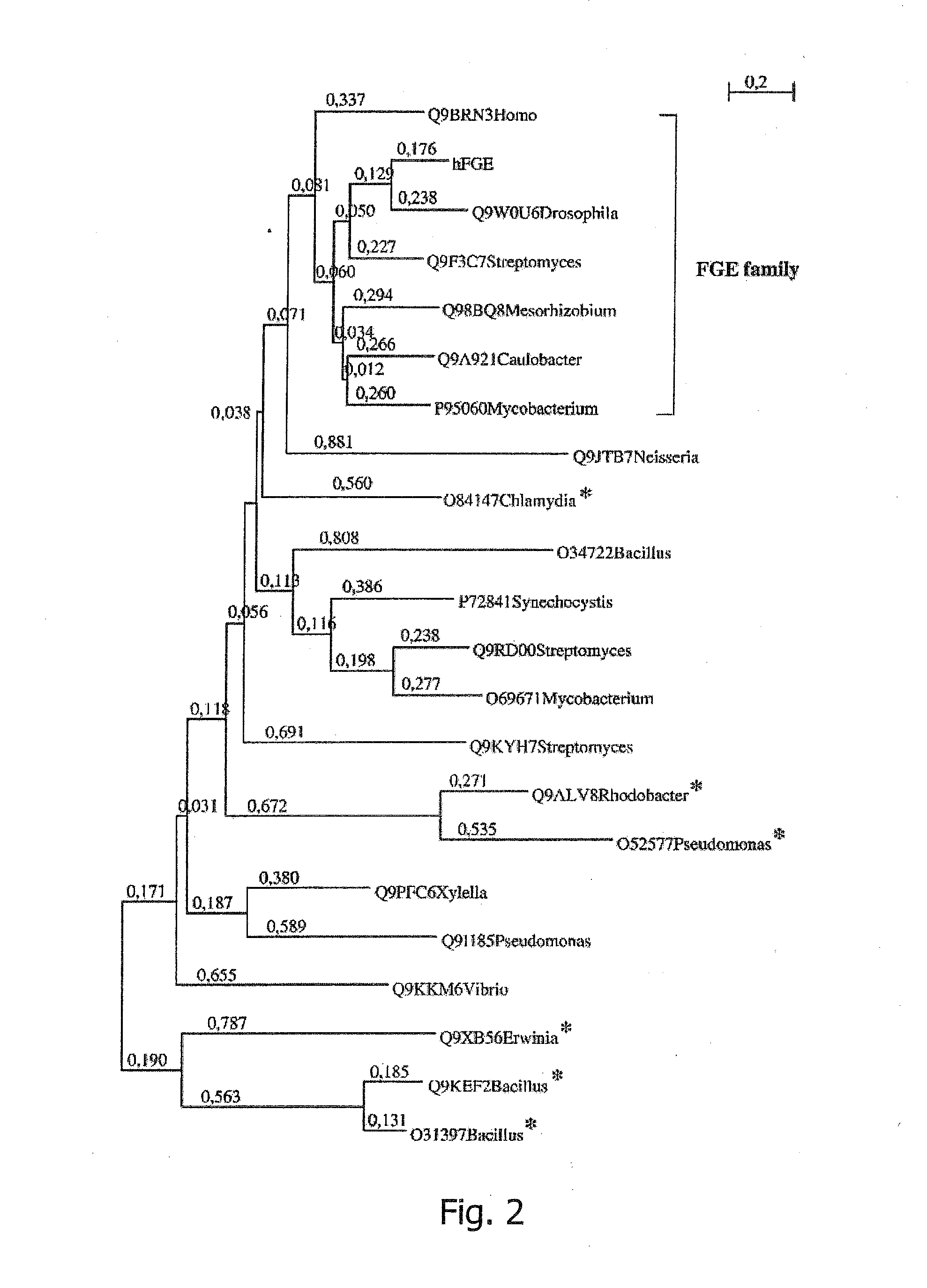
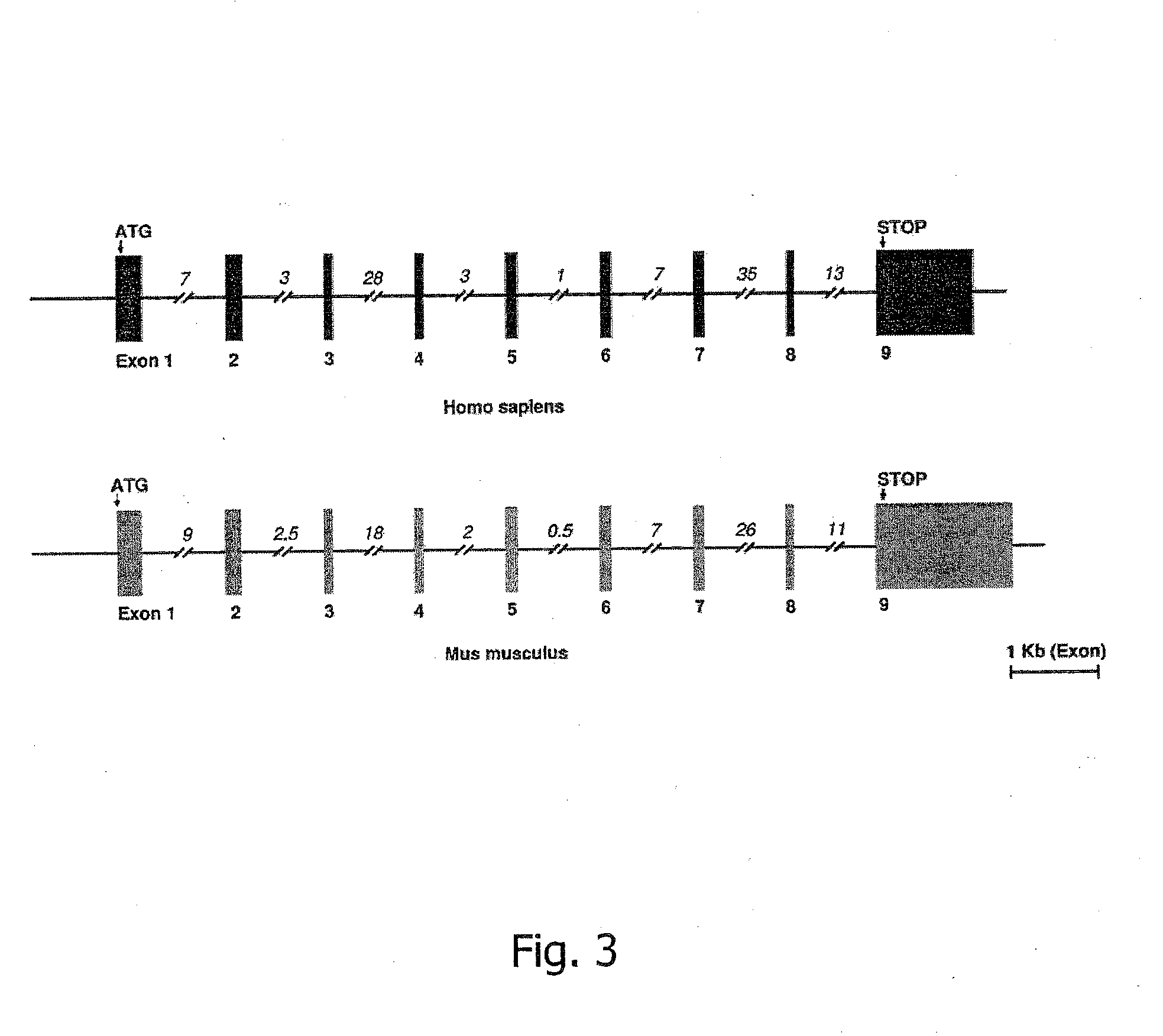
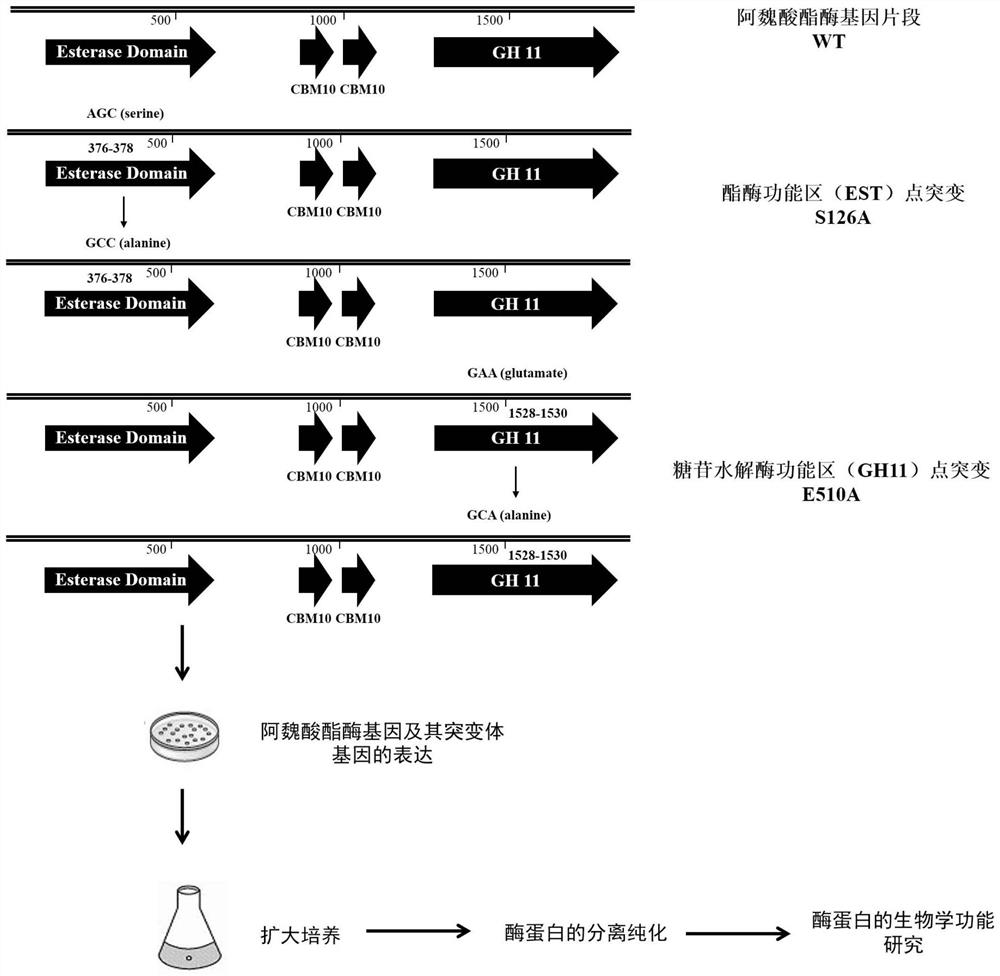
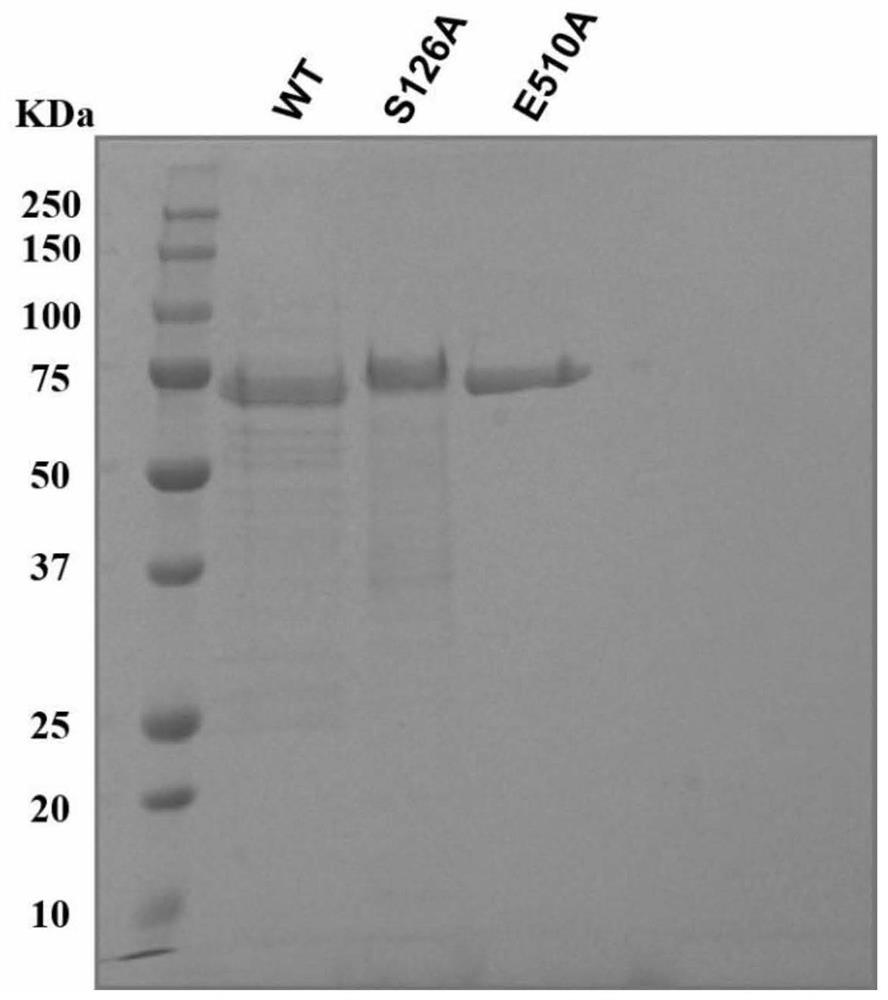
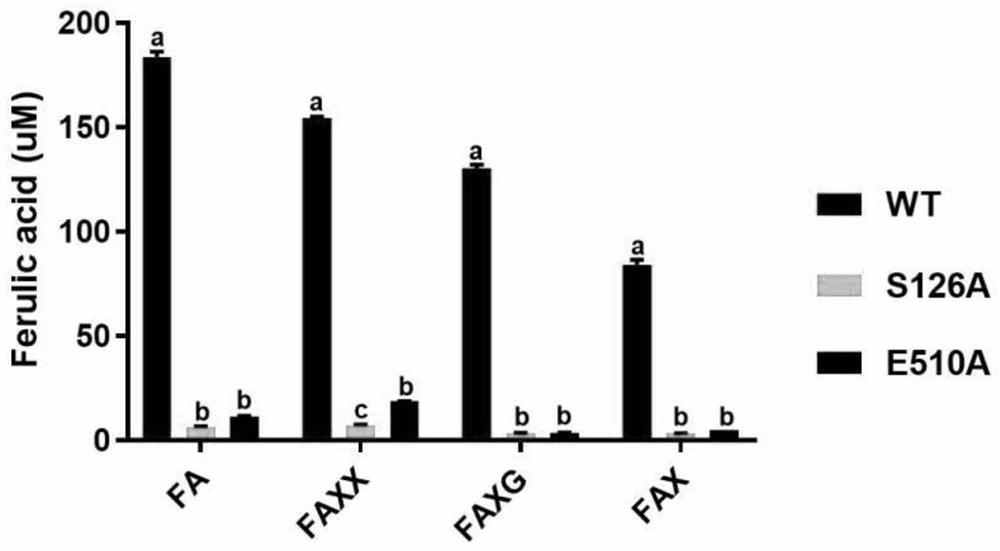
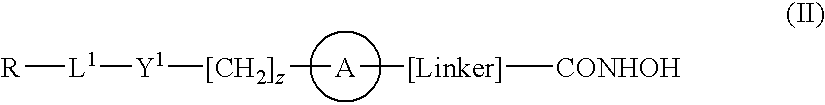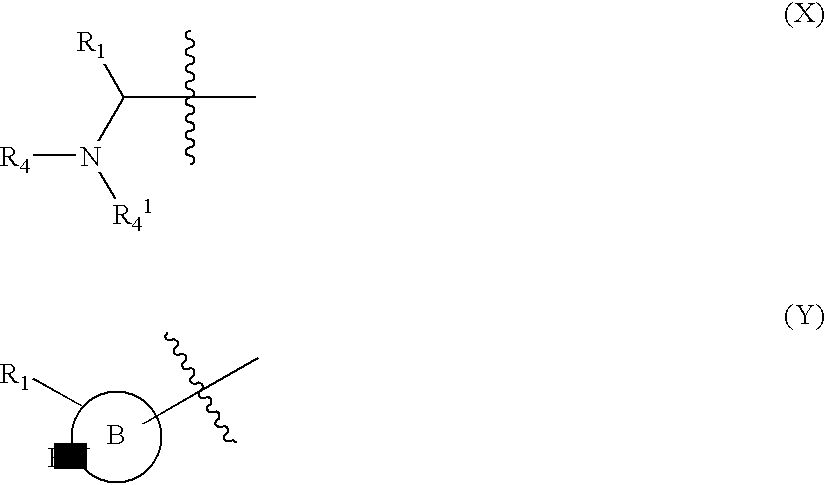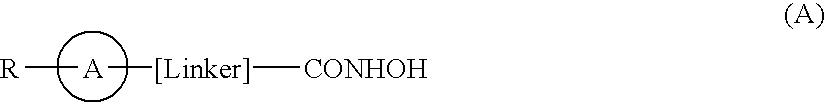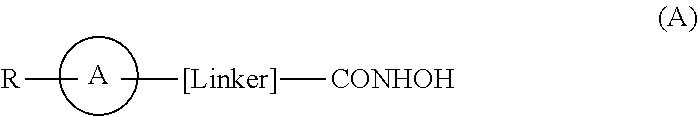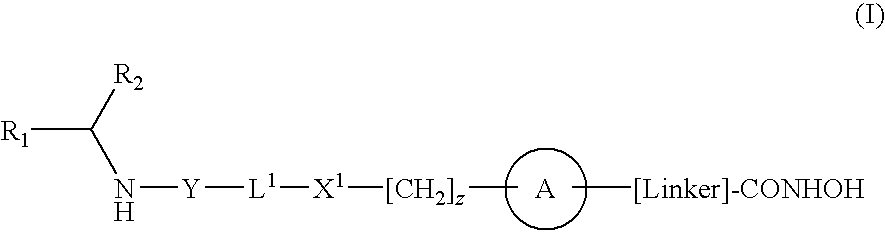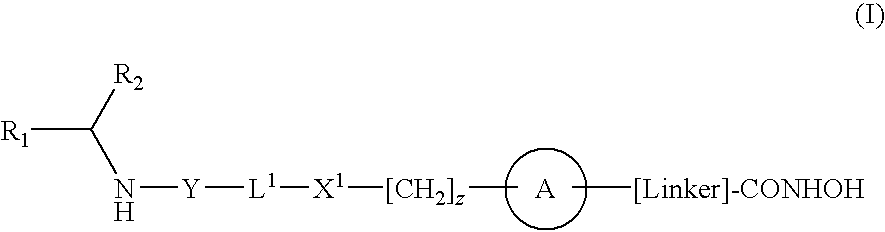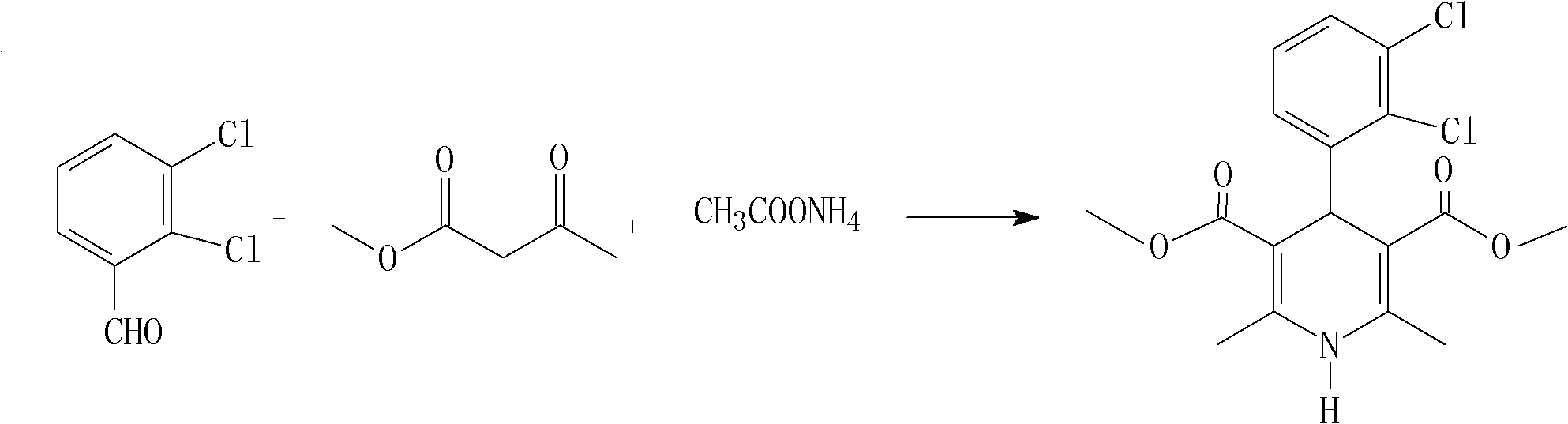Patents
Literature
104 results about "Acid Esterase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Esterase /es·ter·ase/ (es´ter-ās) any enzyme which catalyzes the hydrolysis of an ester into its alcohol and acid. esterase [es′tərās] any enzyme that splits esters. ... Most of the esterases from lactic acid bacteria are active towards short carbon chain fatty acid esters.
