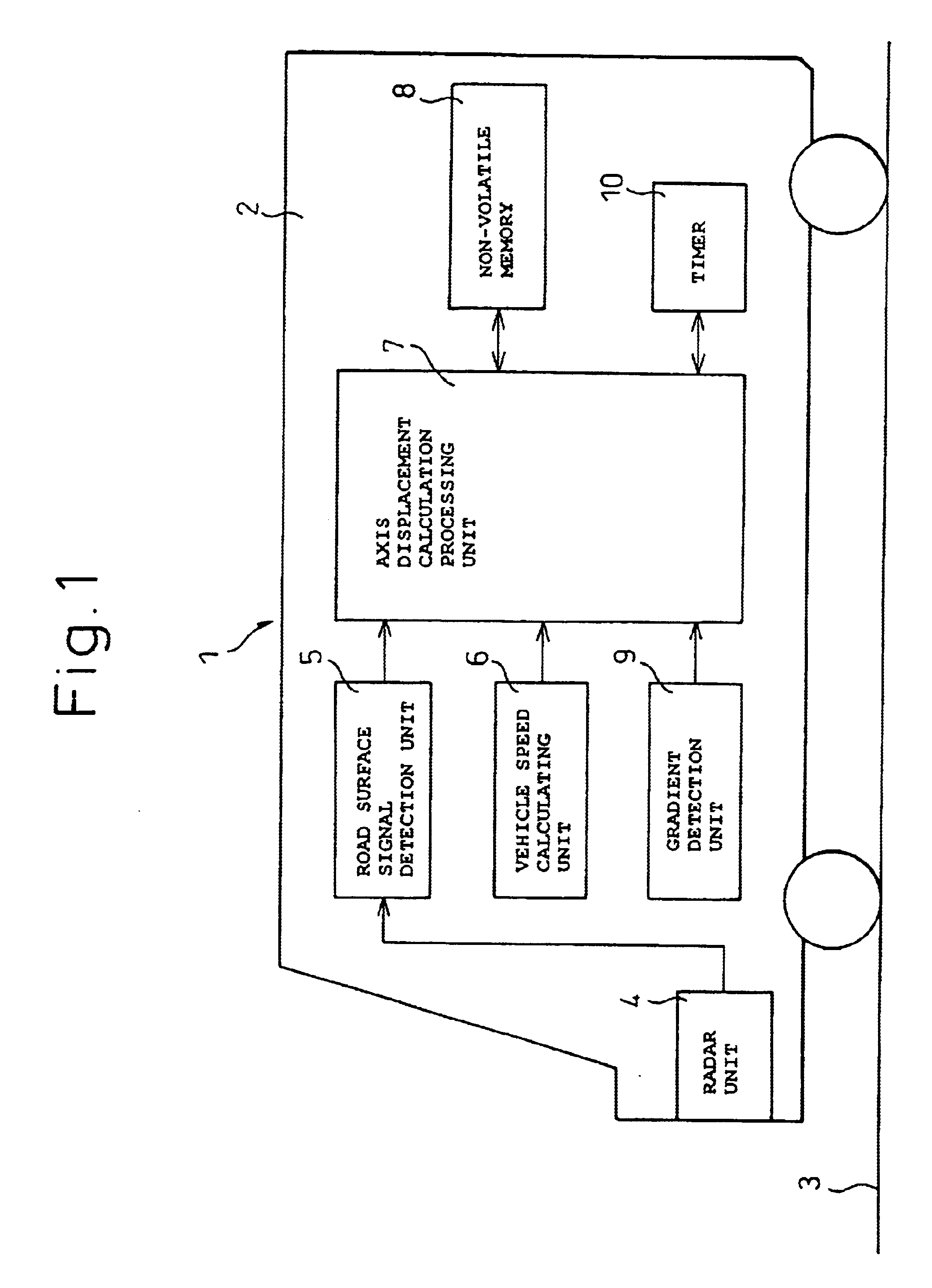
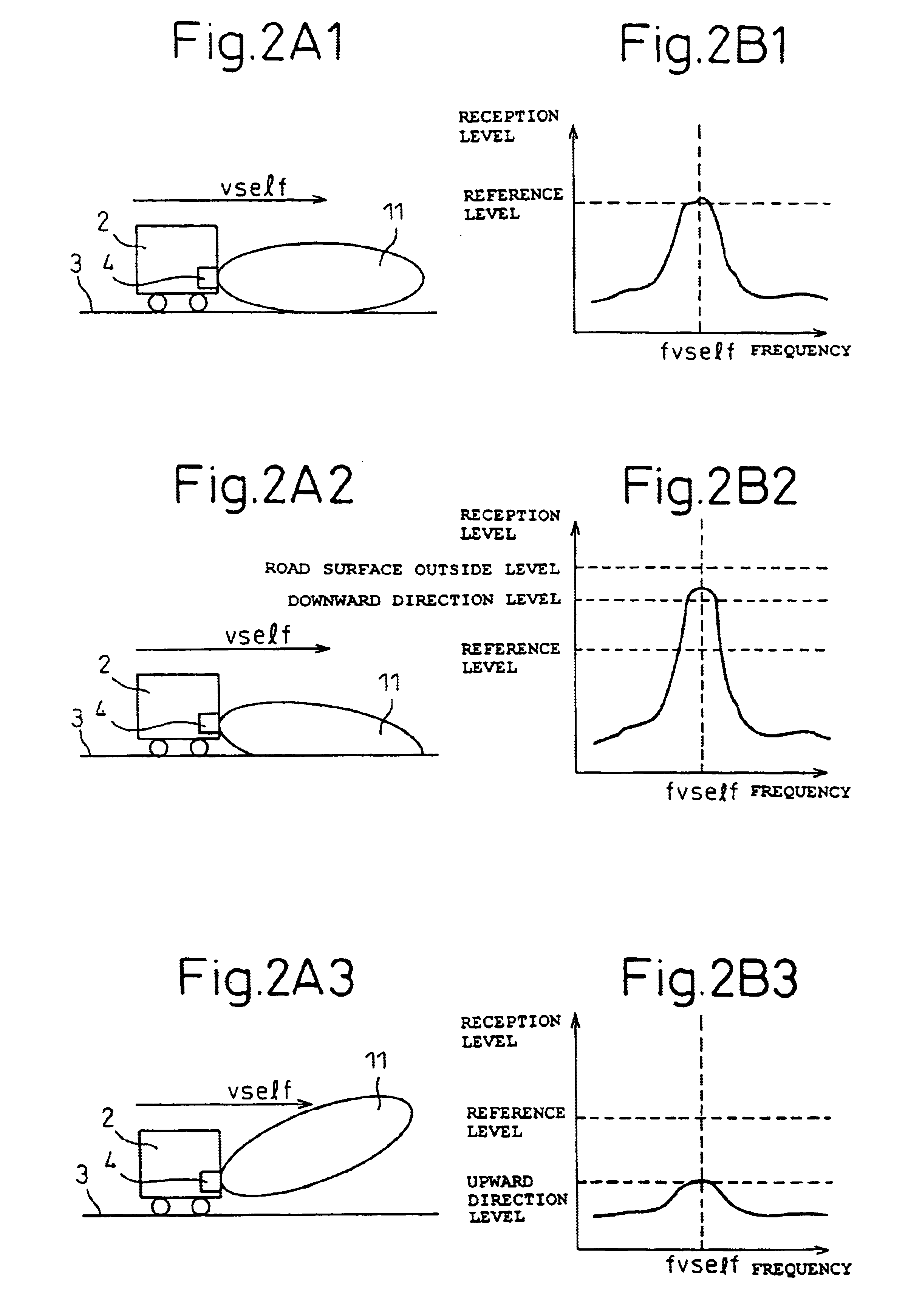
Road surface detection apparatus and apparatus for detecting upward/downward axis displacement of vehicle-mounted radar
InactiveUS6896082B2Simple and accurate mannerEnsure correct executionVehicle fittingsAutomatic initiationsRoad surfaceAcoustics
A road surface detection apparatus capable of detecting an upward / downward displacement in radar axis when detecting a road surface by projecting a radar beam. The apparatus projects a radar beam signal onto the road surface on which the radar-equipped vehicle is traveling, and receives a signal containing a reflected signal of the radar beam signal. Then, the apparatus compares the level of the road surface reflected signal contained in the received signal with a predetermined reference level and, if the result of the comparison lies outside a predefined range, then the apparatus determines that the axis defining the projection direction of the radar beam signal is displaced.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Technique for changing a range gate and radar coverage
InactiveUS6977609B2Increase probabilityImprove accuracyMultiple-port networksVehicle fittingsRadar detectionRange gate
A radar detection process includes computing a derivative of an FFT output signal to detect an object within a specified detection zone. In one embodiment, a zero crossing in the second derivative of the FFT output signal indicates the presence of an object. The range of the object is determined as a function of the frequency at which the zero crossing occurs. Also described is a detection table containing indicators of the presence or absence of an object within a respective radar beam and processing cycle. At least two such indicators are combined in order to detect the presence of an object within the detection zone and with changing range gates in each of the antenna beams the coverage of the detection zone can be varied.
