Patents
Literature
734 results about "Voltage regulator module" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
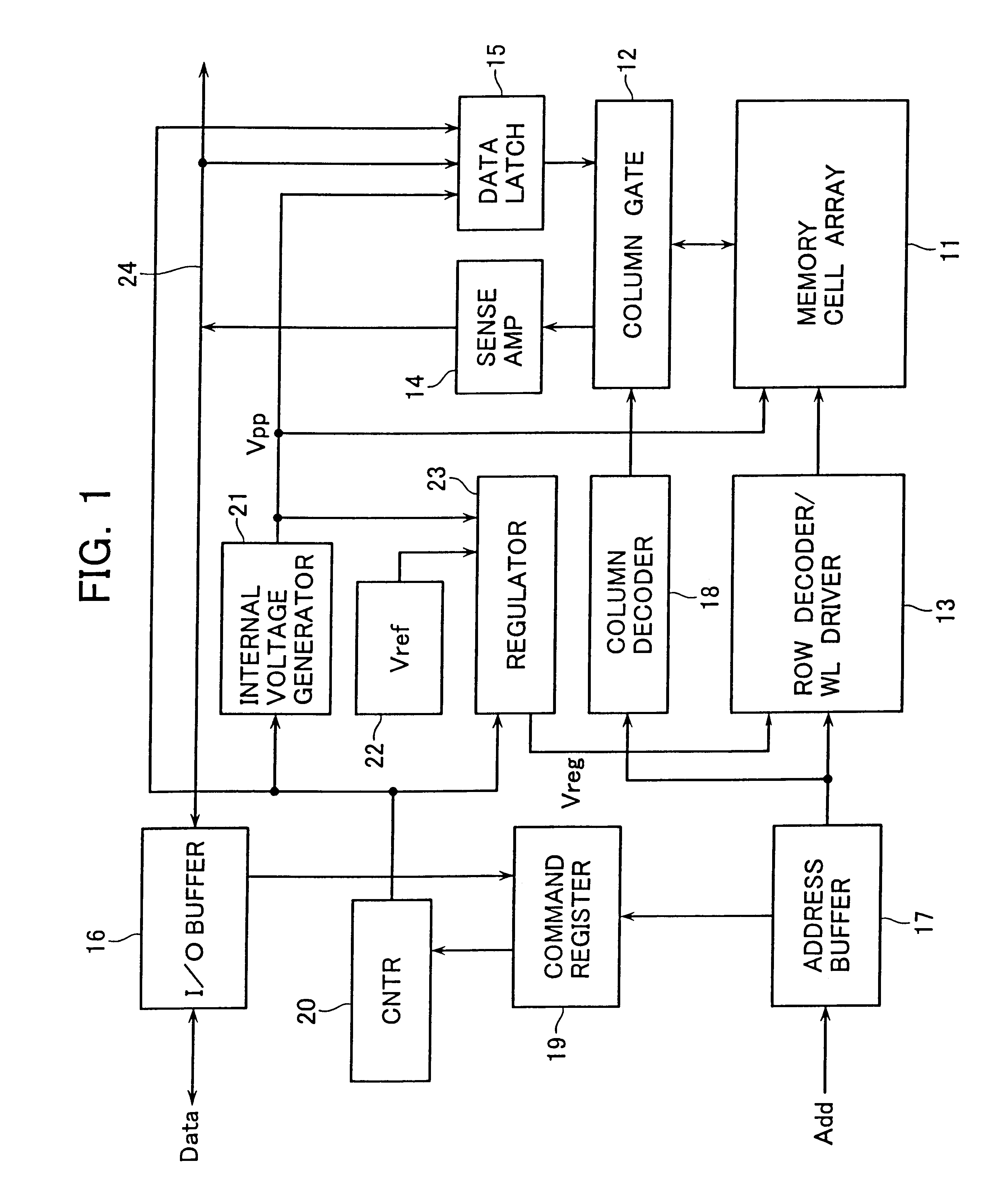
A voltage regulator module (VRM), sometimes called processor power module (PPM), is a buck converter that provides a microprocessor the appropriate supply voltage, converting +5 V or +12 V to a much lower voltage required by the CPU, allowing processors with different supply voltage to be mounted on the same motherboard.
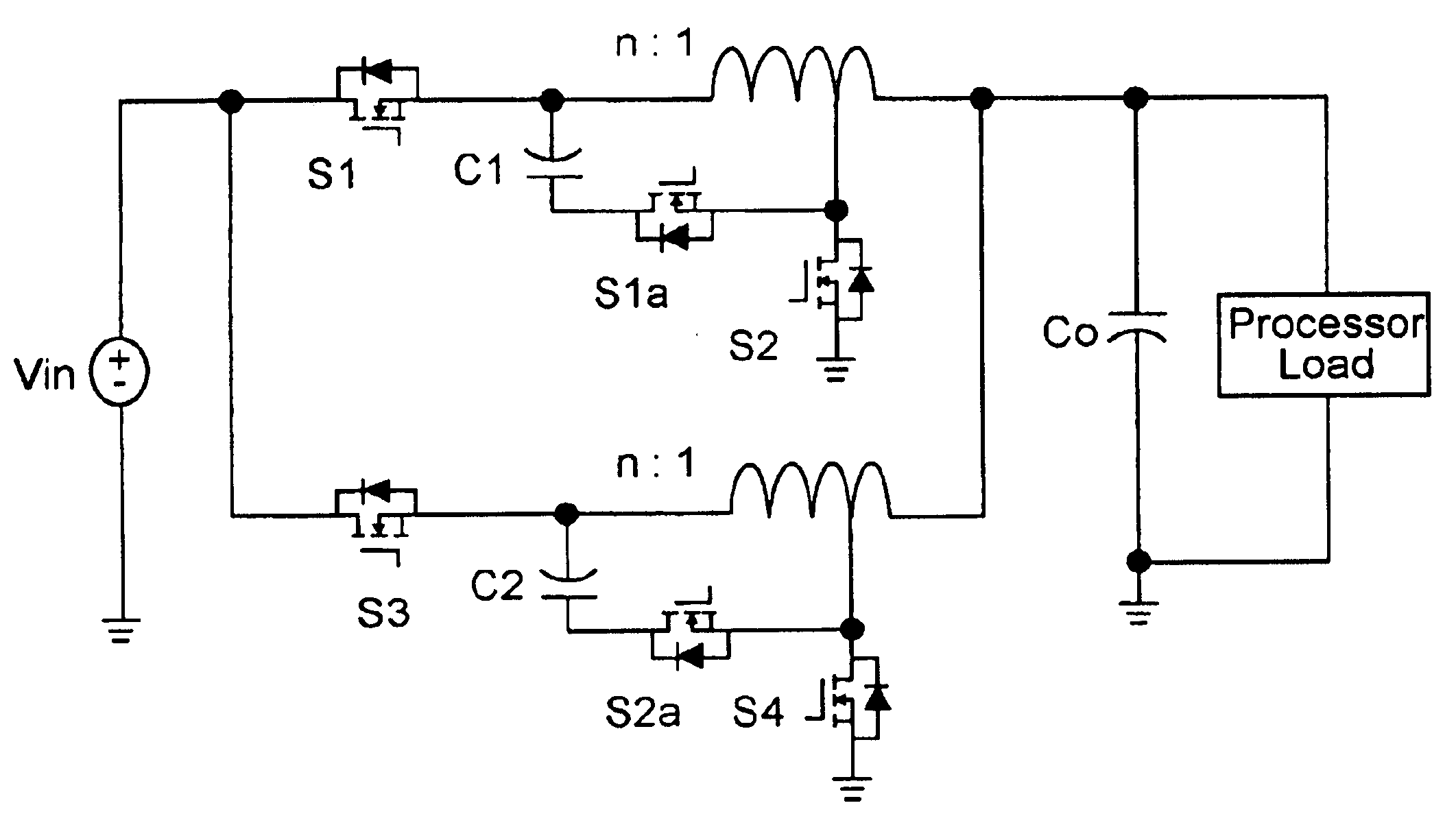
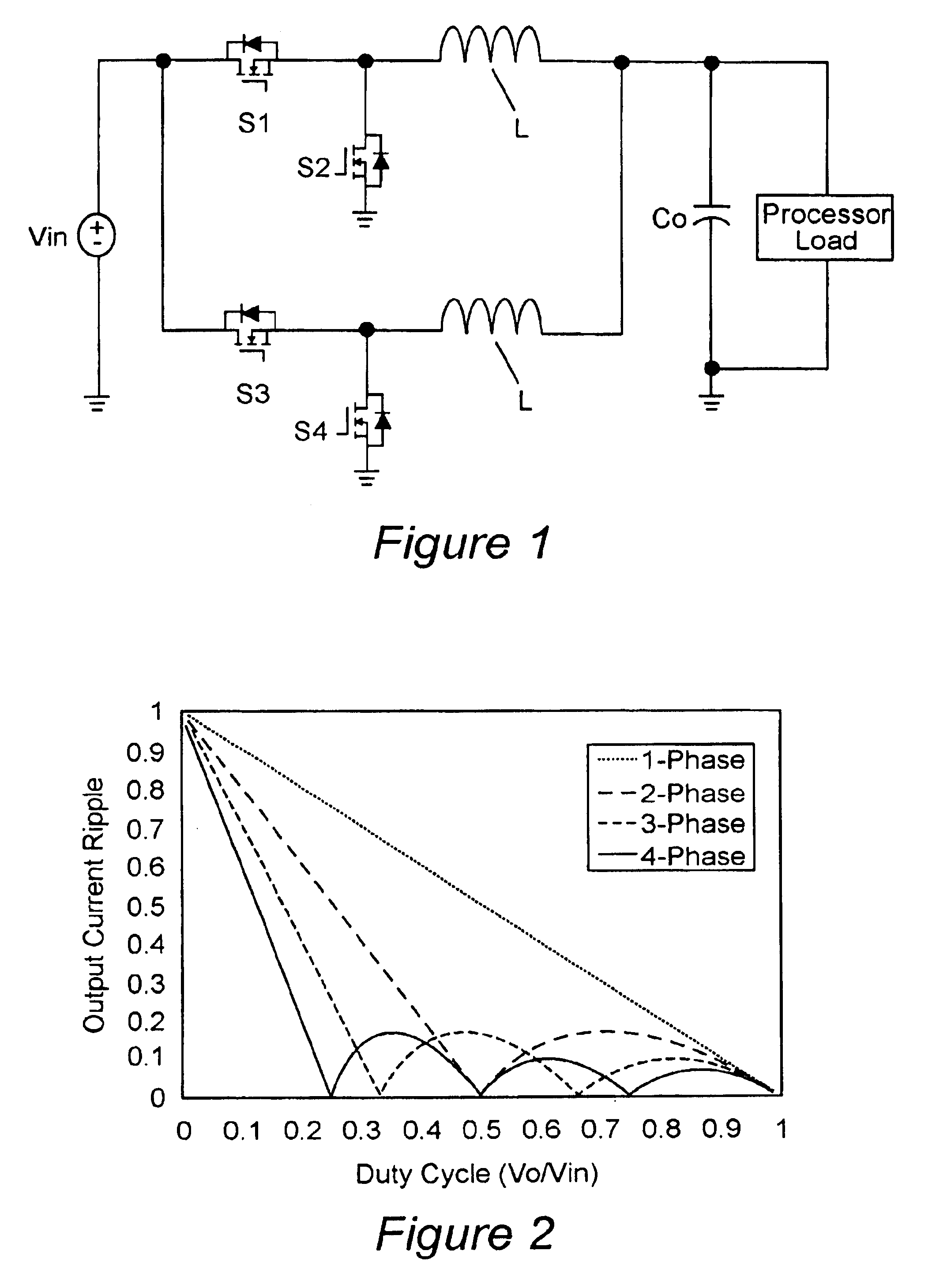
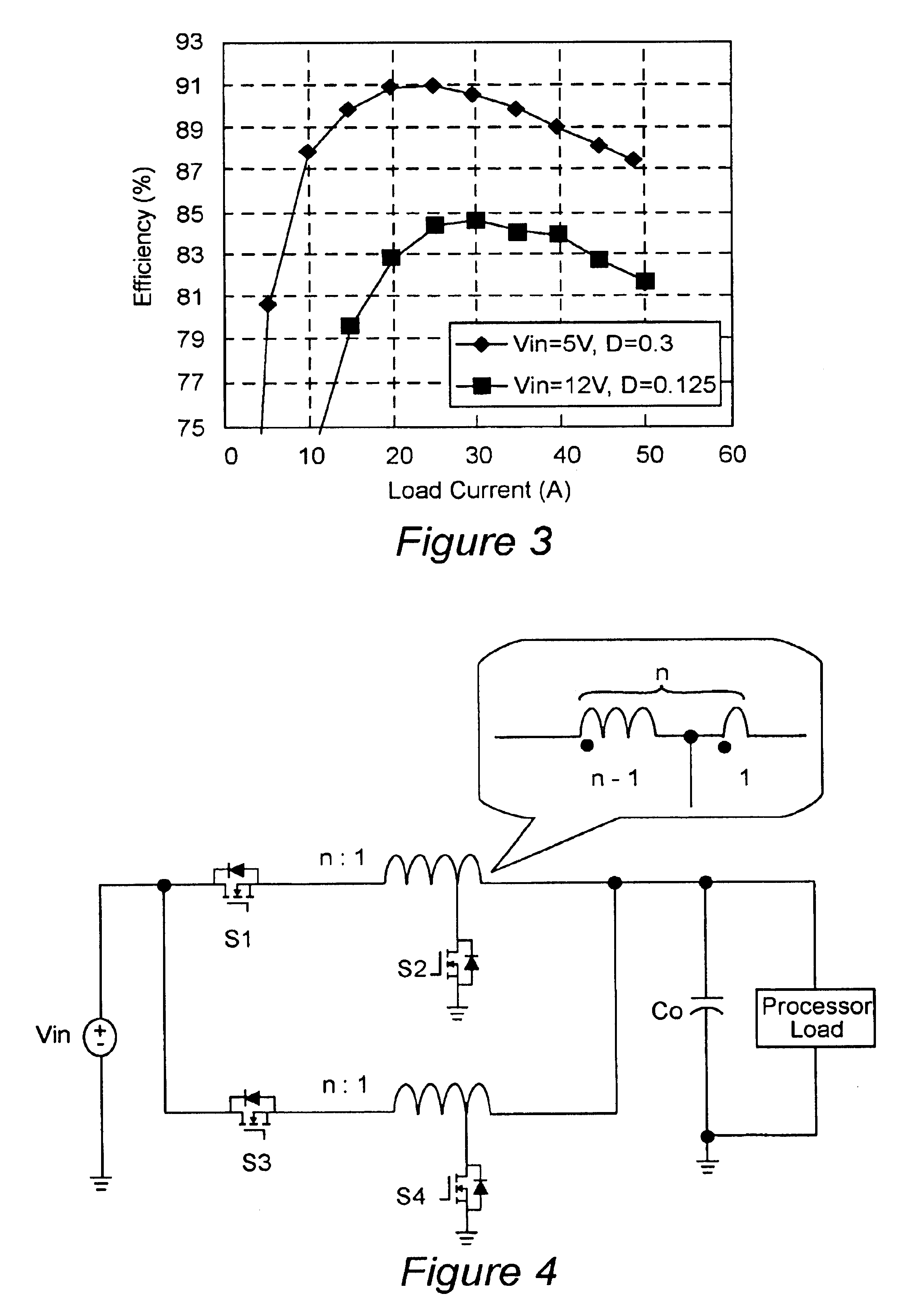
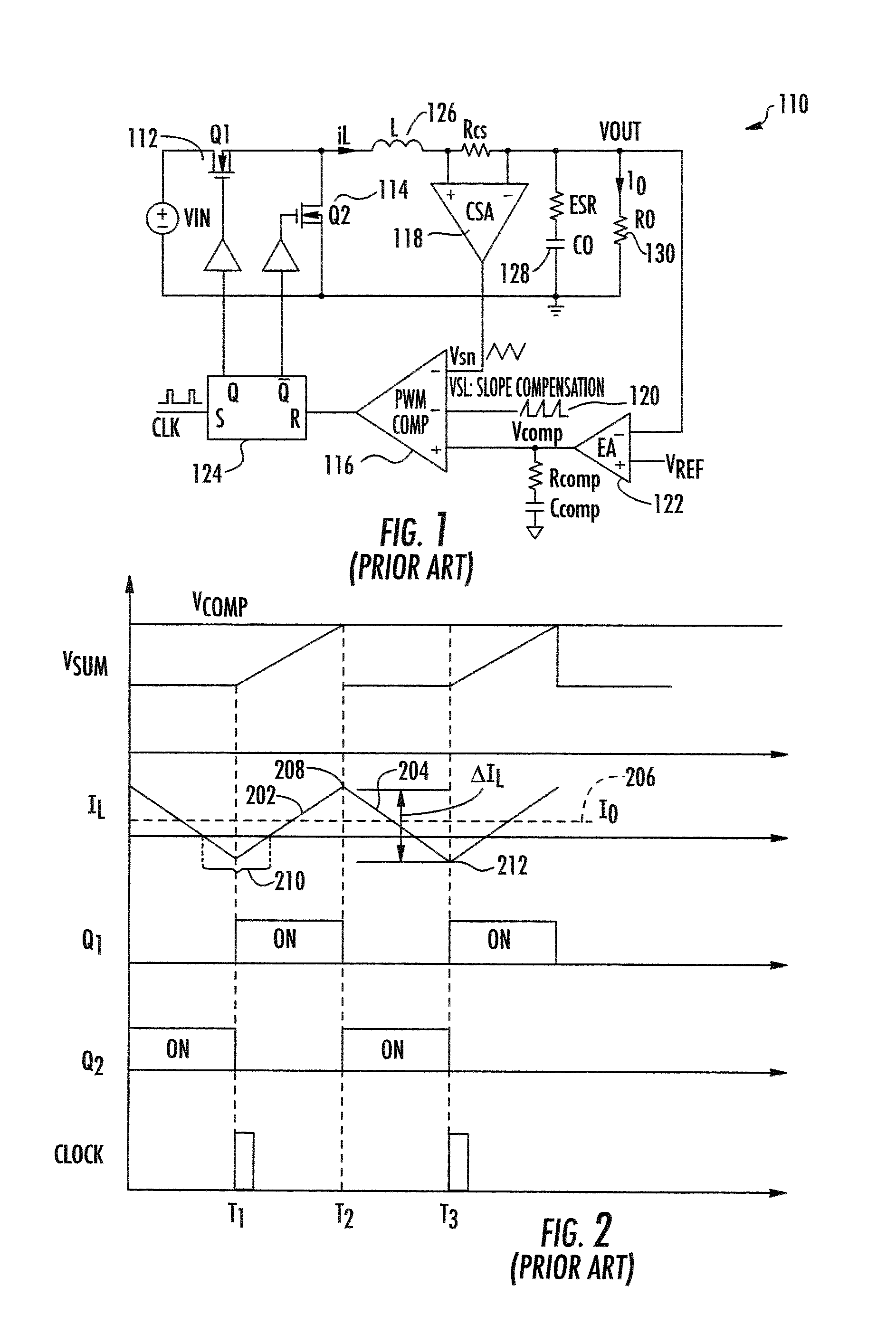
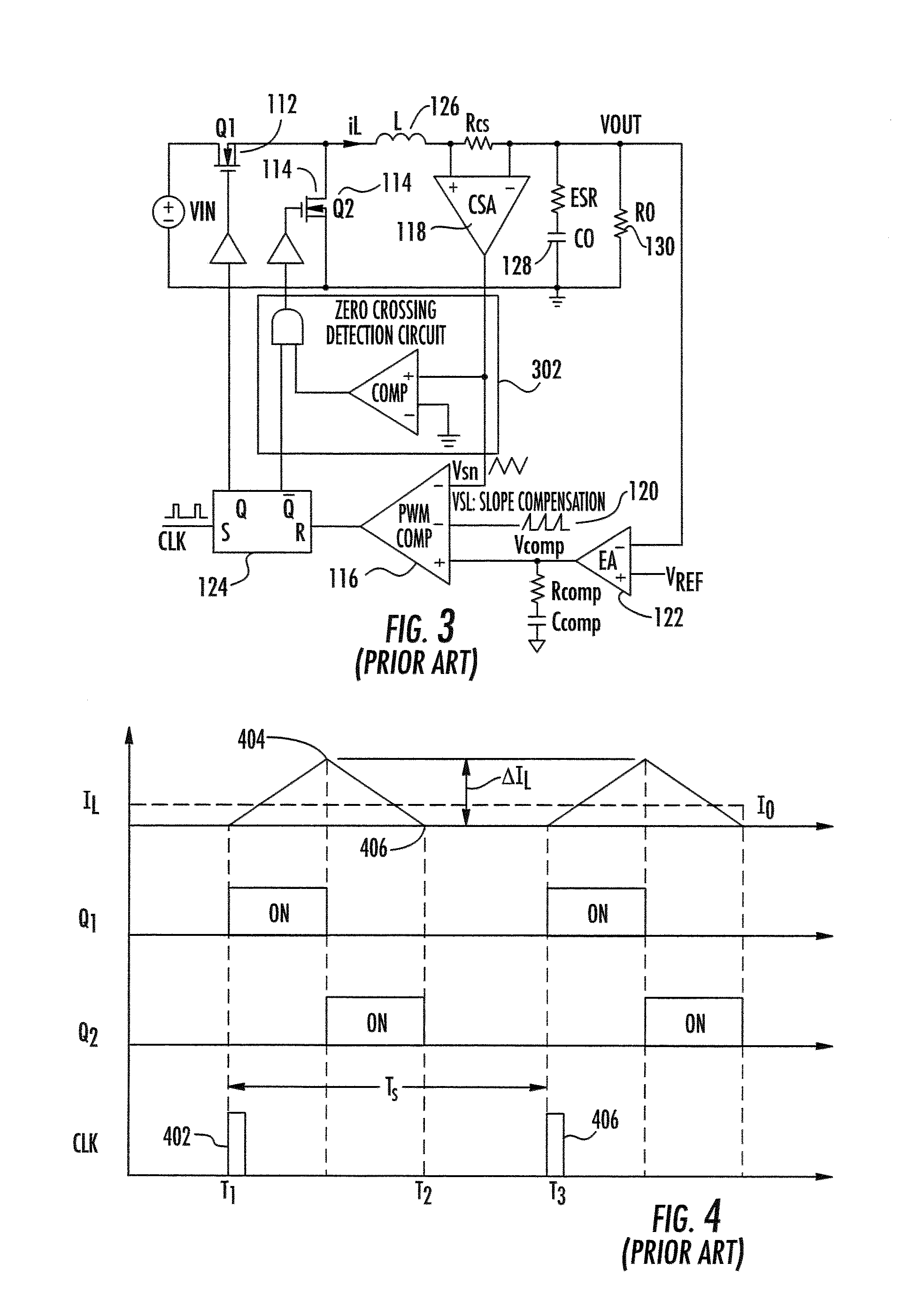
Multiphase clamp coupled-buck converter and magnetic integration
InactiveUS6784644B2Emergency protective circuit arrangementsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage regulator modulePush pull
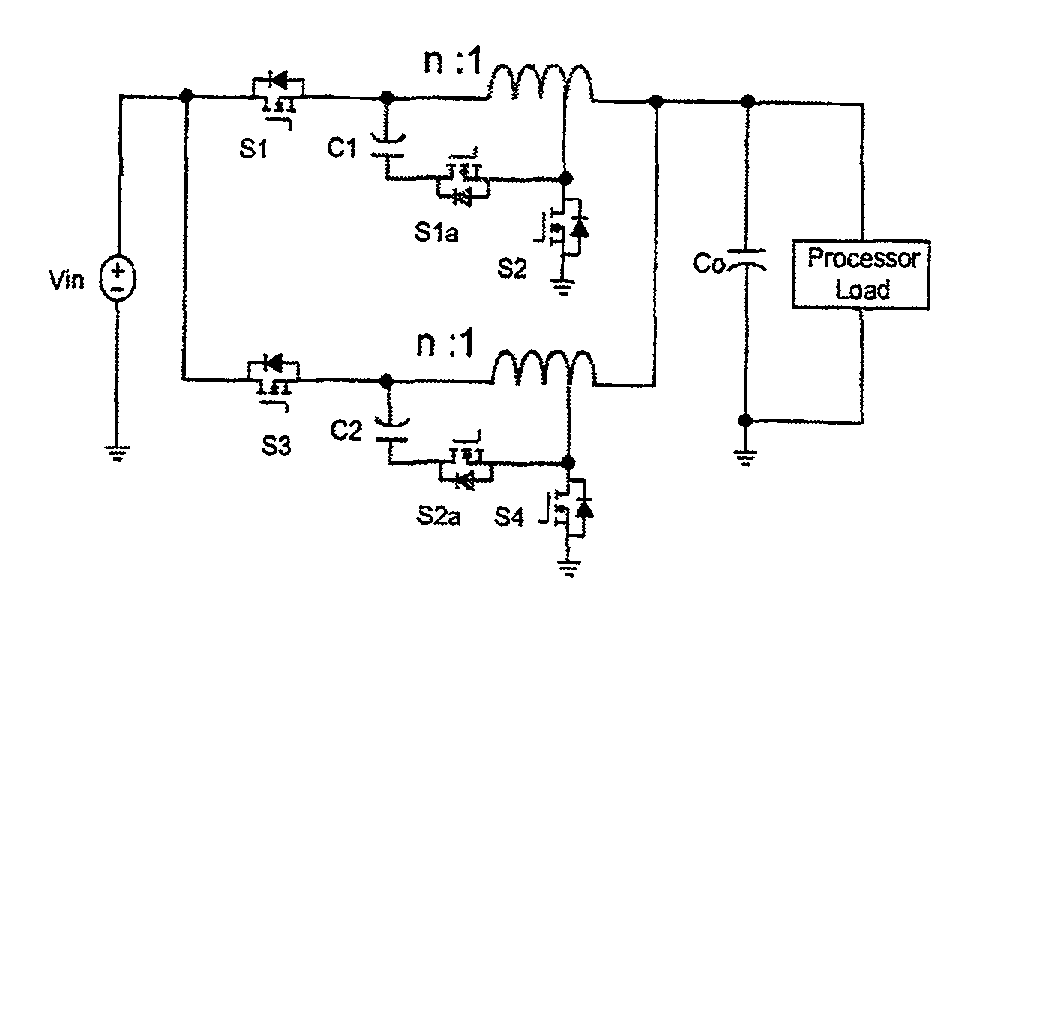
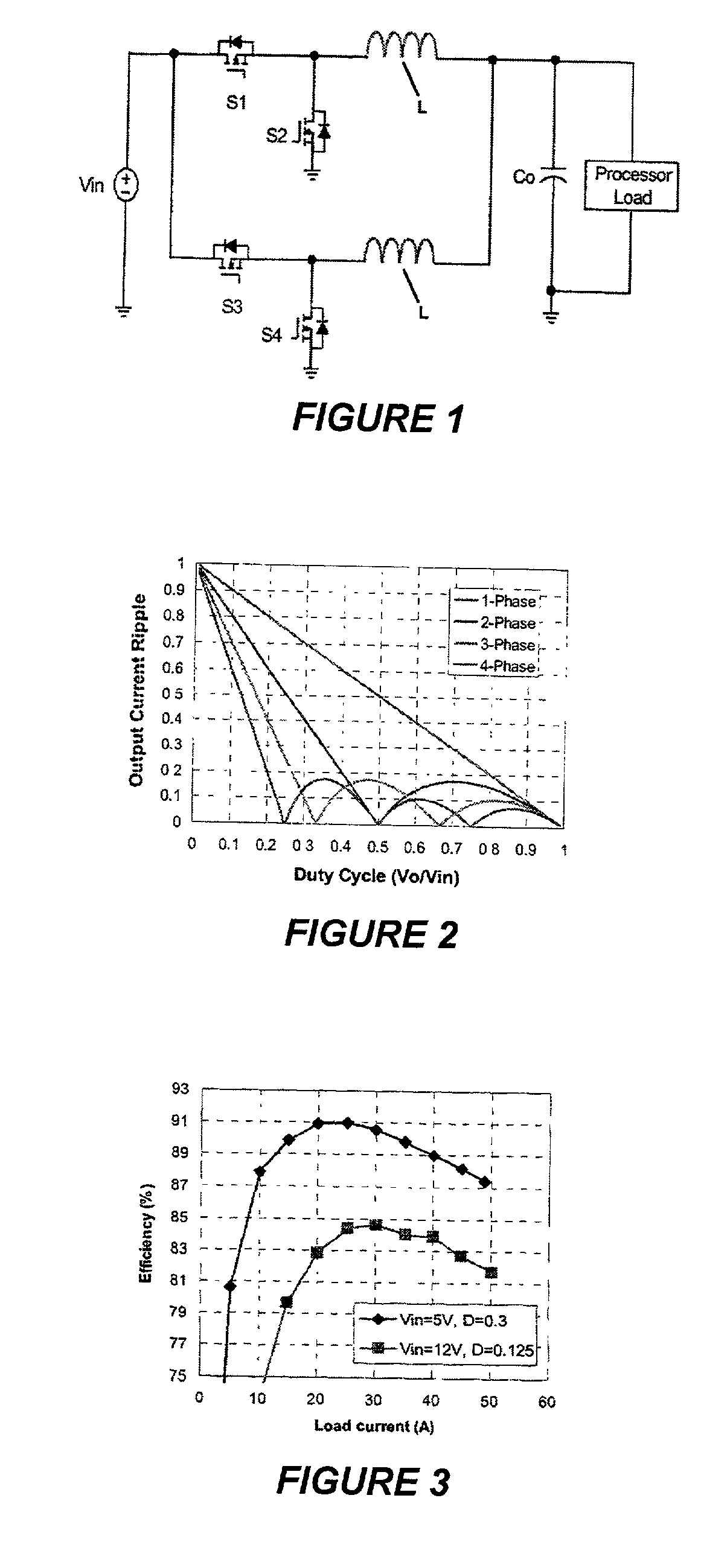
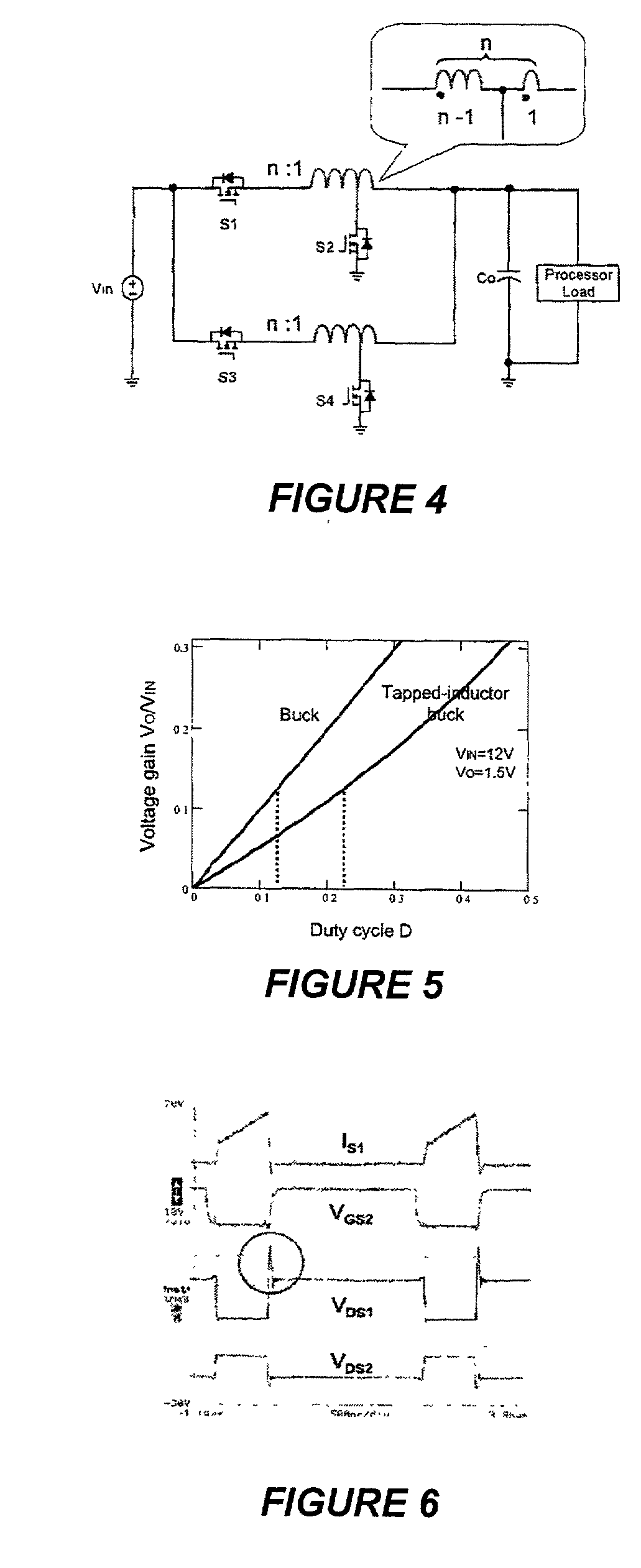
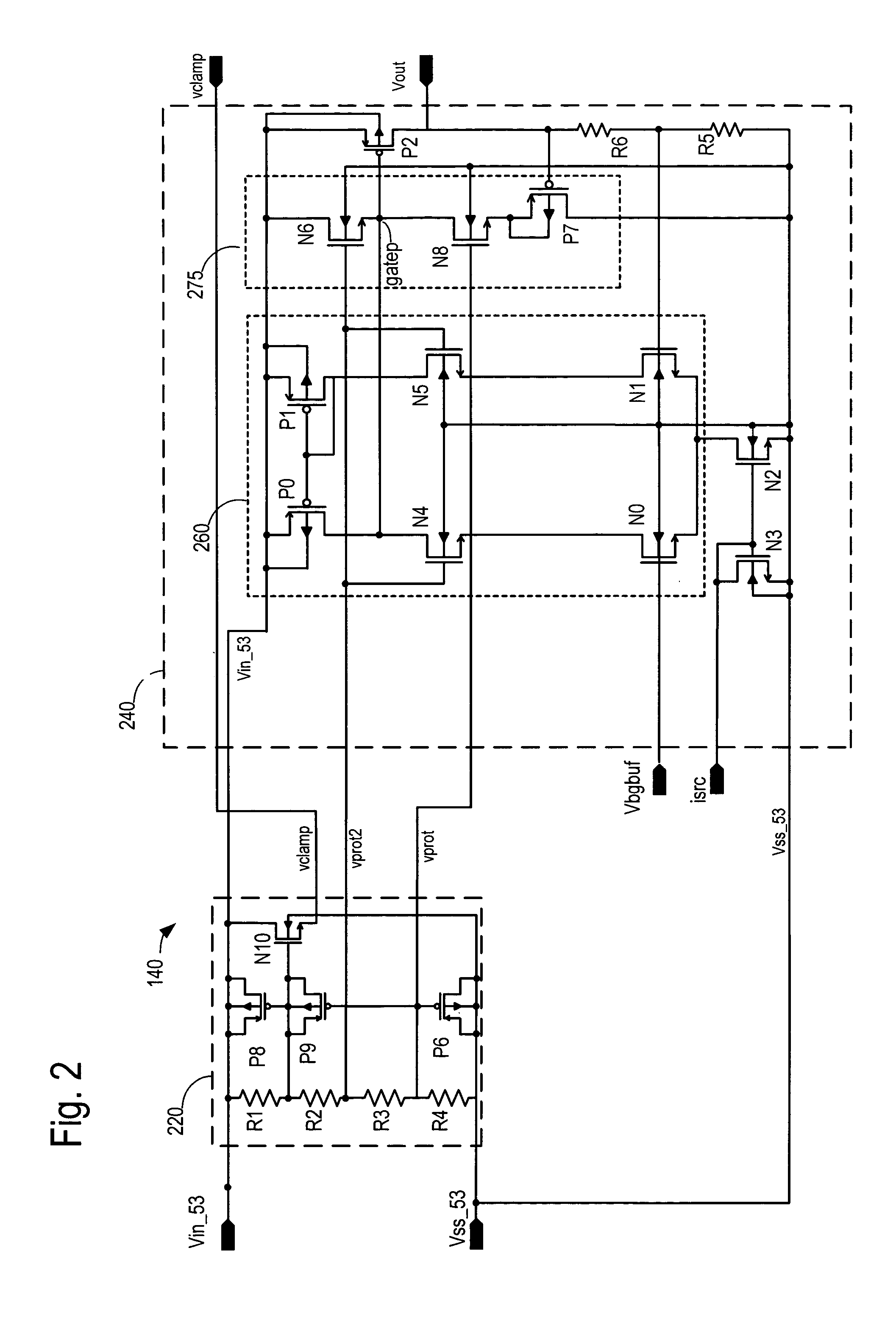
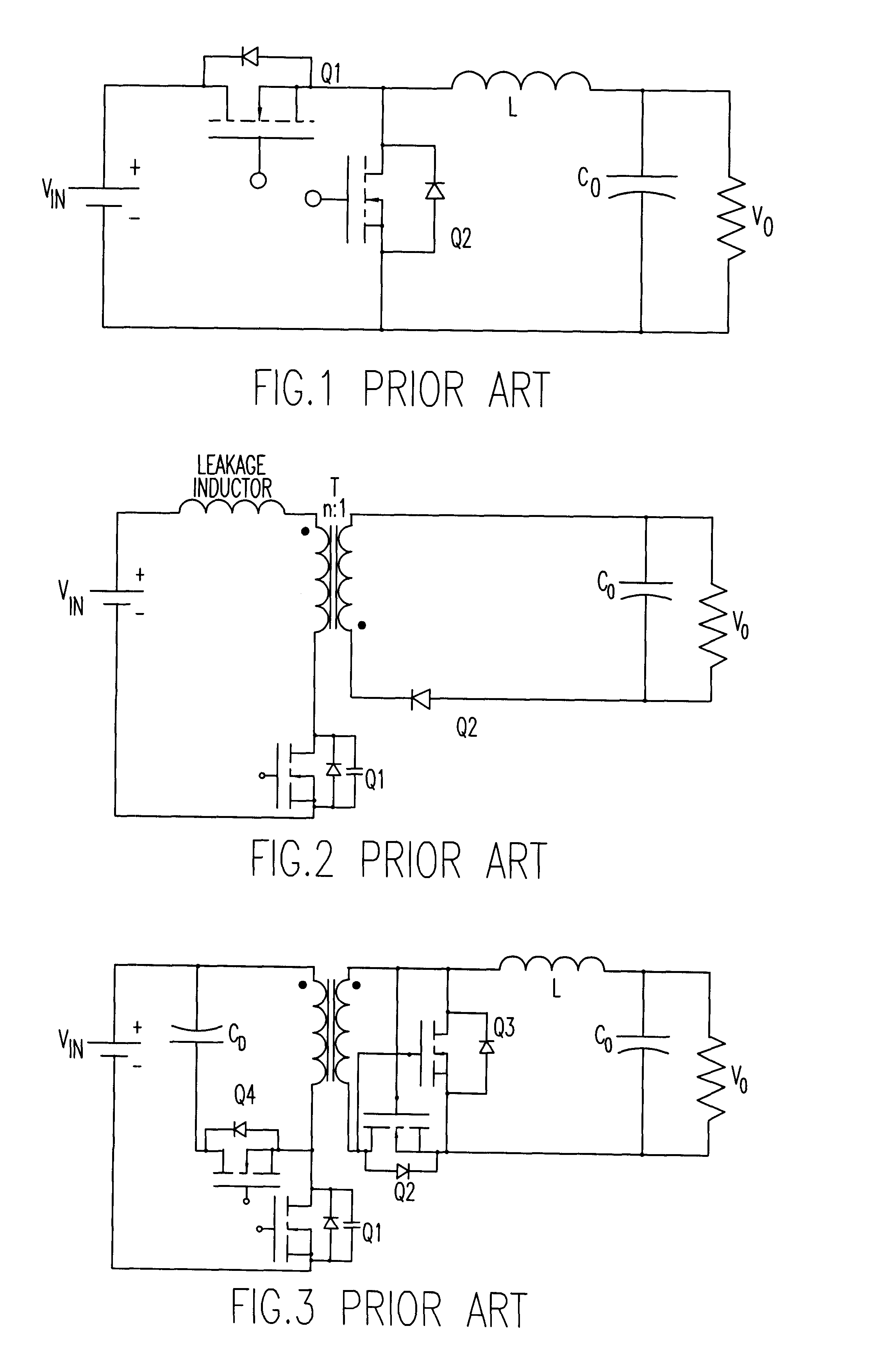
Voltage regulation, transient response and efficiency of a voltage regulator module (VRM) is improved where short duty cycles are necessitated by large differentials of input and output voltage by including at least one clamping of a tap of an inductance in series with an output of each of a plurality of parallel branches or phases which are switched in a complementary fashion or providing coupling between inductors of respective phases. Such coupling between inductors is achieved in a small module with an integrated magnetic structure. Reduced component counts are achieved while deriving built-in input and output filters. Principals of the invention can be extended to isolation applications and push-pull forward converts, in particular. A lossless clamping circuit is also provided allowing spike currents to be suppressed while returning power to the output of the VRM.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
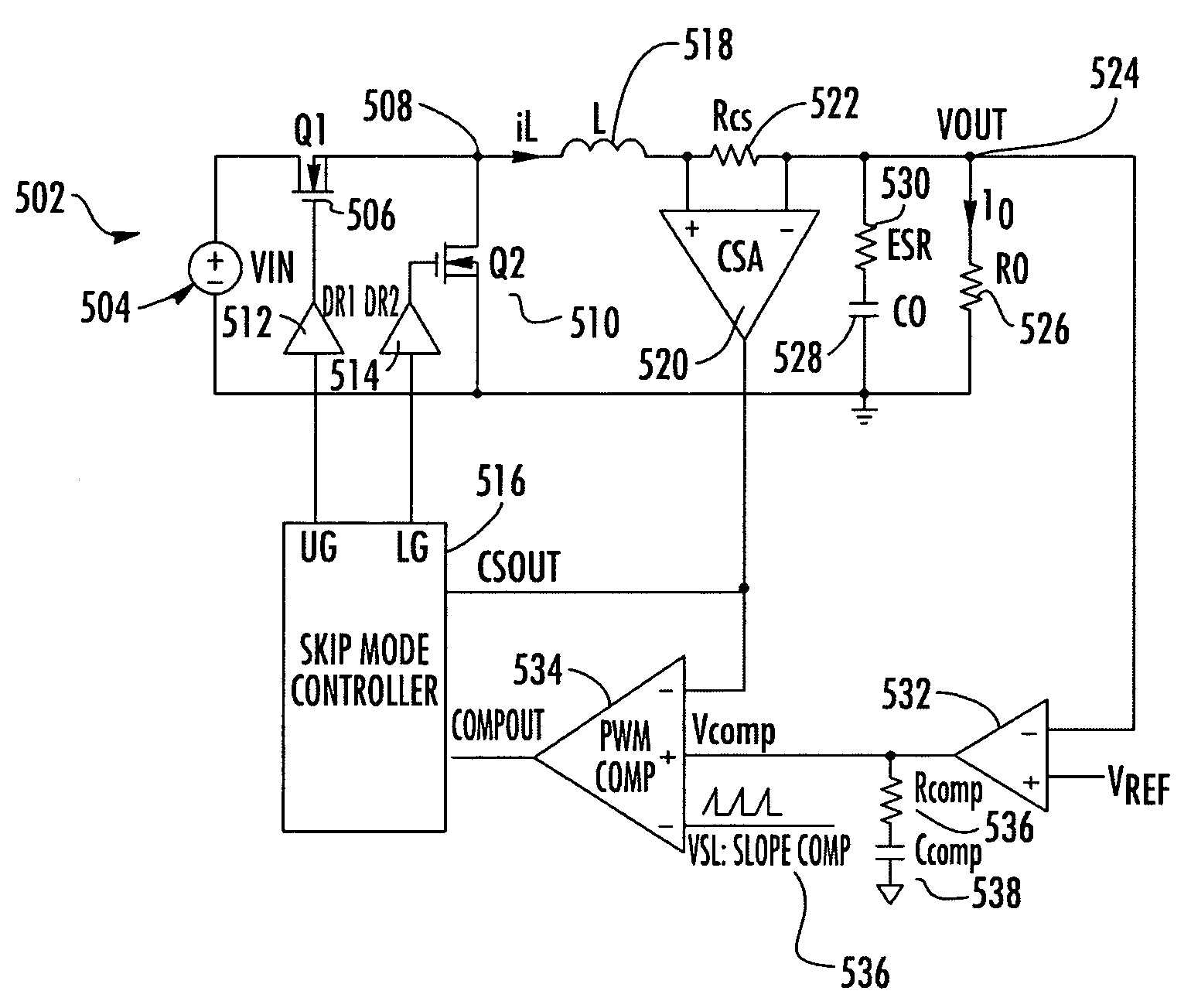
High light load efficiency synchronous buck regulator with pulse skipping control
InactiveUS7245113B2Minimize conduction loss and switching lossEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage regulator moduleVoltage regulation
A voltage regulator includes a voltage source for providing an input voltage and circuitry for regulating the input voltage to provide an output voltage. The circuitry for regulating the input voltage includes at least a high side switch and a low side switch. A skip mode controller controls the high side switch and the low side switch in order to minimize conduction losses and switching losses within the voltage regulator.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Electronic cigarette and method for supplying constant power therein
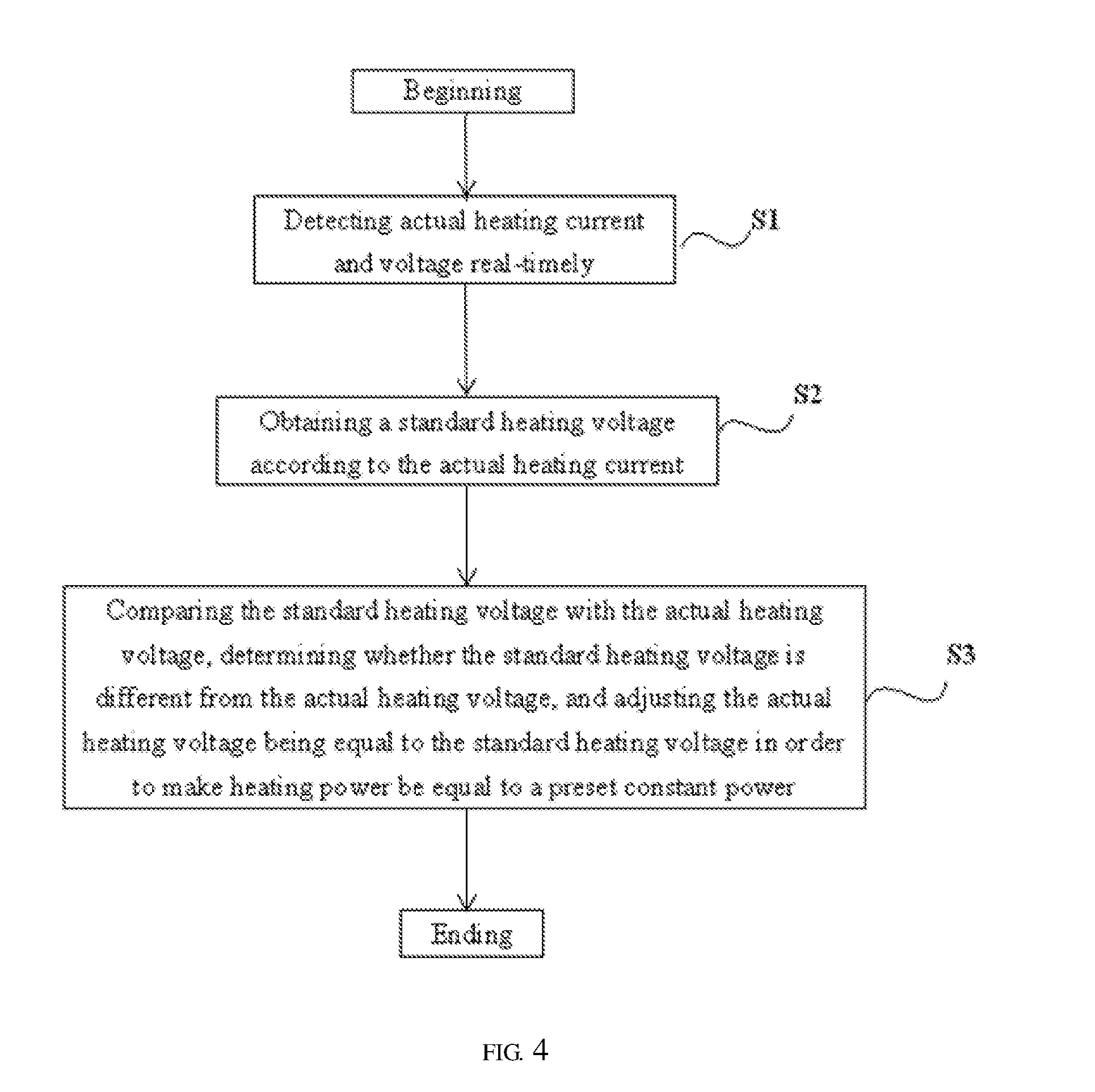
InactiveUS20160143359A1Meeting demandMeet needsSteam generation using steam absorptionElectric heatingVoltage regulator moduleConstant power
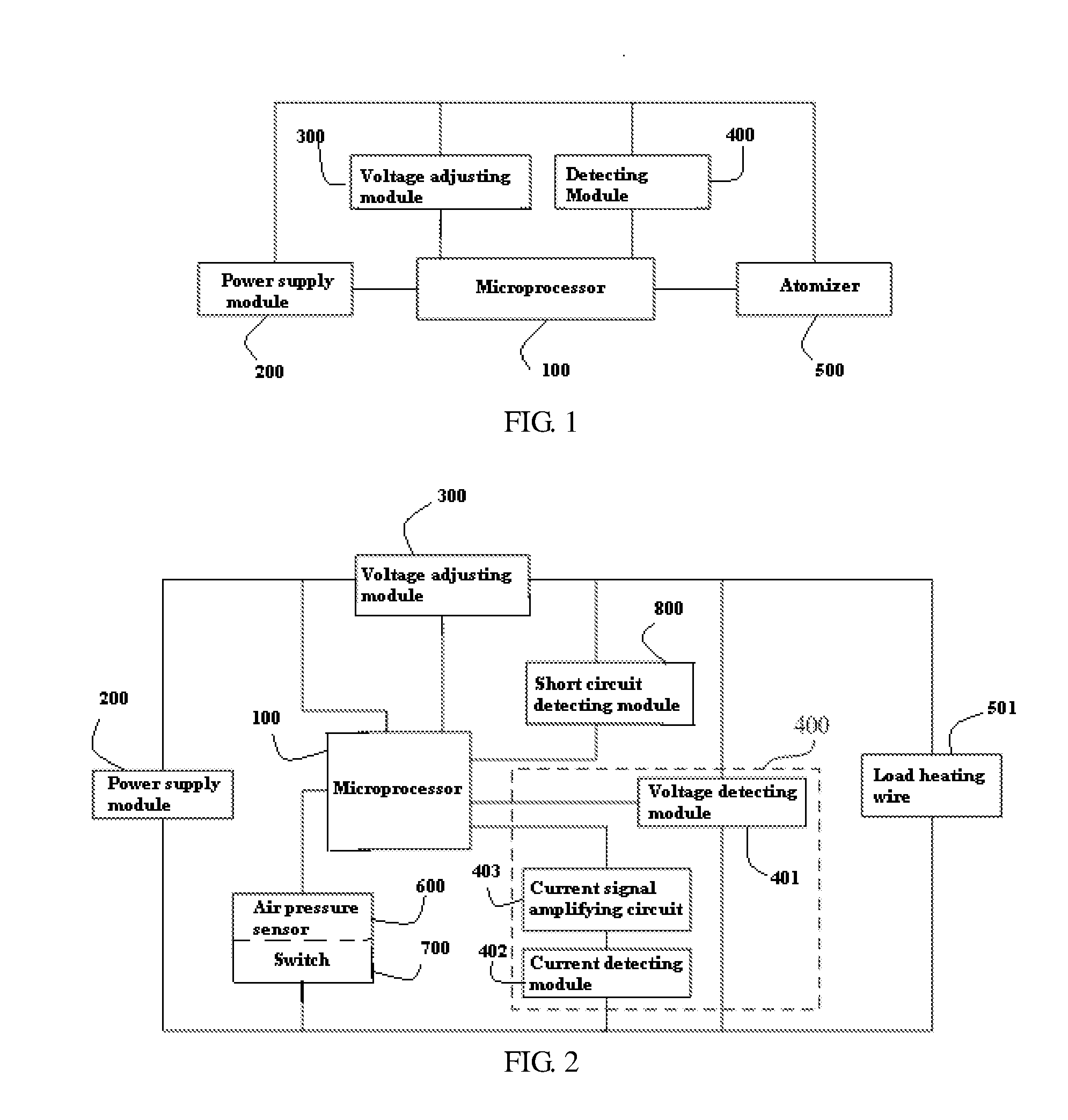
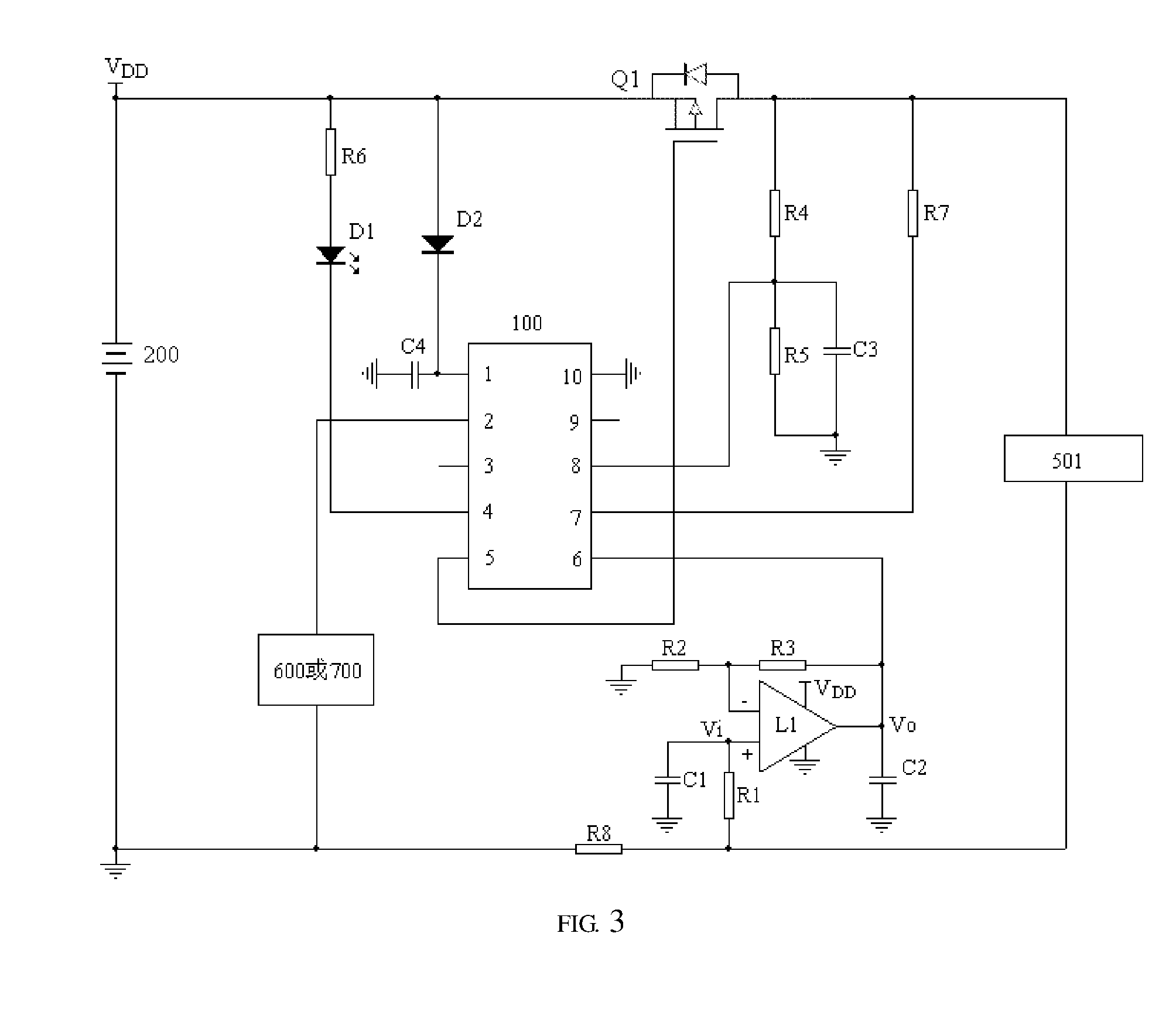