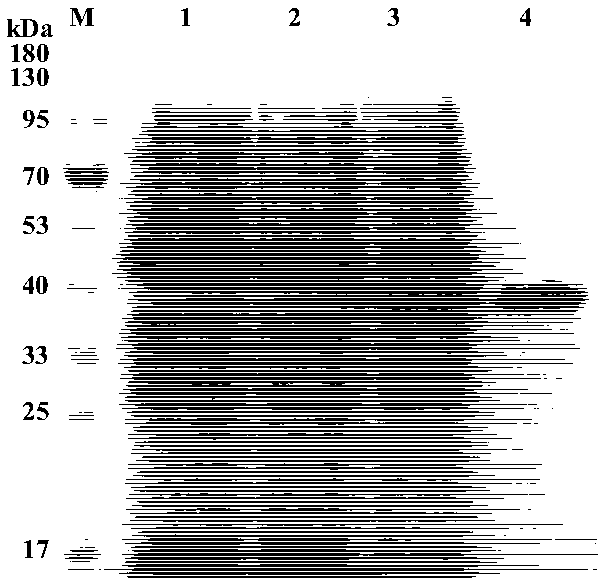
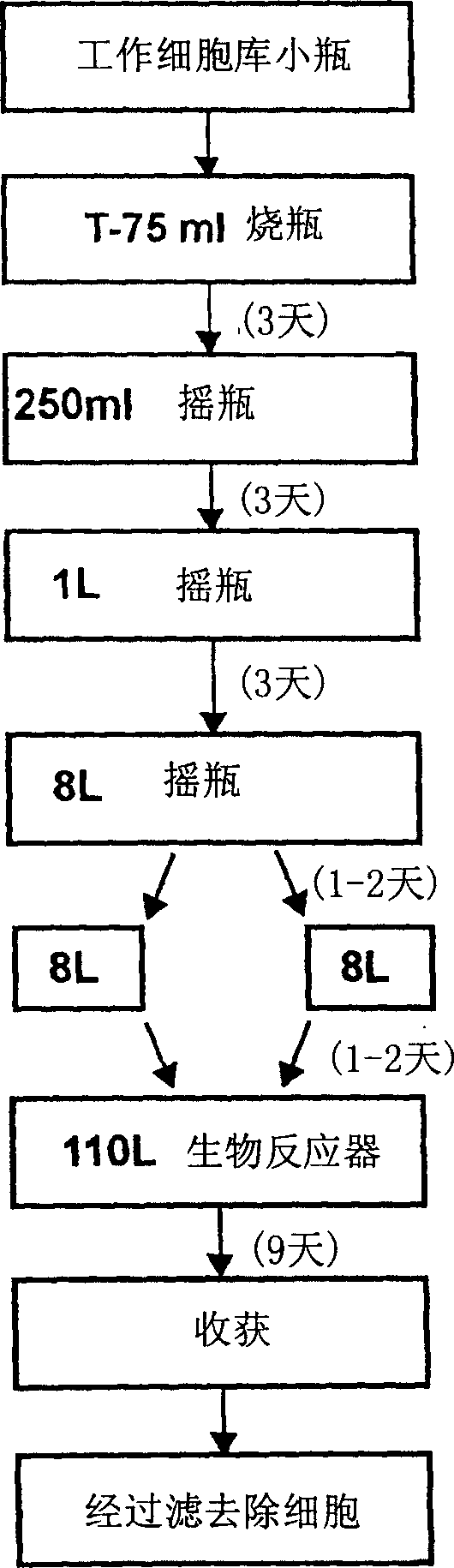
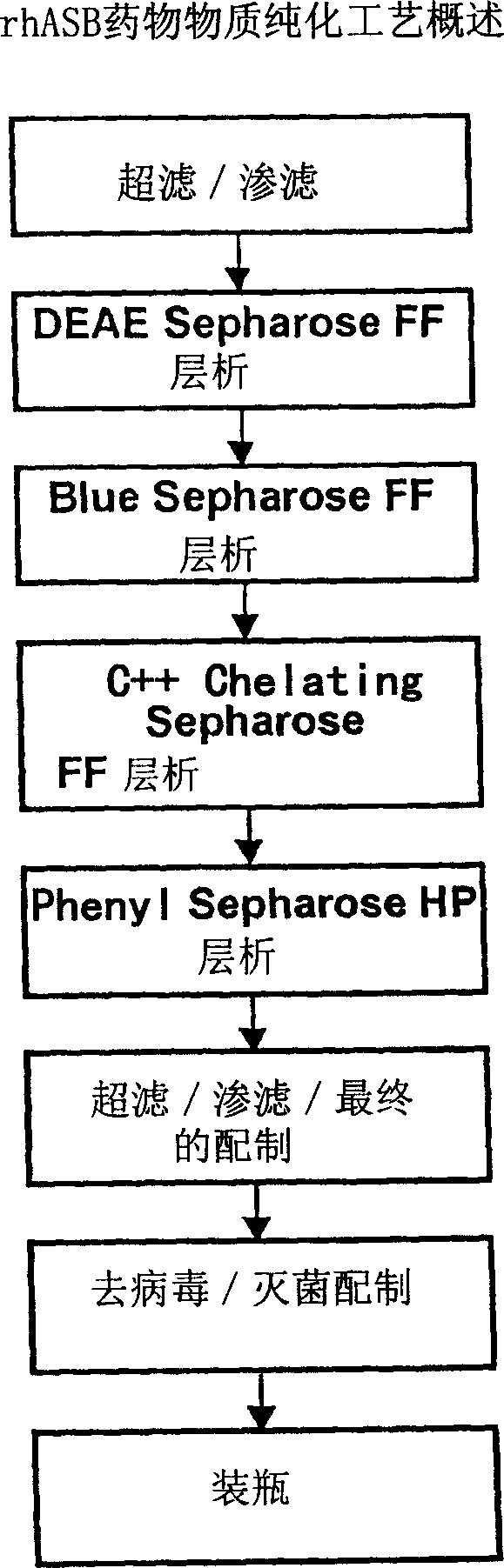
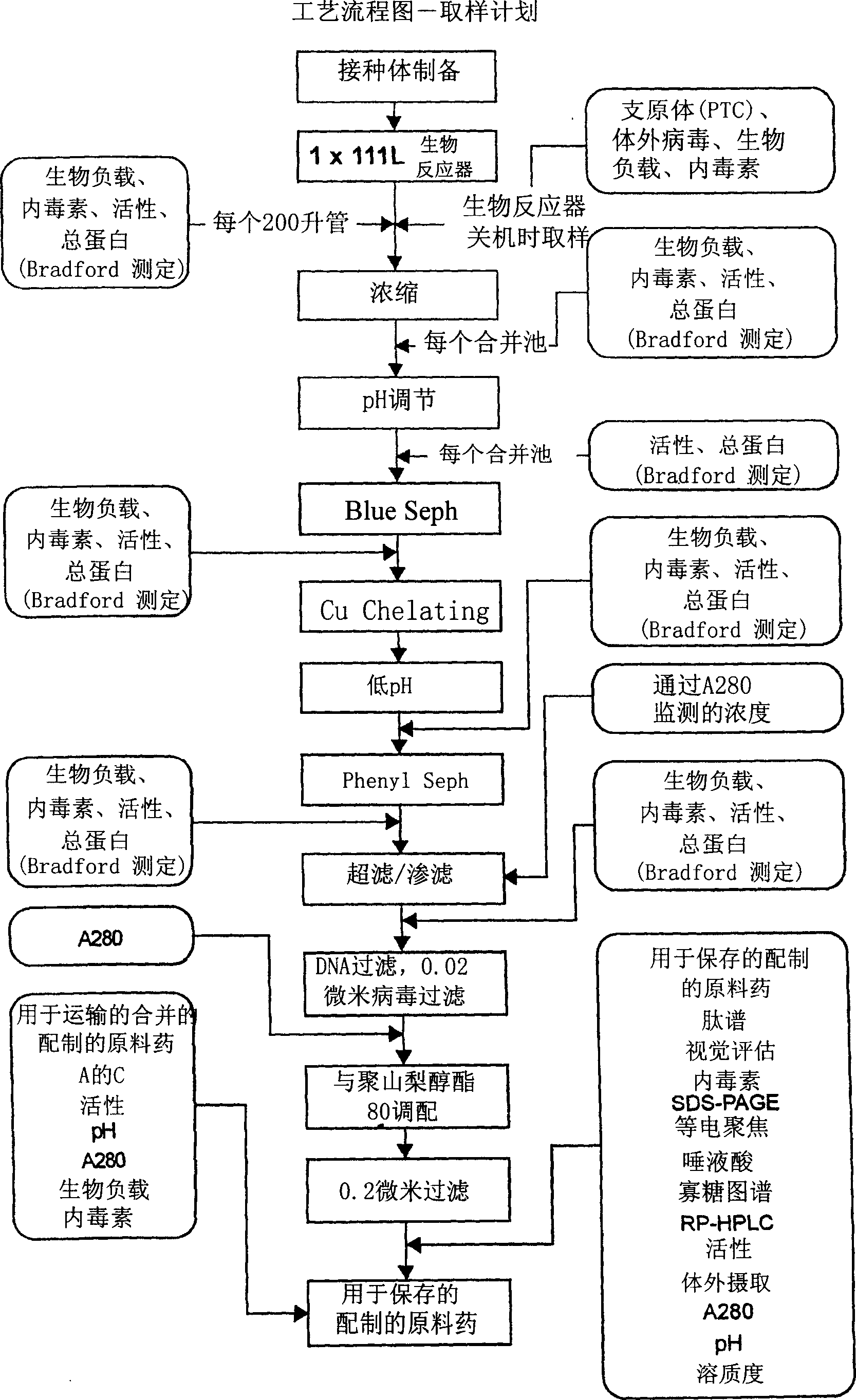
Manufacture of active highly phosphorylated human lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and uses thereof
ActiveUS8128925B2High yieldAvoid material lossCompound screeningNervous disorderPhosphorylationLysosome
This invention provides compositions of active highly phosphorylated lysosomal sulfatase enzymes, their pharmaceutical compositions, methods of producing and purifying such lysosomal sulfatase enzymes and compositions and their use in the diagnosis, prophylaxis, or treatment of diseases and conditions, including particularly lysosomal storage diseases that are caused by, or associated with, a deficiency in the lysosomal sulfatase enzyme.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Thermostable carboxylesterase gene, coding protein and application thereof
The invention discloses a thermostable carboxylesterase gene, coding protein and application thereof, the esterase has amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1. Compared with the prior art, the esterase containing EstW is thermostable esterase obtained from streptomycete in known mesophilic bacteria, can be widely applied to production of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or ferulic acid.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
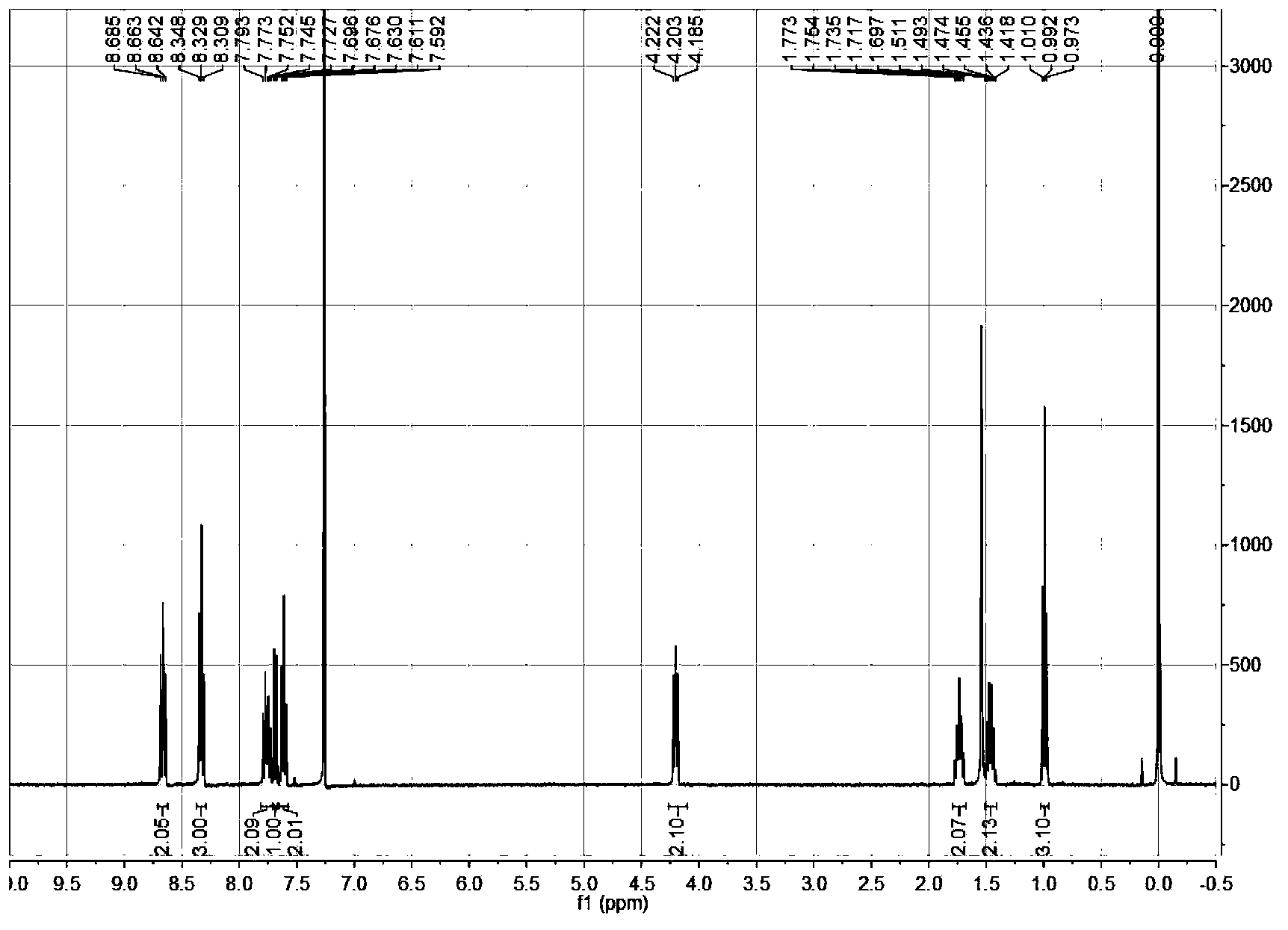
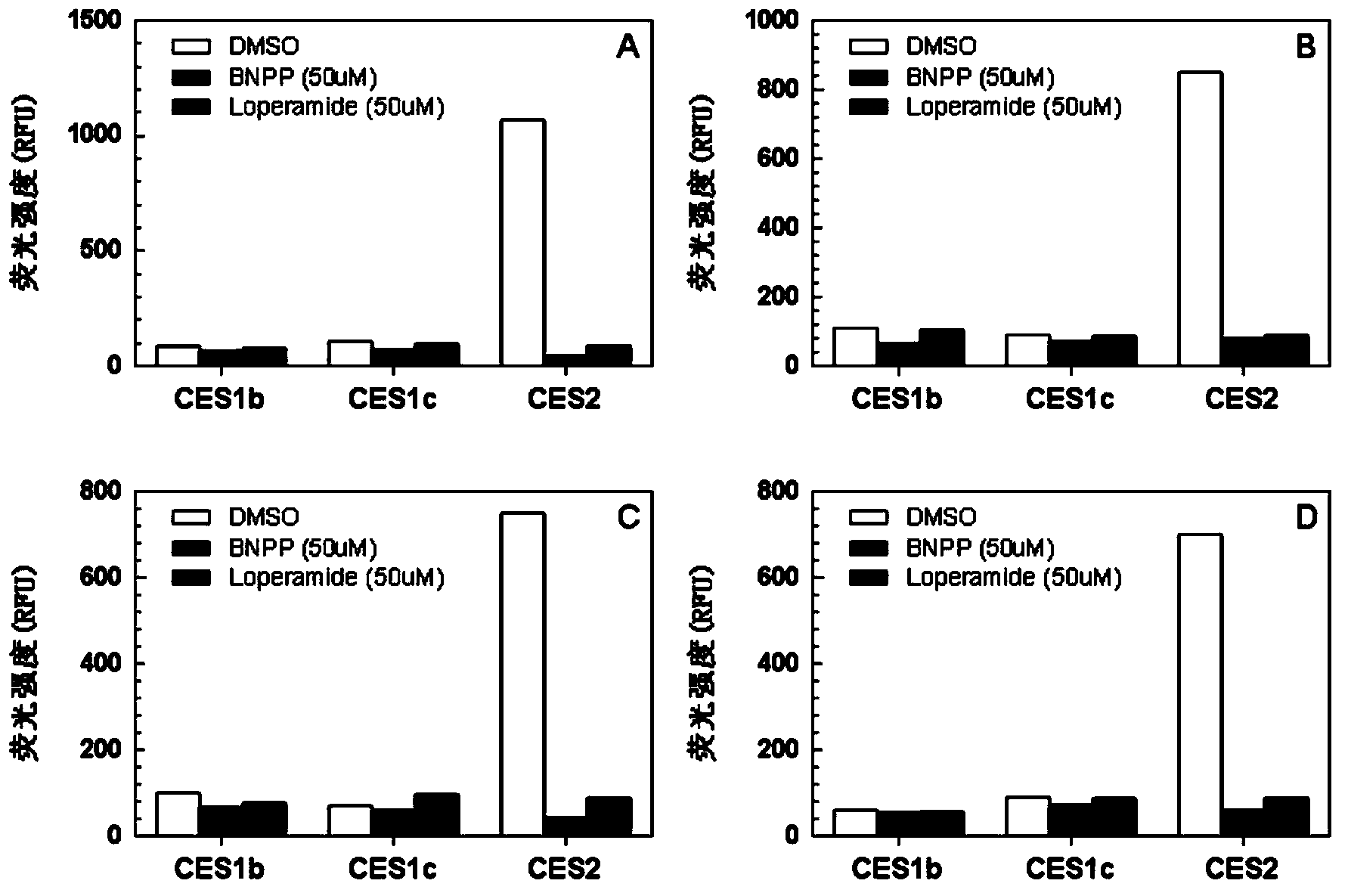
Specific fluorescence probe substrates of human carboxylesterase 2 and application thereof
InactiveCN104120164AEasy to detectThe synthesis process is simpleOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteHydrolysis
The invention provides a specific fluorescence probe substrates of human carboxylesterase 2 (CES2) and application thereof. The specific probe substrate is a benzoateb compound of a C4 hydroxyl naphthalimide, and is applicable to determine the enzyme activity of CES2 in a biological system. The CES2 enzyme activity determination flow comprises: selecting a hydrolysis benzoyl-removal reaction of the benzoate compound of the C4 hydroxyl naphthalimide as a probe reaction, and quantitatively determining the generation amount of a hydrolysis metabolite of the compound in a unit time, so as to determine the enzyme activity of CES2 in all biological samples, cells, bodies and integral organs. The probe is applicable to quantitative assessment of CES2 enzyme activity in biological samples of different species and different individual sources, and quantitative determination on CES2 enzyme activity in different sources of animal tissue cell culture fluids and cell preparation substances, so that the probe is expected to help to realize assessment on medicine disposal capability of important drug metablic enzyme CES2. Additionally, the probe also is applicable as an inhibitor for rapidly screening CES2 in vitro by means of the probe reaction.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