Owner:VALEO RADAR SYST
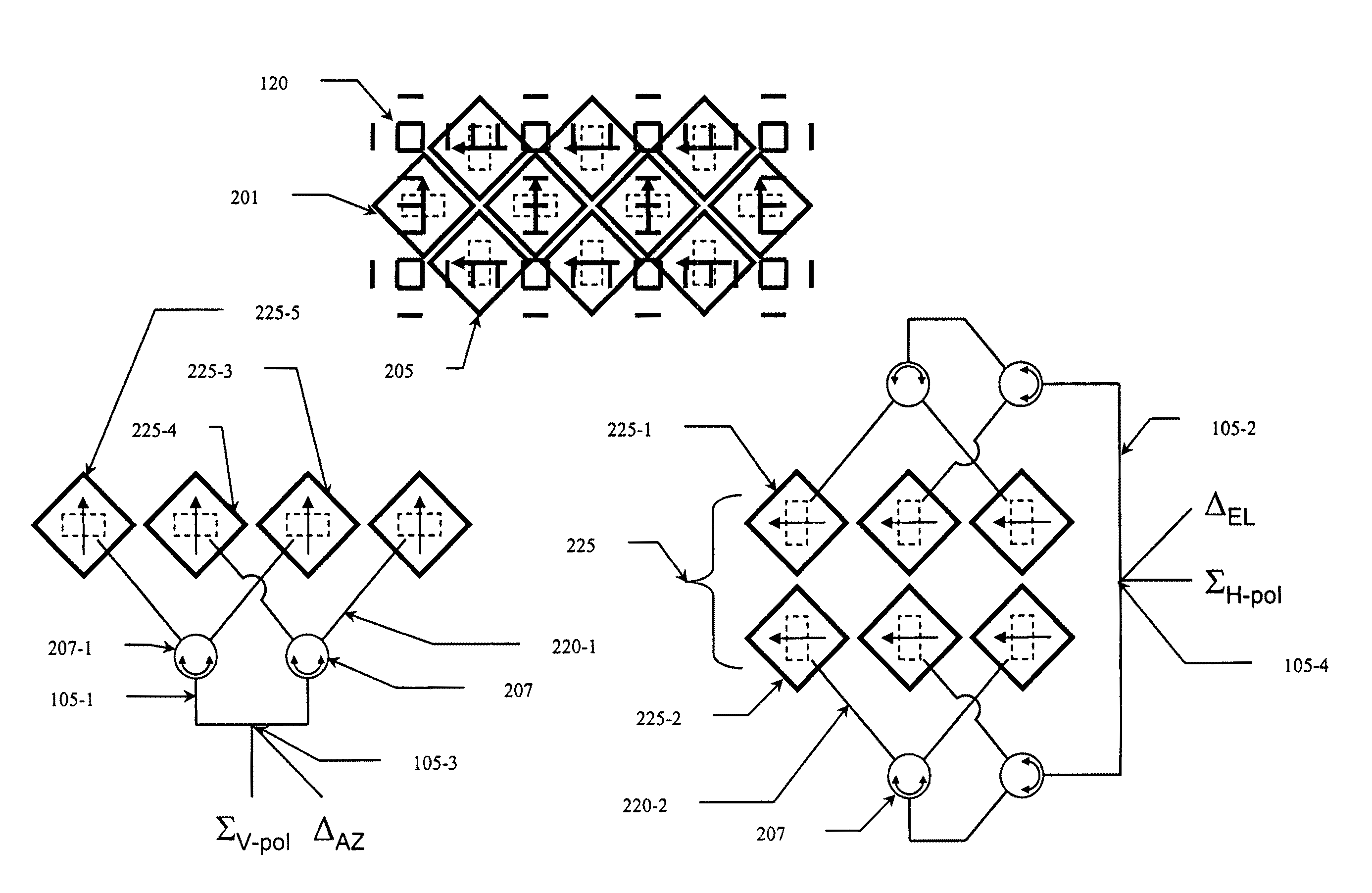
Electronically steered, dual-polarized, dual-plane, monopulse antenna feed
InactiveUS20100052987A1Reduce weight and costSmall sizePolarised antenna unit combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAntenna feedElectron
A method and apparatus for electronically steering a RADAR beam across an array of feed horns by moving the phase center of the beam to different origination points on the array—each origination point being the phase center of a feed horn pair. Variations include polarized beams, polarized feed horns, dual-beam systems, dual direction steering, diagonal steering, and cross-polarized wire grids to control beamwidth.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Imaging apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050104763A1Low costFeasible effortRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar observationsContour analysis
An imaging apparatus 6 has means for illuminating a selected surface with a radar beam footprint, and means for profiling / processing the resultant radar returns in an efficient and logical fashion such as to derive radar attitude information in real time about a number of predefined axes associated with the radar which depends upon the relative dispositions of the radar and the selected surface and upon the radar beam footprint