An electronic cigarette and a method for supplying a constant power therein, the electronic cigarette comprises an atomizer with a heating wire. The electronic cigarette also comprises a power supply module for supplying power to the heating wire to heat the heating wire, and further comprises a microprocessor, a detecting module connected to the microprocessor, and a voltage adjusting module. A preset constant power can supply to the heating wire of the atomizer in the electronic cigarette, so that a consistent heating power can be applied to each of the electronic cigarettes produced in batch production, and smoke amount and flavor of each of the electronic cigarettes are more consistent, thereby better meeting demands of consumers.
Owner:HUIZHOU KIMREE TECH
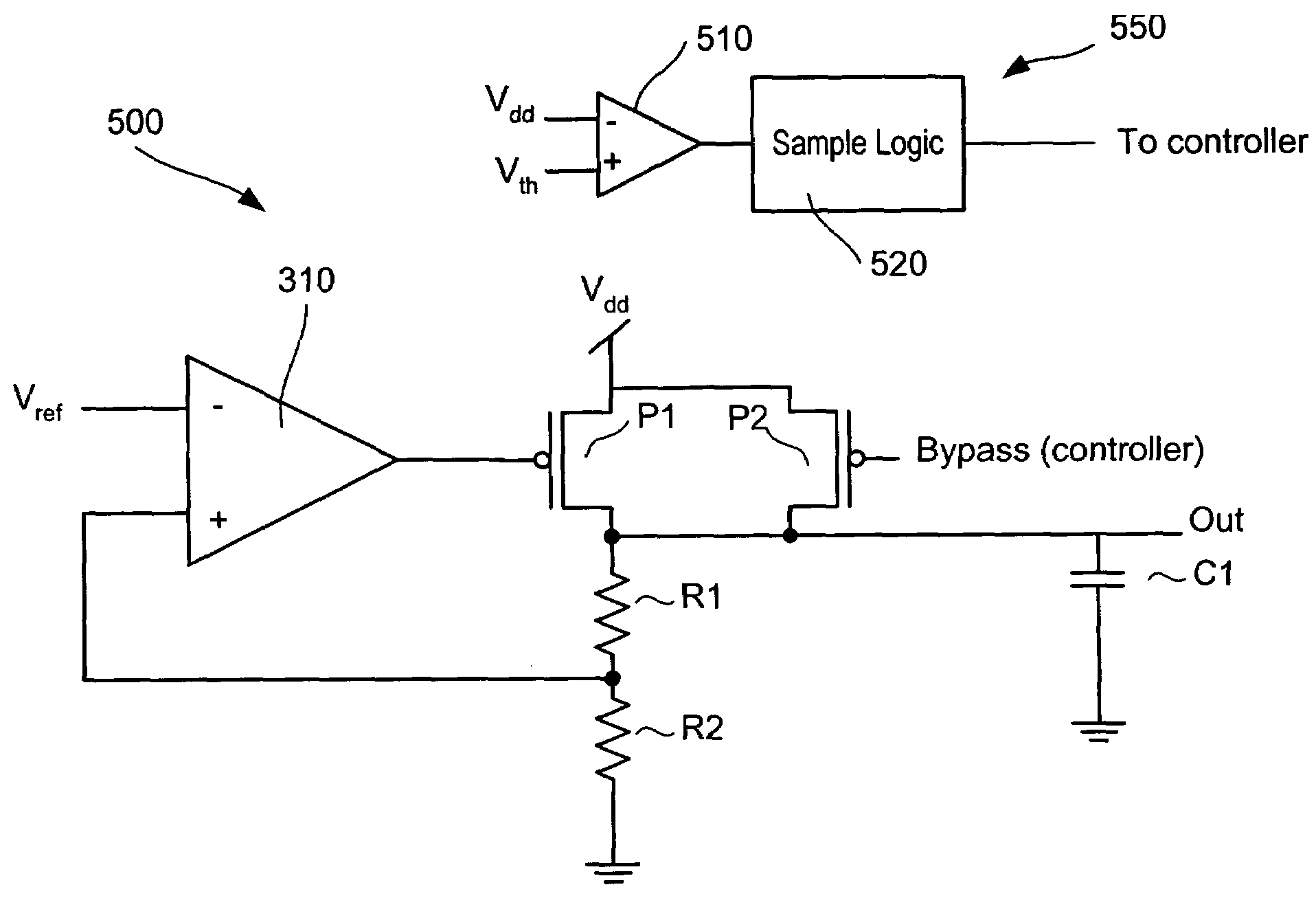
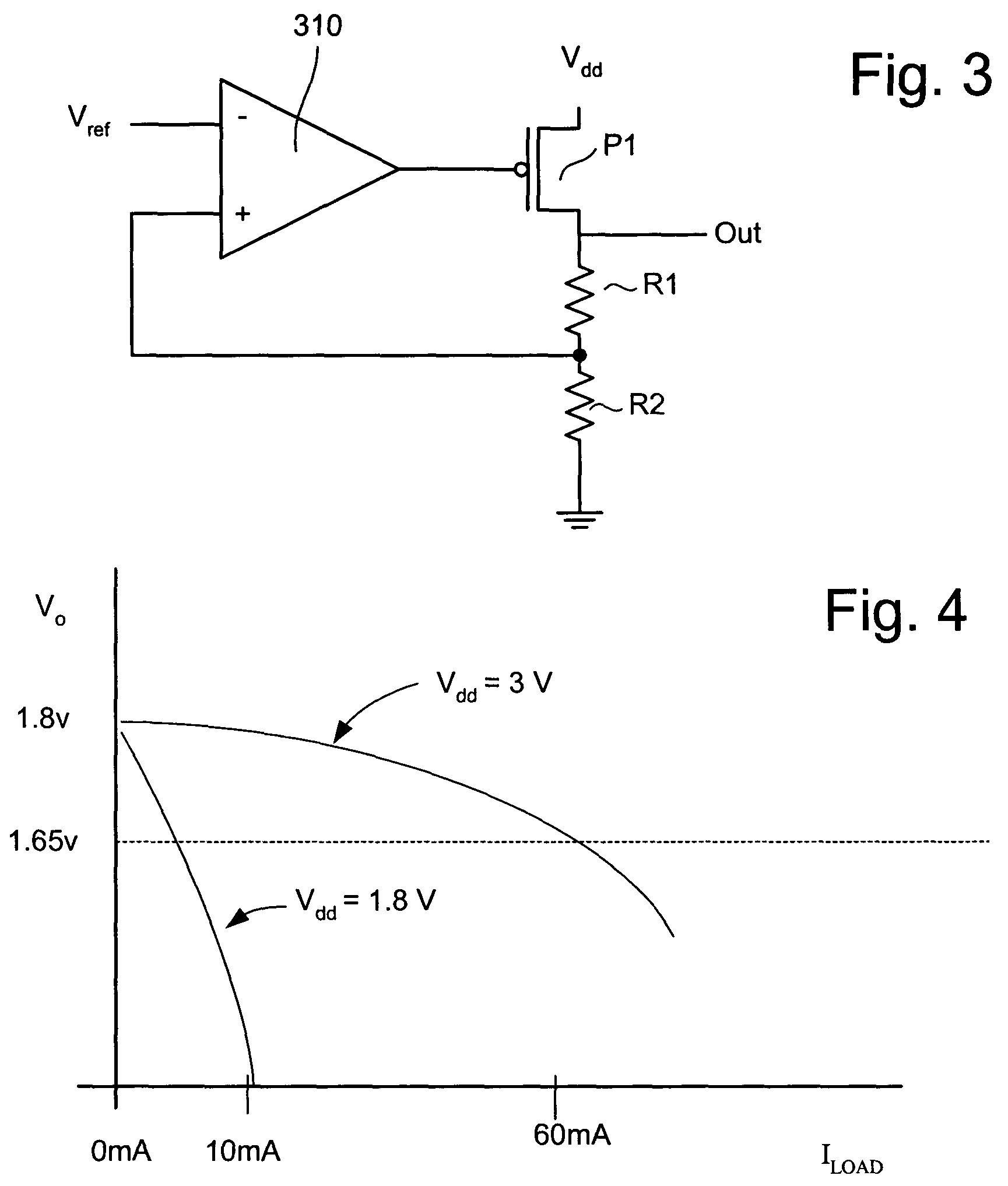
Voltage regulator with bypass for multi-voltage storage system
InactiveUS7212067B2Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingVoltage regulator moduleElectricity
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Multiphase clamp coupled-buck converter and magnetic integration
InactiveUS20020118000A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionVoltage regulator modulePush pull
Voltage regulation, transient response and efficiency of a voltage regulator module (VRM) is improved where short duty cycles are necessitated by large differentials of input and output voltage by including at least one clamping of a tap of an inductance in series with an output of each of a plurality of parallel branches or phases which are switched in a complementary fashion or providing coupling between inductors of respective phases. Such coupling between inductors is achieved in a small module with an integrated magnetic structure. Reduced component counts are achieved while deriving built-in input and output filters. Principals of the invention can be extended to isolation applications and push-pull forward converts, in particular. A lossless clamping circuit is also provided allowing spike currents to be suppressed while returning power to the output of the VRM.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
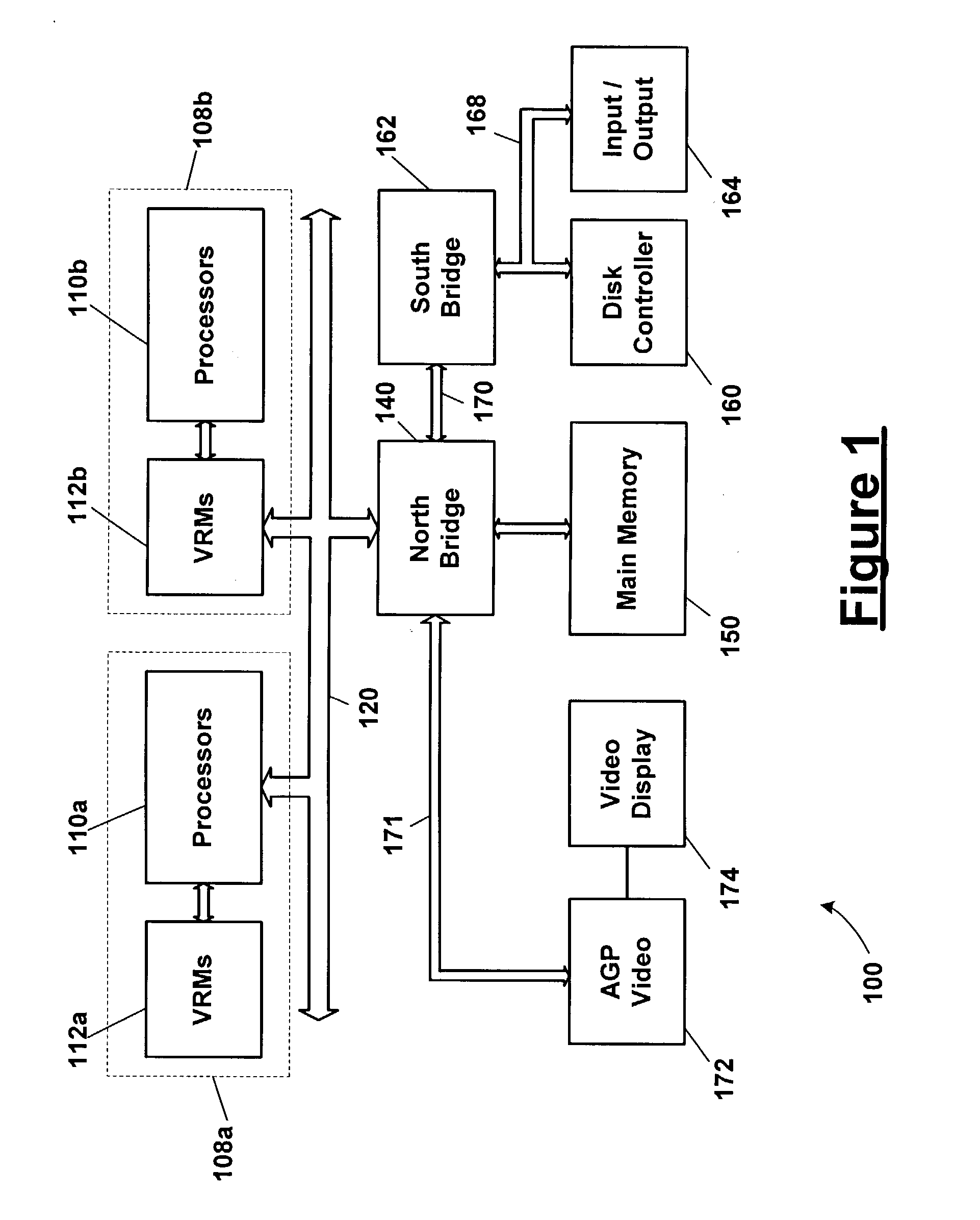
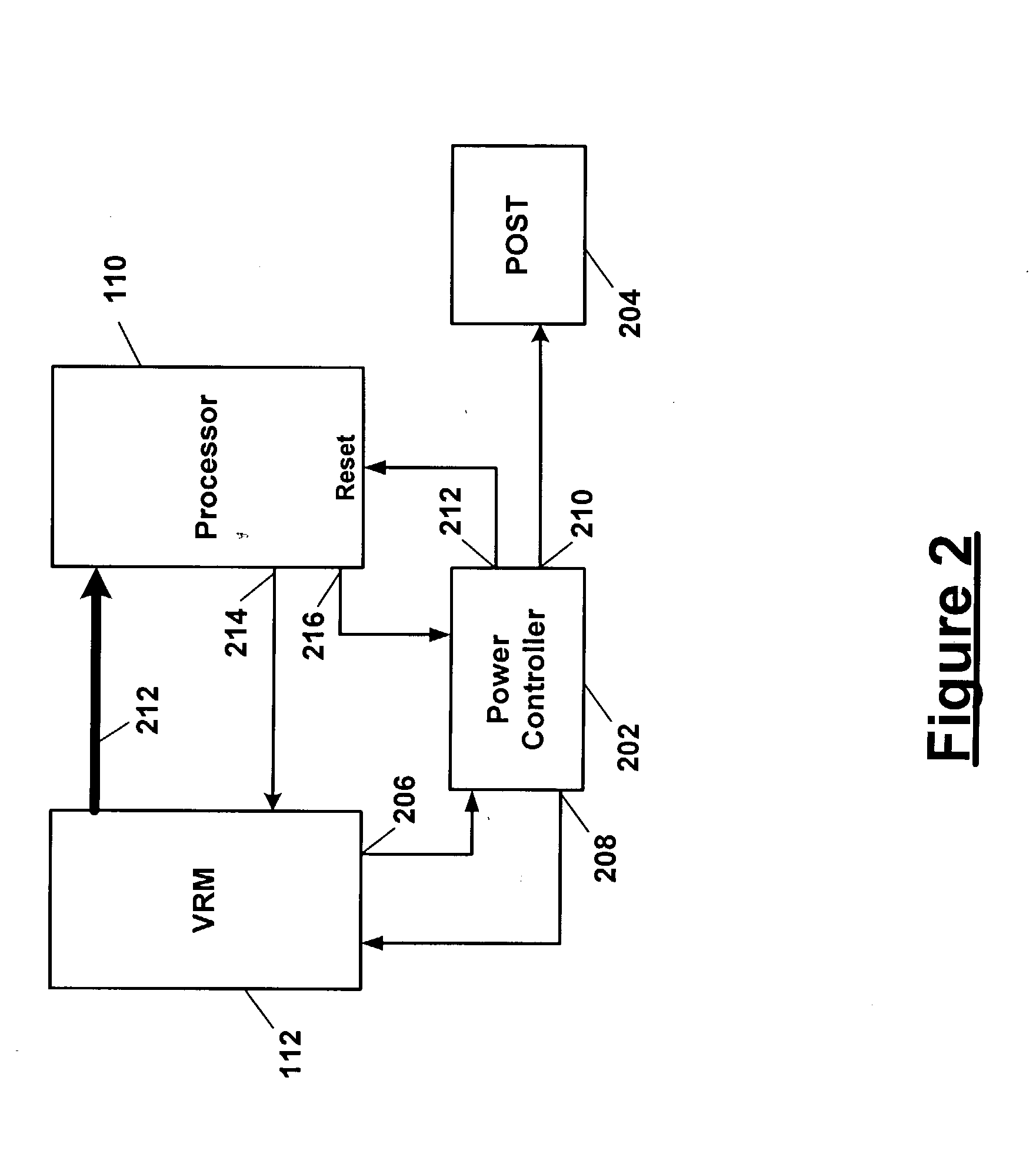
Power-up of multiple processors when a voltage regulator module has failed
InactiveUS20040215991A1Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingInformation processingVoltage regulator module
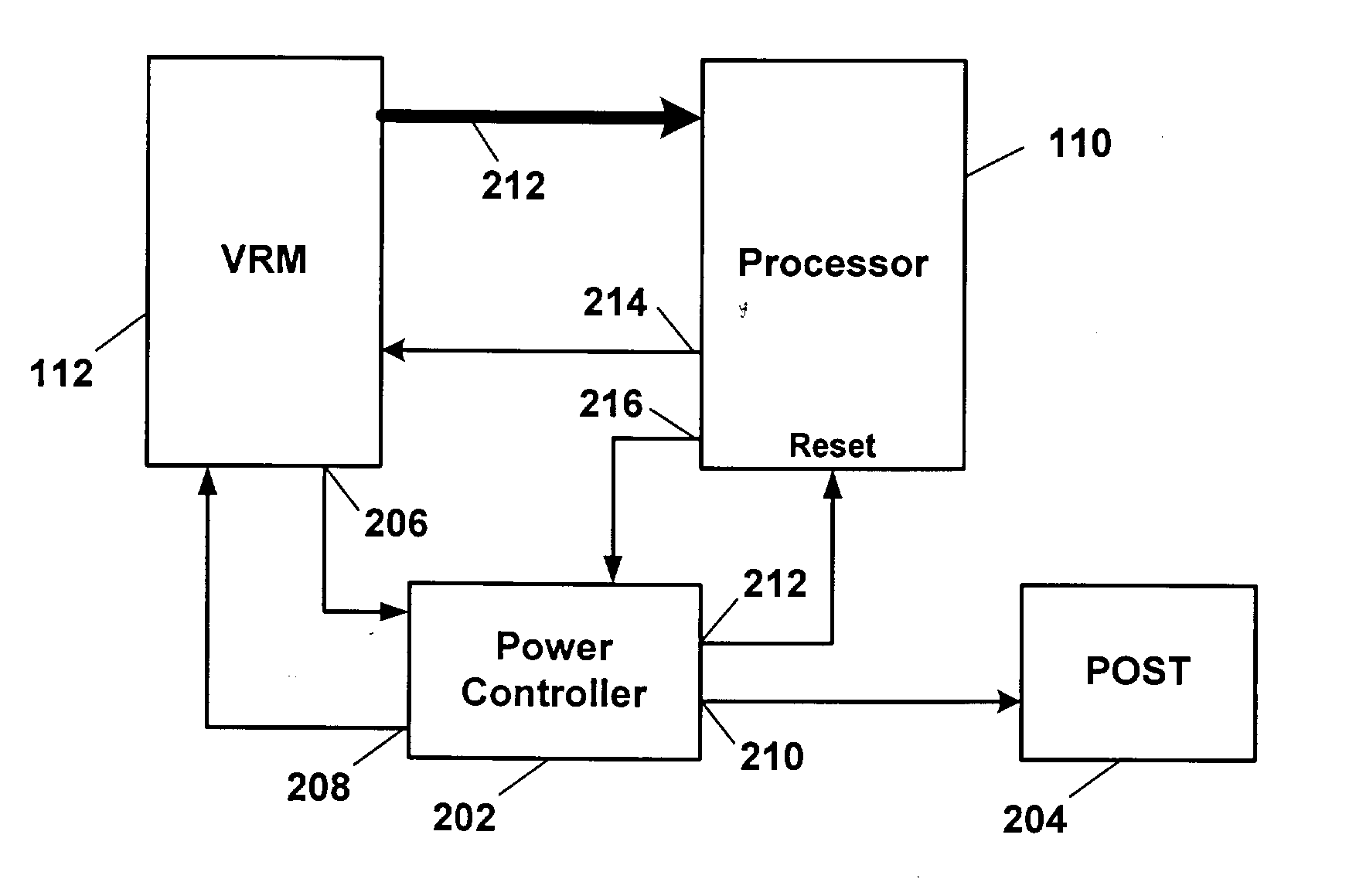
In an information handling system, voltage regulator modules (VRM) are first enabled and determined to be operational before enabling an associated processor. If a VRM is determined not to be operational, then the associated processor is disabled. Once all VRMs are determined to be operational or not operational and the associated processors are enabled or disabled as the case may be, the information handling system is operationally started-up with all operational VRMs and associated processors functioning.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
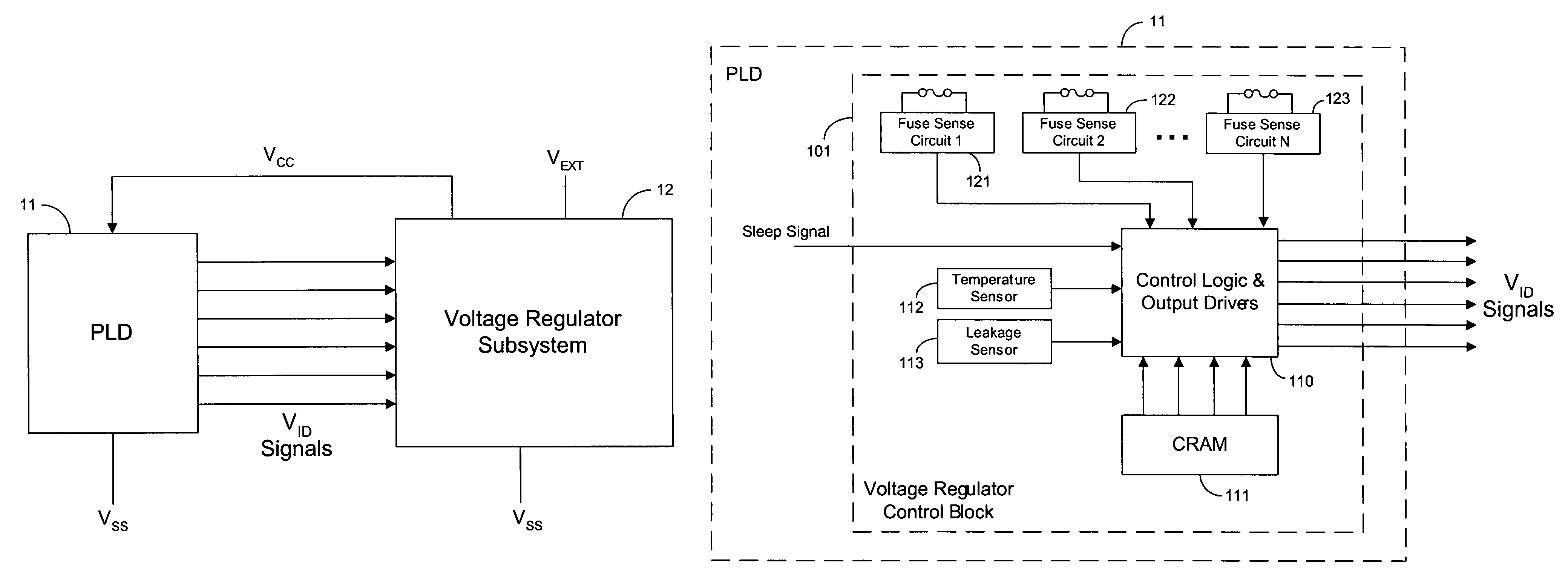
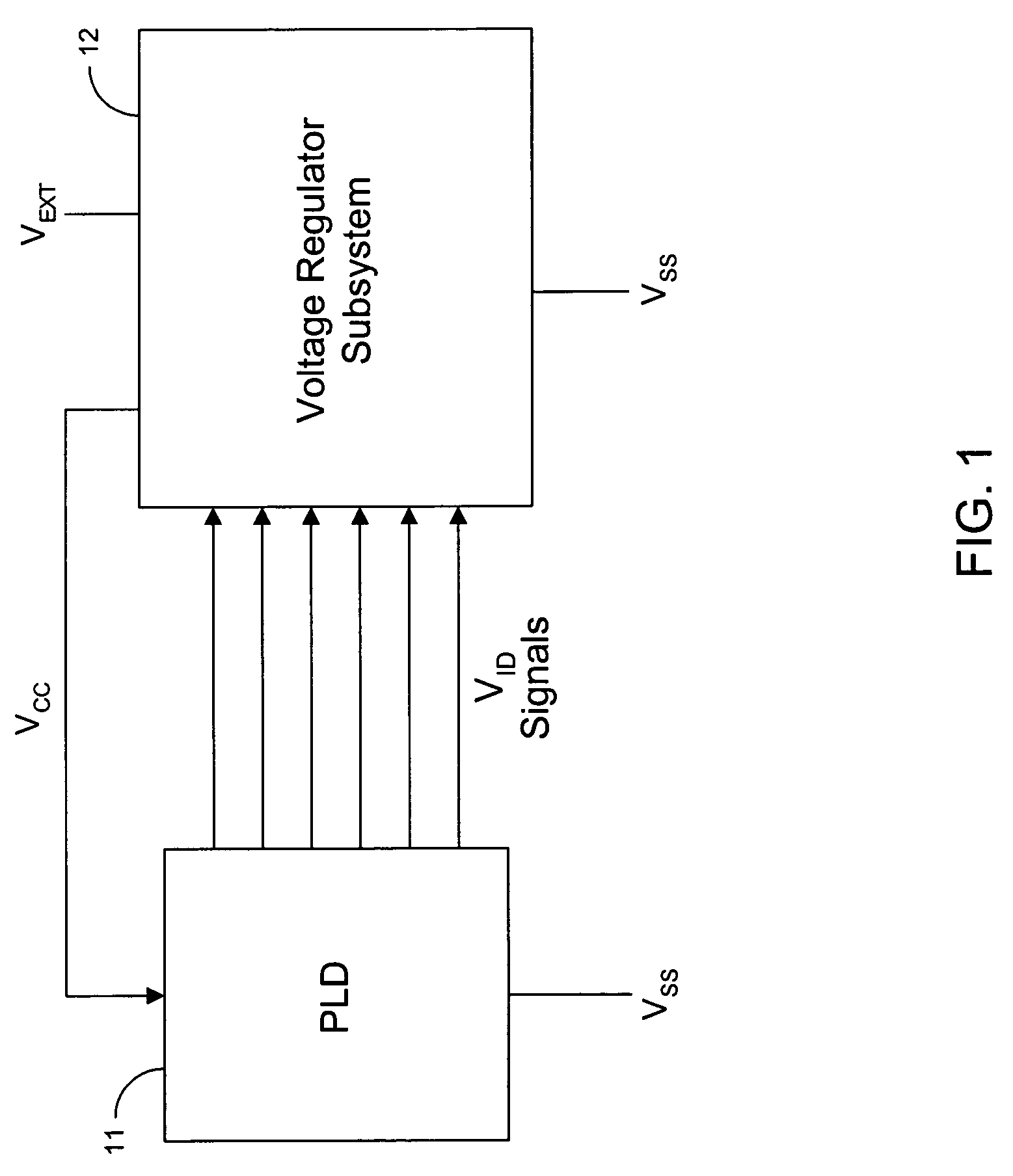
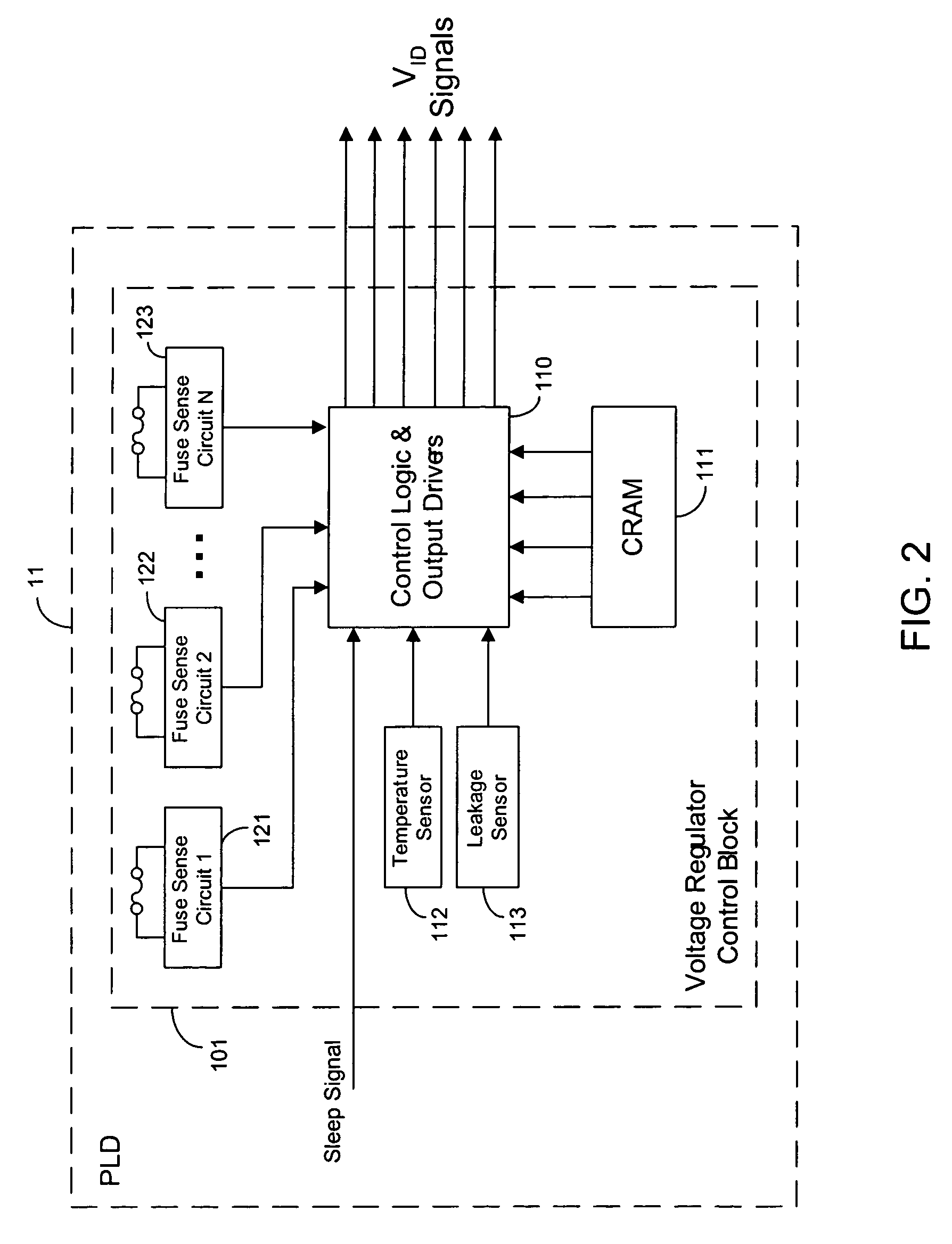
Adaptive power supply voltage regulation for programmable logic
ActiveUS7142009B1Reduce power consumptionPower consumption reductionVolume/mass flow measurementVoltage regulator moduleProgrammable logic device