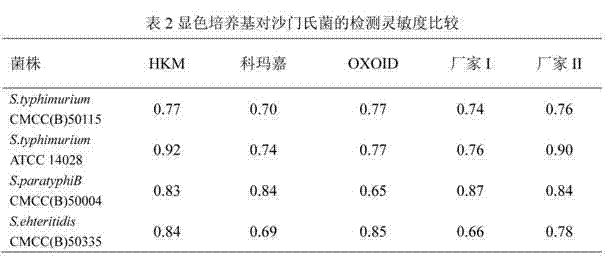
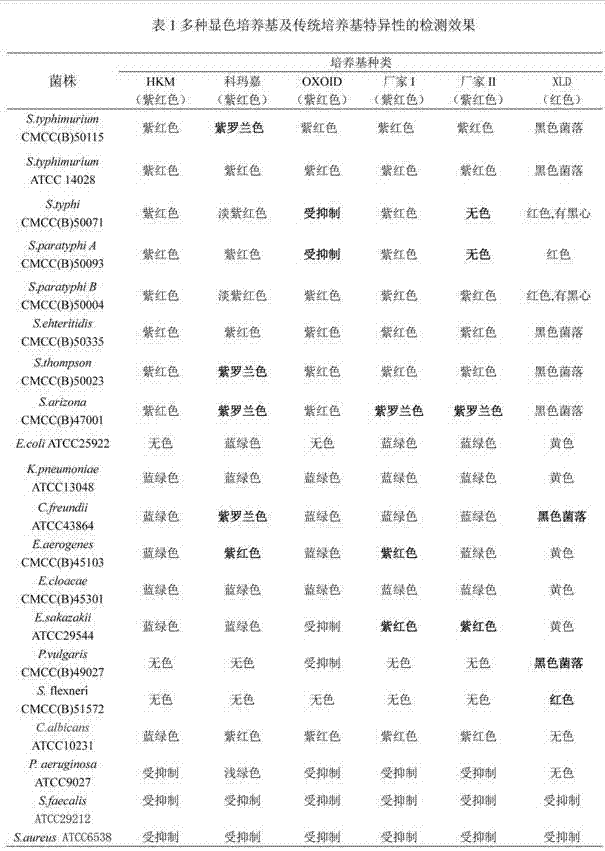
Chromogenic medium for detecting salmonella
InactiveCN102827918AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyActive agent
The invention discloses a chromogenic medium for detecting salmonella, which belongs to the fields of food safety and clinical microbiological detection. The culture medium contains agar, peptone, beef extract powder, sodium chloride, a surfactant, cholate, an enzyme inducer, an octoate enzyme chromogenic substrate, a beta-galactosidase chromogenic substrate, a hexosaminidase chromogenic substrate and robiocina. The chromogenic medium disclosed by the invention is used for detecting salmonella, has high detection sensitivity and high specificity, and can be used for initially identifying strains directly according to the color of a colony; the chromogenic medium has high operability, and suitable for treating large-reflux samples, and can be used for comprehensively, systematically and accurately detecting and initially identifying salmonella in food production, clinical disease diagnosis and the environment; and a new way is provided for rapid detection of microorganisms.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
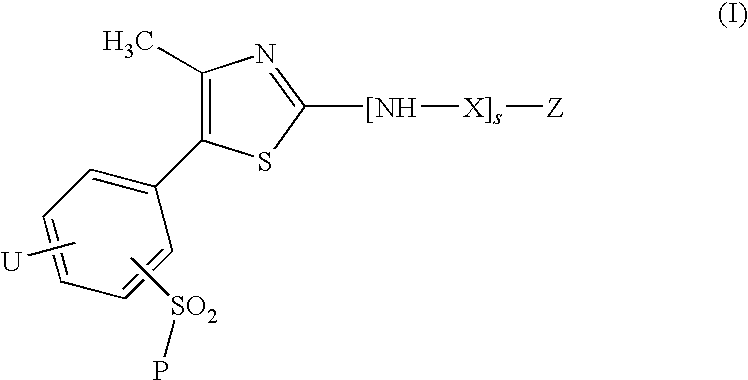
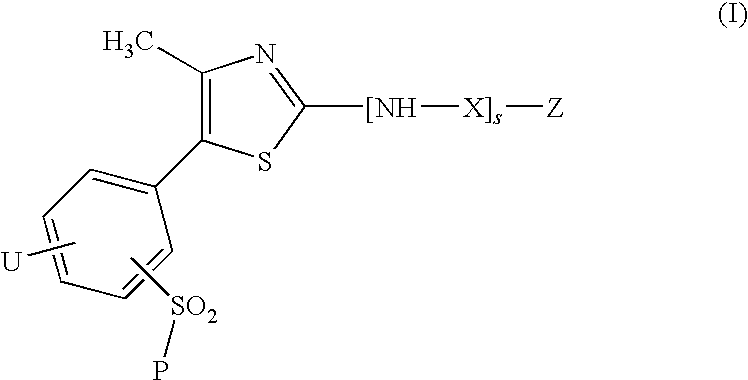
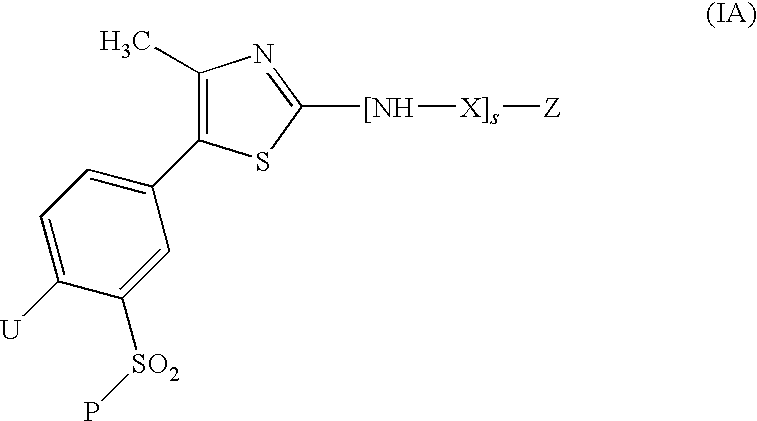
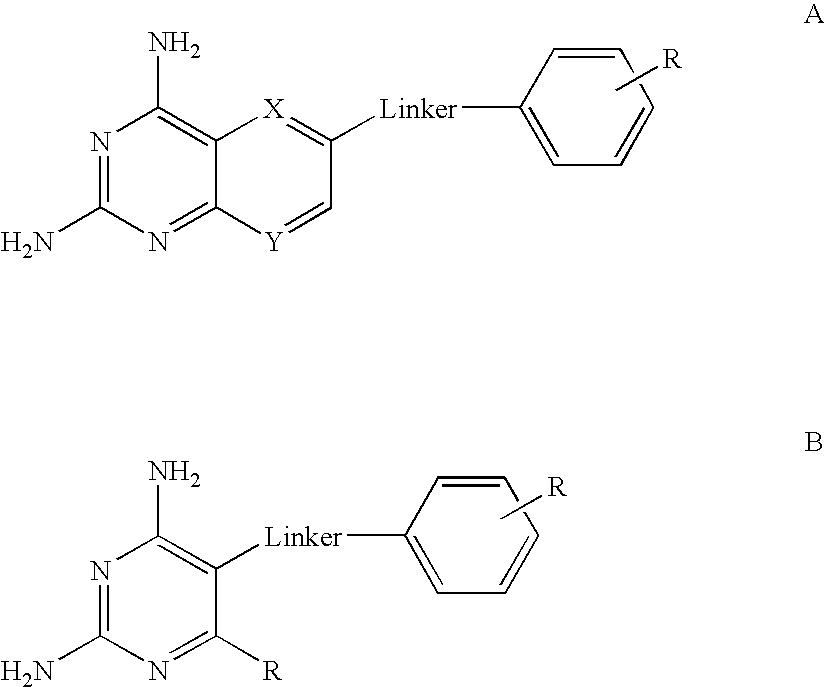
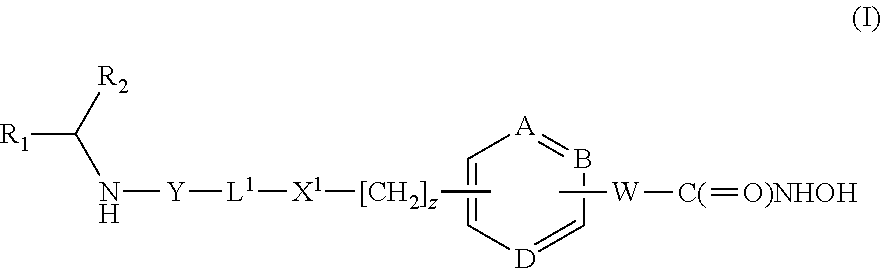
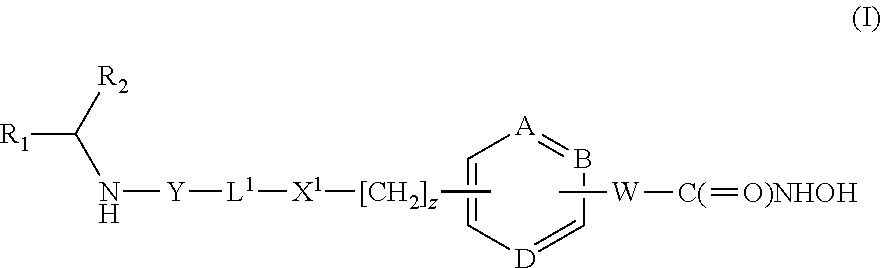
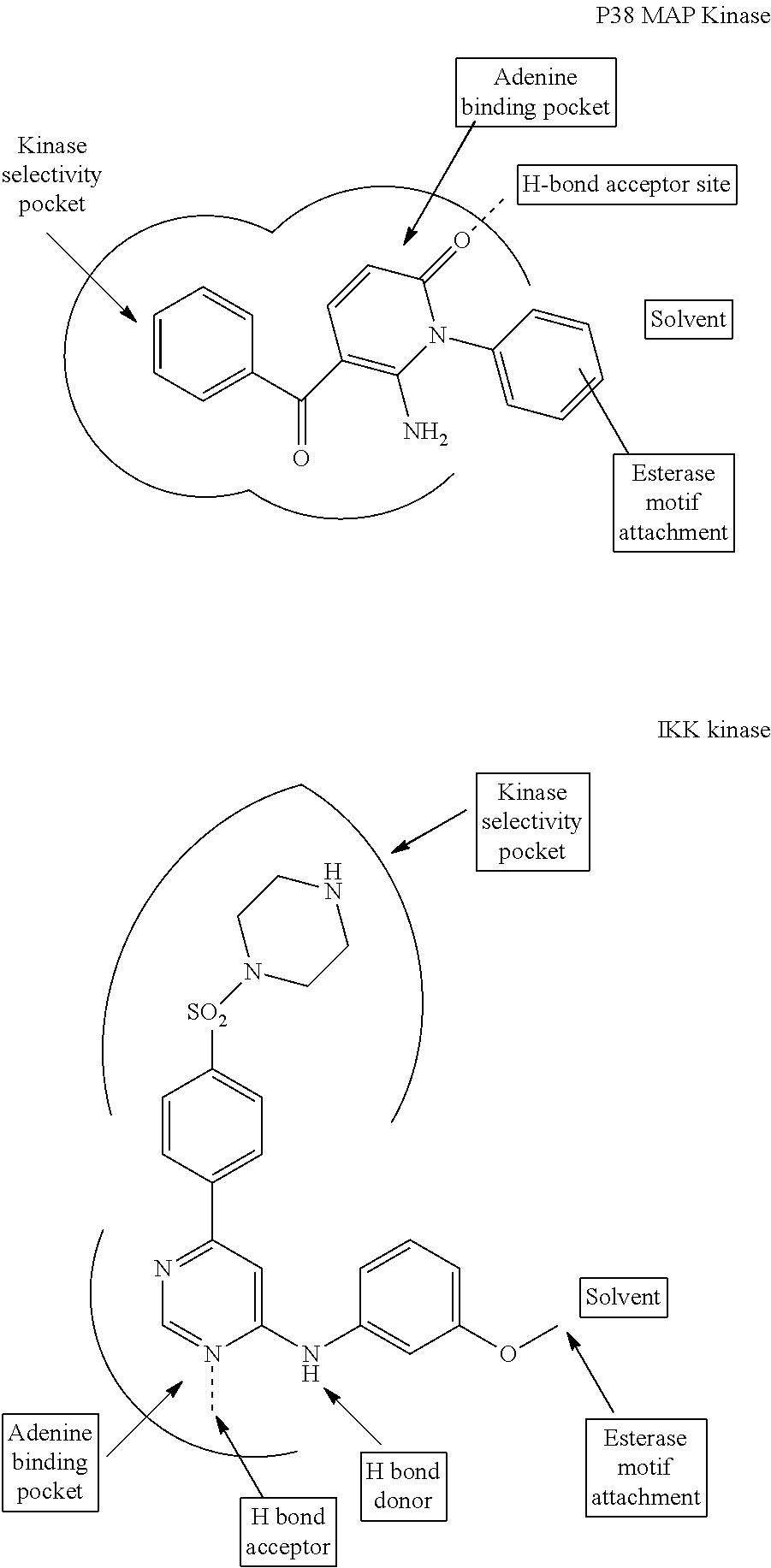
Thiazole derivatives as inhibitors of p13 kinase
Compounds of formula (I) are inhibitors of P13 kinase activity, and useful in treatment of, inter alia, autoimmune, inflammatory and proliferative diseases: wherein: s is 0 or 1; U is hydrogen or halogen; X is —(C═O), an optionally substituted divalent phenylene, pyridinylene, pyrimidinylene, or pyrazinylene radical, or a bond; P is optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl and Z is —(CH2)Z—X1-L1-NHCHR1R2; or Z is optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl and P is —(CH2)Z—X1-L1-NHCHR1R2; R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R2 is the side chain of a natural or non-natural alpha amino acid; X1 is (i) a bond; —NR4C(═O)NR5— or —NR4S(═O)2—; or except when X is —(C═O)— (ii) —C(═O)—, —S(═O)2—, or —S(═O)2NR4— wherein R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; and z and L1 are as defined in the specification.
