Patents
Literature
1375results about "Special recording techniques" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
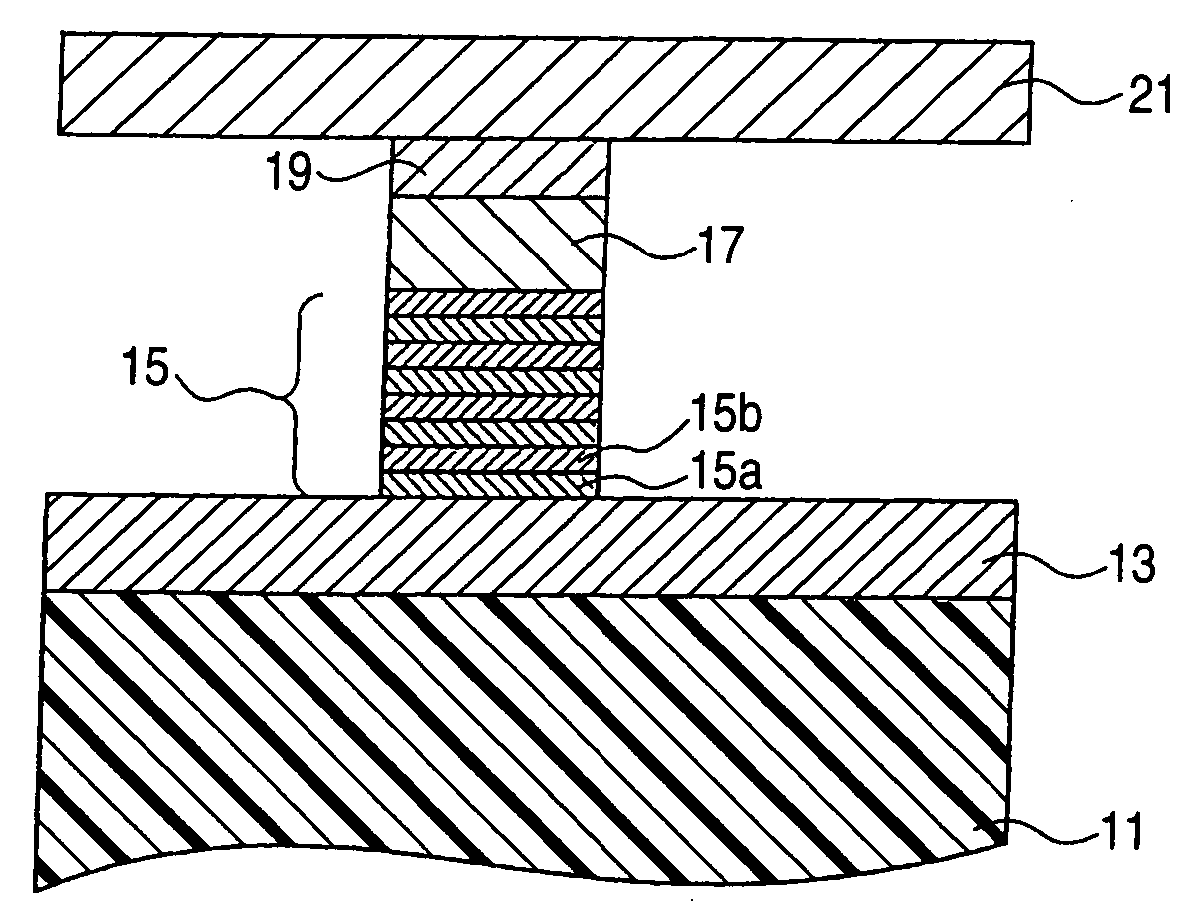
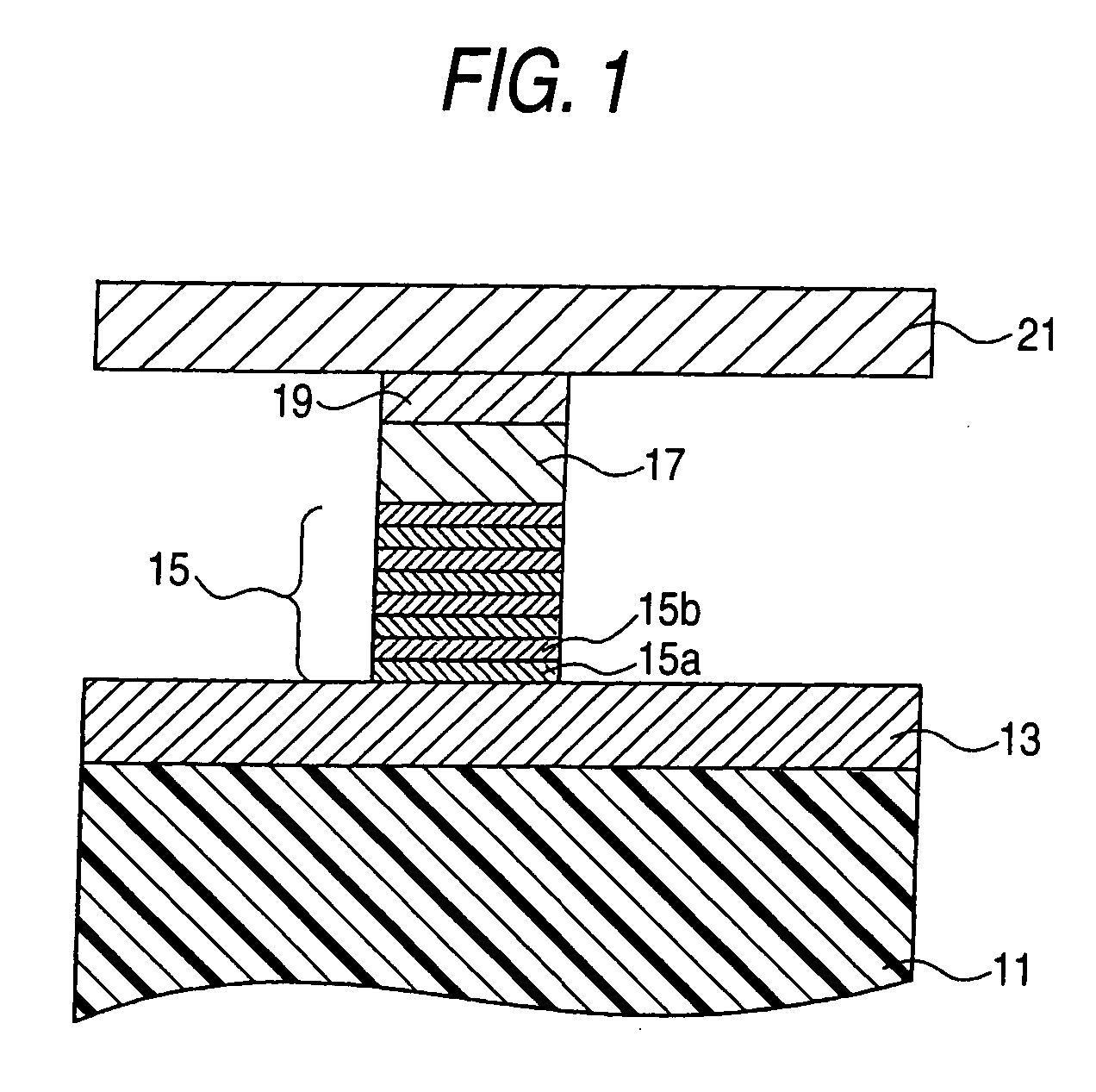
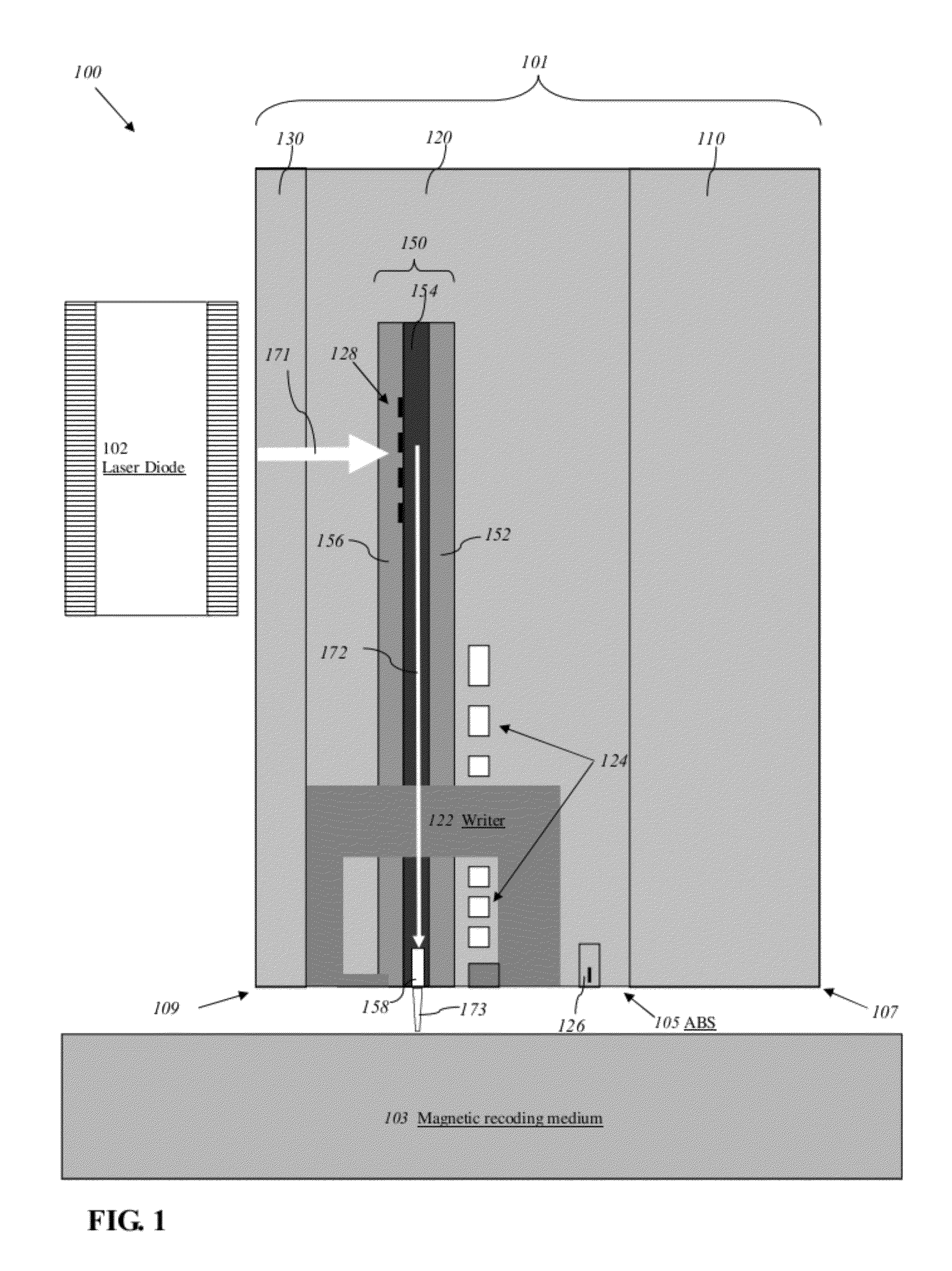
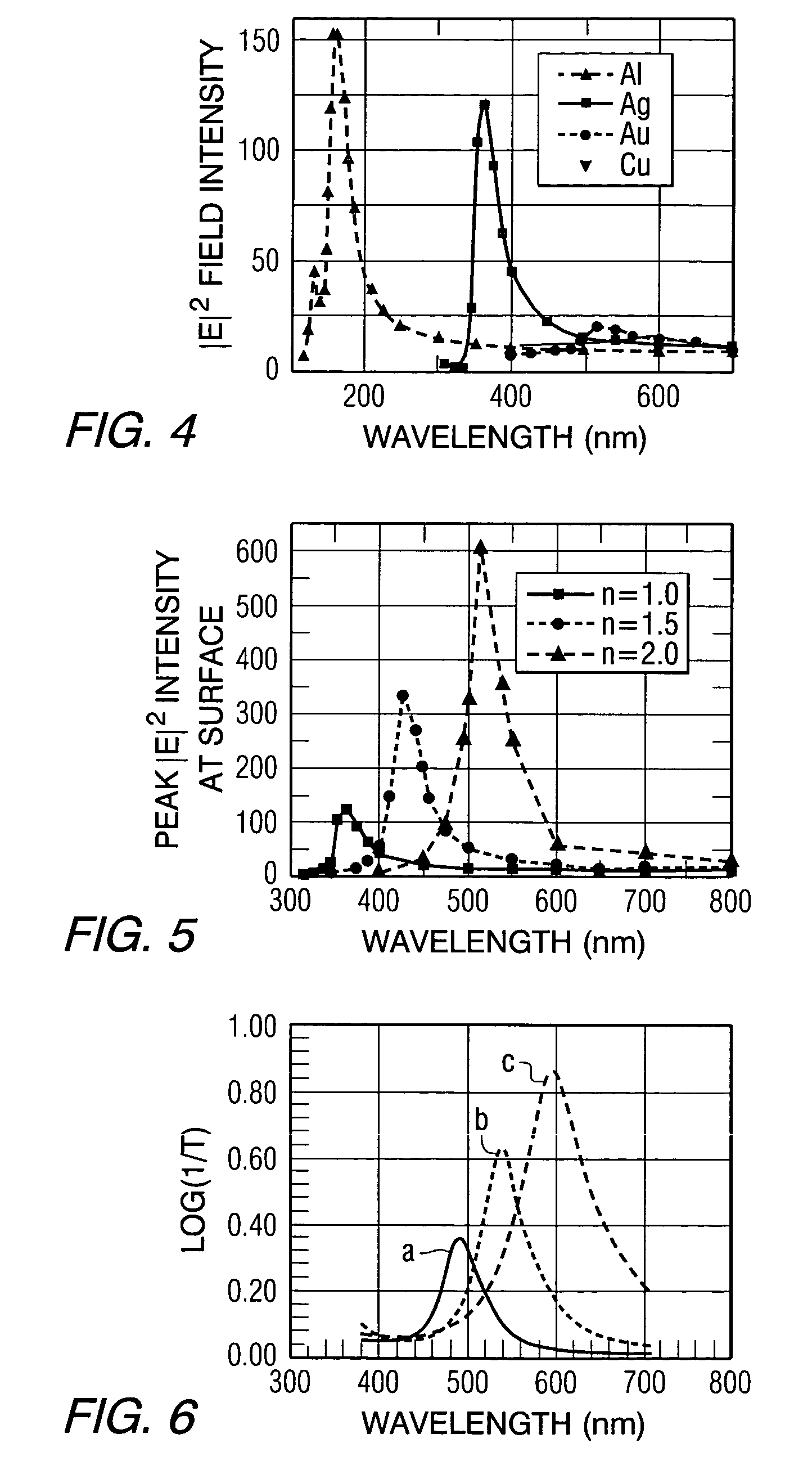
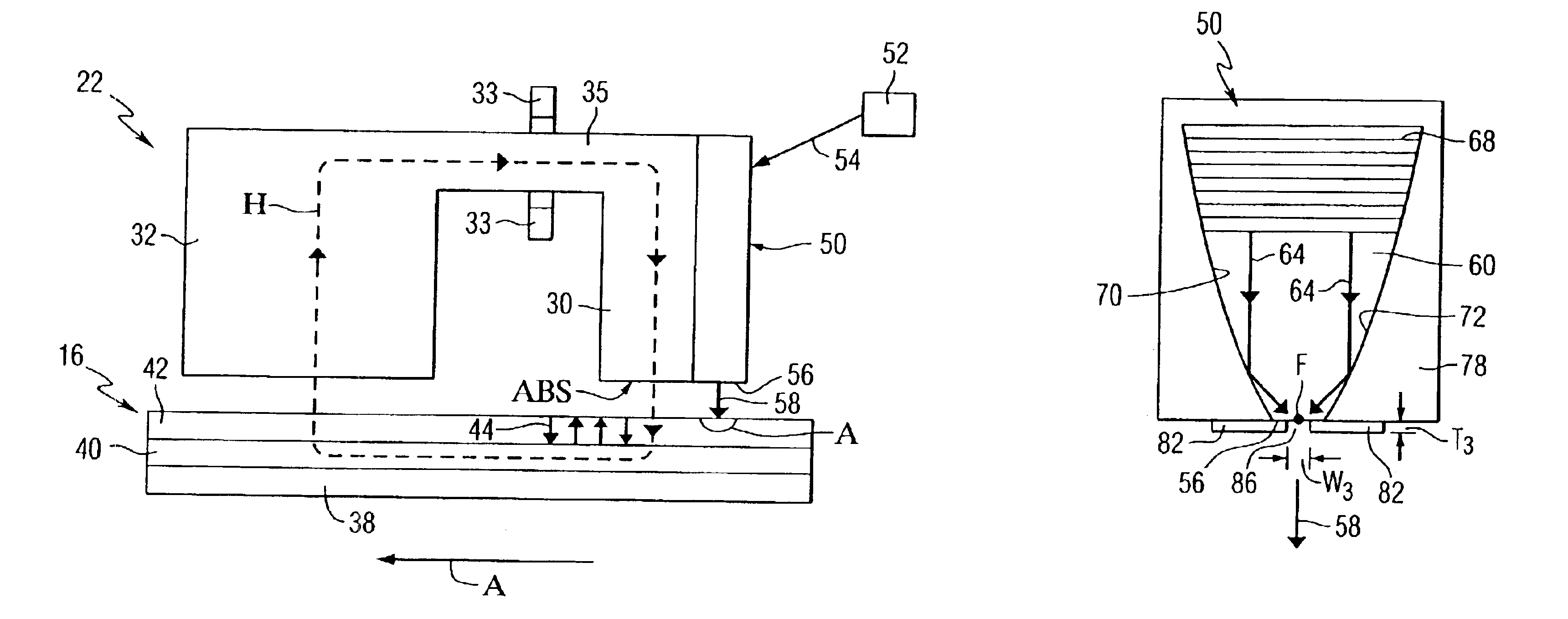
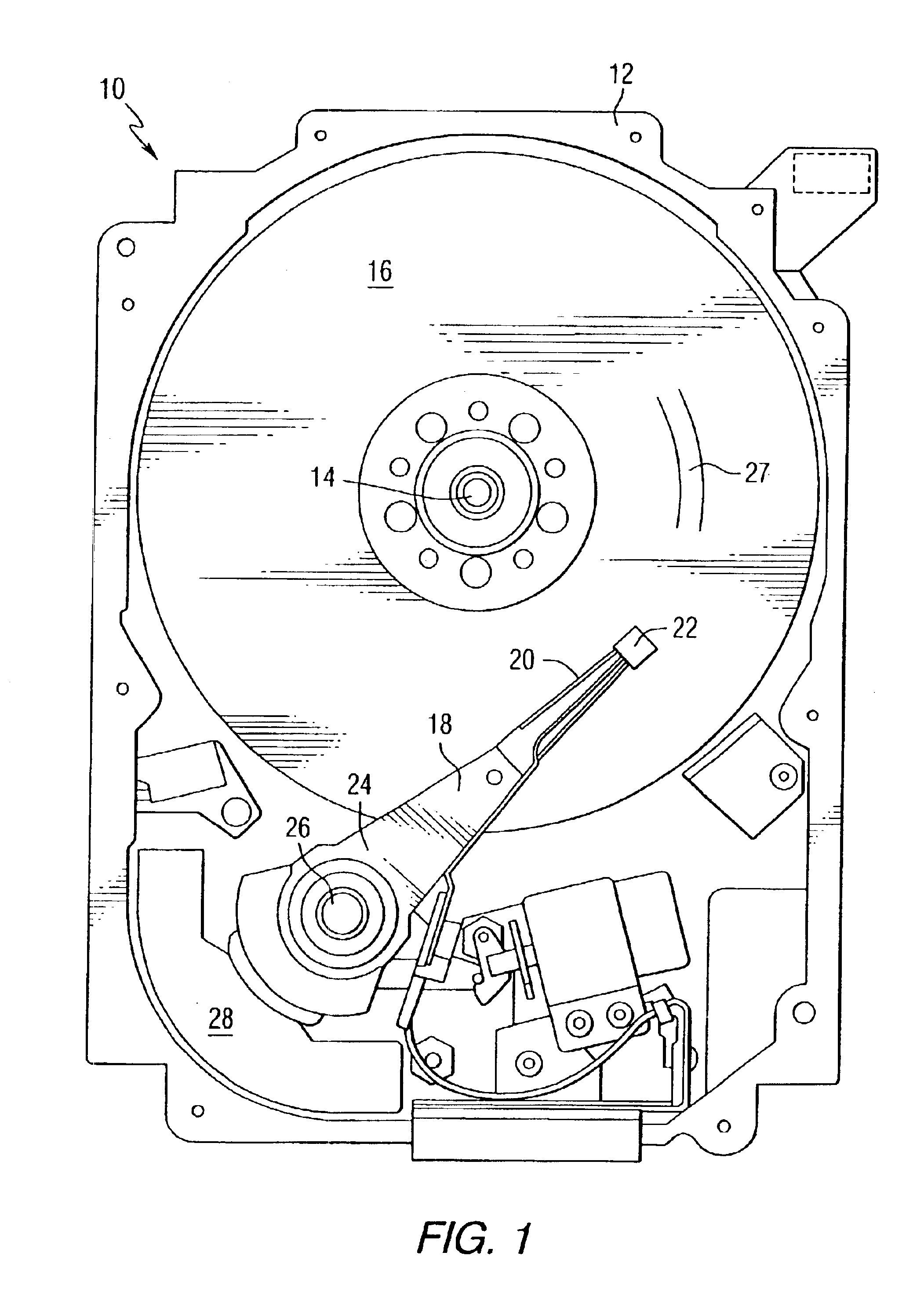
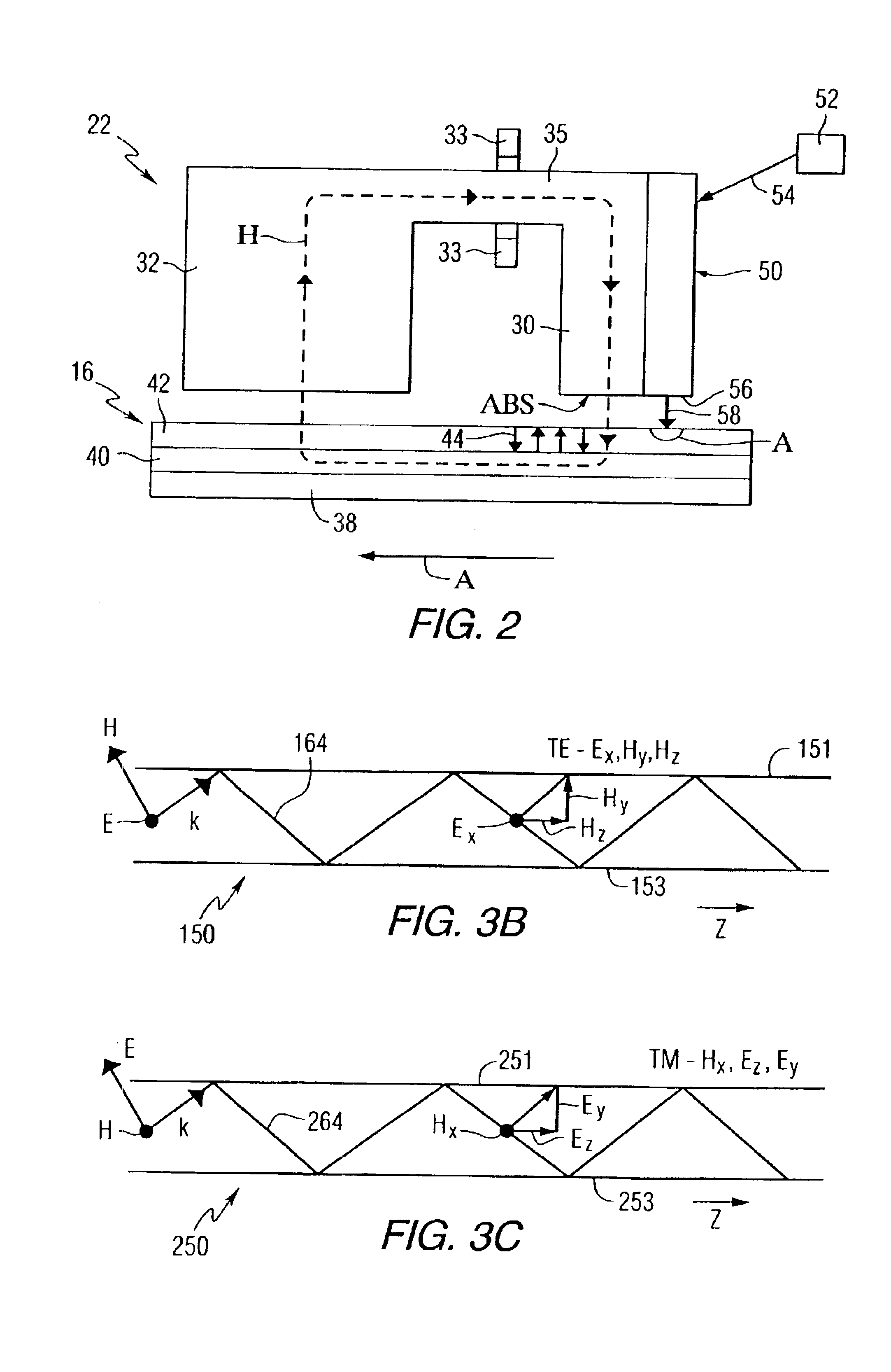
Near-field optical transducers for thermal assisted magnetic and optical data storage
ActiveUS7330404B2Recording by magnetic meansRecord information storageSurface plasmonRefractive index
An optical transducer comprises an optical element for directing an electromagnetic wave to a focal region and a metallic nano-structure having a longitudinal axis substantially parallel to an electric field of the electromagnetic wave, the metallic nano-structure being positioned outside of the optical element, wherein the electromagnetic wave produces surface plasmons on the metallic nano-structure. A cladding material having a refractive index differing from the refractive index of the optical element can be positioned adjacent to a surface of the metallic nano-structure. Magneto-optical recording heads that include the transducers and disc drives that include the magneto-optical recording heads are also included.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
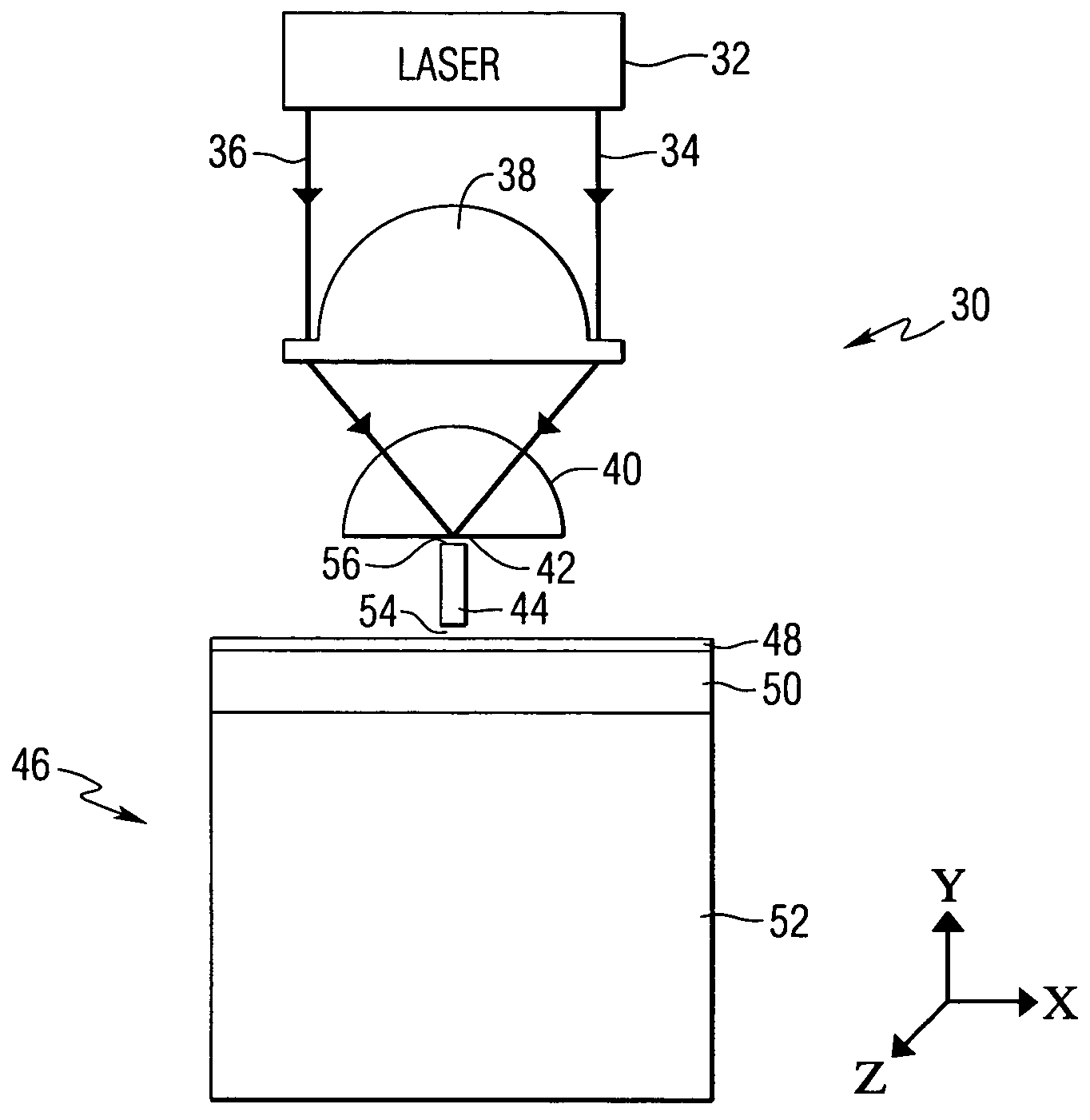
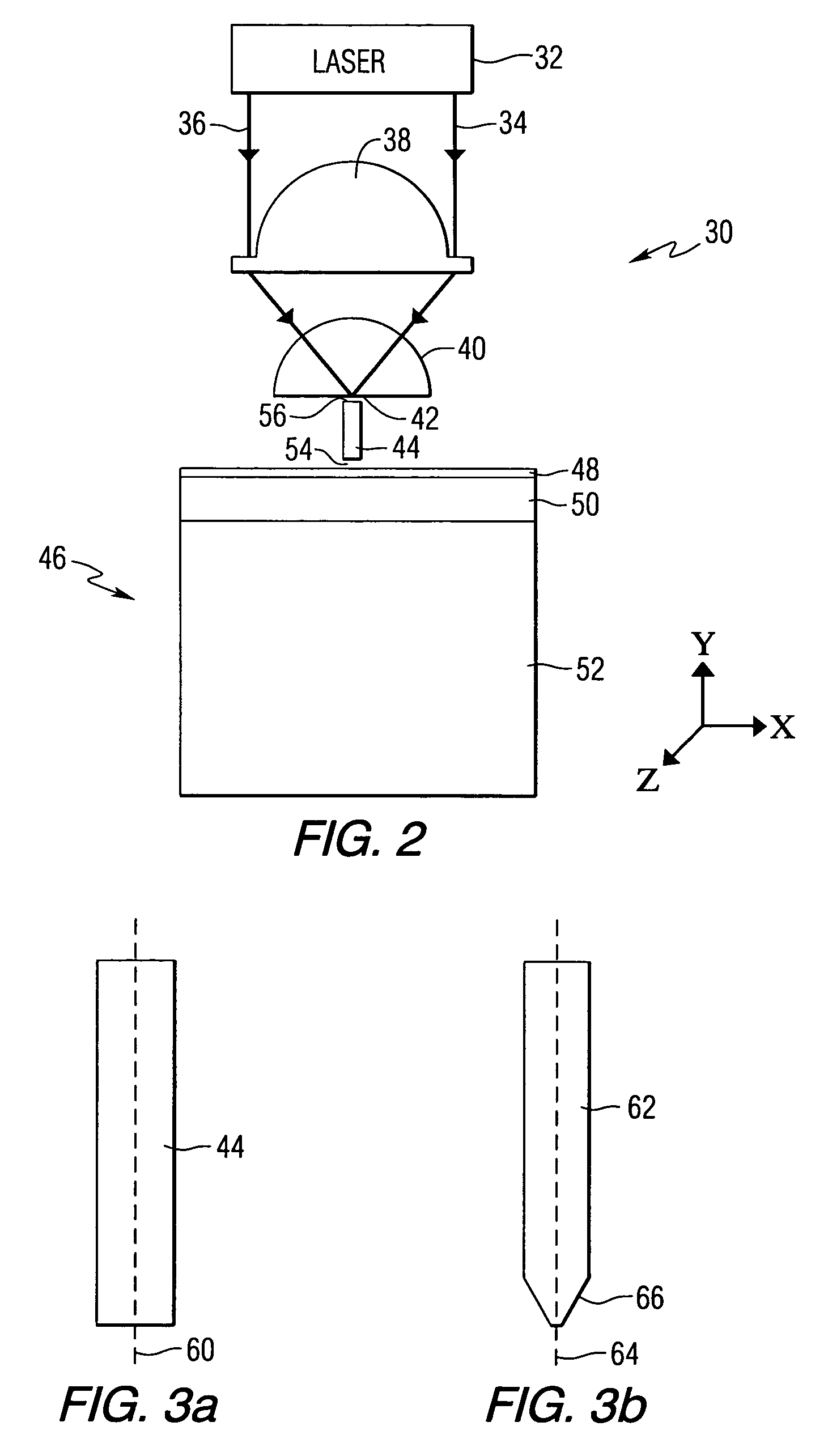
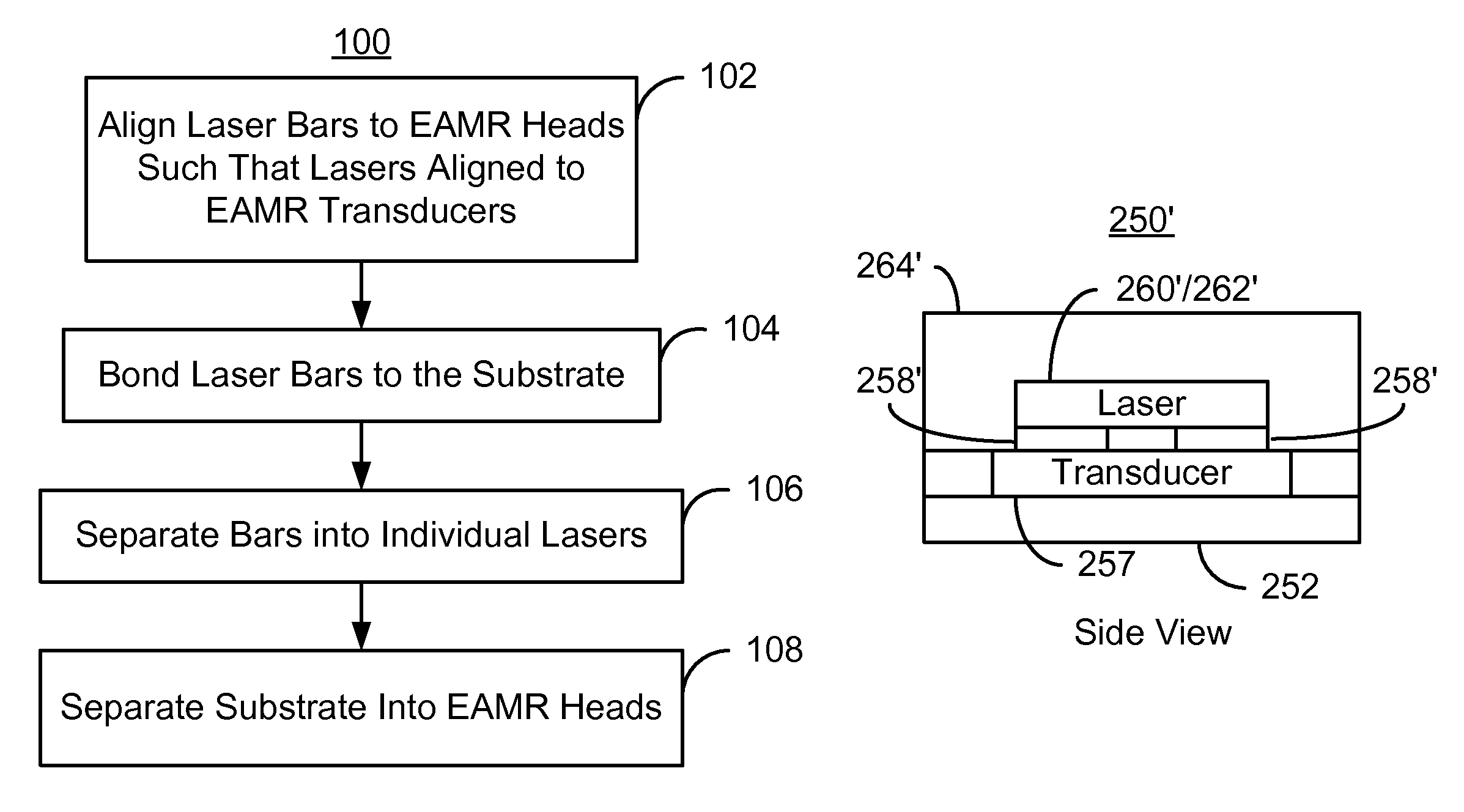
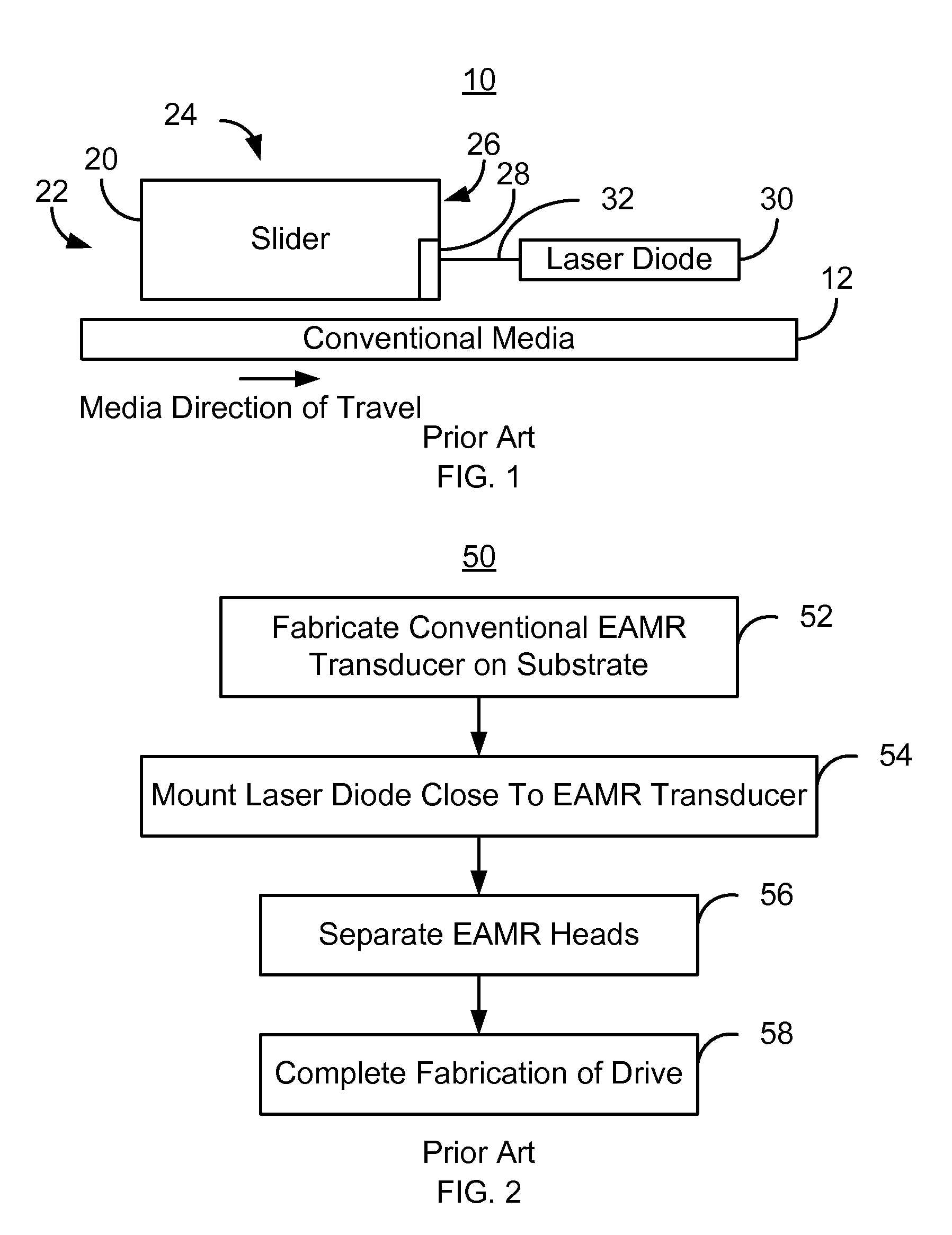
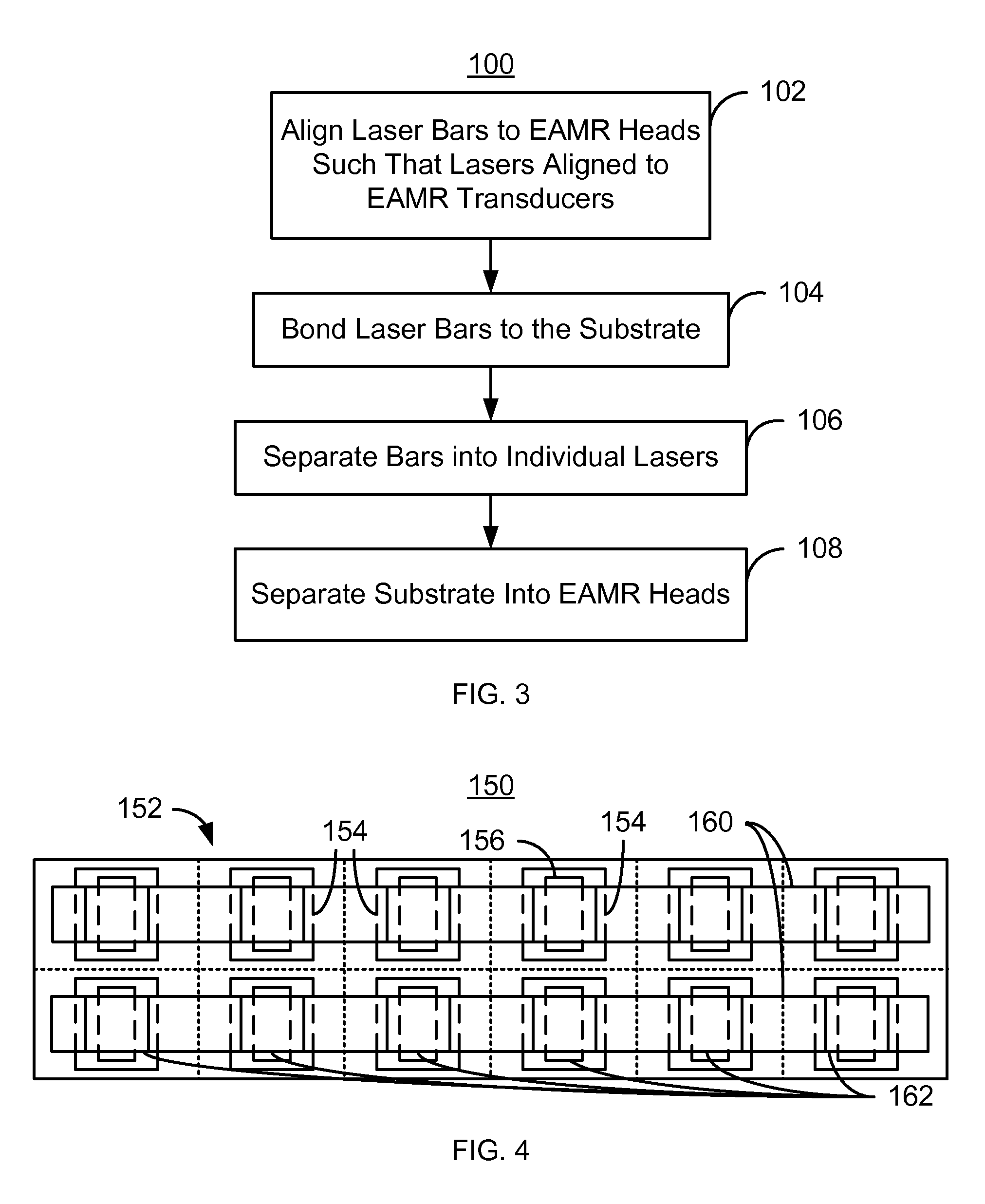
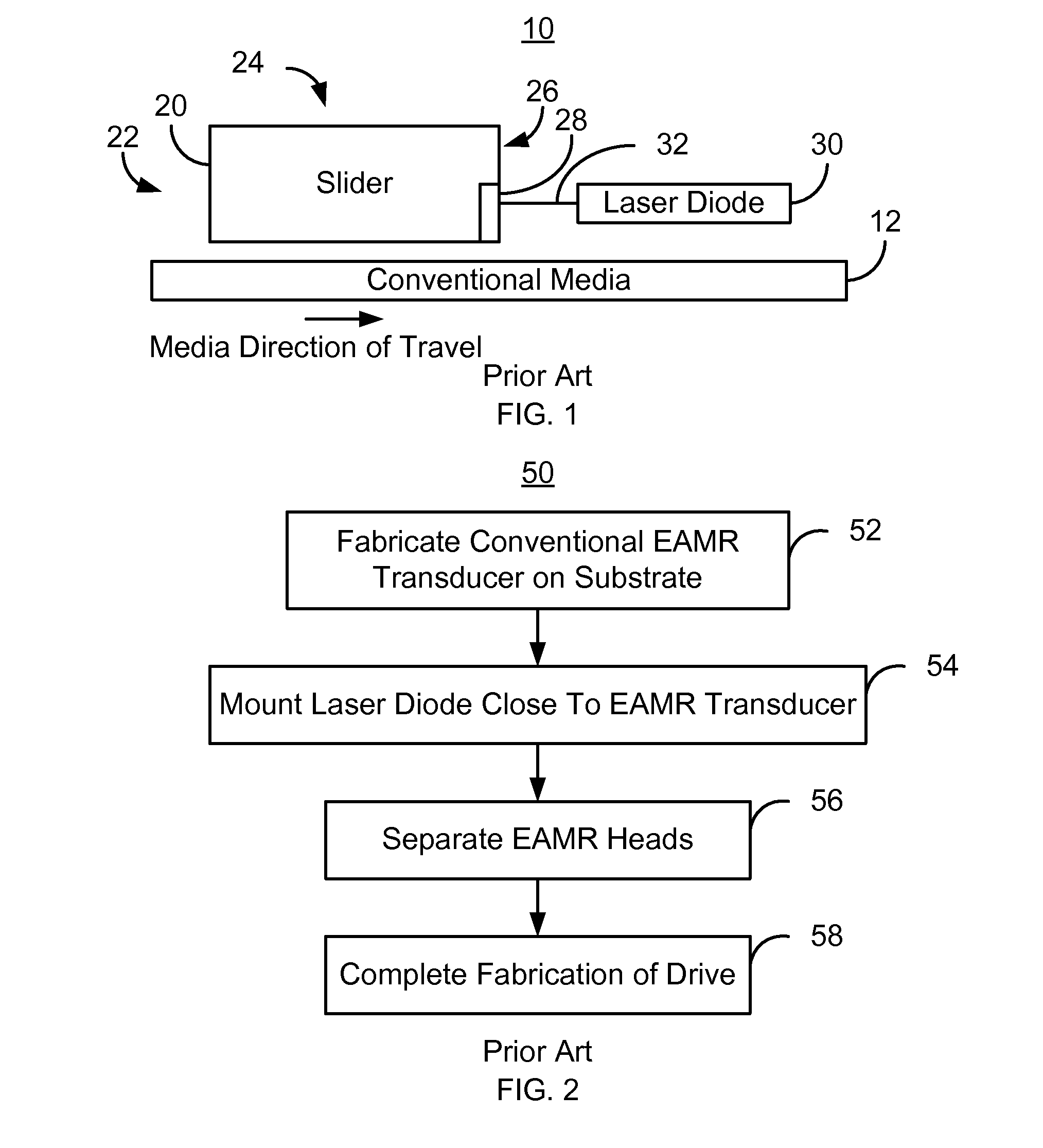
Method and system for mounting lasers on energy assisted magnetic recording heads
A method and system for providing energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) heads including EAMR transducers are described. The method and system include aligning a laser bar to the EAMR heads on a substrate. The laser bar includes lasers in locations corresponding to a portion of the EAMR transducers. The method and system also include bonding the laser bar to the substrate and removing a portion of the laser bar to separate the plurality of lasers. The substrate is separated into the EAMR heads.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic disk with a guard band arrangement
A magnetic disk including a substrate, a recording track section which is made of a magnetic member for recording and reproducing information magnetically and is provided on the substrate, and a guard band member which is provided between the recording track sections adjacent to each other so that they are substantially continued in a track direction and is harder than the magnetic member and is made of a non-magnetic material. Moreover, the magnetic member is not provided or magnetic members with a different thickness from the magnetic member forming the recording track section is provided on a lower area of the guard band member.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
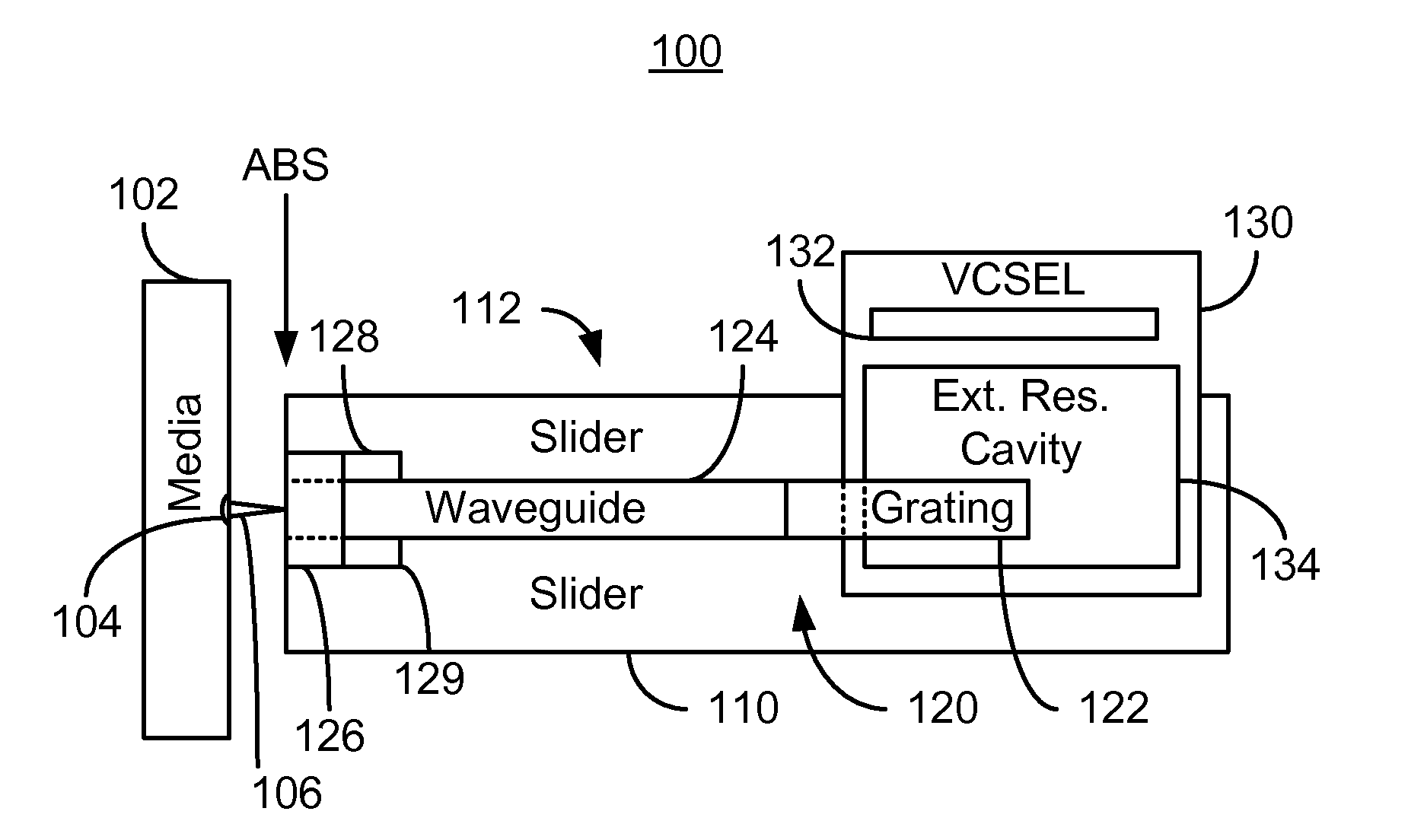
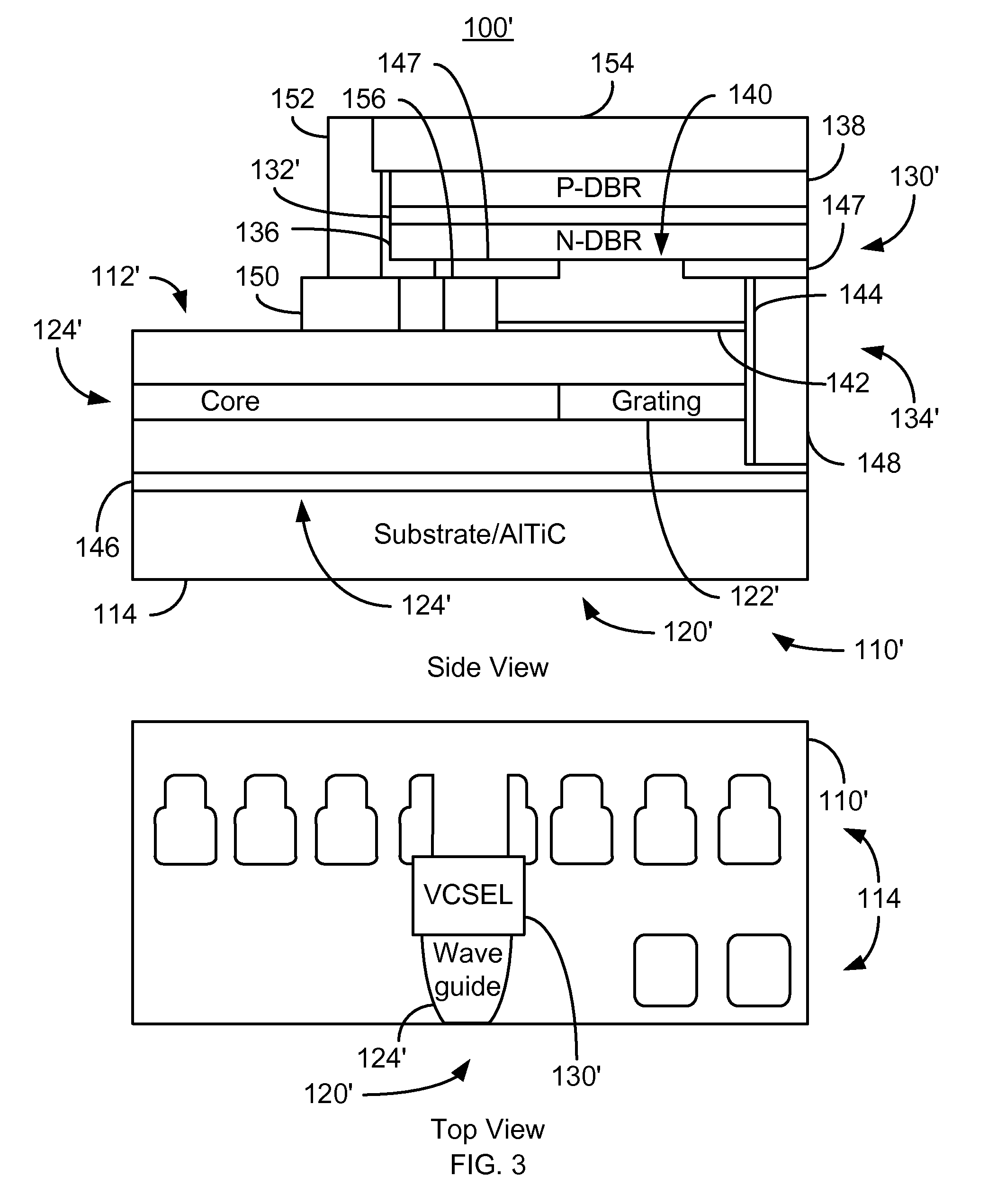
Method and system for providing energy assisted magnetic recording disk drive using a vertical surface emitting laser
