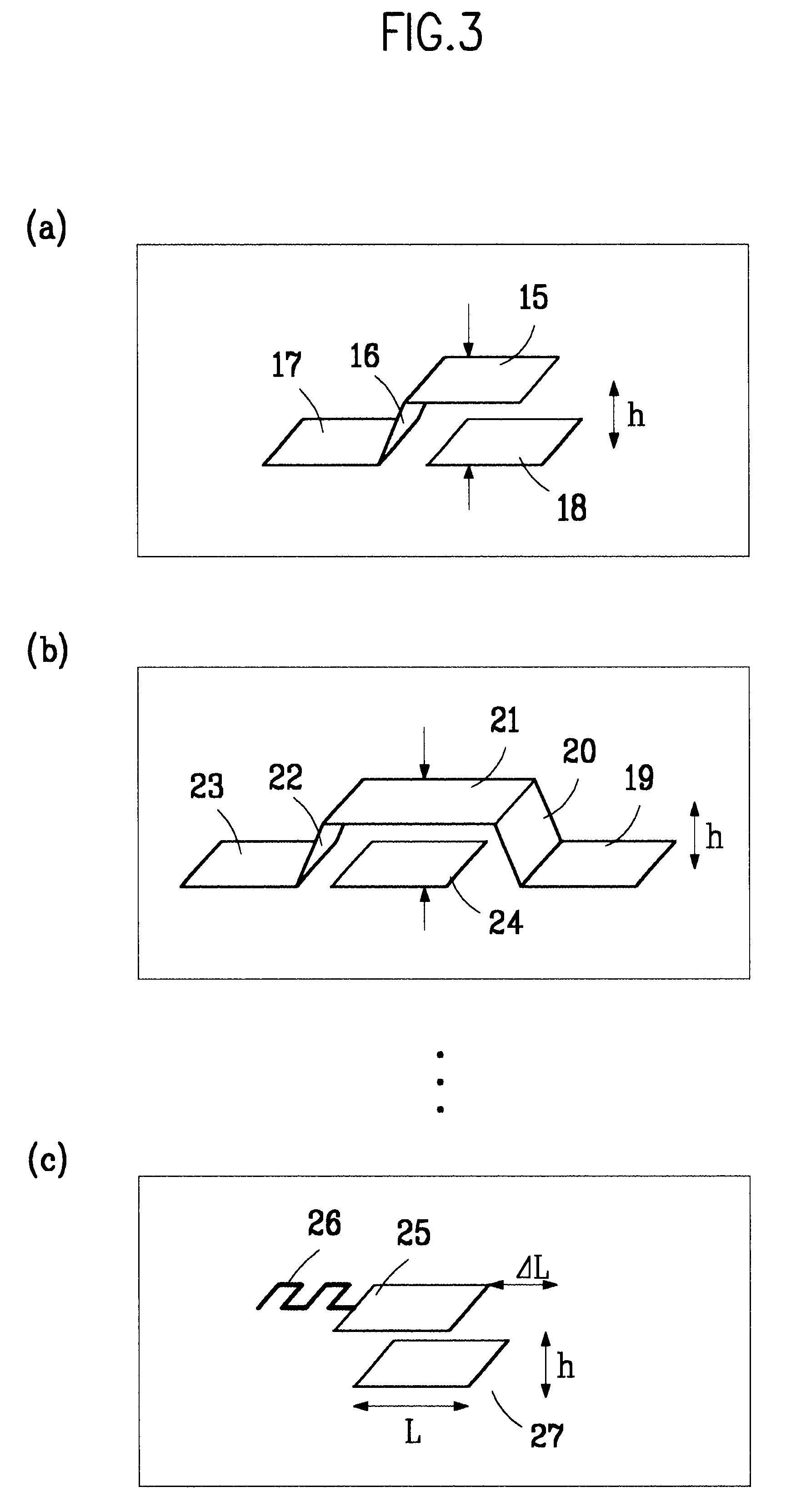
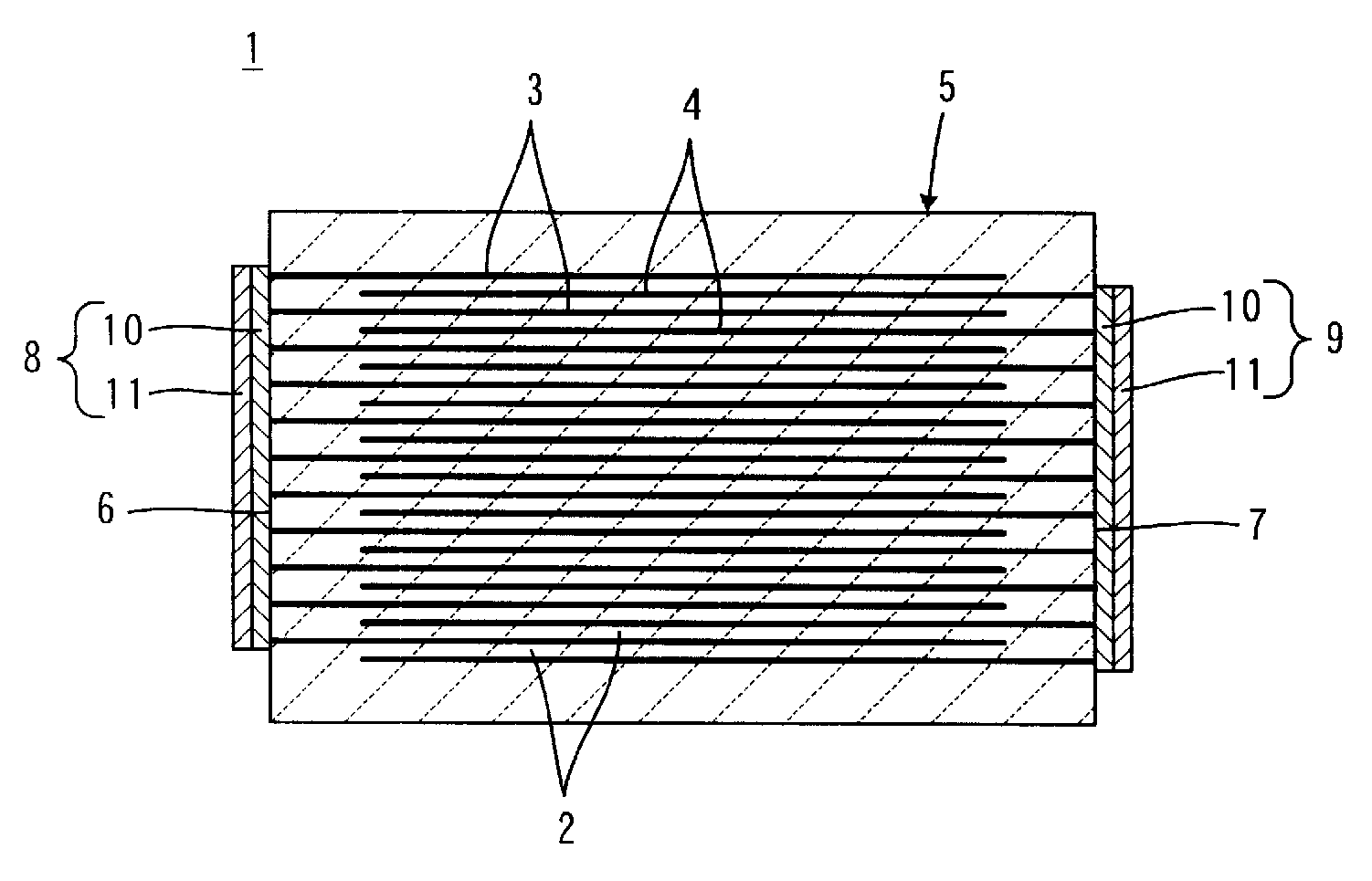
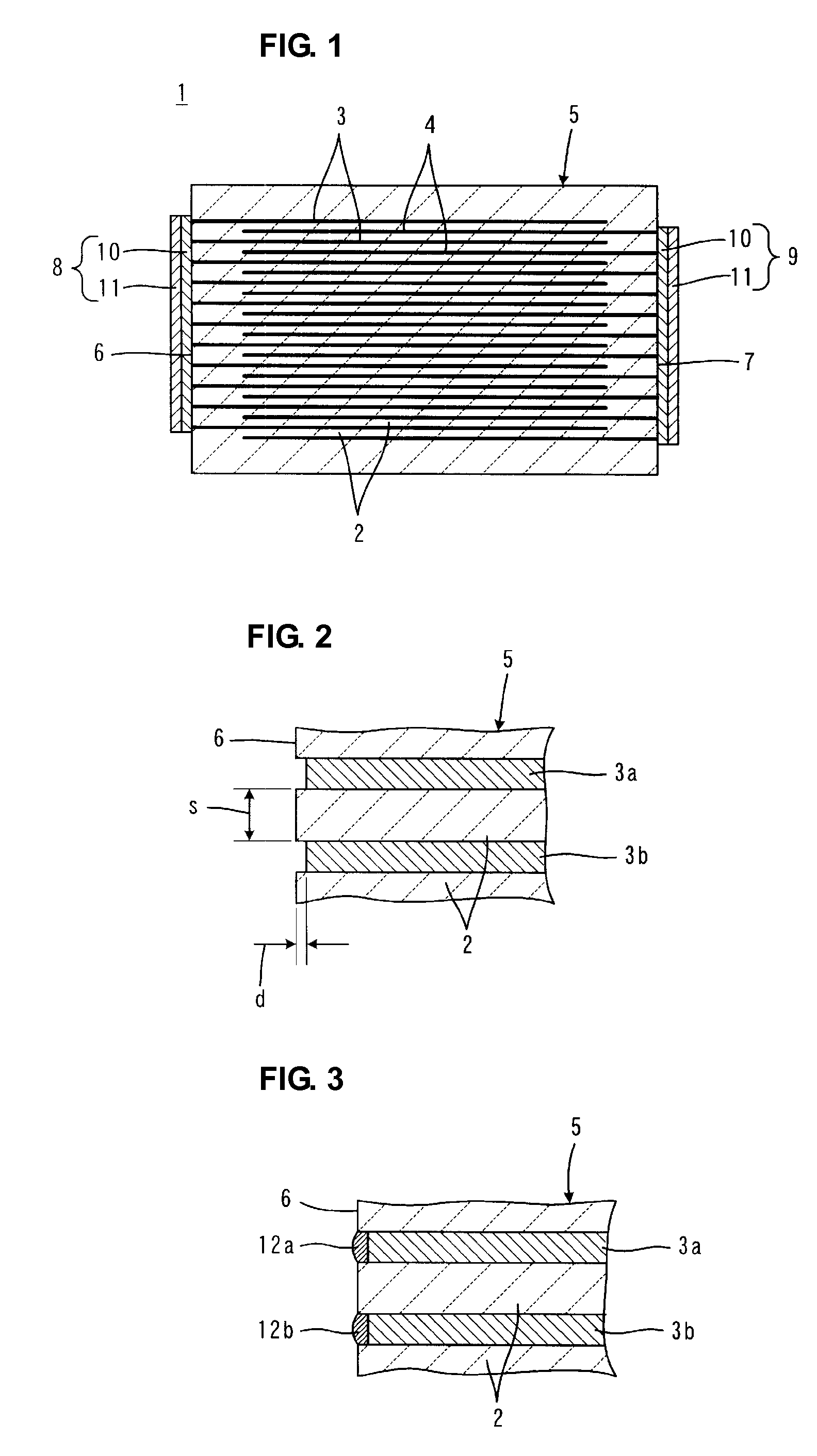
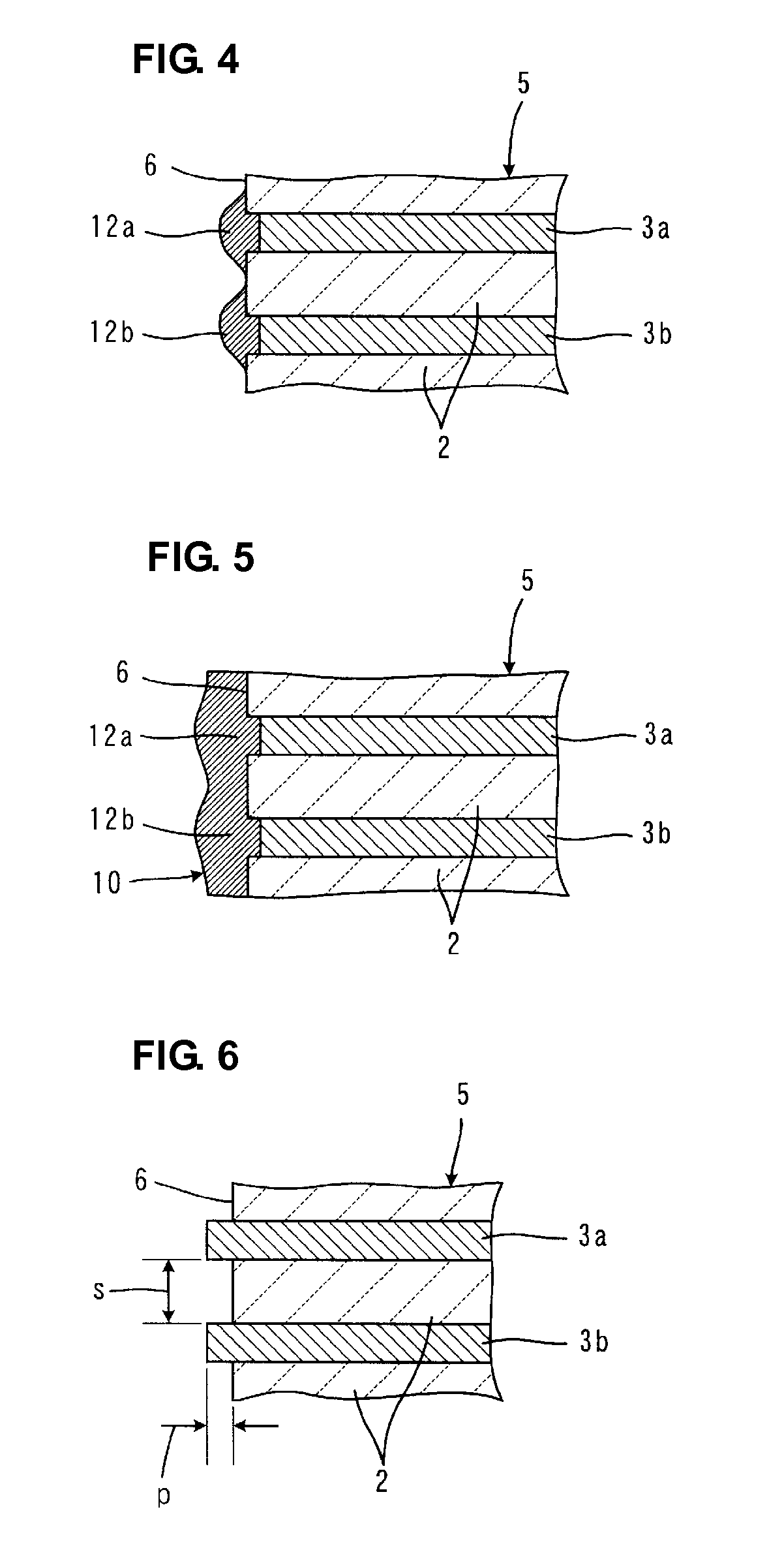
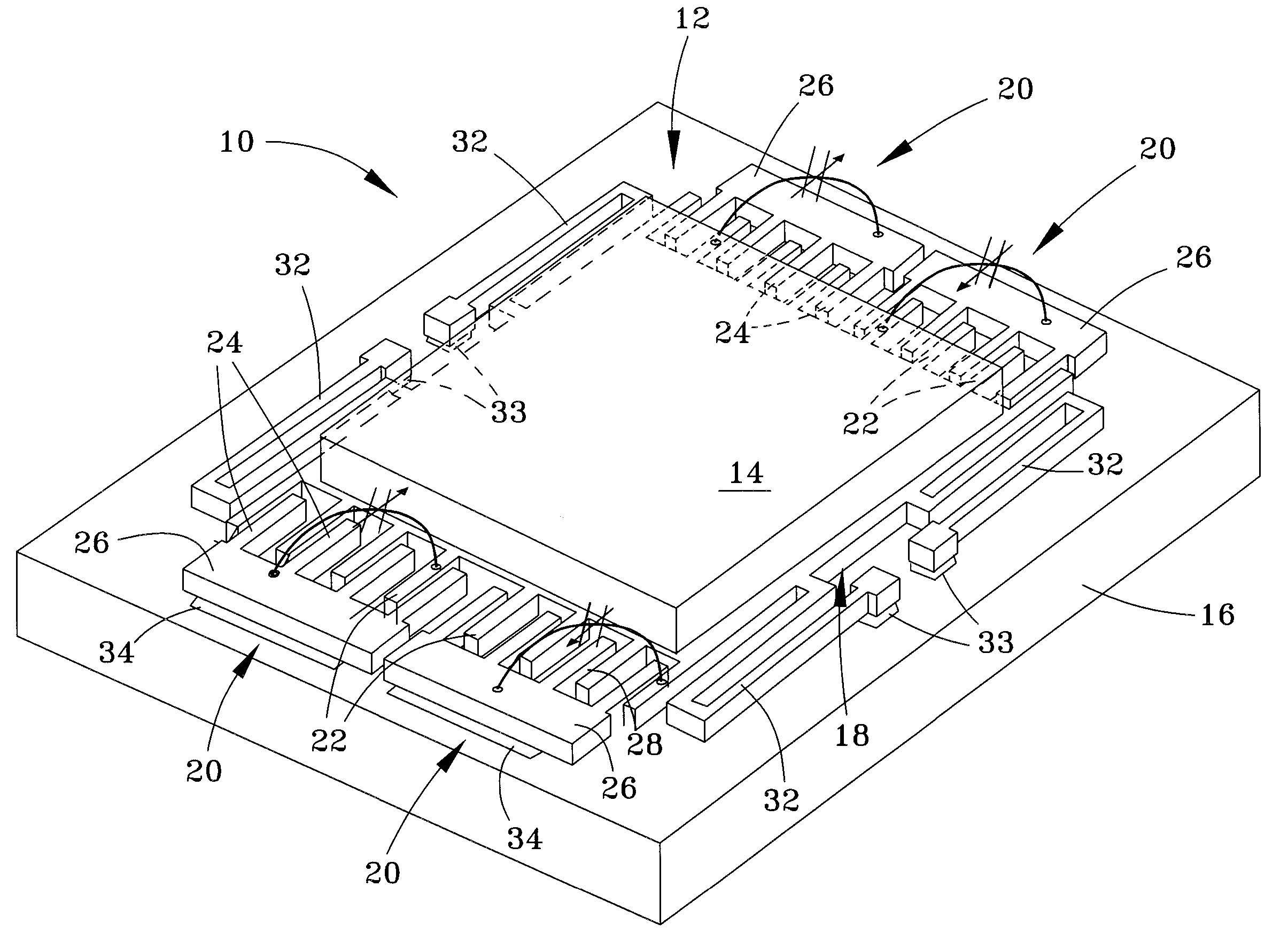
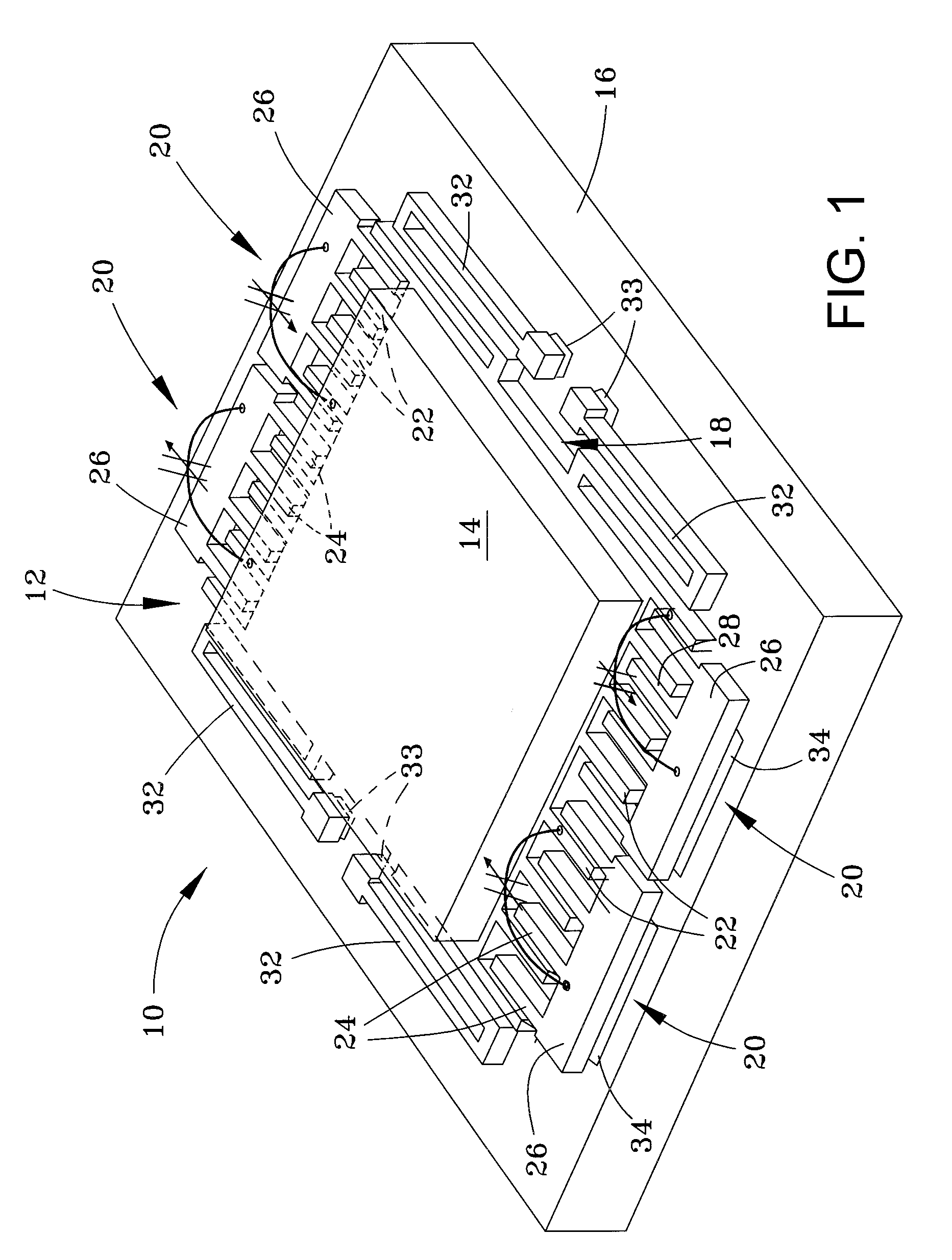
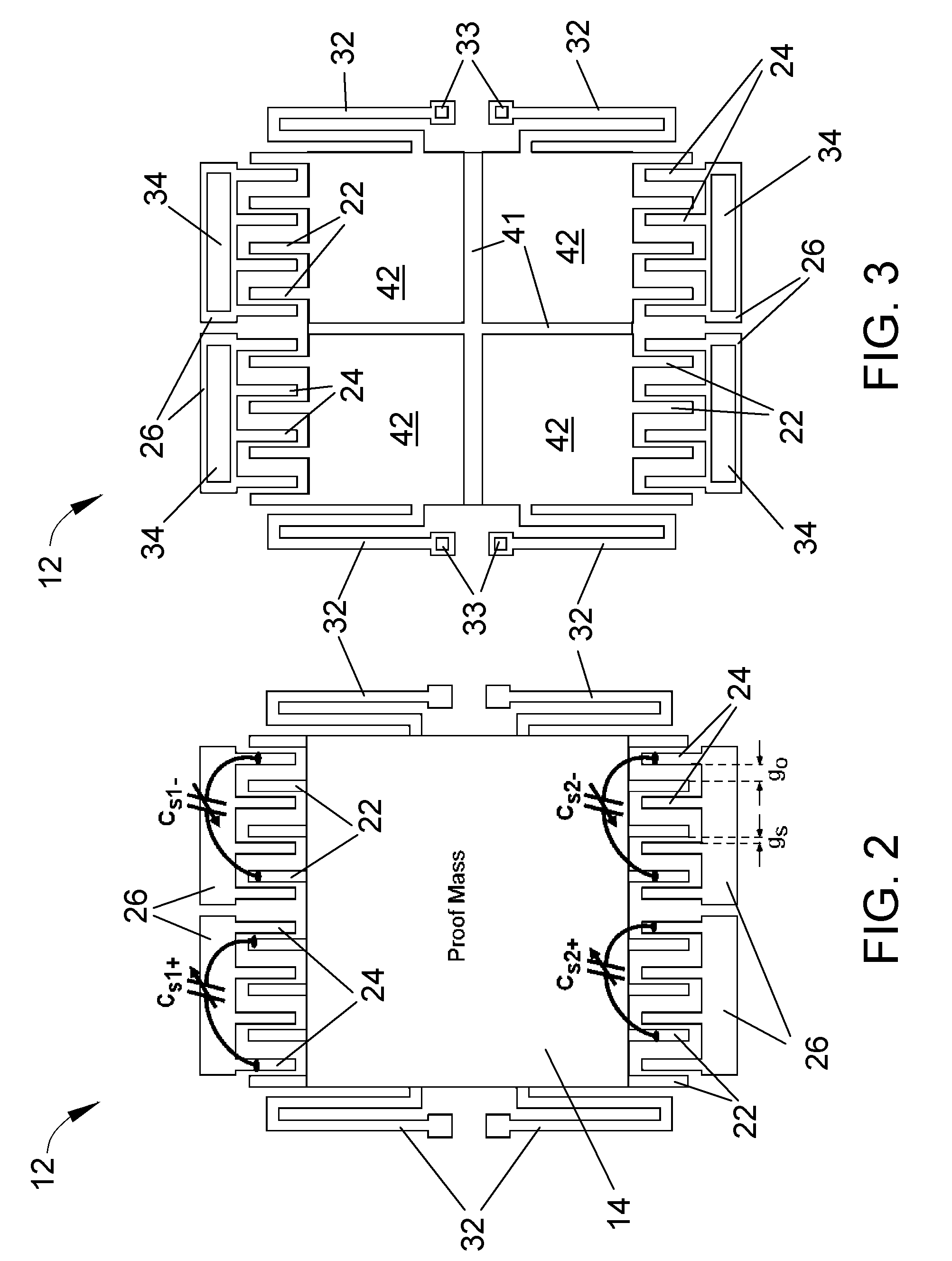
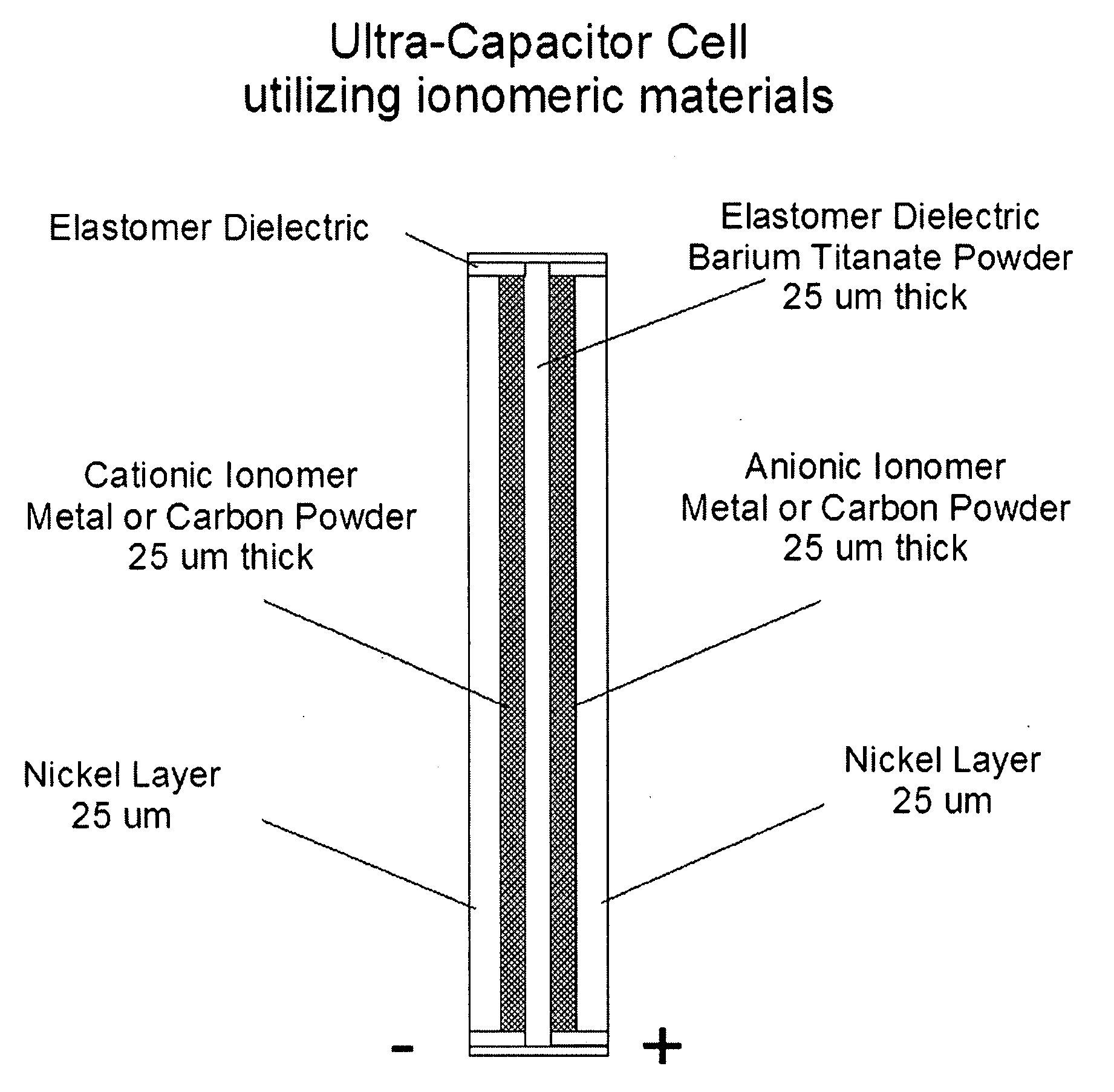
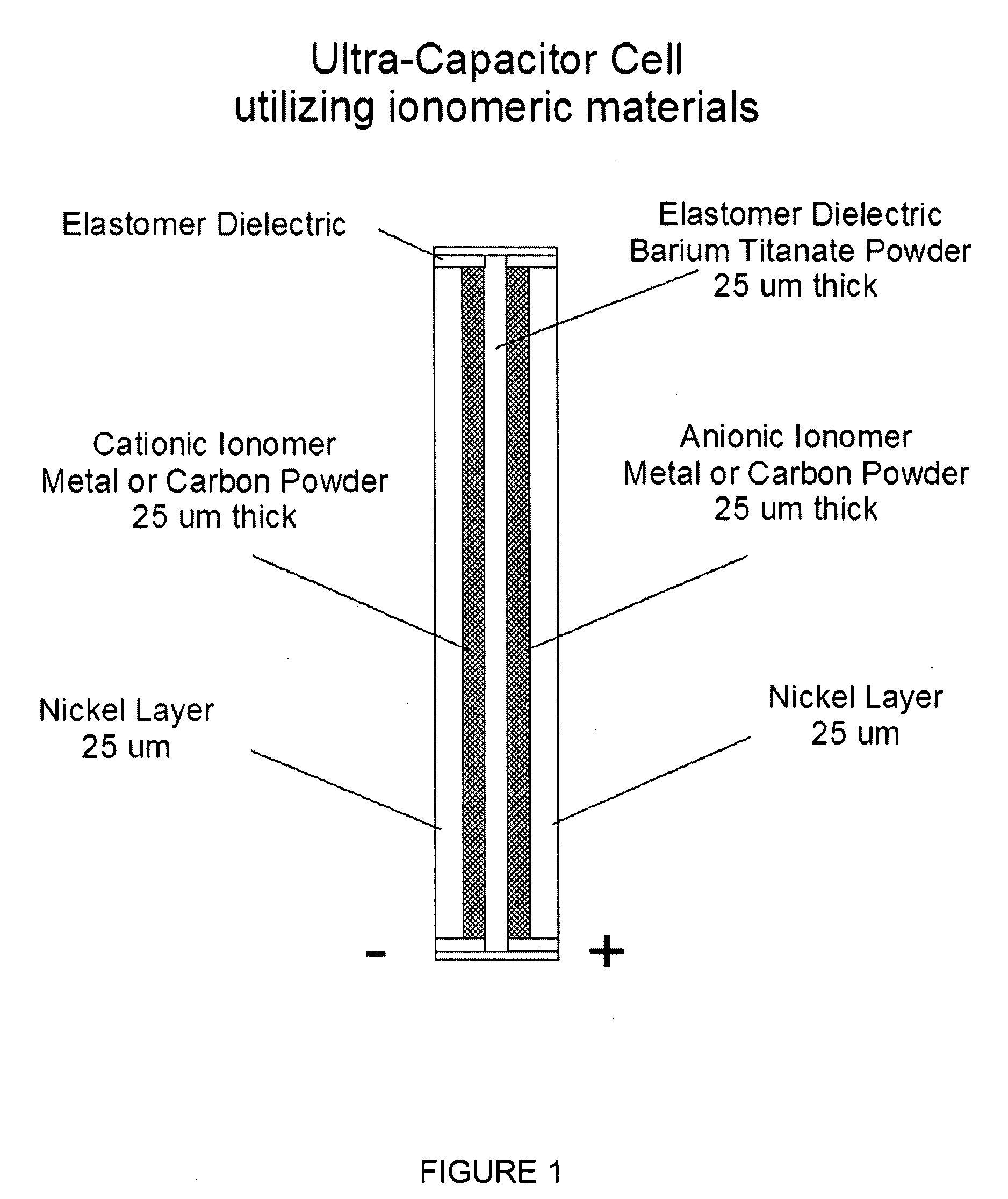
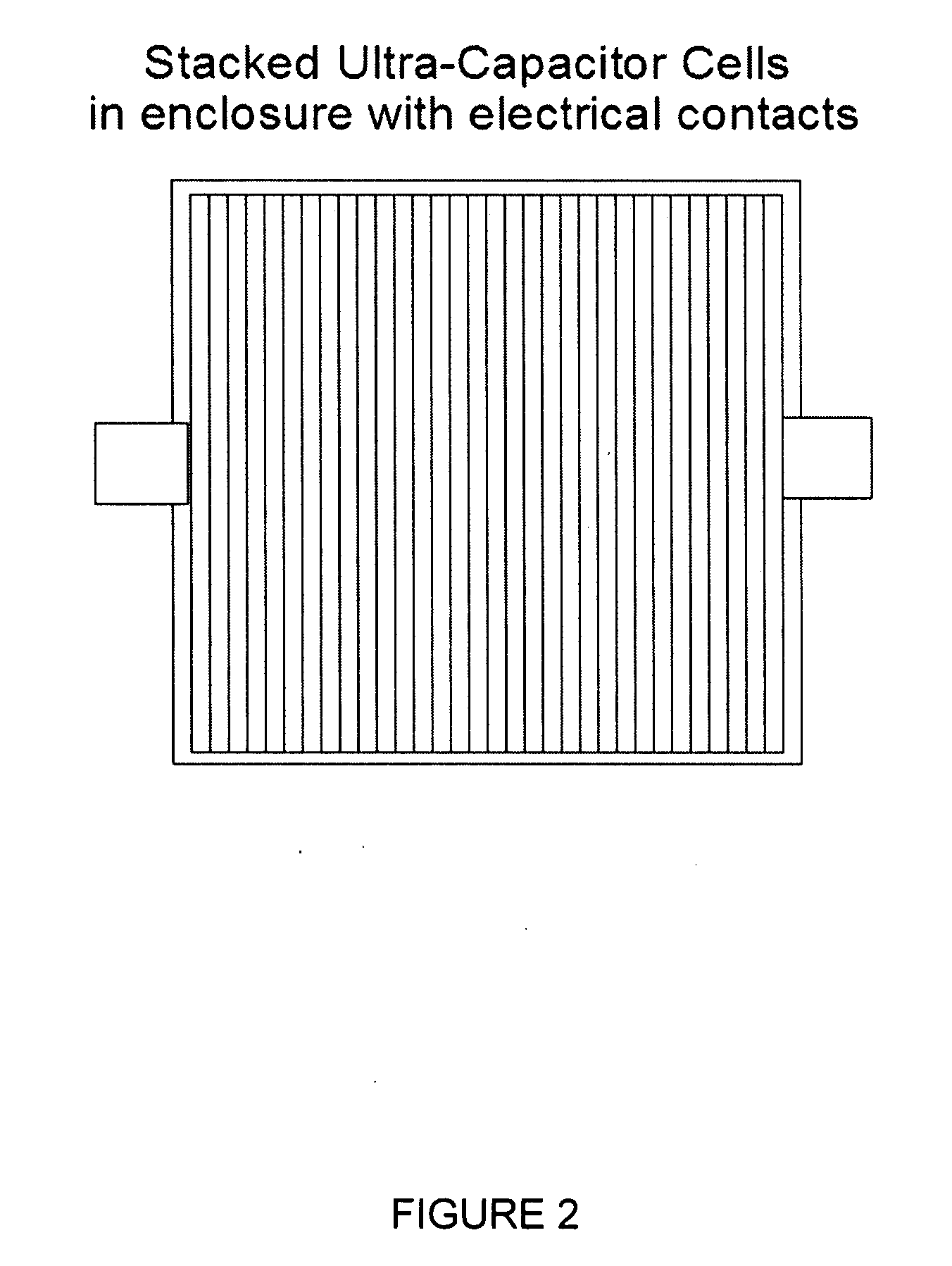
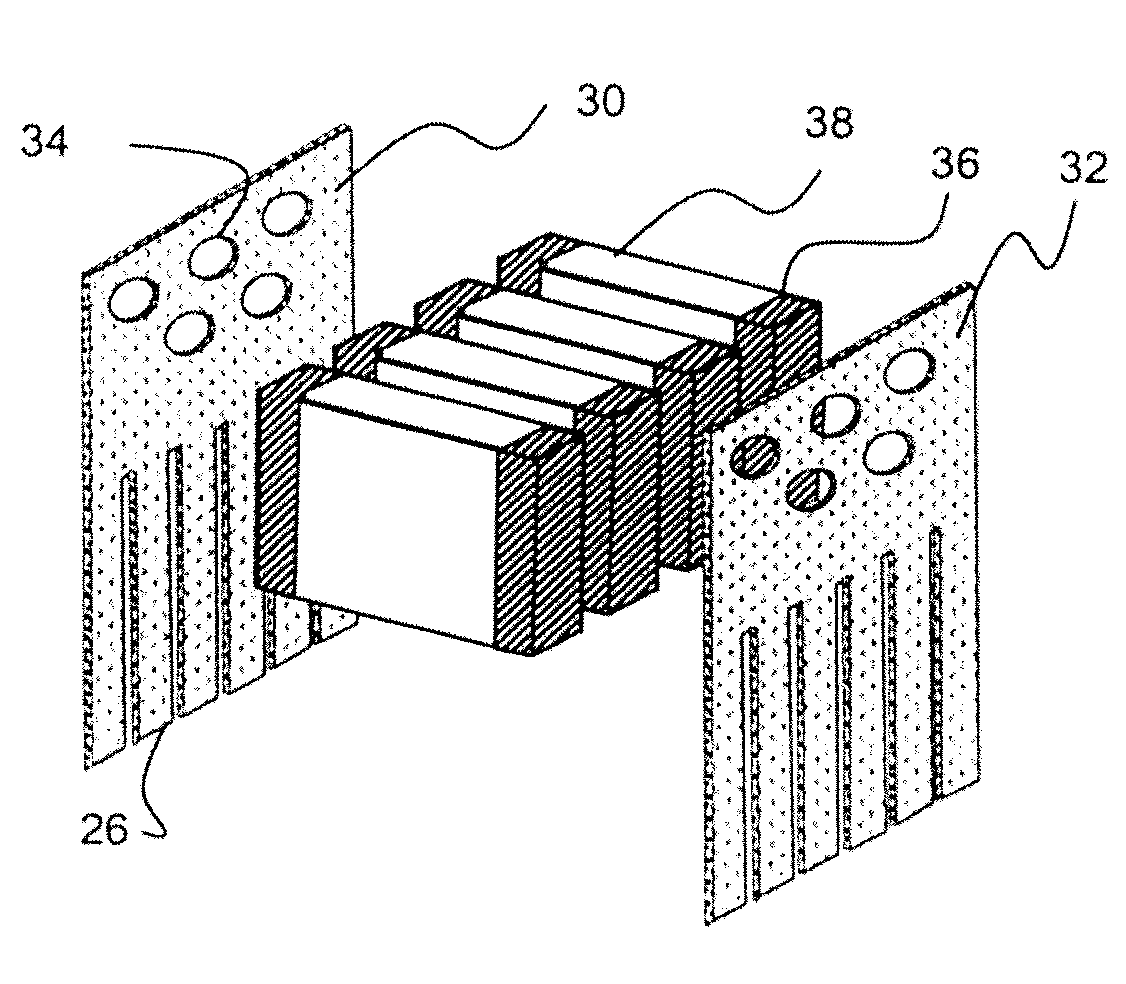
Patents
Literature
1401results about "Non-mechanically variable capacitors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
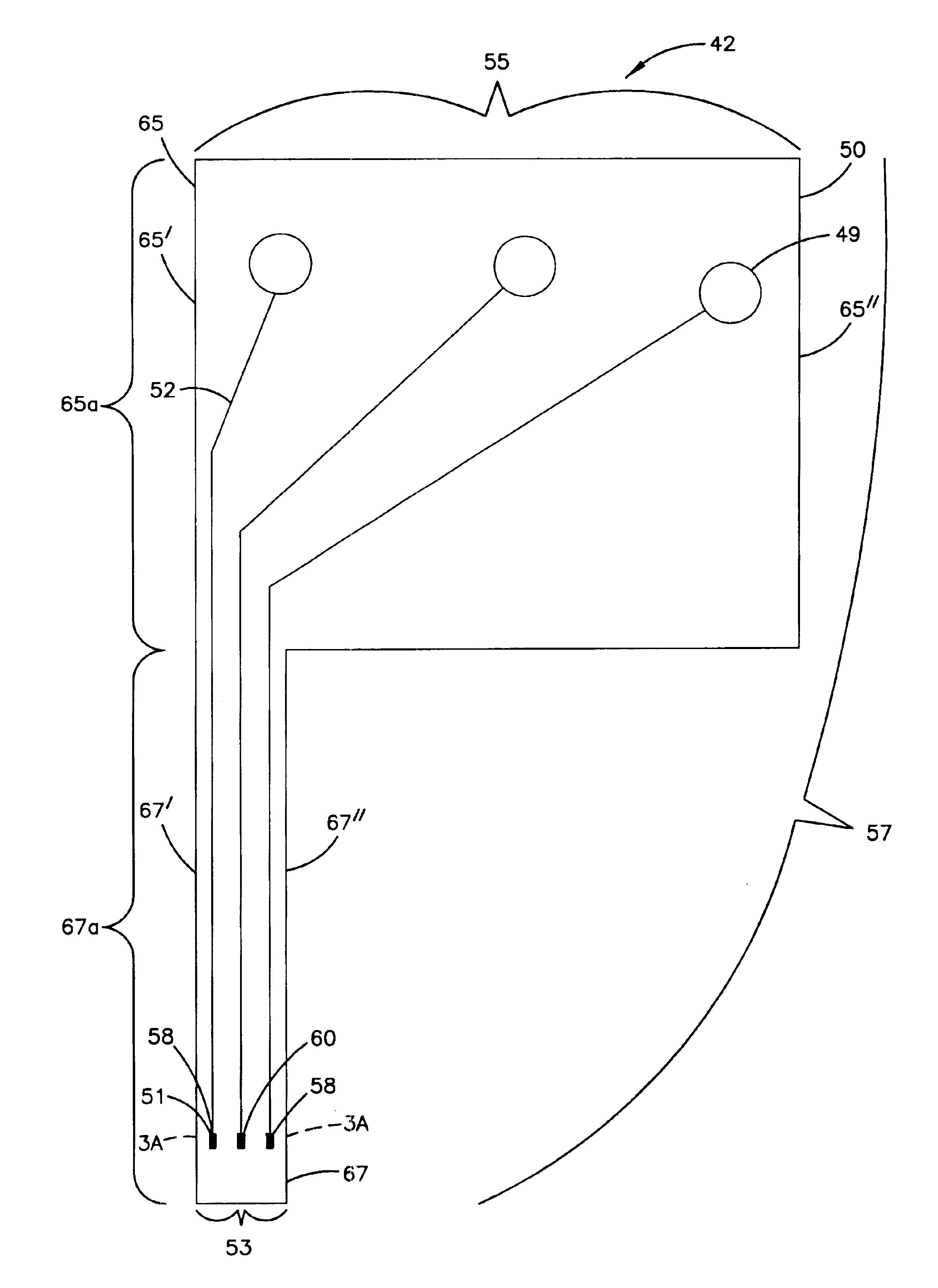
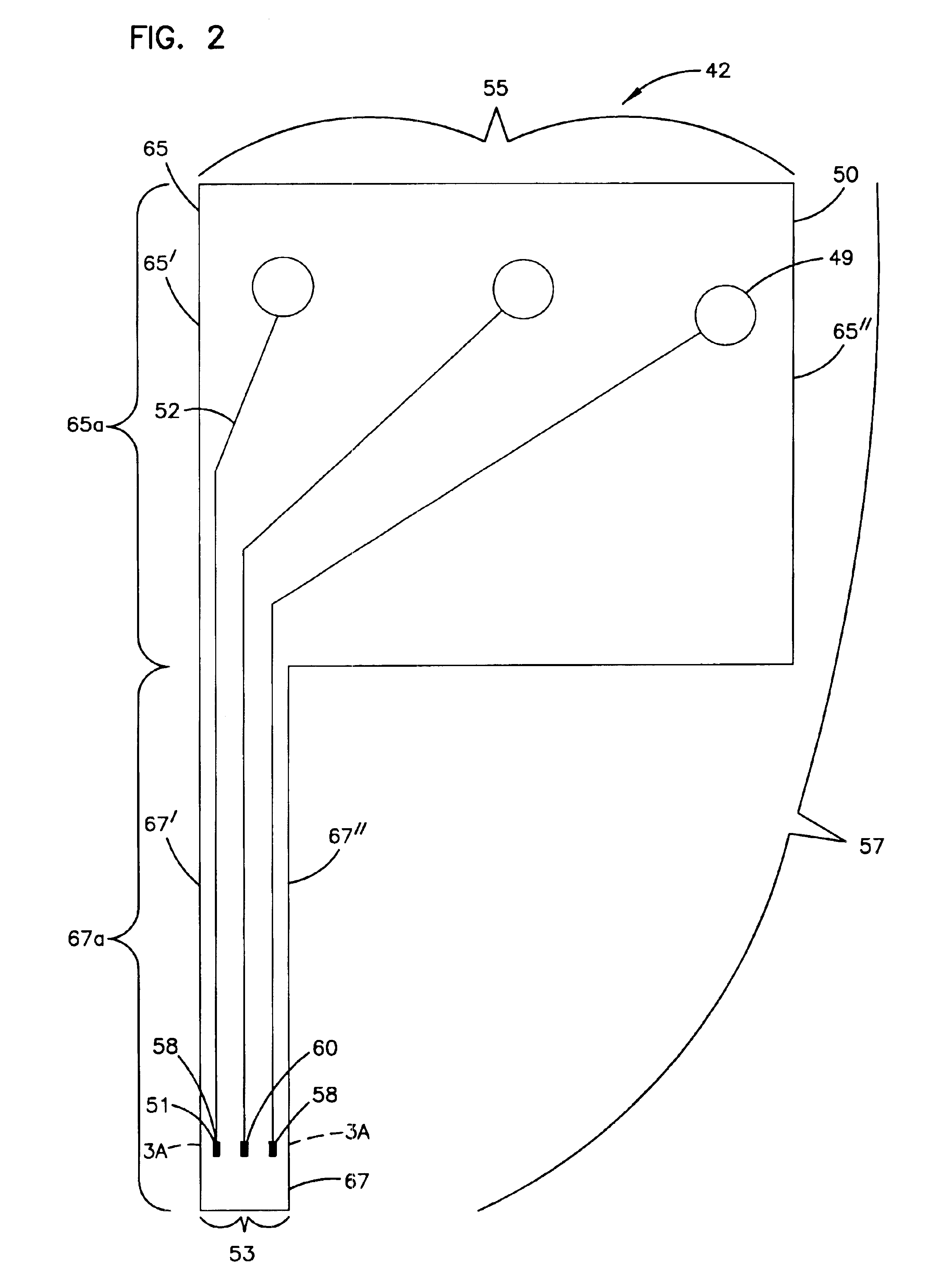
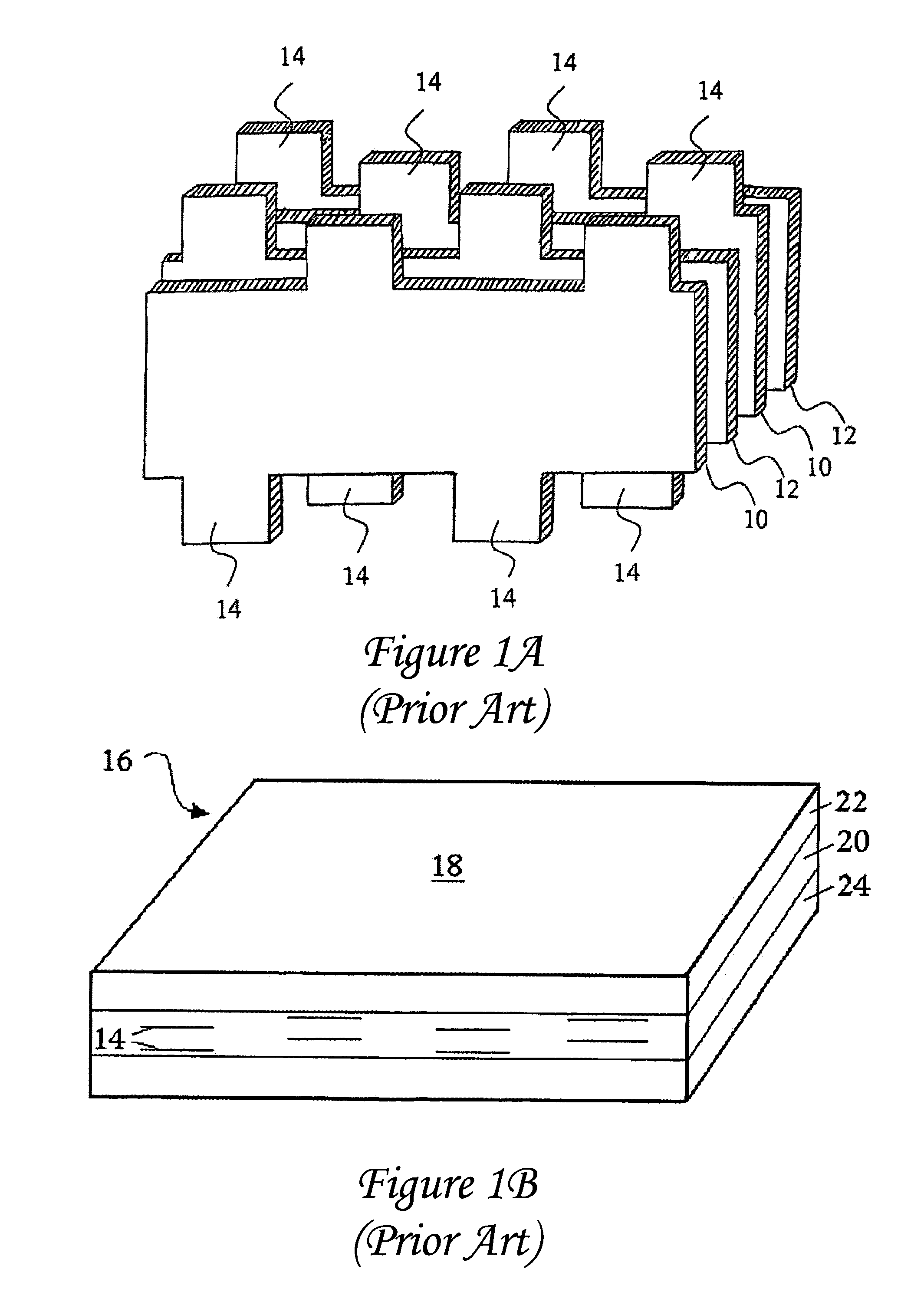
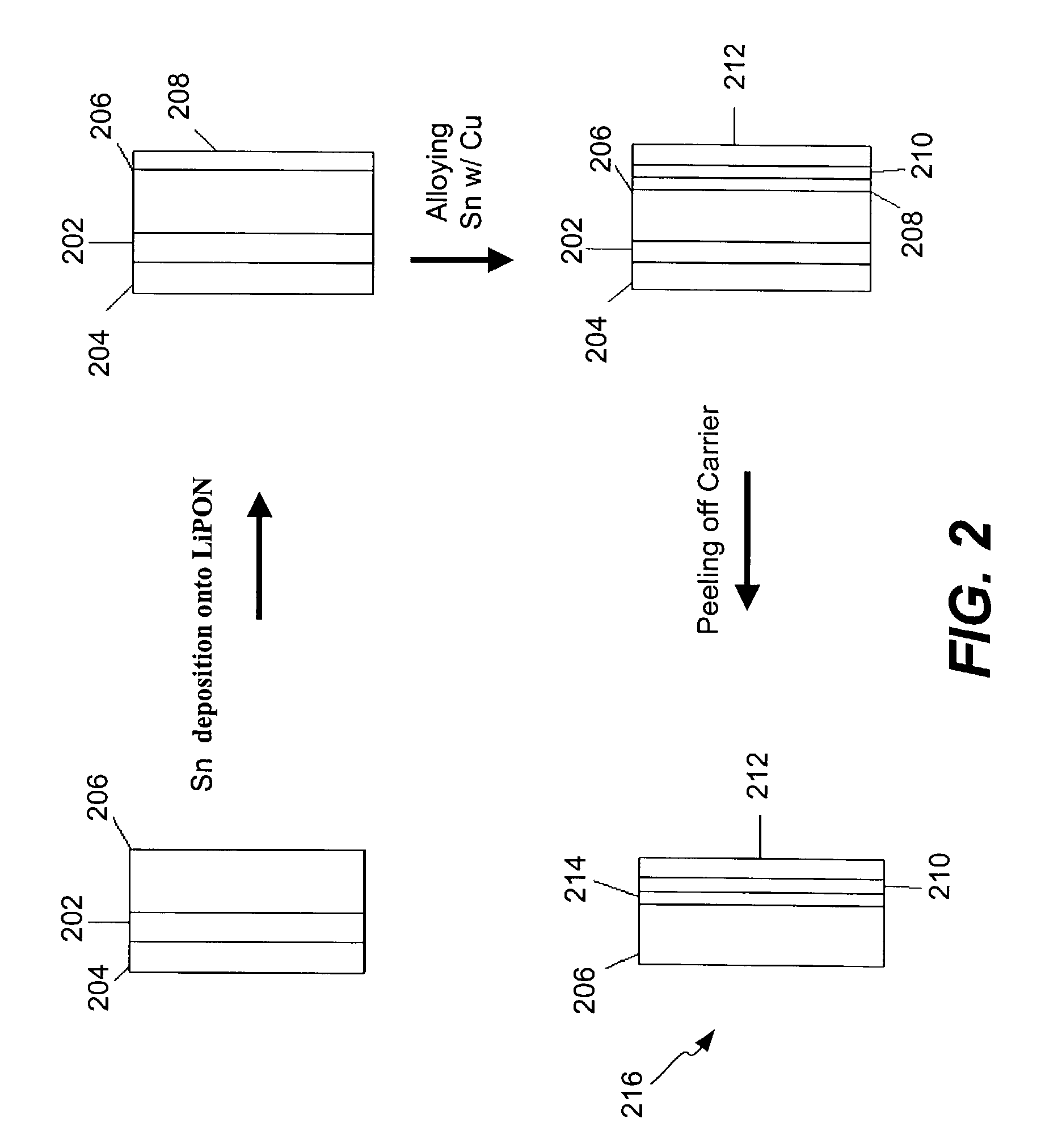
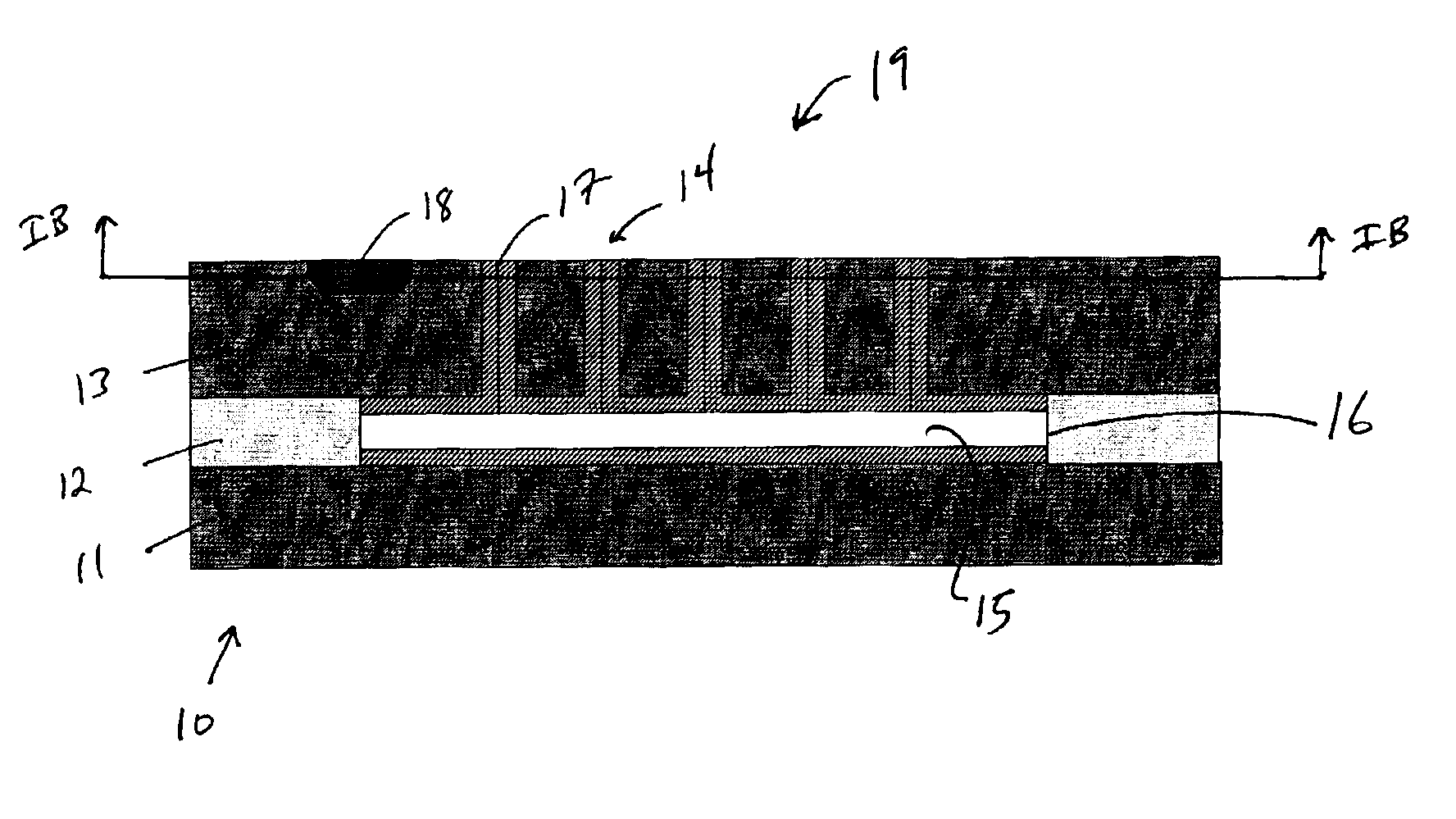
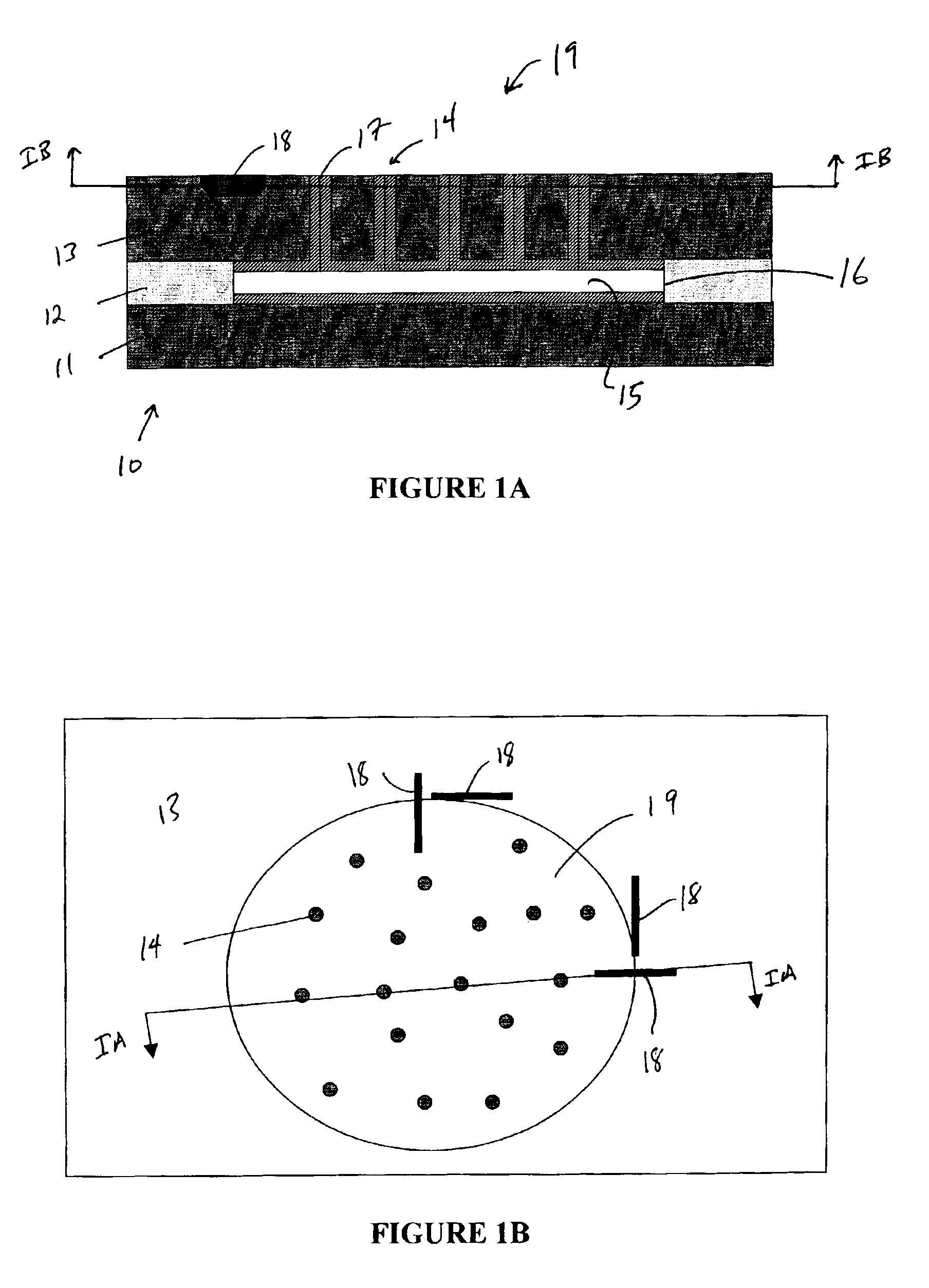
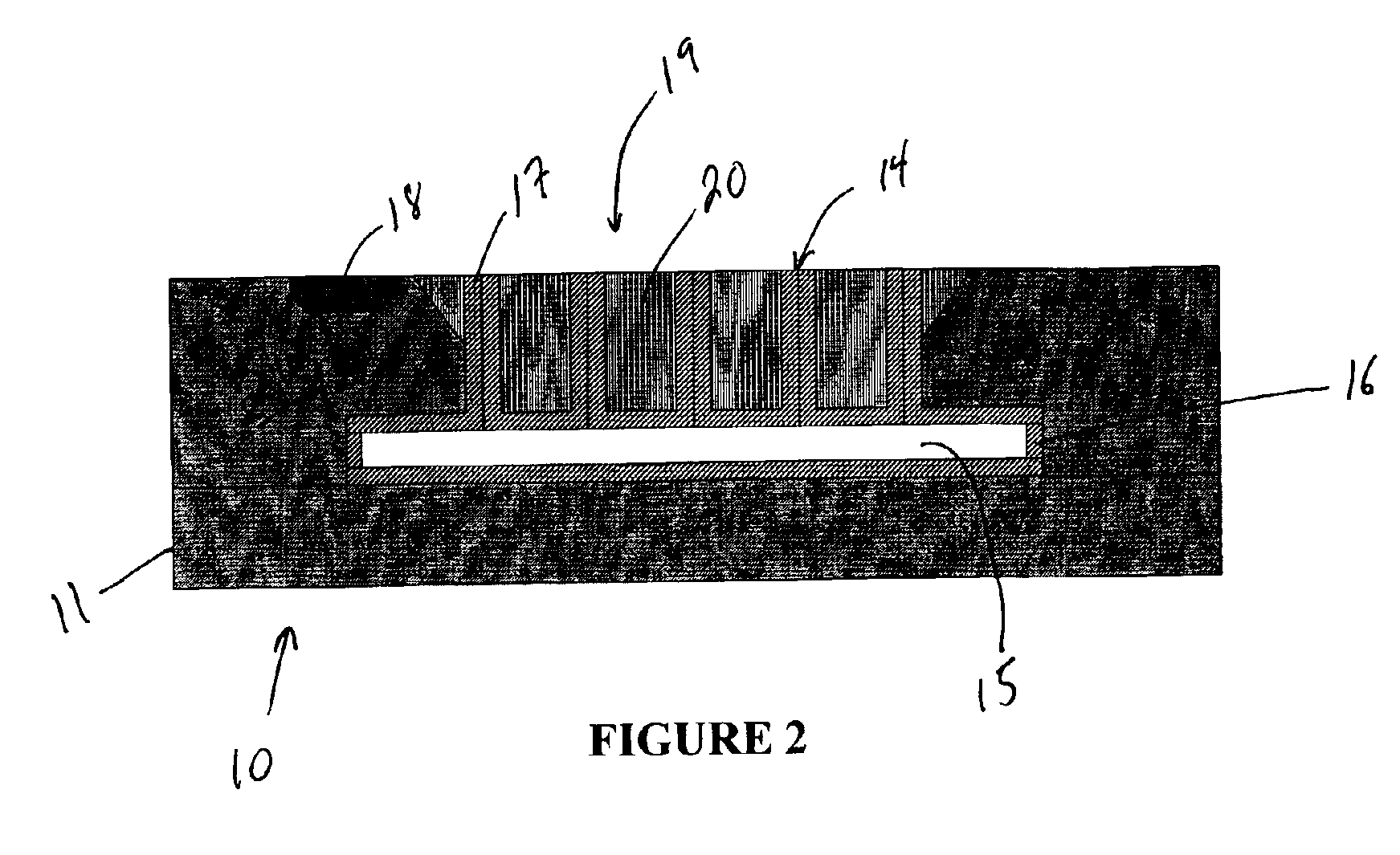
Method of making a transcutaneous electrochemical sensor
InactiveUS6973706B2Efficient productionWave amplification devicesDecorative surface effectsEngineeringConductive materials