characteristics. Advantageously, a plurality of transmit beams 10,11,12 are used to image the surface and the processing arrangement has the capability of determining roll, pitch and / or yaw pointing data associated with the radar, such pointing data being determined by derivation of the attitude information and by selective input of terrain elevation data so as to take account of variations in the radar viewing geometry with terrain elevation. The inventive radar bears a definite low cost advantage over known radar designs, and retains utility for many applications, for example spaceborne and airborne applications.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
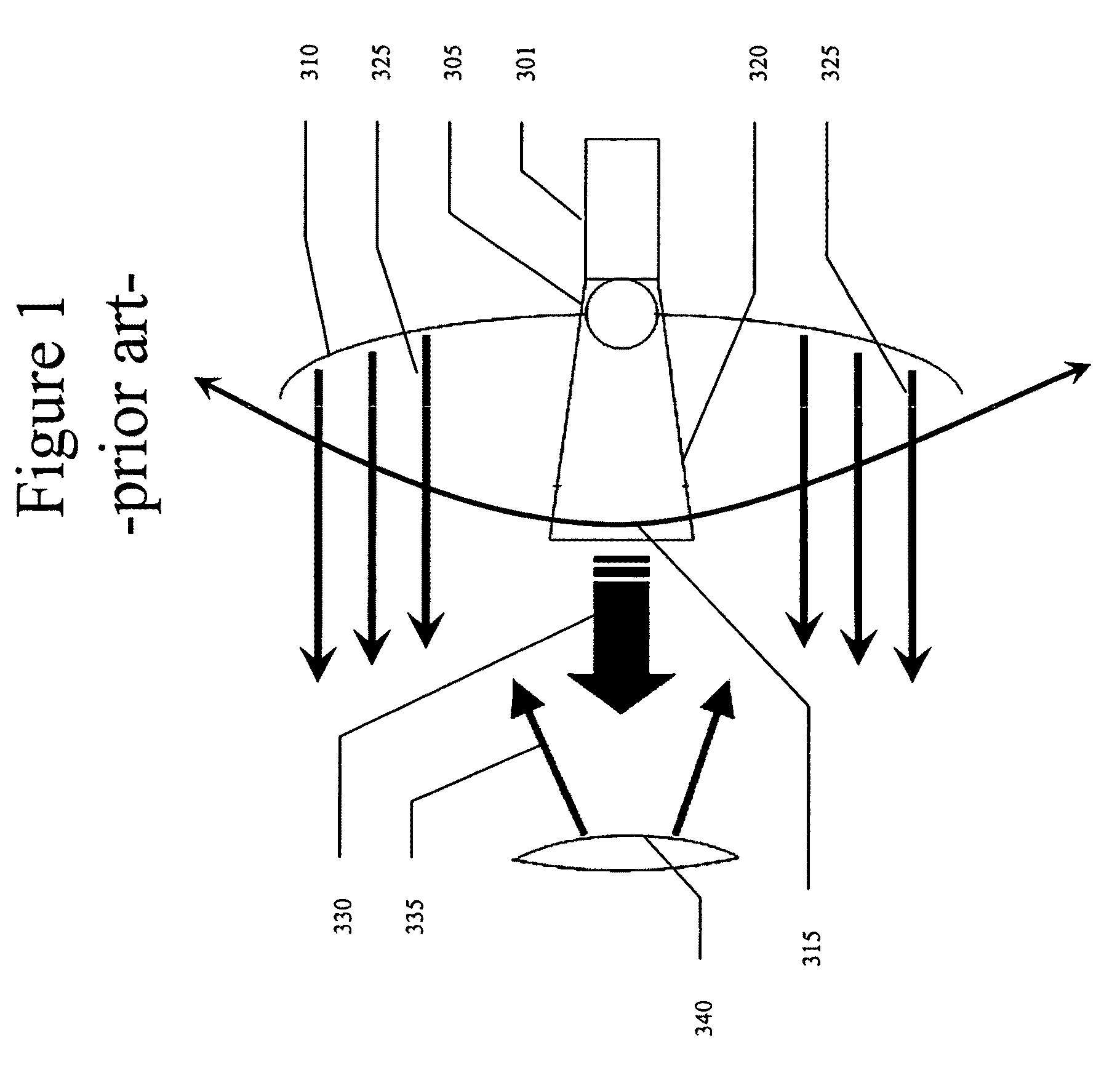
Process for side lobe suppression and amplitude or phase monopulse radar device
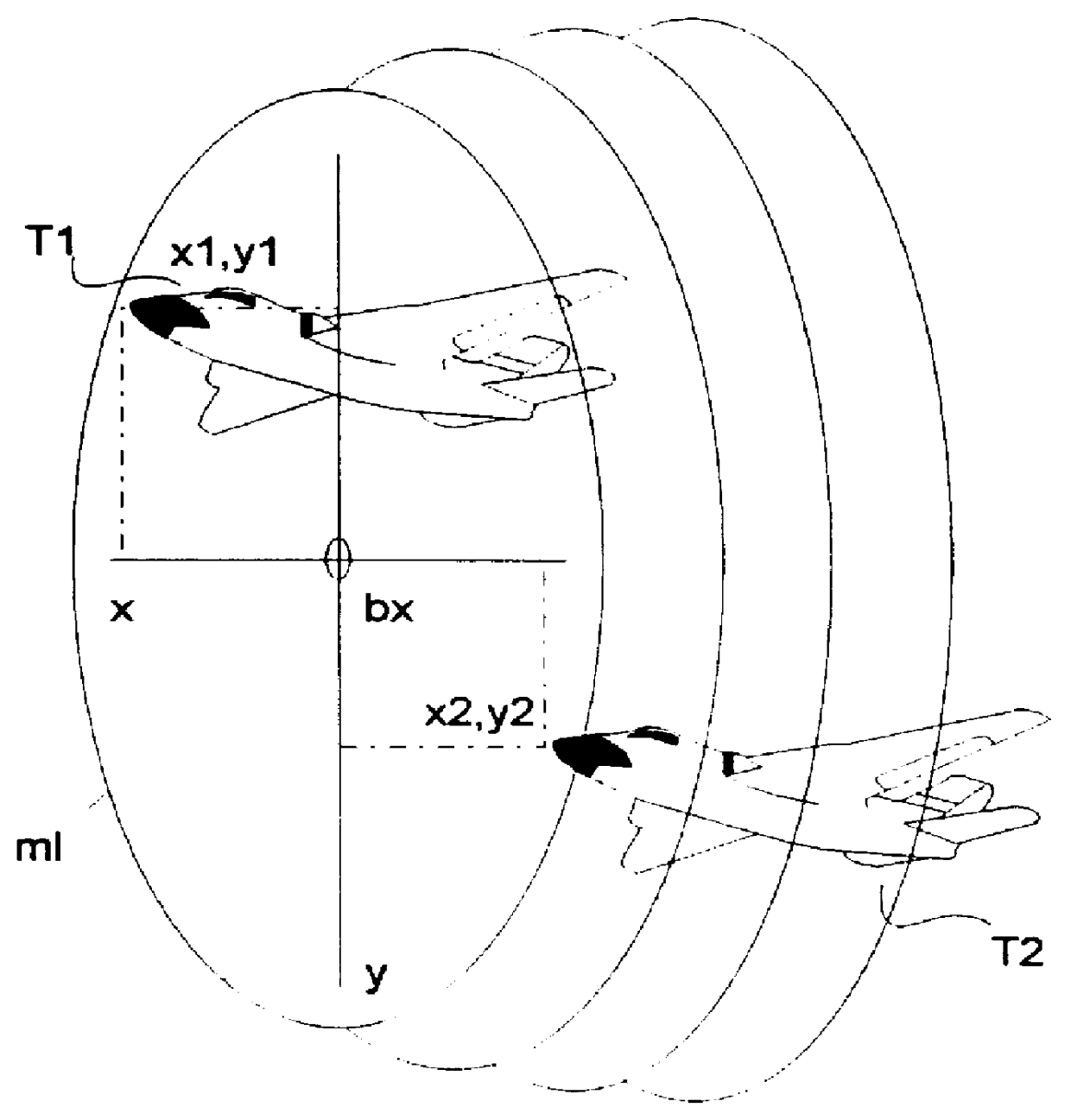
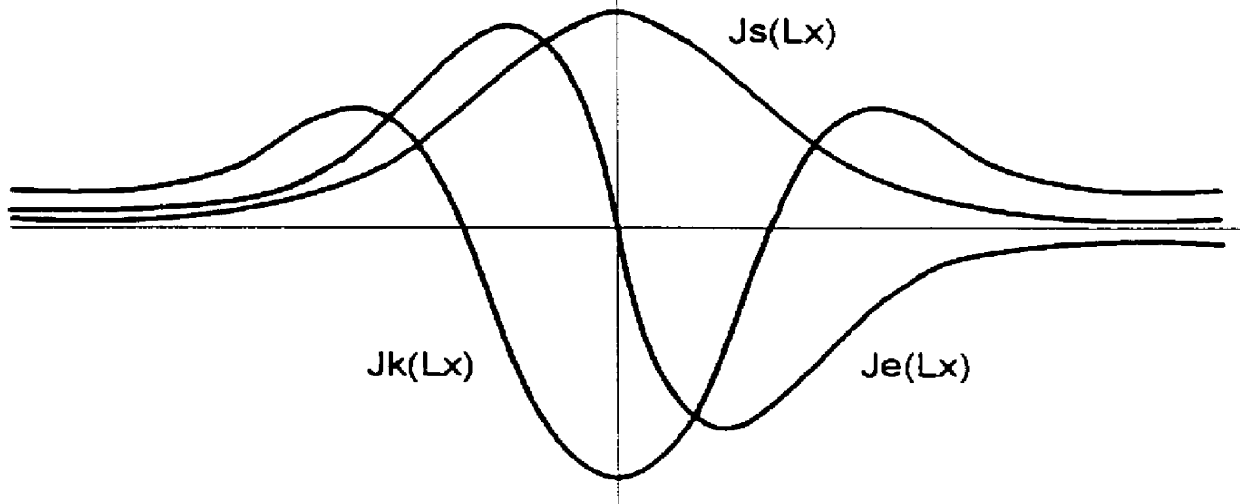
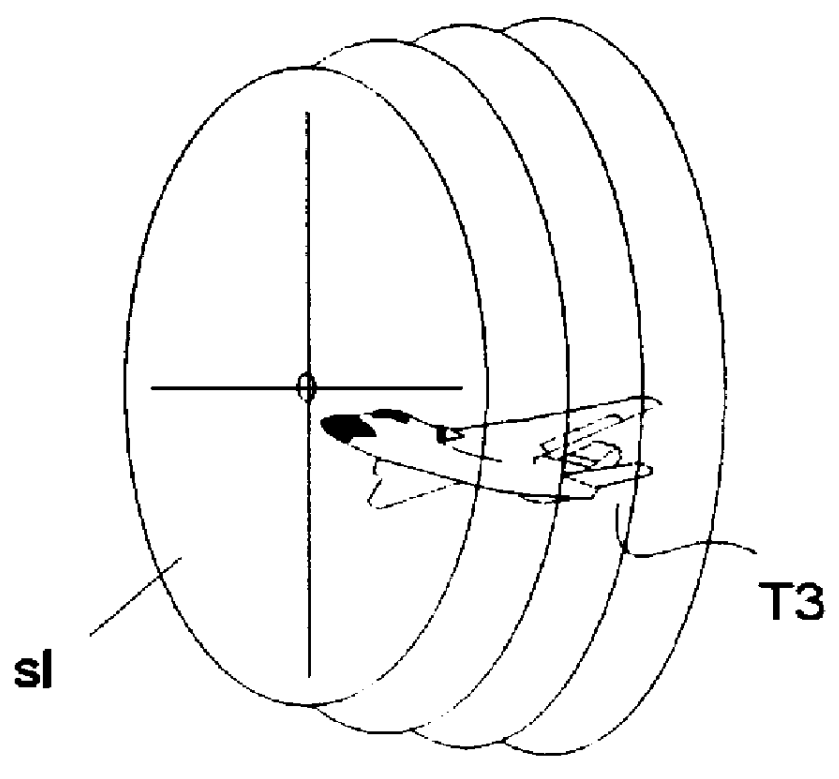
The process is used for suppressing the effect of signals that are received or sent via side lobes of an antenna (PA; HA) of an amplitude or phase monopulse radar device, in which for the purpose of position measurement of a first and, if need be, a second target (T1, T2) detected by the radar beam, three illumination functions Je(Lx), Jk(Lx) and Js(Lx) for the antenna (PA; HA) are provided for each measurement axis, as well as antenna functions Fe(X), Fk(X), and Fs(X) resulting