Adaptive regulated power supply voltages are applied to programmable logic integrated circuits. Control circuitry in a programmable logic IC generates control signals that are transmitted to an external voltage regulator. The voltage regulator generates one or more power supply voltages in response to the control signals. The values of control signals determine the target values of the supply voltages. The control circuitry can adapt the power supply voltages to compensate for temperature and process variations on the IC. The power supply voltages can be programmed by a manufacturer or by a user to achieve desired target values. The control circuitry can also put a programmable logic IC into a sleep mode by dropping the high supply voltage to a low value to reduce power consumption during periods of low usage.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
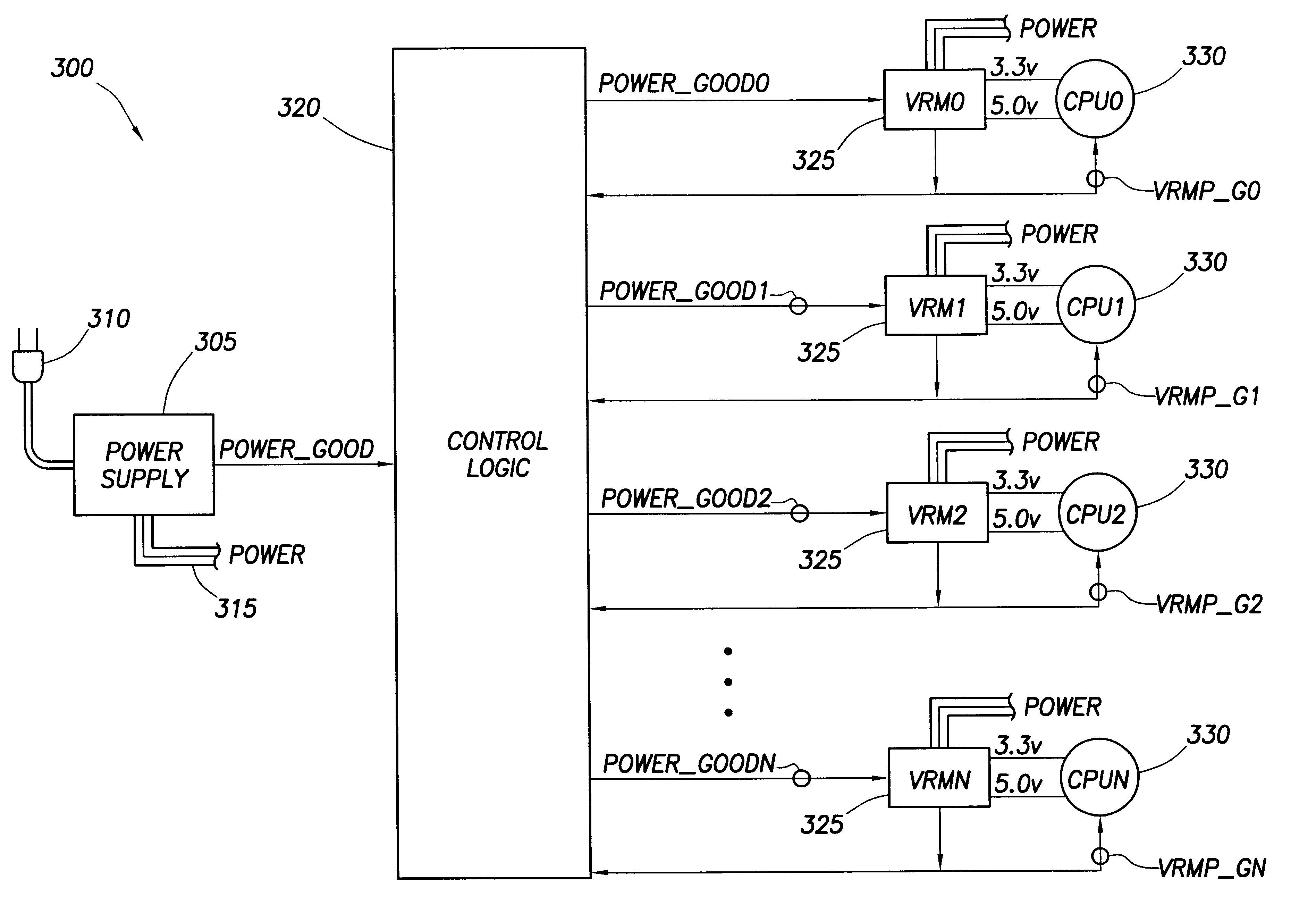
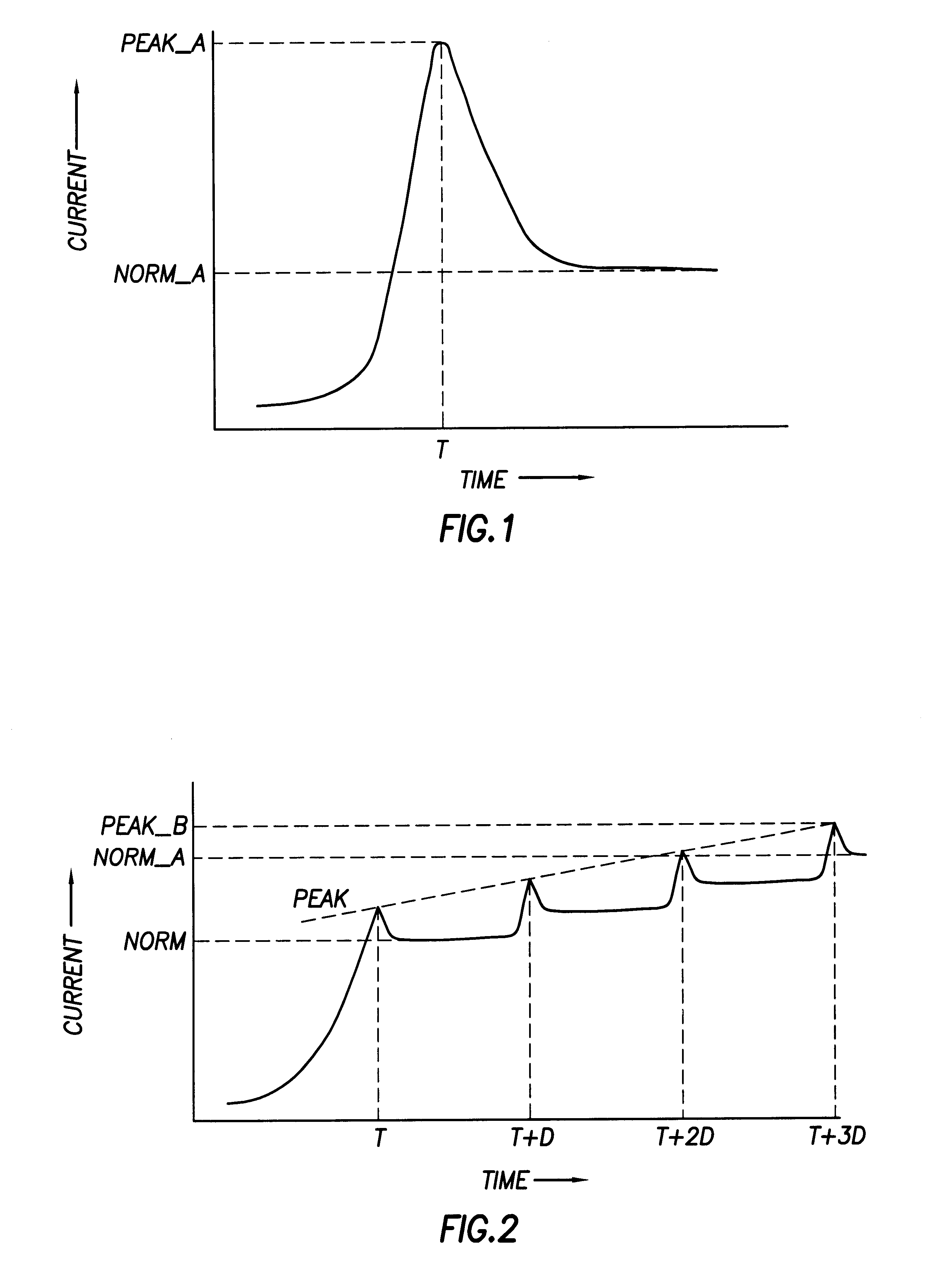
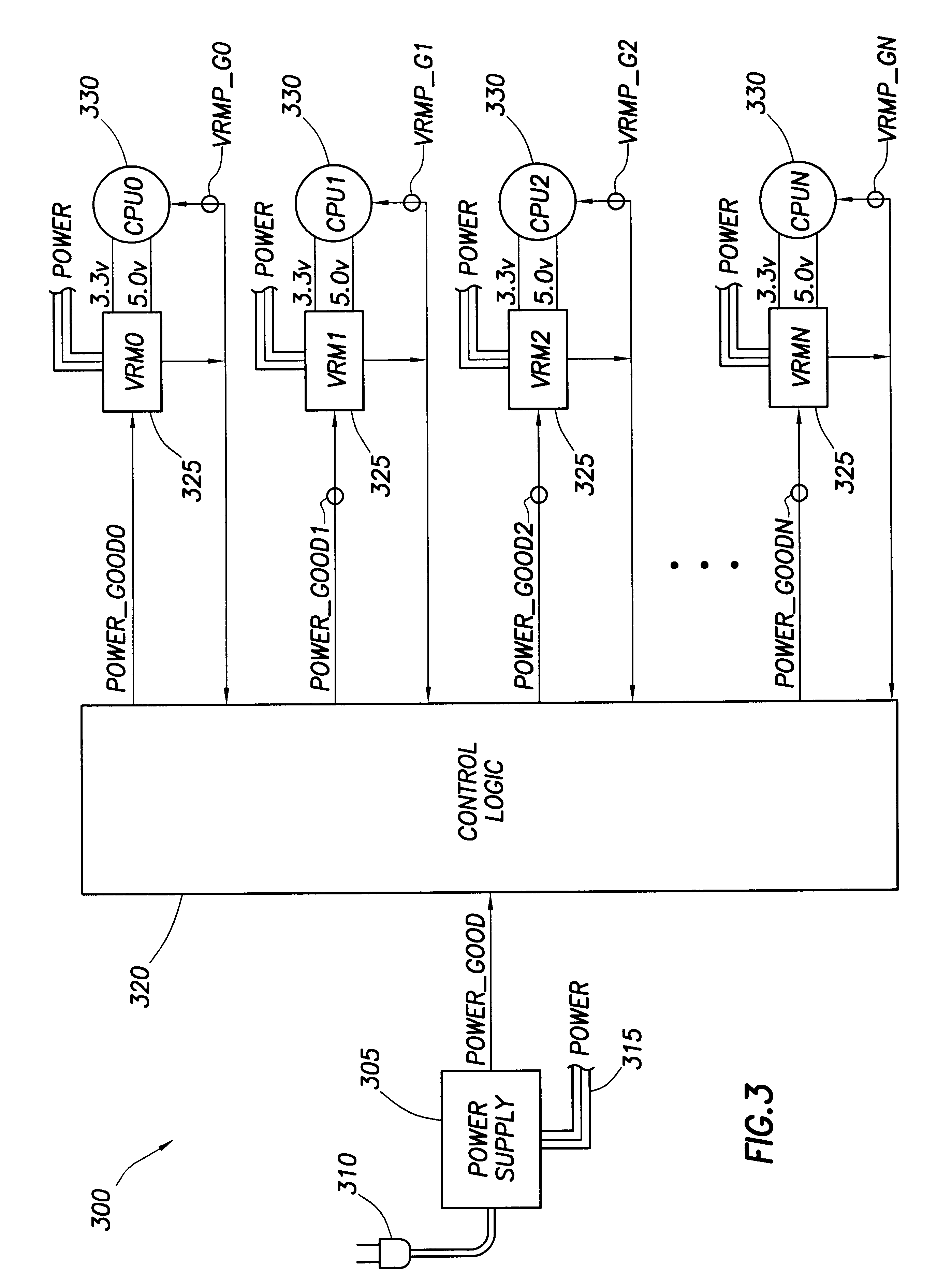
CPU power sequence for large multiprocessor systems
InactiveUS6792553B2Pulse automatic controlVolume/mass flow measurementVoltage regulator moduleElectricity
A computer system includes a power supply coupled to a control logic, the power supply including a power_good output signal and Power output lines. The power_good signal notifies the control logic when the Power output lines have stabilized. The computer system also includes a plurality of voltage regulator modules ("VRM") coupled to the control logic, wherein each VRM receives a power good signal from the control logic. A plurality of processors is also present in the computer system, each of the processors coupled to a VRM. Each of the VRMs transmits voltage to a processor to power-on the processor. Each VRM also transmits to its processor and to the control logic a voltage regulator module power good ("VRMP_G") signal. The control logic includes means to control the sequential power-on of the processors so as to reduce the current sourcing requirements of the power supply and eliminate power supply surges.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
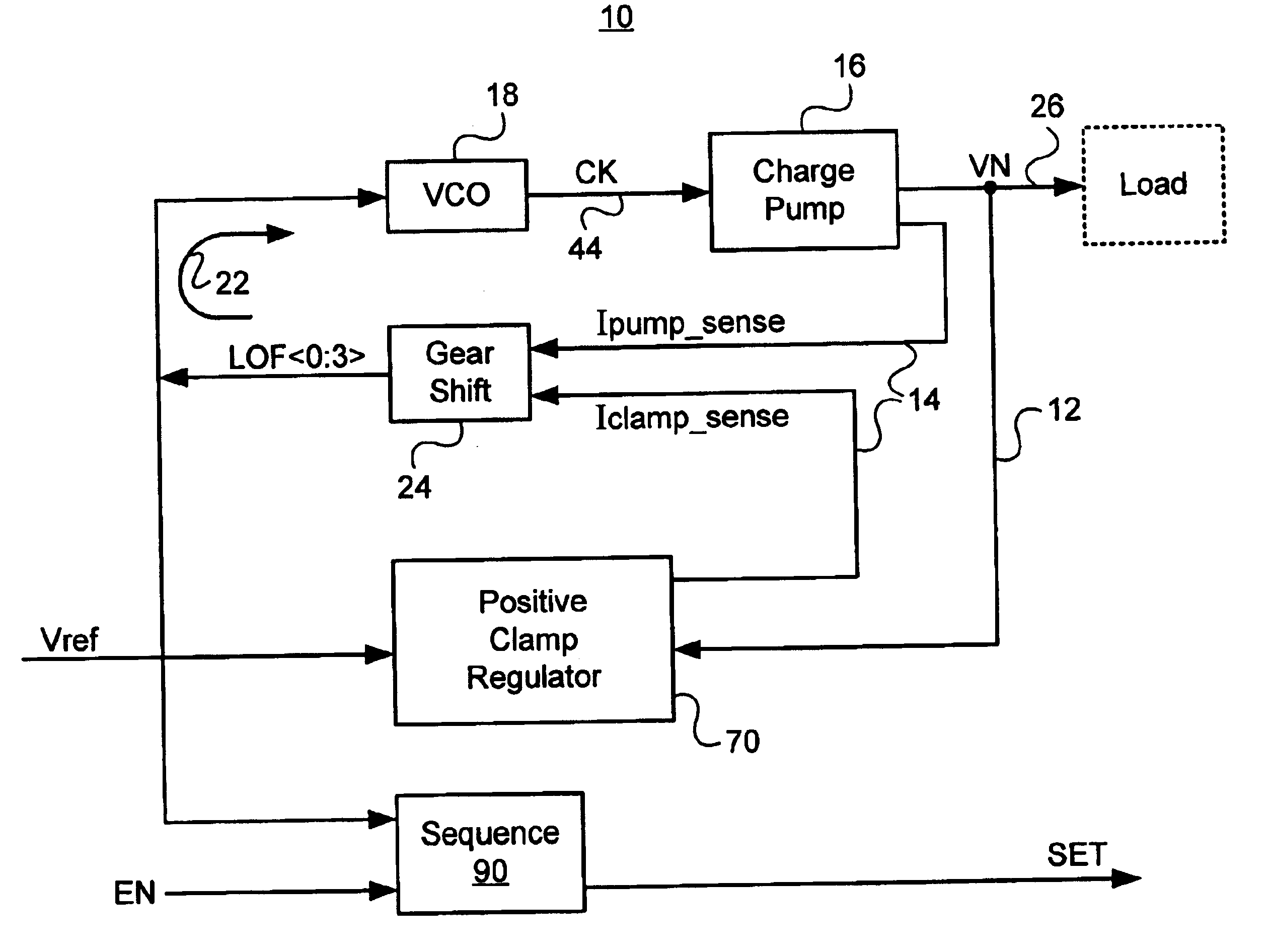
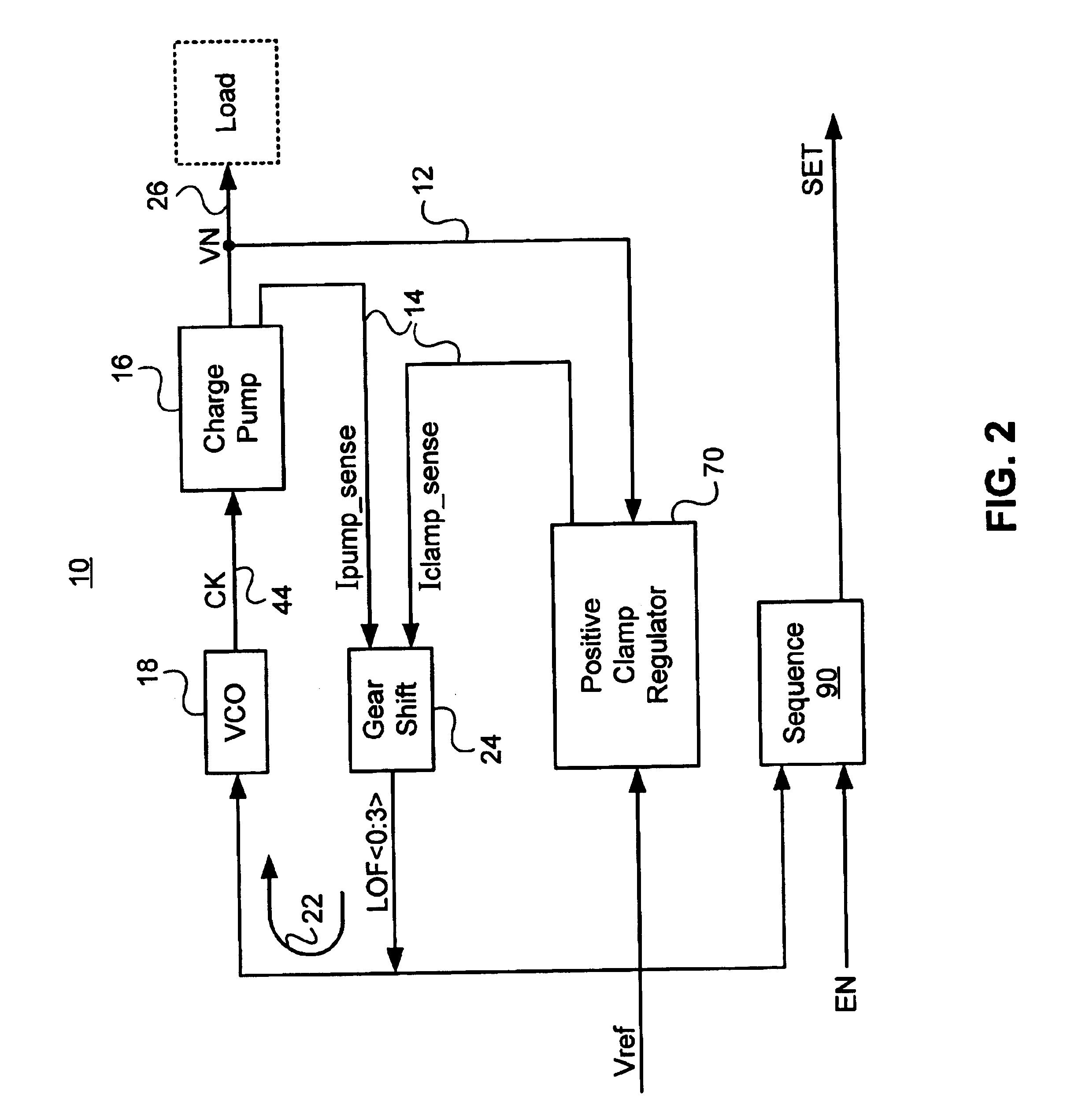
Charge pump based voltage regulator with smart power regulation
InactiveUS6756838B1Apparatus without intermediate ac conversionDigital storageVoltage regulator moduleControl signal
A charge pump based voltage regulator with smart power regulation employs an architecture that requires that the charge pump current be a linear combination of the load current and a clamp current with a possible offset current. The smart power regulation is based on automatic load activity (or load current) detection using the clamp current. The clamp current and the filtered charge pump current are compared with one another; and the charge pump current is then adjusted accordingly by stepping the frequency of the clock driving the charge pump, optimizing the power consumption of the entire voltage regulator with varying load activity. The negative voltage regulation is independent of the integrated circuit positive supply voltage. In one embodiment, a derivative of the desired output voltage is compared with a reference voltage to generate a clamp current control signal. In another embodiment, the reference voltage is solely positive.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC +1
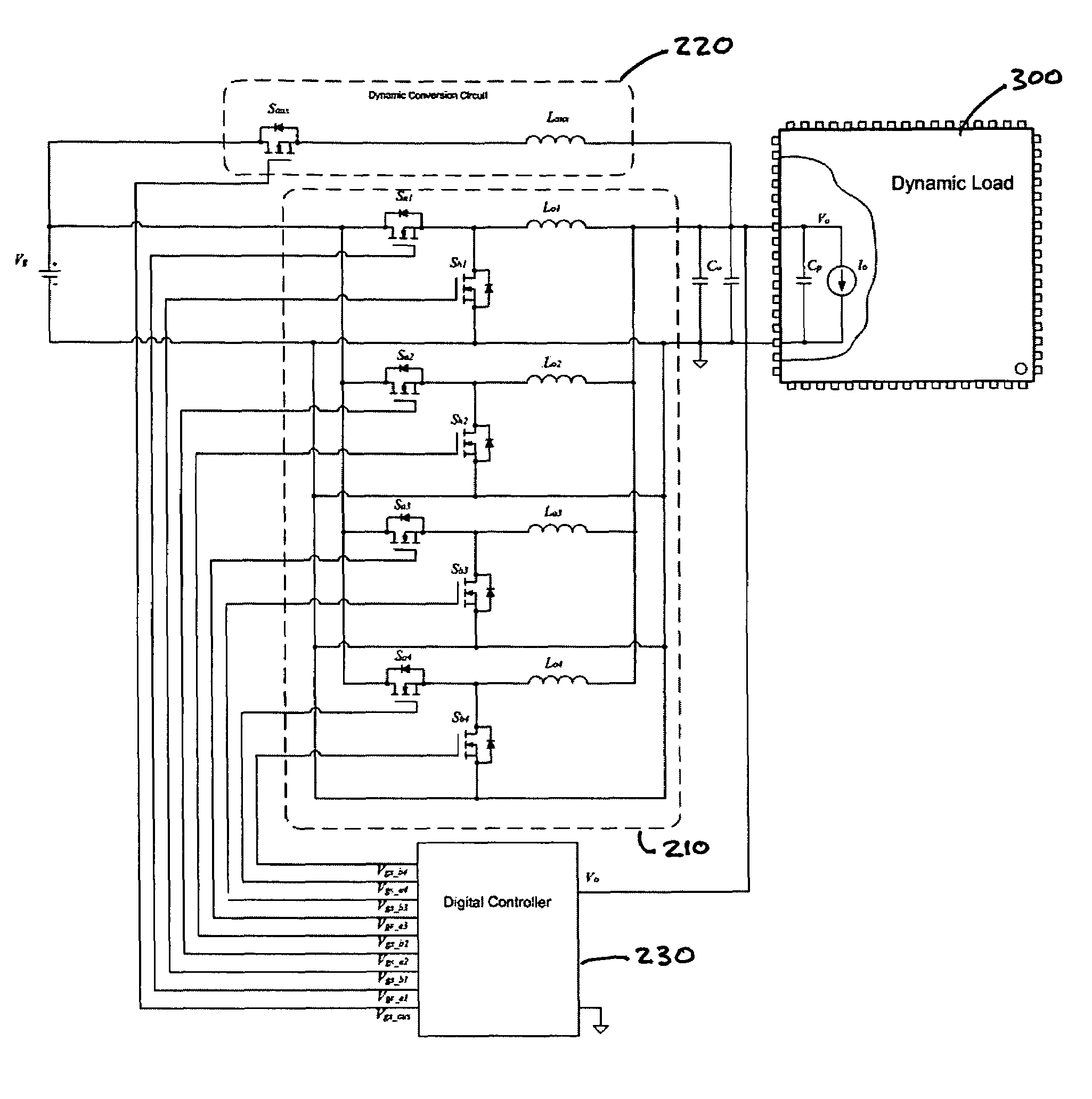
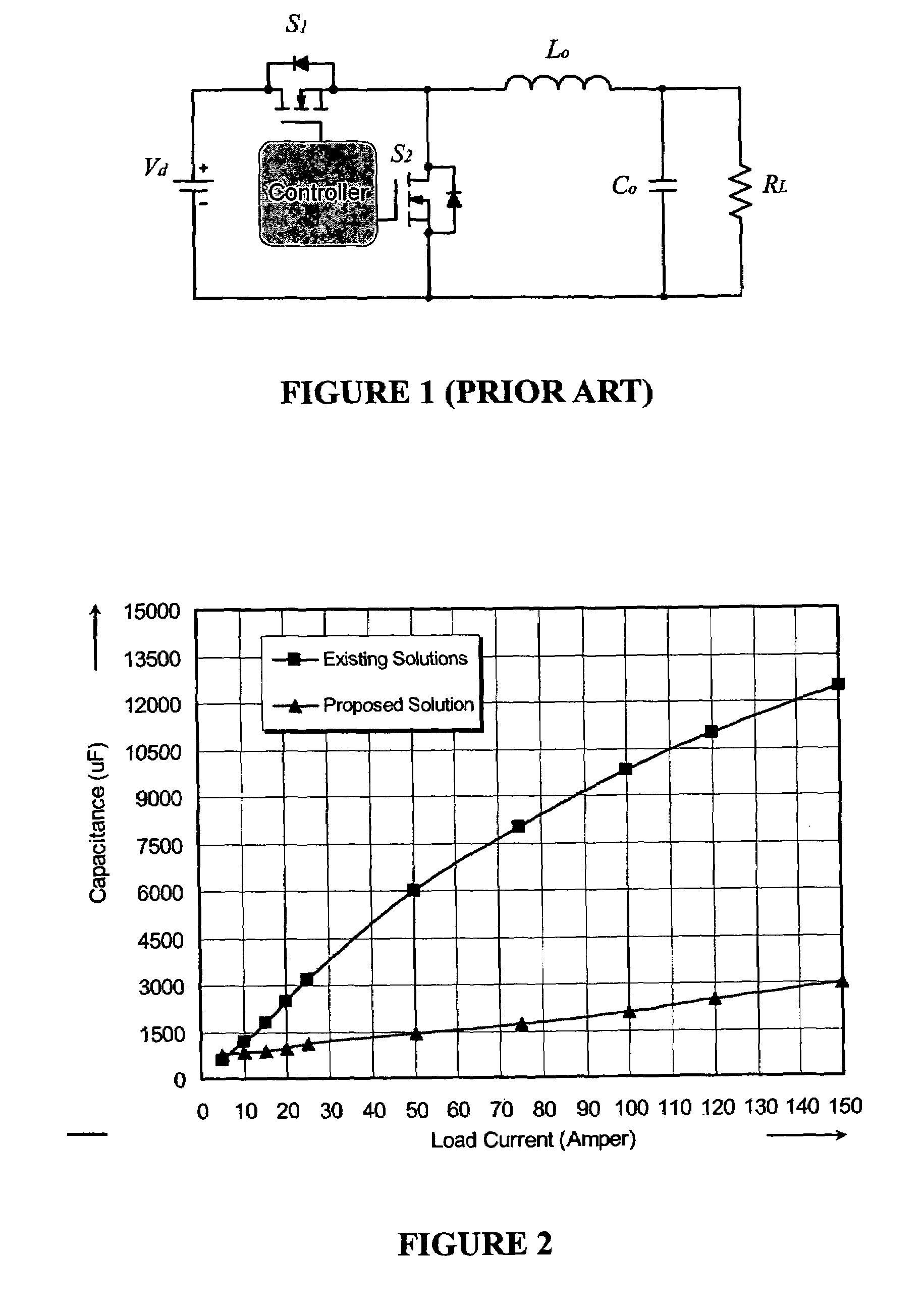
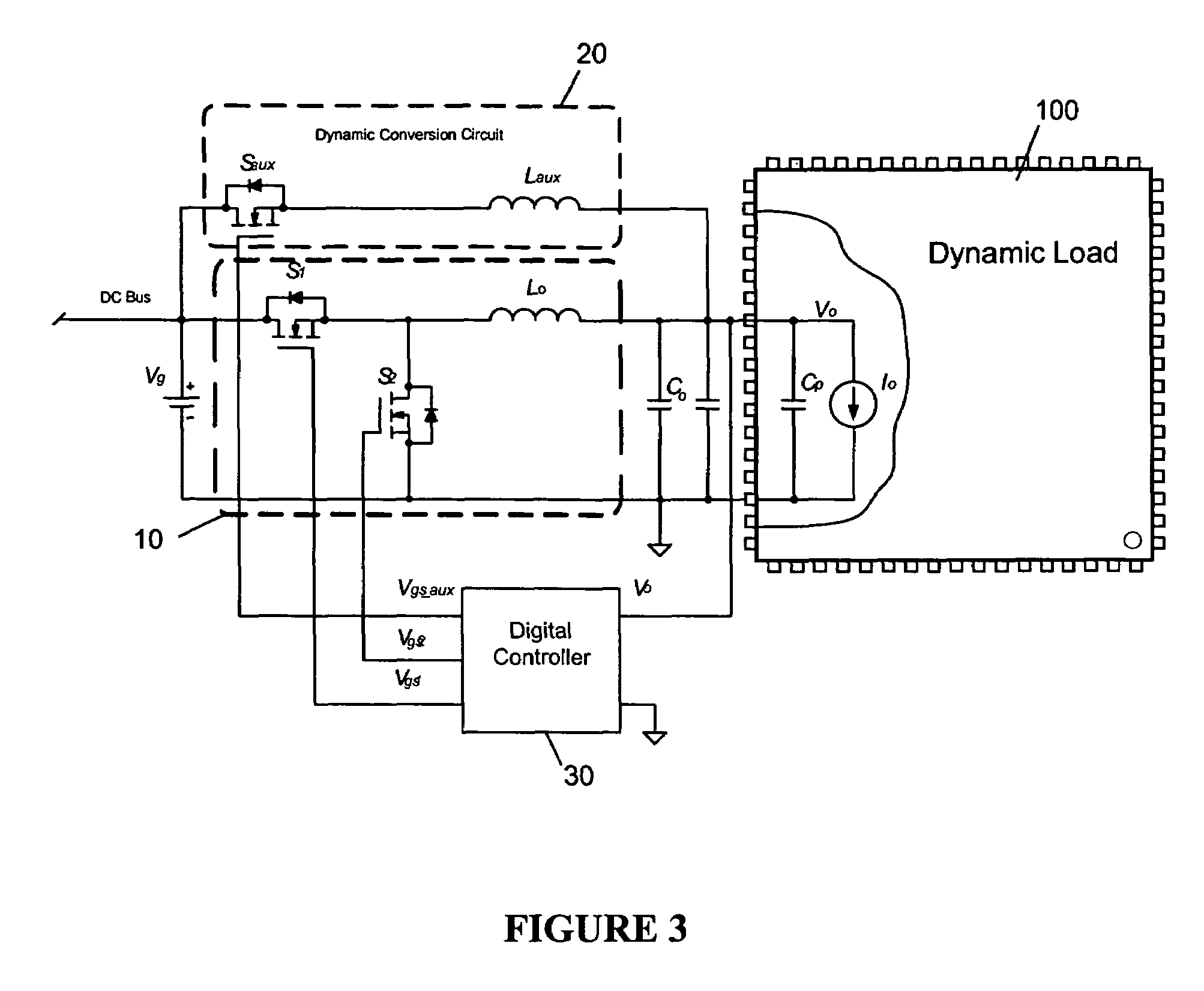
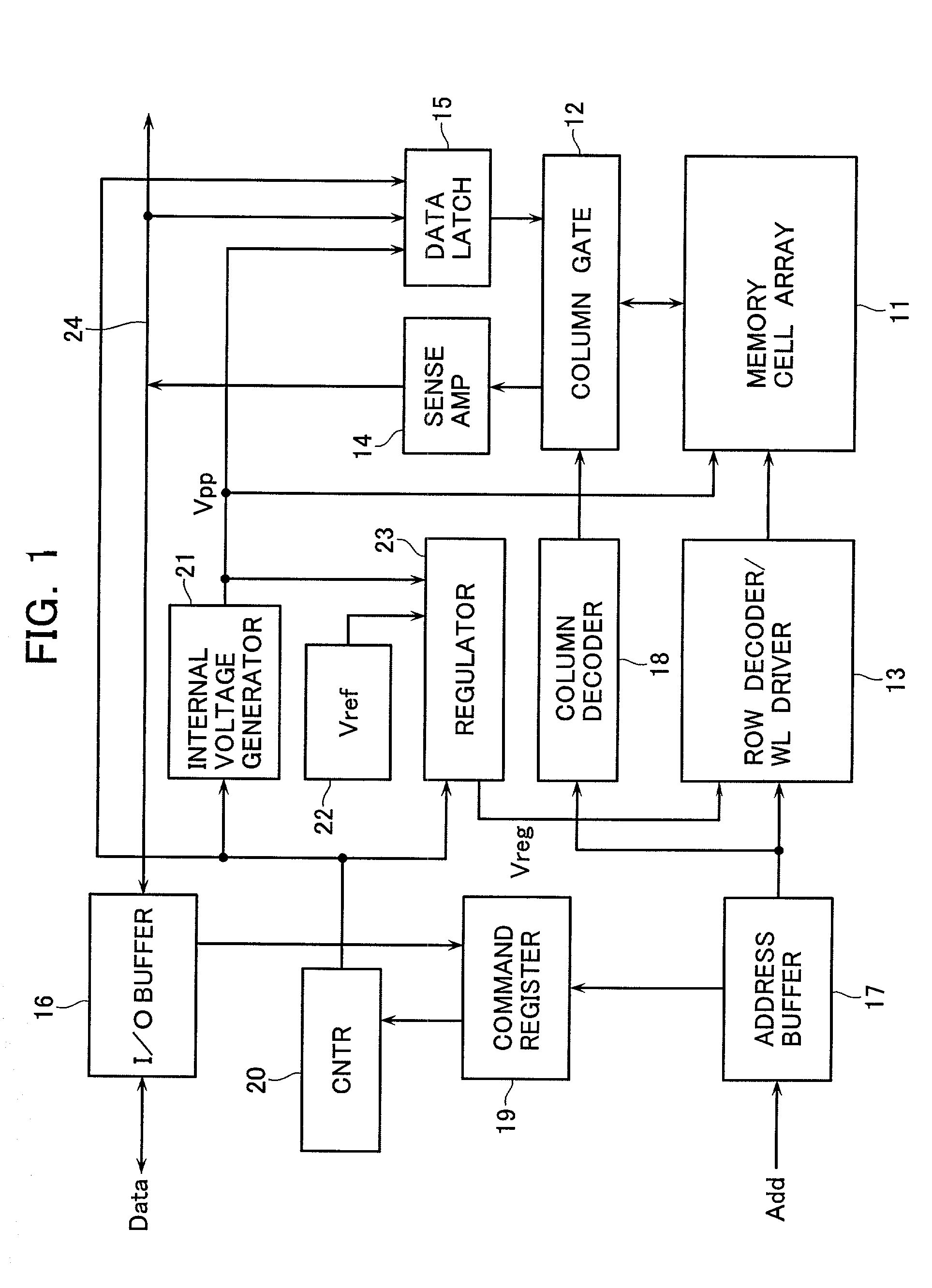
Digital controller for a voltage regulator module
