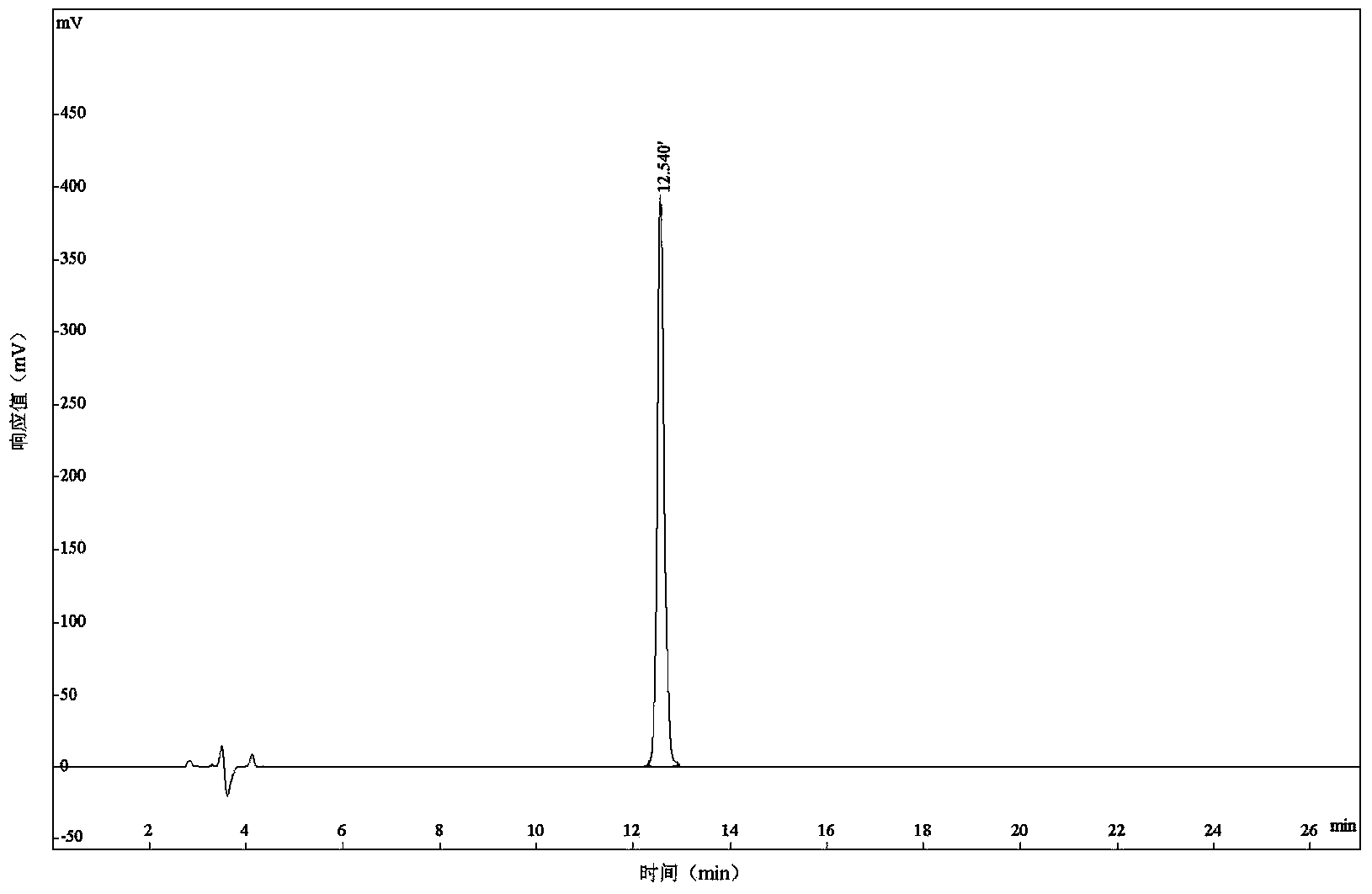
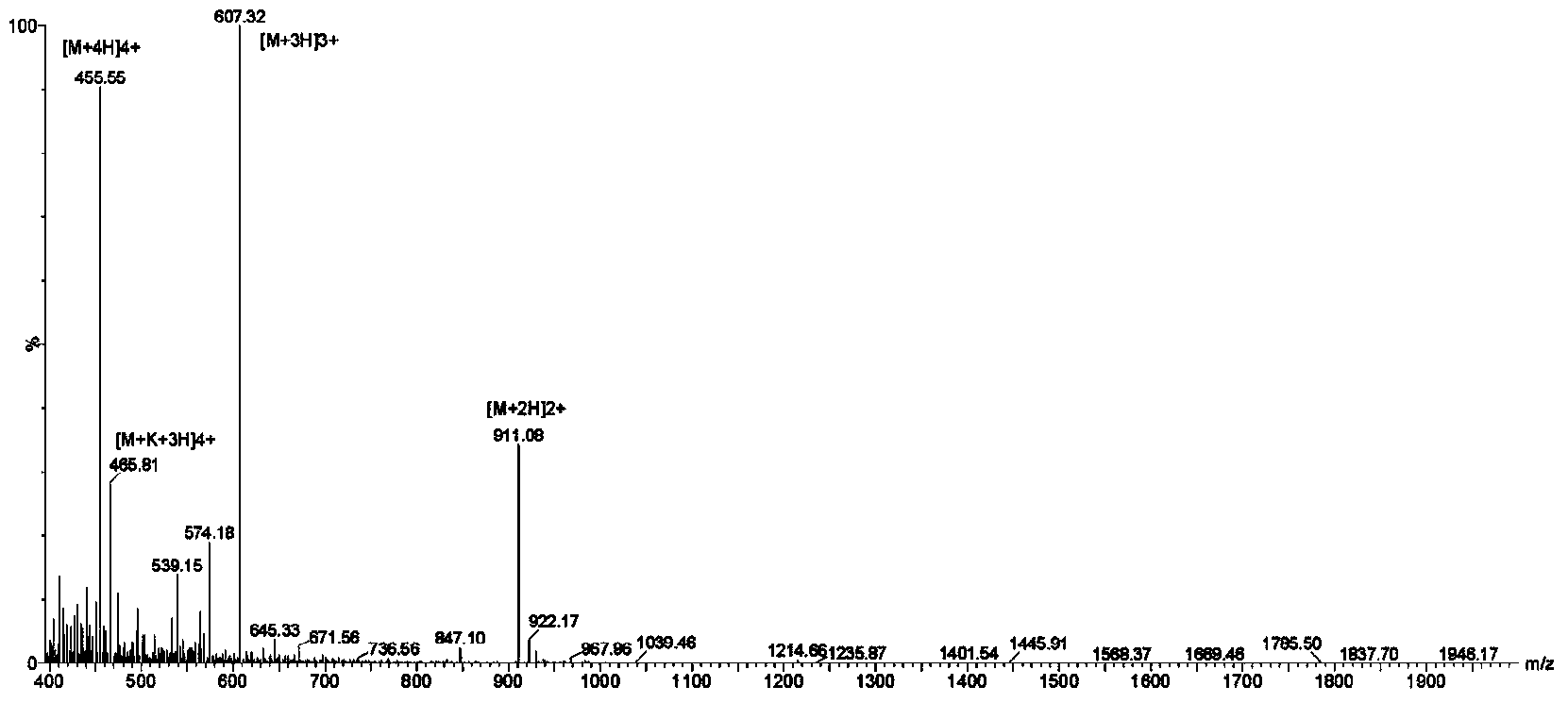
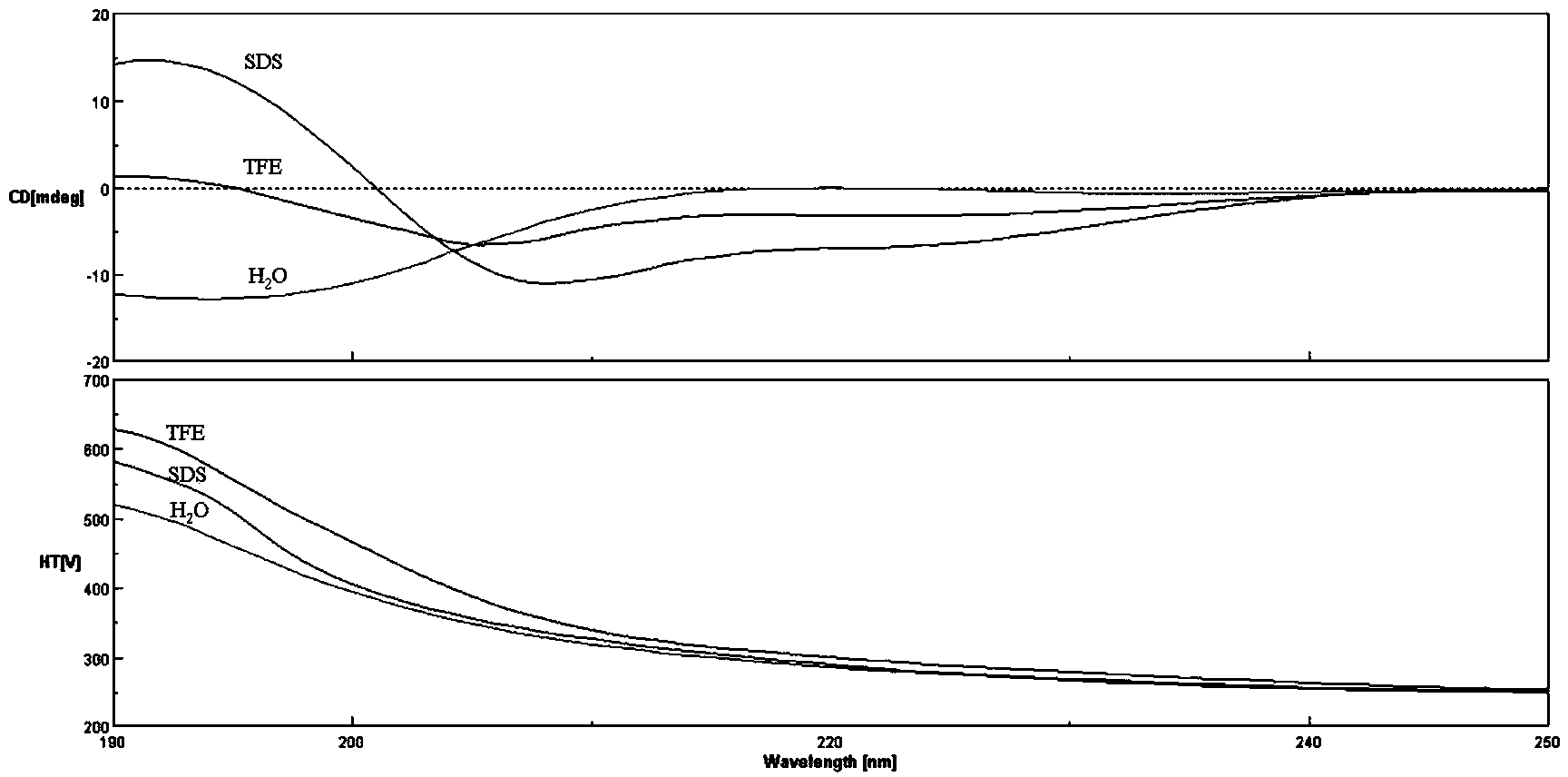
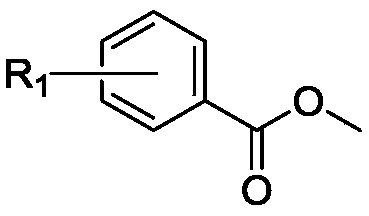
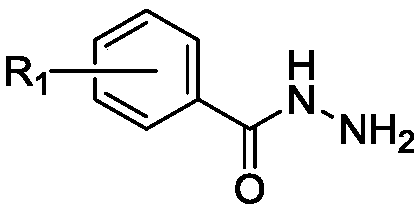
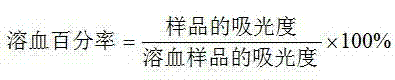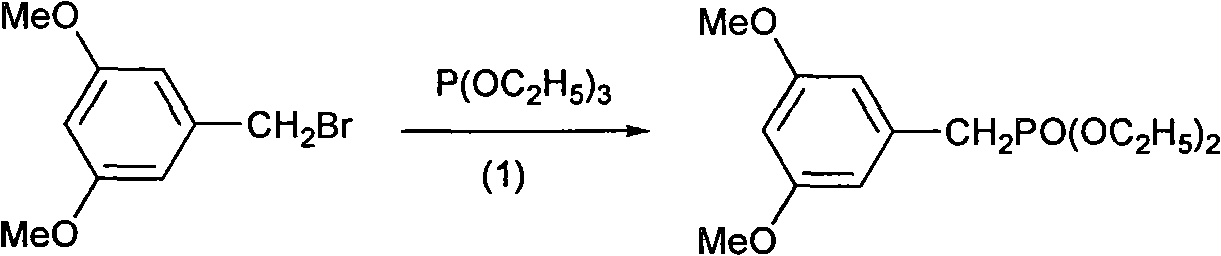Patents
Literature
68 results about "Pandrug resistant bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method to reduce inflammatory response in transplanted tissue
InactiveUS20050182018A1Inhibit inflammationLower immune responseBiocideSugar derivativesPandrug resistant bacteriaDisease cause
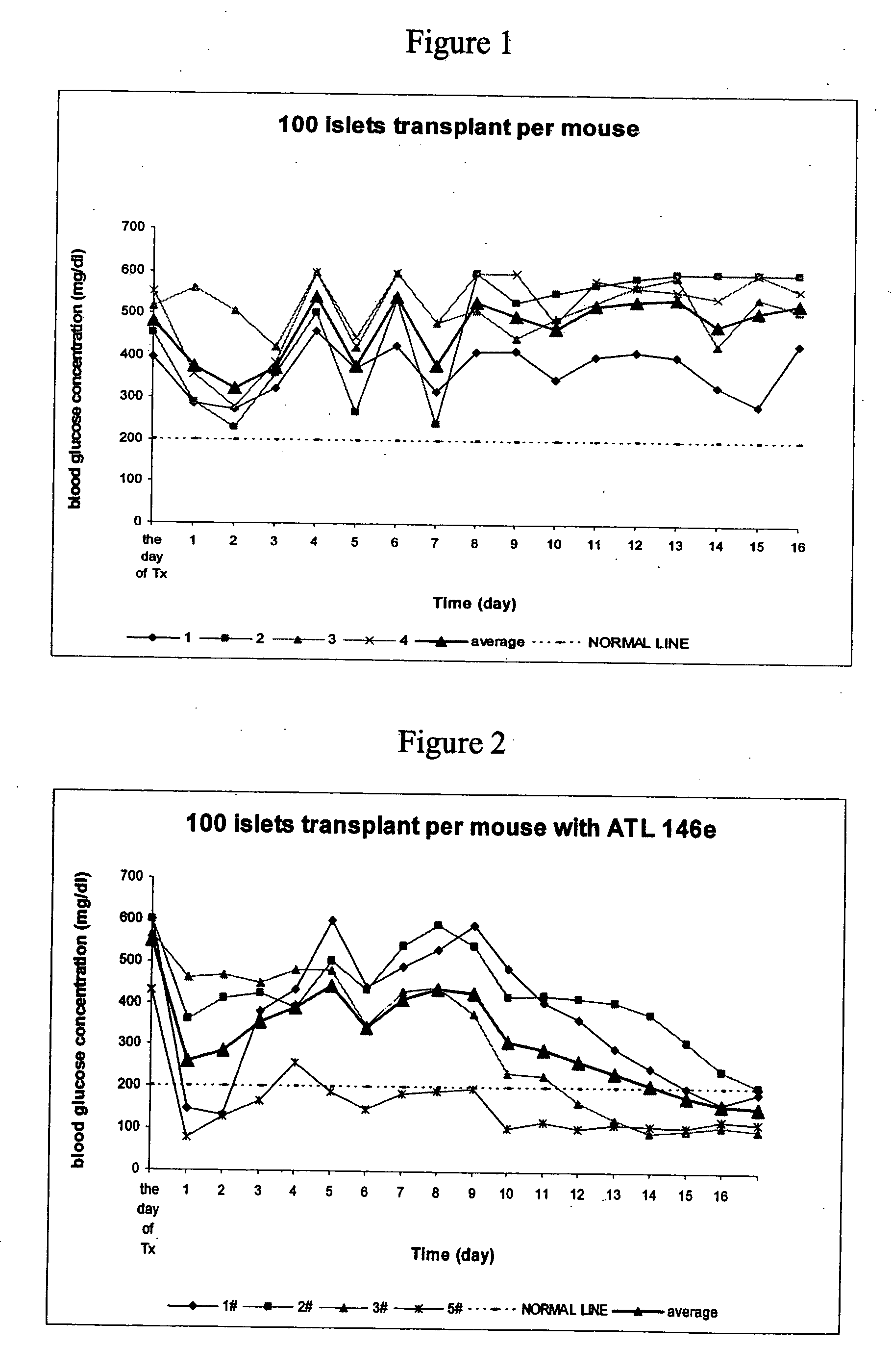
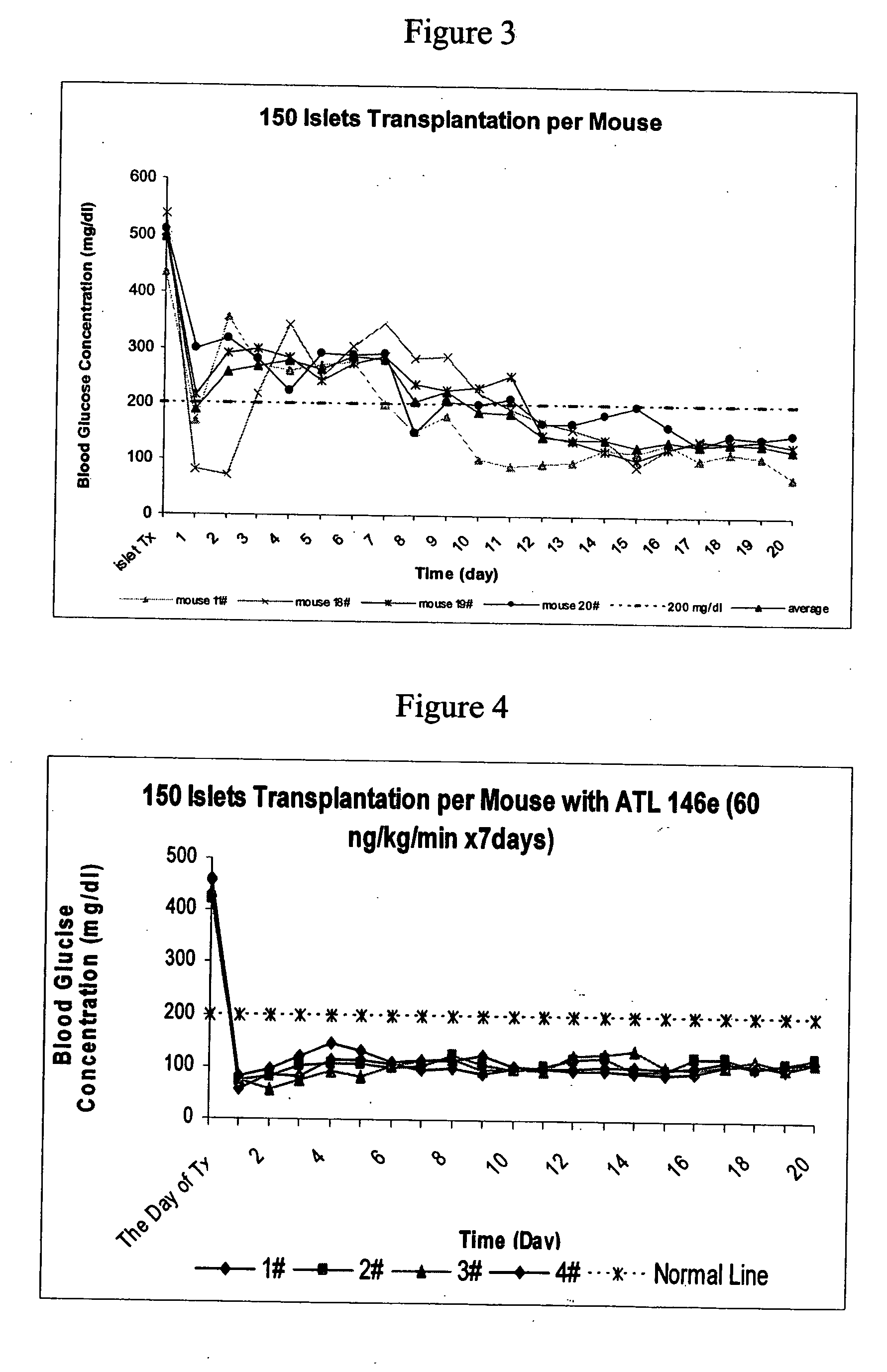
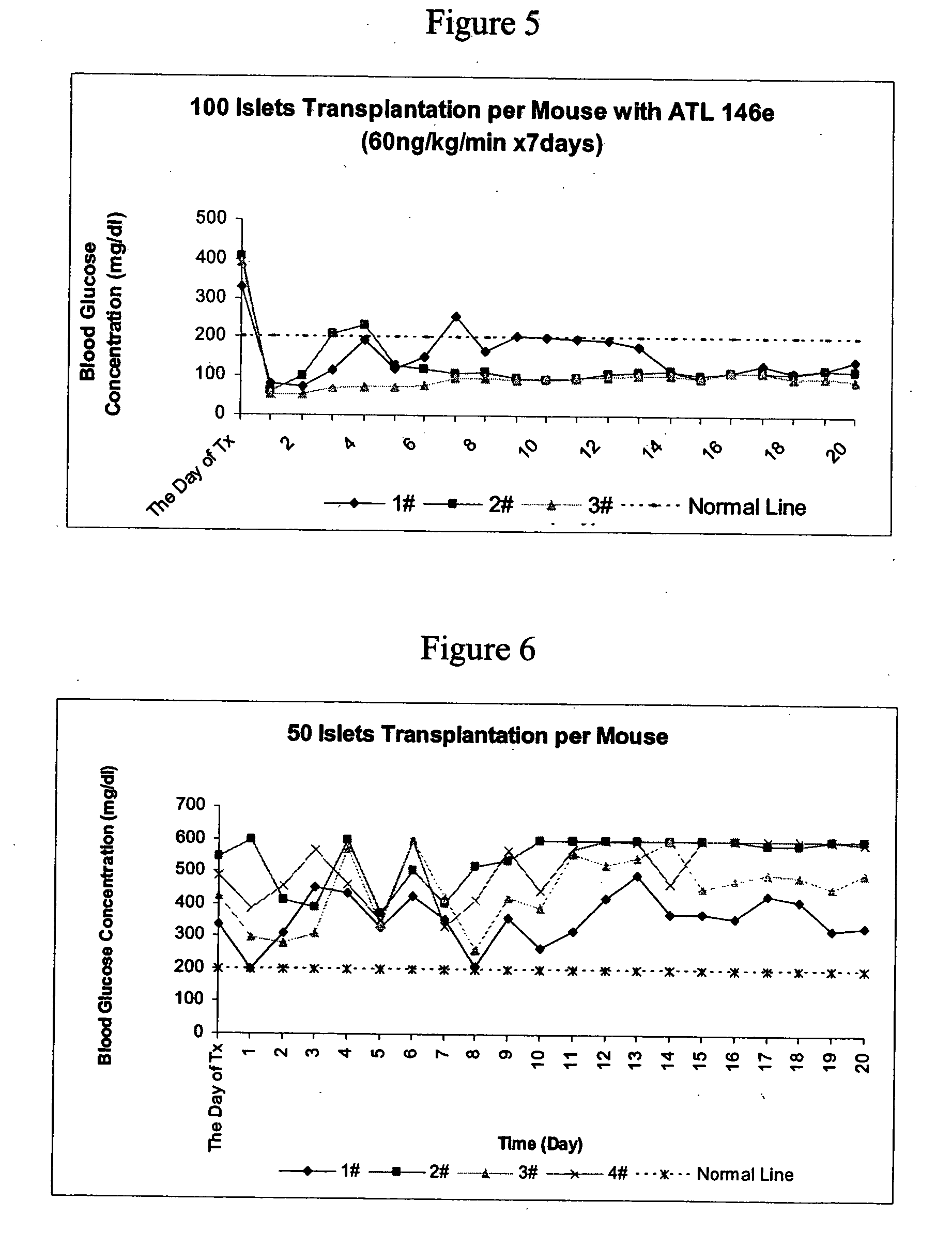