A method and system for providing an energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) disk drive are described. The EAMR disk drive includes a media, a slider having a trailing face, at least one EAMR head on the slider, and at least one vertical surface emitting laser (VCSEL). The VCSEL(s) includes a plurality of quantum wells and an extended resonance cavity. The VCSEL(s) provides energy to the EAMR disk drive. The extended resonance cavity extends into the slider and is oriented substantially perpendicular to the trailing face of the slider. The EAMR head(s) include grating(s), waveguide(s), a write pole, and coil(s) for energizing the write pole. At least a portion of the grating(s) reside in the extended resonance cavity and couple energy from the VCSEL to the waveguide(s). The waveguide(s) direct the energy from the grating(s) toward the media.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
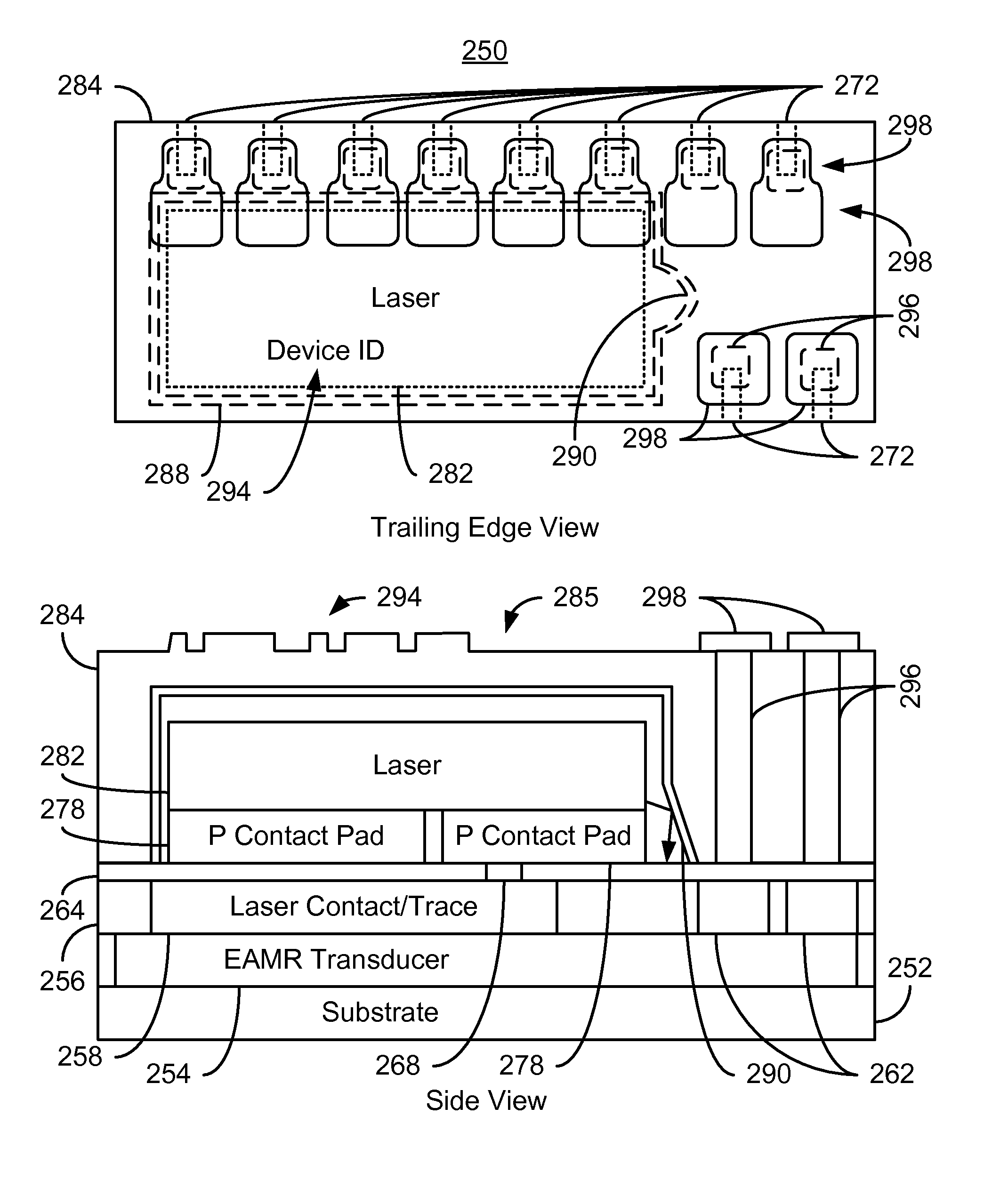
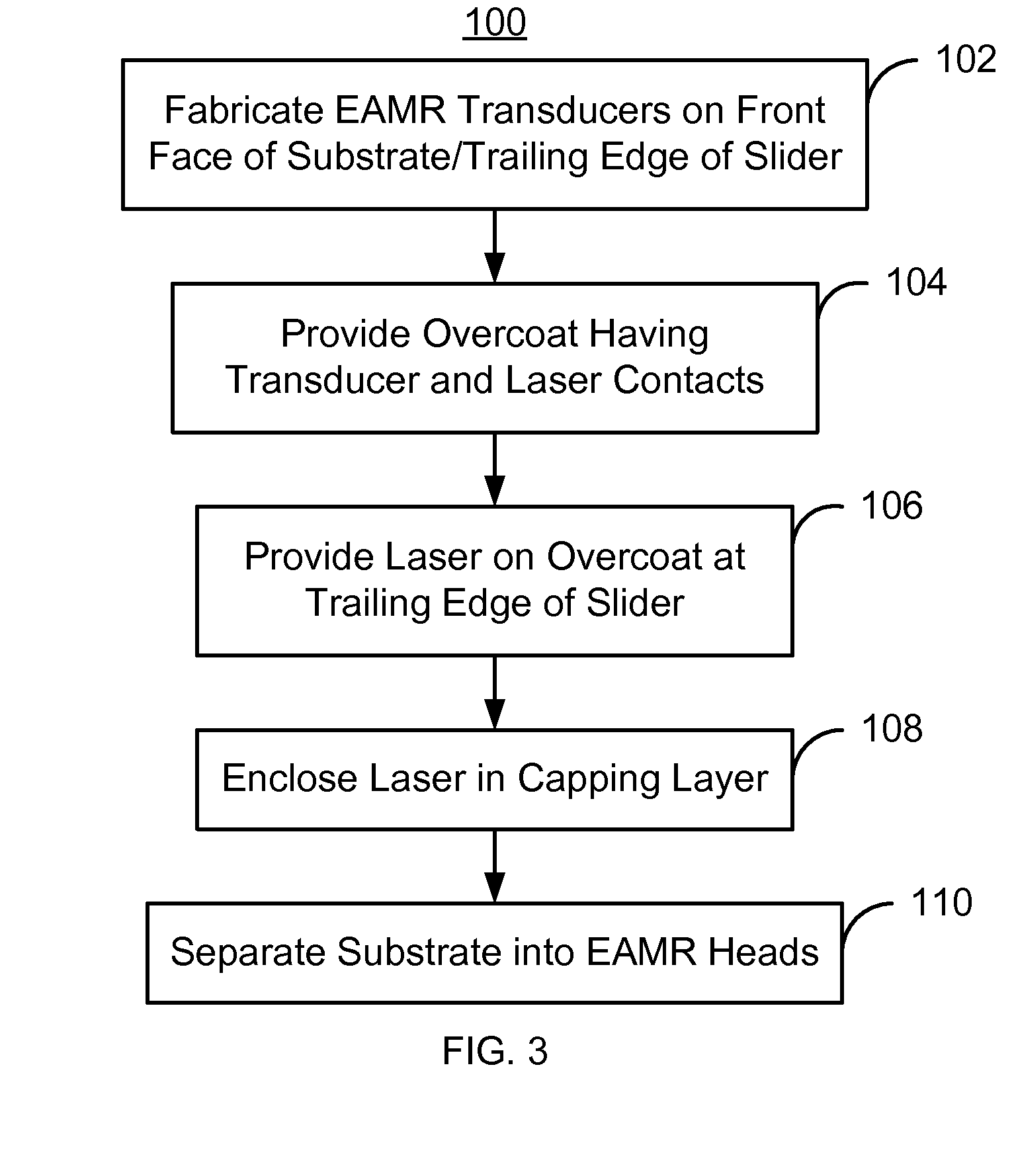
Method and system for providing an energy assisted magnetic recording head in a wafer packaging configuration
A method and system for providing energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) heads are described. The heads include sliders having leading and trailing edges. An EAMR transducer for each head is fabricated on a front face of a substrate that corresponds to the trailing edge of the slider. An overcoat layer that includes transducer and laser contact(s) is provided on the transducer. A laser for providing light to the transducer is provided on each slider. The laser is electrically coupled to the laser contact(s) and electrically insulated from at least part of the transducer contacts. The laser is enclosed in a capping layer, which has a laser-facing surface including a laser cavity, via(s), a trailing surface, and pads on the trailing surface. The laser cavity encloses the laser between the overcoat and capping layers. The via(s) provide electrical connection to the transducer contacts. The substrate is separated into the heads.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
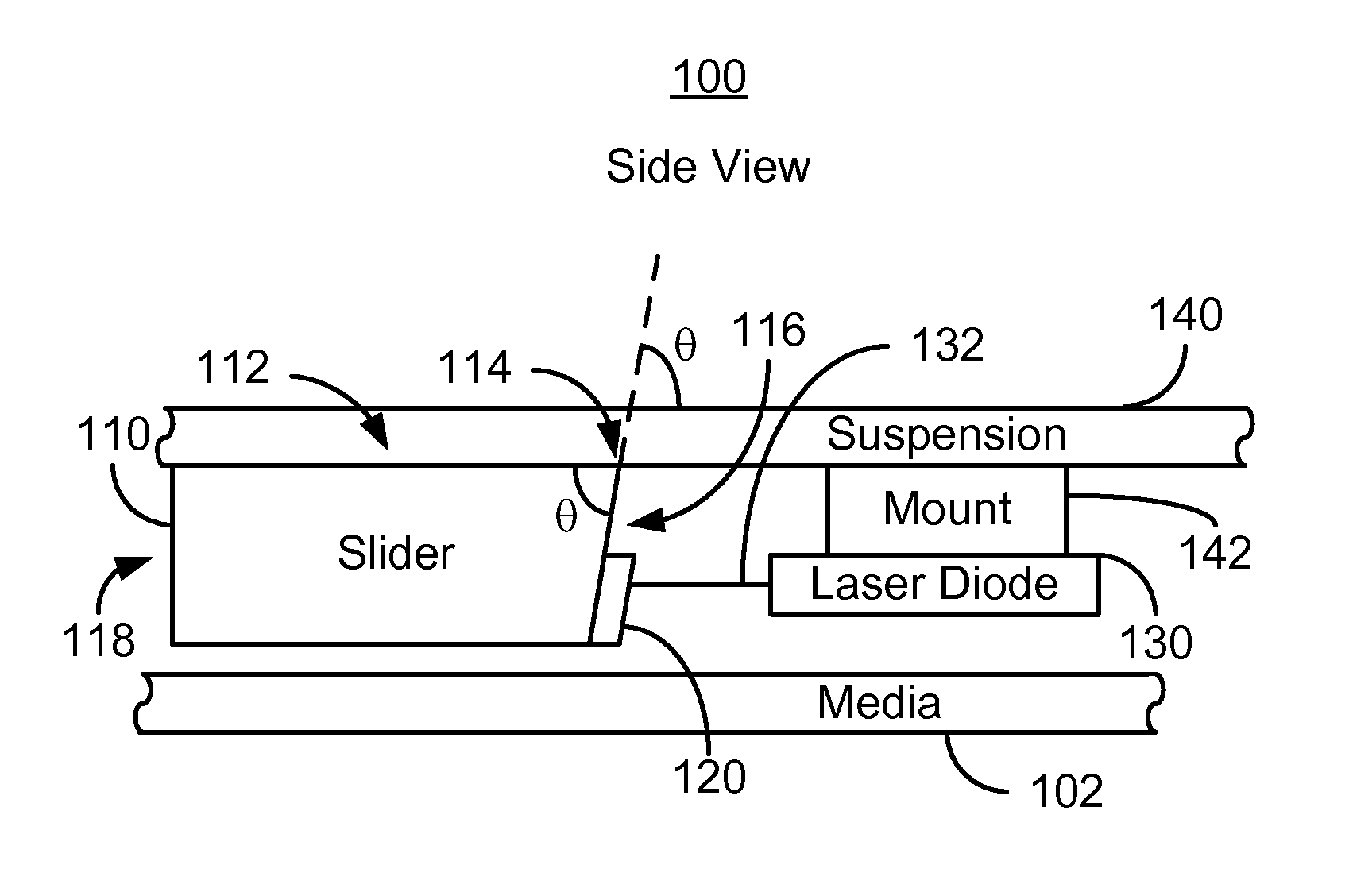
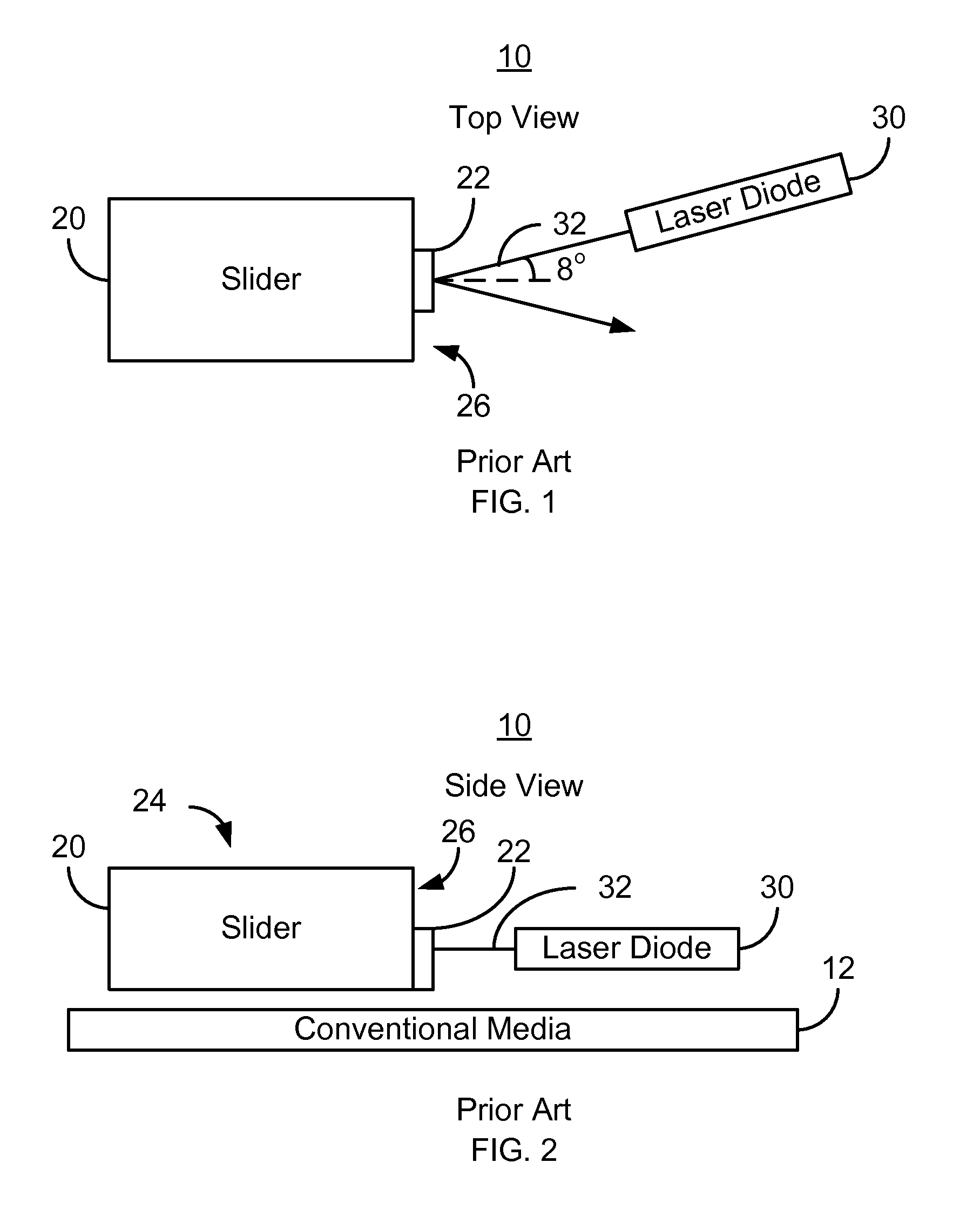
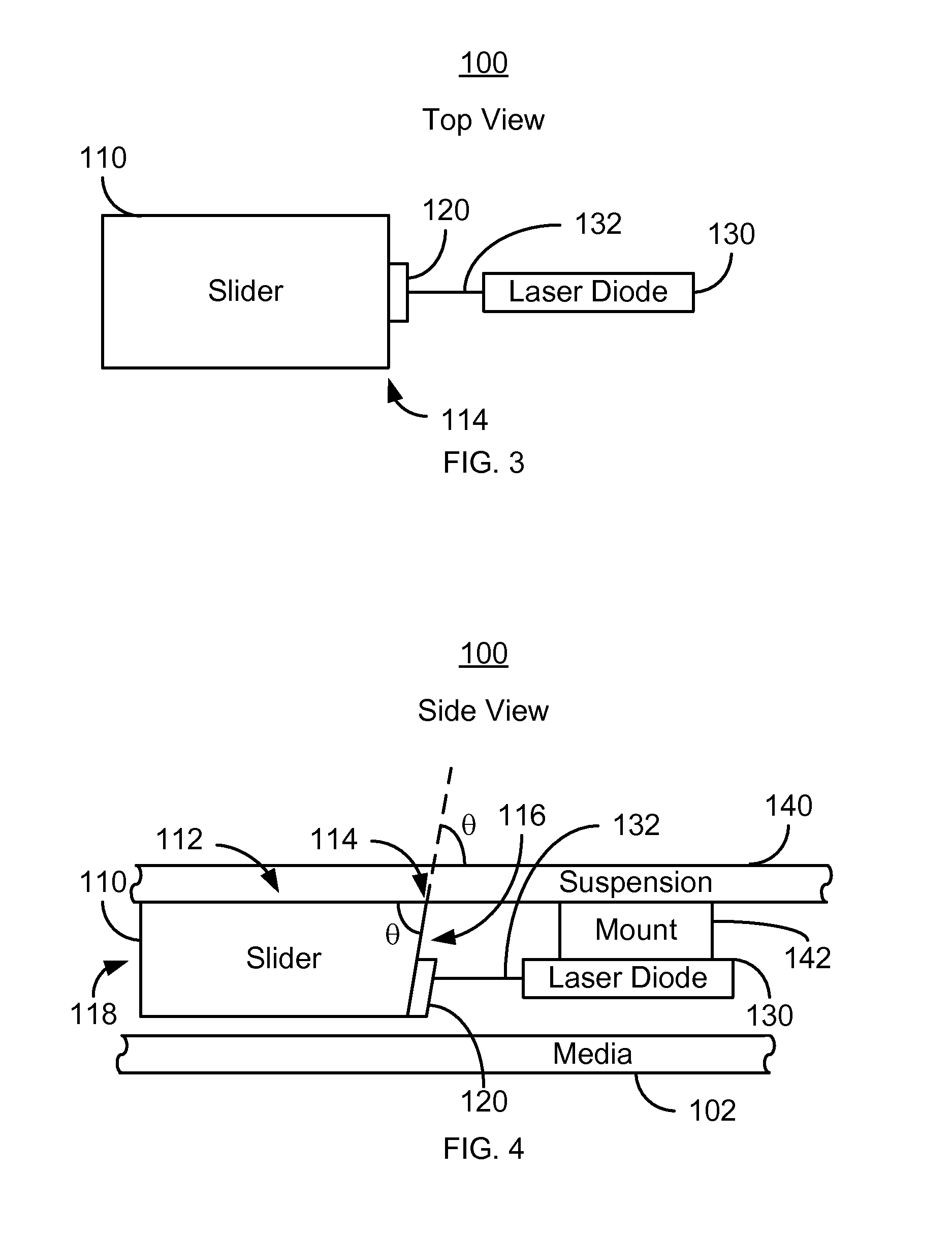
Method and system for coupling a laser with a slider in an energy assisted magnetic recording disk drive
A method and system for providing an energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) disk drive are described. The EAMR disk drive includes a slider, at least one EAMR transducer on the slider, and at least one laser coupled with the slider. The slider has a slider back side, a trailing face, and an intersection. The trailing face and the slider back side meet at the intersection. The trailing face makes an angle different from ninety degrees with the slider back side at the intersection. The laser(s) have an optical axis and are optically coupled with the trailing face of the slider. The optical axis is substantially perpendicular to the intersection and parallel to the slider back side.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
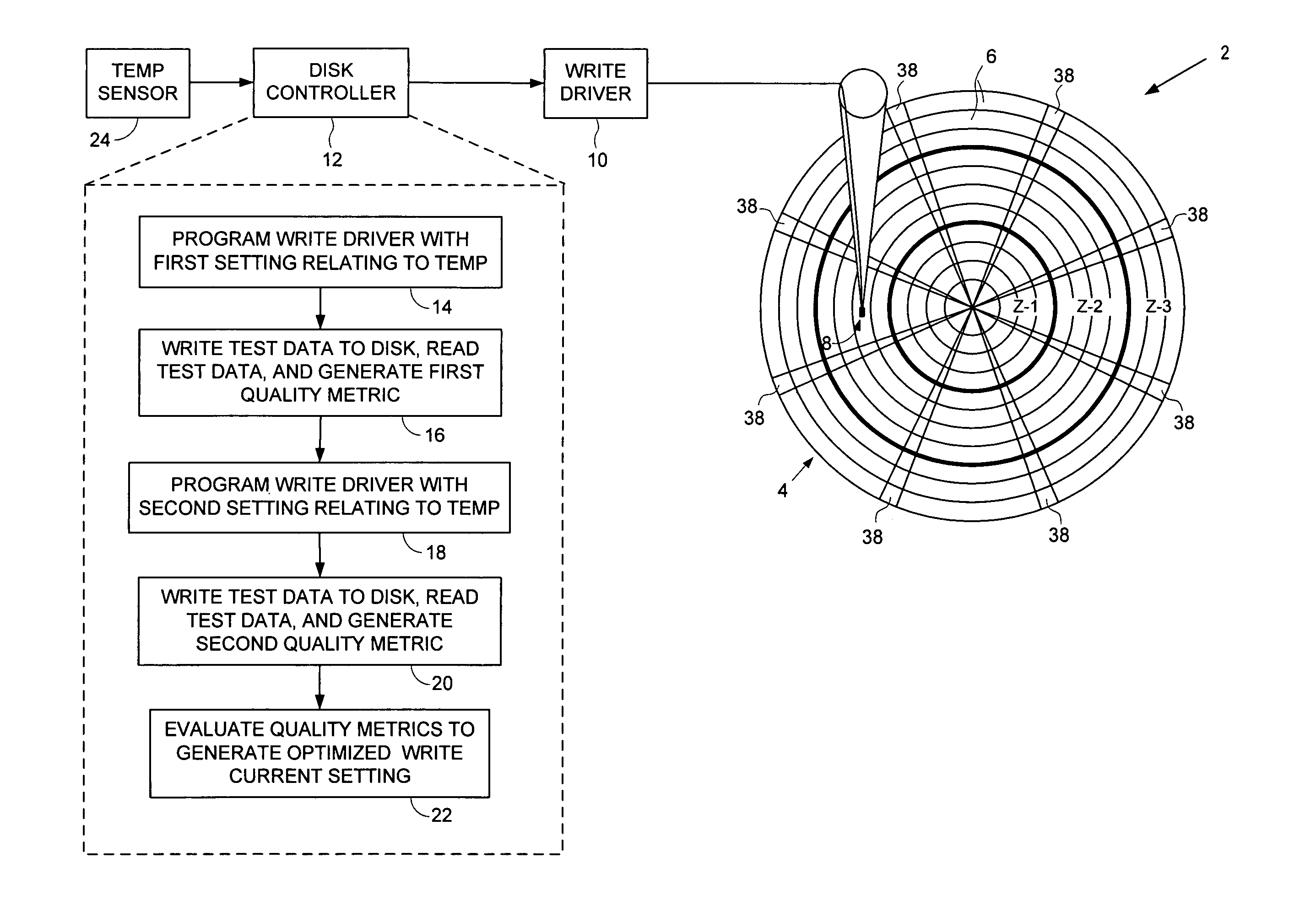
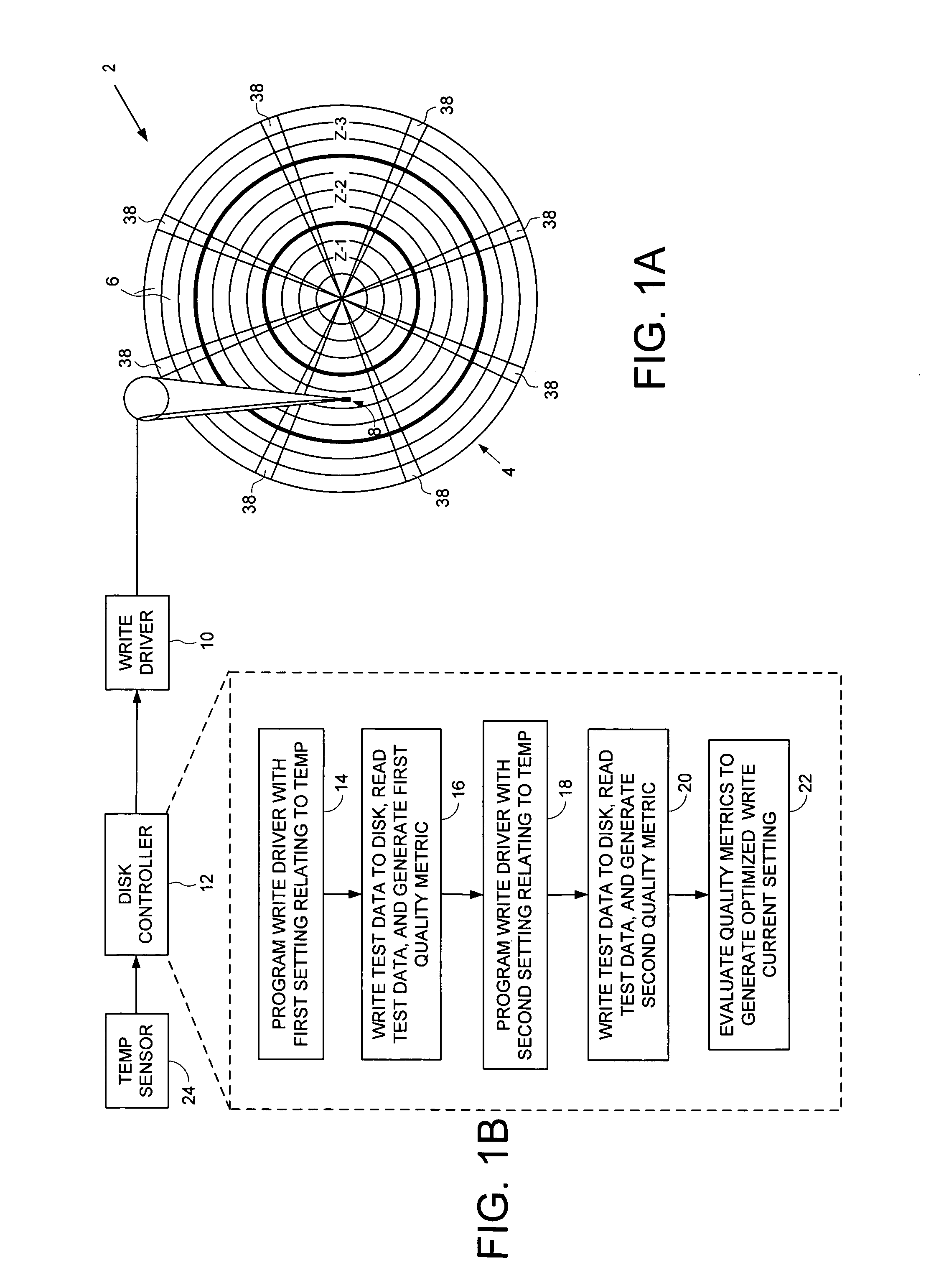
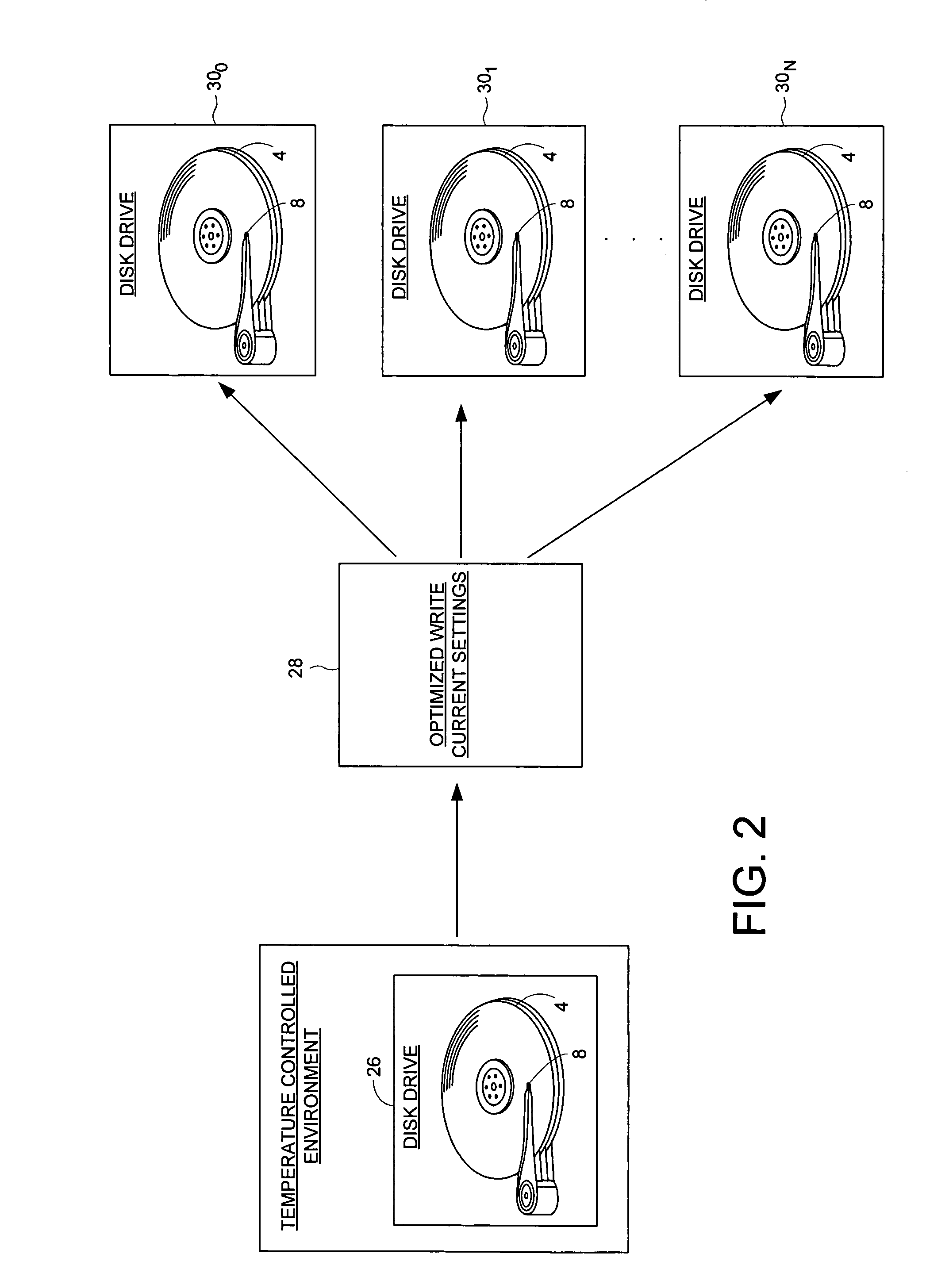
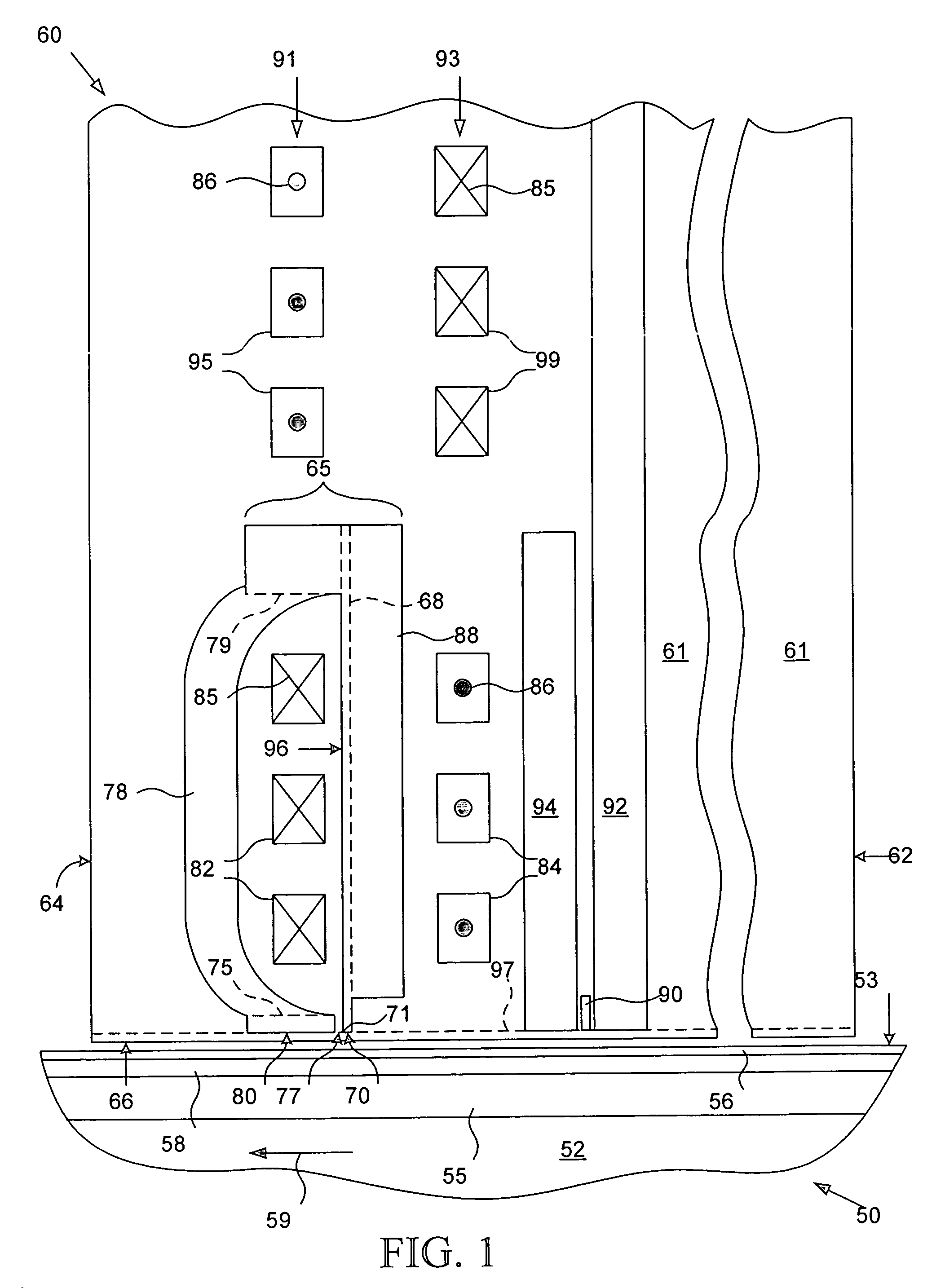
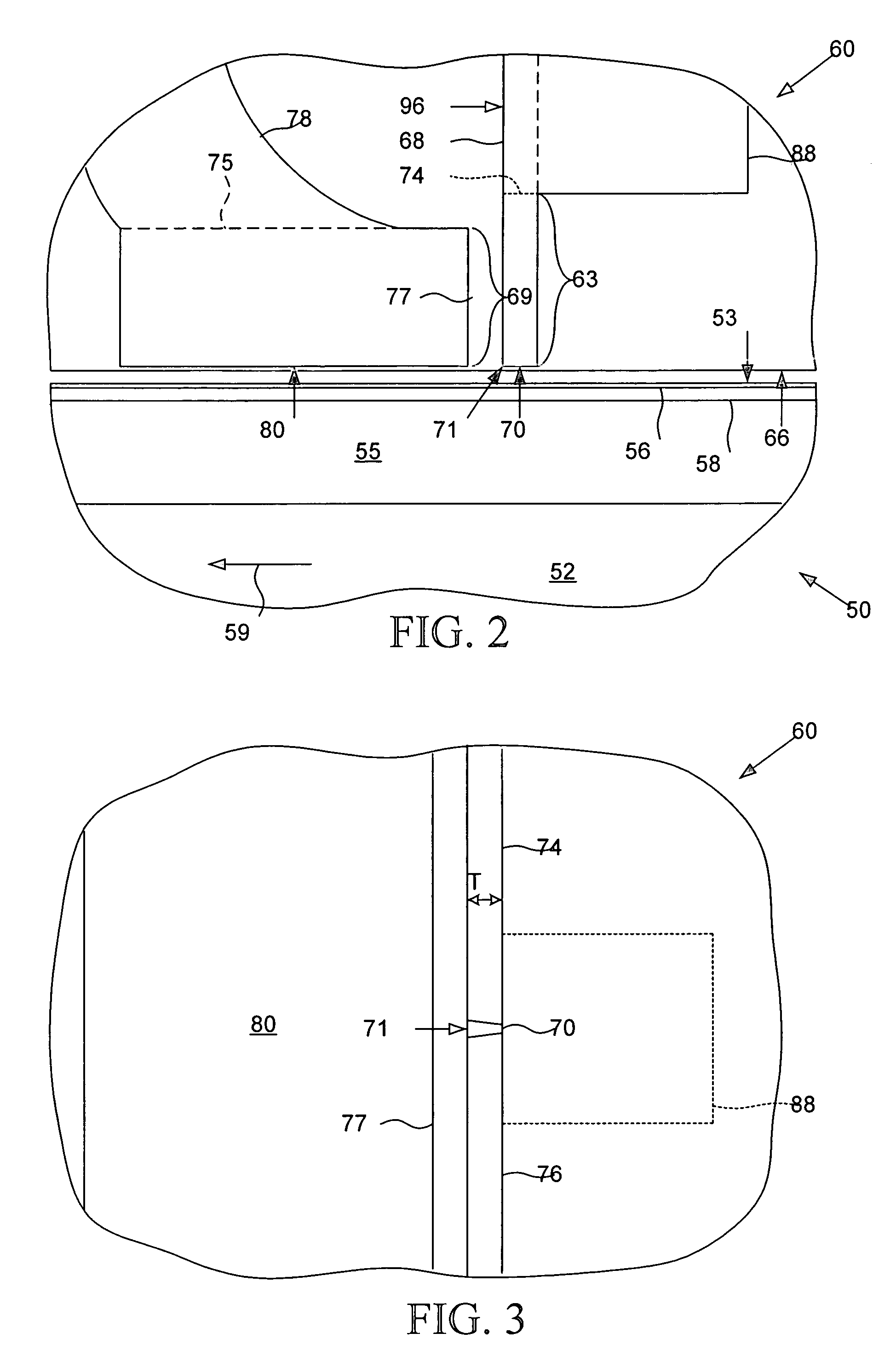
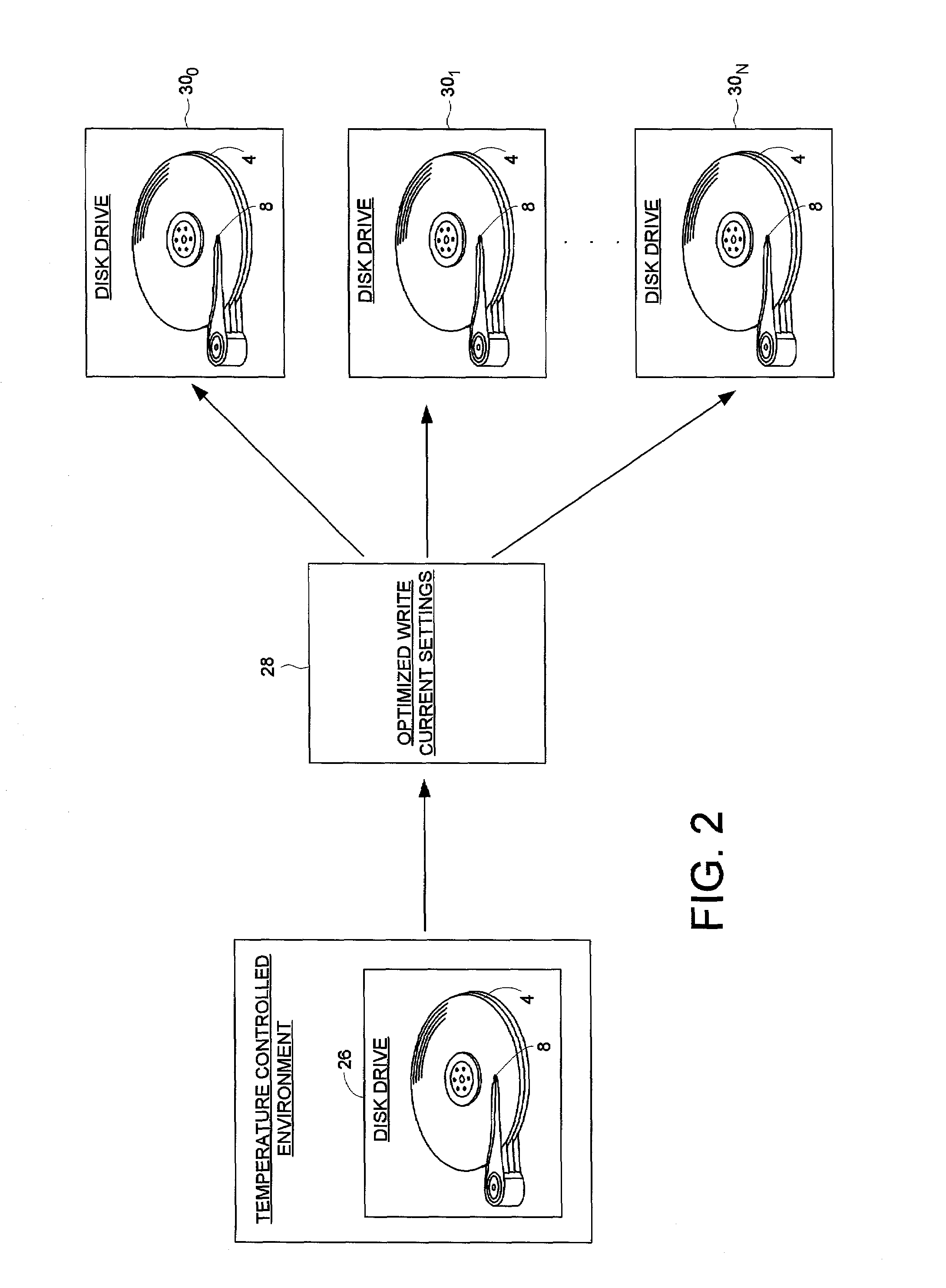
Disk drive for optimizing write current settings relative to drive operating characteristics and ambient temperature readings
InactiveUS7095577B1Record information storageFunctional testing of recording headsComputer scienceElectrical current