from them. The first, second, and third illumination functions Je(Lx); Jk(Lx), and Js(Lx) are selected in this connection so that a quotient function Qe(X)=Fe(X) / Fs(X) or Qk(X)=Fk(X) / Fs(X), which is linearly or quadratically dependent on the target direction, is produced by normalizing the first and the second antenna functions Fe(X); Fk(X) with the third antenna function Fs(X). The power of this quotient is compared with at least one threshold value the or thk that is selected in accordance with the magnitude of the main antenna lobe, and when the threshold value the or thk is exceeded, the effect of the received signal is suppressed. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the provision is made that the zero points of the antenna functions Fe(X), Fk(X), and Fs(X) are shifted slightly in relation to one another.
Owner:SIEMENS SWITZERLAND
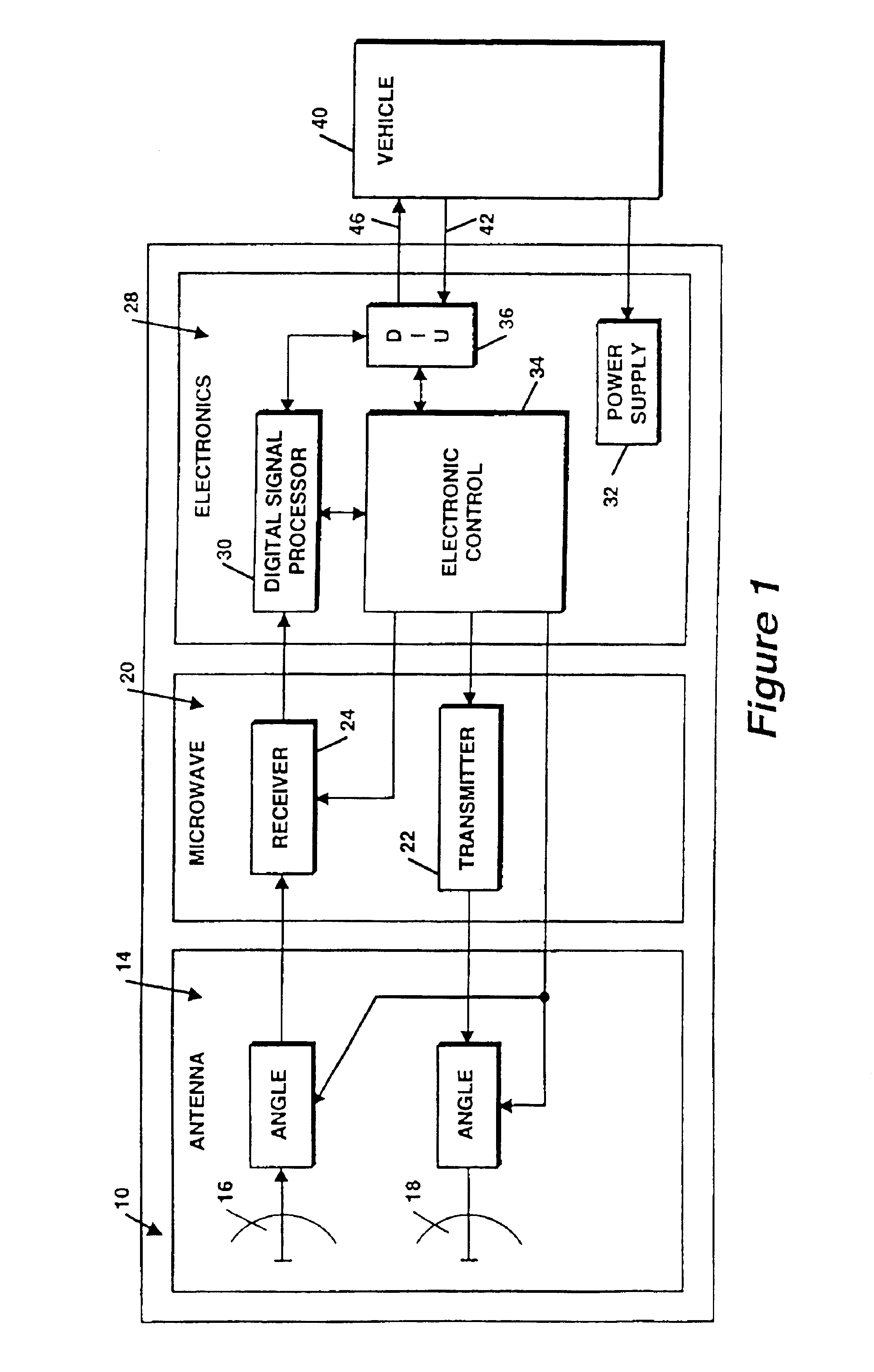
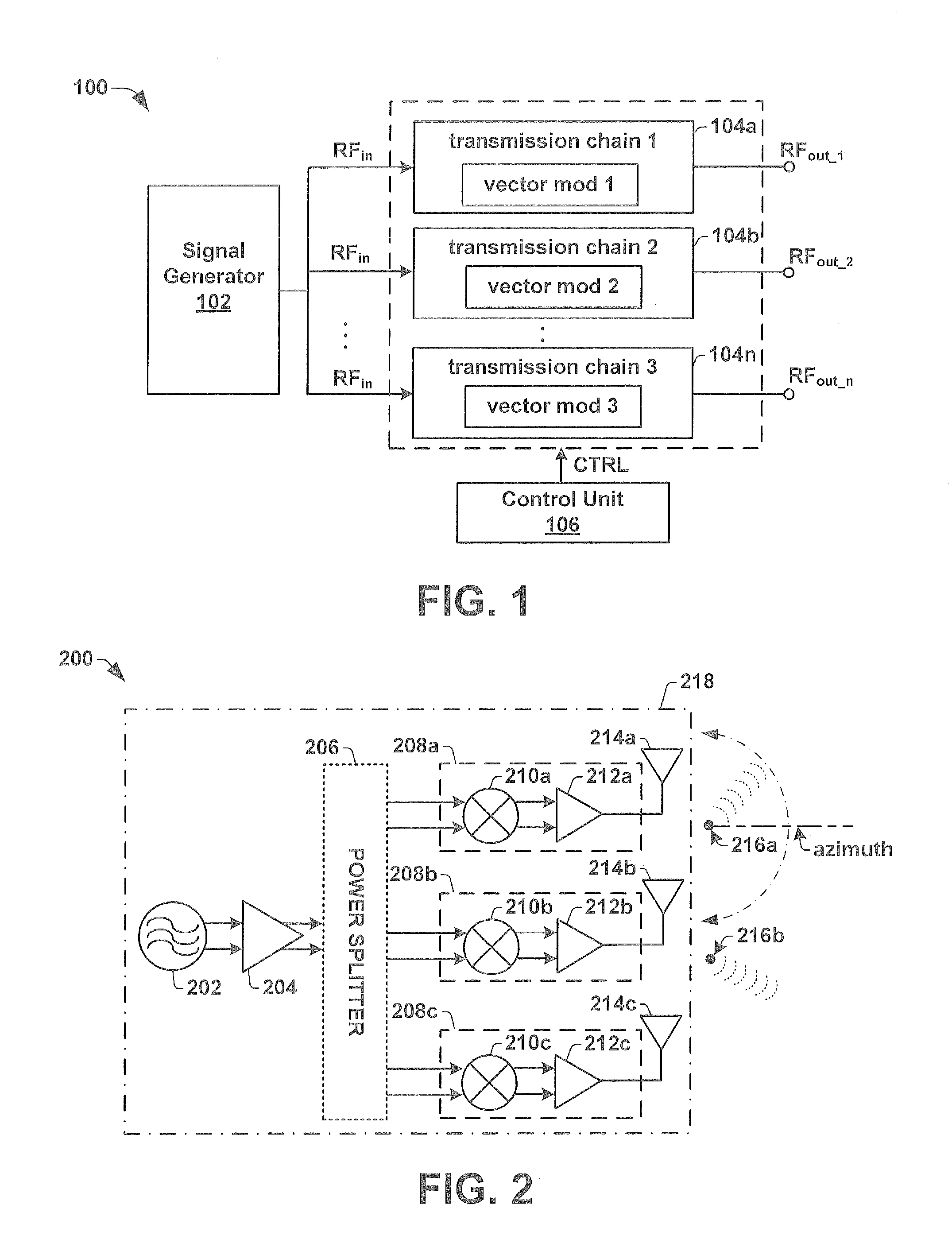
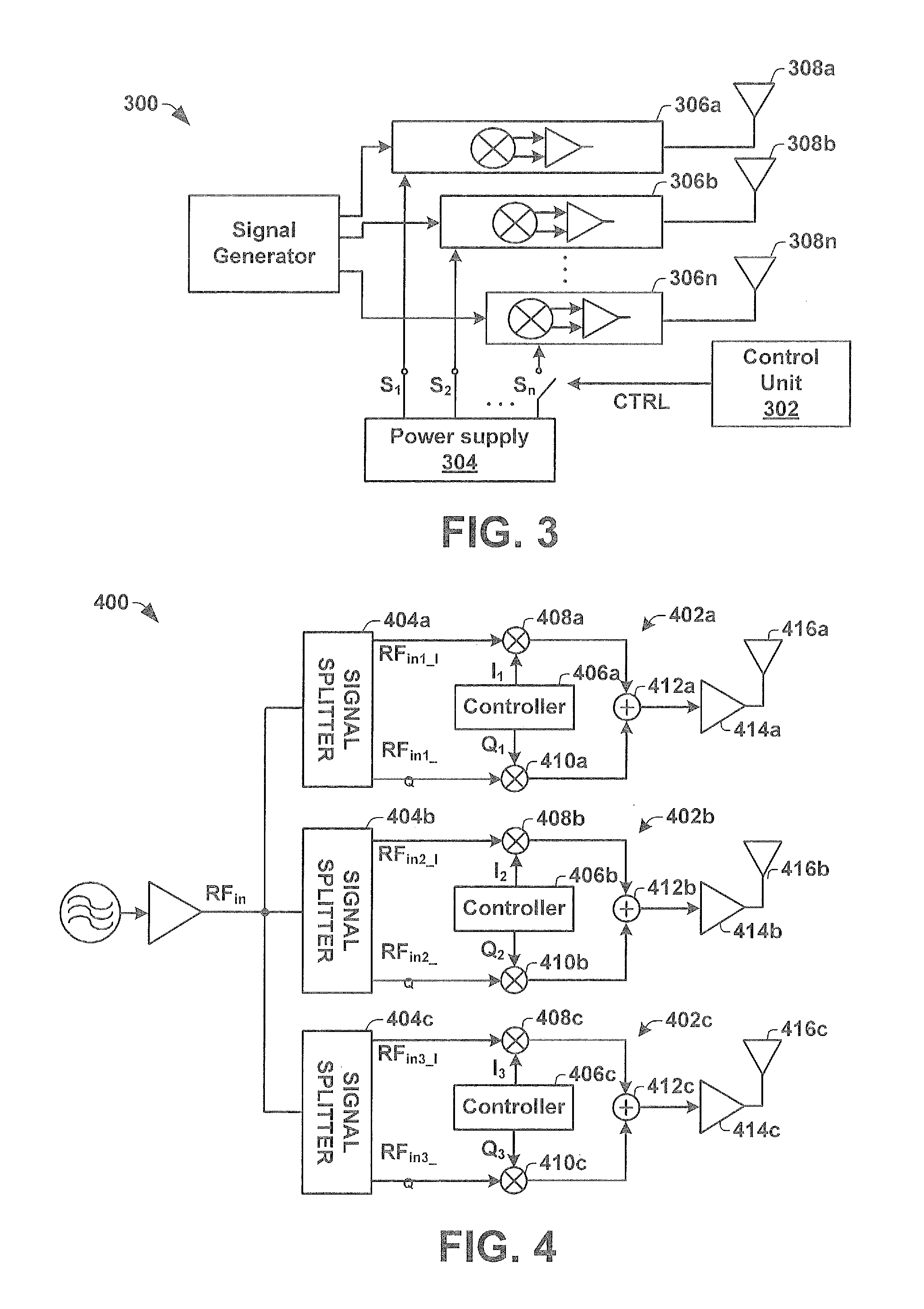
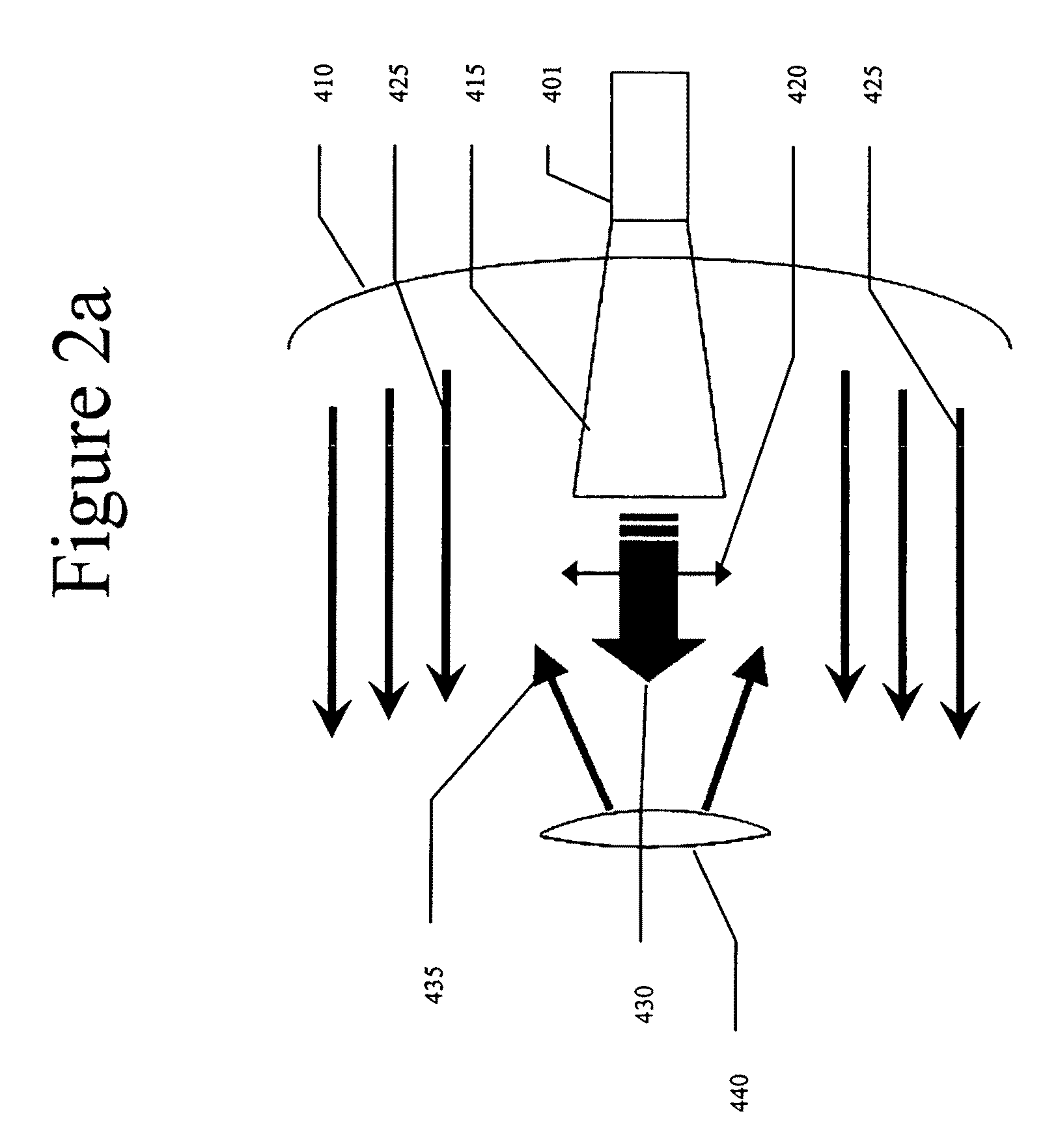
Automotive Radar Transmitter Architecture
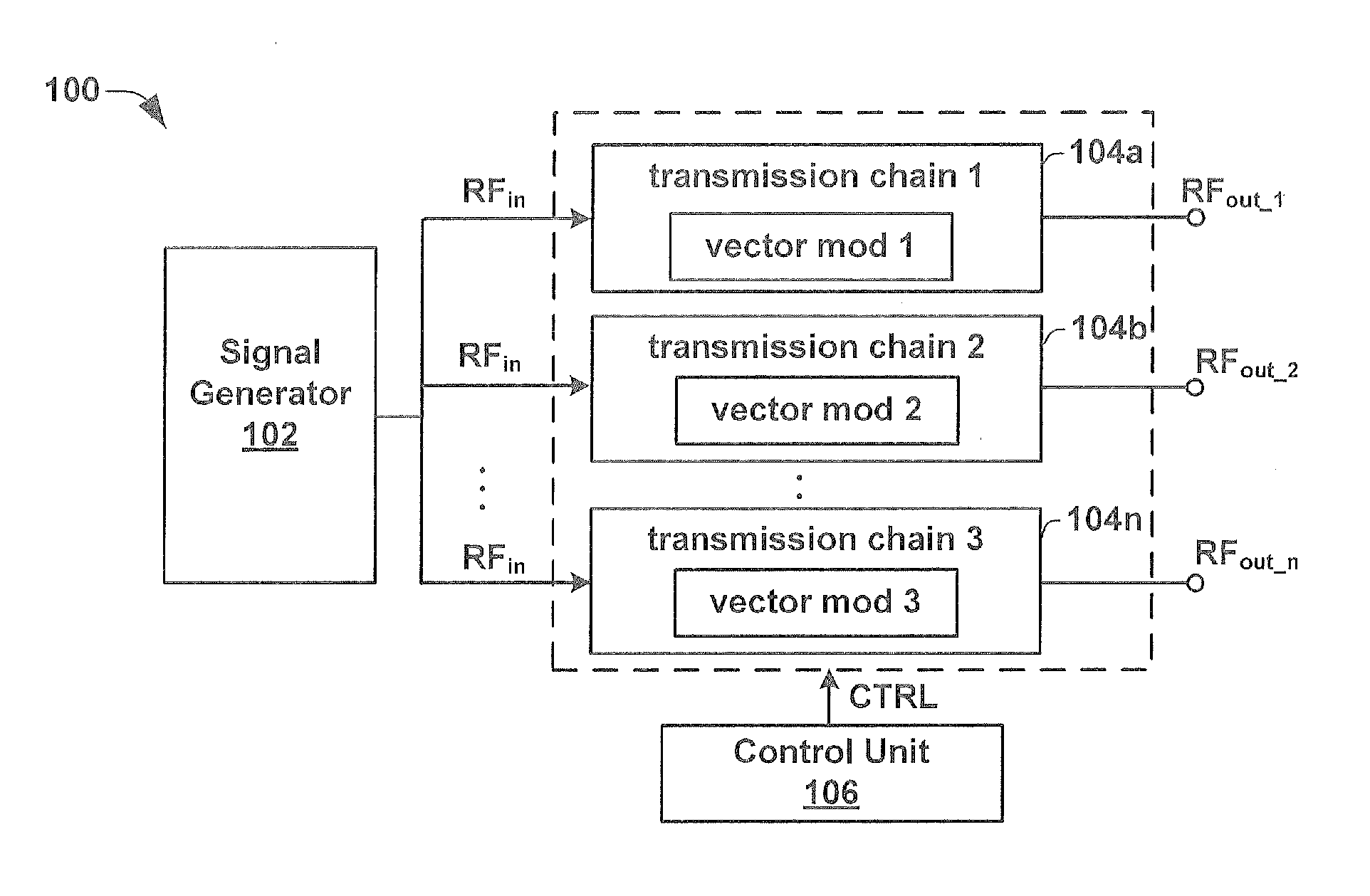
ActiveUS20130088383A1Radio transmissionIndividually energised antenna arraysBeam steeringEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a radar transmitter comprised within a single integrated chip substrate, which is capable of continuous beam steering of a