Owner:CHROMA THERAPEUTICS
Diagnosis and treatment of multiple sulfatase deficiency and other sulfatase deficiencies
InactiveUS20130028881A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMultiple sulfatase deficiencyPost translational
This invention relates to methods and compositions for the diagnosis and treatment of Multiple Sulfatase Deficiency (MSD) as well as other sulfatase deficiencies. More specifically, the invention relates to isolated molecules that modulate post-translational modifications on sulfatases. Such modifications are essential for proper sulfatase function.
Owner:SHIRE HUMAN GENETIC THERAPIES INC
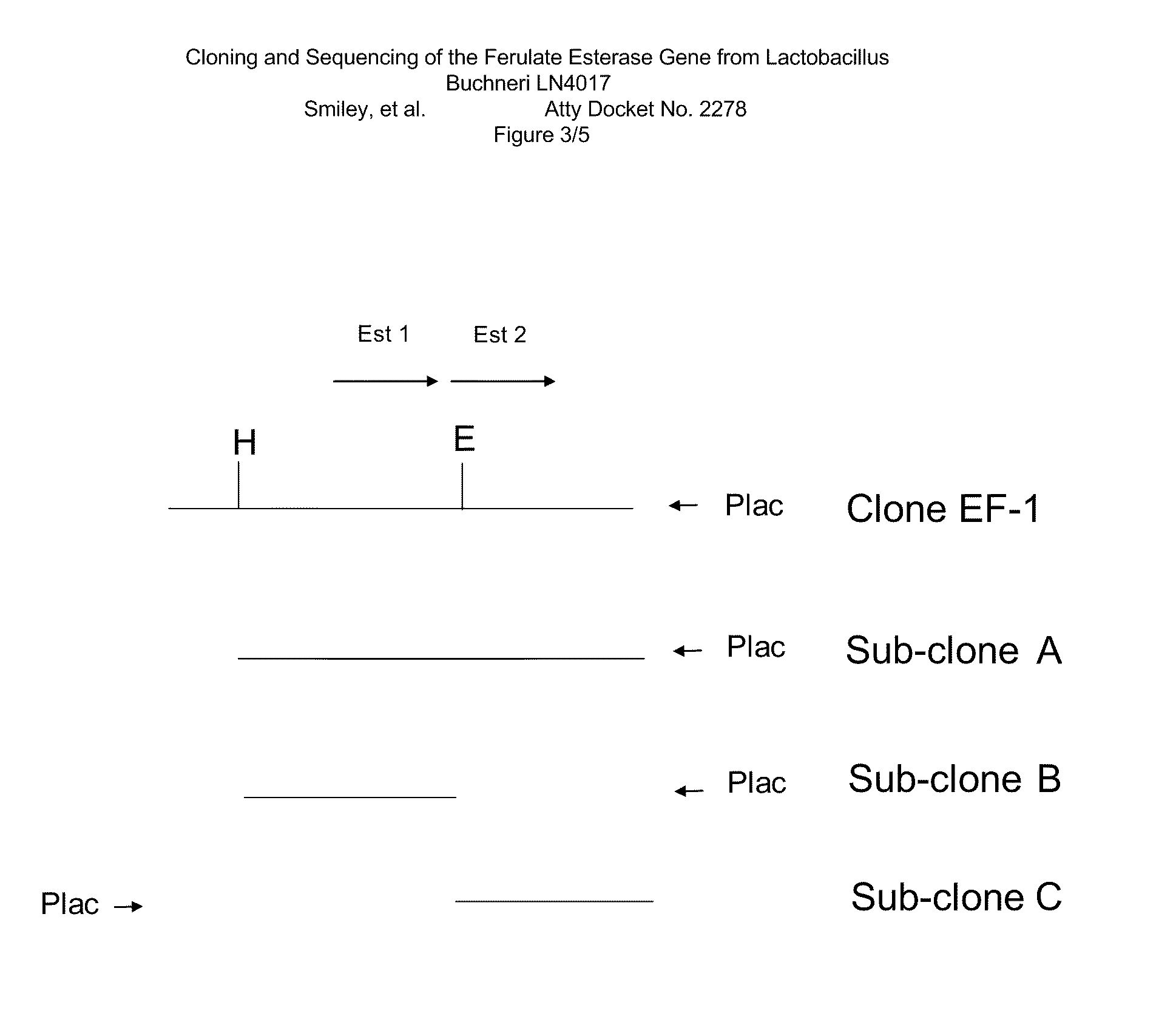
Cloning and sequencing of the ferulate esterase gene from Lactobacillus buchneri LN4017
Embodiments of the present invention include polypeptides having ferulate esterase activity and the nucleic acid sequences that encode them. Methods of the embodiments utilize these ferulate esterase polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences to enhance the digestibility of plant cell walls and the accessibility of carbohydrates in plants. The invention provides for transgenic plants transformed with expression vectors containing a DNA sequence encoding ferulate esterase from Lactobacillus buchneri. Methods of using same to enhance plant fiber digestion in animals, are disclosed. Uses of this invention include, but are not limited to, forage and silage with improved digestibility for livestock, and enhanced biomass conversion.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Manufacture of active highly phosphorylated human n-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase and uses thereof
This invention provides compositions of active highly phosphorylated human N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (GALNS), and pharmaceutical compositions and formulations thereof, methods of producing and purifying GALNS, and its use in the diagnosis, prophylaxis, or treatment of diseases and conditions, including particularly lysosomal storage diseases that are caused by, or associated with, a deficiency in the GALNS enzyme, e.g., Mucopolysaccharidosis IVa (MPS IVa or Morquio A syndrome).
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
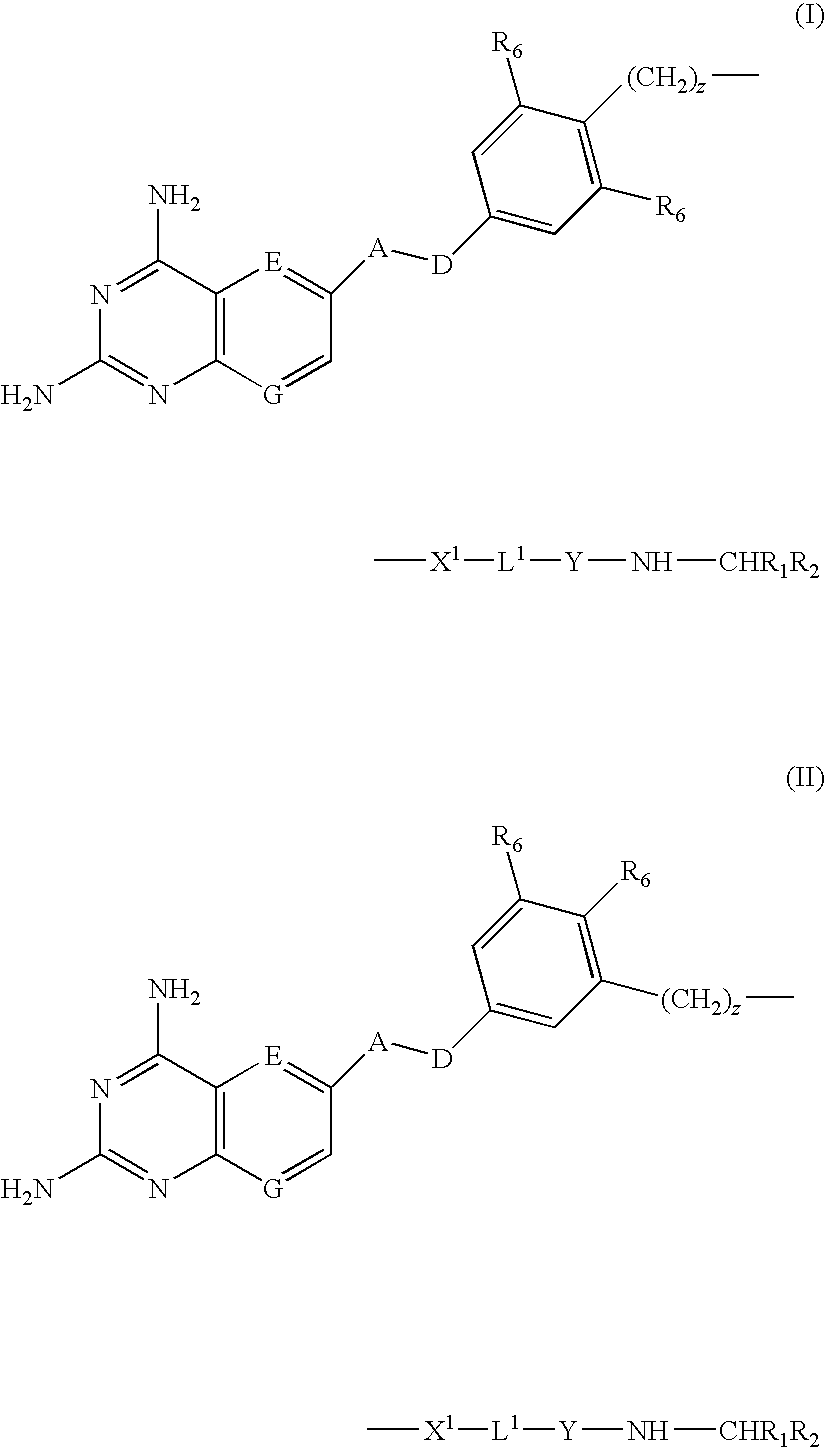
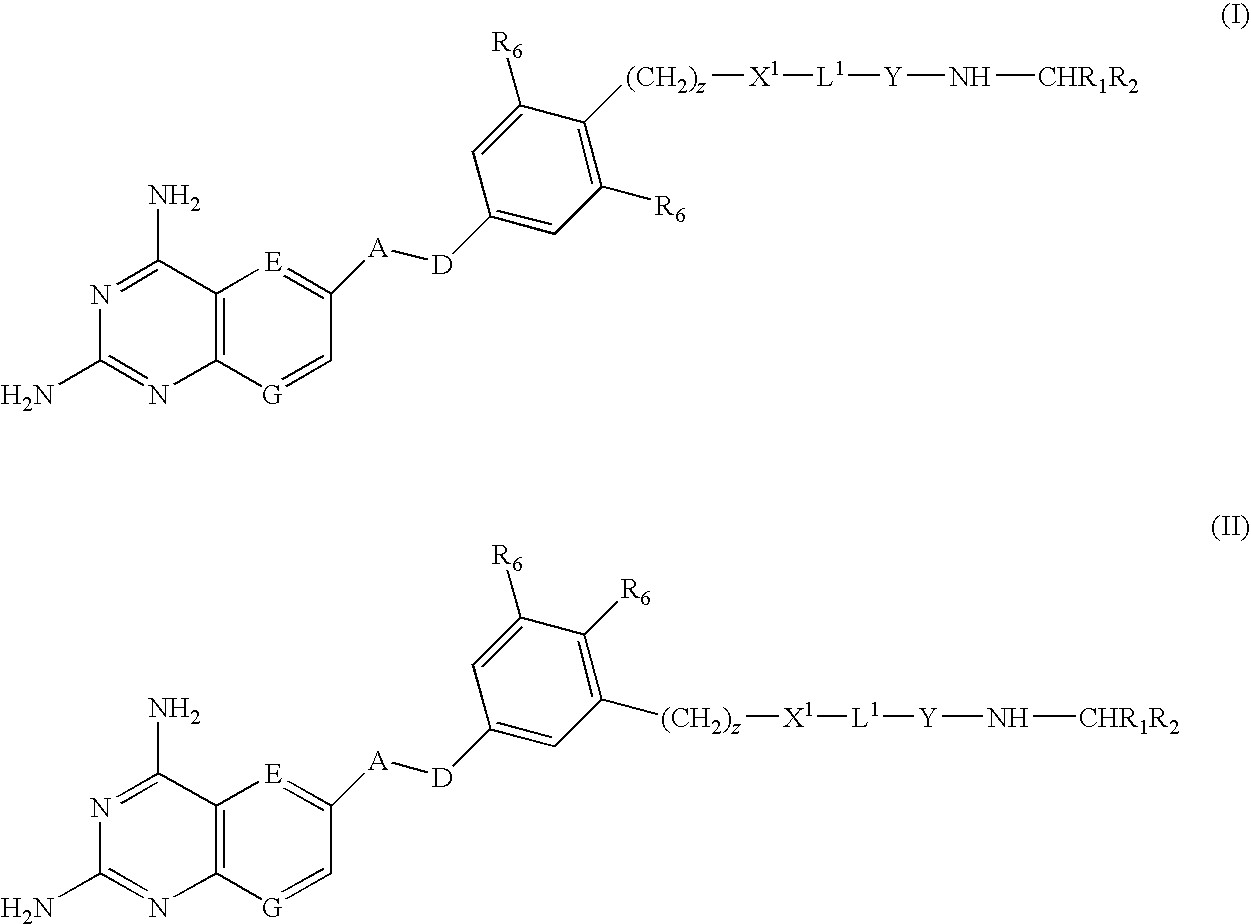
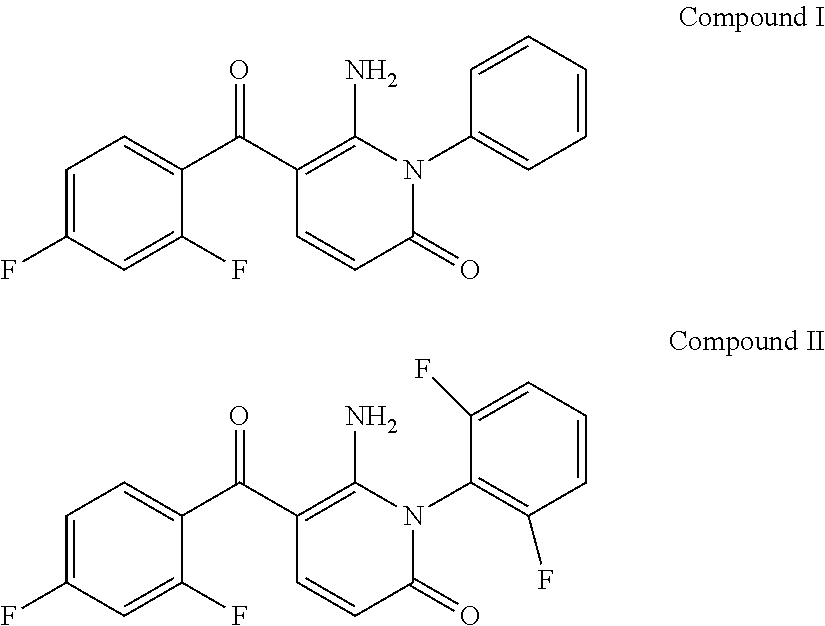
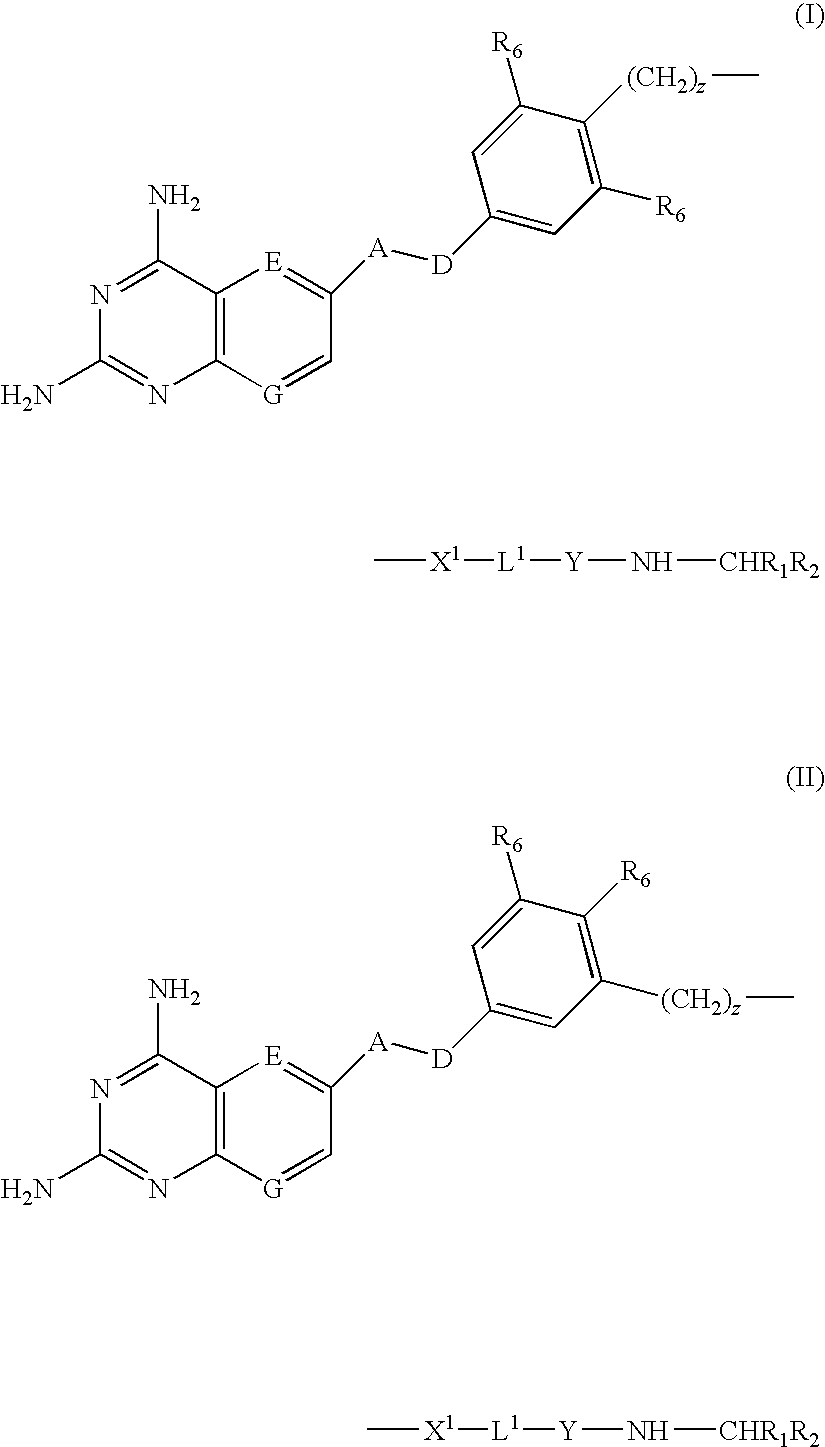
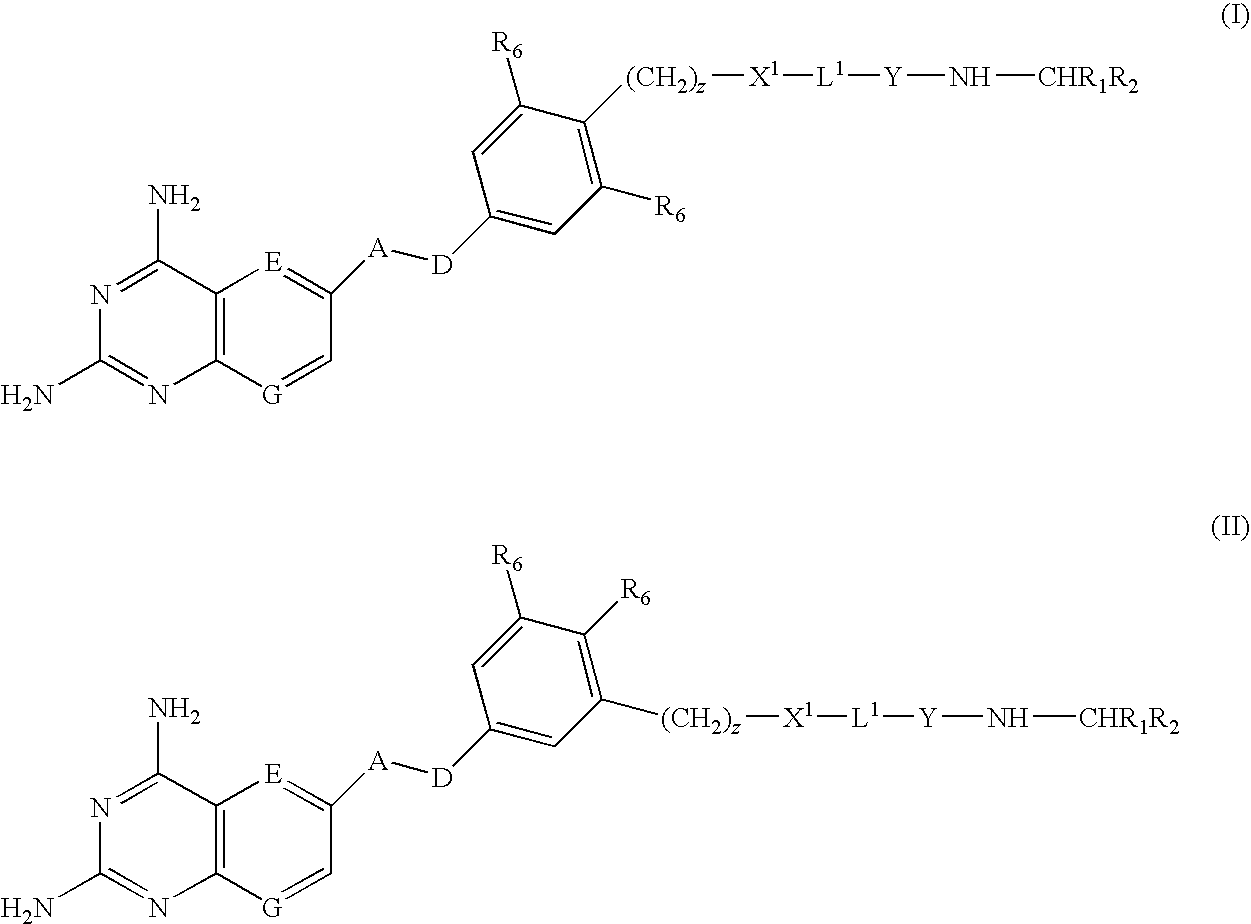
DHFR enzyme inhibitors
Compounds of formula (I) or (II) are dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors, useful for the treatment of, for example, cell proliferative diseases:wherein A and D are independently —CHR7— or —NR7—; E and G are independently ═CR7— or ═N—; each R6 independently represents hydrogen or —OR7; R7 is hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl; R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R2 is the side chain of a natural or non-natural alpha amino acid which does not contain a carboxyl, or carboxyl ester group; Y is a bond, —C(═O)—, —S(═O)2—, —C(═O)NR3—, —C(═S)—NR3, —C(═NH)NR3 or —S(═O)2NR3— wherein R3 is hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; L1 is a divalent radical of formula -(Alk1)m(Q)n(Alk2)p- wherein m, n and p are independently 0 or 1, and Q, Alk1 and Alk2 are as defined in the claims; X1 represents a bond; —C(═O); or —S(═O)2—; —NR4C(═O)—, —C(═O)NR4—, —NR4C(═O)NR5—, —NR4S(═O)2—, or —S(═O)2NR4— wherein R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; and z is 0 or 1.
Owner:CHROMA THERAPEUTICS
Feruloyl esterase and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN109652392AIncrease enzyme activityHigh hydrolytic activityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliCefazolin
The invention provides feruloyl esterase and a preparing method and application thereof. A feruloyl esterase gene coming from a soil macro gene library have the nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The gene contains a tetrapeptide SXXK sequence motif which is rarely seen, and after the esterase gene is inserted into plasmid pET28a(+), the gene is transformed into escherichia coli BL21(DE3) to achieve heterogeneous expression. The molecular weight of purified recombinase (DLFae4) is 38.3 kDa. Besides, it is put forward for the first time that novel feruloyl esterase can hydrolyze penbritin, penicillin, cefazolin and other lactam antibiotics. As is shown by site-directed mutagenesis experiments, a catalysis triplet of DLFae4 is composed of serine(S11), histidine (H74) and aspartic acid (D302), and the mutation of any of serine (S11), histidine (H74) and aspartic acid (D302) can cause loss of the catalysis capability of DLFae4. DLFae4 has a high hydrolytic activity on methyl ferulate and has good heat stability. In the presence of cellulase, DLFae4 can obviously increase the amount of ferulic acid released from destarched wheat bran. Due to peculiar activities and enzymatic characteristics of novel feruloyl esterase, novel feruloyl esterase can be applied to feed, paper making, food, pharmacy and other fields.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
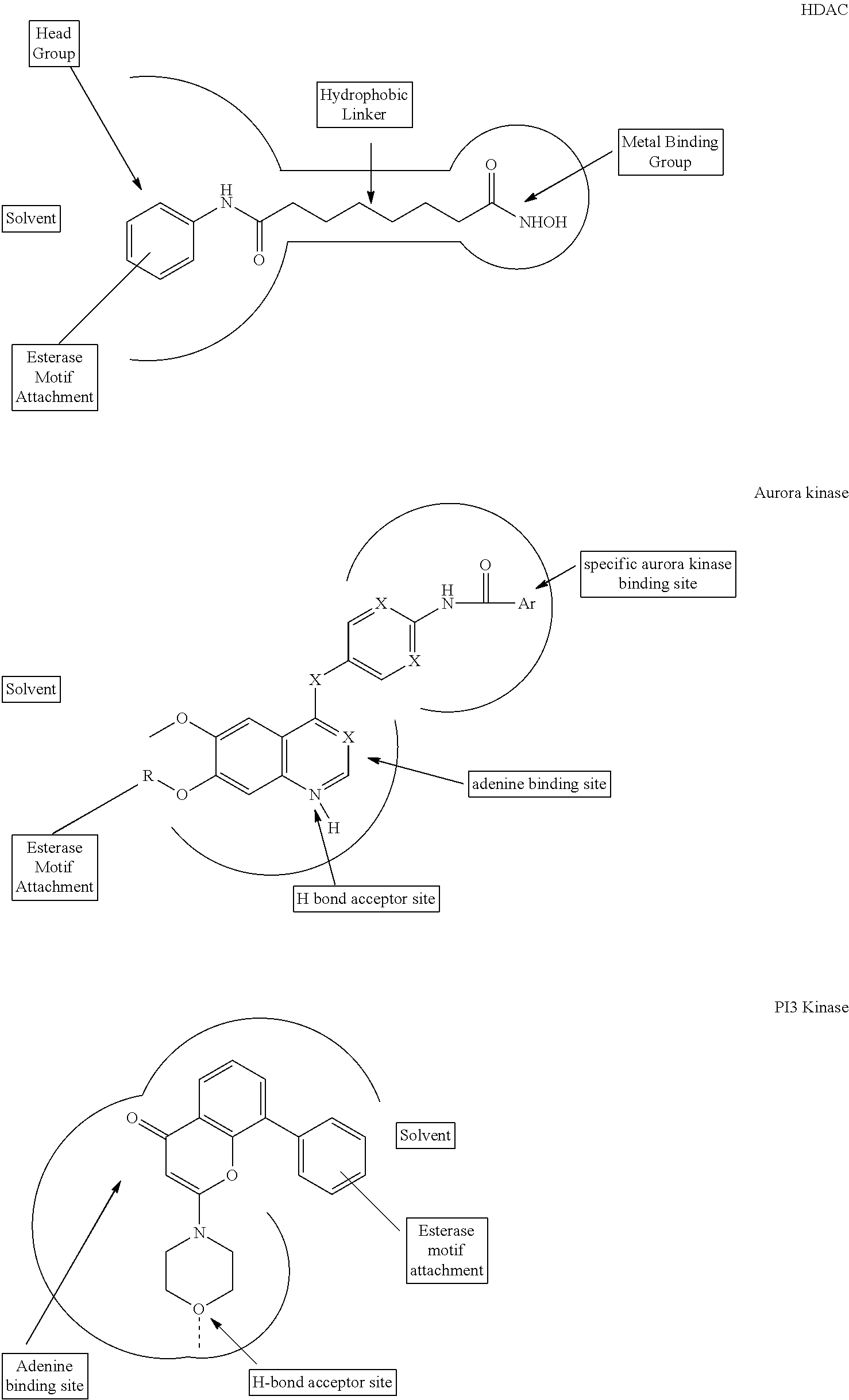
Hydroxamic acid derivatives as inhibitors of HDAC enzymatic activity
Compounds of formula (I) are inhibitors of histone deacetylase activity, and are useful in the treatment of, for example, cancers:wherein Y1 is a bond, —(C═O)—, —S(O2)—, —C(═O)O—, —OC(═O)—, —(C═O)NR3—, —NR3(C═O)—, —S(O2)NR3—, —NR3S(O2)—, or —NR3(C═O)NR5—, wherein R3 and R5 are independently hydrogen or optionally substituted (C1-C6)alkyl, L1 is a divalent radical of formula -(Alk1)m(Q)n(Alk2)p wherein m, n, p, Alk1, Alk2 and Q are as defined in the claims; z is 0 or 1; A represents an optionally substituted mono-, bi— or tri-cyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring system; -[Linker]- represents a divalent linker radical; R is a radical of formula (X) or (Y):wherein R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R4 is hydrogen; or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl, C3-C7cycloalkyl, aryl, aryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-, heteroaryl, heteroaryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-, —(C═O)R3, —(C═O)OR3, or —(C═O)NR3 wherein R3 is hydrogen or optionally substituted (C1-C6)alkyl, C3-C7 cycloalkyl, aryl, aryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-, heteroaryl, or heteroaryl(C1-C6 alkyl)-; R41 is hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; and B is a monocyclic heterocyclic ring of 5 or 6 ring atoms wherein R1 is linked to a ring carbon adjacent the ring nitrogen shown, and ring B is optionally fused to a second carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring of 5 or 6 ring atoms in which case the bond shown intersected by a wavy line may be from a ring atom in said second ring.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
HDAC inhibitors
InactiveUS20130197042A1Improve permeabilityProlong the action timeBiocideNervous disorderSide chainCarboxylic acid
Compounds of formula (I) inhibit HDAC activity:wherein A, B and D independently represent ═C— or ═N—; W is a divalent radical —CH═CH— or CH2CH2—; R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxyesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R2 is the side chain of a natural or non-natural alpha amino acid; z is 0 or 1; and Y, L1, and X1 are as defined in the claims.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
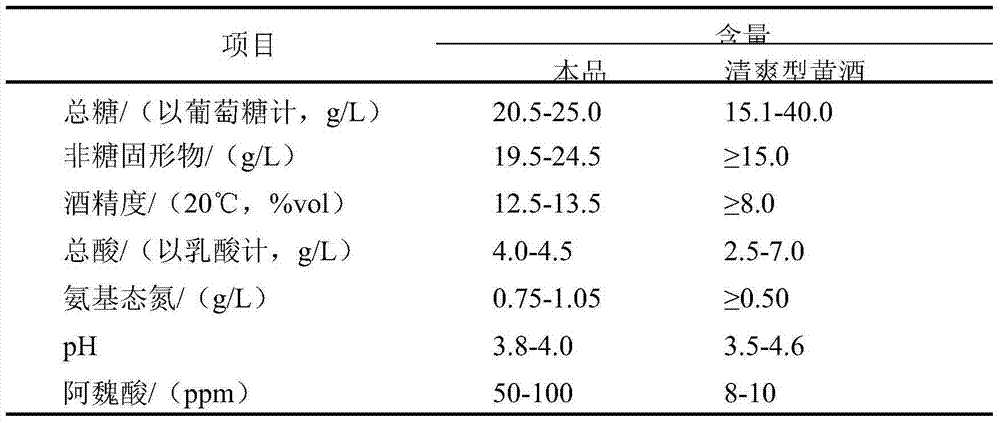