The present invention provides a therapeutic method for treating biological diseases that includes the administration of an effective amount of a suitable antibiotic agent, antifungal agent or antiviral agent in conjunction with an A2A adenosine receptor agonist. If no anti-pathogenic agent is known the A2A agonist can be used alone to reduce inflammation, as may occur during infection with antibiotic resistant bacteria, or certain viruses such as those that cause SARS or Ebola. Optionally, the method includes administration of a type IV PDE inhibitor.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
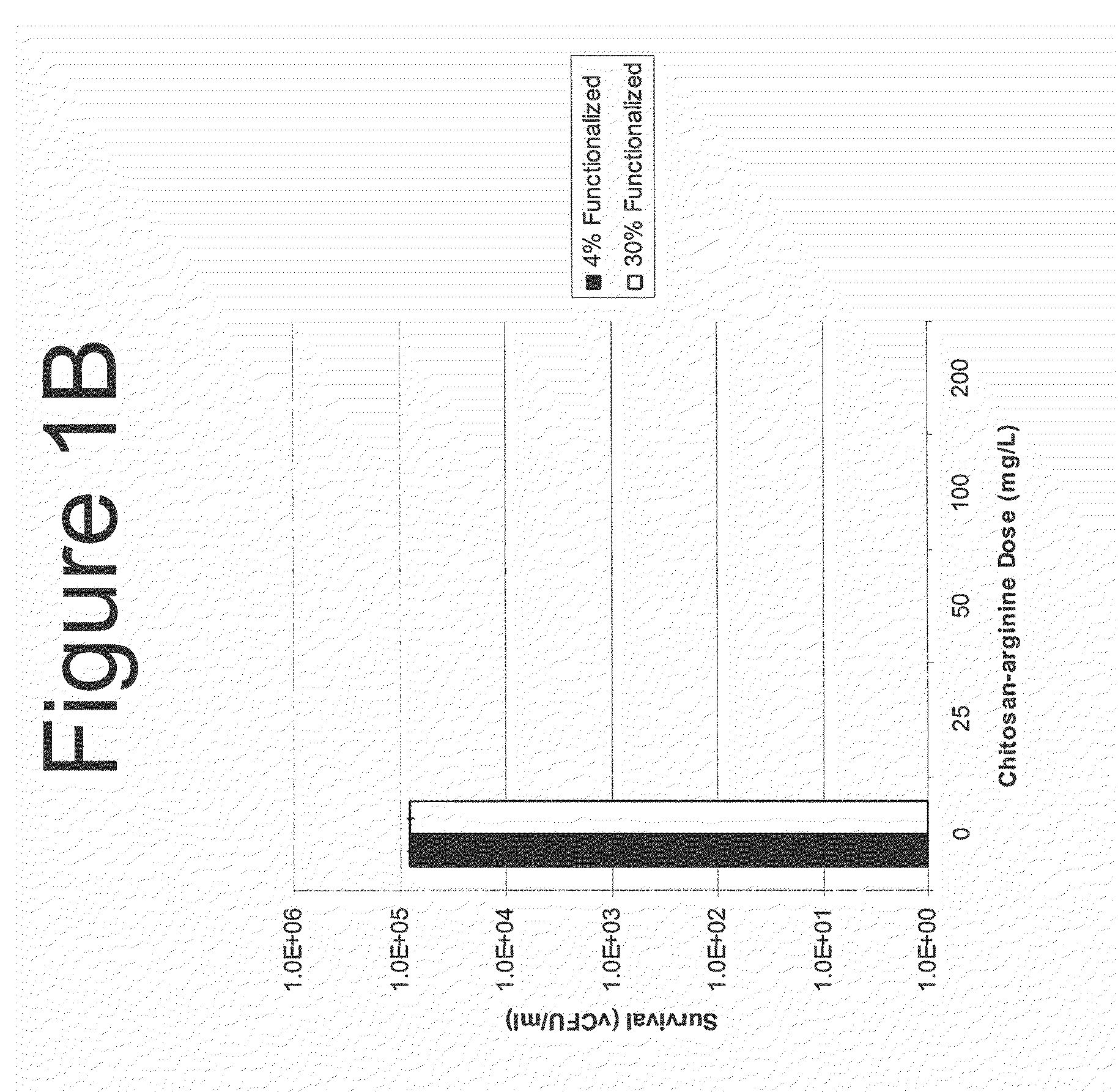
Methods and Compositions for the Prevention of and Treatment of Infections Utilizing Chitosan-Derivative Compounds