A digital controller for a voltage regulator module (VRM) having single phase or multiphase power converters, and an optional dynamic conversion circuit, is disclosed. The digital controller improves the transient response of the VRM during harsh load current transients, and permits a substantial reduction in output capacitance of the VRM. When used with multiphase interleaved power converters, for a given load current requirement, the digital converter permits the number of interleaved phases of the VRM to be minimized. A VRM with the digital controller demonstrates low cost, high power density, high efficiency, and fast transient response.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
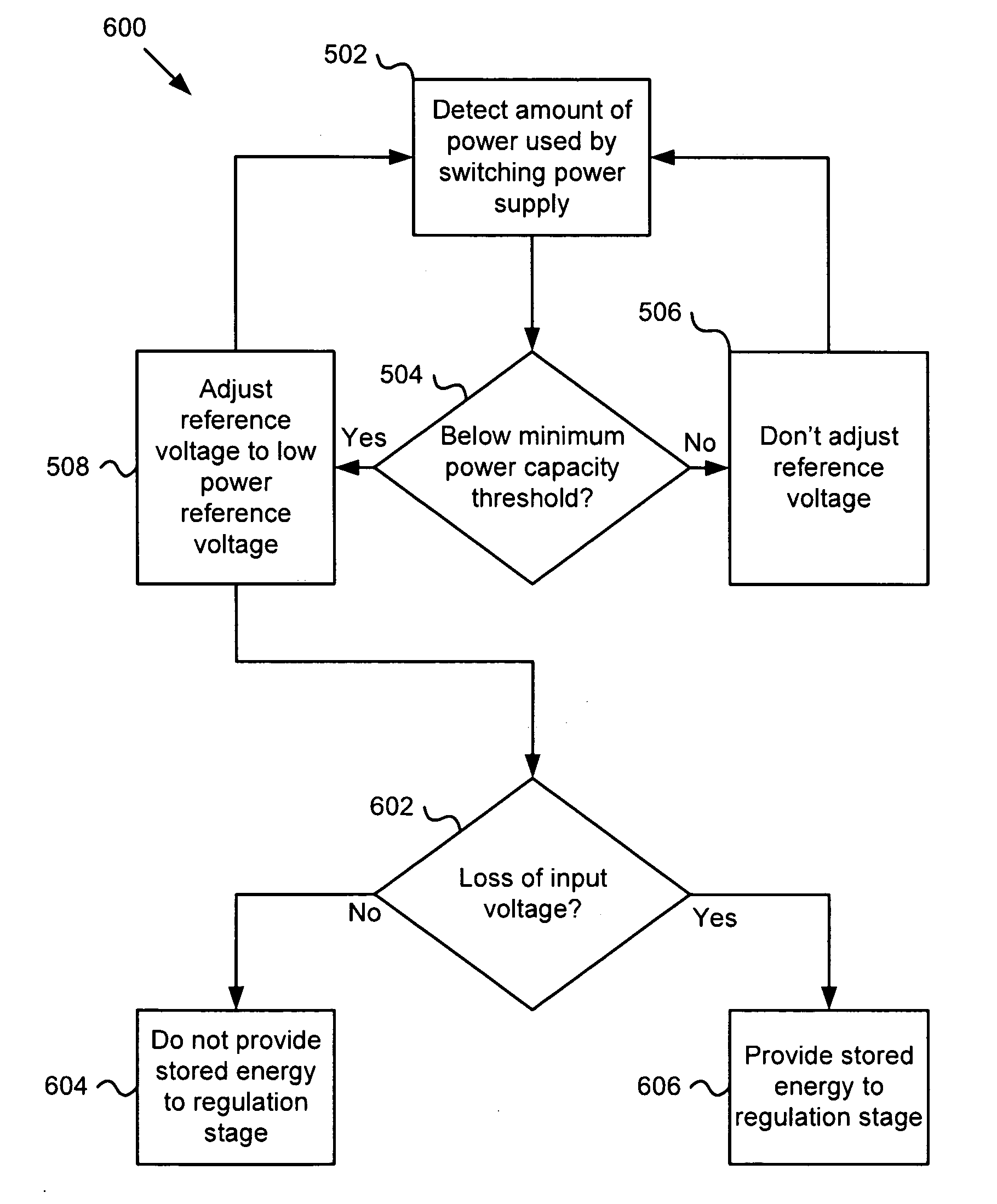
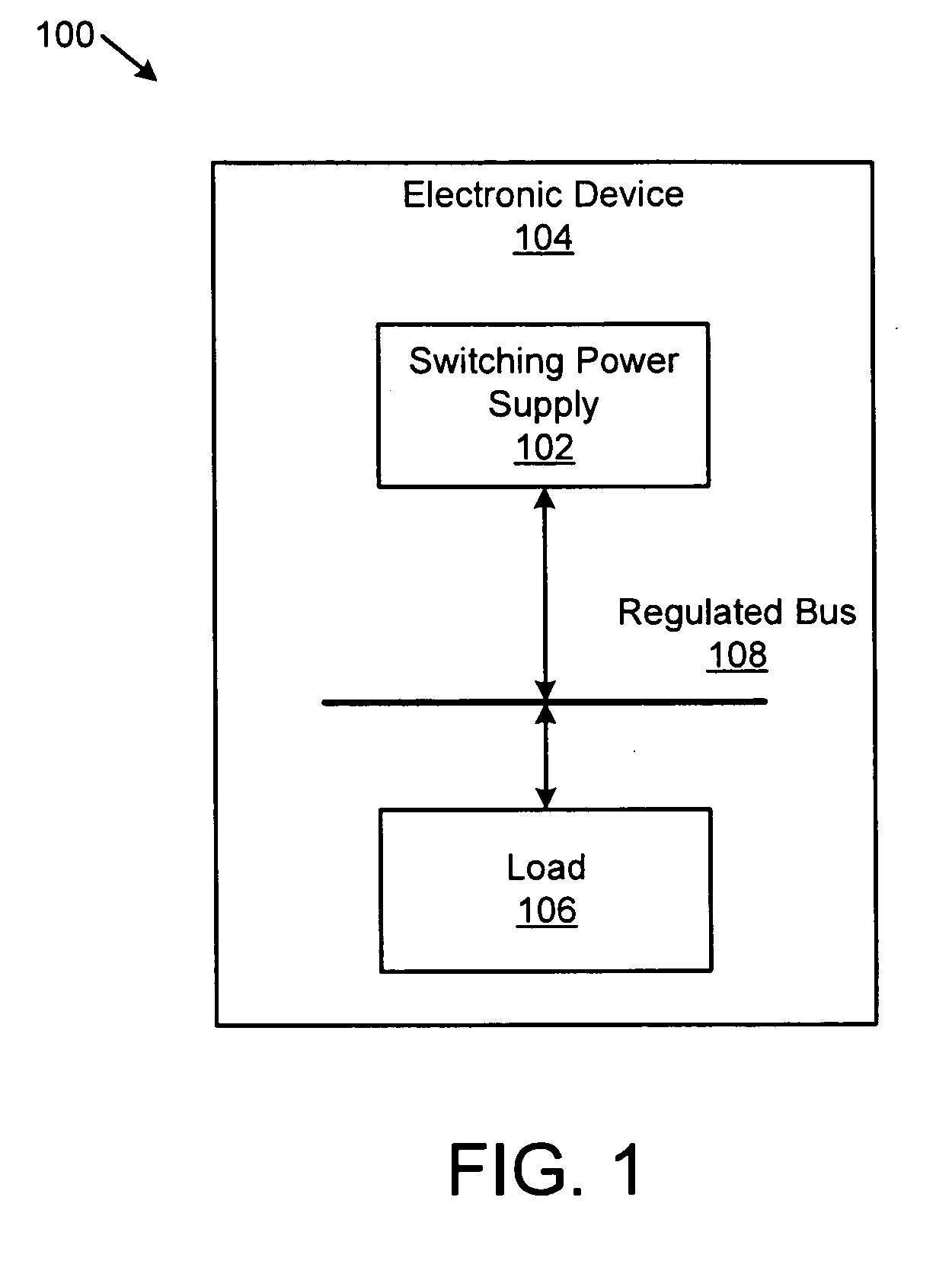
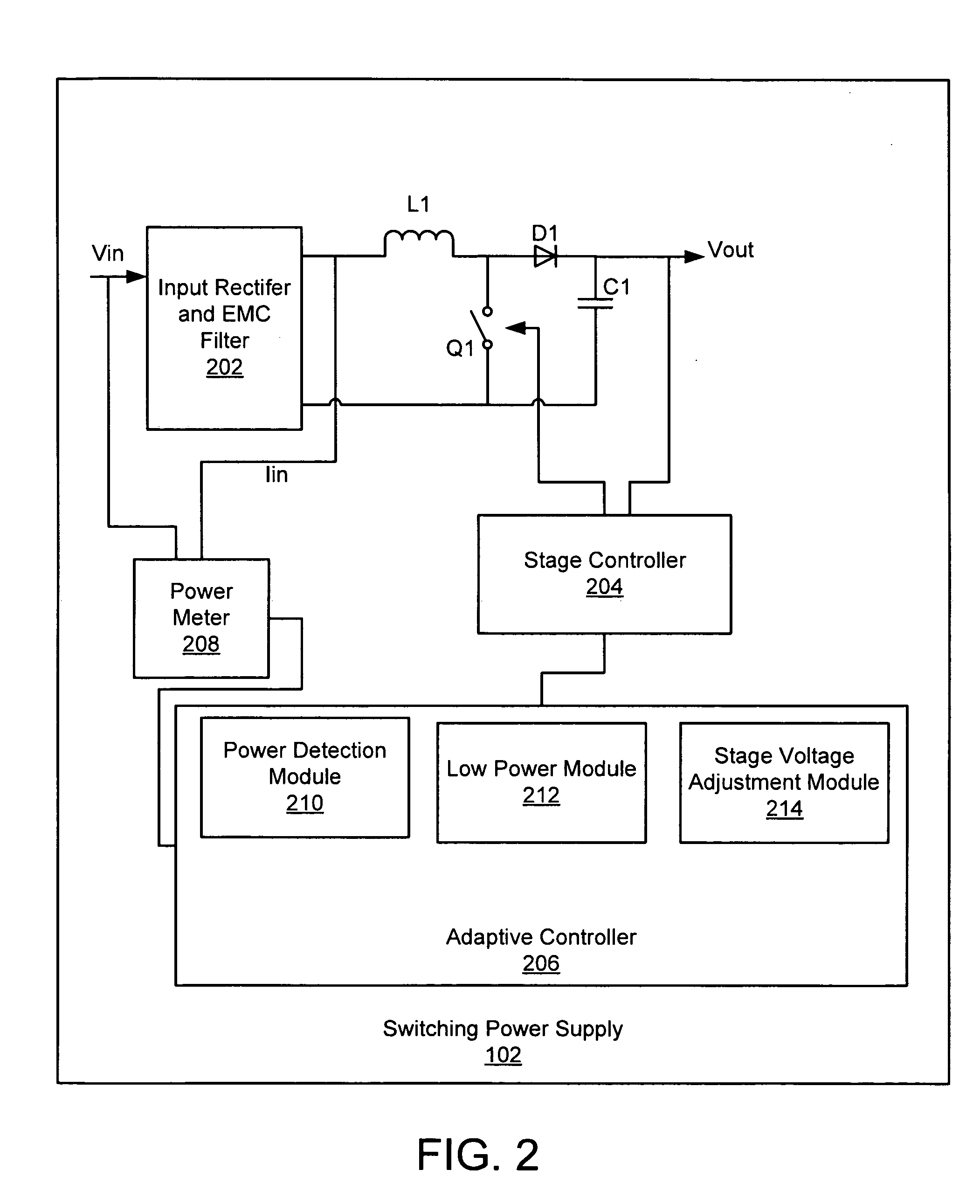
Apparatus, system, and method for an adaptive high efficiency switching power supply
ActiveUS20090237057A1Easy to operateEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionVoltage regulator moduleVoltage regulation
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for an adaptive high efficiency switching power supply. The switching power supply has a regulation stage with a stage controller that operates to regulate a voltage of the regulation stage relative to a reference voltage. A power detection module detects an amount of power used by the switching power supply. A low power module determines if the power supply is operating below a minimum power capacity threshold. A stage voltage adjustment module adjusts the reference voltage from a high power reference voltage to a low power reference voltage in response to the low power module determining that the power supply is operating below the minimum power capacity threshold. The low power reference voltage causes a regulated voltage adjustment such that the switching power supply operates more efficiently below the minimum power threshold.
Owner:IBM CORP
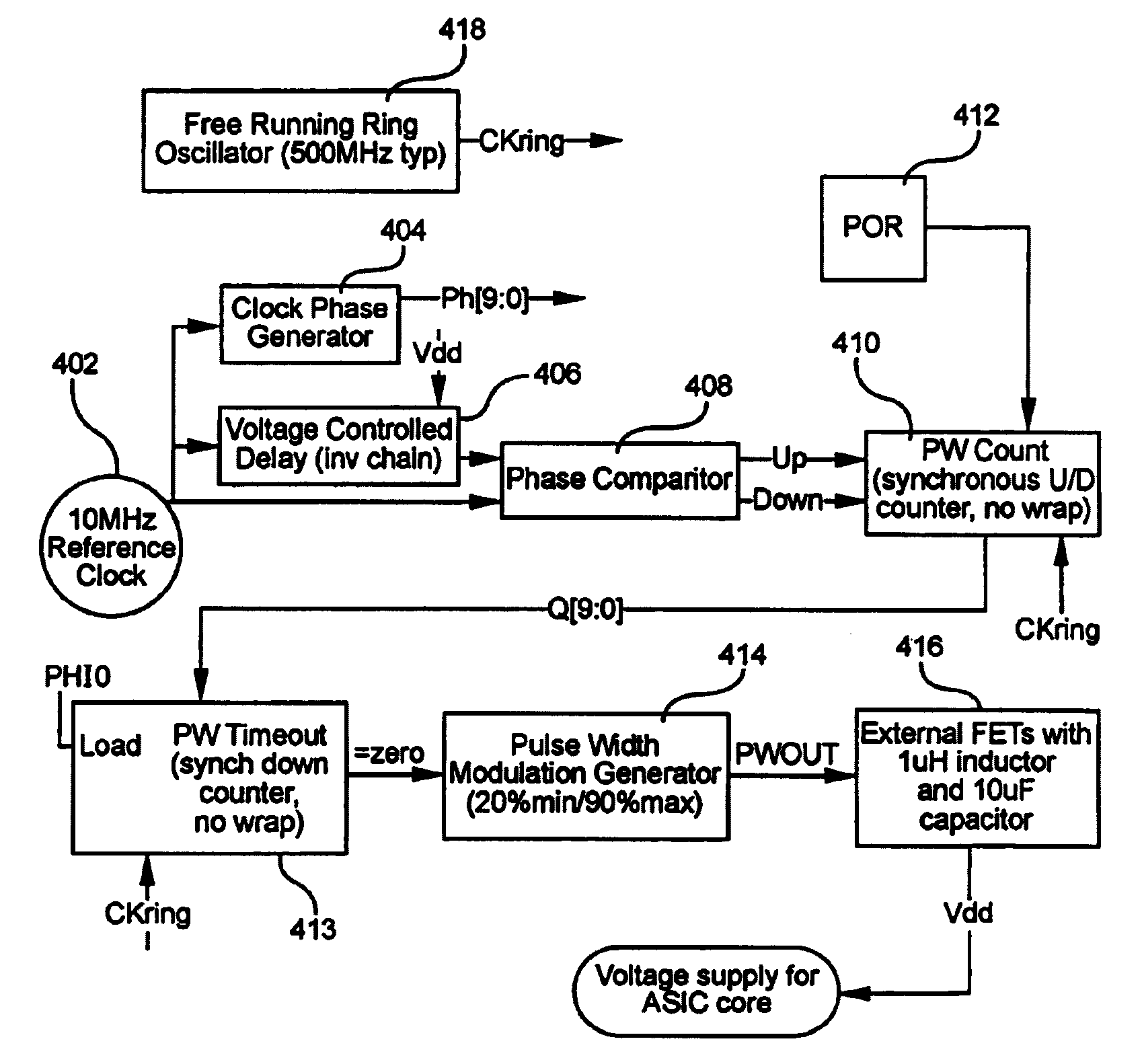
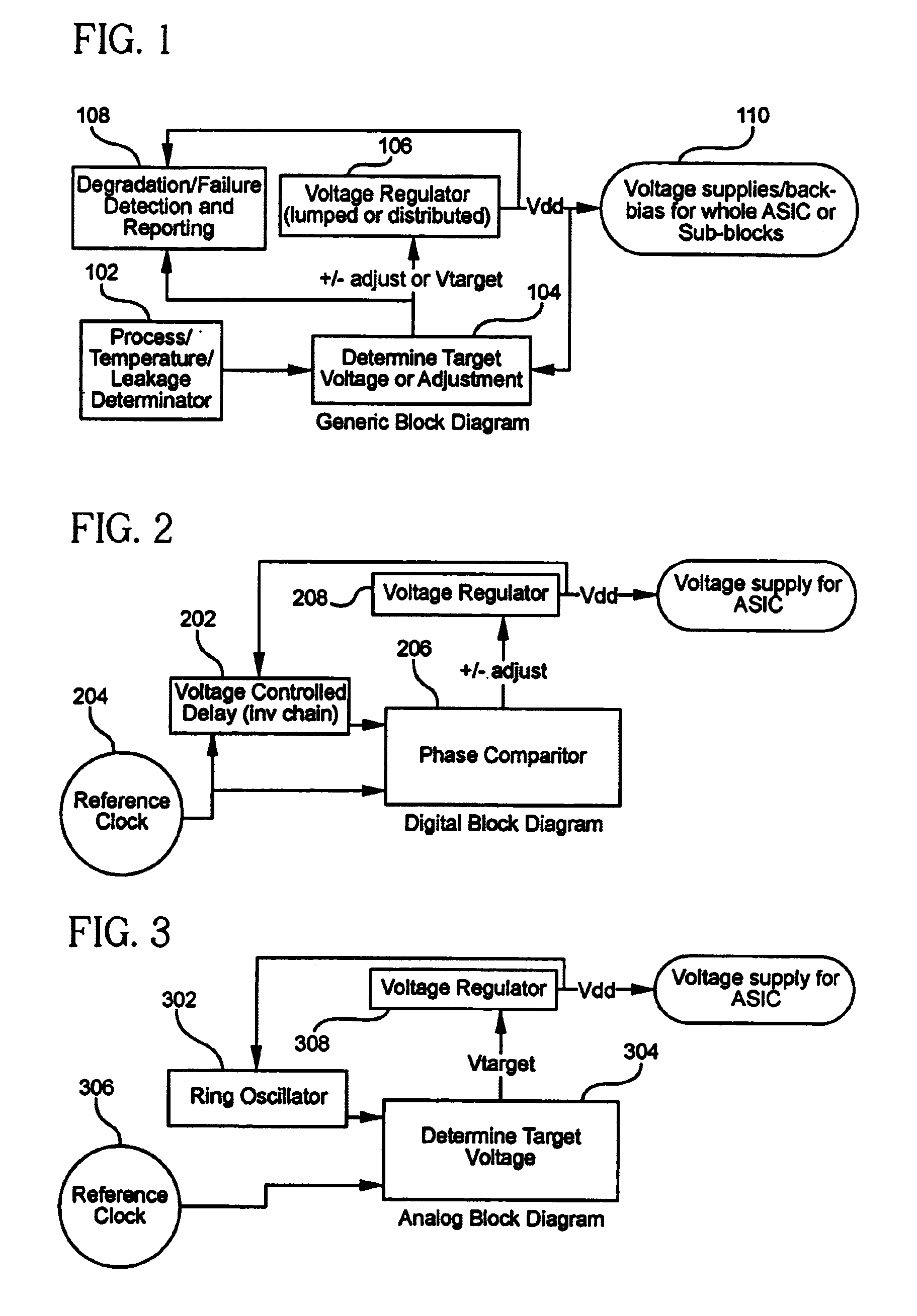
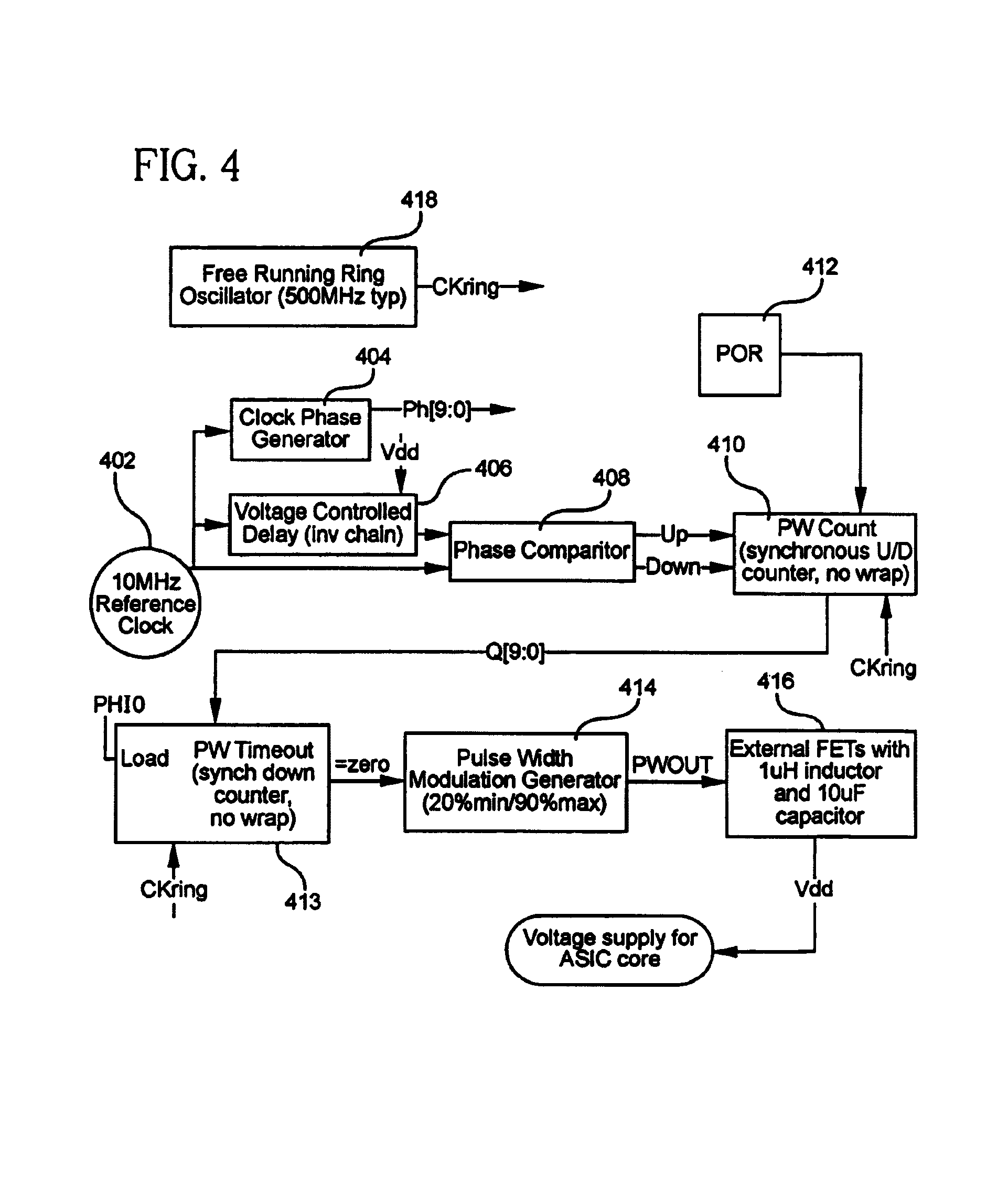
On-chip compensation control for voltage regulation
InactiveUS7075276B2Pulse automatic controlEfficient power electronics conversionVoltage regulator moduleControl signal
Manufacturing and / or operational variations that affect performance of an integrated circuit (IC) are at least partially compensated for, by determining the magnitude of these variations and providing one or more corresponding control signals to a voltage regulator, which, responsive thereto, increases or decreases the magnitude of the output voltage. The output voltage of the voltage regulator is typically provided to a power supply node of the IC. Similarly, the output of the voltage regulator may be provided to a substrate portion of the IC, so as to provide a substrate bias that is variable in response to changes in the performance of the IC. In various embodiments, a determination of the magnitude of the variations is made by comparing the performance of a digital delay circuit or a ring oscillator to a reference clock; speed characterization of the IC may be obtained from the voltage regulator control signals; and information regarding reliability degradation of the IC may be obtained from the control signals that are generated for control of the voltage regulation circuitry.