transmitted radar beam as well as an option to change the physical position of the origin of the transmit radar beam. The radar transmitter has a signal generator that generates an RF signal. The RF signal is provided to a plurality of independent transmission chains, which contain independently operated vector modulators configured to introduce an individual phase adjustment to the high frequency input signal to generate separate RF output signals. A control unit is configured to selectively activate a subset of (e.g., two or more) the independent transmission chains. By activating the subset of independent transmission chains to generate RF output signals with separate phases, a beam steering functionality is enabled. Furthermore, the subset defines a changeable position of the transmitted radar beam.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
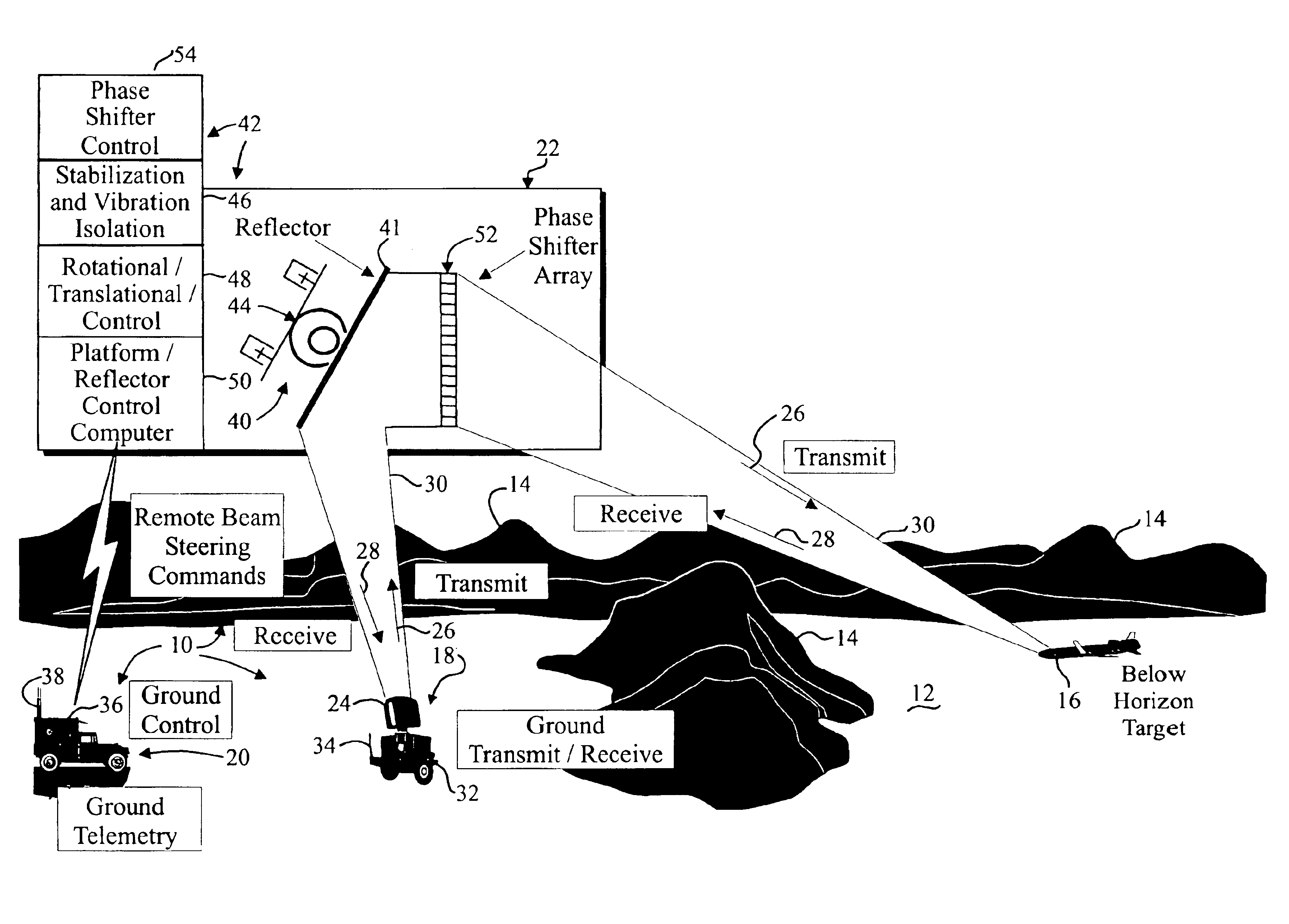
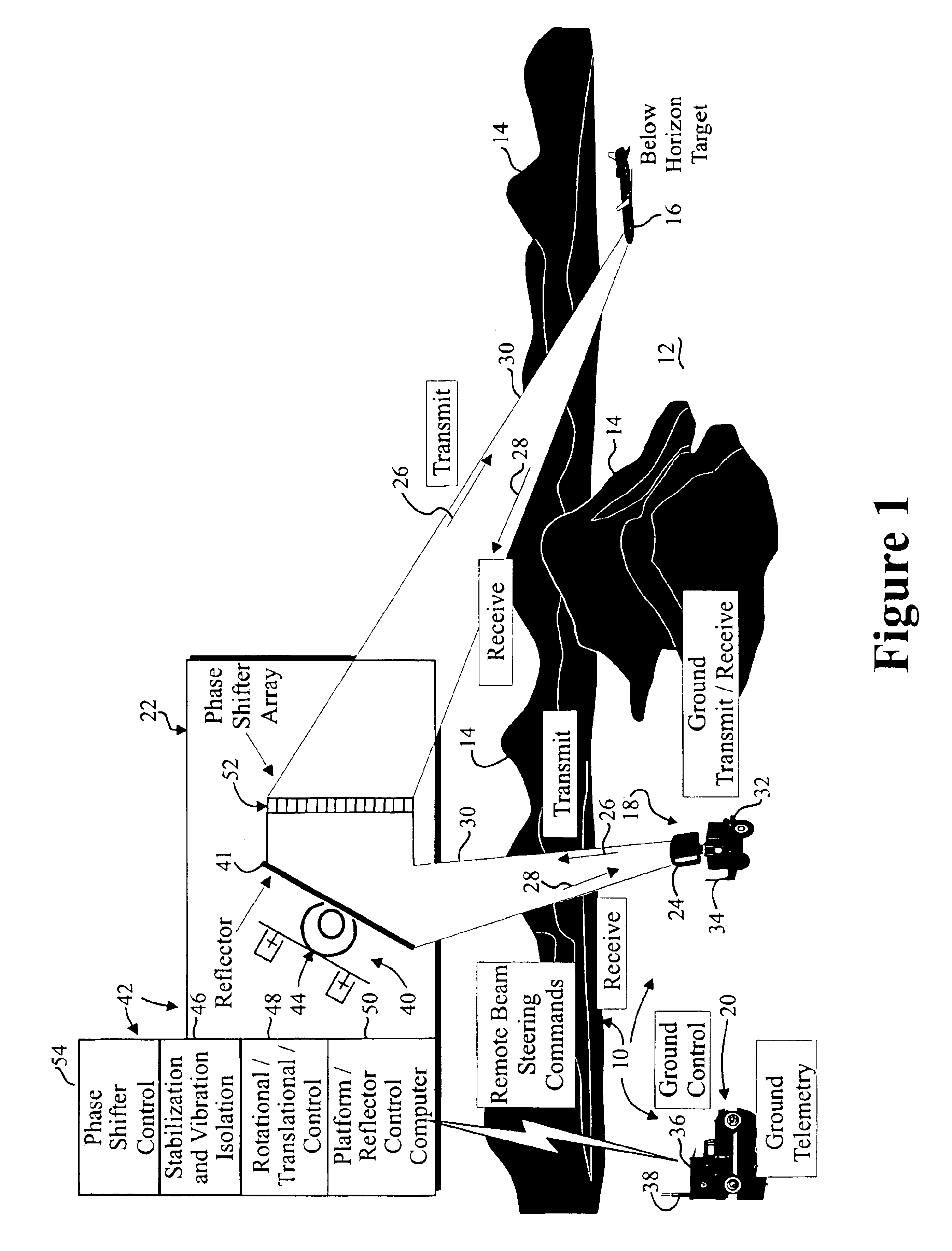
Radar beam steering with remote reflectors/refractors
A reflected energy detecting device includes a transmitter for transmitting an electromagnetic signal and a receiver for receiving a reflected electromagnetic signal. An antenna may be operatively connected with the transmitter and the receiver for radiating the electromagnetic signal and capturing the reflected electromagnetic signal and the antenna may be movable. A main controller may