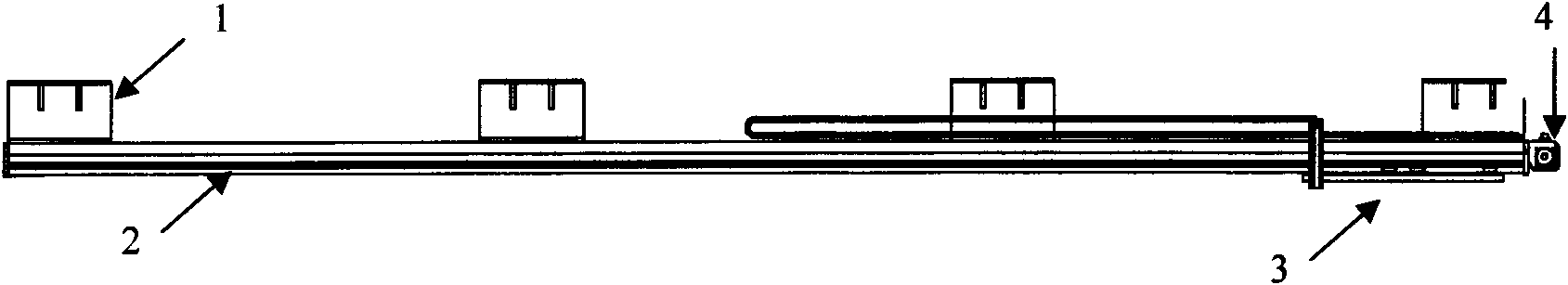Patents
Literature
48 results about "Induced movement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
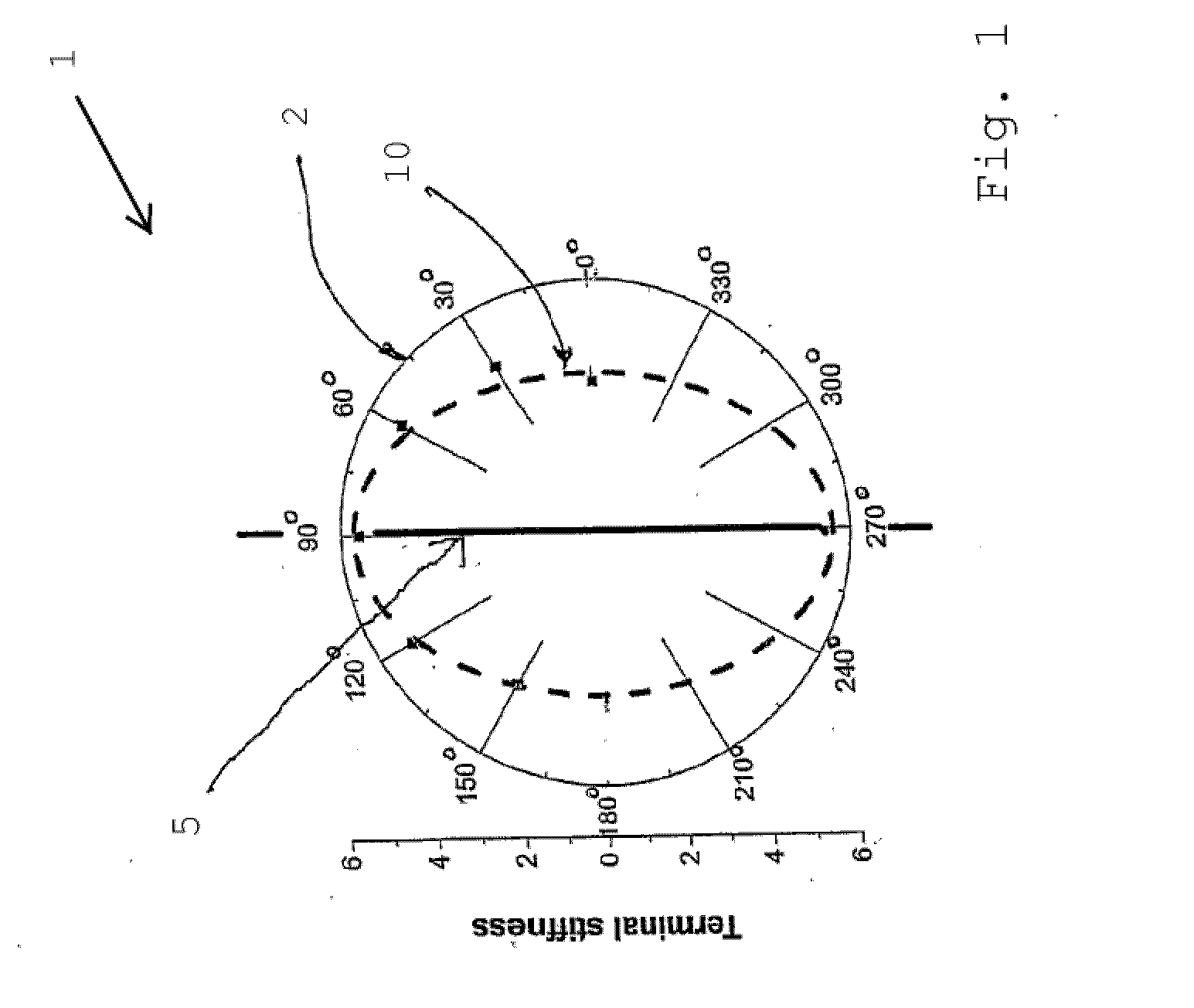
Induced movement or induced motion is an illusion of visual perception in which a stationary or a moving object appears to move or to move differently because of other moving objects nearby in the visual field. It is interpreted in terms of the change in the location of an object due to the movement in the space around it. The object affected by the illusion is called the target, and the other moving objects are called the background or the context (Duncker, 1929).
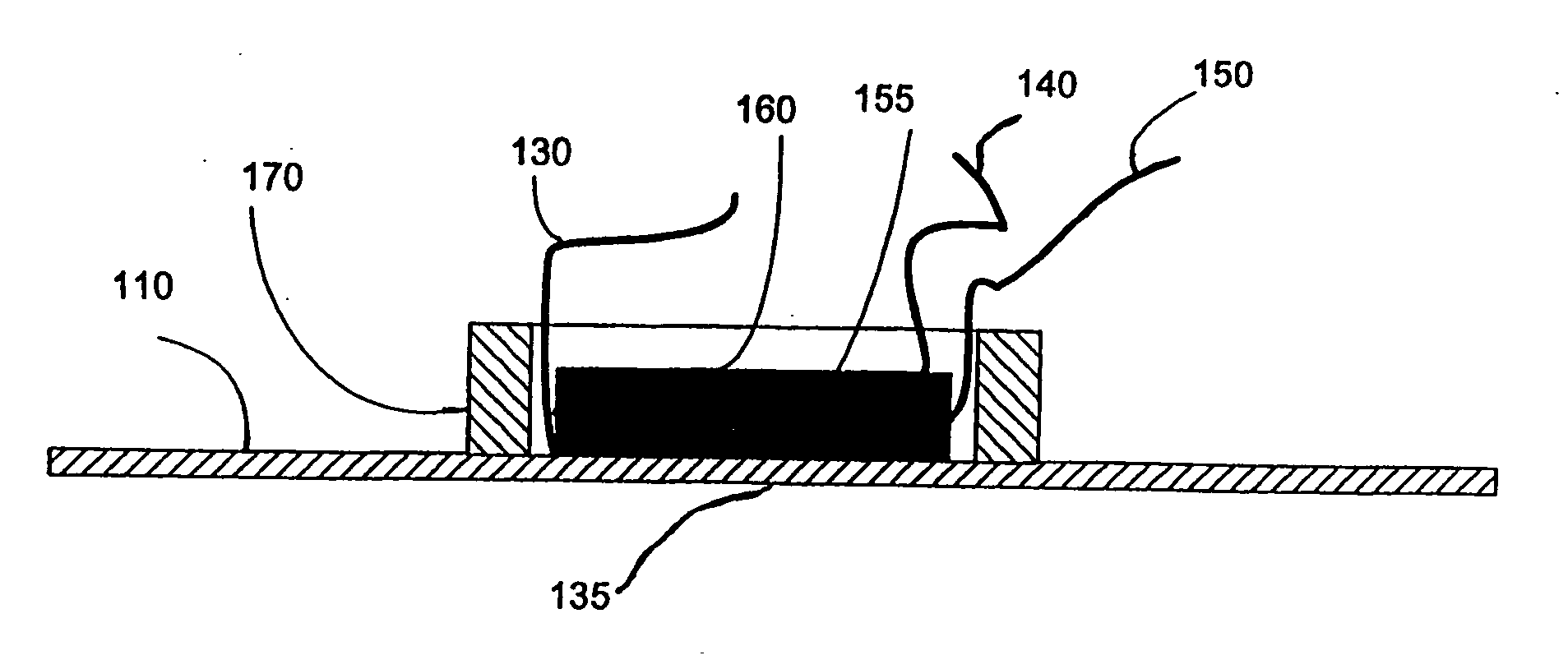
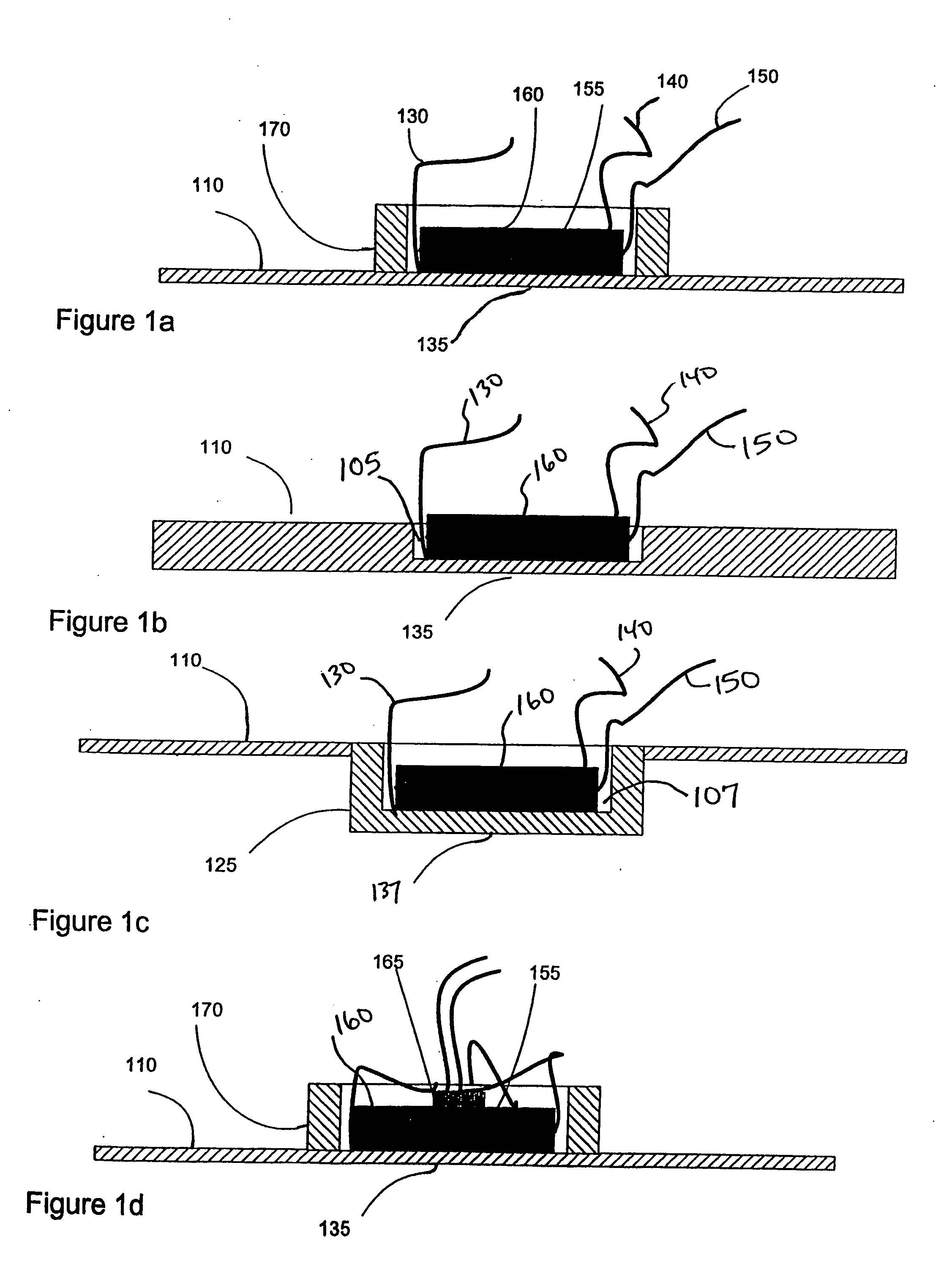
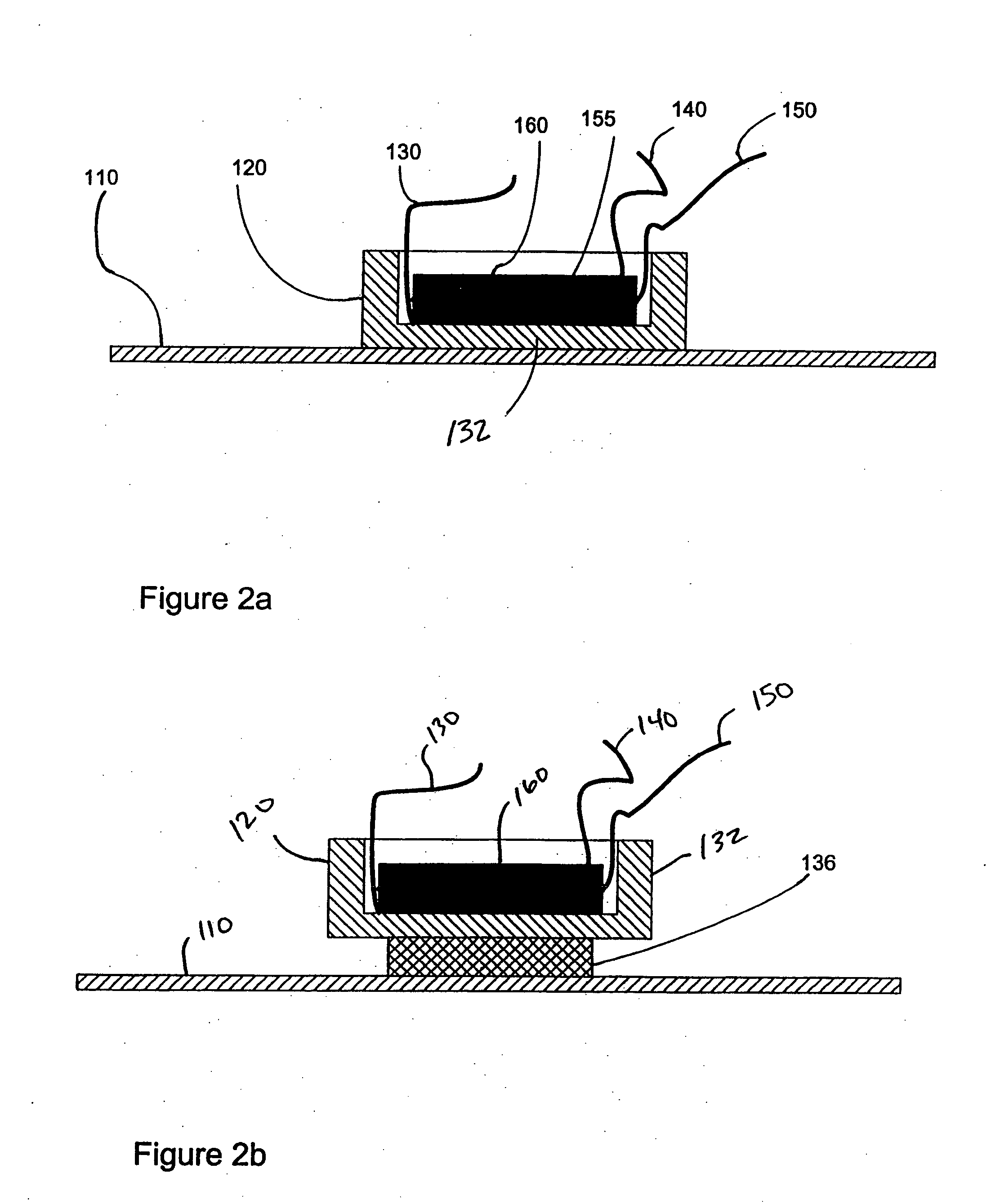
Method and Apparatus Using Electric Field for Improved Biological Assays
ActiveUS20090032401A1Avoid corrosionIncrease electric fieldElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentPresent methodEngineering
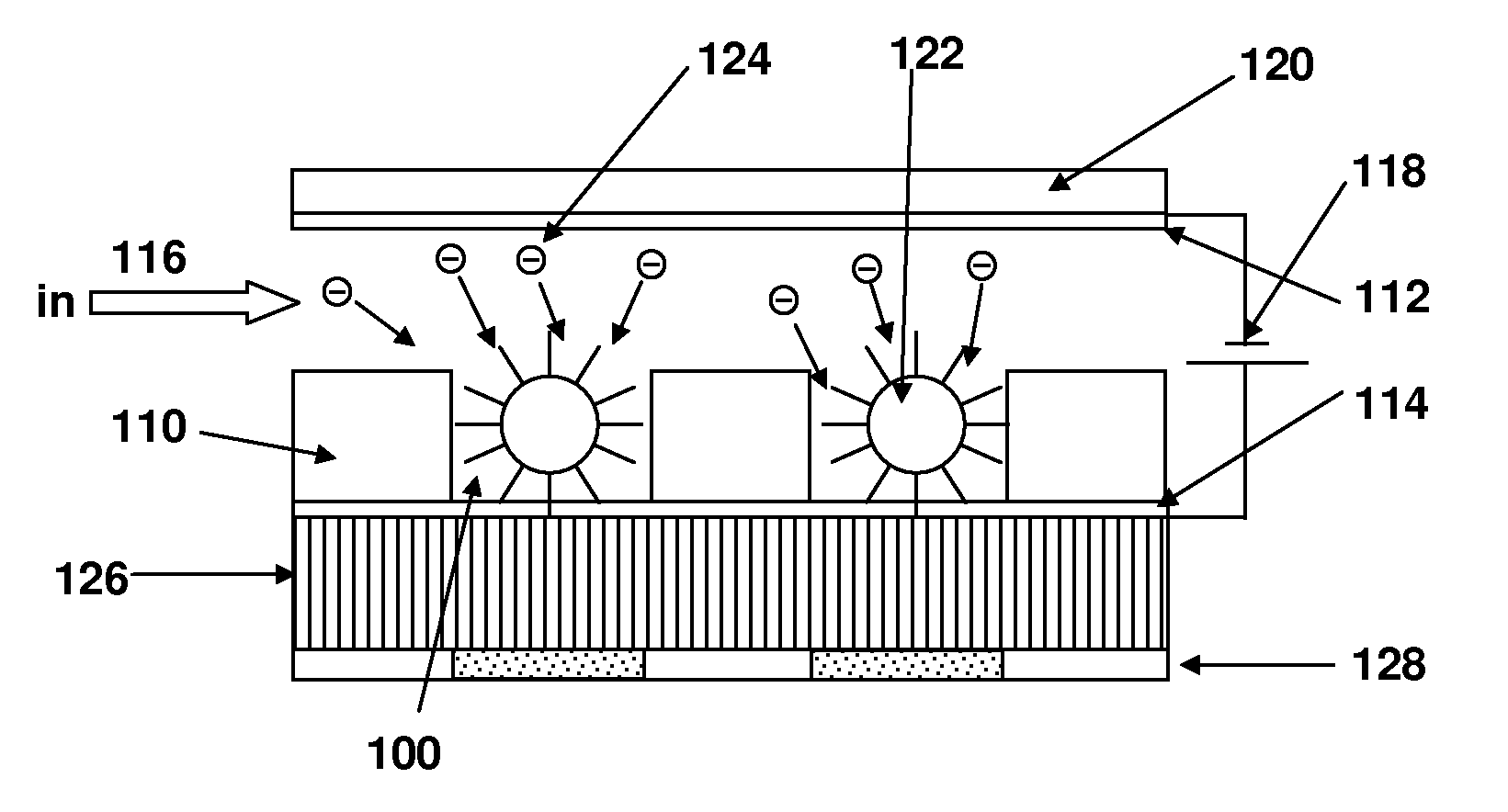
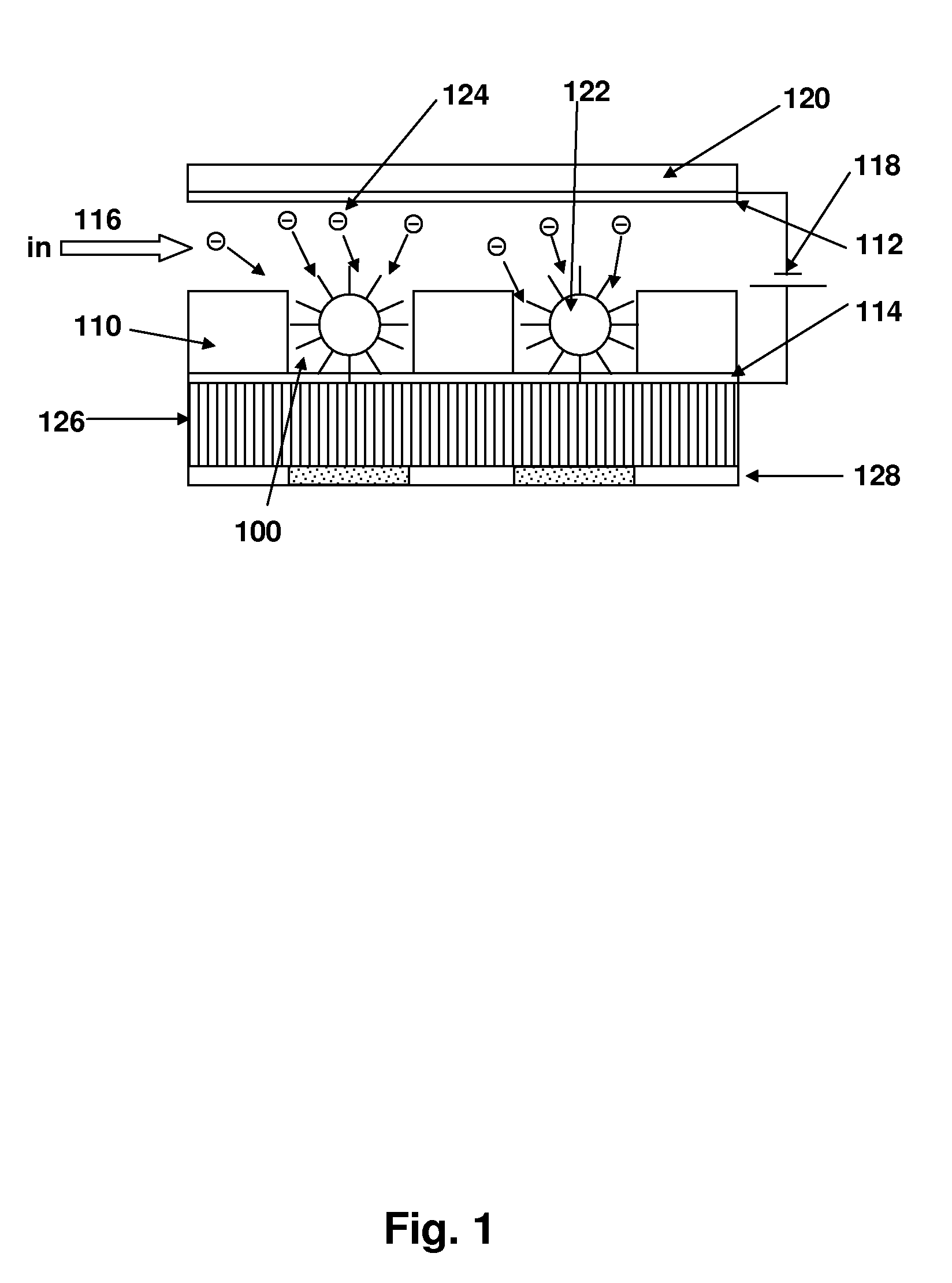
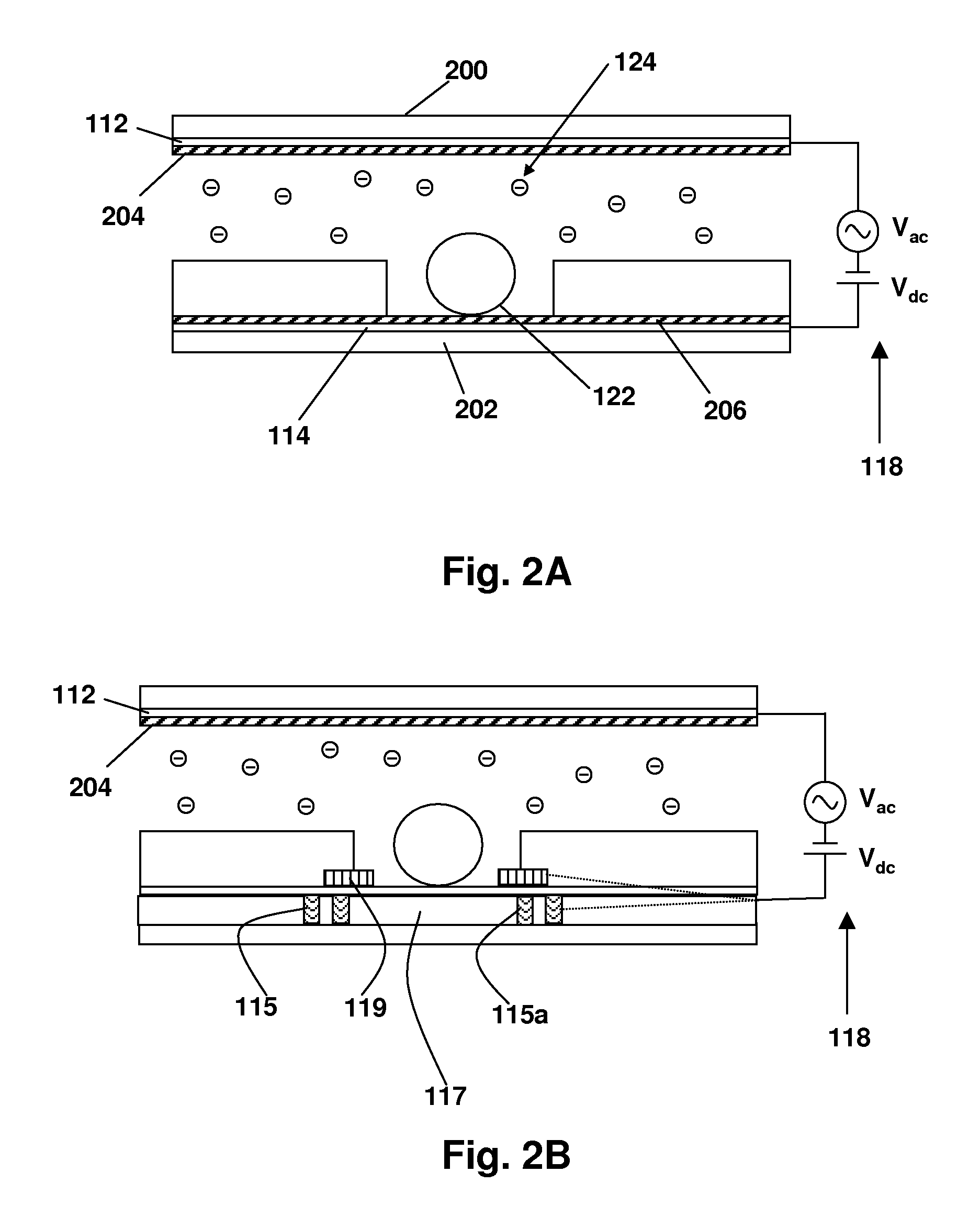
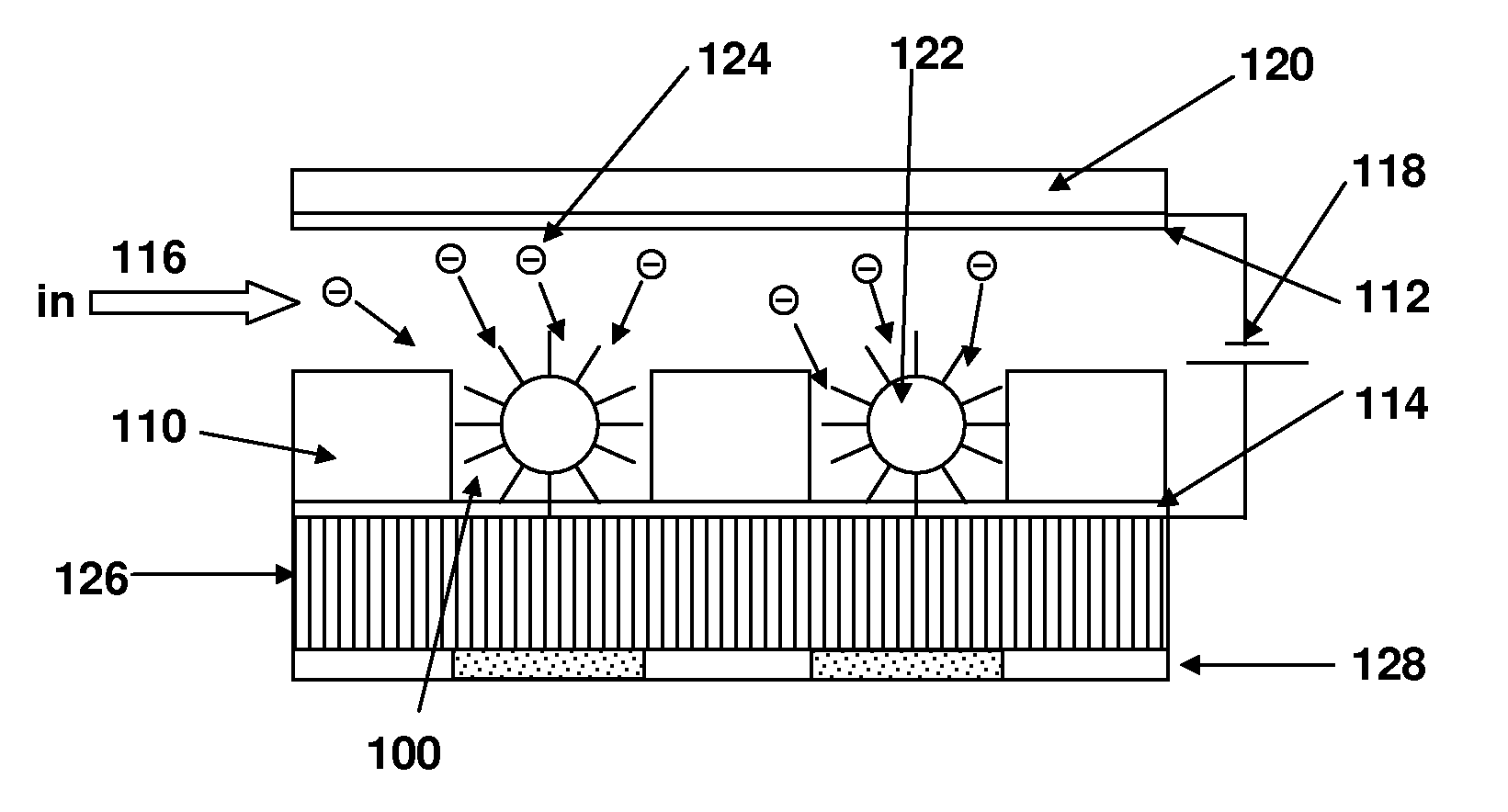
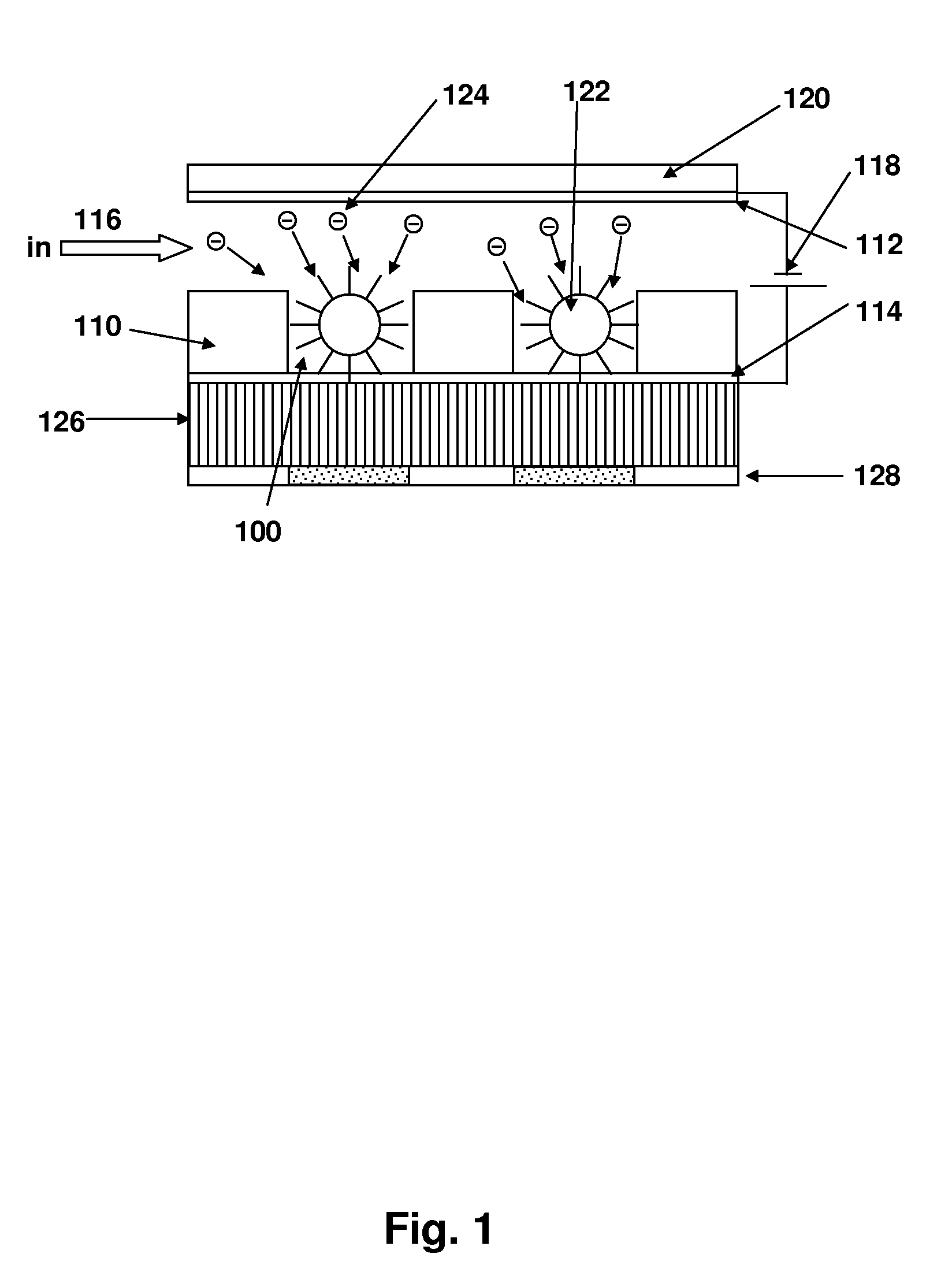
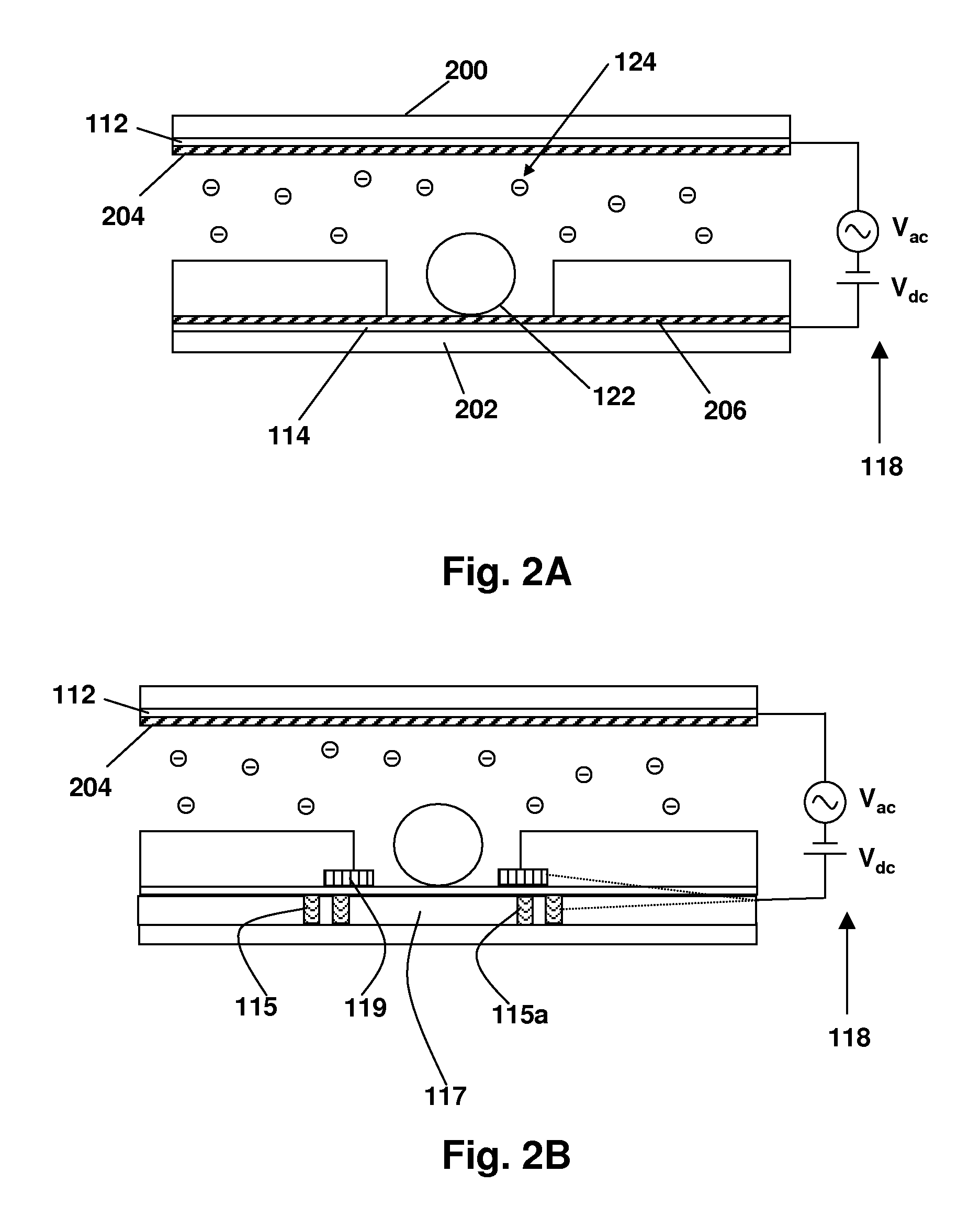
Disclosed are a method and apparatus that use an electric field for improved biological assays. The electric field is applied across a device having wells, which receive reactants, which carry a charge. The device thus uses a controllable voltage source between the first and second electrodes, which is controllable to provide a positive charge and a negative charge to a given electrode. By controlled use of the electric field charged species in a fluid in a fluid channel are directed into or out of the well by an electric field between the electrodes. The present method involves the transport of fluids, as in a microfluidic device, and the electric field-induced movement of reactive species according to various assay procedures, such as DNA sequencing, synthesis or the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
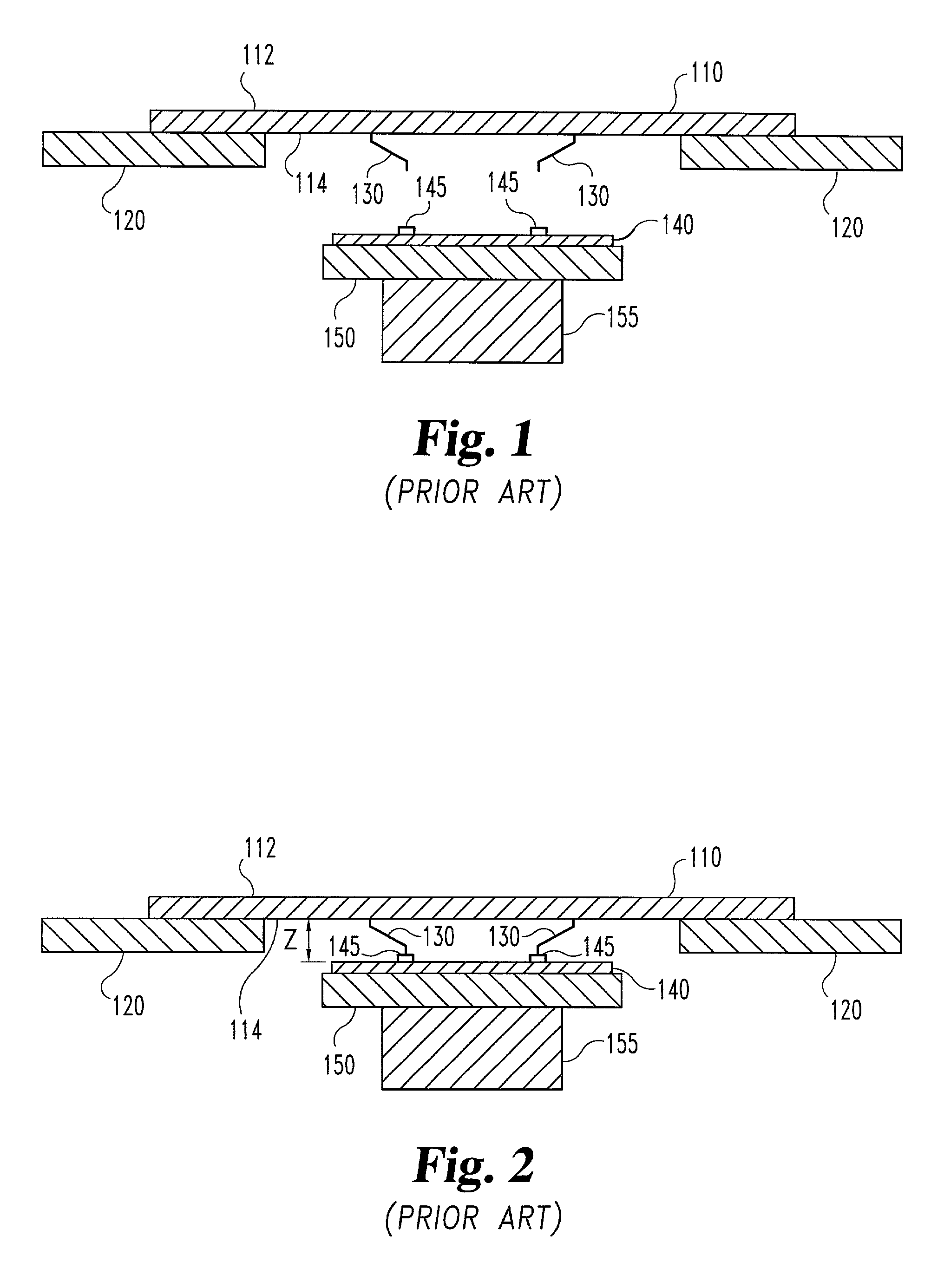
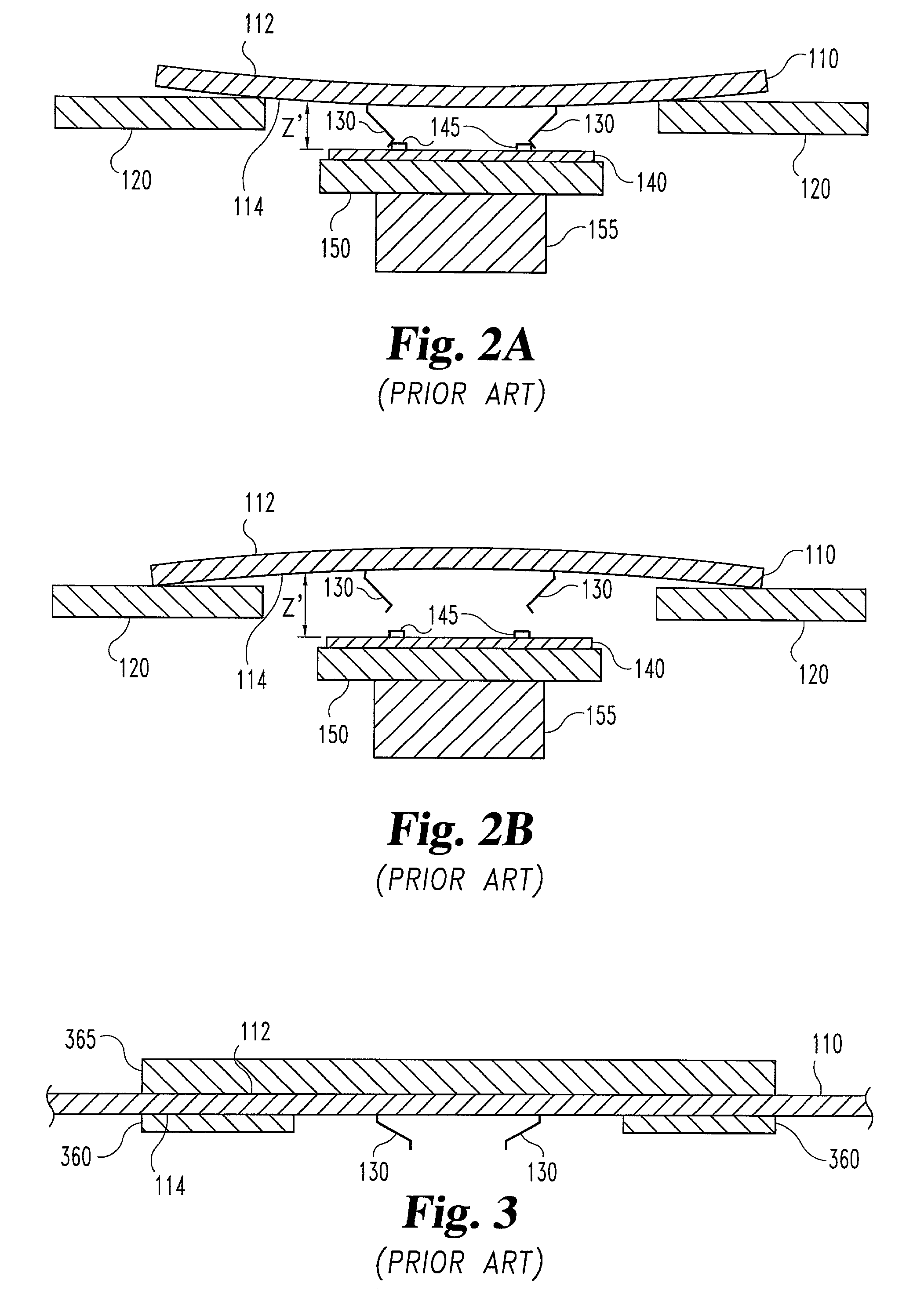
Method and system for compensating thermally induced motion of probe cards
InactiveUS7002363B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementTemperature controlProbe card