A disk drive is disclosed for optimizing write current settings relative to drive operating characteristics and an ambient temperature reading. Test data is written to and read from the disk using different write current settings to generate a plurality of corresponding quality metrics. The quality metrics are evaluated to generate an optimized write current setting for the ambient temperature reading. In one embodiment, the first write current setting is selected relative to a previously optimized write current setting that corresponds to the ambient temperature reading. This embodiment expedites the optimization process by testing write current settings surrounding a previous write current setting rather than testing the entire range of write current settings.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
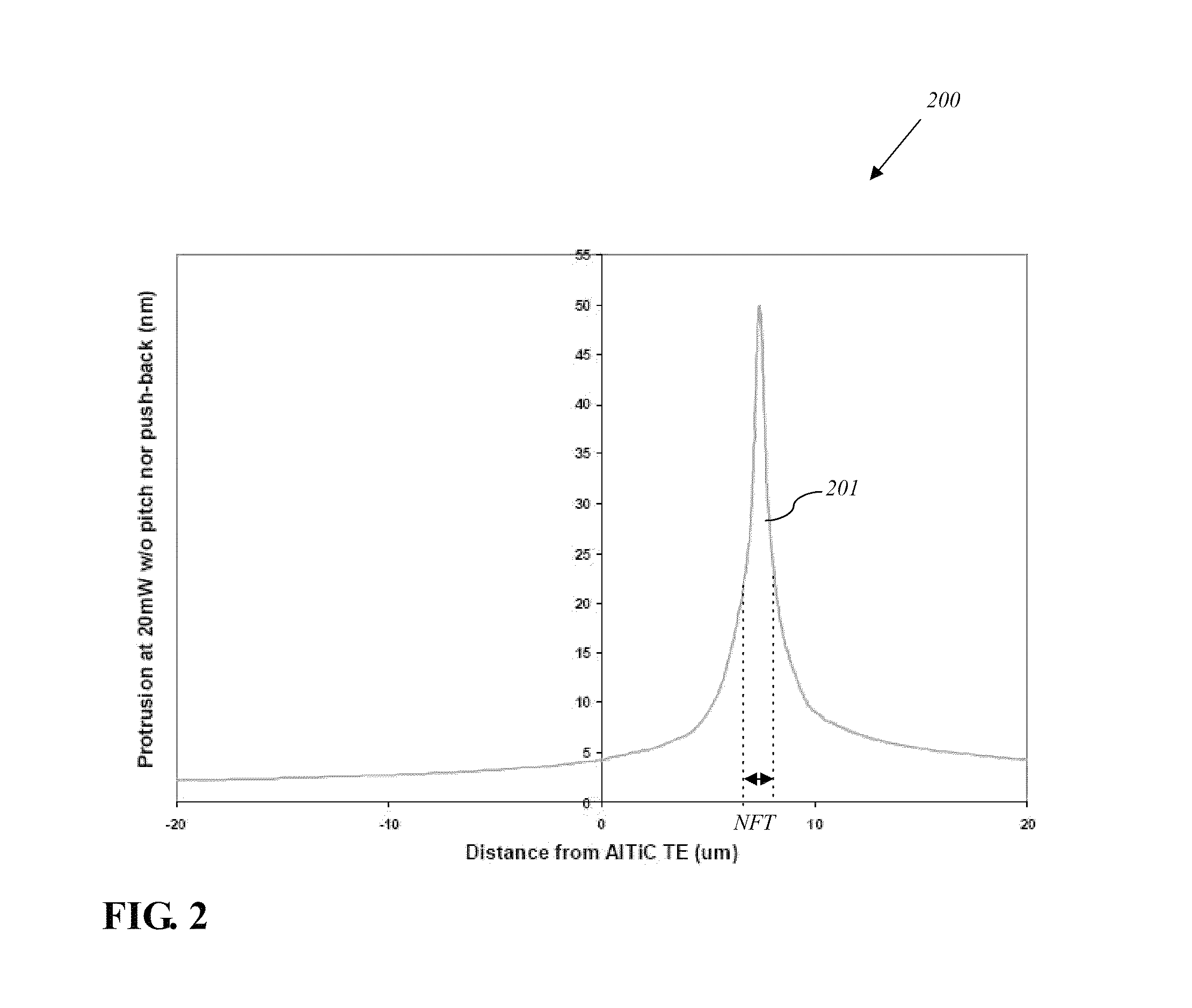
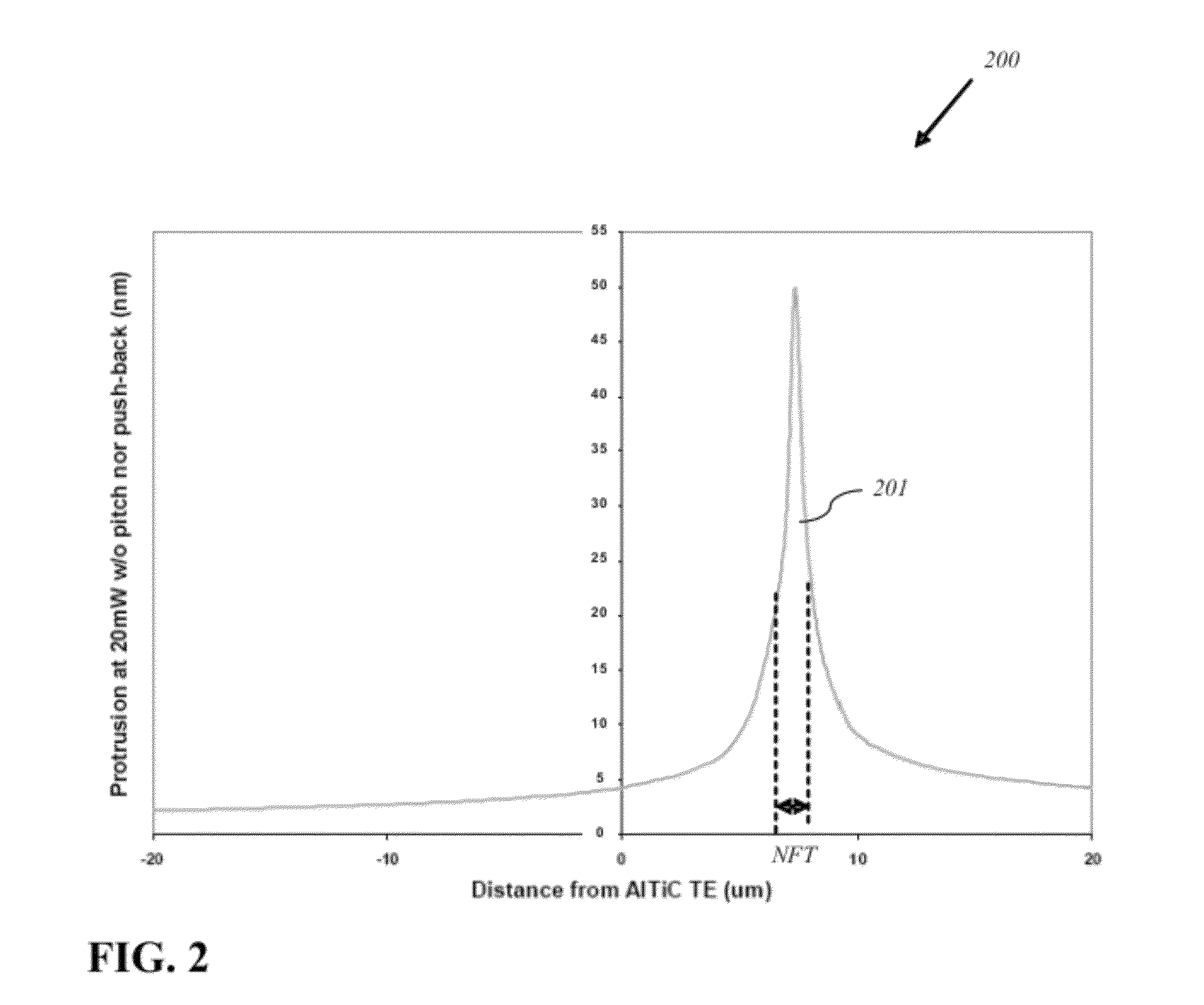
Reducing thermal protrusion of a near field transducer in an energy assisted magnetic recording head
ActiveUS8077418B1Preventing protrusion-related damageImprove reliabilityCombination recordingElectrical transducersTransducerOptical power
Methods of fabricating an energy-assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) head to compensate for a heat-induced protrusion of a near field transducer formed therein are disclosed. The methods can include applying optical power to the near field transducer to generate heat therein. The near field transducer protrudes beyond an air bearing surface of the EAMR head by the generated heat. The methods can further include removing a protruded portion of the near field transducer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
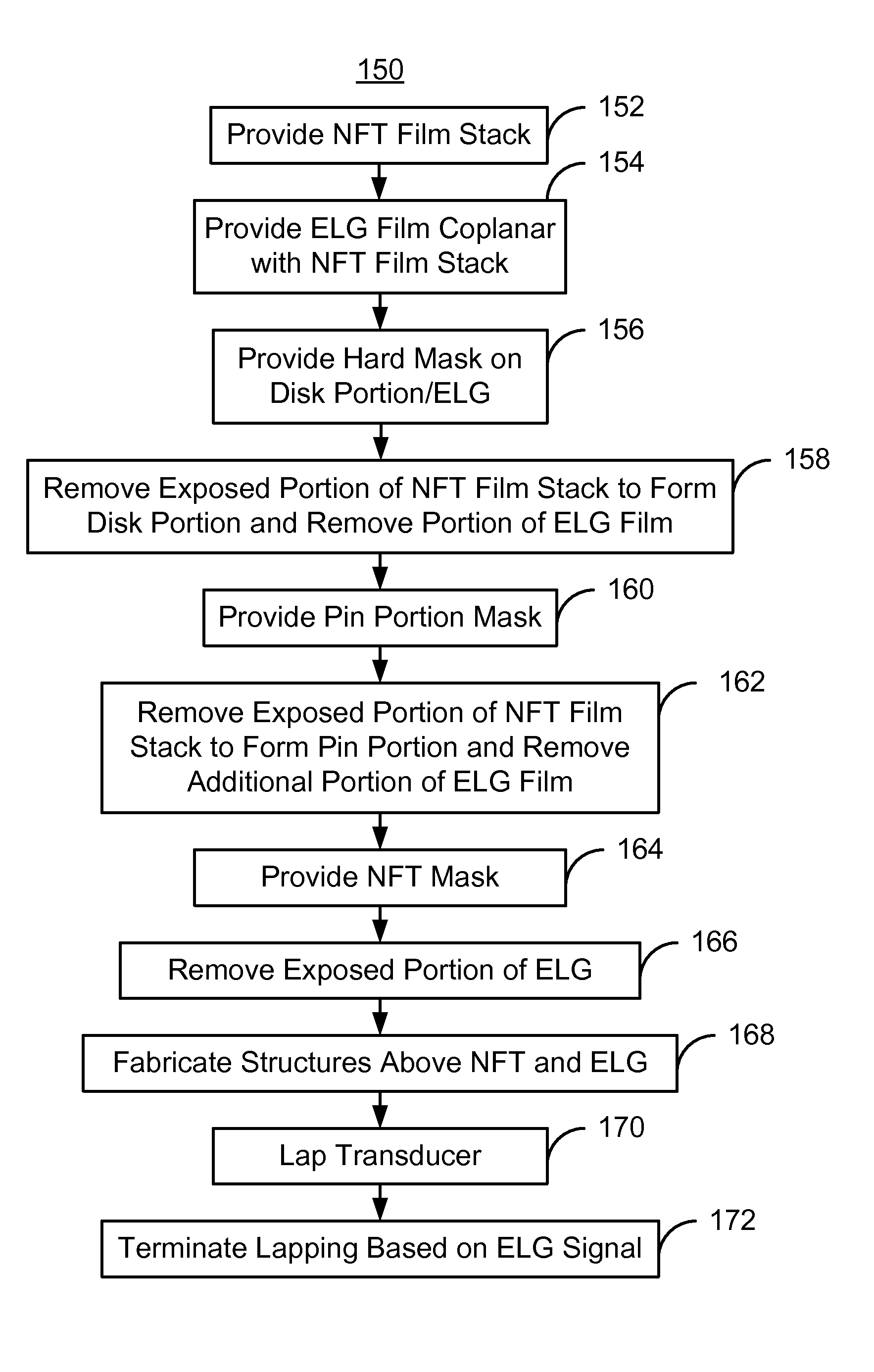
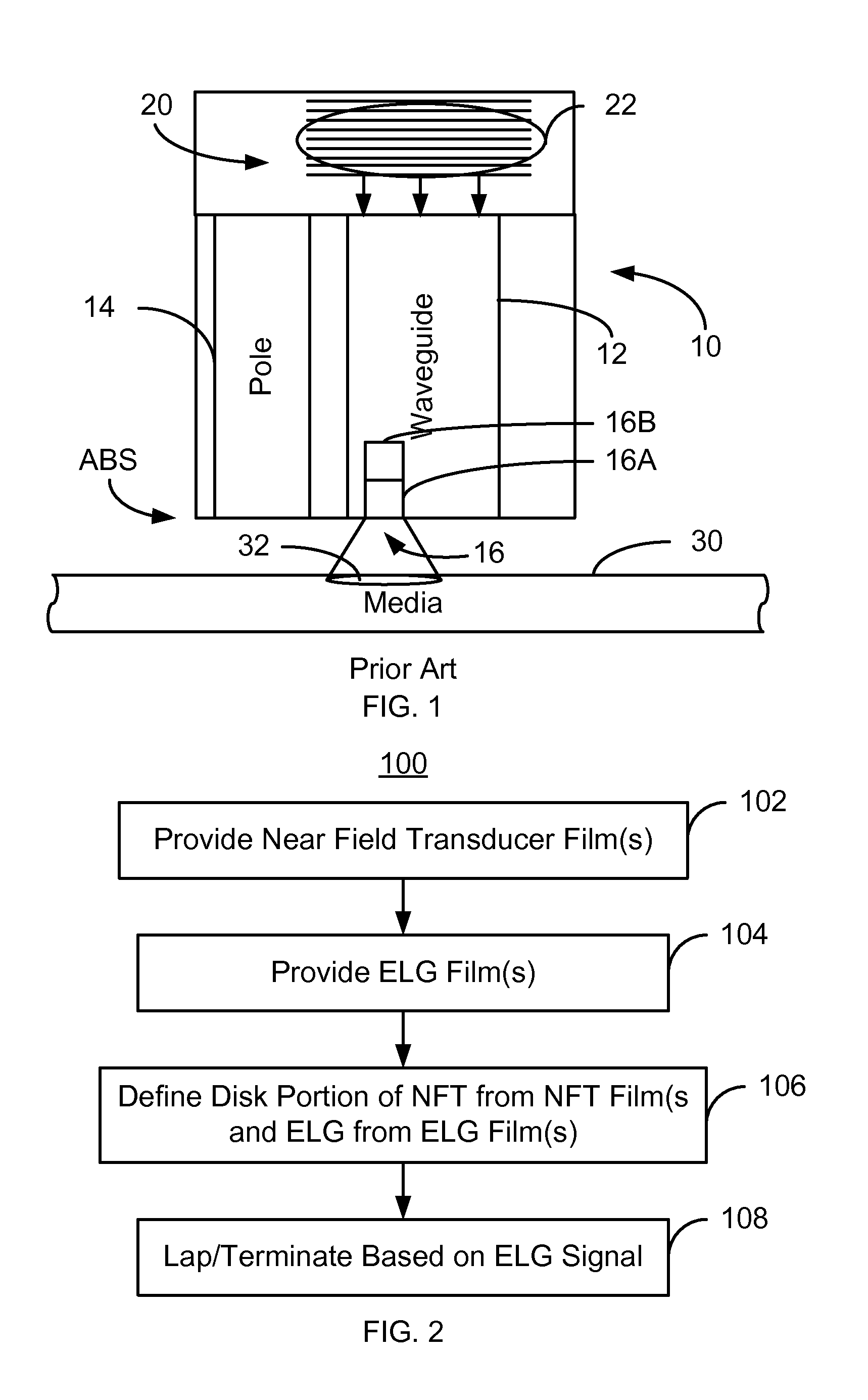
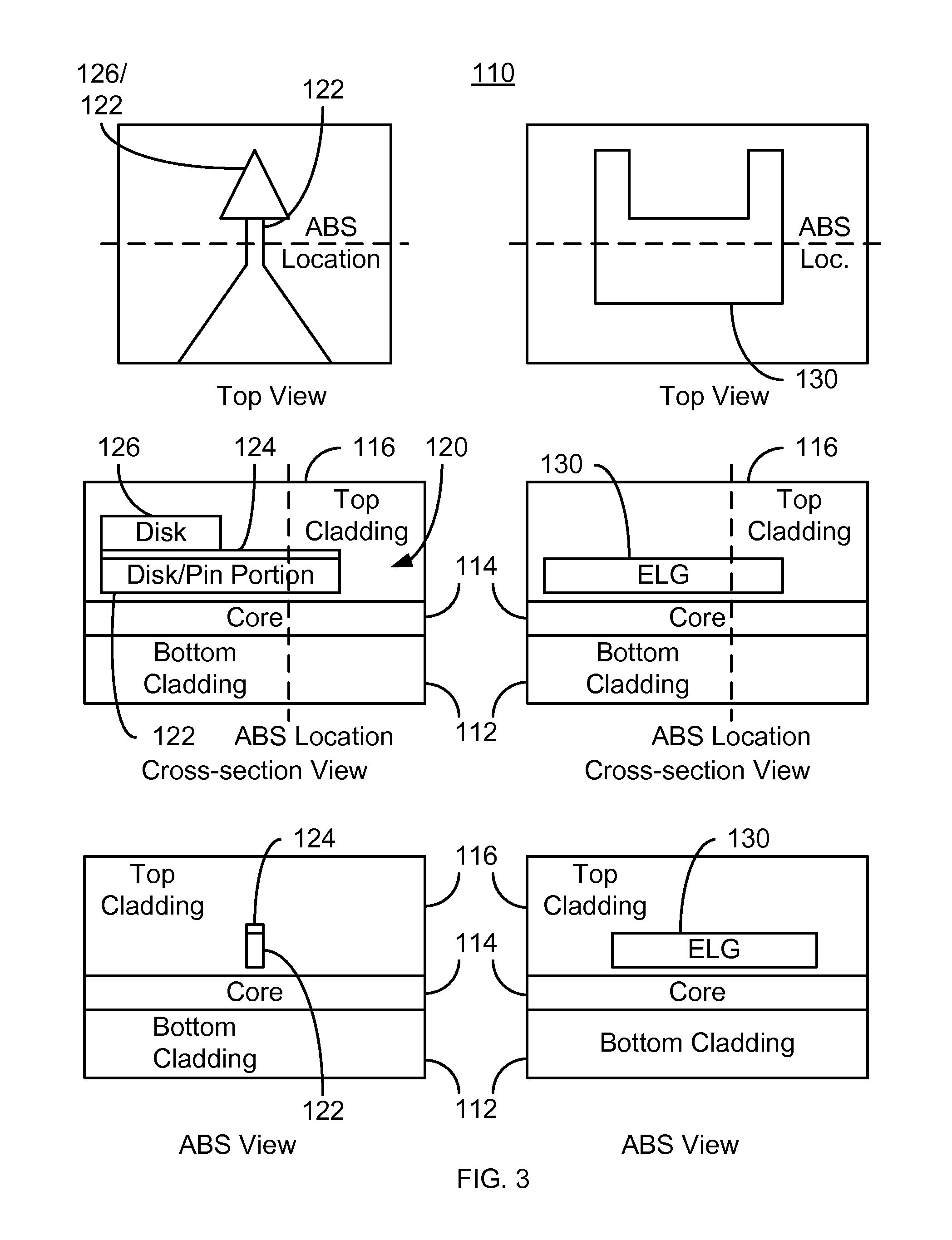
Method for providing an electronic lapping guide corresponding to a near-field transducer of an energy assisted magnetic recording transducer
A method fabricates a transducer having an air-bearing surface (ABS). The method includes providing at least one near-field transducer (NFT) film and providing an electronic lapping guide (ELG) film substantially coplanar with a portion of the at least one NFT film. The method also includes defining a disk portion of an NFT from the portion of the at least one NFT film and at least one ELG from the ELG film. The disk portion corresponds to a critical dimension of the NFT from an ABS location. The method also includes lapping the at least one transducer. The lapping is terminated based on a signal from the ELG.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic head for perpendicular recording with hard bias structure for write pole tip
A magnetic head for writing information on a relatively-moving medium is disclosed, the head having a leading end, a trailing end and a medium-facing surface, the head comprising: a soft magnetic write pole that terminates in a pole tip that is disposed adjacent to the medium-facing surface; at least one coil section that is disposed adjacent to the write pole to induce a magnetic flux in the write pole; and a hard magnetic bias structure disposed within one micron of the pole tip to magnetically bias the pole tip.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
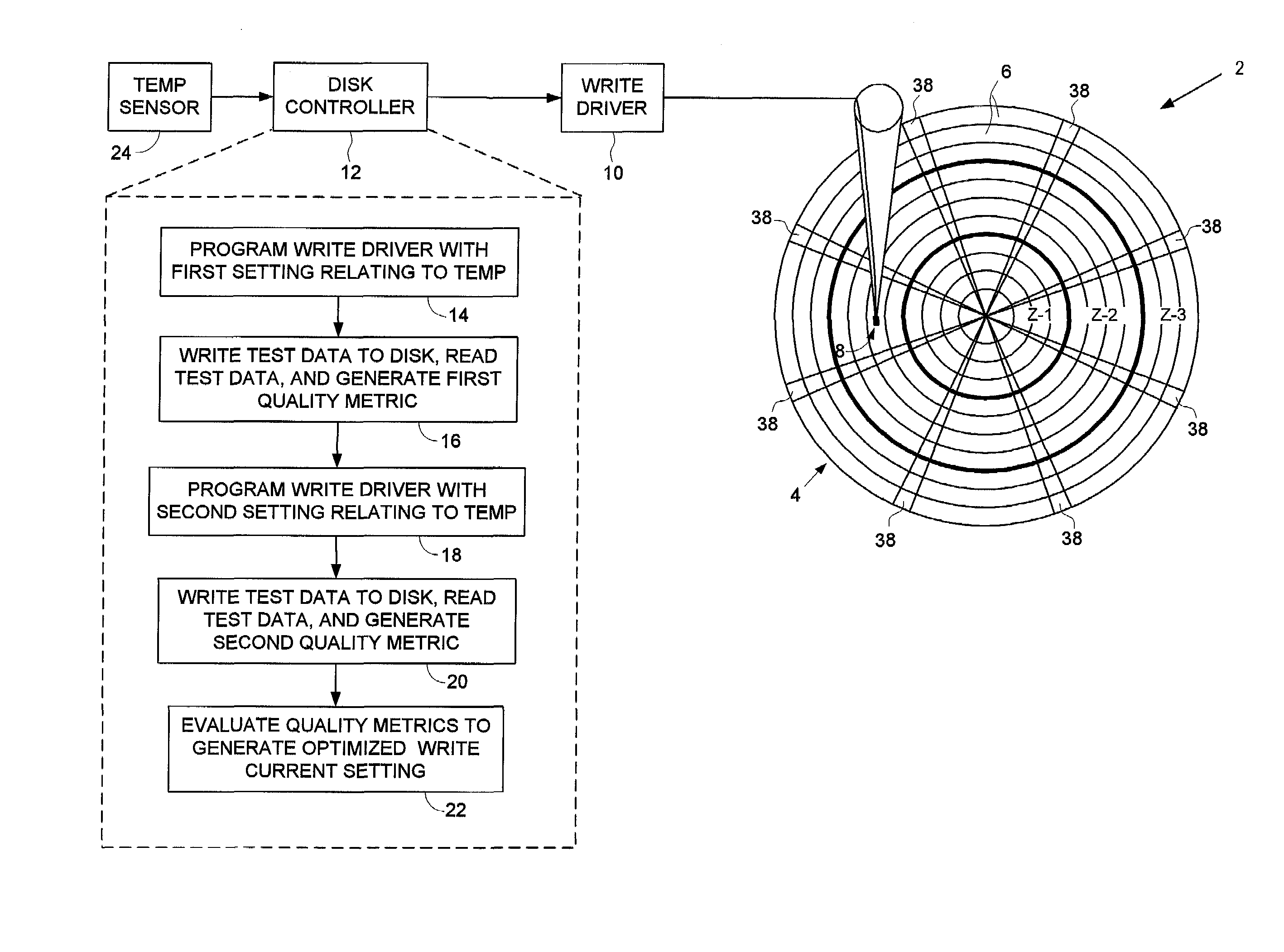
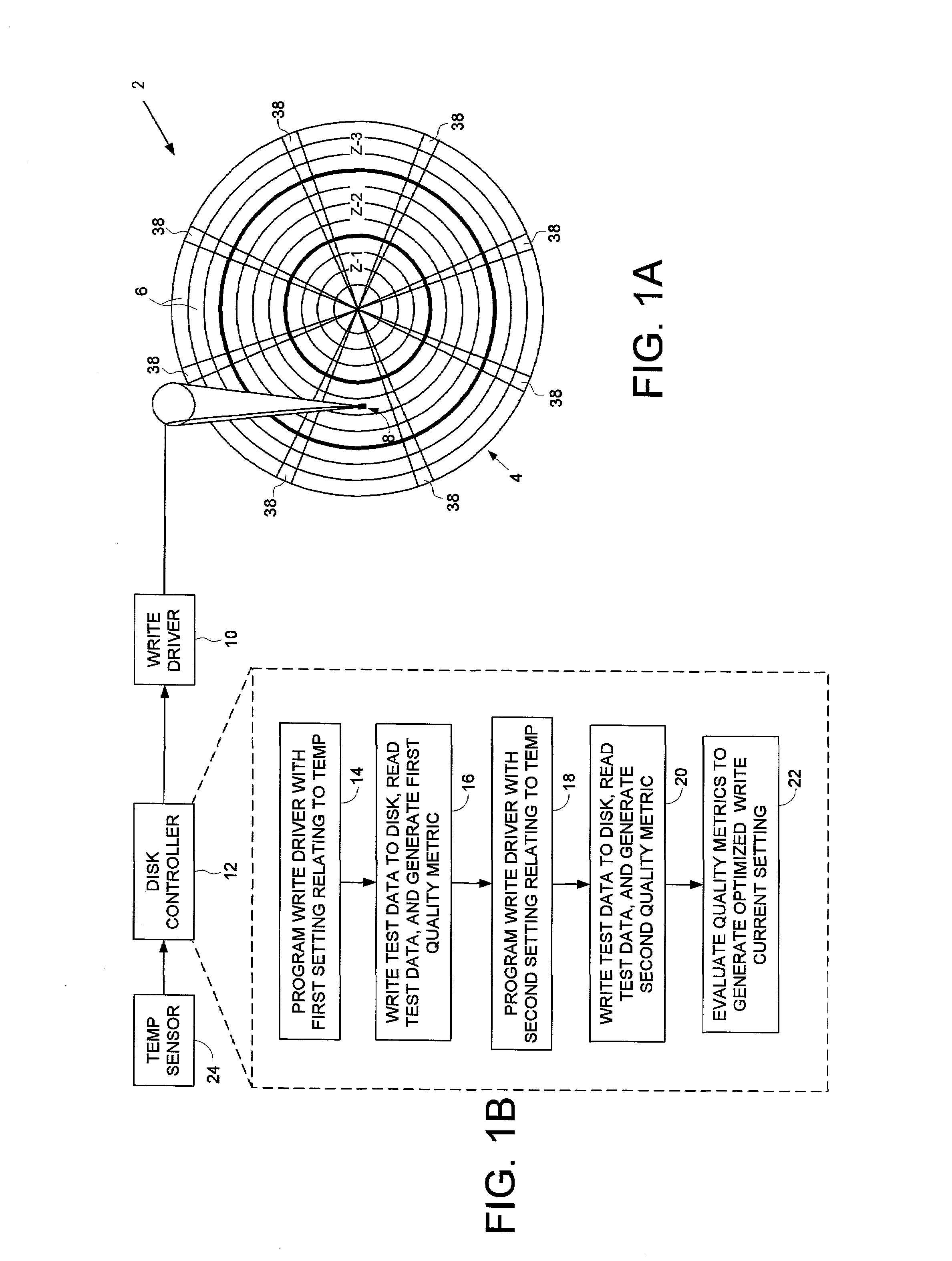