A process for the manufacture of small sensors with reproducible surfaces, including electrochemical sensors. One process includes fanning channels in the surface of a substrate and disposing a conductive material in the channels to form an electrode. The conductive material can also be formed on the substrate by other impact and non-impact methods. In a preferred embodiment, the method includes cutting the substrate to form a sensor having a connector portion and a transcutaneous portion, the two portions having edges that define one continuous straight line.
Owner:THERASENSE
Capacitive type touch panel
ActiveUS7864503B2Overcomes drawbackContact materialsMechanically variable capacitor detailsElectrical conductorEngineering
A capacitive type touch panel includes: a transparent substrate; an array of first conductors formed on a surface of the transparent substrate; an array of second conductors formed on the surface of the transparent substrate; a plurality of conductive first bridging lines, each of which interconnects two adjacent ones of the first conductors; a plurality of conductive second bridging lines, each of which interconnects two adjacent ones of the second conductors and each of which intersects insulatively a respective one of the first bridging lines; and a plurality of spaced apart insulators, each of which is disposed at an intersection of a respective one of the first bridging lines and a respective one of the second bridging lines to separate the respective first and second bridging lines.
Owner:TAZIK SOLUTIONS (SUZHOU) LTD
Capacitive type touch panel
ActiveUS20080277259A1Overcomes drawbackContact materialsMechanically variable capacitor detailsElectrical conductorTouch panel
A capacitive type touch panel includes: a transparent substrate; an array of first conductors formed on a surface of the transparent substrate; an array of second conductors formed on the surface of the transparent substrate; a plurality of conductive first bridging lines, each of which interconnects two adjacent ones of the first conductors; a plurality of conductive second bridging lines, each of which interconnects two adjacent ones of the second conductors and each of which intersects insulatively a respective one of the first bridging lines; and a plurality of spaced apart insulators, each of which is disposed at an intersection of a respective one of the first bridging lines and a respective one of the second bridging lines to separate the respective first and second bridging lines.