The present invention discloses a method and system compensating for thermally induced motion of probe cards used in testing die on a wafer. A probe card incorporating temperature control devices to maintain a uniform temperature throughout the thickness of the probe card is disclosed. A probe card incorporating bi-material stiffening elements which respond to changes in temperature in such a way as to counteract thermally induced motion of the probe card is disclosed including rolling elements, slots and lubrication. Various means for allowing radial expansion of a probe card to prevent thermally induced motion of the probe card are also disclosed. A method for detecting thermally induced movement of the probe card and moving the wafer to compensate is also disclosed.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
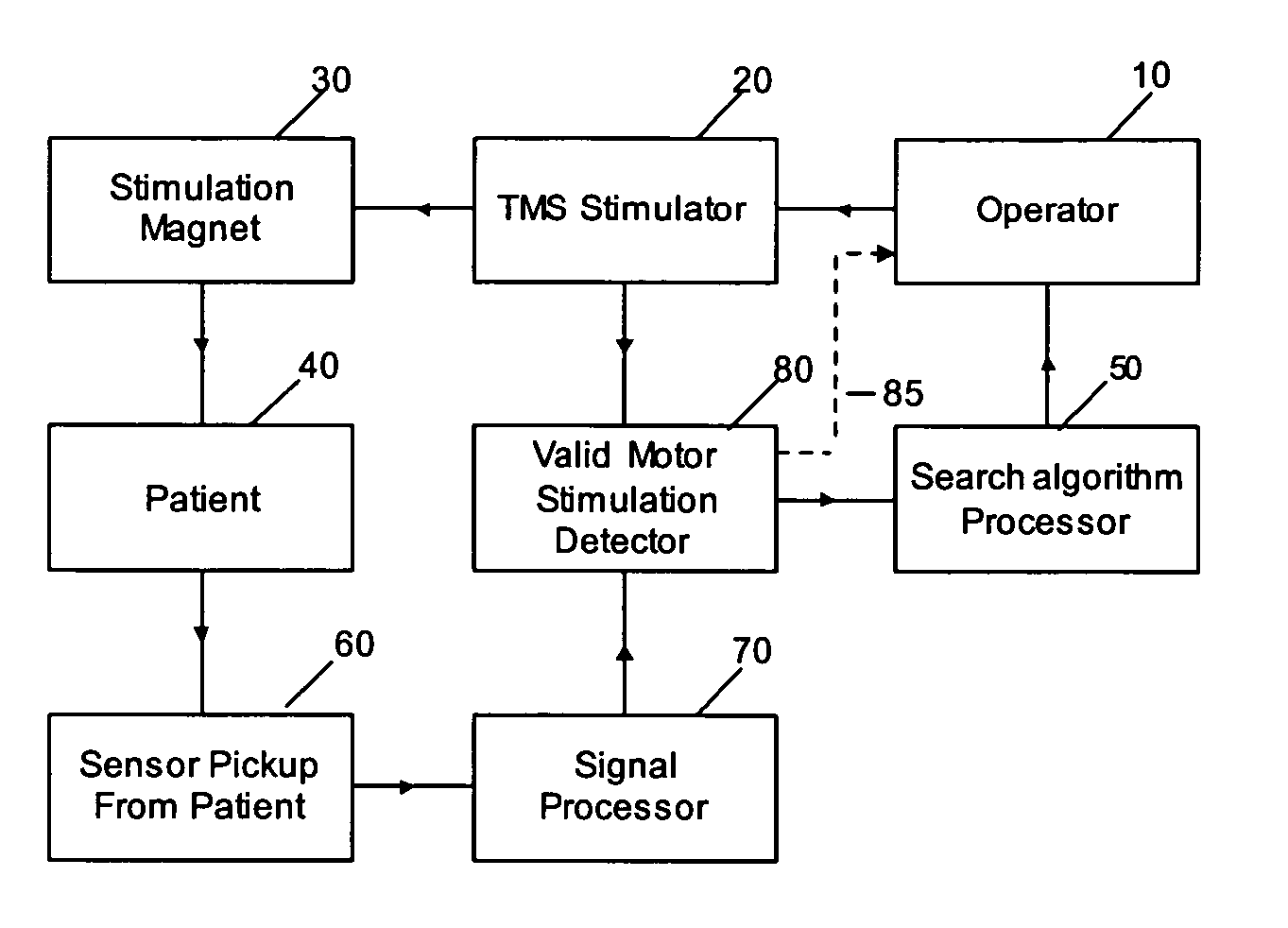
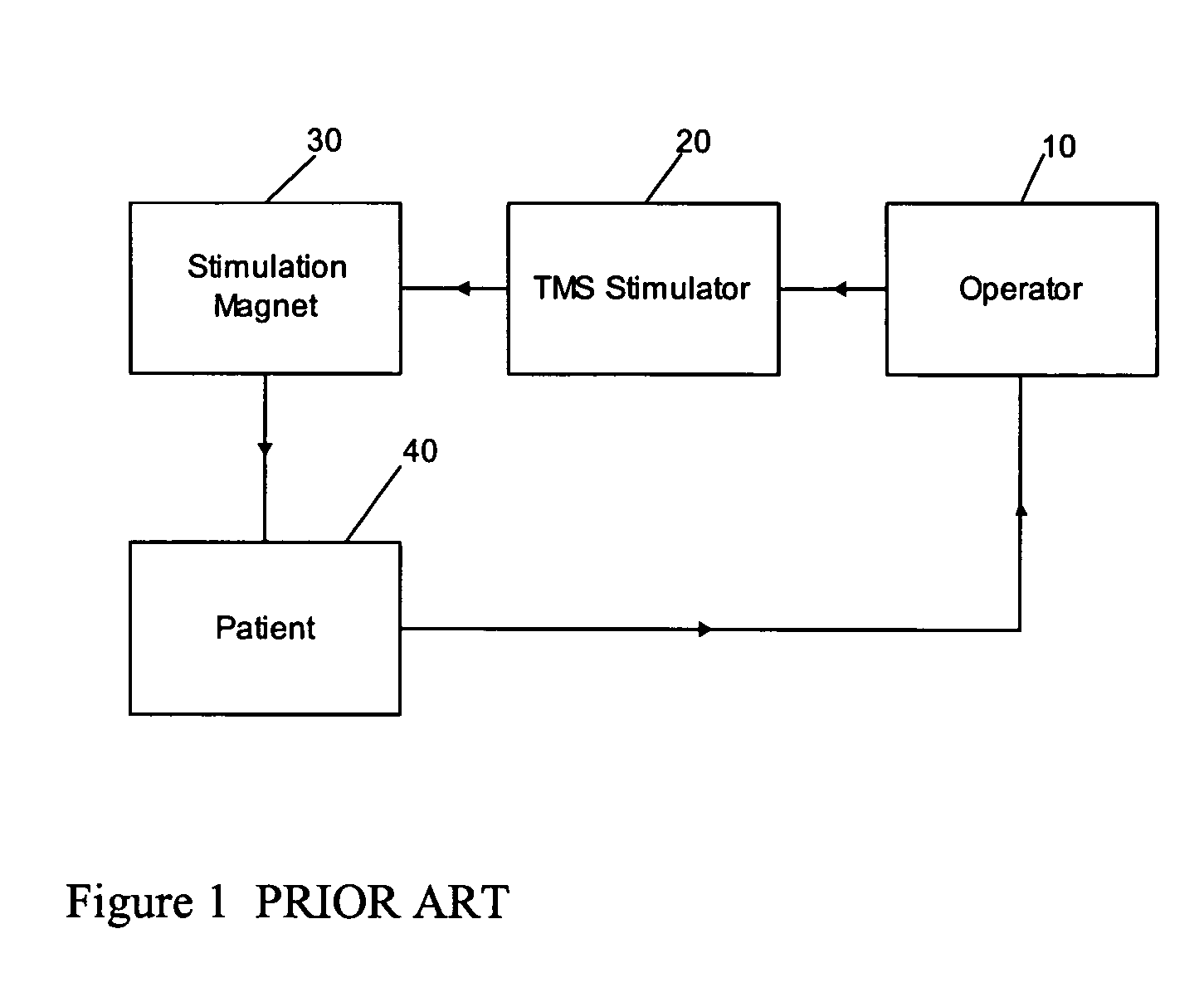
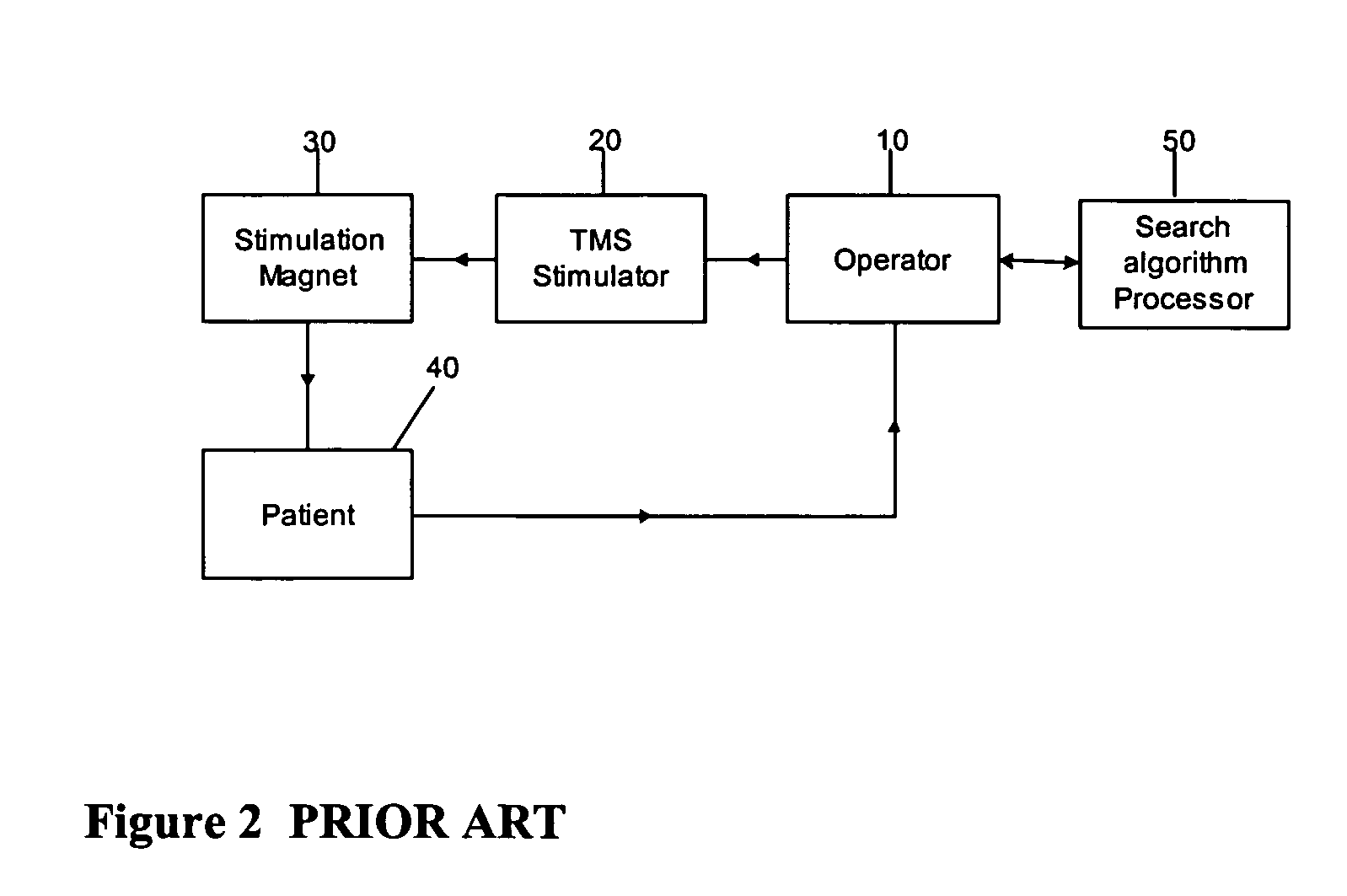
Determining stimulation levels for transcranial magnetic stimulation
ActiveUS7104947B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyMotion detectorREFLEX DECREASE
Owner:NEURONETICS
Method and apparatus using electric field for improved biological assays
ActiveUS8277628B2Quality improvementEfficient removalElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentPresent methodEngineering
Disclosed are a method and apparatus that use an electric field for improved biological assays. The electric field is applied across a device having wells, which receive reactants, which carry a charge. The device thus uses a controllable voltage source between the first and second electrodes, which is controllable to provide a positive charge and a negative charge to a given electrode. By controlled use of the electric field charged species in a fluid in a fluid channel are directed into or out of the well by an electric field between the electrodes. The present method involves the transport of fluids, as in a microfluidic device, and the electric field-induced movement of reactive species according to various assay procedures, such as DNA sequencing, synthesis or the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Implantable medical device with integrated acoustic
InactiveUS20060149329A1Noise minimizationMinimize parasitic effectElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringTransducerEngineering
An implantable medical device comprises a hermetically sealed housing having a housing wall with an interior surface, and an ultrasonic acoustic transducer, the transducer comprising one or more piezoelectric discs fixed to the interior surface of the housing wall, such that the housing wall acts as a diaphragm in response to induced movement by the one or more piezoelectric material discs.
