Method for rapidly and quantitatively calculating inherent drought resistance of plants
A quantitative calculation and anti-drought technology, which is applied in agricultural engineering, crop information detection, and drought-resistant seed selection. It can solve the problems of long measurement time and slow response to plant water changes, and achieve fast speed, timely response to fluorescence information, and high accuracy. high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] In the first step, before the experiment, fresh branches of syringa plants with relatively consistent growth were picked on the campus of Jiangsu University, and the base of the branches of the plants was wrapped with a damp cloth to slow down the water loss.
[0032] The second step is to quickly return to the laboratory. After cleaning the dust on the surface of the leaves, pick 6 fresh leaves of the mulberry tree of the same size and put them in a basin filled with water to soak for 30 minutes.
[0033] Step 3: After soaking the leaves for 30 minutes, they become saturated with water. Take out the saturated leaves after soaking, quickly and gently absorb the water on the surface of the leaves with a dry towel and facial tissue, and then place them on a dry and ventilated table.
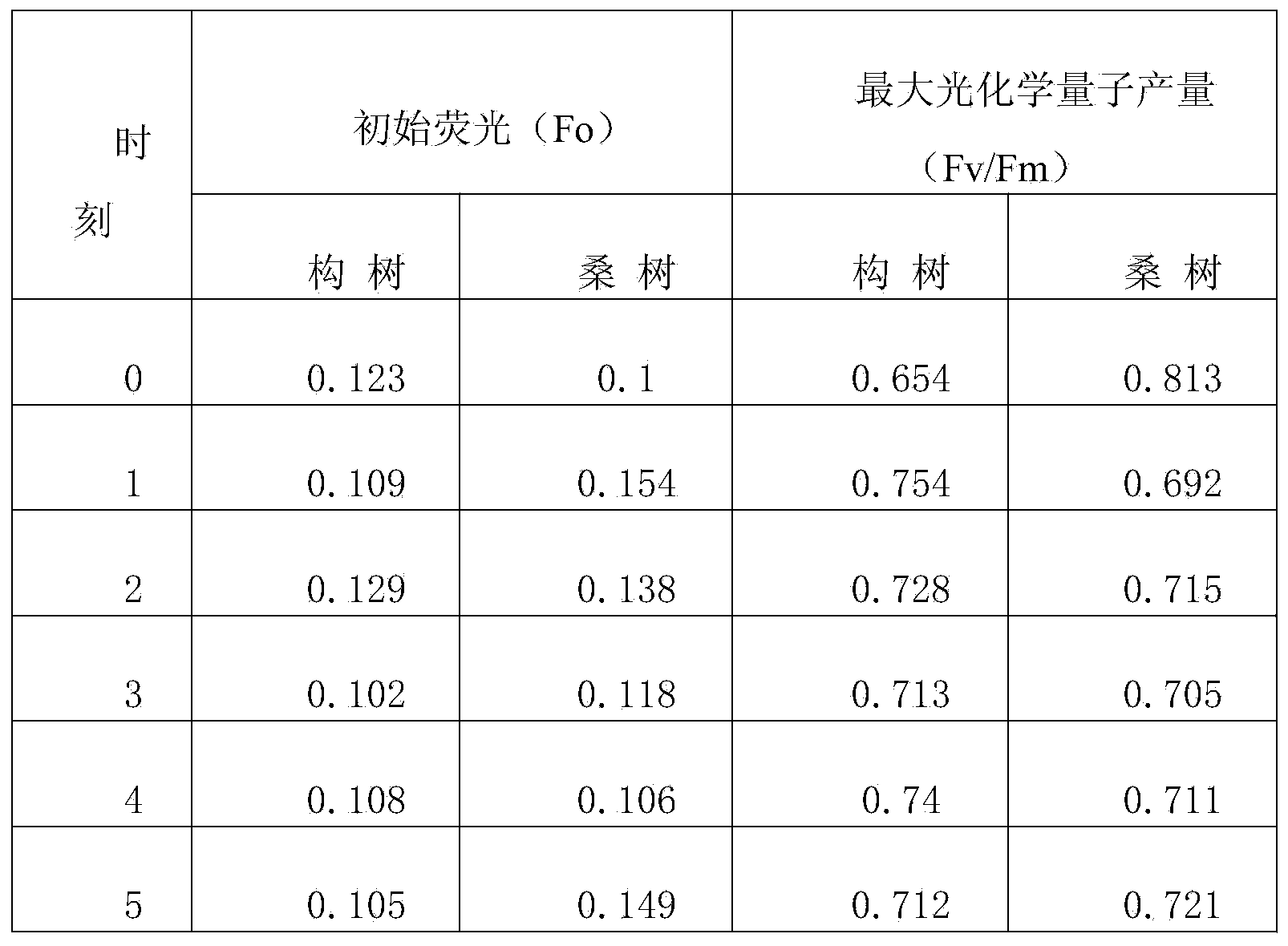
