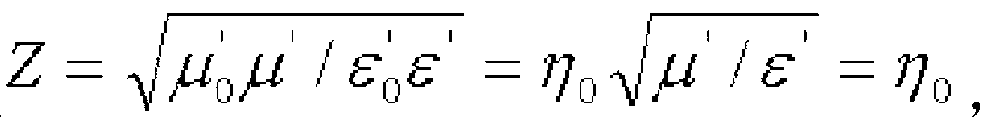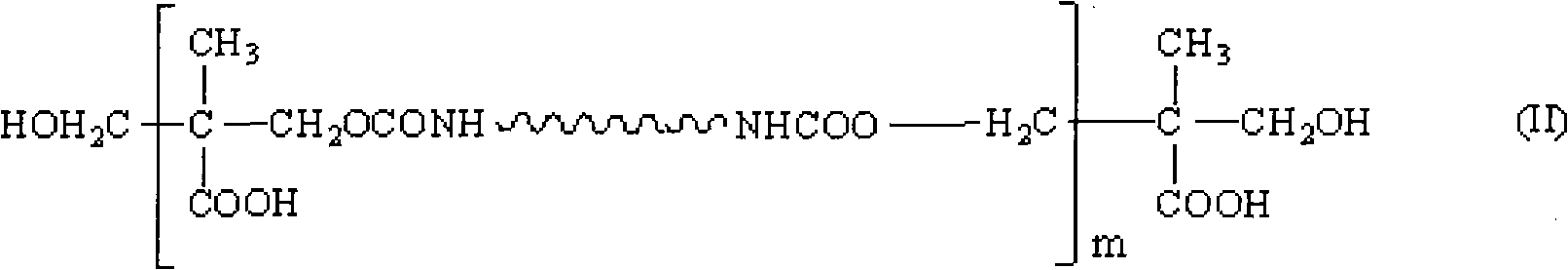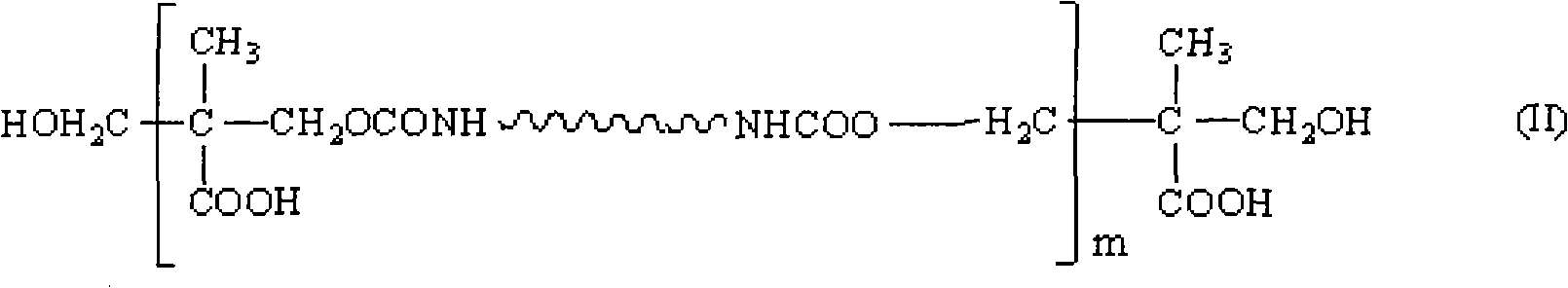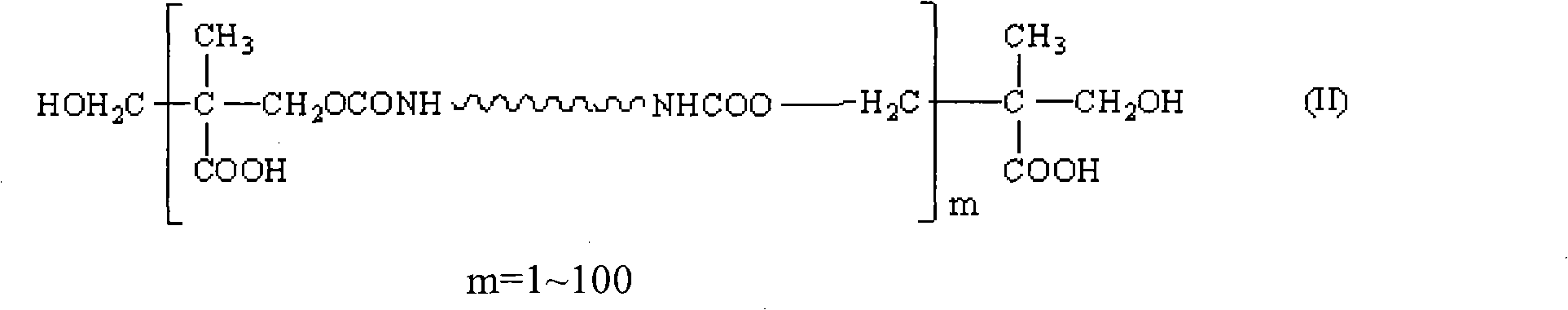Patents
Literature
479 results about "Antenna substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
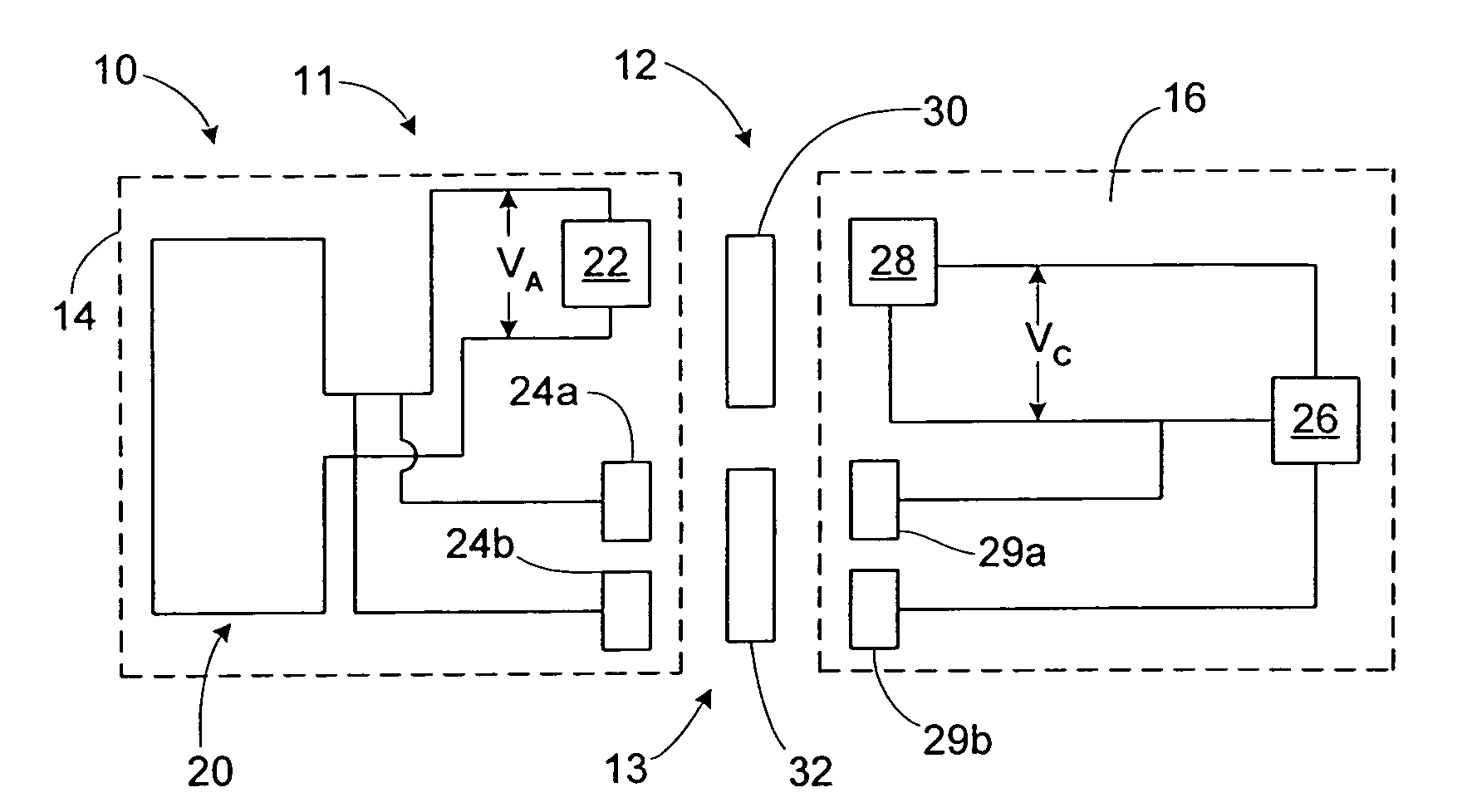
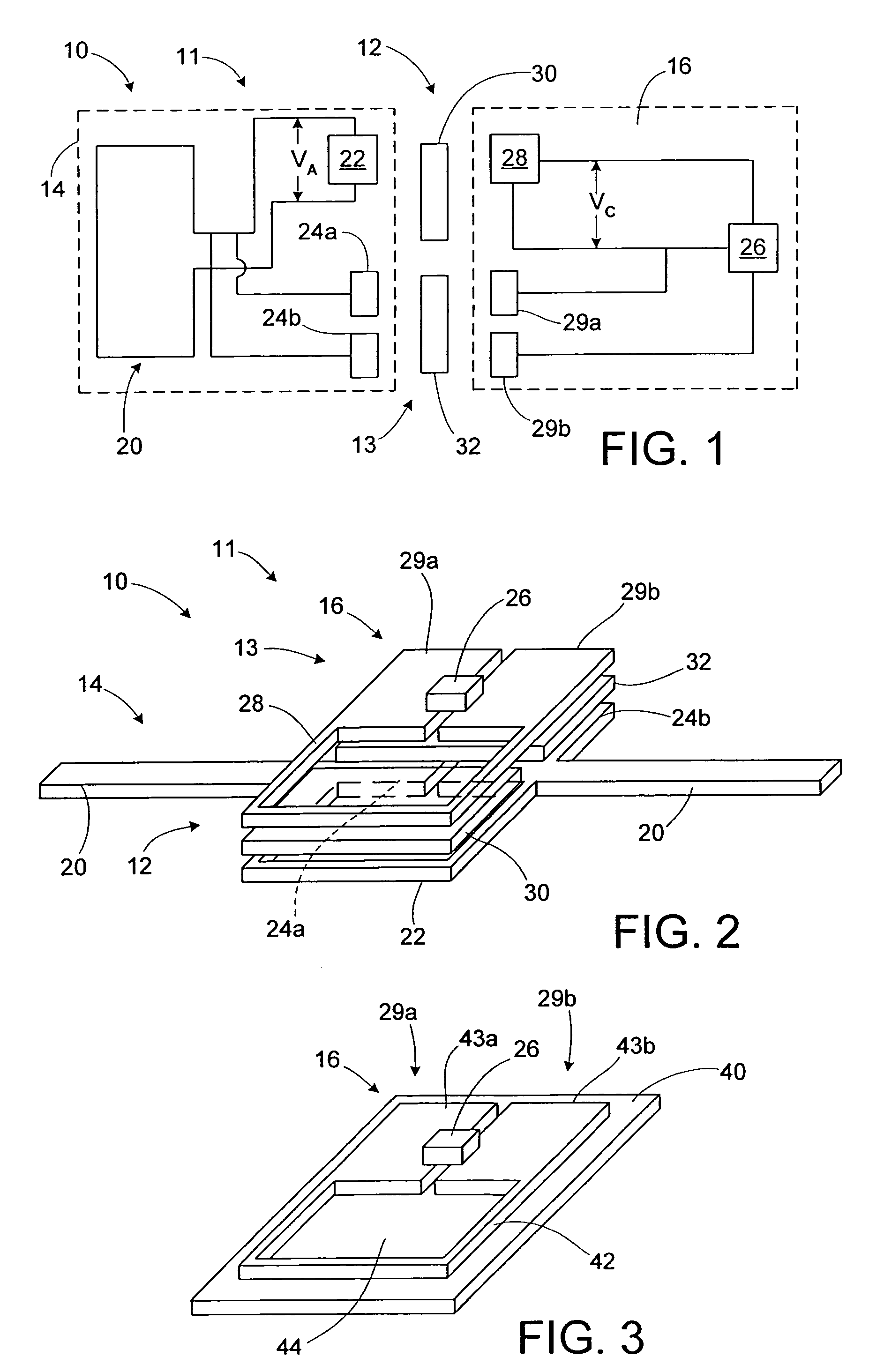
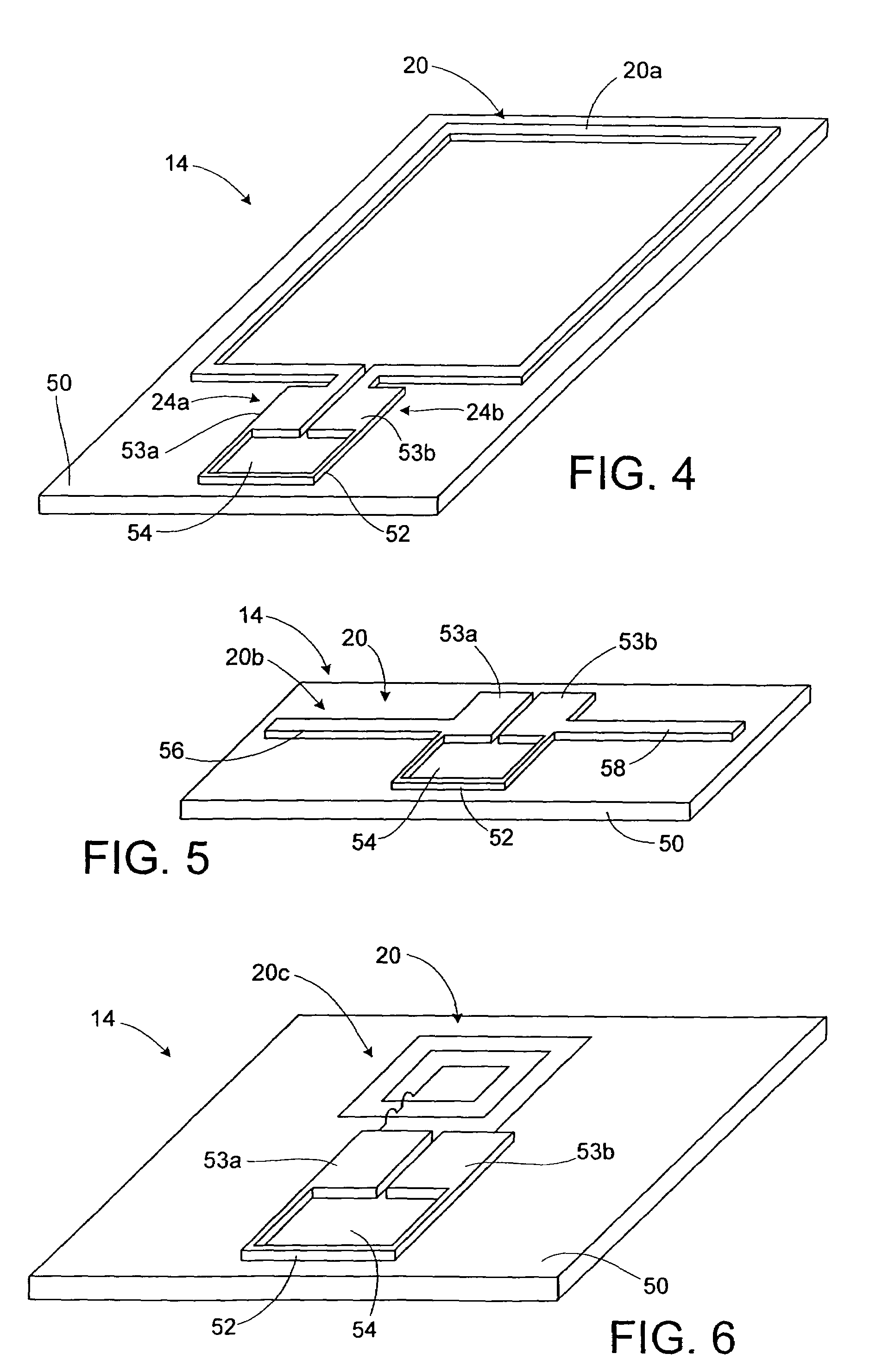
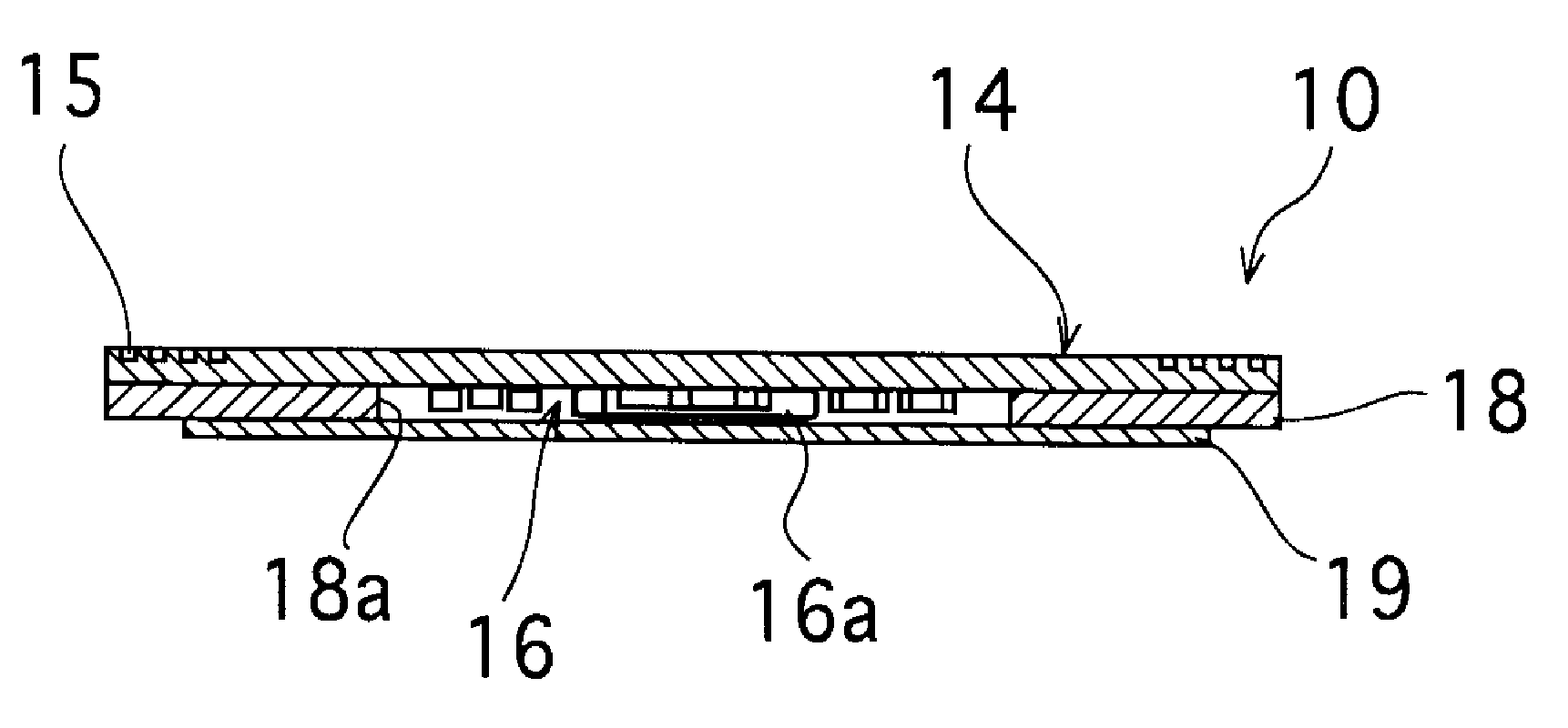
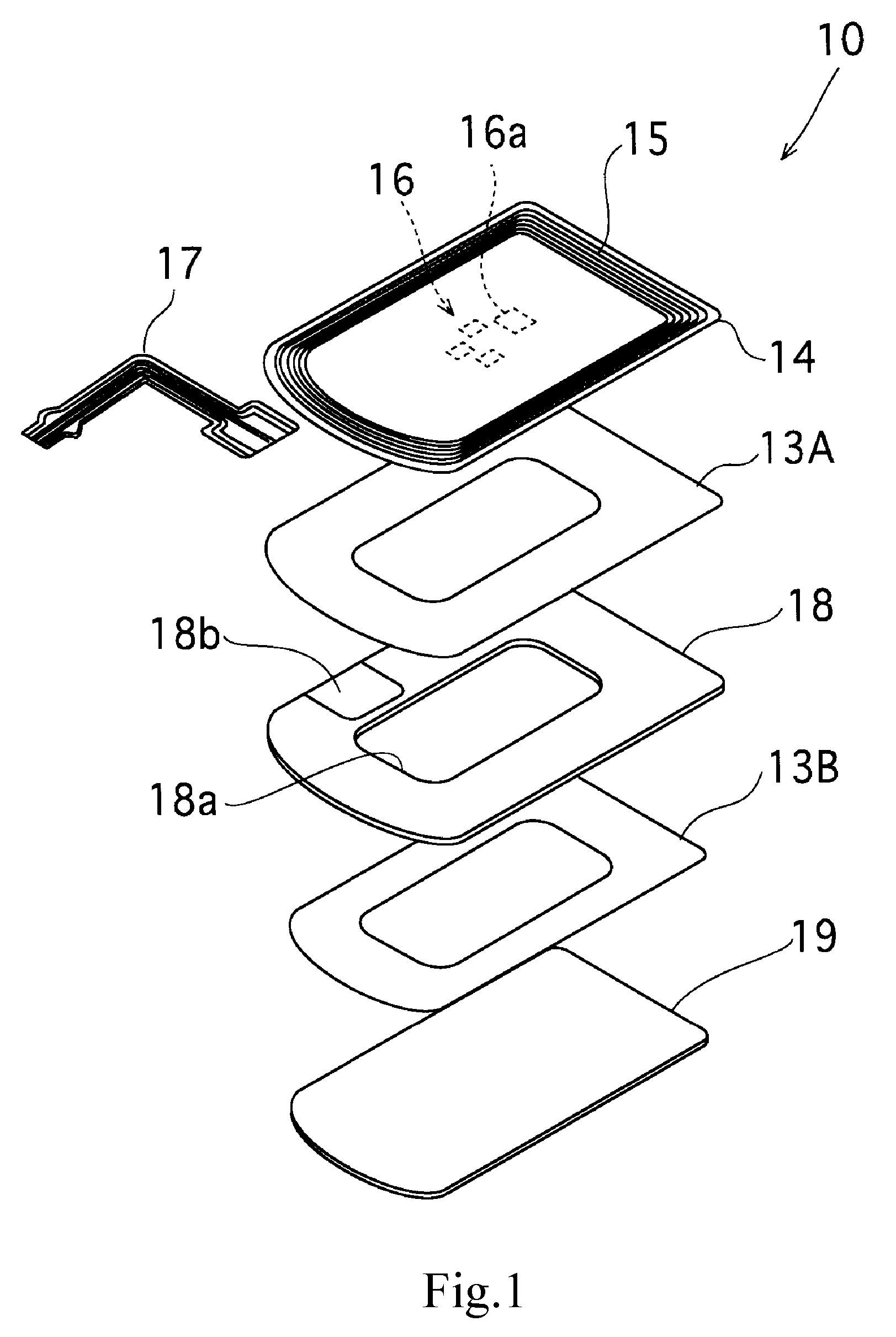