Owner:REMON MEDICAL TECH
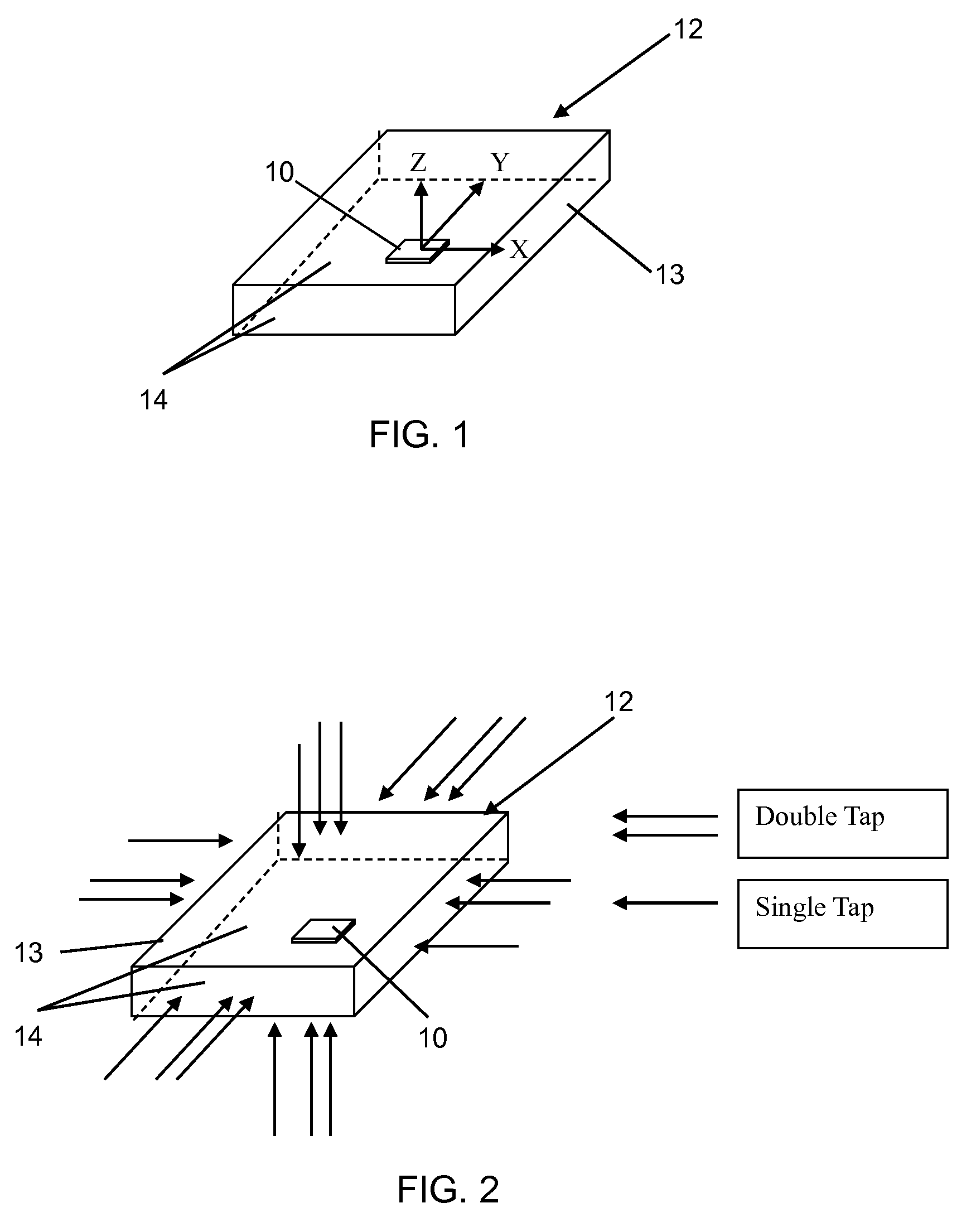
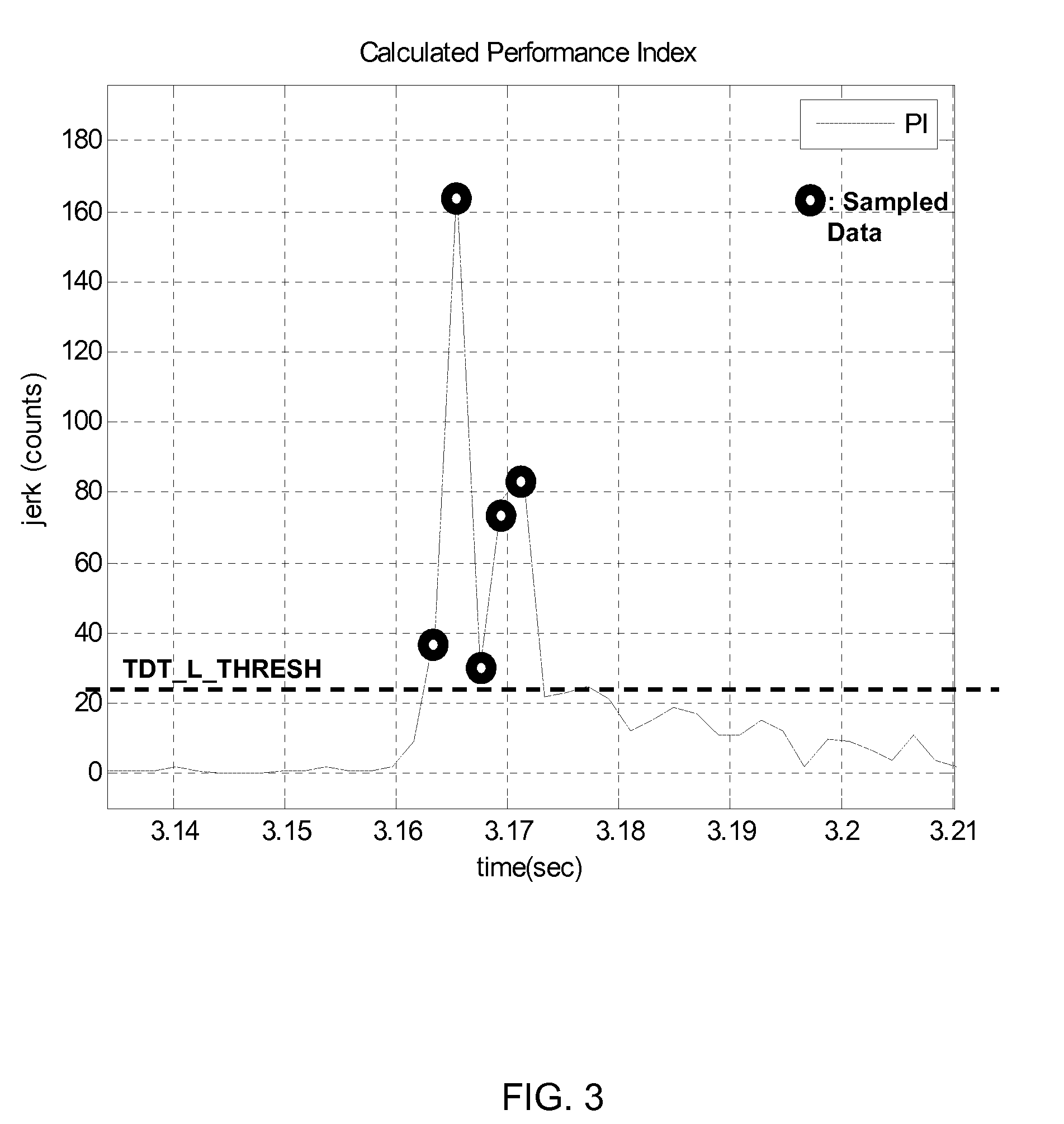
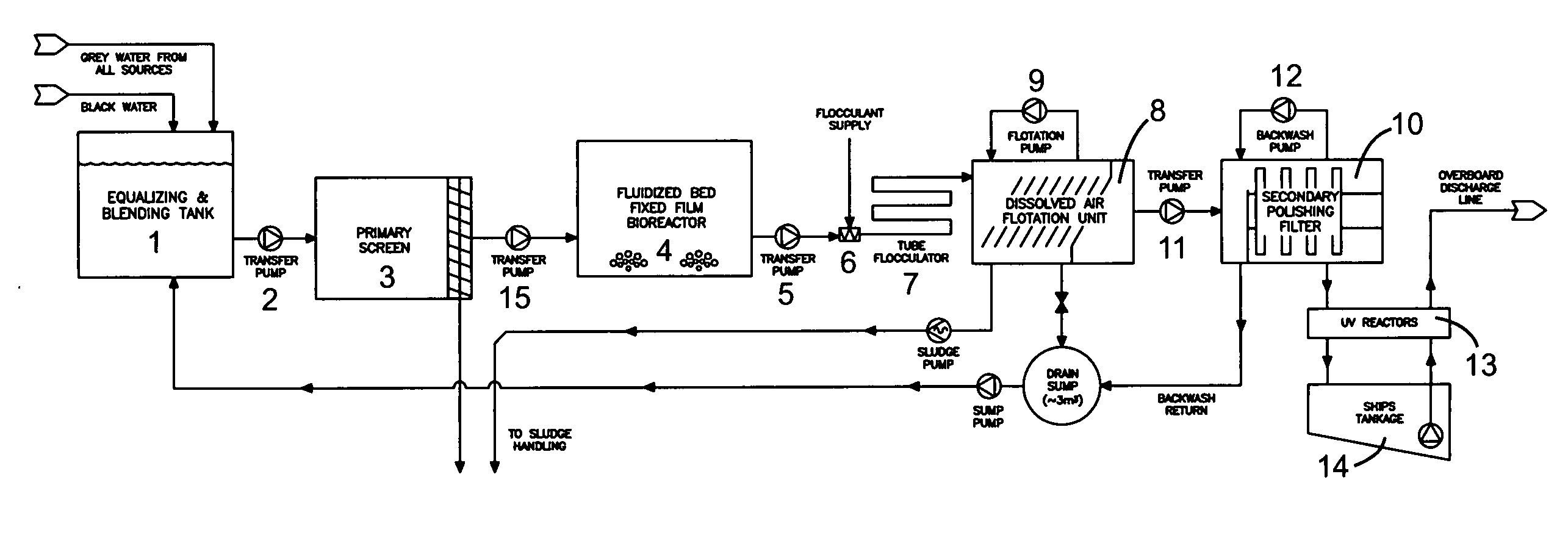
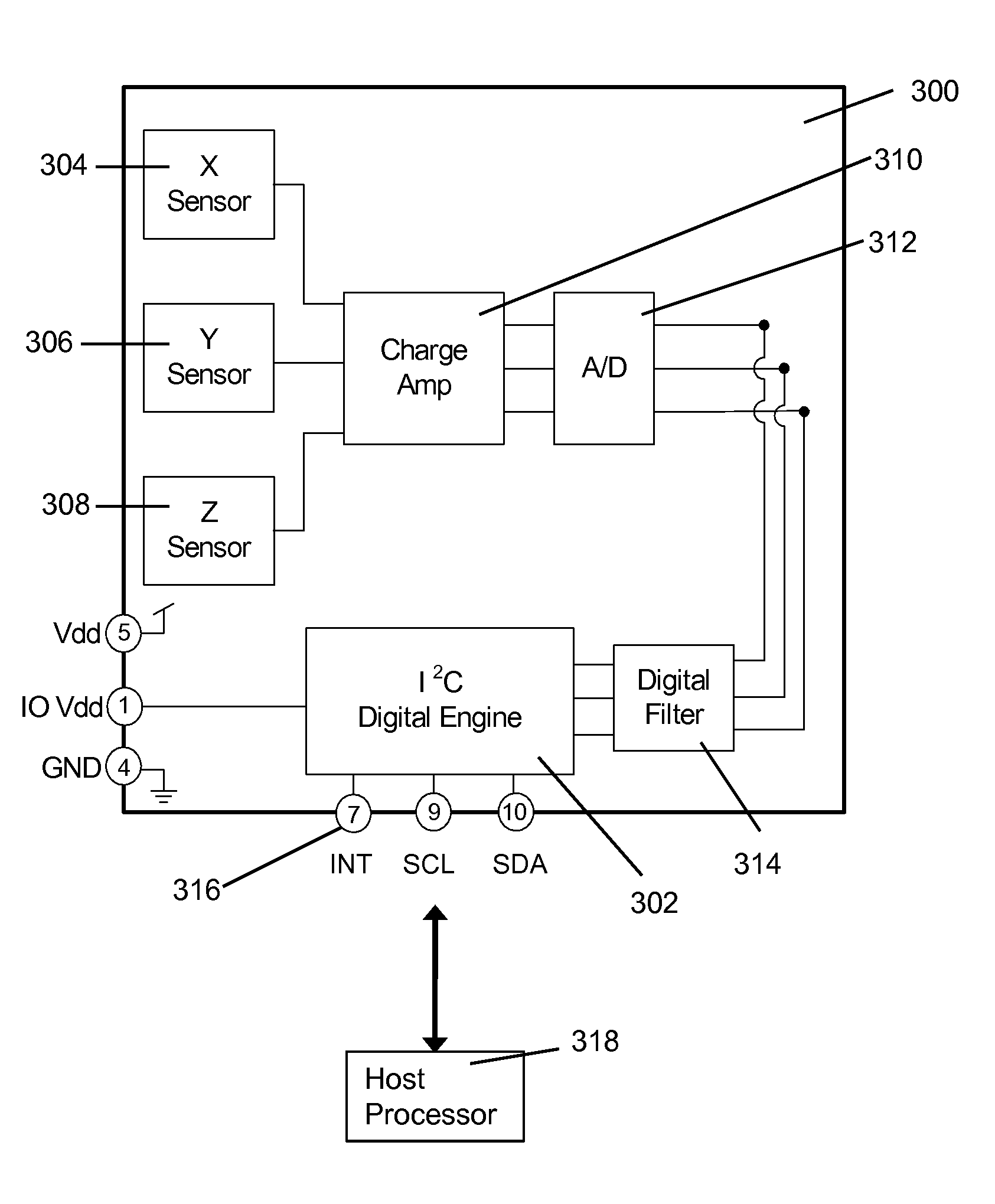
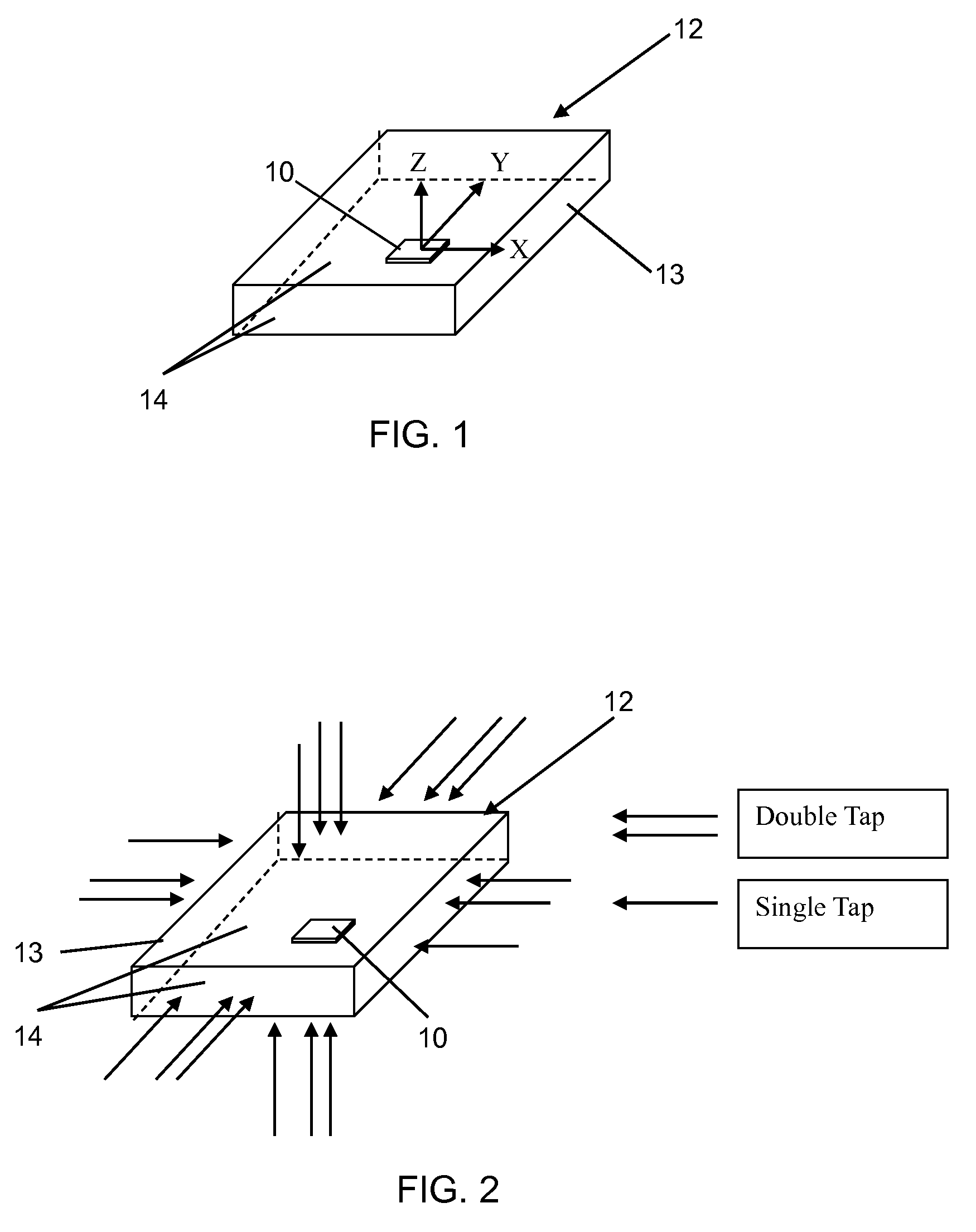
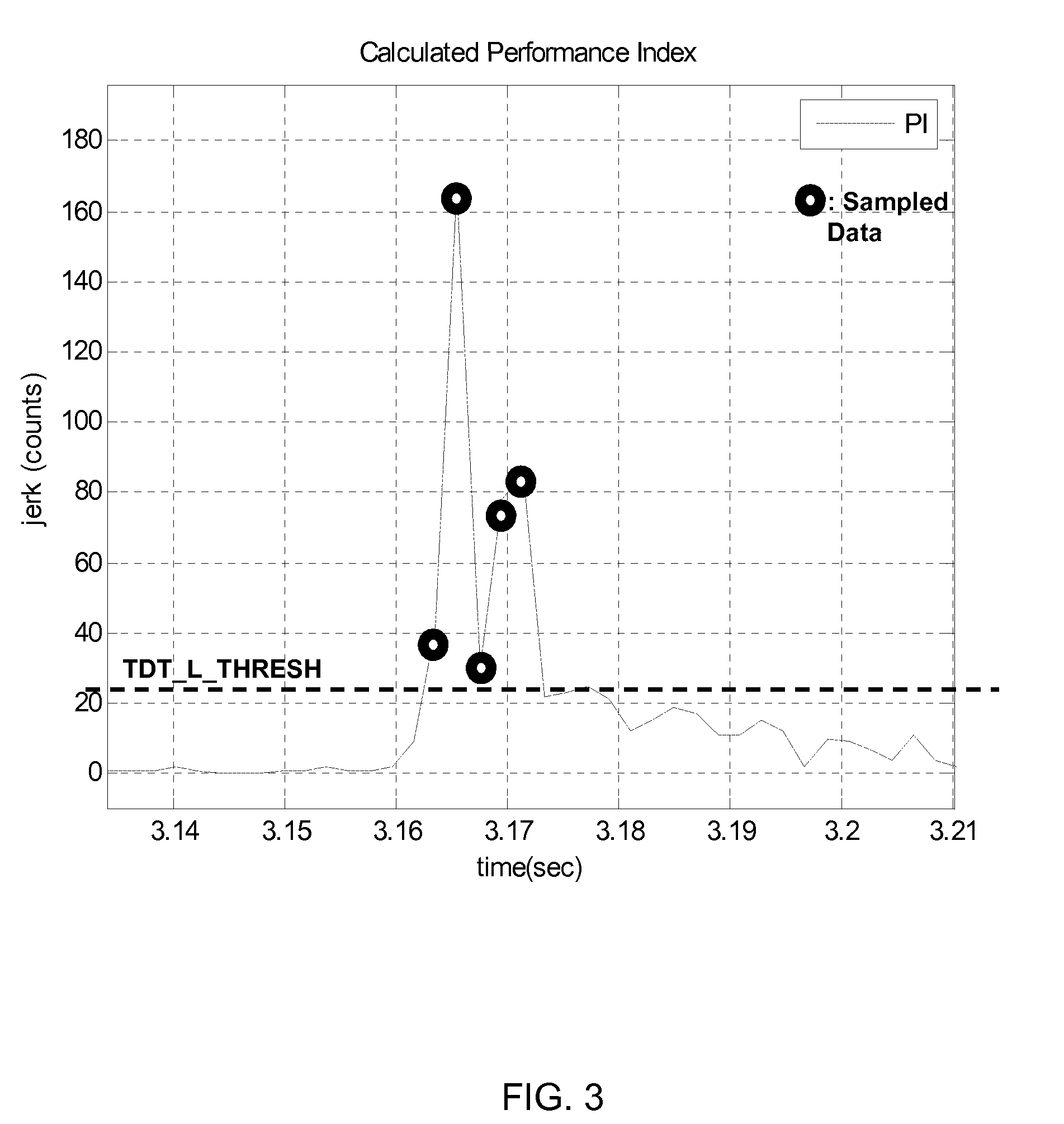
Directional tap detection algorithm using an accelerometer
ActiveUS20100256947A1Increase the number ofForce measurementAcceleration measurementTriaxial accelerometerPerformance index
A directional tap detection algorithm and a single tri-axis accelerometer (10) are employed to extend the number of unique button less input commands available for a small mobile electronic device (12) such as a cell phone or a MP3 player. The algorithm analyzes acceleration data from the tri-axis accelerometer (10) to detect the direction and number of taps imparted to any of the six sides (14) of a housing (13) of the device (12), yielding 12 unique inputs. The algorithm employs a parameter referred to as the performance index (PI) to identify tap induced movements. The PI is determined by calculating the time derivative of each acceleration signal for each axis and then calculating the sum of the absolute values of the calculated acceleration derivatives. A tap is determined to have occurred if the sum exceeds a threshold value for a predetermined amount of time. If a second tap is detected within a predetermined time after the first tap, then a double tap is determined to have occurred.
Owner:KIONIX CORP
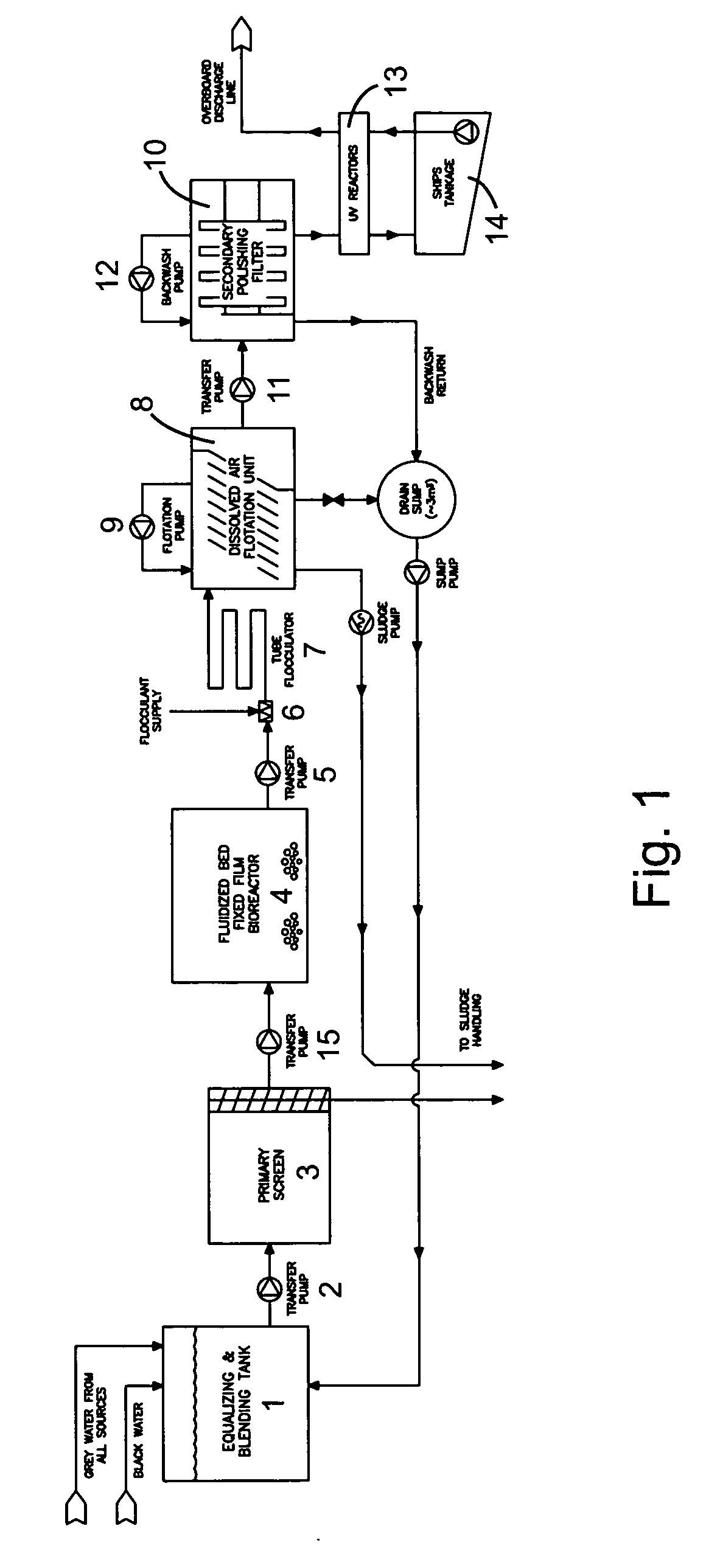
Wastewater treatment system for a marine vessel
InactiveUS20070114182A1Reduce movementAvoid erratic movementTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment involving filtrationCompound (substance)Membrane bioreactor
A wastewater treatment system for use on a marine vessel comprising an aerobic fixed film biological reactor, a tubular flocculator and a dissolved air flotation (DAF) unit. The process units desirably include means for reducing erratic movement of the wastewater due to sea-induced movement of the marine vessel. The DAF unit includes a plurality of inclined baffles arranged to create a plurality of parallel inverted U-shaped flow paths that effect combined co-current and counter-current flotation separation while reducing erratic movement of the wastewater. The selection of process units and operating conditions advantageously reduces the footprint of the wastewater treatment system and reduces cost and complexity associated with the handling of wastewater treatment chemicals.
