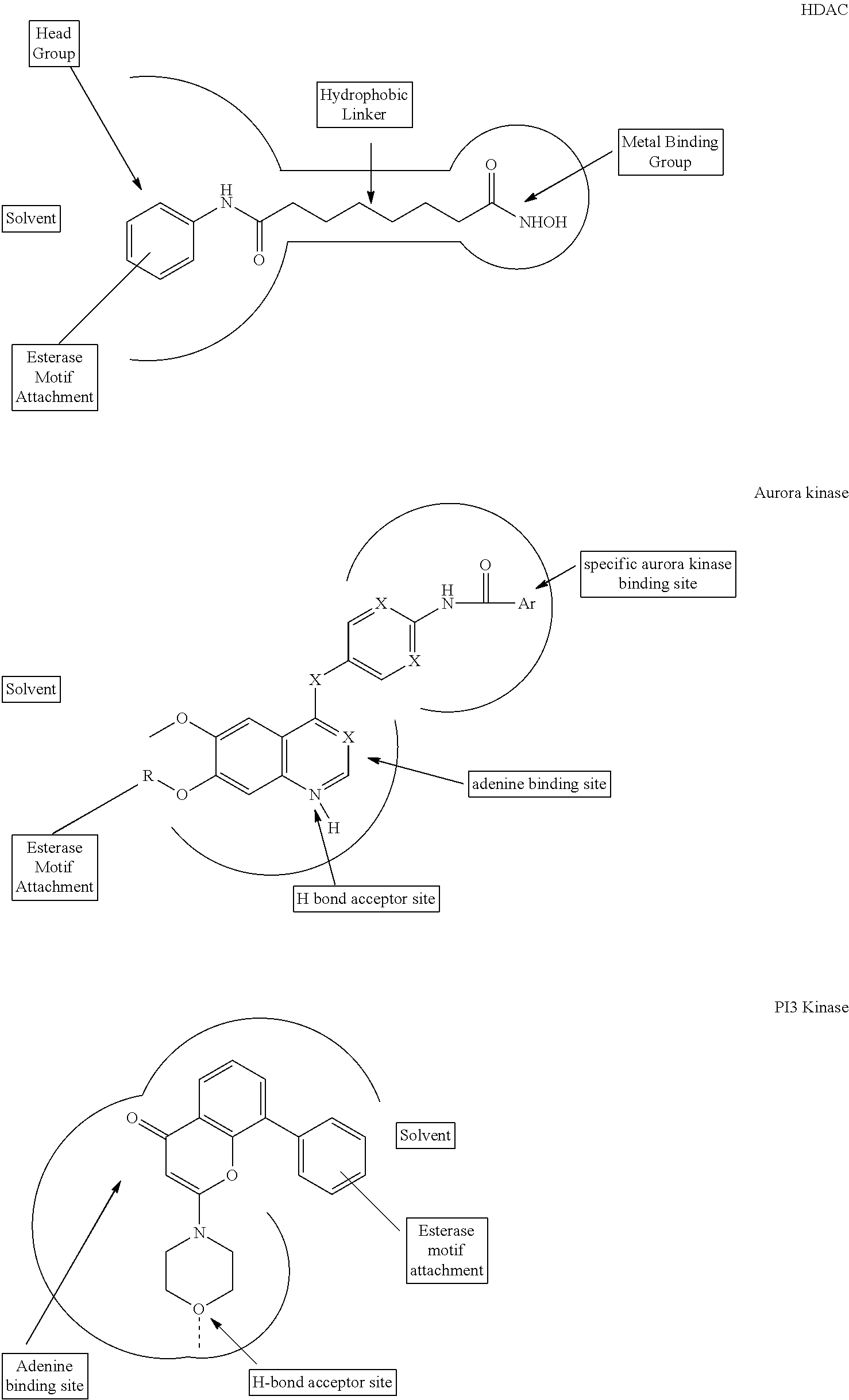
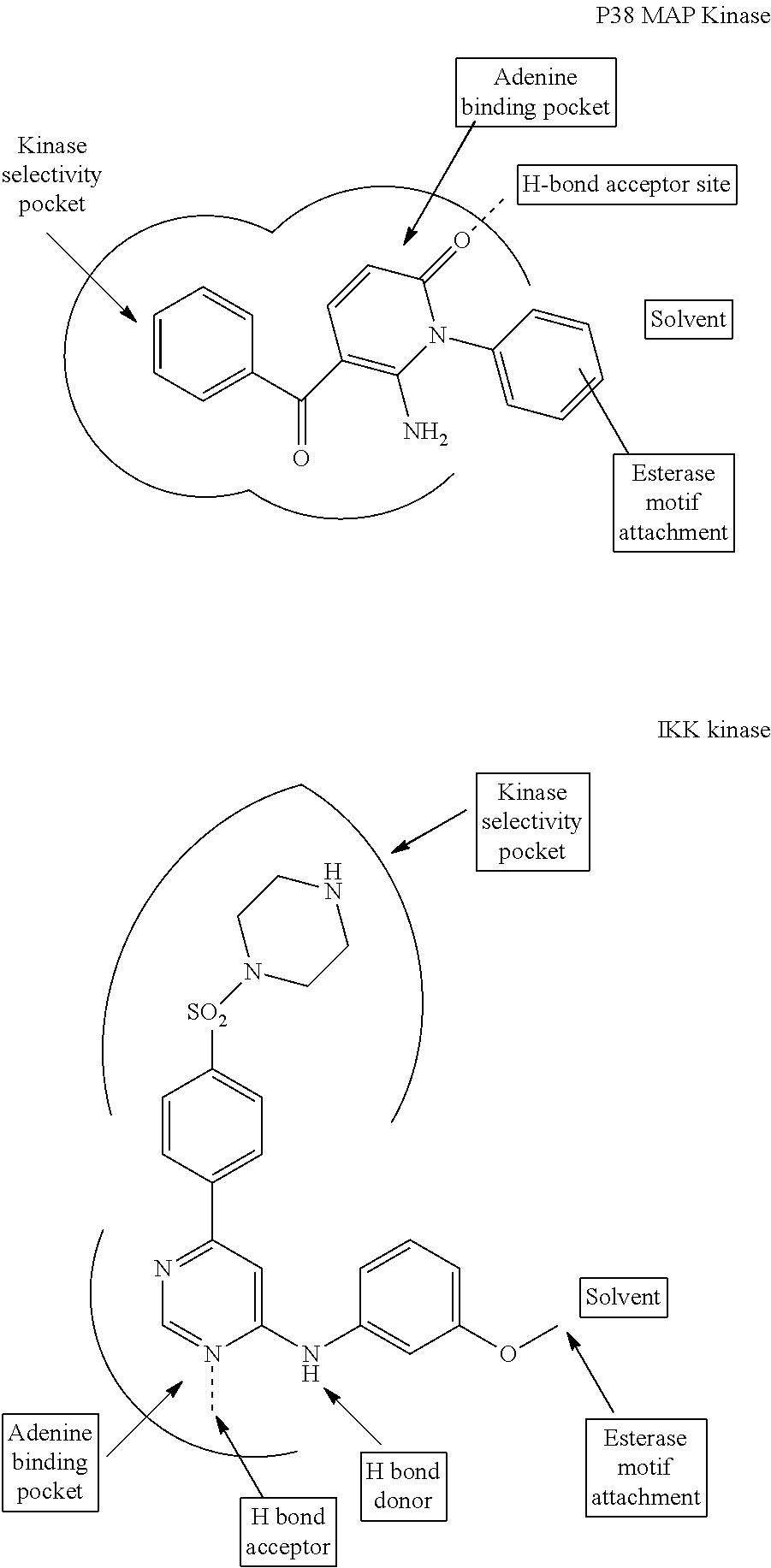
Enzyme and receptor modulation
a technology of enzymes and receptors, applied in the field of enzymes and receptor modulation, can solve the problems of poor potency of modulators, and achieve the effect of prolonging and/or increasing activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-6
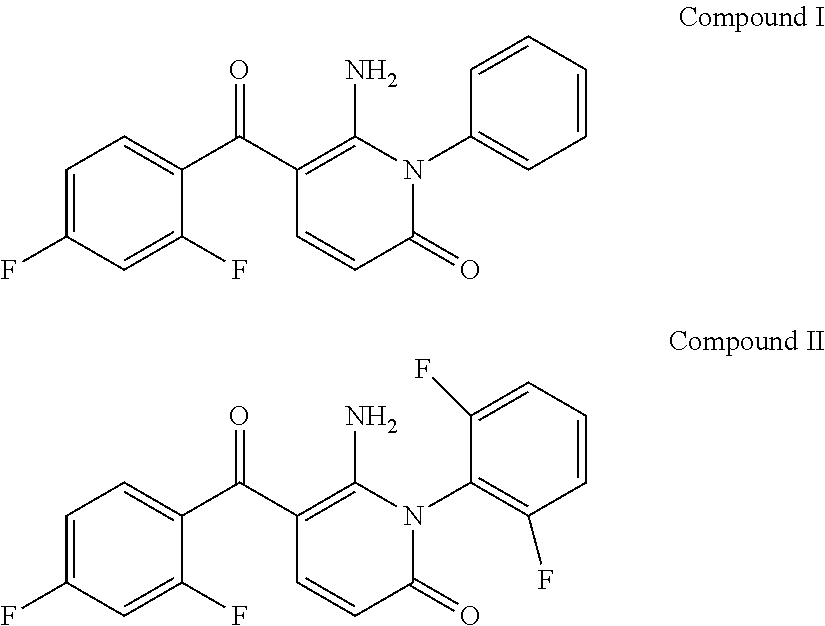
[0100]The compounds 6-amino-5-(2,4-difluoro-benzoyl-1-phenyl-1H-pyridin-2-one (Compound I) and 6-amino-5-(2,4-difluoro-benzoyl-1-(2,5-difluorophenyl-1H-pyridin-2-one (Compound II):
are known inhibitors of the intracellular enzyme p38 MAP kinase (WO 03 / 076405). Examples 1, 3 and 5 below relate to the covalent conjugation of esterase motifs with di-substitution at the alpha carbon of the amino acid ester to these compounds, in a position remote from the binding interface between the inhibitor and the target enzyme (see the comments above concerning the binding mode of a model p38 MAP kinase inhibitor). Examples 2, 4 and 6 below relate to the carboxylic acid esterase hydrolysis products of Examples 1, 3 and 5 respectively.
Synthesis of Examples 1-6
Intermediate 1