Disk drive for optimizing write current settings relative to drive operating characteristics and ambient temperature readings
InactiveUS6995933B1Record information storageFunctional testing of recording headsProcess engineeringElectrical current
A disk drive is disclosed for optimizing write current settings relative to drive operating characteristics and a plurality of ambient temperature readings. Test data is written to and read from the disk to generate quality metrics that are evaluated to generate an optimized write current setting for each ambient temperature reading. In one embodiment, the optimized write current settings are derived during manufacturing and used in-the-field during normal operation. In another embodiment, the optimized write current settings are re-optimized in-the-field to compensate for changes in the drive operating characteristics that occur over time (e.g., environmental changes and electrical and mechanical changes).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
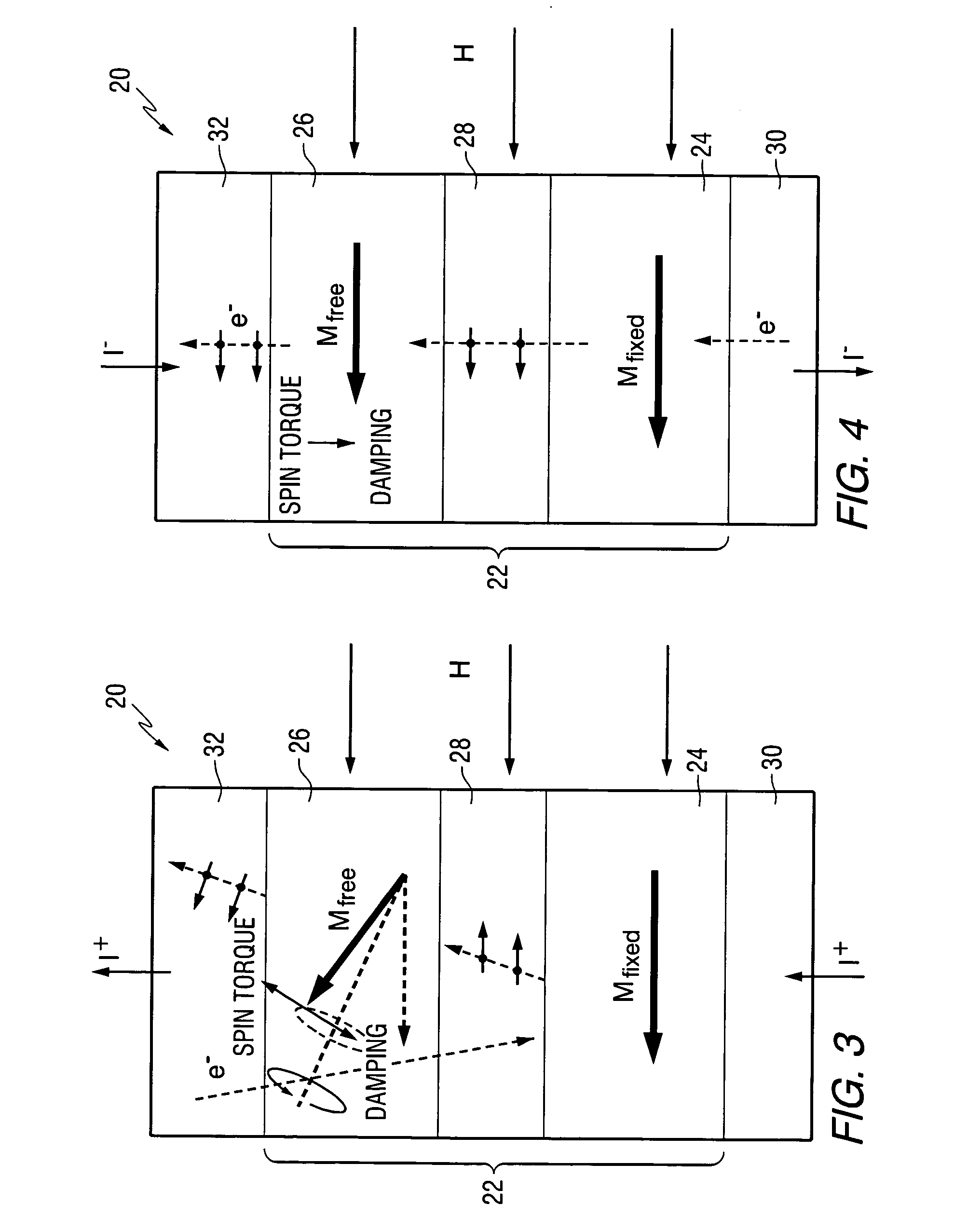
Magnetic recording head and magnetic recording apparatus
ActiveUS20080304176A1Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetic poles
A magnetic recording head includes a recording magnetic pole, and a spin oscillation device including a first magnetic layer having at least one magnetic material layer, a second magnetic layer having at least one magnetic material layer, and a first nonmagnetic layer provided between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer are antiferromagnetically coupled and / or magnetostatically coupled to each other. The first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer are laminated in a direction generally parallel to a medium facing surface and generally parallel to a side surface of the recording magnetic pole intersecting with the medium facing surface.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High-frequency oscillation element, magnetic information recording head, and magnetic storage device
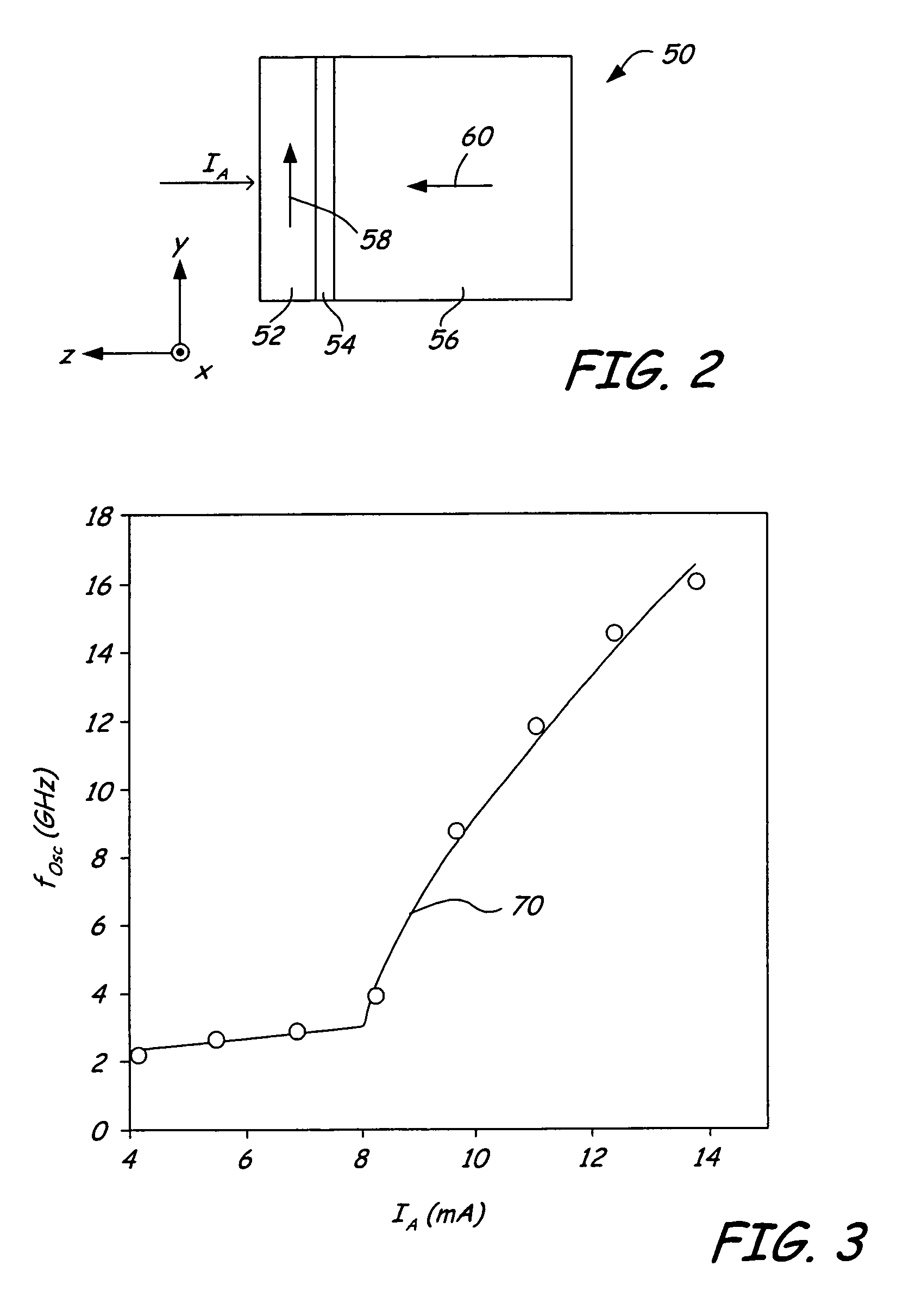
ActiveUS20050023938A1Increase temperatureIncrease speedPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSolid-state devicesMagnetic storageResonance
A high-frequency oscillation element has a ferromagnetic material which exhibits thermal fluctuation of magnetization and generates spin fluctuations in conduction electrons, a nonmagnetic conductive material which is laminated on the first magnetic material and transfers the conduction electrons, a magnetic material which is laminated on the nonmagnetic conductive material, generates magnetic resonance upon injection of the conduction electrons, and imparts magnetic dipole interaction to magnetization of a neighboring magnetic area by means of magnetic vibration stemming from the magnetic resonance, a first electrode electrically coupled with the first magnetic material, and a second electrode electrically coupled with the second magnetic material.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
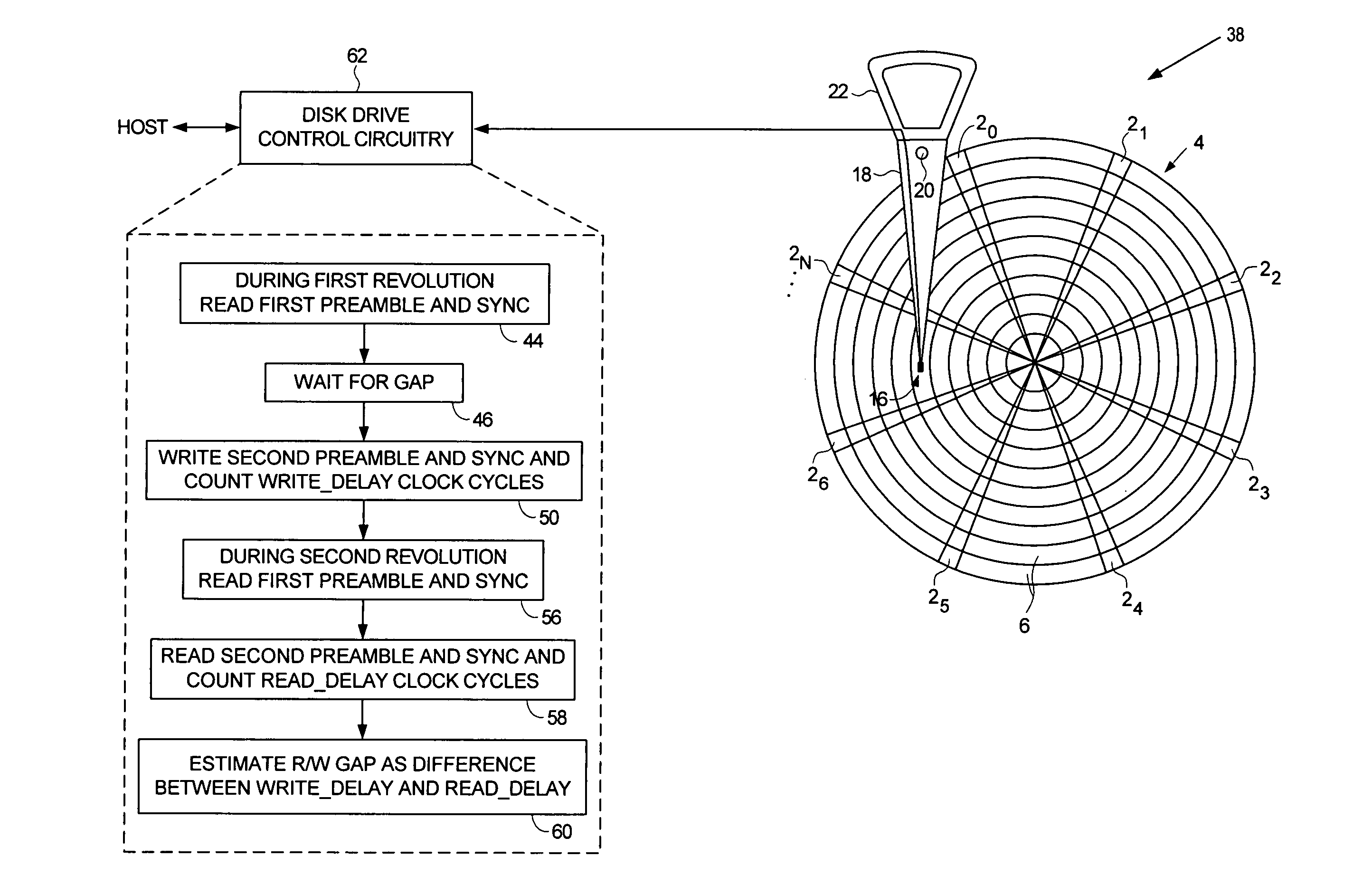
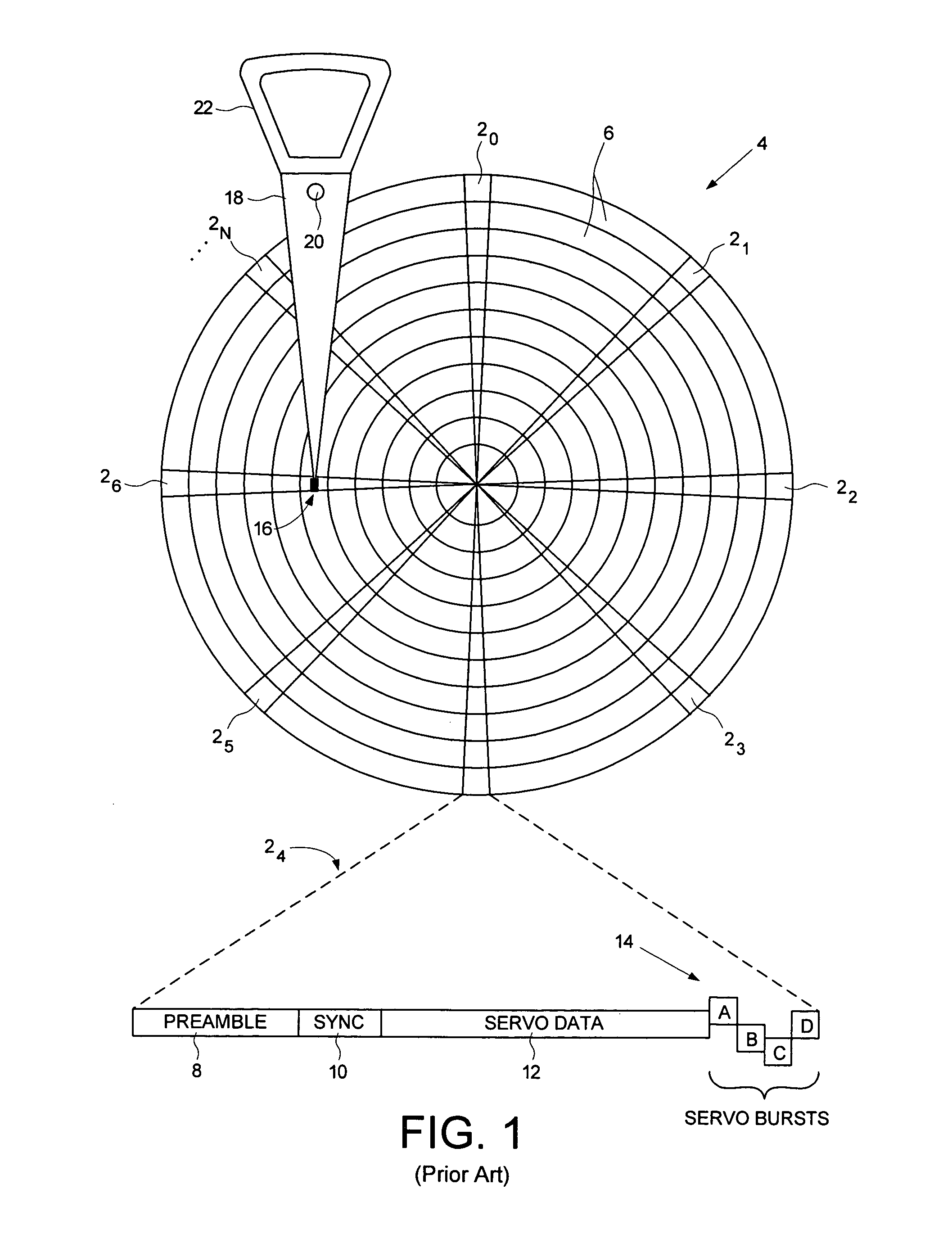
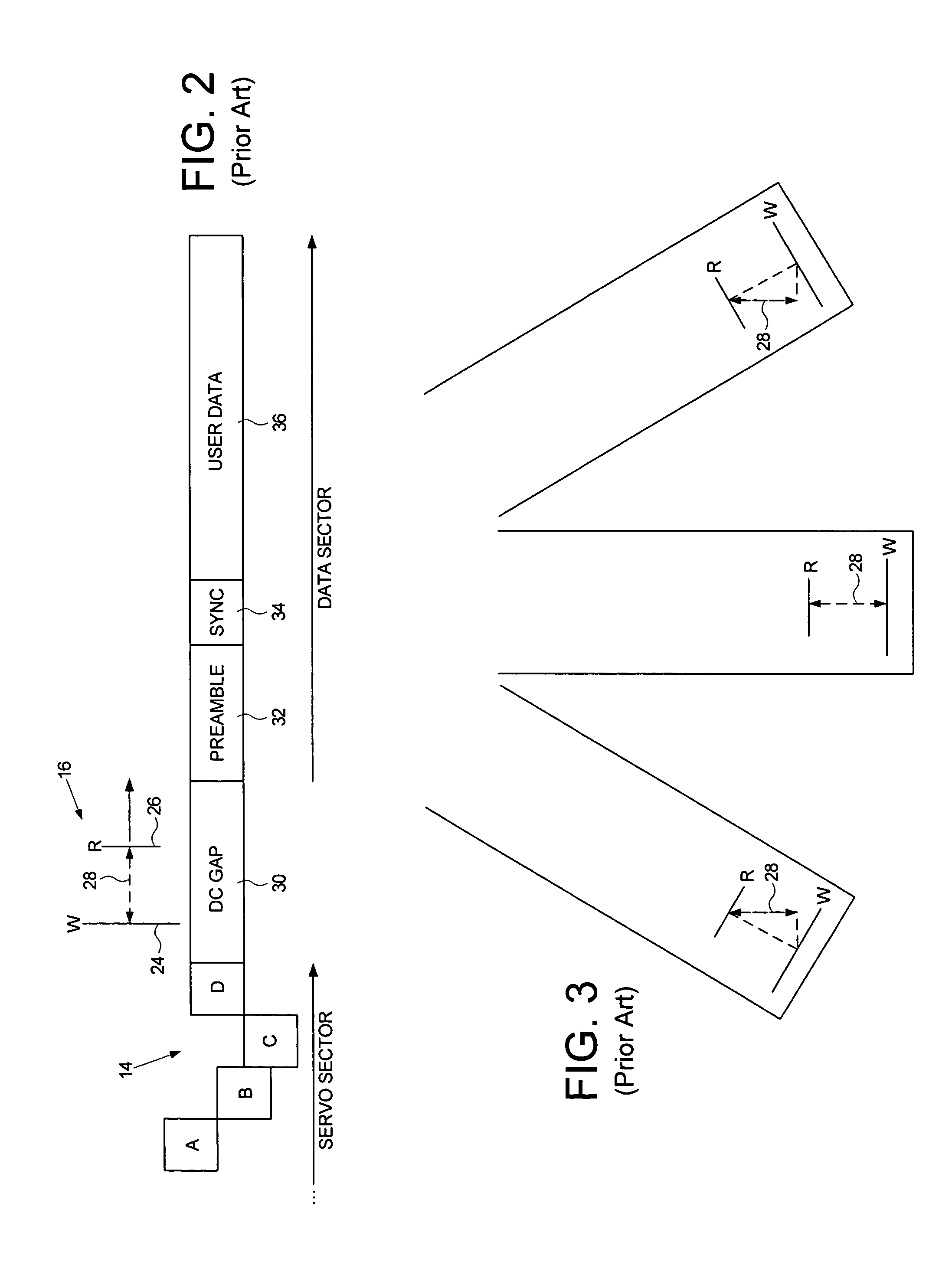
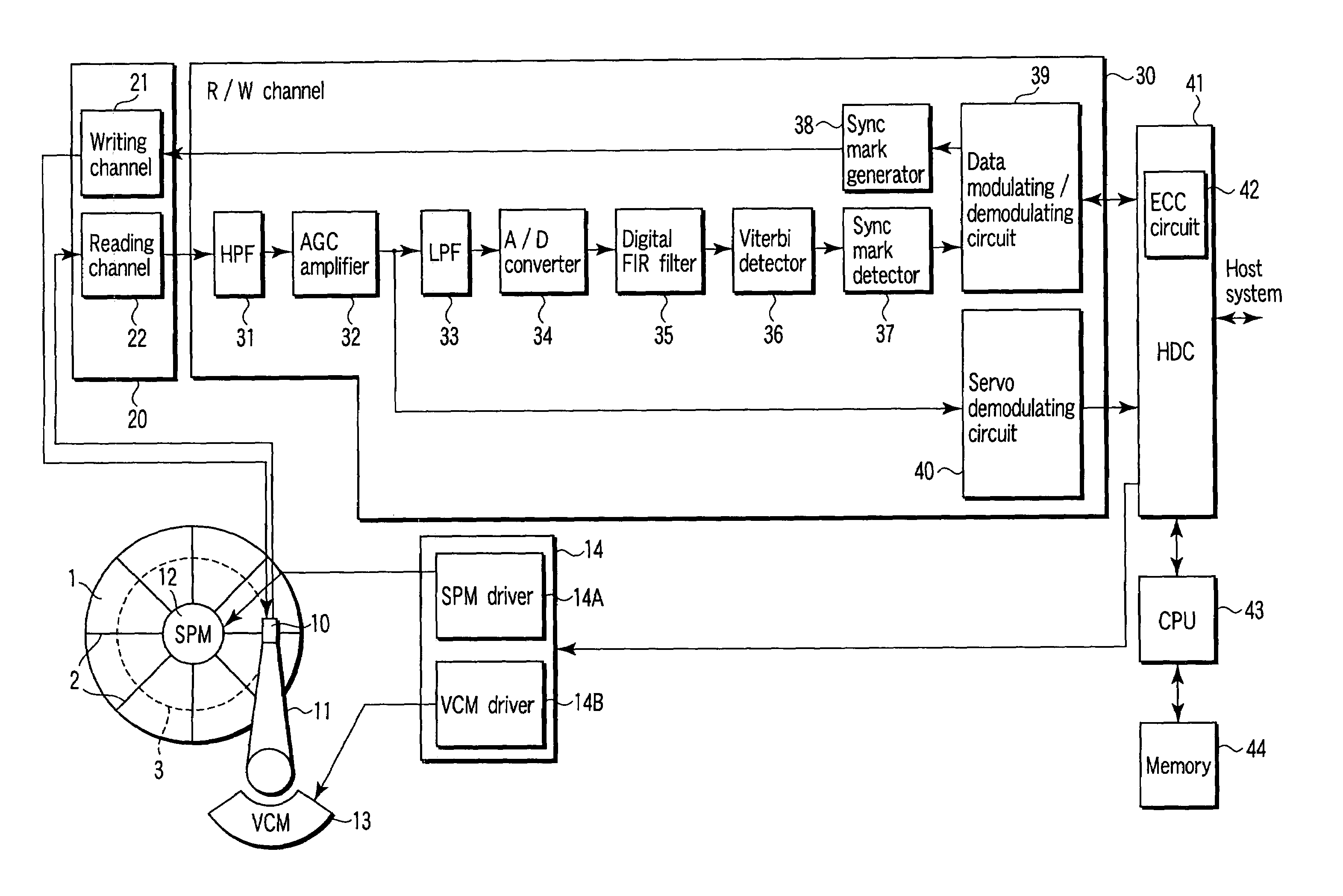
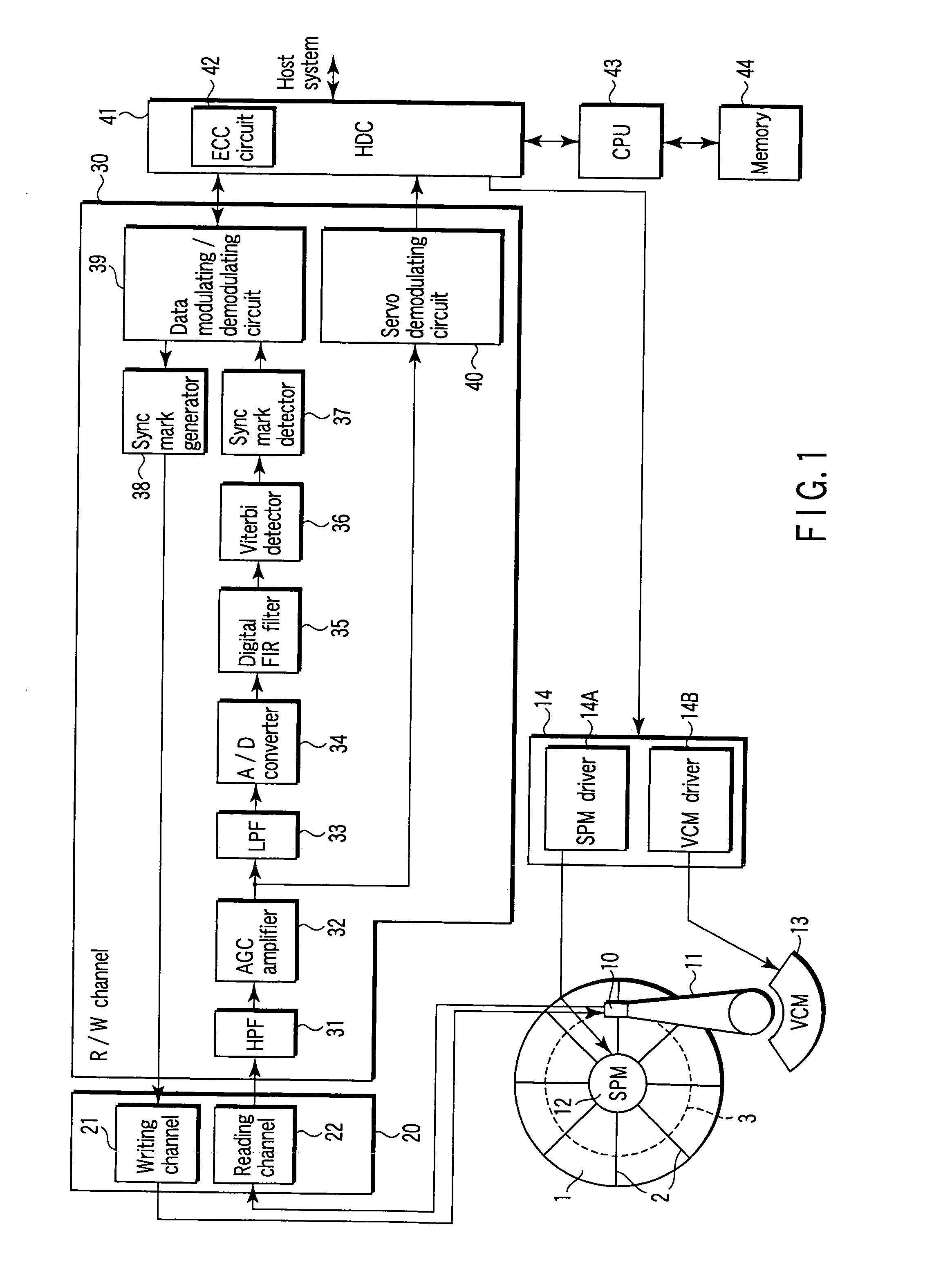
Estimating a writer/reader gap in a disk drive by measuring write/read times relative to a sync mark