be provided for controlling operation of the transmitter and the receiver and the movement of the antenna and the reflected energy detecting device may further include at least one platform. The at least one platform may support a remote reflector that is dimensioned and configured to redirect the transmitted electromagnetic signal in a desired direction and a platform controller that is configured to communicate with the main controller and to maintain alignment between the remote reflector and the antenna.
Owner:SEC OF THE ARMY
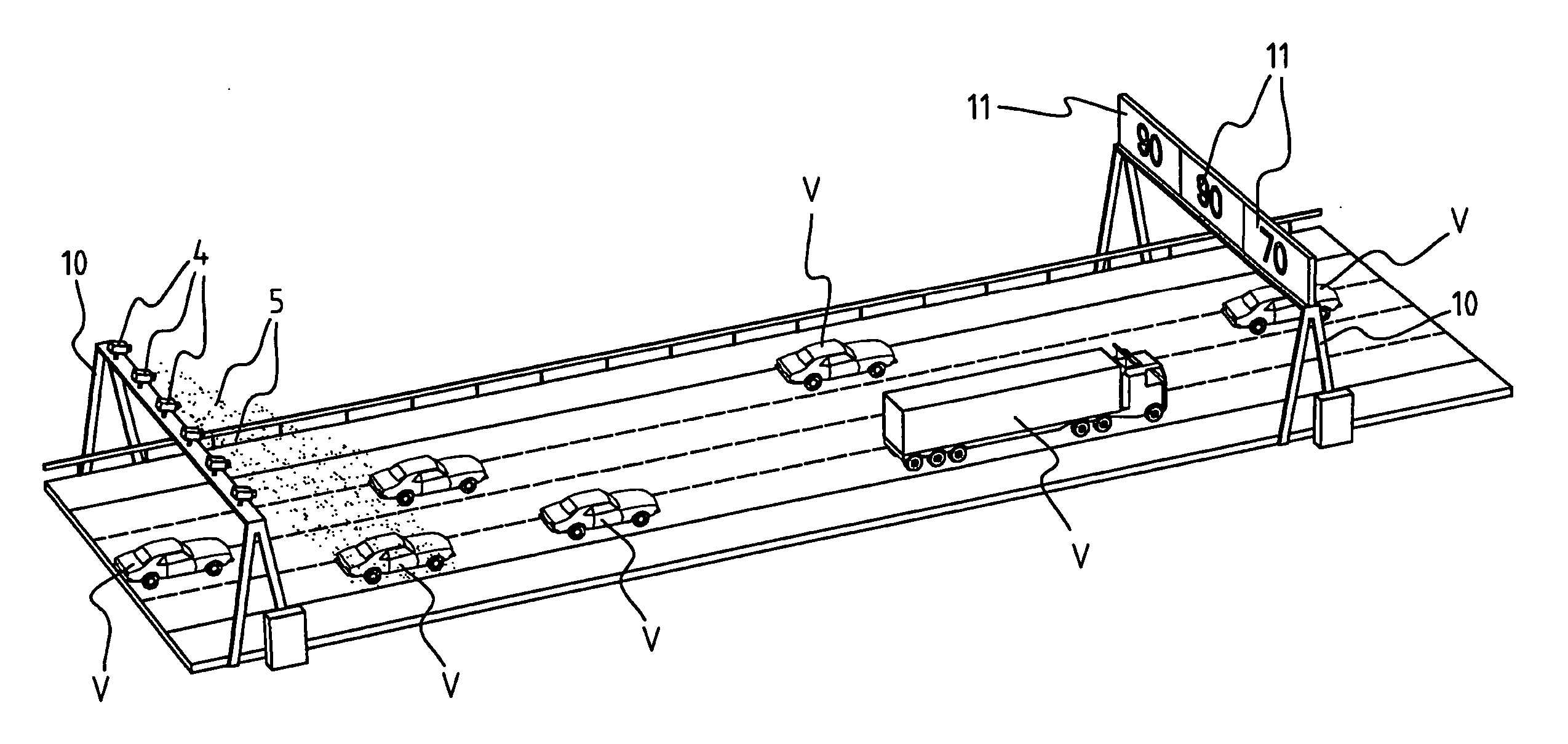
Method for detecting and documenting traffic violations at a traffic light
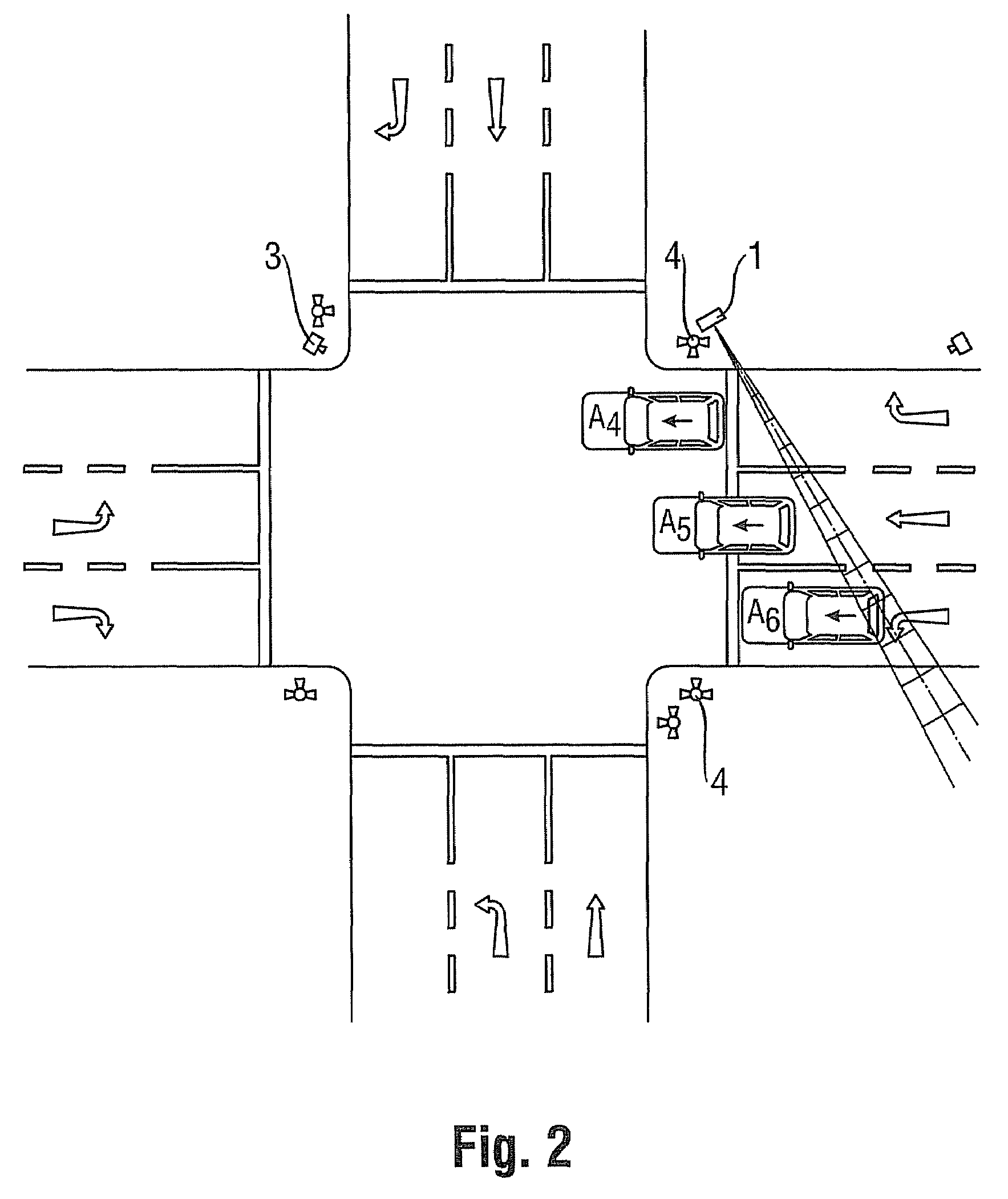
ActiveUS7633433B2Improve accuracyDetection of traffic movementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTraffic violationRadar beam
A method for detecting and documenting red-light violations and / or speeding violations in which a radar beam is directed across all lanes of a roadway of interest and in which the speed and the position of a vehicle which passes through the radar beam are determined from the radar signals so as to be able to predict the probability of a red-light violation from the speed and the determined distance of the measured vehicle from a stop line and to trigger the recording of images of the violating vehicle at predetermined distances from the stop line.