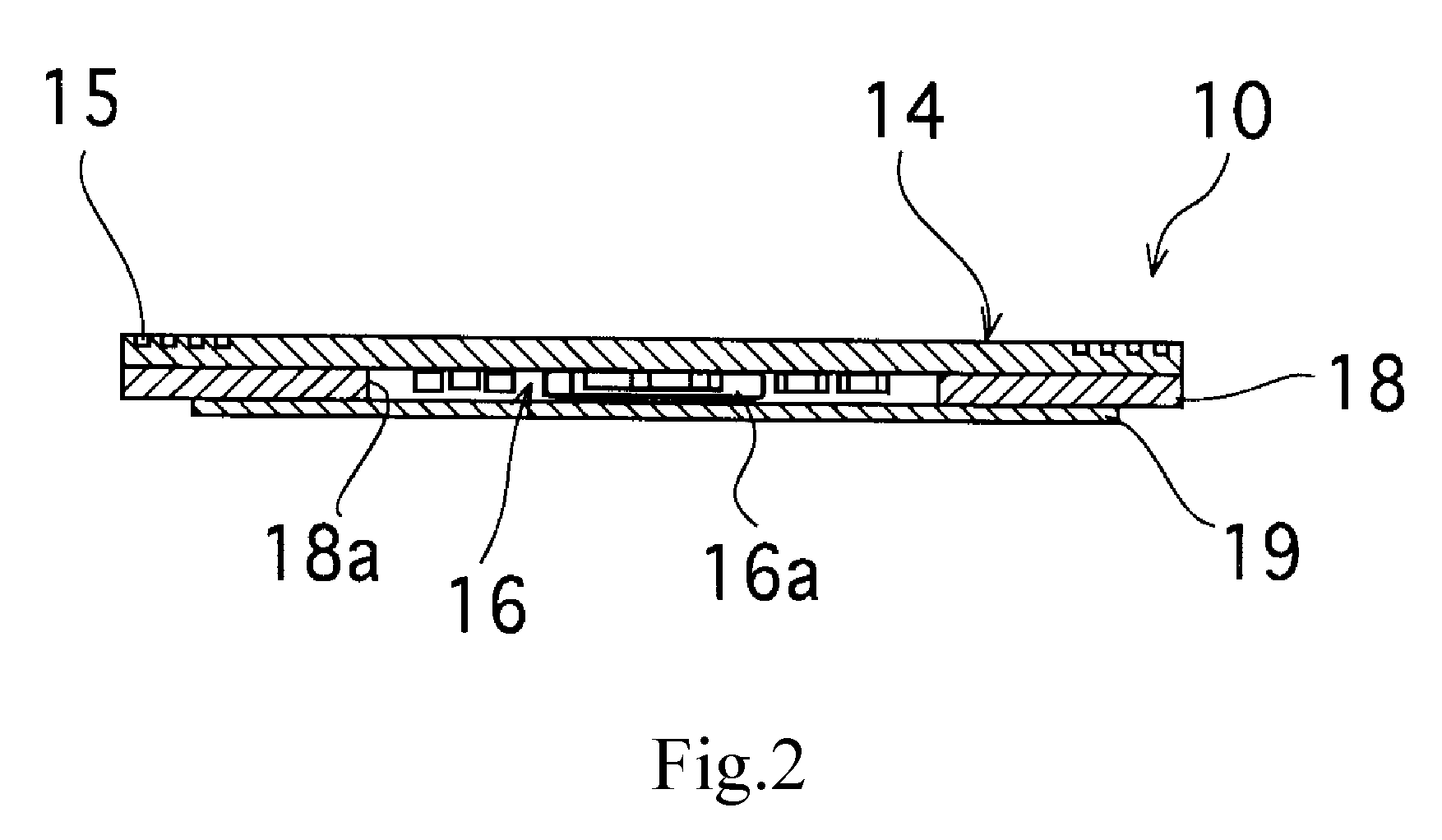
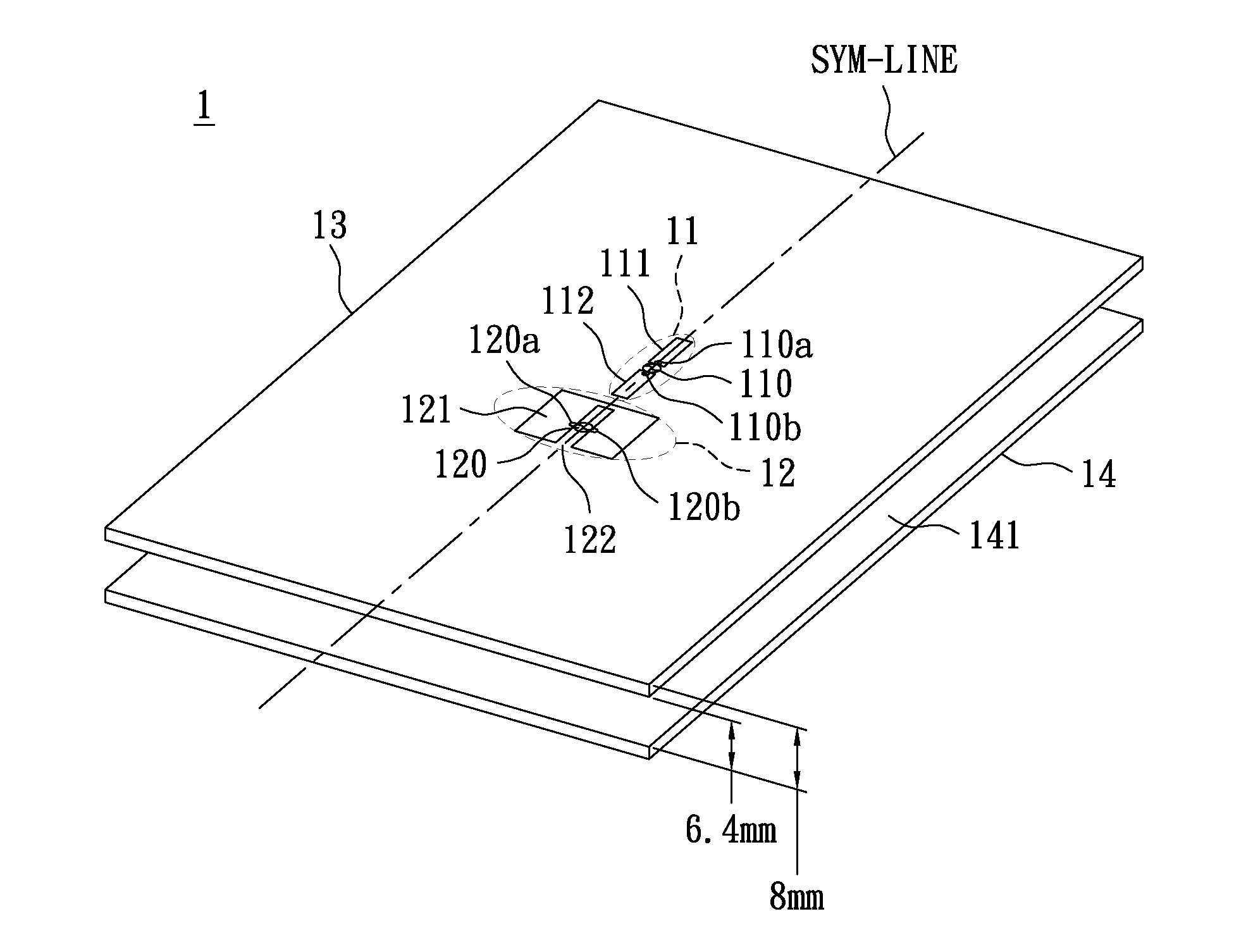
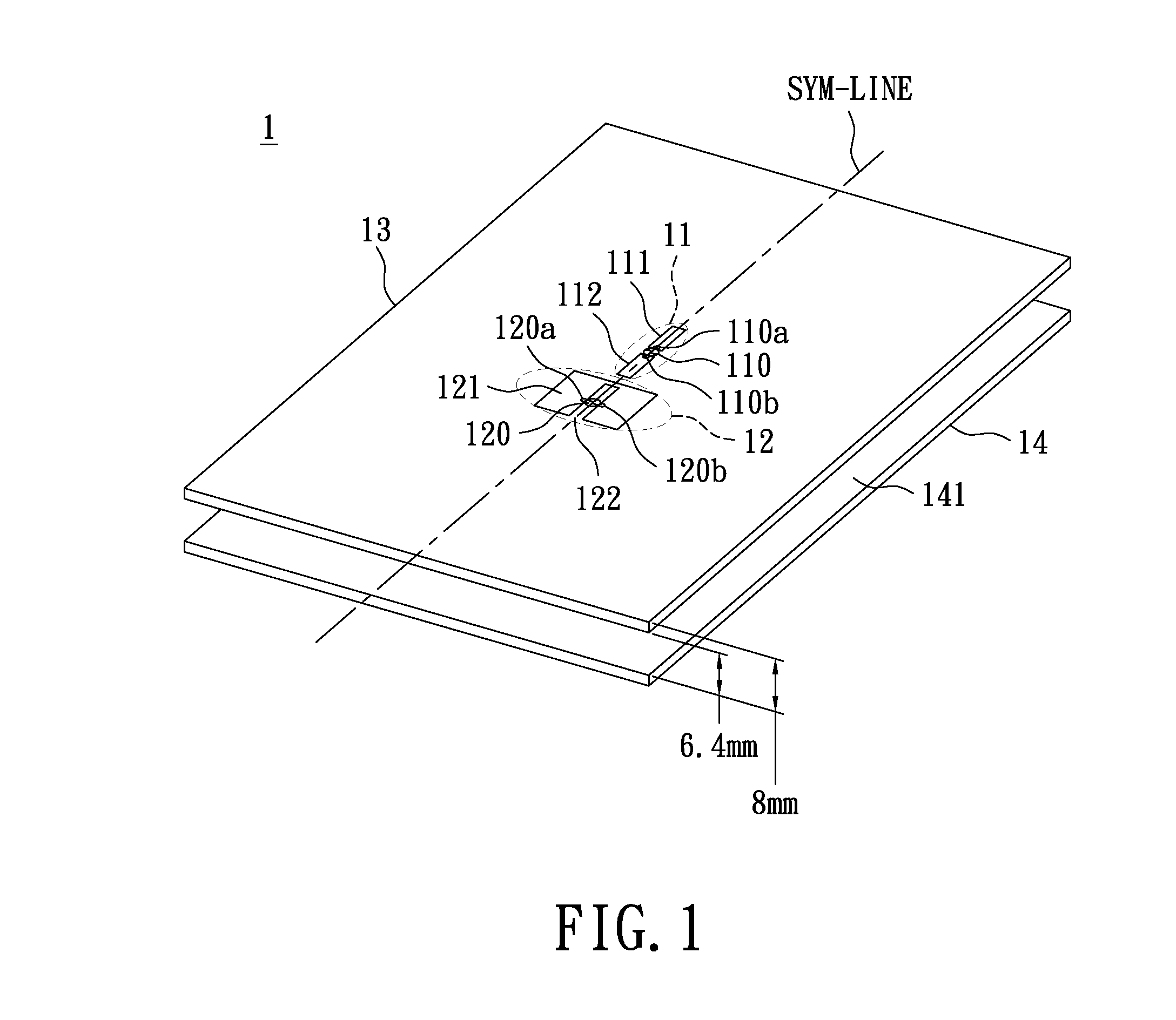
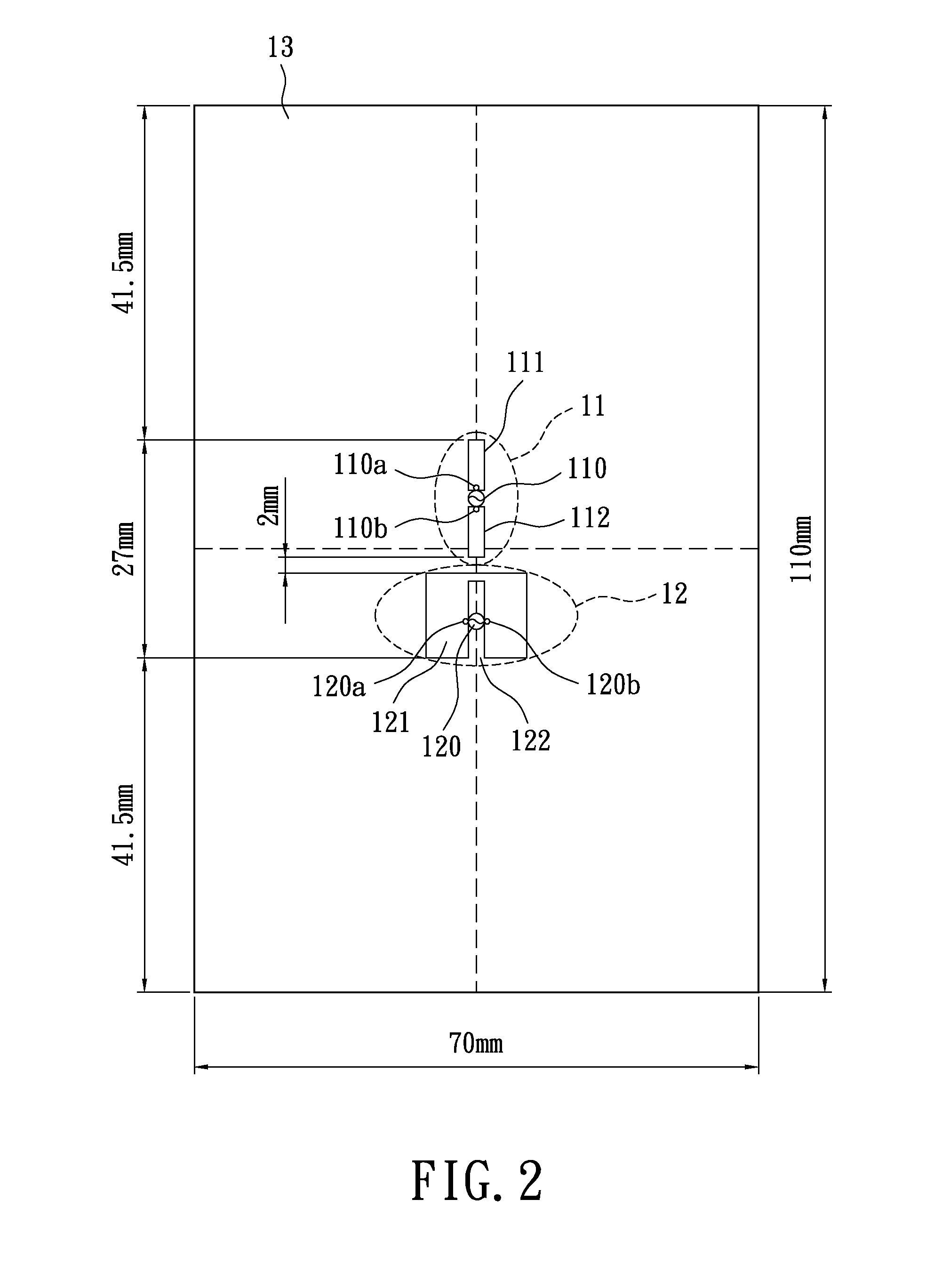
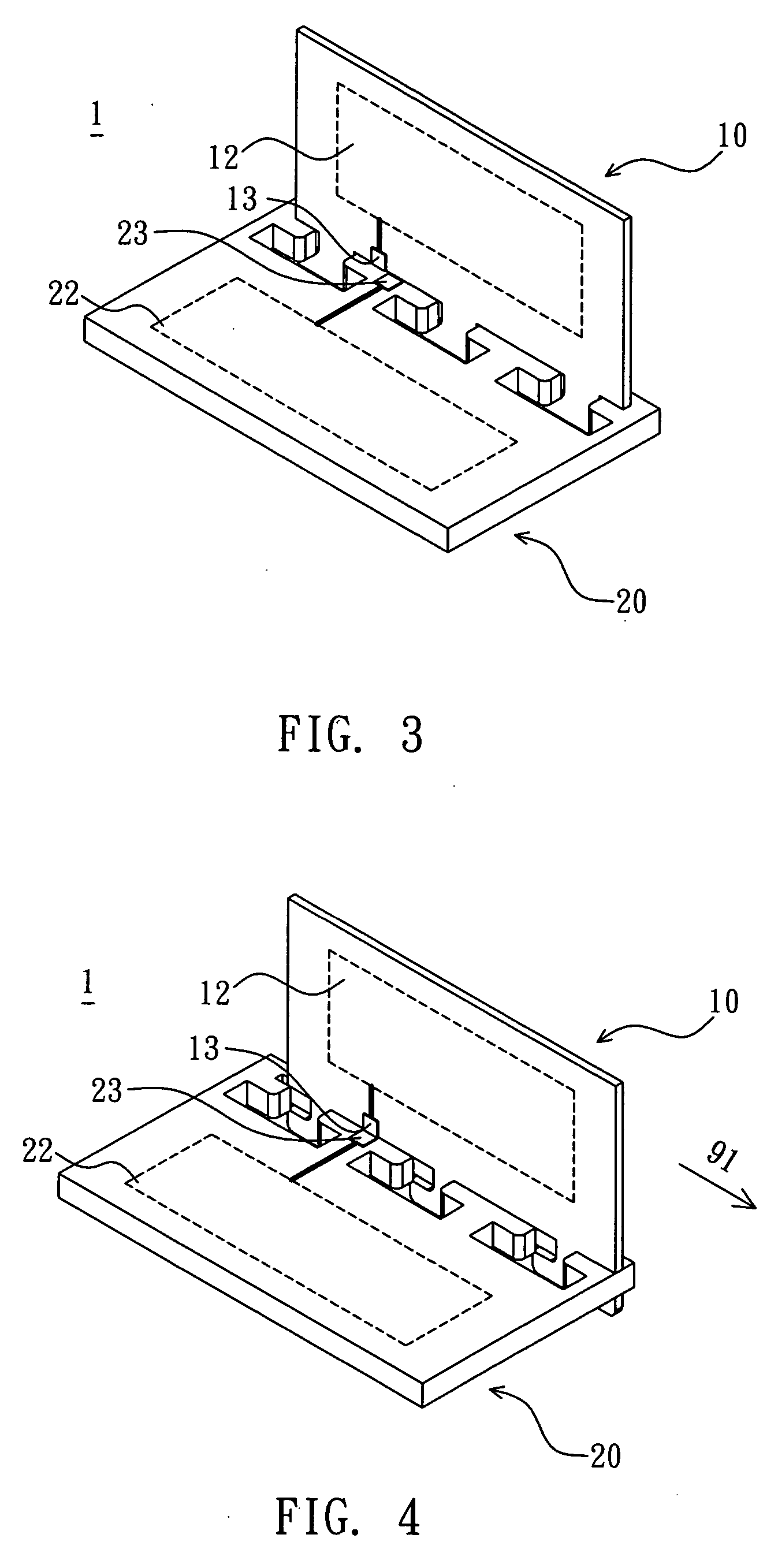
A substrate antenna that includes one or more conductive traces supported on a dielectric substrate having a predetermined thickness. Appropriate dimensions are selected for the lengths and widths of traces, based on the wavelength of interest, connecting elements, and space allocated.