Owner:HYDROXYL SYST
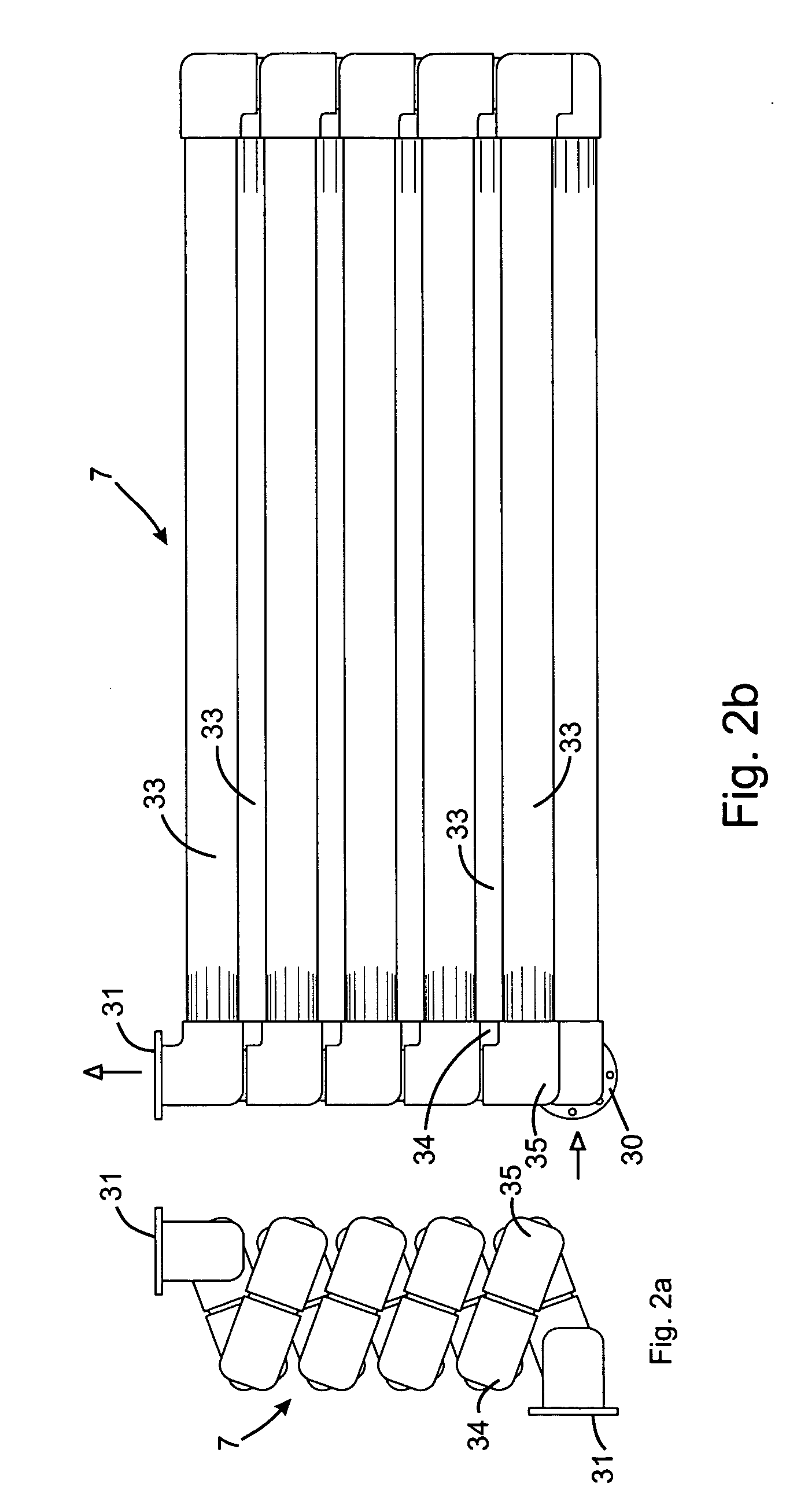
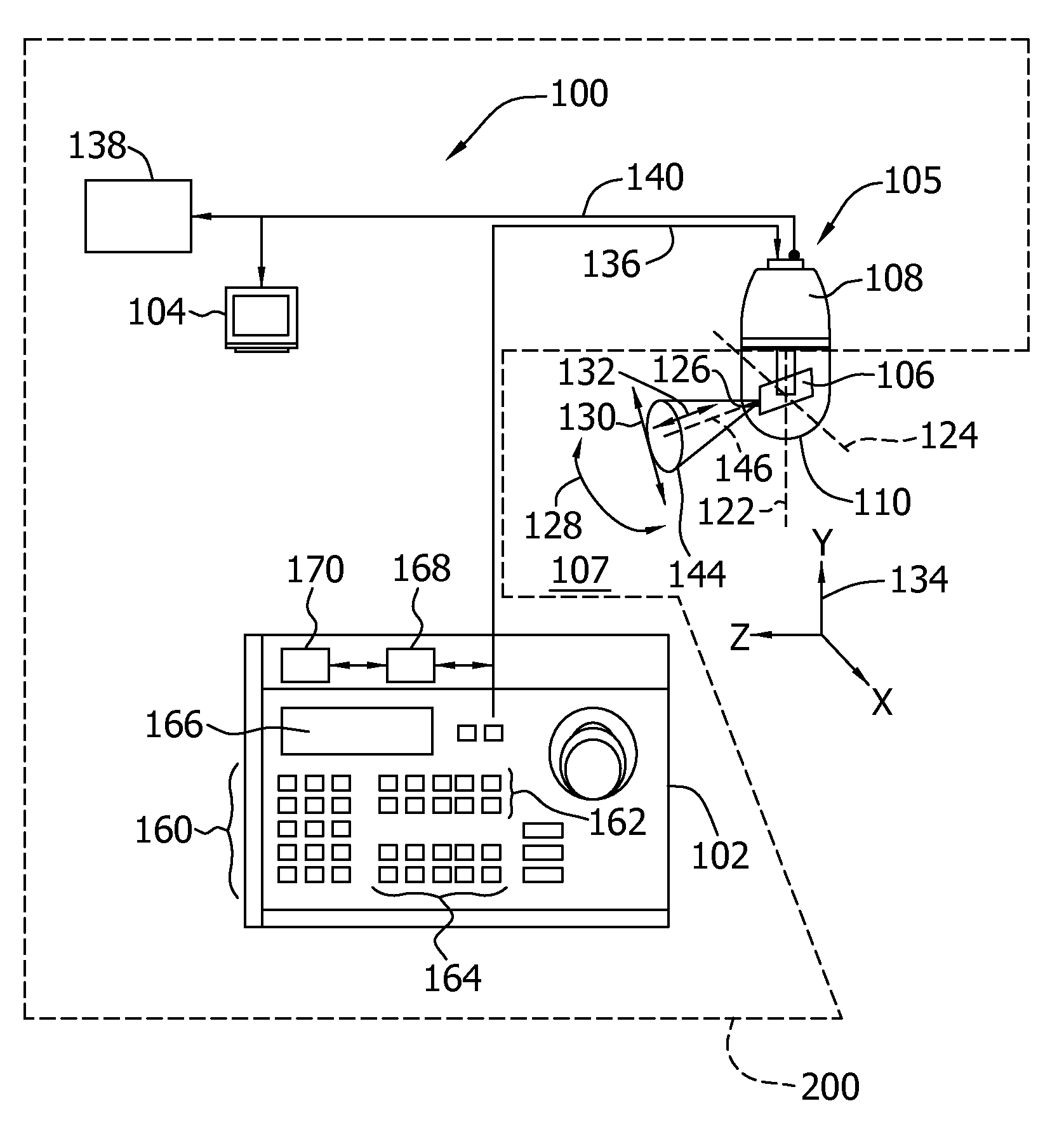
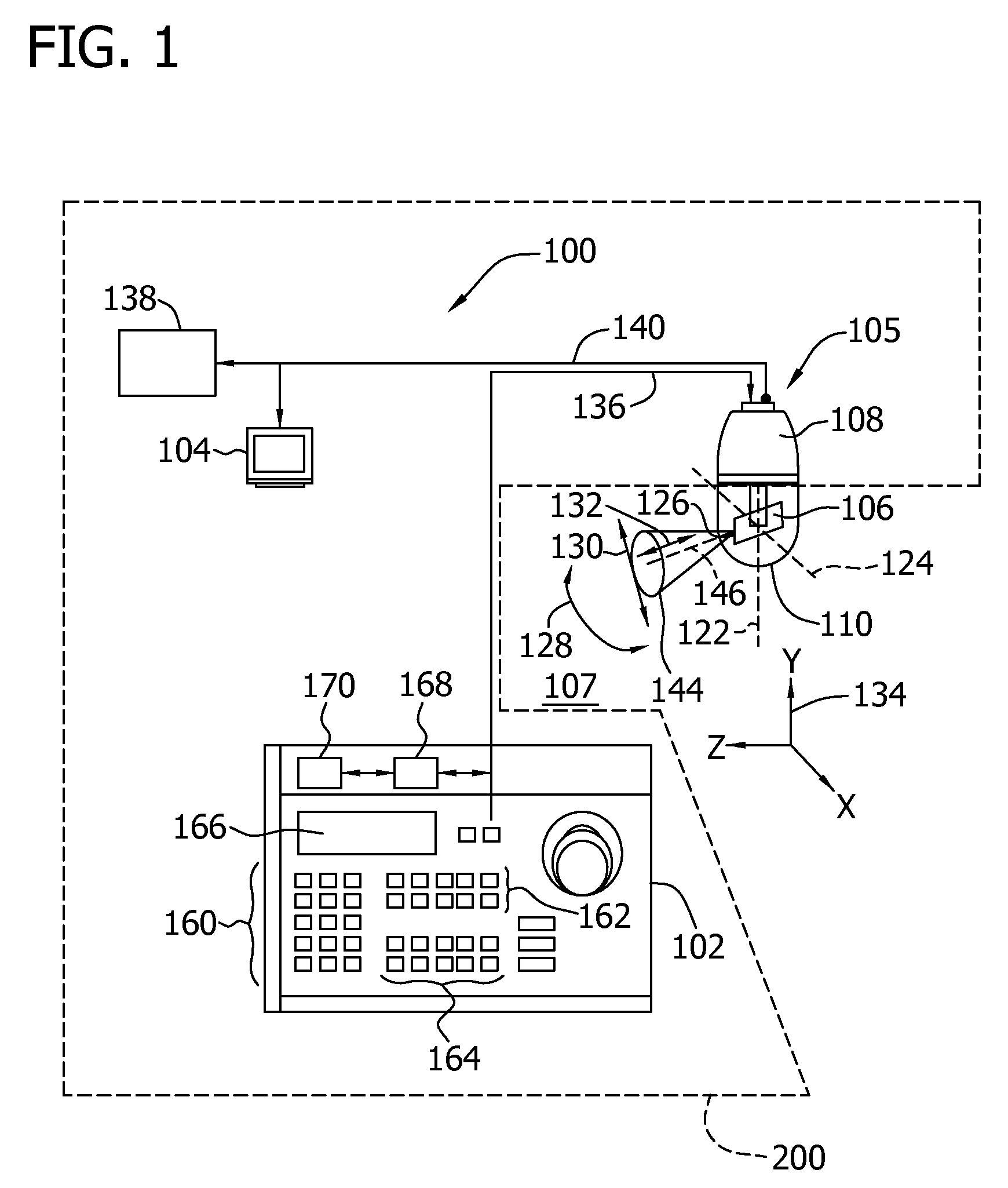
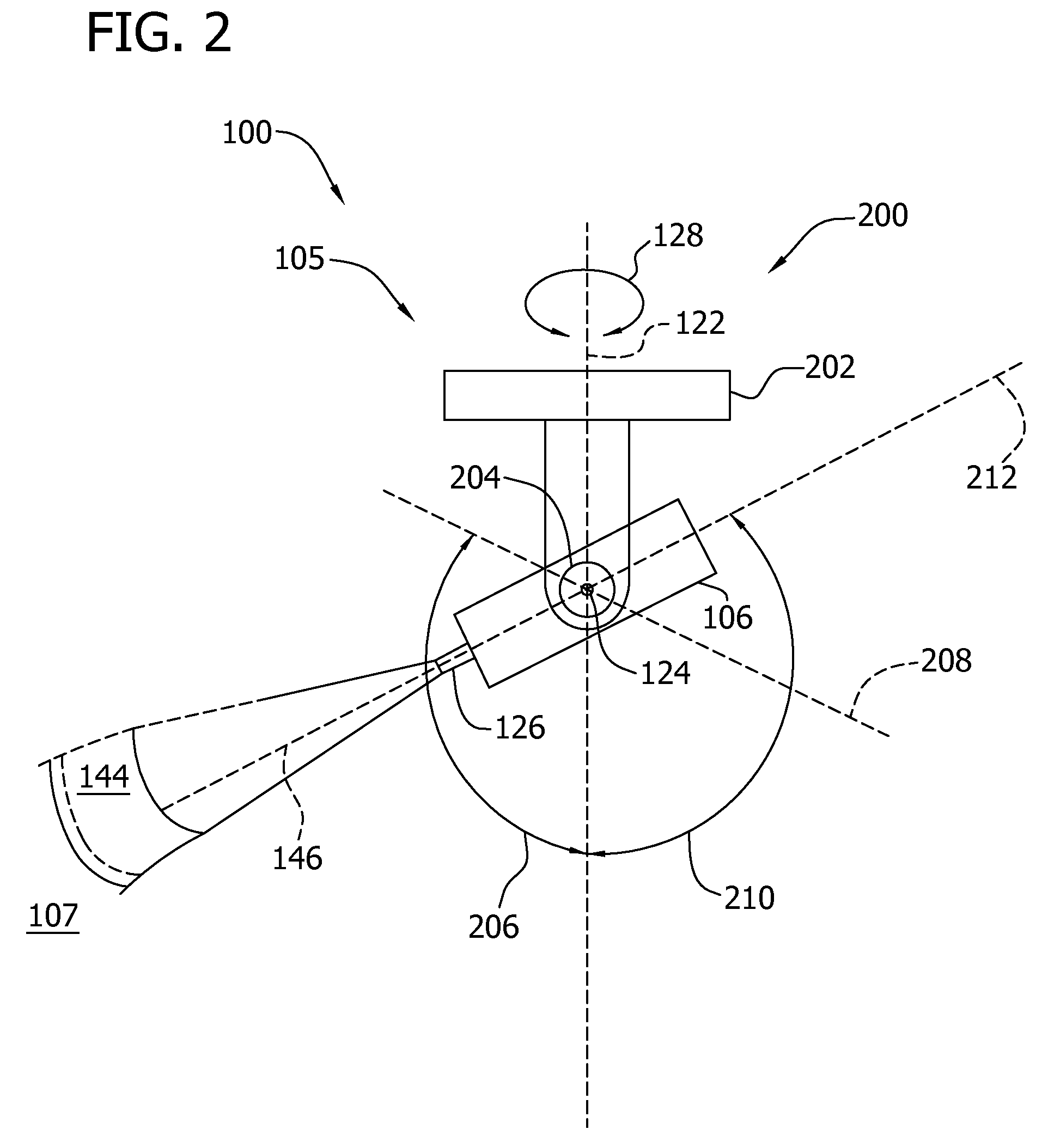
Surveillance system and method for operating same
ActiveUS20110149072A1Facilitates discriminationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMonitoring systemControl area
A method for operating a surveillance system includes performing a first portion of an automated visual surveillance tour of a predetermined control area by inducing movement of at least one visual surveillance camera at a first camera tour speed. The method also includes recording at least one first video image frame of the predetermined control area. The method further includes recording at least one second video image frame of the predetermined control area. The method also includes automatically determining whether a region of interest exists within the predetermined control area. The method further includes performing a second portion of the automated visual surveillance tour by shifting the induced movement of the at least one visual surveillance camera to a second camera tour speed. The method also includes automatically dwelling on the region of interest.
Owner:UTC FIRE & SECURITY AMERICAS CORPORATION INC
Single force strut for dual sided cargo box
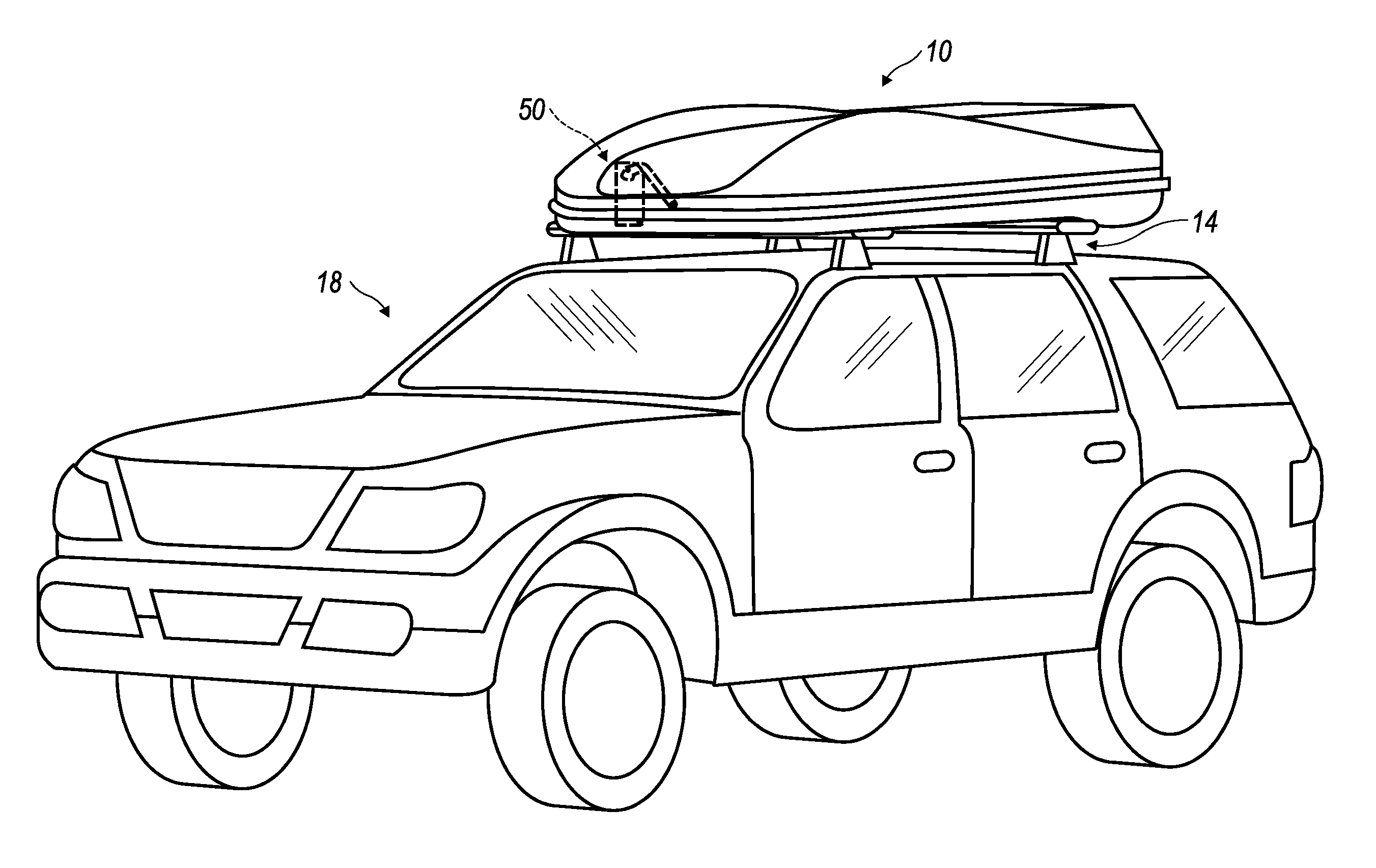
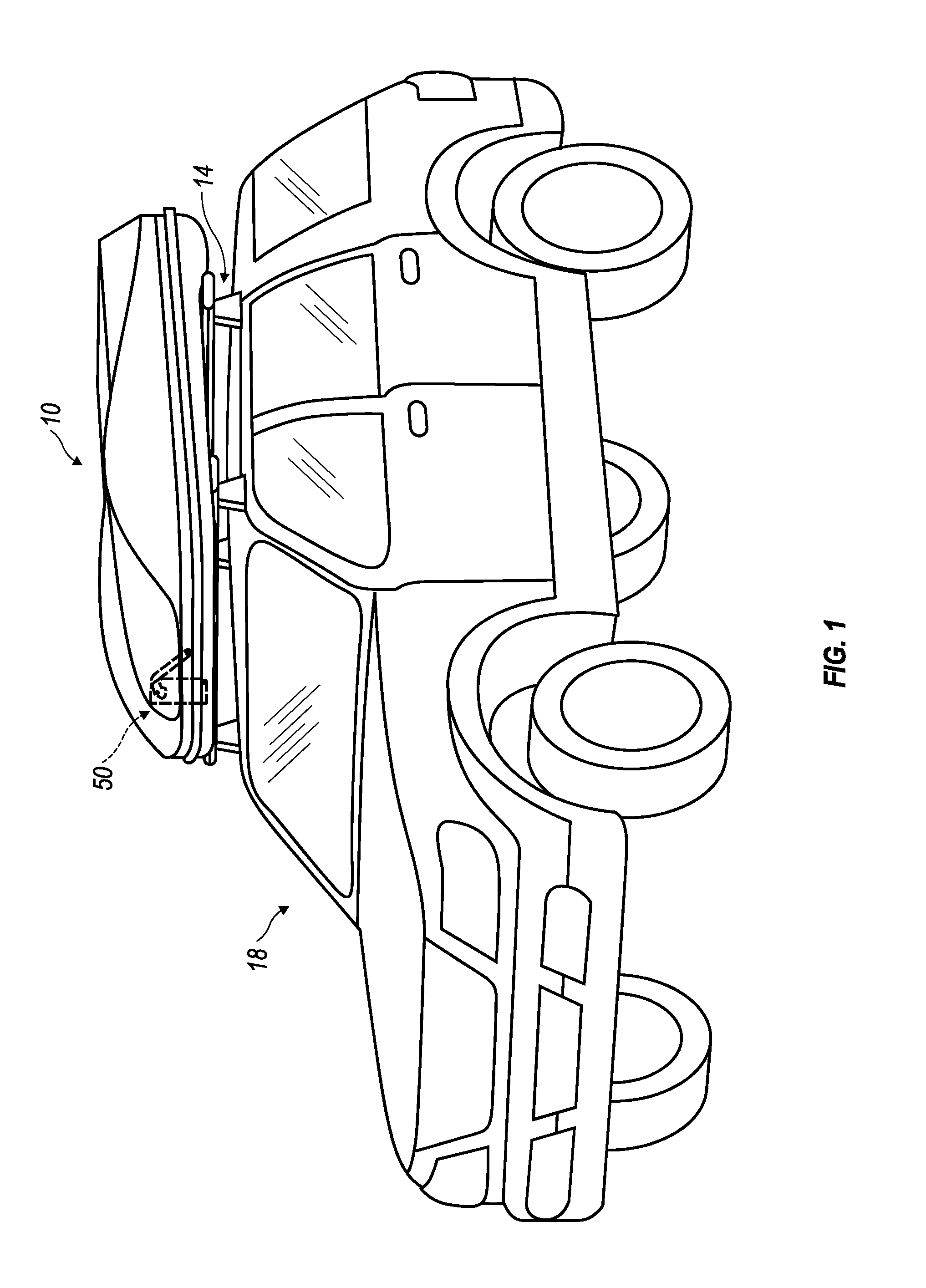
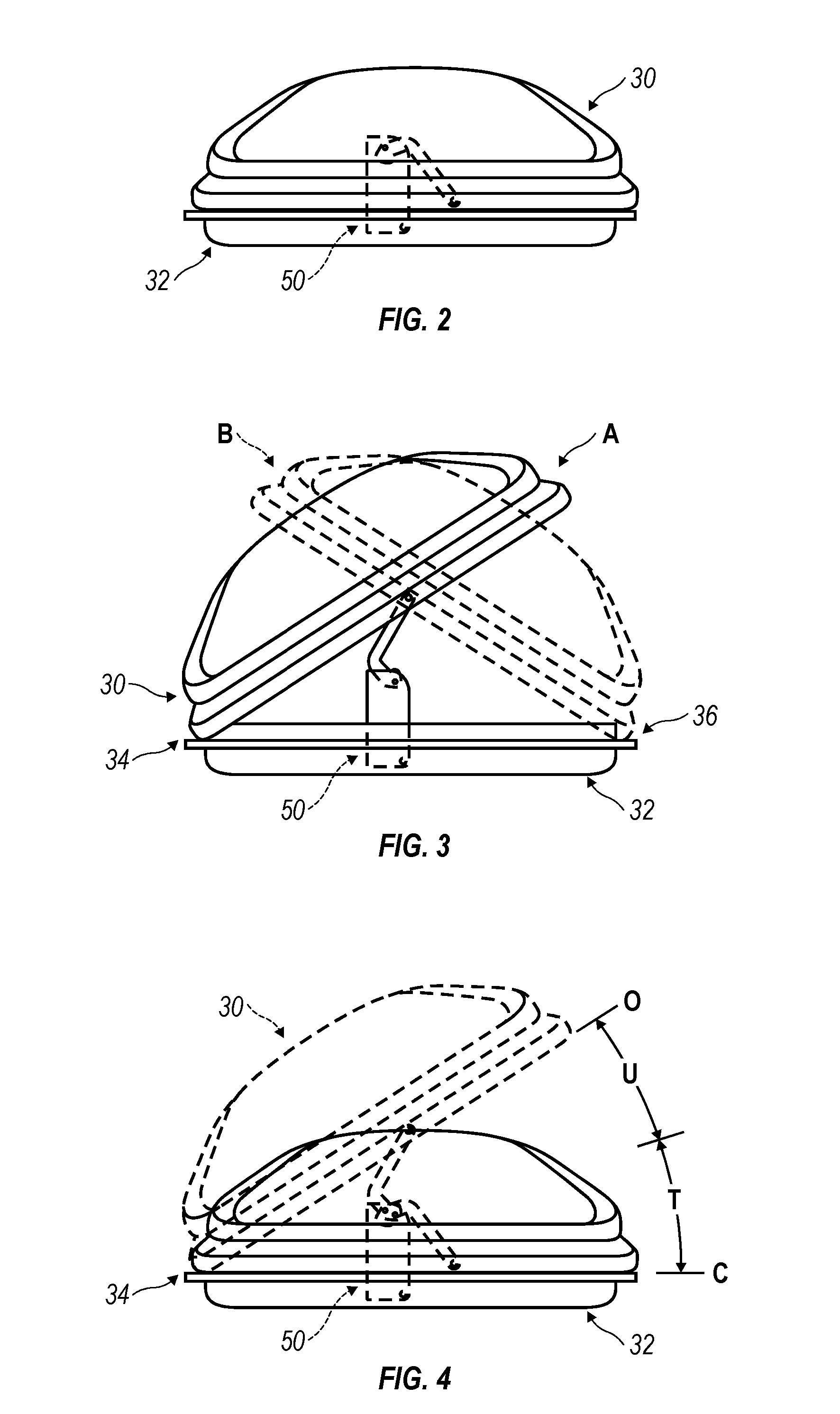
ActiveUS20050145639A1Open smoothlyWing fastenersSupplementary fittingsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Method and arrangement for providing and controlling operation of a dual sided opening roof mount cargo box (10) for a carrying vehicle. A dual sided opening roof mount cargo box (10) is provided and which has a lid portion (30) releasably hinge-connected at two lateral sides to a bottom portion (32) of the cargo box (10) for alternate pivotation at each of the two lateral sides between open and closed configurations. The bottom portion (32) is adapted to be mounted to a carrying vehicle and the lid portion (30) is manufactured from a semi-flexible material sufficiently pliable to permit two opposite end regions thereof to be at different relative distances from the bottom portion (32) of the cargo box (1) during transition between the open and closed configurations. A pair of spring-biased struts (50) are also provided, each operatively interposed between the lid portion (30) and the bottom portion (32) of the cargo box (10), and one each of the pair of spring-biased struts (50) being located at the two opposite end regions of the cargo box. An expansively directed force is imposed on the lid portion (30), utilizing the pair of spring-biased struts (50), across a substantial entirety of travel of the lid portion (30) during operator induced movement from the closed configuration to the open configuration and thereby assisting the operator to smoothly open the cargo box (10).
Owner:THULE SWEDEN AB
Method and system for compensating thermally induced motion of probe cards
InactiveUS6972578B2Motion compensationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingTemperature controlProbe card
The present invention discloses a method and system compensating for thermally induced motion of probe cards used in testing die on a wafer. A probe card incorporating temperature control devices to maintain a uniform temperature throughout the thickness of the probe card is disclosed. A probe card incorporating bi-material stiffening elements which respond to changes in temperature in such a way as to counteract thermally induced motion of the probe card is disclosed including rolling elements, slots and lubrication. Various means for allowing radial expansion of a probe card to prevent thermally induced motion of the probe card are also disclosed. A method for detecting thermally induced movement of the probe card and moving the wafer to compensate is also disclosed.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Forced ion migration for chalcogenide phase change memory device
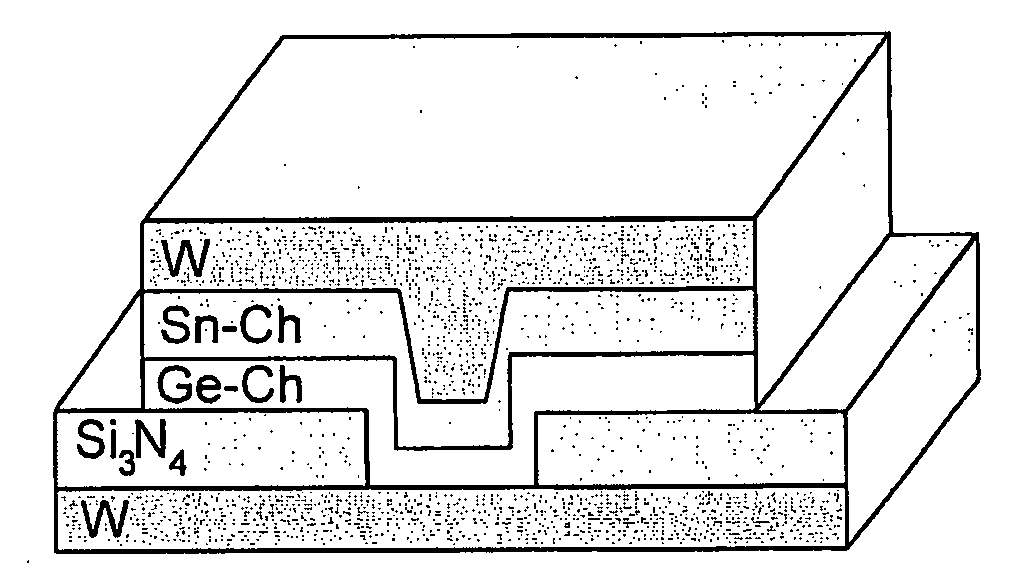
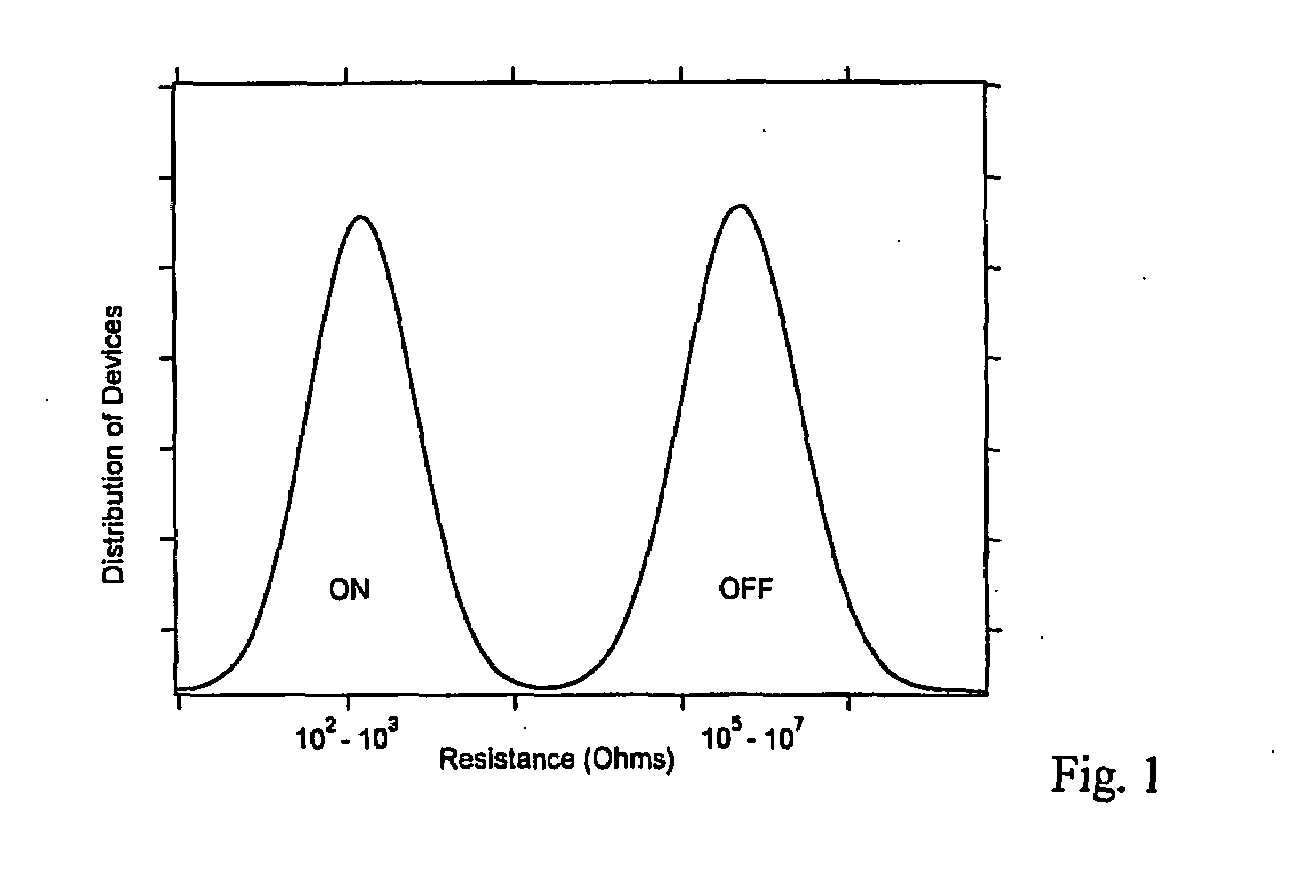
ActiveUS20080121859A1Improve adhesionAvoid layeringNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryElectron
Non-volatile memory devices with two stacked layers of chalcogenide materials comprising the active memory device have been investigated for their potential as phase change memories. The devices tested included GeTe / SnTe, Ge2Se3 / SnTe, and Ge2Se3 / SnSe stacks. All devices exhibited resistance switching behavior. The polarity of the applied voltage with respect to the SnTe or SnSe layer was critical to the memory switching properties, due to the electric field induced movement of either Sn or Te into the Ge-chalcogenide layer. One embodiment of the invention is a device comprising a stack of chalcogenide-containing layers which exhibit phase change switching only after a reverse polarity voltage potential is applied across the stack causing ion movement into an adjacent layer and thus “activating” the device to act as a phase change random access memory device or a reconfigurable electronics device when the applied voltage potential is returned to the normal polarity. Another embodiment of the invention is a device that is capable of exhibiting more that two data states.