Functional yellow wine enriched in ferulic acid and production method of functional yellow wine
ActiveCN104762220AIncrease ferulic acid contentIncreased ferulic acid contentFungiHydrolasesAmylaseThrombus
The invention discloses functional yellow wine enriched in ferulic acid and a production method of the functional yellow wine, belonging to the technical field of food brewing. The aspergillus niger CCTCC NO:M 2015202 feruloyl esterase, amylase and cellulase are high in activity, when the enzymes are added into the yellow wine fermentation process, normal fermentation of the yellow wine is not influenced, saccharifying of raw materials in the yellow wine production process is accelerated, the yellow wine production and fermentation cycle is shortened, and the original flavor and taste of the yellow wine can be maintained. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: by taking sticky rice as a raw material, inoculating aspergillus niger strain spore suspension containing high-yield feruloyl esterase during jar dropping, adding wheat bran with high ferulic acid content, performing primary fermentation, secondary fermentation, pressing, boiling wine, filling, sealing the jar and the like. The yellow wine produced by the method disclosed by the invention is enriched in ferulic acid and has the effects of resisting oxidation, reducing blood pressure, resisting thrombus, reducing blood fat, resisting bacteria, diminishing inflammation, preventing cancers, protecting the liver, treating the diabetes and the like. Moreover, the production process is energy saving and environmentally friendly, and the additional value of byproducts of wheat production is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Feruloyl esterase gene, genetically engineered strain, and preparation method and application of feruloyl esterase
The invention provides a feruloyl esterase gene. The feruloyl esterase gene is originated from microbes in the rumen of a Chinese yak and has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, wherein the nucleotide sequence codes an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The invention also provides a recombinant Kluyveromyces marxianus expression vector containing the gene, a genetically engineered strain, a preparation method for feruloyl esterase and application of prepared feruloyl esterase. Feruloyl esterase is subjected recombinant expression in a Kluyveromyces marxianus expression system; and after high-density fermentation for 48 h, intracellular and extracellular feruloyl esterase vitalities are 686.35 U / mL and 346.34 U / mL, respectively. Feruloyl esterase having undergone recombinant expression by Kluyveromyces marxianus can release ferulic acid in corn bran. Feruloyl esterase prepared in the invention can be applied to food processing, feed addition, biomedicine, biotransformation of cellulosic substances, bioenergy and other fields.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Novel feruloyl esterase, mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111748538ARich sources of bacteriaRich sourcesHydrolasesFood processingEscherichia coliGenetics genomics
The invention discloses novel feruloyl esterase, a mutant and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, successfully screening out a feruloyl esterase gene from anaerobic fungi Neocallimatix sp. by utilizing a genomics technology; according to the preference of a prokaryotic system codon, the GC content of a feruloyl esterase gene and the secondary structure of mRNA, and codon optimization is carried out on the feruloyl esterase gene to obtain a novel feruloyl esterase gene sequence. The enzyme has an esterase regionand a glucoside hydrolase 11 region, site-specific mutagenesis is carried out on the two regions; the obtained mutant gene is also expressed in escherichia coli; separation and purification results show that the novel feruloyl esterase and the mutant thereof are successfully expressed in escherichia coli, and the esterase activity of the mutant is far lower than that of a non-mutant, so that the strain source of the feruloyl esterase is enriched, and the feruloyl esterase has theoretical guiding significance in the aspects of improving the digestibility of feed fibers and improving the production performance of animals.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Precursor of N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase, methods of treatment using said enzyme and methods for producing and purifying said enzyme
InactiveUS6972124B2High puritySufficient amountBacteriaHydrolasesN-Acetylgalactosamine-4-SulfataseMutant
The present invention provides a highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase and biologically active mutants, fragments and analogs thereof as well as pharmaceutical formulations comprising highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase. The invention also provides methods for treating diseases caused all or in part by deficiencies in human N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase including MPS VI and methods for producing and purifying the recombinant precursor enzyme to a highly purified form.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Enzyme Inhibitors
InactiveUS20090291978A1Improve permeabilityProlong the action timeBiocideNervous disorderHydroxamic acidSide chain
Compounds of formula (I) are inhibitors of histone deacetylase activity, and are useful in the treatment of, for example, cancers, wherein R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxyesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R2 is the side chain of a natural or non-natural alpha amino acid; Y is a bond, C(═O)—, —S(═O)2—, —C(—O)O—, —C(O)NR3—, —C(═S)—NR3, —C(═NH)NR3 or —S(═O)2NR3— wherein R3 is hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; L is a divalent radical of formula -(Alk1)m(O)n(Alk2)p— wherein m, n and p are independently 0 or 1, Q is (i) an optionally substituted divalent mono- or bicyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic radical having 5-13 ring members, or (ii), in the case where both m and p are 0, a divalent radical of formula —X2-Q1- or -Q1-X2— wherein X2 is —O—, S— or NRA— wherein RA is hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C3 alkyl, and Q1 is an optionally substituted divalent mono- or bicyclic carbocyclic or hetero-cyclic radical having 5-13 ring members, AIk1 and AIk2 independently represent optionally substituted divalent C3-C7 cycloalkyl radicals, or optionally substituted straight or branched, C1-C6 alkylene, C2-C6 alkenylene, or C2-C6 alkynylene radicals which may optionally contain or terminate in an ether (—O—), thioether (—S—) or amino (—NRA-) link wherein RA is hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C3 alkyl; X represents a bond; —C(═O); or —S(═O)2—; —NR4C(═O)—, —C(═O)NR4—, —NR4C(═O)NR5—, —NR4S(═O)2—, or —S(═O)2NR4— wherein R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; z is 0 or 1; A represents an optionally substituted mono-, bi- or tri-cyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring system wherein the radicals R1R2NH—Y-L1-X1—[CH2]z— and HONHCO-[LINKER]- are attached different ring atoms; and -[Linker]- represents a divalent linker radical linking a ring atom in A with the hydroxamic acid group CONHOH, the length of the linker radical, from the terminal atom linked to the ring atom of A to the terminal atom linked to the hydroxamic acid group, is equivalent to that of an unbranched saturated hydrocarbon chain of from 3-10 carbon atoms.
