Patents
Literature
96 results about "Modulation doping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Modulation doping is a technique for fabricating semiconductors such that the free charge carriers are spatially separated from the donors. Because this eliminates scattering from the donors, modulation-doped semiconductors have very high carrier mobilities.
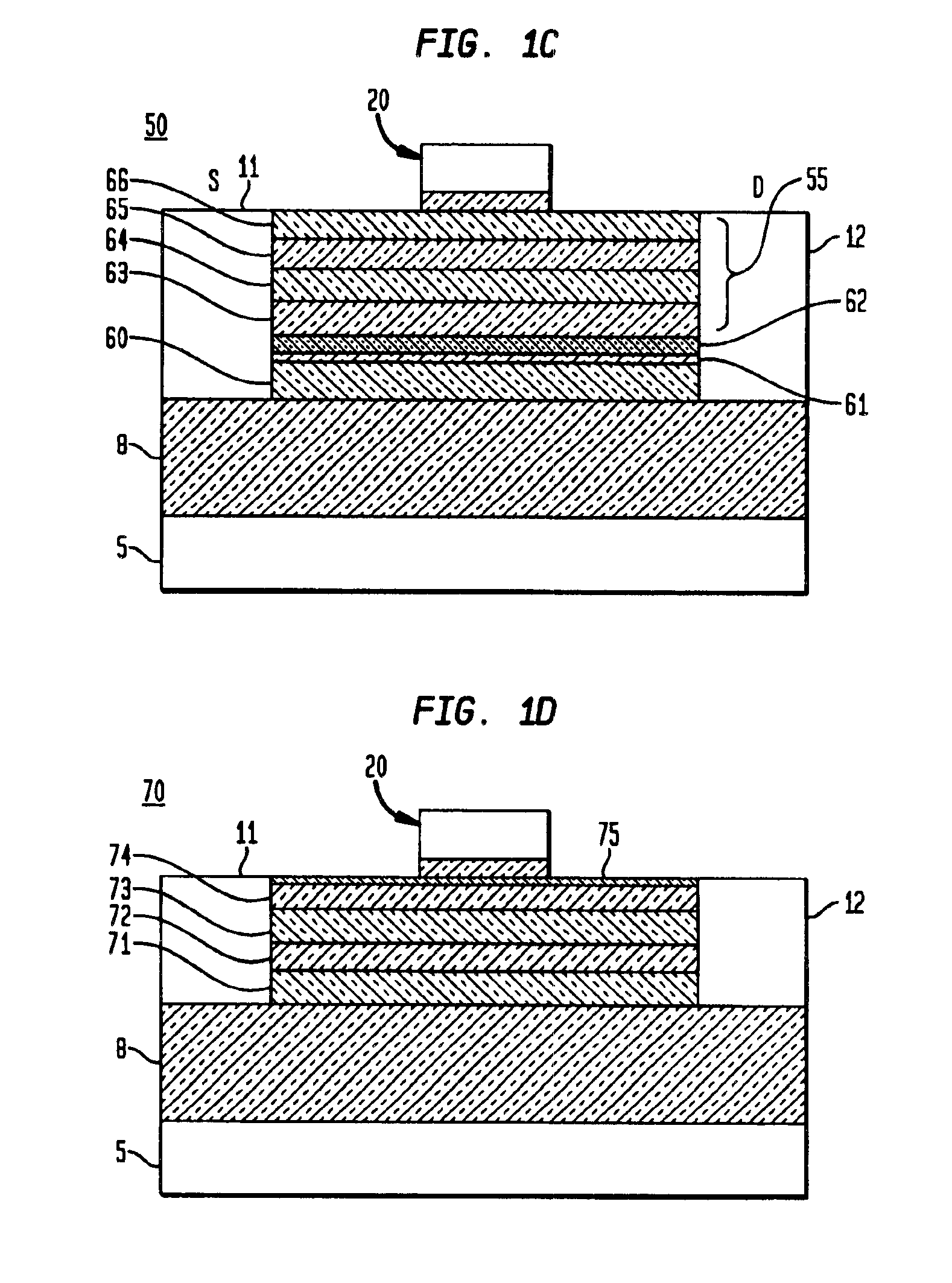
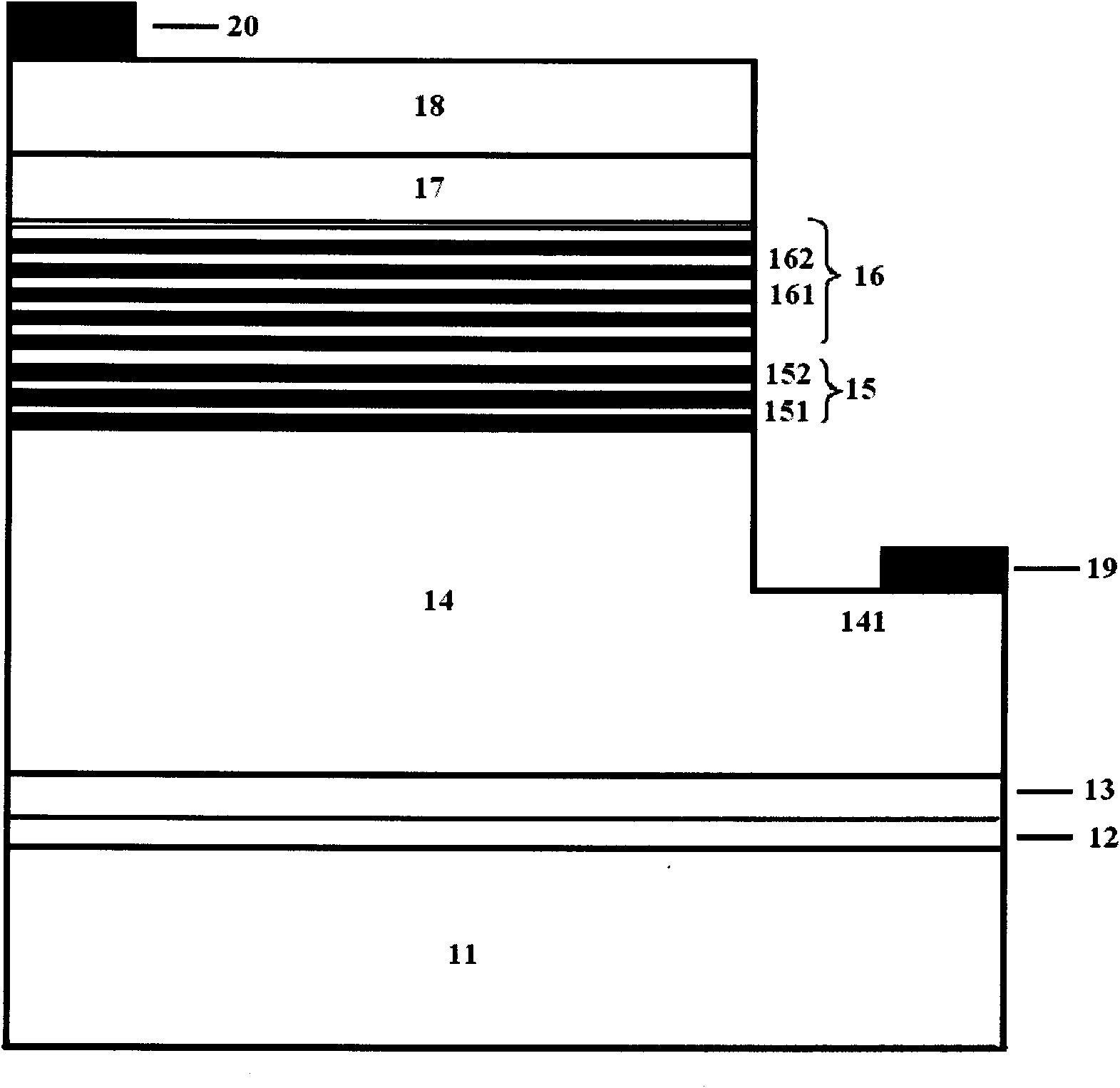
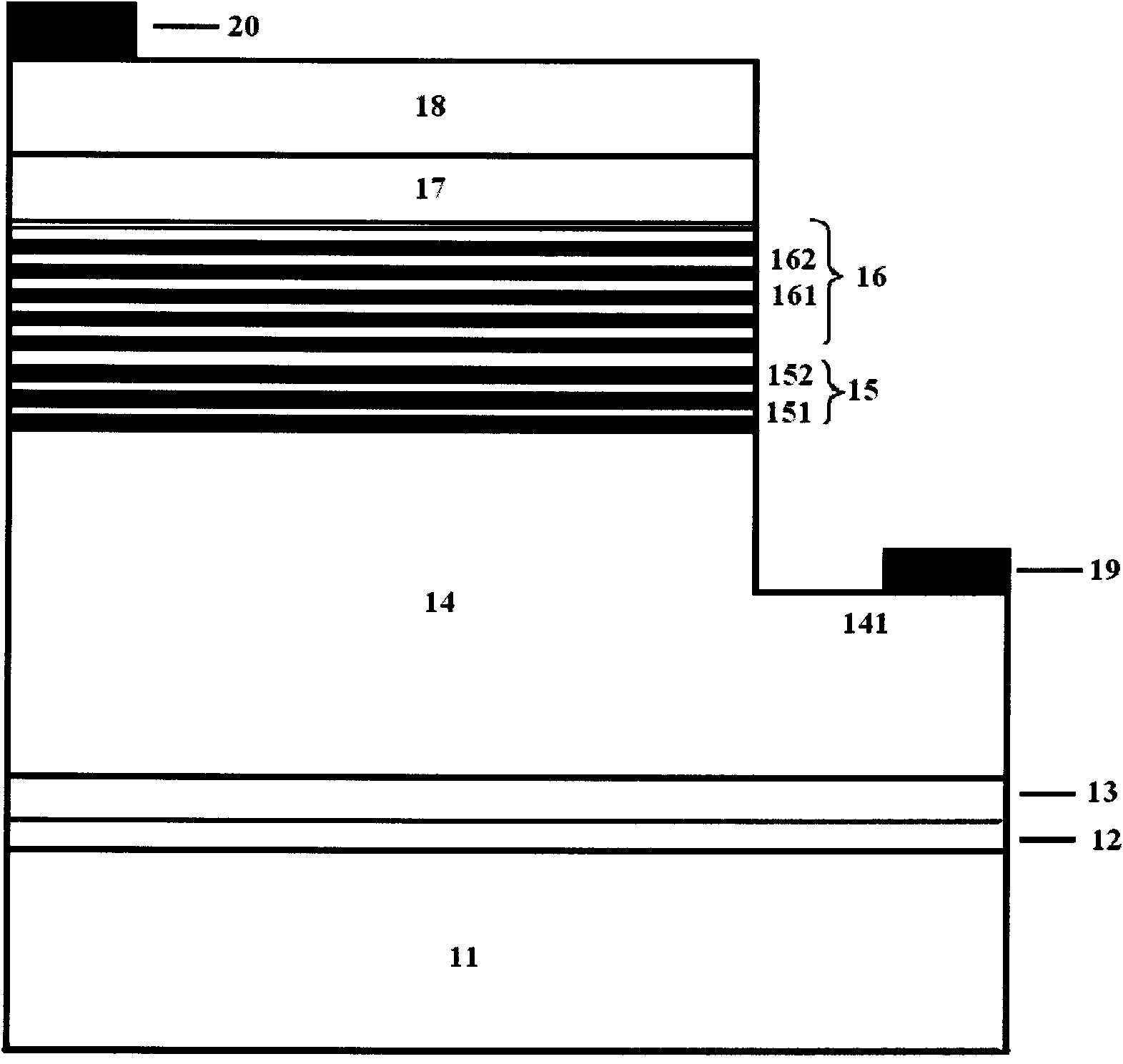
Nanowhiskers with PN junctions, doped nanowhiskers, and methods for preparing them
InactiveUS20050006673A1Good electrical conductivityPermitted diffusionPolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsHeterojunctionP–n junction
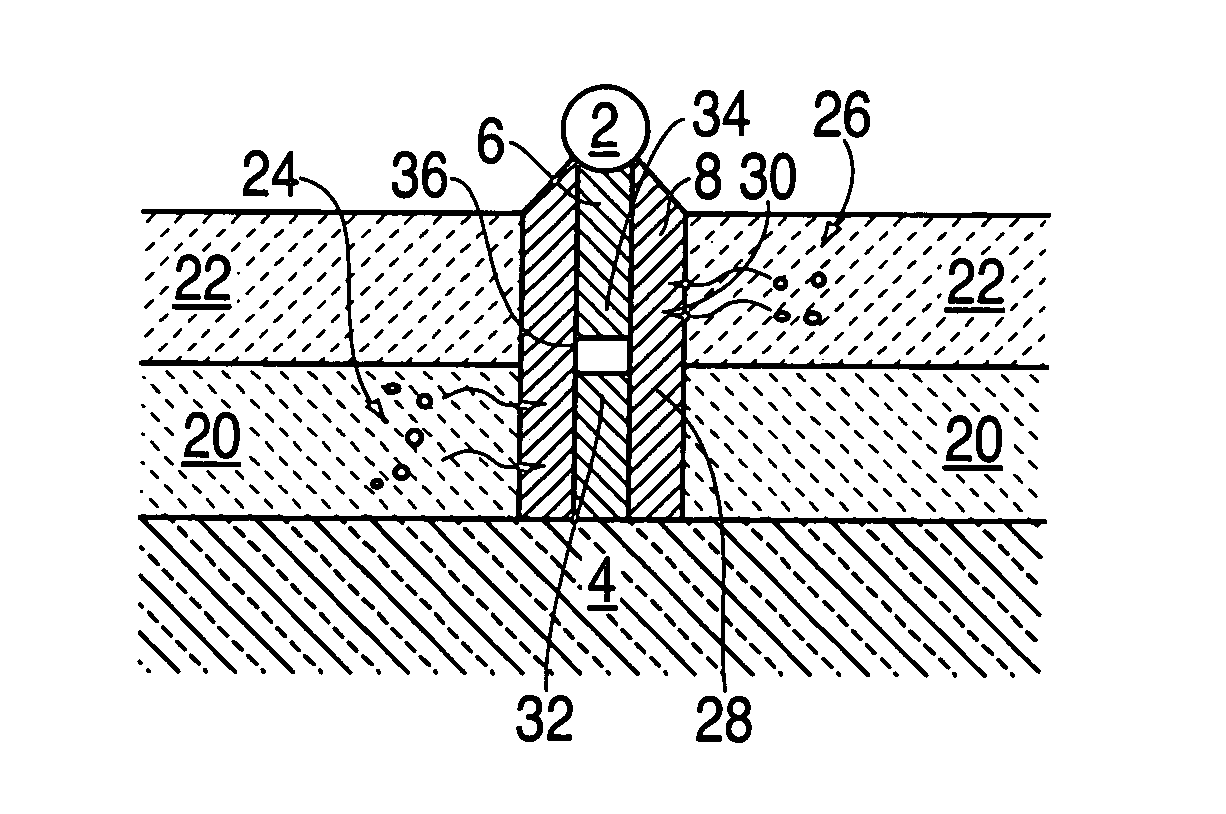
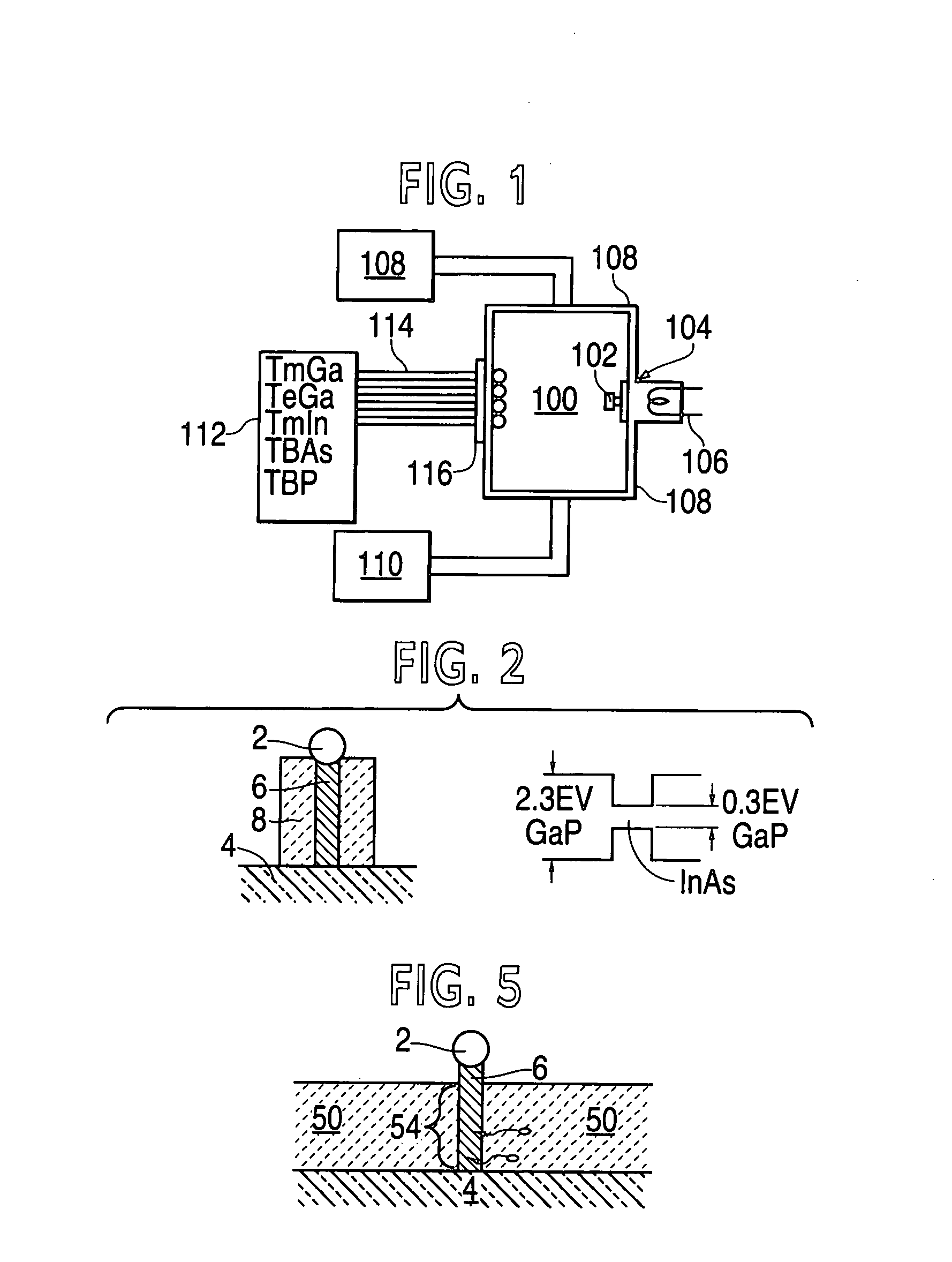
Nano-engineered structures are disclosed, incorporating nanowhiskers of high mobility conductivity and incorporating pn junctions. In one embodiment, a nanowhisker of a first semiconducting material has a first band gap, and an enclosure comprising at least one second material with a second band gap encloses said nanoelement along at least part of its length, the second material being doped to provide opposite conductivity type charge carriers in respective first and second regions along the length of the of the nanowhisker, whereby to create in the nanowhisker by transfer of charge carriers into the nanowhisker, corresponding first and second regions of opposite conductivity type charge carriers with a region depleted of free carriers therebetween. The doping of the enclosure material may be degenerate so as to create within the nanowhisker adjacent segments having very heavy modulation doping of opposite conductivity type analogous to the heavily doped regions of an Esaki diode. In another embodiment, a nanowhisker is surrounded by polymer material containing dopant material. A step of rapid thermal annealing causes the dopant material to diffuse into the nanowhisker. In a further embodiment, a nanowhisker has a heterojunction between two different intrinsic materials, and Fermi level pinning creates a pn junction at the interface without doping.
Owner:QUNANO
III-V charge coupled device suitable for visible, near and far infra-red detection
InactiveUS6870207B2Optimized drift velocityLower resistanceSolid-state devicesNanoopticsFar infraredElectron
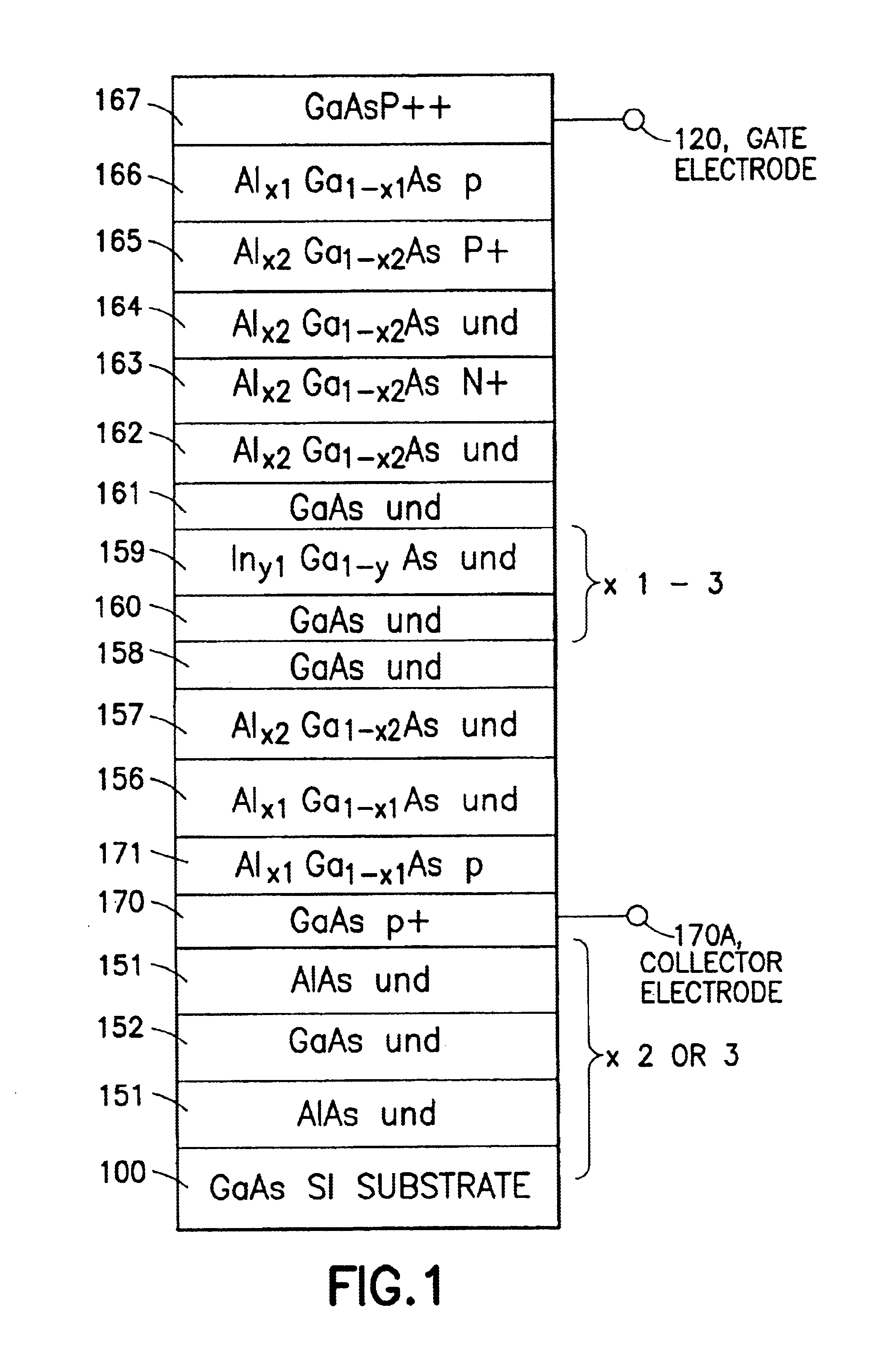
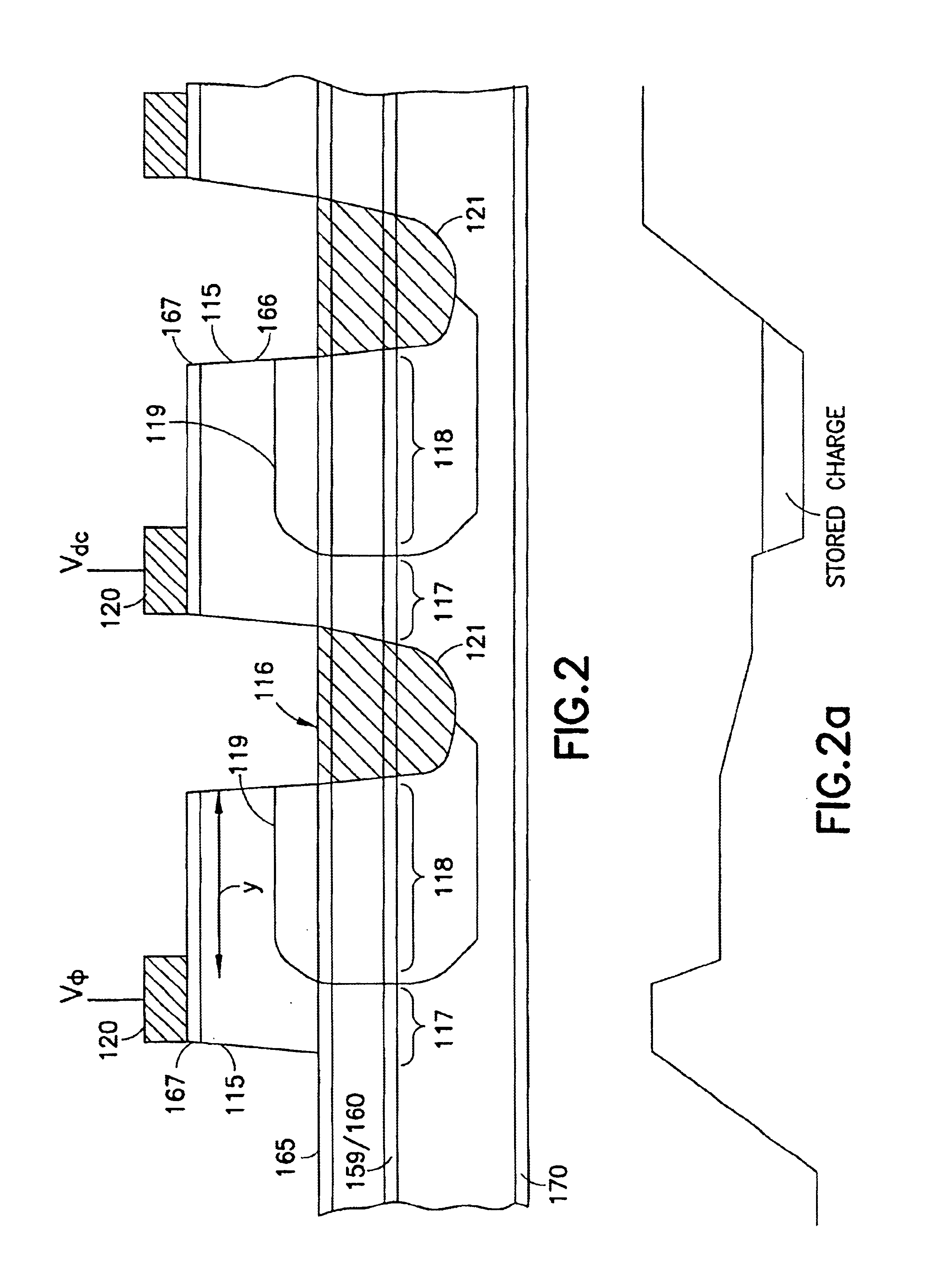
A photon detector is obtained by using the intersubband absorption mechanism in a modulation doped quantum well(s). The modulation doping creates a very high electric field in the well which enables absorption of input TE polarized light and also conducts the carriers emitted from the well into the modulation doped layer from where they may recombine with carriers from the gate contact. Carriers are resupplied to the well by the generation of electrons across the energy gap of the quantum well material. The absorption is enhanced by the use of a resonant cavity in which the quantum well(s) are placed. The absorption and emission from the well creates a deficiency of charge in the quantum well proportional to the intensity of the input photon signal. The quantity of charge in the quantum well of each detector is converted to an output voltage by transferring the charge to the gate of an output amplifier. The detectors are arranged in the form of a 2D array with an output amplifier associated with the entire array or a row of the array as in the known charge coupled devices, or a separate amplifier could be dedicated to each pixel as in the known architecture of the active pixel device. This detector has the unique advantage of near room temperature operation because the dark current is limited to the generation across the semiconductor bandgap and not the emission over the quantum well barrier. The detector also has the advantage that the readout circuitry is implemented monolithically by the HFETs formed in the GaAs substrate simultaneously, with the detecting elements.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Nonvolatile memory and three-state FETs using cladded quantum dot gate structure
ActiveUS20090173934A1TransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryField-effect transistor
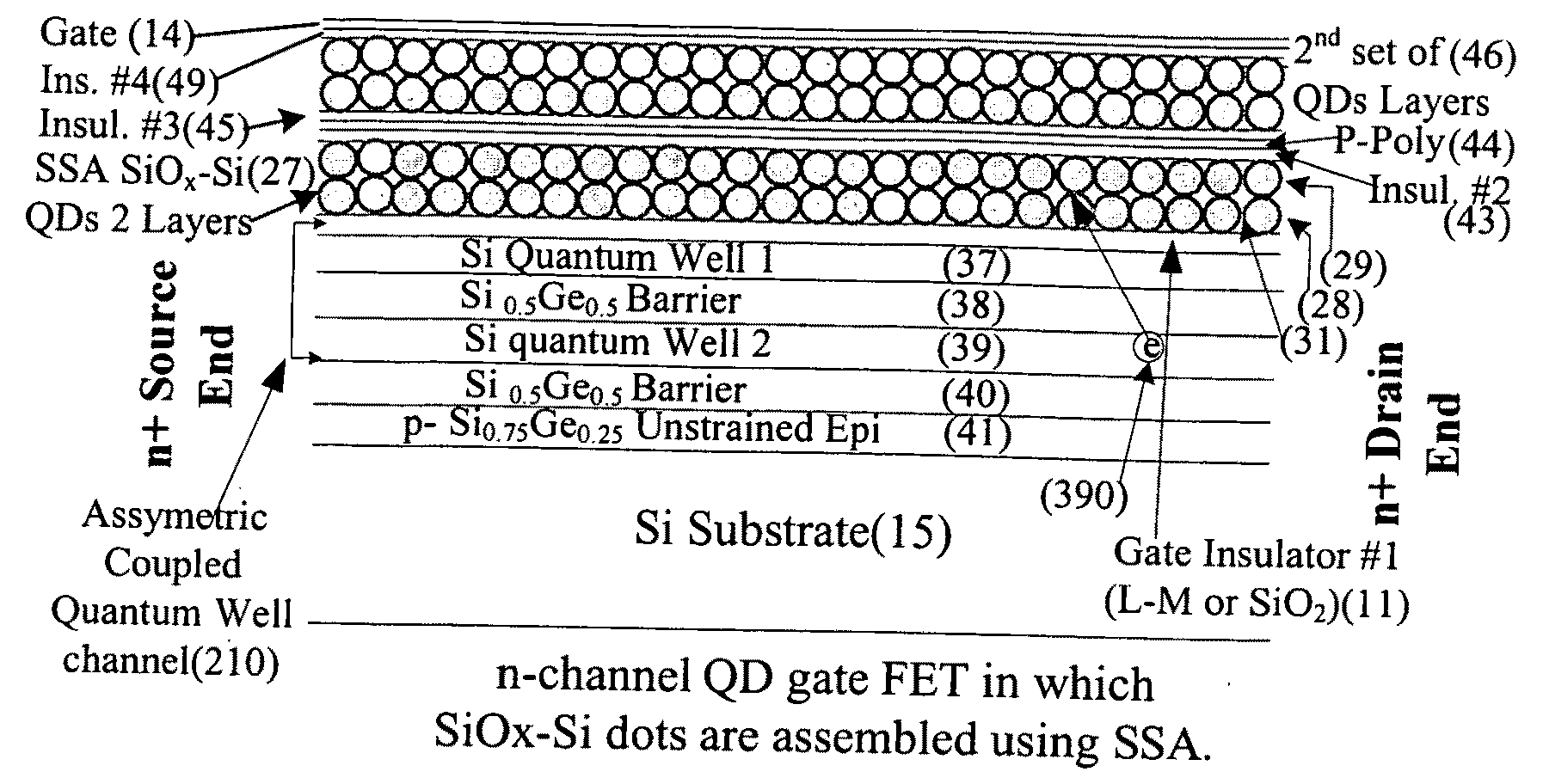
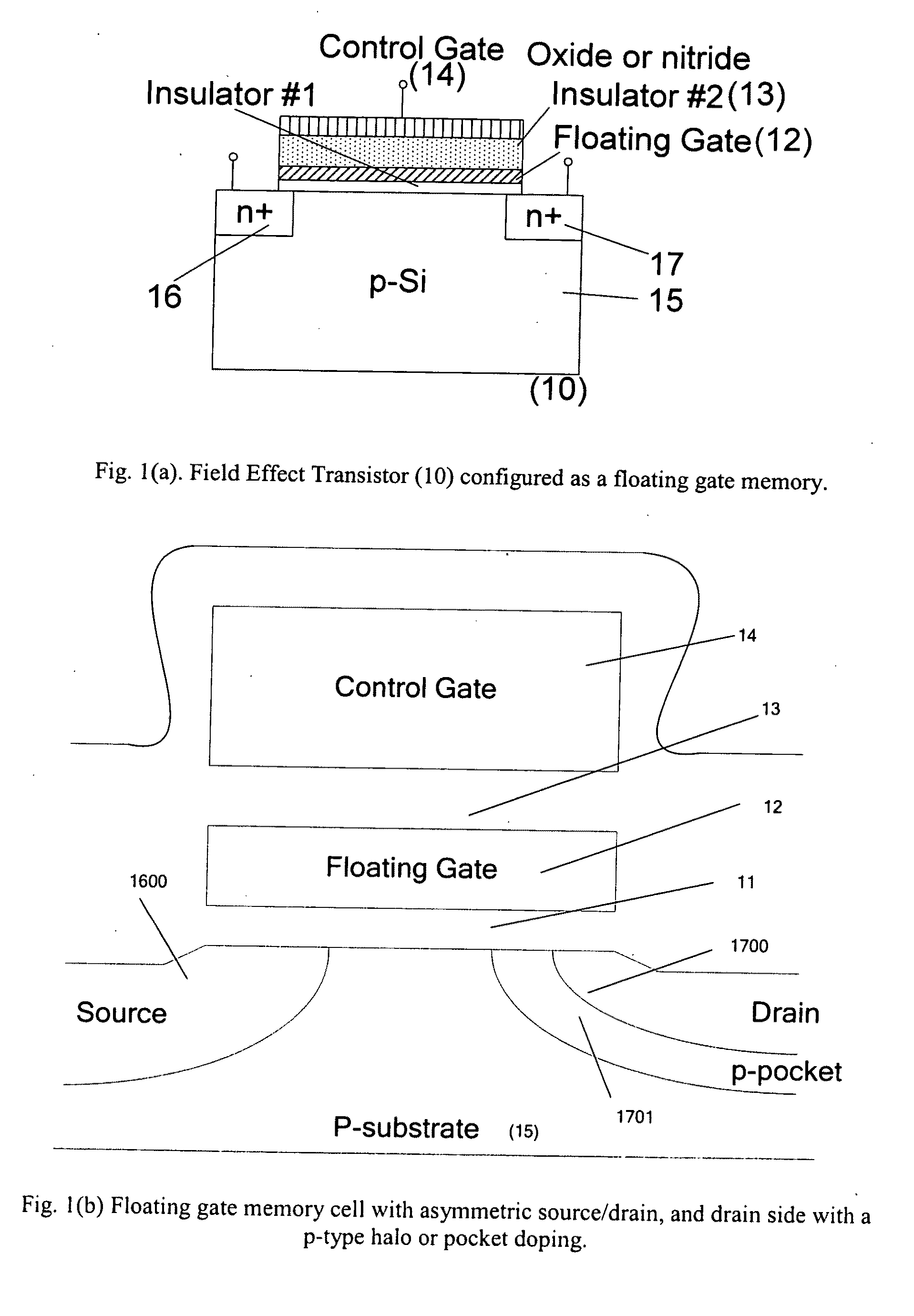
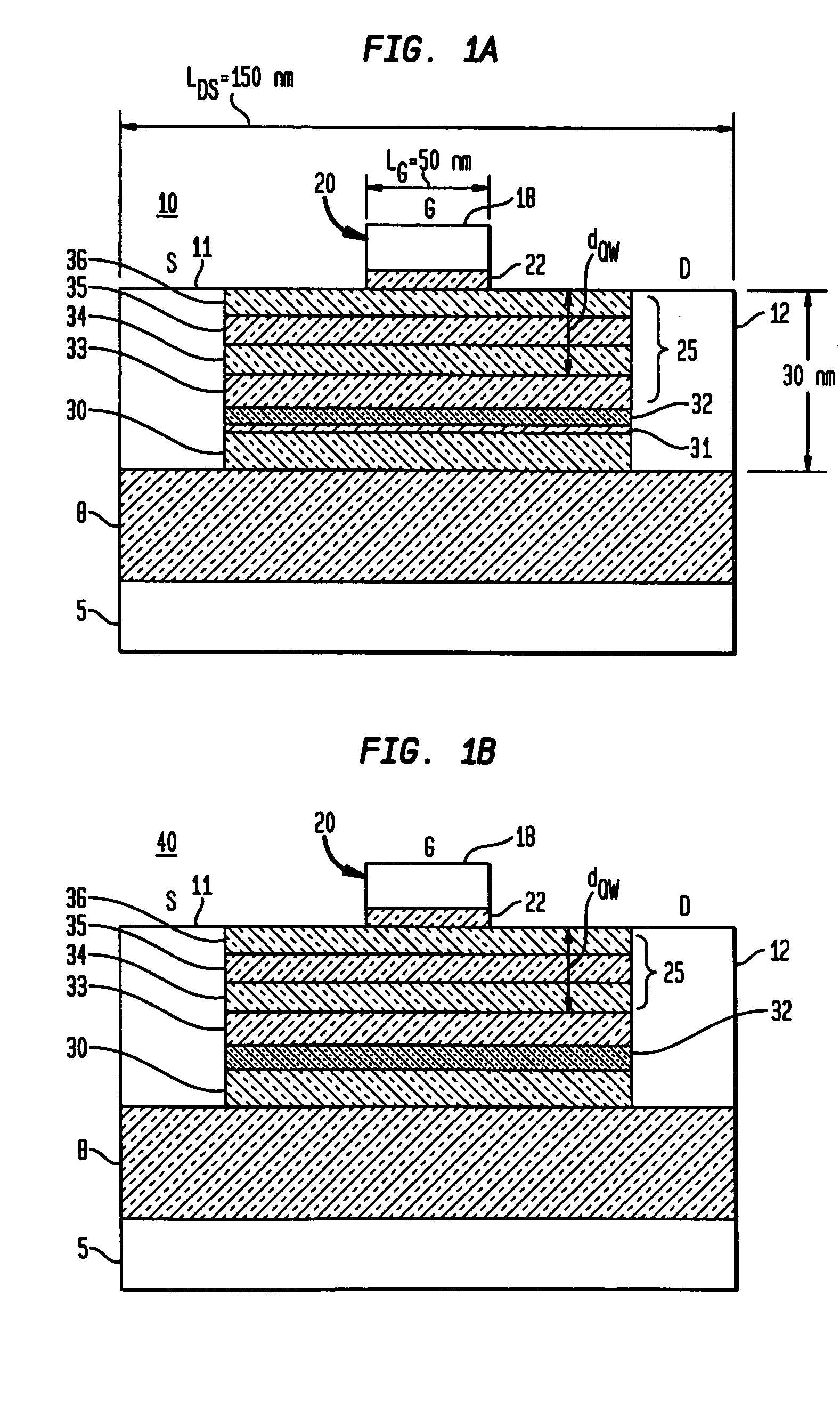
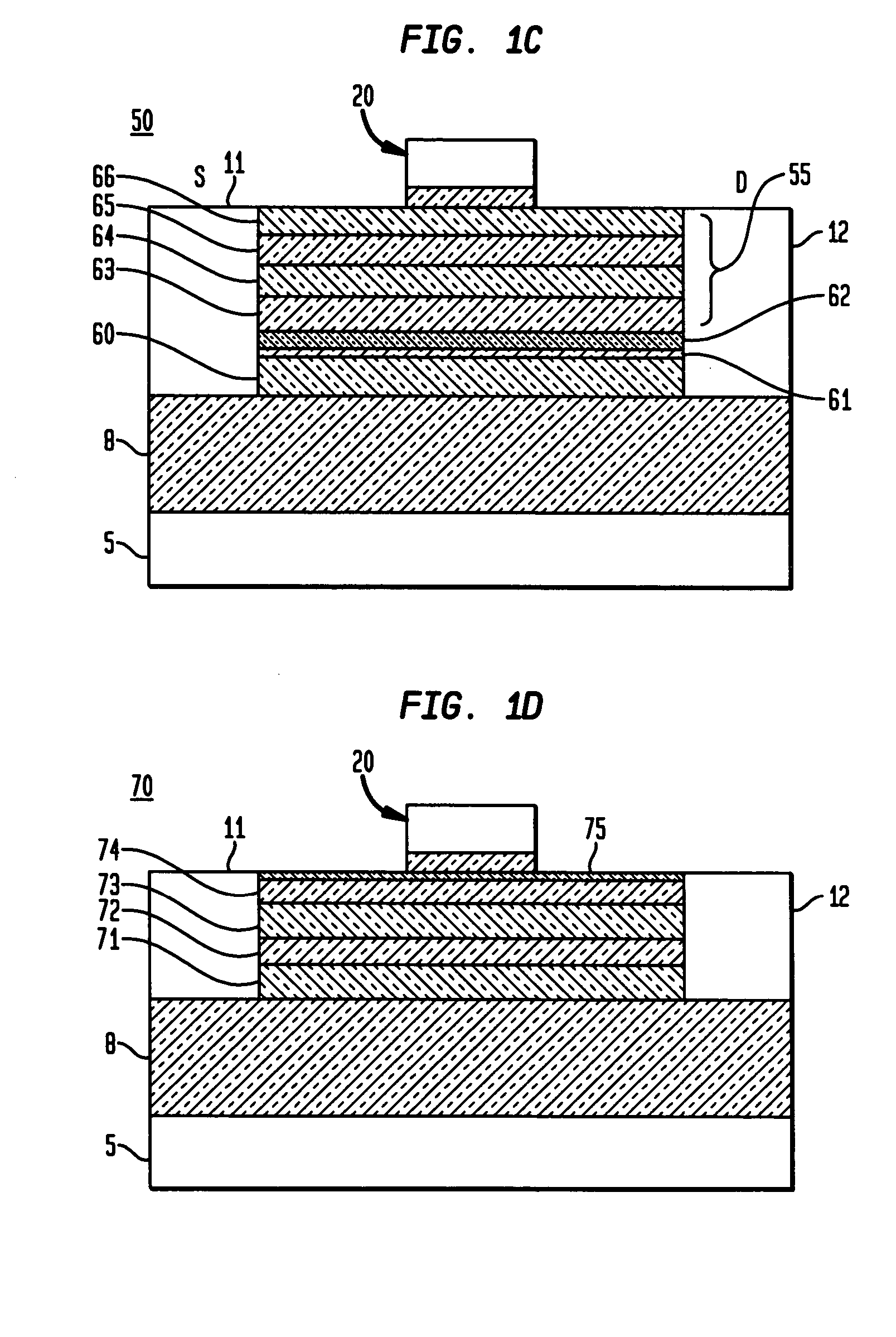
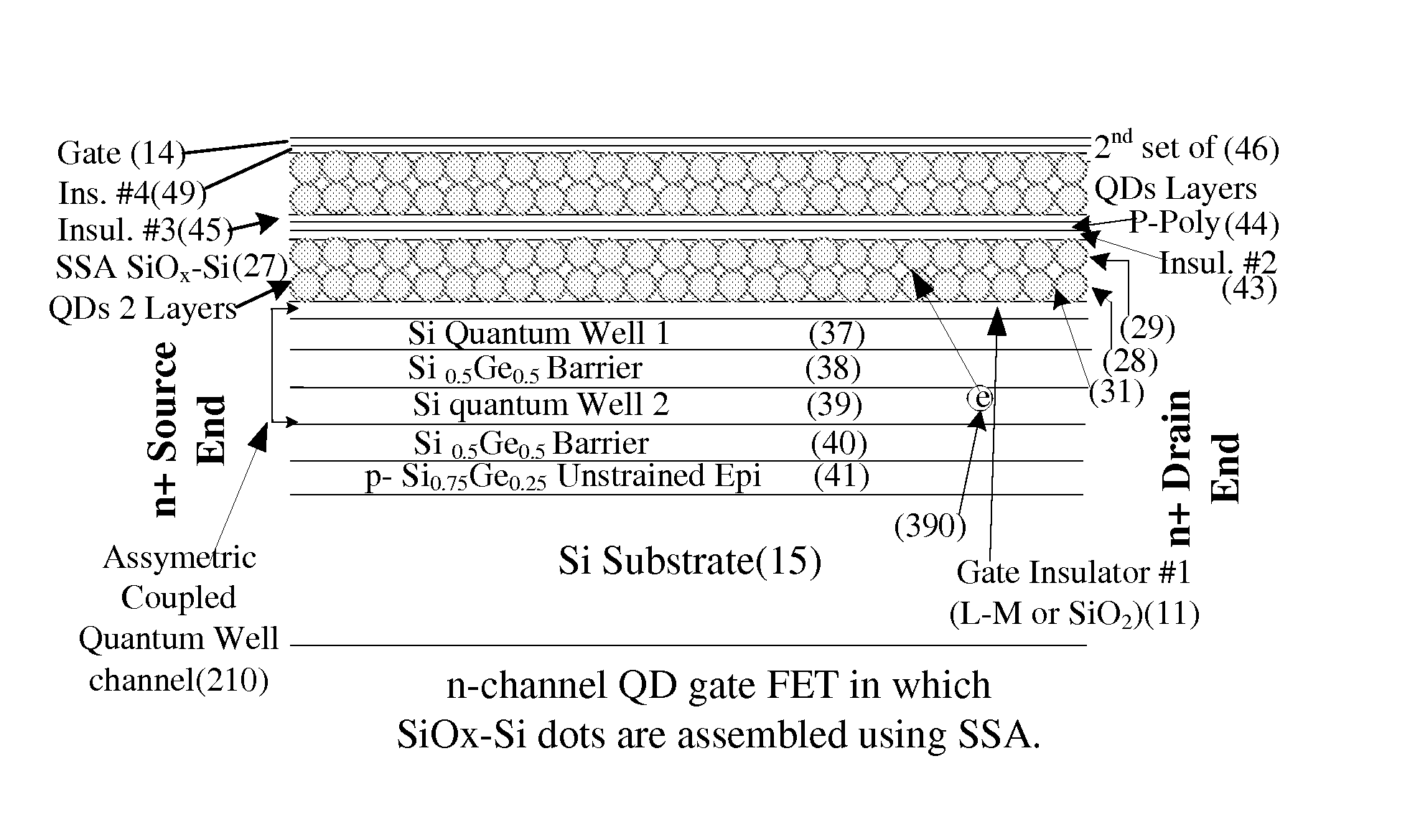