The present invention is directed to the treatment and prevention of nosocomial infections or MRSA infections utilizing soluble chitosan or chitosan derivative compounds. These chitosan-derivative compounds, e.g., chitosan-arginine and chitosan-acid amines, exhibit bactericidal activity against bacterial pathogens, e.g., drug resistant bacteria such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Owner:SYNEDGEN
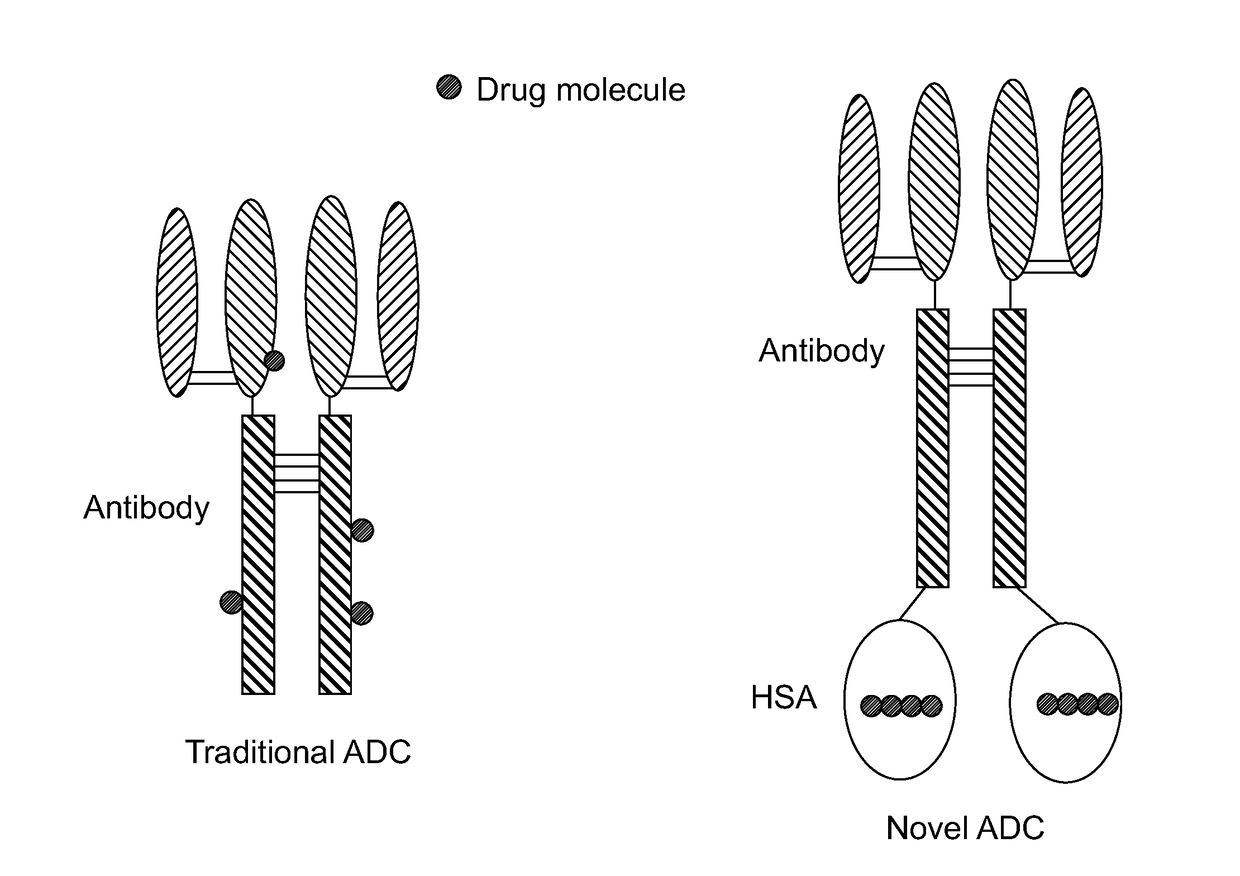
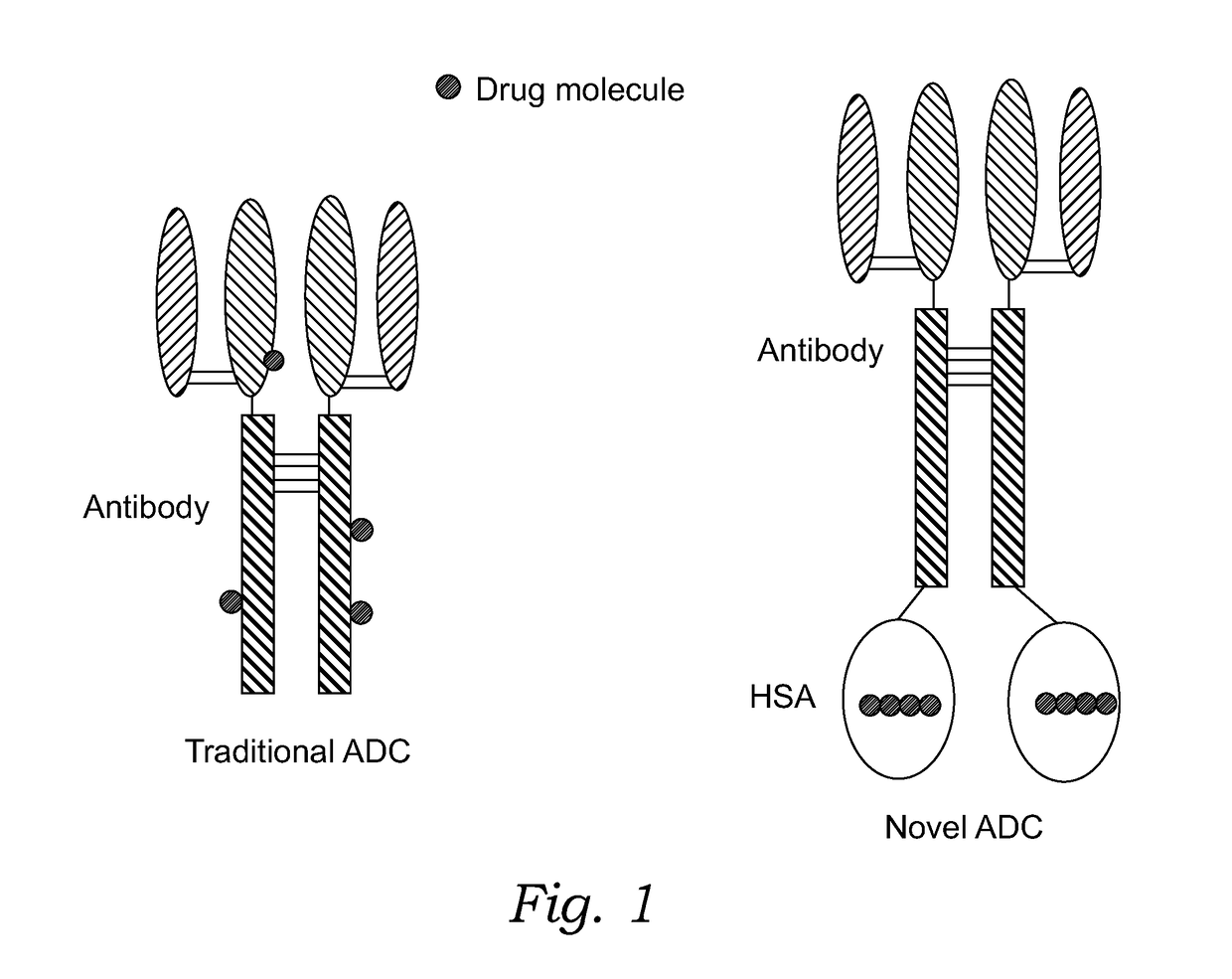
Novel antibody-albumin-drug conjugates (AADC) and methods for using them
InactiveUS20180055944A1Reduce decreaseReduce hydrophobicitySerum albuminTetrapeptide ingredientsCancer cellDrug conjugation
The present invention relates to compositions and methods using an isolated chimeric molecule, wherein the isolated chimeric molecule comprises an antibody, one or more albumin motifs, optional peptide linkers, and two or more antibiotics or cytotoxic drug molecules conjugated to the unpaired cysteine residues, optionally through linkers. In one embodiment, each of the said albumin motifs in the isolated chimeric molecule contains 2 or more unpaired cysteine residues. In another embodiment, the said antibody in the isolated chimeric molecule targets antigens on cancer cells or drug-resistant bacteria. In another embodiment, the cancer cells have upregulated macropinocytosis. In another embodiment, the cancer cells contain one or more mutations in their RAS family genes. The compositions of the invention are used to treat drug-resistant bacterial infections and cancers, preferably the ones with upregulated macropinocytosis, and the ones containing one or more mutations in their RAS family genes.