ActiveUS7006316B1Record information storageFunctional testing of recording headsComputer sciencePreamble
A method of estimating a writer / reader gap in a disk drive is disclosed. During a first revolution of the disk, a clock is synchronized to a first preamble and used to measure a write delay to write a second sync mark to the disk relative to a first sync mark. During a second revolution of the disk, the clock is again synchronized to the first preamble and used to measure a read delay required to detect the second sync mark relative to the first sync mark. The writer / reader gap is then estimated in response to the measured write delay and the measured read delay, for example, by computing a difference between the measured write delay and the measured read delay.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Energy assisted magnetic recording head having a near field transducer with reduced thermal protrusion
ActiveUS8208350B1Preventing protrusion-related damageImprove reliabilityCombination recordingElectrical transducersLeading edgeTransducer
An energy assisted magnetic recording head comprises a slider having a leading edge, a trailing edge, and an air bearing surface (ABS), and a near field transducer (NFT) disposed in the slider and having a distal end proximate the ABS. The distal end is recessed from the ABS when no optical power is applied to the NFT, and is co-planar with the ABS when a predetermined amount of optical power is applied to the NFT. A portion of the slider surrounding the distal end forms a concave surface having a continuously varying slope when no optical power is applied to the NFT, and a flat surface coplanar with the ABS and the distal end when the predetermined amount of optical power is applied to the NFT. Applying optical power comprises coupling light into a waveguide formed in the head and directing the coupled light to the NFT via the waveguide.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
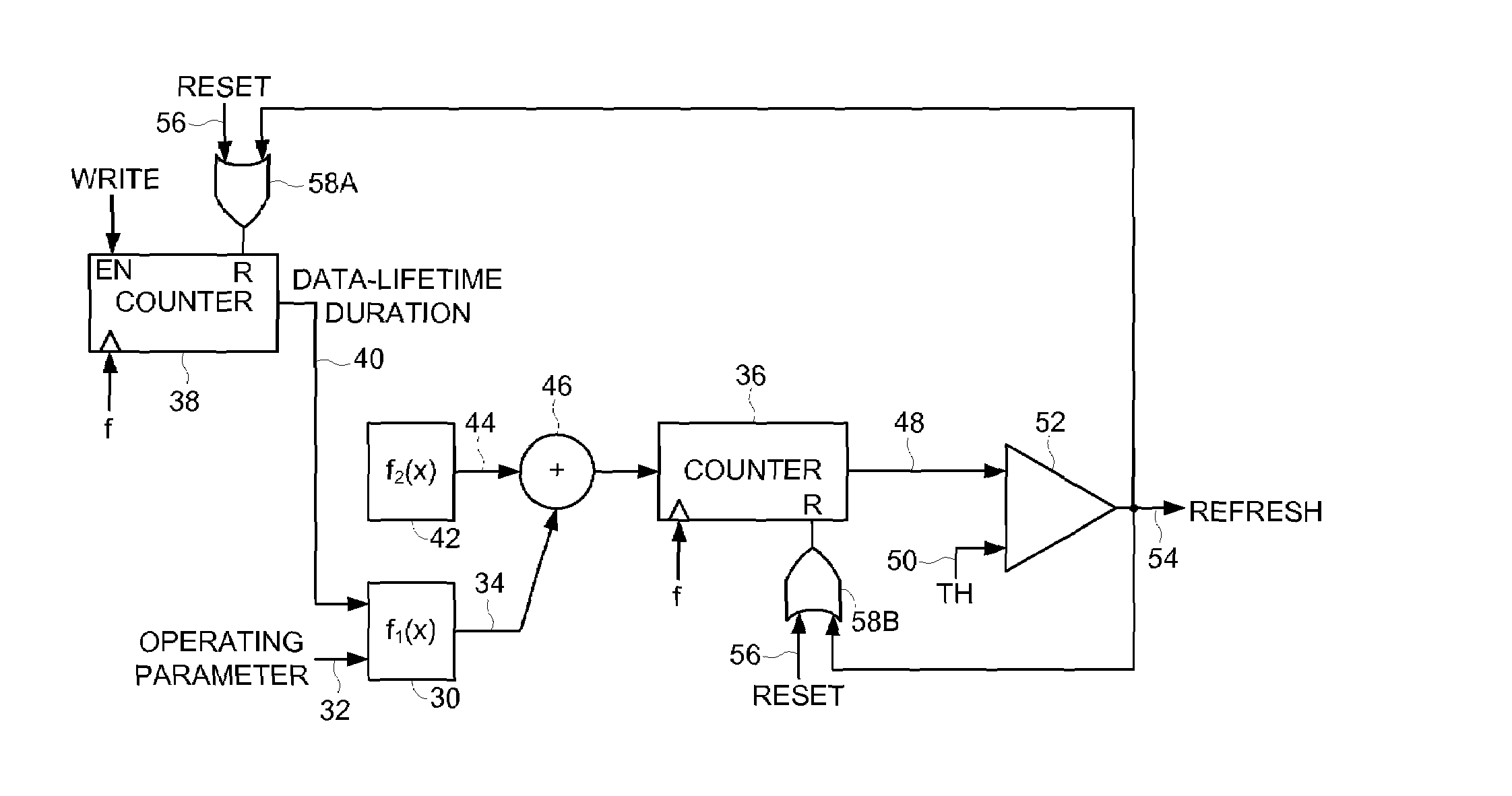
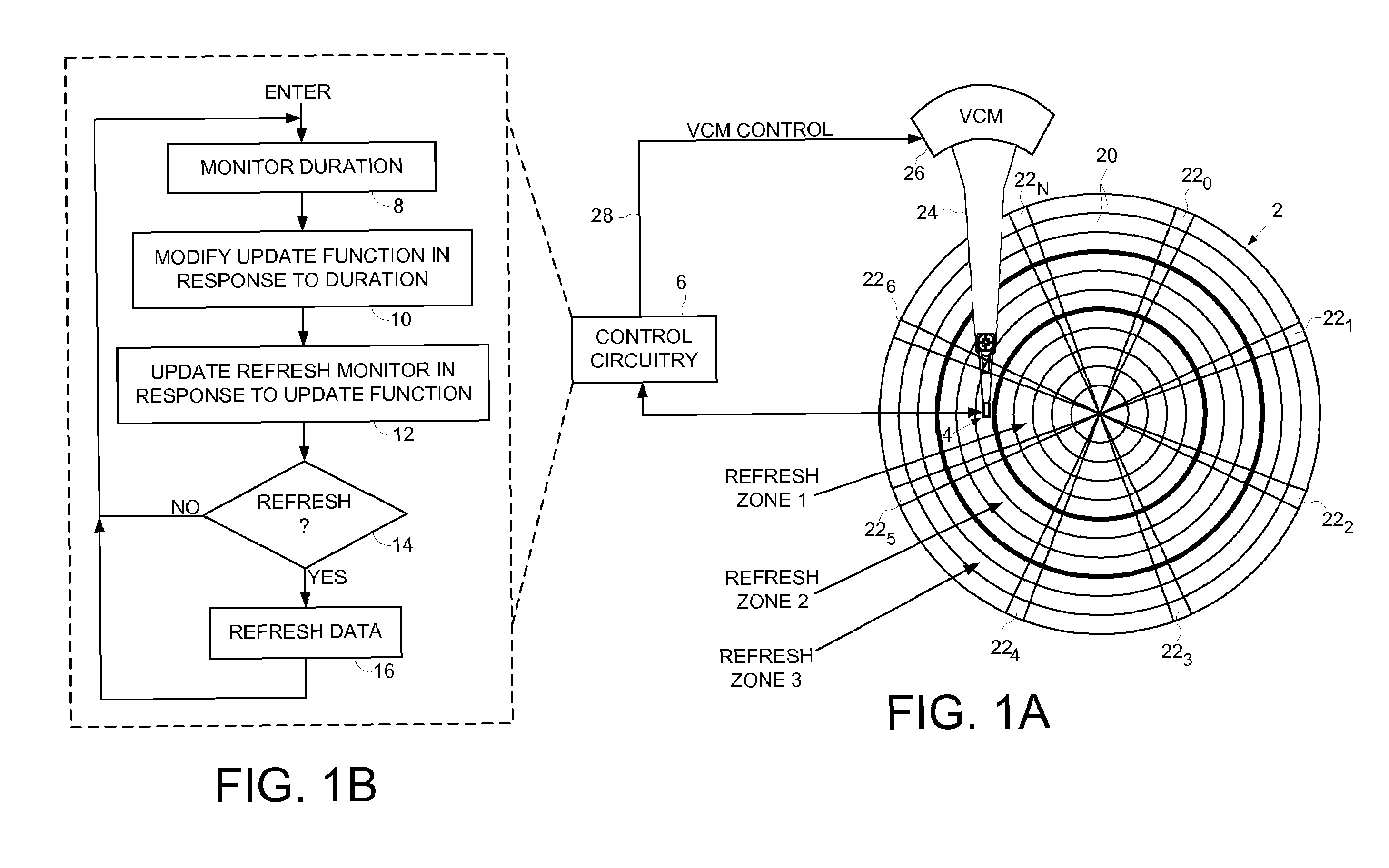
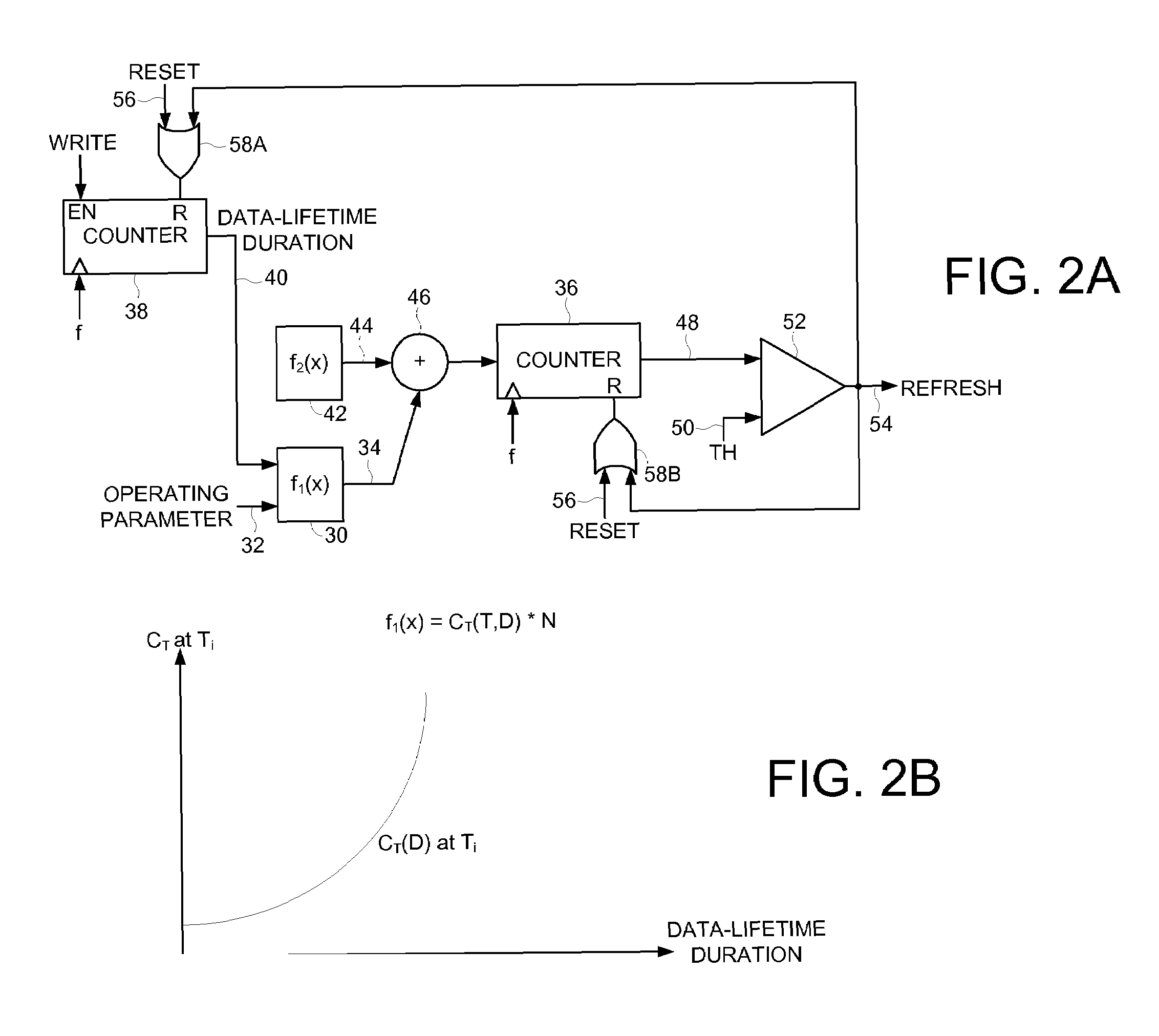
Disk drive modifying an update function for a refresh monitor in response to a measured duration
InactiveUS7672072B1Electronic editing digitised analogue information signalsUsing non-detectable carrier informationData storingEmbedded system
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Techniques for ultrahigh density writing with a probe on erasable magnetic media
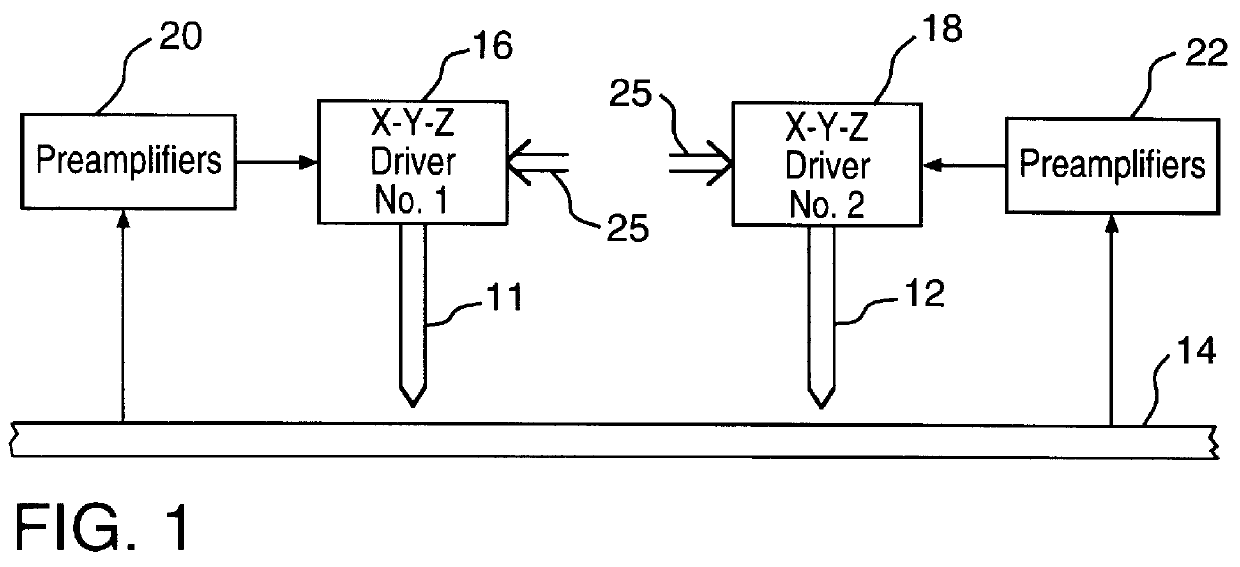
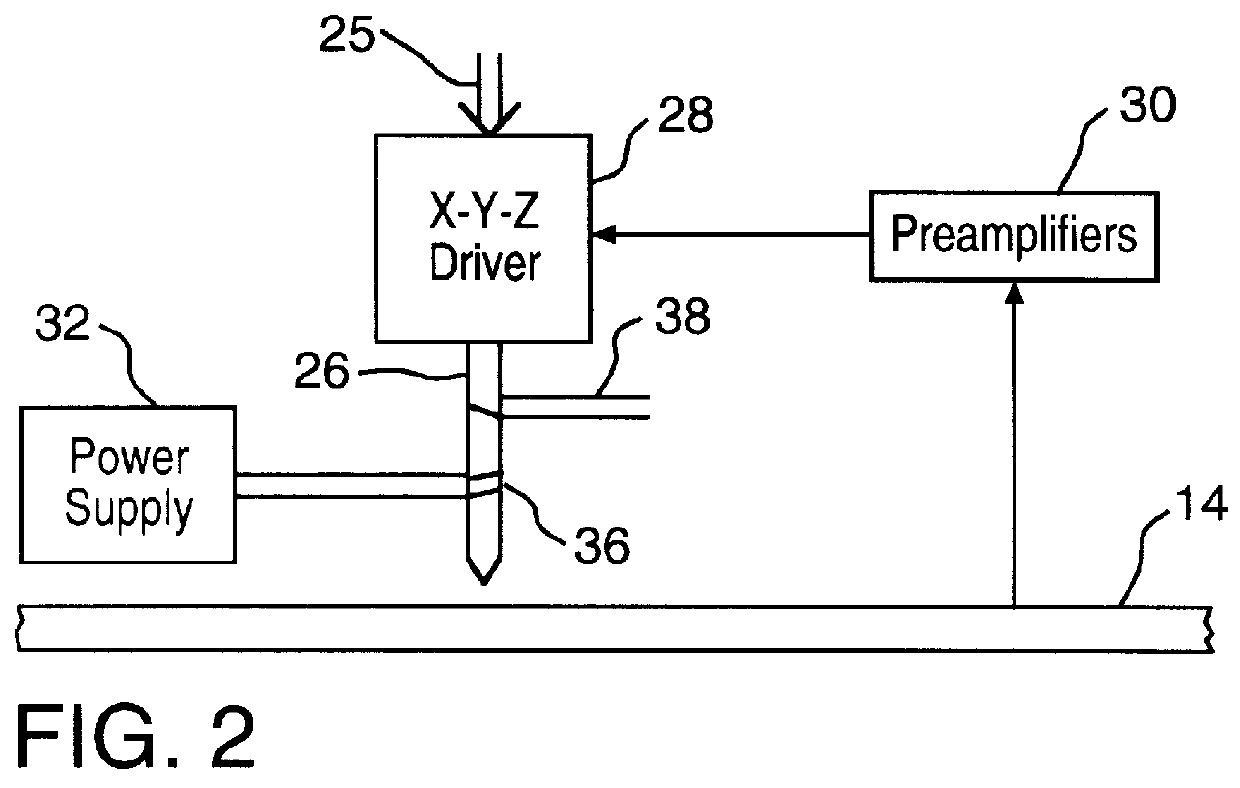
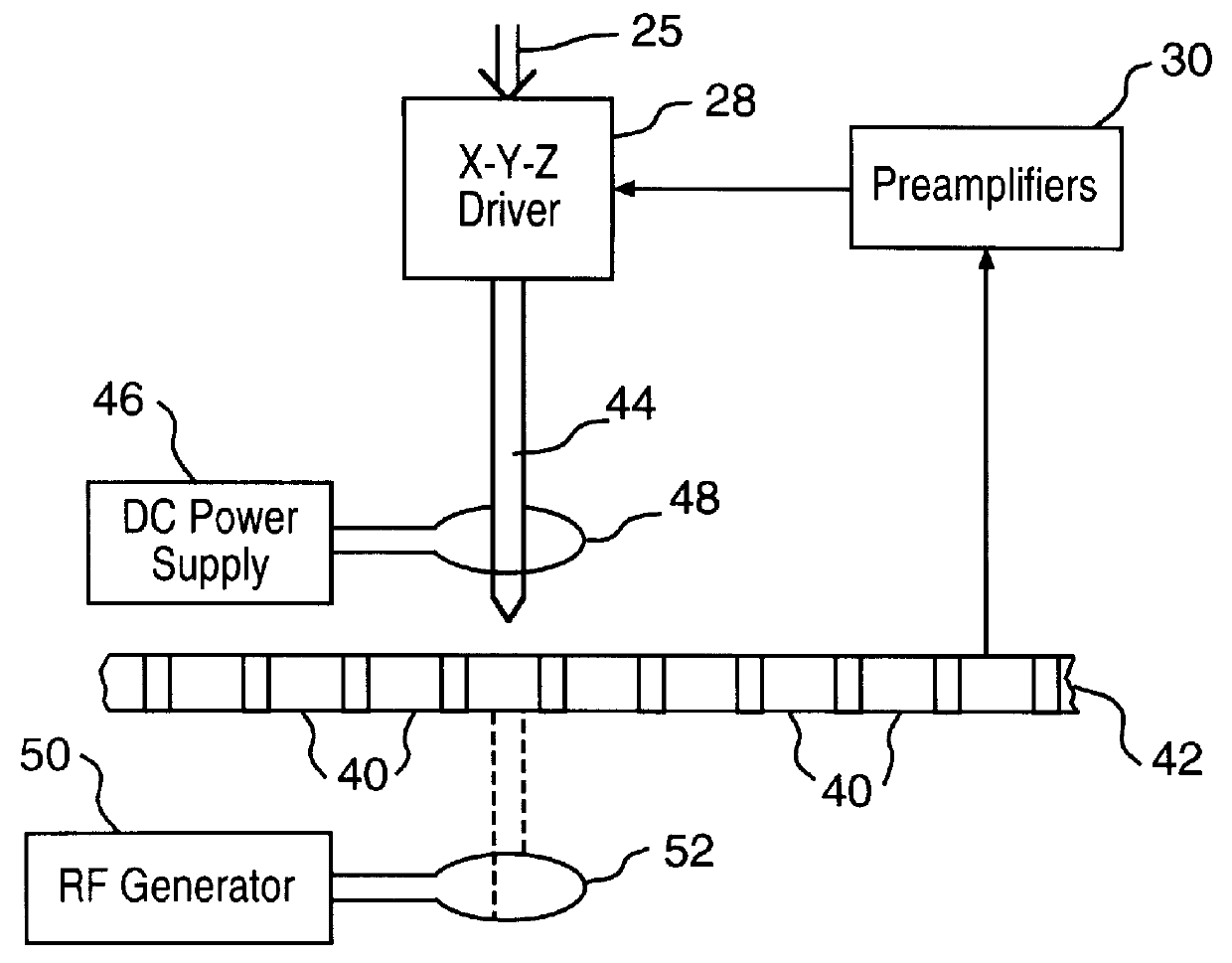
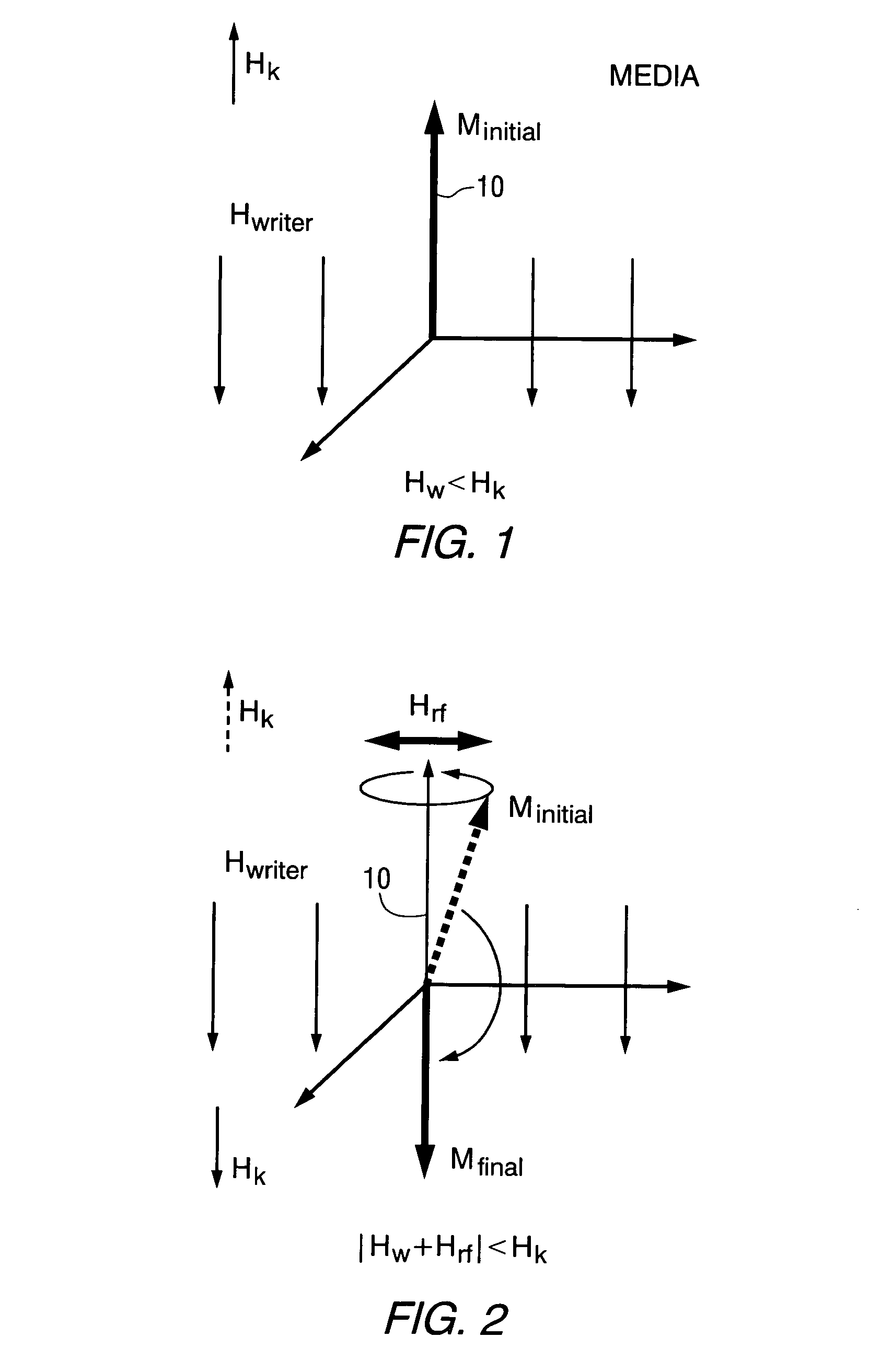
Techniques for ultrahigh density writing on an erasable magnetic medium include using a micromachined mechanism having two probes for writing to the medium. Use of the two probe embodiment eliminates the need to change the magnetic orientation of the probe. In another embodiment, a single probe is provided which is heated to the vicinity of its Curie temperature to enable the magnetic orientation of the probe to be switched. The probe may be heated to its Curie temperature through the use of a heating element or a focused laser. In another embodiment of the present invention, either the magnetic orientation of the probe or the magnetic orientation of the medium may be switched through the combination of a static magnetic field, a radio frequency magnetic field and, under certain circumstances, the magnetic field of the probe. In all cases, the writing techniques enable information to be written to a magnetic medium in a manner which enables the information to be erased and the medium rewritten.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