Owner:CHROMA THERAPEUTICS
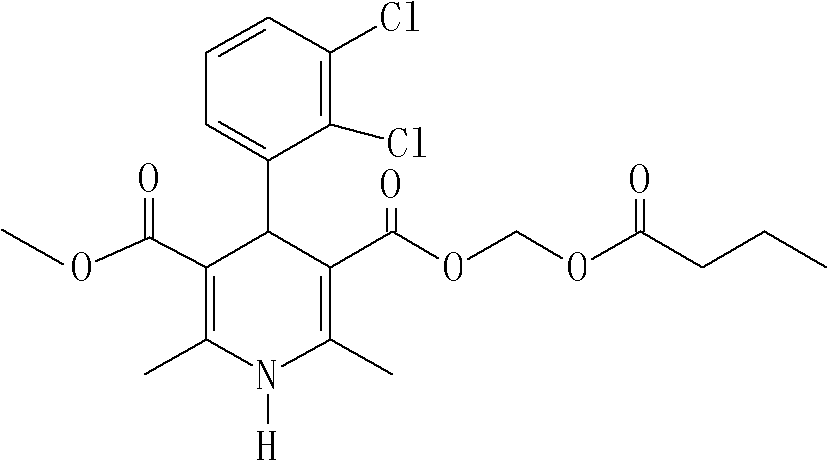
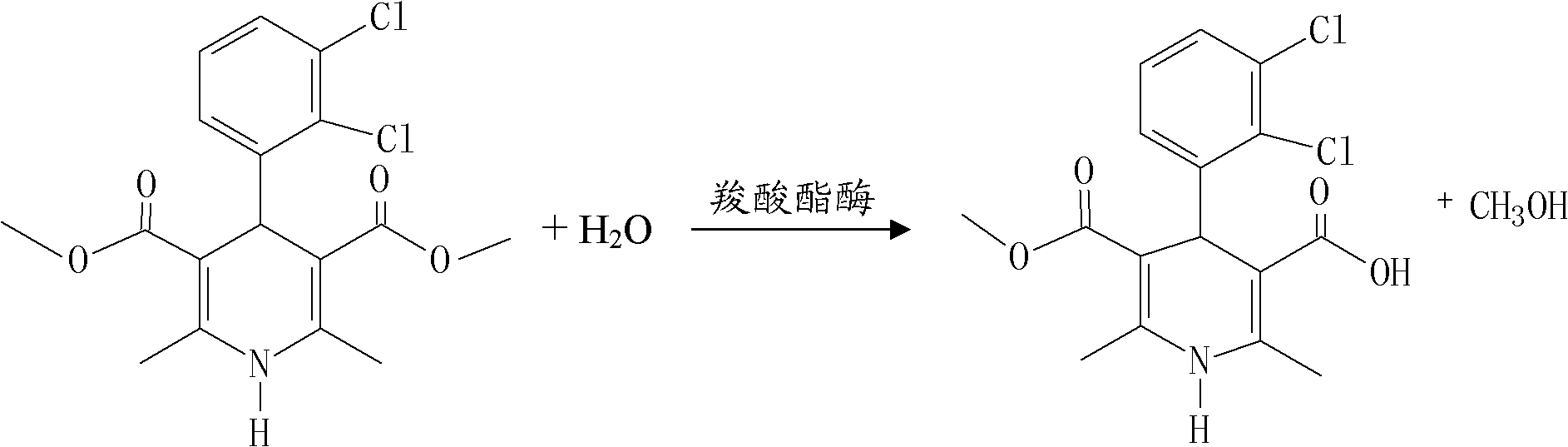
Method for preparing clevidipine butyrate
ActiveCN102432527AHigh selectivityReduce generationOrganic chemistryFermentationClevidipineCarboxylic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing clevidipine butyrate and also relates to a method for preparing 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-methoxycarbonyl-3-picolinic acid methyl ester (an intermediate I) and 4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-methoxycarbonyl-3-pyridine carboxylic acid (an intermediate II) which are used as intermediates of the clevidipine butyrate. The intermediate I is prepared by using 2,3-dichlorobenzaldehyde, ammonium acetate and methyl acetoacetate as raw materials and performing a reaction by using ultrasound. The intermediate II is prepared by carrying out enzyme hydrolysis on the intermediate I. When the clevidipine butyrate is prepared by using the method disclosed by the invention, ammonia water is not used as the raw material, so that no irritant gas is generated. Moreover, the cyclizative condensation is carried out by using ultrasonic waves and the hydrolysis is carried out by using carboxy lesterase, so that the reaction time can be shortened and the reaction yield is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIUXU PHARMA
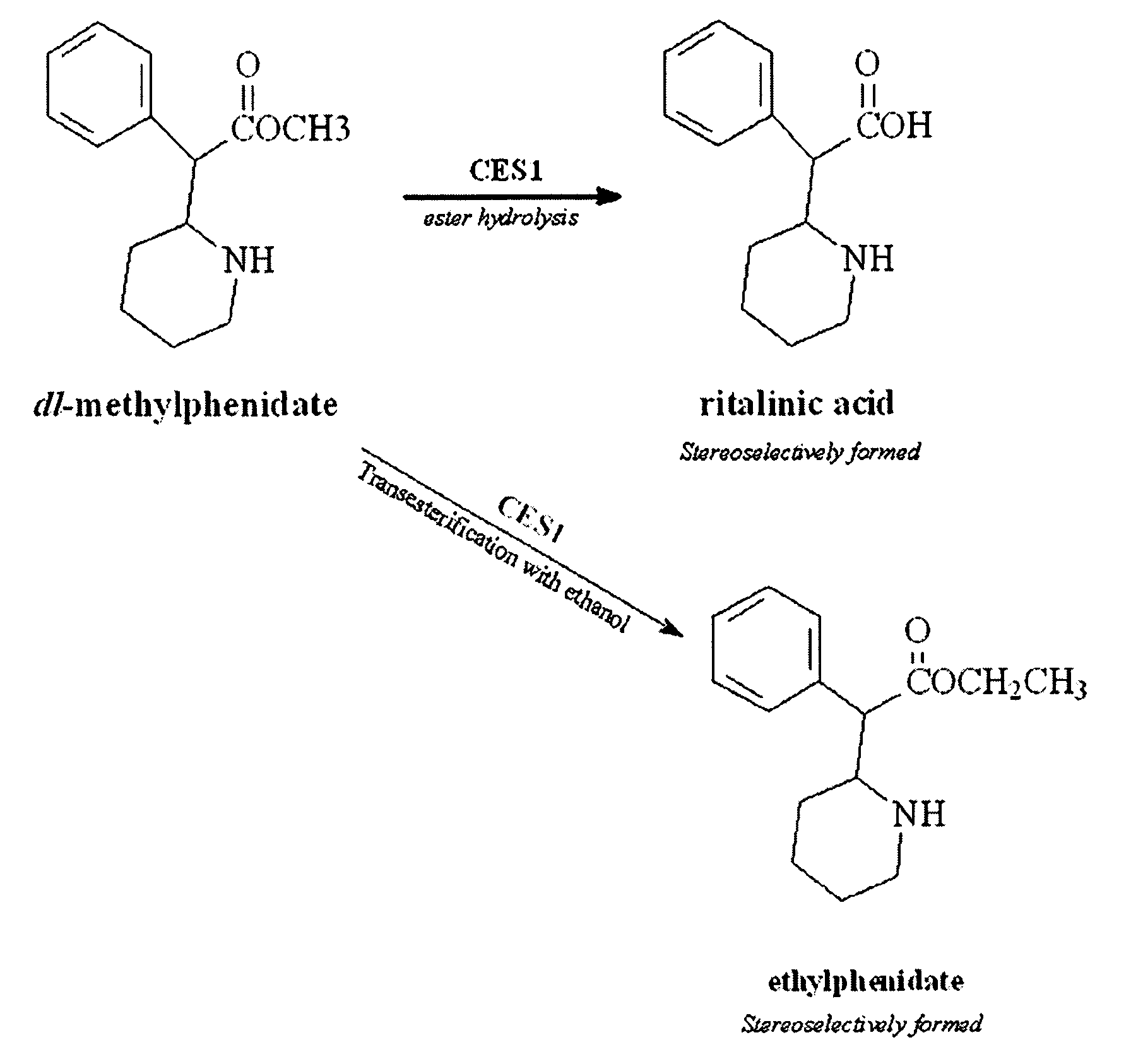
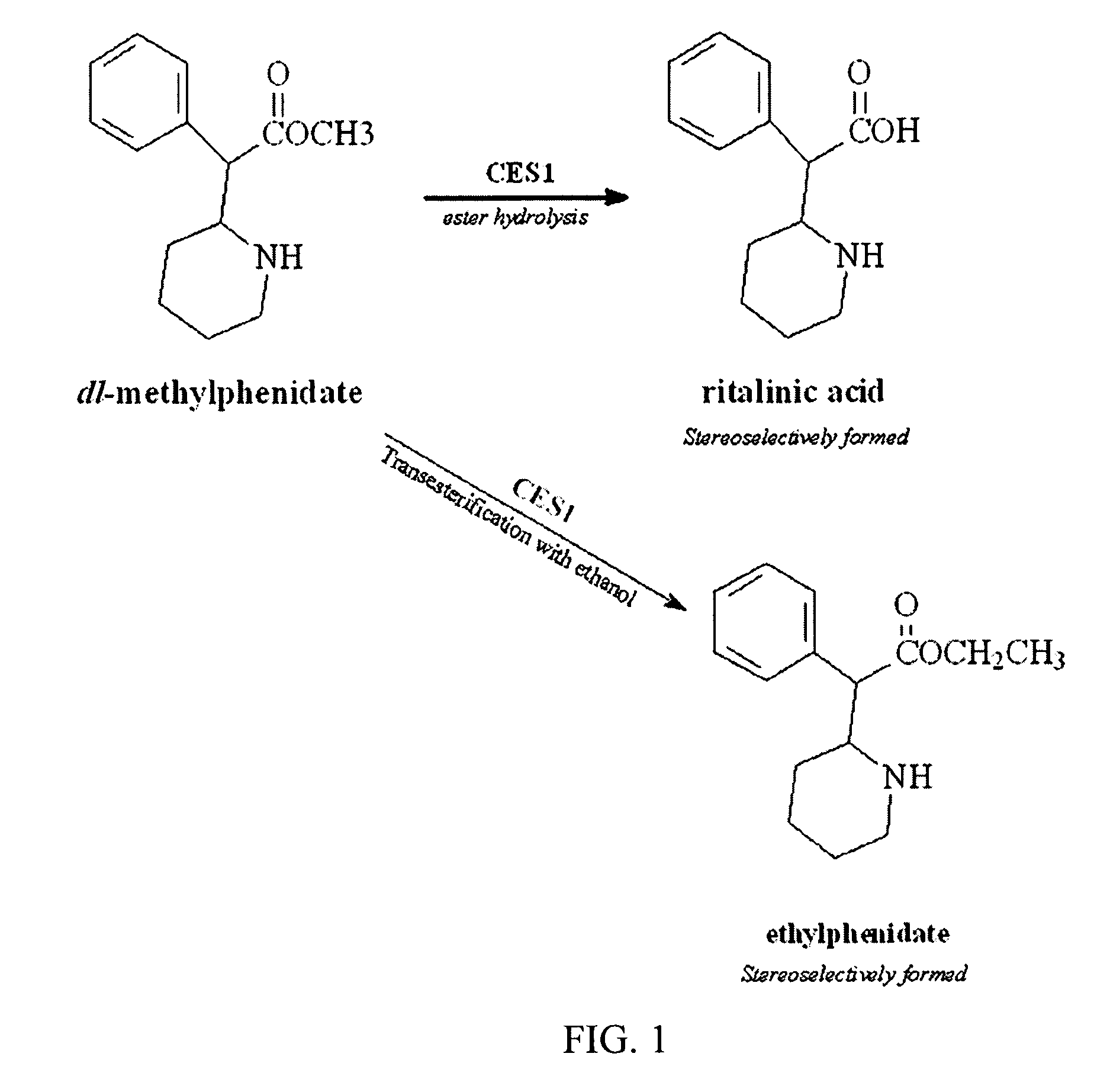
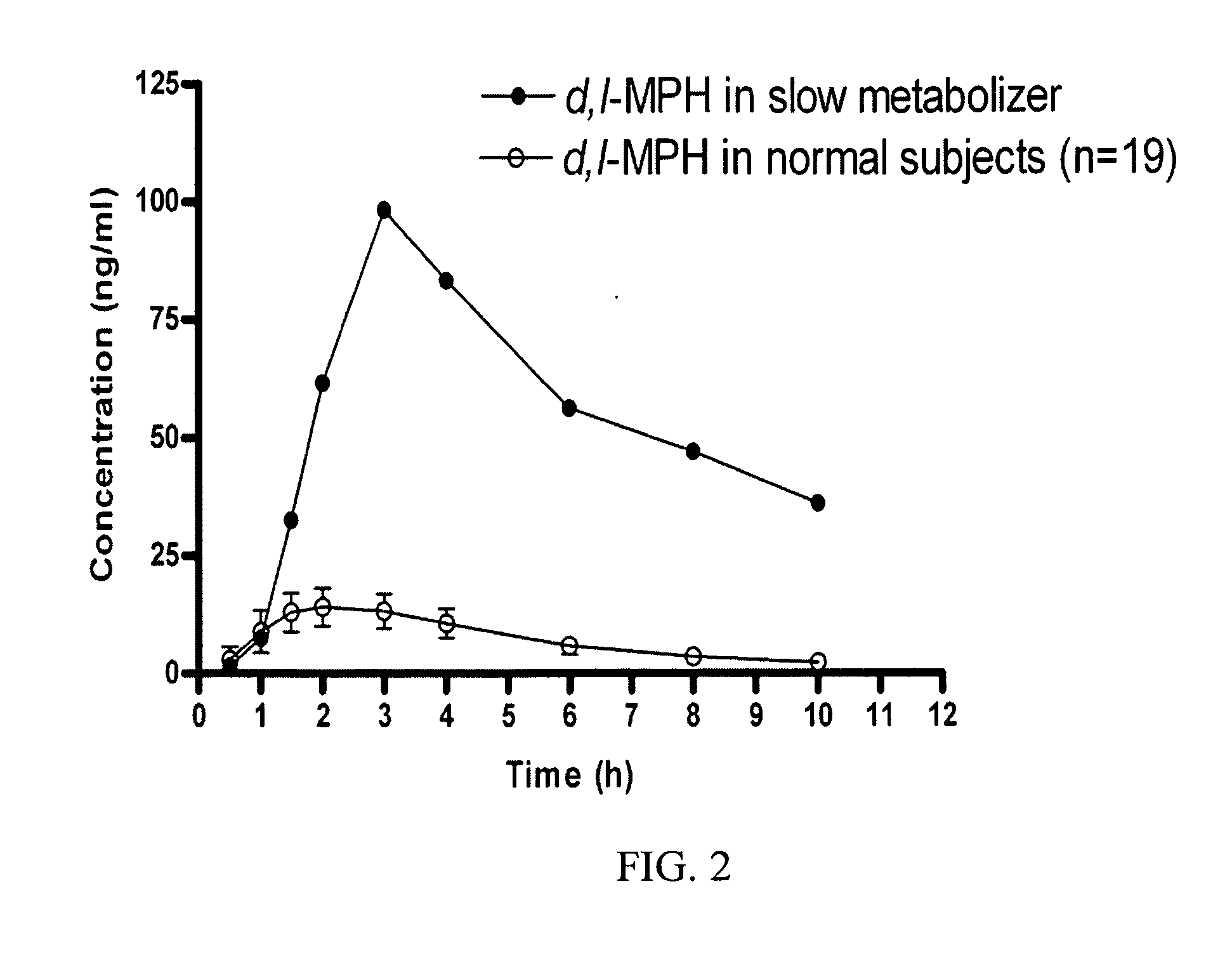
Carboxylesterase-1 Polymorphisms and Methods of Use Therefor
InactiveUS20110020801A1Improve throughputEfficient CatalysisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCaucasian populationNucleotide
Methods and kits are provided for detecting polymorphisms in carboxylesterase-1 (CES1). Several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in CES1 in humans, and methods for detecting the same, are provided (e.g., Gly143Glu, 12754T>del). Results indicate that the Gly143Glu (9486G>A) polymorphism has an allelic frequency of 1.5% in the Caucasian population. Polymorphisms of the present invention may alter the function of the carboxylesterase-1 enzyme (hCES1). Thus, the methods and kits of the present invention may be used to personalize a therapy and / or avoid adverse consequences of altered metabolism of a therapeutic or compound (e.g., enalapril, methylphenidate, etc.) which may result due to a CES1 polymorphism. In addition, recombinant cells lines overexpressing wild-type CES1 or expressing CES1 mutants are provided. Such cell lines may be used to assess the effects of candidate compounds on CES1, and the action of CES1 on these candidate compounds.