Owner:ASKGENE PHARM INC
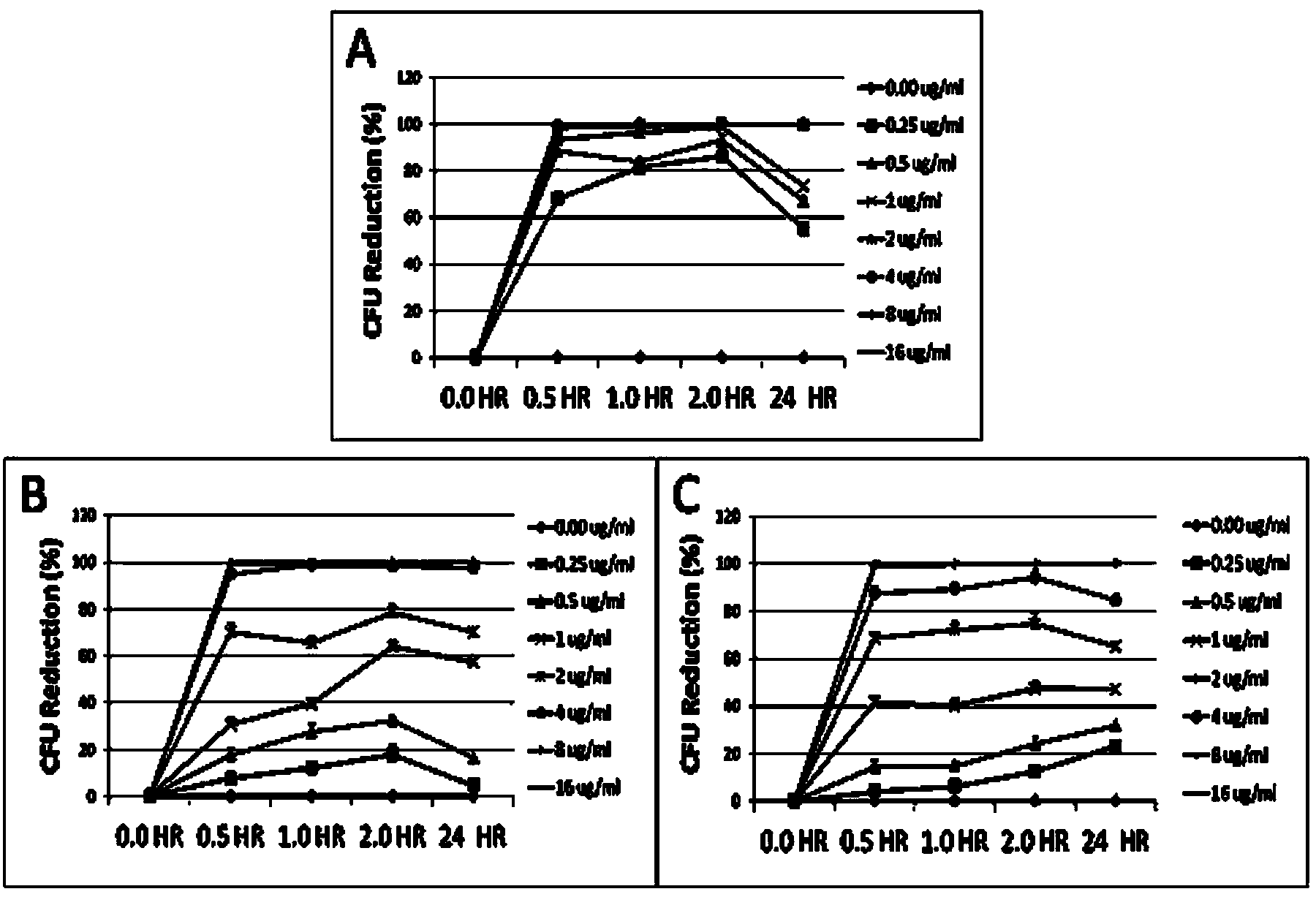
Polypeptide Cbf-14 resisting infection of drug-resistant bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN103435686AStrong inhibitory activityLow production costAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisDisease
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine and in particular relates to an antibacterial polypeptide. Part of active amino acids of the antibacterial polypeptide of Cathelicidin family is mutated based on the antibacterial polypeptide of Cathelicidin family, and then the antibacterial polypeptide with high inhibitory activity to penicilin-resistant bacterium is obtained by solid phase chemical synthesis. The result of pharmacodynamic tests shows that the antibacterial polypeptide provided by the invention has good in vitro antibacterial activity and is applicable to treating diseases about drug-resistant bacterial infection.
Owner:NANJING YINGHAIYUE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Antibacterial peptides and application of antibacterial peptides to preparation of medicament resisting drug-resistant bacteria
InactiveCN102807610ANo residueHigh activity against drug-resistant bacteriaAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsResistant bacteriaHemolysis
The invention discloses antibacterial peptides and application of the antibacterial peptides to preparation of a medicament resisting drug-resistant bacteria. The antibacterial peptides consist of 21 amino acids, wherein the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQIDNO.1. The in-vivo and in-vitro research shows that six kinds of antibacterial peptides have a strong inhibiting and killing action for the mostly clinically-separated drug-resistant bacteria and can remarkably reduce the mortality of a septicemia model caused by the drug-resistant bacteria; and a hemolytic test and an acute local stimulus test results show that six kinds of derivates have no hemolytic test or acute toxic stimulus reaction when the concentration is 2.5mg / mL.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