Owner:JENOPTIK ROBOT GMBH
Electronically steered, dual-polarized, dual-plane, monopulse antenna feed
InactiveUS7834803B2Reduce weight and costSmall sizePolarised antenna unit combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAntenna feedElectron
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
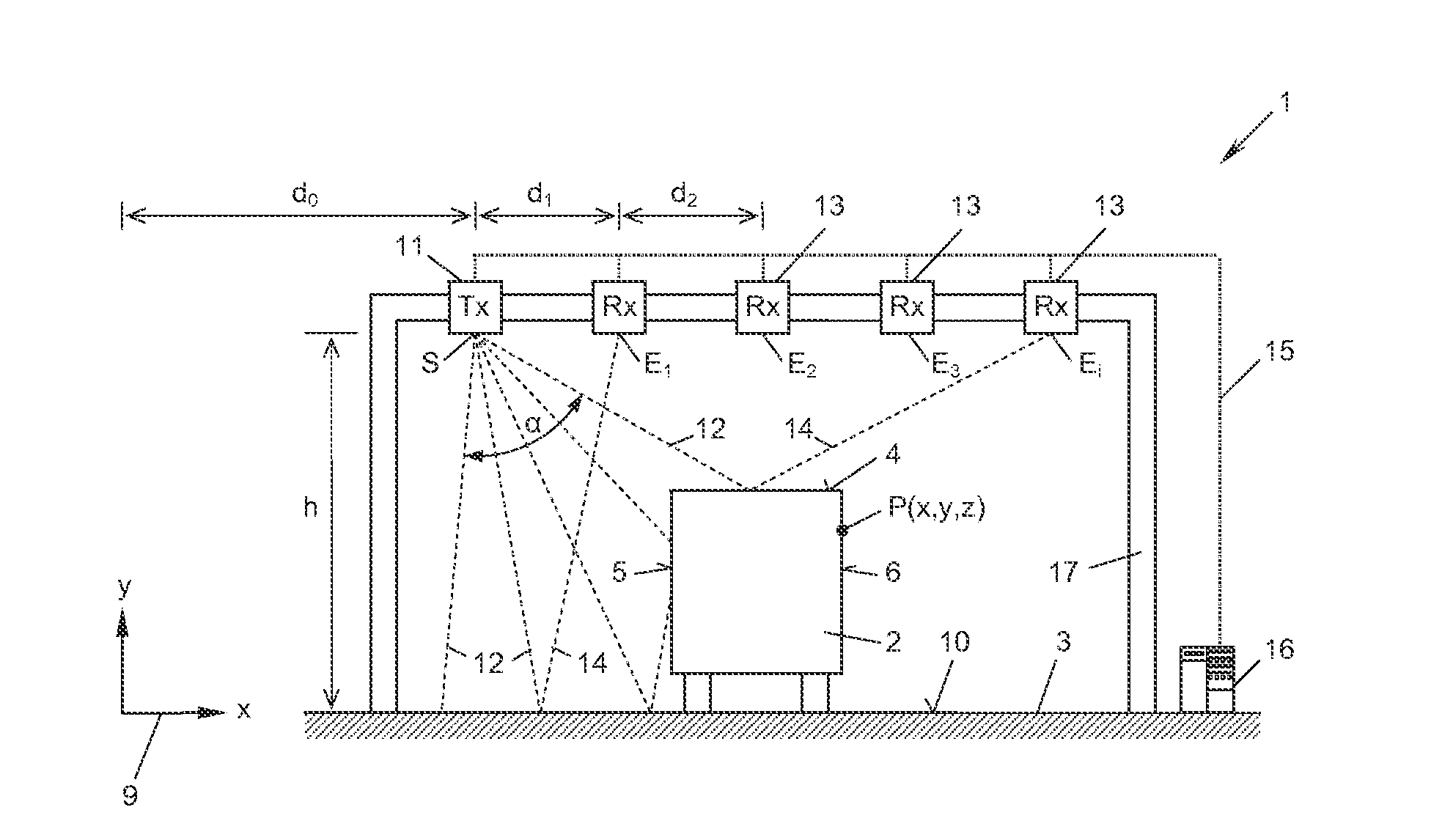
Apparatus for measuring the position of a vehicle or a surface thereof
InactiveUS20140333472A1More cost-effectivelyAccuracy of the position measurement apparatusTicket-issuing apparatusDetection of traffic movementRadar beamRadar transmitter
An apparatus is disclosed for measuring the position of a vehicle or a surface thereof on a roadway. The apparatus comprises at least one radar transmitter, which is arranged in a transmitting position above the plane of the roadway and transmits radar beams downwardly, a plurality of radar receivers, which are distributed above the plane of the roadway in different receiving positions at distances from one another, receive reflections of the radar beams from beneath, and convert the reflections into a received signal, and an evaluation device, which is connected to the radar transmitter and the radar receivers and is configured to measure the said position from the transmitting position, the receiving positions and the received signals.
Owner:KAPSCH TRAFFICCOM AG
High-Resolution Stripmap SAR Imaging
ActiveUS20160109570A1High resolutionExtend integration timeImage enhancementImage analysisElevation angleFlight direction
A SAR imaging method performs N SAR acquisitions in stripmap mode of the earth's surface using a synthetic aperture radar transported by an aerial or satellite platform and including a single, non-partitioned antenna and a single receiver coupled thereto. All N SAR acquisitions are performed using the same predetermined elevation angle relative to the nadir of the synthetic aperture radar and using a respective squint angle relative to the flight direction of the synthetic aperture radar. Radar transmission and reception operations are time interleaved with other N-1 SAR acquisitions, resulting in the respective acquisition directions being parallel to each other and not parallel to acquisition directions of other N-1 SAR acquisitions. Radar beams in two immediately successive time instants and related to two different SAR acquisitions are contiguous along the azimuth. SAR images may be generated using all the N SAR acquisitions having an enhanced azimuth resolution.