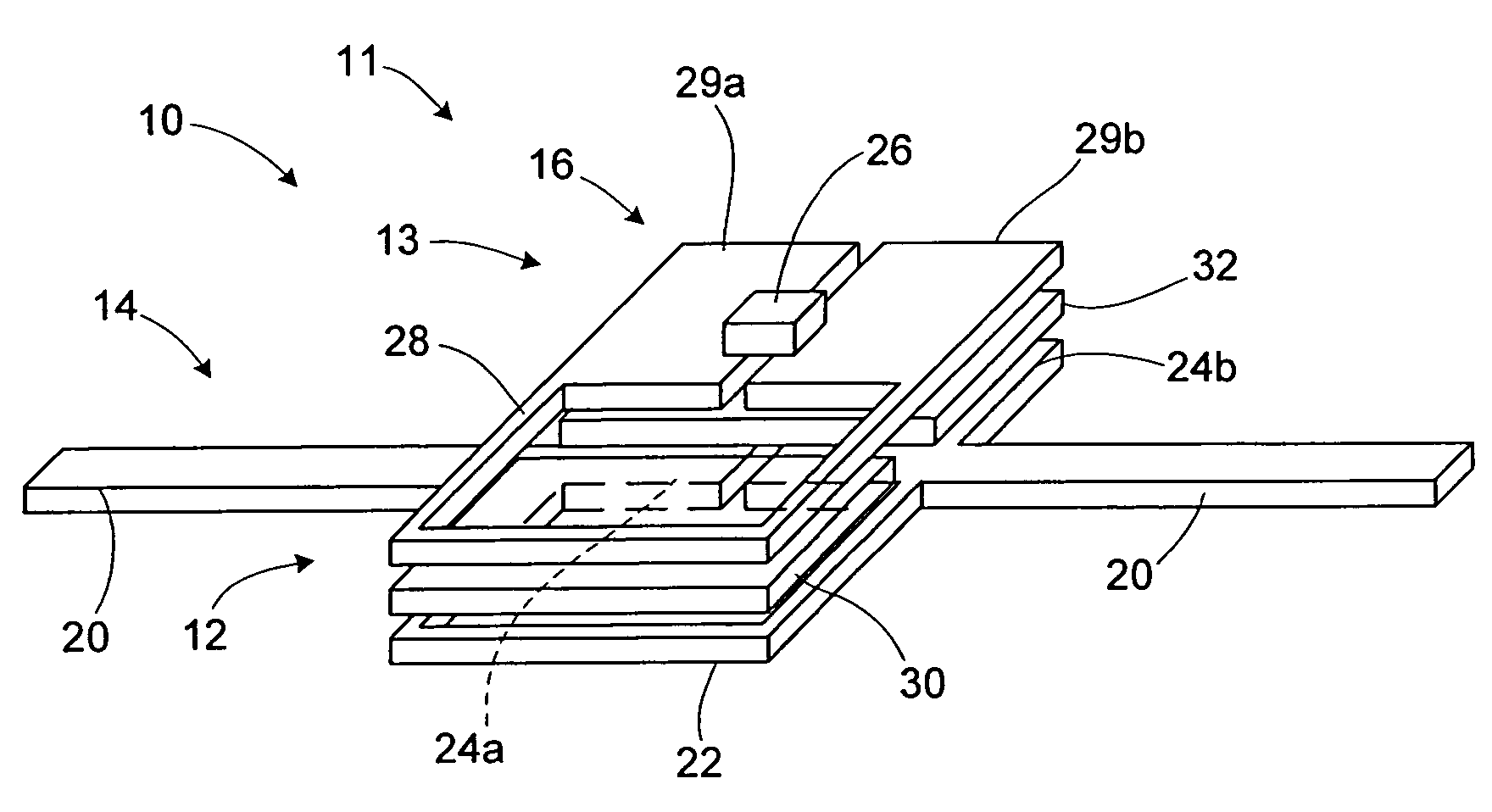
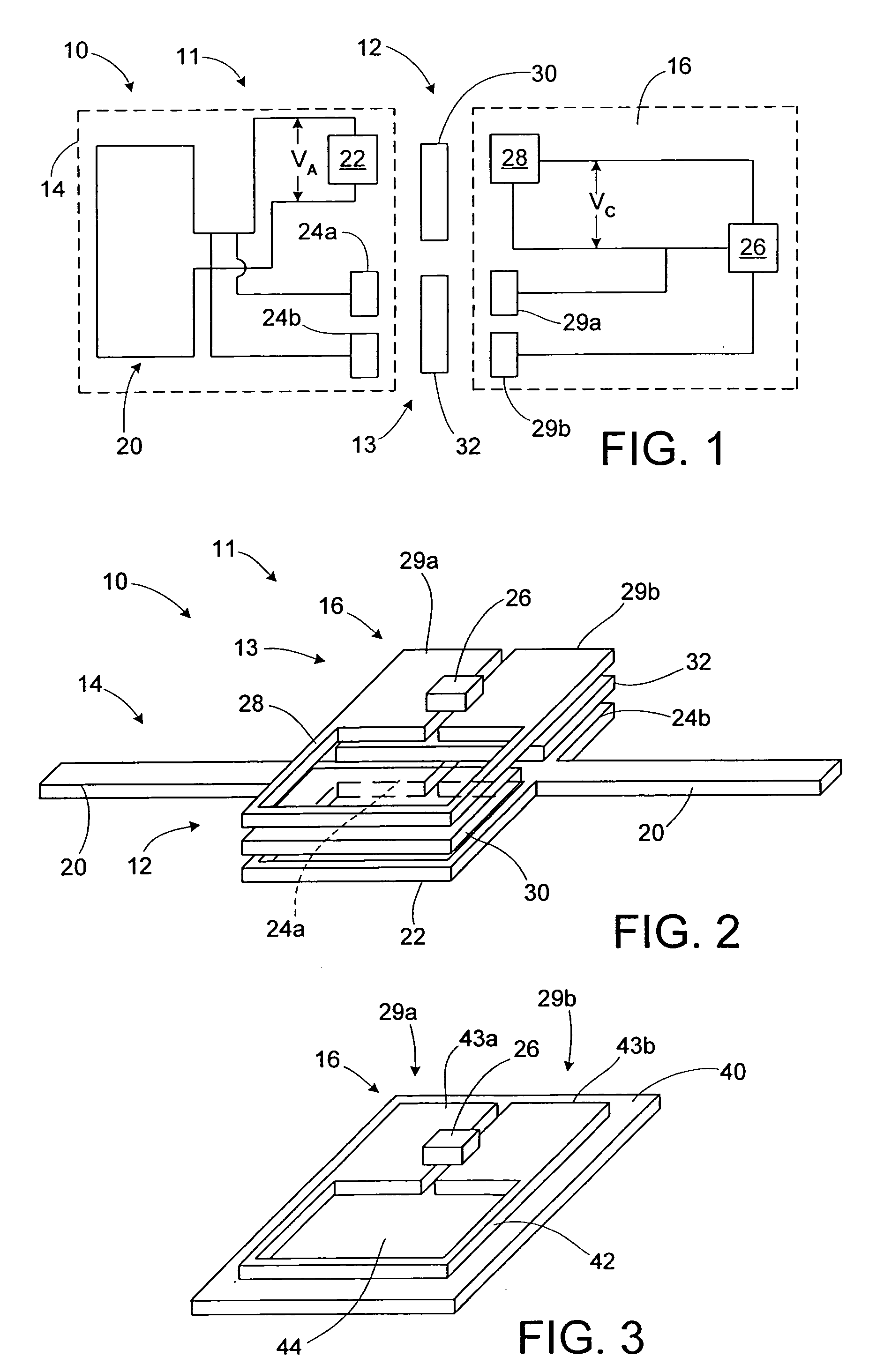
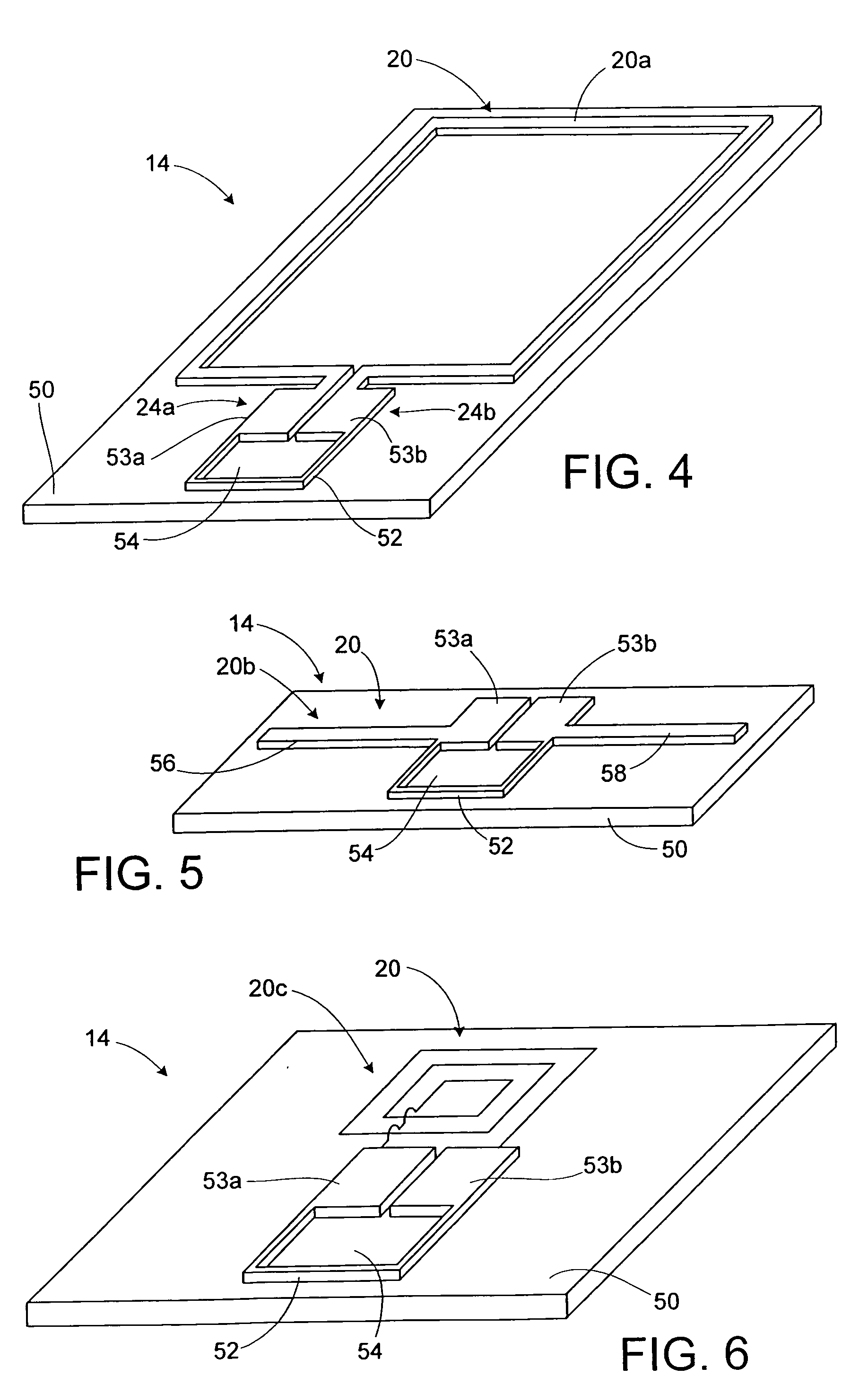
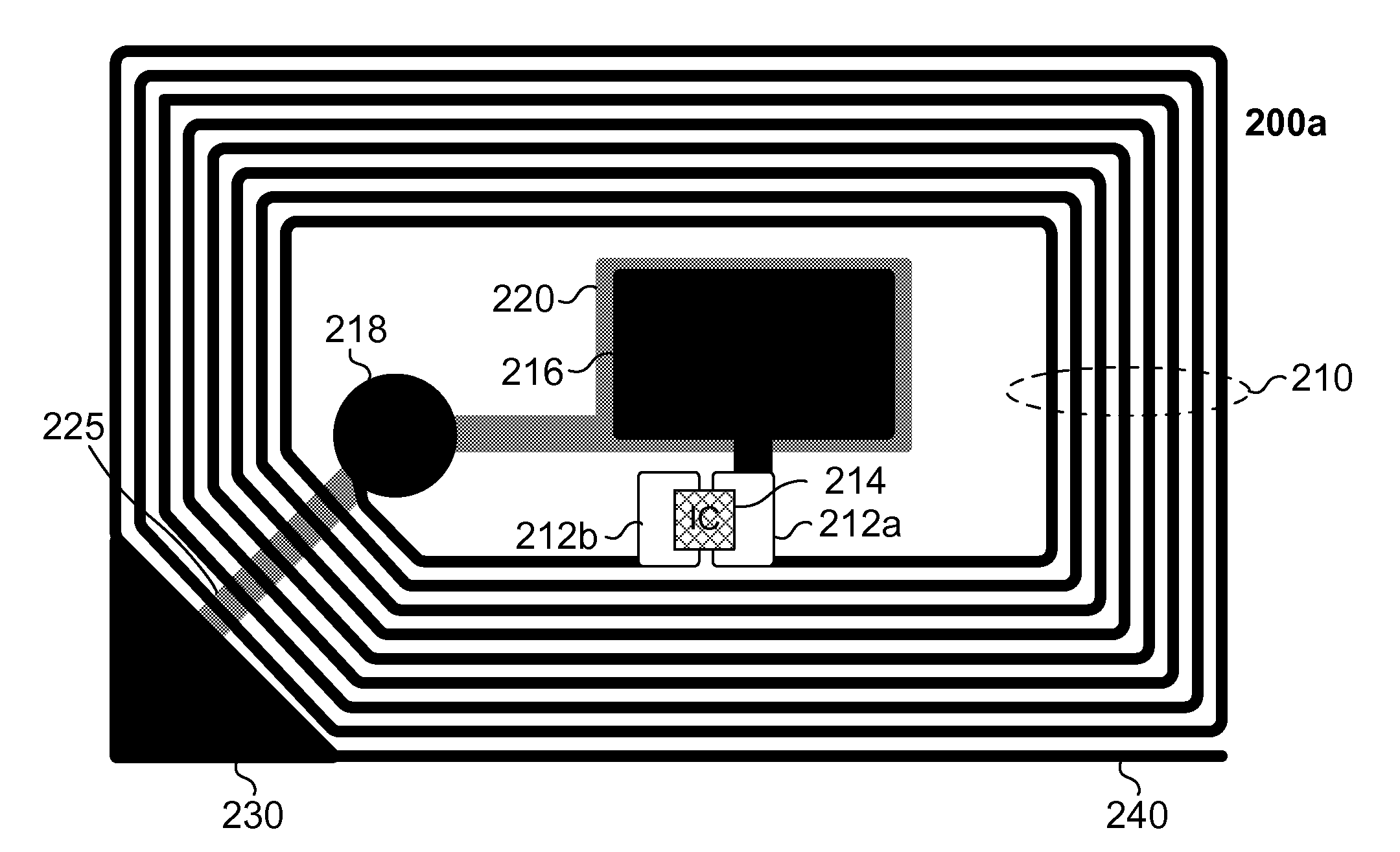
RFID device with combined reactive coupler
ActiveUS20060043198A1Simultaneous aerial operationsLoop antennasCapacitive couplingAntenna substrate
An RFID device, such as an RFID tag or label, includes a combined reactive coupler electrically coupling a transponder chip to an antenna. The combined reactive coupler includes a magnetic coupler and a capacitive coupler. The magnetic coupler and the reactive coupler may have respective coupling elements on both the interposer and on an antenna substrate.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
RFID device and method of forming
InactiveUS7102520B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsInterposerAntenna substrate
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Indefinite materials
InactiveUS20060125681A1Protective material radiating elementsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAntenna substrateWavelength
A compensating multi layer material includes two compensating layers adjacent to one another. A multi-layer embodiment of the invention produces subwavelength near-field focusing, but mitigates the thickness and loss limitations of the isotropic “perfect lens”. An antenna substrate comprises an indefinite material.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
RFID device with combined reactive coupler
An RFID device, such as an RFID tag or label, includes a combined reactive coupler electrically coupling a transponder chip to an antenna. The combined reactive coupler includes a magnetic coupler and a capacitive coupler. The magnetic coupler and the reactive coupler may have respective coupling elements on both the interposer and on an antenna substrate.
Owner:AVERY DENNISON CORP
Antenna Module-Use Magnetic Core Member, Antenna Module, and Portable Information Terminal Having the Same
InactiveUS20090146898A1Improve permeabilityTotal current dropLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna supports/mountingsComputer moduleComputer terminal
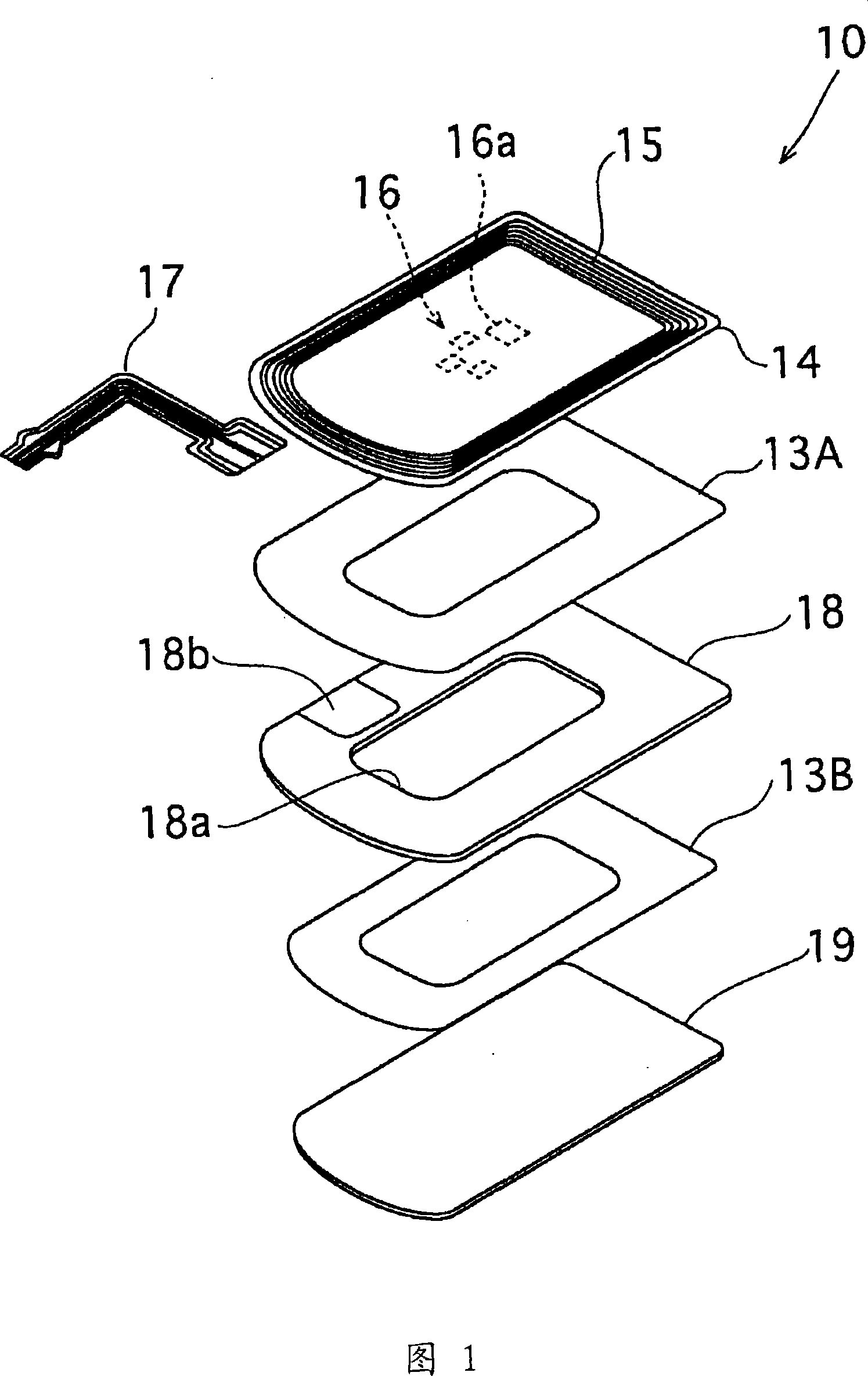
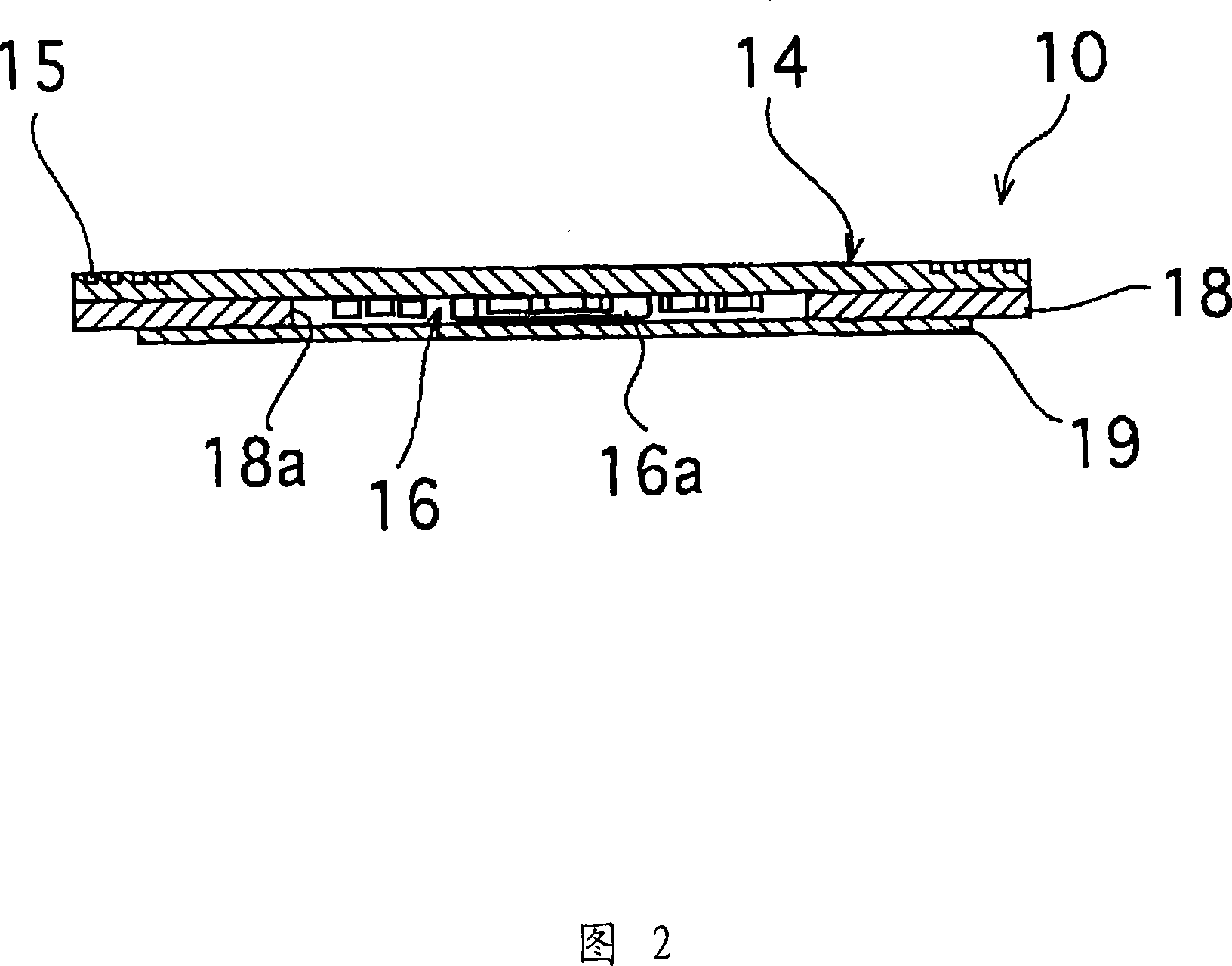
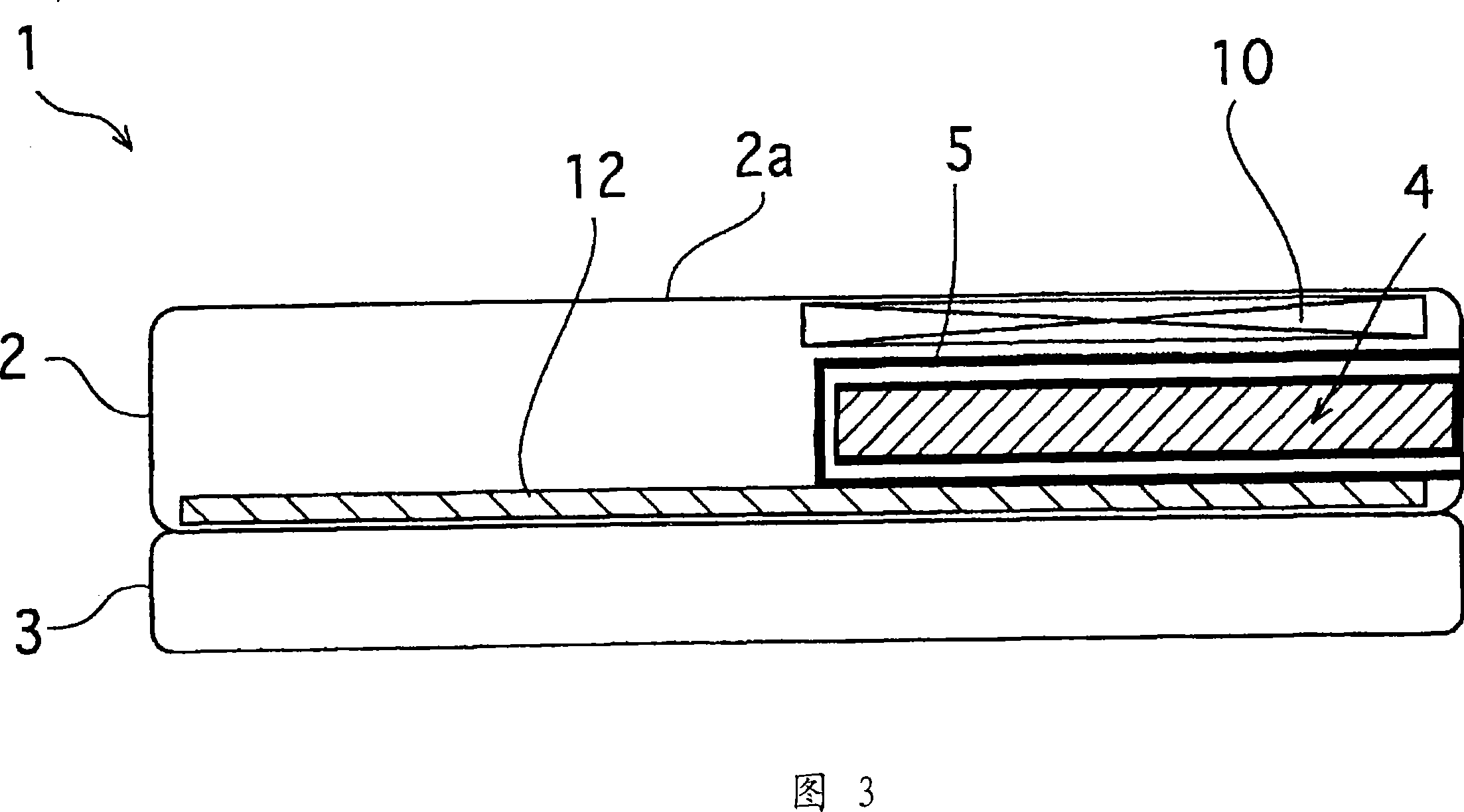
There are provided an antenna module-use magnetic core member, an antenna module and a portable information terminal provided with the same, capable of improving a communication distance without increasing a module thickness. In an antenna module (1) in which a sheet-formed magnetic core member (4) is stacked on an antenna substrate (2) on which a looped antenna is formed, one having a performance index, expressed by μ′×Q, of 300 or higher when Q is a reciprocal of a loss factor (tan δ=μ″ / μ′) expressed by a real part μ′ and an imaginary part μ″ of a complex permeability at an applied frequency is used as the magnetic core member (4).