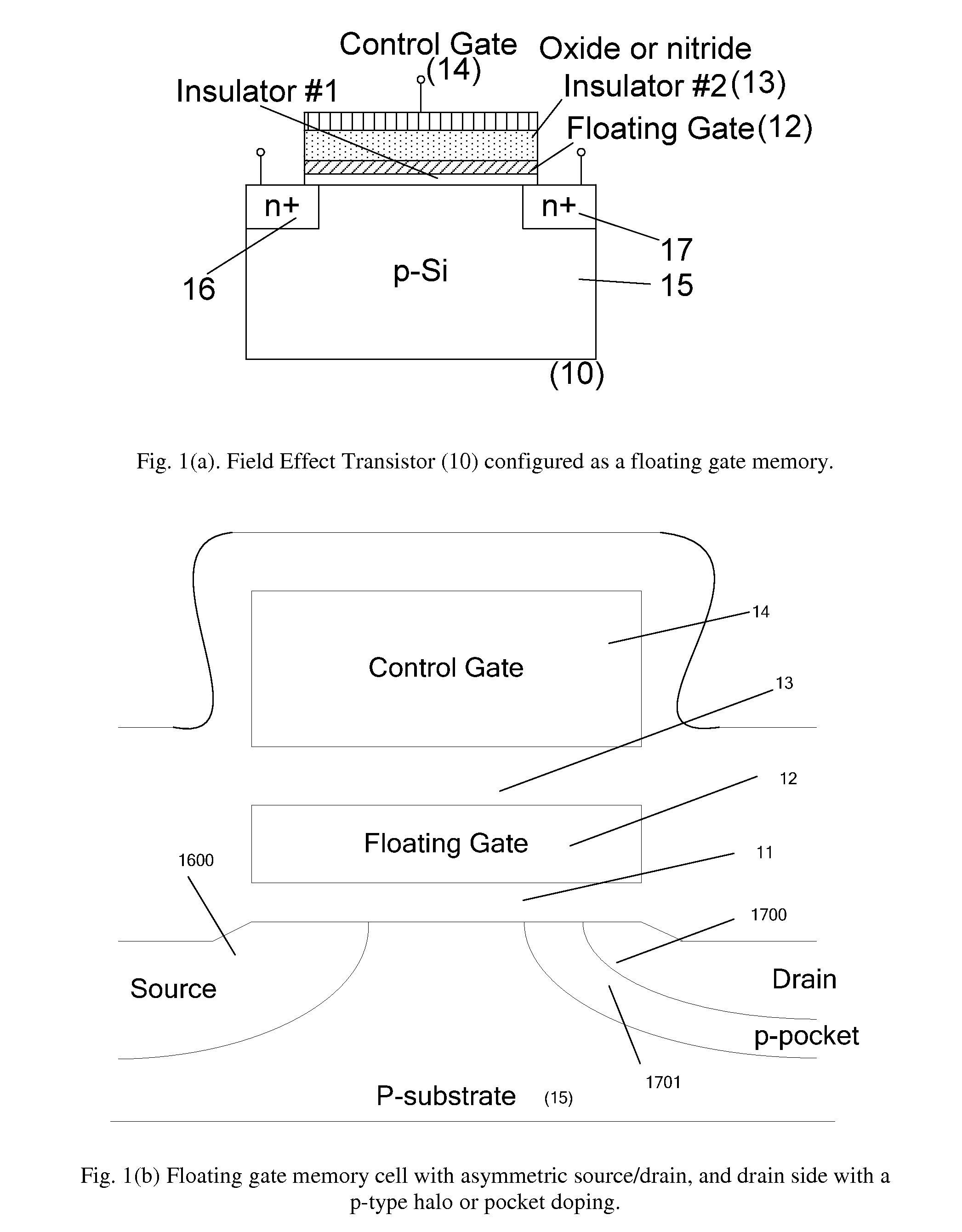
The present invention discloses use of quantum dot gate FETs as a nonvolatile memory element that can be used in flash memory architecture as well as in a nonvolatile random access memory (NVRAM) configuration that does not require refreshing of data as in dynamic random access memories. Another innovation is the design of quantum dot gate nonvolatile memory and 3-state devices using modulation doped field-effect transistors (MODFETs), particularly MOS-gate field effect transistors. The cladded quantum dot gate MODFETs can be designed in Si—SiGe, InGaAs—InP and other material systems. The incorporation of 3-state FET devices in static random access memory (SRAM) cell is described to result in advanced multi-state memory operation. Unlike conventional SRAMs, the 3-state QD-FET based of SRAMs provides 3 and 4-state memory operation due to the utilization of the intermediate states particularly in CMOS configuration. QD-gate FETs, potentially suitable for 8 nm channel lengths, in vertical configuration (VFET) are also described.
Owner:JAIN FAQUIR C
Light emitting diode having modulation doped layer
InactiveUS20100044674A1Avoid misalignmentExtension of timeSemiconductor devicesHigh concentrationContact layer
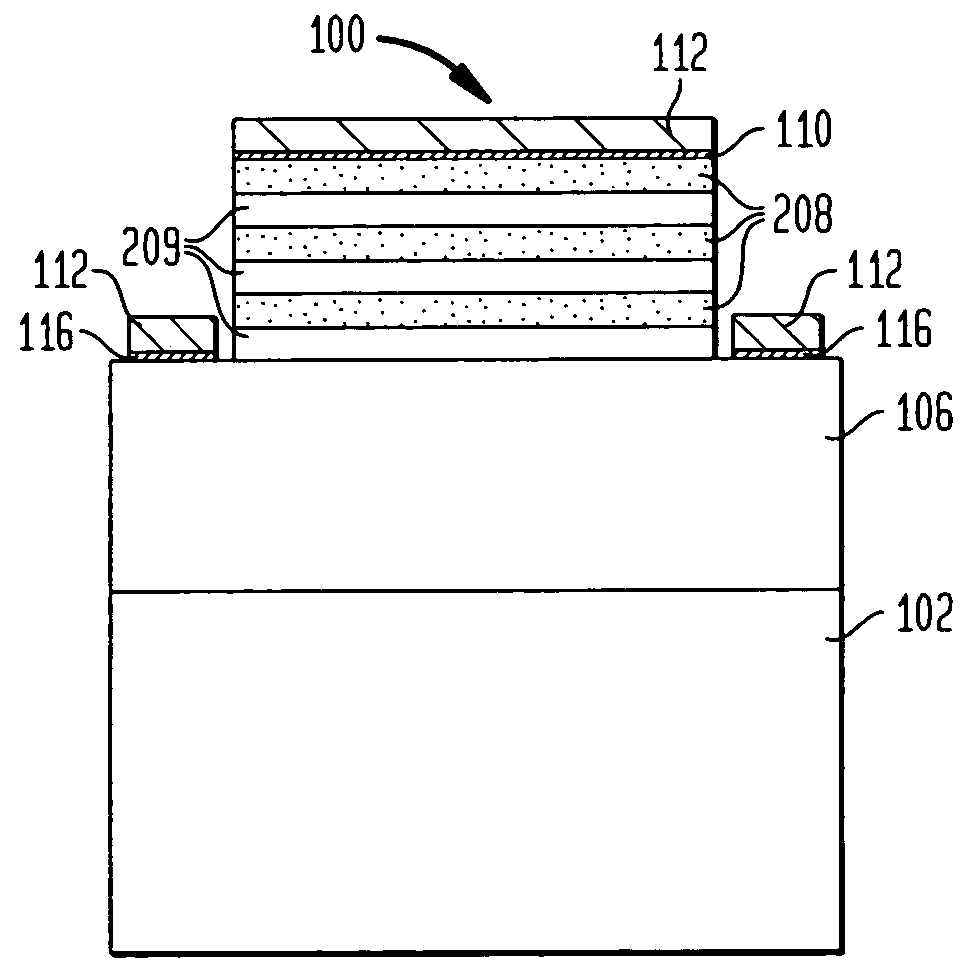
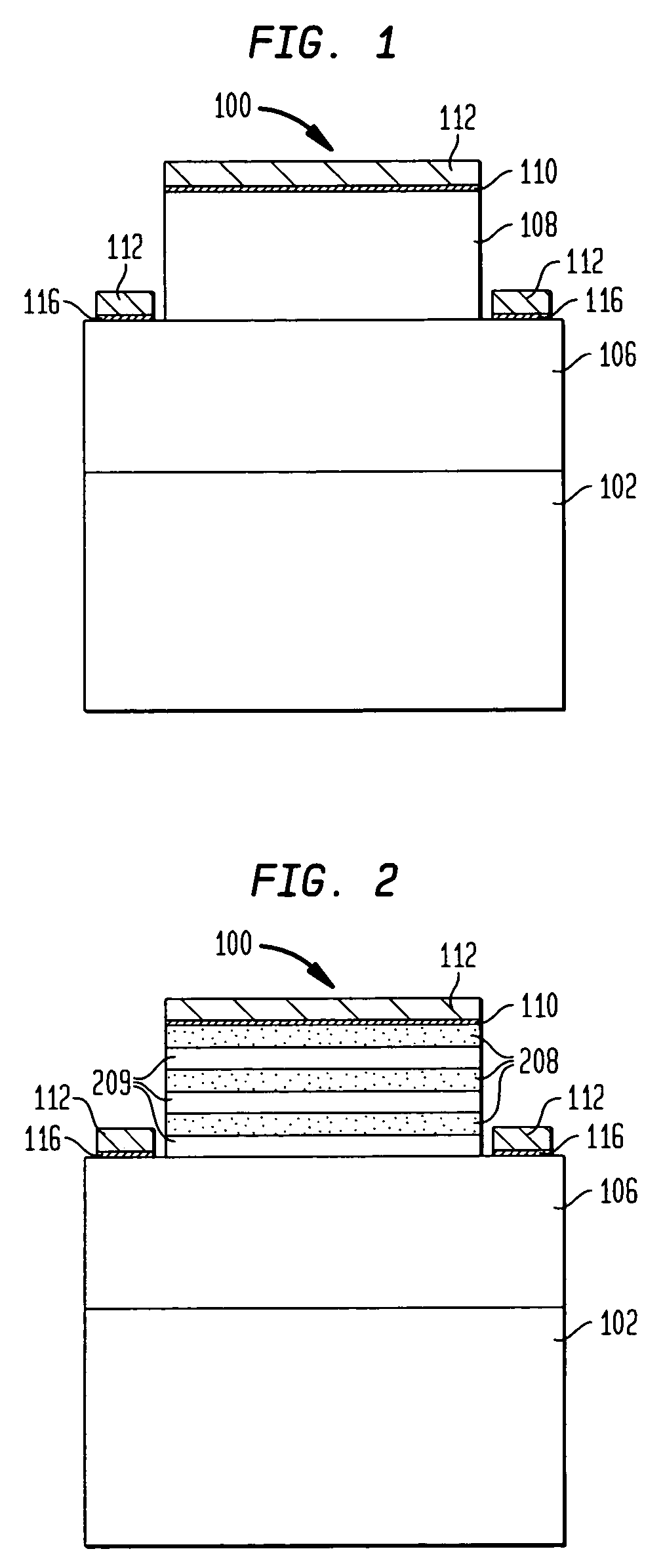
A light emitting diode (LED) having a modulation doped layer. The LED comprises an n-type contact layer, a p-type contact layer and an active region of a multiple quantum well structure having an InGaN well layer. The n-type contact layer comprises a first modulation doped layer and a second modulation doped layer, each having InGaN layers doped with a high concentration of n-type impurity and low concentration of n-type impurity InGaN layers alternately laminated. The InGaN layers of the first modulation doped layer have the same composition, and the InGaN layers of the second modulation doped layer have the same composition. The second modulation doped layer is interposed between the first modulation doped layer and the active region, and an n-electrode is in contact with the first modulation doped layer. Accordingly, an increase in process time is prevented and strains induced in a multiple quantum well structure are reduced.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
Ultra high-speed si/sige modulation-doped field effect transistors on ultra thin soi/sgoi substrate
InactiveUS20050045905A1Improve RF performanceUltra-high speed performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow noiseUltra high speed
A silicon and silicon germanium based semiconductor MODFET device design and method of manufacture. The MODFET design includes a high-mobility layer structure capable of ultra high-speed, low-noise for a variety of communication applications including RF, microwave, sub-millimeter-wave and millimeter-wave. The epitaxial field effect transistor layer structure includes critical (vertical and lateral) device scaling and layer structure design for a high mobility strained n-channel and p-channel transistor incorporating silicon and silicon germanium layers to form the optimum modulation-doped heterostructure on an ultra thin SOI or SGOI substrate capable of achieving greatly improved RF performance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Nonvolatile memory and three-state FETs using cladded quantum dot gate structure
The present invention discloses use of quantum dot gate FETs as a nonvolatile memory element that can be used in flash memory architecture as well as in a nonvolatile random access memory (NVRAM) configuration that does not require refreshing of data as in dynamic random access memories. Another innovation is the design of quantum dot gate nonvolatile memory and 3-state devices using modulation doped field-effect transistors (MODFETs), particularly MOS-gate field effect transistors. The cladded quantum dot gate MODFETs can be designed in Si—SiGe, InGaAs—InP and other material systems. The incorporation of 3-state FET devices in static random access memory (SRAM) cell is described to result in advanced multi-state memory operation. Unlike conventional SRAMs, the 3-state QD-FET based of SRAMs provides 3 and 4-state memory operation due to the utilization of the intermediate states particularly in CMOS configuration. QD-gate FETs, potentially suitable for 8 nm channel lengths, in vertical configuration (VFET) are also described.
