Method for fast judging enzyme activity in grain and predicting enzyme adaptation temperature
A technology for rapid determination of enzyme activity, applied in measuring devices, testing food, testing starch contaminants, etc., can solve the problems of high variability of iodine colorimetry, little total enzyme activity, small coefficient of variation, etc. The effect of operability, small error and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A simple method for quickly determining the enzyme activity in grains and predicting the optimum temperature of the enzyme, characterized in that the method comprises the following specific steps:
[0040] (1) Rice pretreatment: extract rice starch, the starch content is 95%, and pass through a 100-mesh sieve.
[0041] (2) Determining the water content of the sample, taking 14% as the water content, weighing 3 g of the sample on a dry basis.
[0042] (3) The specific procedure is as follows: keep warm at 60°C for 1min, increase the speed at 12°C / min to 95°C and hold for 2.5min, then decrease the same speed to 50°C and hold for 1.4min, and keep the stirring speed at 160r / min.
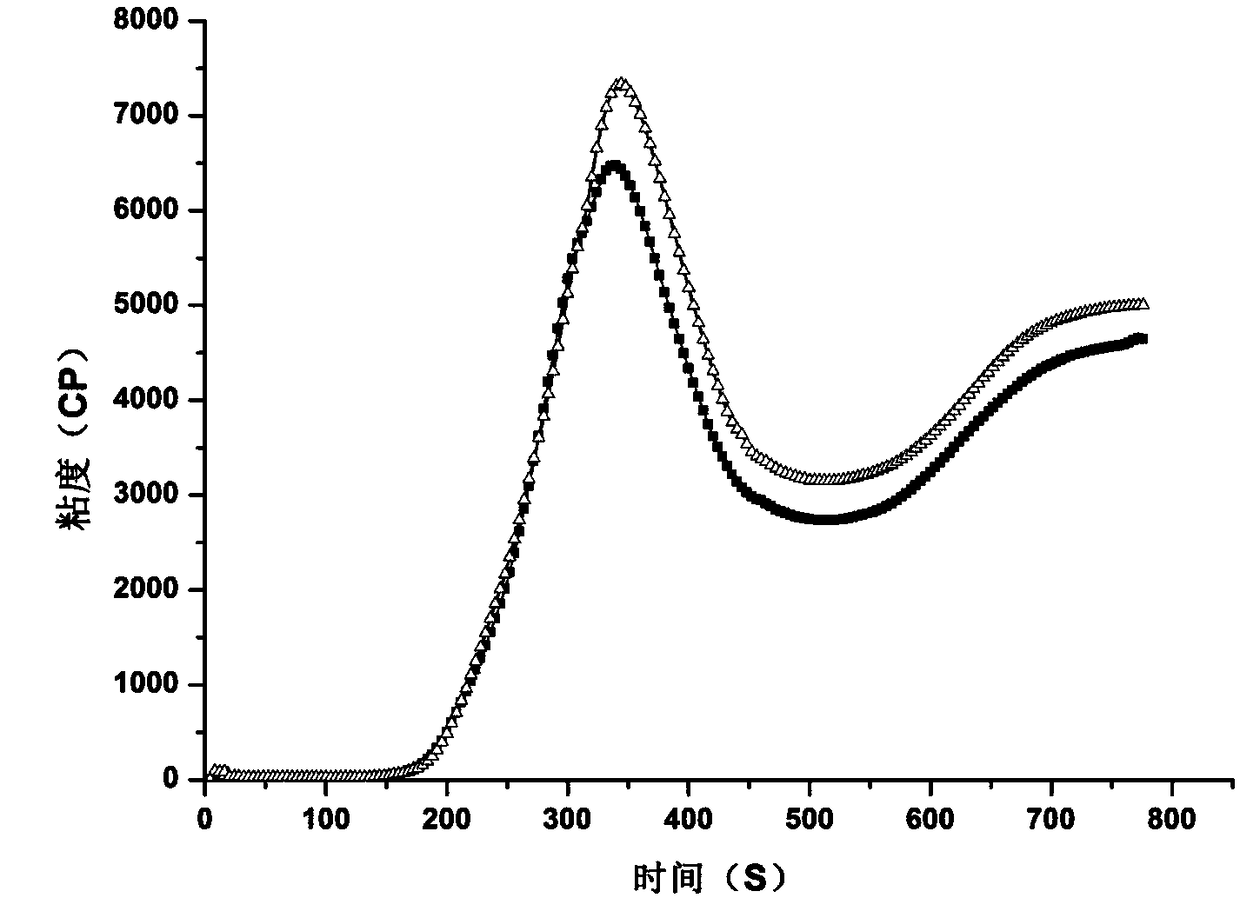
[0043](4) Weigh 25g of deionized water and mix with the sample evenly, as a control sample. At the same time, weigh 25g of the enzyme inhibitor solution and mix it with the powder as a test sample. The samples were placed in a rapid viscosity analyzer (RVA) to measure the viscosity characteristi...