Owner:TAZIK SOLUTIONS (SUZHOU) LTD
Method and apparatus for use in digitally tuning a capacitor in an integrated circuit device
ActiveUS20110002080A1Easy to controlHigh Power Handling CapabilityAnalogue/digital conversionImpedence matching networksCapacitanceLeast significant bit
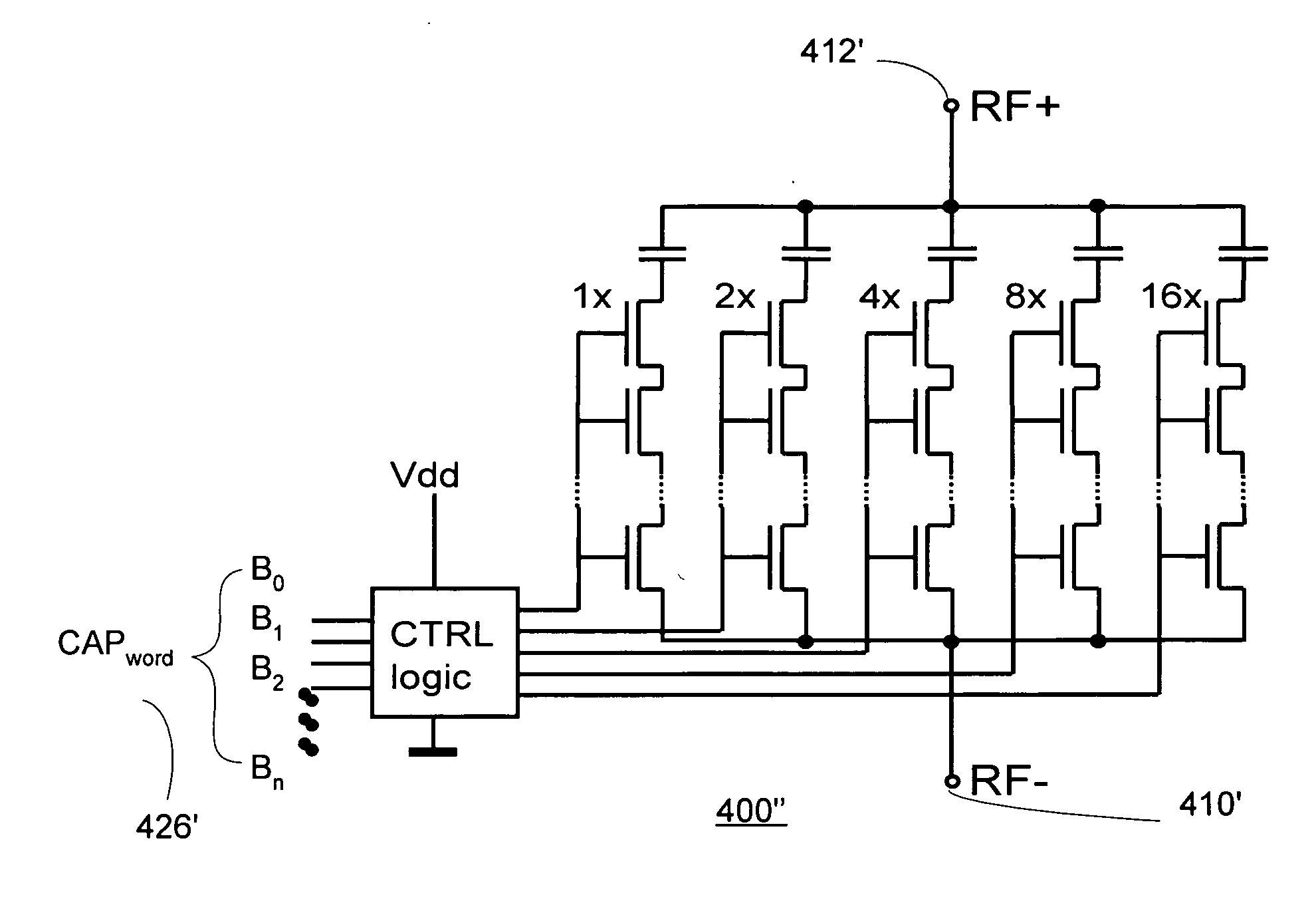
A method and apparatus for use in a digitally tuning a capacitor in an integrated circuit device is described. A Digitally Tuned Capacitor DTC is described which facilitates digitally controlling capacitance applied between a first and second terminal. In some embodiments, the first terminal comprises an FW+ terminal and the second terminal comprises an RF terminal. In accordance with some embodiments, the DTCs comprises a plurality of sub-circuits ordered in significance from least significant bit (LSB) to most significant bit (MSB) sub-circuits, wherein the plurality of significant bit sub-circuits are coupled together in parallel, and wherein each sub-circuit has a first node coupled to the first RF terminal, and a second node coupled to the second FW terminal. The DTCs further include an input means for receiving a digital control word, wherein the digital control word comprises bits that are similarly ordered in significance from an LSB to an MSB.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Plated terminations
InactiveUS7177137B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricHigh densityEngineering
A multilayer electronic component includes a plurality of dielectric layers interleaved with a plurality of internal electrode elements and a plurality of internal anchor tabs. Portions of the internal electrode elements and anchor tabs are exposed along the periphery of the electronic component in one or more aligned columns. Each exposed portion is within a predetermined distance from other exposed portions in a given column such that bridged terminations may be formed by depositing one or more plated termination materials over selected of the respectively aligned columns. Internal anchor tabs may be provided and exposed in prearranged relationships with other exposed conductive portions to help nucleate metallized plating material along the periphery of a device. External anchor tabs or lands may be provided to form terminations that extend to top and / or bottom surfaces of the device. Selected of the conductive elements may be formed by a finite volume percentage of ceramic material for enhanced durability, and external lands may be thicker than internal conductive elements and / or may also be embedded in top and / or bottom component surfaces. A variety of potential internal electrode configurations are possible including ones configured for orientation-insensitive component mounting and for high density peripheral termination interdigitated capacitors.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
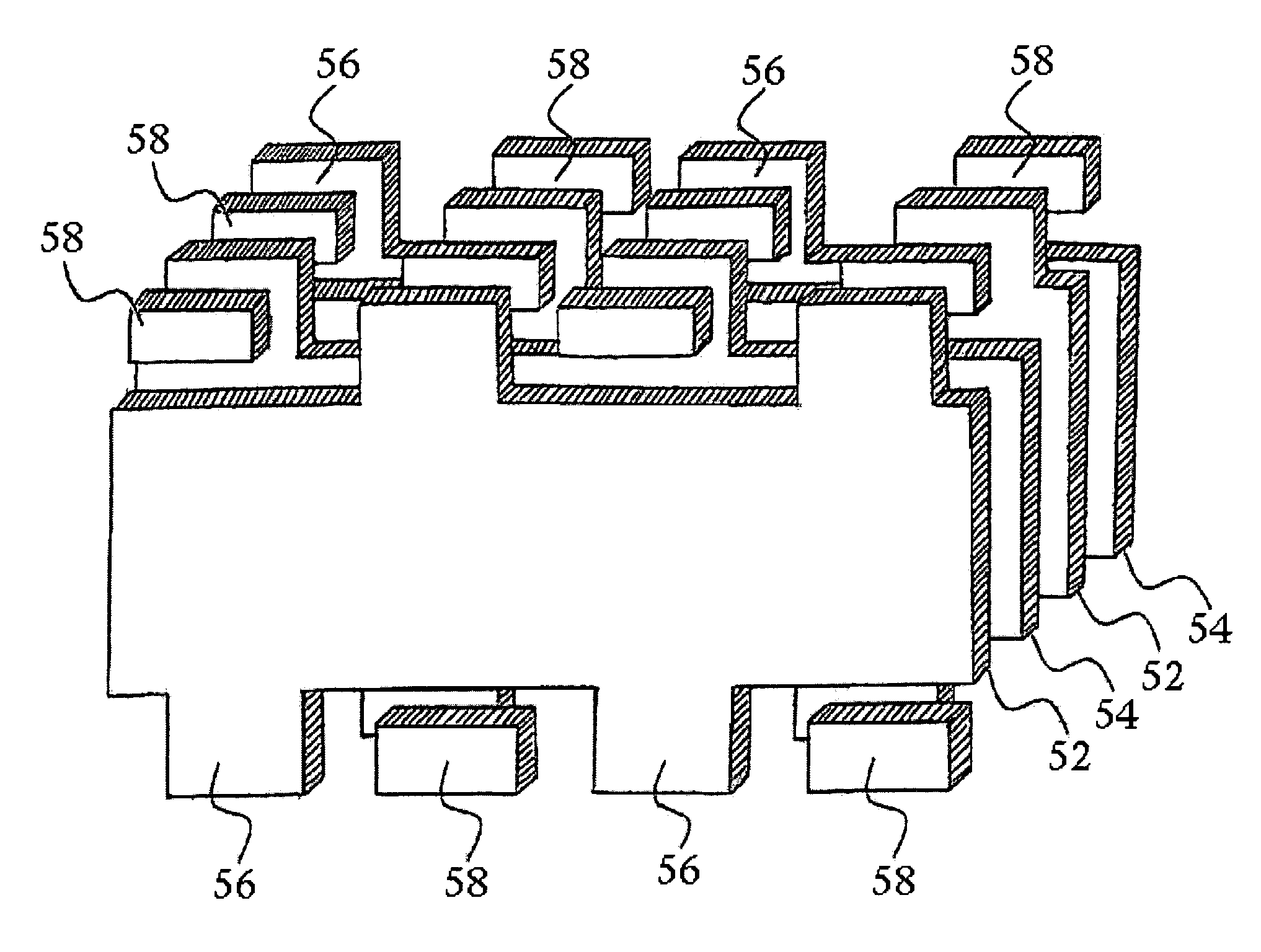
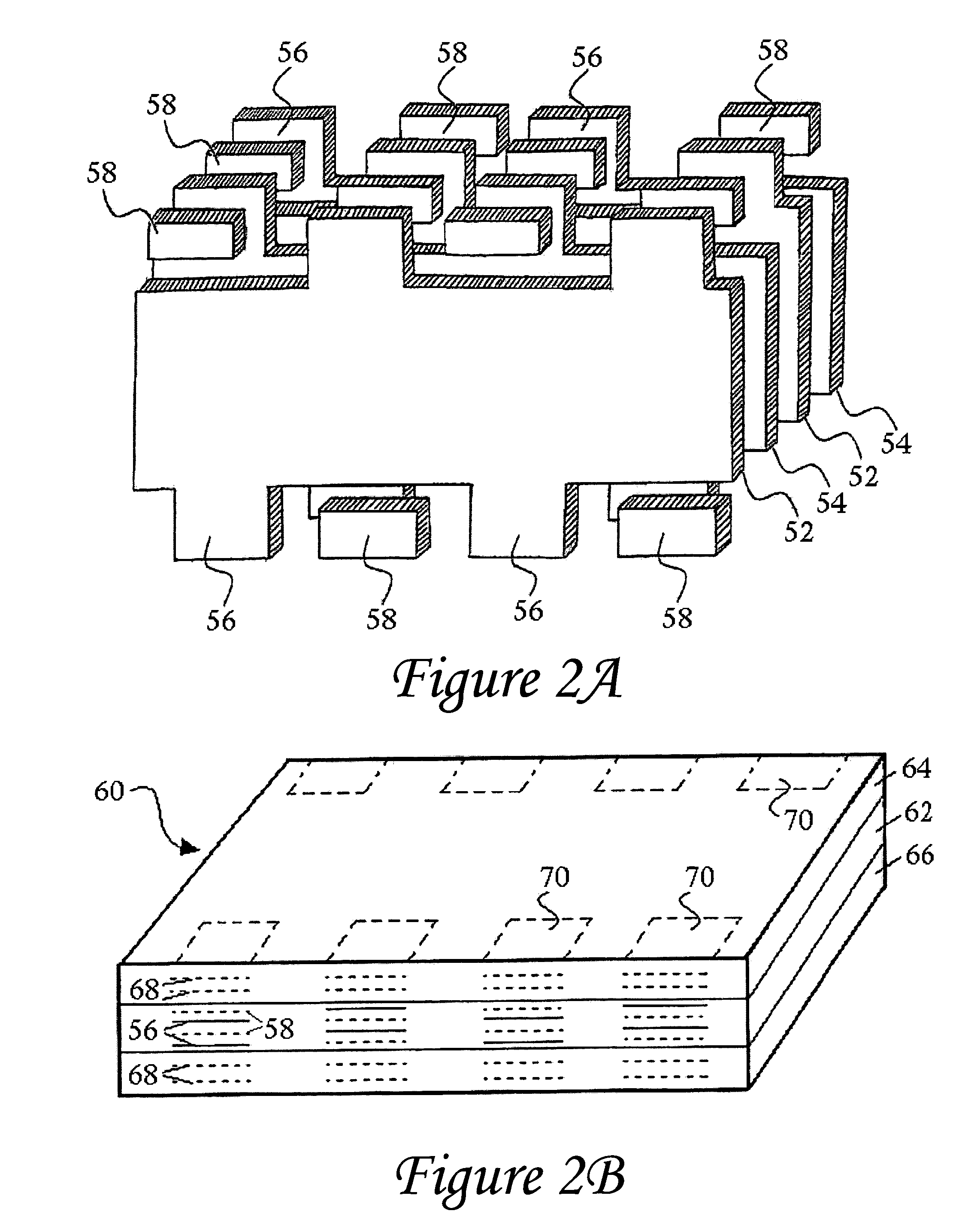
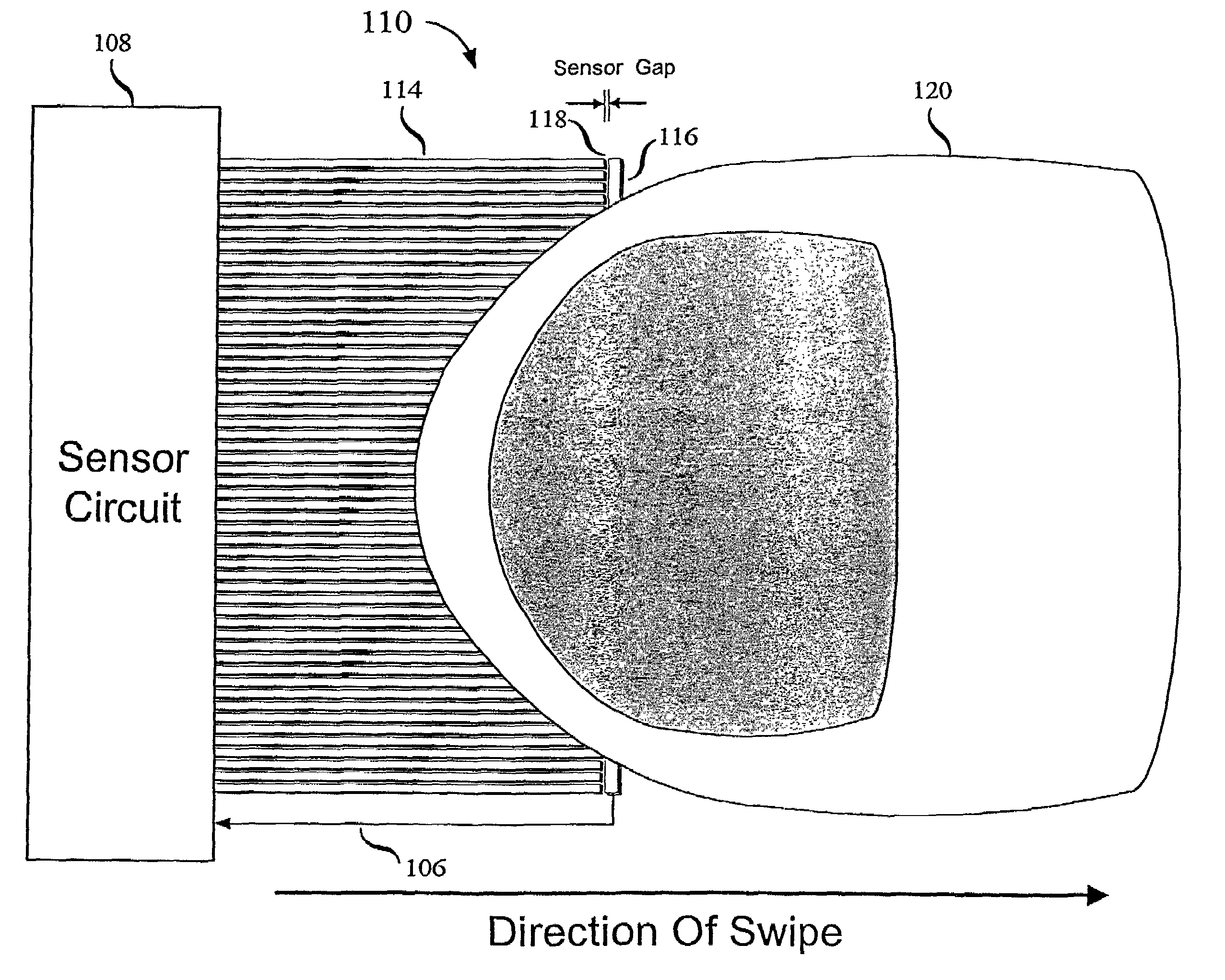
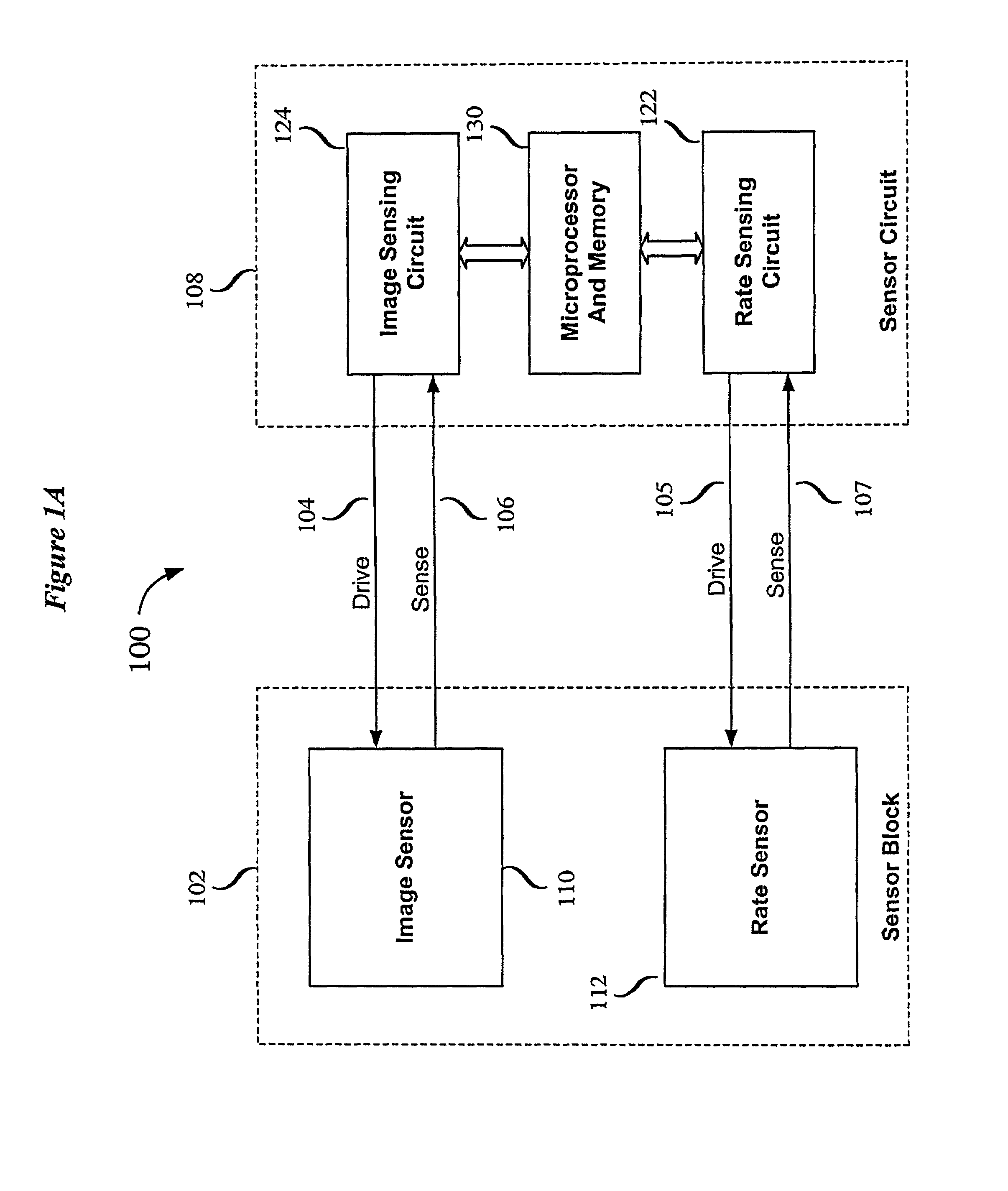
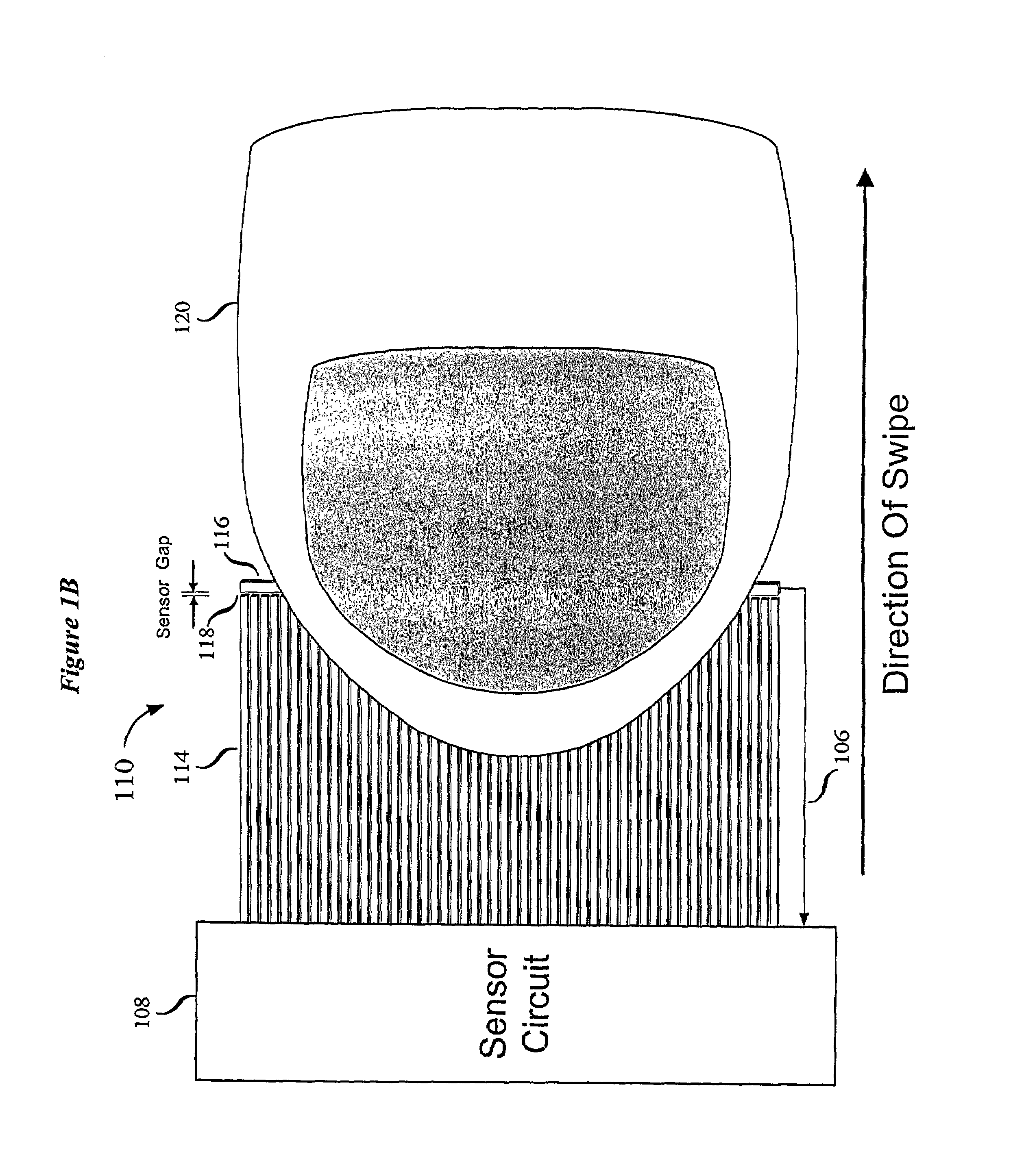
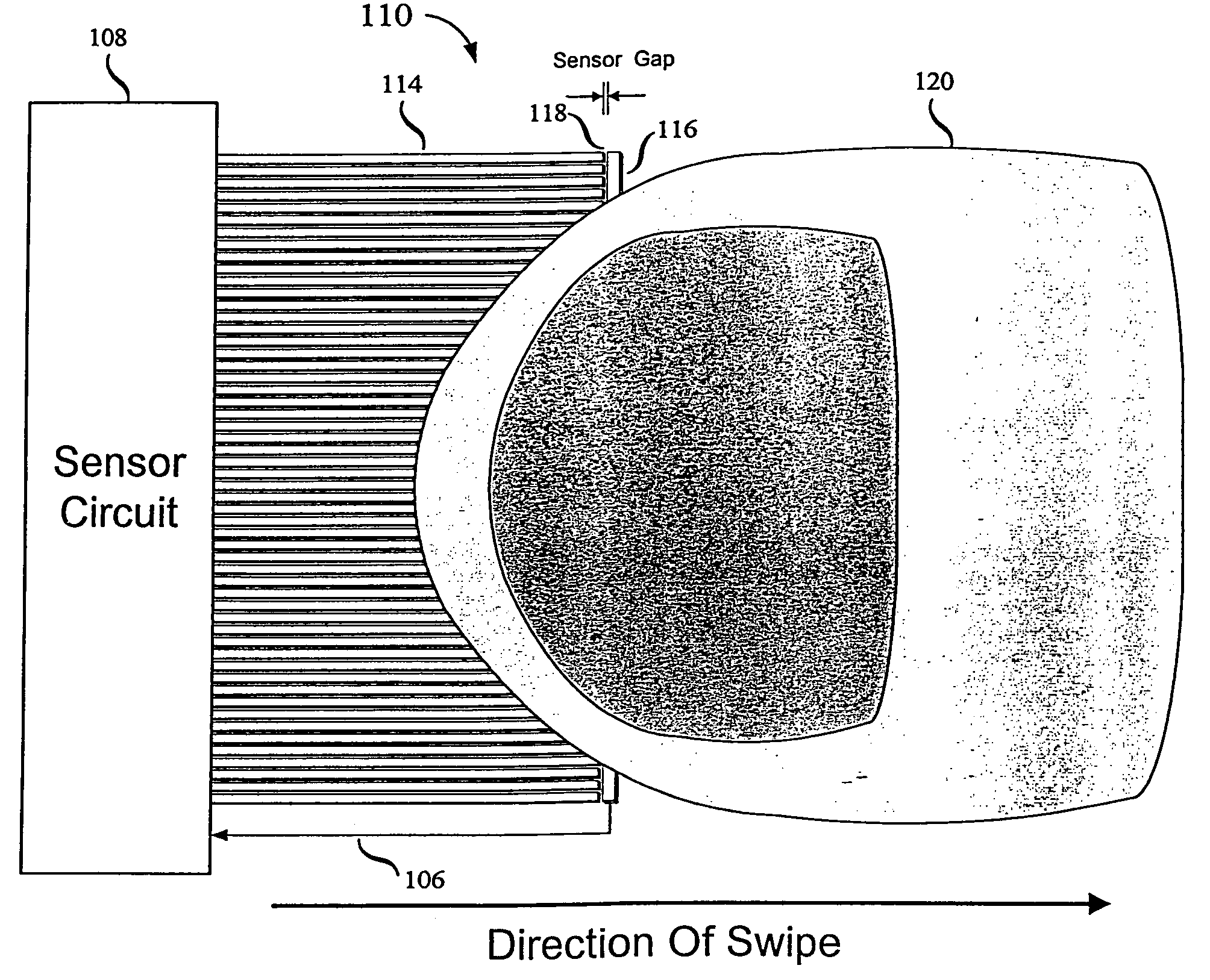
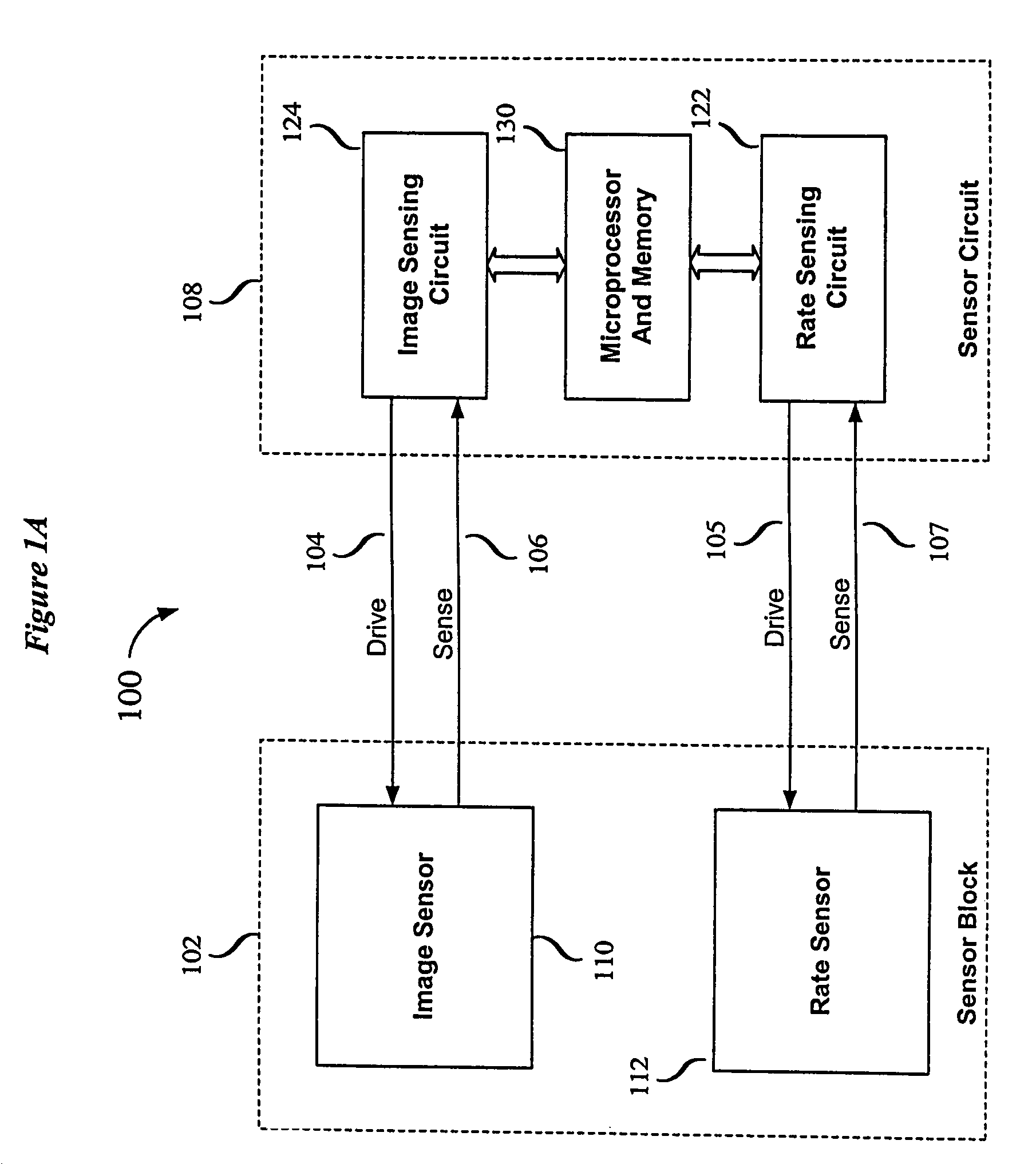
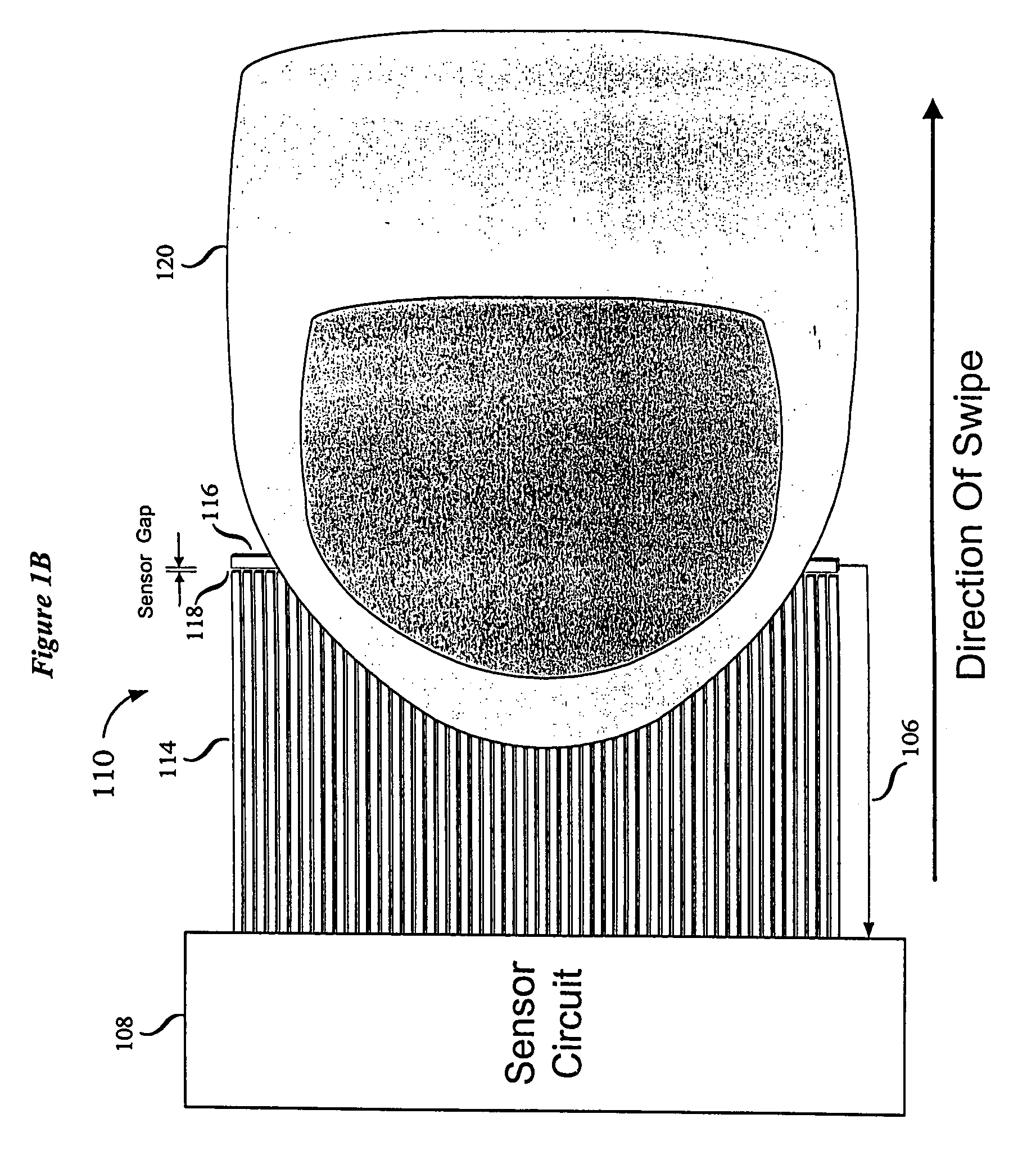
Swiped aperture capacitive fingerprint sensing systems and methods
InactiveUS7099496B2Faster rateResistance/reactance/impedenceAcceleration measurementEngineeringFlexible electronics
A fingerprint sensing system includes an image sensor, a rate sensor and a sensor circuit. The image sensor includes a linear array of capacitive sensors for capacitive sensing of ridge peaks and ridge valleys of a fingerprint on a swiped finger. The rate sensor senses the speed of the finger as it is swiped across the image sensor. The sensor circuit supplies image drive signals to the image sensor and detects image signals in response to the drive signals. The sensor circuit supplies rate drive signals to the rate sensor and detects rate signals in response to the rate drive signals. The sensor circuit further coordinates the image signals and the rate signals to provide a fingerprint image. The image sensor may be configured as an image pickup plate and multiple image drive plates formed on a substrate, such as a flexible printed circuit board or other flexible substrate which may conform to the shape of the finger.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Plated terminations
InactiveUS6960366B2Improved termination featureEliminate and greatly simplifyResistor terminals/electrodesFinal product manufactureTermination problemEngineering
