Booster circuit and semiconductor device having same
a booster circuit and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of electric variable regulation, process and machine control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of the inability to meet the phase lag, and the inability to control the peak current at start-up, so as to achieve lower power supply voltage, higher speed, and the effect of reducing the voltage of the power supply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
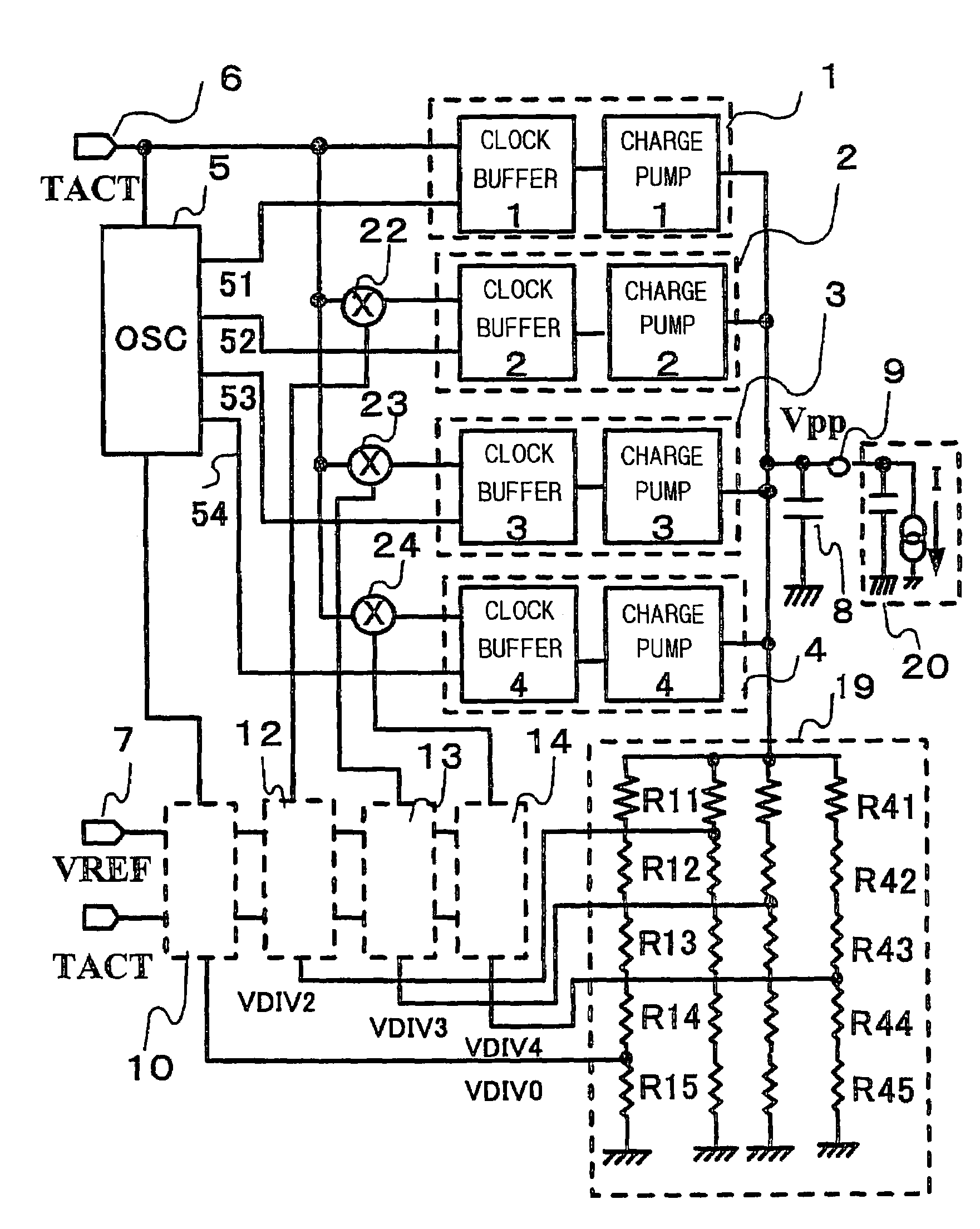
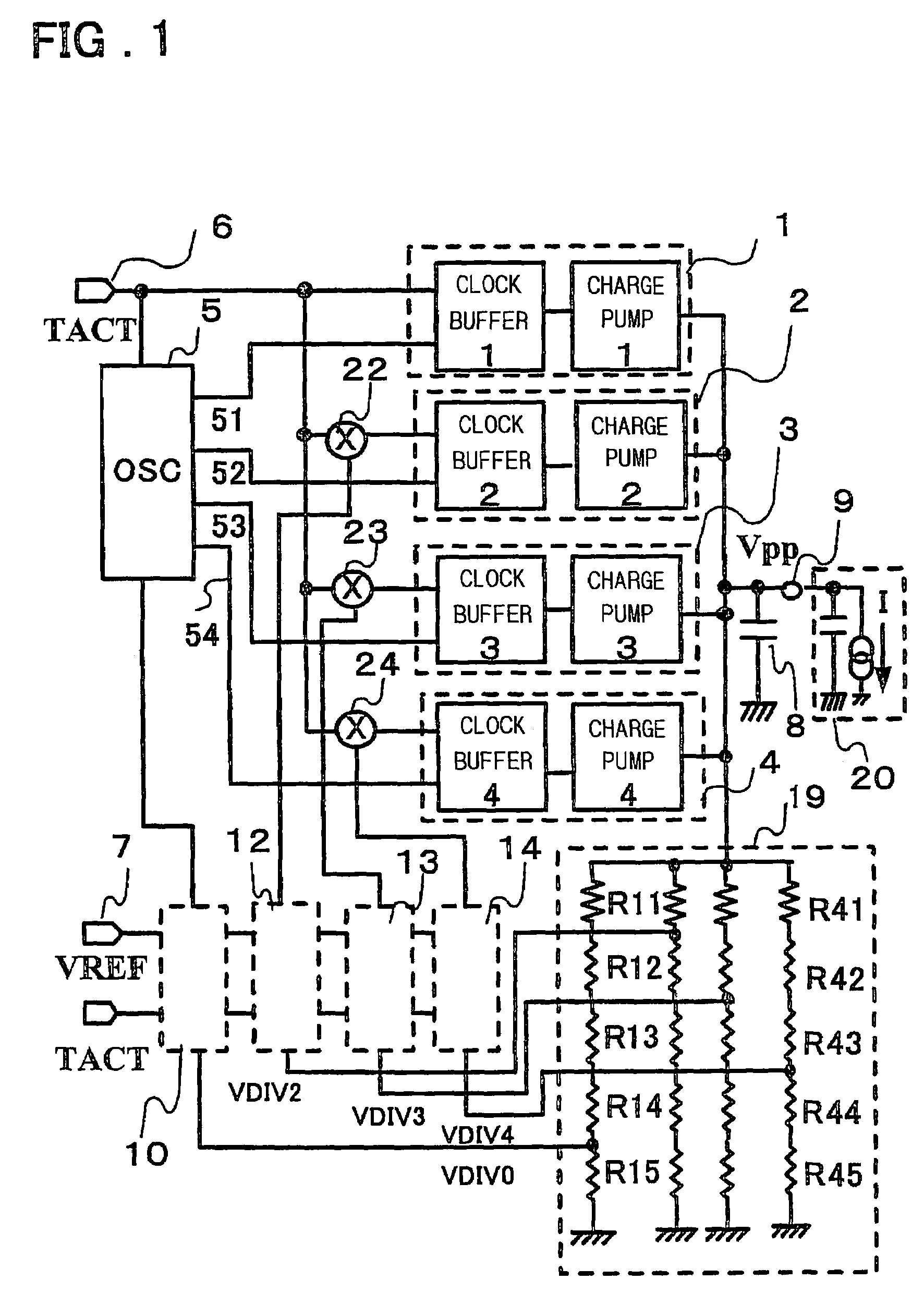
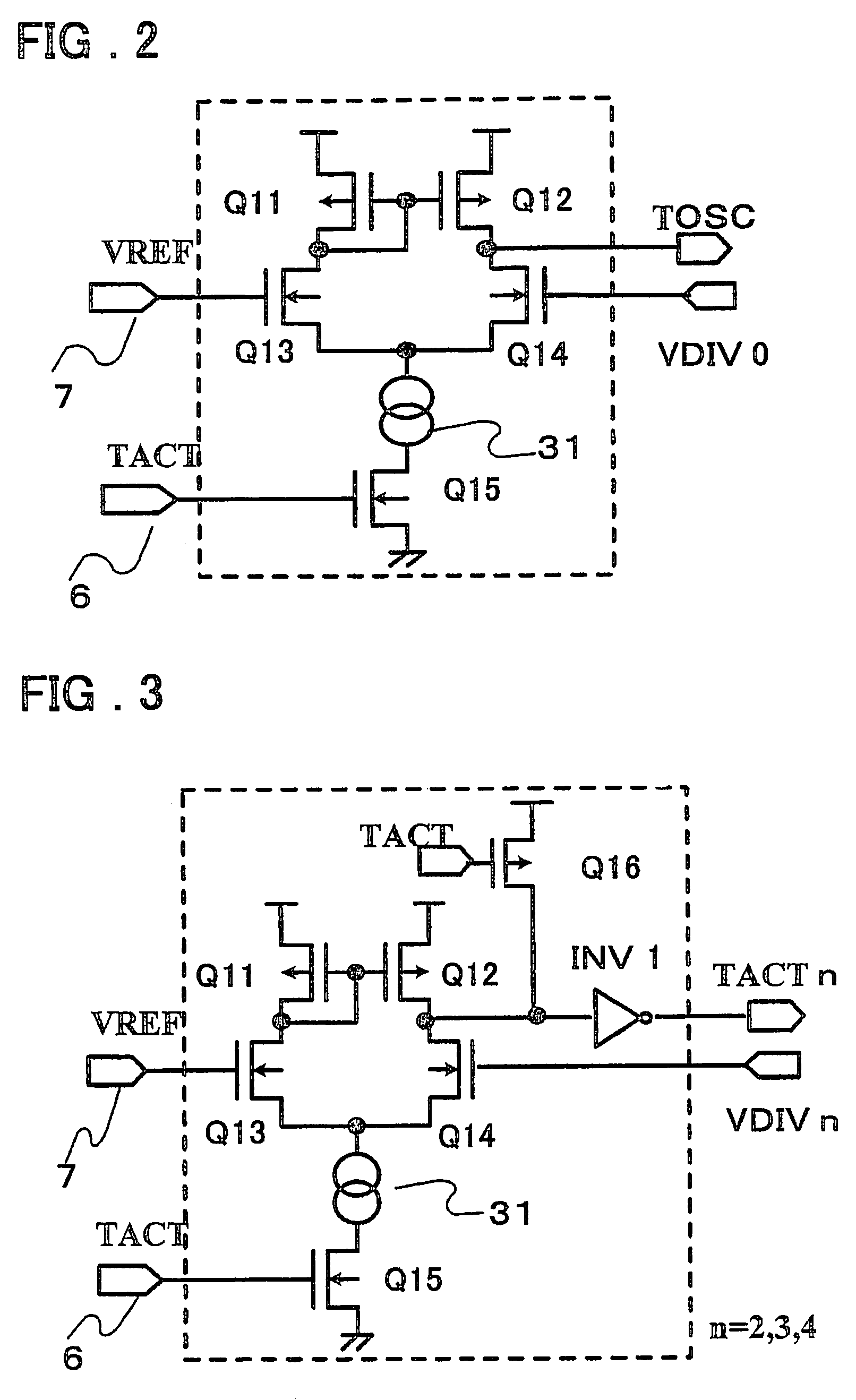
[0033]FIG. 1 is a circuit block diagram illustrating a booster circuit according to a first embodiment of the prior art, FIG. 2 is a circuit diagram of first comparison unit, FIG. 3 is a circuit diagram of second comparison unit, FIG. 4 is a circuit diagram illustrating a changeover device for changing over a clock buffer control signal, and FIG. 5 is a timing chart illustrating operation.
[0034]The booster circuit shown in FIG. 1 comprises charge pump units 1 having a clock buffer #1 and a charge pump circuit #1; charge pump unit 2, 3 and 4 similarly having clock buffers #2, #3 and #4 and charge pump circuits #2, #3 and #4, respectively; a clock generating circuit 5 for generating a basic clock 51 and clocks 52, 53 and 54 each of which is shifted in phase relative to the basic clock; a capacitor 8; voltage dividing unit 19 for dividing a boosted voltage; comparison units 10, 12, 13 and 14; and control signal changeover devices 22, 23 and 24. The booster circuit has an input terminal...
second embodiment
[0070]FIG. 6 illustrates the circuit structure of second voltage dividing unit for dividing boosted voltage in a second embodiment of the present invention. In the second embodiment, the voltage dividing unit of the first embodiment for dividing boosted voltage and outputting the divided boosted voltage is modified to have the structure shown in FIG. 6. This embodiment is such that when the boosted voltage has declined owing to supply of current to the load of the booster circuit, a charge pump unit, once it has starting the boosting operation, is prevented from suspending the boosting operation and is allowed to continue performing boosting.
[0071]In comparison with the voltage dividing unit 19 for dividing boosted voltage in FIG. 1, it will be understood that the voltage dividing unit of this embodiment differs in that the second, third and fourth resistor groups are each additionally provided with a transistor and an inverter. Structural elements identical with those of FIG. 1 are...
third embodiment
[0081]FIG. 7 illustrates a third embodiment of the present invention. The embodiment in FIG. 7 differs in the arrangement of the comparison units and voltage dividing units that outputs divided boosted voltage. Structural elements identical with those in FIG. 1 are designated by like reference characters and need not be described again. The voltage dividing unit for outputting divided boosted voltage comprises resistors R51 and R52, with divided boosted voltage VDIV1 being output from the node of resistors R51 and R52. Comparison units 15, 16, 17 and 18 compare the commonly applied divided boosted voltage with different reference voltages 71 to 74, and output clock generation control signals or charge pump control signals.
[0082]In the comparison means of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1, a common reference voltage is applied to these comparison units, which compare the reference voltage with respective ones, respectively, of divided boosted voltages having voltage values that di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com