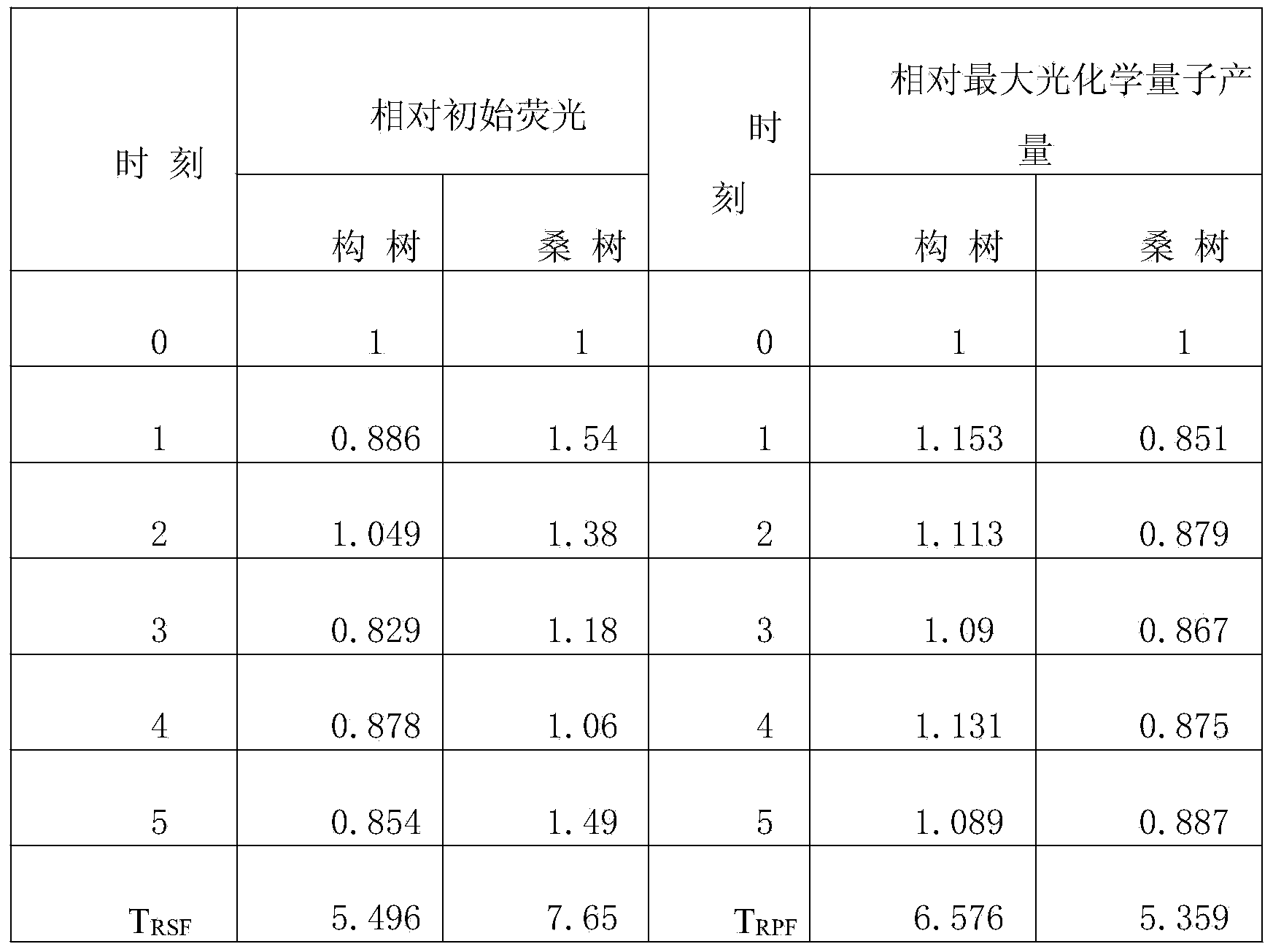
[0034] The fourth step is to take the above-mentioned leaves and use the IMAGING-PAM modulated chlorophyll fluorescence meter to measure the initial fluorescence value (Fo) and PSⅡ maximum ph...
Embodiment 2
[0040] In the first step, before the experiment, 6 leaves of mulberry trees with relatively uniform growth were picked on the campus of Jiangsu University and put into fresh-keeping bags.
[0041] The second step is to quickly return to the laboratory, and put the picked fresh leaves into a basin filled with water to soak for 30 minutes.
[0042] The third step is to take out the soaked leaves after 30 minutes, dry the water on the surface of the leaves with a dry towel and tissue paper, etc., and place them on a dry and ventilated desktop.
[0043] The 4th step, take above-mentioned leaf and measure the initial fluorescence value (Fo) and PSⅡ maximum photochemical quantum yield (Fv / Fm) of mulberry leaf when measuring 0 level fluorescence with IMAGING-PAM modulation type chlorophyll fluorescence meter, repeat measurement 3 times, average value is taken as The measured value at this moment.
[0044] In the fifth step, the fourth step is repeated every hour to measure the chlor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com