Improved termination features for multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions which may optionally extend to the cover layers of a multilayer component. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. External anchor tabs positioned on one or both of top and bottom surfaces of a monolithic structure can facilitate the formation of selective wrap-around plated terminations. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Capacitive Touch Panel with Low Impedance
ActiveUS20090085891A1Reduce resistanceSystem coupling capacitance and resistanceElectronic circuit testingStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceDielectric layer
A capacitive touch panel and a display device using the capacitive touch panel are provided. The capacitive touch panel includes a first electrode layer, a second electrode layer, and a dielectric layer disposed between two layers. The first electrode layer has a plurality of first A electrode strings and first B electrode strings extended along a first direction. The first A electrode string and the first B electrode string respectively has a plurality of first direction electrodes. The second electrode layer has a plurality of second direction electrodes connected in series along a second direction. The first A and B electrode strings are disconnected in the first electrode layer while they are simultaneously detected for presence of signal variation.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Method of fabricating silicon capacitive sensor
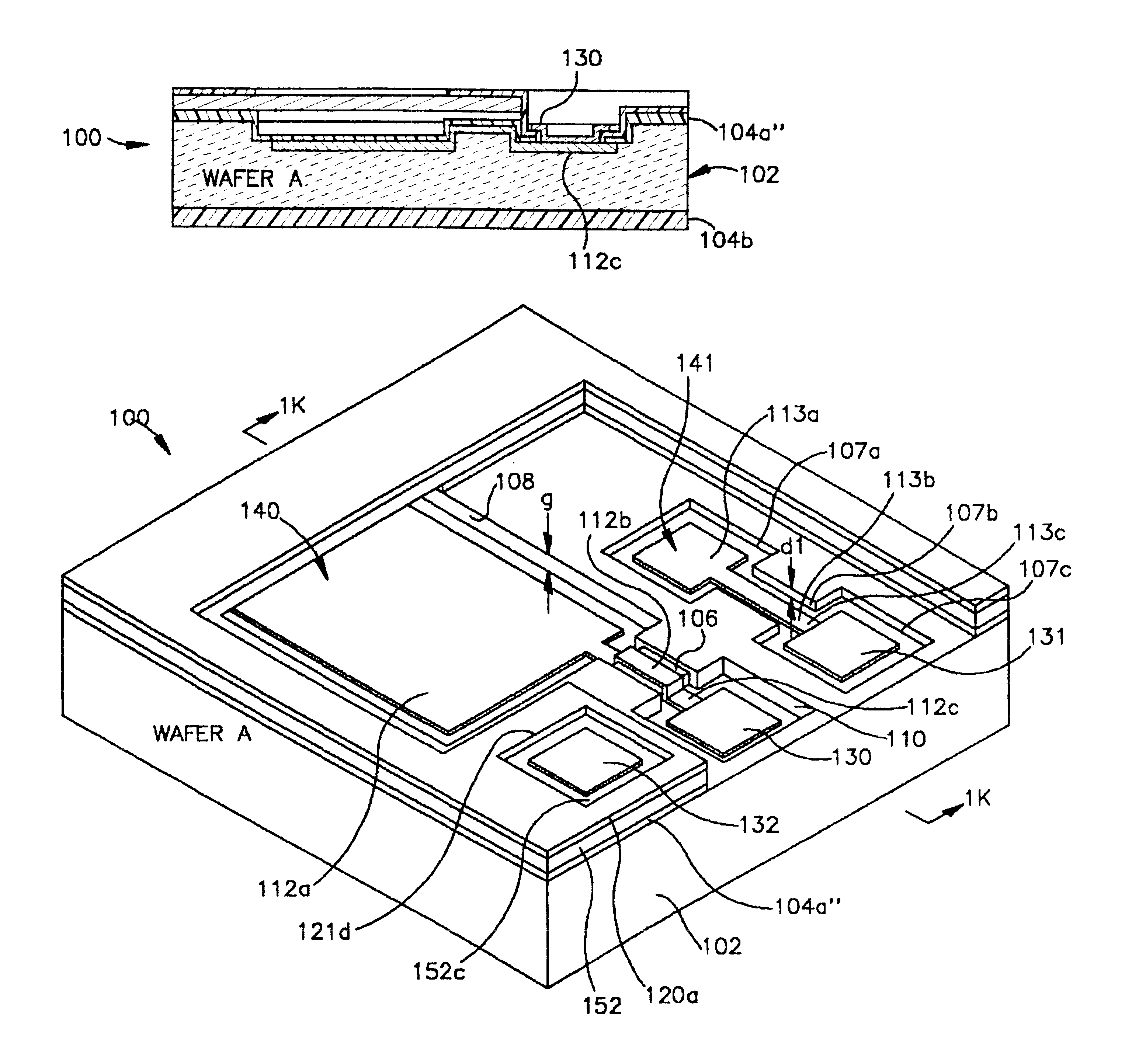
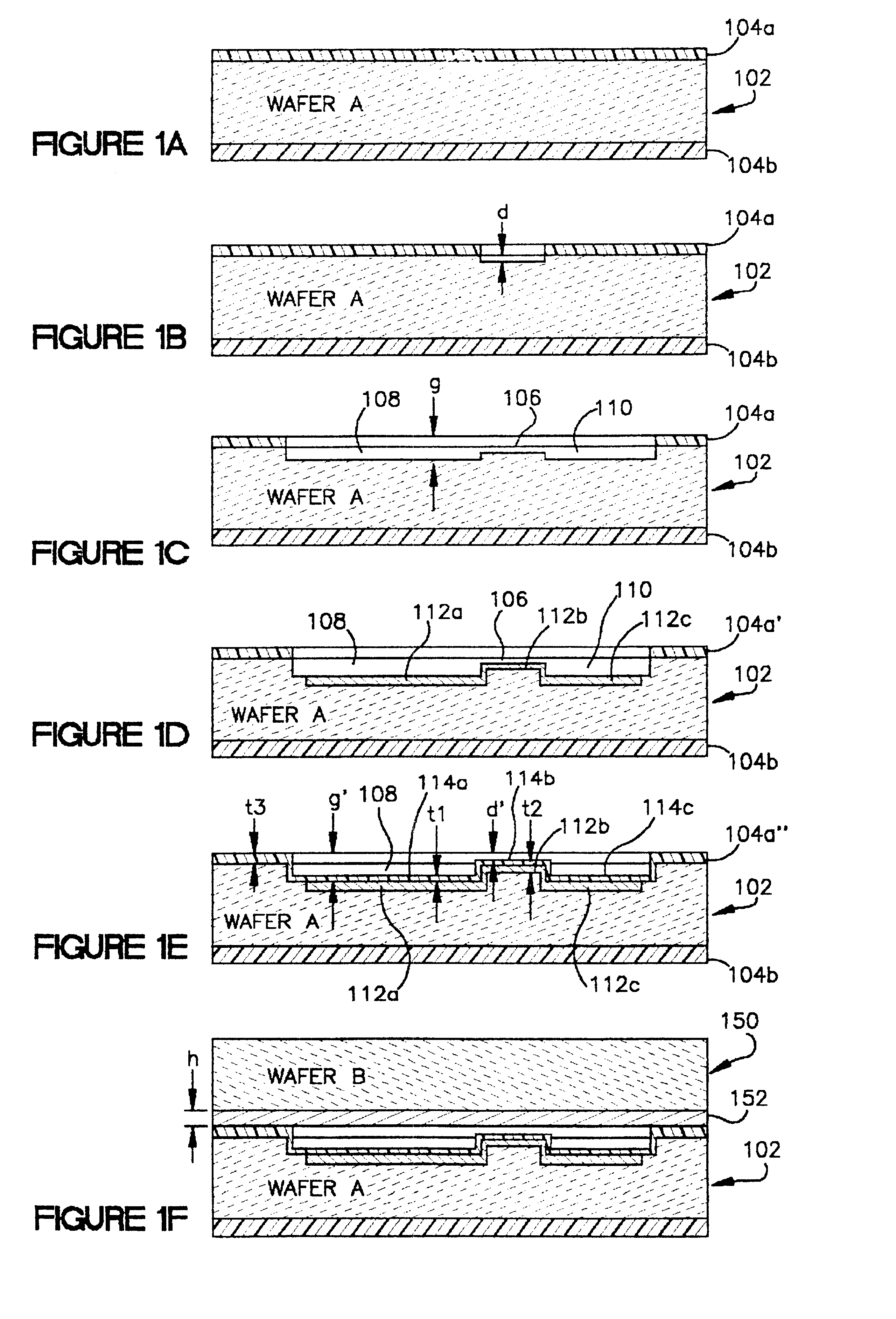
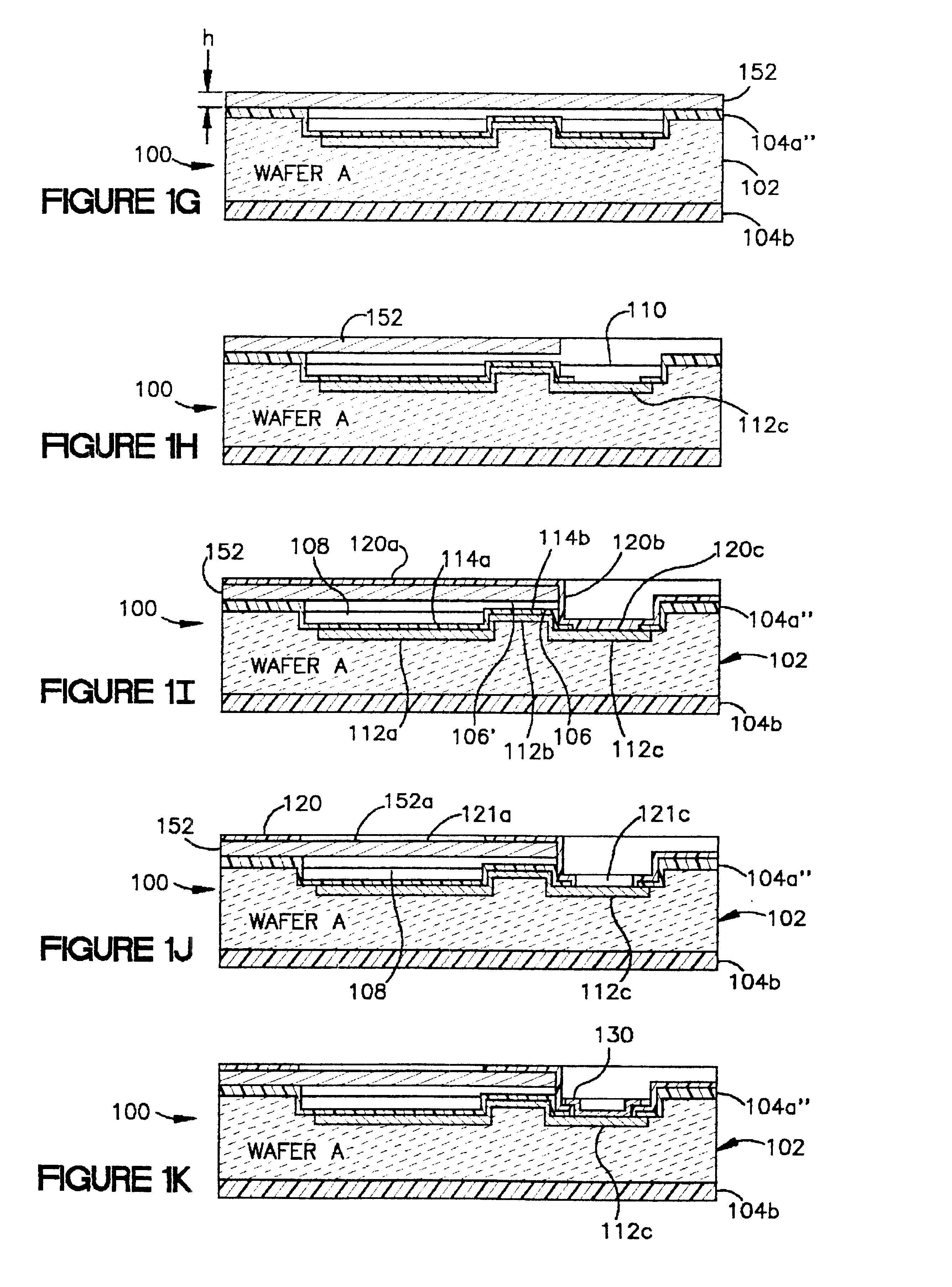
InactiveUS6465271B1Good linear sensitivityLong-term stabilityInflated body pressure measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitive pressure sensorDiffusion
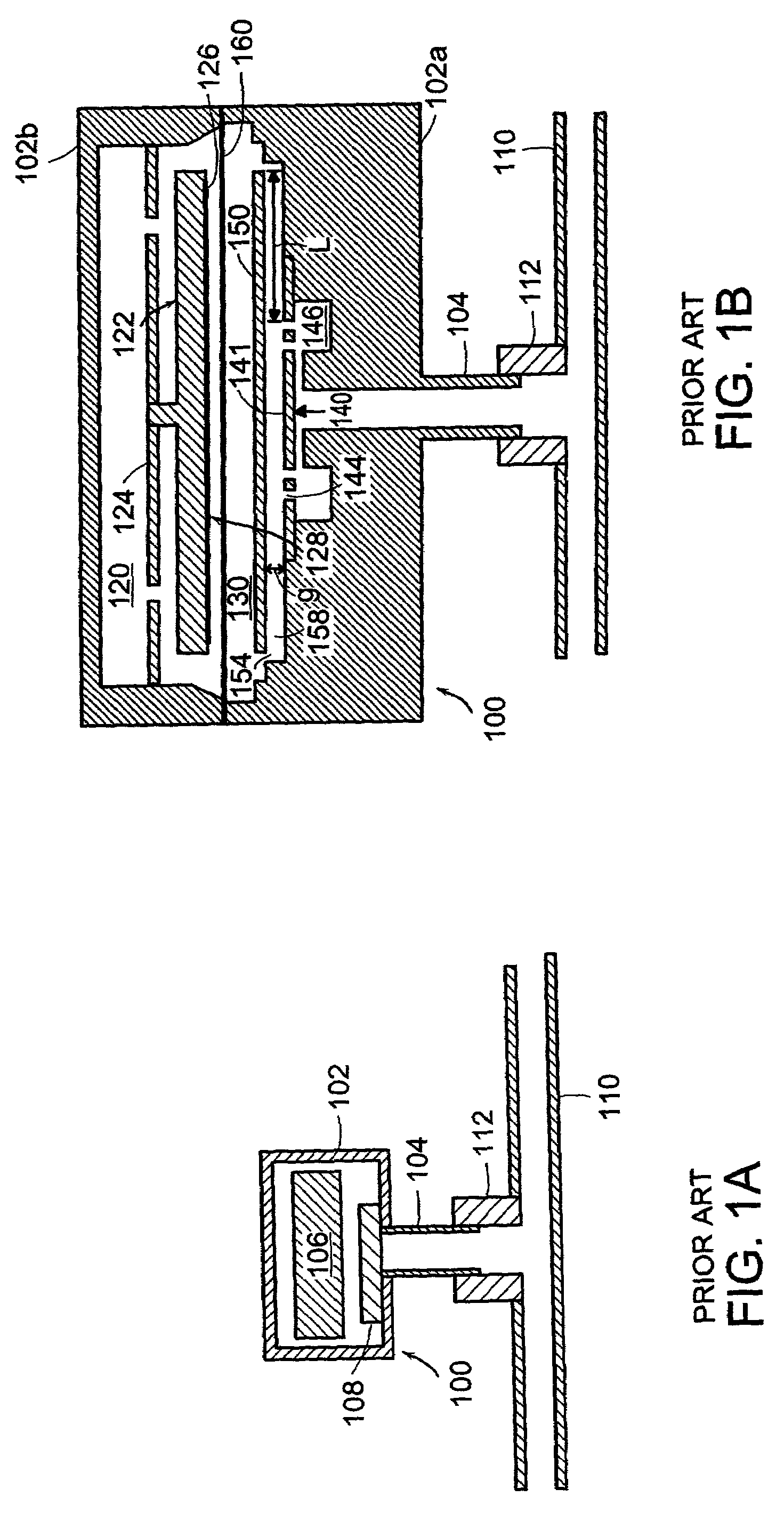
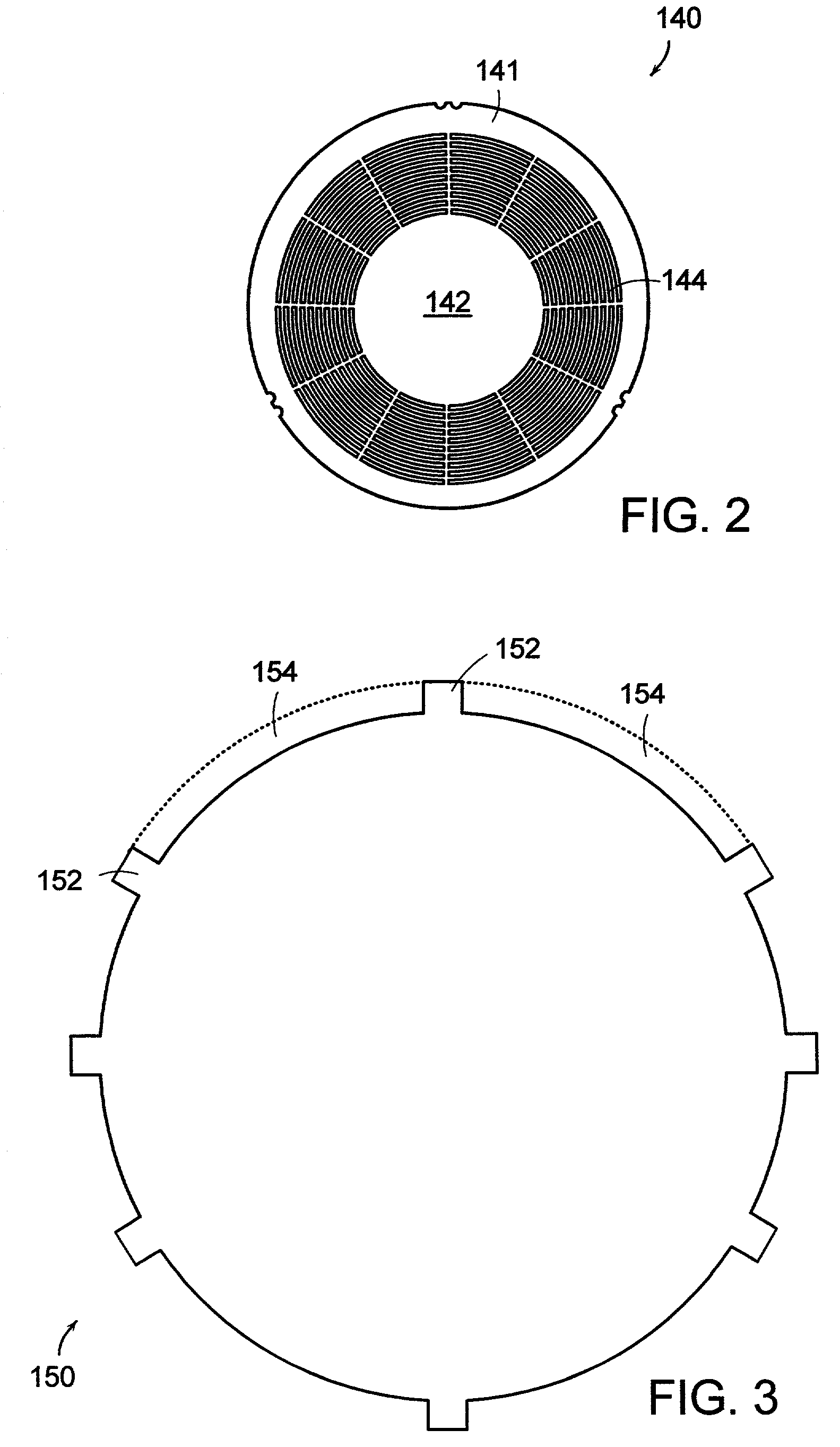
Manufacturing all-silicon force sensors, such as capacitive pressure sensors (100, 200) that have long term stability and good linear sensitivity, and can be built into of a pneumatic tire. The sensors include buried electrical feedthrough (112b) to provide an electrical connection into a sealed silicon cavity (108). The buried feedthrough consists of a conductor (112b) in a shallow groove (106) in a substrate (102), communicating between the sensing cavity (108) and an external contact area (110). The sensor designs also feature a method for forming a silicon-to-silicon fusion bond (SFB) wherein at least one of the two surfaces (152, 252) to be has a tough silicon surface unsuitable for good SFB joints because it was bonded heavily boron-doped by means of diffusion. The method of this invention includes preparing each doped surface (152, 252) for SFB by polishing the surface with a Chemical-Mechanical Polishing (CMP) process. The sensor designs can also include optional reference capacitors (141, 241) on the same chip (100, 200) as the sensing capacitor (140, 240). The reference capacitors (141, 241) are insensitive to pressure (force), but respond to ambient temperature changes in the same way as the sensing capacitor. Suitable external interface circuits can utilize the reference capacitors (141, 241) to pull out the majority of ambient temperature effects.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Concentric tilted double-helix dipoles and higher-order multipole magnets
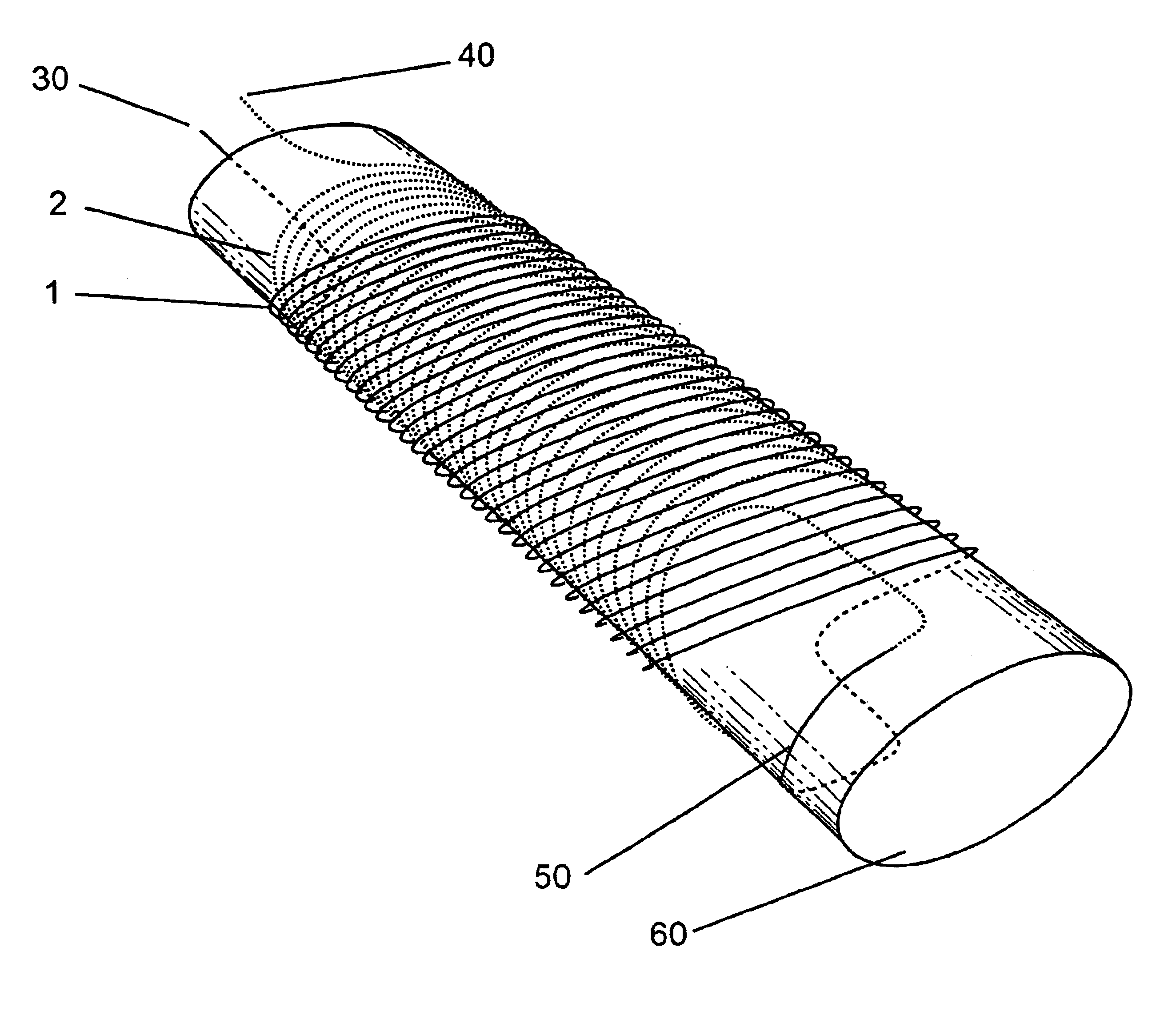
InactiveUS6921042B1Simple processLess costlyElectromagnets without armaturesFilament handlingElectric machineryMagneto hydrodynamic
Concentric tilted double-helix magnets, which embody a simplified design and construction method for production of magnets with very pure field content, are disclosed. The disclosed embodiment of the concentric tilted double-helix dipole magnet has the field quality required for use in accelerator beam steering applications, i.e., higher-order multipoles are reduced to a negligibly small level. Magnets with higher multipole fields can be obtained by using a simple modification of the coil winding procedure. The double-helix coil design is well-suited for winding with superconducting cable or cable-in-conduit conductors and thus is useful for applications that require fields in excess of 2 T. The coil configuration has significant advantages over conventional racetrack coils for accelerators, electrical machinery, and magneto-hydrodynamic thrusting devices.
Owner:GOODZEIT CARL L +2
Plated terminations
InactiveUS20050046536A1Improved termination featureEliminate and greatly simplifyWave amplification devicesResistor terminals/electrodesTermination problemEngineering