Owner:THALES ALENIA SPACE ITAL SPA
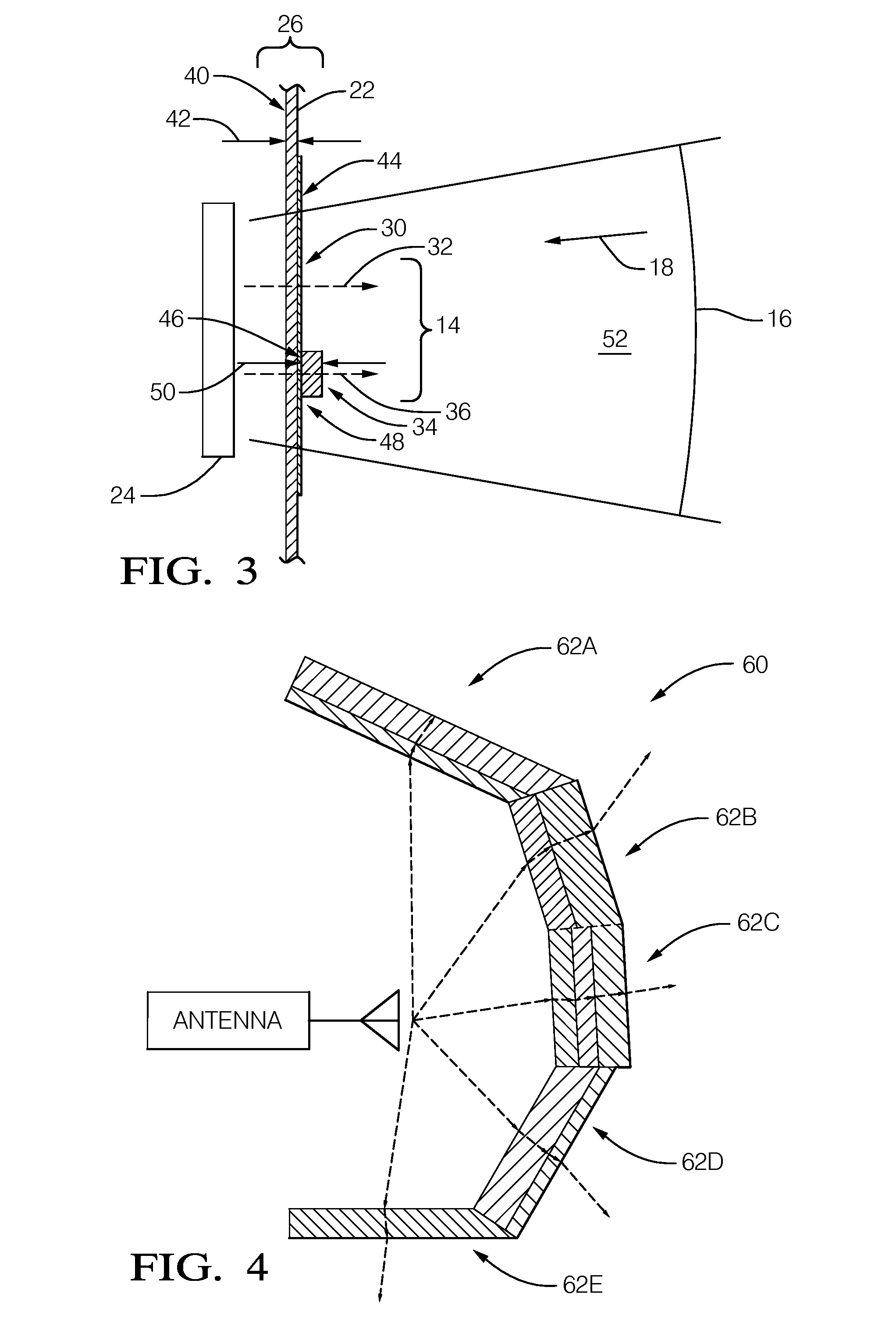
Partial covering radome for a radar unit
A sensor assembly that integrates a camera and a radar sensor is described herein. The sensor assembly includes a housing configured to partially enclose the camera and the radar sensor, and define a partial radome that partially intrudes into the radar beam. The partial radome is configured such that after passing through the partial radome a first phase angle of the first portion of the radar beam differs from a second phase angle of the second portion of the radar beam by an amount substantially corresponding to an integer number of three hundred sixty degrees (360°) of phase angle shift. The partial radome provides glare shield to the camera, protection to assembly, and is configured to minimally effect radar performance.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Fast Realization method for simulation 3D scene SAR radar echo based on forward method
InactiveCN106324571AMeet real-time processing needsGuaranteed Simulation AccuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionProperty distributionMain processing unit
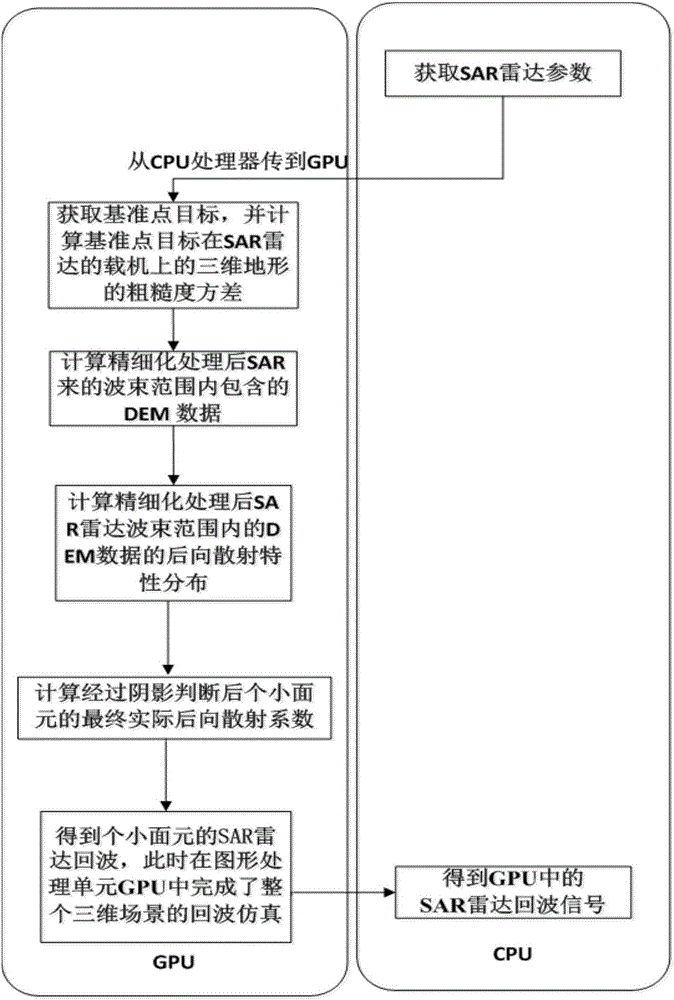
The invention discloses a fast Realization method for simulation 3D scene SAR radar echo based on forward method. The main idea of the fast Realization method comprises the following steps: acquiring digital elevation model (DEM) data within SAR radar beam range, wherein the data comprises K point targets; randomly distributing the K point targets on a 2D ground in the geographic coordinate system, and calculating DEM data within the SAR radar beam range after refinement processing; acquiring back scattering property distribution of the DEM data within the SAR radar beam range after refinement processing; utilizing an improved downward angle comparison method to determine shaded areas of Q small surface elements, calculating final actual back scattering coefficients of the Q small surface elements after shaded area determination, and then calculating SAR radar echo of the Q small surface elements. At this time, the whole 3D scene echo simulation is completed in a graphic processing unit (GPU), and finally an echo signal in the GPU is sent to a CPU processor to be output.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A Ground Clutter Removal Method for Airborne Weather Radar Based on Terrain Elevation Data
ActiveCN102269809AAccurate removalSimple methodRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationJet aeroplaneWeather radar
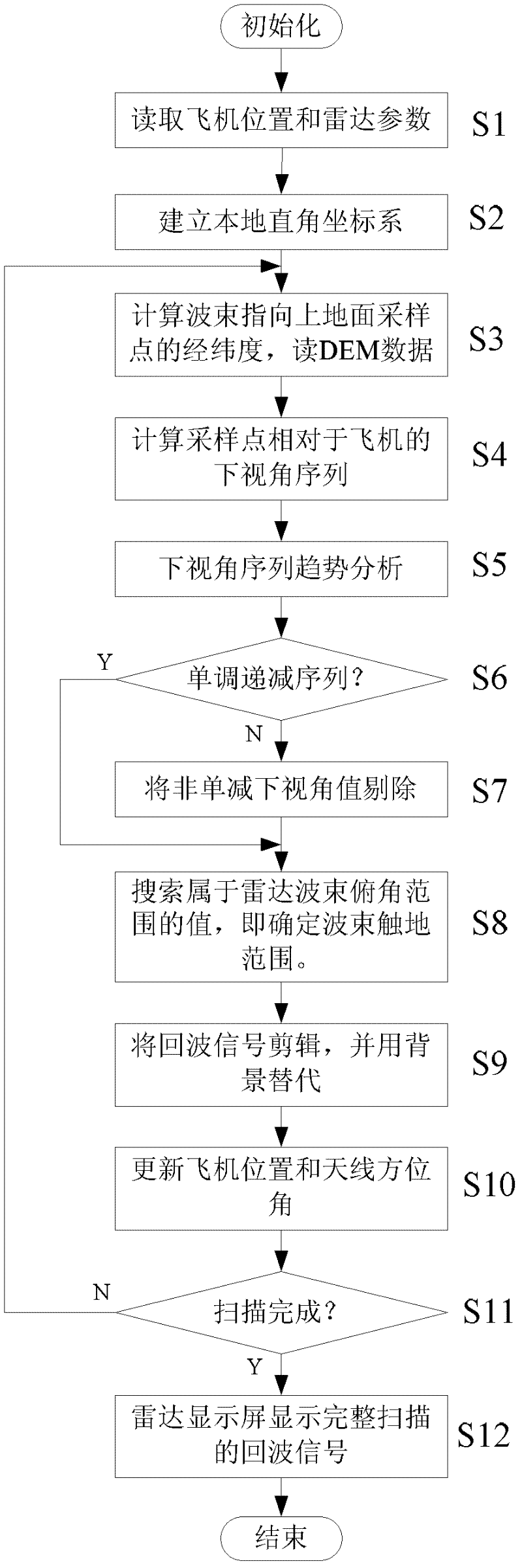
The invention provides a method for eliminating terrestrial clutters of an airborne weather radar based on terrain altitude data. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: reading airplane position and radar parameters, establishing a local rectangular coordinate system, calculating longitudes and latitudes of ground sampling points in a beam direction, reading DEM (Digital Elevation Model) data, calculating a lower view angle sequence of the sampling points relative to an airplane, analyzing a tendency of the lower view angle sequence, judging a monotonically decreasing sequence, eliminating a non-monotonically-decreasing lower view angle value, determining a beam grounding range, editing echo signals and replacing by a background, updating the airplane position and an antenna azimuth angle, judging whether the scanning is finished, displaying complete scanning echo signals by a radar display screen and the like. According to the method provided by the invention, by utilizing the characteristics that the terrestrial clutters of the airborne weather radar echoes and weather targets are respectively located at units with different distances and can be separated in the distance and adopting the discipline characteristics of the lower view angle, the grounding position of the radar beam is analyzed, and the terrestrial clutters is eliminated by utilizing and utilizes the terrain altitude data; and the method has the advantages of simple method, calculation accuracy, good inhibition effect, capability of effectively eliminating terrestrial cluttersof the airborne weather radar in a time domain and the like.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com