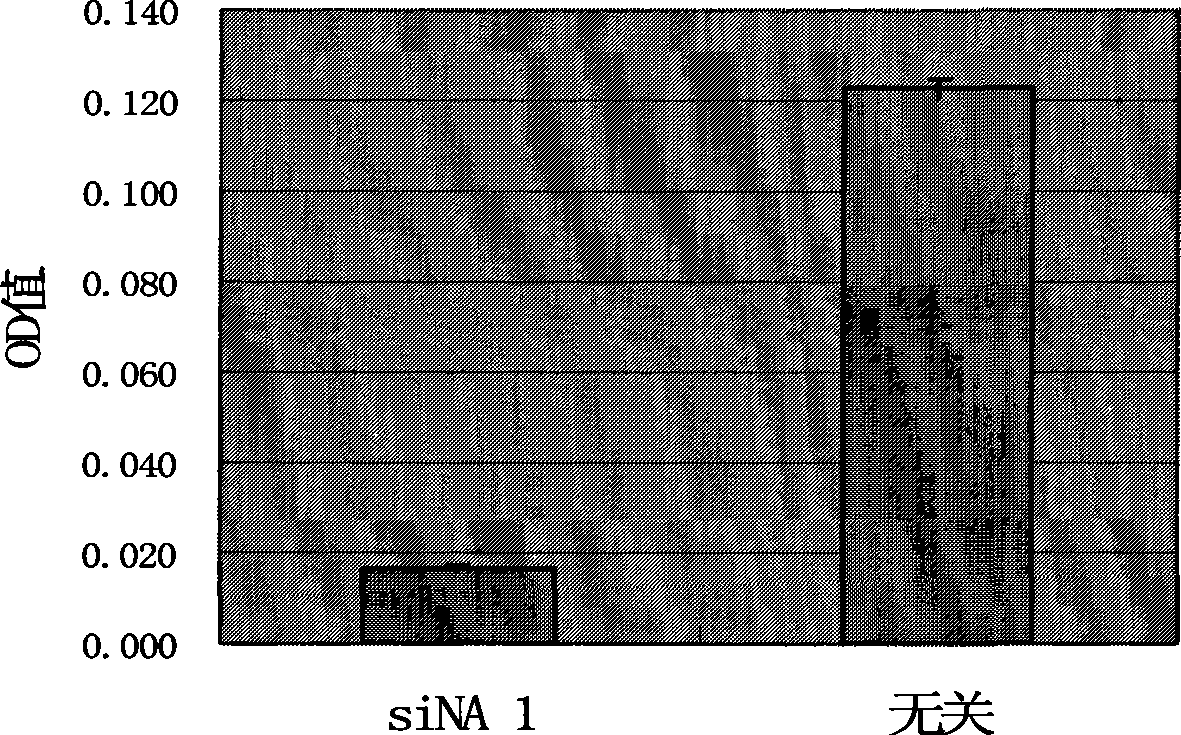
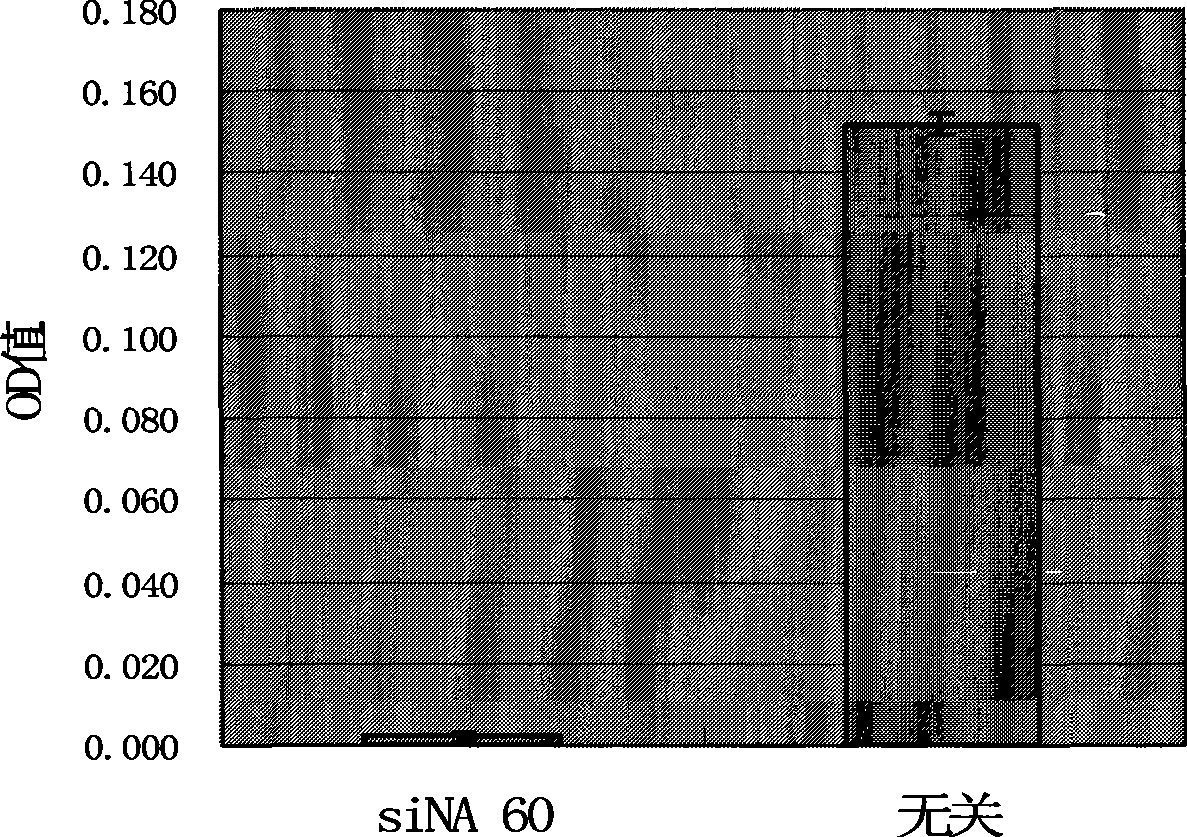
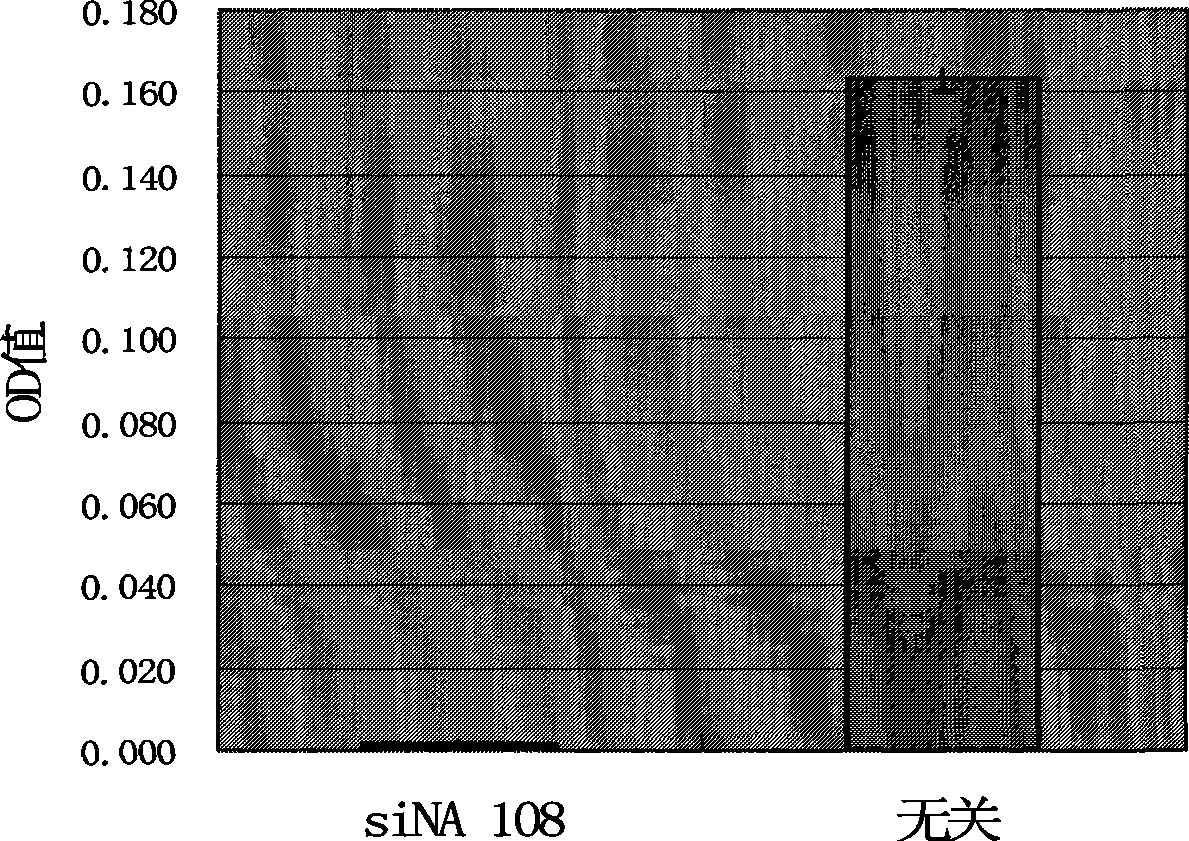
Double-chain small molecule interference nucleic acid for inhibiting and killing drug tolerant bacteria and composition thereof
InactiveCN101457222ADrug resistance is reversibleInhibition is effectiveAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesMethicillin resistance geneHuman DNA sequencing
The invention relates to a double-chain small molecule interference nucleic acid for inhibiting and killing various drug tolerance bacteria using methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aurous as represents. The siNA of the invention is a double-chain molecule with 19 base pairs. A sense strand and a antisense strand respectively have two overhanging bases dT at 5' terminals, the GC content is 40-55; the aimed target sequence is selected from the genes relative with the vital movements of copy, transcription and translation in the staphylococcus aurous genome and an mecA gene correlative with the drug tolerance; said target sequence is preserved in 900f staphylococcus aurous; said target sequence is in a conservative sequence area in more than 900f staphylococcus aurous with distinct source with all the gene sequences in the human genome; the target sequence of the said siNA double-chain molecule is selected from SEQ ID NO. 1-325, the sense strand is a corresponding DNA or RNA sequence with the target sequence and the antisense strand is a corresponding RNA or DNA with the sense strand according to the complementary base law.