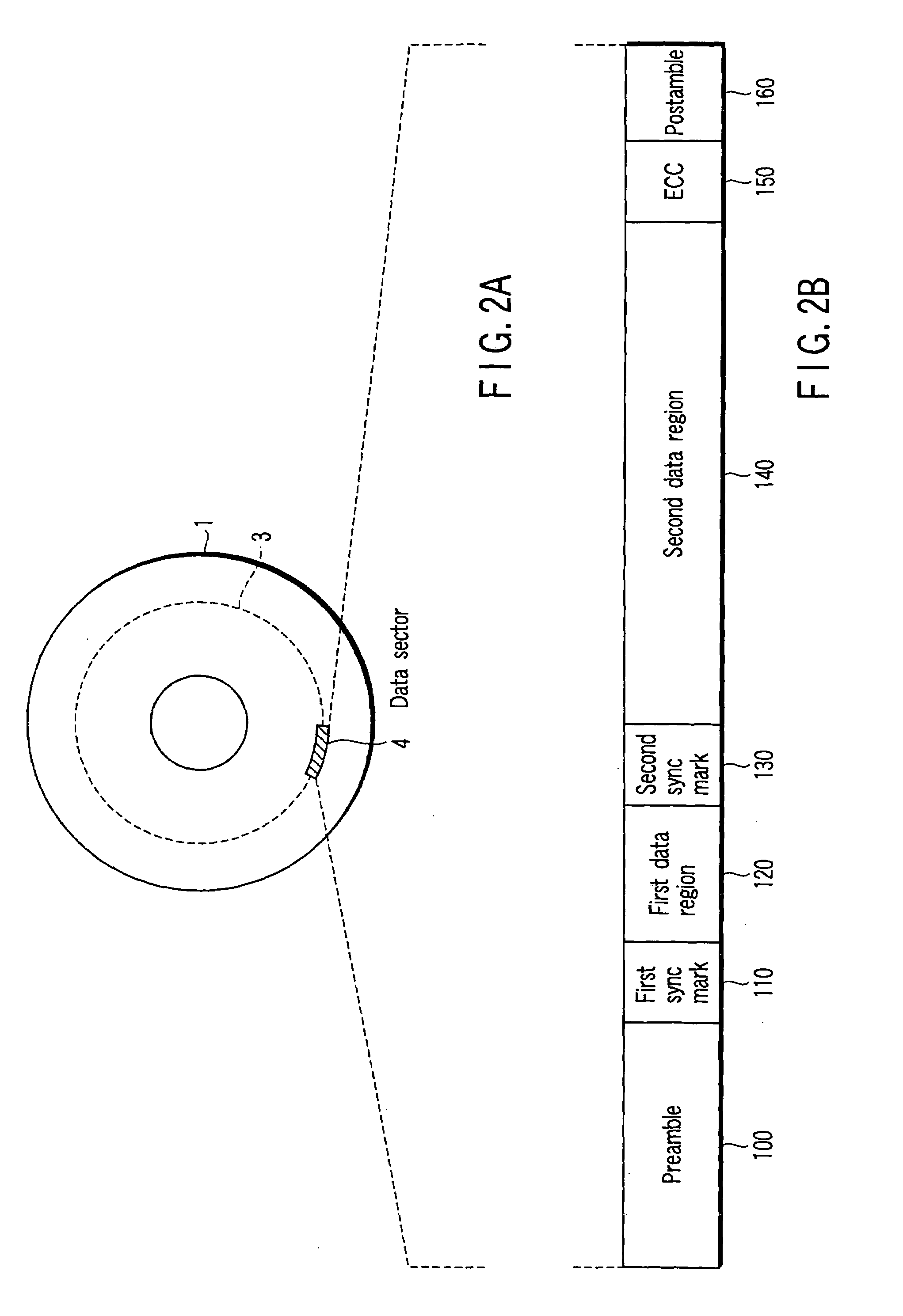
Method and apparatus for decoding sync marks in a disk
InactiveUS7203015B2High error rateIncrease probabilityModification of read/write signalsDisc-shaped record carriersComputer scienceBit-length
In a disk drive that performs perpendicular magnetic recording, the read / write channel has a sync mark generator. The sync mark generator generates a second sync mark before the read / write channel operates to write data on a disk. The second sync mark has a bit pattern including a series of bits representing positive polarity and a series of bits representing negative polarity. The series of bits, which is longer than the other, has a bit length that is at least 50% but less than 85% of the total bit length of the second sync mark.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
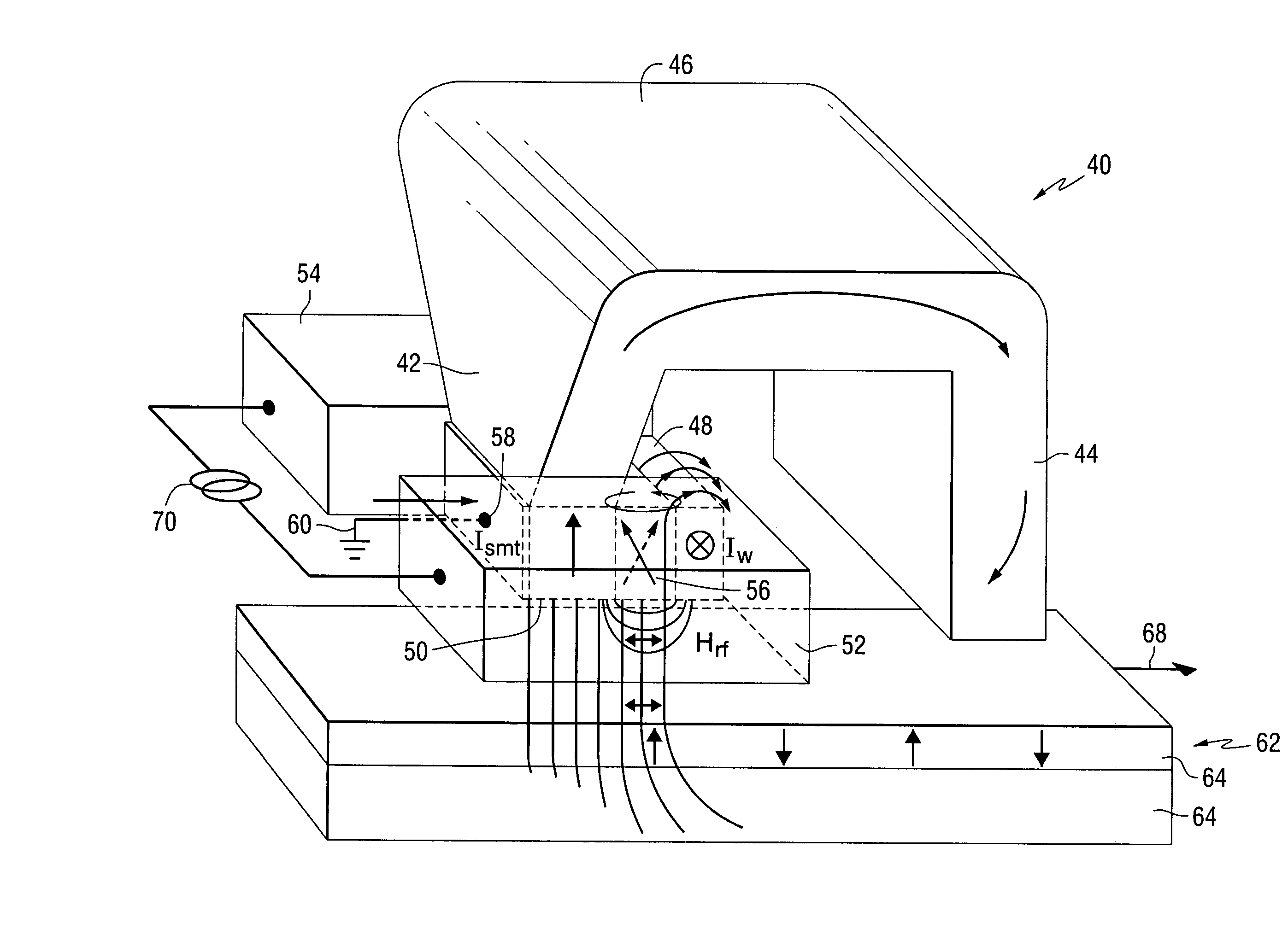
WAMR writer with an integrated spin momentum transfer driven oscillator for generating a microwave assist field
InactiveUS20080112087A1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsInter layerSpins
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
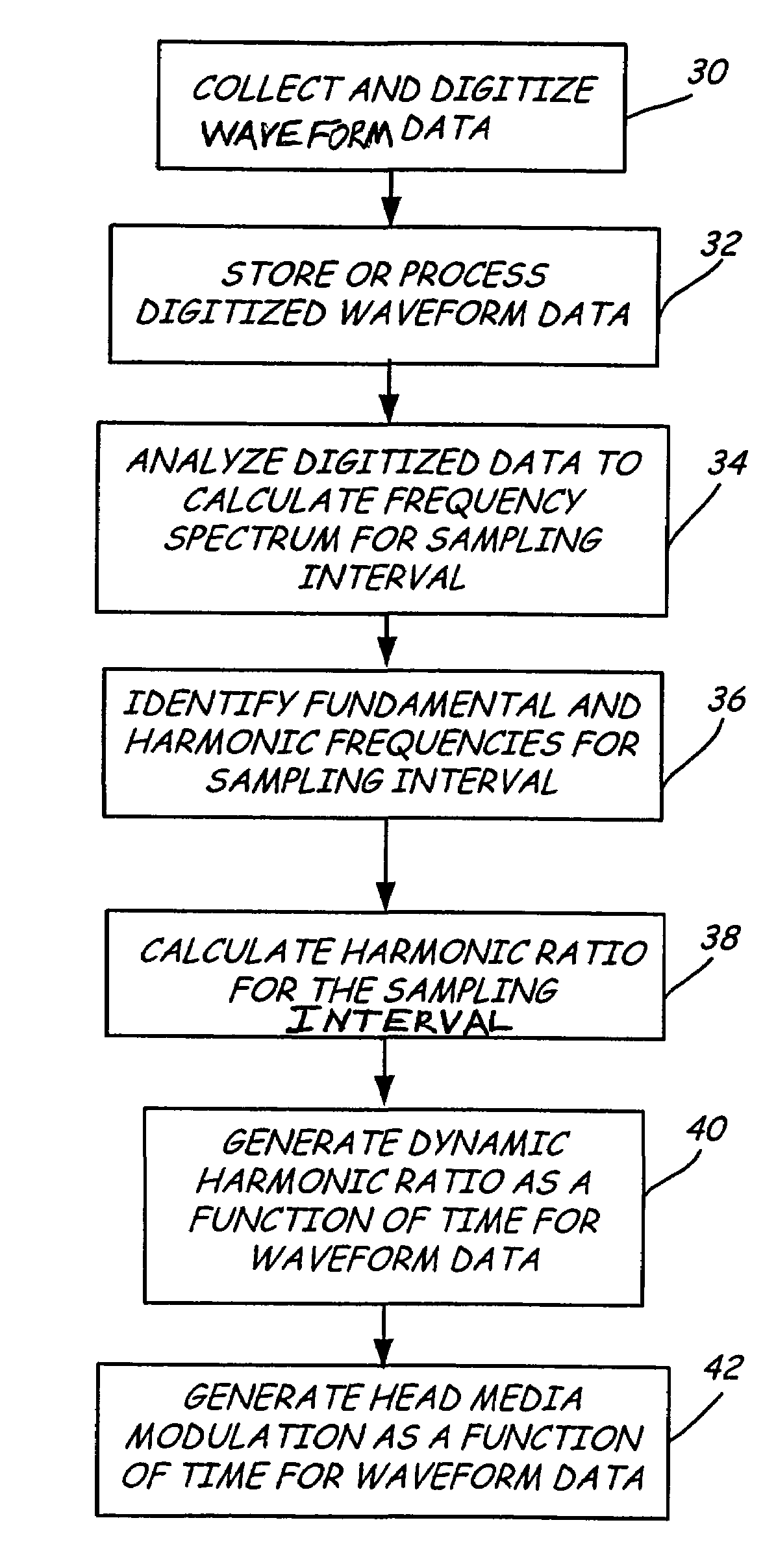
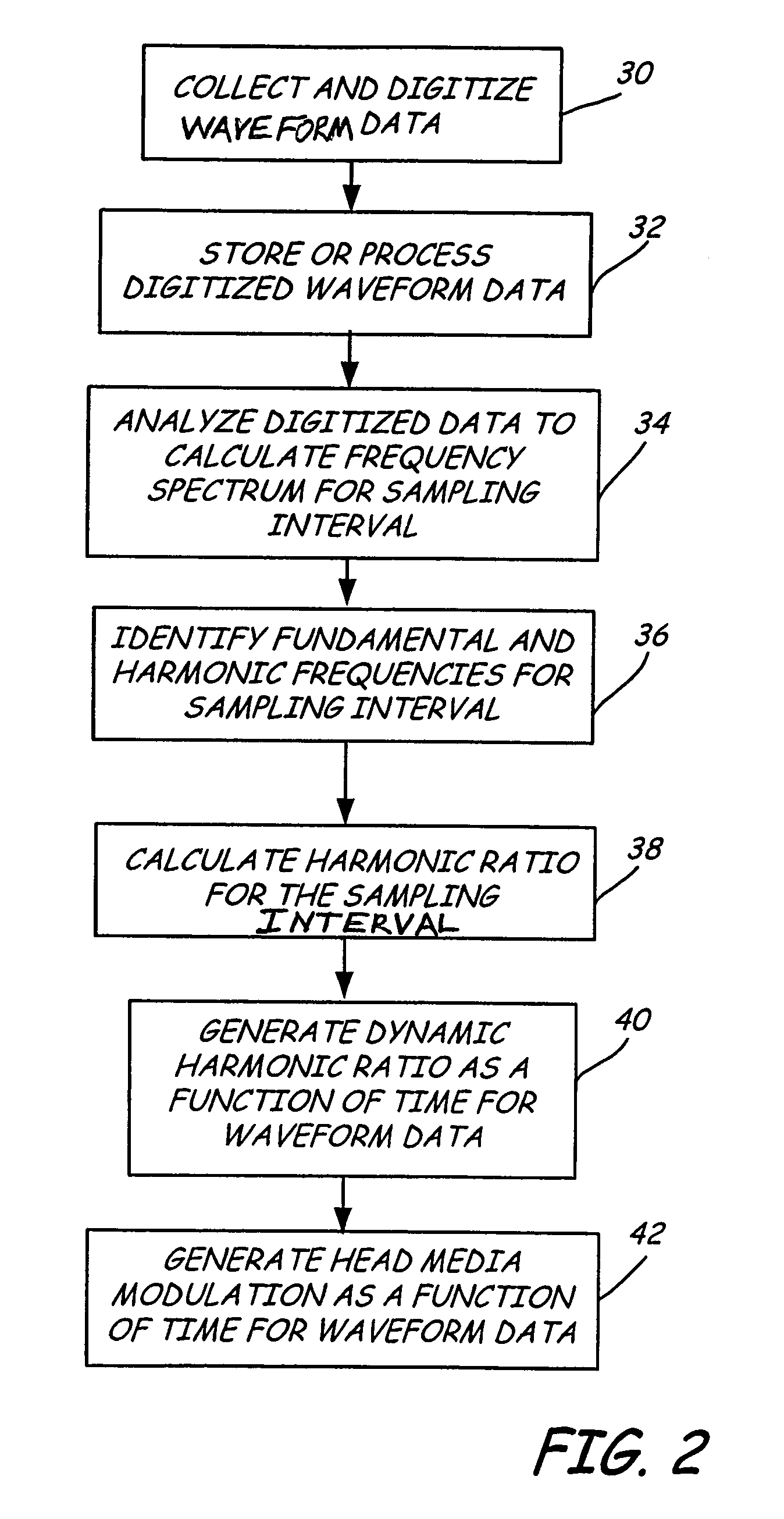
Dynamic measurement of head media spacing modulation
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
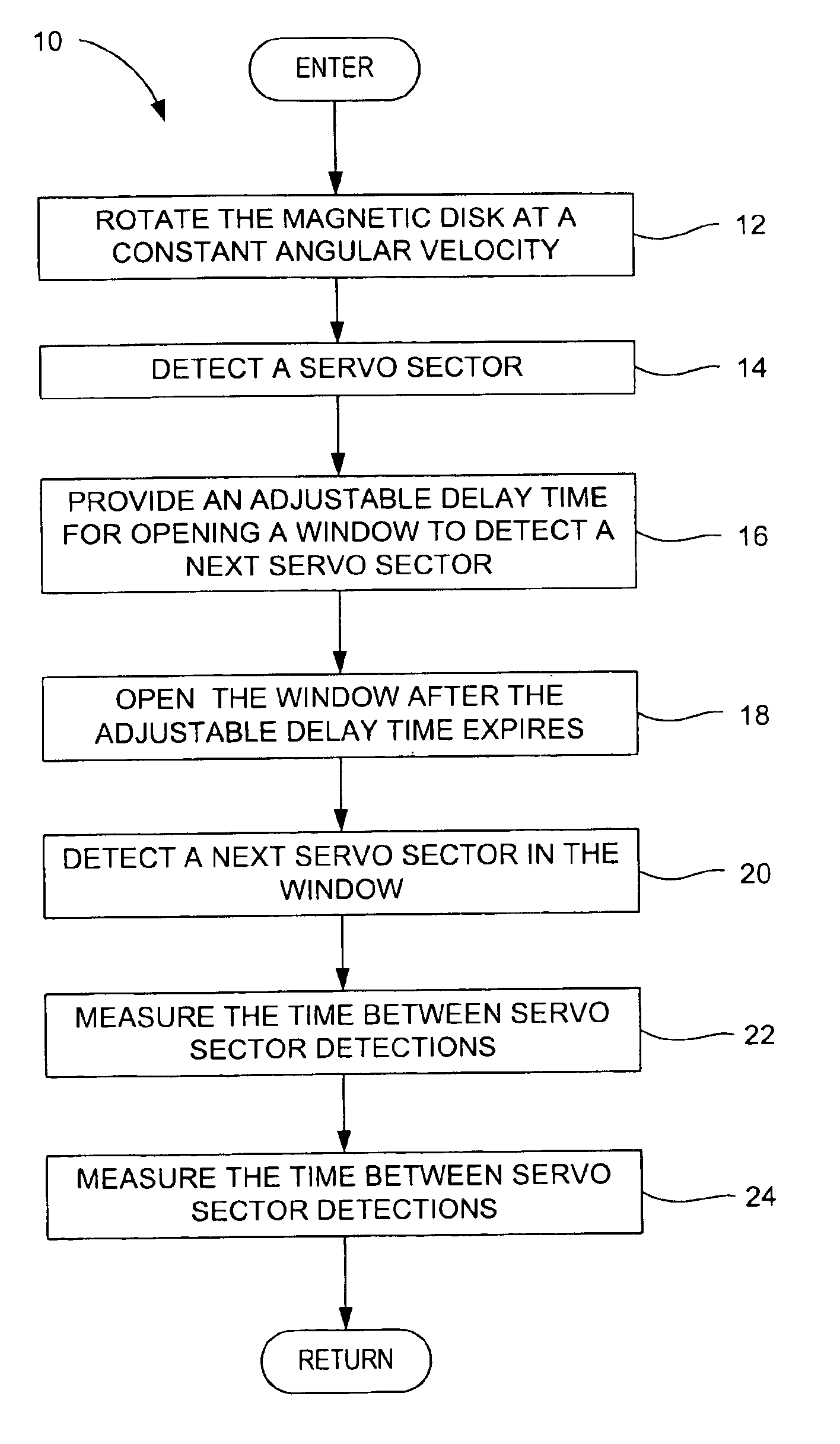
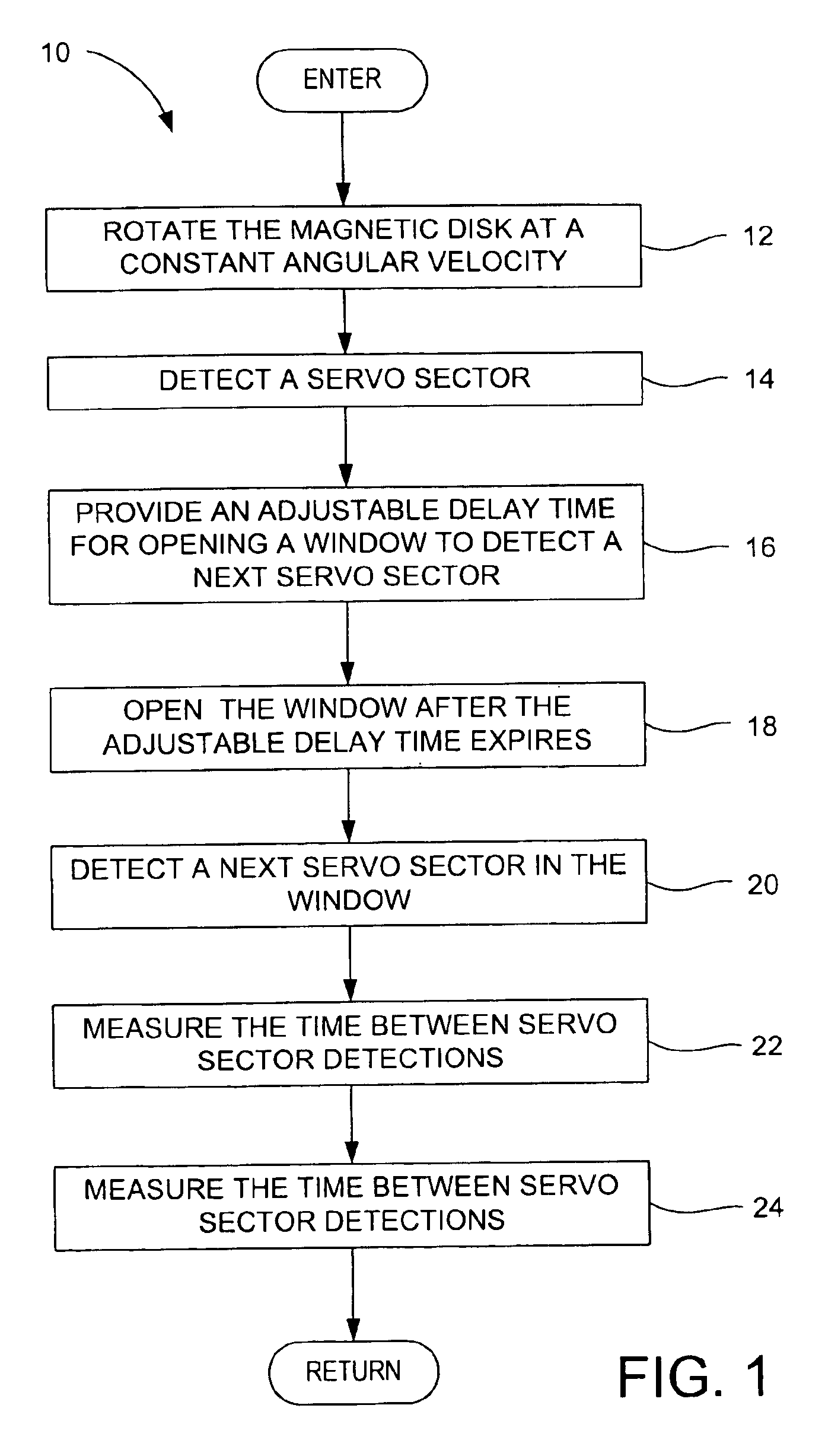
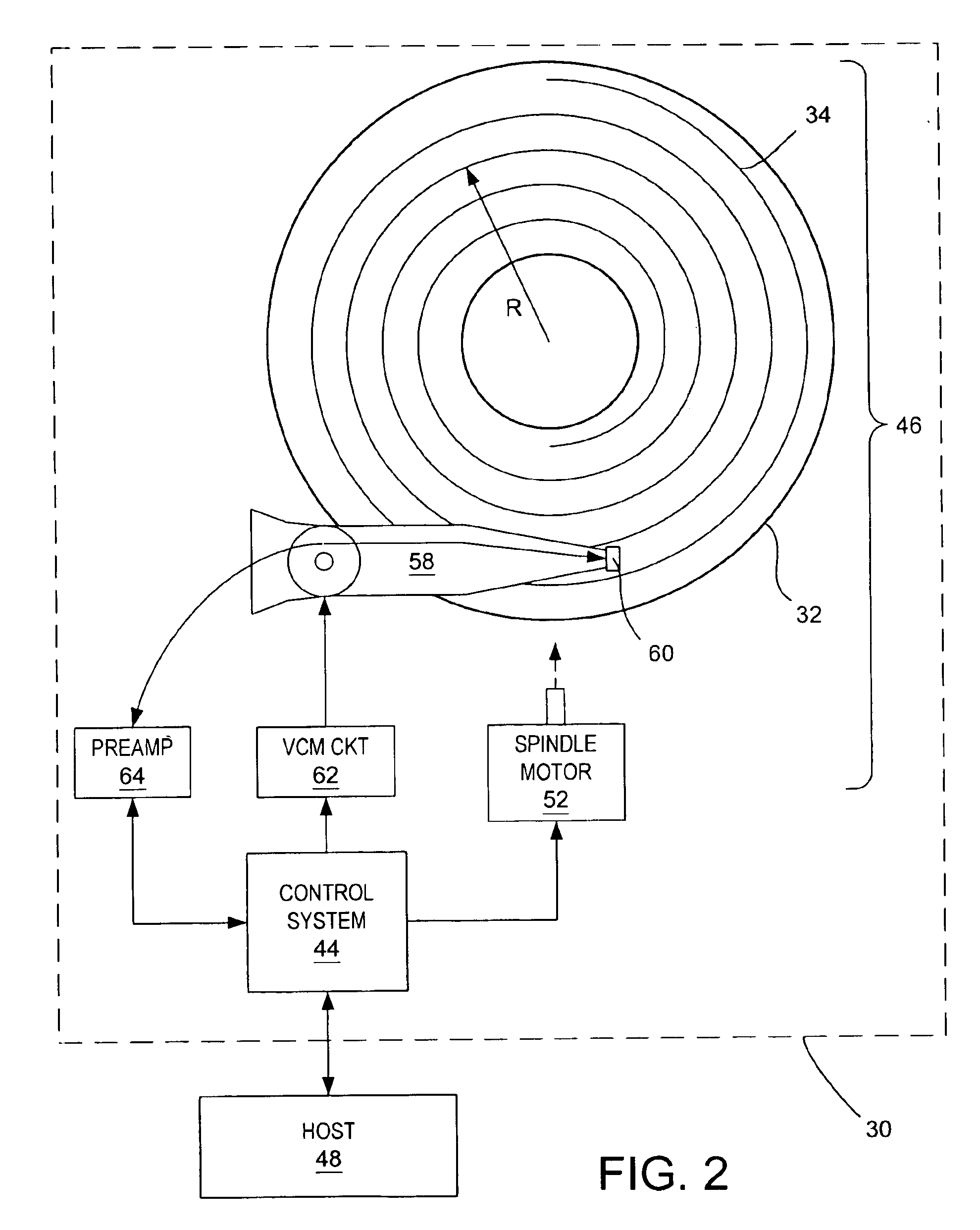
Method for adjusting a delay time for opening a servo sector detection window in a disk drive having a spiral track
InactiveUS6920004B1Disc-shaped record carriersRecord information storageLinear densityControl theory
The present invention may be embodied in a method for adjusting a servo sector detection delay time between detection windows in a disk drive. The disk drive includes a magnetic disk with a spiral track having contiguous storage segments. Each storage segment has a servo sector and a predetermined number of uniformly-sized data sectors. The storage segments are written at a relatively constant linear density along the spiral track. In the method, the magnetic disk is rotated at a constant angular velocity. A servo sector is detected. An adjustable delay time is provided for opening a window to detect a next servo sector. The window is opened after the adjustable delay time expires. A next servo sector is detected in the window. A time between the servo sector detections is measured and the adjustable delay time is adjusted based on the measured time.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic head and magnetic recording device
InactiveUS20090080106A1Suppress mutationDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageSpin torque oscillatorsMagnetic poles
It is made possible to restrict the variation of the oscillation frequency of a spin torque oscillator placed in the vicinity of the recording magnetic pole. A magnetic head includes: a recording magnetic pole to generate a recording magnetic field; a spin torque oscillator formed in the vicinity of the recording magnetic pole; and a magnetic field applying unit configured to apply a magnetic field to the spin torque oscillator. The magnetic field applied to the spin torque oscillator by the magnetic field applying unit is perpendicular to a recording magnetic field generated from the recording magnetic pole.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