Owner:INNOTECH SYST
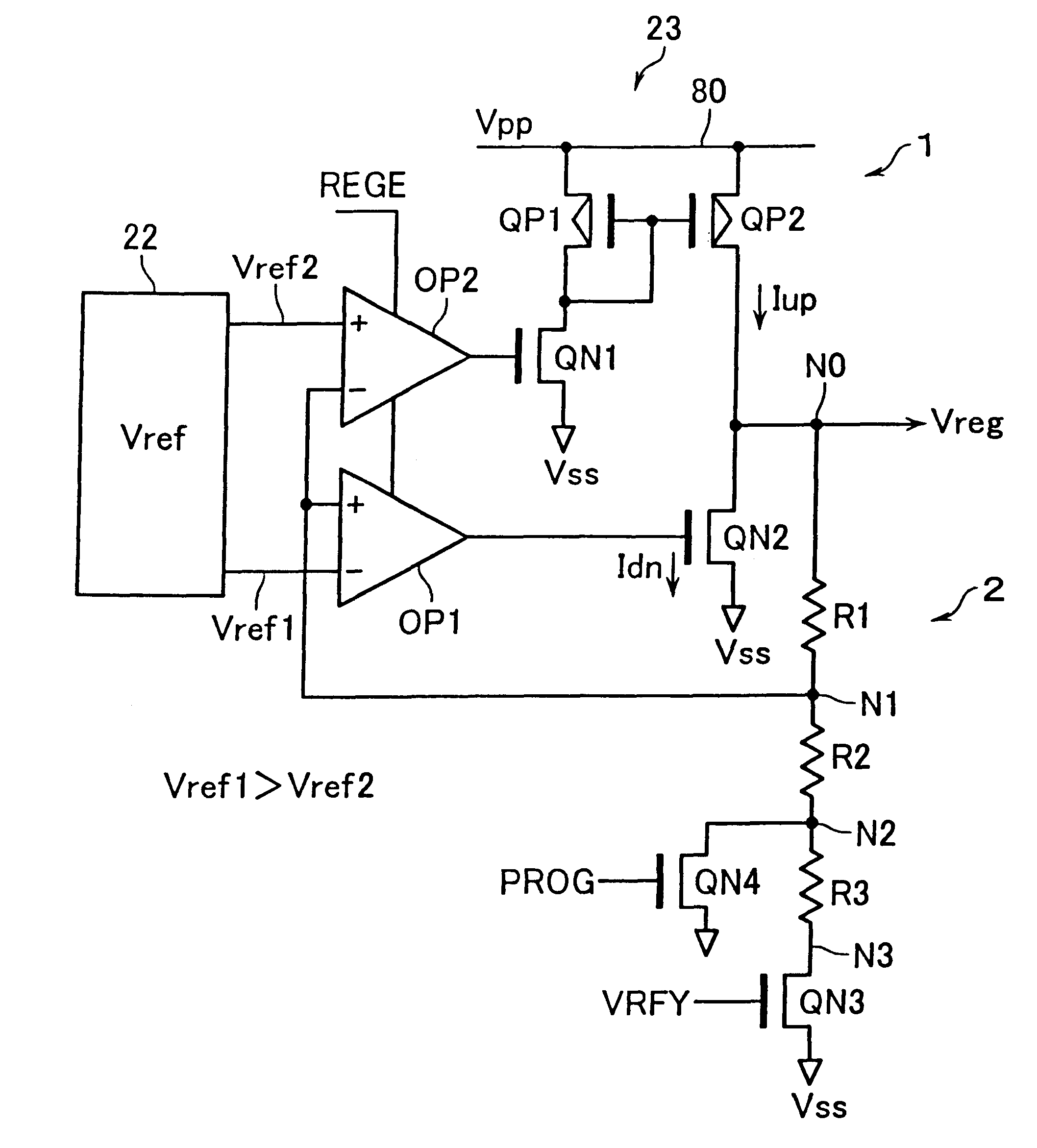
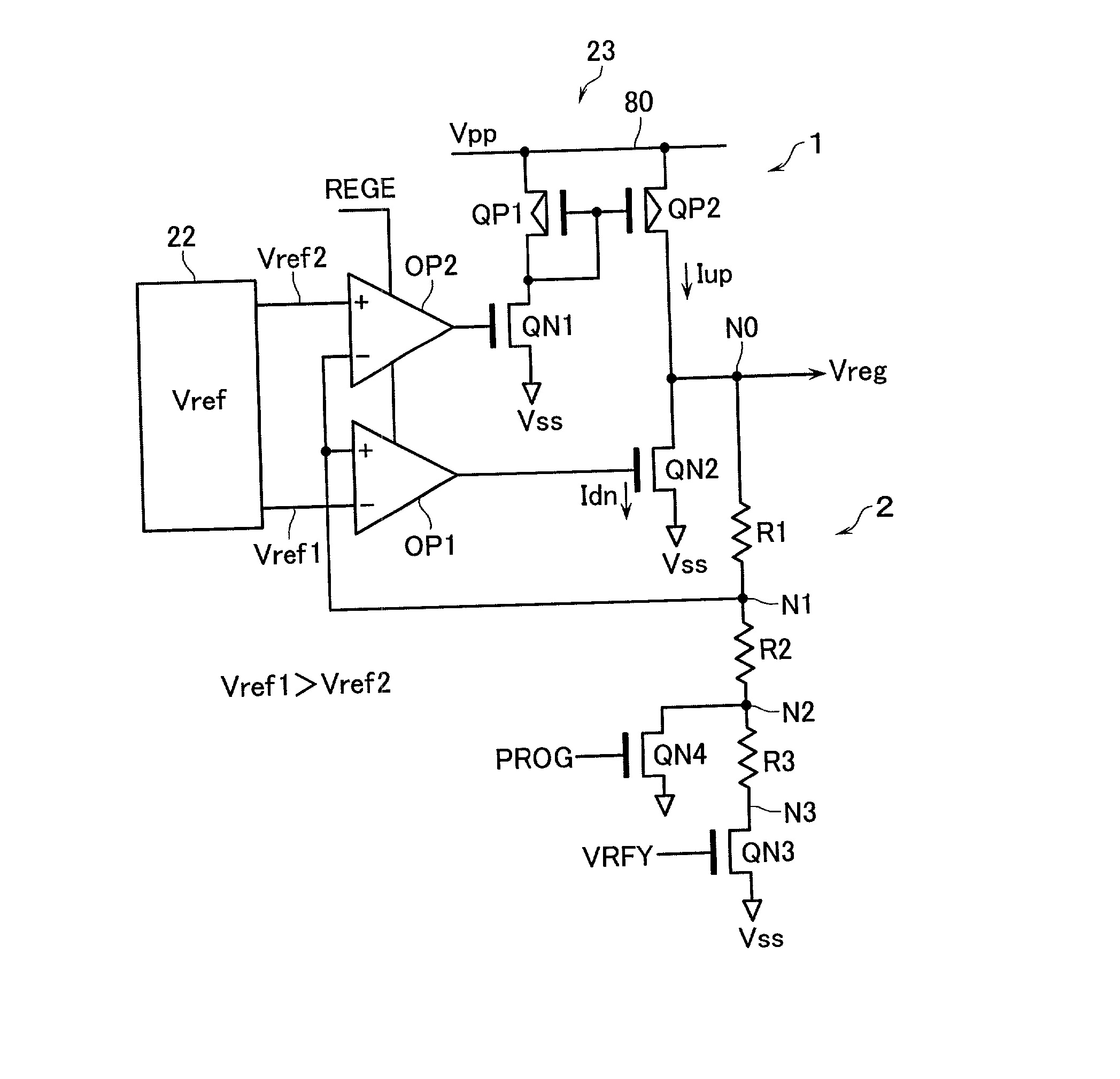
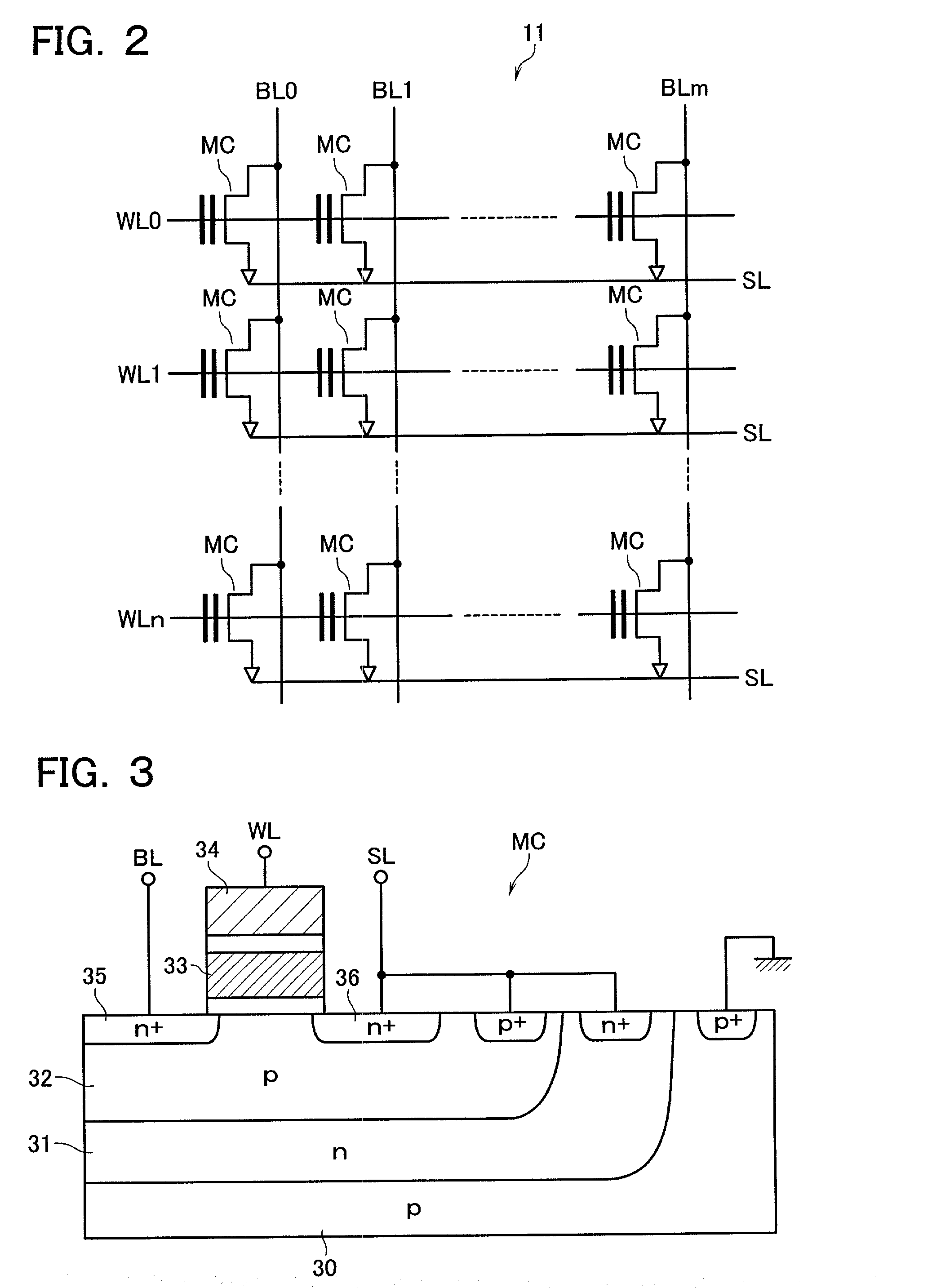
Semiconductor device with a voltage regulator
InactiveUS6600692B2Solid-state devicesRead-only memoriesVoltage regulator moduleAudio power amplifier
A semiconductor device with a voltage regulator is disclosed. The voltage regulator includes: a driver including pull-up and pull-down transistors serially connected between an output node of an internal voltage generation circuit and a reference potential terminal, for outputting a regulated voltage at its regulated voltage output node corresponding to the connection node of the pull-up and pull-down transistors; a voltage divider circuit for subdividing the regulated voltage output to the regulated voltage output node; a first operational amplifier for controlling current drivability of the pull-down transistor in accordance with a difference between a first reference voltage and a divided output of the voltage divider circuit; and a second operational amplifier for controlling current drivability of the pull-up transistor in accordance with a difference between a second reference voltage and the divided output of the voltage divider circuit in such a way as to vary in a reverse direction to the current drivability of the pull-down transistor.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Semiconductor device with a voltage regulator
InactiveUS20020118568A1Solid-state devicesRead-only memoriesVoltage regulator moduleAudio power amplifier
A semiconductor device with a voltage regulator is disclosed. The voltage regulator includes: a driver including pull-up and pull-down transistors serially connected between an output node of an internal voltage generation circuit and a reference potential terminal, for outputting a regulated voltage at its regulated voltage output node corresponding to the connection node of the pull-up and pull-down transistors; a voltage divider circuit for subdividing the regulated voltage output to the regulated voltage output node; a first operational amplifier for controlling current drivability of the pull-down transistor in accordance with a difference between a first reference voltage and a divided output of the voltage divider circuit; and a second operational amplifier for controlling current drivability of the pull-up transistor in accordance with a difference between a second reference voltage and the divided output of the voltage divider circuit in such a way as to vary in a reverse direction to the current drivability of the pull-down transistor.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
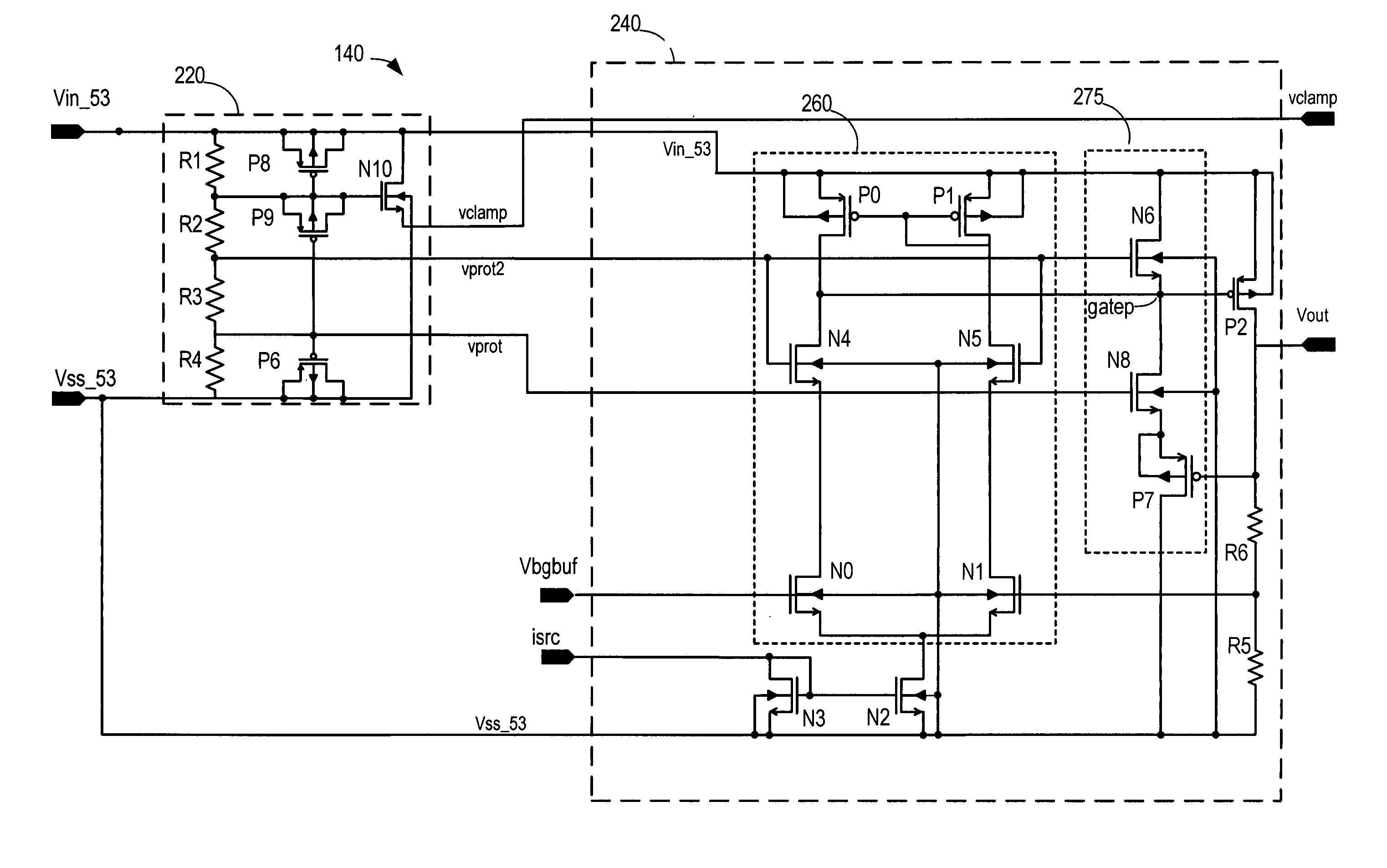
Voltage regulator using protected low voltage devices
ActiveUS7164561B2Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingVoltage regulator moduleLow voltage
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Systems, apparatus and method for reducing dust on components in a computer system
InactiveUS7113402B2Digital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityVoltage regulator module
An apparatus and method for reducing dust on components in a computer system is disclosed. Embodiments include a system that generally includes an enclosure, a component mounted with the enclosure, and a fan adapted to induce an airflow towards the component to provide cooling. The system also generally includes a dust ionizer adapted to provide an electrical charge to dust particles within the airflow and a dust reflector having an electrical charge adapted to deflect the charge dust particles away from the component. In some embodiments, the component may be a processor, heat sink, video chip, memory module, voltage regulator module, etc.
Owner:LENOVO (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Pixel circuit, organic electroluminescent display panel and display device
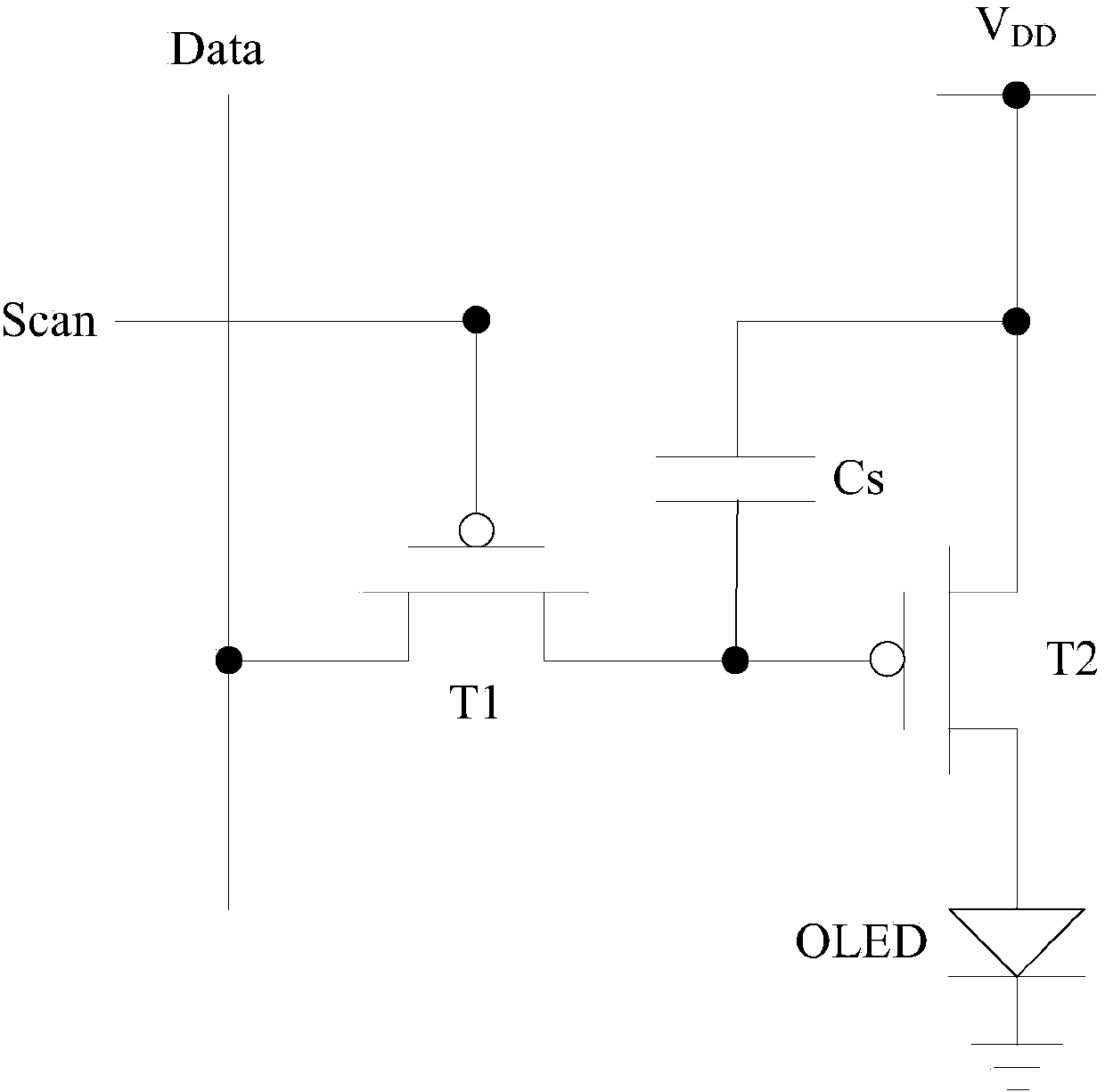
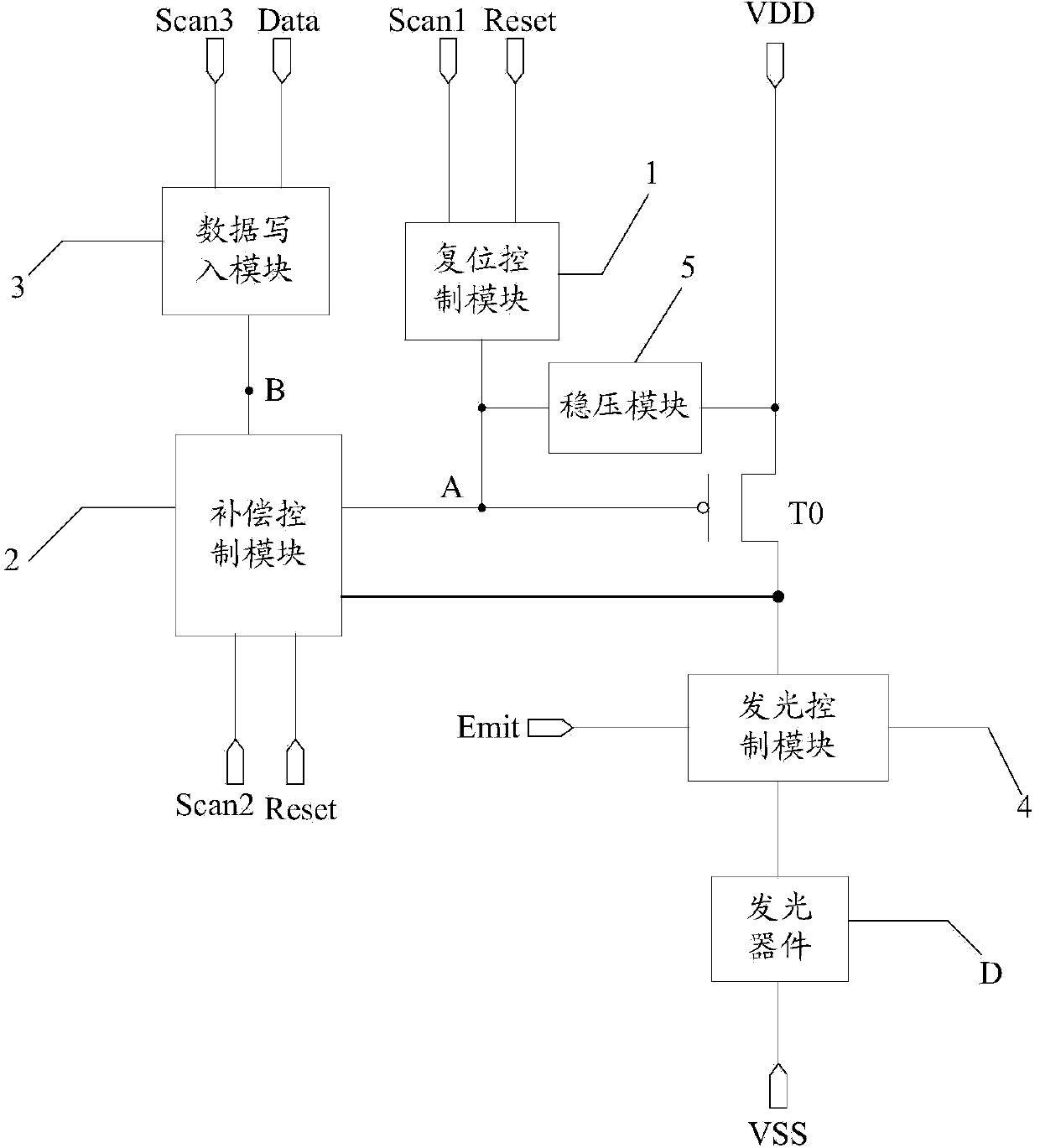
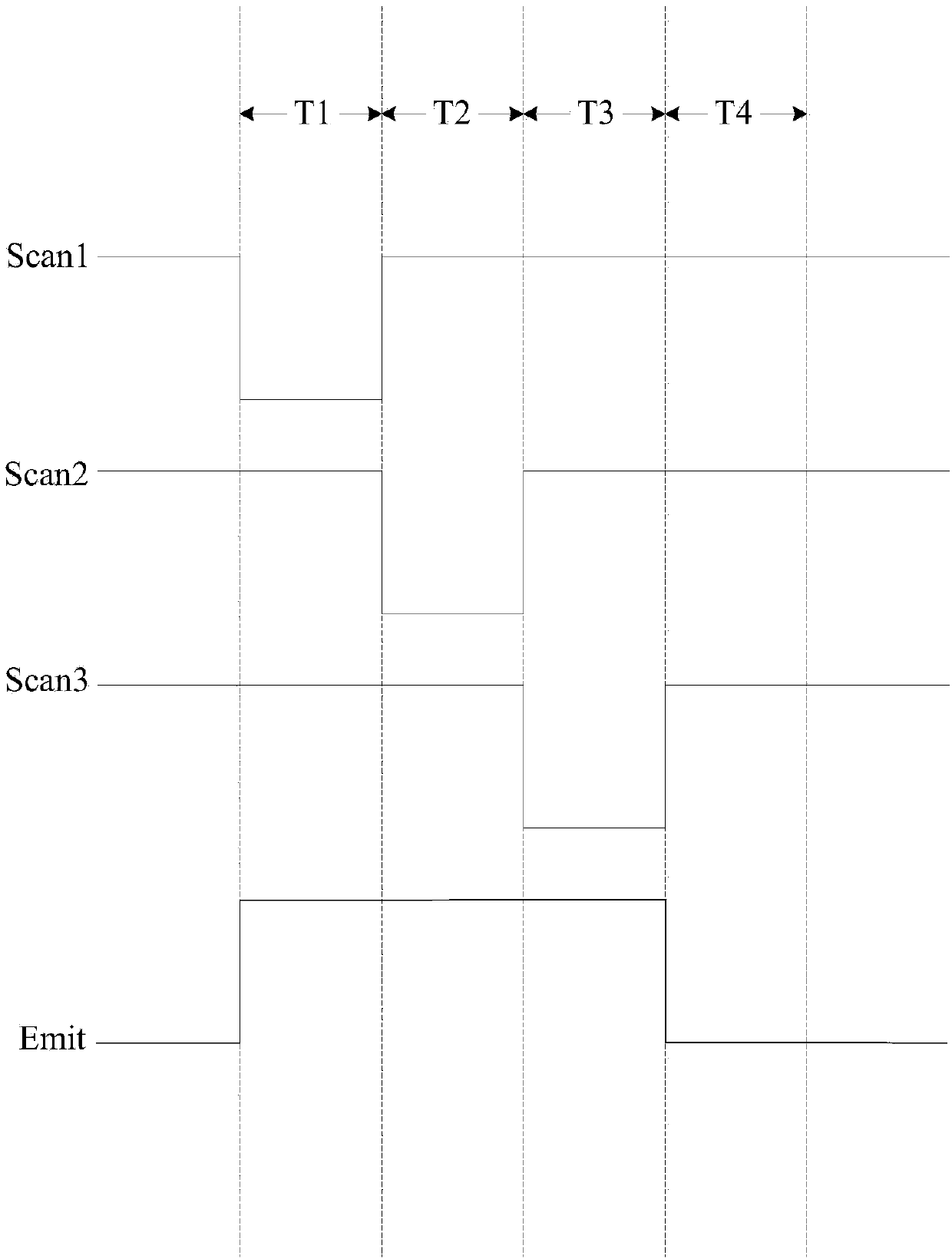
InactiveCN104217682AImprove uniformityAvoid influenceStatic indicating devicesVoltage regulator moduleData signal
The invention discloses a pixel circuit, an organic electroluminescent display panel and a display device, which comprise a driving transistor, a light-emitting device, a reset control module, a compensation control module, a data writing module, a light emission control module and a voltage regulator module. Due to the fact that the compensation control module in a pixel device is capable of compensating drift of a threshold voltage, working currents for driving the light-emitting device to light in the driving transistor is made to be only related to voltage of a data signal and a reset signal regardless of the threshold voltage and a second voltage source. As a result, effects of the threshold voltage and resistance drop on currents flowing through the light-emitting device are avoided, the working currents for driving the light-emitting device to light are consistent, and uniformity of brightness of the image in a display area of the display device is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI TIANMA AM OLED +1
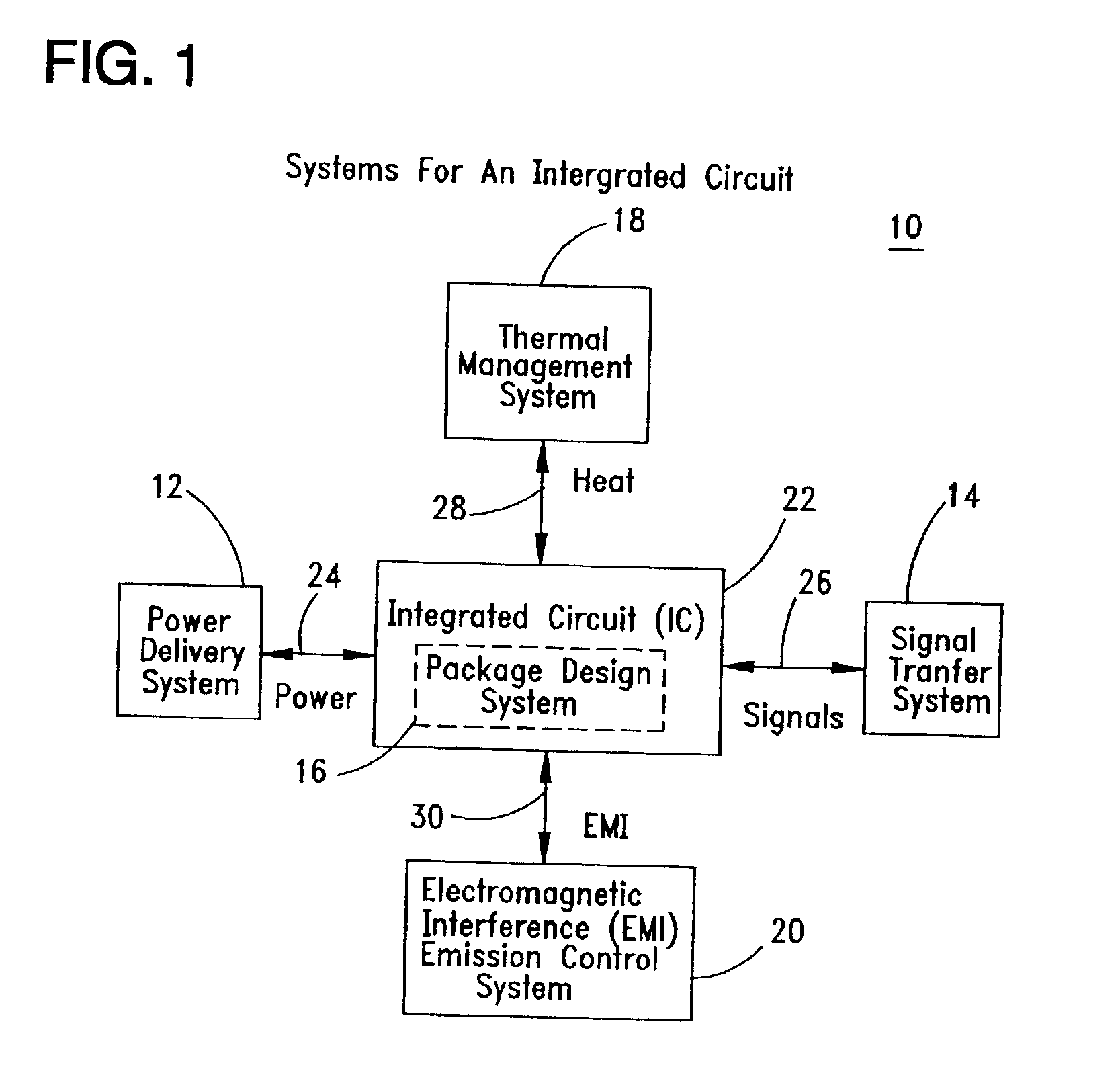
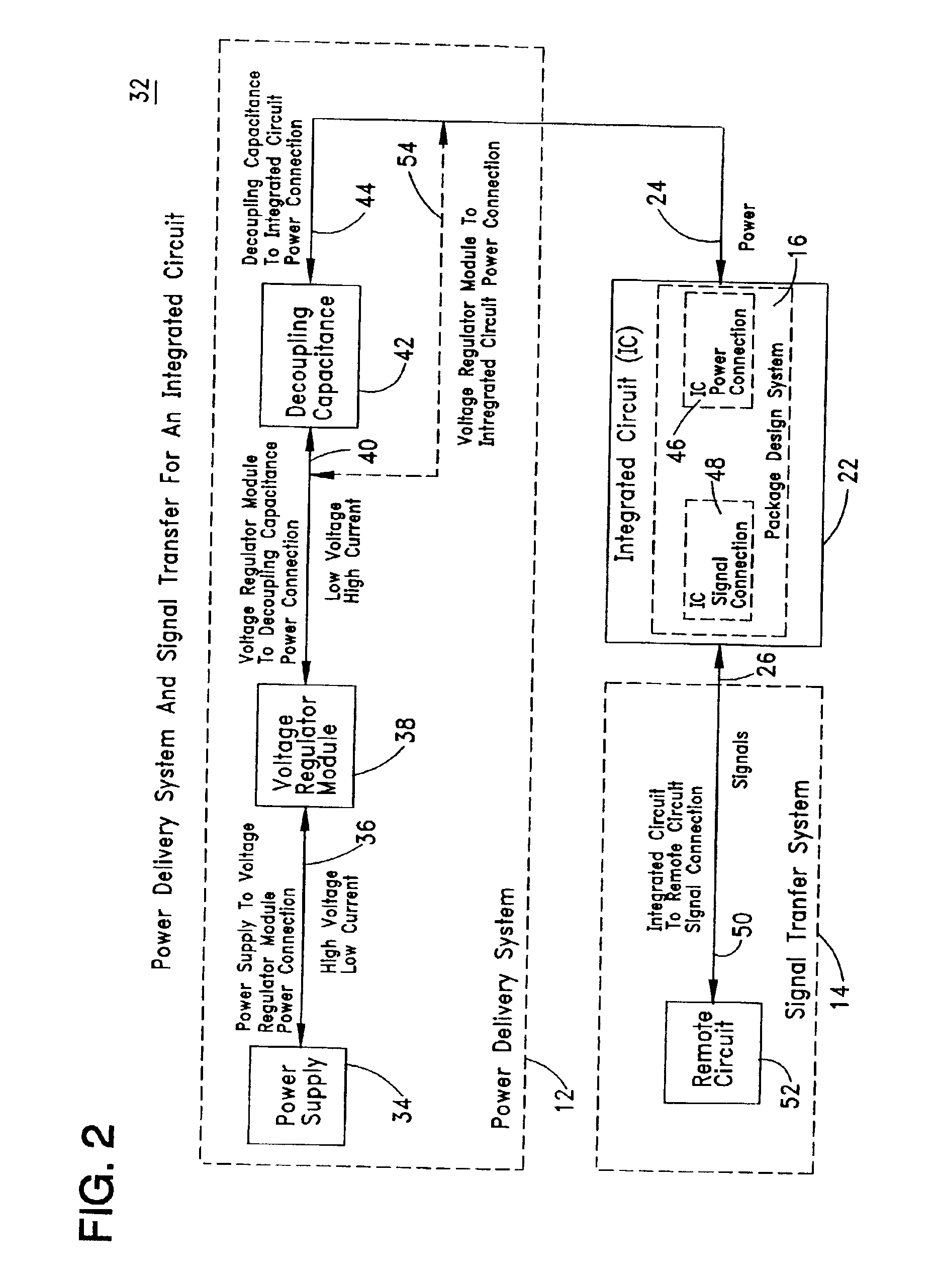
Power delivery and other systems for integrated circuits
InactiveUS6885563B2Reduce in quantityLittle strengthElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVoltage regulator moduleCapacitance
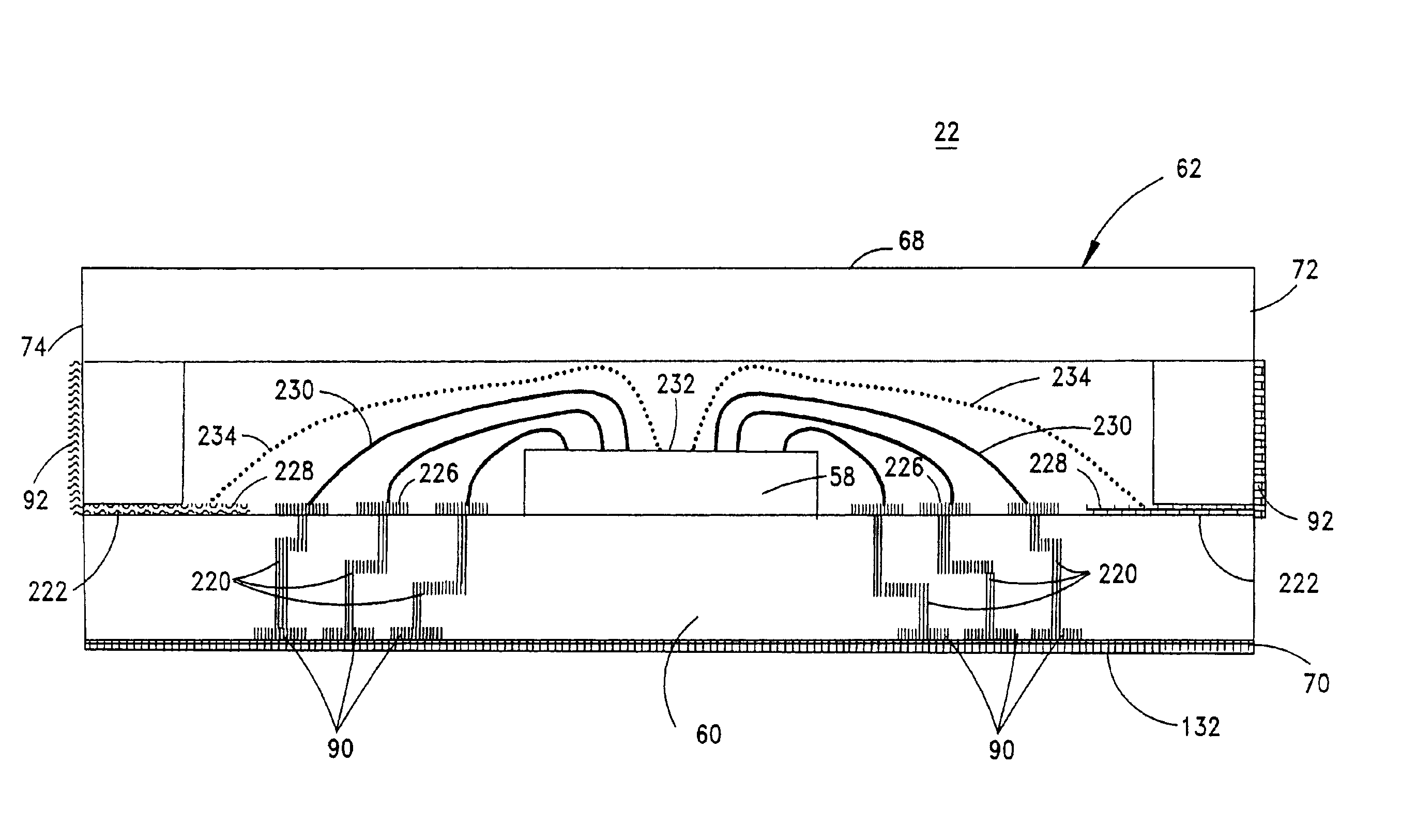
Systems for power delivery, signal transfer, package design, thermal management, and electromagnetic interference (“EMI”) control are provided to support an integrated circuit (“IC”). The power delivery system includes a power supply, a voltage regulator module and a decoupling capacitance in the form of discrete and / or integral capacitors. The voltage regulator module and decoupling capacitance are located in a connector that may be formed as a cover, socket or a frame for the IC. The power delivery system delivers power to the IC along top, bottom or sides of the IC. The signal transfer system couples signals from the IC to one or more circuits on a circuit board. The package design system for the IC permits signals and / or power to be coupled to selected sides of the IC at connections outside, flush with, recessed or inside the IC package. The package design system also permits the transferred signals to have different frequencies, such as high and low frequencies, and to utilize different types of signal interfaces, such as galvanic, capacitive or the like. The thermal management system utilizes a heat sink, a fan and / or a heat spreader to dissipate heat generated by the IC and / or voltage regulator module. The EMI control system blocks EMI generated by the IC.