Owner:SONY CORP
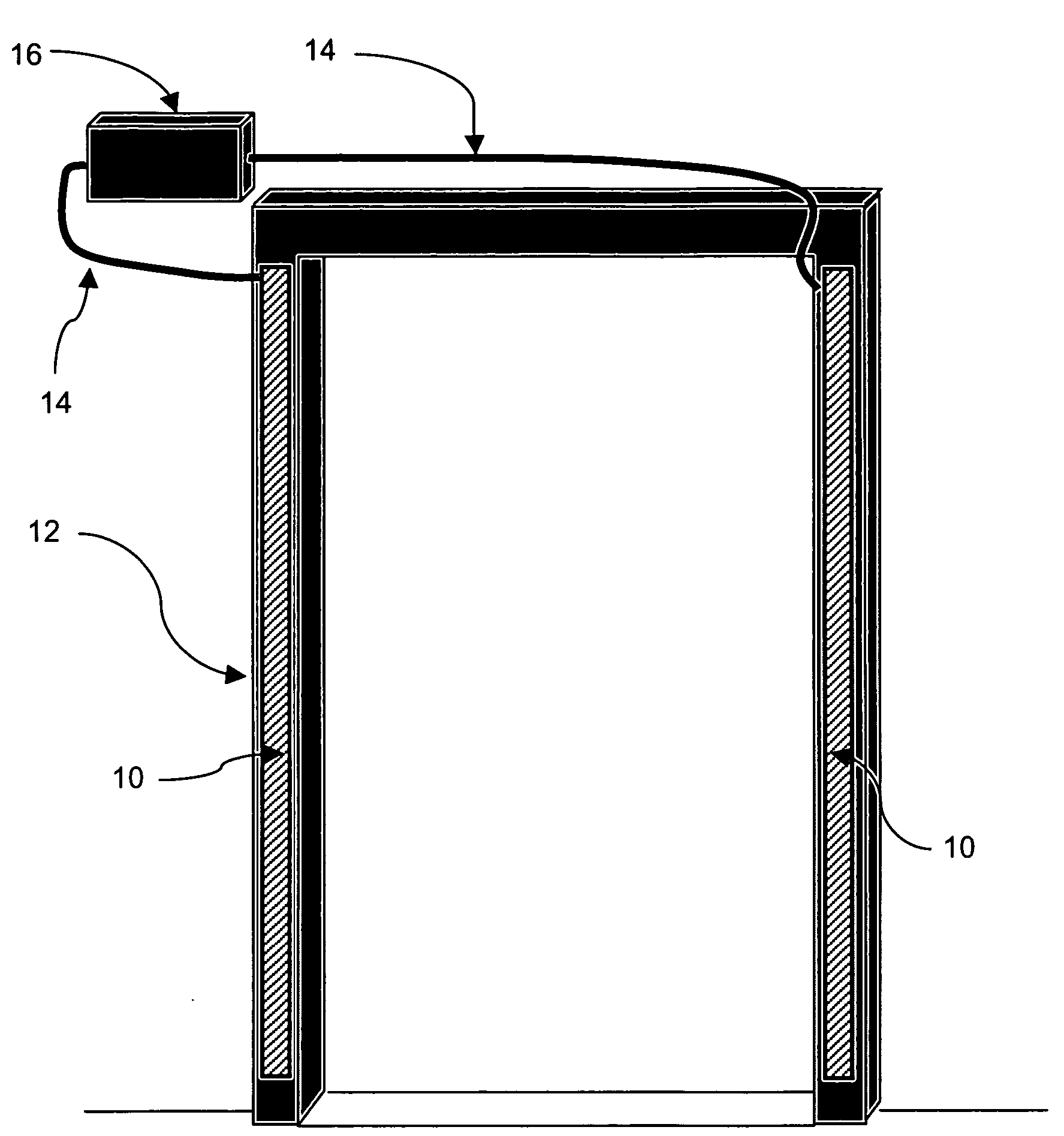
Portal antenna for radio frequency identification
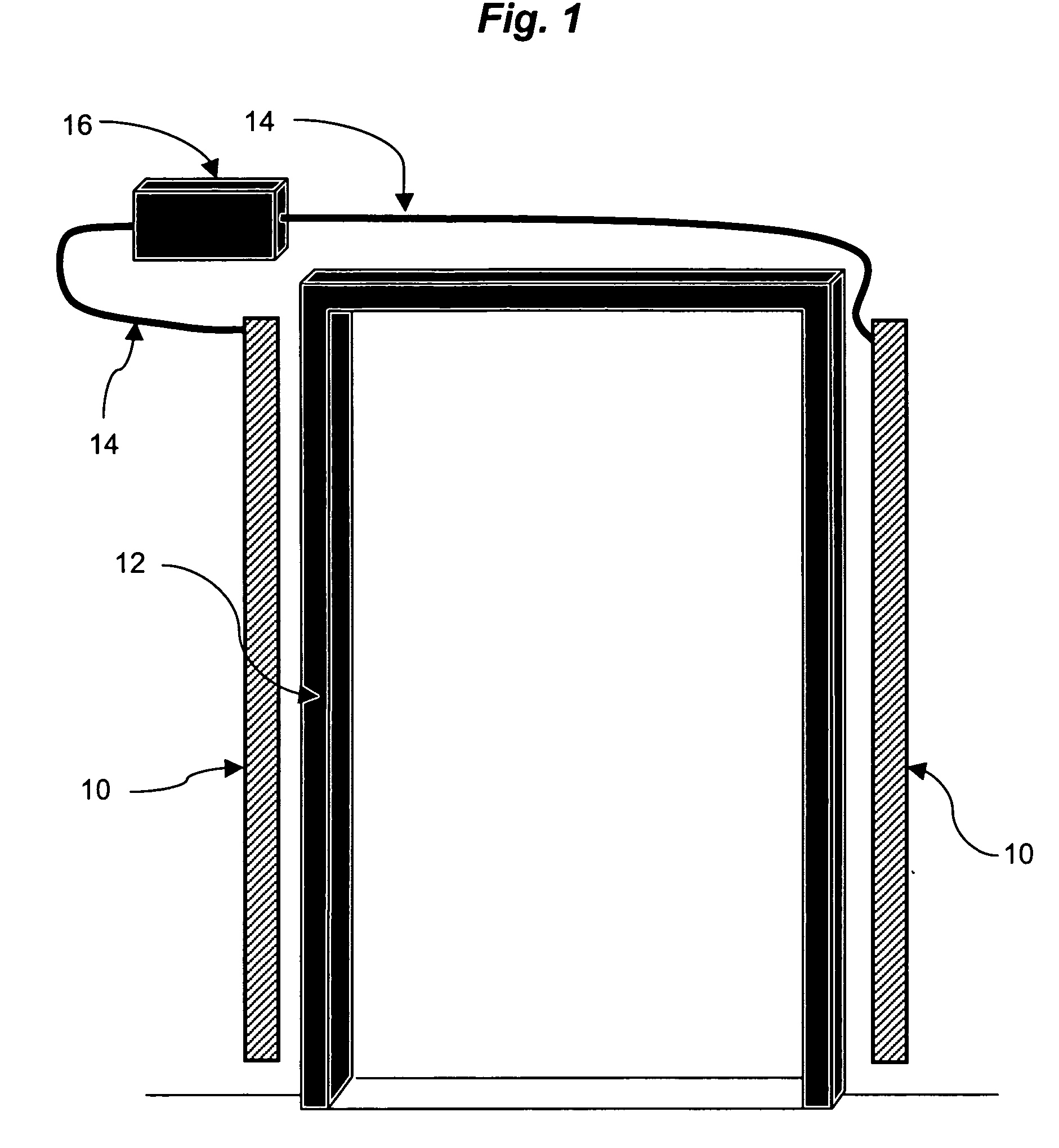
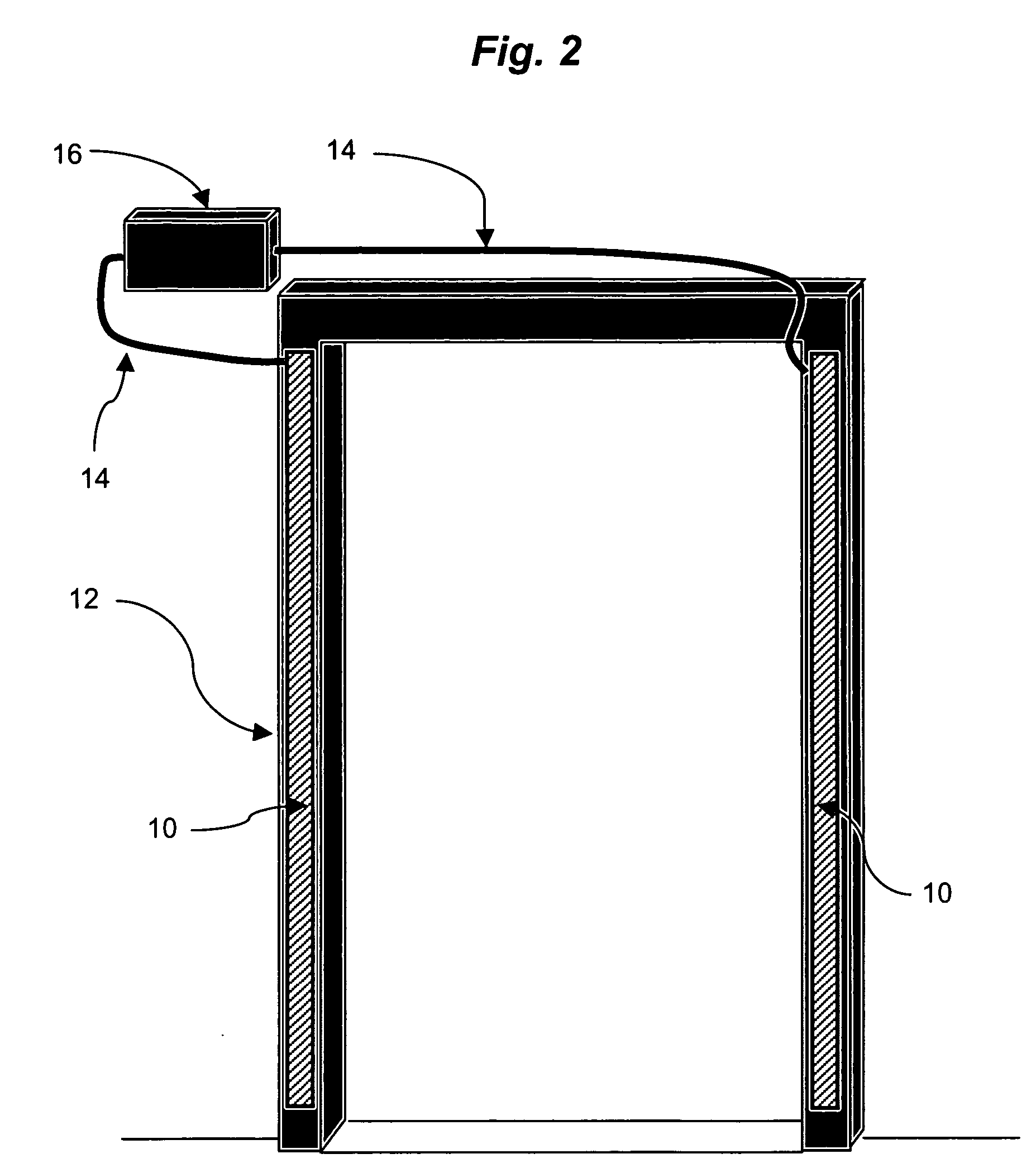
InactiveUS20060132312A1Lighting and heating apparatusAntenna supports/mountingsEngineeringAntenna substrate
An antenna that is used to read and / or write radio frequency identification tags is integrated into the structure of a door frame or other portal. The antenna may incorporate multiple radiating elements and frequency diversity to increase the reliability and accuracy of tag reads or writes, and to provide compatibility with a variety of RFID tags. The design of the antenna may also incorporate a Photonic Band Gap (PBG) antenna substrate.
Owner:TAVORMINA JOSEPH J
Indefinite materials
InactiveUS7522124B2Protective material radiating elementsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAntenna substrateWavelength
A compensating multi layer material includes two compensating layers adjacent to one another. A multi-layer embodiment of the invention produces subwavelength near-field focusing, but mitigates the thickness and loss limitations of the isotropic “perfect lens”. An antenna substrate comprises an indefinite material.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi-band monopole antennas for mobile communications devices
InactiveUS7423592B2Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandElectrical conductor
Antennas for use in mobile communication devices are disclosed. The antennas disclosed can include a substrate with a base, a top, a front side and a back side; a first conductor can be located on the first side of the antenna substrate; and a second conductor can be located on the second side of the antenna substrate. The conductors can have single or multiple branches. If a conductor is a single branch it can, for example, be a spiral conductor or a conducting plate. If a conductor has multiple branches, each branch can be set up to receive a different frequency band. A conductor with multiple branches can have a linear branch and a space-filling or grid dimension branch. A conducting plate can act as a parasitic reflector plane to tune or partially tune the resonant frequency of another conductor. The first and second conductors can be electrically connected.
Owner:FRACTUS
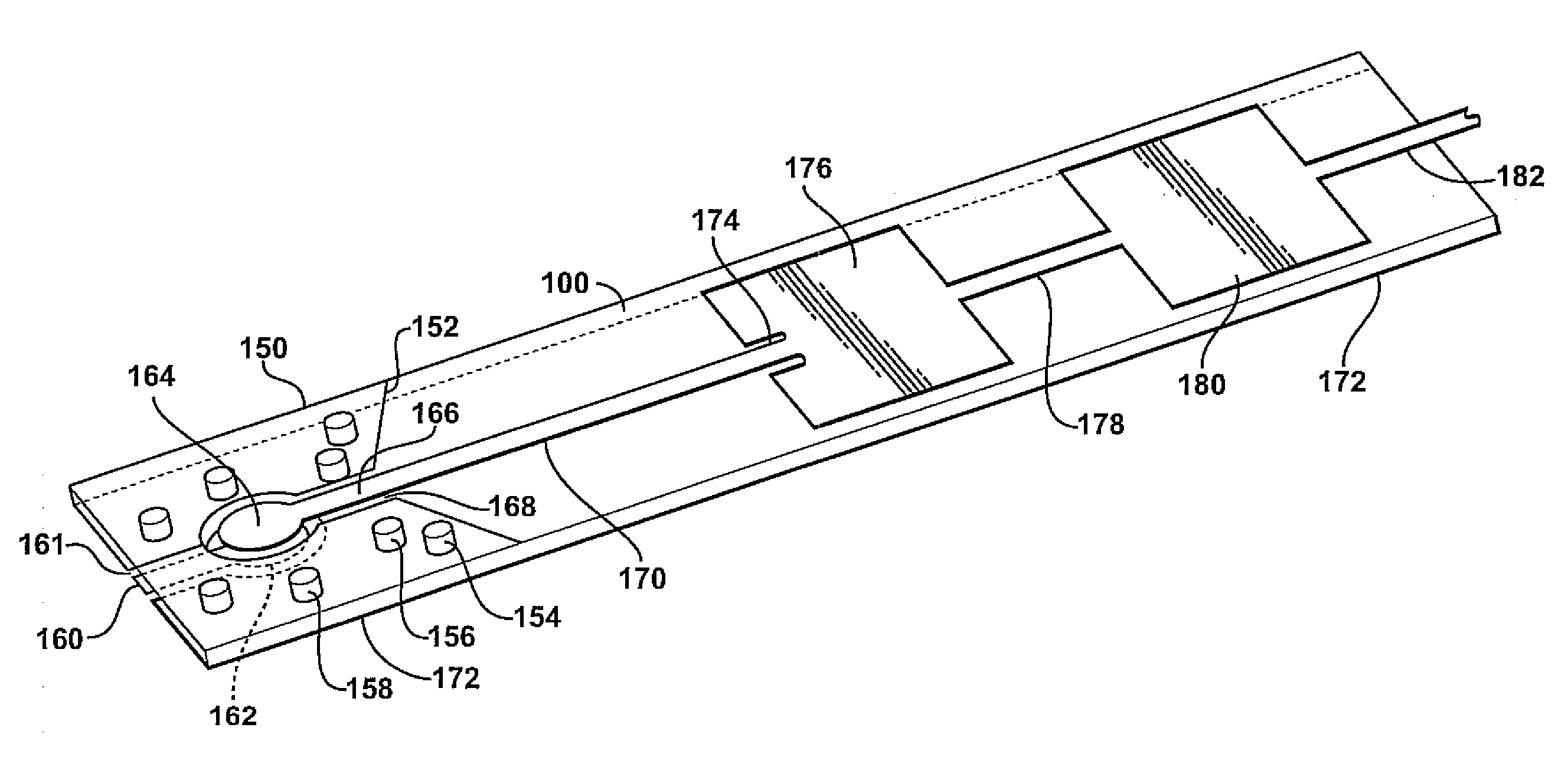
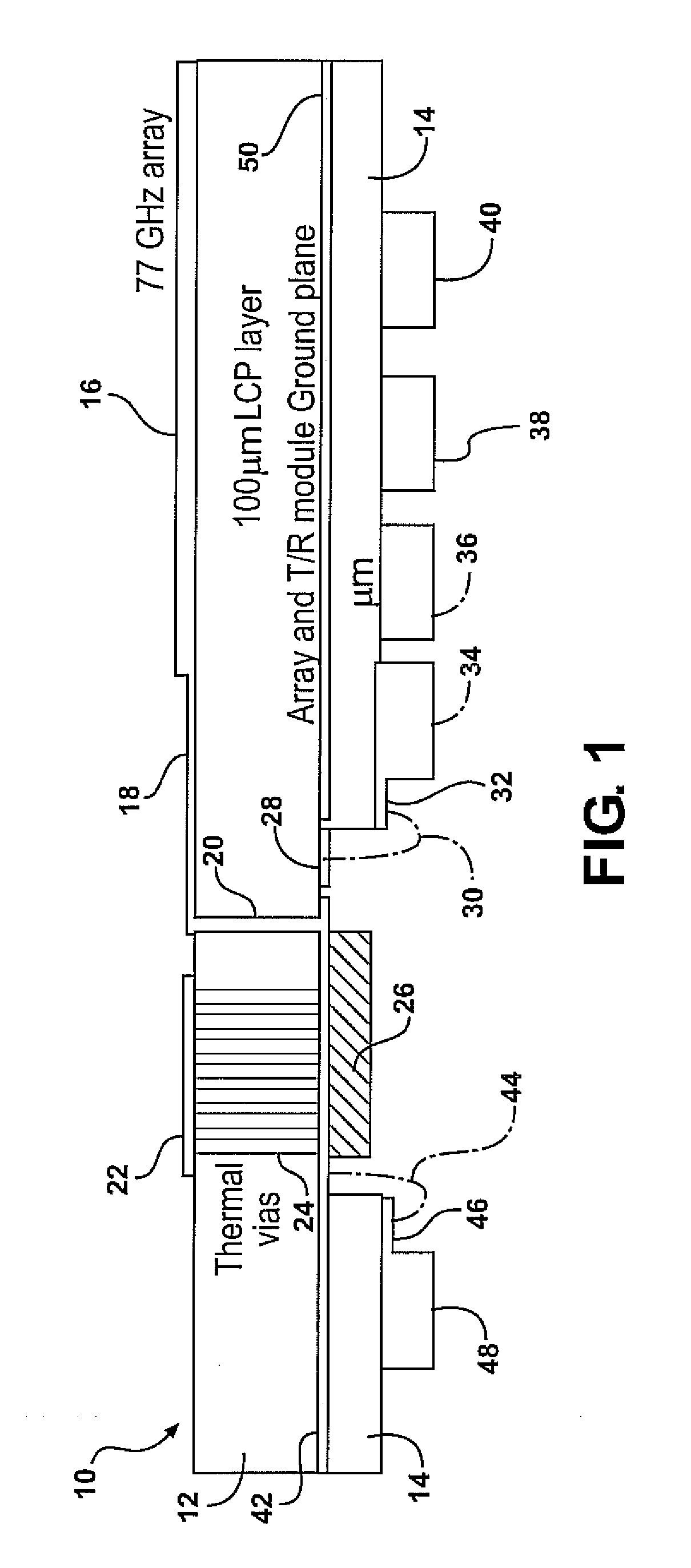
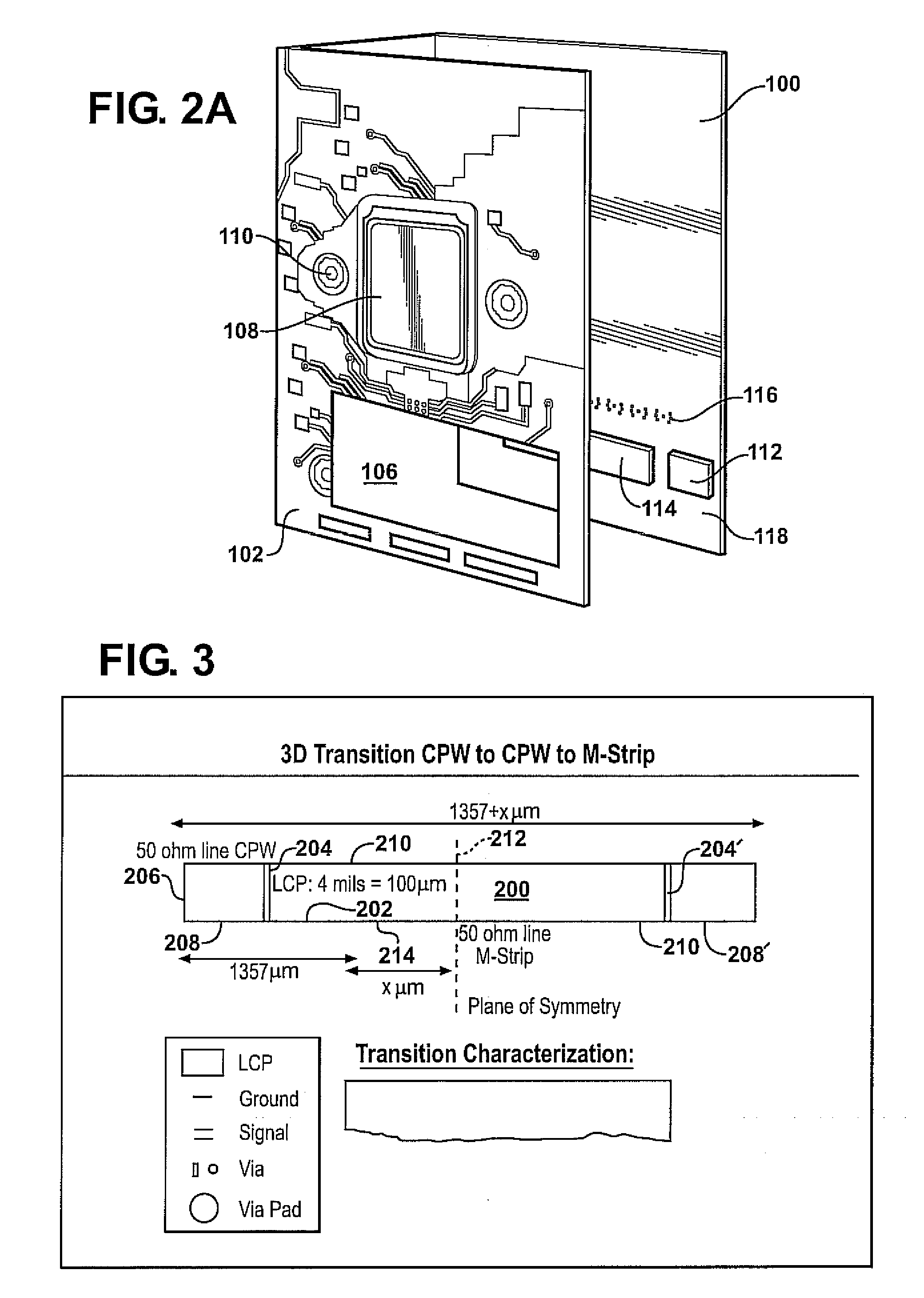
Wideband RF 3D transitions
InactiveUS20100134376A1Reduce return lossReduce lossesSimultaneous aerial operationsSolid-state devicesElectricityElectrical connection
Apparatus and methods according to examples of the present invention include providing an electrical interconnection between an RF circuit and an antenna, the electrical interconnection including a transition via through an antenna substrate. The electrical connection can be configured so as to provide low losses.