Owner:BOISE STATE UNIVERSITY
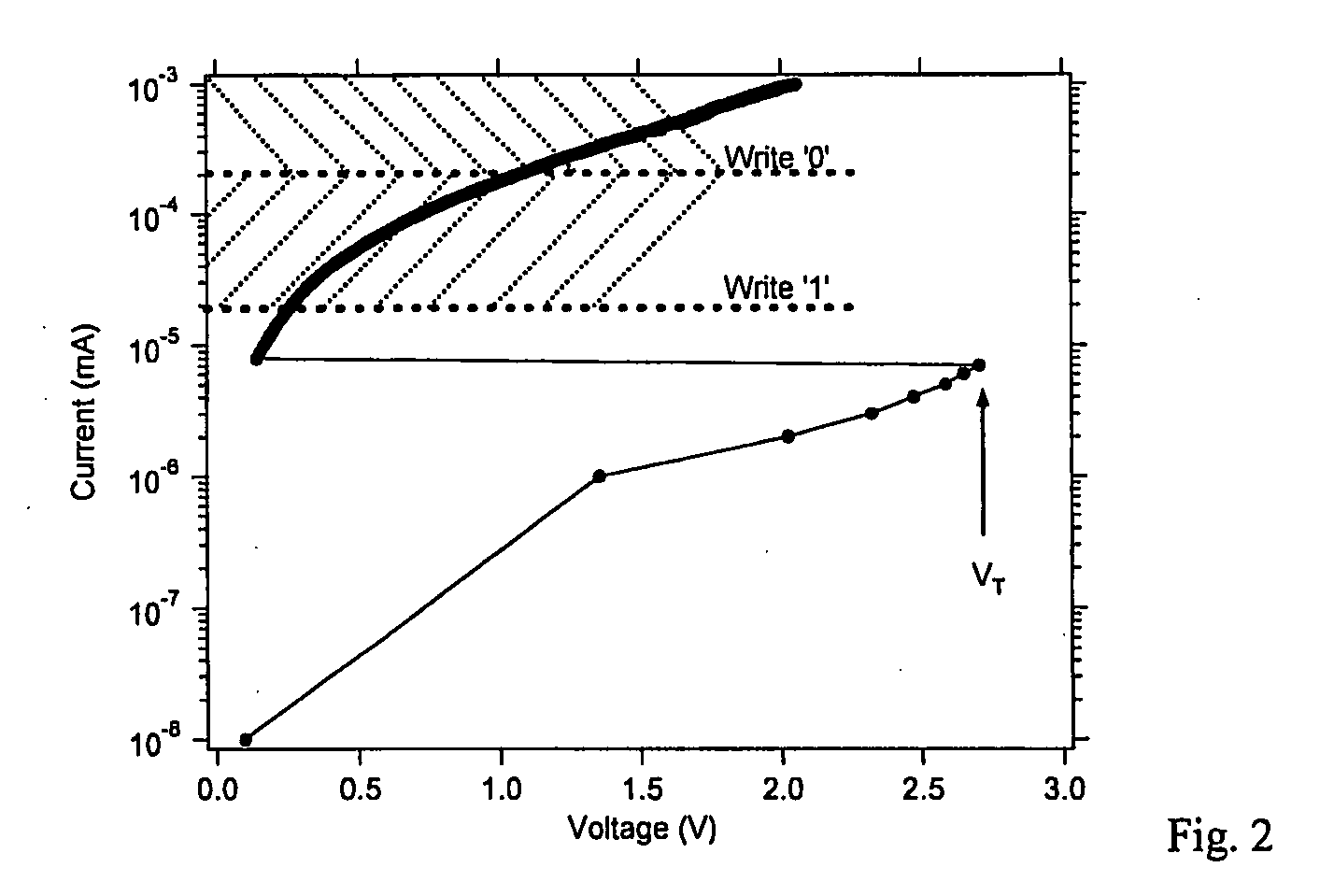
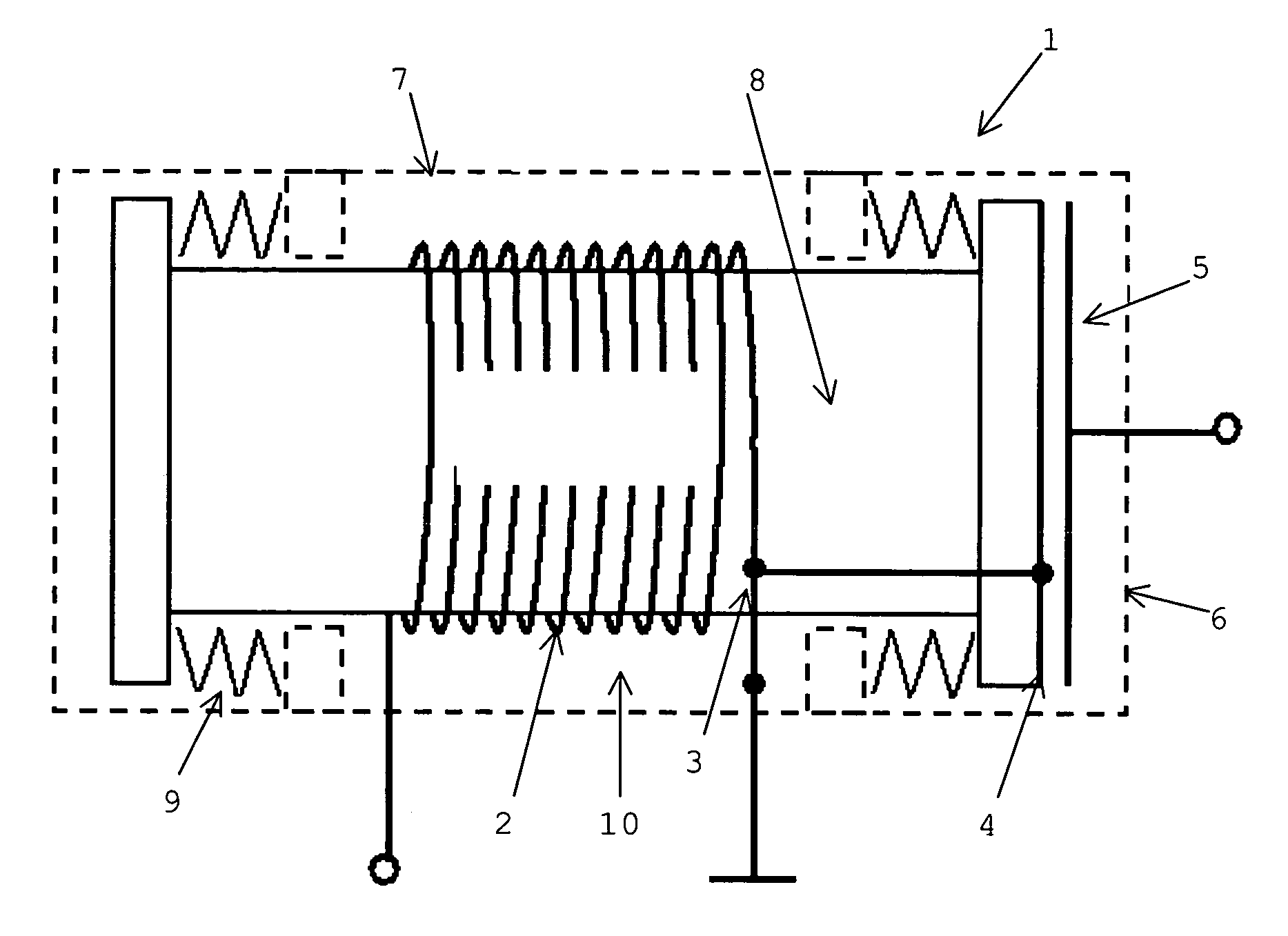
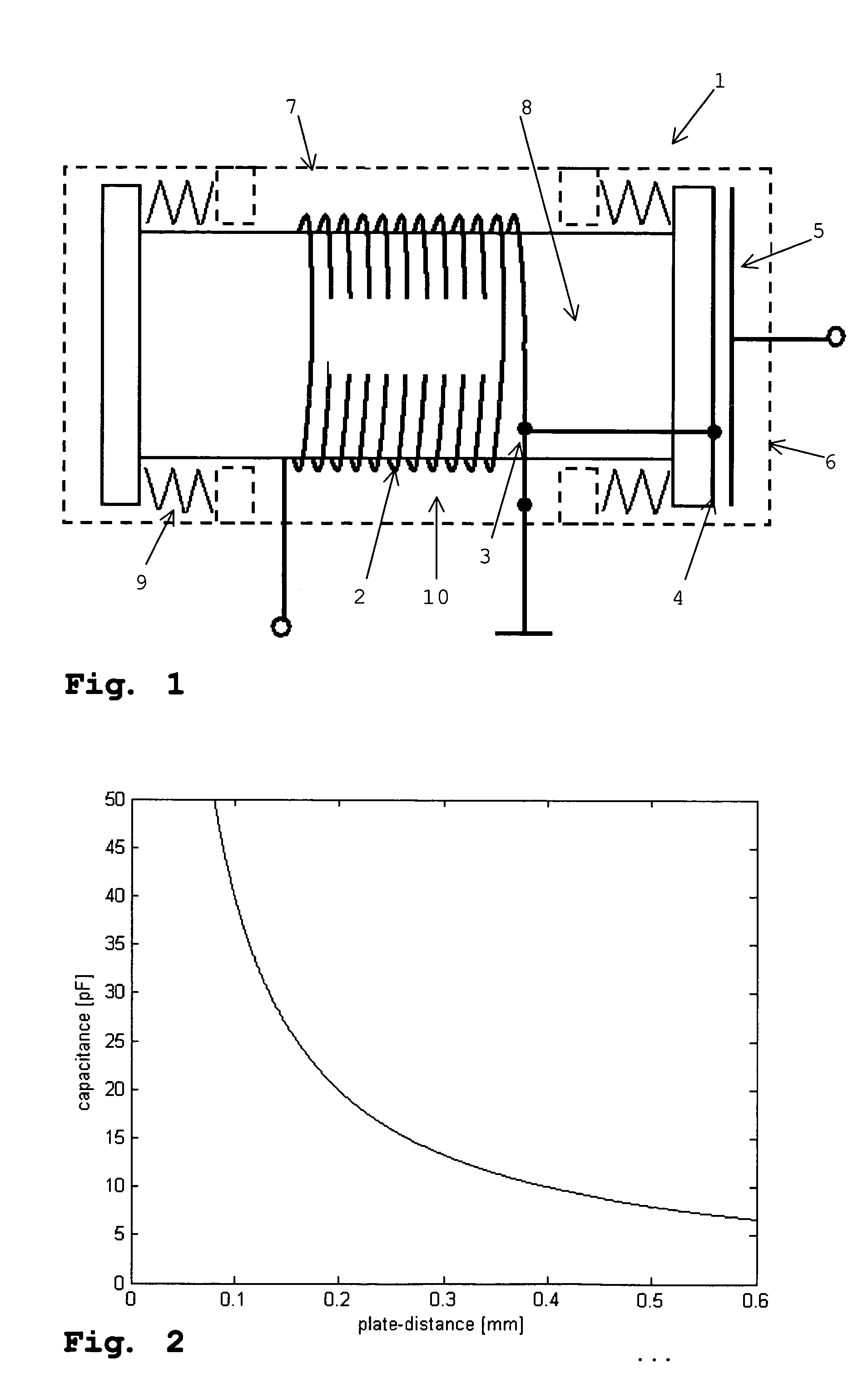
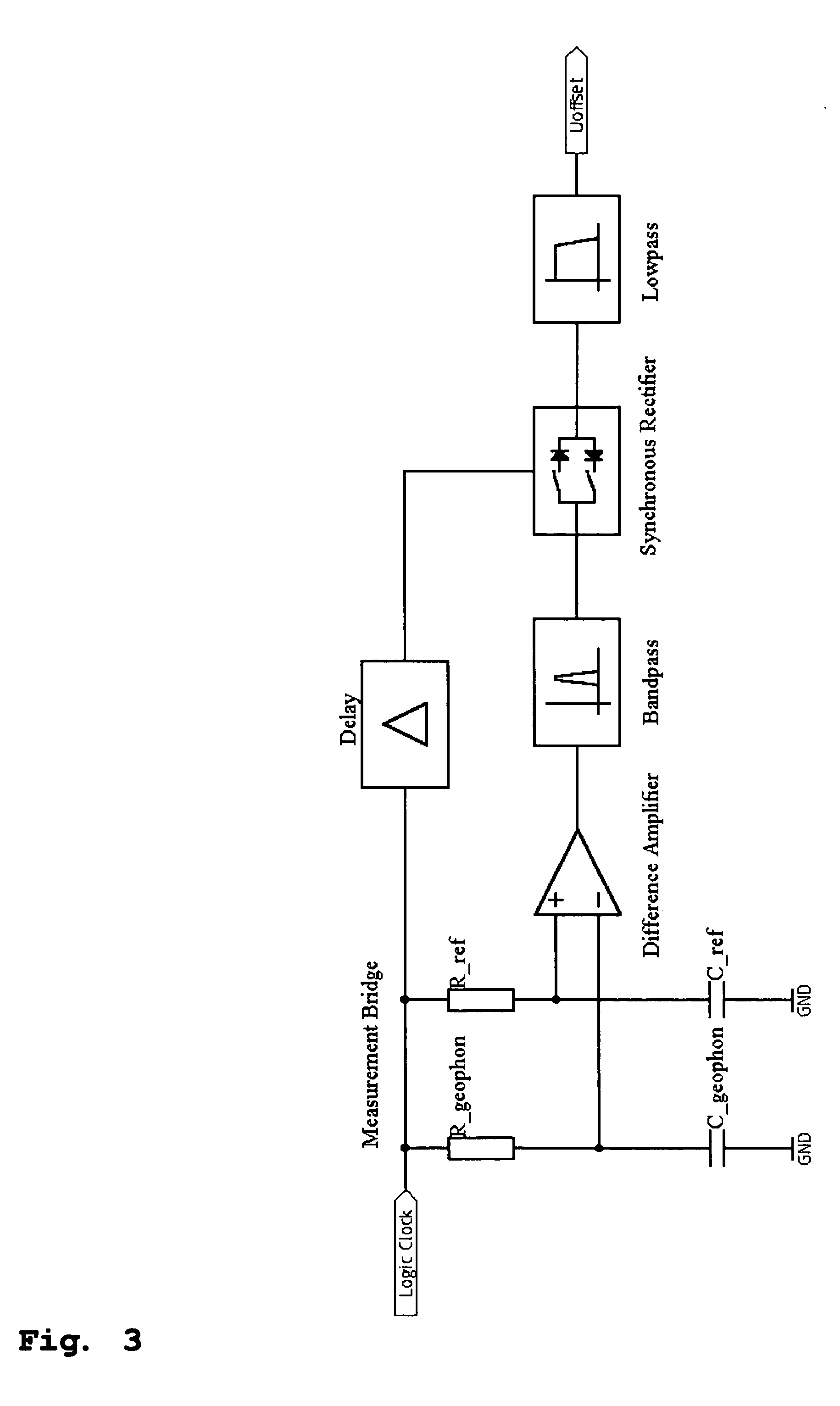
Method and apparatus for the acquisition of seismic movements
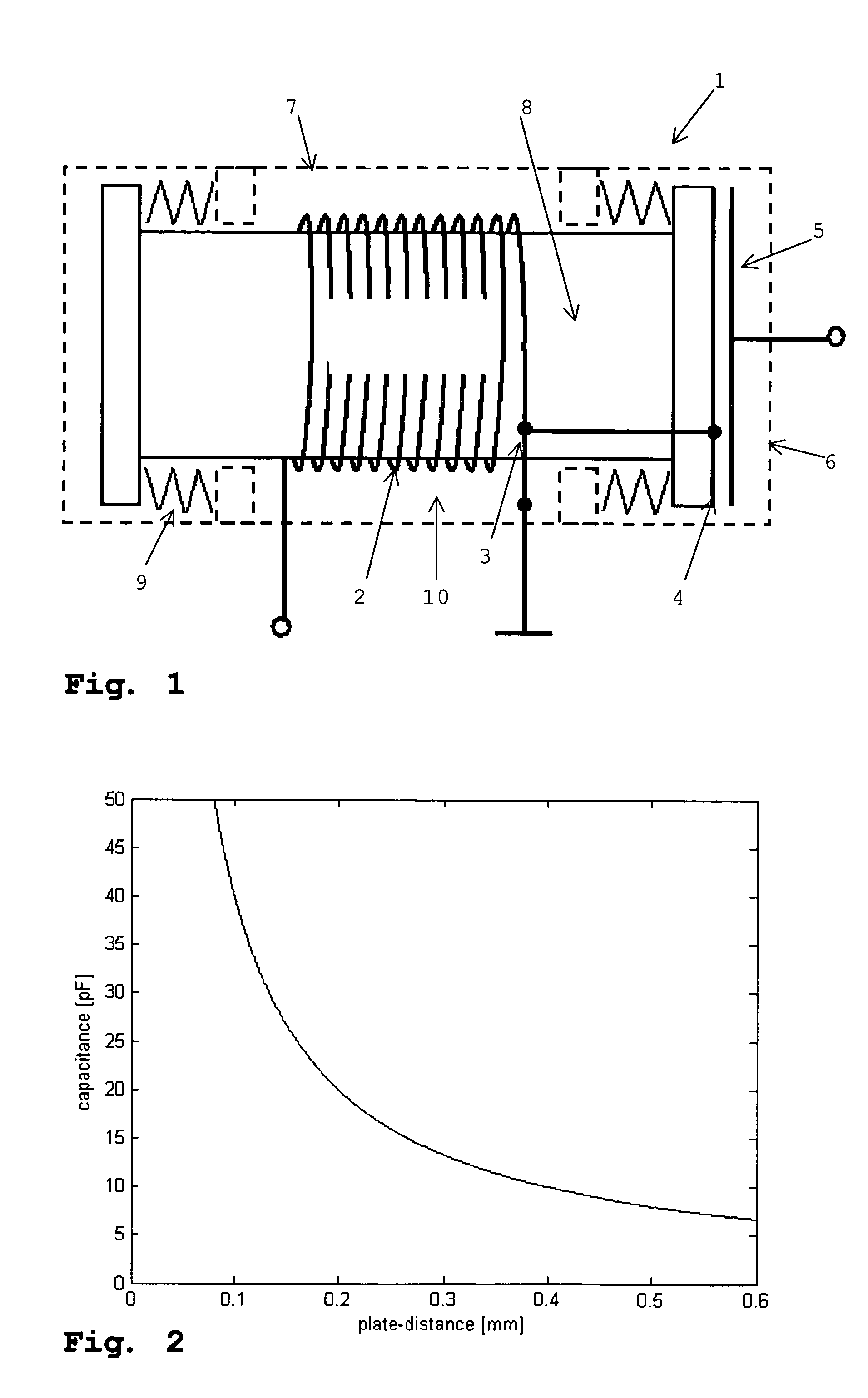
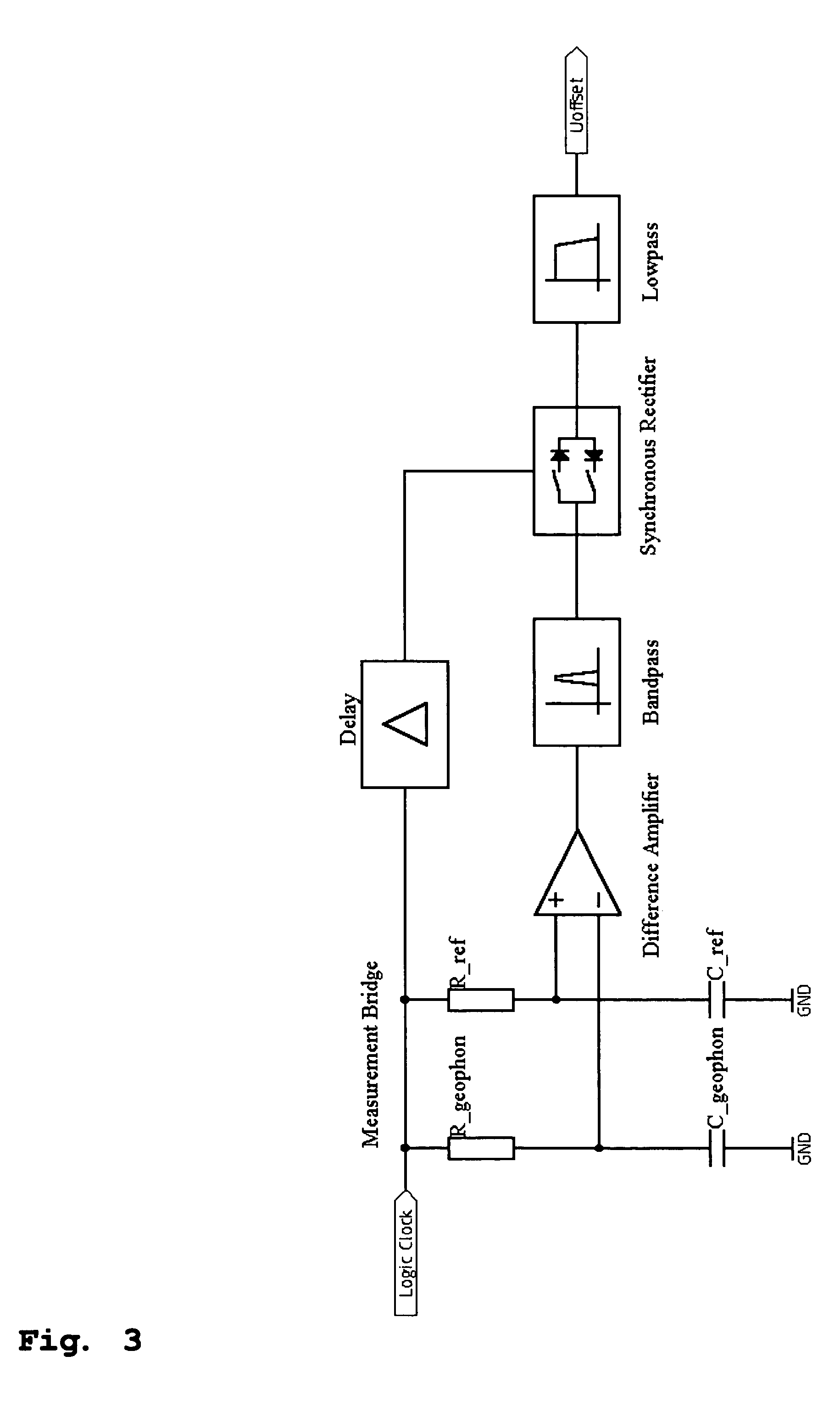
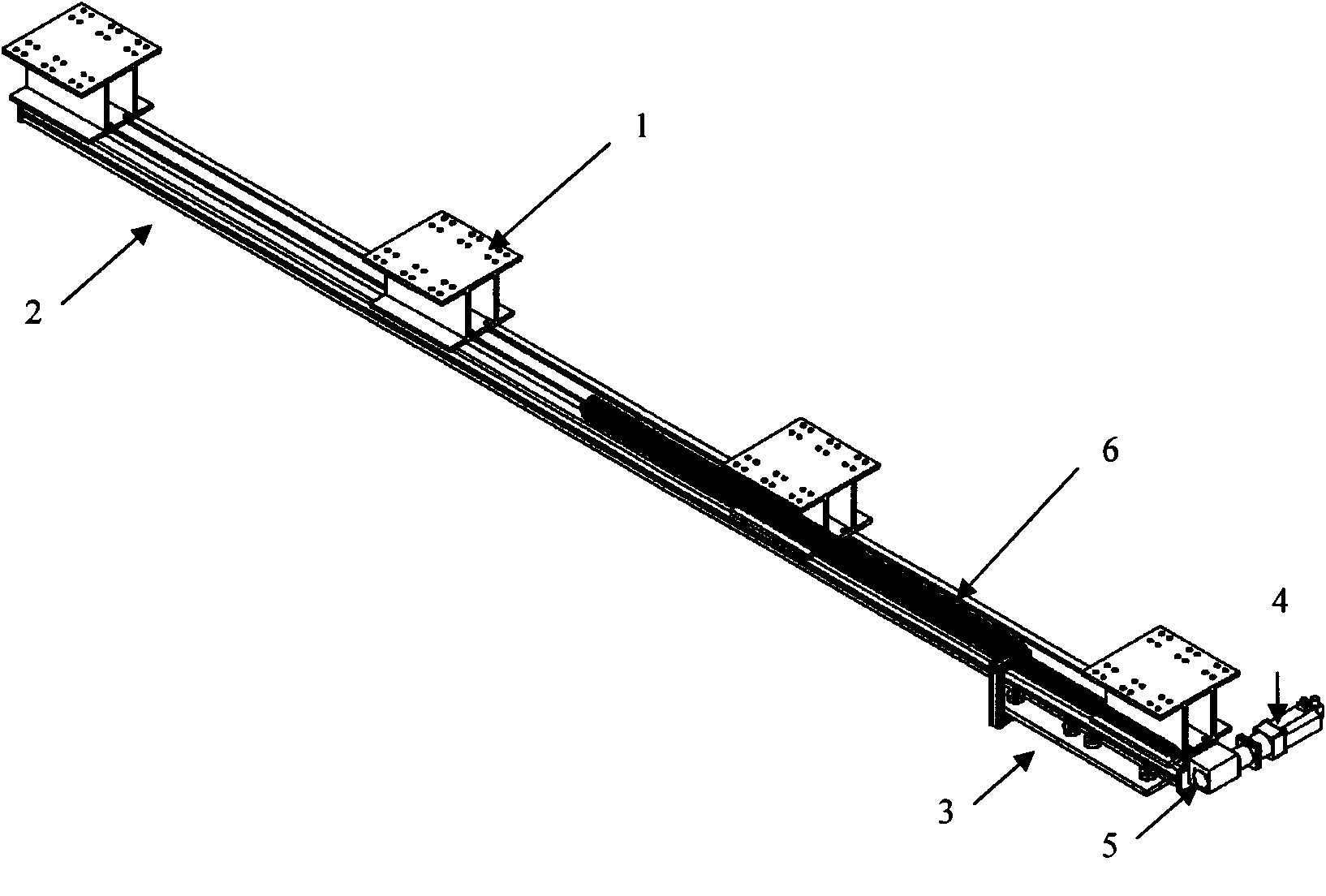
InactiveUS20050068851A1Avoid distortionPrecise and small detectionElectrical transducersSeismic signal receiversClosed loopAcoustics
The method and the apparatus disclosed serve to acquire seismic induced movements. A coil and a permanent magnet are contained in an enclosure and the seismic movements induce a relative movement between said coil and said magnet. The current induced into the coil is appraised as a measure of said seismic movement. The position of the coil in relation to the permanent magnet is monitored by a position sensor. A closed loop control generates a current that is fed into the coil so that the coil settles at a given neutral position relative to the permanent magnet.