Improved termination features for multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions which may optionally extend to the cover layers of a multilayer component. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. External anchor tabs positioned on top and bottom sides of a monolithic structure can facilitate the formation of wrap-around plated terminations. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Plated terminations
InactiveUS7154374B2Improved termination featureEliminate or greatly simplify thick-film stripesResistor terminals/electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTermination problemEngineering
Improved termination features for multilayer electronic components are disclosed. Monolithic components are provided with plated terminations whereby the need for typical thick-film termination stripes is eliminated or greatly simplified. Such termination technology eliminates many typical termination problems and enables a higher number of terminations with finer pitch, which may be especially beneficial on smaller electronic components. The subject plated terminations are guided and anchored by exposed internal electrode tabs and additional anchor tab portions which may optionally extend to the cover layers of a multilayer component. Such anchor tabs may be positioned internally or externally relative to a chip structure to nucleate additional metallized plating material. External anchor tabs positioned on top and bottom sides of a monolithic structure can facilitate the formation of wrap-around plated terminations. The disclosed technology may be utilized with a plurality of monolithic multilayer components, including interdigitated capacitors, multilayer capacitor arrays, and integrated passive components. A variety of different plating techniques and termination materials may be employed in the formation of the subject self-determining plated terminations.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Surface area deposition trap
InactiveUS7252011B2Raise the possibilityEasy to addFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesFluid pressure measurement using capacitance variationCouplingTransducer
The disclosed pressure transducer assembly includes a housing, a pressure sensor disposed within the housing, a coupling establishing a sealed pathway between the housing and an external source of gas or fluid, and a deposition trap disposed in the pathway. The deposition trap provides a plurality of channels, each of the channels being narrower than the pathway.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Swiped aperture capacitive fingerprint sensing systems and methods
InactiveUS7146024B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceAcceleration measurementEngineeringFlexible electronics
A fingerprint sensing system includes an image sensor, a rate sensor and a sensor circuit. The image sensor includes a linear array of capacitive sensors for capacitive sensing of ridge peaks and ridge valleys of a fingerprint on a swiped finger. The rate sensor senses the speed of the finger as it is swiped across the image sensor. The sensor circuit supplies image drive signals to the image sensor and detects image signals in response to the drive signals. The sensor circuit supplies rate drive signals to the rate sensor and detects rate signals in response to the rate drive signals. The sensor circuit further coordinates the image signals and the rate signals to provide a fingerprint image. The image sensor may be configured as an image pickup plate and multiple image drive plates formed on a substrate, such as a flexible printed circuit board or other flexible substrate which may conform to the shape of the finger.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
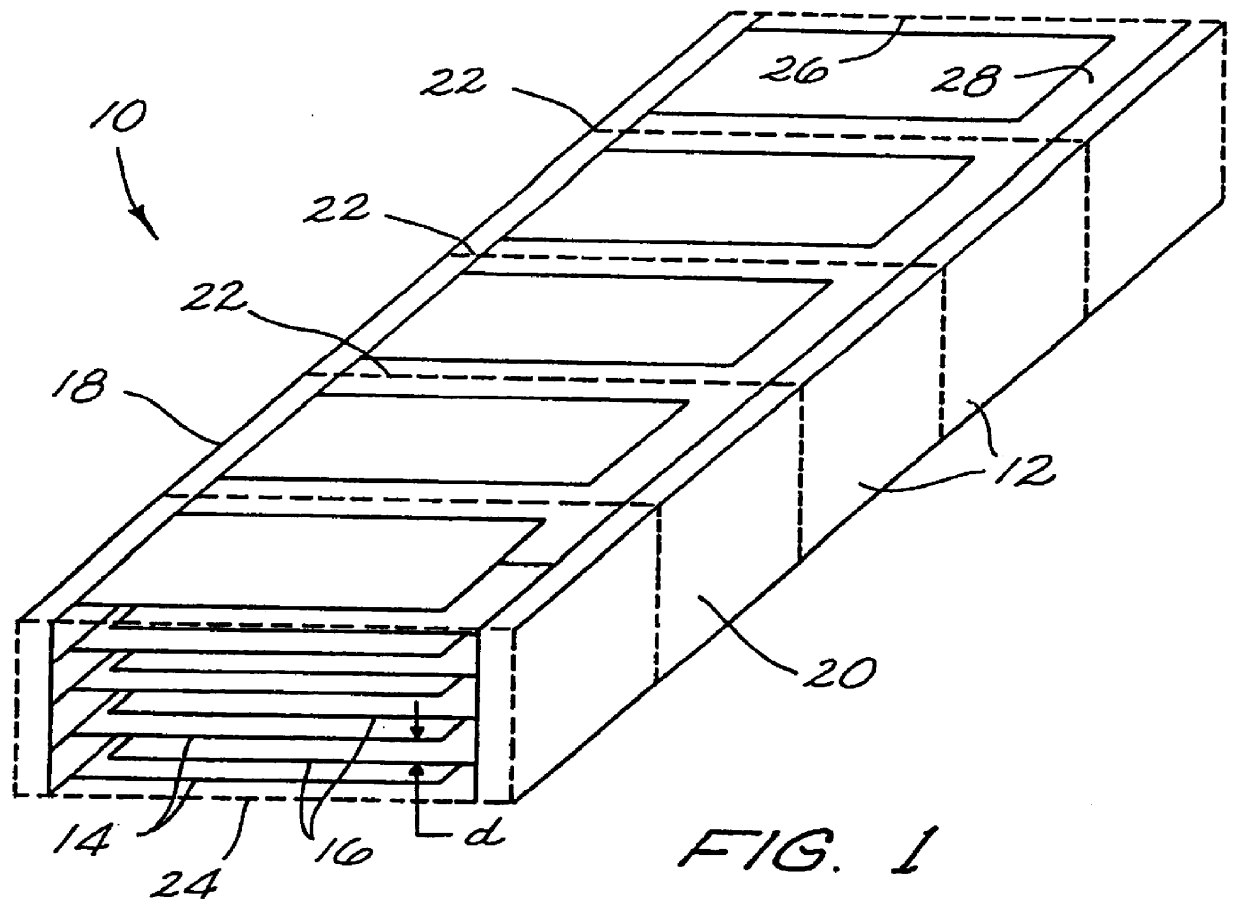
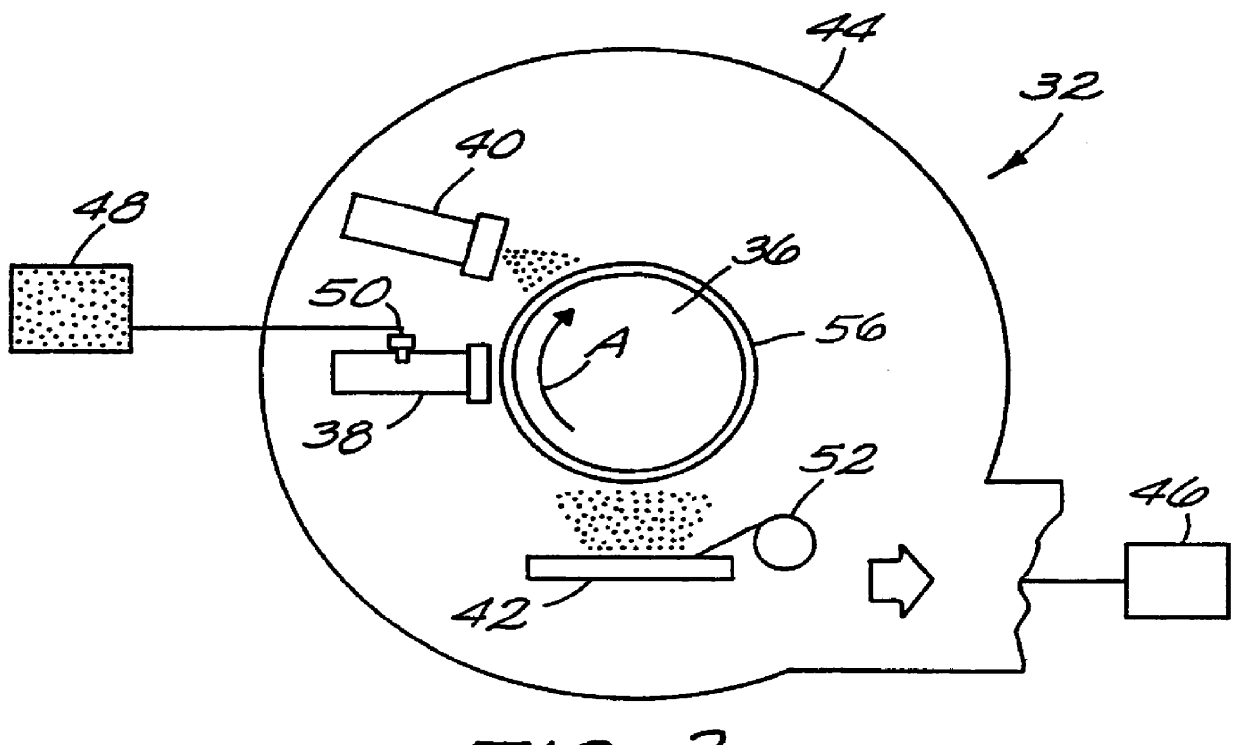
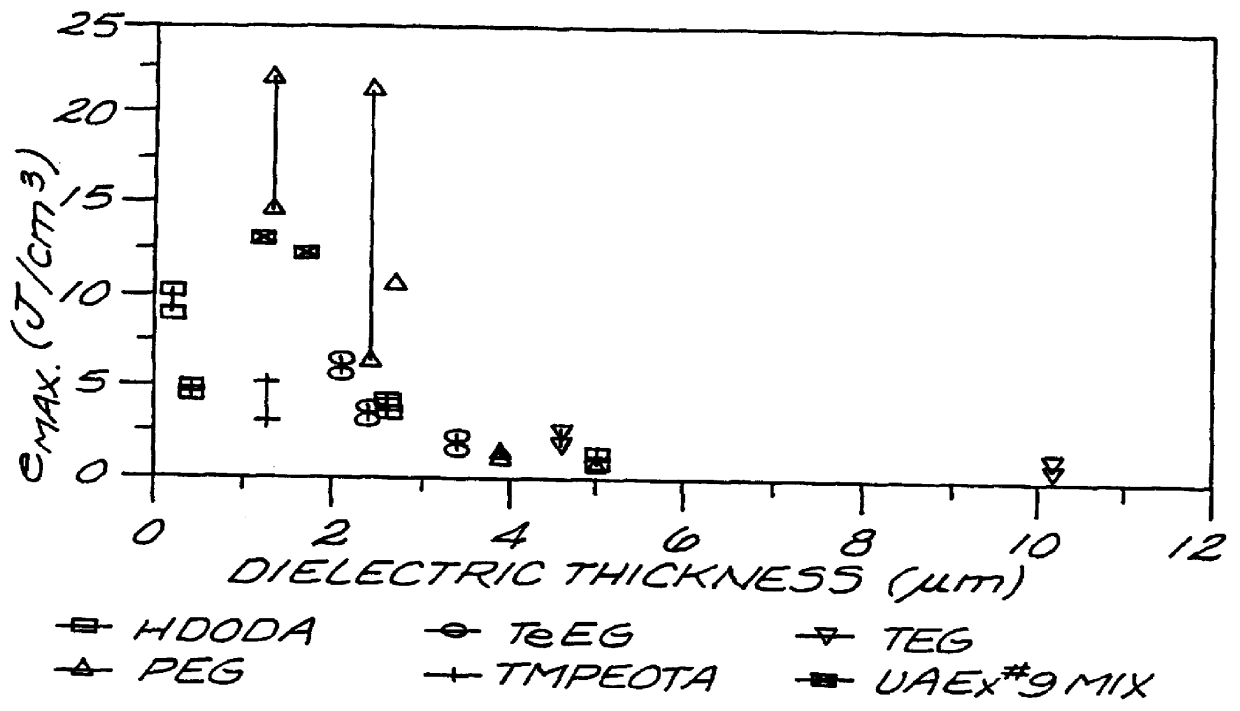
High energy density capacitor
A high energy density, high power density capacitor having an energy density of at least about 0.5 J / cm3 is provided. The capacitor comprises a plurality of interleaved metal electrode layers separated by a polymer layer. The interleaved metal electrode layers terminate at opposite ends in a solder termination strip. The high energy density aspect of the capacitors of the invention is achieved by at least one of the following features: (a) the dielectric thickness between the interleaved metal electrode layers is a maximum of about 5 mu m; (b) the polymer is designed with a high dielectric constant kappa of at least about 3.5; (c) the metal electrode layers within the polymer layer are recessed along edges orthogonal to the solder termination strips to prevent arcing between the metal electrode layers at the edges; and (d) the resistivity of the metal electrode layers is within the range of about 10 to 500 ohms per square, or a corresponding thickness of about 200 to 30 ANGSTROM .