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR ENGINEERING & MANUFACTURING NORTH AMERICA
Reader/writer and mobile communication apparatus
ActiveUS20070051807A1Improve efficiencyFacilitate communicationLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreMemory record carrier reading problemsCouplingEngineering
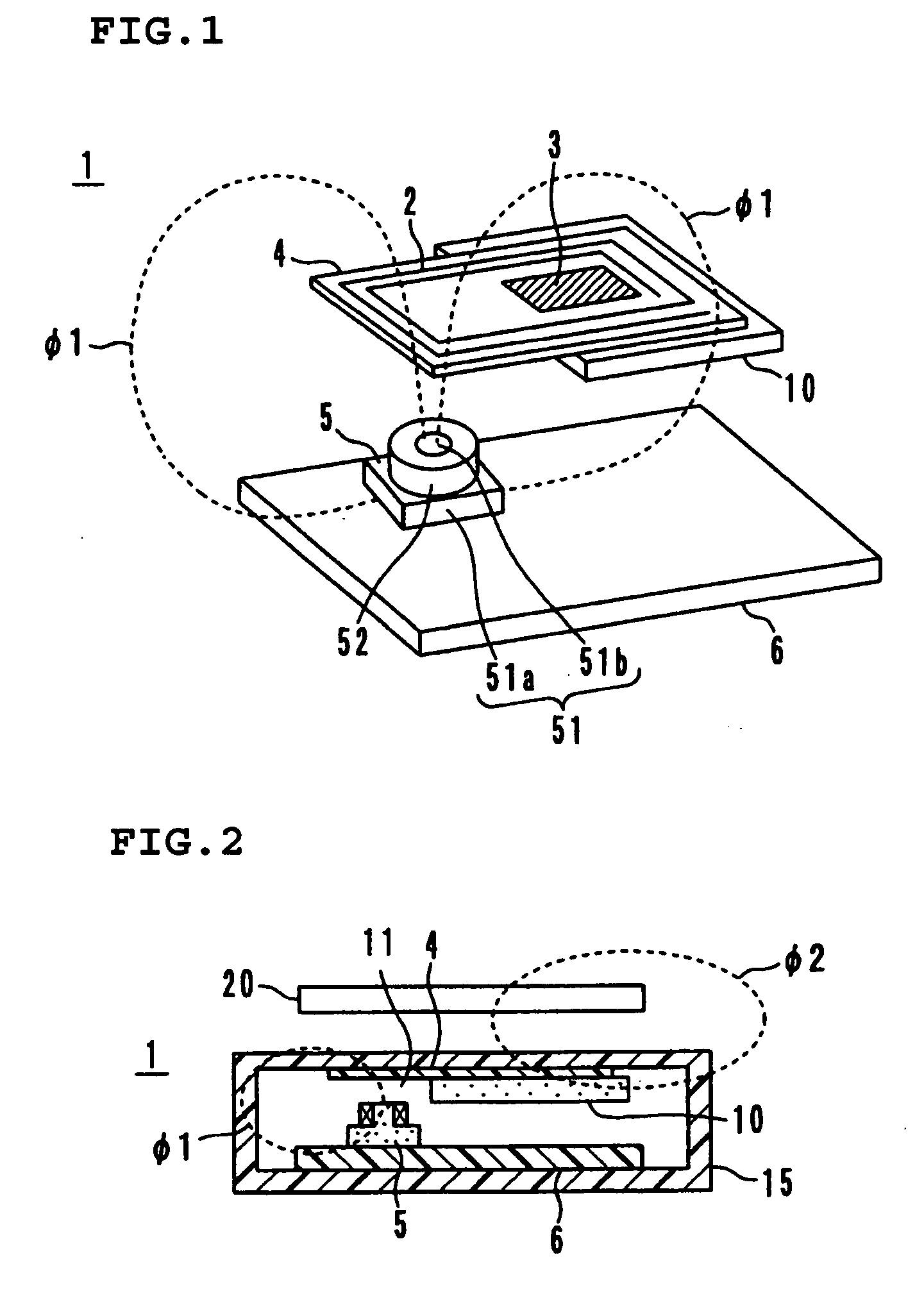
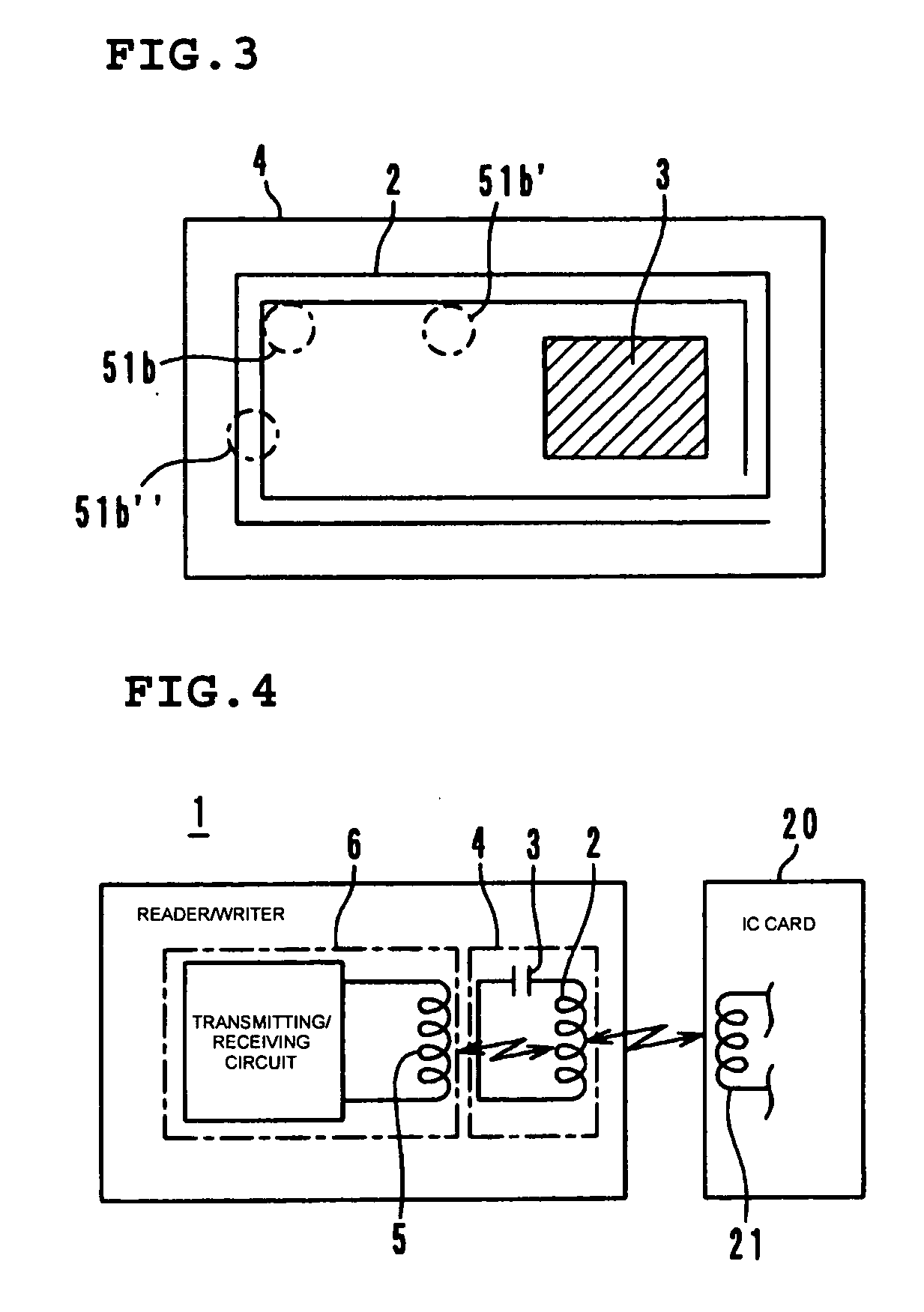
A non-contact reader / writer for an IC card includes an antenna substrate provided with a loop antenna and a capacitor on its upper surface, a control substrate provided with a transmitting / receiving circuit and a chip coil on its upper surface, and a magnetic sheet disposed between the antenna substrate and the control substrate. A magnetic flux generated by the chip coil on the control substrate passes through the loop antenna to cause magnetic coupling, so that the loop antenna and the transmitting / receiving circuit need not be connected to each other through a communication cable.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Chip package structure and device
ActiveCN103247581AReduce lossSmall sizeAntenna supports/mountingsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCommunications systemSemiconductor materials
The invention relates to a chip package structure and a device. Wafer-scale packaging structures and methods are provided for integrally packaging antenna structures with semiconductor RFIC (radio frequency integrated circuit) chips to form compact integrated radio / wireless communications systems for millimeter wave (mmWave) and Terahertz (THz) applications. For example, a chip package includes an RFIC chip, an antenna structure and an interface layer. The RFIC chip includes a semiconductor substrate having an active surface and an inactive surface, and a BEOL (back end of line) structure formed on the active surface of the semiconductor substrate. The antenna structure includes an antenna substrate and a planar antenna radiator formed on a surface of the antenna substrate, wherein the antenna substrate is formed of a low loss semiconductor material. The interface layer connects the antenna structure to the BEOL structure of the RFIC chip.
Owner:TESSERA INC
Transferring antenna structures to RFID components
InactiveUS20120040128A1Easy transferLayered productsSolid-state devicesComputer moduleAntenna substrate
Forming antenna structures having turns of wire, foil or conductive material on a an antenna substrate or in a layer of adhesive layer on a carrier substrate, transferring the antenna structures individually or many at once to corresponding transponder sites on an inlay substrate and connecting the aligned termination ends of the antenna structures to terminal areas of RFID chip modules at the transponder sites. Transferring may be performed by various means such as laminating (heat and pressure), or heating the antenna structures directly or indirectly. The antenna substrate may be in web format or sheet format. Automated manufacturing procedures are disclosed. Kits having components for manufacturing inlay substrates, inlays and secure documents are disclosed. Various features of an inlay substrate and chip module are disclosed.
Owner:AMATECH GRP LTD
Hybrid multi-antenna system and wireless communication apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20120169552A1Antenna structure is simpleSmall sizeElectrically short antennasSeparate antenna unit combinationsPhase differenceAntenna substrate
A hybrid multi-antenna system includes a system circuit board, an antenna substrate, at least a dipole antenna, and at least a monopole-slot antenna. The system board has at least a system ground plate, and the system ground plate is served as a reflector of the hybrid multi-antenna system. The antenna substrate and the system ground plate have a first distance therebetween. The dipole antenna having a first signal feed-in source and the monopole-slot antenna having a second signal feed-in source respectively provide a first and second operating band, and they are on a surface of the antenna substrate. The monopole-slot antenna is located nearby the dipole antenna. The monopole-slot antenna and the dipole antenna have a second distance therebetween. The first and second signal feed-in sources are vertical to each other, and have the phase difference of 90°.
Owner:LITE ON ELECTRONICS (GUANGZHOU) LTD +1
RFID Label With Shielding Element
InactiveUS20120055998A1Improve performanceNear-field transmissionRecord carriers used with machinesContact padAntenna substrate
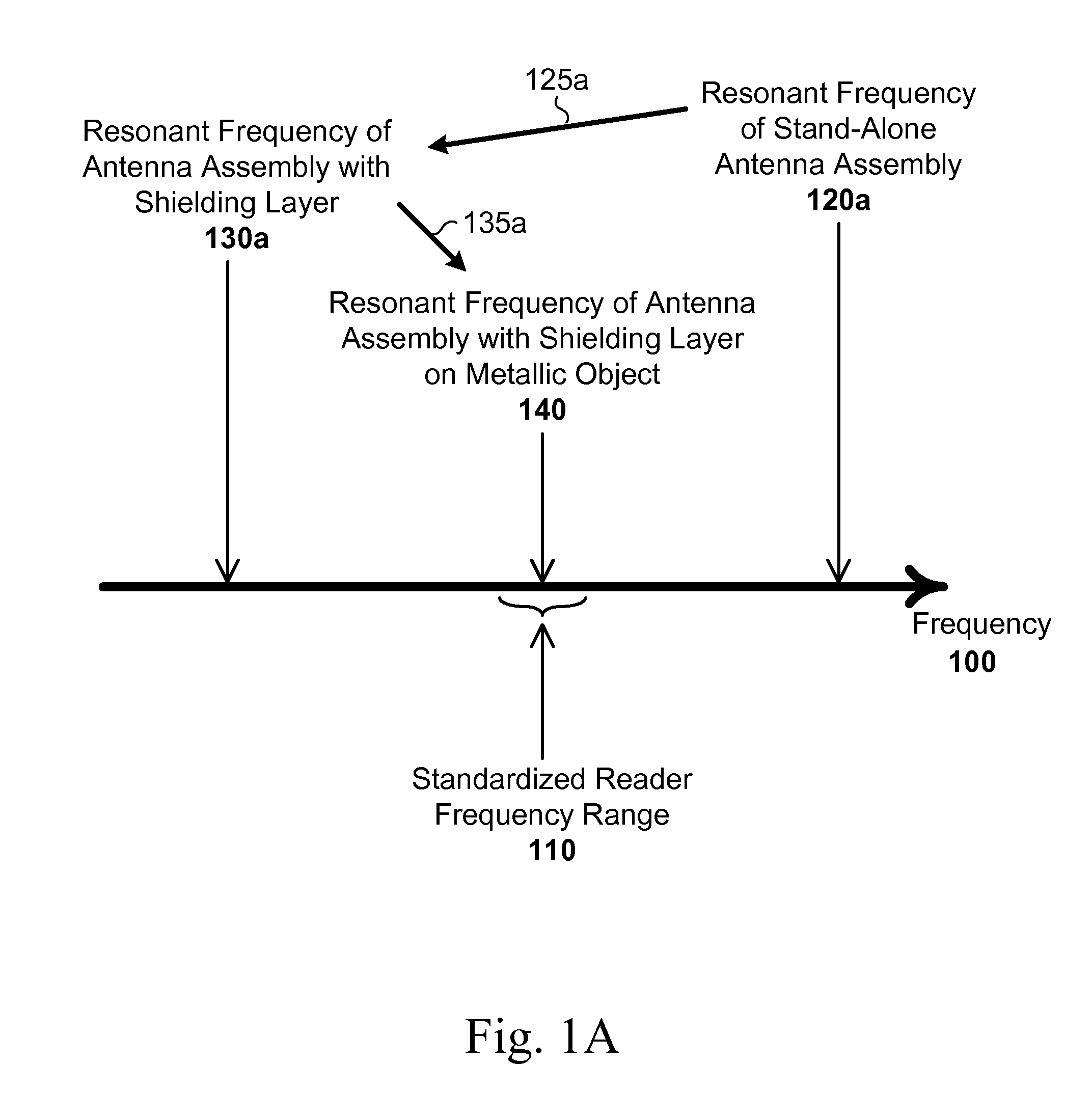
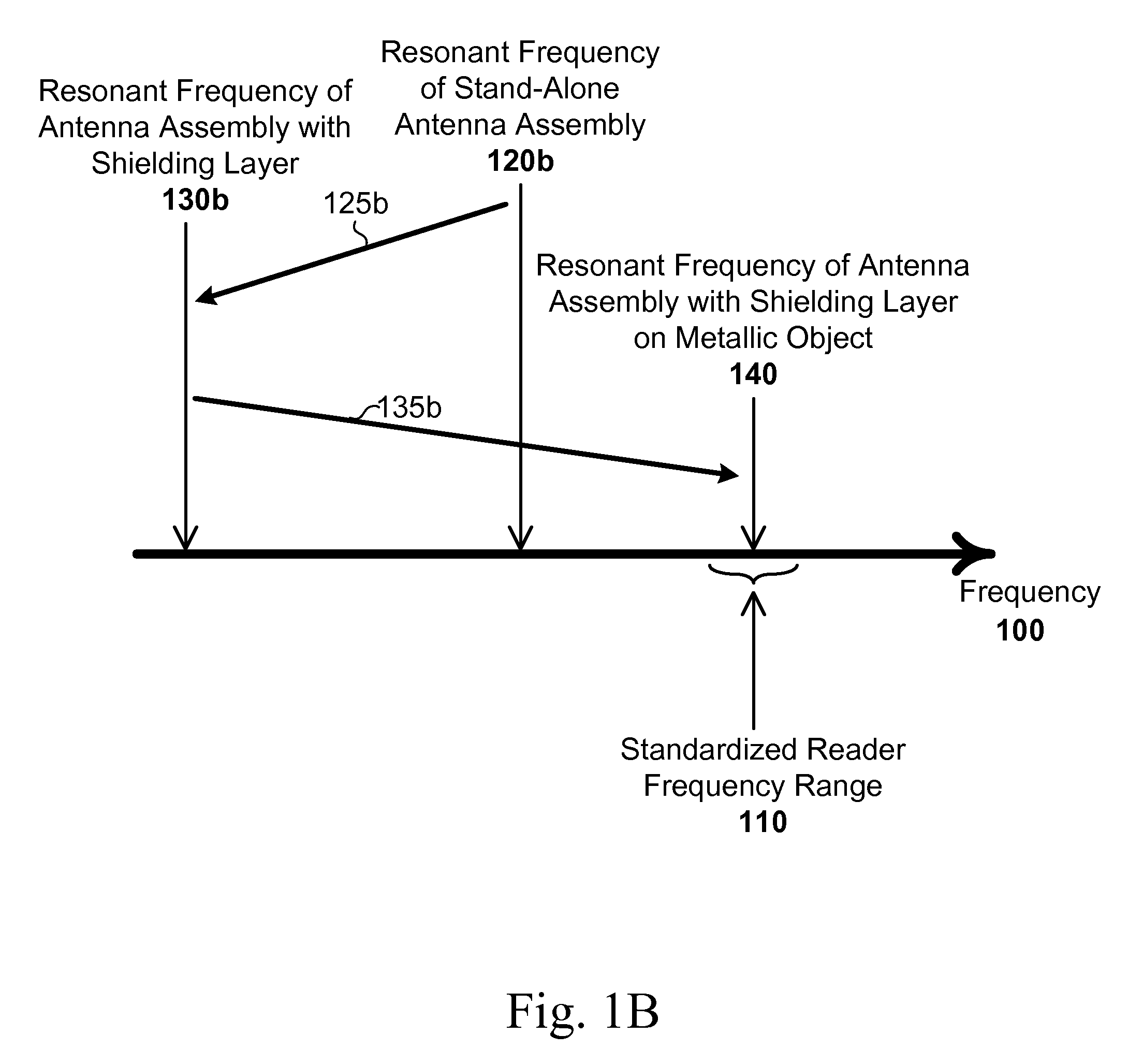
Described are RFID structures and methods for forming RFID structures. An RFID structure includes a loop antenna assembly, an antenna substrate supporting the loop antenna assembly, and a shielding layer parallel with a plane defined by the antenna substrate. The loop antenna assembly has a stand-alone resonant frequency of ƒ1 above or below a standardized reader frequency range. The loop antenna includes an antenna track and at least two contact pads. The loop antenna assembly in combination with the shielding layer has a resonant frequency of ƒ2 below the standardized reader frequency range. If positioned against a metallic surface, the loop antenna assembly in combination with the shielding layer has a resonant frequency within the standardized reader frequency range.
Owner:TAGSTAR SYST
Circuit board
InactiveUS20070096995A1Easy to modifyMinimized volumeAntenna supports/mountingsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringAntenna substrate
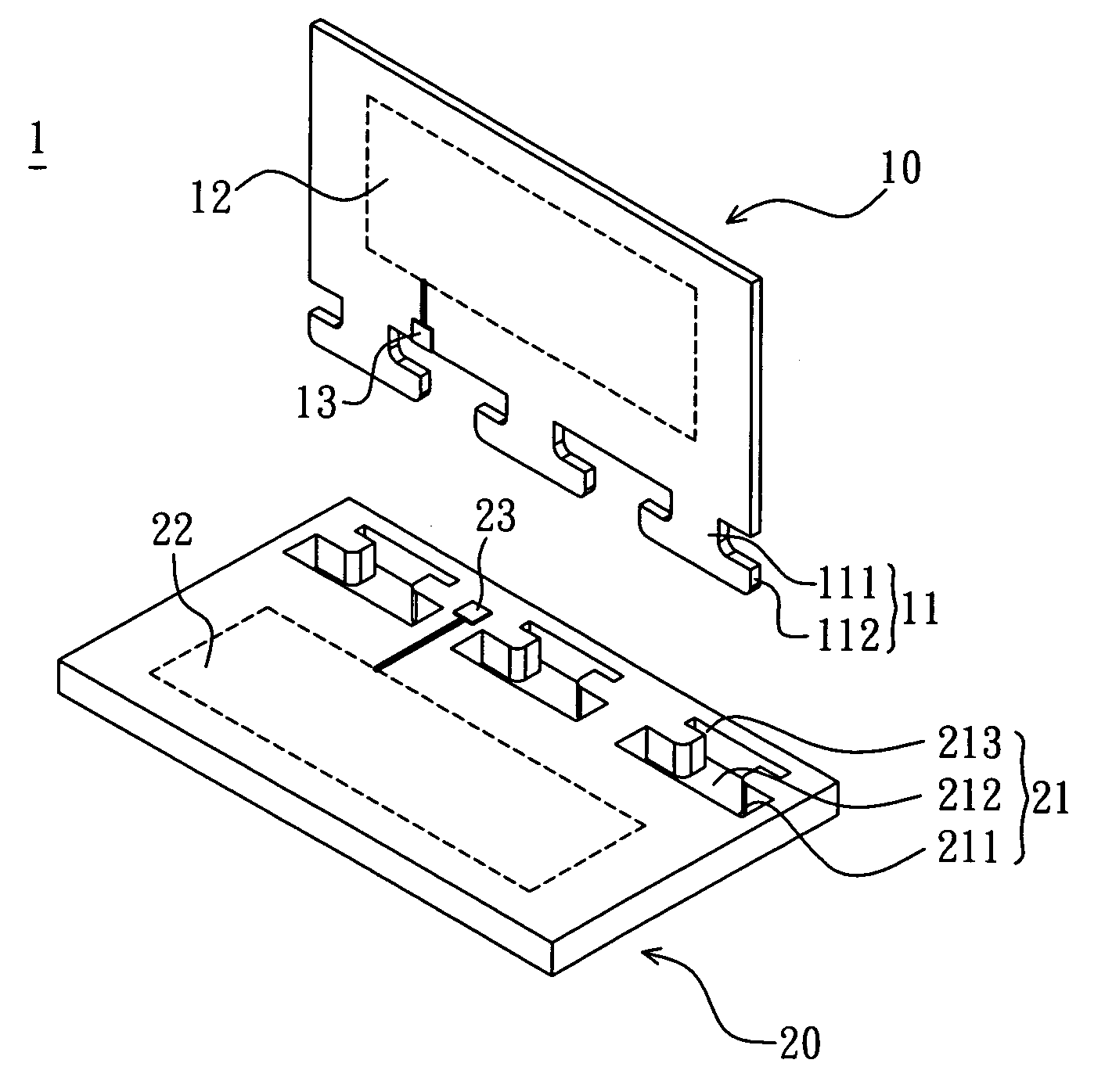
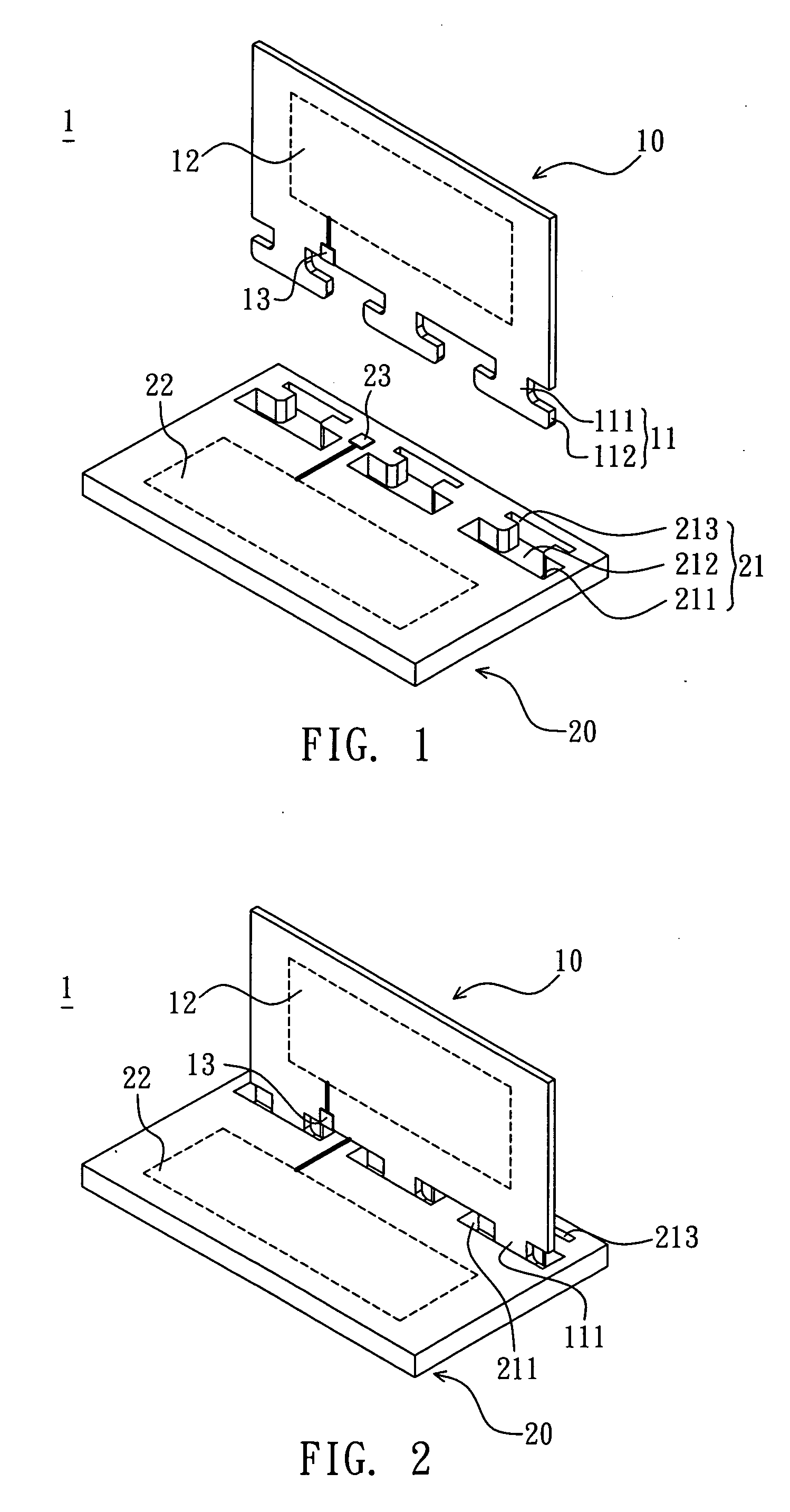
A circuit board includes an antenna substrate and a main substrate. The antenna substrate has at least one first linking portion. The main substrate has at least one second linking portion. The first linking portion connects with the second portion so that the antenna substrate assembles with the main substrate. Herein, the antenna is substantially perpendicular to the main substrate.