Owner:JAIN FAQUIR C
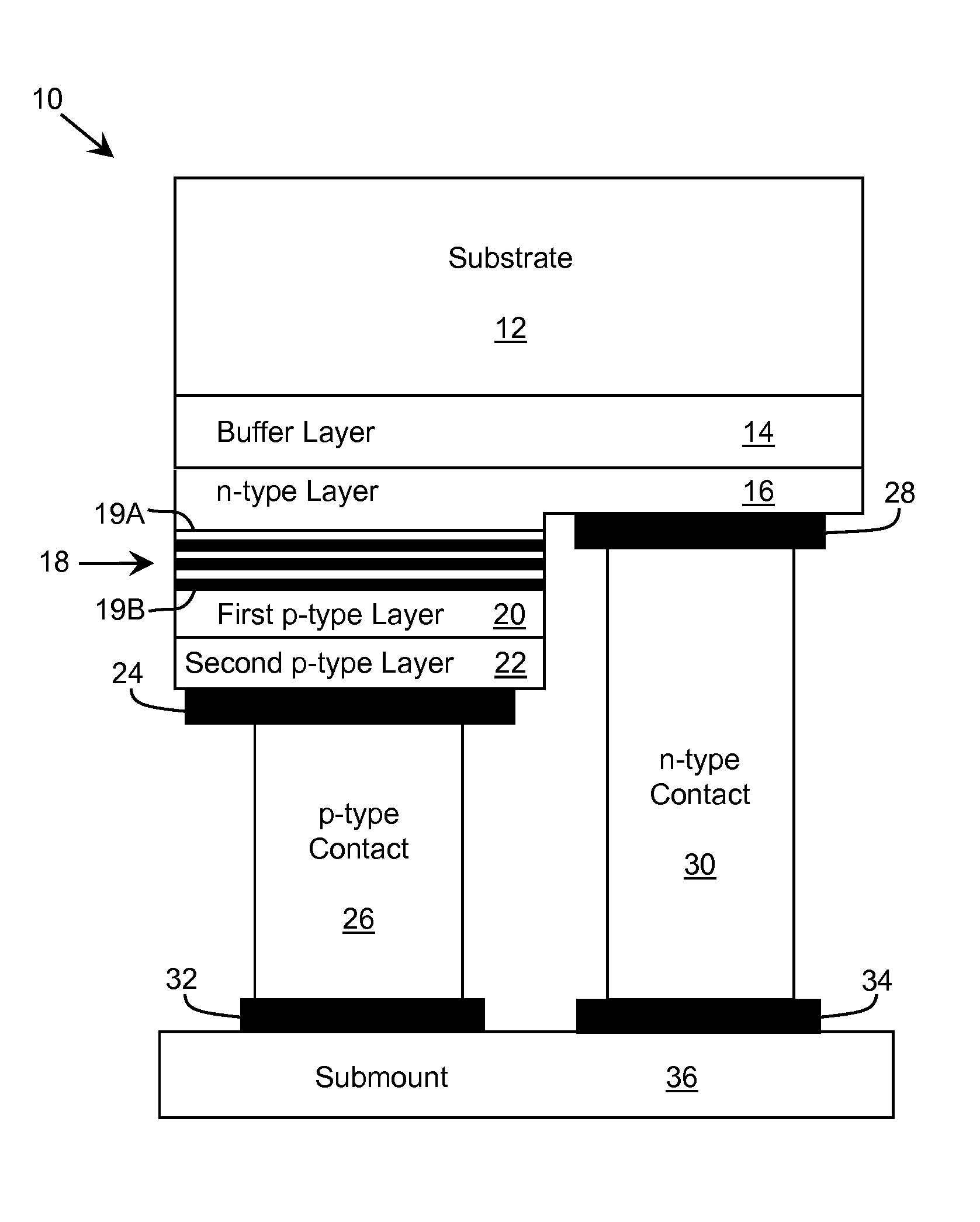
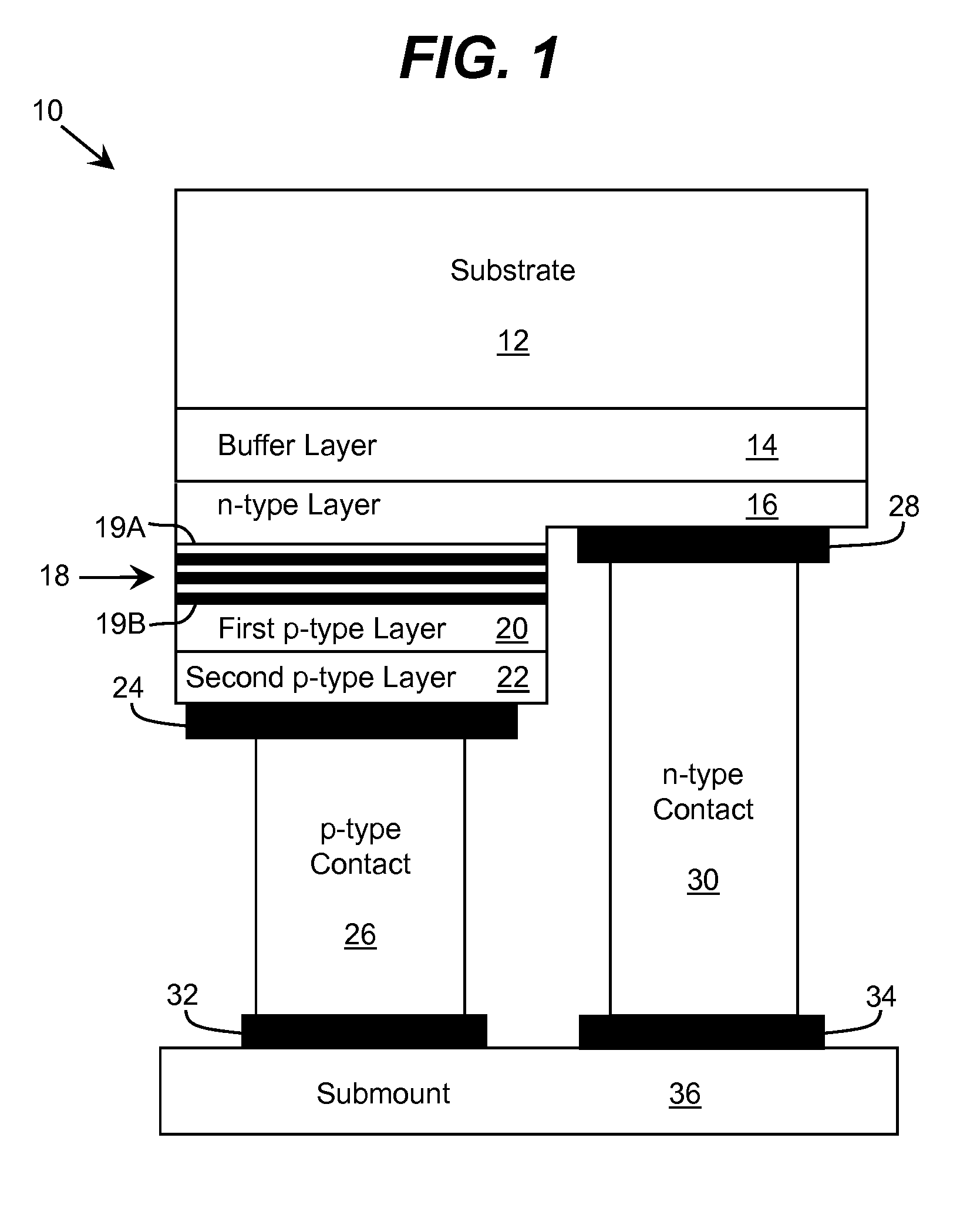
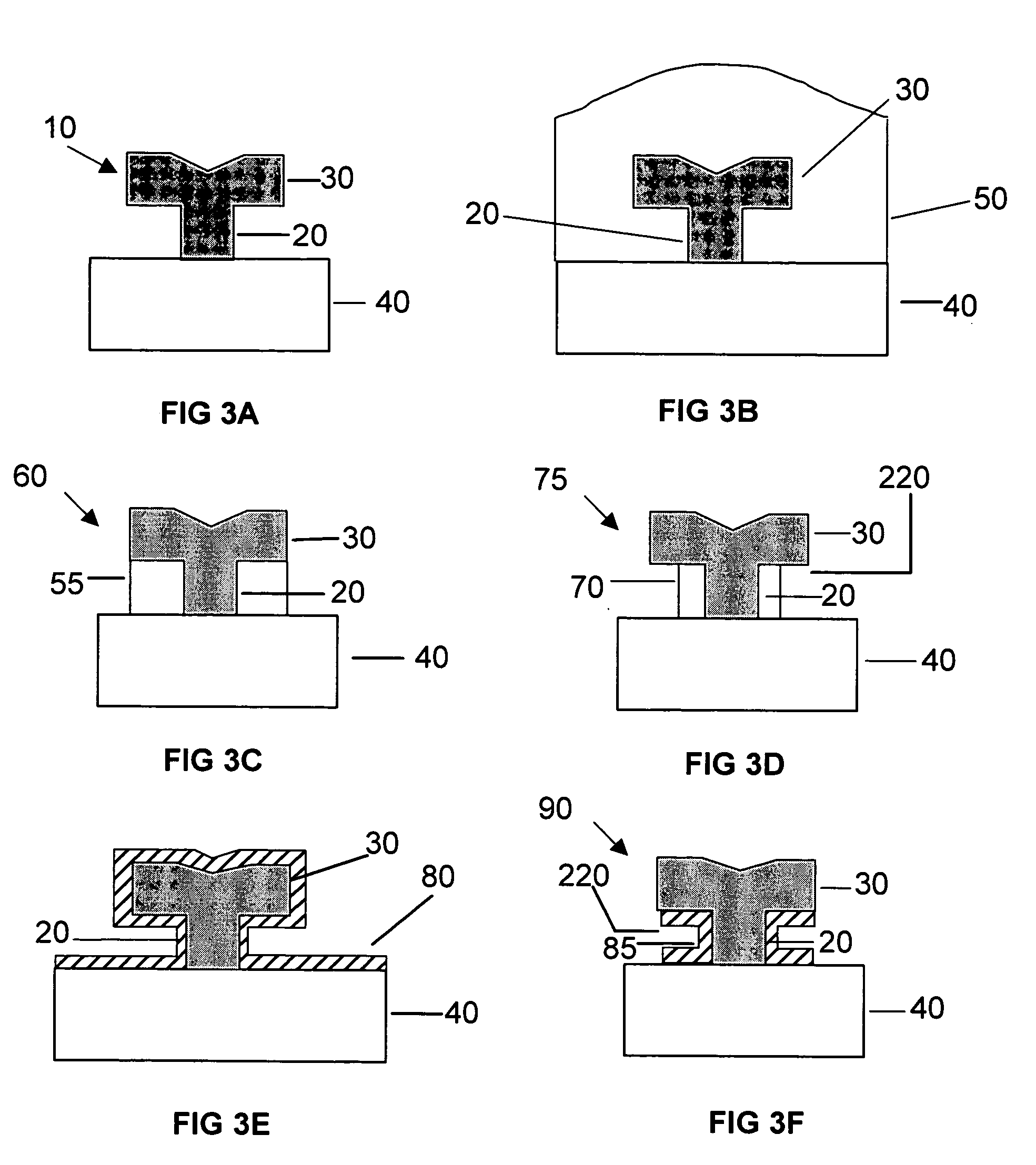
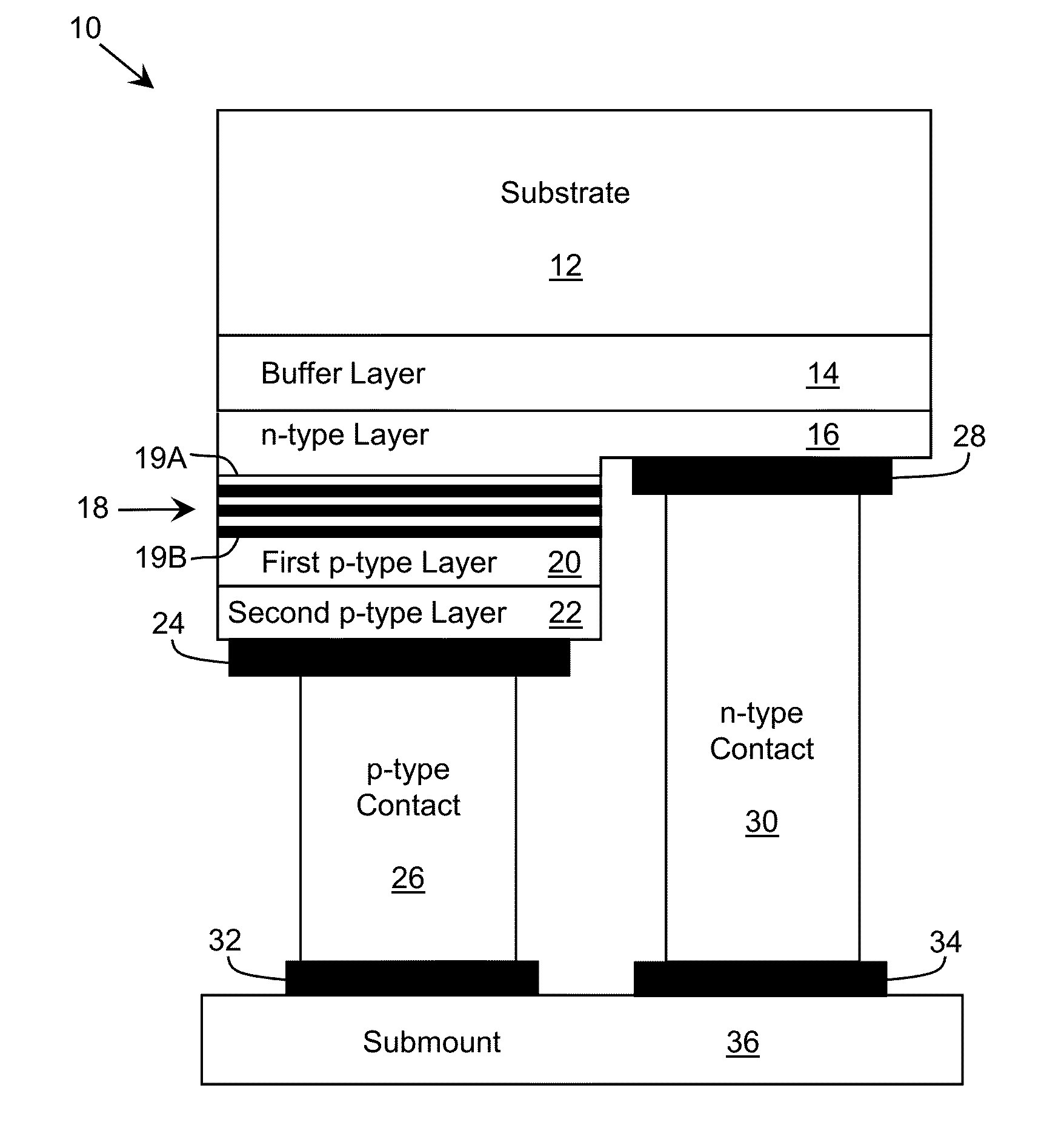
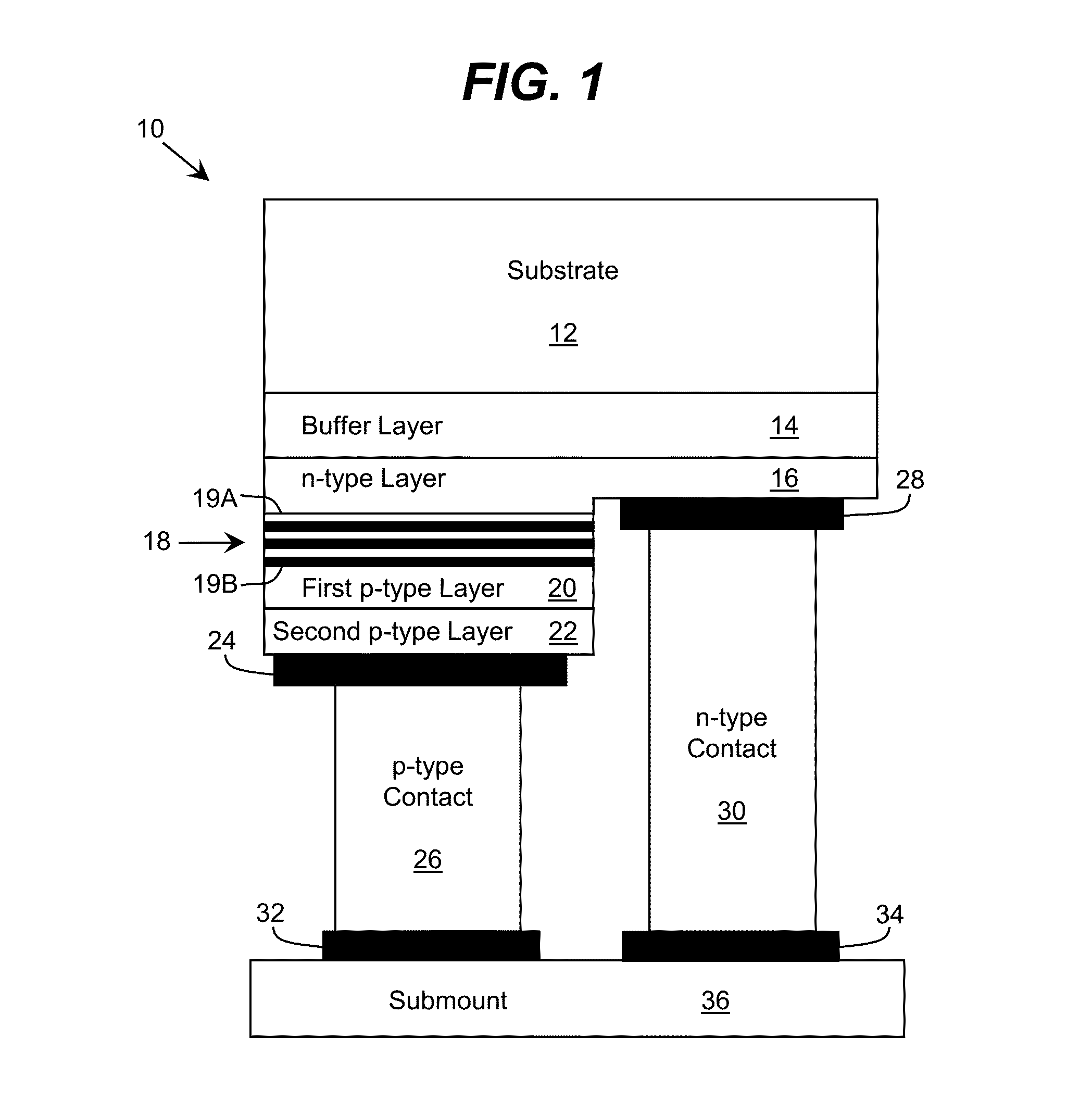
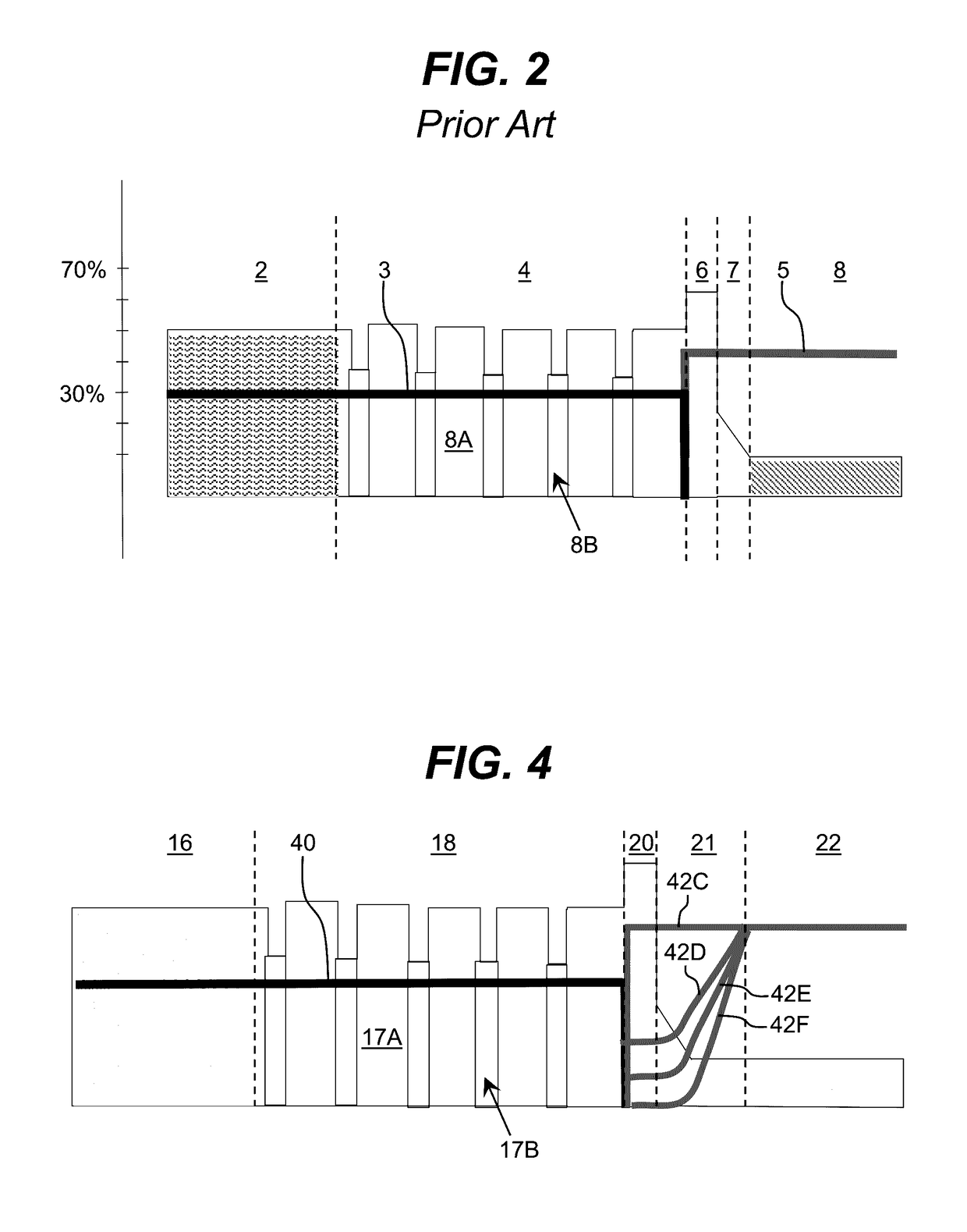
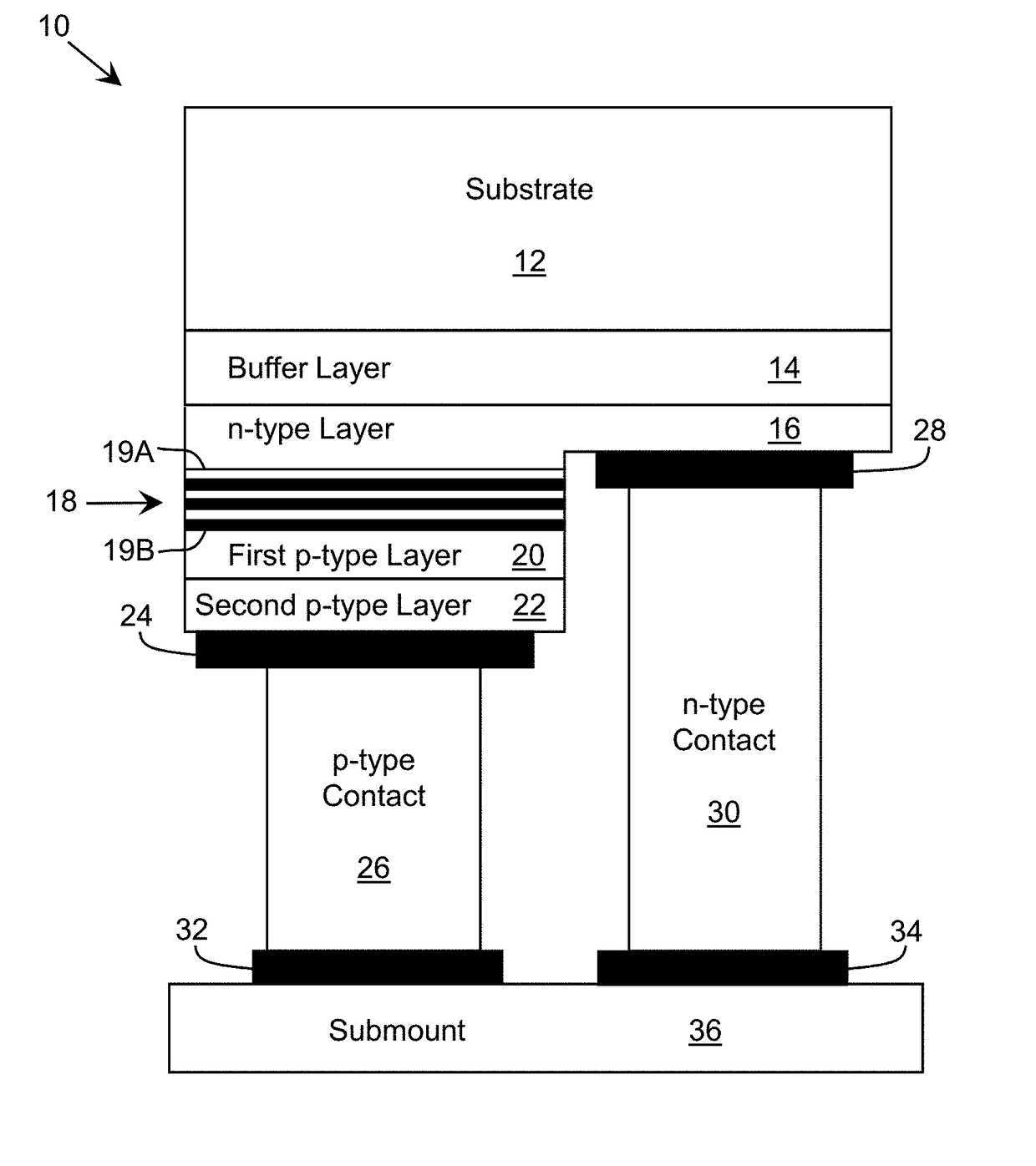
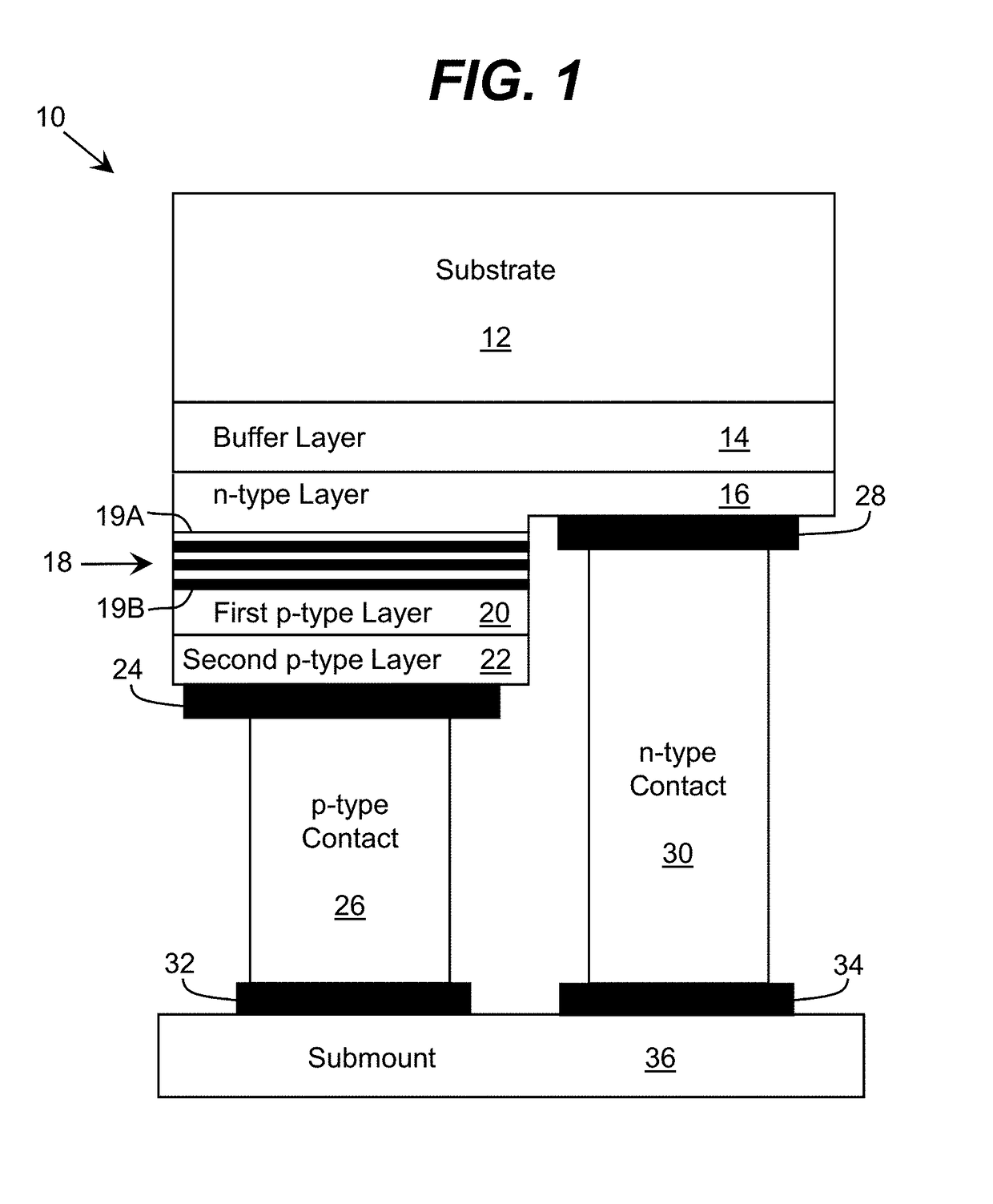
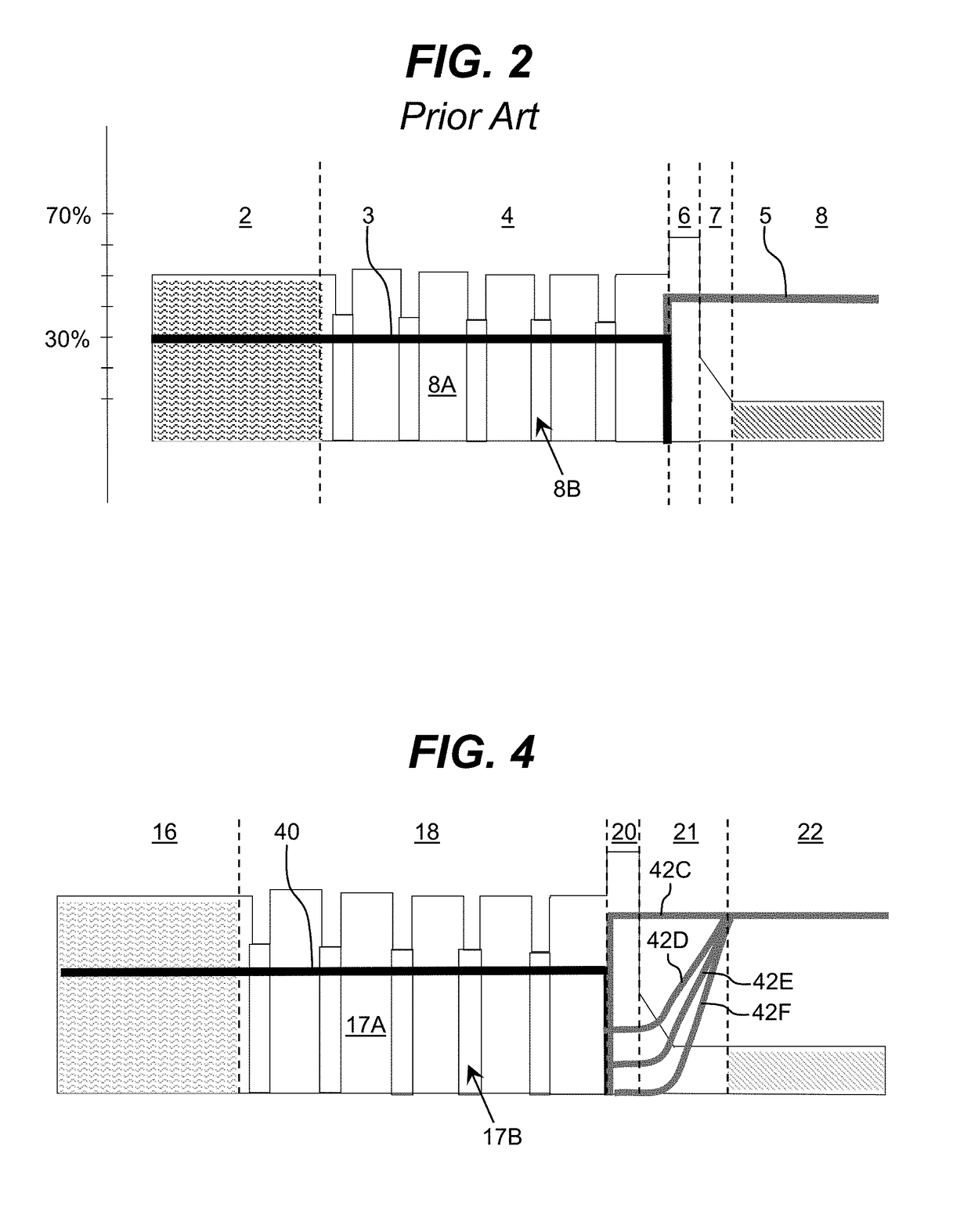
Optoelectronic Device with Modulation Doping
ActiveUS20150060908A1Reduce formationImprove reliabilityLaser detailsSolid-state devicesDopantHeterojunction
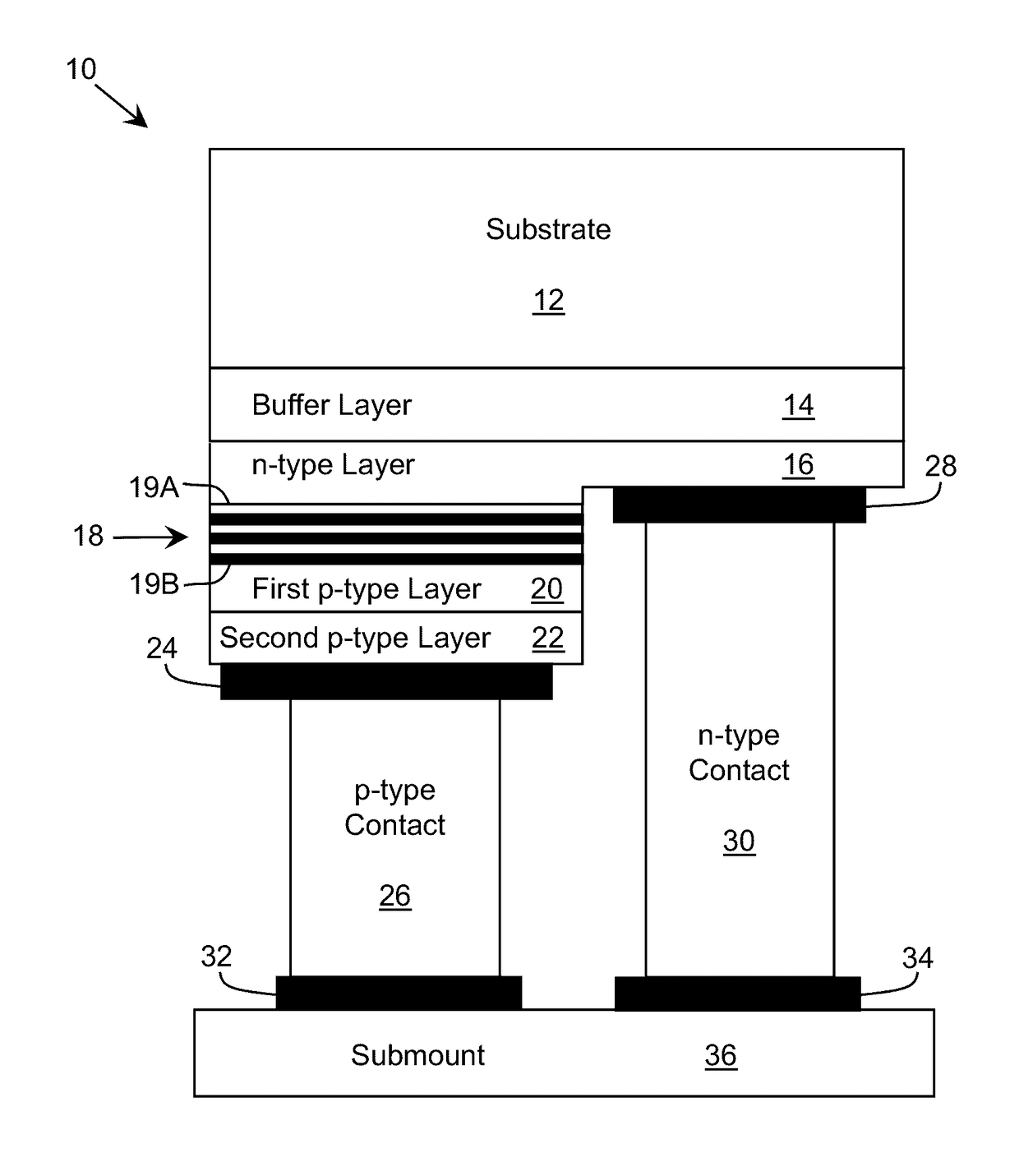
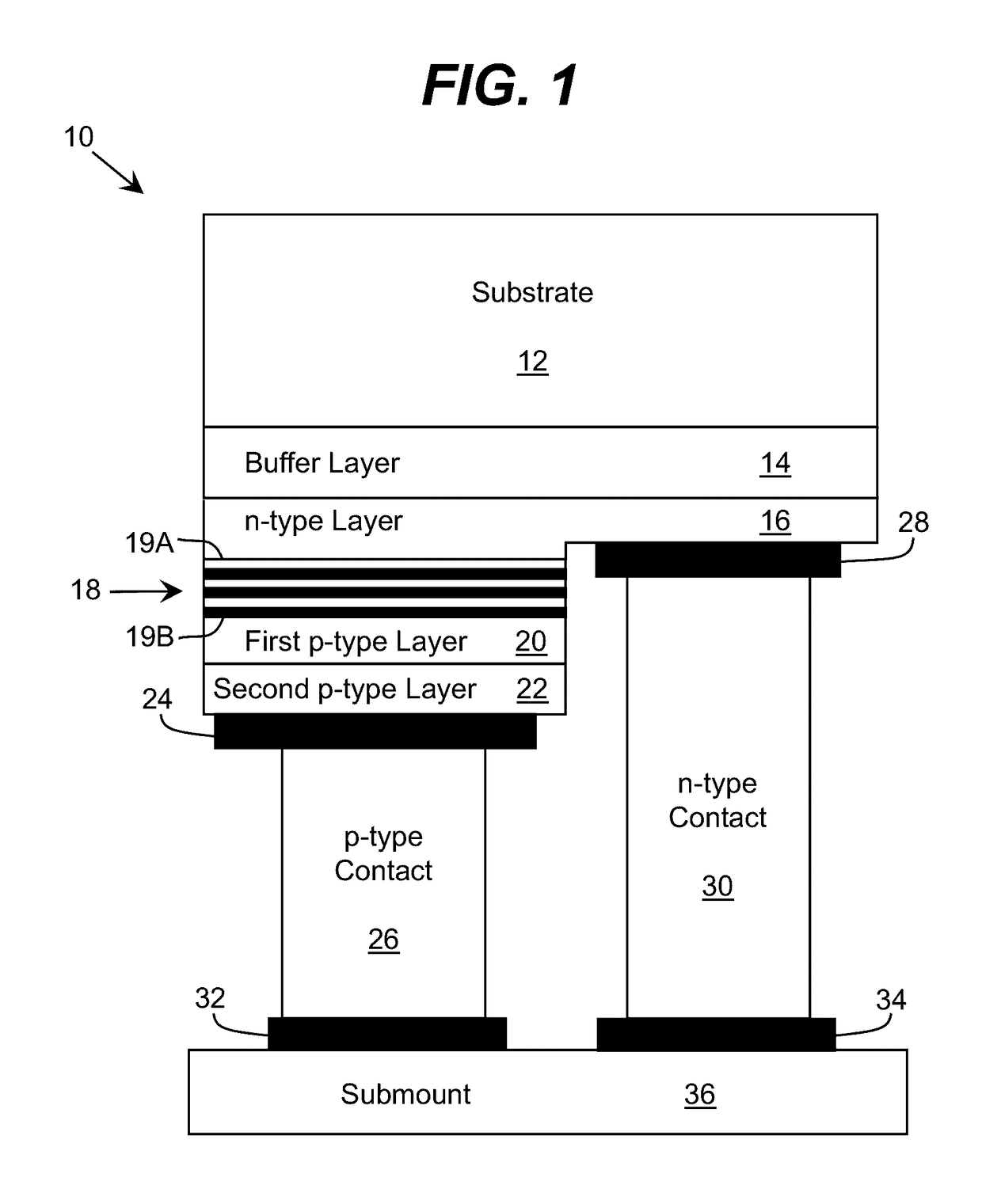
An improved heterostructure for an optoelectronic device is provided. The heterostructure includes an active region, an electron blocking layer, and a p-type contact layer. The p-type contact layer and electron blocking layer can be doped with a p-type dopant. The dopant concentration for the electron blocking layer can be at most ten percent the dopant concentration of the p-type contact layer. A method of designing such a heterostructure is also described.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Single crystal graphene pn node and preparation method thereof
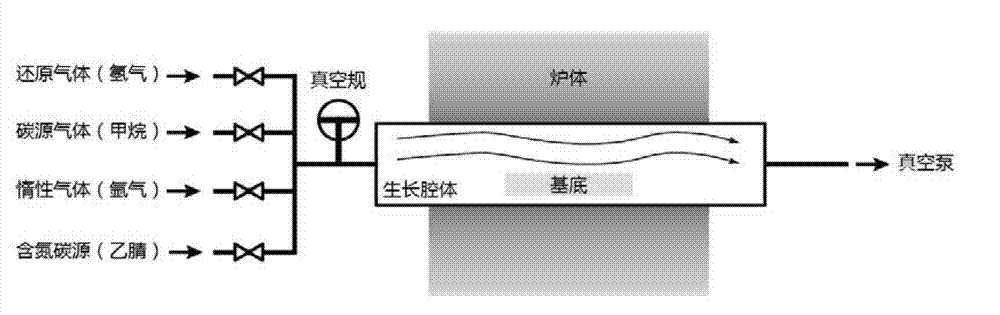
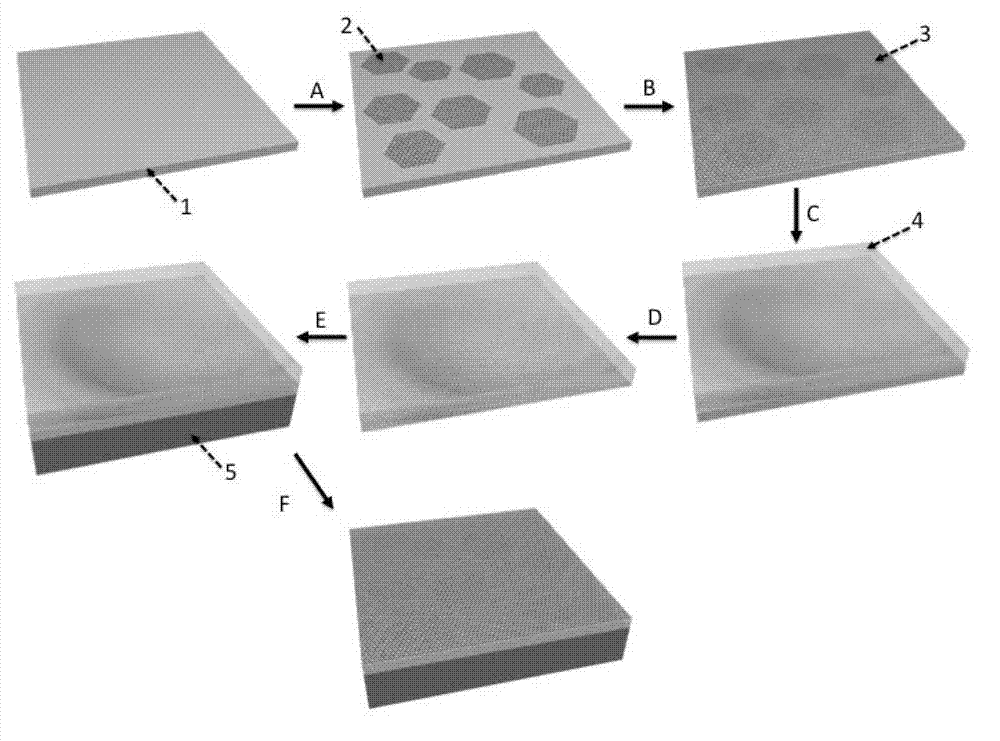
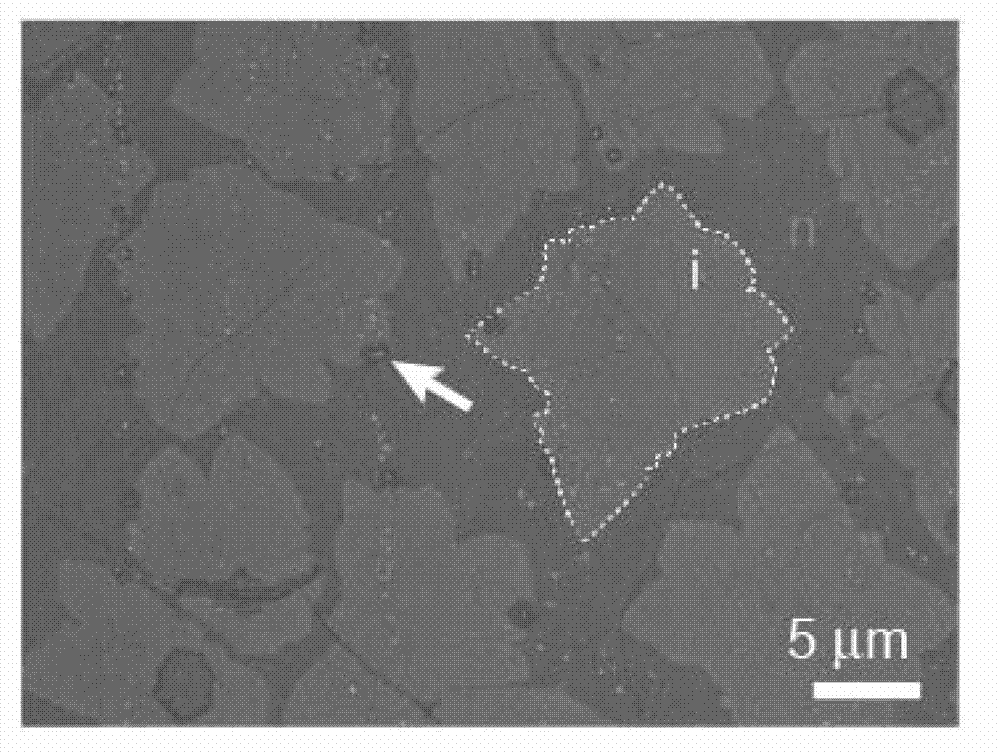
ActiveCN102953118AQuality improvementImprove mobilityPolycrystalline material growthGrapheneDoped grapheneFrequency multiplier
The invention discloses a single crystal graphene pn node and a preparation method thereof. The modulated and doped graphene pn node is prepared according to the method which comprises the following steps of 1, annealing a copper foil substrate; 2, growing a sub-monolayer intrinsic graphene island on the surface of a copper foil by taking methane as a carbon source; 3, cleaning a growing system by using inert gas; 4, taking acetonitrile steam as a nitrogen-containing carbon source and growing nitrogen doped graphene on the boundary of the intrinsic graphene island; 5, repeating the steps 2, to 4, for at least zero time to obtain the single-level or multi-level graphene pn node; 6, quickly reducing the temperature to stop a growing process; and 7, transferring the graphene pn node which is obtained through modulating, doping and growing onto any target substrate by using polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) as a medium. The modulated and doped graphene pn node with high quality is obtained by regulating the carbon source in the graphene growing process. The product has very high migration rate and photon to current conversion efficiency; and a transfer characteristic curve of the product has a double-Dirac point, so that the single crystal graphene pn node can be applied to logic devices, such as a phase inverter and a frequency multiplier.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Nanowhiskers with pn junctions, doped nanowhiskers, and methods for preparing them
InactiveUS7432522B2Permitted diffusionReduce the amount requiredPolycrystalline material growthNanoinformaticsHeterojunctionNon doped