4-Chlorophenyl 3-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-oxopropanimidothioate
[0101]
[0102]Intermediate 1 can be prepared using experimental procedures described in WO 2003076405.
Intermediate 2
{4-[6-Amino-5-(2,4-difluorobenzoyl)-2-oxopyridin-1(2H)y...
example 1
Cyclopentyl N-(2-{4-[6-amino-5-(2,4-difluorobenzoyl)-2-oxopyridin-1 (2H)-yl]phenyl}ethyl)-2-methylalaninate
[0141]
[0142]In this example compound of the invention, a dimethyl glycine cyclopentyl ester motif is covalently conjugated to the parent p38 MAP kinase inhibitor via the amino group of the dimethyl glycine cyclopentyl ester and through a —CH2CH2— linker radical.
[0143]The compound was synthesised using Intermediate 2 and Intermediate 3 as described below.
[0144]To a solution of Intermediate 2 (189 mg, 0514 mmol) in anhydrous THF (4 mL) were added cyclopentyl 2-methylalaninate hydrochloride (Intermediate 3) (160 mg, 0.77 mmol, 1.5 eq) and NaBH(OAc)3 (326 mg, 1.54 mmol, 3 eq). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 16 hours, and then quenched with water (20 mL). The aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc (3×20 mL), and the combined organic extracts washed with brine (40 mL), dried over MgSO4, filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by pre...
example 2
N-(2-{4-[6-Amino-5-(2,4-difluorobenzoyl)-2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-yl]phenyl}ethyl)-2-methylalanine
[0146]
[0147]This Example relates to the carboxylic acid hydrolysis product of the compound of Example 1.
[0148]The compound was synthesised using Intermediate 2 and Intermediate 4 as described below in Scheme 6.
Stage 1—tert-Butyl N-(2-{4-[6-amino-5-(2,4-difluorobenzoyl)-2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-yl]phenyl}ethyl)-2-methylalaninate
[0149]To a solution of Intermediate 2 (180 mg, 0.489 mmol) in THF (3 mL) was added tert-butyl 2-methylalaninate (Intermediate 4) (117 mg, 0.73 mmol), stirred for 30 minutes, and then NaBH(OAc)3 (310 mg, 1.467 mmol). The reaction was stirred for 24 hours, diluted with EtOAc and the organic washed with sat NaHCO3, brine, dried (MgSO4) and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by preparative HPLC to provide the title compound (120 mg, 48% yield).
[0150]LC / MS: m / z 512 [M+H]+. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 10.41 (1H, br s), 7.51-7.34 (4H, m), 7.28-7.26 (2H, m), 7.05-6.90 (2H...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com