Owner:ARCADYAN
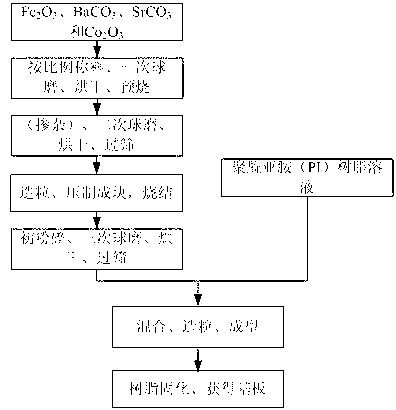
Ferrite-base composite magnetic dielectric antenna substrate material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a ferrite-base composite magnetic dielectric antenna substrate material and a preparation method thereof. The ferrite-base composite magnetic dielectric antenna substrate material is formed by combining a main phase material which accounts for 85-90wt% and an auxiliary phase material which accounts for 15-10% in percentage by mass, wherein the main phase material is Co2Z type hexagonal ferrite, with molecular formula represented as Ba3-xSrxCo2Fe24-yO41, wherein x ranges from 0 to 1.5 and y ranges from 0 to 4; the auxiliary phase material is polyimide resin. The magnetic dielectric composite substrate material has a relatively low magnetic conductivity and a relatively high dielectric constant within a frequency range of 300MHz-3GHz, and the composite substrate material is comparatively high in miniaturization factor and is simultaneously comparatively low in both magnetic loss and dielectric loss; the composite substrate material, in comparison with the conventional ceramic substrate material, is better in mechanical shock resistance. The ferrite-base composite magnetic dielectric antenna substrate material is not only favorable for reducing the weight and size of an antenna, but also conductive to improving the bandwidth of the micro-strip antenna and for inhibiting the generation of a surface wave.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
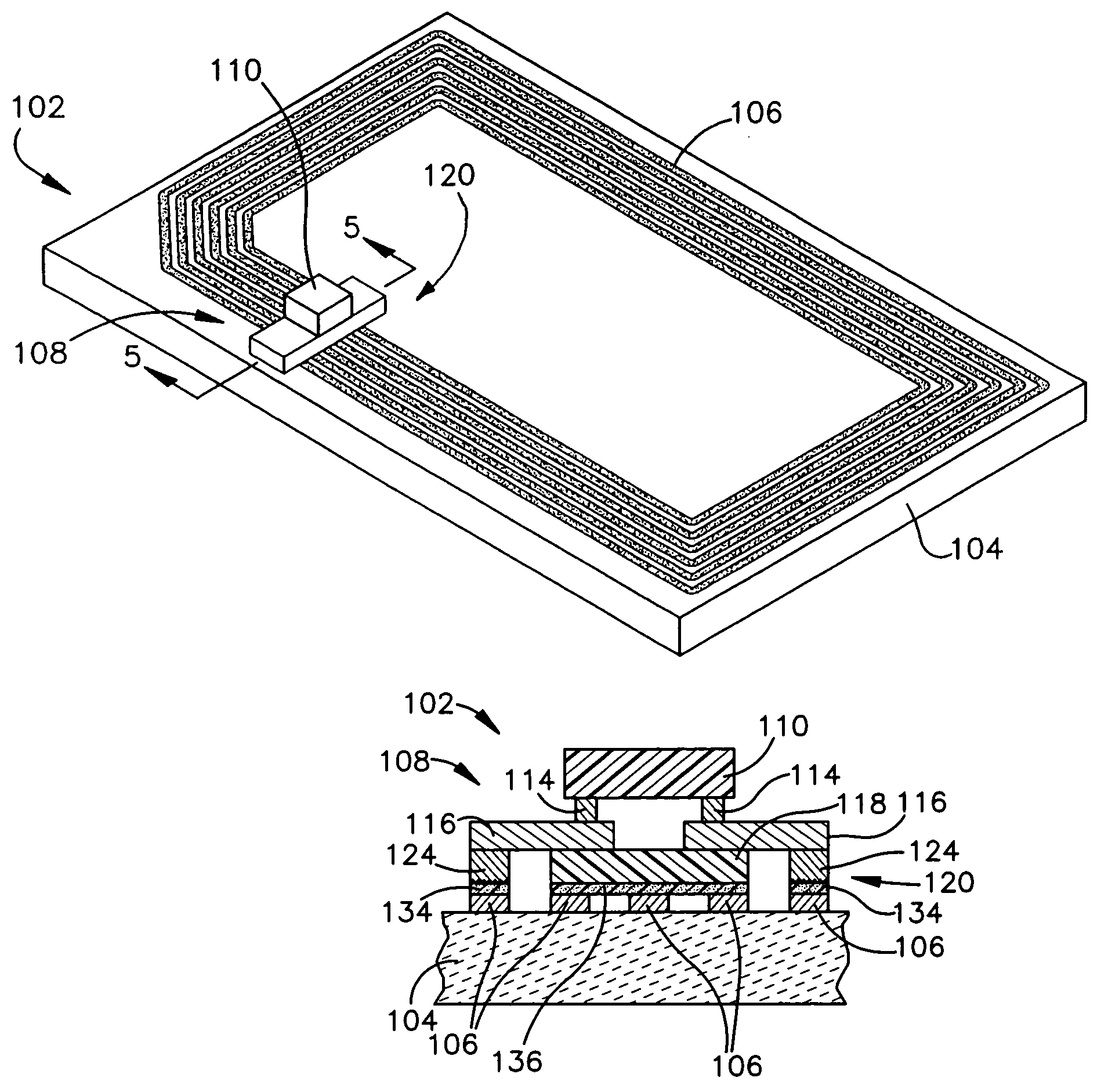
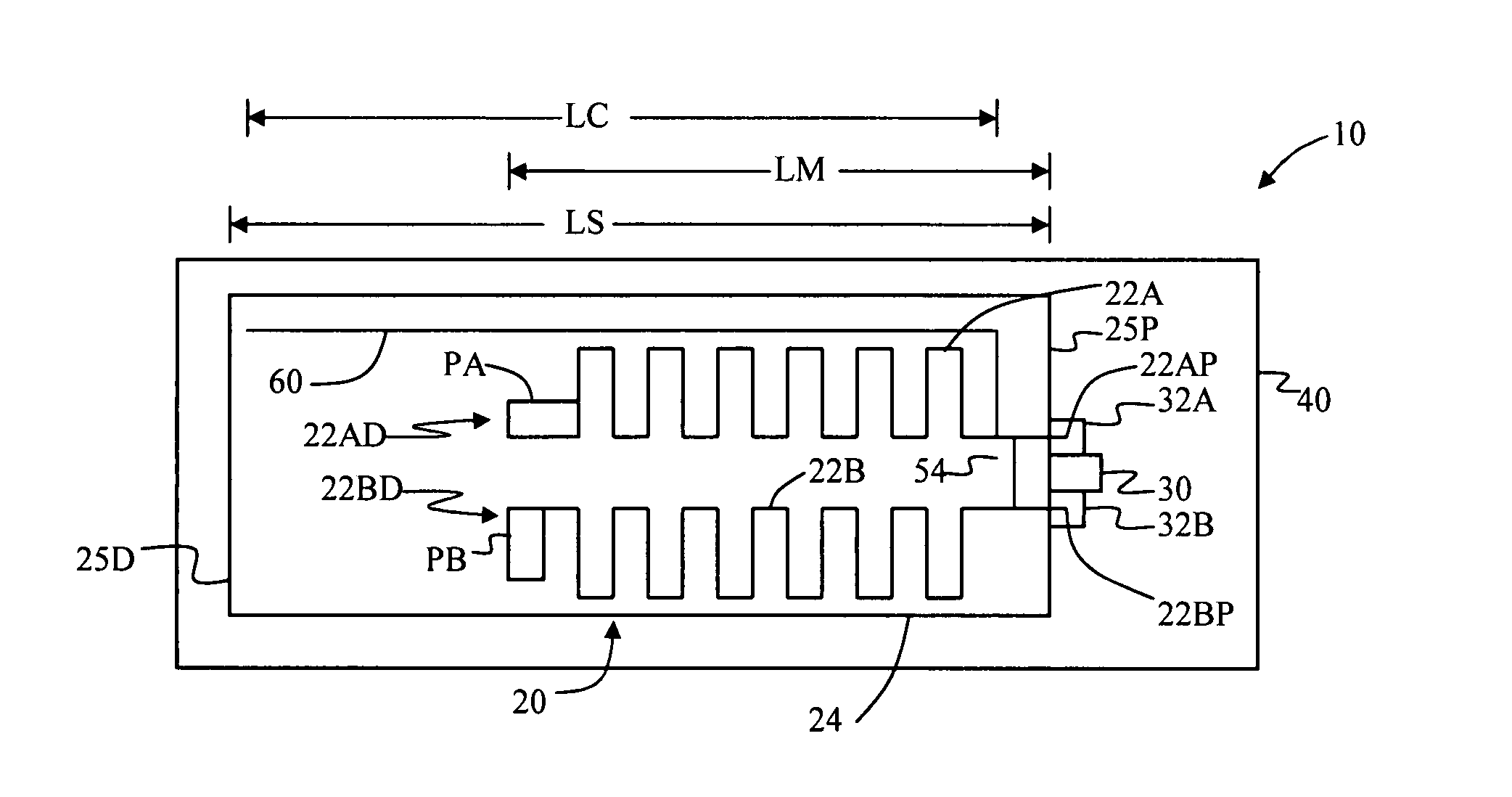
Antenna systems for passive RFID tags
ActiveUS7855697B2Facilitate currentImproving Impedance MatchingSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsTag antennaSmall form factor
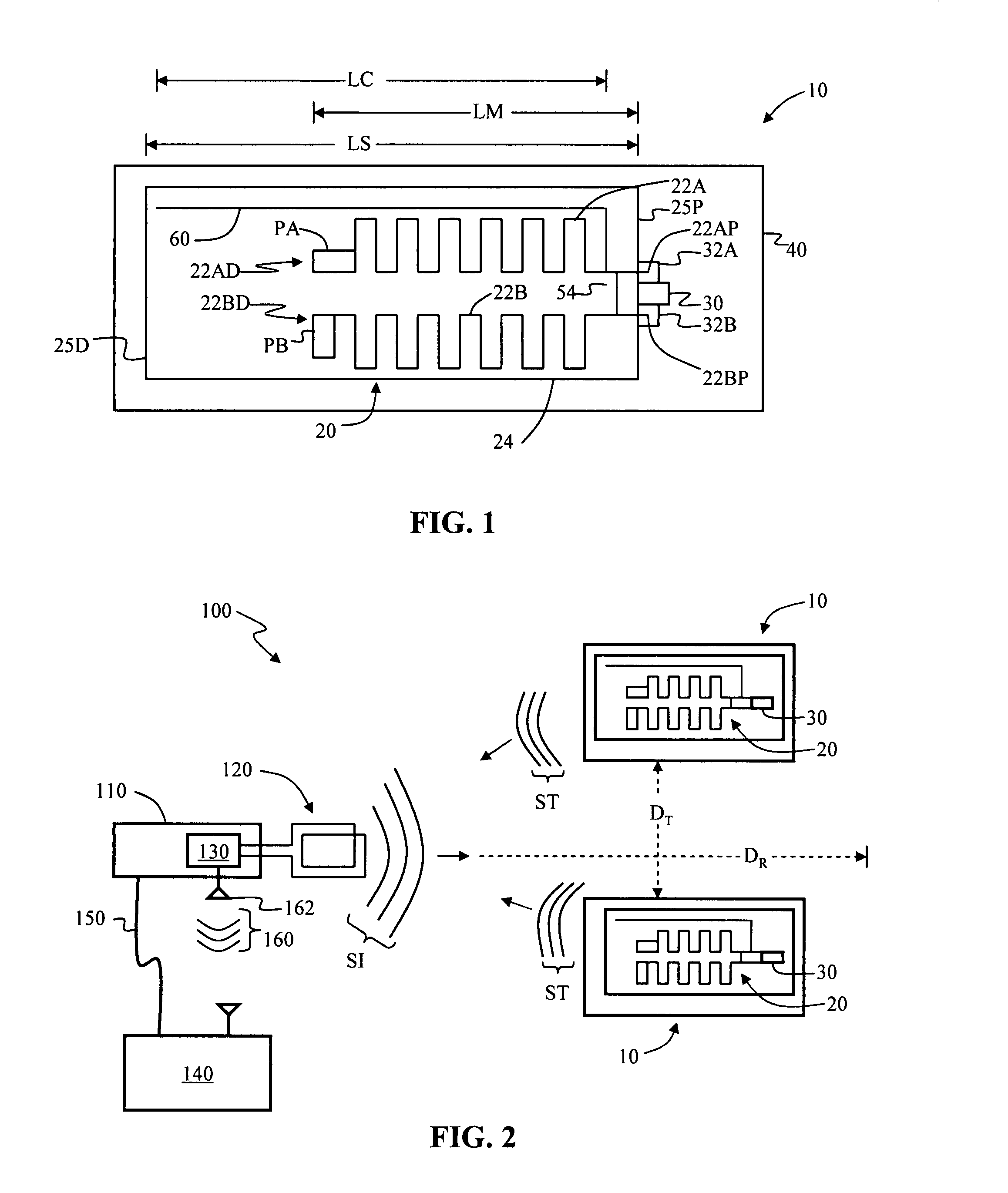
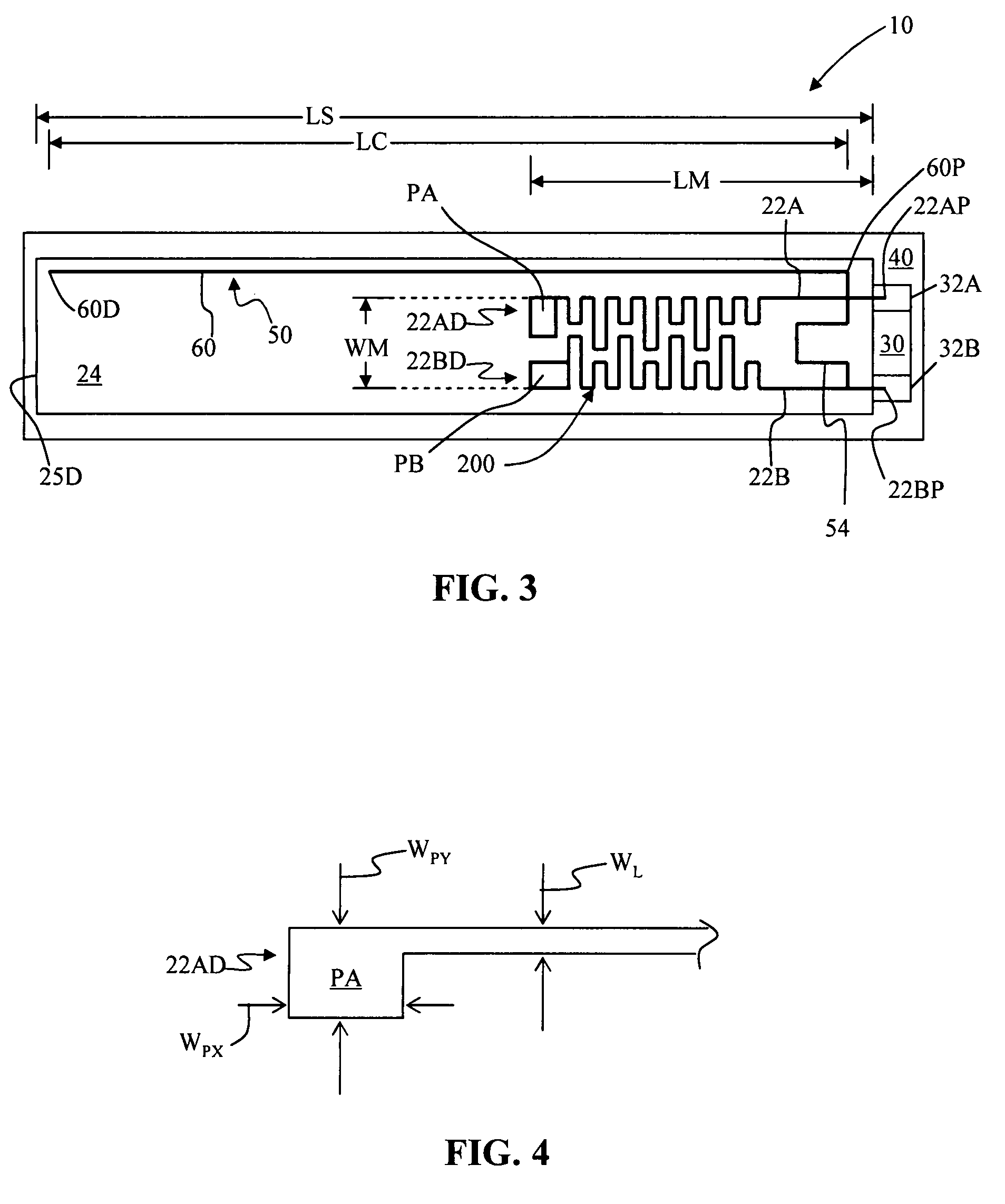
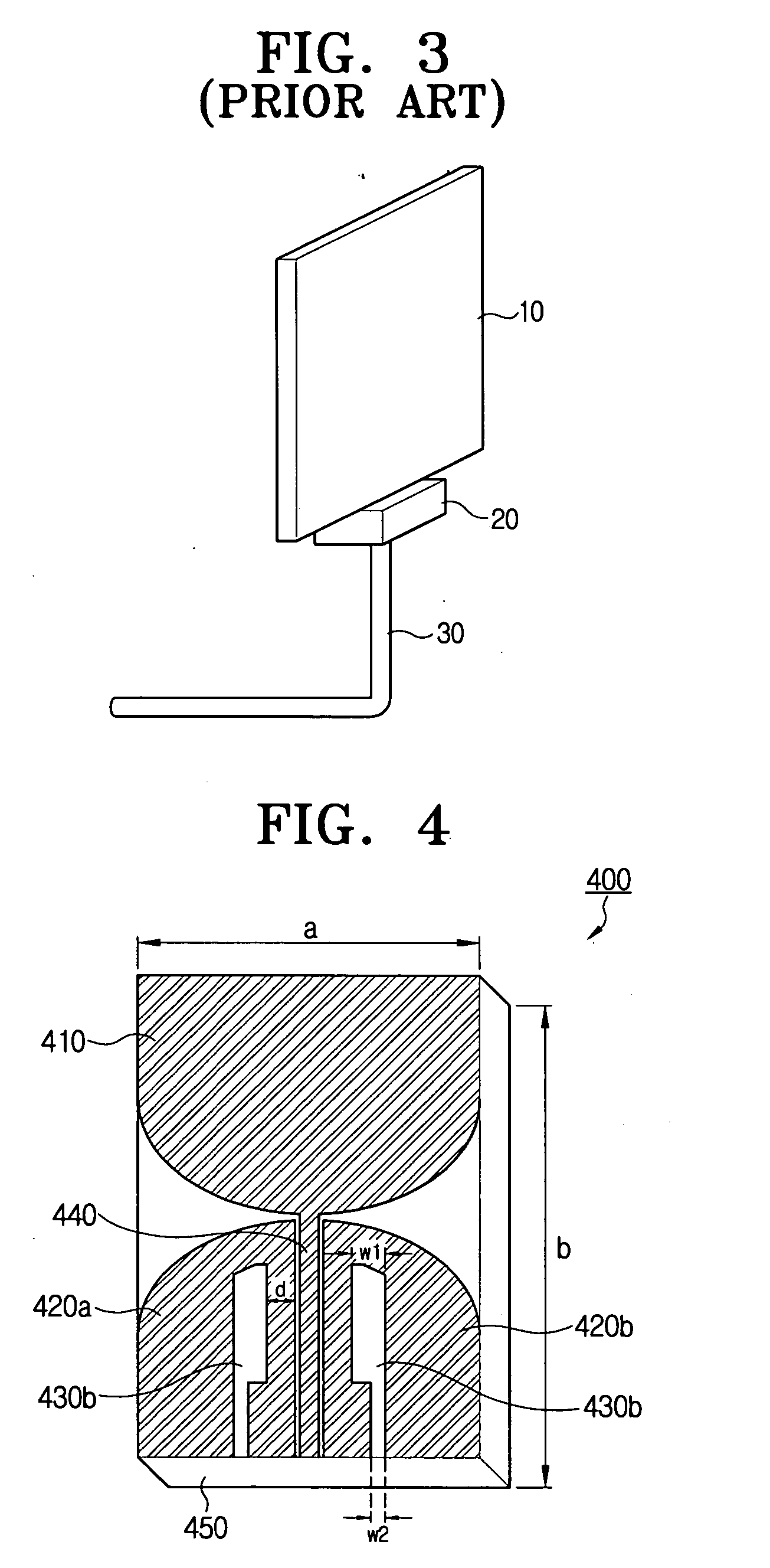
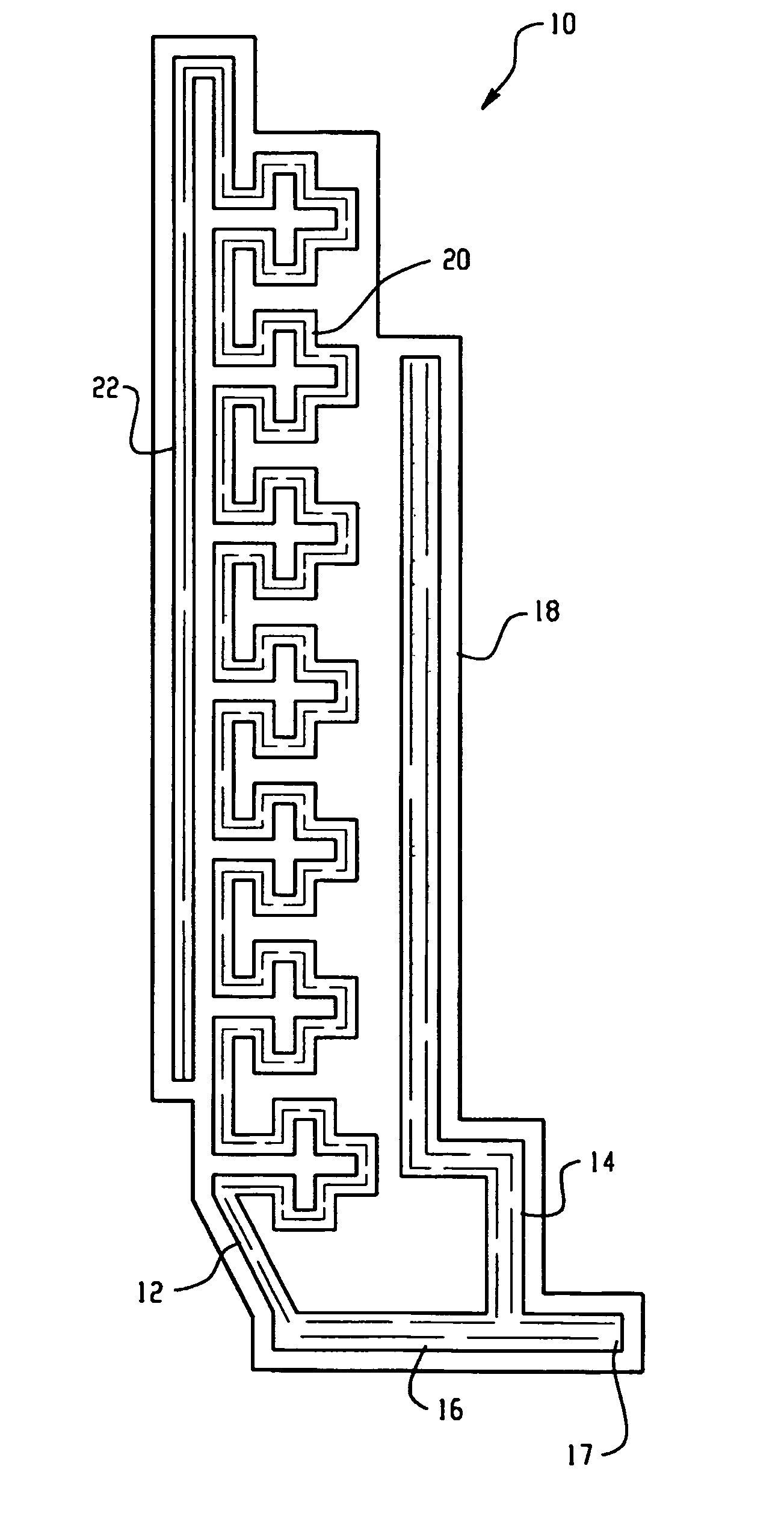
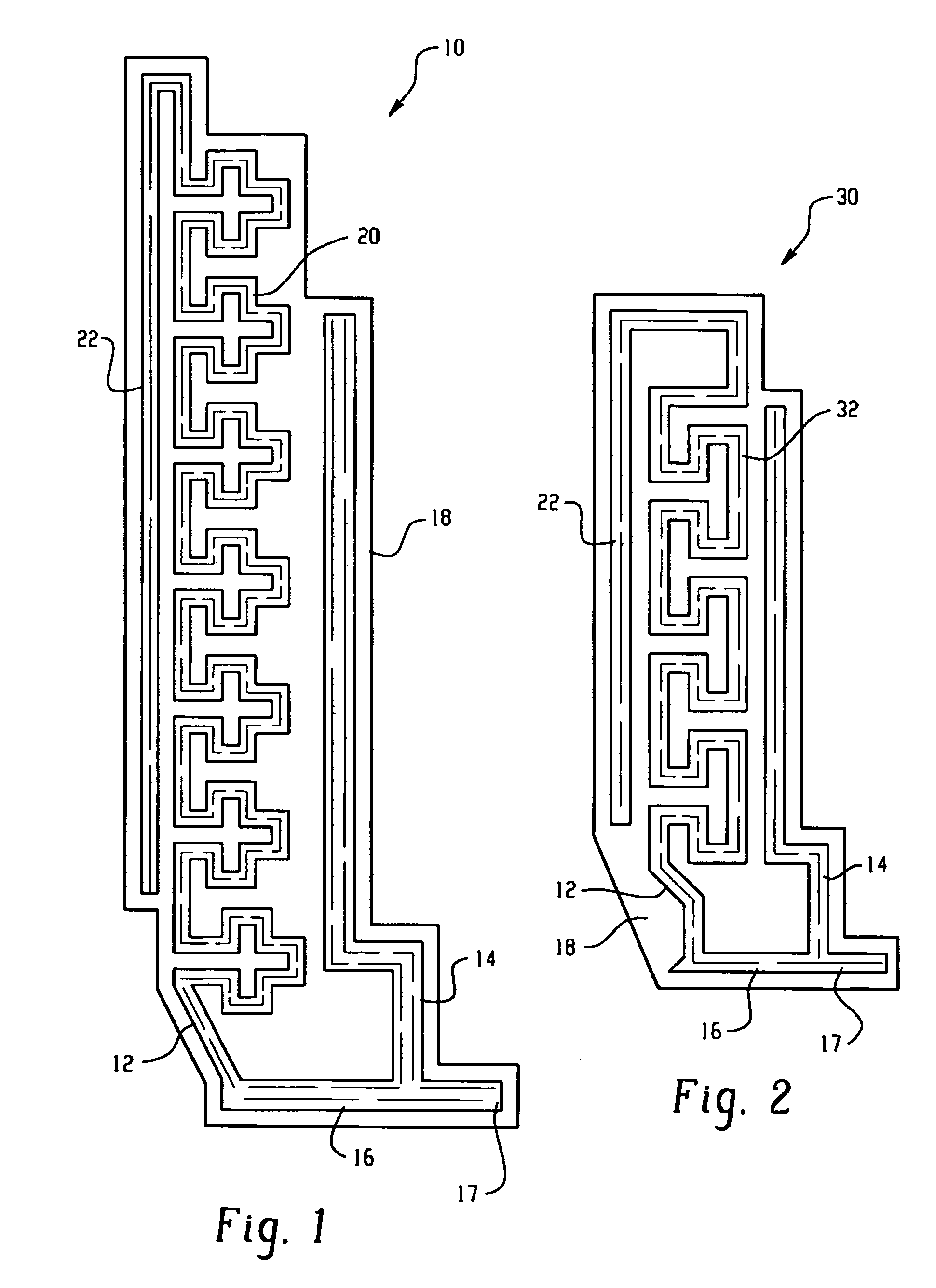
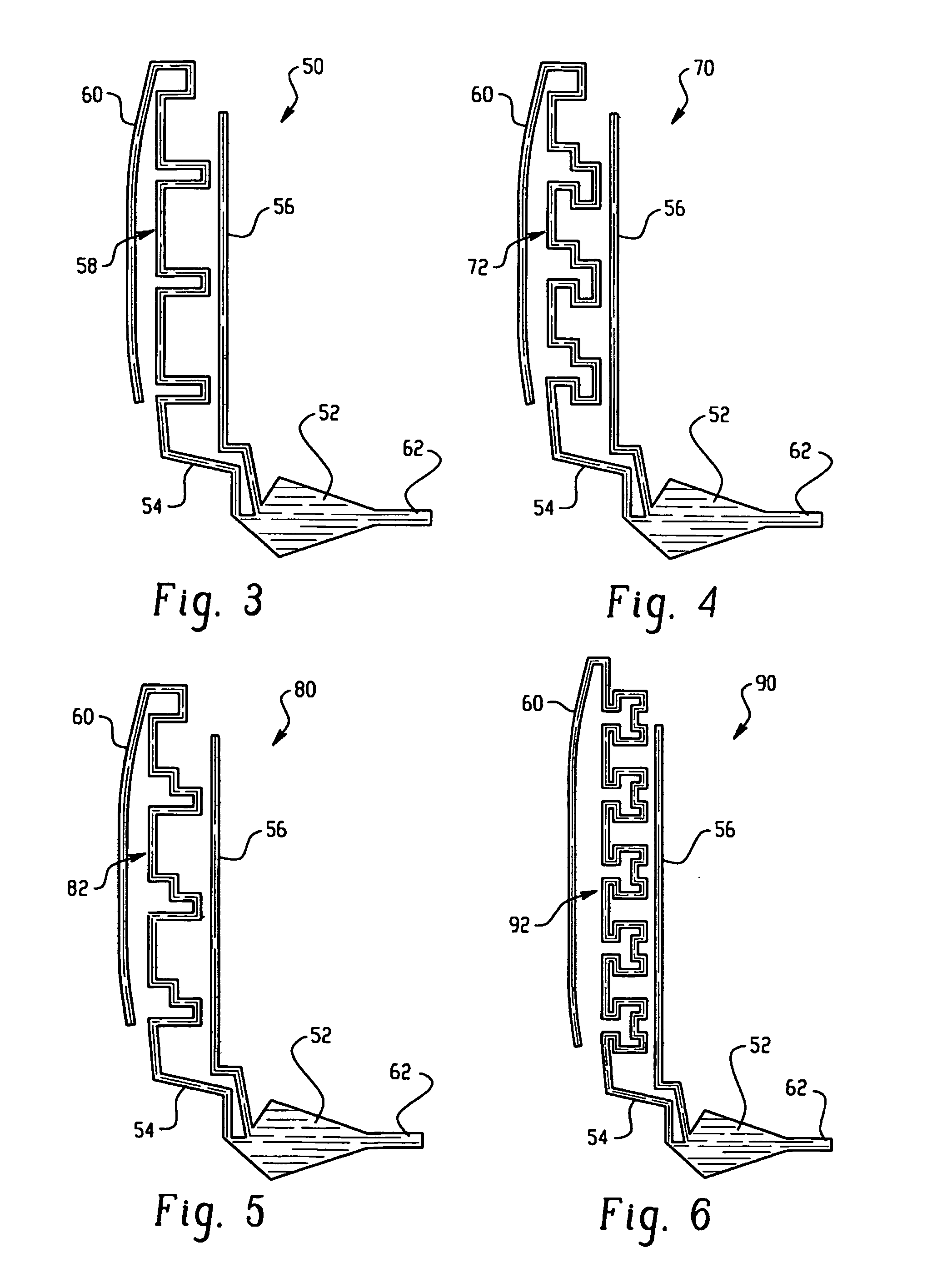
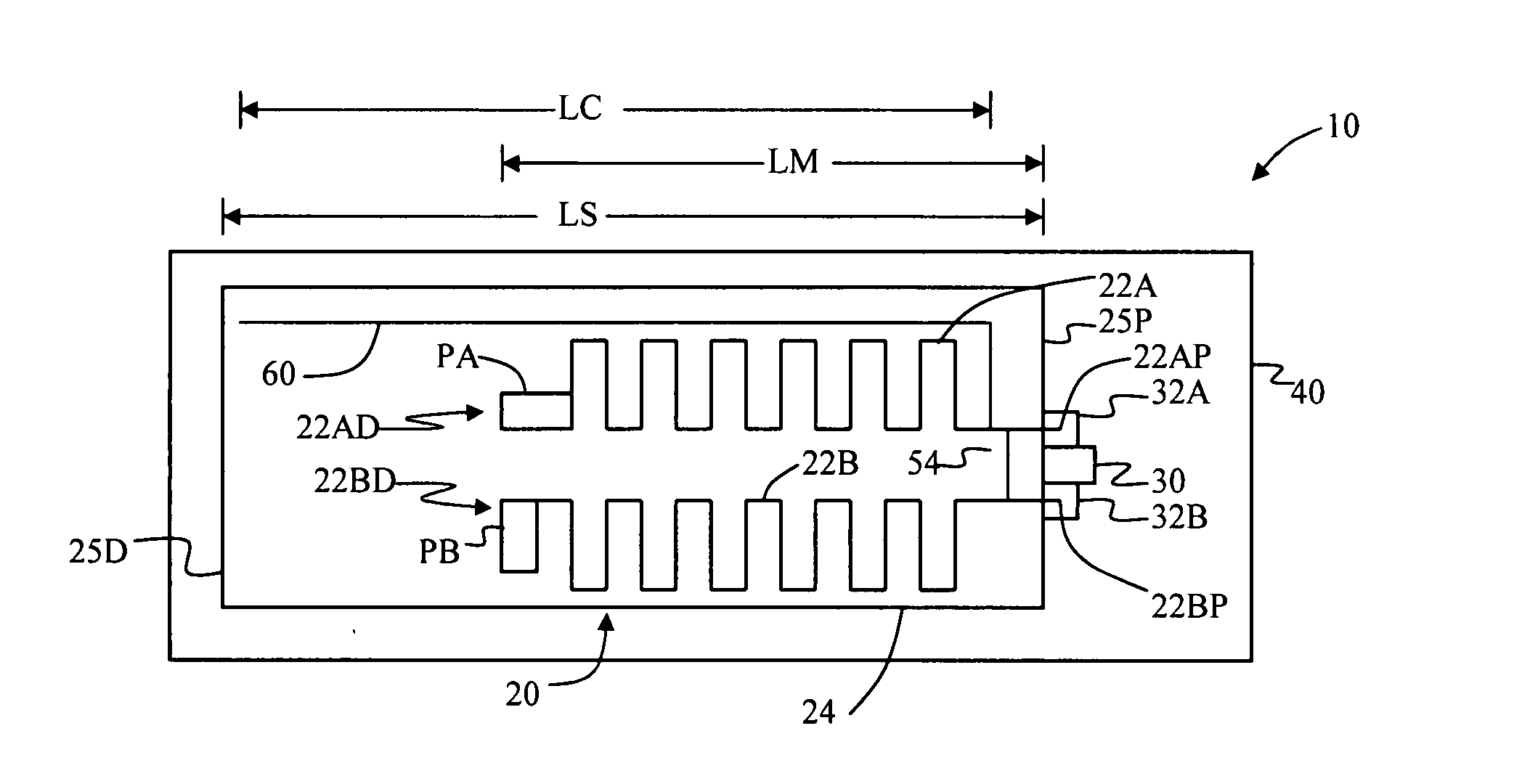
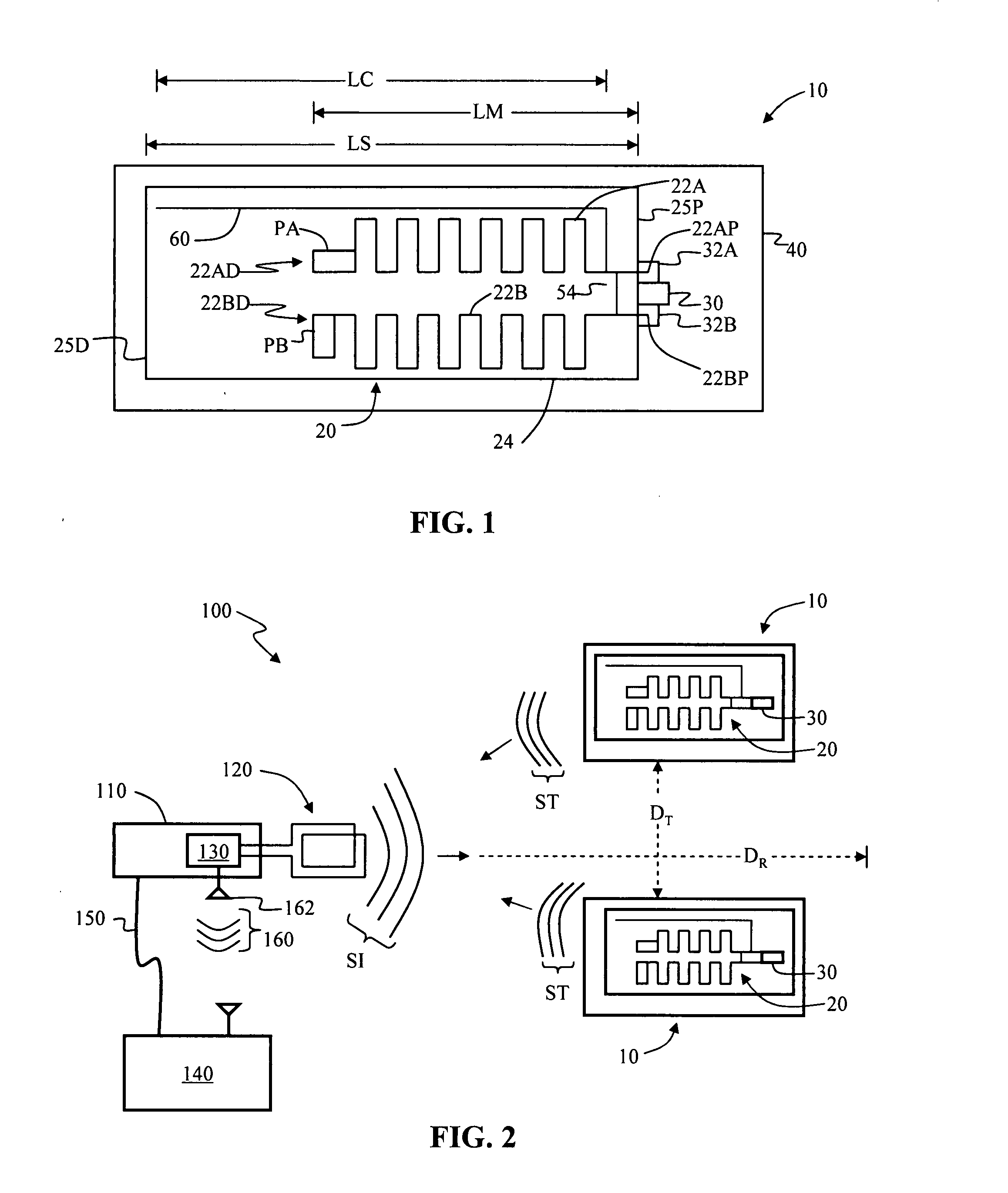
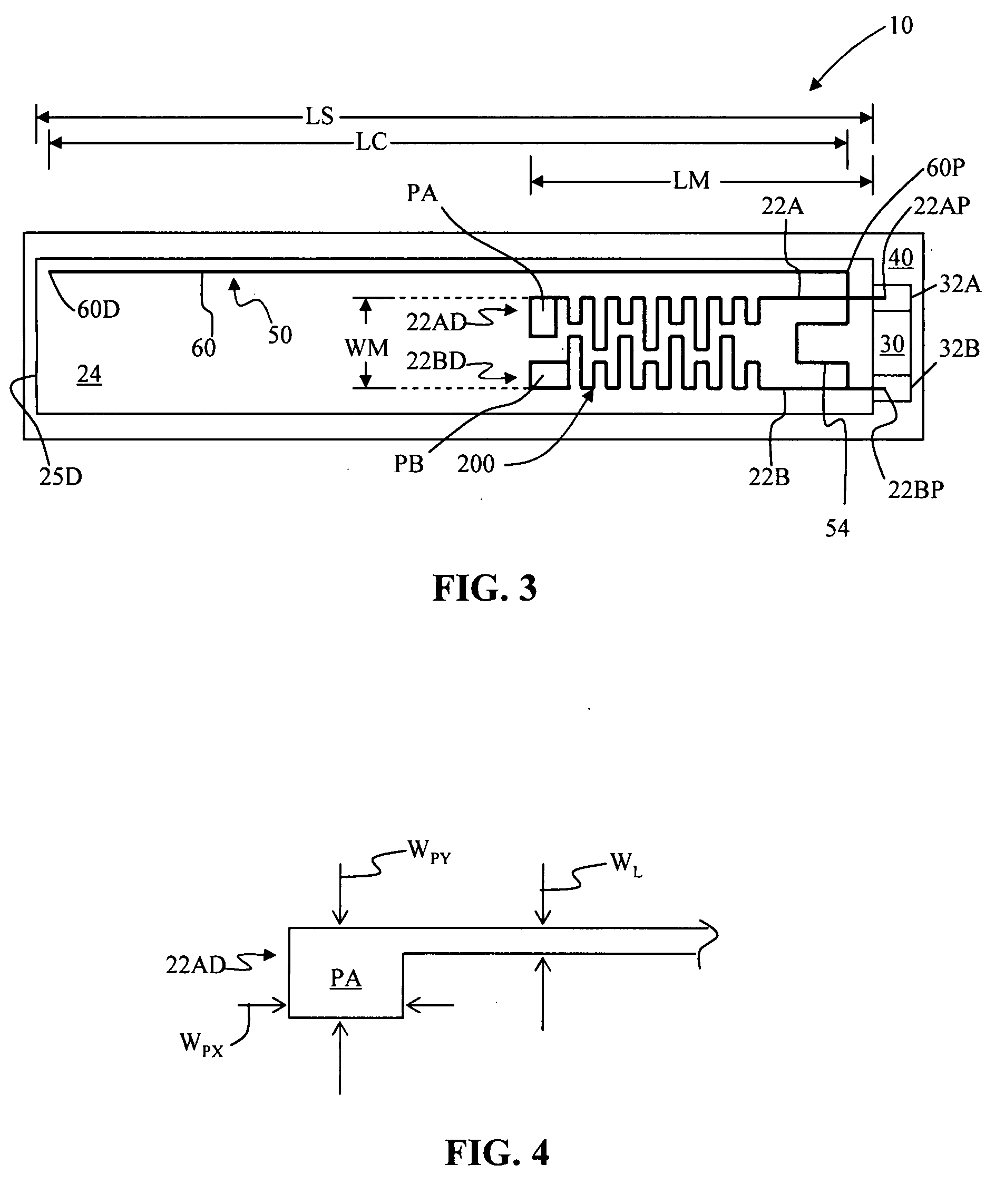
Antenna systems for passive radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags. The antenna systems have a very small form factor with good power harvesting and good performance in proximity to other antennas. The antenna system includes at least one, and preferably two, parallel serpentine antenna elements formed on, or otherwise supported by, an antenna substrate so that a RFID-tag integrated circuit (IC) can be electrically contacted to the antenna system at one end of the antenna substrate. A conducting wire that runs in the same direction as the at least one serpentine antenna element is used to match impedance and enhance antenna performance and power flow between the antenna and the IC. An impedance-matching circuit may be employed in place of the conducting wire to facilitate impedance matching between the antenna and the IC.