Embodiment 2
[0047] A simple method for quickly determining the enzyme activity in grains and predicting the optimum temperature of the enzyme, characterized in that the method comprises the following specific steps:
[0048] (1) Pre-treatment: the rice sample is pulverized and passed through a 100-mesh sieve.
[0049] (2) Determining the water content of the sample, taking 14% as the water content, weighing 4 g of the sample on a dry basis.
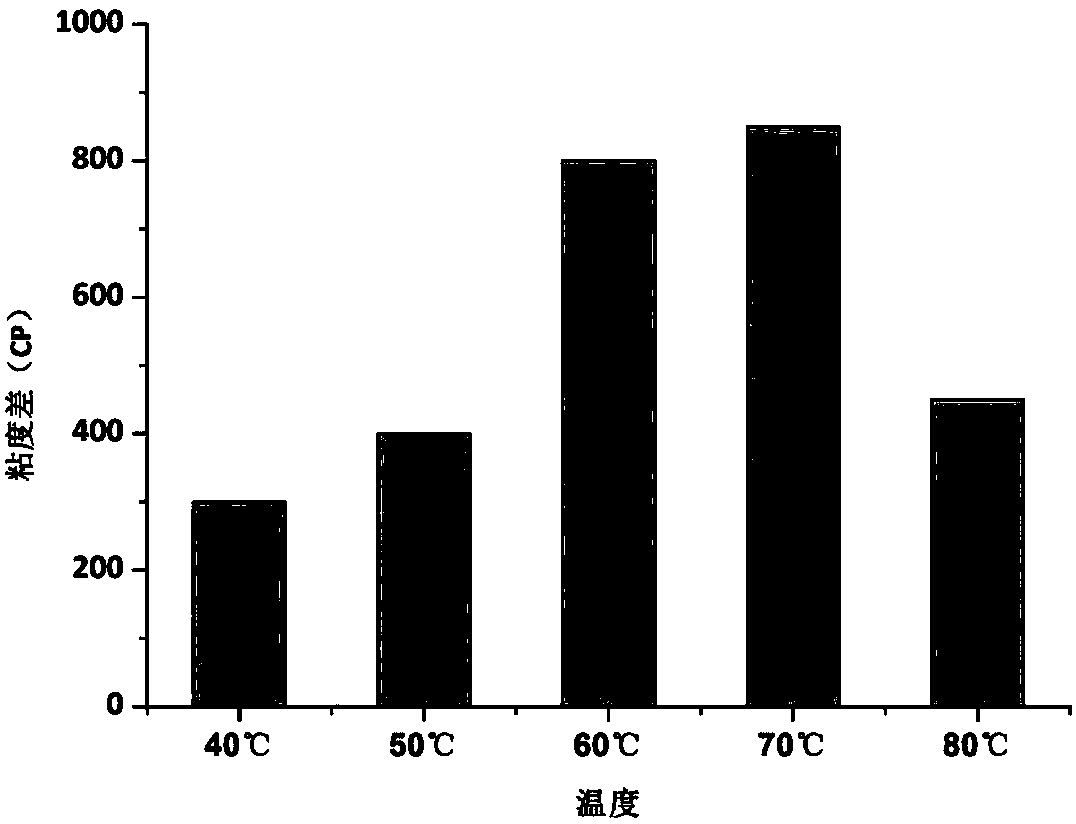
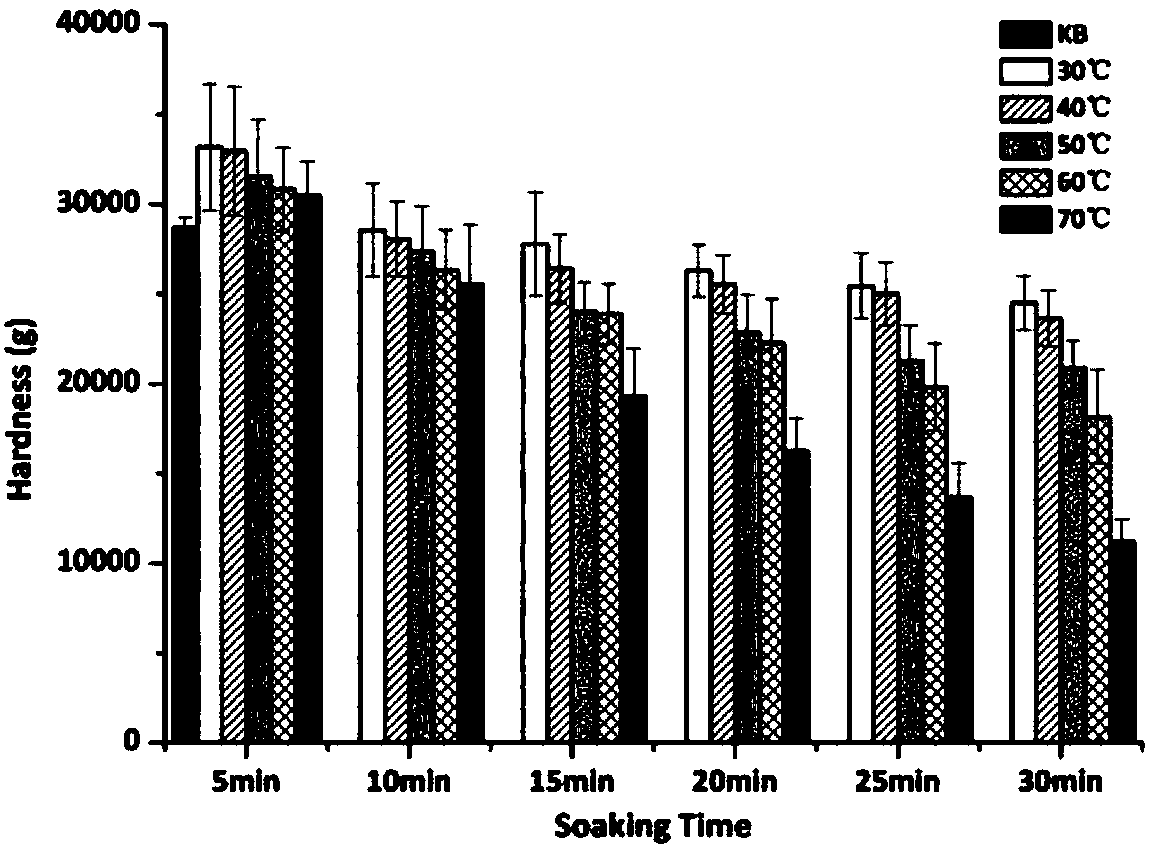
[0050] (3) The specific procedure is as follows: set different holding times respectively, keep warm at 30-90°C for 5 minutes, then rise to 95°C at a speed of 12°C / min and hold for 2.5 minutes, then drop to 50°C at the same rate for 1.4 minutes, stir The speed is kept at 160r / min.
[0051] (4) Weigh 25g of deionized water and mix with the sample evenly, as a control sample. At the same time, weigh 25g of the enzyme inhibitor solution and mix it with the powder as a test sample. The samples were placed in a rapid viscosity analyzer (RVA) to measure...
Embodiment 3
[0056] A simple method for quickly determining the enzyme activity in grains and predicting the optimum temperature of the enzyme, characterized in that the method comprises the following specific steps:
[0057] (1) Pre-treatment: the corn sample is ground and passed through a 100-mesh sieve.
[0058] (2) Determining the water content of the sample, taking 14% as the water content, weighing 5 g of the sample on a dry basis.
[0059] (3) The specific procedures are as follows:
[0060] Incubate at 60°C for 5 minutes, increase the speed at 12°C / min to 95°C and maintain for 5 minutes, then decrease the same rate to 50°C and maintain for 3 minutes, and keep the stirring speed at 160r / min.
[0061] (4) Weigh 25g of deionized water and mix with the sample evenly, as a control sample. At the same time, weigh 25g of the enzyme inhibitor solution and mix it with the powder as a test sample. The samples were placed in a rapid viscosity analyzer (RVA) to measure the viscosity charact...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com