Owner:MOLEX INC
Power delivery to base of processor
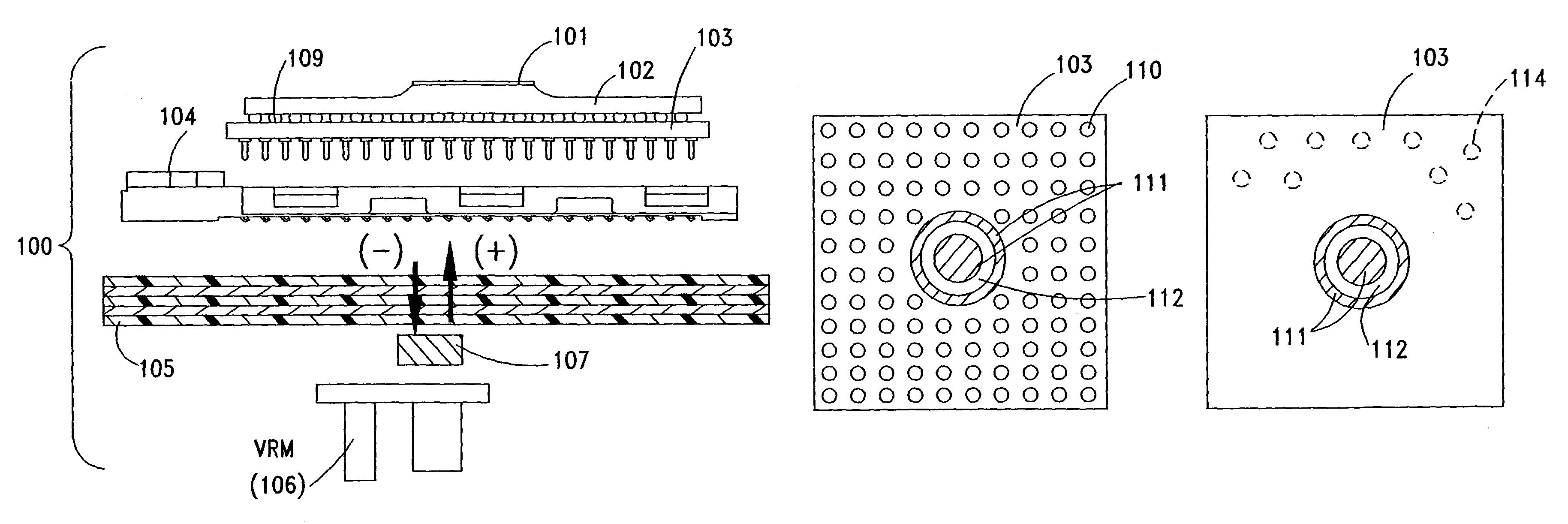
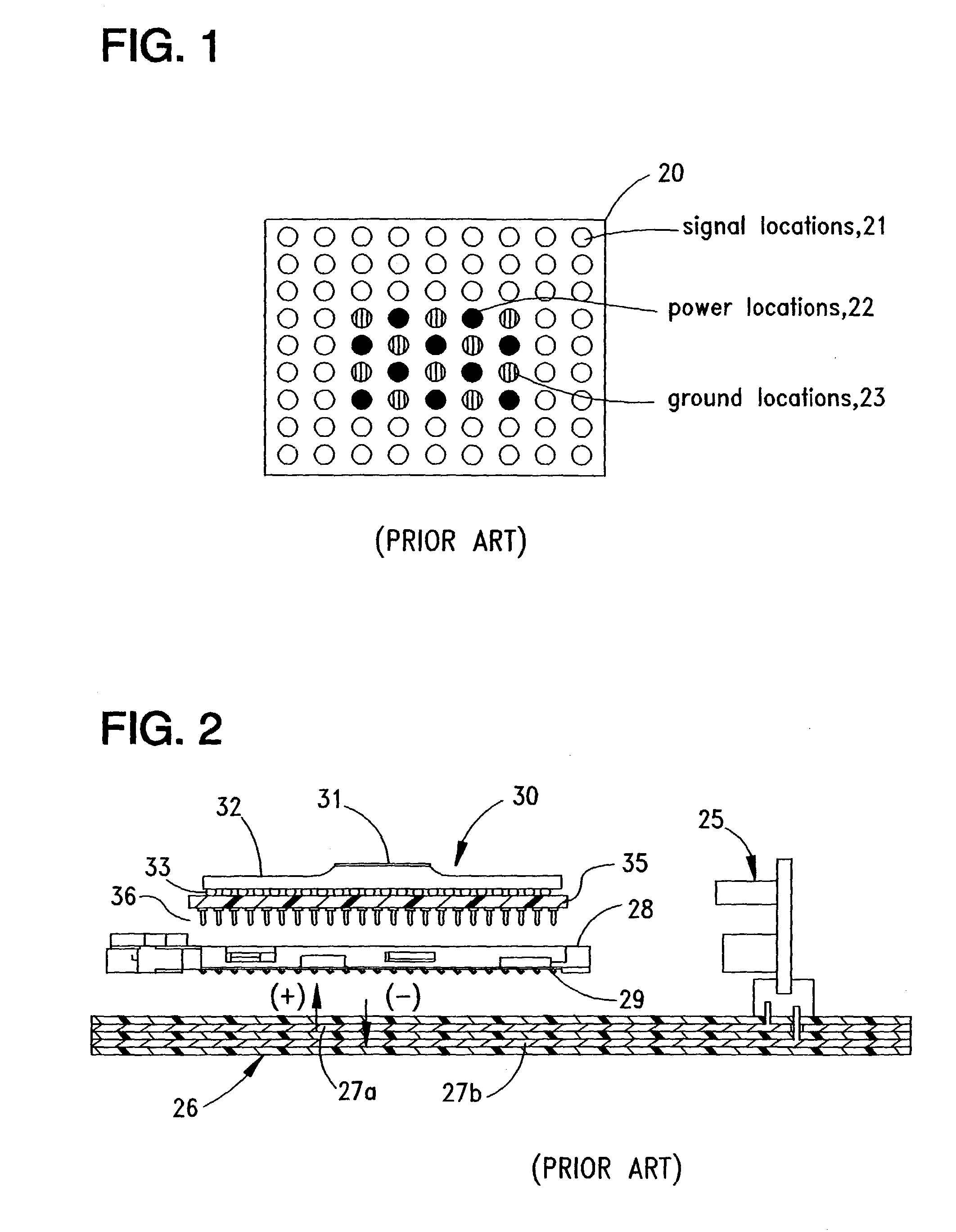
InactiveUS7095619B2Coupling for high frequencyPrinted circuit aspectsVoltage regulator moduleElectrical conductor
A processor mounted to a circuit board is provided with regulated voltage through lower-inductance circuit board traces by mounting a voltage regulator module for the processor, on the side of the circuit opposite to the processor. Current from the voltage regulator is provided to the processor by way of one or more conductors between the regulator and processor that extend through the circuit board from one side to the other. Inductance attributable to lead length is reduced by locating the voltage regulator close to its load. Circuit board space on the processor side of the circuit board is increased by moving the voltage regulator to the opposite side.
Owner:MOLEX INC
Current-source gate driver
ActiveUS20100019807A1Electronic switchingElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceVoltage regulator module
Provided is a current-source gate driver for use with a switching device having a gate capacitance, including an input terminal for receiving a DC voltage; a first switch connected between the input terminal and an output terminal; a second switch connected between the output terminal and a circuit common; a series circuit comprising a first capacitor and an inductor, the series circuit connected between the input terminal and the output terminal; wherein the gate capacitance of the switching device is connected between the output terminal and the circuit common. The current-source gate driver improves efficiency of the power switching devices of a voltage regulator module or other switching converter.
Owner:GANPOWER SEMICON FOSHAN CO LTD
Hot plug control of MP based computer system
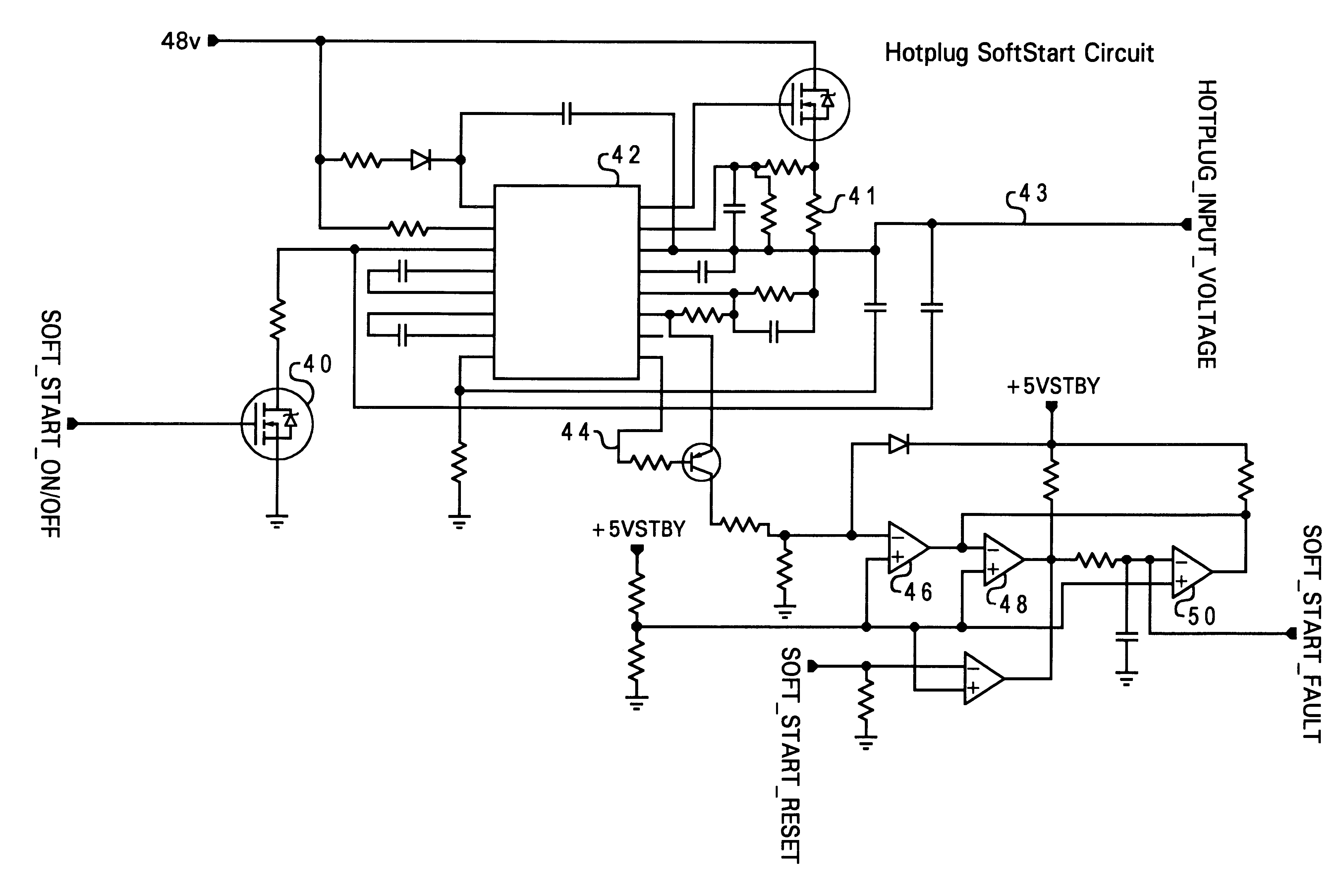
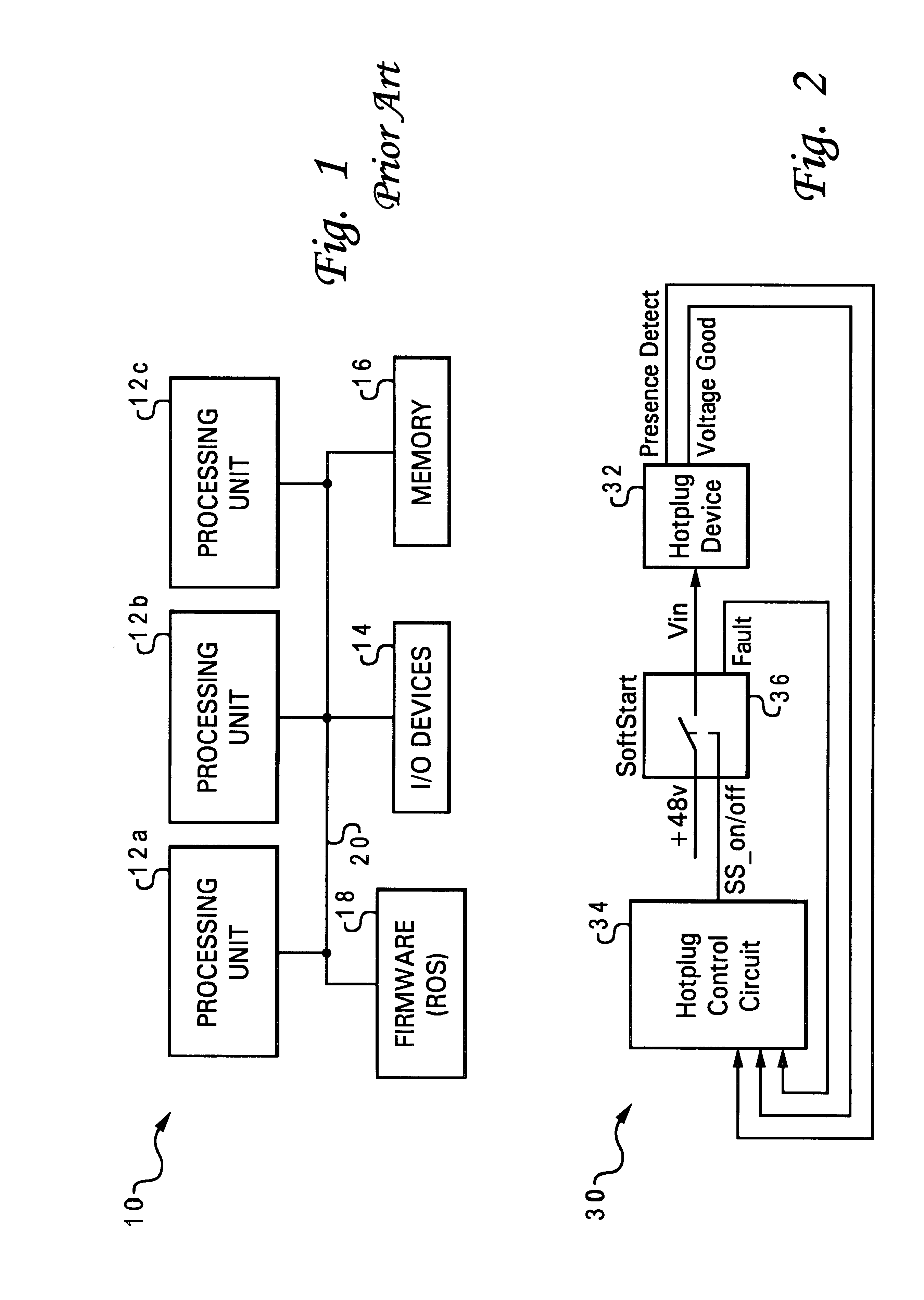
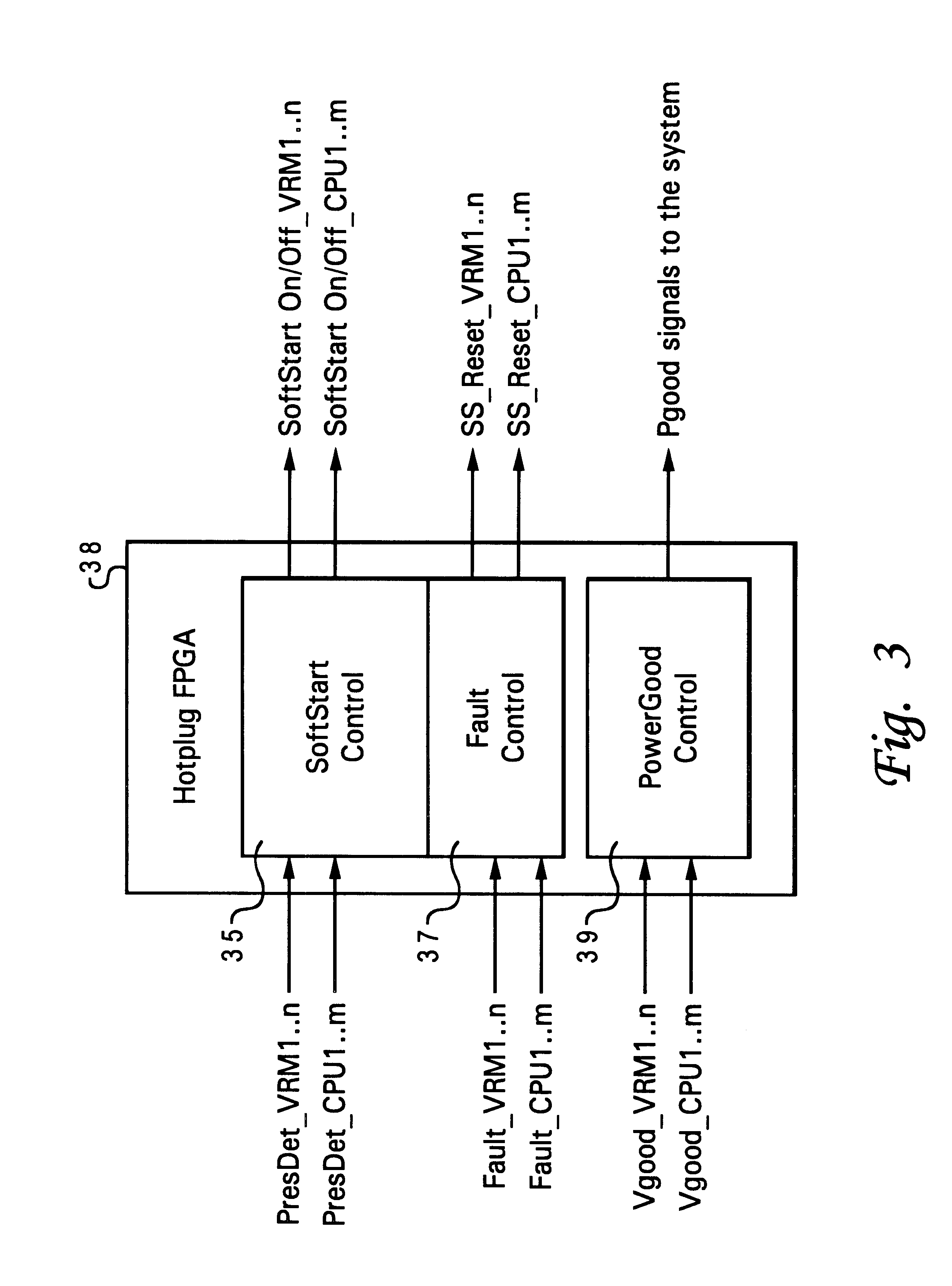
InactiveUS6535944B1Hardware monitoringPower supply for data processingVoltage regulator moduleVoltage regulation
A method of servicing a computer system without interrupting operation of the computer system, by connecting a computer component to a board of the computer system, detecting connection of the computer component to the system board using a control circuit, supplying power to the voltage input of the computer component in response to detecting the connection, and thereafter monitoring the power supplied to the voltage input of the computer component. The method may be used for core computer components such as CPU modules and voltage regulator modules. Power to the voltage input of the computer component is turned off in response to a determination that a current level of the power supplied to the voltage input exceeds a specified level. A fault signal is latched in an active state in response to the determination; the fault signal is reset when the component is removed from the system. The method also applies to a plurality of hot-pluggable components, wherein the power supplied to each component is individually monitored.
Owner:IBM CORP
Photovoltaic air conditioning system and control method thereof
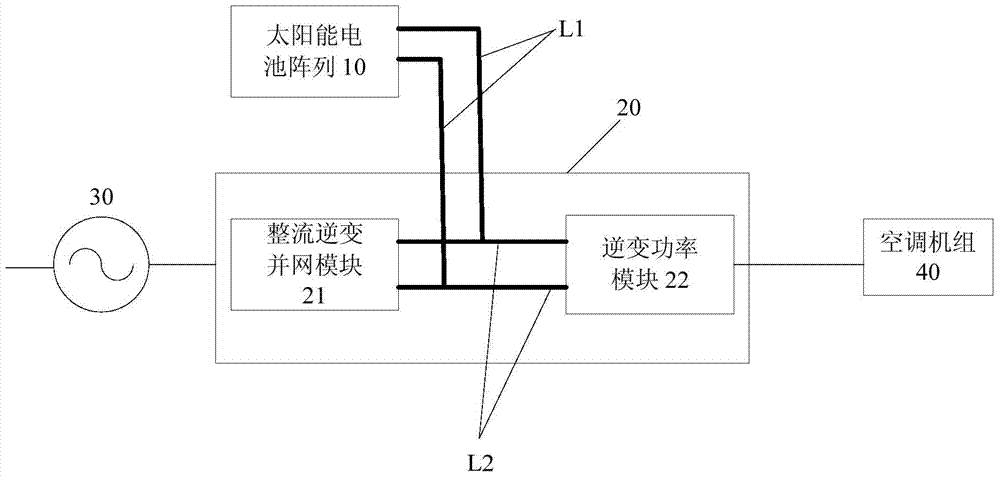
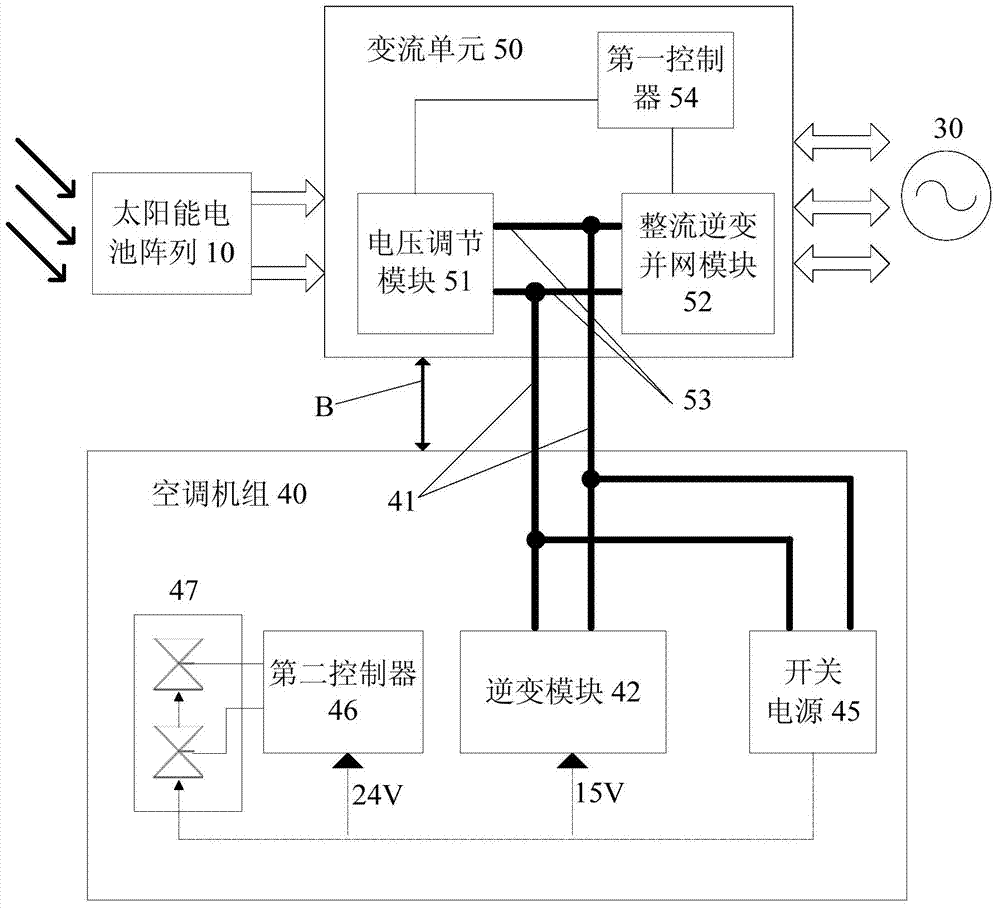
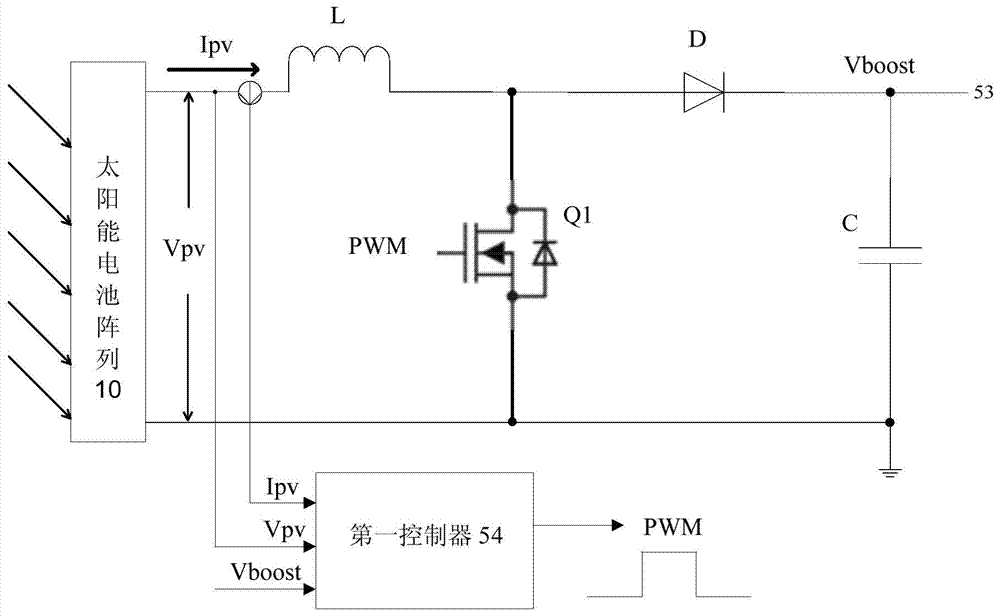
ActiveCN104713176ASolve the problem of not being able to run off the gridReduce dependenceMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsVoltage regulator modulePower grid
The invention discloses a photovoltaic air conditioning system and a control method thereof. The photovoltaic air conditioning system comprises a solar battery array, a current change unit and an air conditioning set, wherein the current change unit is connected between the solar battery array and a public power grid, and is provided with a first direct-current bus, a voltage adjusting module and a rectification inversion synchronization module connected through the first direct-current bus and a first controller both connected with the voltage adjusting module and the rectification inversion synchronization module; and the air conditioning set has a second direct-current bus connected to the first direct-current bus, an inversion module and a switching power supply connected with the second direct-current bus, and a second controller. The photovoltaic air conditioning system solves the problem that a photovoltaic air conditioning system in the prior art cannot operate off network, achieves the reduction of the dependence of the photovoltaic air conditioning system on the power grid, and reduces the cost of the photovoltaic air conditioning system.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
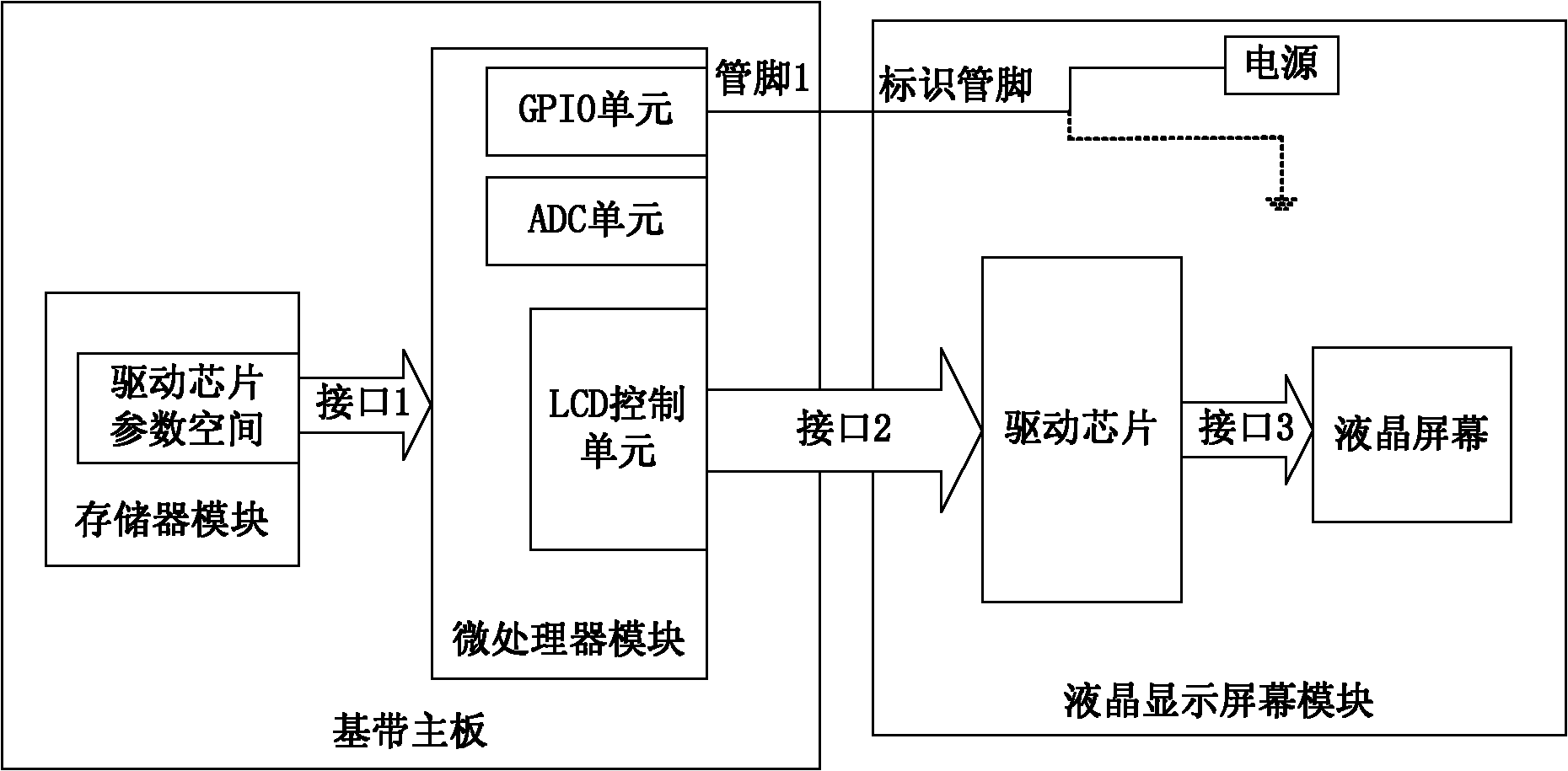
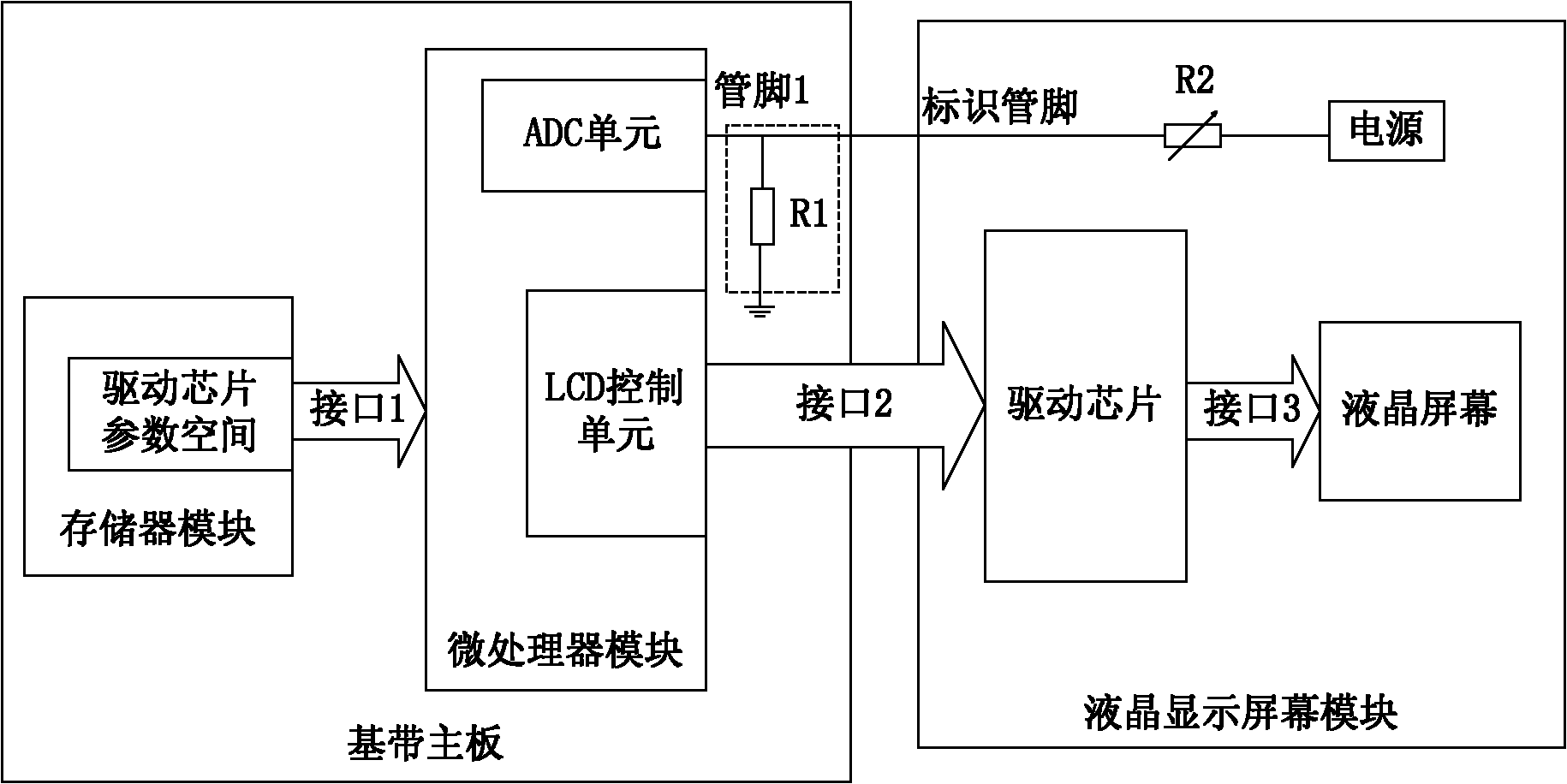
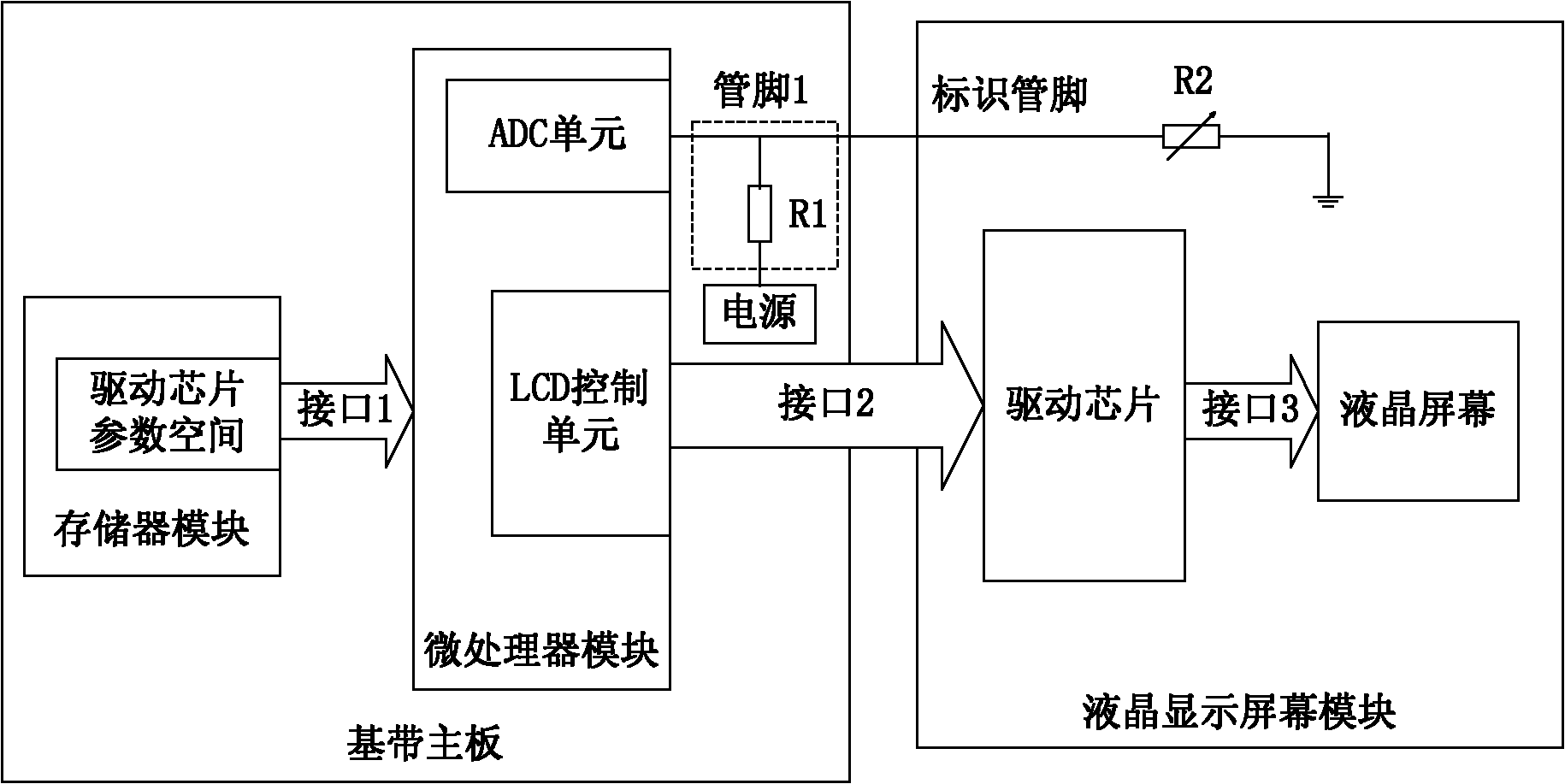
Method and device for recognizing liquid crystal display screen and terminal
InactiveCN101986381ACurrent/voltage measurementStatic indicating devicesVoltage regulator moduleLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a method and a device for recognizing a liquid crystal display screen and a terminal, which can be automatically compatible with a plurality of liquid crystal display screens. The device comprises a storage module, a voltage regulating module and a recognition module, wherein the storage module is used for storing the driving chip parameter of the liquid crystal display screen; the voltage regulating module is used for regulating an output voltage of the liquid crystal display screen to the processing range of the recognition module according to a fixed voltage when connected to the liquid crystal display screen so as to obtain a regulating voltage; and the recognition module is used for storing the corresponding relation between the driving chip parameter and the regulating voltage of a corresponding type of liquid crystal display screen, receiving the regulating voltage of the voltage regulating module, and searching the driving chip parameter corresponding to the regulating voltage according to the regulating voltage and a preset corresponding relation.
