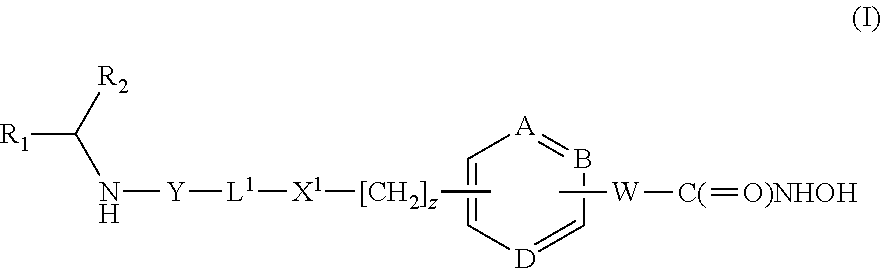
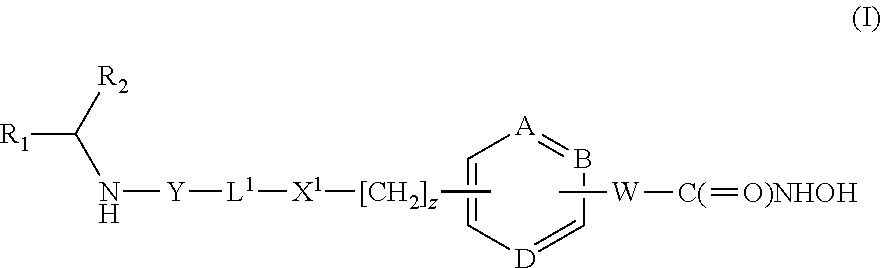
HDAC inhibitors
a technology of hdac inhibitors and inhibitors, which is applied in the field of hdac inhibitors, can solve the problems of increasing potency and duration of action, and achieve the effects of overcoming the poor pharmacokinetic properties of parent drugs, enhancing the delivery to target organs and tissues, and reducing the risk of side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
(2S)-[({3-[(1E)-3-(Hydroxyamino)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl]phenyl}sulfonyl)amino](phenyl)acetate
[0142]
[0143]The title compound was prepared by the following methodology:
Stage 1—Preparation of 3-formylbenzenesulfonate sodium salt
[0144]Benzaldehyde (10 g, 94 mmol) was added dropwise to 20% sulfur trioxide in fuming sulfuric acid (25 mL) and stirred under an atmosphere of nitrogen, maintaining the reaction temperature below 40° C. The reaction was stirred at 40° C. for 18 h. The reaction was then quenched onto ice (60 g) and the aqueous extracted with EtOAc (100 mL). The aqueous phase was treated with CaCO3 until the evolution of CO2 ceased (pH ˜6). The resultant precipitate was filtered, washed with water and the filtrate basified with Na2CO3 to pH ˜8. The precipitate was removed by filtration and the filtrate evaporated to dryness in vacuo. The residue was washed with MeOH, filtered and the washings concentrated to give the desired product as a white solid (7.94 g, 81%). 1H NMR (300 MHz, C...
example 5
Cyclopentyl (2S)-cyclohexyl({3-[(1E)-3-(hydroxyamino)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl]benzoyl}amino)acetate
[0152]
[0153]The title compound was prepared by the following methodology:
Stage 1—Preparation of 3-[(1E)-3-methoxy-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl]benzoic acid
[0154]3-Carboxybenzaldehyde (25 g, 0.167 mol) and K2CO3 (69 g, 0.499 mol) were added to water (250 mL) and cooled to 0-5° C. Trimethyl phosphonoacetate (32.3 mL, 0.2 mol) was charged dropwise maintaining the reaction temperature below 15° C. The reaction was warmed and stirred at RT for 17 h. The mixture was acidified to pH ˜1, filtered and dried in vacuo to afford the product as an off-white solid (37.25 g, >100%—slightly wet). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CD3OD) δ: 8.23 (1H, s), 8.06 (1H, d, J=7.8 Hz), 7.86 (1H, d, J=7.5 Hz), 7.75 (1H, d, J=15.9 Hz), 6.61 (1H, d, J=16.2 Hz), 7.54 (1H, t), 3.81 (3H, s).
Stage 2—Preparation of methyl (2E)-3-(3-{[(1S)-1-cyclohexyl-2-(cyclopentyloxy)-2-oxoethyl]carbamoyl}phenyl)acrylate
[0155]Stage 1 product (5 g, 24 mmol) was a...
example 9
Cyclopentyl (2S)-cyclohexyl[(3-{4-[(1E)-3-(hydroxyamino)-3-oxoprop-1-en-1-yl]phenoxy}propyl)amino]acetate
[0160]
[0161]The title compound was prepared by the following methodology:
Stage 1—Preparation of (2E)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(1-isobutoxyethoxy)acrylamide
[0162]4-Hydroxycinnamic acid (1 g, 6.1 mmol), EDCl (1.76 g, 9.1 mmol) and HOBt (1.24 g, 9.1 mmol) were added to DCM (20 mL) and stirred at RT for 45 minutes. Intermediate I (4.2 mL, 30.5 mmol) and triethylamine (4.1 mL, 30.5 mmol) were added and the reaction stirred at RT for 1.5 h. The reaction was separated with water, the aqueous phase extracted with DCM (20 mL) and the combined organics dried (MgSO4) and concentrated in vacuo. The crude material was purified by column chromatography to afford the product as a clear oil (1.39 g, 82%). m / z=278 [M−H]−.
Stage 2—Preparation of (2E)-3-[4-(3-bromopropoxy)phenyl]-N-(1-isobutoxyethoxy)acrylamide
[0163]Stage 1 product (0.66 g, 2.4 mmol), 3-bromopropan-1-ol (0.24 mL, 2.6 mmol) and tripheny...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com