Owner:李宝健
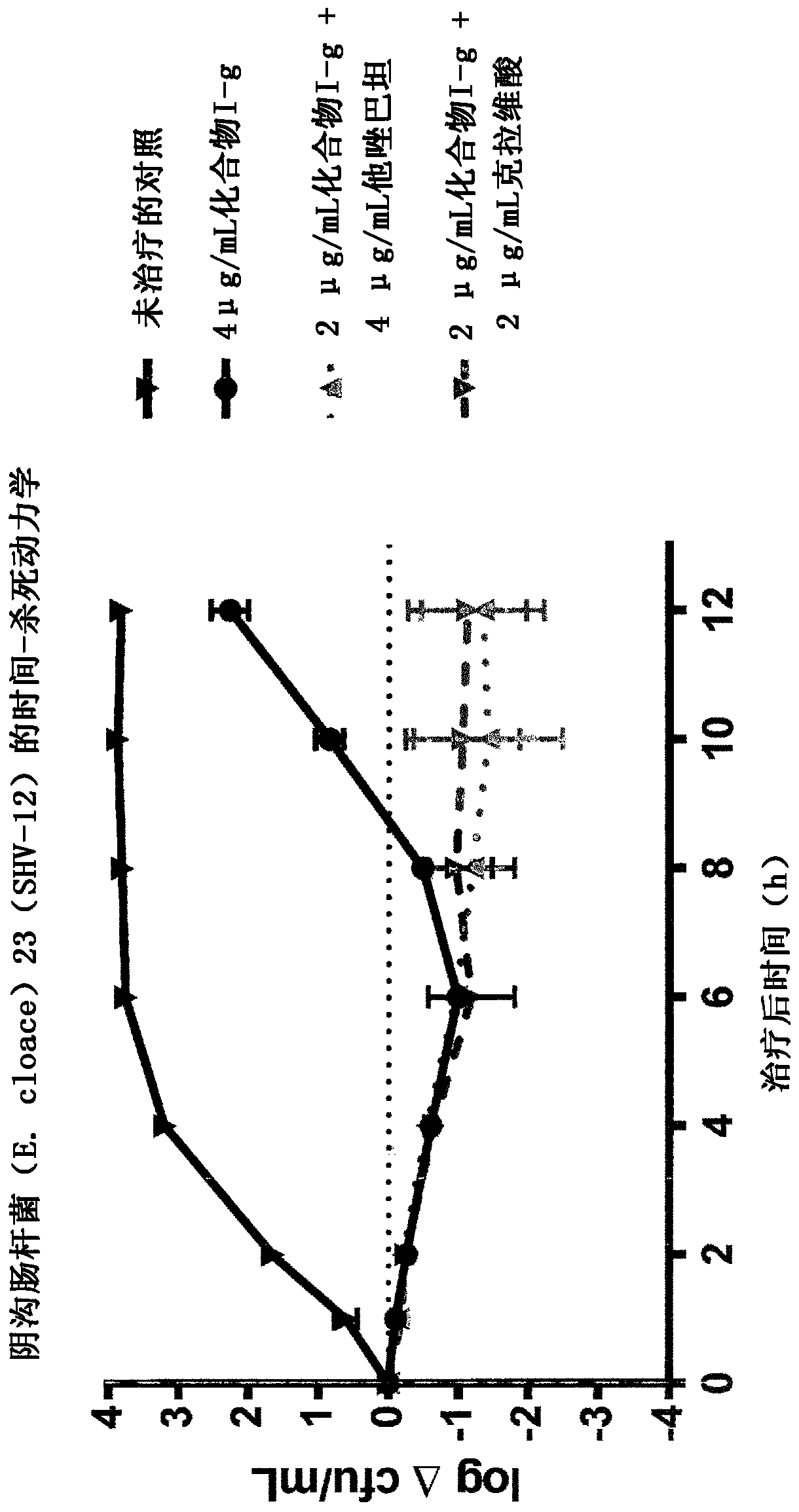
COMBINATION THERAPY WITH AMIDINE SUBSTITUTED beta-LACTAM COMPOUNDS AND beta-LACTAMASE INHIBITORS FOR INFECTIONS WITH ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANT BACTERIAL STRAINS
This invention relates to beta-lactam compounds in combination with further drugs, e.g. beta-lactamase inhibitors (BLIs), for use in the treatment and prophylaxis of infections caused by resistant bacteria.
Owner:AICURIS GMBH & CO KG
Production and use of high expression, high purity, high activity gene recombinant human lysozyme
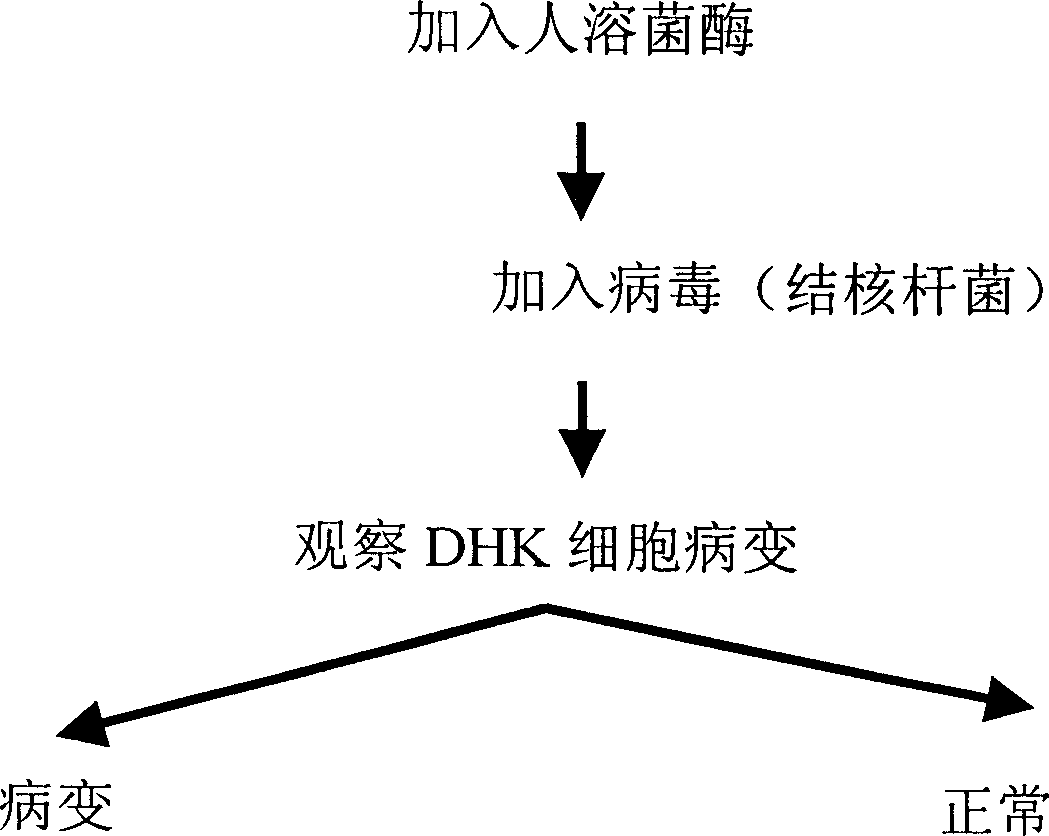
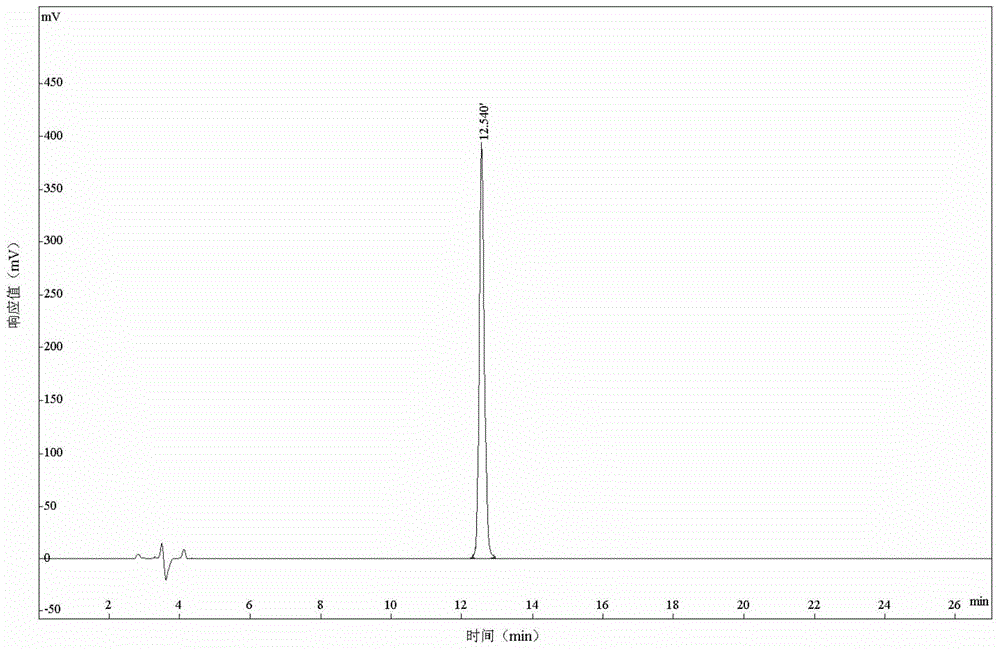
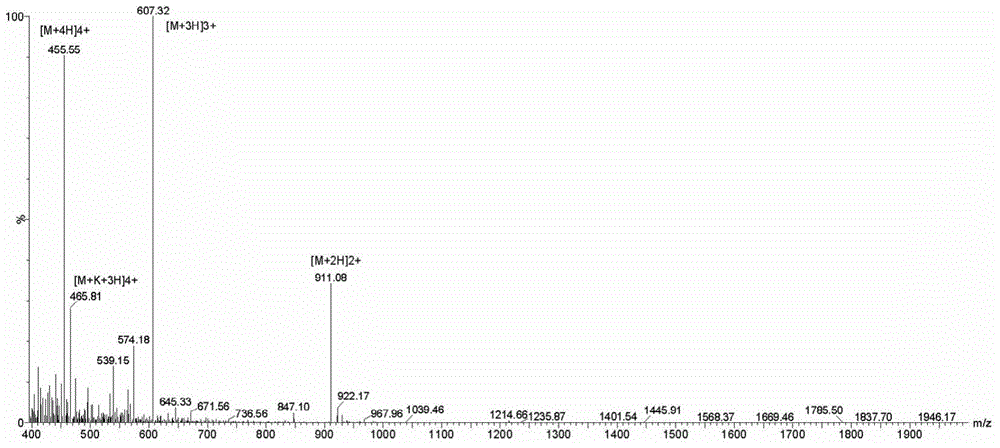
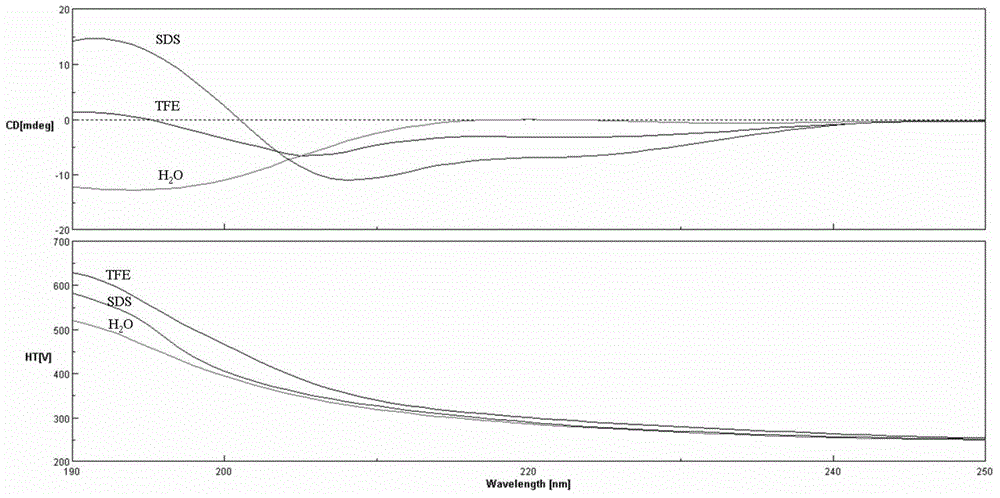
A high-expression, high-purity and high-activity gene-recombinant human lysozyme, its preparing process and the medical composition of antibiotic and the said human lysozyme for treating bacterial and fungus infection, drug-resistant bacteria infection, and the sequela caused by gram-negative bacteria infection are disclosed.