Nano-engineered structures are disclosed, incorporating nanowhiskers of high mobility conductivity and incorporating pn junctions. In one embodiment, a nanowhisker of a first semiconducting material has a first band gap, and an enclosure comprising at least one second material with a second band gap encloses said nanoelement along at least part of its length, the second material being doped to provide opposite conductivity type charge carriers in respective first and second regions along the length of the of the nanowhisker, whereby to create in the nanowhisker by transfer of charge carriers into the nanowhisker, corresponding first and second regions of opposite conductivity type charge carriers with a region depleted of free carriers therebetween. The doping of the enclosure material may be degenerate so as to create within the nanowhisker adjacent segments having very heavy modulation doping of opposite conductivity type analogous to the heavily doped regions of an Esaki diode. In another embodiment, a nanowhisker is surrounded by polymer material containing dopant material. A step of rapid thermal annealing causes the dopant material to diffuse into the nanowhisker. In a further embodiment, a nanowhisker has a heterojunction between two different intrinsic materials, and Fermi level pinning creates a pn junction at the interface without doping.
Owner:QUNANO
Ultra high-speed Si/SiGe modulation-doped field effect transistors on ultra thin SOI/SGOI substrate
ActiveUS6855963B1Improve RF performanceUltra-high speed performanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLow noiseUltra high speed
A silicon and silicon germanium based semiconductor MODFET device design and method of manufacture. The MODFET design includes a high-mobility layer structure capable of ultra high-speed, low-noise for a variety of communication applications including RF, microwave, sub-millimeter-wave and millimeter-wave. The epitaxial field effect transistor layer structure includes critical (vertical and lateral) device scaling and layer structure design for a high mobility strained n-channel and p-channel transistor incorporating silicon and silicon germanium layers to form the optimum modulation-doped heterostructure on an ultra thin SOI or SGOI substrate capable of achieving greatly improved RF performance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
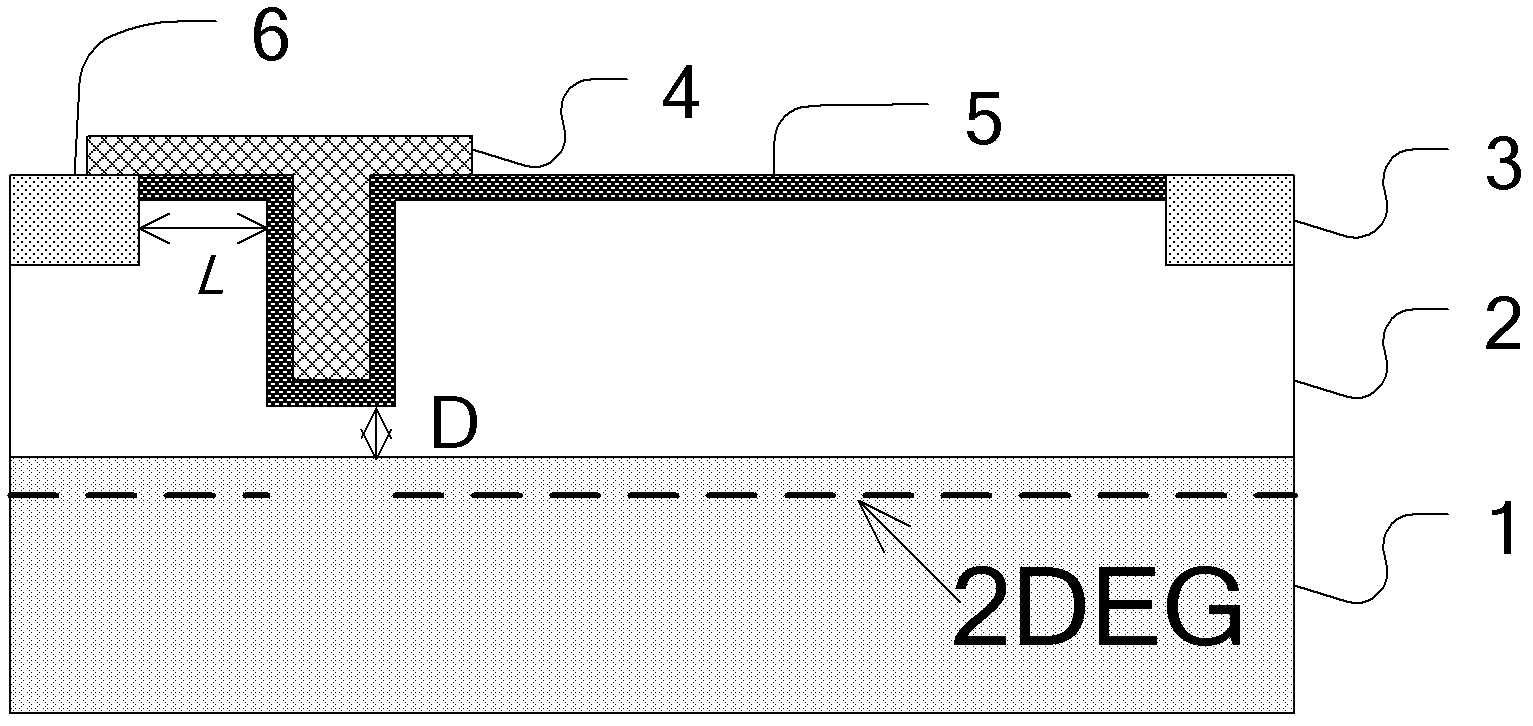
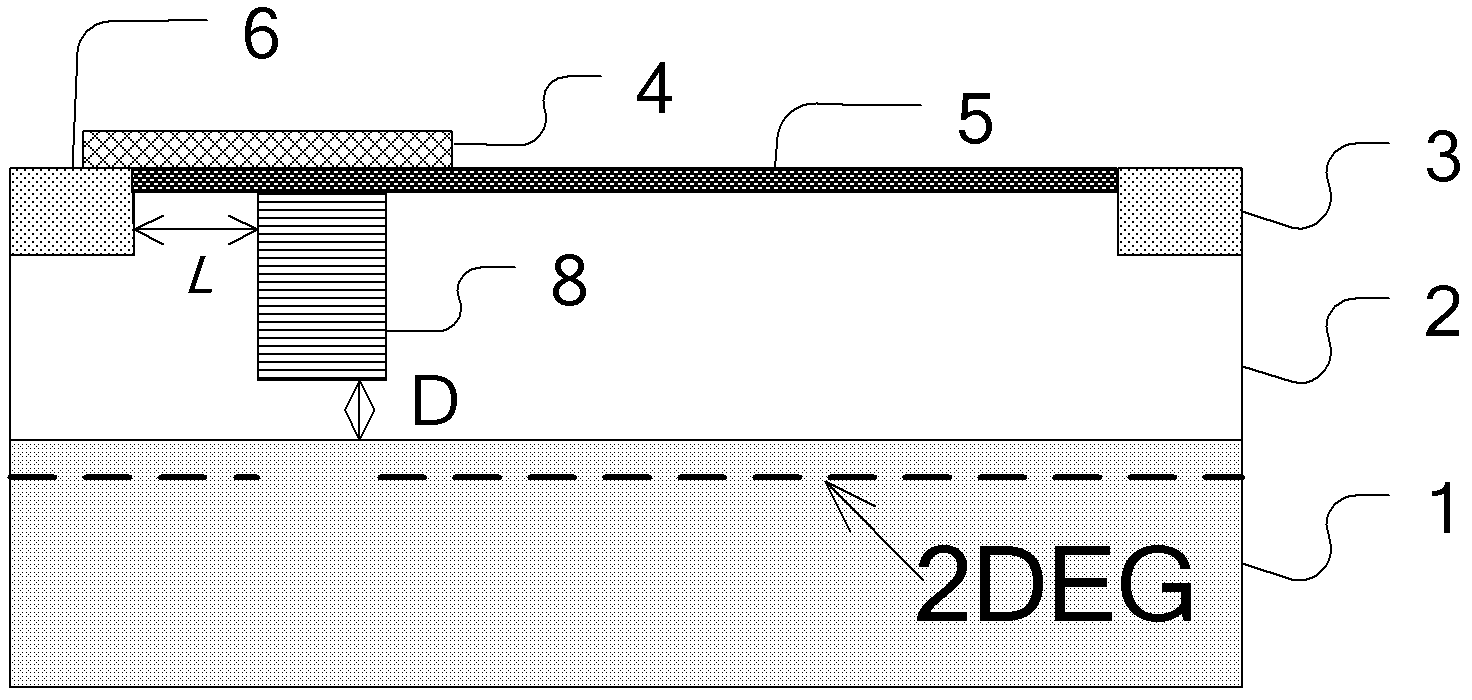
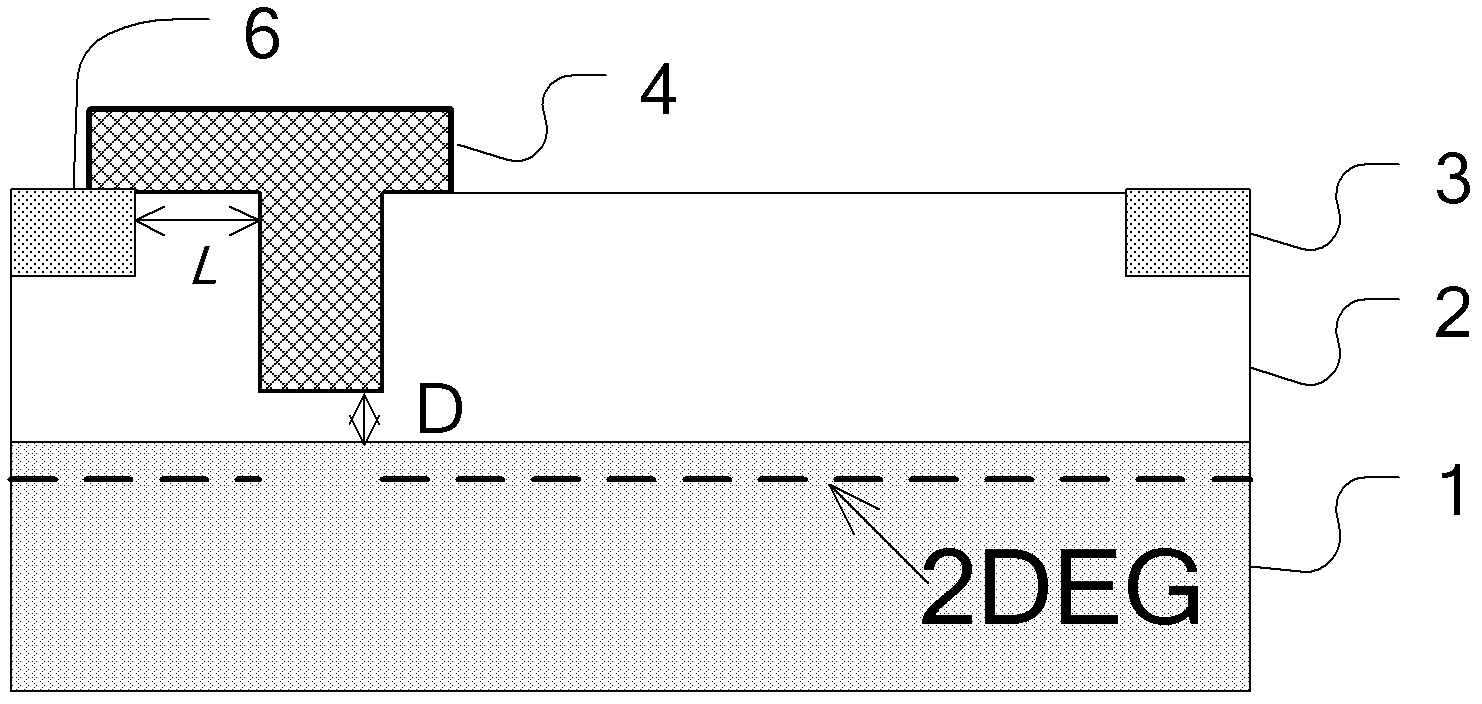
Normally-off field-controlled channel gan heterojunction diode
InactiveCN102280494AImplement field control featuresEfficient use ofSemiconductor devicesControl channelPositive power
A normally-off type field-controlled channel GaN heterojunction diode belongs to the technical field of semiconductor devices. The invention adopts the technology of combining insulating layer-groove, modulation doping and groove-modulation doping to change the conductive channel structure of the existing GaN heterojunction diode, and convert the original normally-on spontaneously polarized GaN heterojunction The junction conductive channel is changed into a normally-off field-controlled conductive channel combining spontaneous polarization and piezoelectric polarization in the present invention, which realizes the field-controlled characteristics of the GaN heterojunction diode conductive channel and reduces the forward conduction resistance and enhanced reverse cut-off capability. The invention has lower forward conduction resistance and power consumption, stronger reverse cut-off ability, and is compatible with AlGaN / GaN HEMT power switching device technology, which is beneficial to the application of the device.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Ultra high-speed Si/SiGe modulation-doped field effect transistors on ultra thin SOI/SGOI substrate
InactiveUS20050127392A1Improve RF performanceImprove noise figureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow noiseEngineering