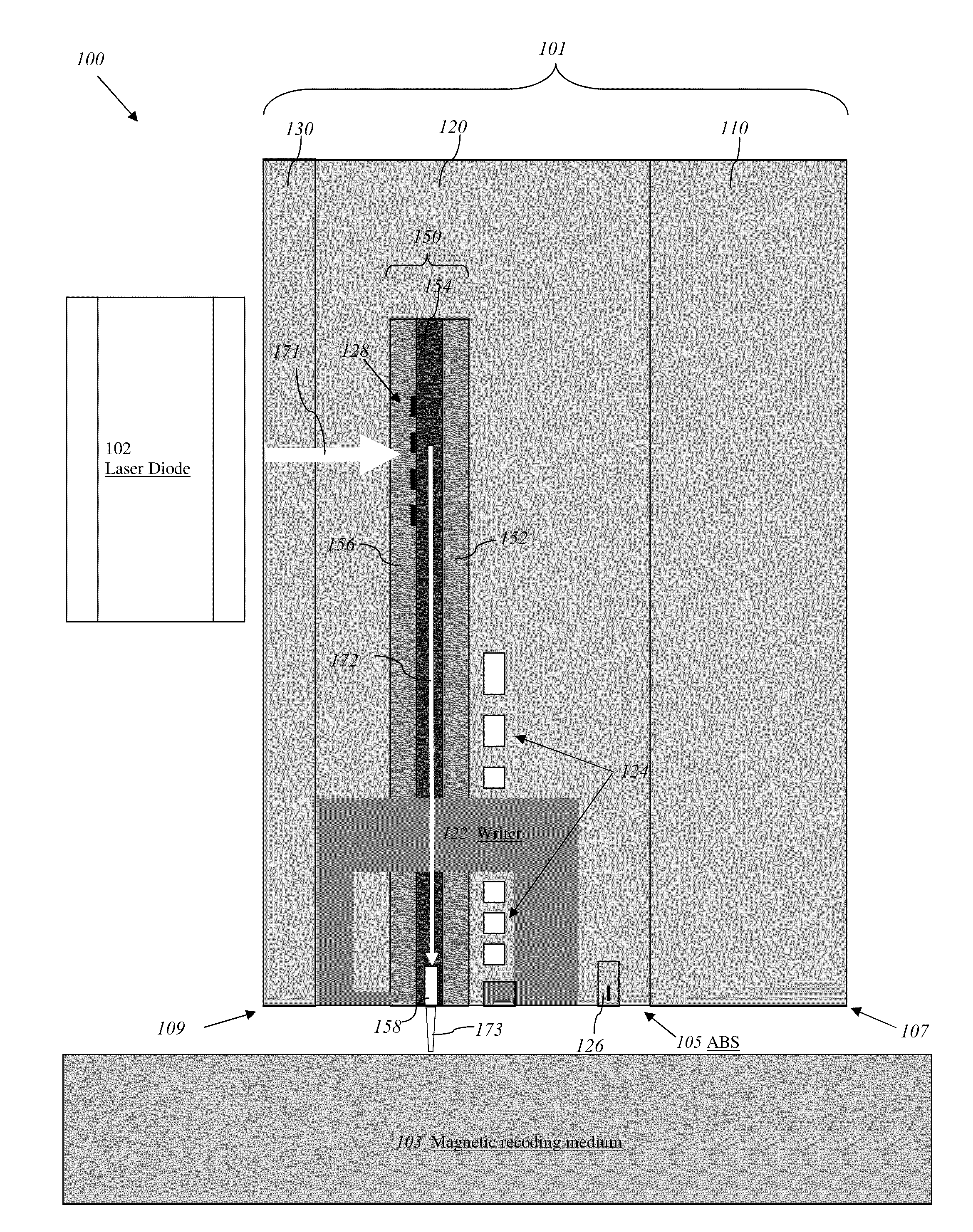
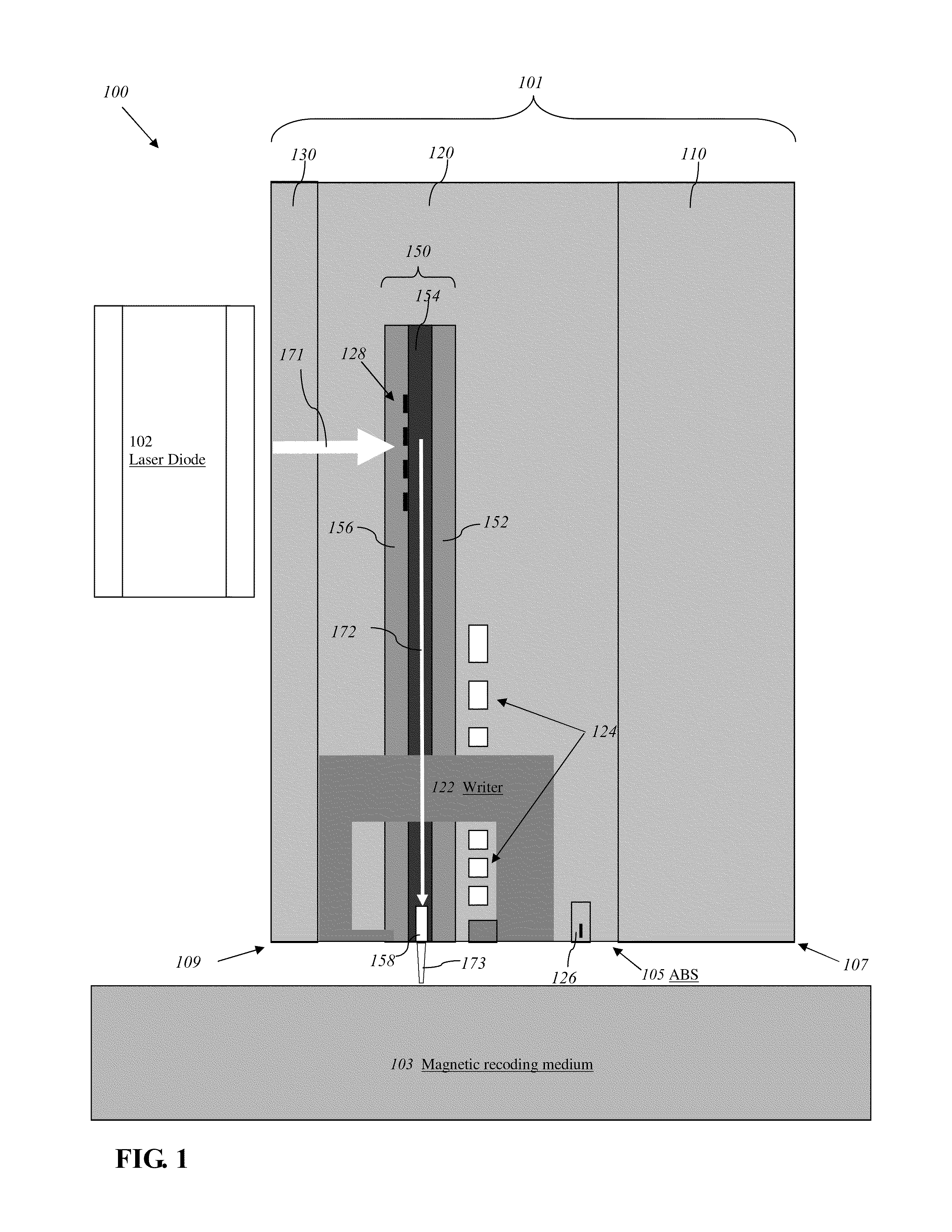
Transducer for heat assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS7272079B2Combination recordingNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic storage
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Heat assisted magnetic recording head with a planar waveguide
InactiveUS6944112B2Combination recordingRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingWaveguide
A heat assisted magnetic recording head having a planar waveguide for heating a recording medium proximate to where a write pole of the recording head applies a magnetic write field thereto. The planar waveguide includes at least one edge, which may have a substantially parabolic shape, that is shaped to reflect an electromagnetic wave to a focal point within the planar waveguide. The planar waveguide includes a truncated end adjacent the focal point such that the truncated end intersects the focal point.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic recording head and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20090052095A1Construction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceInter layerMagnetic poles
A magnetic recording head includes:a main magnetic pole; a laminated body; and a pair of electrodes. The laminated body includes a first magnetic layer having a coercivity lower than magnetic field applied by the main magnetic pole, a second magnetic layer having a coercivity lower than the magnetic field applied by the main magnetic pole, and an intermediate layer provided between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The pair of electrodes are operable to pass a current through the laminated body.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic recording head, magnetic head assembly, magnetic recording apparatus, and magnetic recording method
ActiveUS20100134922A1Construction of head windingsRecord information storageSpin torque oscillatorsMagnetic poles
A magnetic recording head includes a first magnetic pole, a second magnetic pole, a spin torque oscillator, a first coil, a second coil, and a third coil. The first magnetic pole applies a recording magnetic field to a magnetic recording medium. The second magnetic pole is provided parallel to the first magnetic pole. At least a portion of the spin torque oscillator is provided between the first magnetic pole and the second magnetic pole. The first coil magnetizes the first magnetic pole. A current is passed through the second coil independently of the first coil. A current is passed through the third coil independently of both the first coil and the second coil.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic head and magnetic recording device
ActiveUS20090080120A1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsSpin torque oscillatorsMagnetic poles