Owner:SIGMA LAB OF ARIZONA
Arrangement for authentication of a person
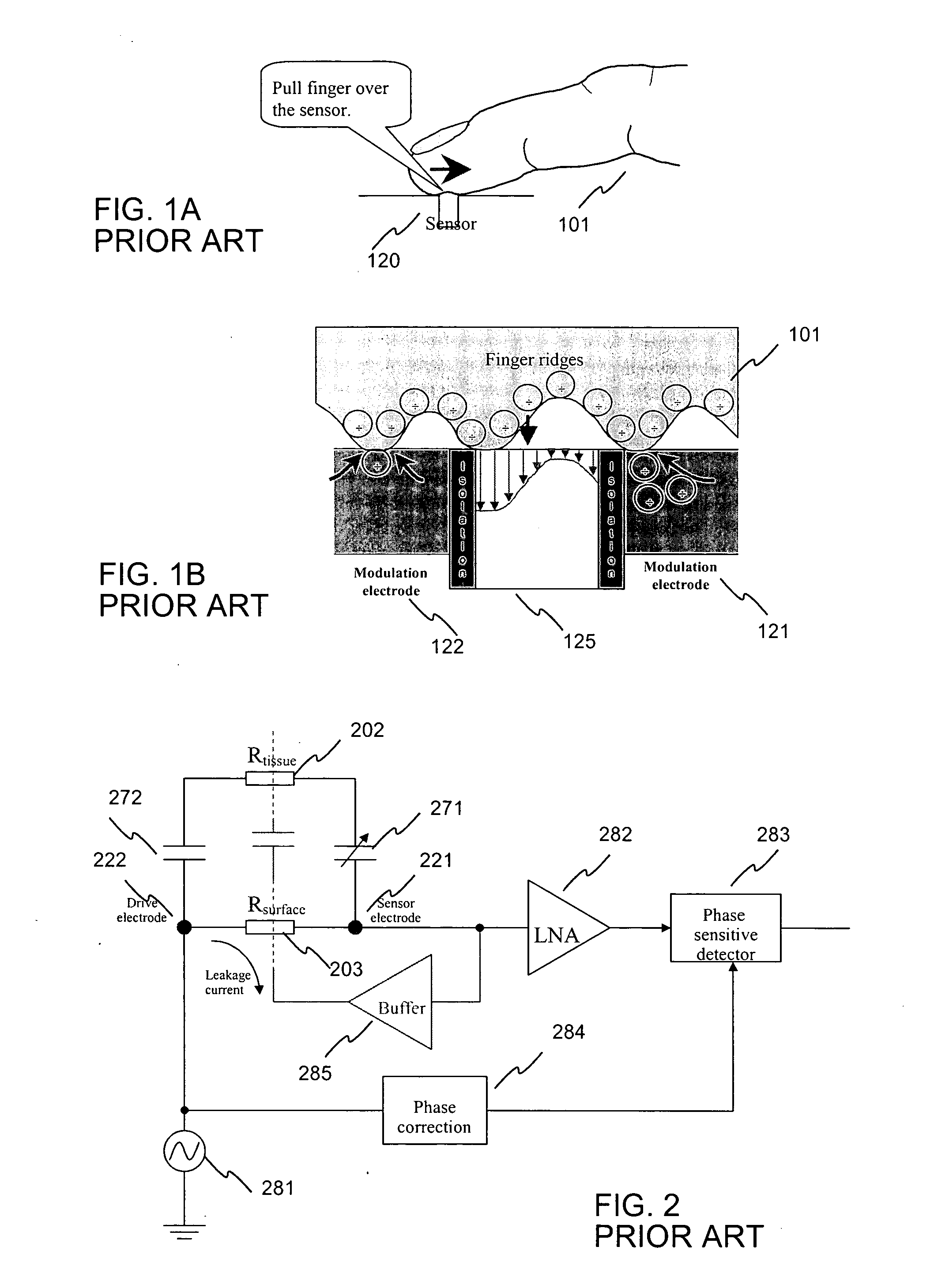
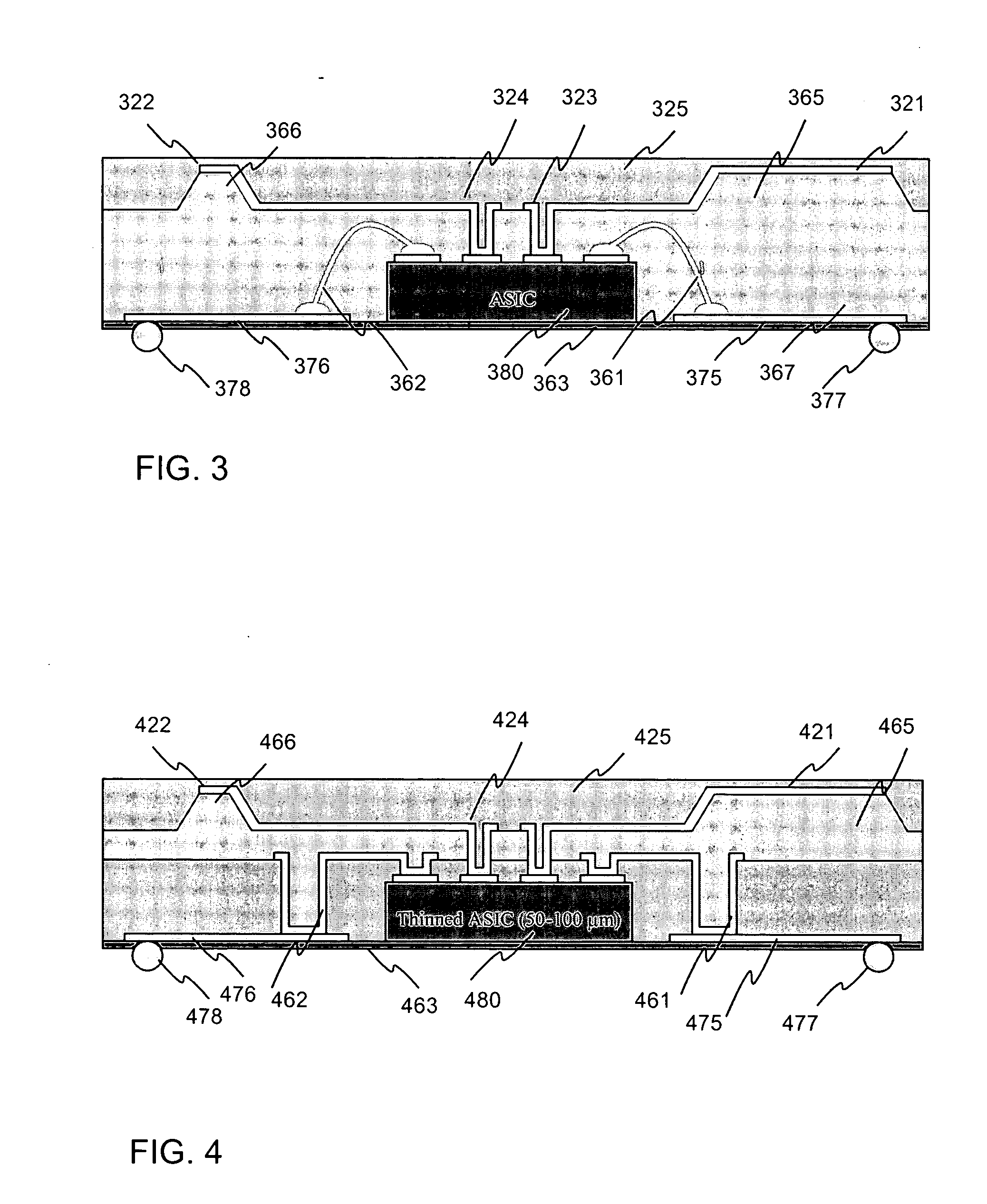
ActiveUS20050031174A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceIntegrated circuit
A capacitive fingerprint sensor is fabricated on a plastic substrate (363) with an embedded integrated circuit chip (380). The invention describes a way to create two or three dimensional forms for electrode structures (321, 322, 325, 365, 366) that can be used to optimize the performance of the sensor. When the three dimensional structure is designed to follow the shape of a finger, a very small pressure is required when sliding the finger along the sensor surface. This way the use of the sensor is ergonomic and the measurement is made very reliable. The inventive fabrication method describes the way, how to connect and embed an integrated circuit containing measurement electronics with a batch processed larger scale electrode configuration that is used for capturing the capacitive image of the fingerprint.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
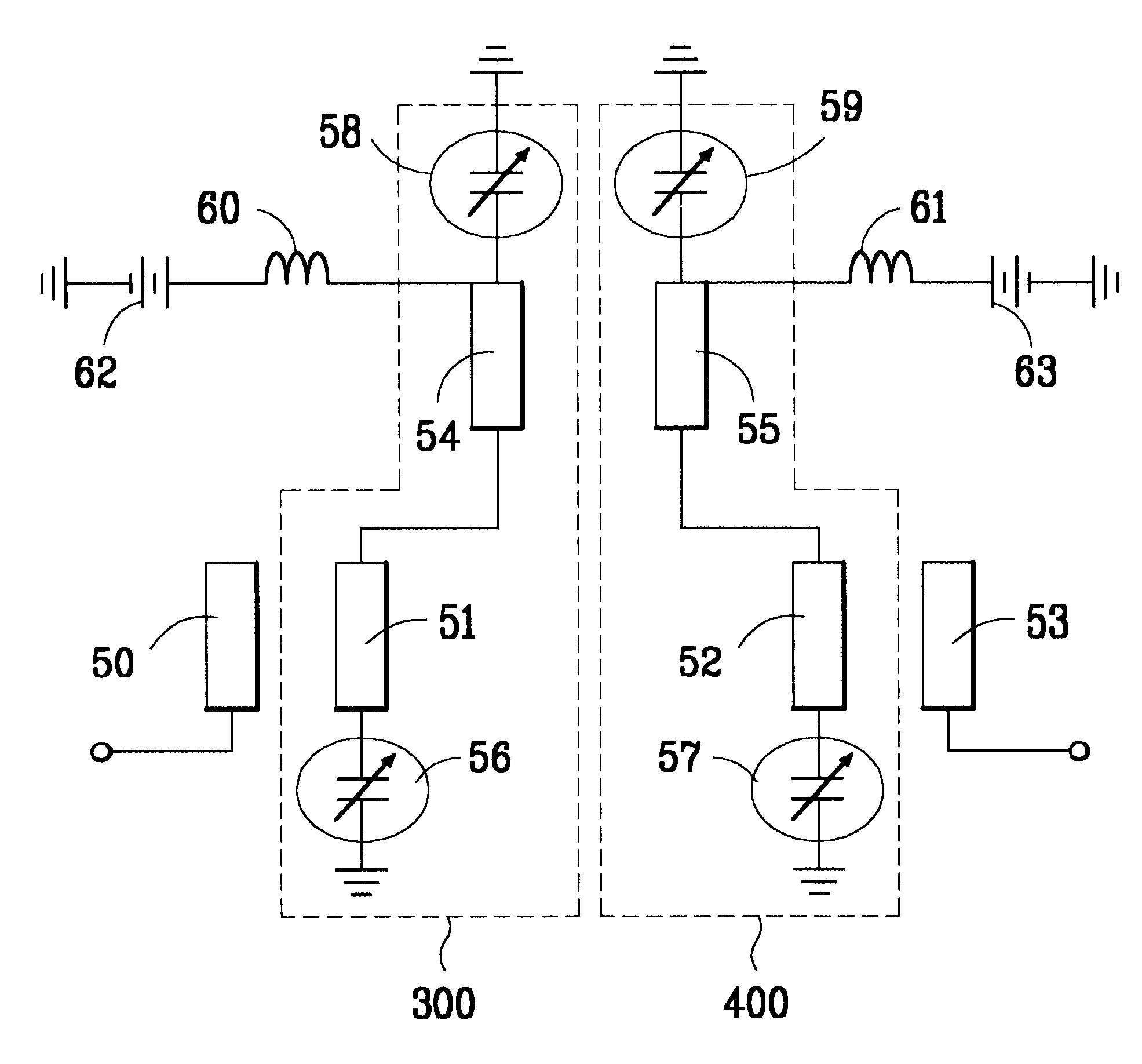
Microwave tunable filter using microelectromechanical (MEMS) system
A microwave tunable filter having some advantages as follows: a) the integration of MEMS tunable filter and MMIC; b) the very low signal transmission loss and low dispersion; and c) the drastic variation and linear characteristic of frequency by means of MEMS capacitor and an external control signal. The microwave tunable MEMS filter includes a plurality of unit resonant cells, each unit resonant cell being formed by various serial and parallel combination of an inductor, a capacitor, a transmission line, and a variable MEMS capacitor, whereby capacitance variation of the variable MEMS capacitor in the unit resonant cell converts a resonant frequency of the unit resonant cell to thereby convert a center frequency of the filter.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
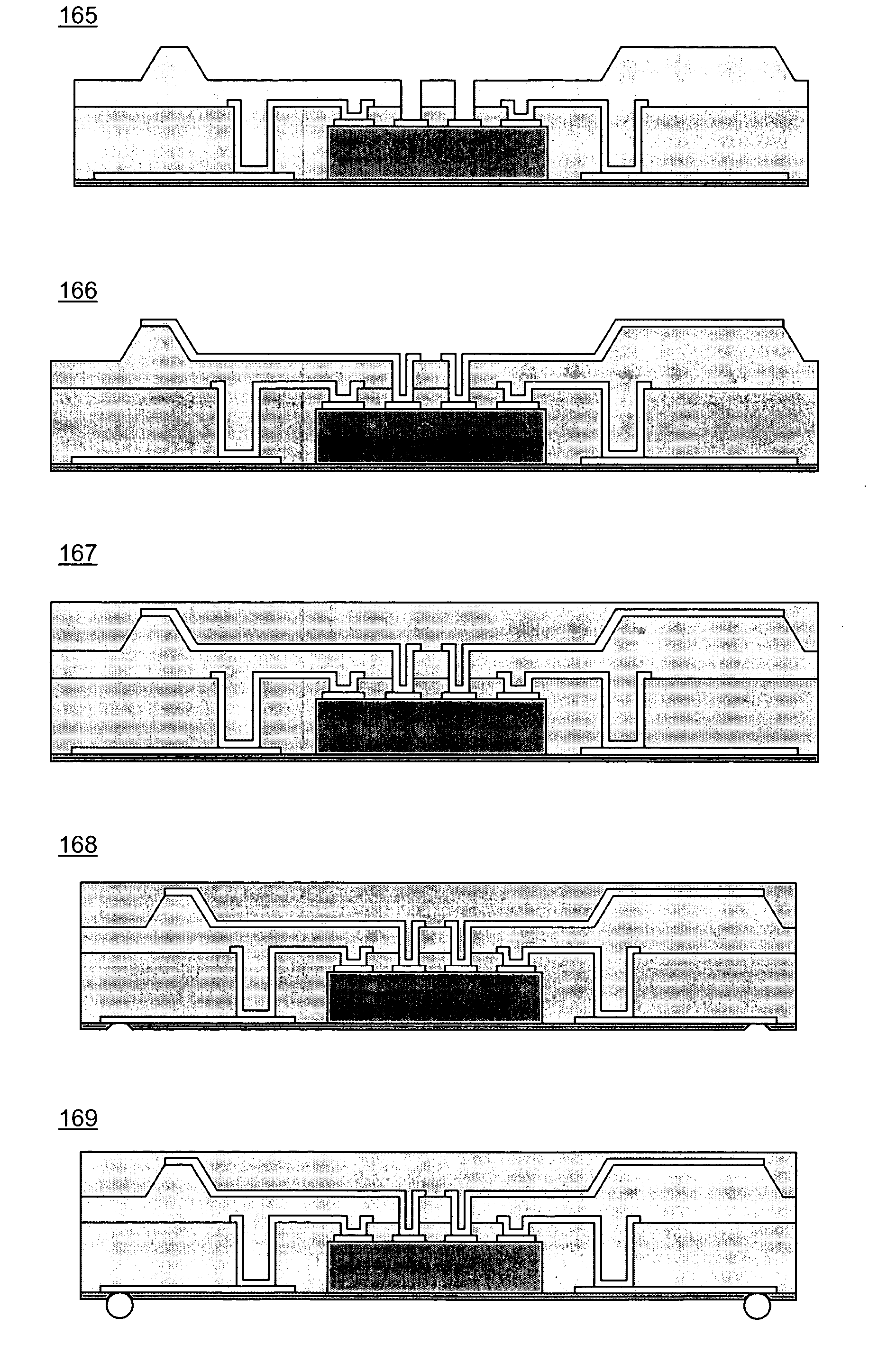
Laminated electronic component and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080123249A1Improve the effective volume ratioImprove reliabilityFixed capacitor dielectricStacked capacitorsElectronic componentElectron
A laminated body is prepared, in which at an end surface at which internal electrodes are exposed, the internal electrodes disposed adjacently are electrically isolated from each other, and a distance between the internal electrodes disposed adjacently is about 20 μm or less when measured along the thickness direction of an insulator layer, and a withdrawn-depth of the internal electrodes is about 1 μm or less when measured from the end surface. In a step of electroless plating, plating deposits formed at the end portions of the plurality of internal electrodes are increased in size so as to be connected to each other.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Integrated sensor and circuitry and process therefor
ActiveUS20070029629A1Large mechanical sensitivityReduce input parasiticsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceFull bridge
A micromachined sensor and a process for fabrication and vertical integration of a sensor and circuitry at wafer-level. The process entails processing a first wafer to incompletely define a sensing structure in a first surface thereof, processing a second wafer to define circuitry on a surface thereof, bonding the first and second wafers together, and then etching the first wafer to complete the sensing structure, including the release of a member relative to the second wafer. The first wafer is preferably a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafer, and the sensing structure preferably includes a member containing conductive and insulator layers of the SOI wafer. Sets of capacitively coupled elements are preferably formed from a first of the conductive layers to define a symmetric capacitive full-bridge structure.