A silicon and silicon germanium based semiconductor MODFET device design and method of manufacture. The MODFET design includes a high-mobility layer structure capable of ultra high-speed, low-noise for a variety of communication applications including RF, microwave, sub-millimeter-wave and millimeter-wave. The epitaxial field effect transistor layer structure includes critical (vertical and lateral) device scaling and layer structure design for a high mobility strained n-channel and p-channel transistor incorporating silicon and silicon germanium layers to form the optimum modulation-doped heterostructure on an ultra thin SOI or SGOI substrate capable of achieving greatly improved RF performance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
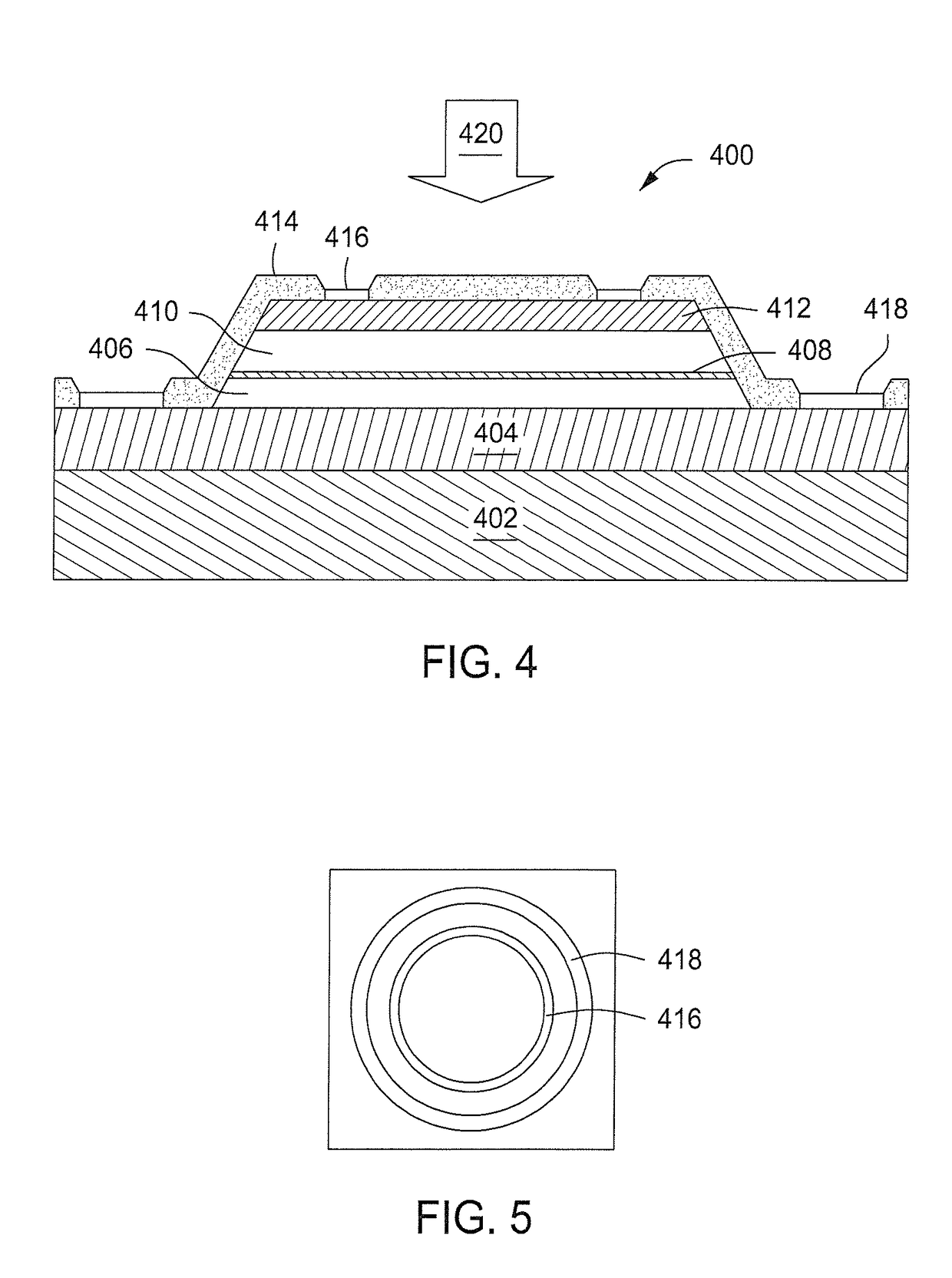
Low doped layer for nitride-based semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050179107A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialSchottky diode
A repeatable and uniform low doped layer is formed using modulation doping by forming alternating sub-layers of doped and undoped nitride semiconductor material atop another layer. A Schottky diode is formed of such a low doped nitride semiconductor layer disposed atop a much more highly doped nitride semiconductor layer. The resulting device has both a low on-resistance when the device is forward biased and a high breakdown voltage when the device is reverse biased.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
III-group nitride light-emitting diode (LED) and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102185062AIncreased longitudinal resistivityImprove crystal qualitySemiconductor devicesNitrideLight-emitting diode
The invention discloses a III-group nitride light-emitting diode (LED) and a manufacturing method thereof. The LED comprises a substrate and a semiconductor epitaxial laminate which is laminated on the substrate, wherein the semiconductor epitaxial laminate sequentially comprises an N type layer, a luminescent layer and a P type layer from top to bottom. The LED is characterized in that: an N type layer table face is formed in the N type layer by etching a part of the semiconductor epitaxial laminate; an N type electrode is arranged on the N type layer table face; a P type electrode is arranged on the upper surface of the un-etched part of the P type layer; the N type layer also comprises a uniformly doped layer of which the doping concentration is consistent and a modulation doped layer of which the doping concentration is changeable; and the modulation doped layer is arranged between the uniformly doped layer and the luminescent layer. A doped mode of the modulation doped layer is gradual transition doping which connects uniformly doped layer and the luminescent layer of which the doping concentration is consistent. The concentration change trend is decrease progressively change from the uniformly doped layer to the luminescent layer. By the LED and the manufacturing method, the crystal quality and the luminance uniformity can be obviously improved, and the lighting effect is improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Preparation of strained germanium thin film
InactiveCN101246819AImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystalField-effect transistor
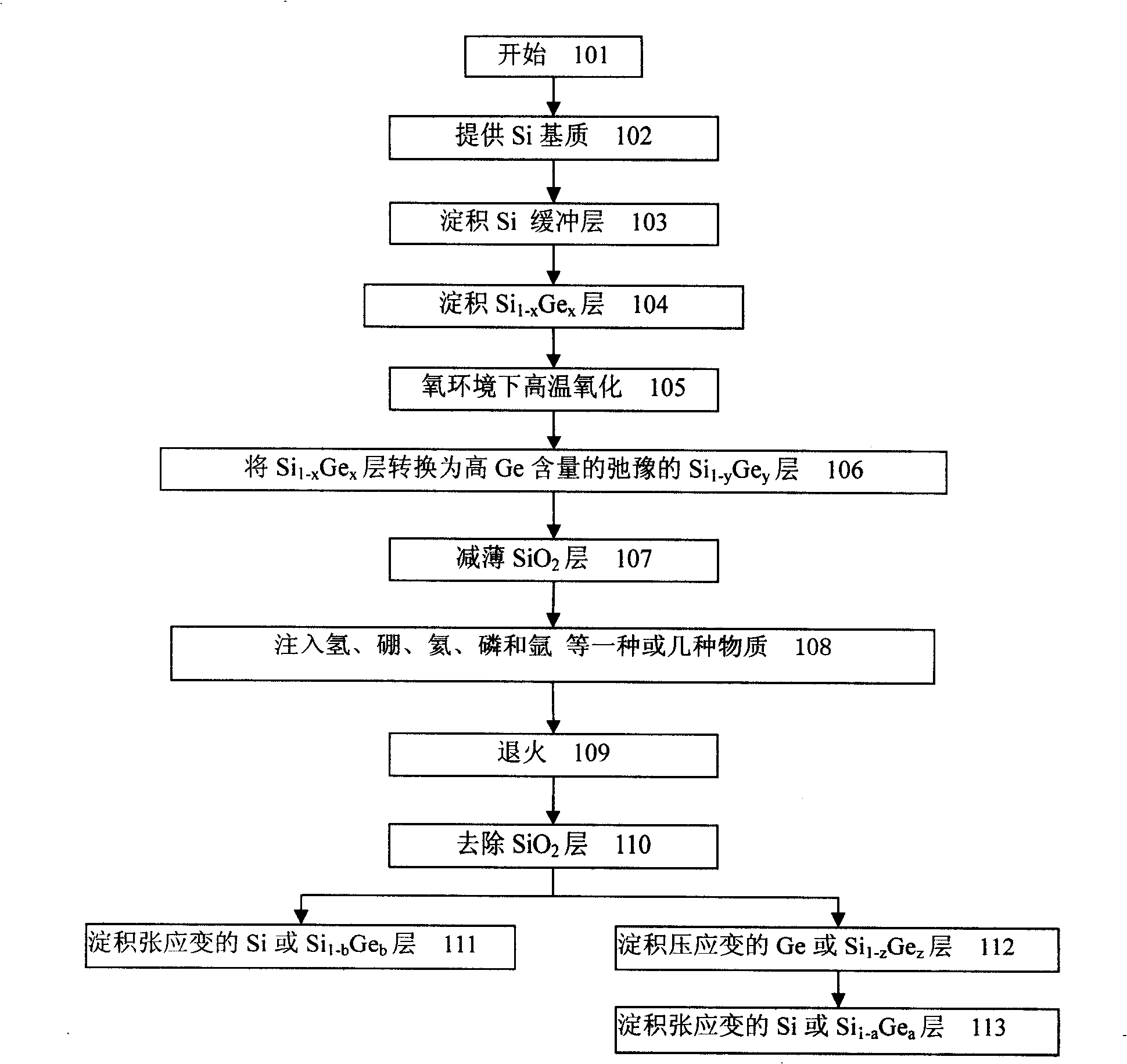
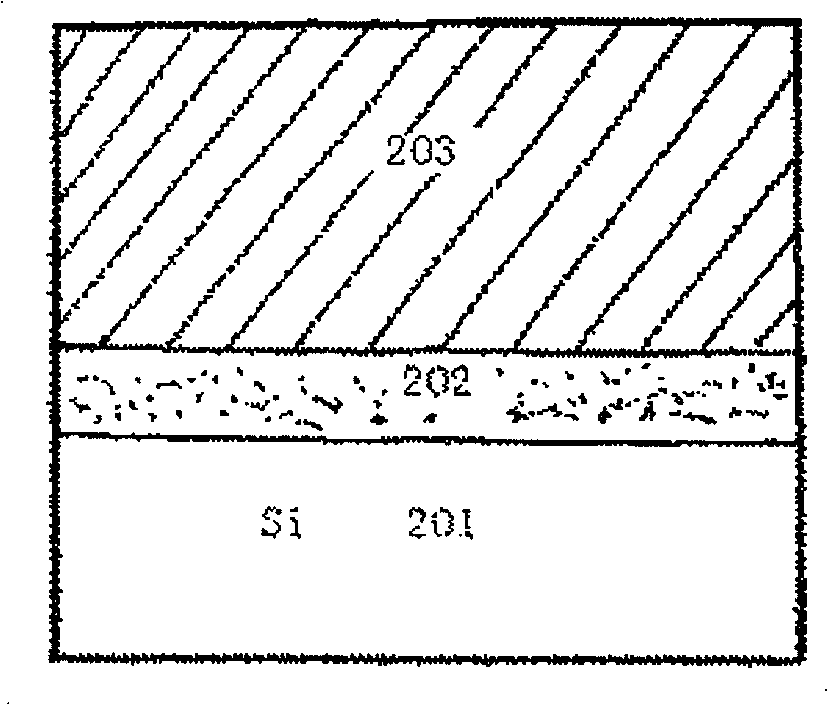
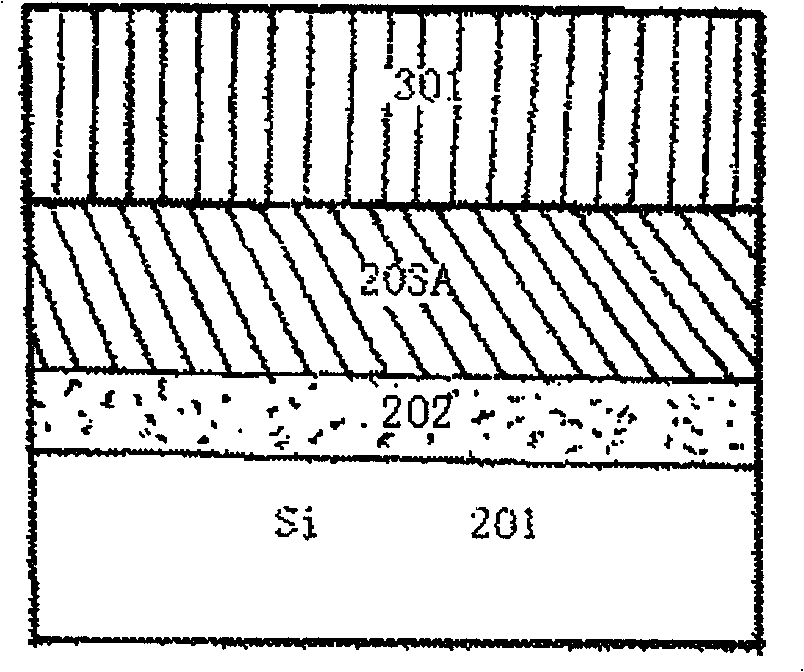