Owner:ZTE CORP
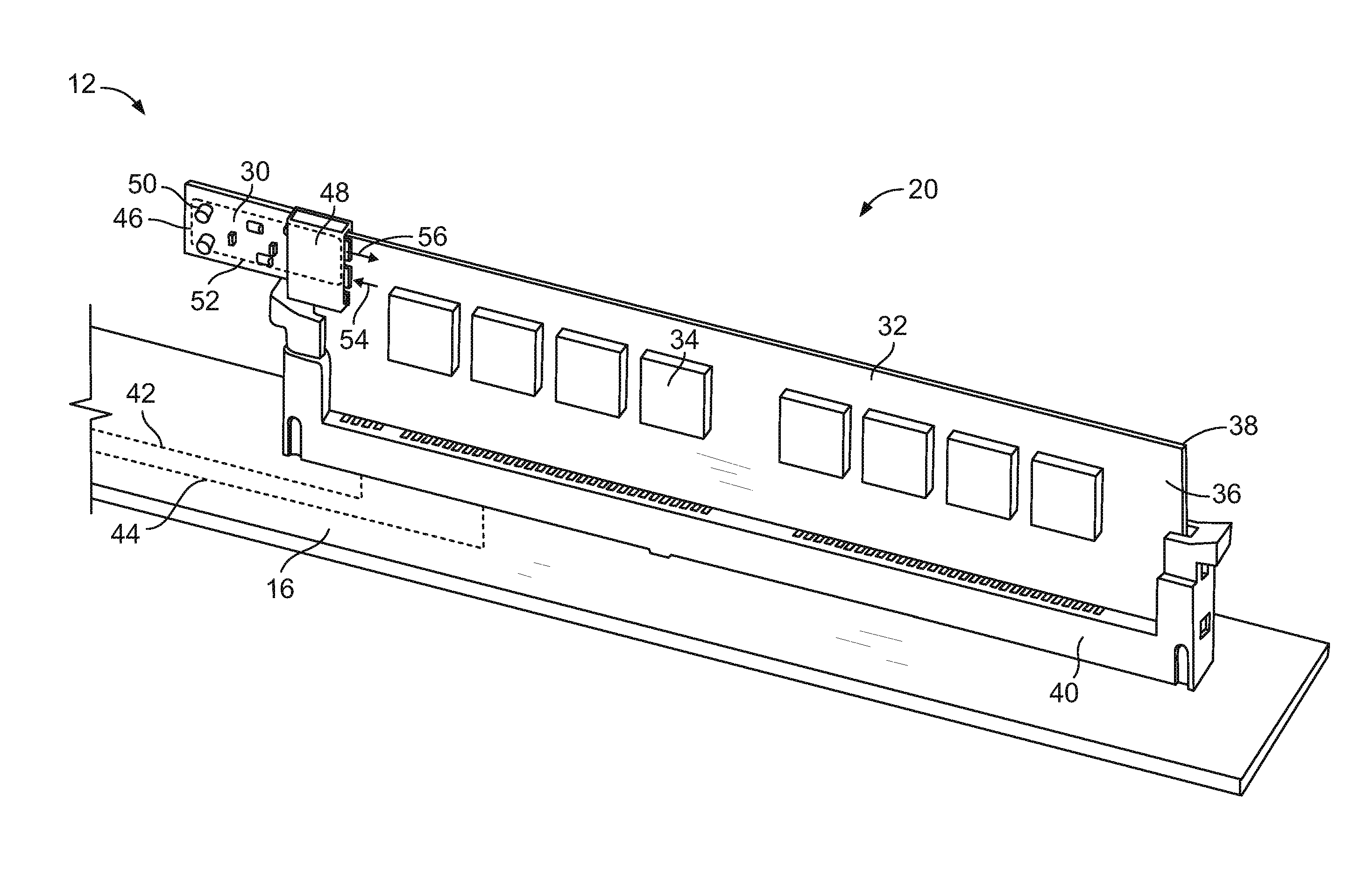
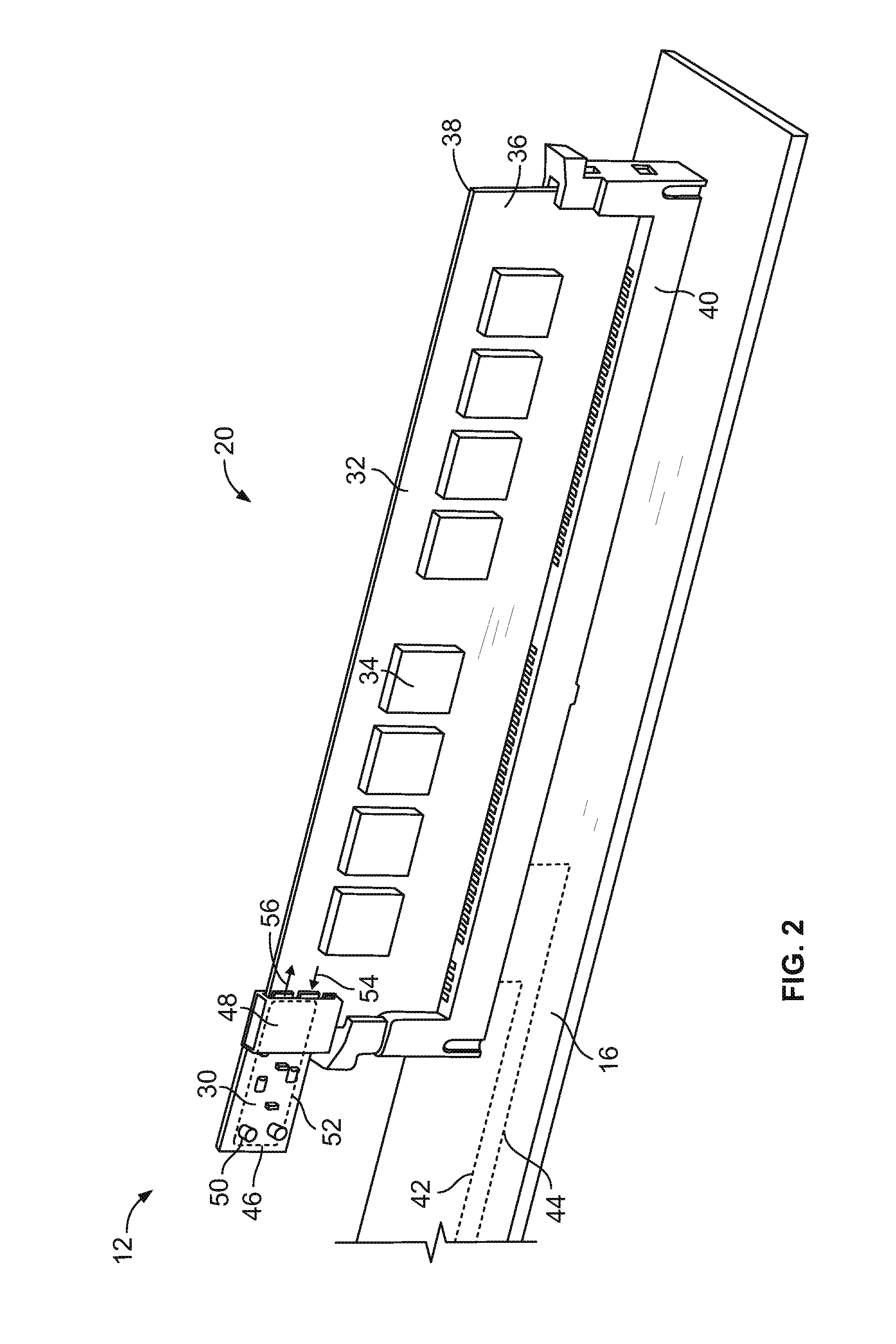
Memory module having voltage regulator module
InactiveUS20100128447A1High voltage circuit adaptationsPrinted circuit manufactureVoltage regulator moduleEngineering
A memory module includes a circuit board having socket mating contacts at a socket interface and VRM contacts at a VRM interface. Memory devices are coupled to the circuit board. The memory devices are electrically connected to corresponding socket mating contacts and the memory devices are electrically connected to corresponding VRM contacts. A voltage regulator module is coupled to the circuit board at the VRM interface. The voltage regulator module is electrically connected to the VRM contacts.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
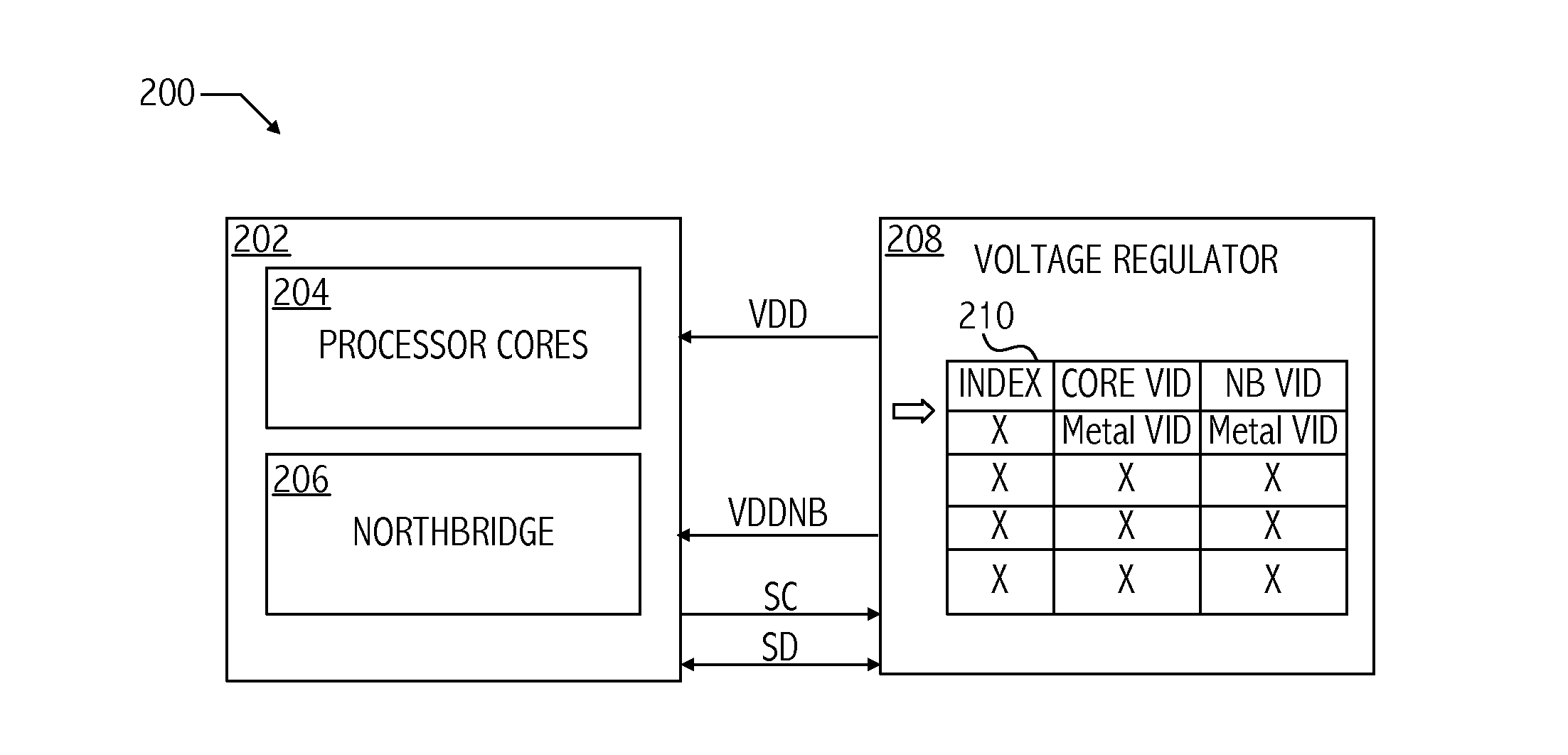
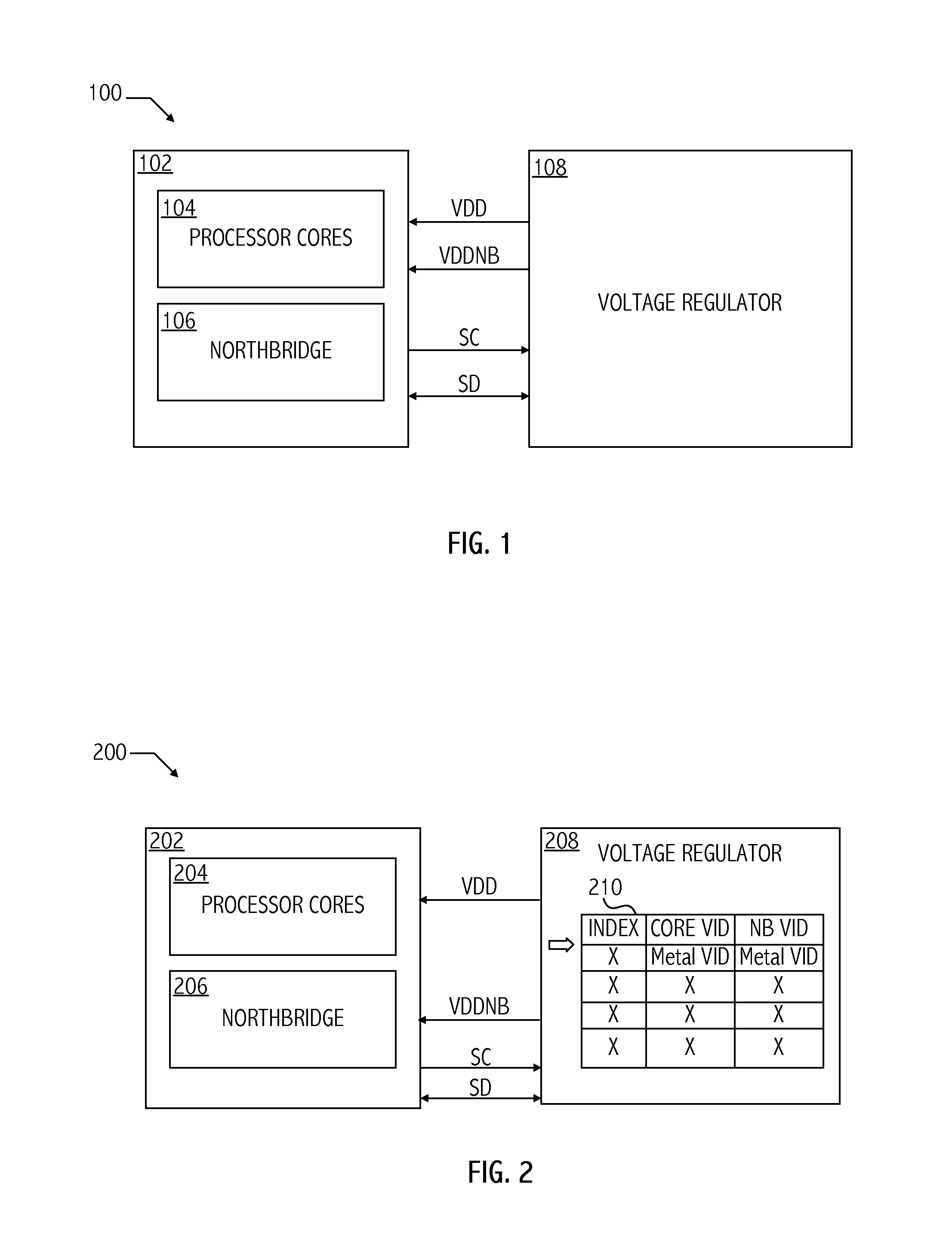
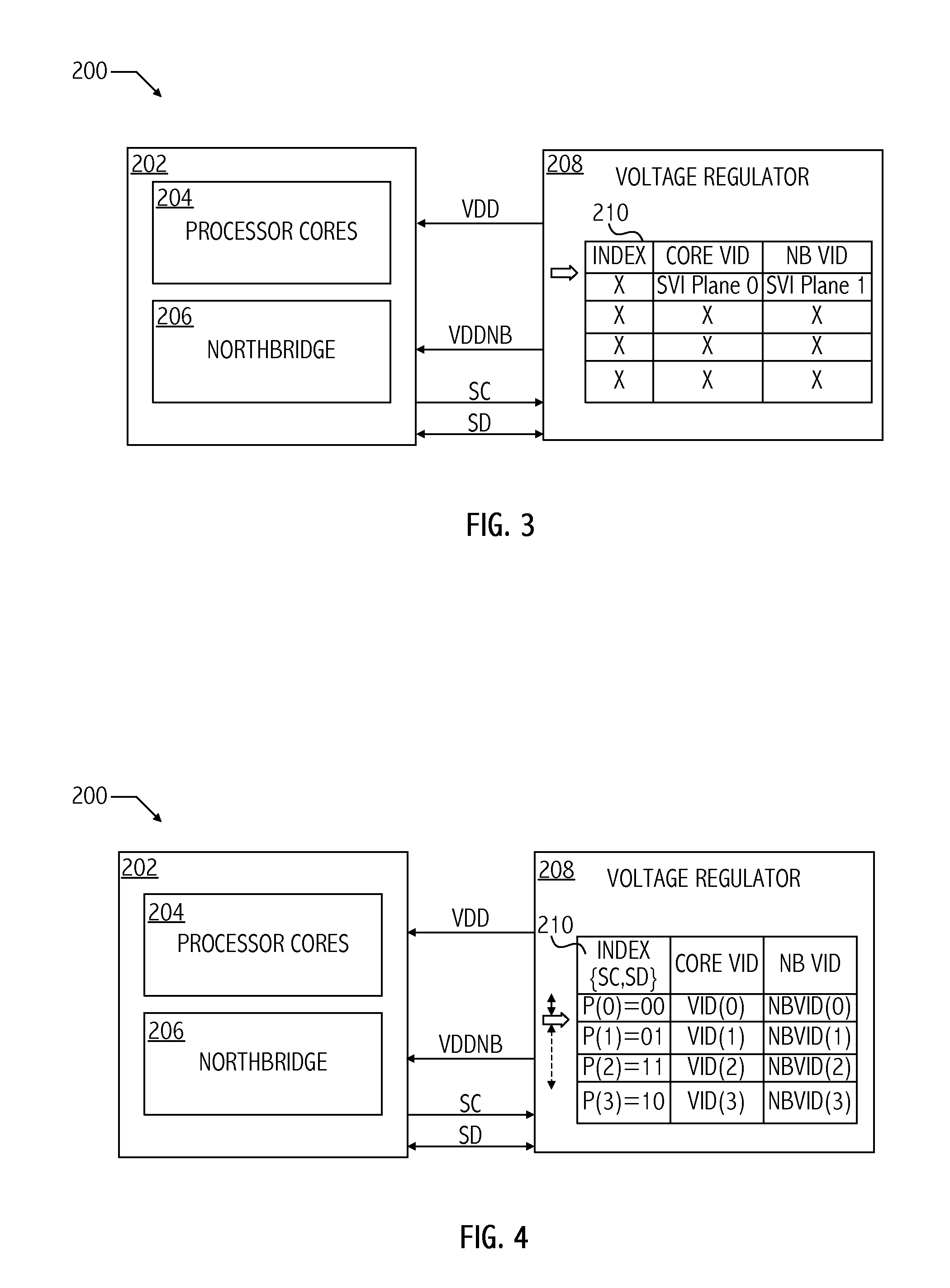
Dynamic table look-up based voltage regulator control
ActiveUS20110087900A1Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementVoltage regulator moduleState dependent
A technique for dynamically controlling microprocessor power plane voltage levels includes storing in a memory on a voltage regulator voltage control identifiers in a table accessible according to performance state. In at least one embodiment of the invention, a method includes transitioning a voltage output of a voltage regulator to a next voltage level associated with a next performance state of a processor coupled to the voltage regulator based on a performance state indicator received from the processor and a corresponding entry of a performance state table. In at least one embodiment, the method includes loading performance state table entries into a storage device on the voltage regulator circuit.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
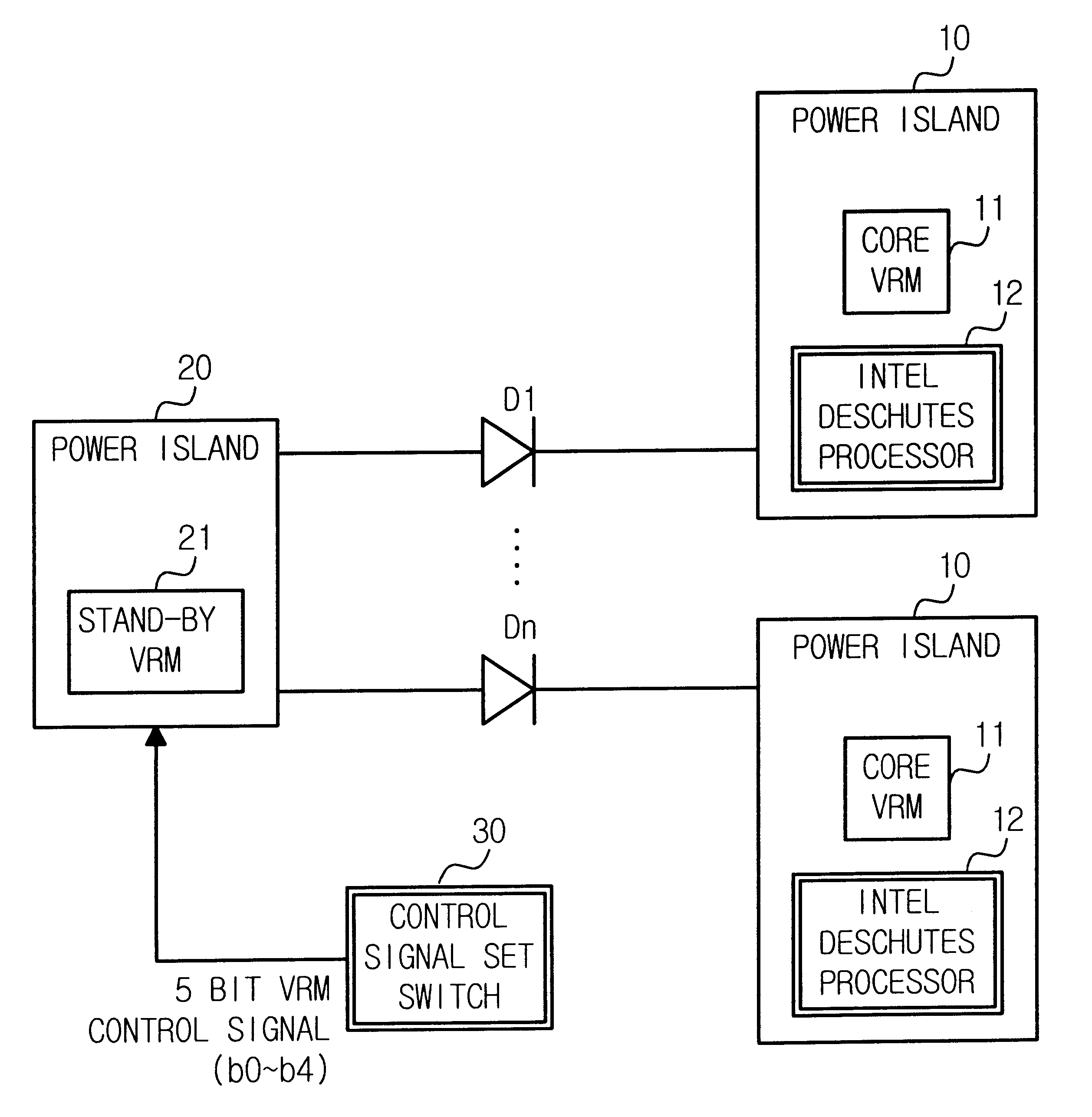
Fault tolerant voltage regulator module circuit for supplying core voltage and cache voltage to a processor
InactiveUS6189107B1Dc network circuit arrangementsPower network operation systems integrationVoltage regulator moduleControl signal
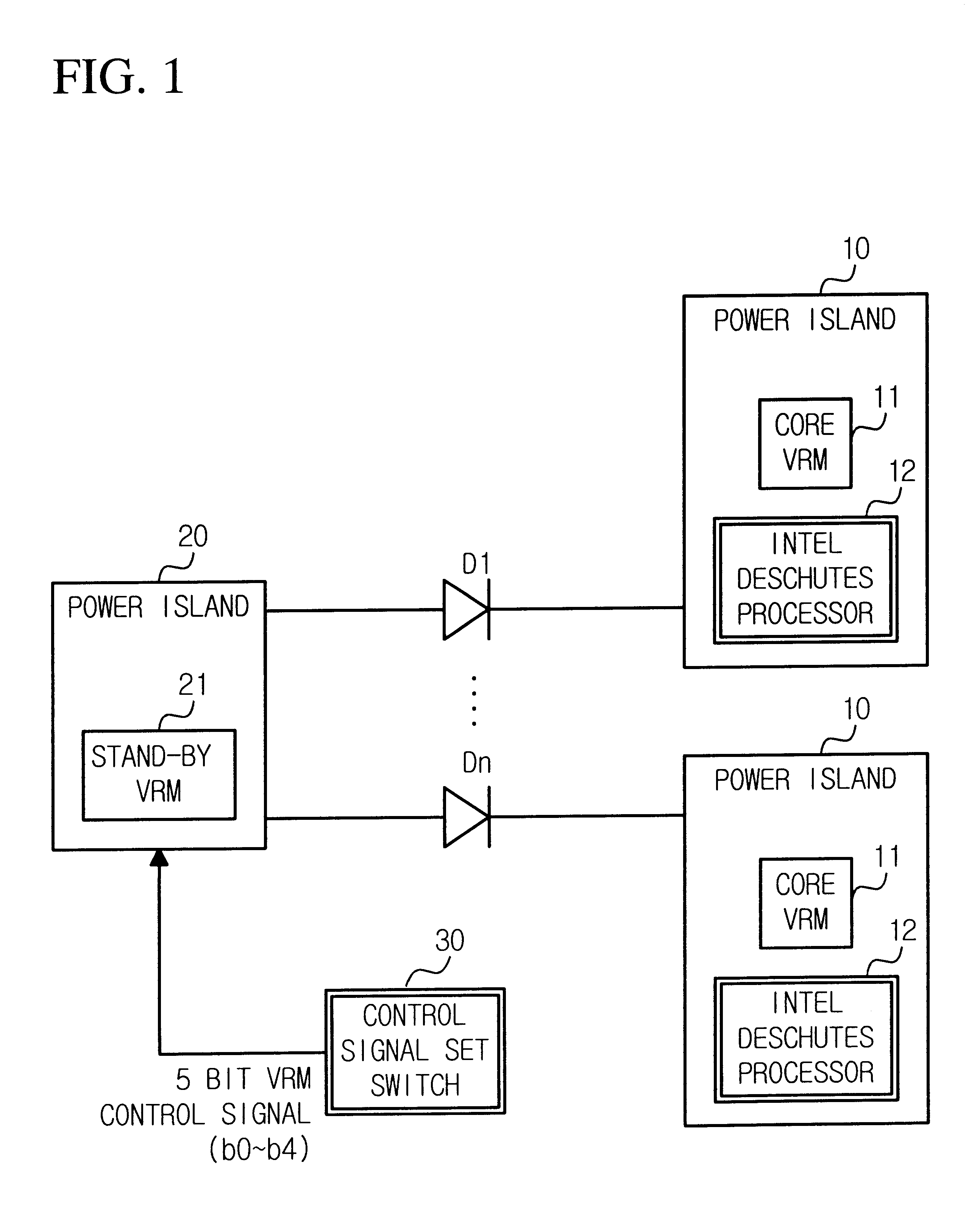
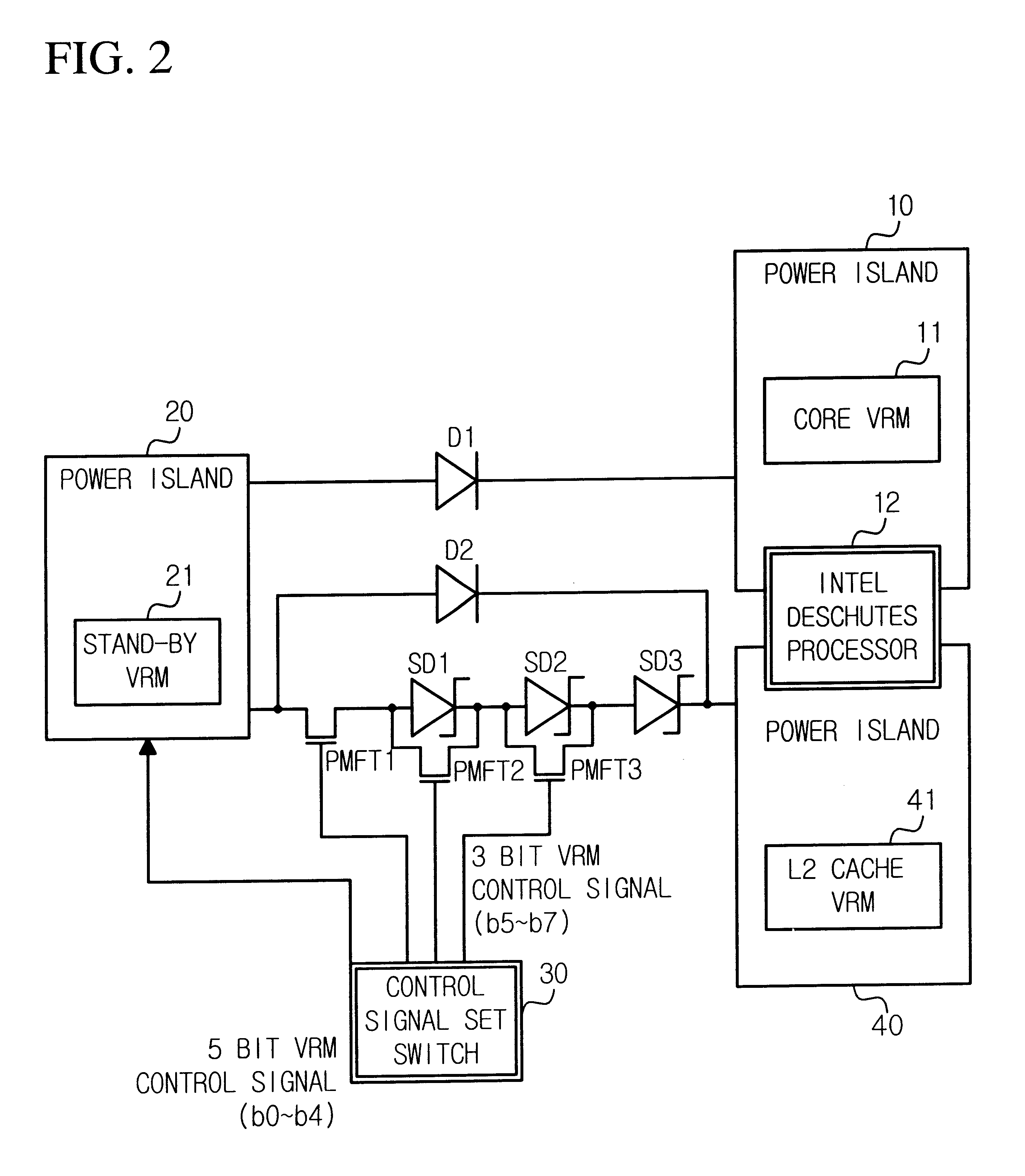
A fault tolerant voltage regulator module (VRM) circuit for a processor simultaneously supplies a core voltage to a plurality of processors, has a plurality of main VRMs (VRM) for supplying the same core voltage to the plurality of processors, a stand-by VRM for use upon a fault occurring in the plurality of main VRMs, a plurality of diodes connected in parallel between each of the main VRMs and the stand-by VRM for automatically supplying power to the stand-by VRM, a plurality of first power islands for connecting each of the plurality of main VRMs to the processor and each of output port of the plurality of diodes, a control signal set switch for setting output voltage level of the stand-by VRM and a second power island for connecting the stand-by VRM to input ports of the plurality of diodes and the control signal set switch. When a processor core voltage level and L2 cache voltage level are different, a fault tolerant VRM circuit further has a plurality of schottky diodes and a plurality of power MOSFETs for by-passing the schottky diodes so that the stand-by VRM can support two different voltage levels. The circuit improves stability of supplying board power owing to a fault tolerant VRM in processors and enables just one stand-by VRM to effect simultaneous support of a plurality of main VRMs and even different voltage level main VRMs using schottky diodes.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Apparatus and method for controlling voltage regulator and power supply apparatus
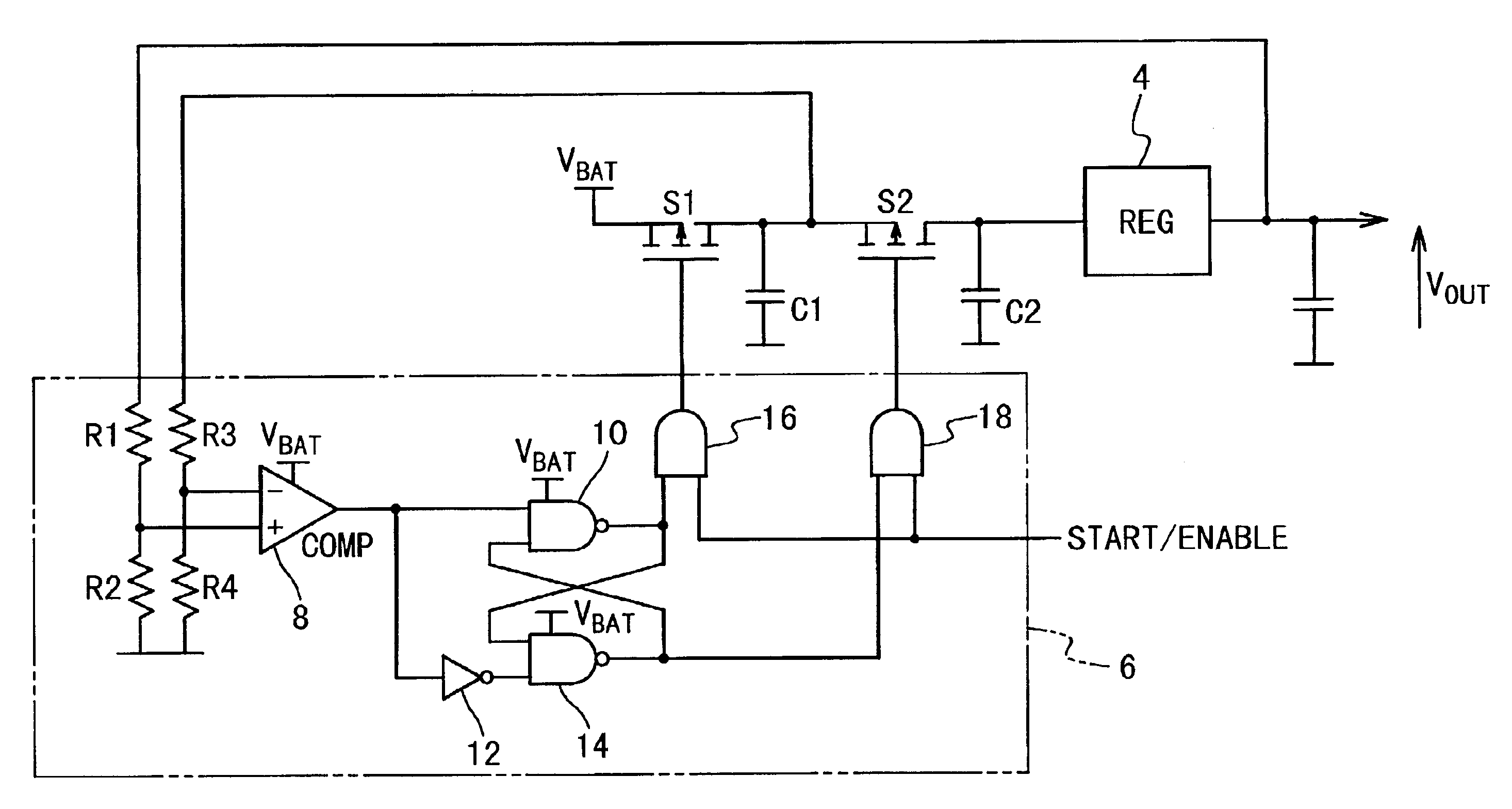
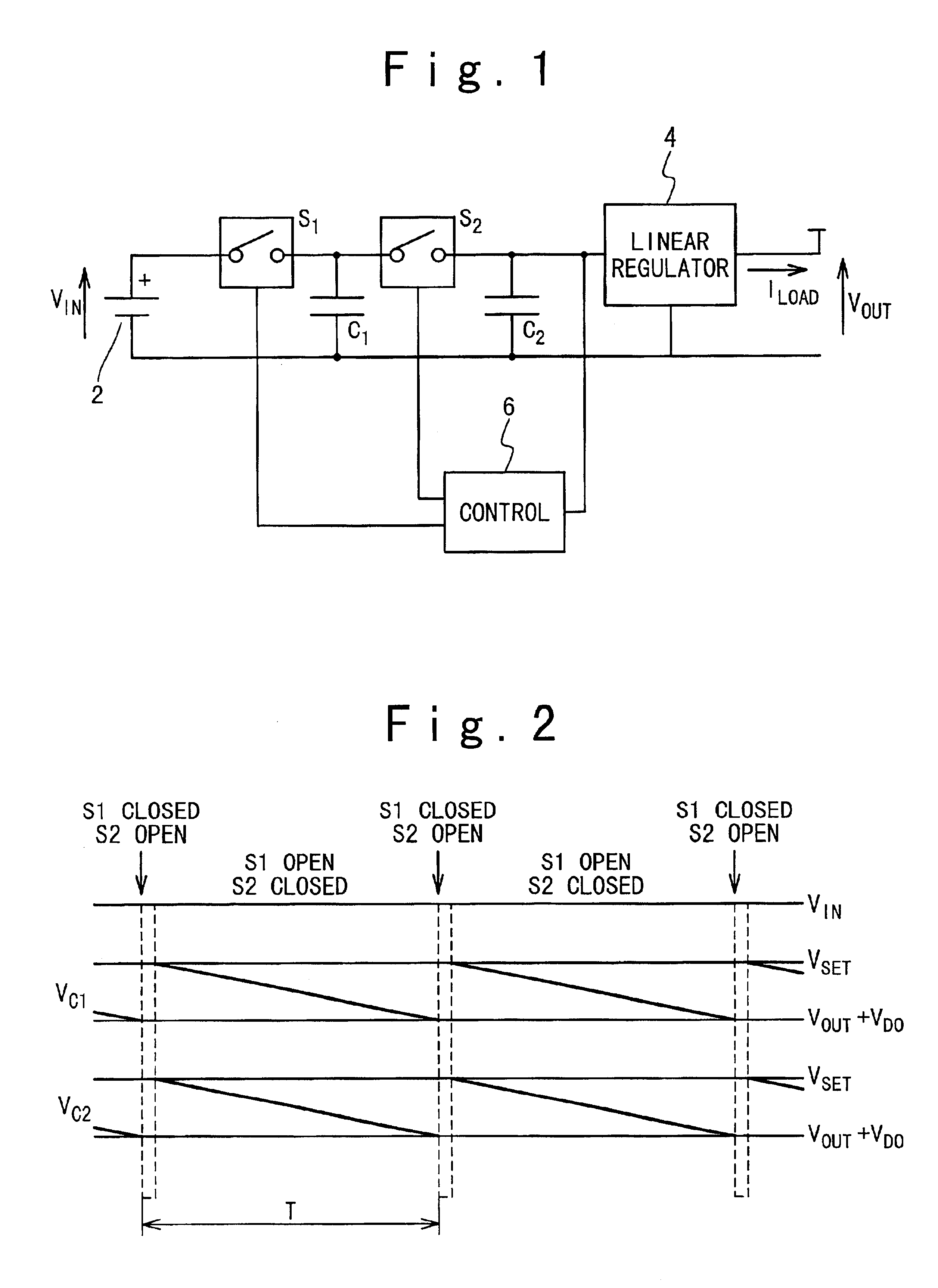
InactiveUS6856525B2Improving efficiency of linearImprove efficiencyDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionVoltage regulator moduleVoltage regulation
In a method for controlling a voltage regulator, first and second charge storage devices are switchably connected between a voltage source and the voltage regulator. The first storage device is switched into connection with the voltage source until the voltage on it reaches a predetermined level. The first storage device is disconnected from the voltage source and switched into connection with the second storage device and the voltage regulator until the voltage input to the voltage regulator falls below a predetermined level. The above operations are repeated.