Owner:MARKOWITZ JOHN S +1
Enzyme and receptor modulation
InactiveUS20140088159A1Extended stayHydrolysed effectivelyBiocideOrganic chemistryGlycineIntracellular
Covalent conjugates of an α,α-disubstituted glycine ester and a modulator of the activity of a target intracellular enzyme or receptor, wherein the ester group of the conjugate is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to the corresponding acid and the α,α-disubstituted glycine ester is conjugated to the modulator at a position remote from the binding interface between the inhibitor and the target enzyme or receptor pass into cells and the active acid hydrolysis product accumulates within the cells.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE INTPROP DEV LTD
Anti-tumor active matter and its preparing method and use
InactiveCN1682771AHas antitumor activityAchieve production controlFungiBacteria material medical ingredientsActive matterTyrosine
The present invention relates to active antitumor matter and its preparation process and use, and belongs to the field of microbiological medicine technology. The active matter is prepared through convenient process with Moinascus ruber 3081 of preservation number CGMCC No. 1319. The test seed is cultured in conventional malt juice culture medijm at 20-30 deg.c for 4-8 days; and the solid fermentation culture medium consists of notoginseng hairy rootlet powder 20-30 wt% and water 70-80 wt% in natural pH. Through further solid culture at 20-30 deg.c for 15-20 days, alcohol leaching with alcohol solution for 2 days, decompression concentrating and evaporating out solvent, the active matter is obtained. The active matter has high inhibiting rate to human leukaemia cell strain K562, human lung cancer strain A549, oncogene Raf1 and c-Myc latent target tyrosine phosphoesterase cdc25a and cdc25b, so that it may be used in preparing antitumor preparation.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
DHFR Enzyme Inhibitors
InactiveUS20090118311A1Facilitates penetration of agentHigh potencyOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSide chainCarboxylic acid
Compounds of formula (I) or (II) are dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors, useful for the treatment of, for example, cell proliferative diseases:wherein A and D are independently —CHR7— or —NR7—; E and G are independently ═CR7— or ═N—; each R6 independently represents hydrogen or —OR7; R7 is hydrogen or C1-C6 alkyl; R1 is a carboxylic acid group (—COOH), or an ester group which is hydrolysable by one or more intracellular carboxylesterase enzymes to a carboxylic acid group; R2 is the side chain of a natural or non-natural alpha amino acid which does not contain a carboxyl, or carboxyl ester group; Y is a bond, —C(═O)—, —S(═O)2—, —C(═O)NR3—, —C(═S)—NR3, —C(═NH)NR3 or —S(═O)2NR3— wherein R3 is hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; L1 is a divalent radical of formula -(Alk1)m(Q)n(Alk2)p- wherein m, n and p are independently 0 or 1, and Q, Alk1 and Alk2 are as defined in the claims; X1 represents a bond; —C(═O); or —S(═O)2—; —NR4C(═O)—, —C(═O)NR4—, —NR4C(═O)NR5—, —NR4S(═O)2—, or —S(═O)2NR4— wherein R4 and R5 are independently hydrogen or optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl; and z is 0 or 1.
Owner:CHROMA THERAPEUTICS
Method for producing feruloyl esterase
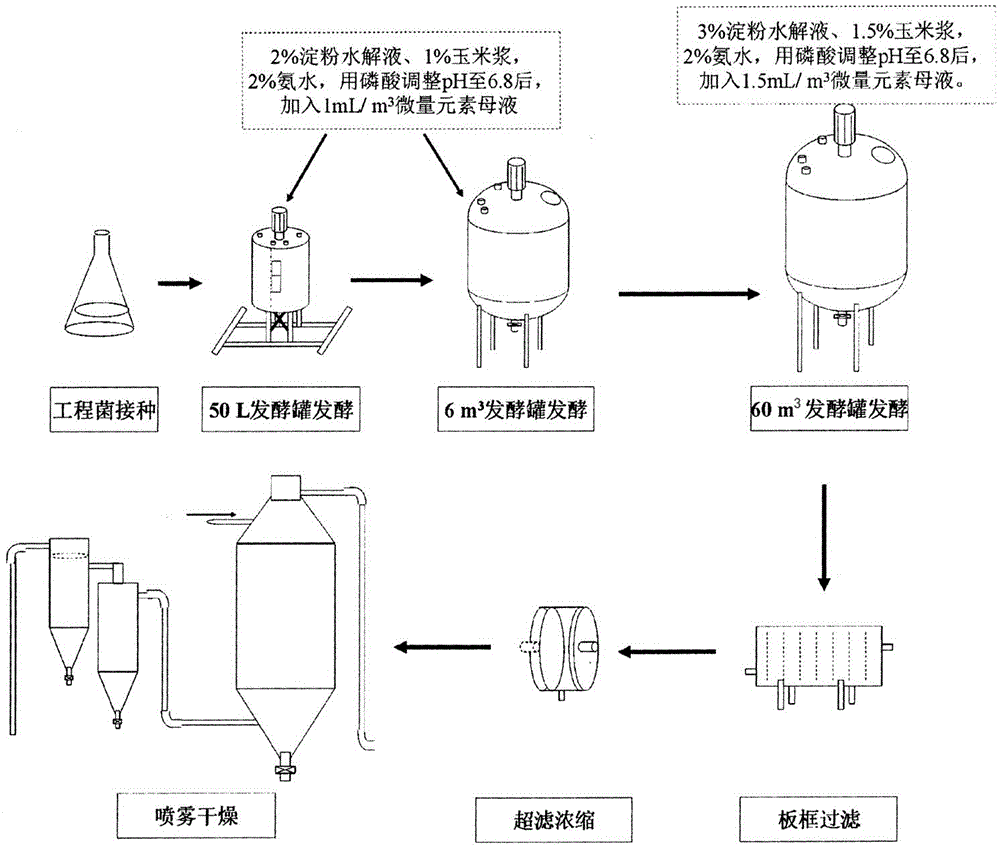
InactiveCN104673767ALow running costShorten the production cycleHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesUltrafiltrationSubmerged fermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing feruloyl esterase and belongs to the technical field of bio-enzyme preparation production. The method comprises the following steps: fermenting by utilizing a genetic engineering strain of the constitutive expressed feruloyl esterase, and by taking the starch saccharification liquid, the maize slurry and the ammonia water as main raw materials, preparing the feruloyl esterase, continuously adding a fermentation culture medium and discharging part of the fermenting fluid in bathes during the fermentation engineering, continuously extending the fermenting period under a no-sundry bacterium contamination condition, and filtering by a plate frame filter, and performing ultrafiltration concentration and spray drying on the fermenting fluid to obtain the high-activity feruloyl esterase preparation. The specific steps are as follows: (1) strain preparation; (2) culture expansion; (3) submerged fermentation and feruloyl esterase production; and (4) feruloyl esterase purification. By adopting the method under the conditions of no serious sundry bacterium contamination and no obvious reduction of the enzyme activity in unit volume of the fermenting fluid, the feruloyl esterase can be continuously fermented and produced, the production period can be shortened and the production cost can be reduced.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
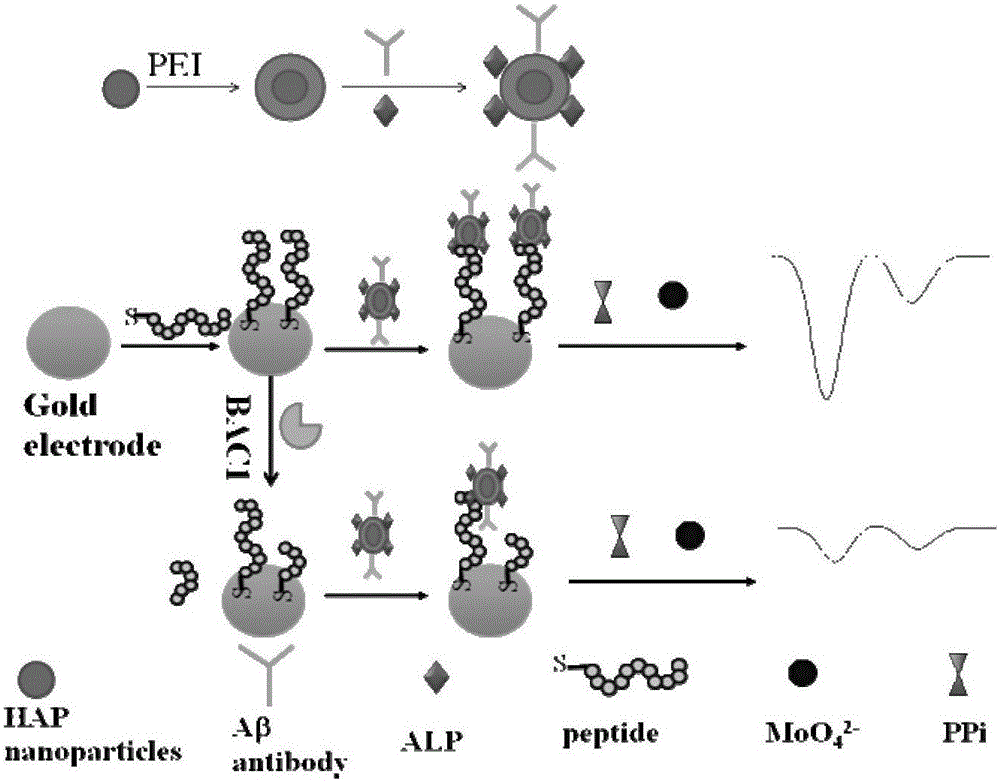
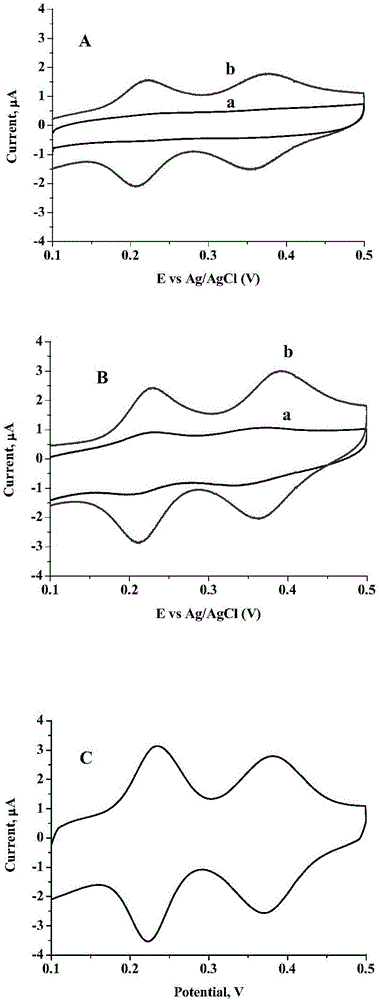
Hydroxyapatite-based electrochemical probe construction method and method for determining activity and inhibition property of BACE1
InactiveCN106093160AEnables sensitive detection of activitySimple and fast operationBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesAntibodyAbnormal alkaline phosphatase
The invention discloses a hydroxyapatite-based electrochemical probe and a construction method thereof, and a method for determining the activity and the inhibition property of BACE1. According to the present invention, an A[beta] antibody and alkaline phosphatase are co-modified on a hydroxyapatite matrix to form the hydroxyapatite-based electrochemical probe; the preparation method comprises: sequentially placing hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in a polyethylenimine solution and carrying out a reaction, placing in a glutaraldehyde solution and carrying out a reaction, and placing in a solution containing an A[beta] antibody and alkaline phosphatase and carrying out a reaction so as to obtain the probe; and the method for determining the activity and the inhibition property of BACE1 by using the hydroxyapatite-based electrochemical probe has advantages of simpleness, rapidness, high sensitivity and wide detection range, and can be widely promoted and applied.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Recombinant expression strain of feruloyl esterase as well as preparation method and application of recombinant expression strain
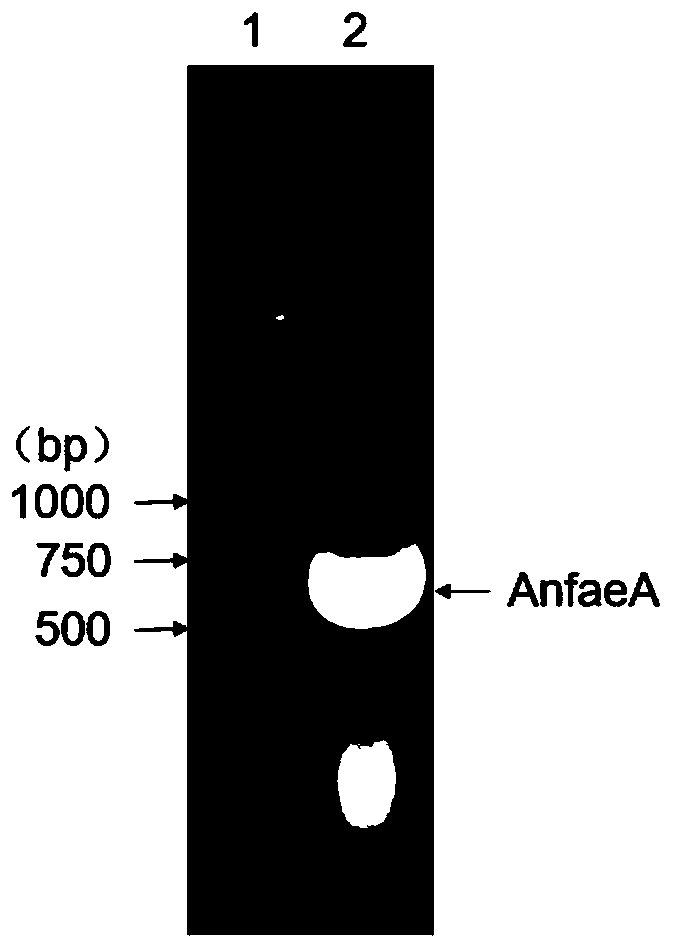
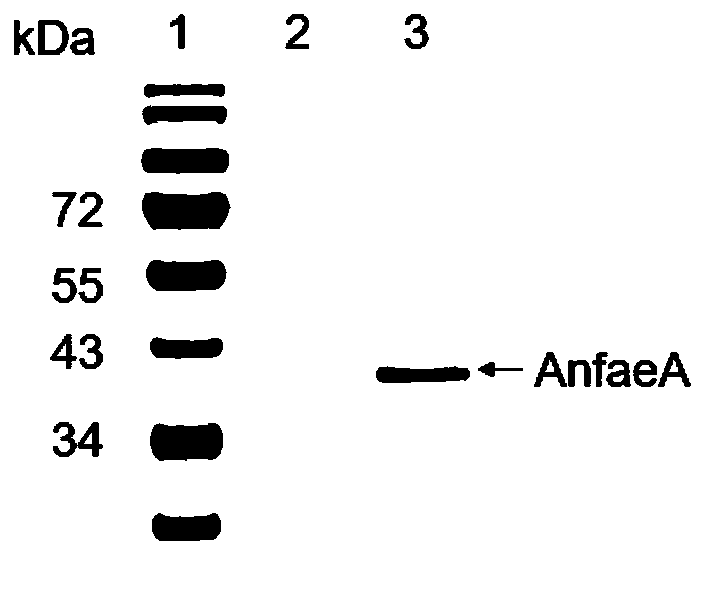
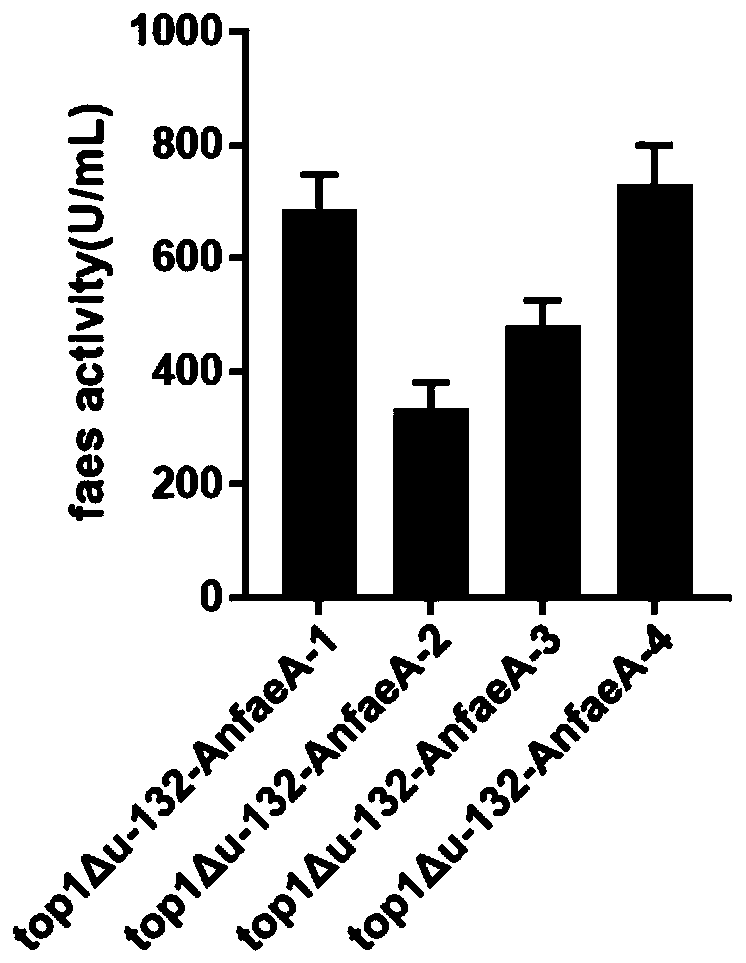
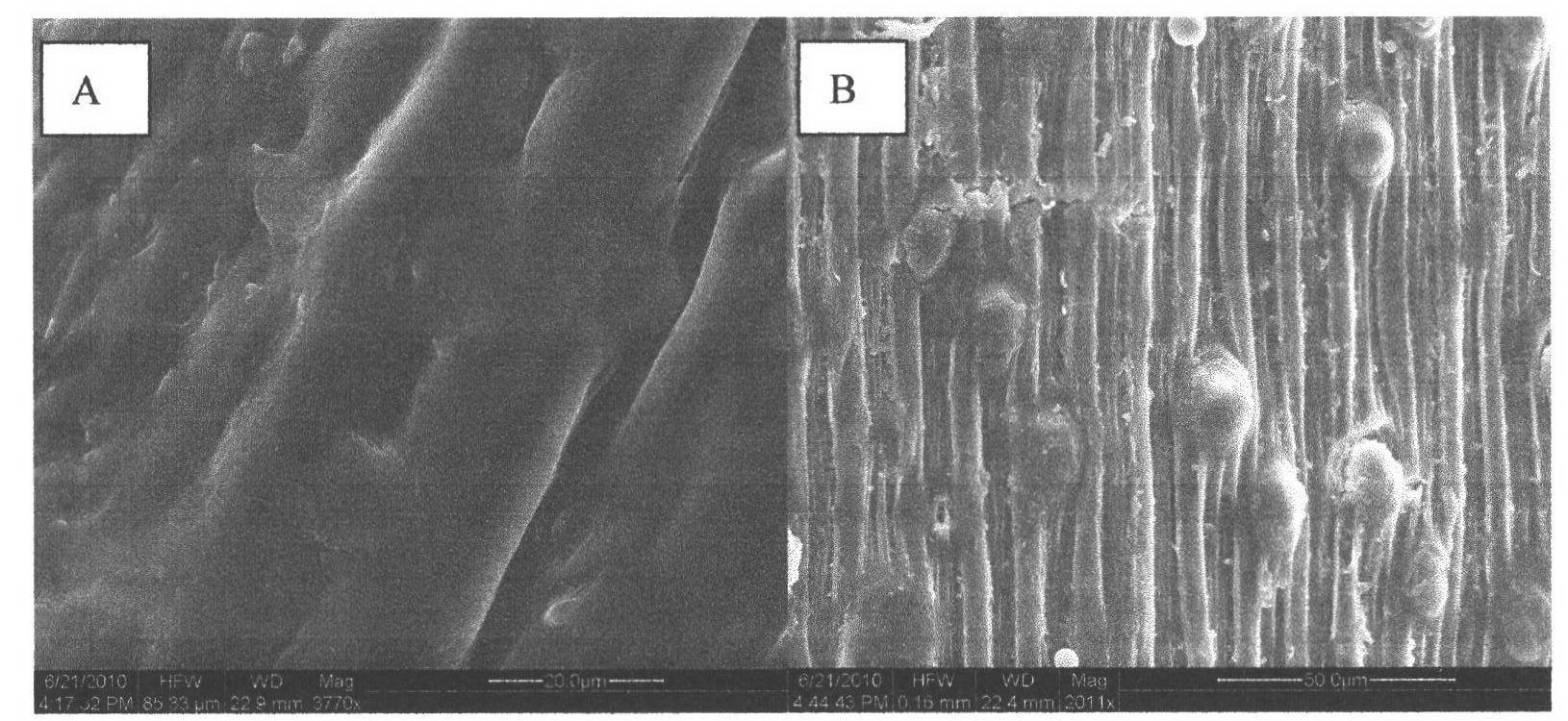