The invention discloses a preparing method for strained germanium, belonging to the field of semiconductor substrate preparation. Single crystal silicon buffer layer is deposited on a silicon substrate; the single crystal silicon buffer layer is covered with a strained single crystal silicon germanium Si1-Gex layer having a thickness less than the critical thickness, then oxidized, and converted into a relax high-germanium component Si1-yGey layer; the high-germanium component Si1-yGey layer is completely relaxed by ion injection and annealing, and covered with compression-strained germanium layer or compression-strained high-germanium component Si1-zGez layer, or the compression-strained germanium layer or compression-strained high-germanium component Si1-zGez layer is covered with tension-strained silicon layer or tension-strained Si1-aGea layer. The method can be used for manufacturing complementary metal oxide semiconductor, modulation-doped field effect transistor, high electron mobility transistor, bipolar transistor and other high-speed devices, and greatly improves the performance of the devices.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
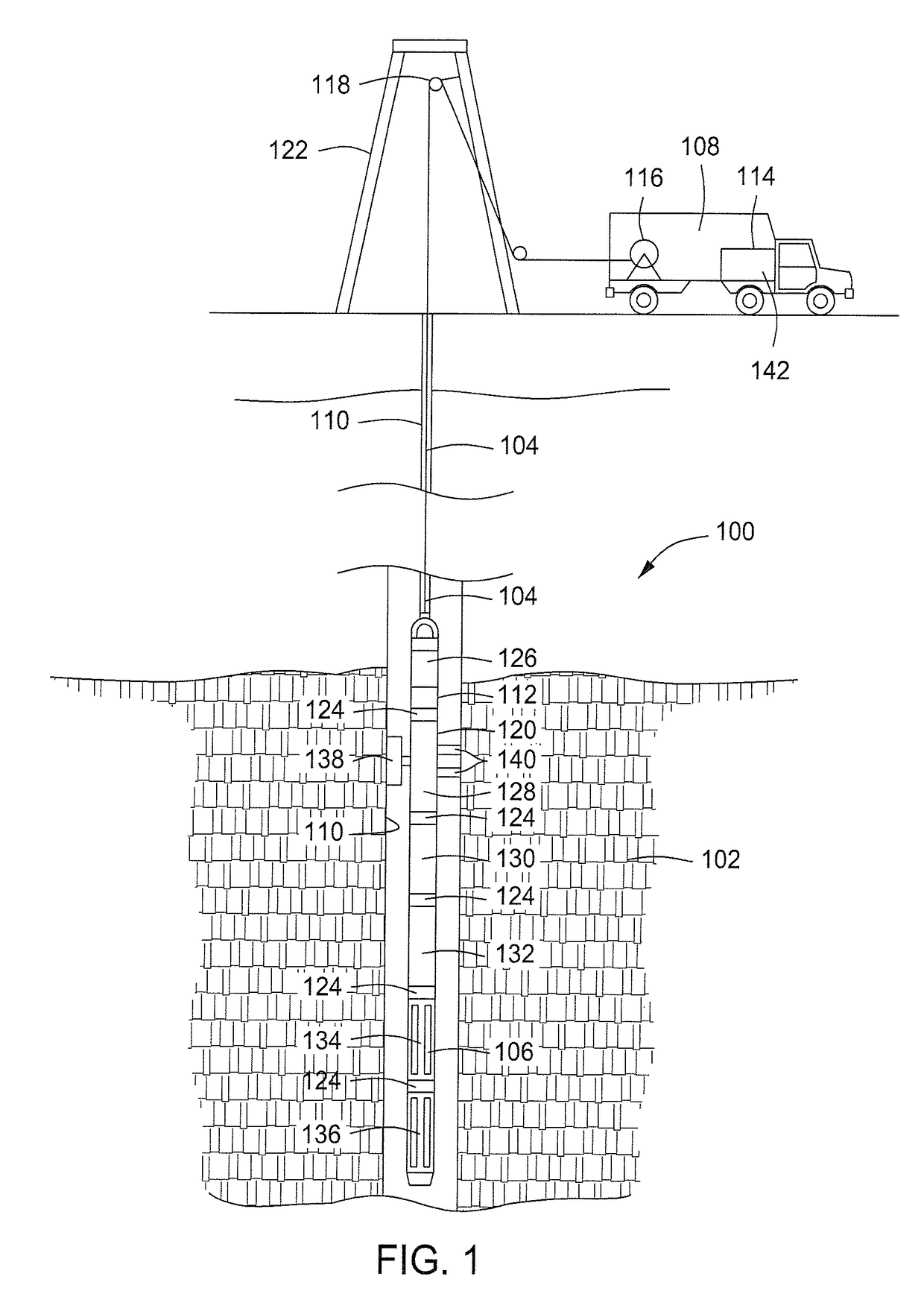
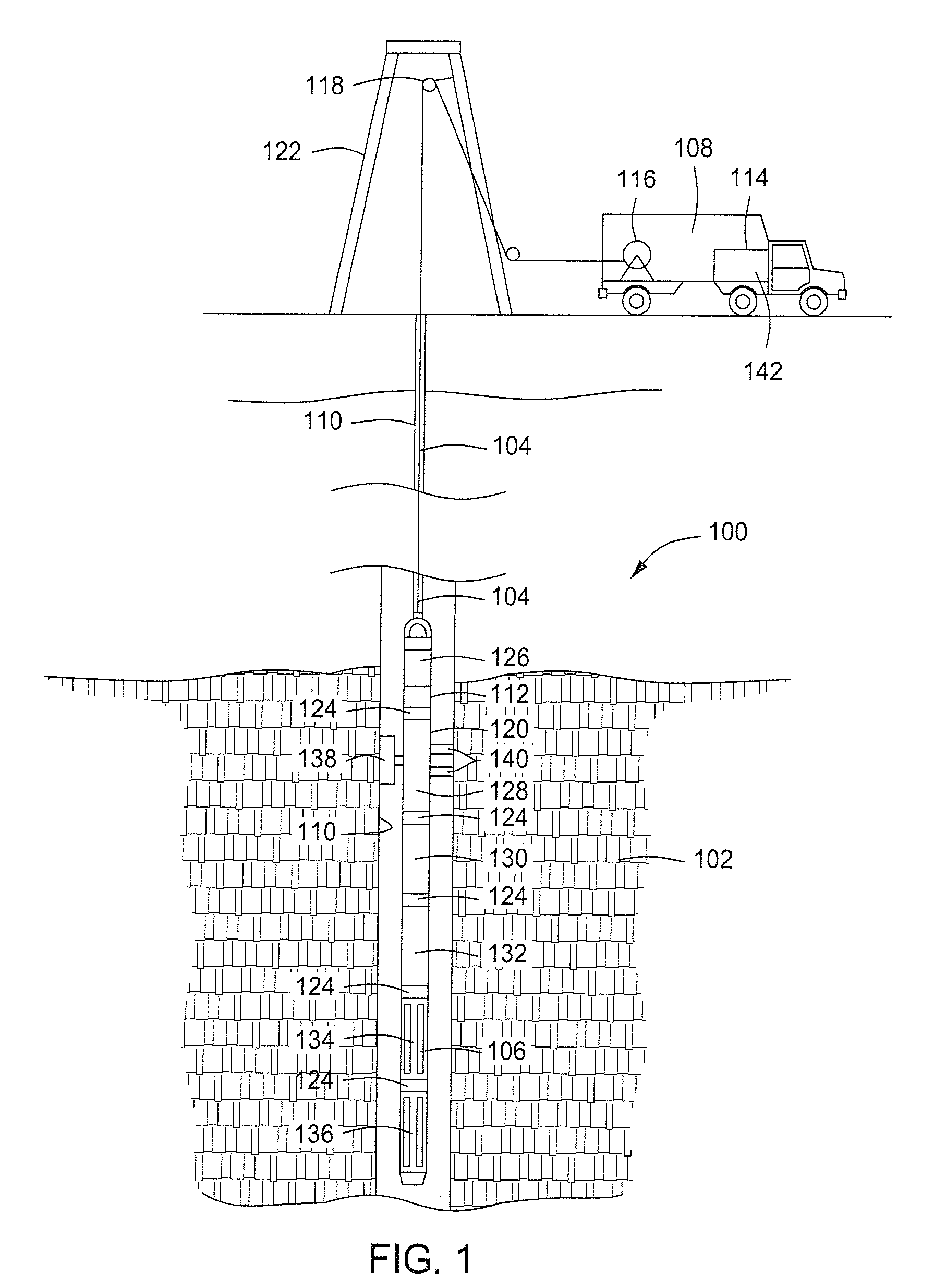
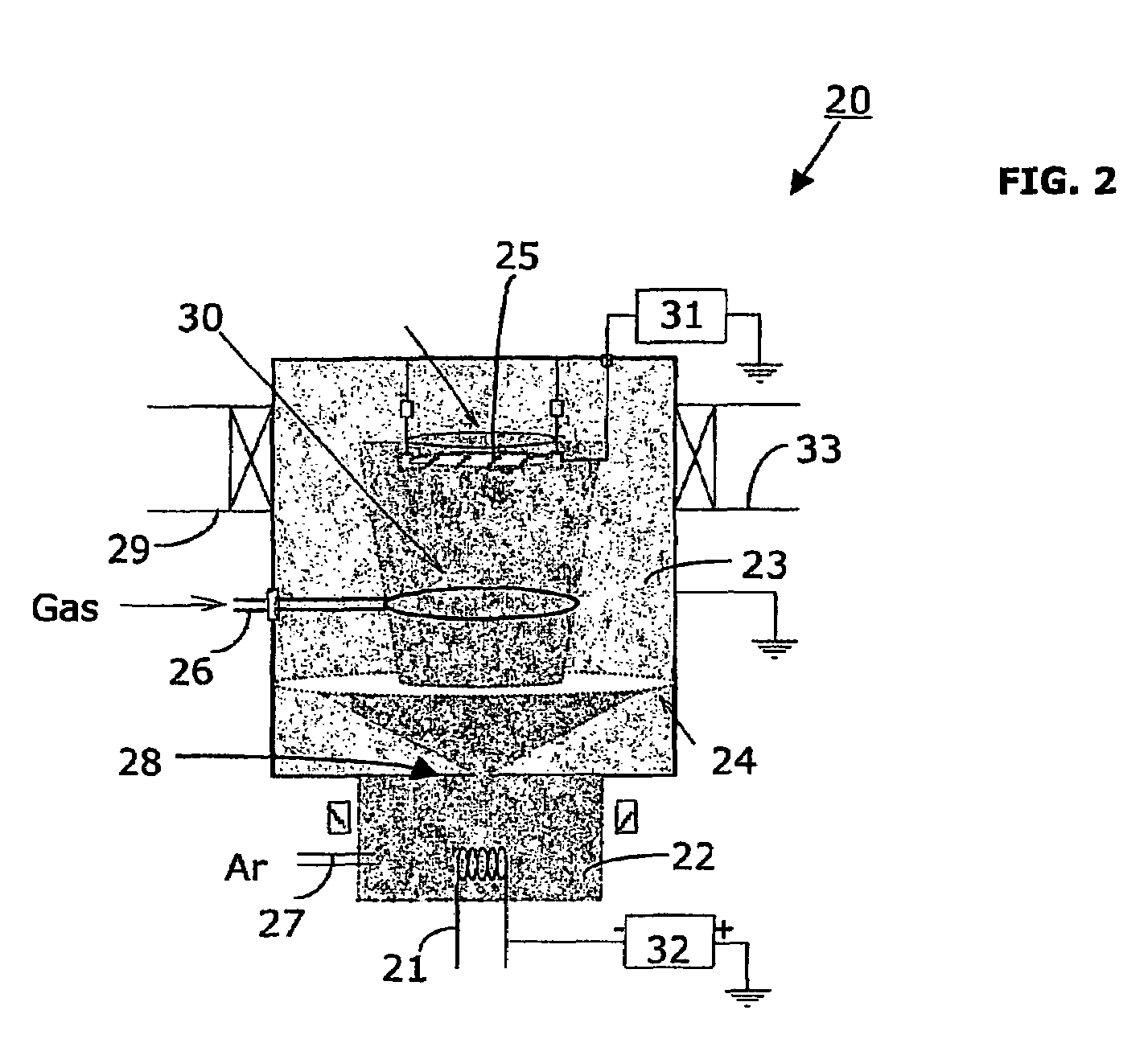
Method and apparatus for downhole spectroscopy
Apparatus and method for estimating a property of a downhole fluid including a carrier that is conveyed in a borehole, and a semiconductor electromagnetic energy source carried by the carrier, the semiconductor electromagnetic energy source having an active region that includes one or more nitride-based barrier layers that are modulation-doped using a nitride-based doped layer.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
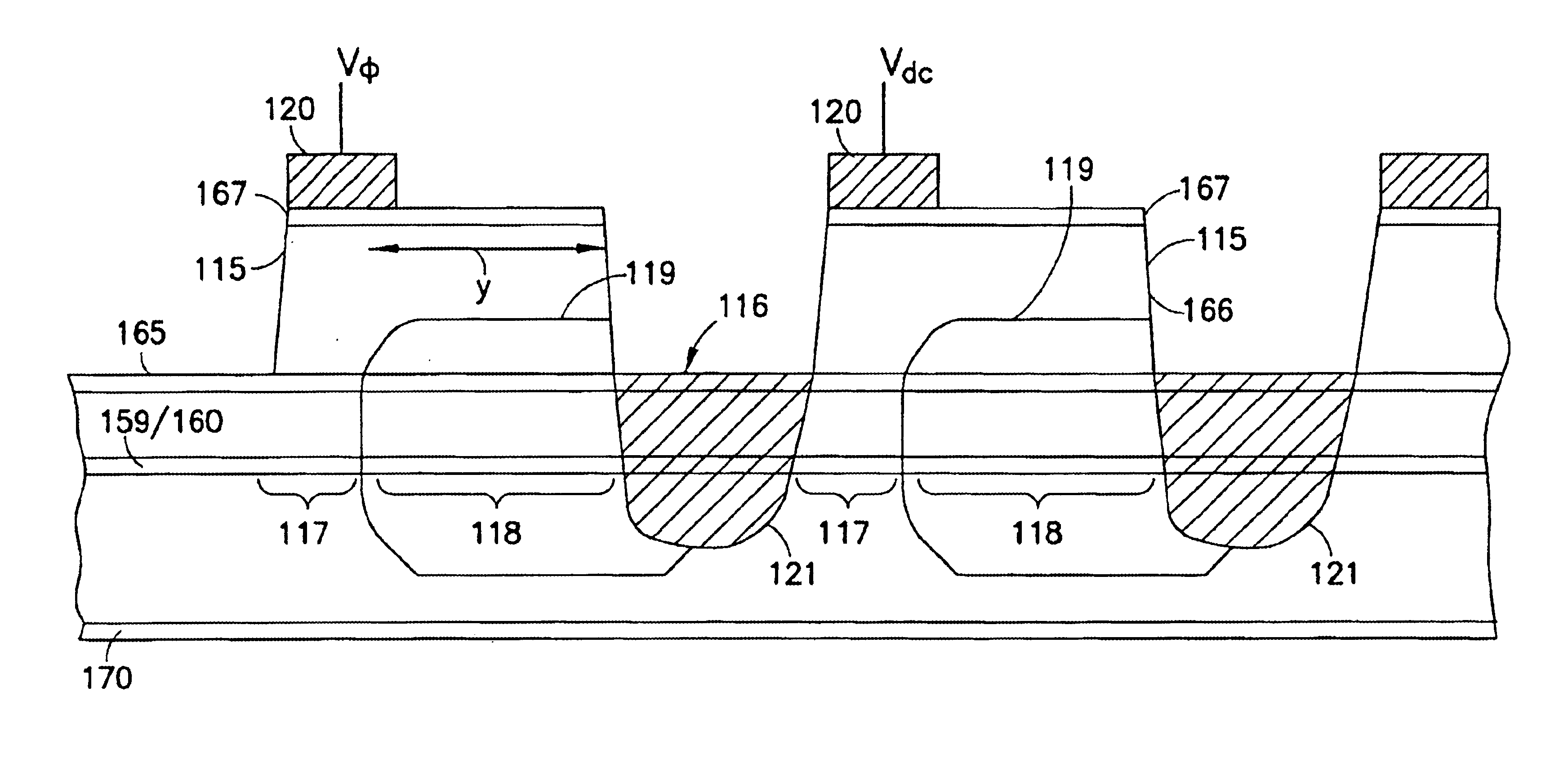
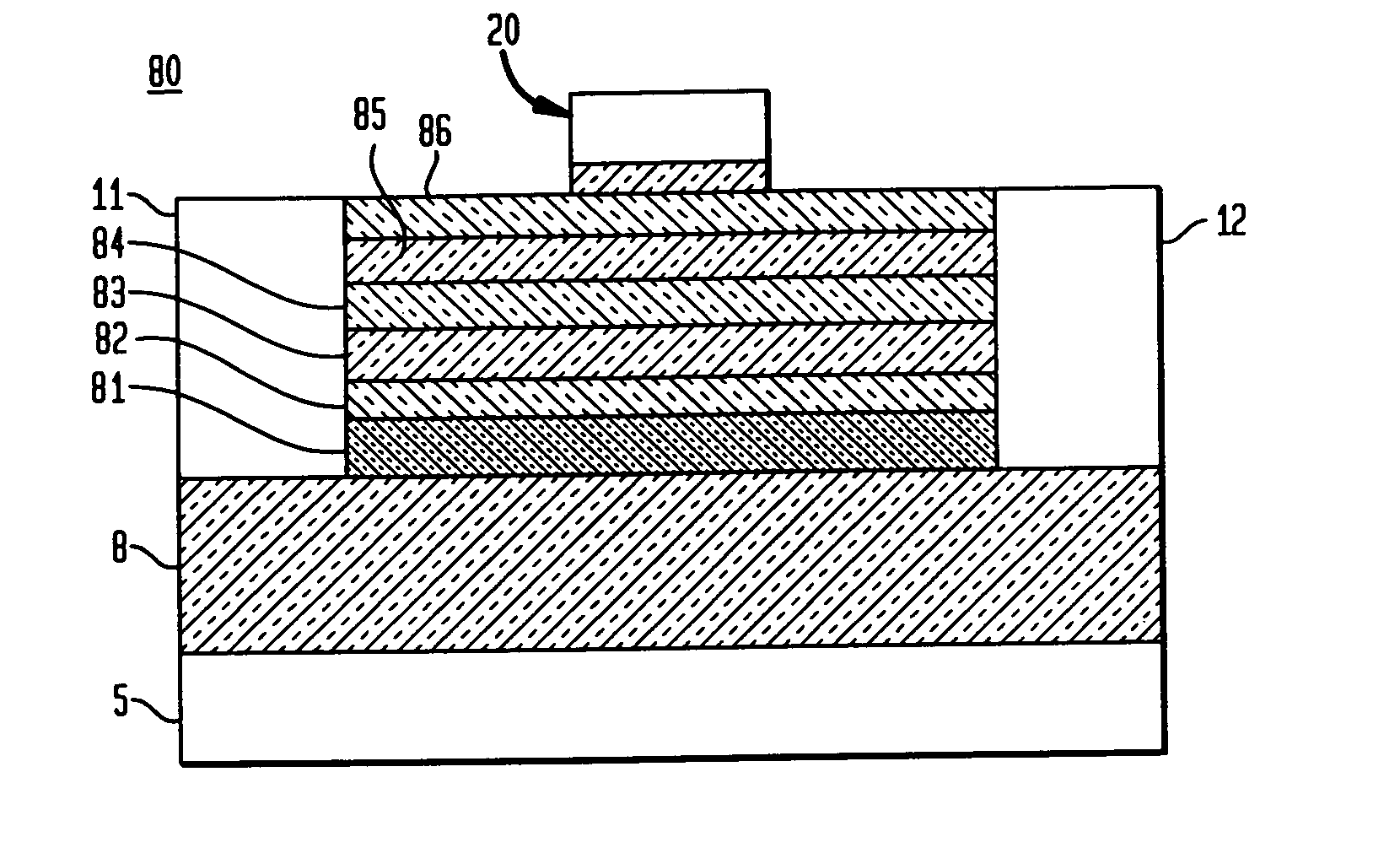
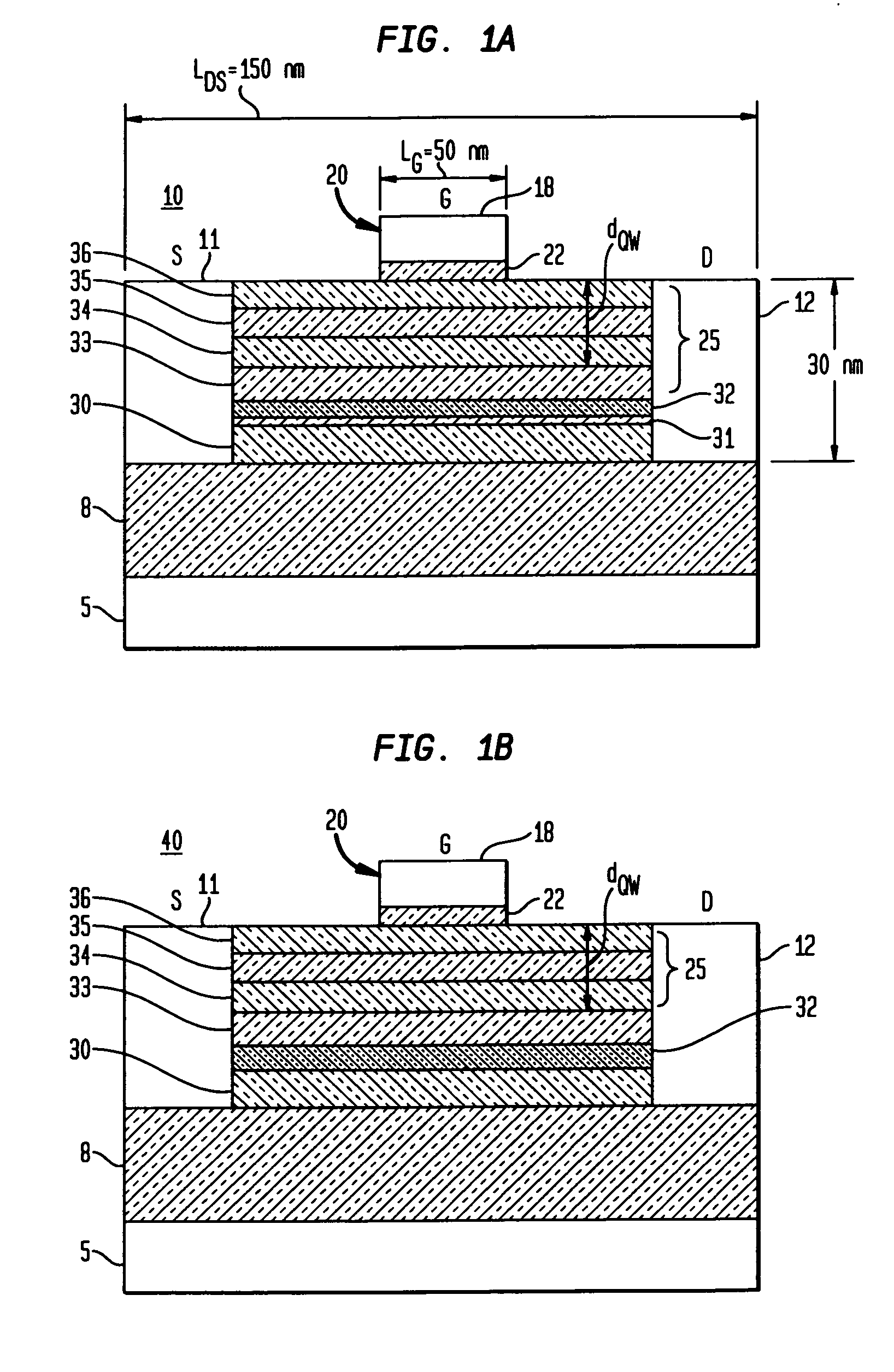
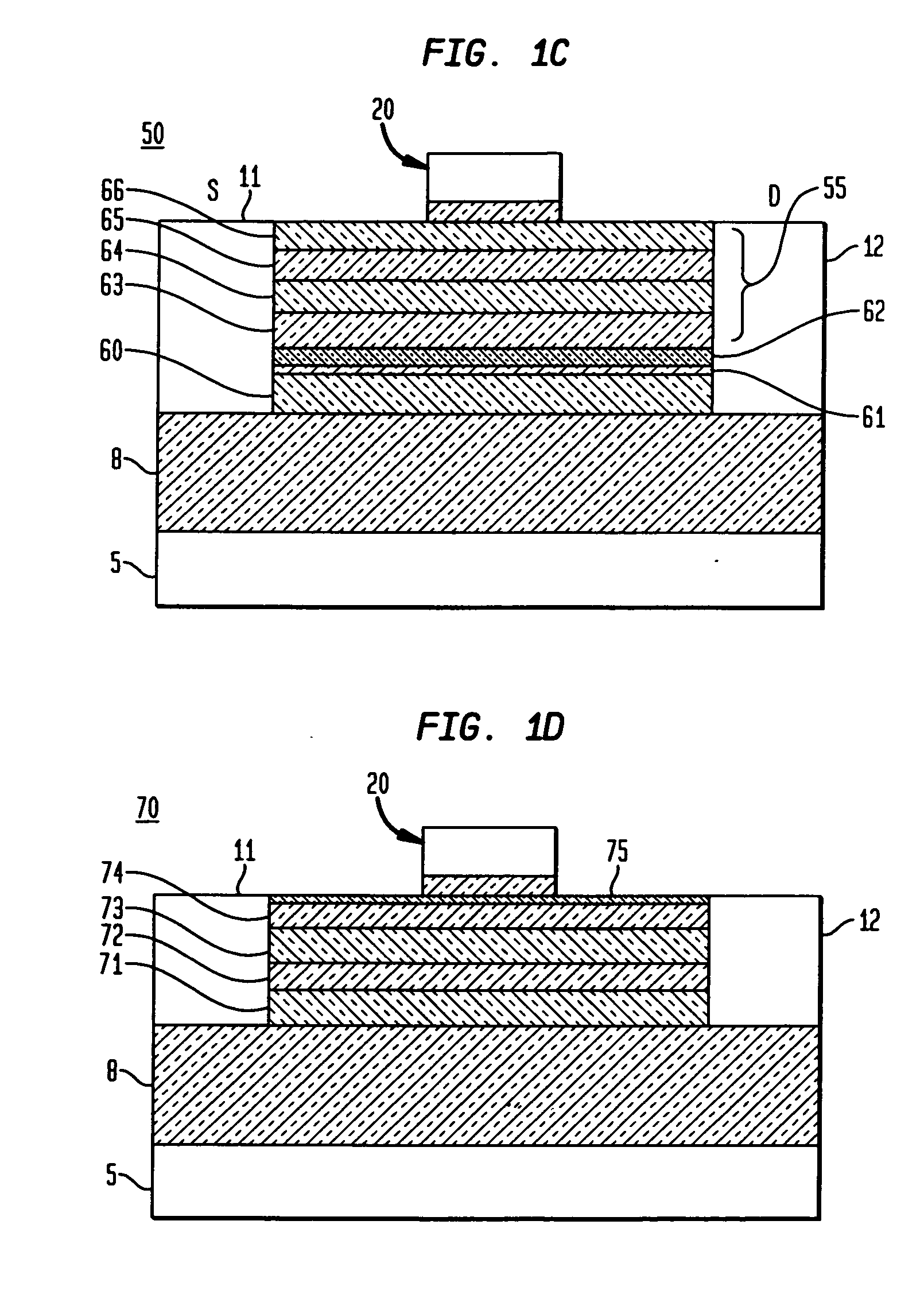
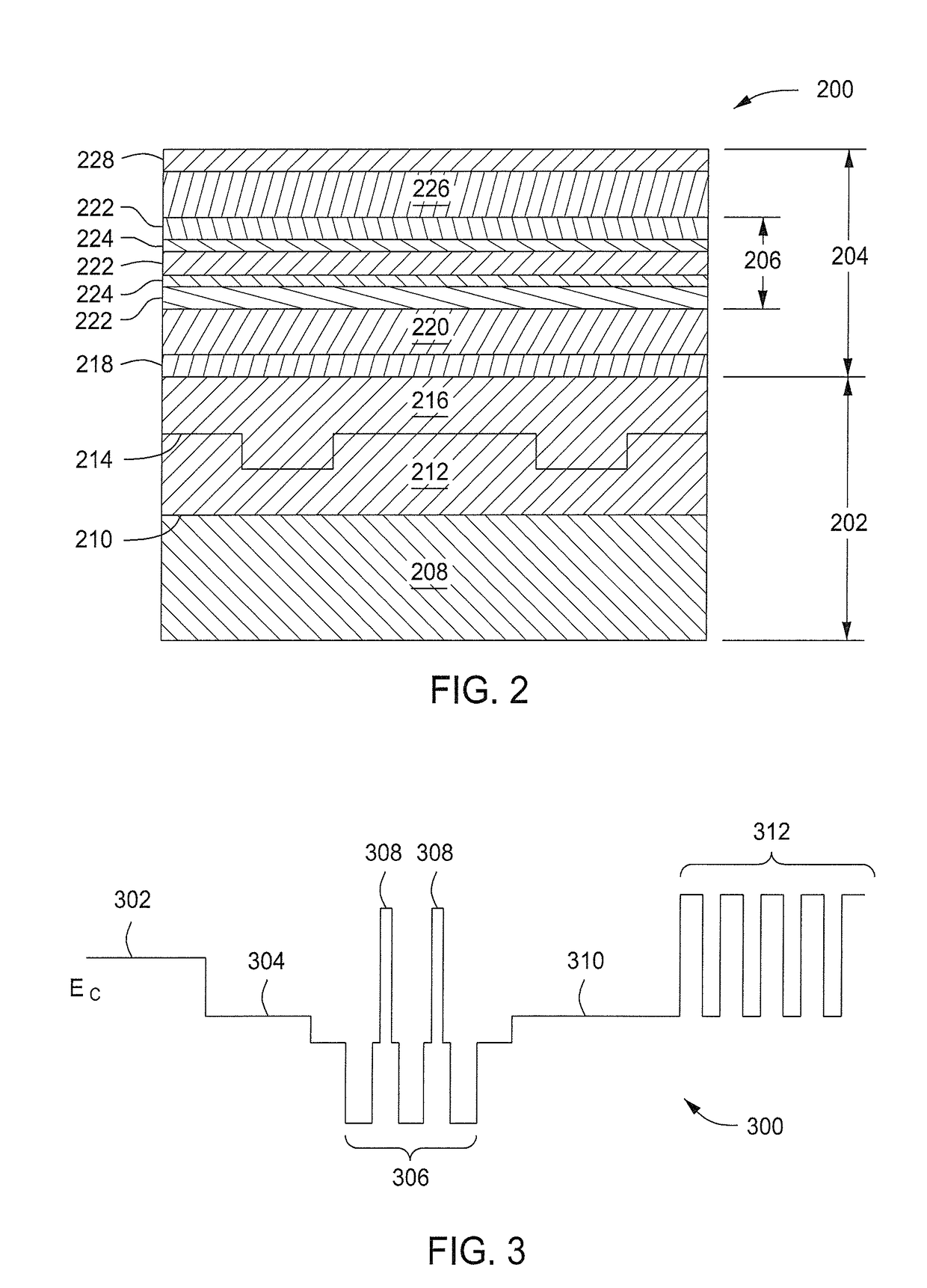
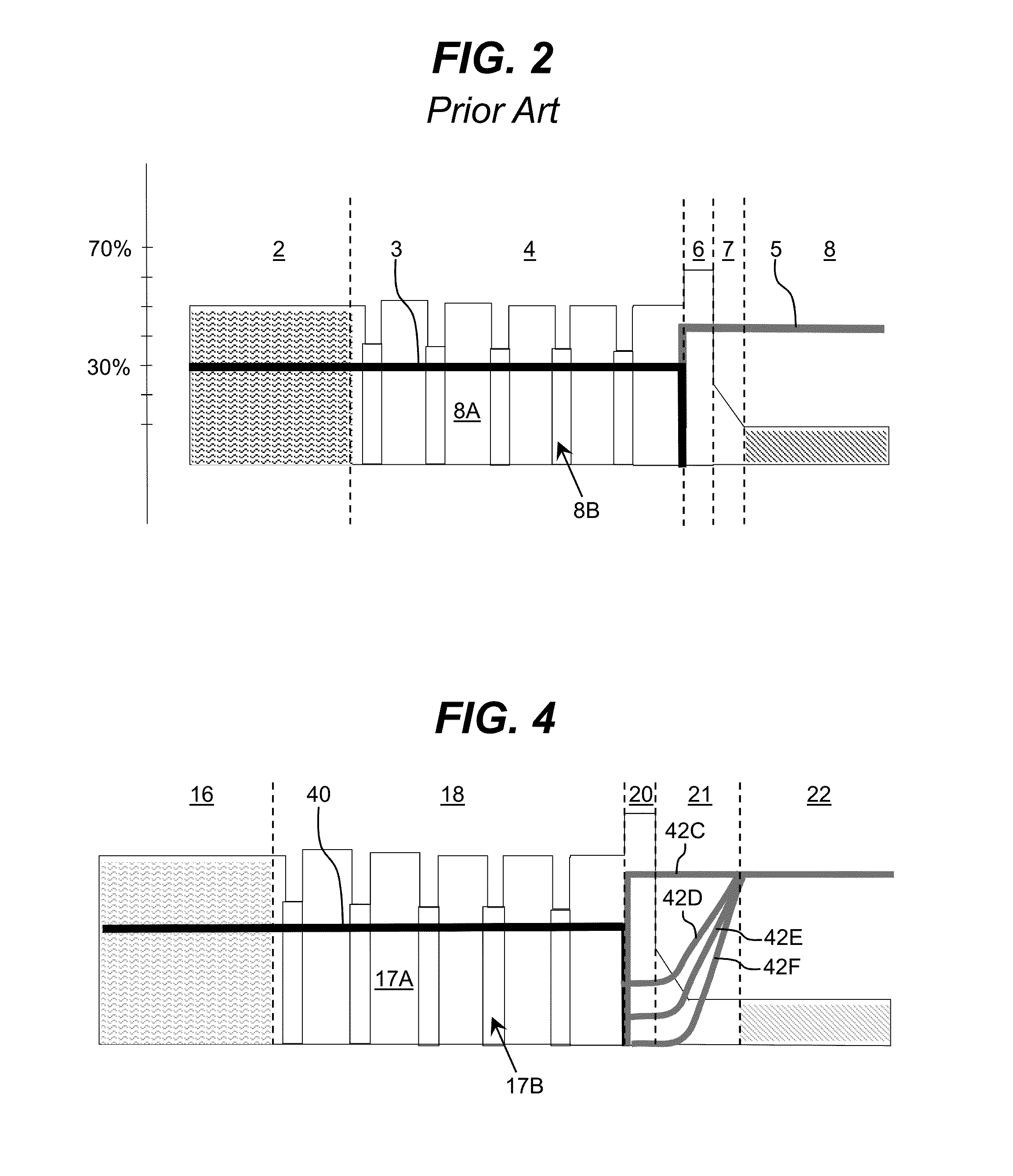
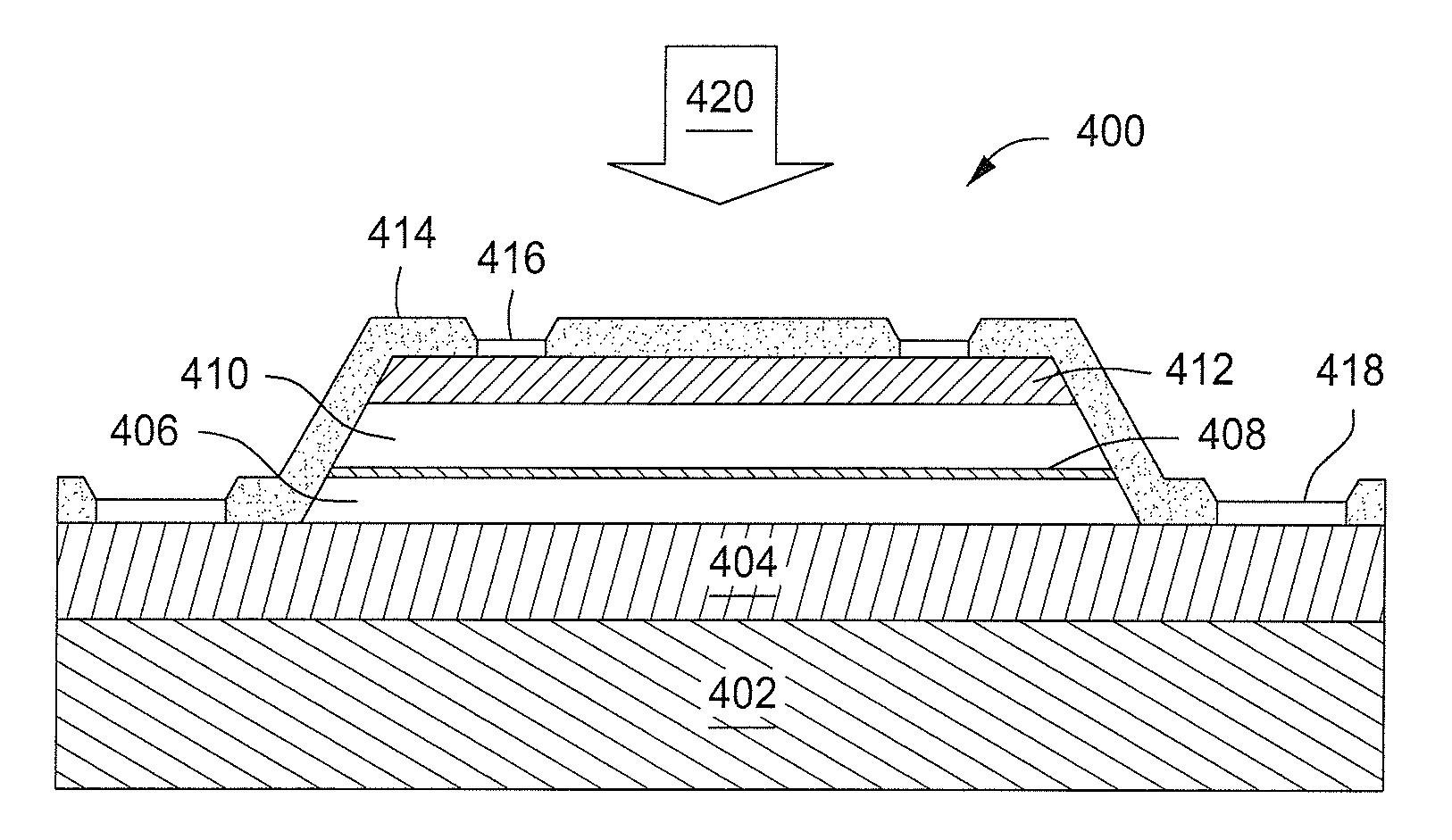
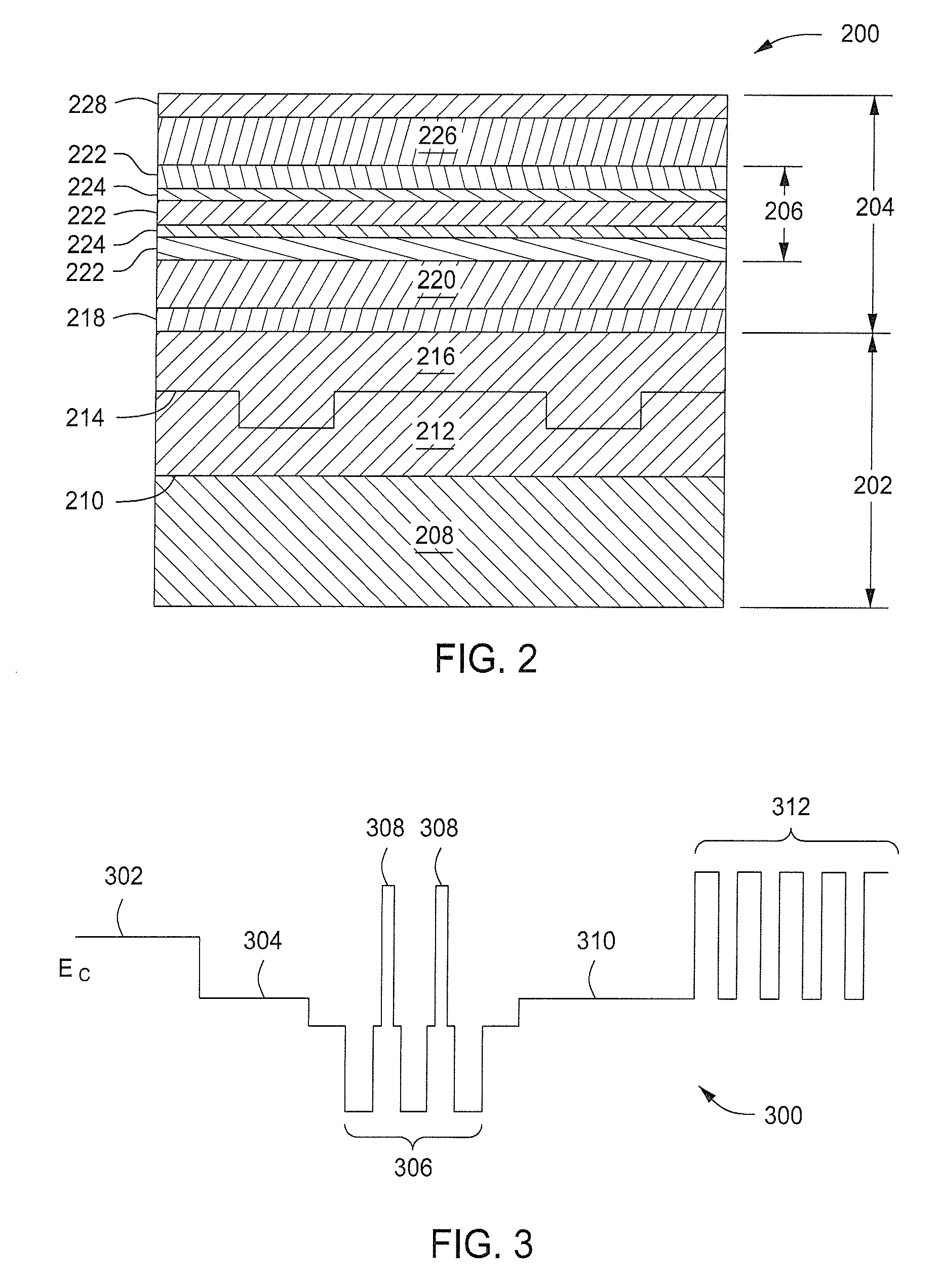
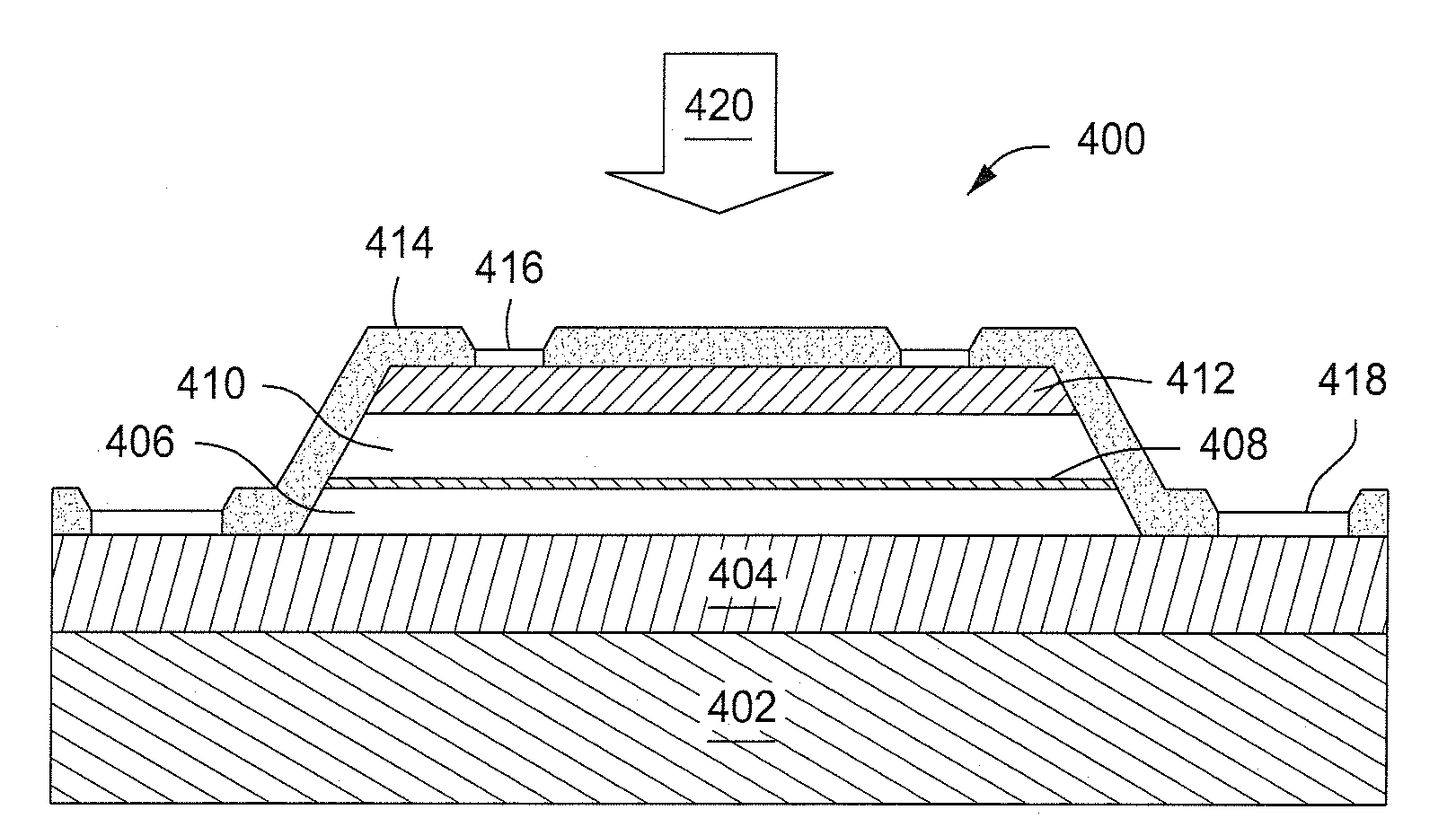
Enhanced T-gate structure for modulation doped field effect transistors
InactiveUS6972440B2Improve scalabilityIncrease productionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesField-effect transistorCondensed matter physics
A structure and a method are disclosed of an enhanced T-gate for modulation doped field effect transistors (MODFETs). The enhanced T-gate has insulator spacer layers sandwiching the neck portion of the T-gate. The spacer layers are thinner than the T-bar portion overhang. The insulating layer provides mechanical support and protects the vulnerable neck portion of the T-gate from chemical attack during subsequent device processing, making the T-gate structure highly scalable and improving yield. The use of thin conformal low dielectric constant insulating layers ensures a low parasitic gate capacitance, and reduces the risk of shorting gate and source metallurgy when source-to-gate spacings are reduced to smaller dimensions.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Optoelectronic Device with Modulation Doping
ActiveUS20160118531A1Reduce formationImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantContact layer
An improved heterostructure for an optoelectronic device is provided. The heterostructure includes an active region, an electron blocking layer, and a p-type contact layer. The p-type contact layer and electron blocking layer can be doped with a p-type dopant. The dopant concentration for the electron blocking layer can be at most ten percent the dopant concentration of the p-type contact layer. A method of designing such a heterostructure is also described.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
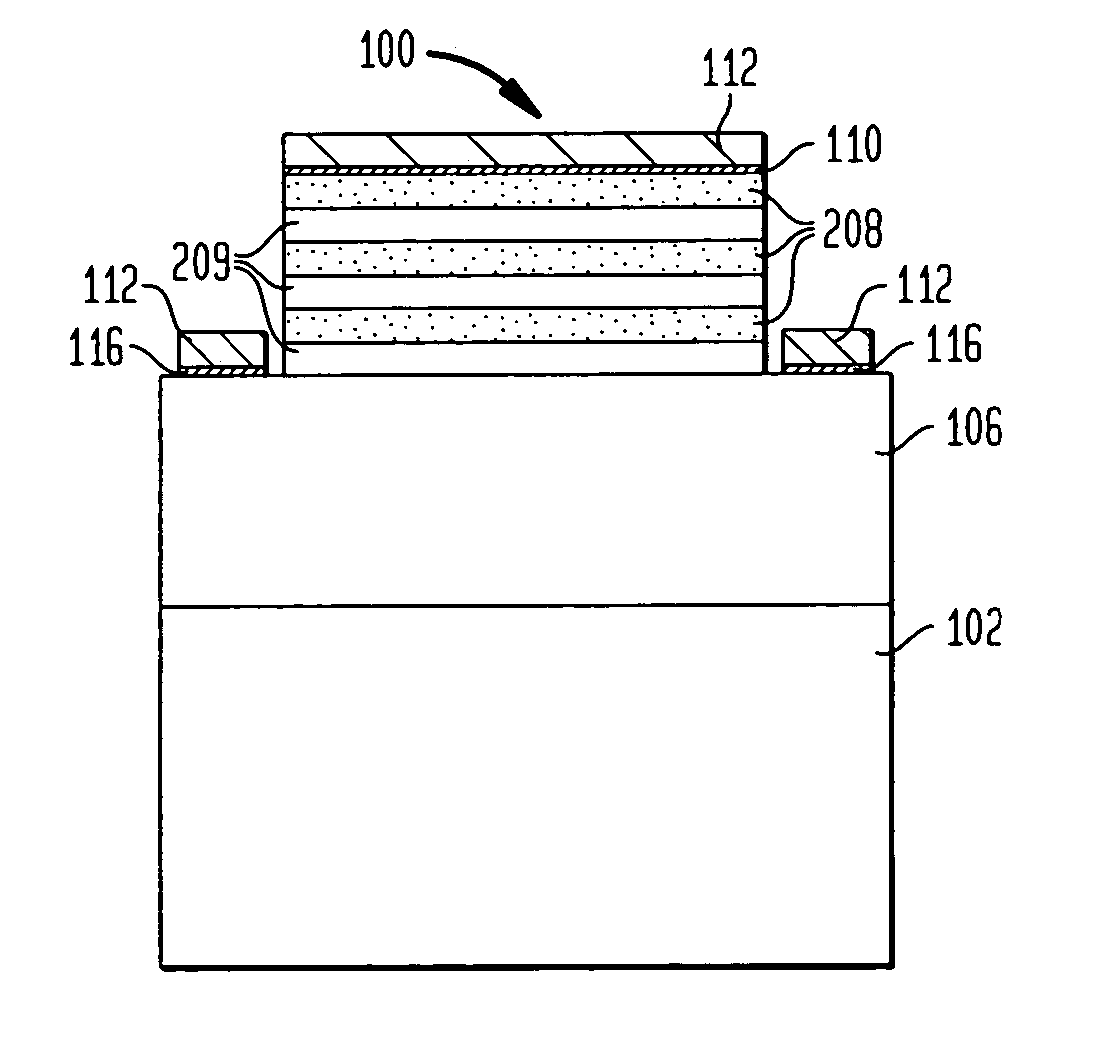
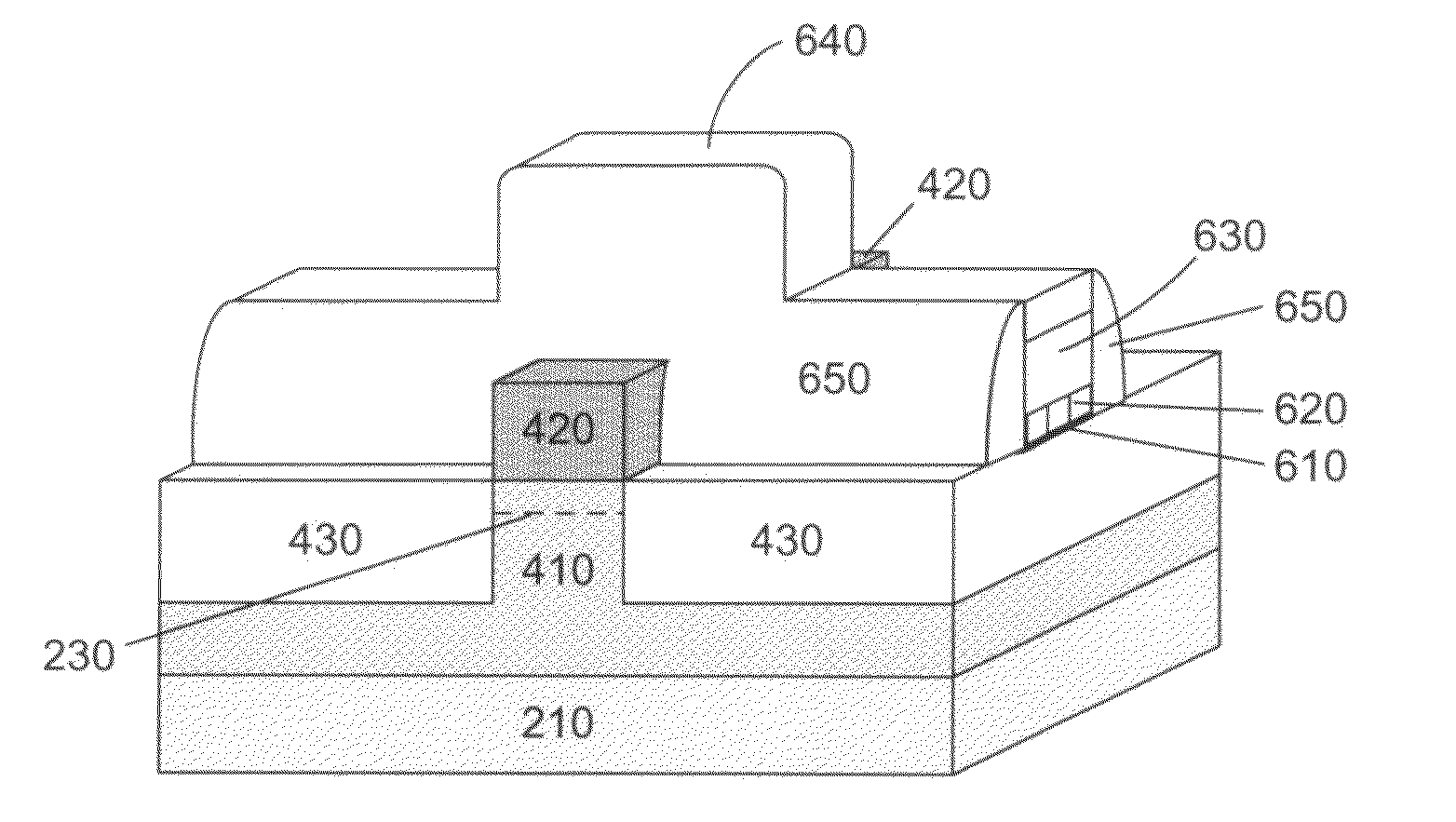
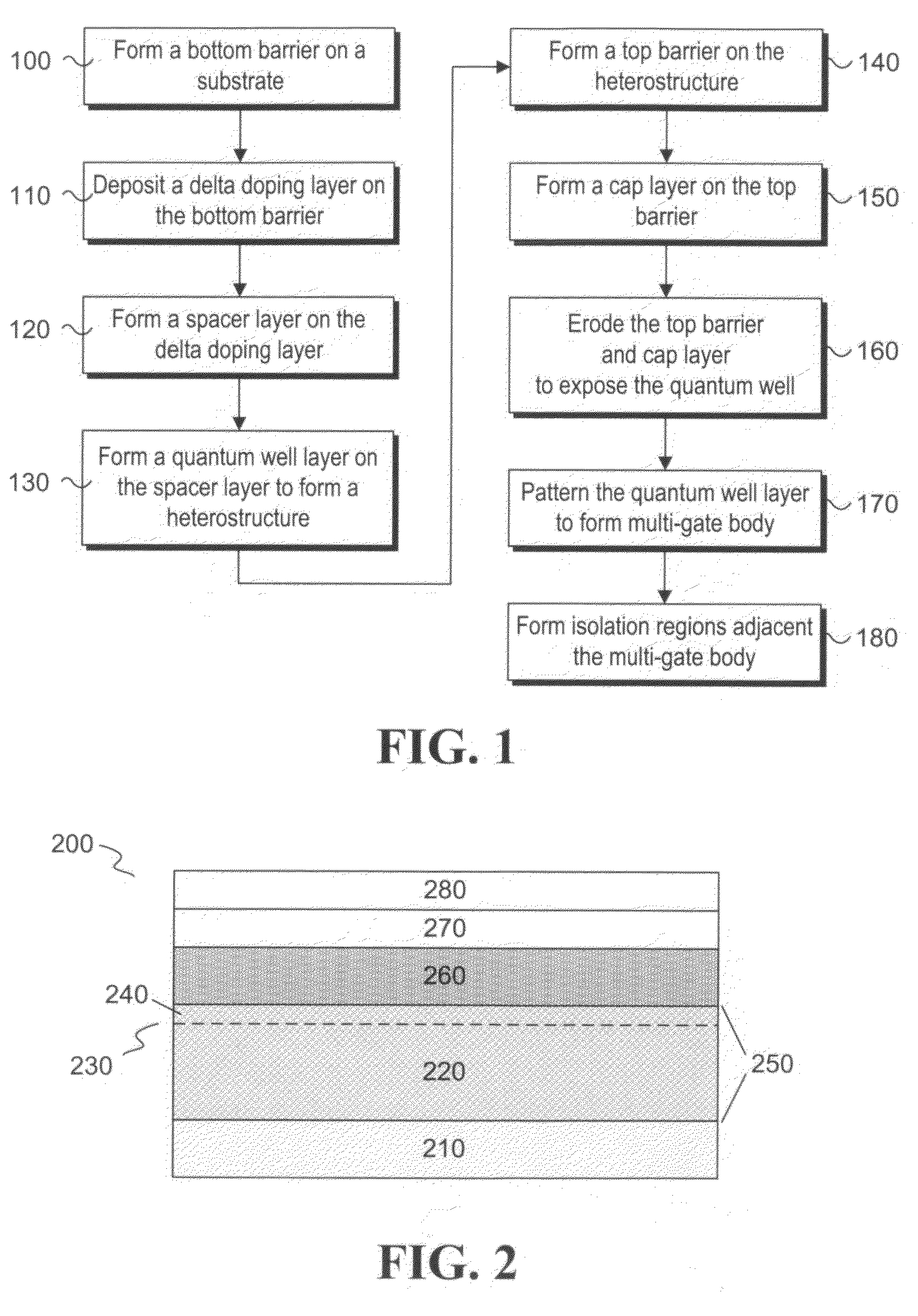