It is made possible to provide a magnetic head that generates a sufficient high-frequency magnetic field for assisting recording operations, and a magnetic recording device that includes the magnetic head. A magnetic head includes: a recording magnetic pole; a return yoke magnetically coupled to the recording magnetic pole; and at least two spin torque oscillators provided near the recording magnetic pole.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Surface plasmon antenna with propagation edge and near-field light generating element
ActiveUS20100103553A1Avoid excessive heatAppropriate heatCombination recordingArm with optical waveguideSurface plasmonMagnetic poles
Provided is a surface plasmon antenna that can be set so that the emitting position on the end surface of the plasmon antenna where near-field light is emitted is located sufficiently close to the end of a magnetic pole. The surface plasmon antenna comprises an edge having a portion for coupling with a light in a surface plasmon mode. The edge is provided for propagating surface plasmon excited by the light and extends from the portion to a near-field light generating end surface that emits near-field light. The edge for propagating surface plasmon is a very narrow propagation region. Therefore, the near-field light generating end surface, which appears as a polished surface processed through polishing in the manufacturing of the plasmon antenna, can be made a shape with a very small size, and further can be set so that surface plasmon propagates to reach the end surface reliably.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Perpendicular magnetic recording write head and system with improved spin torque oscillator for microwave-assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS7982996B2Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsPower flowSpin torque oscillators
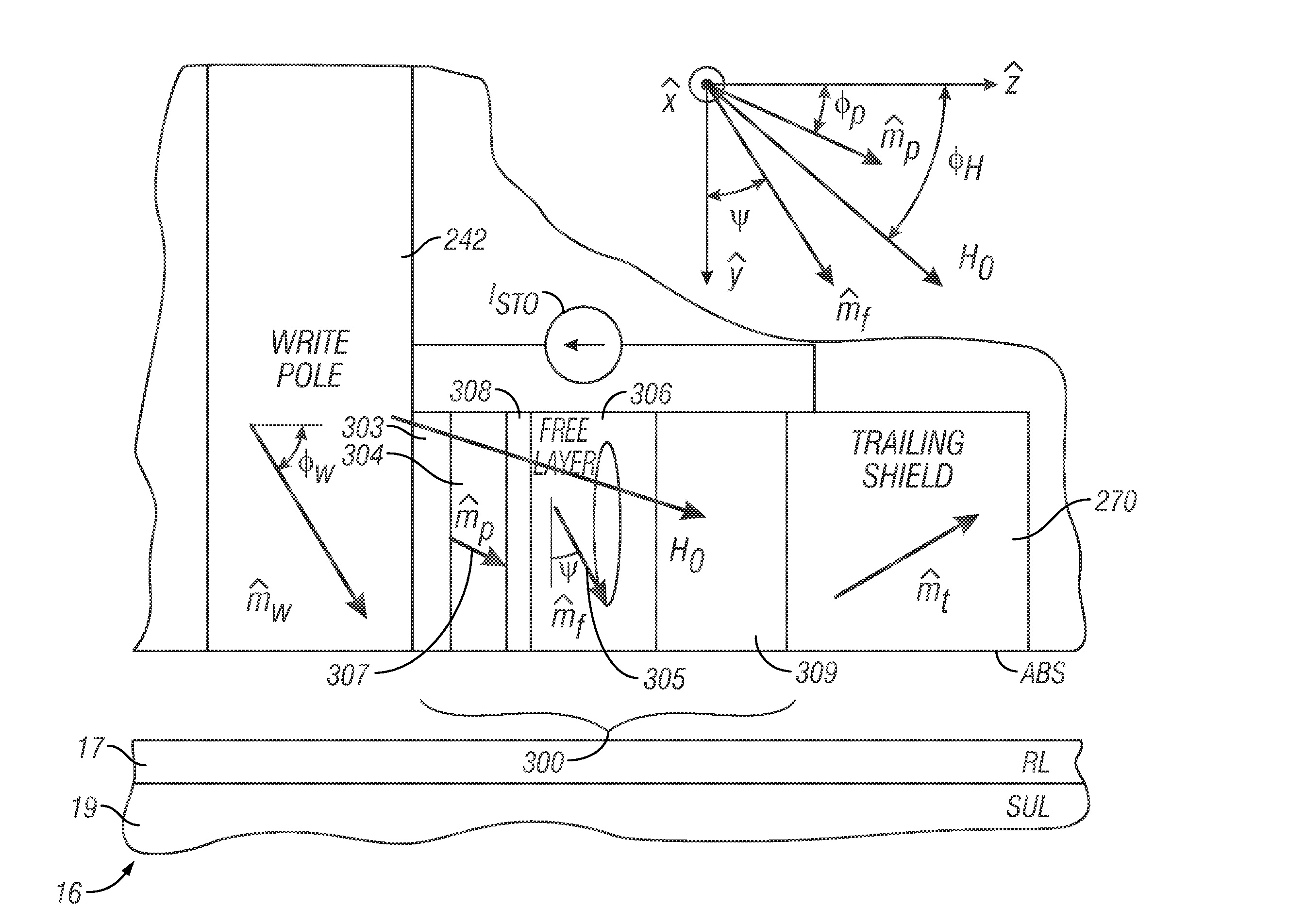
A microwave-assisted magnetic recording (MAMR) write head and system has a spin-torque oscillator (STO) located between the write pole of the write head and a trailing shield that alters the write field from the write pole. The STO is a stack of layers whose planes lie generally parallel to the X-Y plane of an X-Y-Z coordinate system, the stack including a ferromagnetic polarizer layer, a free ferromagnetic layer, and a nonmagnetic electrically conductive spacer between the polarizer layer and the free layer. In the presence of the write field from the write pole the polarizer layer has its magnetization oriented at an angle between 20 and 80 degrees, preferably between 30 and 70 degrees, with the Z-axis. In the presence of a direct electrical current through the STO stack, the free layer magnetization rotates or precesses about the Z-axis with a non-zero angle to the Z-axis.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
High frequency field assisted write device
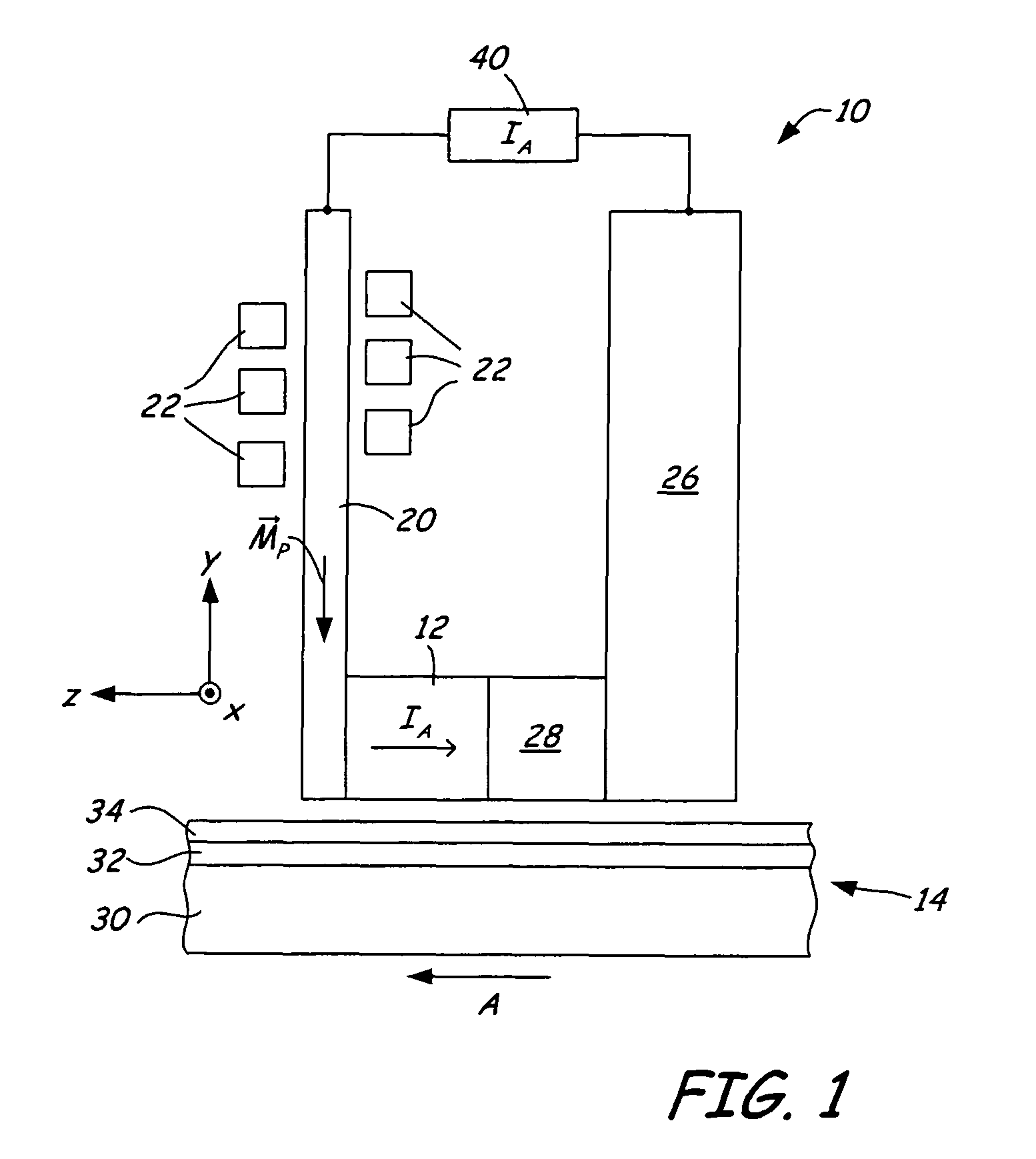
A magnetic writer includes a write element and an oscillation device disposed adjacent to the write element. The first oscillation device includes a first magnetic layer, a second magnetic layer having a magnetization vector including a component perpendicular to a major plane of the first magnetic layer. The first nonmagnetic layer disposed between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The first oscillation device generates a high-frequency oscillation field when a current is directed perpendicular to the major plane of the first magnetic layer.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com