Owner:SCHLEISIEK KLAUS +1
Wall-ceiling slip joint permitting seismic induced movement
Owner:KRUEGER INT INC
Method and system for compensating for thermally induced motion of probe cards
InactiveUS7071714B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingTemperature controlProbe card
The present invention discloses a method and system compensating for thermally induced motion of probe cards used in testing die on a wafer. A probe card incorporating temperature control devices to maintain a uniform temperature throughout the thickness of the probe card is disclosed. A probe card incorporating bi-material stiffening elements which respond to changes in temperature in such a way as to counteract thermally induced motion of the probe card is disclosed including rolling elements, slots and lubrication. Various means for allowing radial expansion of a probe card to prevent thermally induced motion of the probe card are also disclosed. A method for detecting thermally induced movement of the probe card and moving the wafer to compensate is also disclosed.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Directional tap detection algorithm using an accelerometer
ActiveUS8442797B2Increase the number ofForce measurementAcceleration measurementTriaxial accelerometerPerformance index
A directional tap detection algorithm and a single tri-axis accelerometer are employed to extend the number of unique button less input commands available for a small mobile electronic device. The algorithm analyzes acceleration data from the tri-axis accelerometer to detect the direction and number of taps imparted to any of the six sides of a housing of the device, yielding 12 unique inputs. The algorithm employs a parameter referred to as the performance index (PI) to identify tap induced movements. The PI is determined by calculating the time derivative of each acceleration signal for each axis and then calculating the sum of the absolute values of the calculated acceleration derivatives. A tap is determined to have occurred if the sum exceeds a threshold value for a predetermined amount of time. If a second tap is detected within a predetermined time after the first tap, then a double tap is determined to have occurred.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Wave power generator
InactiveUS20120153627A1Improve energy conversion efficiencyImprove practicabilityEngine fuctionsHydro energy generationWave power generationHigh energy
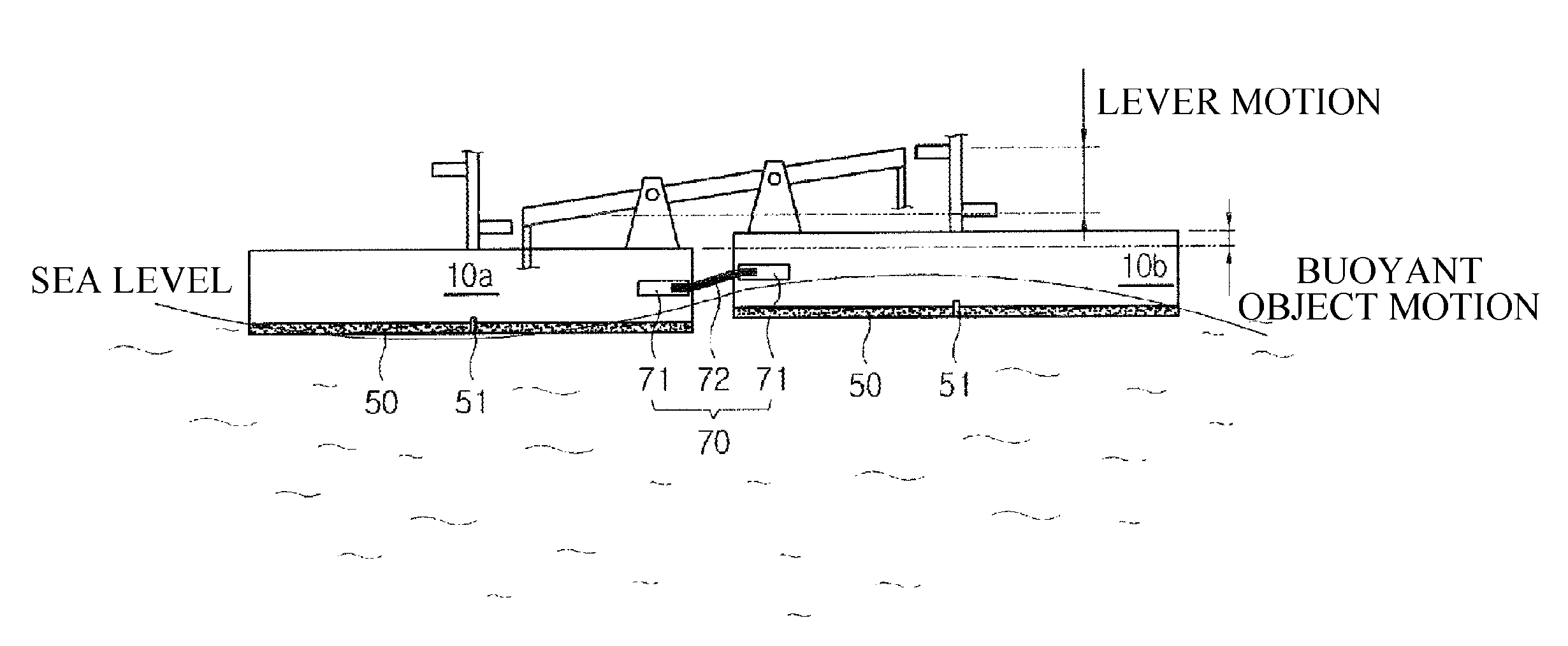
The present invention relates to a wave power generator, and more particularly, to a wave power generator that has comparatively high energy conversion efficiency, so that it can induce active investment and research and development to overcome uncertainties about the natural environment, and which can enhance practicability and value as a clean energy source, especially by virtue of the improved return on investment thereof. For this purpose, the wave power generator of the present invention is characterized in that is comprises: a plurality of rafts arranged on a water surface to move freely with the movement of waves; a plurality of connectors, connecting the plurality of rafts to each other, for performing the conversion of kinetic energy by converting the wave-induced movement of one raft into an amplified lever movement on an adjacent raft; a plurality of generators installed on the plurality of rafts to generate electricity; and an energy-converting unit, connected to the plurality of connectors and to the plurality of generators, for converting the kinetic energy from the plurality of connectors into rotational energy for driving the plurality of generators.
Owner:JO CHANG HUI
Method and apparatus for the acquisition of seismic movements
InactiveUS7406002B2Precise and small detectionAvoid distortionElectrical transducersSeismic signal receiversClosed loopAcoustics
The method and the apparatus disclosed serve to acquire seismic induced movements. A coil and a permanent magnet are contained in an enclosure and the seismic movements induce a relative movement between said coil and said magnet. The current induced into the coil is appraised as a measure of said seismic movement. The position of the coil in relation to the permanent magnet is monitored by a position sensor. A closed loop control generates a current that is fed into the coil so that the coil settles at a given neutral position relative to the permanent magnet.
Owner:SCHLEISIEK KLAUS +1
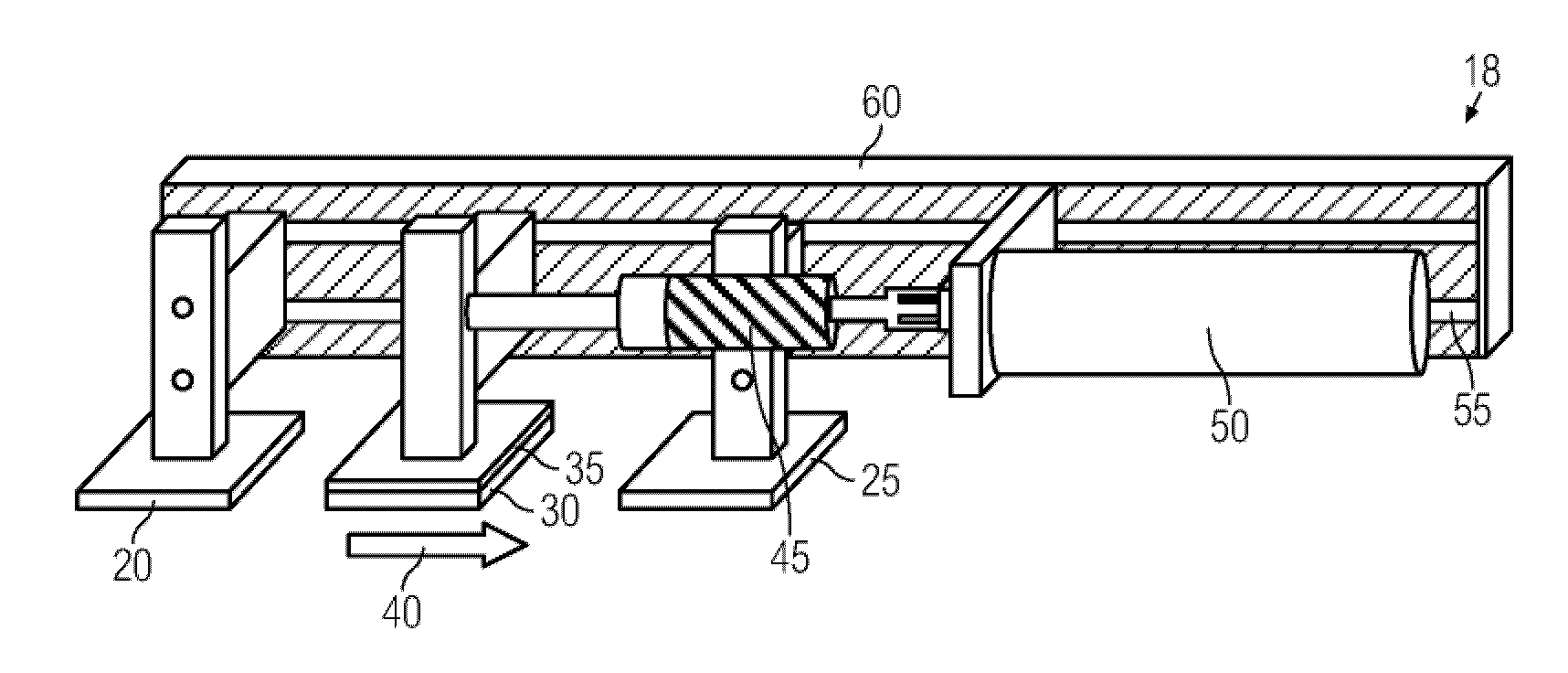
Forced reciprocating movement device of ocean structure
ActiveCN101666703ARealize automatic reciprocating oscillating motionAchieve oscillatory motionHydrodynamic testingSurface oceanReciprocating motion
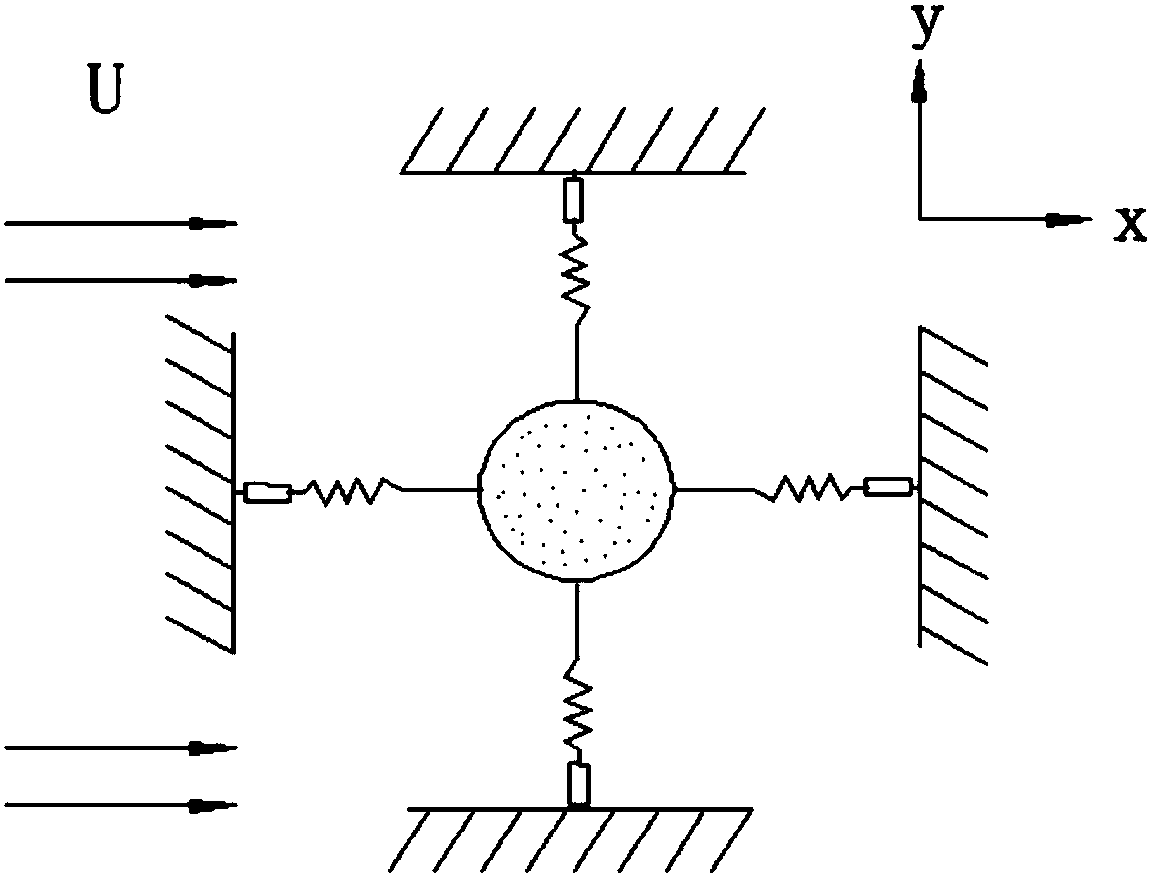
A forced reciprocating movement device of ocean structure in the technical field of ocean engineering includes: a base, a straight track, a sliding block, a driving motor and a speed reducer, whereinthe base is parallelly fixed on the bottom of a trailer, the straight track is fixedly arranged on the lower surface of the base, and the sliding block moves on the straight track by means of pinion and rack and is provided with the driving motor and a planetary speed reducer. The device can fix the ocean structure on the bottom of the sliding block, is driven to do reciprocating movement on the straight track by the driving motor and simulate the phenomena of vortex-induced vibration and vortex-induced movement, and is simple in structure and high in automation degree.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Decorative flag display assembly
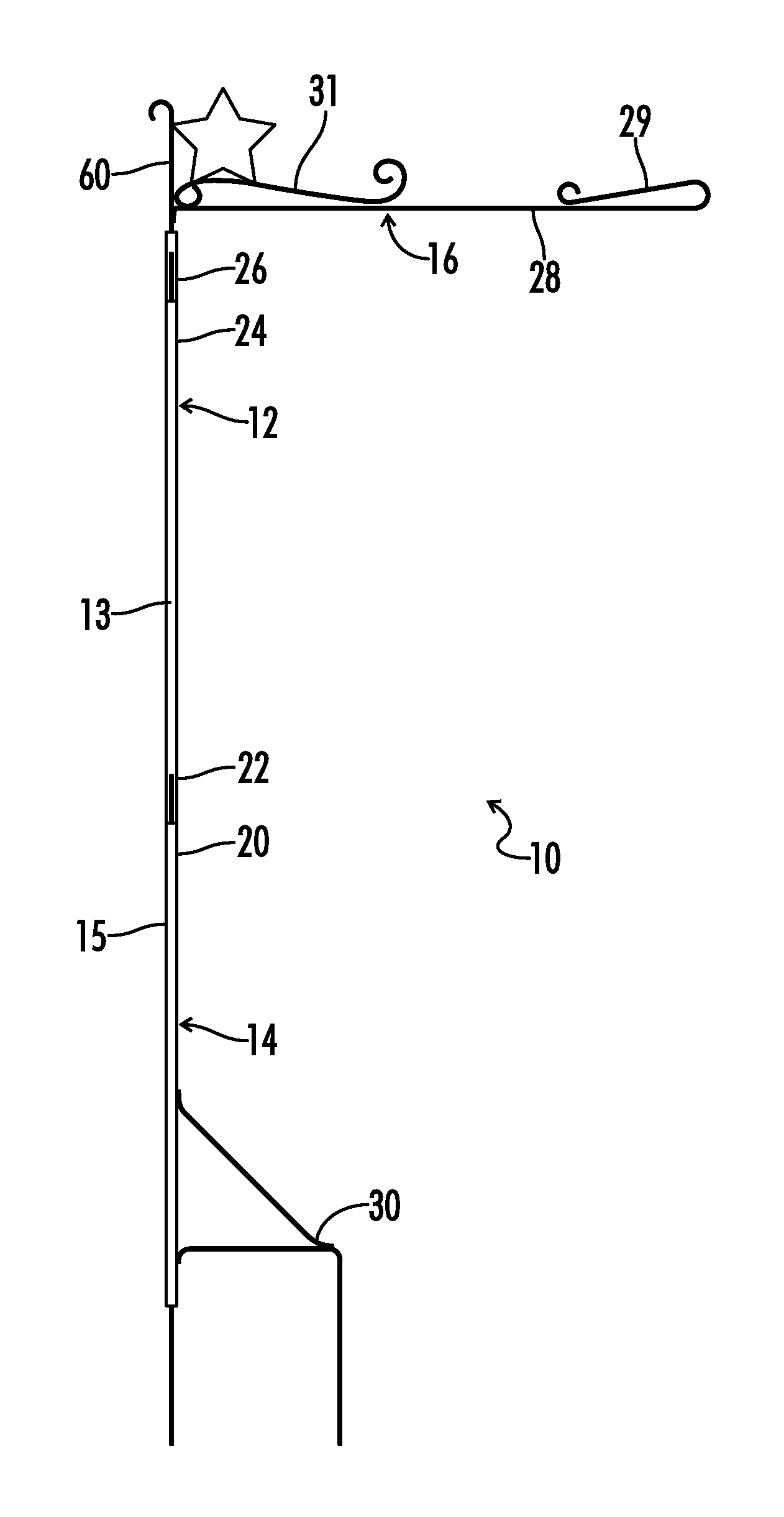
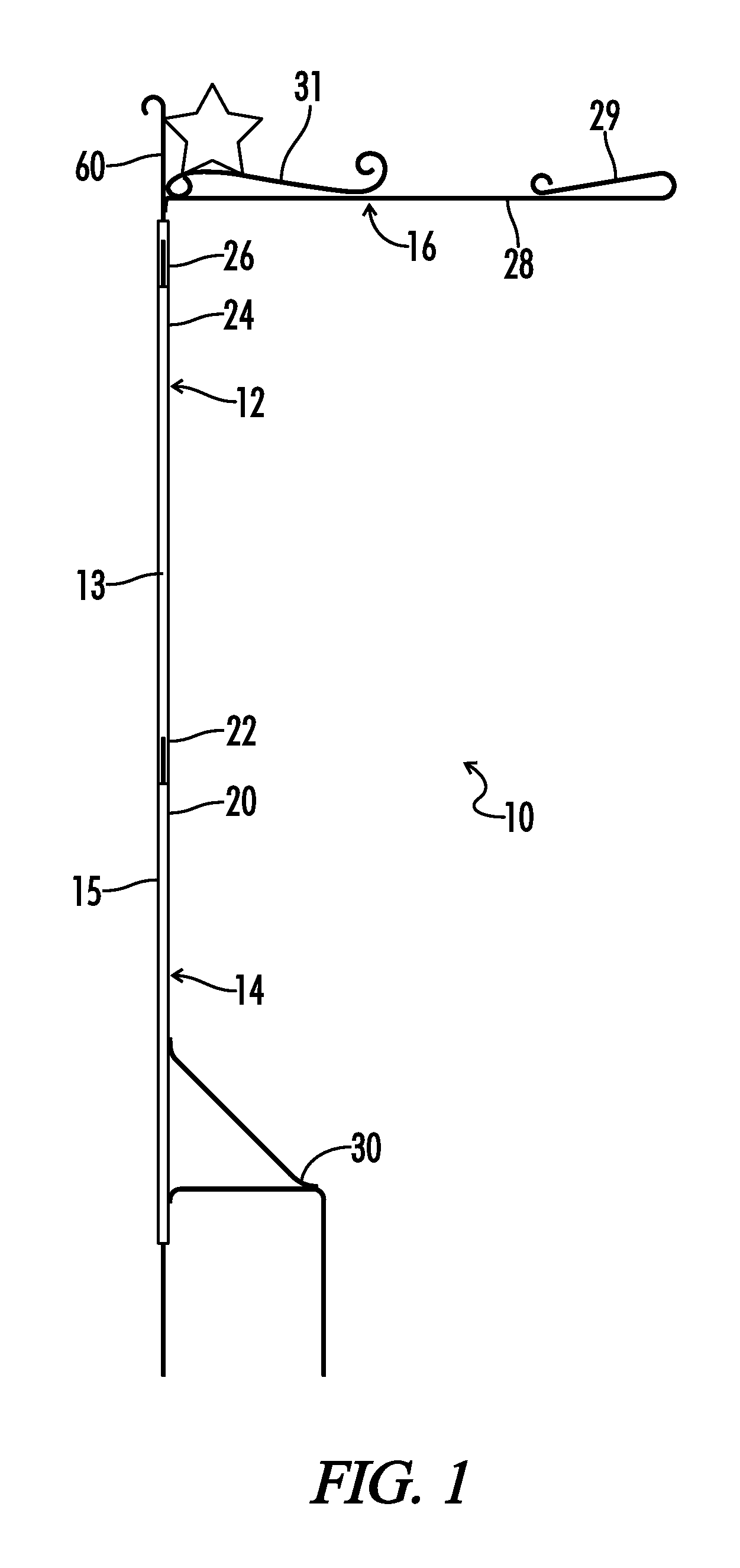
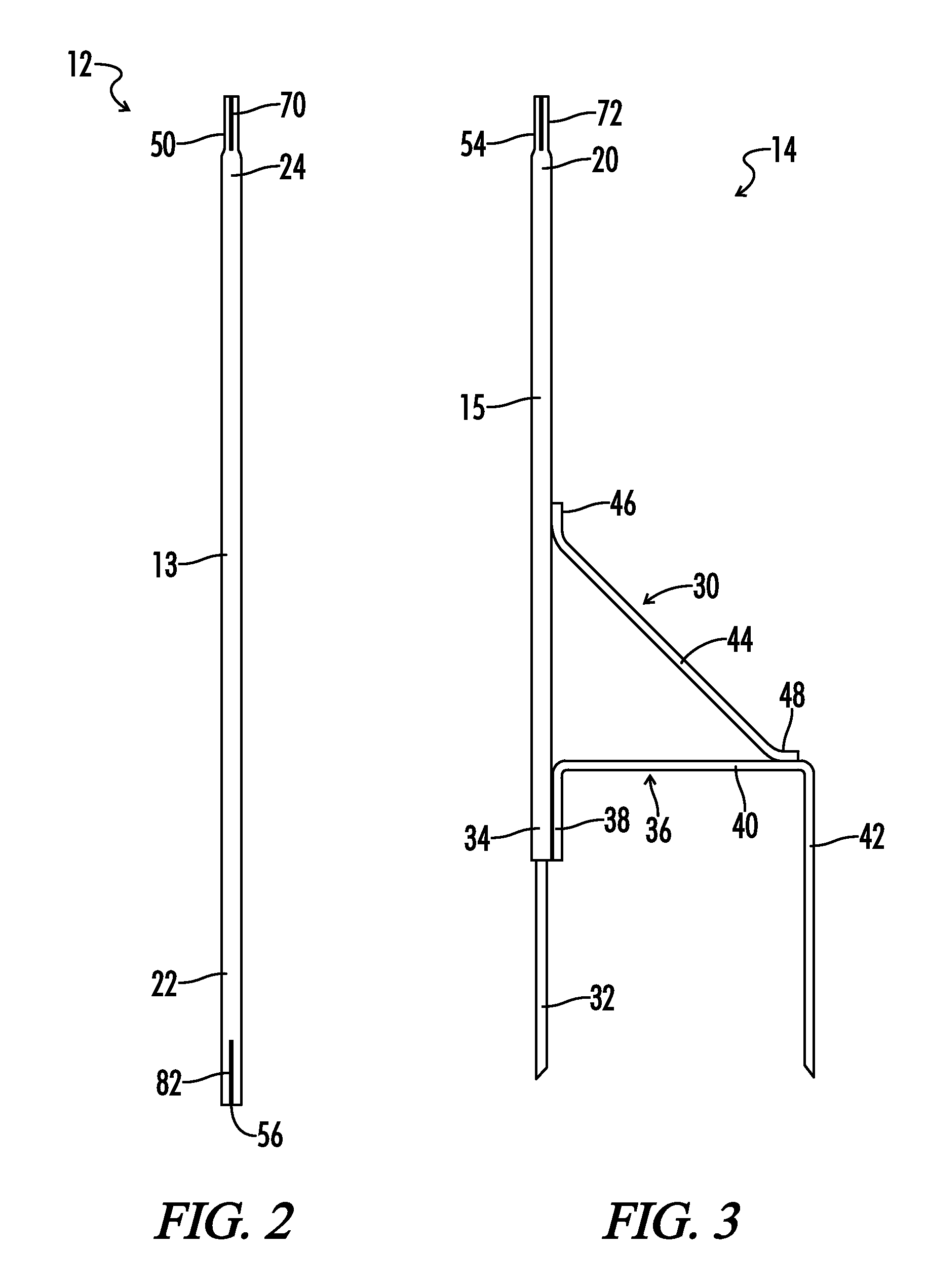
InactiveUS9390640B1Easy and convenient to setEasy and convenient to and retainMachine supportsRod connectionsDisplay deviceEngineering
A large decorative flag mount is formed with a tubular interengaged support construction to provide sufficient stiffness with relative lightness and inhibition of rotation between the tubular support sections by providing a single axial groove pair to the interengaging surfaces of one or more of the tubular sections before interengagement of two sections to inhibit mutual rotation and wherein the invention is useful in preventing undesirable relative rotational wind induced movement between the tubular sections resulting in incorrect orientation of a flag display, and also including a handle and reinforcing member to aid in lifting the assembled mounting.