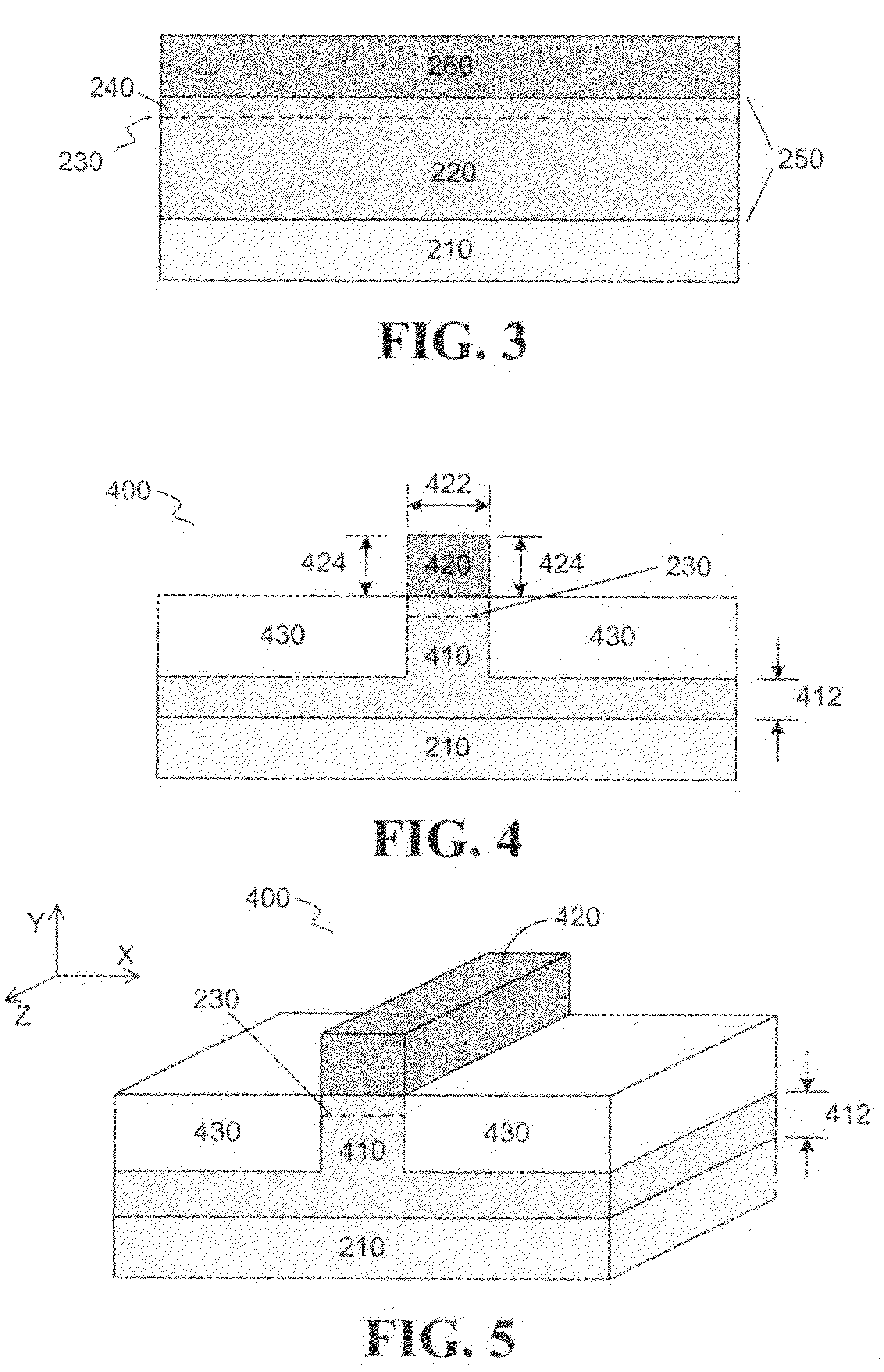
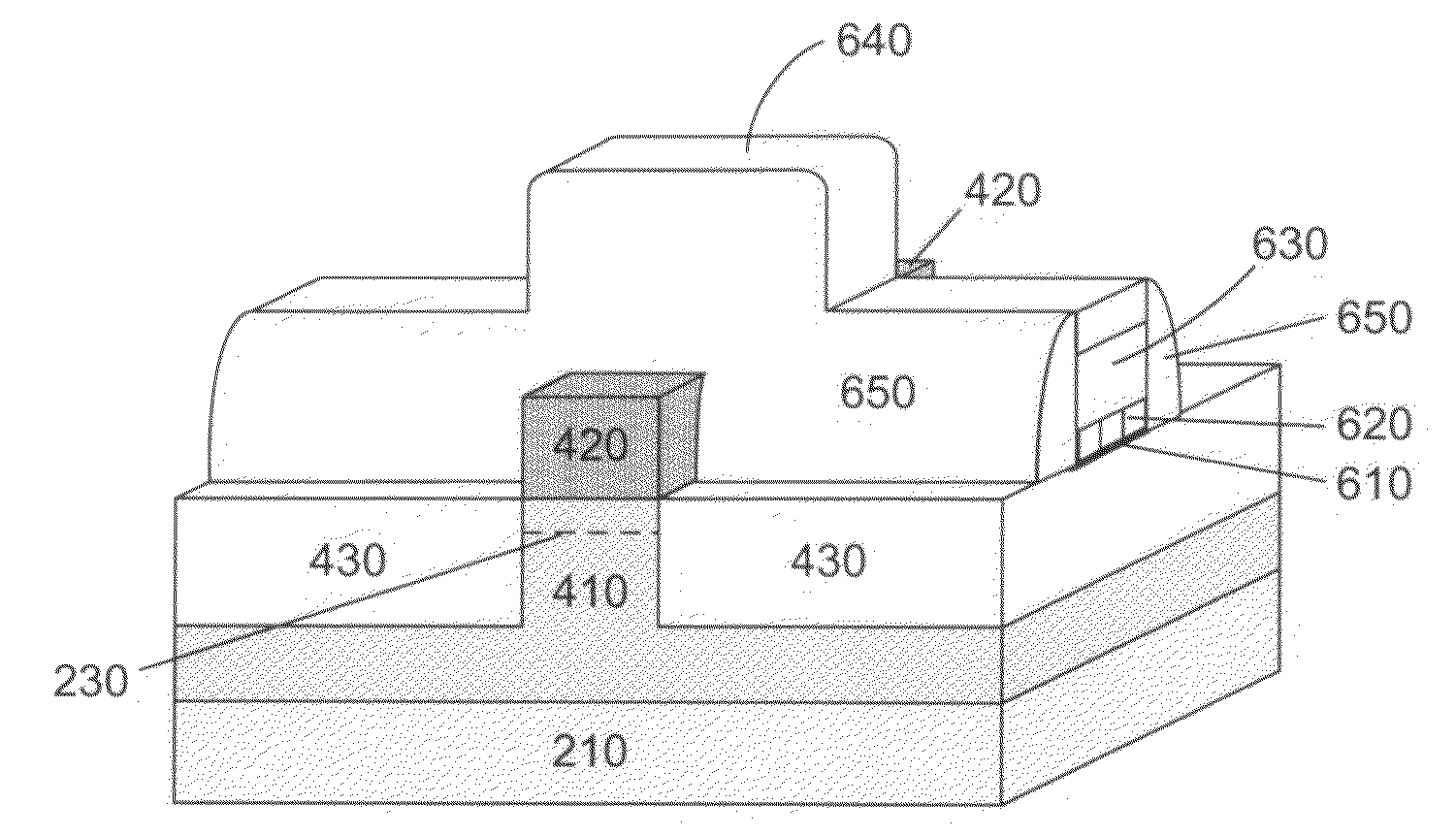
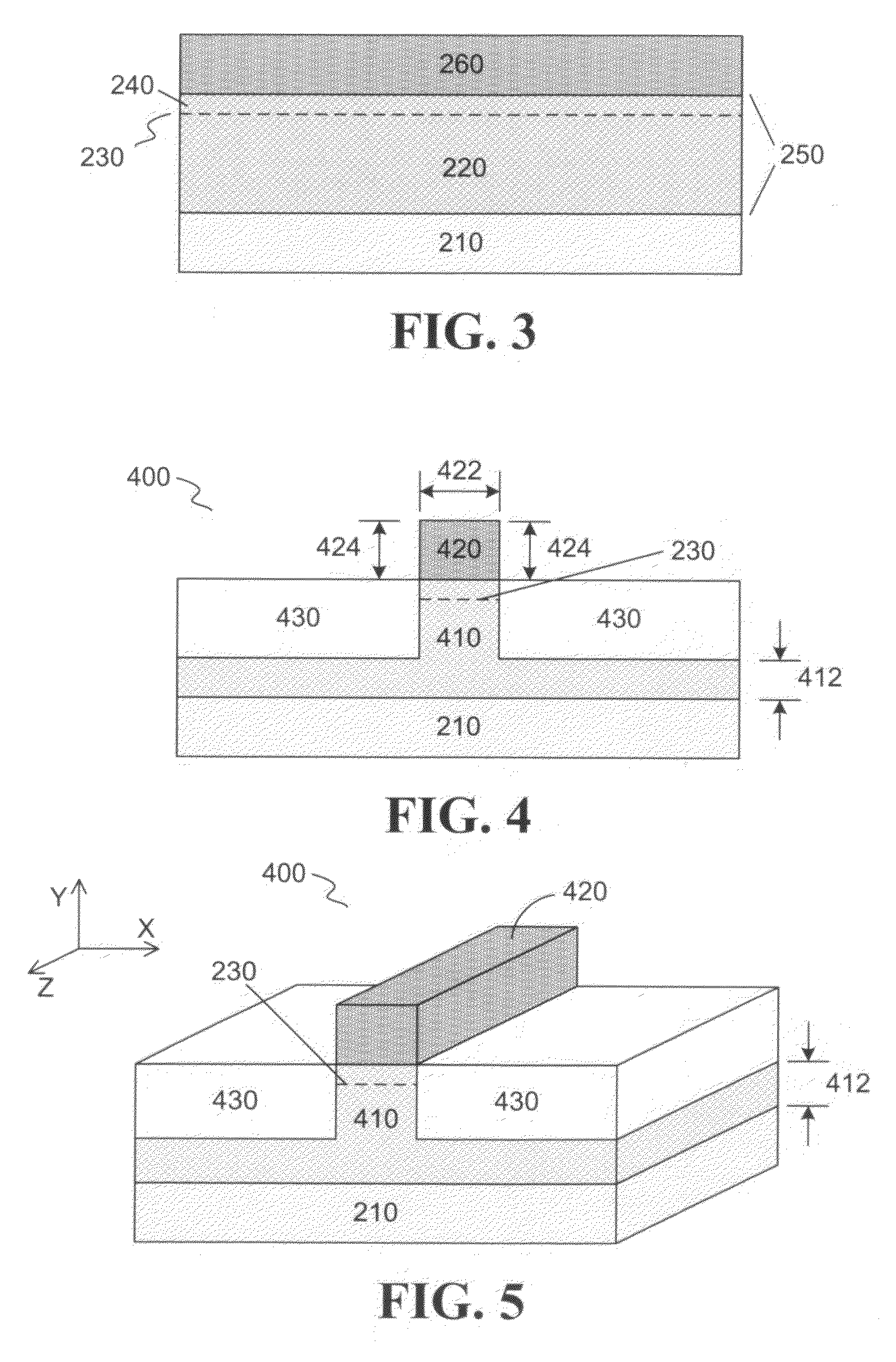
Apparatus and methods for forming a modulation doped non-planar transistor
InactiveUS7915642B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringMaterials science
Embodiments of an apparatus and methods for providing three-dimensional complementary metal oxide semiconductor devices comprising modulation doped transistors are generally described herein. Other embodiments may be described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Apparatus and methods for forming a modulation doped non-planar transistor
InactiveUS20100163927A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCondensed matter physicsSemiconductor
Embodiments of an apparatus and methods for providing three-dimensional complementary metal oxide semiconductor devices comprising modulation doped transistors are generally described herein. Other embodiments may be described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for MOCVD growth nitride light-emitting diode structure extension sheet
InactiveCN1881625AHigh electron mobilityHigh saturation speedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLight-emitting diodeNitride
The invention relates to a method for using MOCVD to grow nitride light emitting diode extensive plate, wherein said growing P-AlGaN carrier baffle layer uses modulated doping growing. The invention can reduce the positive operation voltage of nitride light emitting diode that extending growing, to improve the turn-on voltage and strengthen the breakdown reverse voltage.
Owner:EPILIGHT TECH
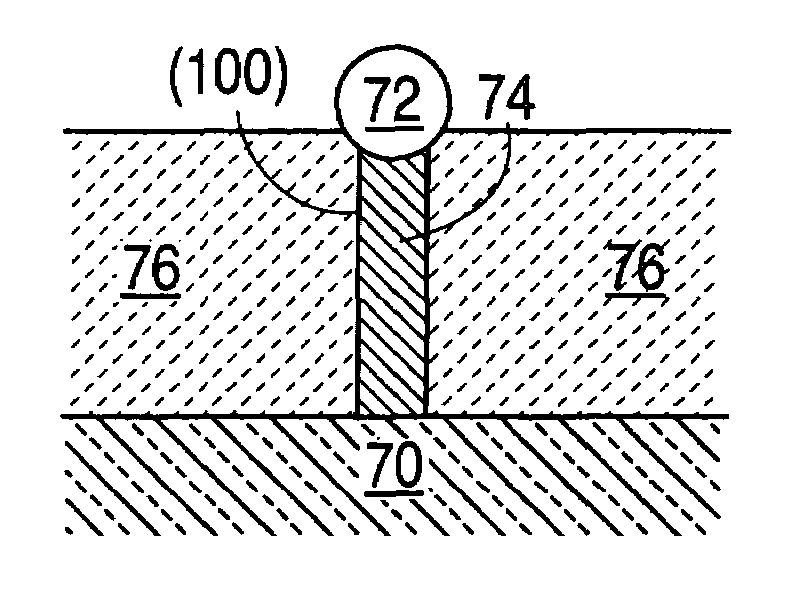
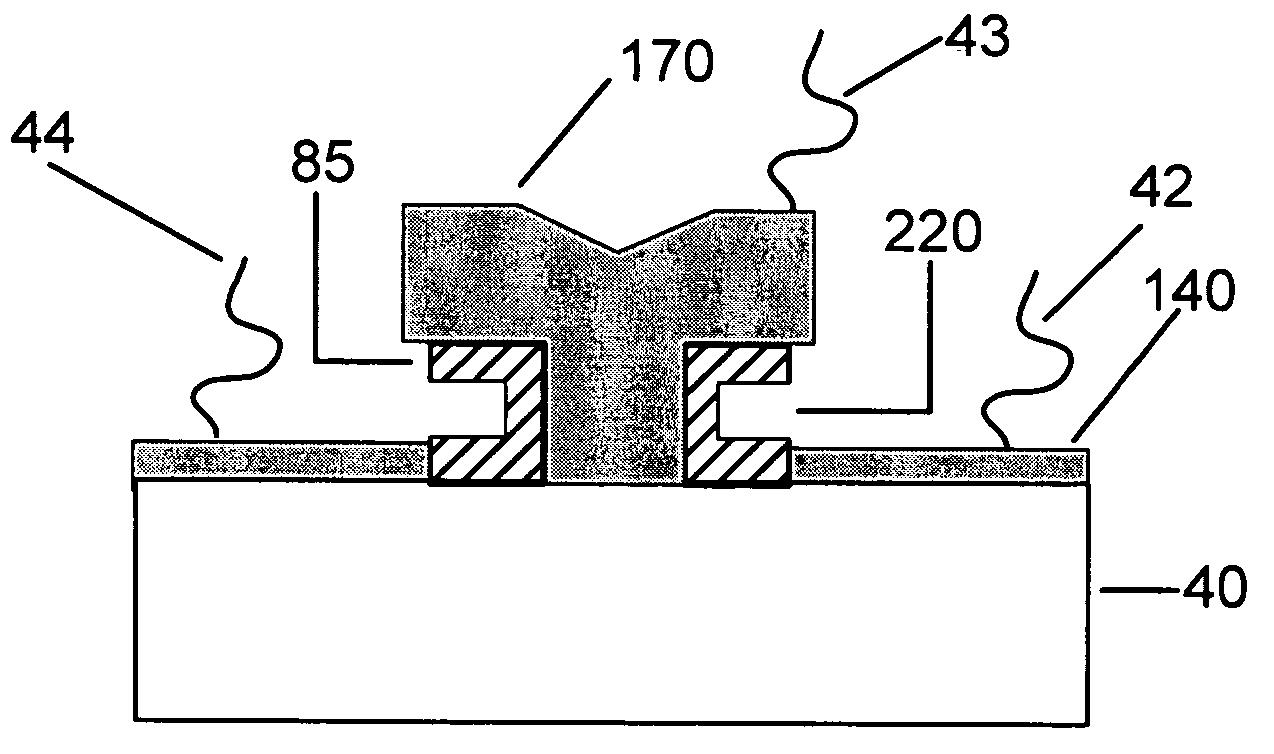
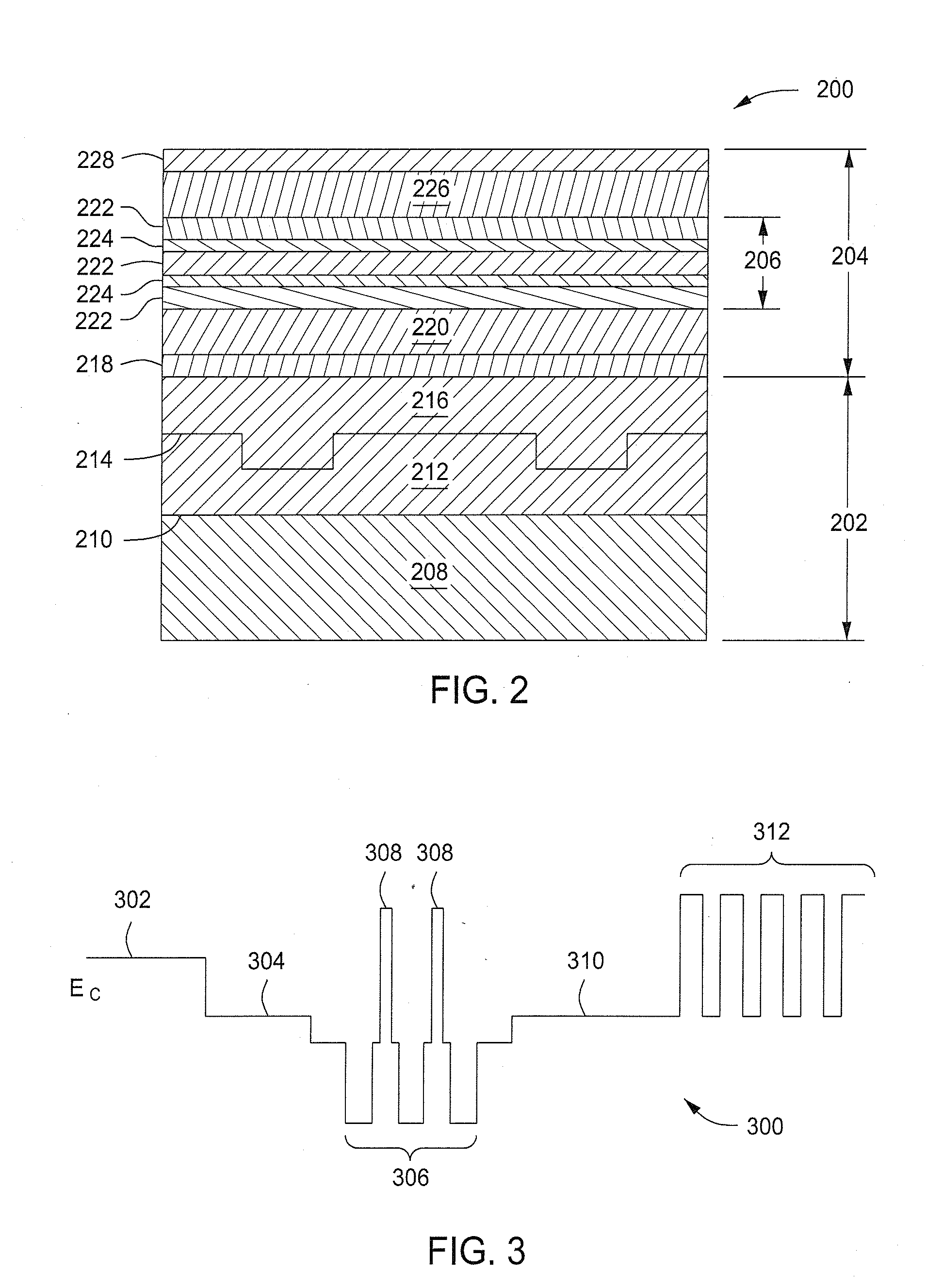
Negative resistance field-effect element
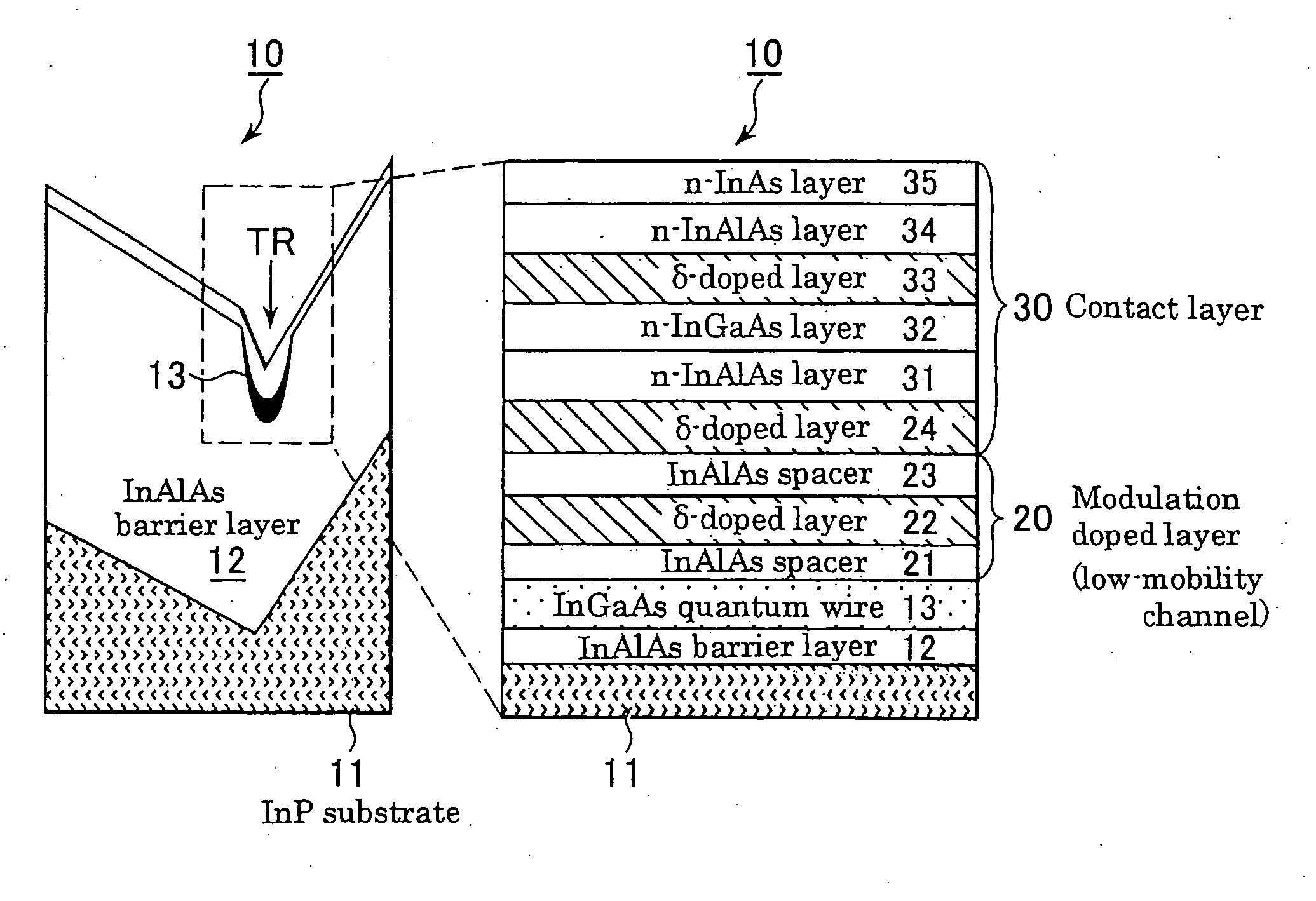
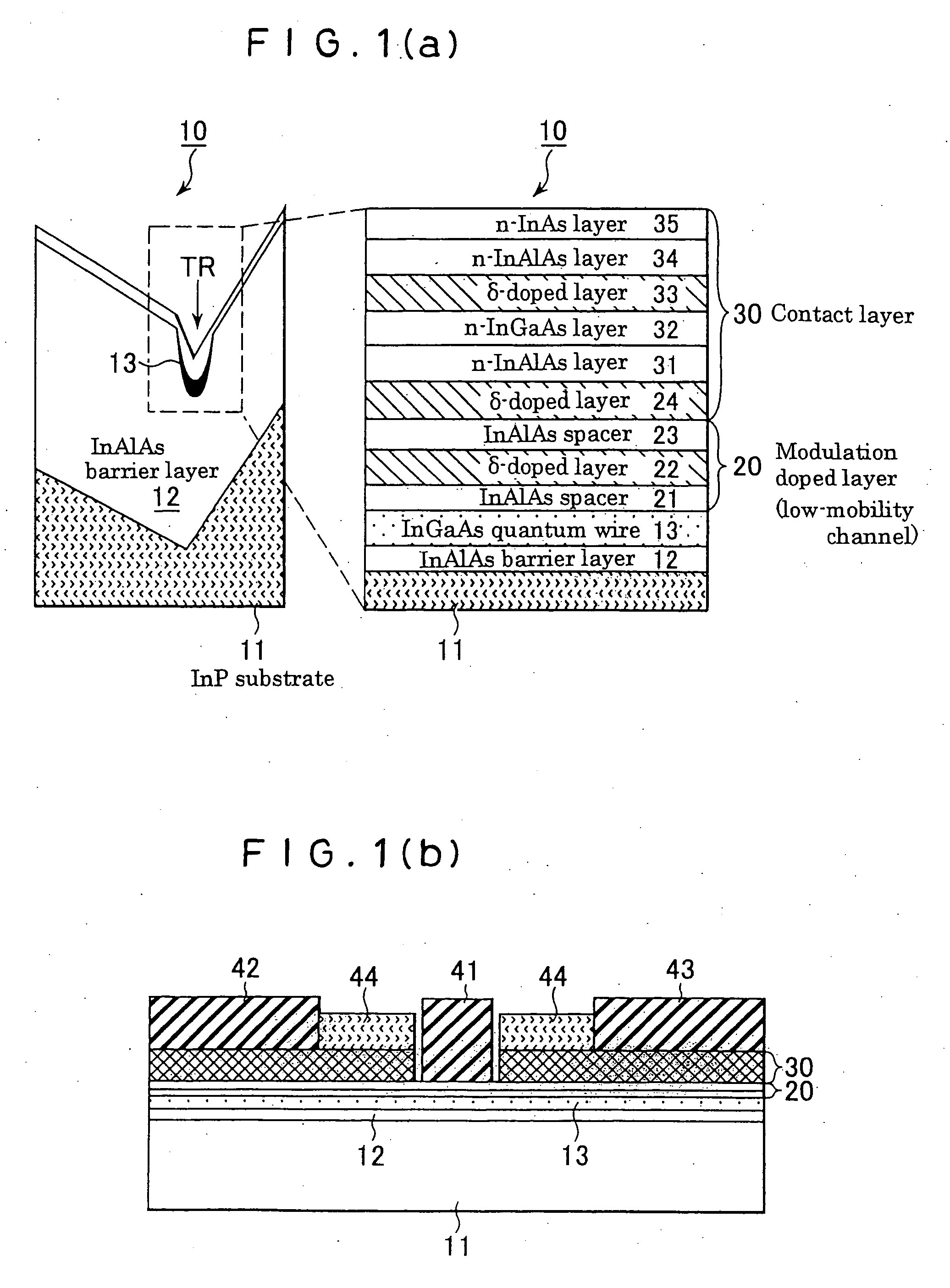
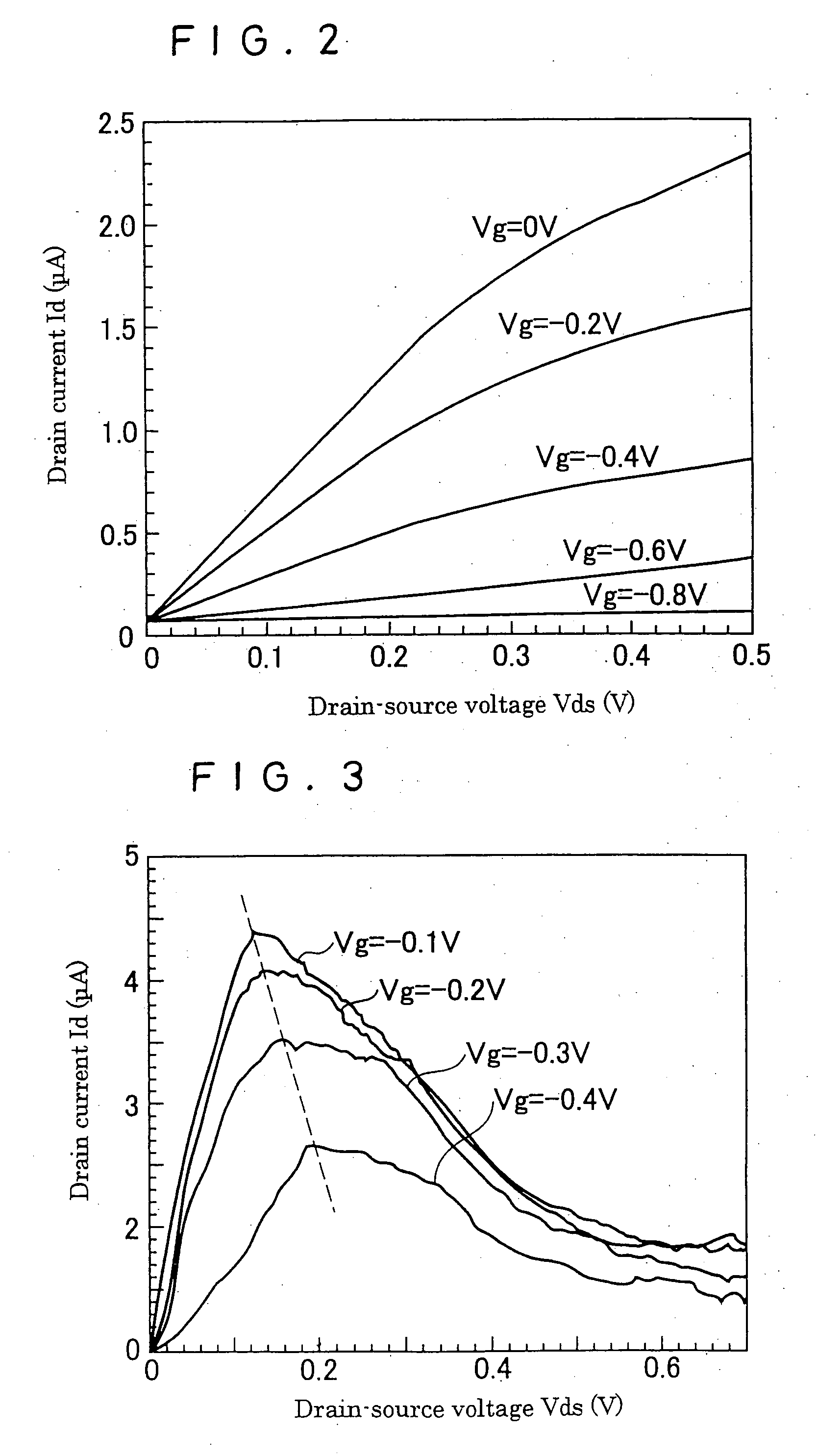
A negative resistance field-effect element that is a negative differential resistance field-effect element capable of achieving negative resistance at a low power supply voltage (low drain voltage) and also enabling securement of a high PVCR is formed on its InP substrate 11 having an asymmetrical V-groove whose surface on one side is a (100) plane and surface on the other side is a (011) plane with an InAlAs barrier layer (12) that has a trench (TR) one of whose opposed lateral faces is a (111) A plane and the other of which is a (331) B plane. An InGaAs quantum wire (13) that has a relatively narrow energy band gap is formed at the trench bottom surface as a high-mobility channel. An InAlAs modulation-doped layer (20) having a relatively wide energy band gap is formed on the quantum wire as a low-mobility channel. A source electrode (42) and a drain electrode (43) each in electrical continuity with the quantum wire (13) constituting the high-mobility channel through a contact layer (30) and extending in the longitudinal direction of the quantum wire (13) as spaced from each other, and a gate electrode (41) provided between the source electrode (42) and the drain electrode (43) to face the low-mobility channel (20) through an insulating layer or a Schottky junction, are provided. Owing to the foregoing configuration, a very narrow-width quantum wire whose lateral confinement size can, without restriction by the lithographic technology limit, be made 100 nm or less is usable as a high-mobility channel, whereby there can be obtained a negative resistance field-effect element that develops a negative characteristic at a low power supply voltage and enables securement of a high PVCR.