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
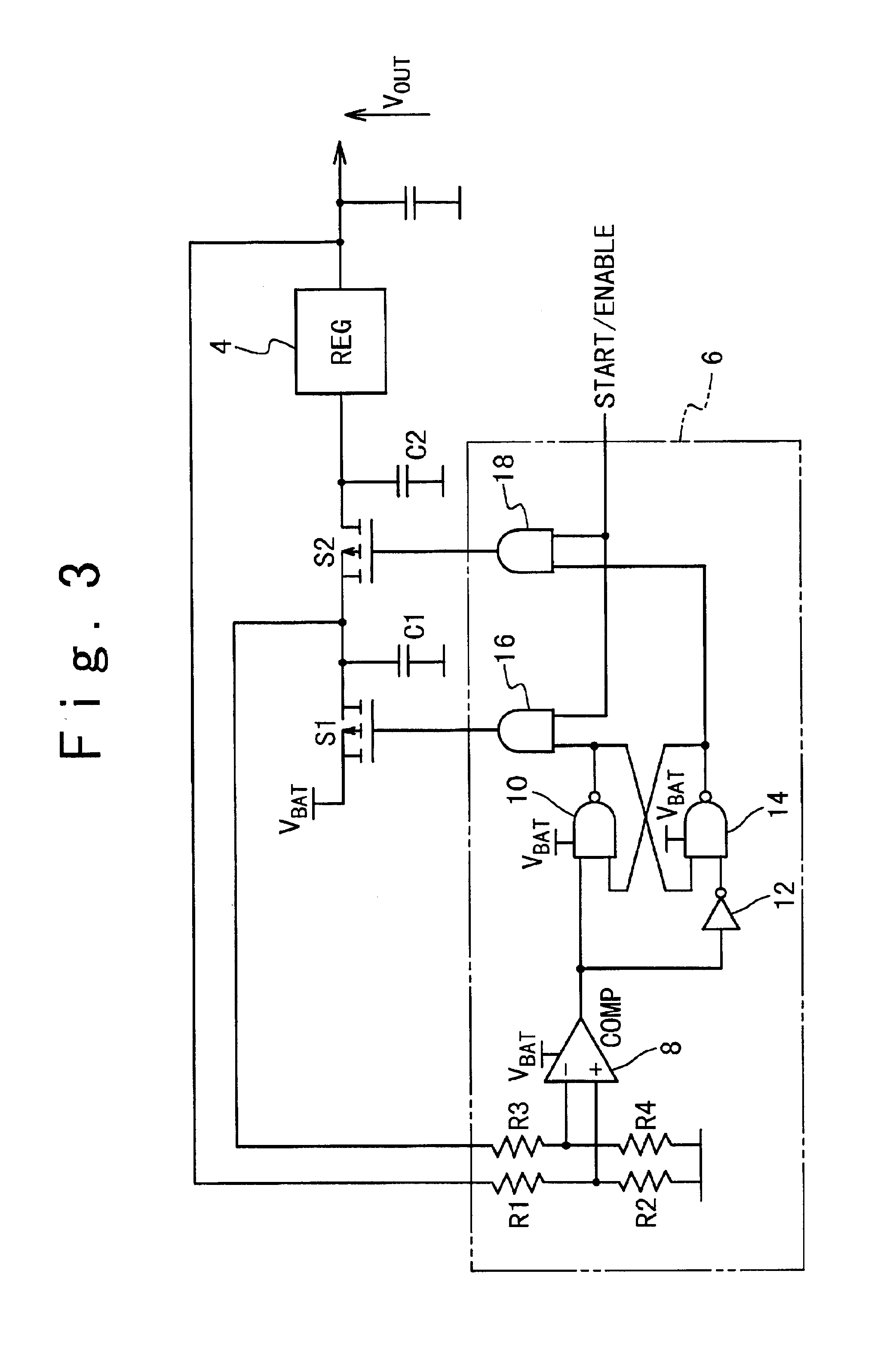
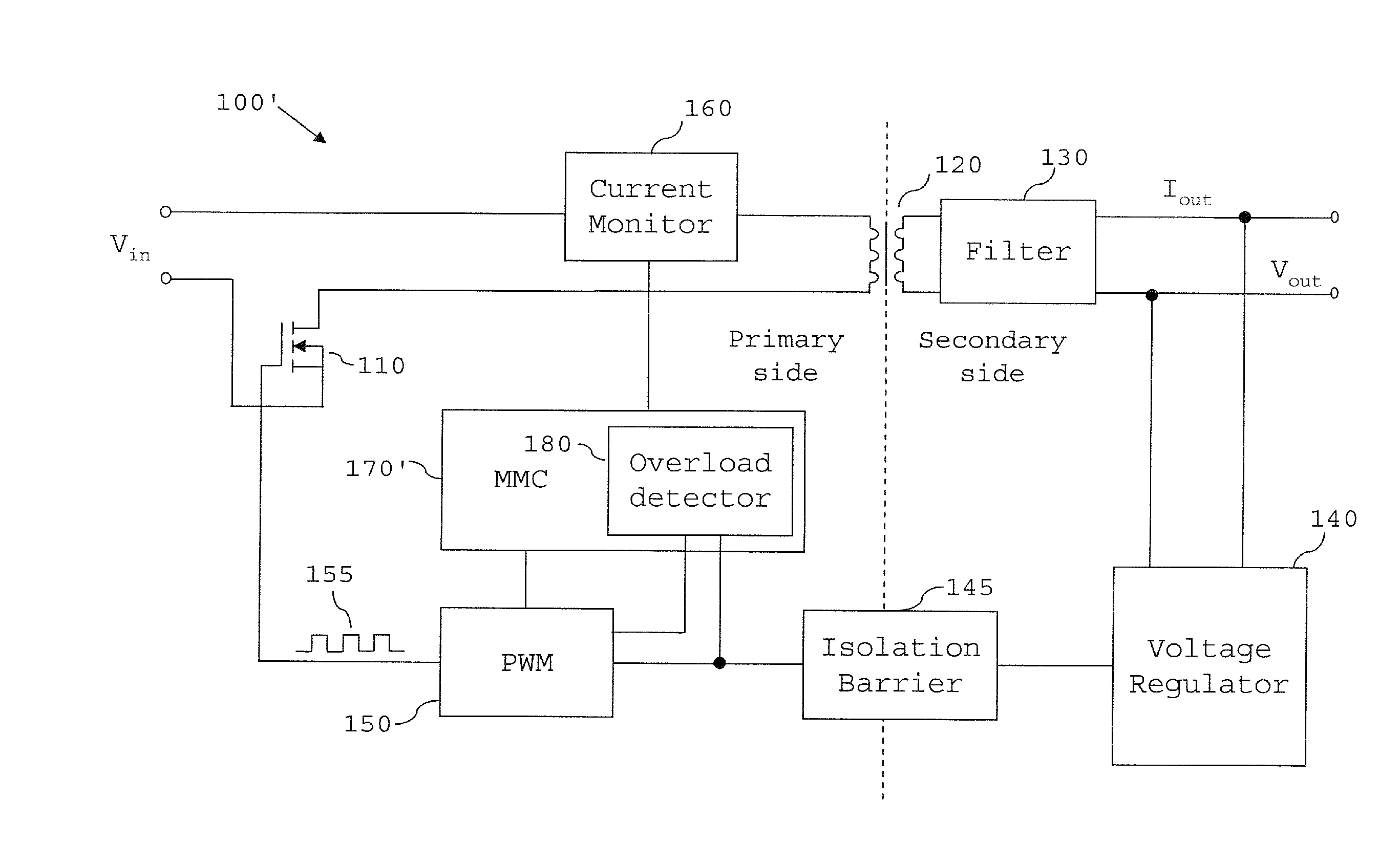
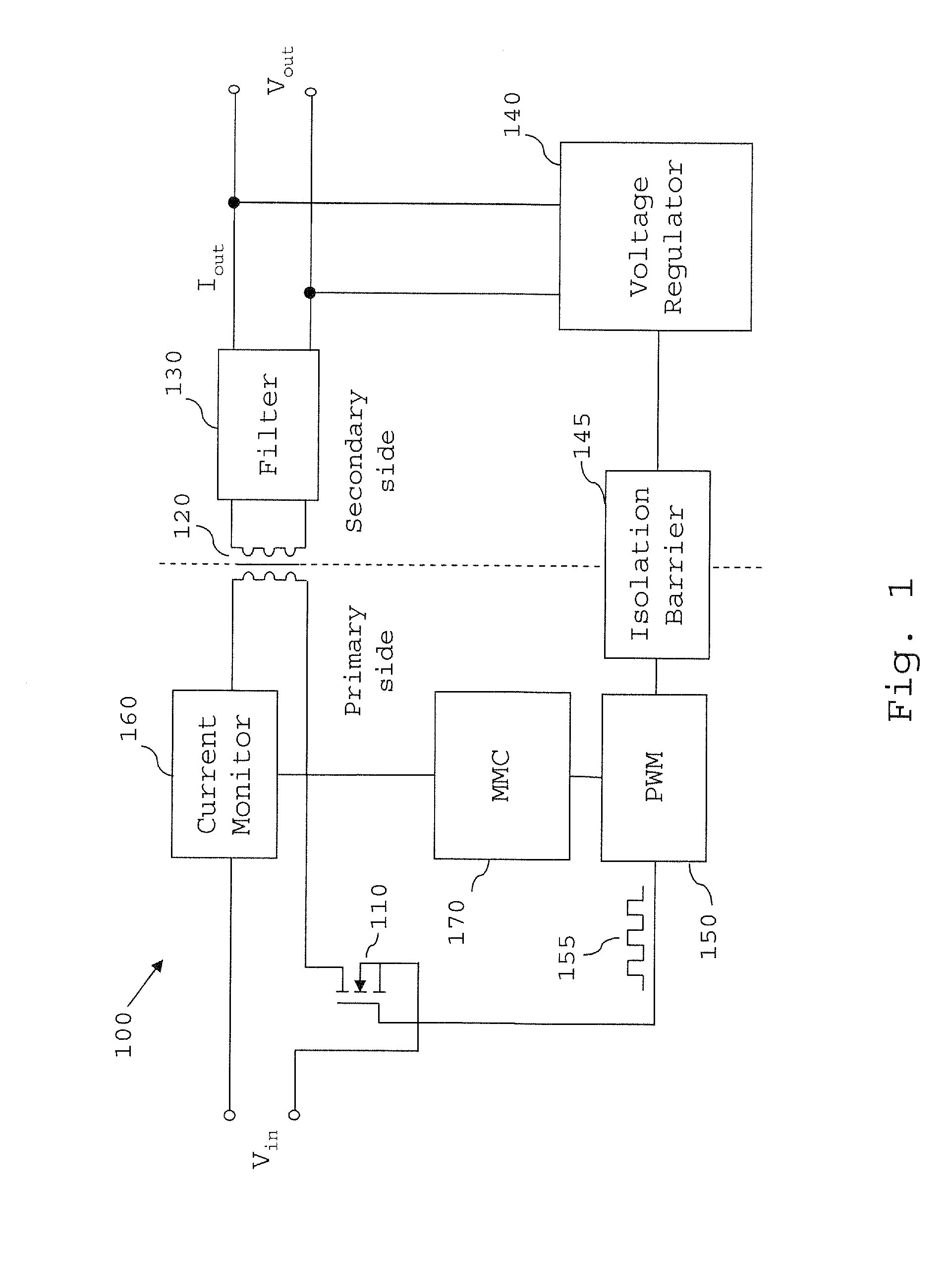
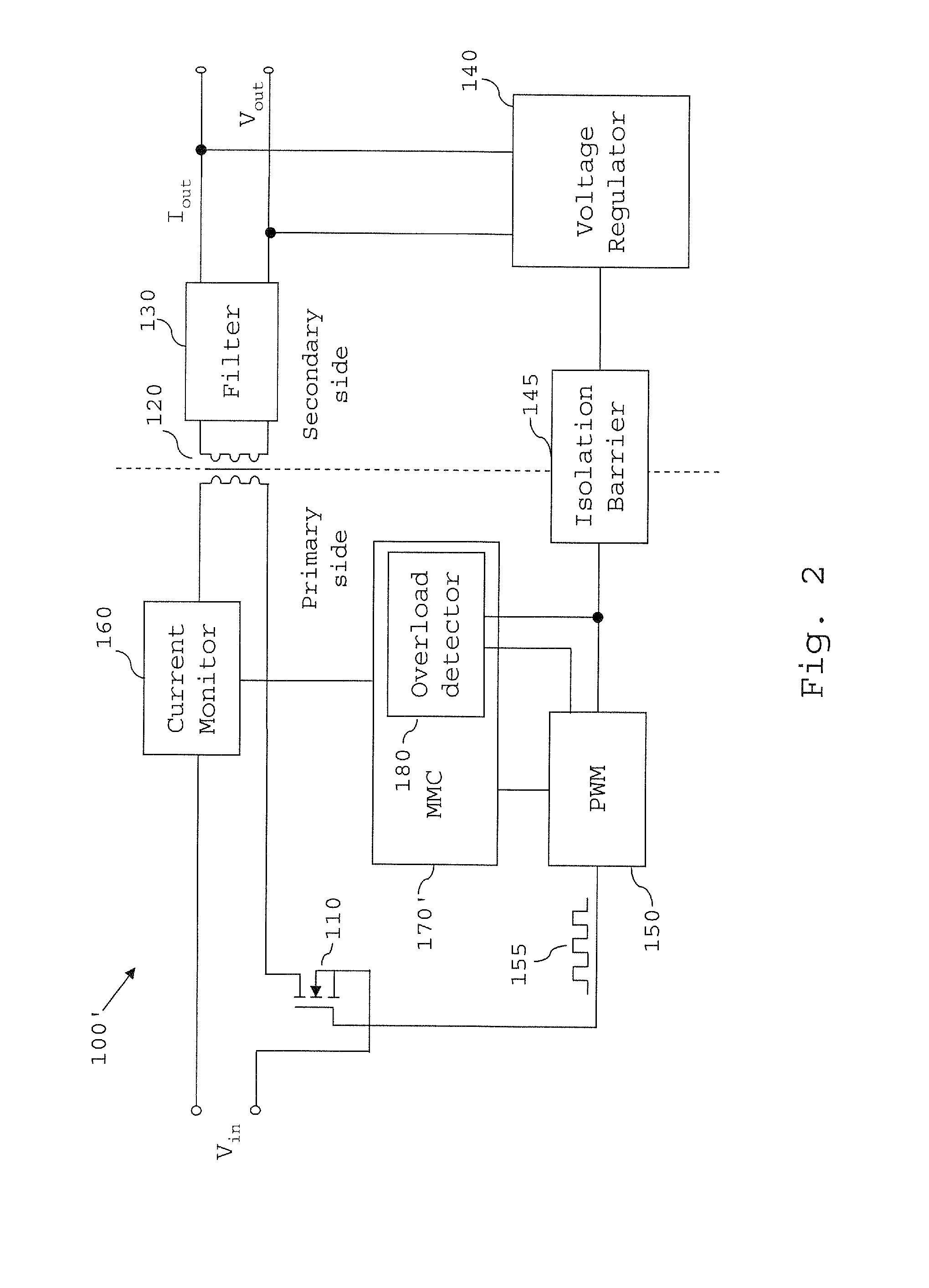
Overload detection in a switched mode power supply
ActiveUS20130294111A1Without risk of breakdownConvenient power supplyEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionVoltage regulator moduleElectrical current
A switched mode power supply includes a switching device, the switched mode power supply being operable to convert an input voltage (Vin) to an output voltage (Vout) by switching the switching device, and a voltage regulator operable to generate a feedback signal based on at least one of the output voltage and an output current of the switched mode power supply. The power supply further comprises an overload detector, which is arranged to receive the feedback signal and operable to determine whether the feedback signal is outside a predetermined range. If the feedback signal is outside the predetermined range, the overload detector is operable to determine that the switched mode power supply is in an overload state, and when an overload state is determined, perform control to place the switched mode power supply in a non-operational state.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Transient electromagnetic logging instrument
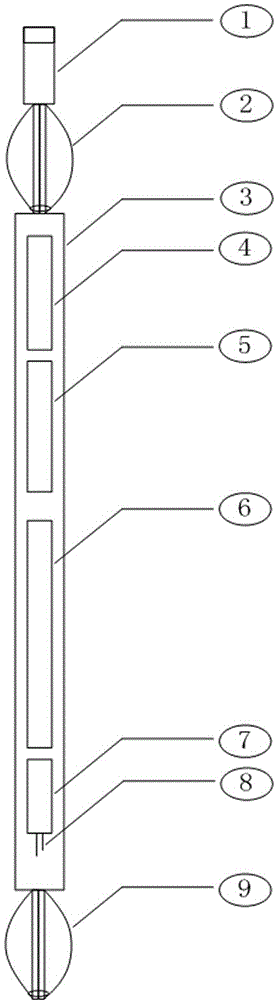
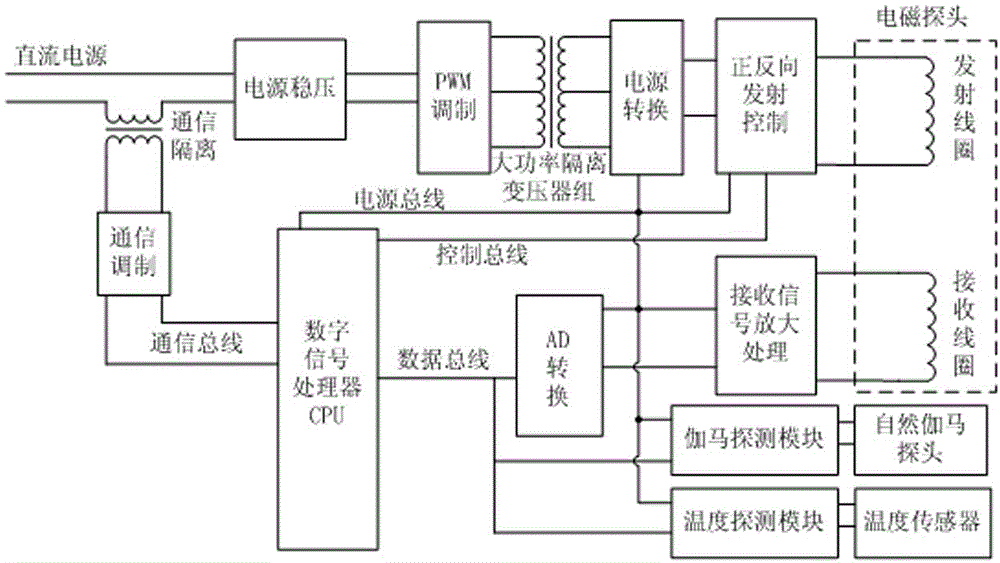
ActiveCN103603650AEffectively pass throughEfficient access through casingSurveyVoltage regulator moduleElectromagnetic field
The invention relates to a transient electromagnetic logging instrument which comprises a shell, a circuit module and an electromagnetic probe system, wherein the circuit module is arranged in the shell, and the electromagnetic probe system is connected with the circuit module. The circuit module is sequentially connected with a power voltage regulator module, a PWM (pulse width modulation) module, a high-power isolating transformer bank and a power conversion module through a direct-current power supply to form a direct-current power supply circuit and a main control circuit taking a digital signal processor as a core, and a communication bus, a power bus, a control bus and a data bus are arranged on the periphery of the main control circuit. The electromagnetic probe system comprises a transmitting coil and a plurality of receiving coils, wherein the transmitting coil is provided with a magnetic core. The instrument detects casing damage and effectively measures the formation resistivity of an open hole well and a cased well in a non-contact mode. High-power transient excitation is realized by the aid of internal iron cores of the coils, the excitation intensity of a transient electromagnetic field is improved, and the formation resistivity is finally obtained by necessarily graduating and processing measured original signals.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +2
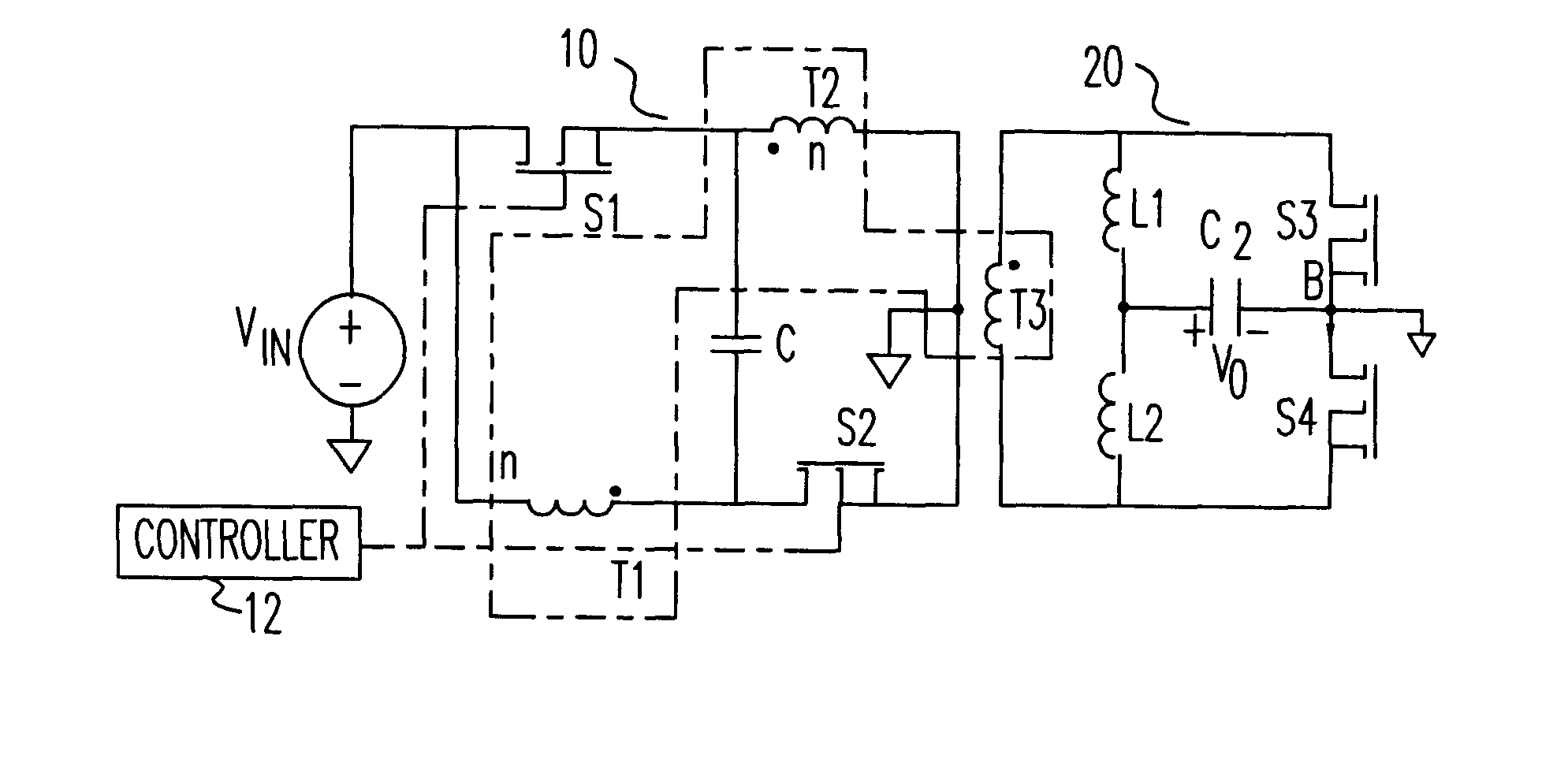
High input voltage, high efficiency, fast transient voltage regulator module (VRM)
InactiveUS6590791B1Efficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitanceVoltage regulator module
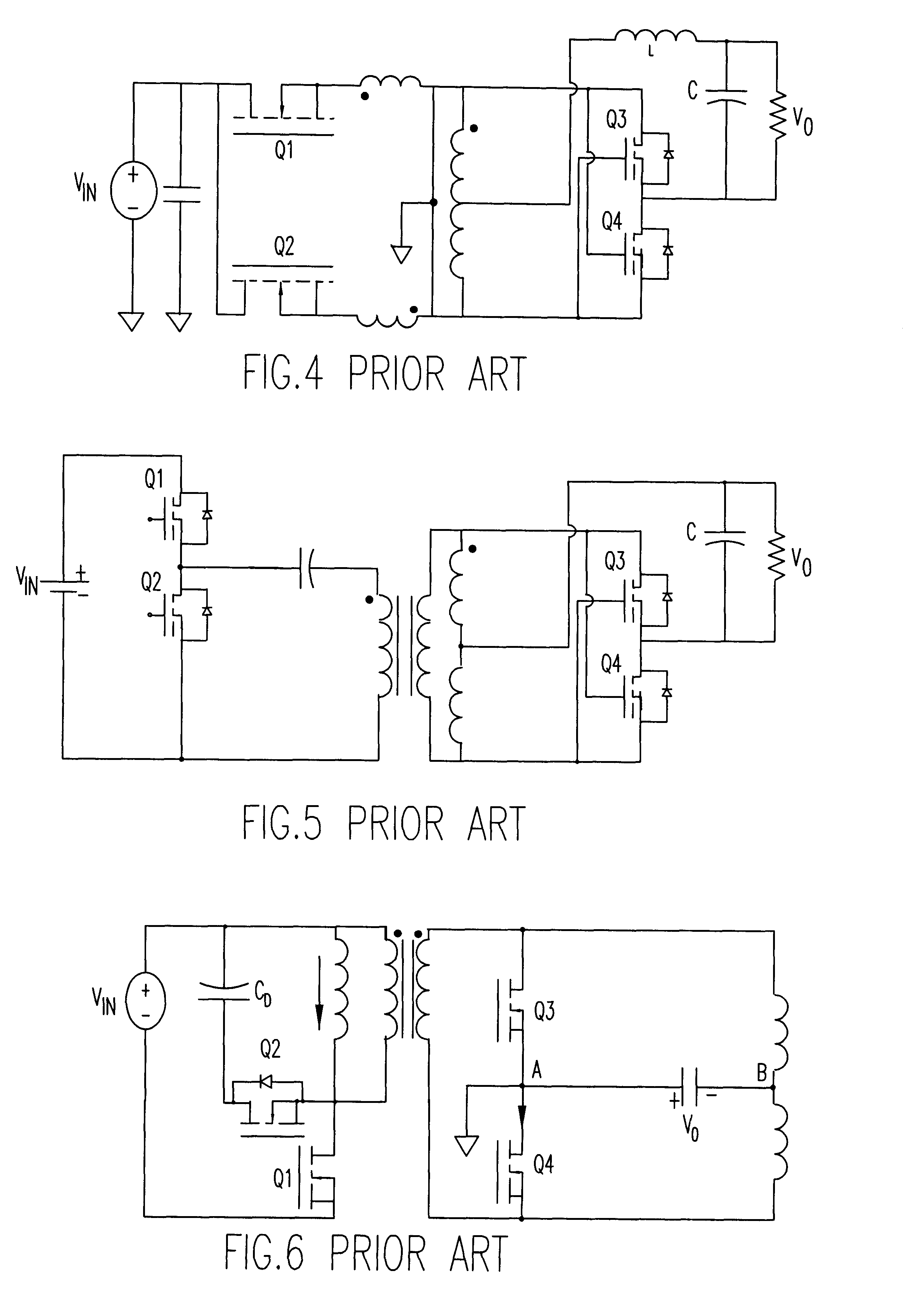
A high input-voltage push-pull forward voltage regulator module (VRM) has high efficiency and fast transient response. The VRM has a primary side wherein two switches and two primary transformer windings are alternately connected in a loop. A capacitor is connected between any of two interleaved terminations. The remaining two terminations are connected to input and ground respectively. The two primary transformer windings have the same number of turns. A number of secondary sides may be used such as, for example, a half wave rectifier or a center tapped secondary. The high input-voltage push-pull forward VRM has high efficiency and fast transient-response with reduced filter capacitance and inductance. Its magnetic components can be easily integrated. As a result, very high power density can be achieved. The device die size needed to achieve the required efficiency is reduced. And control is simple. Therefore, this topology is very cost effective.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com