Owner:COLEMAN ALLEN
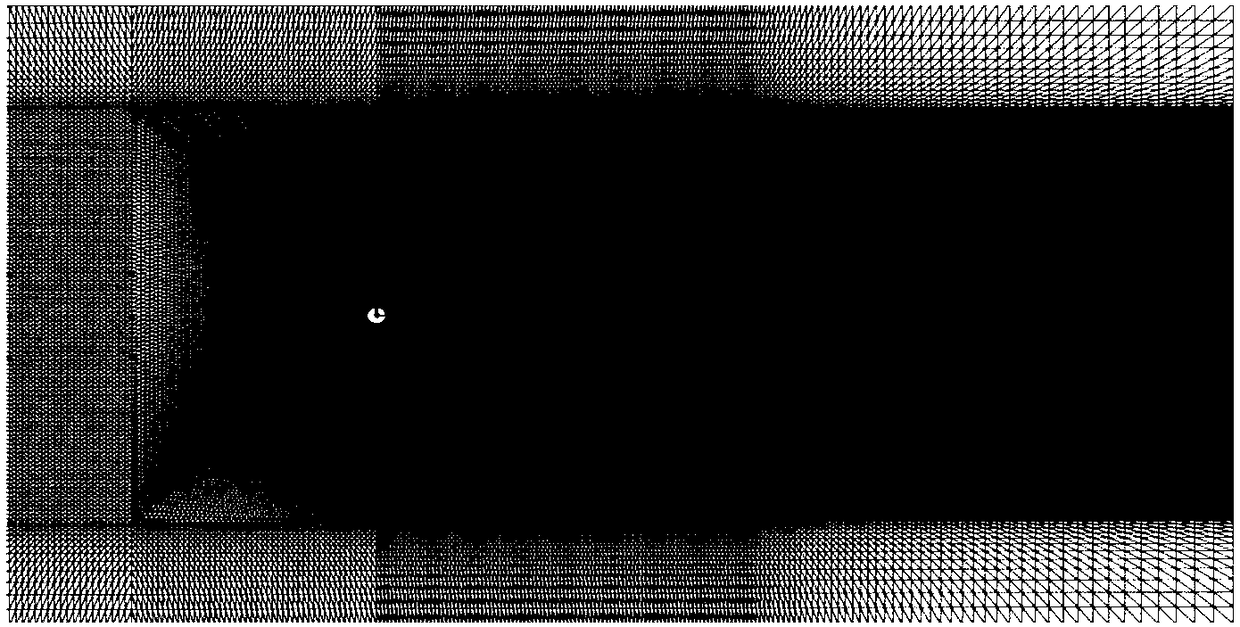
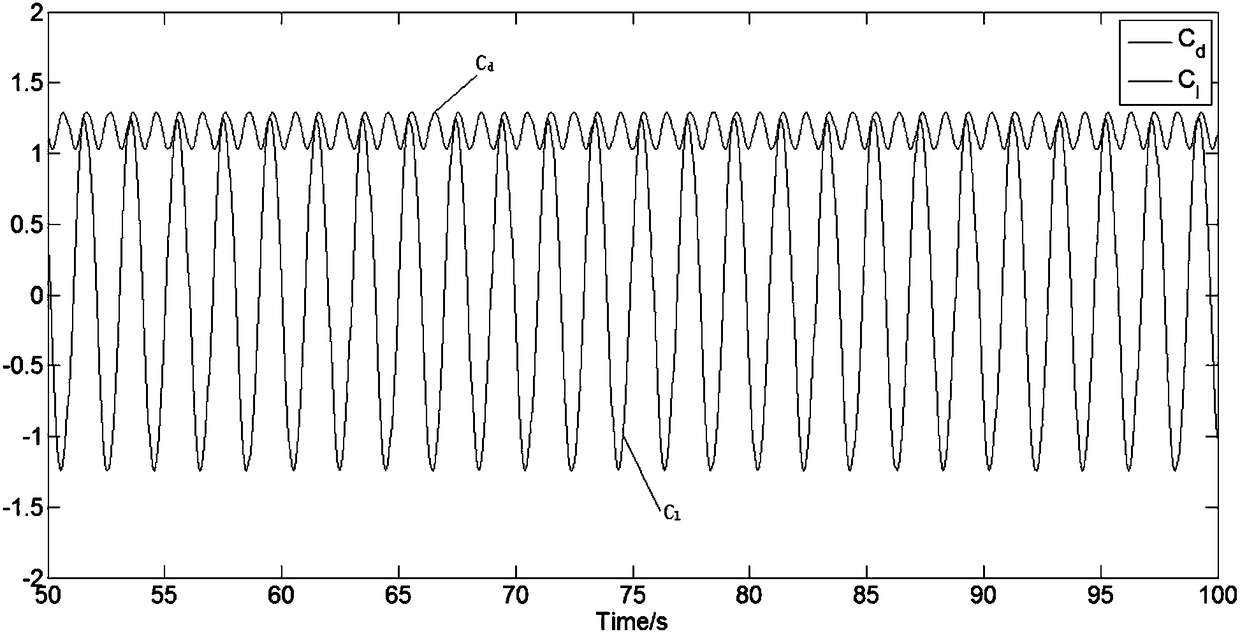
Deep-sea SPAR floating-type draught fan fatigue damage analysis method taking vortex-induced effect into account
InactiveCN108229043AEasy to moveEasy to handleGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsFatigue damageCurrent load
The invention discloses a deep-sea SPAR floating-type draught fan fatigue damage analysis method taking a vortex-induced effect into account. The method includes the following steps of (1) analyzing avortex-induced movement phenomenon of a SPAR-type floating-type draught fan, and obtaining the overall force characteristics, movement trails and response frequency of the SPAR-type floating-type draught fan; (2) on the basis of FAST software, under a working sea condition and a survival sea condition, analyzing a movement response time interval of the SPAR-type floating-type draught fan and theforce condition of tied cables under the combined action of a wind load, a wave load and a current load; (3) according to a Miner linear fatigue damage superposition theory, S-N curves and a rain-flowcounting method, compiling an MATLAB program, conducting fatigue damage analysis under the action of a vortex-induced load and wave load of the draught fan separately, and correspondingly obtaining the total fatigue damage of the tied cables within the design life to provide an effective settlement strategy for accurately evaluating power response of the floating-type draught fan and the fatiguedamage of the tied cables.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
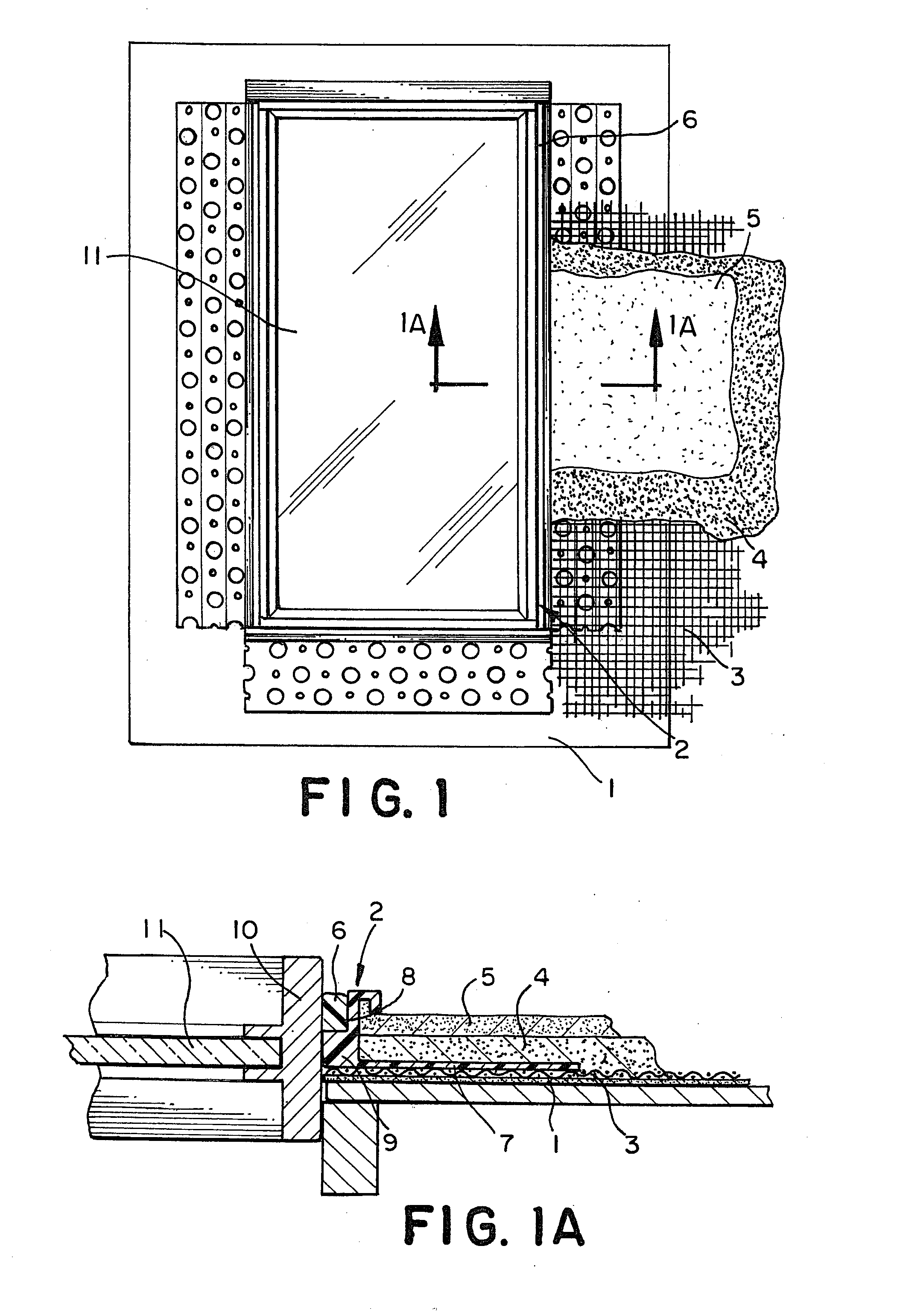
L-bead: a leak prevention system for stucco surfaces
InactiveUS20140245676A1Lower potentialMinimize potentialCeilingsCovering/liningsLeading edgeEngineering
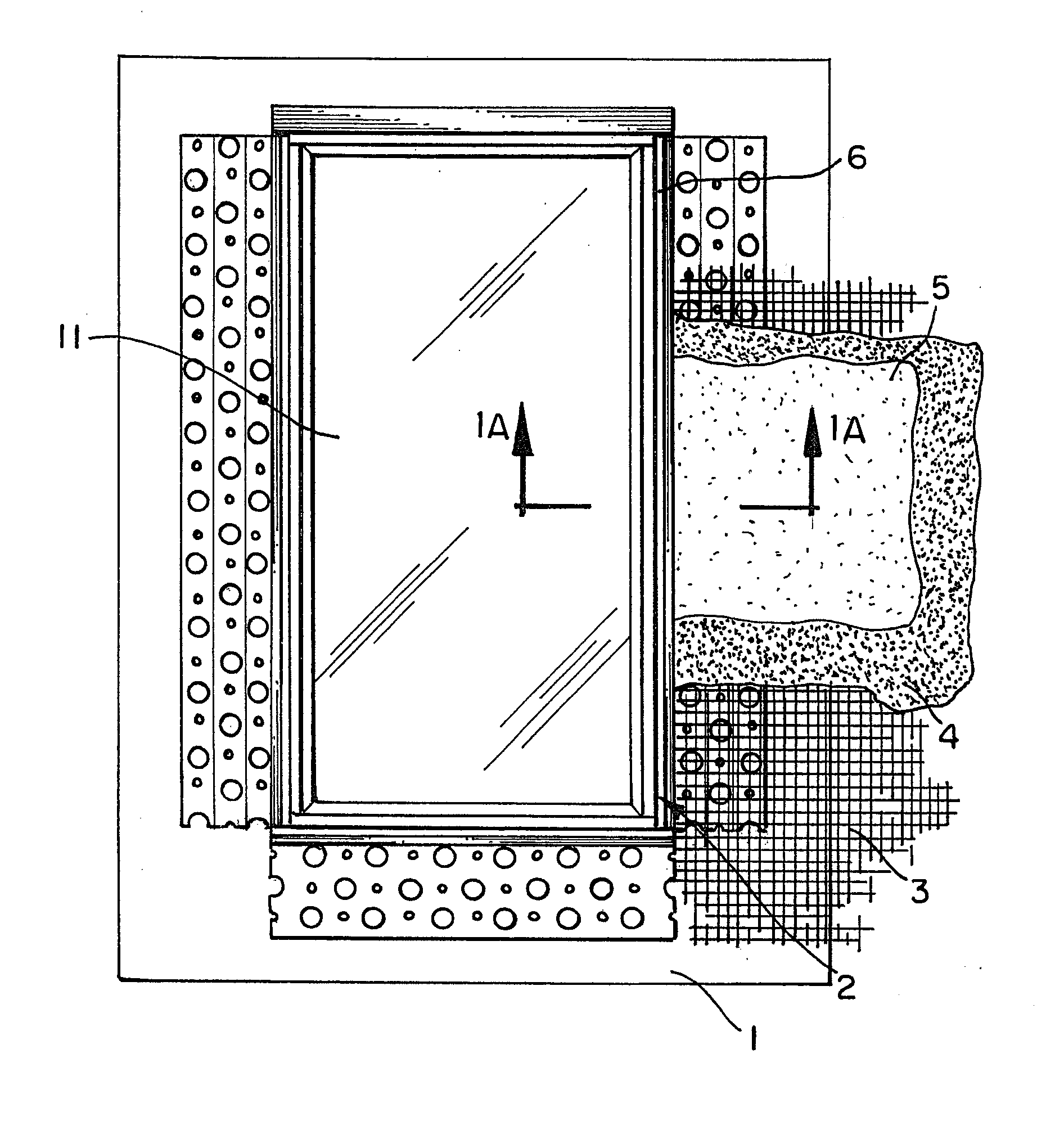
A stop bead for mounting along a frame or jamb of a window or door of a building to separate the frame or jamb from plaster or stucco material during application of the plaster or stucco material to the building comprises a first side end portion and a second side end portion, the first side portion having a leading edge for engaging the frame or jamb when the stop bead is mounted adjacent to the frame or jamb, a base panel having a front face, a stop bead wall formed on the base panel and extending outwardly above the front face of the base panel, the stop bead wall having an engaging surface for engaging plaster or stucco and a frame / jamb facing surface that faces the frame or jamb when the stop bead is mounted adjacent to the frame or jamb, and a spacing member formed on the stop bead and extending outwardly away from the frame / jamb facing surface of the stop bead wall for spacing the stop bead wall a predetermined distance from the frame or jamb when the stop bead is mounted adjacent to the frame or jamb, the spacing member forming the leading edge of the first side portion of the stop bead and forming gap between the stop bead wall and the frame or jamb when the stop bead is mounted adjacent to the frame or jamb for receiving caulk for sealing between the stop bead and the frame or jamb. In a preferred embodiment, the spacing member is flexible to permit movement of the spacing member responsive to movement to weather induced movement of the jamb after the stop bead is mounted adjacent to the jamb.
Owner:E Z BEAD
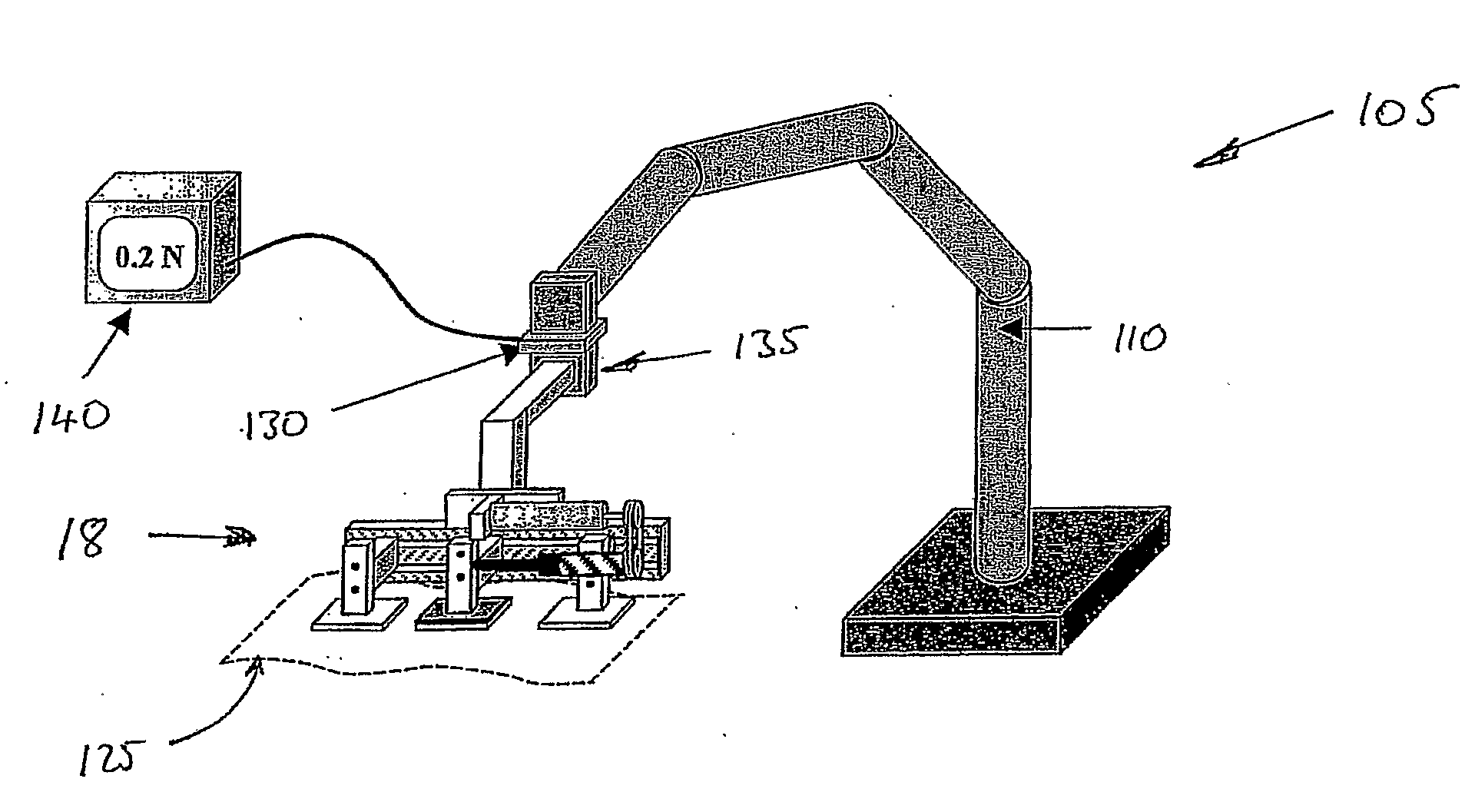
Apparatus and method for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of skin
InactiveUS20110319792A1Approach can be quite invasivePromote healingDiagnostics using pressurePerson identificationMeasurement deviceBiomechanics
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Wall-Ceiling Slip Joint Permitting Seismic Induced Movement
Owner:KRUEGER INT
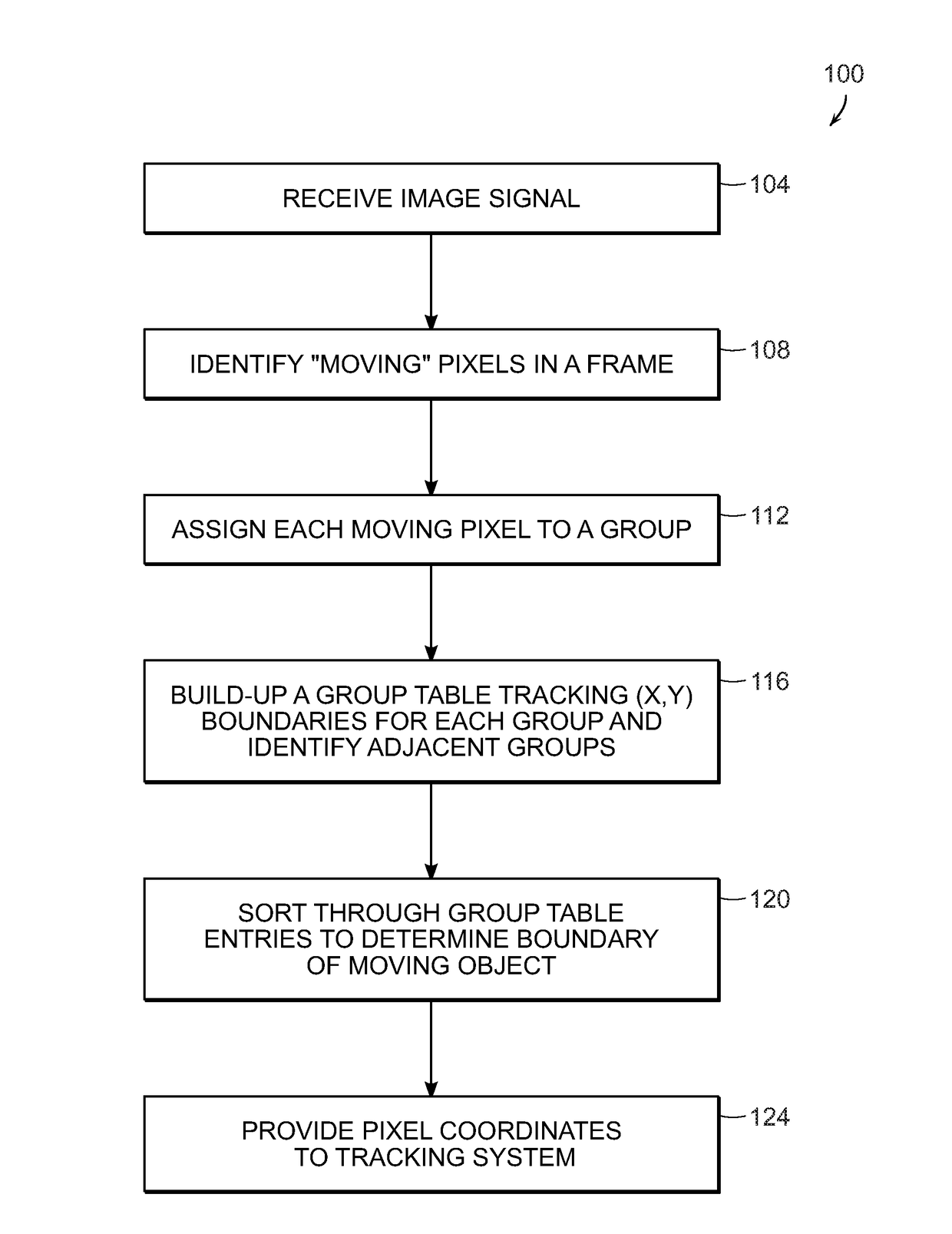
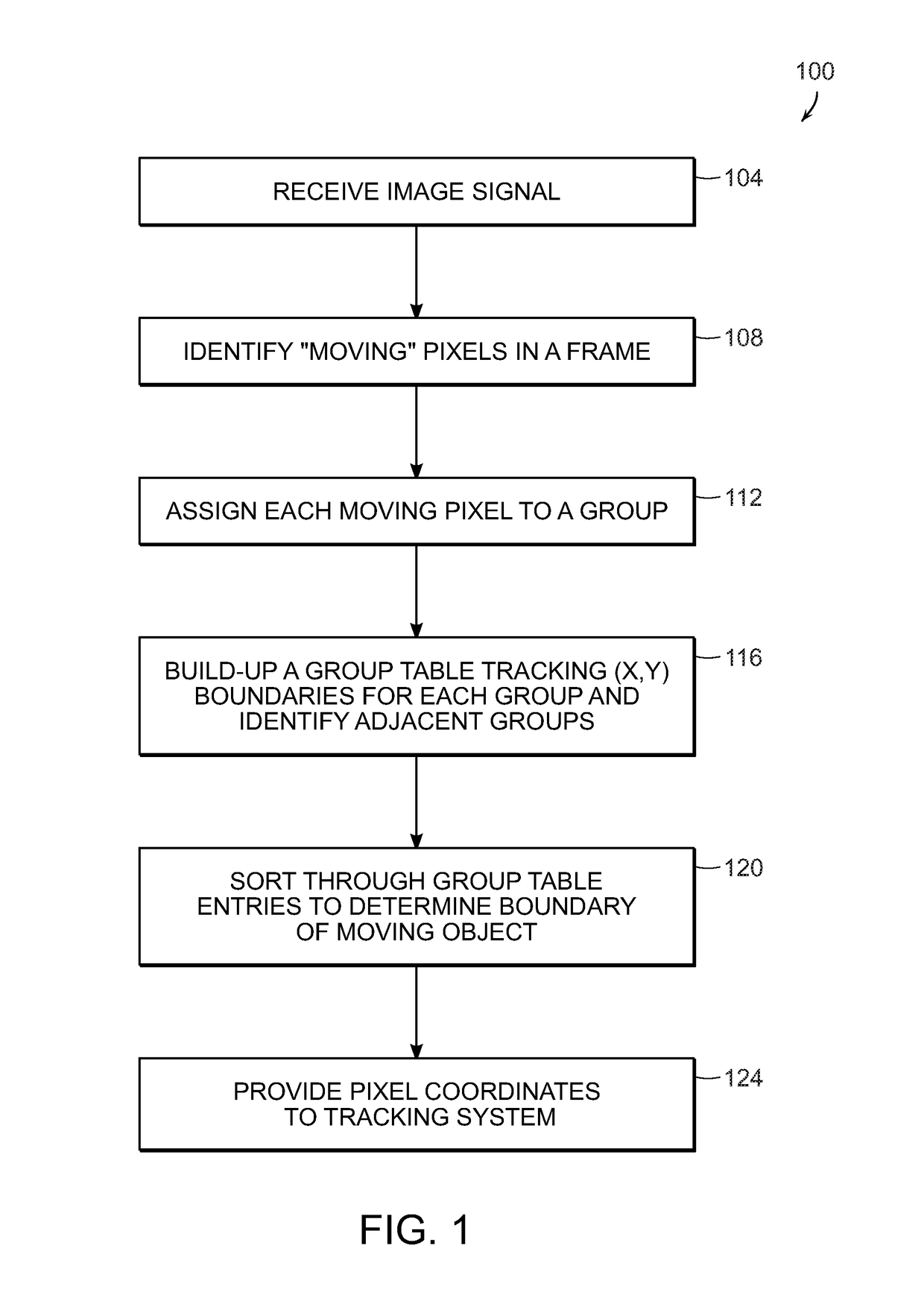
System for real-time moving target detection using vision based image segmentation
A system for processing video signal information to identify those pixels associated with a moving object in the presence of platform and / or sensor pointing induced motion. Frame differencing with self-adjusting noise thresholds is implemented to detect pixels associated with objects that are in motion with respect to the background and a field-by-field motion pixel map of pixels associated with the moving object is generated. A two (2) step pixel grouping process is used where the first pass runs in real-time as the video signal is received and writes the links between pixel groups into entries in a table. The second pass operates on a smaller set of link data and only needs to reorder entries in the table.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method and system for compensating thermally induced motion of probe cards
InactiveUS20060001440A1Motion compensationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical measurement instrument detailsTemperature controlProbe card
The present invention discloses a method and system compensating for thermally induced motion of probe cards used in testing die on a wafer. A probe card incorporating temperature control devices to maintain a uniform temperature throughout the thickness of the probe card is disclosed. A probe card incorporating bi-material stiffening elements which respond to changes in temperature in such a way as to counteract thermally induced motion of the probe card is disclosed including rolling elements, slots and lubrication. Various means for allowing radial expansion of a probe card to prevent thermally induced motion of the probe card are also disclosed. A method for detecting thermally induced movement of the probe card and moving the wafer to compensate is also disclosed.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Wave power generator
InactiveUS8618686B2Improve energy conversion efficiencyImprove practicabilityEngine fuctionsHydro energy generationElectricityWave power generation
The present invention relates to a wave power generator, and more particularly, to a wave power generator that has comparatively high energy conversion efficiency, so that it can induce active investment and research and development to overcome uncertainties about the natural environment, and which can enhance practicability and value as a clean energy source, especially by virtue of the improved return on investment thereof. For this purpose, the wave power generator of the present invention is characterized in that is comprises: a plurality of rafts arranged on a water surface to move freely with the movement of waves; a plurality of connectors, connecting the plurality of rafts to each other, for performing the conversion of kinetic energy by converting the wave-induced movement of one raft into an amplified lever movement on an adjacent raft; a plurality of generators installed on the plurality of rafts to generate electricity; and an energy-converting unit, connected to the plurality of connectors and to the plurality of generators, for converting the kinetic energy from the plurality of connectors into rotational energy for driving the plurality of generators.