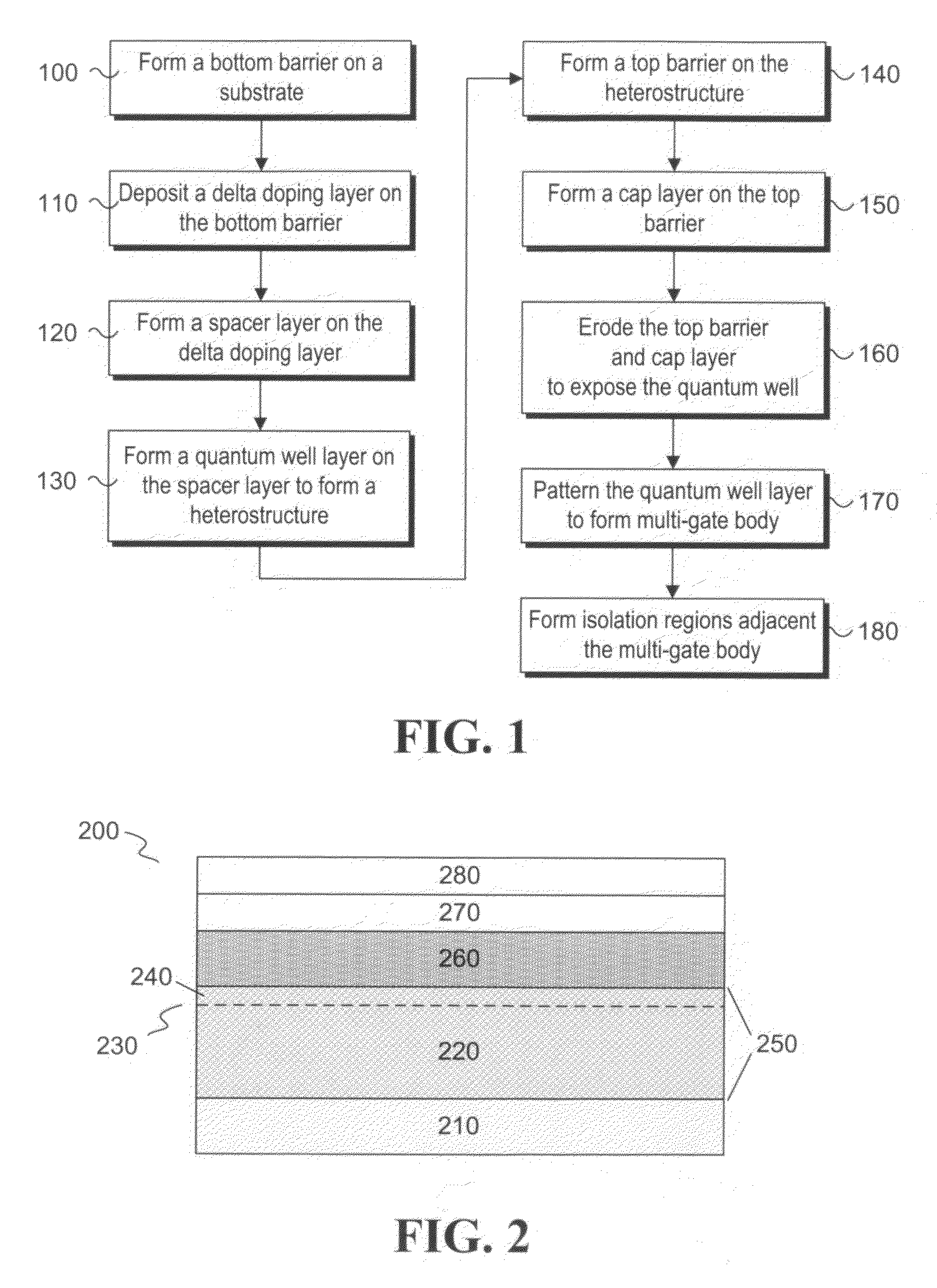
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Manufacturing method of modulation-doped gallium nitride series light-emitting diode
ActiveCN102185052AImprove luminous efficiencyImprove injection efficiencySemiconductor devicesSilanesContact layer
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of a modulation-doped gallium nitride series light-emitting diode. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: step 1, preparing a substrate; step 2, manufacturing a gallium nitride nucleating layer and a gallium nitride buffer layer in sequence on the substrate; step 3, manufacturing an n-type gallium nitride contact layer on the gallium nitride buffer layer, and taking silane as an n-type doping agent; step 4, manufacturing an n-type current expanding layer, an active luminous layer, a p-type electronic blocking layer and a p-type contact layer in sequence on the upper surface of the n-type contact layer, which is not etched; step 5, etching the upper side of the p-type contact layer downwards with the etching depth reaching into the n-type gallium nitride contact layer by adopting an etching method to so that a platform surface is formed at one side of the n-type gallium nitride contact layer; and step 6, manufacturing a negative electrode on the platform surface of the n-type contact layer; and finally manufacturing a positive electrode on the p-type contact layer.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor for use in harsh environments
A gallium-nitride semiconductor apparatus may include an active region having one or more nitride-based barrier layers that are modulation-doped using a nitride-based doped layer. An active region may have at least two nitride-based barrier layers, and a nitride-based blocking layer may be disposed between the at least two barrier layers.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
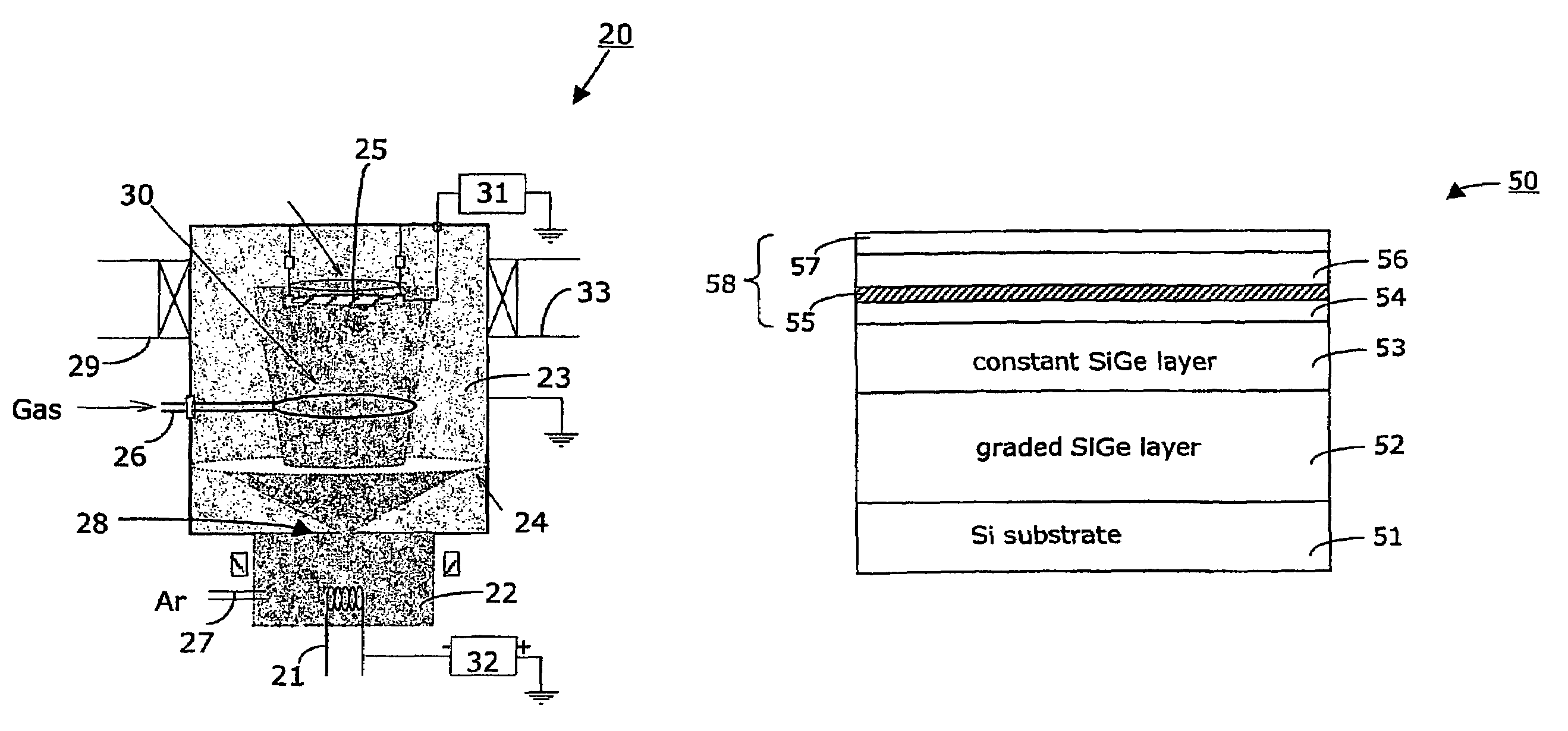
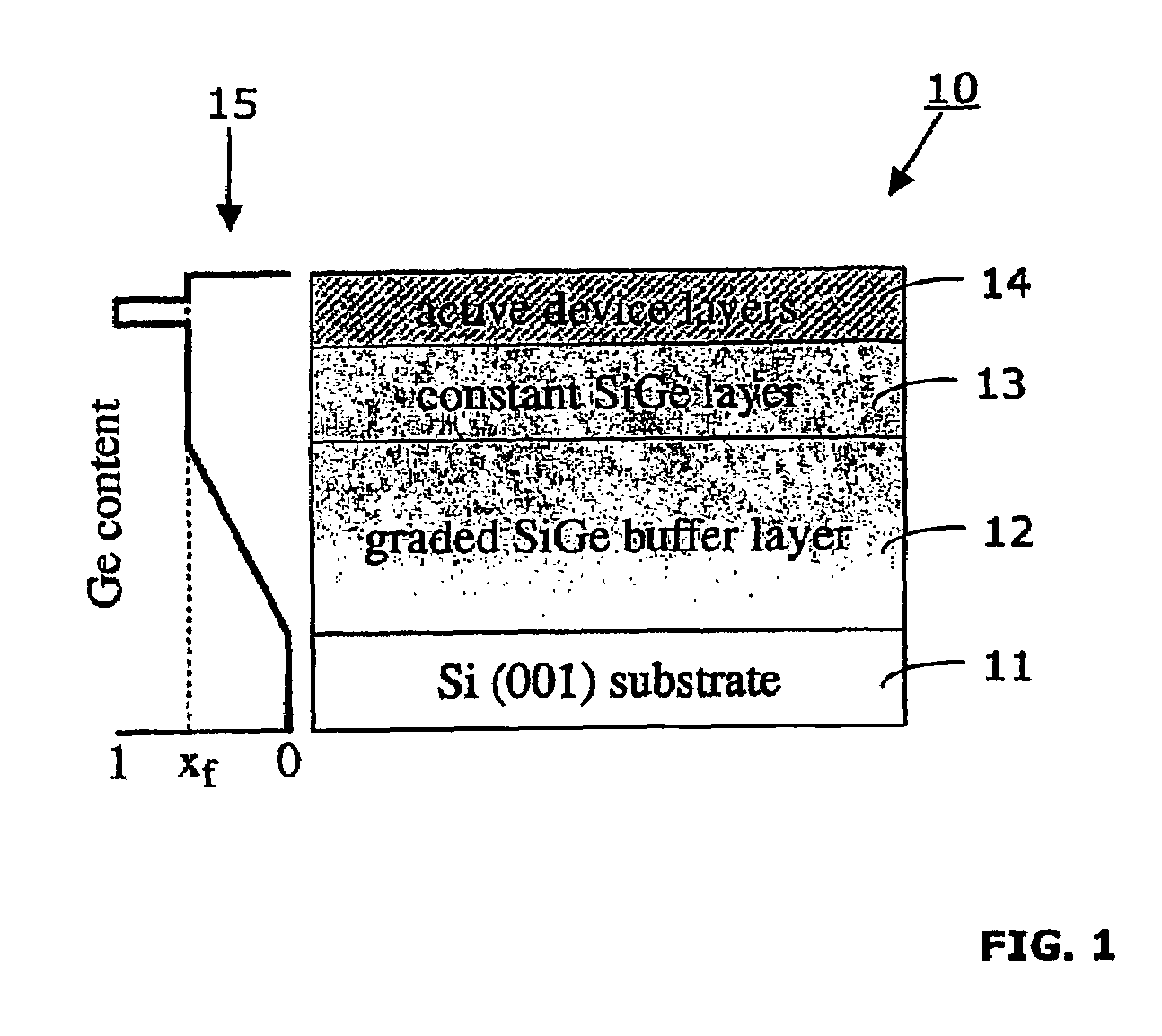
Formation of high-mobility silicon-germanium structures by low-energy plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition
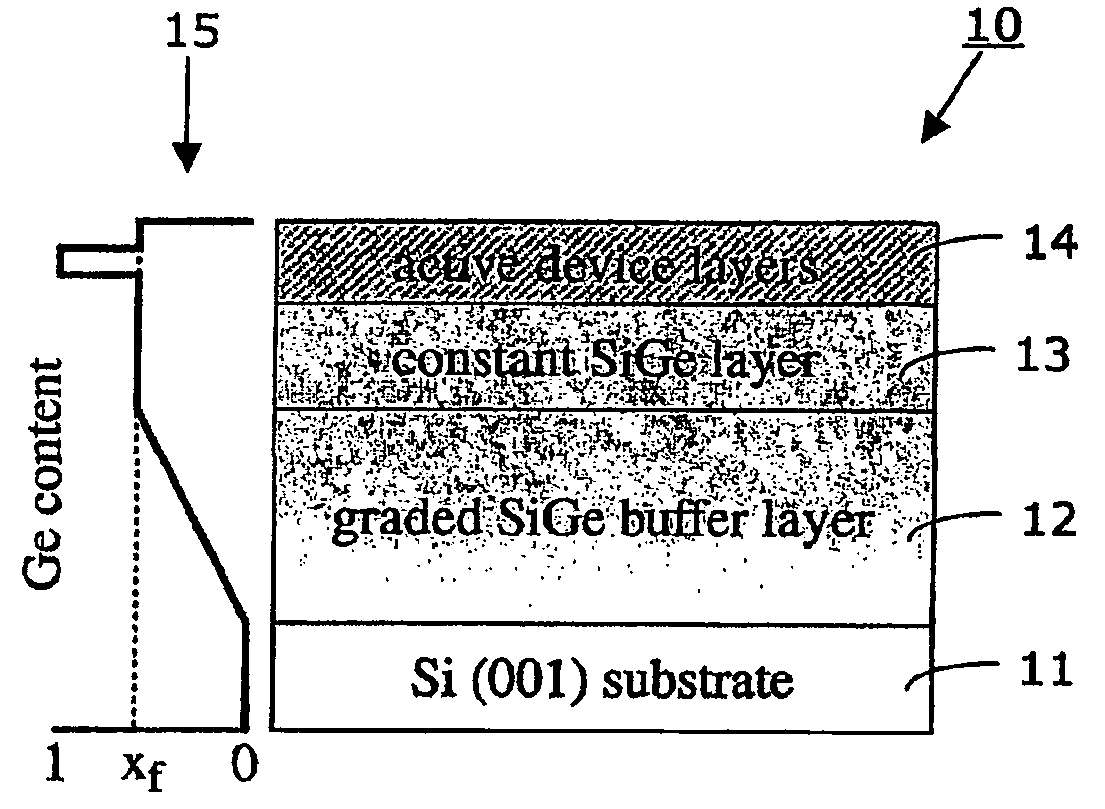
InactiveUS7115895B2Increase probabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDopantHydrogen
Method for making a semiconductor structures comprising the steps:—forming a virtual substrate on a silicon substrate with a graded Si1-xGex layer and a non-graded Si1-xGex layer, using a high-density, low-energy plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (LEPECVD) process with a growth rate above 2 nm / s, a substrate temperature between 400° and 850° C., and a total reactive gas flow at the gas inlet between 5 sccm and 200 sccm;—forming an active region on the virtual substrate that comprises a Ge-channel and at least one modulation-doped layer using a low-density, low-energy plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (LEPECVD) process by introducing hydrogen (H2) into the growth chamber, maintaining a substrate temperature between 400° and 500° C., and by introducing a dopant gas in a pulsed manner into the growth chamber to provide for the modulation-doped layer.
Owner:DICHROIC CELL
Method and apparatus for downhole spectroscopy
ActiveUS20090284259A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingRadiation pyrometrySpectroscopyNitride
Apparatus and method for estimating a property of a downhole fluid including a carrier that is conveyed in a borehole, and a semiconductor electromagnetic energy source carried by the carrier, the semiconductor electromagnetic energy source having an active region that includes one or more nitride-based barrier layers that are modulation-doped using a nitride-based doped layer.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Low doped layer for nitride-based semiconductor device
InactiveUS7253015B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSchottky diodeNitride semiconductors
A repeatable and uniform low doped layer is formed using modulation doping by forming alternating sub-layers of doped and undoped nitride semiconductor material atop another layer. A Schottky diode is formed of such a low doped nitride semiconductor layer disposed atop a much more highly doped nitride semiconductor layer. The resulting device has both a low on-resistance when the device is forward biased and a high breakdown voltage when the device is reverse biased.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
Optoelectronic device with modulation doping
ActiveUS9653631B2Reduce formationImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDopantContact layer
An improved heterostructure for an optoelectronic device is provided. The heterostructure includes an active region, an electron blocking layer, and a p-type contact layer. The p-type contact layer and electron blocking layer can be doped with a p-type dopant. The dopant concentration for the electron blocking layer can be at most ten percent the dopant concentration of the p-type contact layer. A method of designing such a heterostructure is also described.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Optoelectronic Device with Modulation Doping
An improved heterostructure for an optoelectronic device is provided. The heterostructure includes an active region, an electron blocking layer, and a p-type contact layer. The p-type contact layer and electron blocking layer can be doped with a p-type dopant. The dopant concentration for the electron blocking layer can be at most ten percent the dopant concentration of the p-type contact layer. A method of designing such a heterostructure is also described.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Formation of high-mobility silicon-germanium structures by low-energy plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition
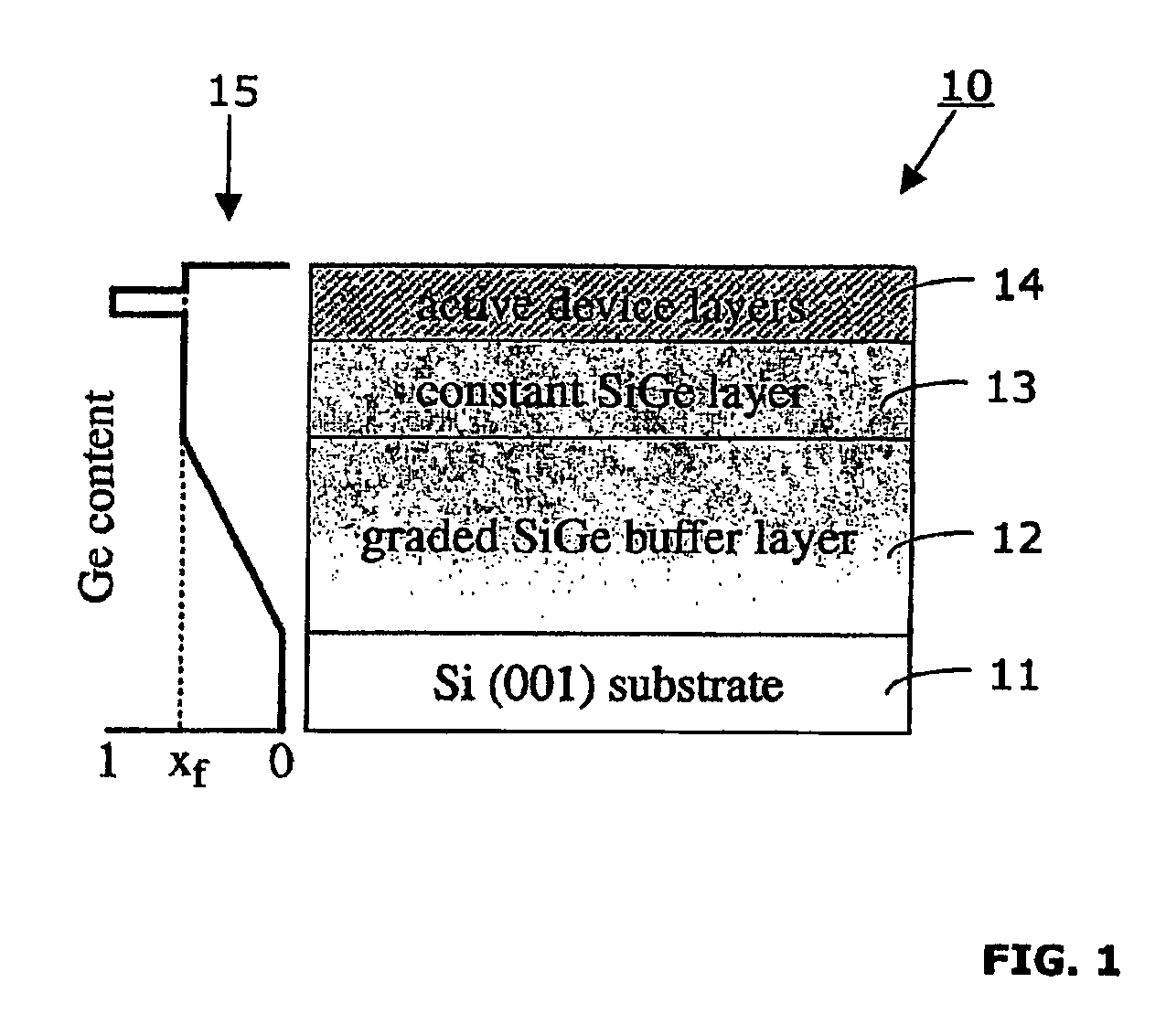
InactiveUS20050116226A1Increase probabilityIncrease ratingsFrom solid stateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseSilicon-germanium
A method for making a semiconductor heterostructure in a growth chamber with gas inlet comprises several steps. In a first step, a virtual substrate is formed on a silicon substrate, comprising a graded Si1-xGex layer followed by a Si1-xGex layer with constant concentration of Ge, using a high-density, low-energy plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (LEPECVD) process. In this step, the growth rate is maintained above 2 nm / s. the substrate temperature between 400° and 850° C., and the total reactive gas flow at the gas inlet between 5 sccm and 200 sccm. In another step, an active region is formed on said virtual substrate comprising a Ge-channel and a modulation-doped layer using a low-density, low-energy plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (LEPECVD) process. In this step, hydrogen (H2) is introduced into the growth chamber to act as a surfactant, a substrate temperature is maintained between 400° and 500° C. and a dopant gas is introduced in a pulsed manner into the growth chamber to provide for the modulation-doped layer.
Owner:DICHROIC CELL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com