The invention provides a Kluyveromyces marxianus recombinant strain capable of being used for preparing feruloyl esterase AnfaeA. The recombinant strain is constructed by cloning an aspergillus nigerferuloyl esterase AnfaeA gene with an optimized sequence to an expression vector and converting a Kluyveromyces marxianus host strain, and the yield of the feruloyl esterase obtained by high-density fermentation of the recombinant strain reaches 120000 U / ml. The invention also provides a method for preparing ferulic acid by hydrolyzing corncob powder with the feruloyl esterase. The feruloyl esterase AnfaeA prepared from the recombinant strain and xylanase have a synergistic effect, so that the corncob powder can be efficiently hydrolyzed to obtain the ferulic acid. The feruloyl esterase provided by the invention can be used for preparing phenolic substances such as ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid and the like through biodegradation of agricultural byproducts such as corncobs, rice bran, cornbran and the like, so that the feruloyl esterase has a wide application value in the fields of foods, papermaking, feeds, medicines and the like. Meanwhile, the preparation method is simple in process, high in yield and very suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for preparing ferulic acid and oligosaccharide by producing enzymes from Salicornia bigelovii straws fermented by Aureobasidium pullulans
InactiveCN102181489APlanting management costs are not highReduce outputMicroorganism based processesFermentationCancer preventionPullulan
The invention relates to application of ferulic acid and oligosaccharide preparation by producing enzymes from Salicornia bigelovii straws fermented by microorganism. The microorganism in the invention refers to Aureobasidium pullulans; the Salicornia bigelovii straws are dried and crushed to a certain particle diameter, and then a mixed enzyme preparation of xylanase and ferulic acid esterase is generated after the metabolism of the Aureobasidium pullulans; the cell walls of the Salicornia bigelovii straws are degraded under the synergistic effect of the mixed enzyme so as to obtain physiologically active substances, such as the ferulic acid and oligosaccharide. The invention has the effects of oxidation resistance, free radical elimination, thrombus resistance, blood fat reduction, coronary heart disease prevention and cure, bacteria resistance, inflammation elimination, mutation resistance and cancer prevention, can be widely applied in industries of medication, food and cosmetics, and can prominently increase the economic value of the straws, i.e., by-products of Salicornia bigelovii.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH +1
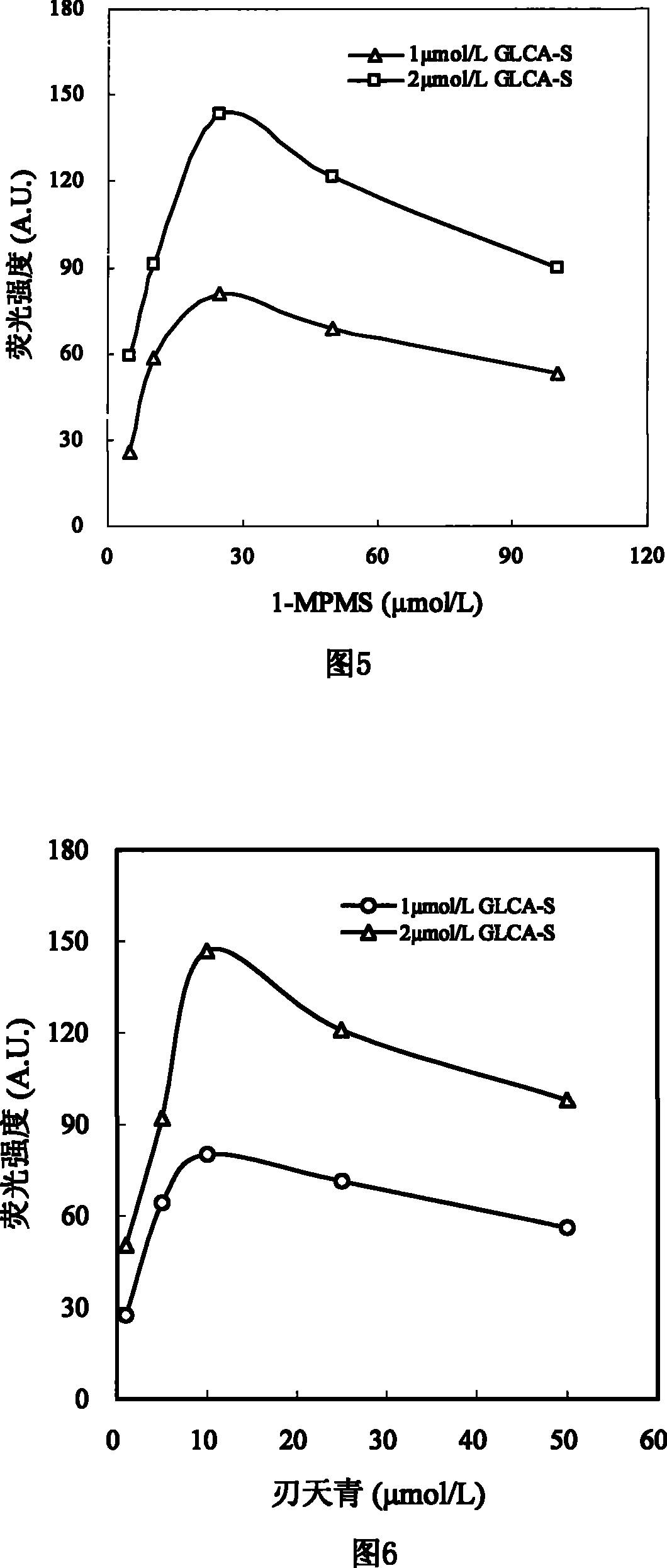
Sulfated bile acid enzyme fluorescence capillary analytical method and enzyme fluorescence quantitative reagent kit
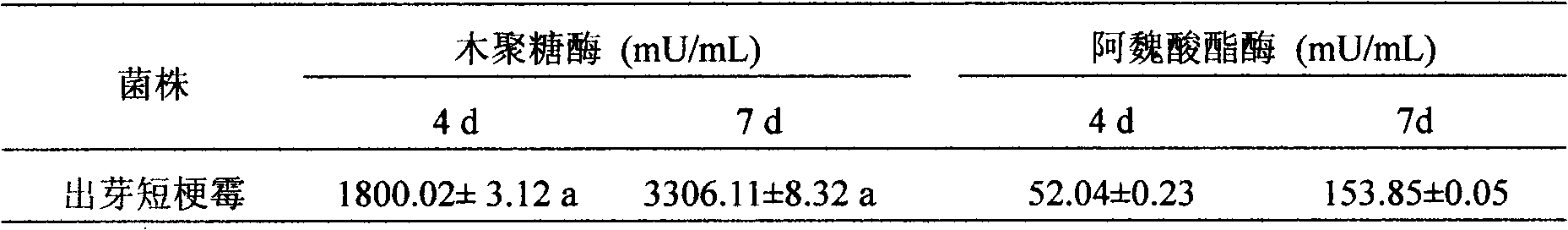
The invention discloses a sulfated bile acid (SBA) enzyme fluorescence capillary analysis and an SBA fluorescence quantitative test kit (SBA-FCA-Kit), which belongs to the field of a clinic biochemistry inspection field and is suitable for the fast screening and diagnosing of liver and gall diseases, more particularly, is suitable for the early period discovery of jaundice in neonatal period and congenital biliary atresia. After being mixed with fluorescence reaction liquid, a biology sample is sucked by an SBA capillary biology reactor (SBA-CBR) which contains sulfated bile acid sulfoacid esterase and Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase to determine the blank fluorescence intensity of the SBA-CBR under a given excitation wavelength and an emission wavelength; then the biology sample is ledto continuously react for a certain time and the fluorescence intensity is determined; the amount of the SBA in the sample is determined by using fluorescence intensity difference value. The SBA-FCA-Kit is composed of an SBA-CBR and fluorescence reaction liquid containing Beta-NAD<+>, an electric transmission body and diazoresorcinal, etc.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for producing feruloyl esterase and application of recombinant bacillus subtilis
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis for producing feruloyl esterase and application of the recombinant bacillus subtilis, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The inventionprovides recombinant bacillus subtilis. The recombinant bacillus subtilis can produce the feruloyl esterase with high yield. Specifically, the recombinant bacillus subtilis is inoculated into a fermentation medium, and fermentation is performed for 14 hours, so that the enzyme activity of the feruloyl esterase in a cell disruption supernatant can reach up to 82.53 U / mL; and therefore, the recombinant bacillus subtilis has a huge application prospect in the production of the feruloyl esterase and ferulic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
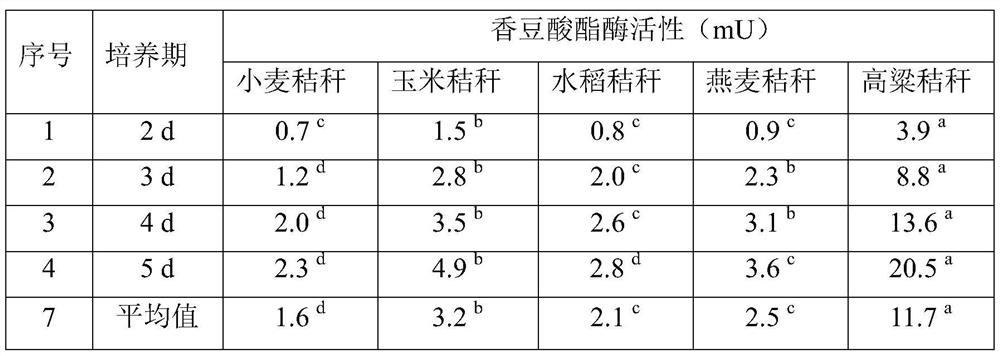
Naturally symbiotic mixed culture and method for producing coumaric acid esterase by degrading straws by using naturally symbiotic mixed culture
The invention relates to the field of renewable energy sources of biotechnology, in particular to a naturally symbiotic mixed culture YakQH5 composed of anaerobic fungi (Neocallimastix frontalis) andmethane bacteria (Methanobrevibacter gottschalkii). The mixed culture is preserved in china general microbiological culture collection center on 09 March 2020, the preservation number is CGMCC No.19299, and the mixed culture YakQH5 can be used for fermenting straws to produce coumaric acid esterase. The invention specifically discloses a fermentation method by using the mixed culture. According tothe mixed culture and the method, the activity of coumaric acid esterase generated by degrading sorghum straws can reach 20.5 mU, and composite antibiotics are added in a fermentation process, so that a mixed culture system can be prevented from being polluted by bacteria, the anaerobic fermentation efficiency is improved, and the important industrial application value is achieved.
Owner:GANSU ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY
Precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4 sulfatase, methods of treatment using said enzyme and methods for producing and purifying said enzyme
InactiveCN1726046ASignificant clinical effectIncrease joint mobilitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical drugPharmaceutical formulation
The present invention provides a highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase and biologically active mutants, fragments and analogs thereof as well as pharmaceutical formulations comprising highly purified recombinant human precursor N -acetylgalactosamirie-4-sulfatase. The invention also provides methods for treating diseases caused all or in part by deficiencies in human N -acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase including MPS Vl and methods for producing and purifying the recombinant precursor enzyme to a highly purified form.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com