Owner:FIBER MOUNTAIN INC
Substrate type dipole antenna having stable radiation pattern
ActiveUS20060158383A1Avoid flowPrevent leakageSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsUltra-widebandElectrical conductor
A Ultra WideBand (UWB) substrate type dipole antenna is provided which has a stable radiation pattern. The UWB substrate type dipole antenna includes a dielectric substrate, a first radiator formed on a side of the dielectric substrate, a signal line transmitting an energy from a coaxial cable to the first radiator, and a plurality of second radiators formed at a predetermined distance from the first radiator and the signal line, and respectively having therein a plurality of slits of a predetermined configuration. Because there is no leakage of electric current to an outer part of an external conductor of the coaxial cable, even when the connection of the connector and the coaxial cable to the antenna, distortion of the radiation pattern of the antenna is prevented. As a result, the same radiation pattern and the direction of maximum radiation may be obtained before and after connection with the connector and the coaxial cable.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-band monopole antennas for mobile communications devices
InactiveUS20070046548A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandElectrical conductor
Antennas for use in mobile communication devices are disclosed. The antennas disclosed can include a substrate with a base, a top, a front side and a back side; a first conductor can be located on the first side of the antenna substrate; and a second conductor can be located on the second side of the antenna substrate. The conductors can have single or multiple branches. If a conductor is a single branch it can, for example, be a spiral conductor or a conducting plate. If a conductor has multiple branches, each branch can be set up to receive a different frequency band. A conductor with multiple branches can have a linear branch and a space-filling or grid dimension branch. A conducting plate can act as a parasitic reflector plane to tune or partially tune the resonant frequency of another conductor. The first and second conductors can be electrically connected.