Owner:JO CHANG HUI
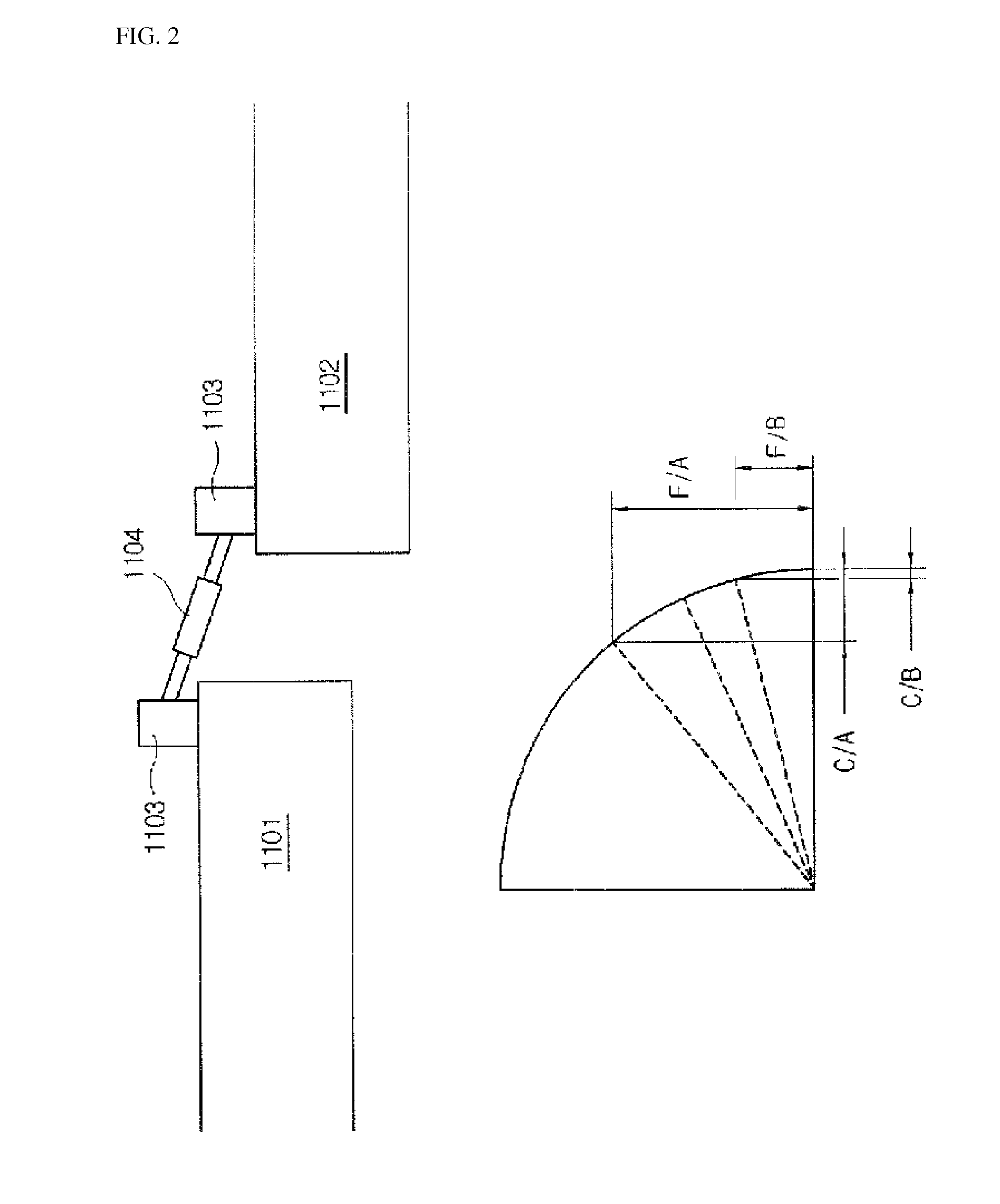
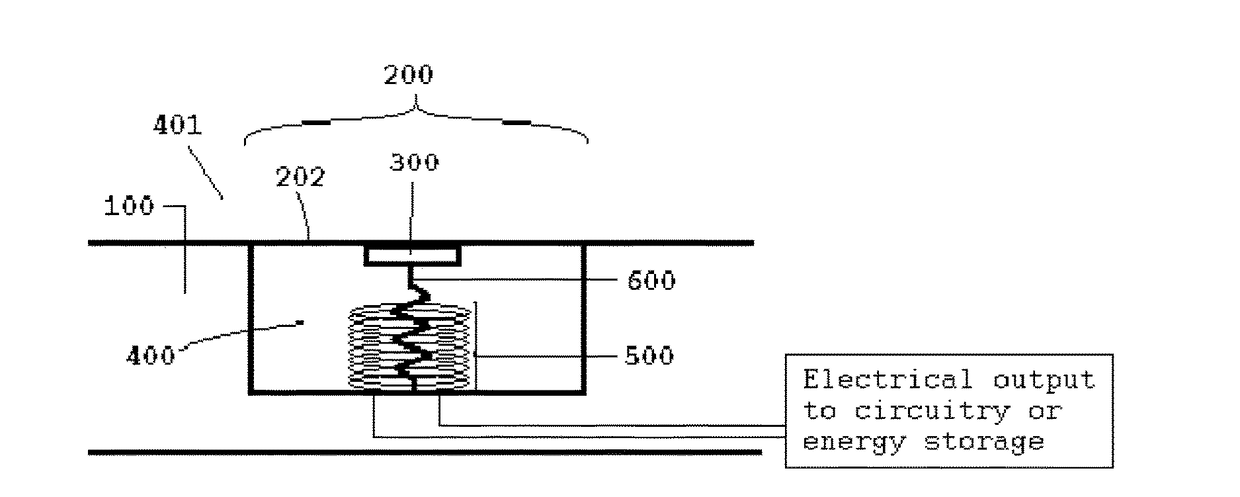
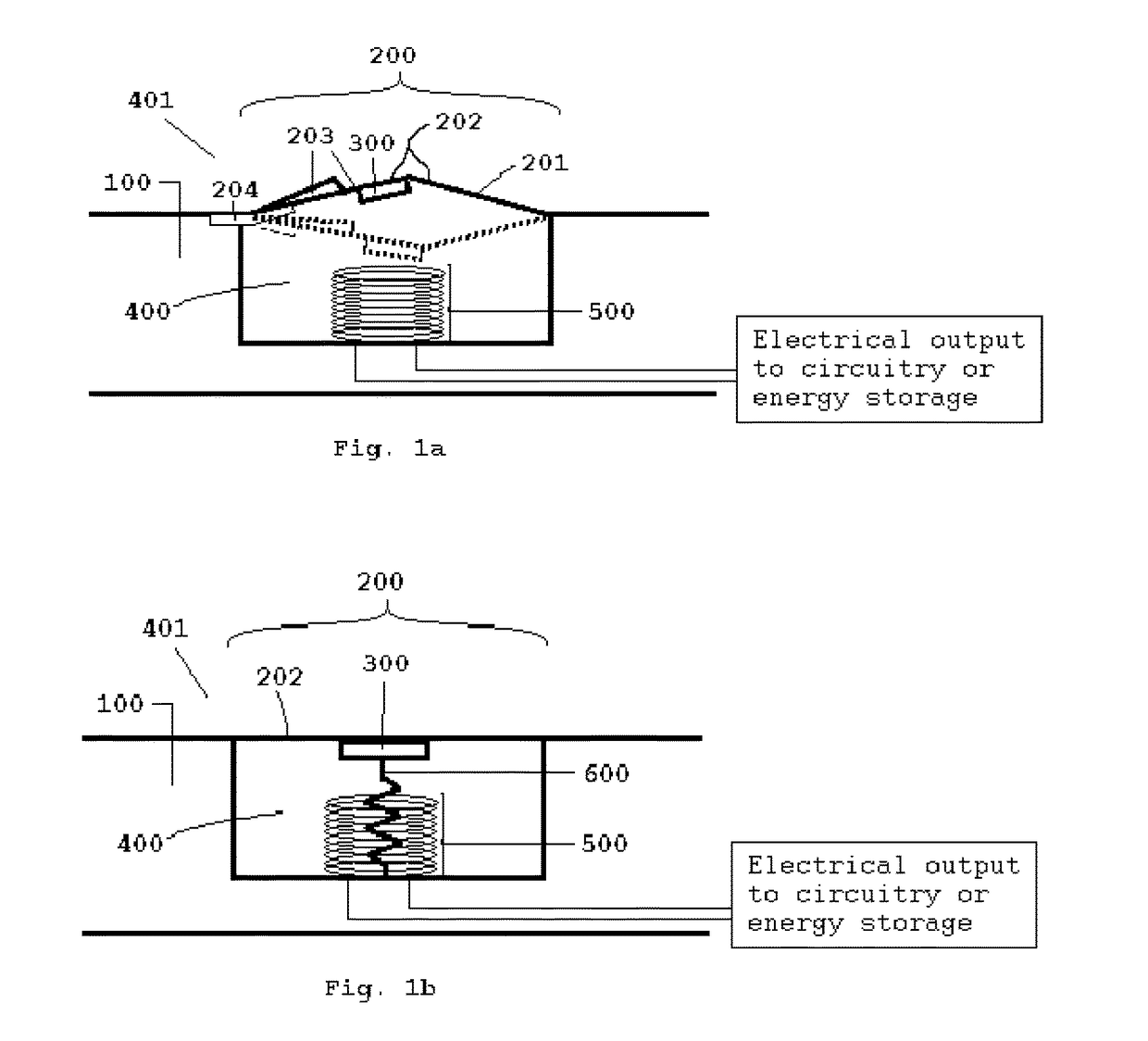
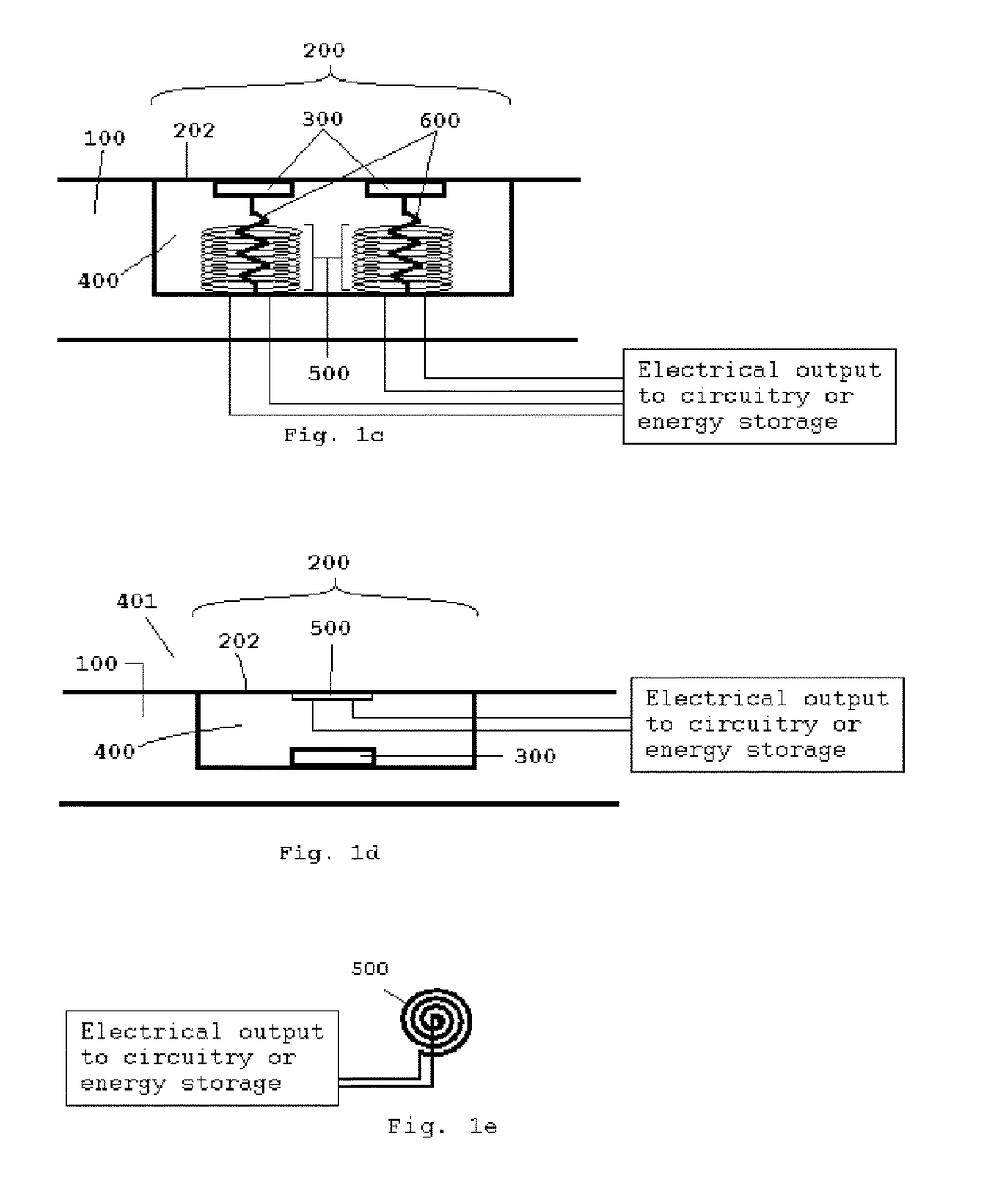
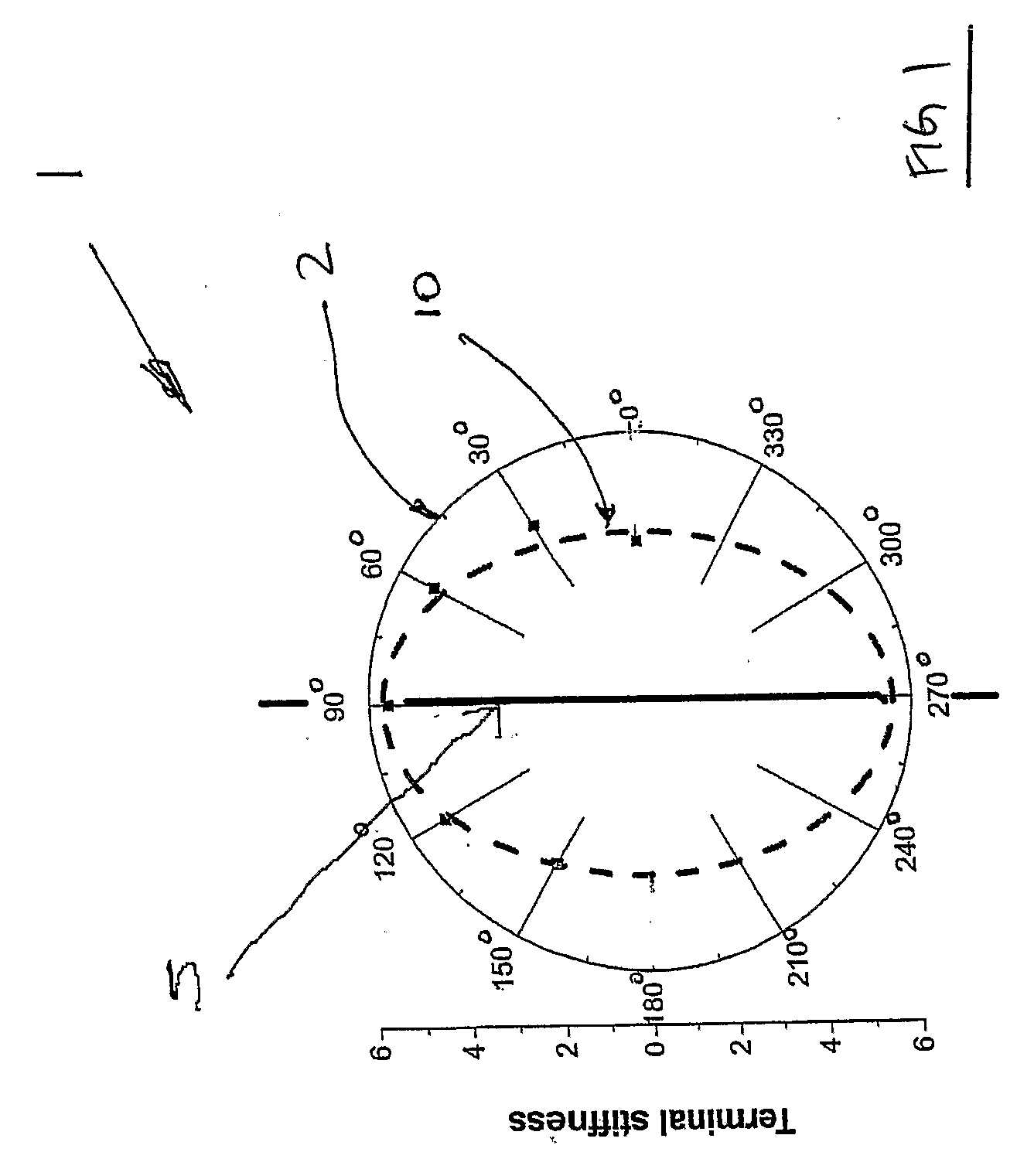
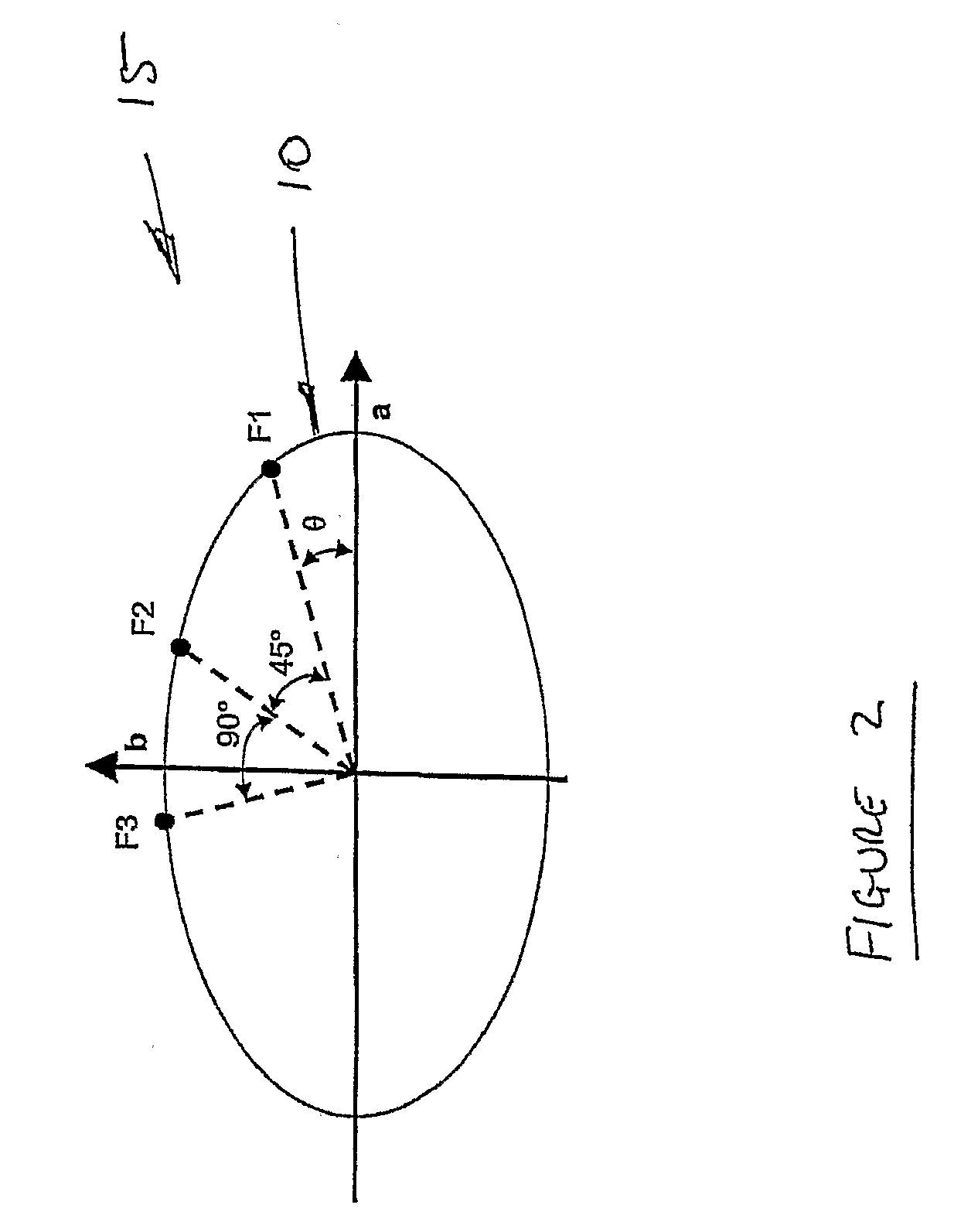
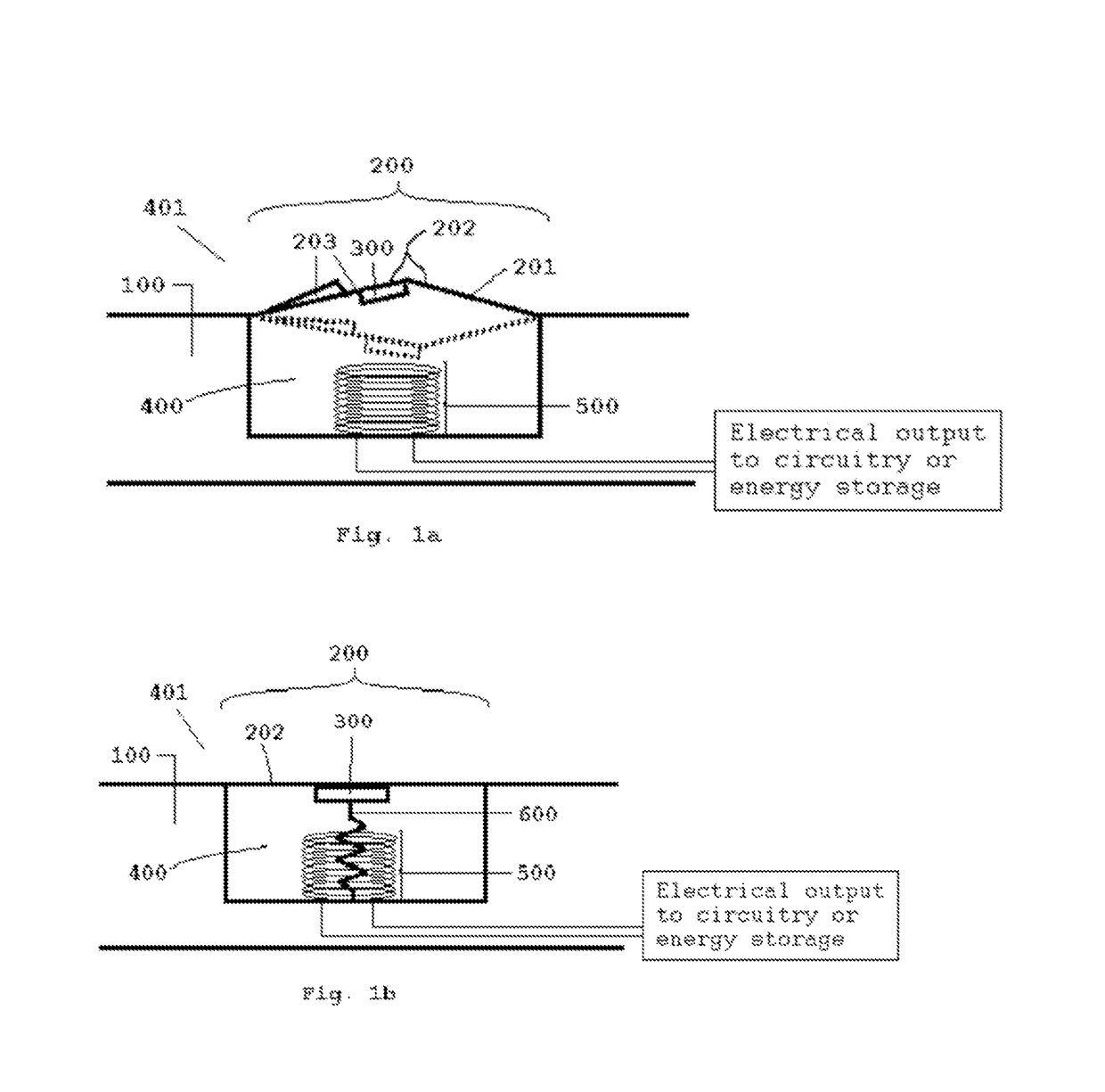
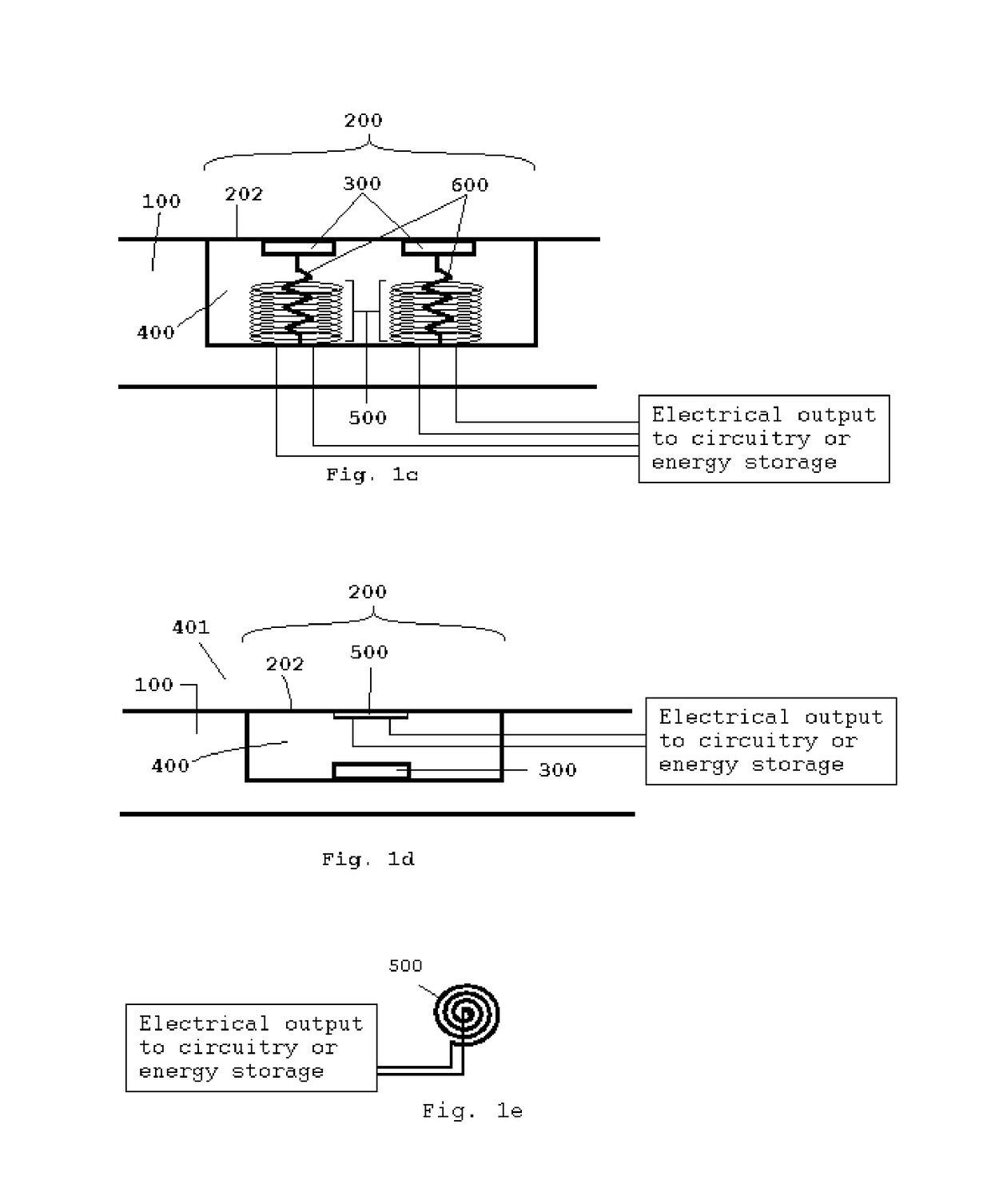
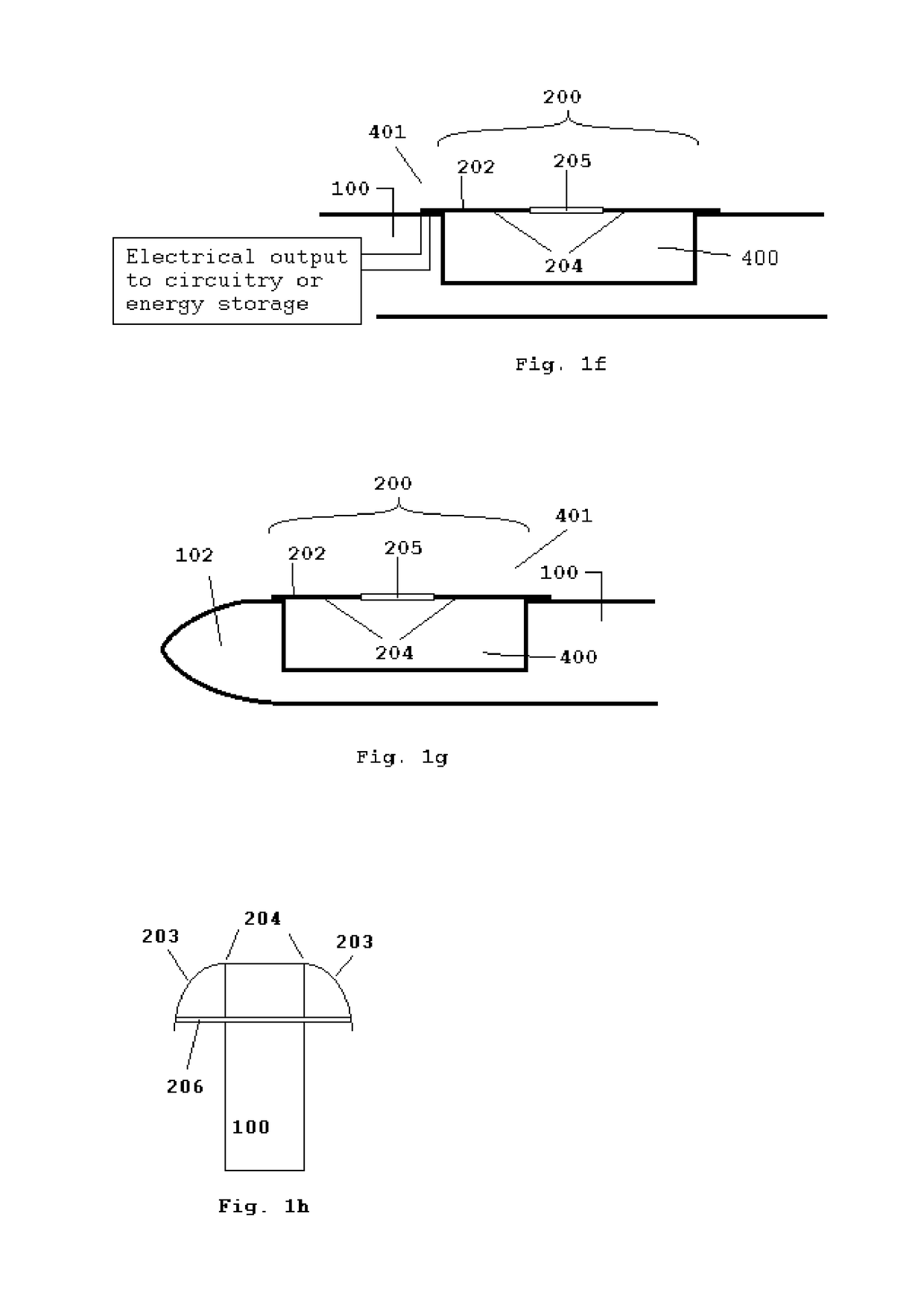
Apparatus for Generating Energy from a Fluid Flow Induced Movement of a Contacting Surface Structure Relative to an Opening to a Cavity in a Frame
InactiveUS20170204839A1Less susceptibleReduced is size and complexity and costPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesHydro energy generationElectricityEngineering
A generator moving through a medium has a contacting surface structure relative to a frame with a spring coupled between the two. The contacting surface structure also has an electrogenerative portion coupled to the contacting surface structure and the frame, such as a piezoelectric or electromagnetic structure, although other types of structures are known within the art. The movement of the frame through the medium exerts forces upon the contacting surface structure which causes contacting surface structure movement relative to the base structure through the electrogenerative portion. The spring provides a force upon the contacting surface structure in response to the force from the fluid flow.
Owner:HSU SEAN NEAN
Two-Dimensional and Multi-Threshold Elastic Button User Interface System and Method
A novel elastic button user interface system and a related method of operation are disclosed. In one embodiment, the elastic button user interface system generates an elastic button that simulates physical characteristics of a button suspended on an elastic string on a touch-sensing display unit. The elastic button first allows selection of a particular item from a display menu, and invokes dynamic transformations to the particular item by correlating a user-induced horizontal and / or vertical movement of the elastic button with application-specific design parameters for two-dimensional and multiple-level thresholds for the elastic button user interface system. Furthermore, releasing the elastic button by removing a finger from the elastic button triggers a “final activation” for the particular item, after dynamic transformations to the particular item during the user-induced movement of the elastic button. Examples of the final activation includes activating a camera shutter and transmitting a message to another electronic device.
Owner:LEE SANG BAEK
Apparatus and Method For Measuring in Vivo Biomechanical Properties of Skin
InactiveUS20080200842A1Approach can be quite invasivePromote healingDiagnostics using pressurePerson identificationMeasurement deviceBiomechanics
An assembly for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of skin, comprising a testing device, said testing device comprising; a first pad attachable to the skin a second pad attachable to the skin, at a known distance from the first pad; said attachability of the pads to the skin to prevent relative movement between the respective pad and the skin to which it is attached; a forcing means for applying a force to the first pad, whilst said pads are attached to the skin, along a first axis connecting the first and second pad, to induce a corresponding relative movement between the pads due to deformation of the skin between said pads; a force measurement device for measuring the applied force, and; a displacement measurement device for measuring the corresponding induced movement.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Apparatus for Generating Energy from a Fluid Flow Induced Movement of a Contacting Surface Structure Relative to an Opening to a Cavity in a Frame
InactiveUS20180355840A1Less susceptibleSmall sizePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesHydro energy generationElectricityEngineering
A generator moving through a medium has a contacting surface structure relative to a frame with a spring coupled between the two. The contacting surface structure also has an electrogenerative portion coupled to the contacting surface structure and the frame, such as a piezoelectric or electromagnetic structure, although other types of structures are known within the art. The movement of the frame through the medium exerts forces upon the contacting surface structure which causes contacting surface structure movement relative to the base structure through the electrogenerative portion. The spring provides a force upon the contacting surface structure in response to the force from the fluid flow.
Owner:HSU SEAN NEAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com