Owner:MICRO INERTIAL LLC
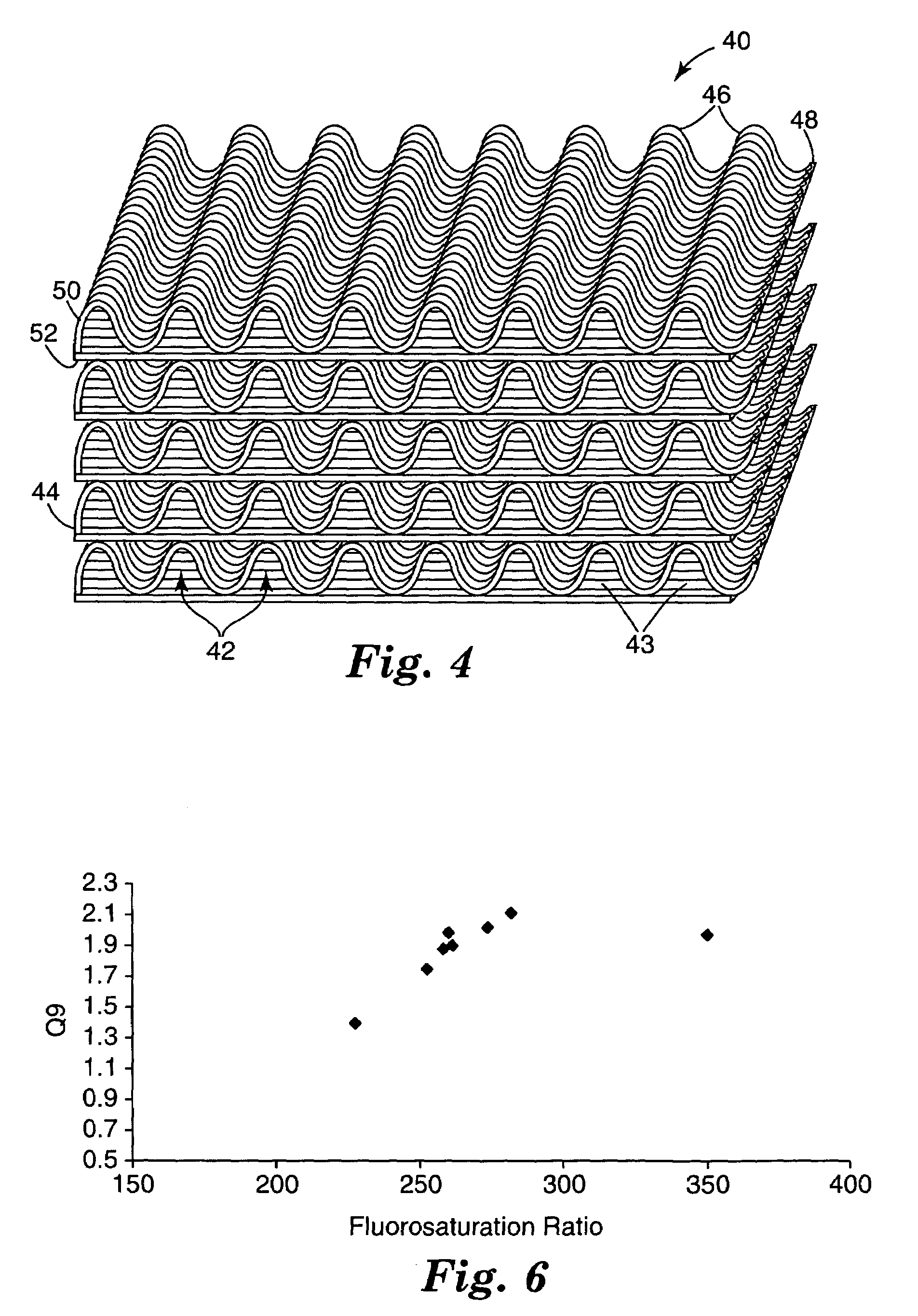
Electret article having high fluorosaturation ratio
ActiveUS7244291B2Improve thermal stabilityIncreased thermal stability—asBreathing filtersElectrostatic separationFiberPolymer chemistry
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
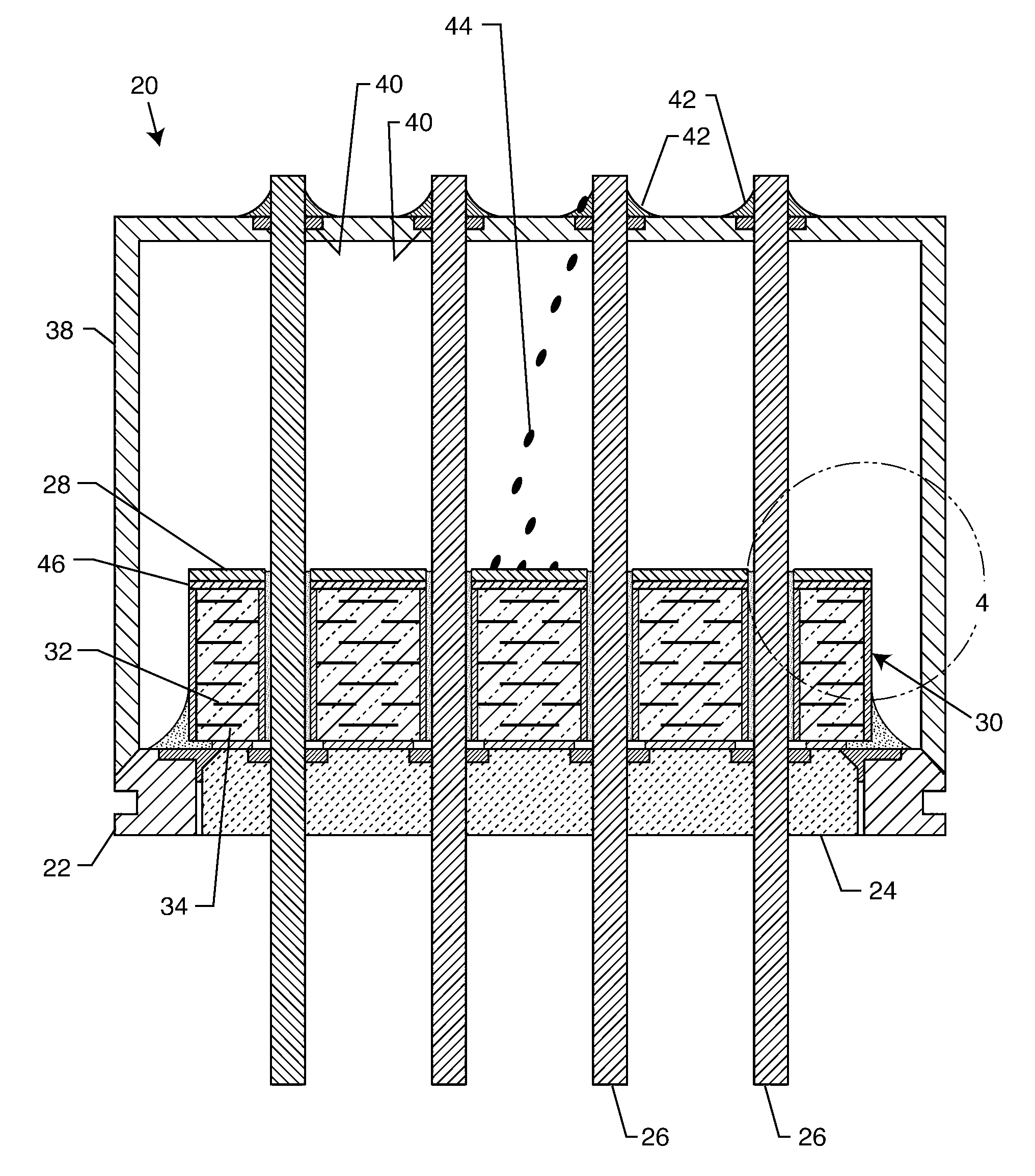
Method for minimizing stress in feedthrough capacitor filter assemblies
A feedthrough terminal pin assembly includes an outer ferrule hermetically sealed through a braze joint to an insulator seated within the ferrule is described. The insulator is also hermetically brazed to at least one terminal pin. The terminal pin is provided with a braze retention structure such as an annular groove that prevents braze material from filleting past the groove. Similarly, either the ferrule or the insulator is provided with a retention structure such as an annular groove that prevents braze material spill out from the insulator / ferrule interface. In that manner, the braze retention structures keep braze material from accumulating in unwanted areas where it could adversely affect hermeticity as well as proper attachment of an EMI filter to the feedthrough assembly.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
High-temperature capacitors and methods of making the same
High-temperature, multiple-layer polymer (MLP) capacitors with a stacked electrode arrangement are disclosed. The capacitor electrodes are separated by a polymer dielectric that is stable at high temperatures. In some embodiments, the polymer dielectric also has a high permittivity and is filled with high-permittivity nanoparticles, which enables the capacitor to achieve a very high capacitance density.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Episeal pressure sensor and method for making an episeal pressure sensor
InactiveUS6928879B2Avoid problemsQuality improvementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsCapacitanceStrain gauge
A method for making a pressure sensor by providing a wafer including a base silicon layer, a buried sacrificial layer, and a top silicon layer. The top silicon layer is arranged over the buried sacrificial layer and the buried sacrificial layer is arranged over the base silicon layer. Etching vents through the top silicon layer to the buried sacrificial layer and removing a portion of the buried sacrificial layer. Depositing silicon to seal the vents and arranging a strain gauge or a capacitance contact on the wafer. A method for making a pressure sensor including providing a bulk wafer and depositing a sacrificial layer on the bulk wafer. Depositing silicon on the sacrificial layer and the bulk wafer to form an encapsulation layer. Etching vents through the encapsulation layer to the sacrificial layer and removing the sacrificial layer. Closing the vents with a silicon deposition and arranging a strain gauge or a capacitance contact on the encapsulation layer. A pressure sensing device including a substrate, an encapsulation layer with vents, and voids between the substrate and the encapsulation layer. A portion of the encapsulation layer above the voids forms a membrane and deposited silicon plugs fill the vents. A strain gauge or a top capacitive contact arranged on the membrane.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Device to protect an active implantable medical device feedthrough capacitor from stray laser weld strikes, and related manufacturing process
An insulative shield is co-bonded to the top of a ceramic capacitor in a feedthrough terminal assembly on an active implantable medical device. The insulative shield is a thin substrate that provides protection against damage and degradation of the feedthrough capacitor and / or its conformal coating from heat, splatter or debris resulting from the electromechanical connection of components during construction of the assembly. Laser welding, thermal or ultrasonic bonding, soldering, brazing or related lead attachment techniques can create such heat, splatter or debris. In a preferred embodiment, the insulative shield is co-bonded using the capacitor's own conformal coating.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Spectral resistor, spectral capacitor, order-infinity resonant tank, EM wave absorbing material, and applications thereof
InactiveUS20070170910A1Improve power qualityReduce performanceOther resistor networksMultiple-port networksElectricityElectric power system
A spectral resistor based on the constitute law of “elasticity of electricity” derived from the Riemann-Lebesgue lemma is provided to build a substantial order-∞ resonant tank. The substantial order-∞ resonant tank according to embodiments of the present invention can function as many different roles such as an electric filter, a harmonic and sub-harmonic power waveform distortion filter, a dynamic damper, a dynamic impedance matching circuit and a kind of electromagnetic wave absorbing material. By attaching an order-∞ resonant tank according to the present invention to an ordinary system with equivalent inductance in a suitable topology as an electric filter, a substantial snubber network, or so-called DeLenzor, is obtained. The duality of an electric system can be handled by coupling the system with an order-∞ resonant tank according to the present invention, and thus the disadvantageous effects caused by the duality of the system can be canceled immediately without any drawbacks. Furthermore, the reactive (or so-called regenerated) power caused by the duality of the electric system can be recycled according to embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:CHANG MING HOO +3
Ultra broadband capacitor
ActiveUS20100039749A1Efficient and less-expensiveReduce in quantityFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricUltra-widebandBroadband
Disclosed are apparatus and methodology for inexpensive realization of one or more secondary capacitors within a monolithic body that already includes a first, larger capacitor to provide ultra wideband structures. Alternating layers of electrodes are provided with arm portions that embrace portions of adjacent electrode layers so as to create additional coupling effects within the capacitor structure thereby producing multiple additional equivalent capacitor structures within the device.
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS CORP
Nanoparticle ultracapacitor
InactiveUS20080316678A1Hybrid capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricCapacitancePolymer science
Particular aspects provide capacitors, and particularly ultracapacitors, comprising molecules suitable to substantially increasing the capacitance of the capacitor, and methods for making same Particular aspects provide ultracapacitors that include nanoparticles optionally coated with molecules, such as polymer electrolytes. Certain aspects provide an energy storage device or capacitor, comprising at least three layers sealed in a fluid-tight covering, wherein a first layer comprises at least one electrolytic polymer molecule of positive charge and at least one nanoparticle; a second dielectric layer comprising at least one insulative polymer; a third layer comprising at least one electrolytic polymer molecule of negative charge and at least one nanoparticle. In certain aspects, the electrolytic polymer of the first layer comprises at least one high charge density polymer electrolyte of positive charge, and wherein the electrolytic polymer of the third layer comprises at least one high charge density polymer electrolyte of negative charge.
Owner:TANGREDI PATRICIA
Low inductance, high rating capacitor devices
InactiveUS20090147440A1Reduce inductanceMultiple fixed capacitorsFinal product manufactureLow inductancePrinted circuit board
Methodologies and structures are disclosed for providing multilayer electronic devices having low inductance and high ratings, such as for capacitor devices for uses involving faster pulsing and higher currents. Plural layer devices are constructed for relatively lowered inductance by relatively altering typical orientation of capacitors such that their electrodes are placed into a vertical position relative to an associated circuit board. Optionally, individual leads may be formed so that the resulting structure can be used as an array. Internal electrodes may be arranged for reducing current loops for associated circuits on a circuit board, to correspondingly reduce the associated inductance of the circuit board mounted device. Leads associated with such devices may have added tab-like structures which serve to more precisely place the lead, to improve the lead to capacitor strength, and to promote lower resistance and inductance. Disclosed designs for reducing associated inductance may be practiced in conjunction with various electric devices, including capacitors, resistors, inductors, or varistors.
Owner:AVX CORP
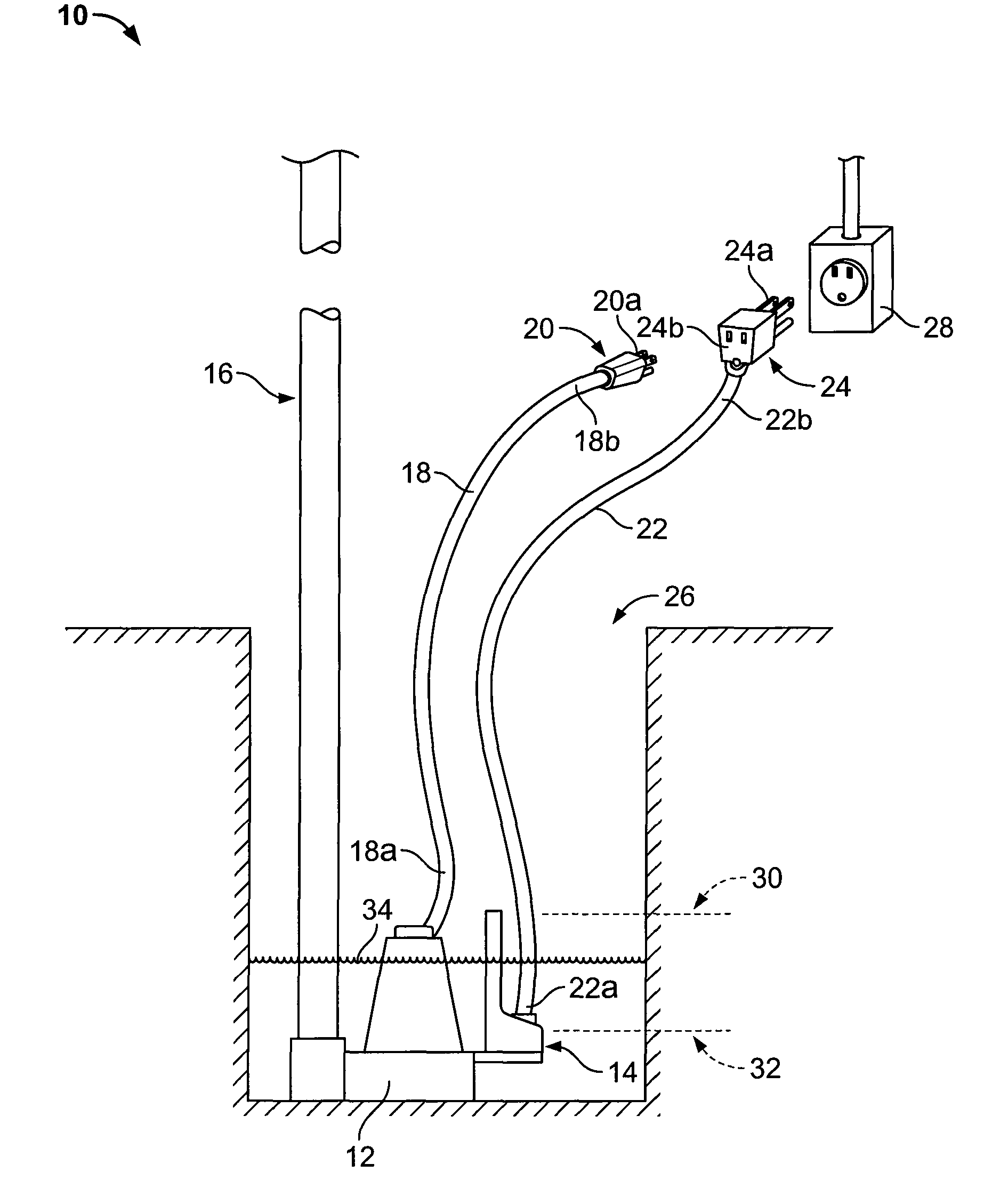
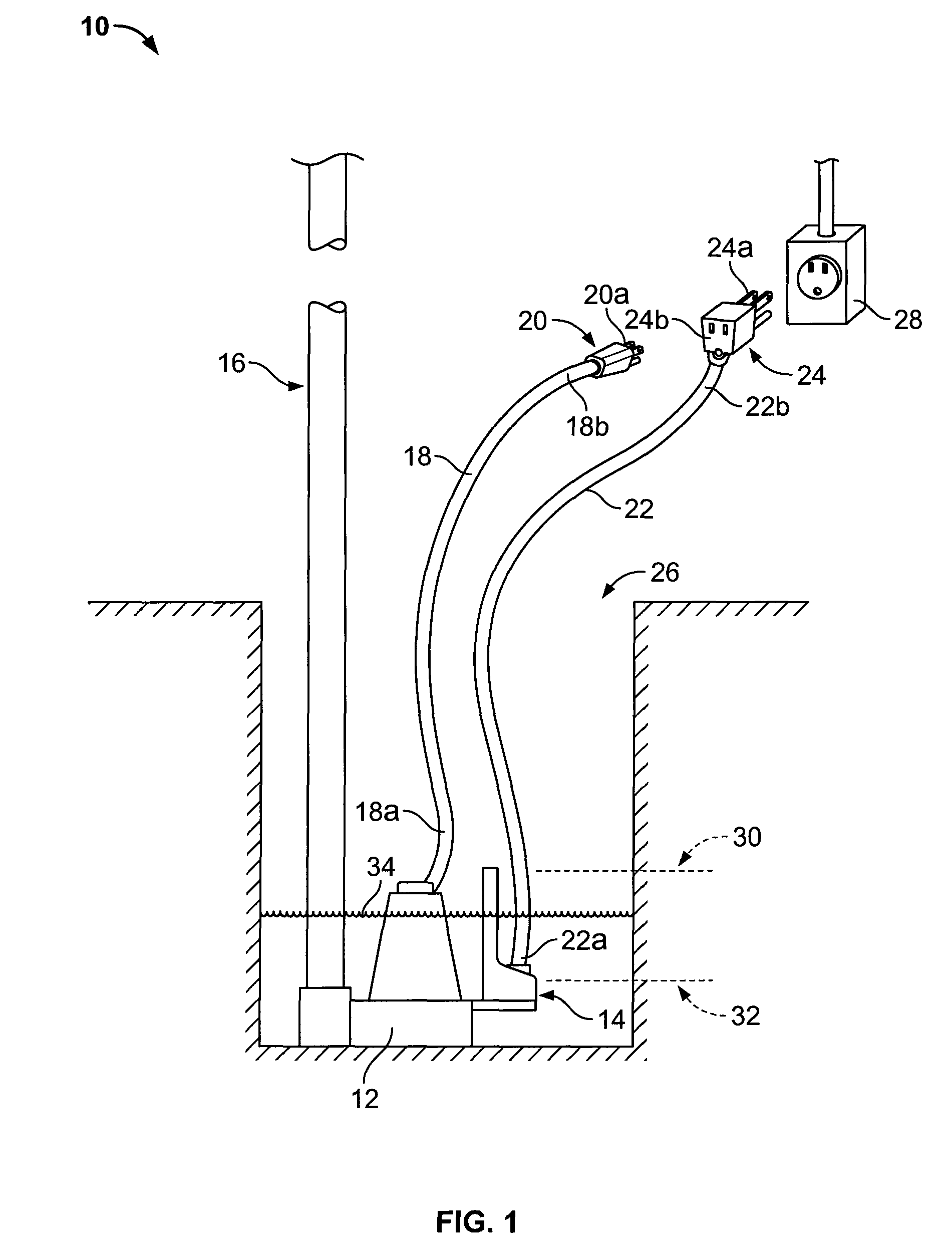
Capacitive sensor and method and apparatus for controlling a pump using same
ActiveUS8380355B2Easy to assembleReduce assemblyNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngine testingControl systemEngineering
A variable capacitor for sensing the level of a liquid. The capacitor provides a readable capacitance that varies with respect to the level of the liquid. A pump control system implementing the capacitive sensor to control the level of a liquid by activating and deactivating the pump depending on the level of the liquid. Methods relating to varying capacitance of a capacitive sensor and controlling a pump based on the level of a liquid. A pump controller for controlling the level of a liquid in a reservoir includes a controller and a capacitor. The capacitor is adapted to provide an activation signal to the controller when the liquid in the reservoir reaches a first predetermined level relative thereto. Additionally, the capacitor is adapted to provide a trigger signal to the controller when the liquid in the reservoir reaches a second predetermined level relative thereto. Based on the trigger signal, the controller determines when to deactivate the pump.
Owner:WAYNESCOTT FETZER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com