Owner:FRACTUS
Planar directional pattern reconfigurable method and antenna with six-wave-beam selectivity
InactiveCN102437423AImplement refactoringSimple structureRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsReconfigurabilityAntenna design
The invention relates to antennas in wireless communication, and provides an antenna which can carry out pattern reconfigurability for more directions and has stronger practicability. The technical scheme in the invention is as follows: the planar directional pattern reconfigurable antenna with six-wave-beam selectivity consists of an antenna substrate, a radiation unit layer and a grounding plate layer, wherein the radiation unit layer consists of a circular active patch positioned at the center of the radiation unit layer and rectangular parasitic patches arranged around the radiation unit layer, and the rectangular parasitic patches are connected with a circular unit at the center of the antenna through strip lines and micro-strip lines; a radio frequency PIN diode is inserted into each micro-strip line; the circumferential rectangular parasitic patches selectively radiate outwards by controlling the on-off status of the diode; the grounding plate layer of the antenna adopts a partial grounding mode and is formed by connecting the center circular patch with the rectangular patches at equal angle-intervals; and the antenna substrate is in a circular disk shape and is made from apolytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) material. The technical scheme is mainly applied to design and manufacture of the antenna.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
High-dielectric-constant resin composition and application thereof
InactiveCN103351581ALow dielectric lossExcellent dielectric propertiesSynthetic resin layered productsMetal layered productsGlass fiberDielectric loss
The invention relates to a high-dielectric-constant resin composition, as well as a prepreg and a copper-clad laminate (CCL) which are manufactured thereby. The prepreg manufactured by the high-dielectric-constant resin composition comprises high-dielectric-constant glass fiber fabric and a high-dielectric-constant resin composition subjected to impregnation drying and then attached to the high-dielectric-constant glass fiber fabric. The CCL manufactured by the high-dielectric-constant resin composition comprises at least one overlapped prepreg and copper foils pressed and coated on both sides of the overlapped prepregs. The CCL manufactured by the high-dielectric-constant resin composition has the performances of high dielectric constant, low dielectric loss, high glass transition temperature, high peel strength and the like and can meet the performance requirement of the high-dielectric-constant antenna substrate.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGYI SCI TECH
Antennas with integrated windings
InactiveUS6018326AReliable and durable and economicalConveniently adaptedLogperiodic antennasPivotable antennasFlexible circuitsAntenna substrate
Radiotelephone antennas include rigid antenna elements integral to the antenna substrate or housing. As such, the present invention configures the antenna without requiring a separate flex circuit winding to provide the conductive windings in the antenna. Methods for fabrication of the antenna are also described. Preferably, the antenna is formed in a two-shot molding process.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Resin composition used for forming dielectric layer of dielectric substrate for antenna and application of resin composition
ActiveCN103351578ASmall coefficient of thermal expansionLittle change in thicknessSynthetic resin layered productsMetal layered productsEpoxyDielectric substrate
The invention relates to a resin composition used for forming a dielectric layer of a dielectric substrate for an antenna. The resin composition comprises (A), epoxy resin containing a naphthalene nucleus or diphenyl structure, (B), any one of or a mixture of at least two of tri(4-hydroxyphenyl) methane type epoxy resin, o-cresol type novolac epoxy resin and phenol type novolac epoxy resin, (C), a resin fusion viscosity modifier, and (D), spherical ceramic powder after presintering treatment. With the adoption of the resin composition, the obtained dielectric substrate has a high dielectric constant, high peeling strength, a low thermal expansion coefficient and very good thickness consistency, and can meet a performance requirement of the high dielectric constant antenna substrate.
Owner:江苏生益特种材料有限公司
Antenna module-use magnetic core member, antenna module and portable information terminal provided with it
InactiveCN1965444ALoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna supports/mountingsComputer moduleComputer terminal
The invention provides an antenna module-use magnetic core member capable of improving a communication distance without increasing a module thickness, and an antenna module and a portable information terminal provided with this. An antenna module (1) comprising a sheet-formed magnetic core member (4) layered on a looped antenna coil-formed antenna substrate (2), wherein a magnetic core member (4) having a performance index, expressed by mu' * Q, of 300 or higher is used when Q is a reciprocal of a loss factor (tan delta=mu'' / mu') expressed by the real part mu' and the imaginary part mu'' of a complex permeability at a frequency used.
Owner:SONY CORP
Waterborne polyurethane adhesive for RFID antenna substrate
ActiveCN101899277APolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesRadiating elements structural formsPolyesterPolyurethane adhesive
The invention relates to a waterborne polyurethane adhesive for an RFID antenna substrate. The adhesive comprises polyurethane emulsion, a waterborne curing agent and a filler, and the composition according to weight percentage is as follows: 45%-65% of polyurethane emulsion, 25%-35% of waterborne curing agent, 5%-20% of filler, 0.2%-0.6% of deformer and 0.3%-0.7% of stabilizer, wherein the polyurethane emulsion comprises polyol, diisocyanate, a chain extender and an organic solvent, a prepolymer as shown in formula (II) is obtained by polycondensation in the presence of an organic tin type catalyst, m in the formula is equal to 1-100, and the formula (II) is dispersed in water containing an emulsifier, thereby preparing the emulsion with the solid content of 20-50% by weight. The adhesive is used for adhering a paper thin film or a polyester thin film with an aluminum foil or a copper foil. A prepared polyester or paper-based aluminum-coated plate and a polyester or paper-based copper-coated plate can be used for the RFID antenna substrate, and have high peeling strength, good acid and alkali resistance, good storage stability, excellent comprehensive performance and low cost.
Owner:华烁电子材料(武汉)有限公司
Antenna substrate for non-contact communication apparatus and non-contact communication apparatus
InactiveUS20090091501A1Increase costThickness of device is increasedResonant long antennasNear-field transmissionEngineeringAntenna substrate
An antenna substrate for a non-contact communication apparatus includes a support substrate and an antenna coil provided on or inside of the support substrate. The antenna coil has a first opening and an auxiliary coil. The auxiliary coil has a second opening which has an opening area smaller than the first opening. The auxiliary coil is insulated and isolated from the antenna coil, and arranged so that the second opening is opposed to a part of the first opening when viewed from a direction orthogonal to a surface of the support substrate.
Owner:SONY CORP
Antenna element-waveguide converter and radio communication device using the same
InactiveUS20110234466A1Improve reliabilityWithout complicating manufacturing processWaveguide hornsWaveguide mouthsEngineeringAntenna substrate
An antenna element-waveguide converter includes an antenna substrate having, on one surface, an antenna element and rectangular metal plates arranged in a plurality of rows to surround this antenna element, and a waveguide having, at one end, an opening opposed to the one surface of the antenna substrate. Surfaces of the rectangular metal plates and the opening of the waveguide are arranged with a predetermined gap left therebetween in a direction perpendicular to the one surface of the antenna substrate. Thus arranging the antenna substrate and the waveguide avoids a stress due to assembly variations, which can achieve favorable antenna characteristics.
Owner:SHARP KK
Antenna systems for passive RFID tags
ActiveUS20090045961A1Improving Impedance MatchingFacilitate currentRadiating elements structural formsAntenna feed intermediatesTag antennaPower flow
Antenna systems for passive radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags. The antenna systems have a very small form factor with good power harvesting and good performance in proximity to other antennas. The antenna system includes at least one, and preferably two, parallel serpentine antenna elements formed on, or otherwise supported by, an antenna substrate so that a RFID-tag integrated circuit (IC) can be electrically contacted to the antenna system at one end of the antenna substrate. A conducting wire that runs in the same direction as the at least one serpentine antenna element is used to match impedance and enhance antenna performance and power flow between the antenna and the IC. An impedance-matching circuit may be employed in place of the conducting wire to facilitate impedance matching between the antenna and the IC.
Owner:FIBER MOUNTAIN INC
Microstrip antenna composite substrate material and its preparation method
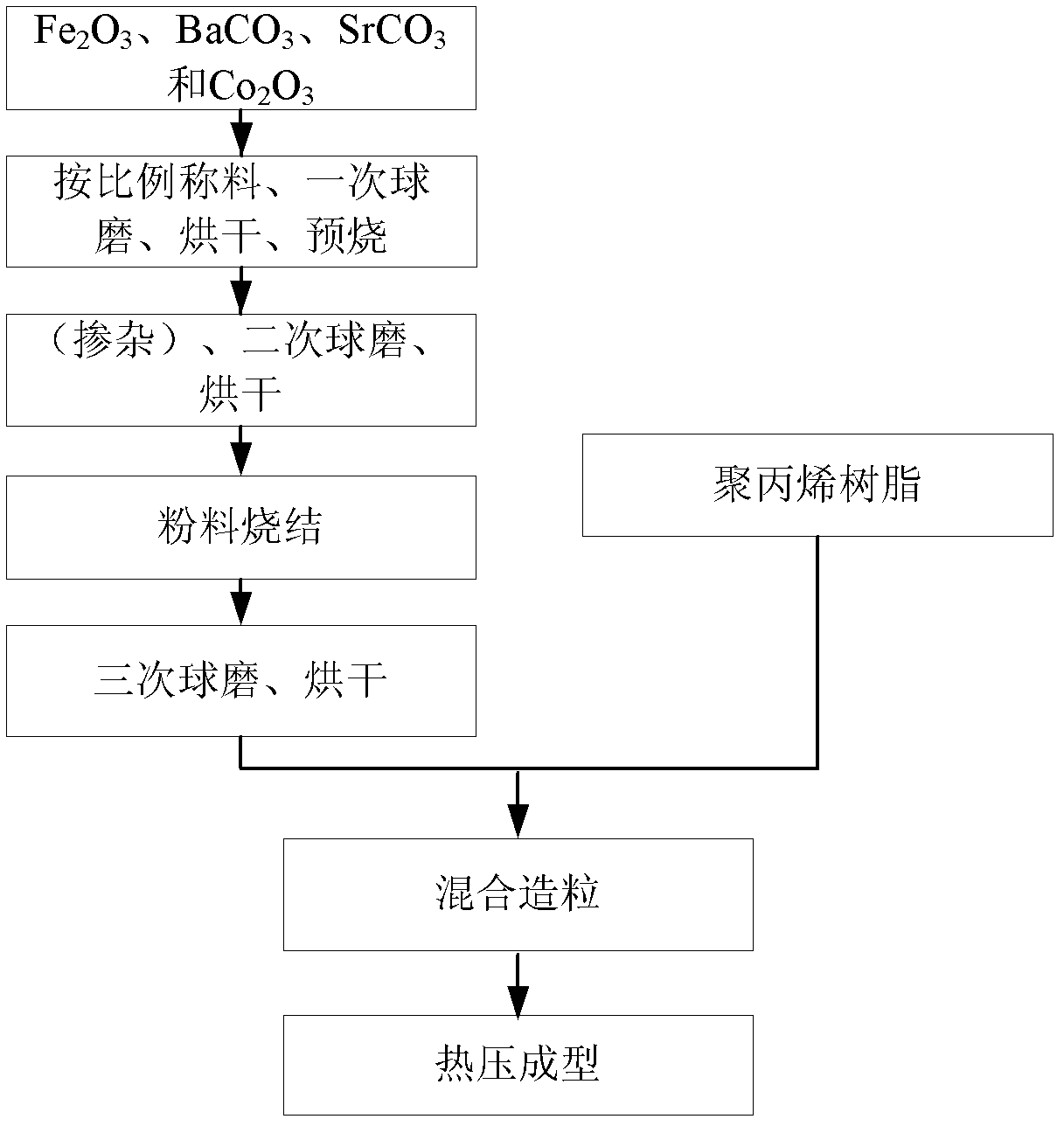
Belonging to the technical field of electronic materials, the invention relates to a microstrip antenna composite substrate material and its preparation method. The composite substrate material is formed by compounding 70-90 parts by mass of a main phase material and 10-30 parts by mass of an auxiliary phase material, wherein, the main phase material is a Co2Z hexagonal ferrite which has a molecular formula of Ba3-xSrxCo2Fe24O41 (with x located in the range of 0-1.5), and the auxiliary phase material is polypropylene resin. The preparation method consists of: 1) material weighing, mixing, first ball milling and drying; 2) presintering; 3) secondary ball milling and drying; 4) sintering; 5) tertiary ball milling and drying; 6) compounding and granulation; 7) thermoforming, etc. The composite substrate material has an isomagnetic dielectric property and low loss in a frequency scope of 300MHz-3GHz, and has certain flexibility at the same time. The preparation method in the invention is simple and easy to operate, and convenient for mastering and popularization. Employment of the composite substrate material as a microstrip antenna substrate is conducive to reduce microstrip antenna weight and volume, and is in favor of enhancing the bandwidth and radiation efficiency of microstrip antennas.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
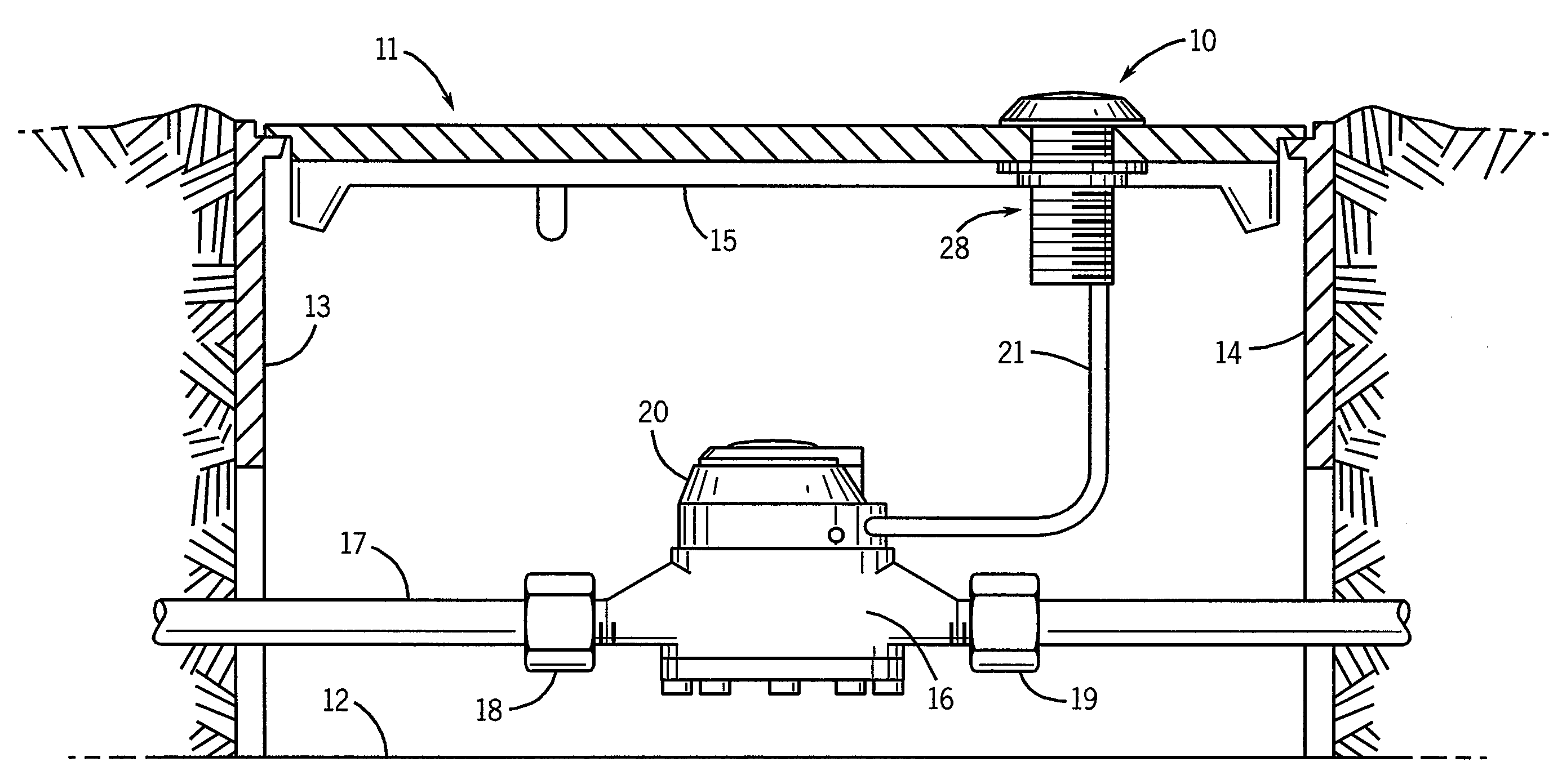
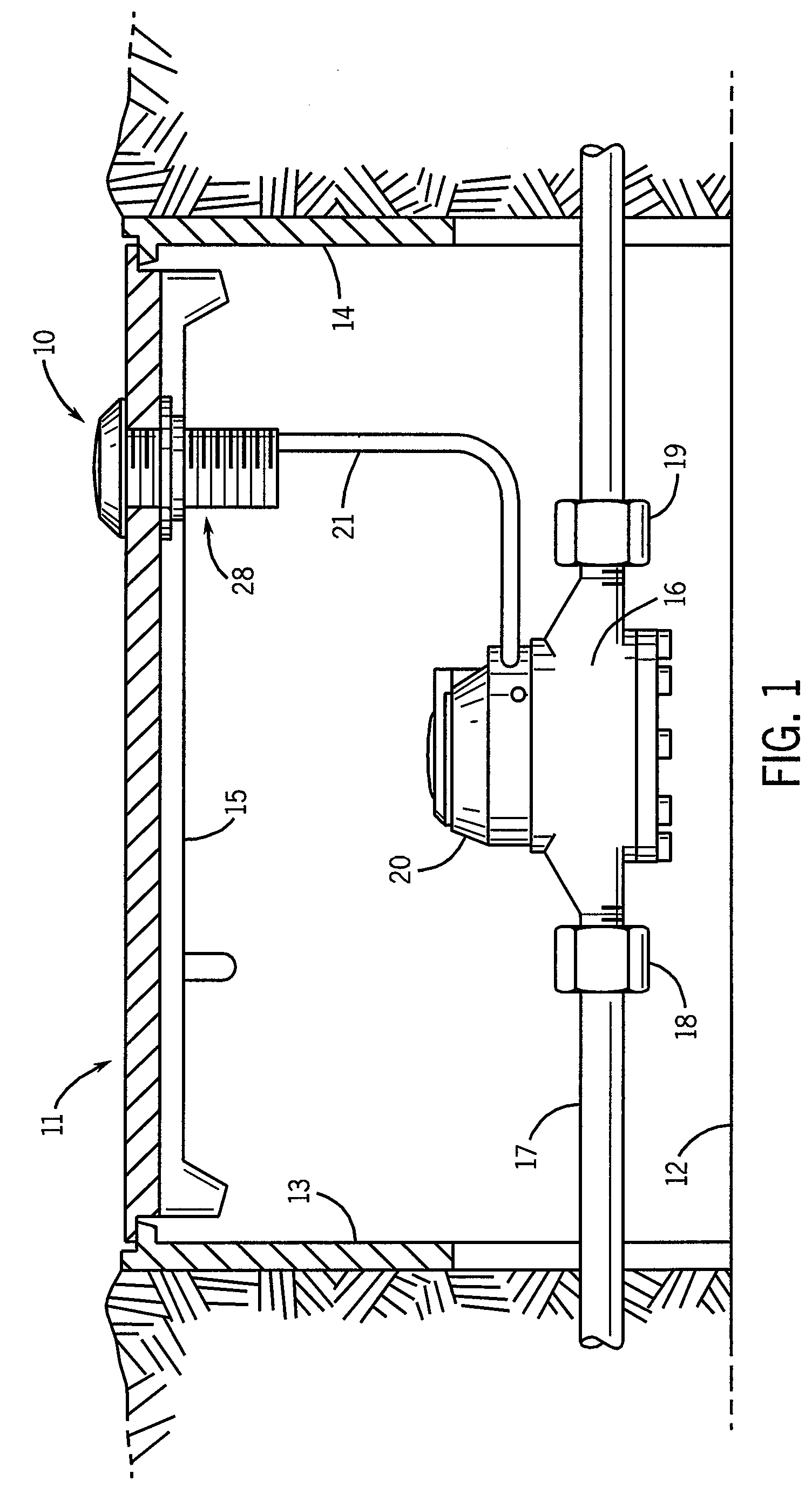
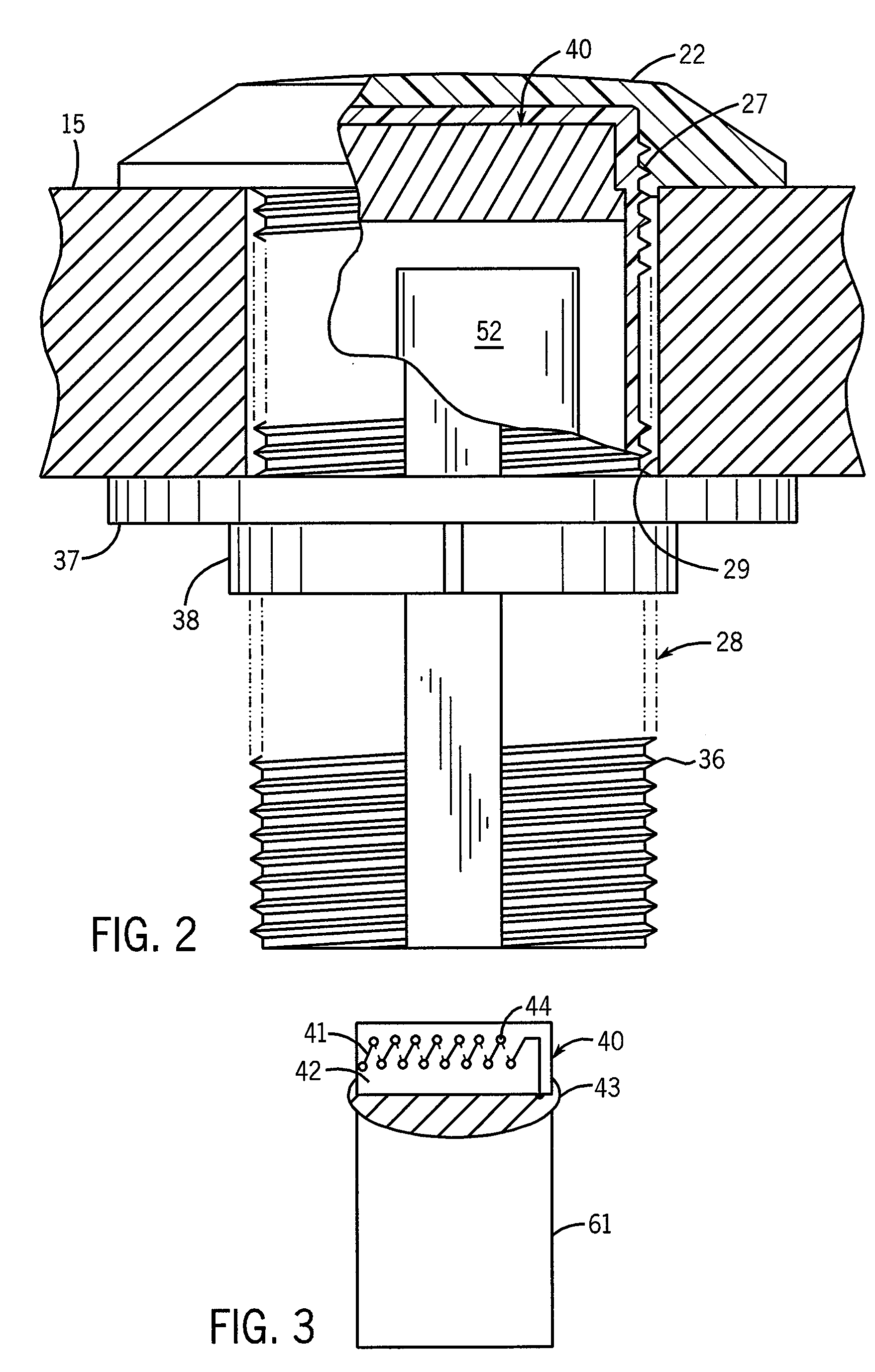
Utility Metering System With Compact And Robust Antenna For Subsurface Installation
InactiveUS20100026515A1Electric signal transmission systemsTariff metering apparatusElectrical conductorAntenna substrate
A pit transmitter assembly (10) for RF communication of signals representing utility meter data, includes a transmitter (60) supported by a transmitter substrate (61), a planar ground conductor (43) disposed over the transmitter (60), an antenna substrate (42) disposed on edge on the planar ground conductor (43), a flat coil antenna conductor (41) disposed on two opposite sides of the antenna substrate (42) and in which the transmitter (60) includes an L-C circuit (50) connected to the antenna conductor (41) to provide operation of the antenna in the 450 Mhz-470 Mhz frequency range.
Owner:BADGER METER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com