Owner:长春奇龙生物技术研究所 +2
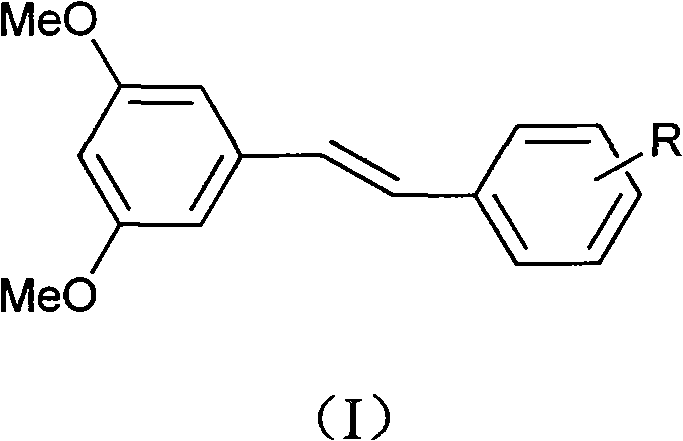
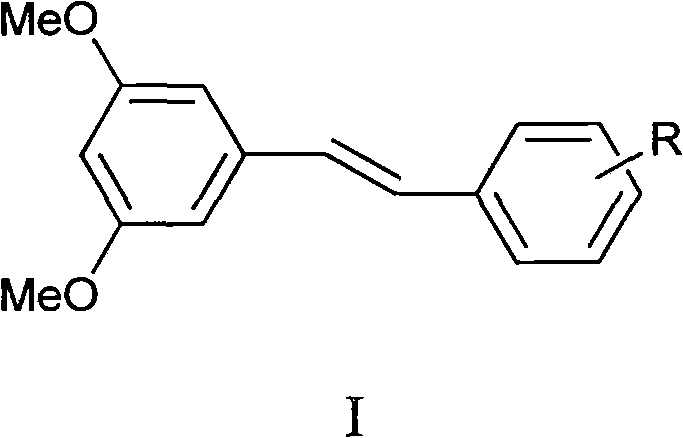
3,5-dimethoxystilbene derivative, preparation method and application thereof in anti-drug resistant bacteria
InactiveCN102001949ASimple reaction conditionsEasy to operateAntibacterial agentsOrganic compound preparationResistant bacteriaTriethylphosphite
The invention discloses a 3,5-dimethoxystilbene derivative, a preparation method and an application thereof, in particular relating to the synthesis of the 3,5-dimethoxystilbene derivative as shown in structural formula (1) and anti-drug resistant bacterial activity thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly mixing 3,5-dimethoxybenzyl bromide with triethyl phosphate to obtain 3,5-dimethoxybenzyl phosphonate; and then carrying out Wittig-Honner reaction to obtain the 3,5-dimethoxystilbene derivative. The preparation method has the advantages of high yield, simple and convenient operation, low cost, good industrialization prospect and the like. A bacterial inhibiting test result shows that the synthesized 3,5-dimethoxystilbene derivative has obvious inhibition activity on drug resistant bacteria and is of great significance on research and development of a novel anti-drug resistant bacterial drug.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
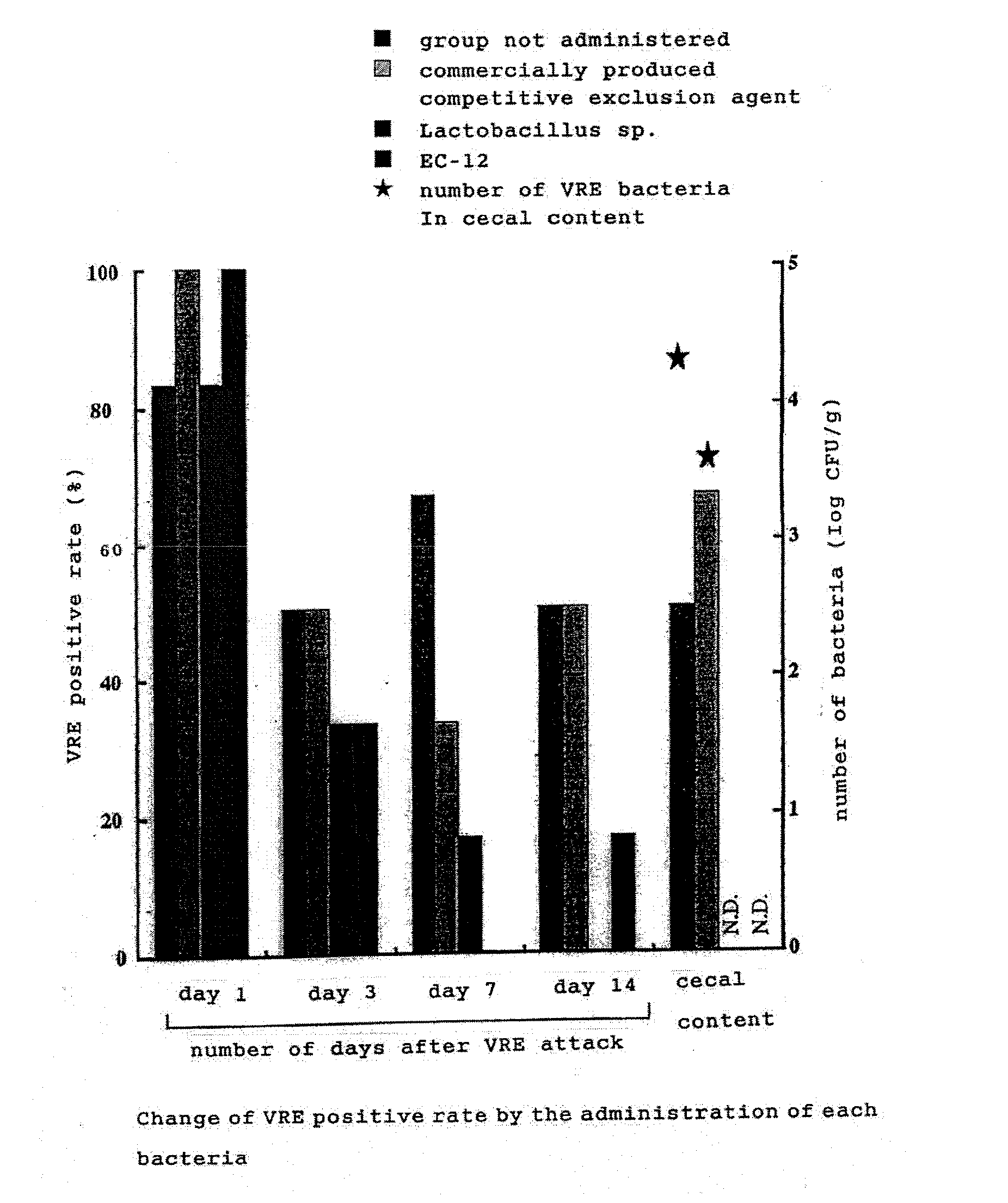
Preventing Agent Against Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infection
InactiveUS20080206380A1Avoid bacterial infectionAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesMicrobial agent
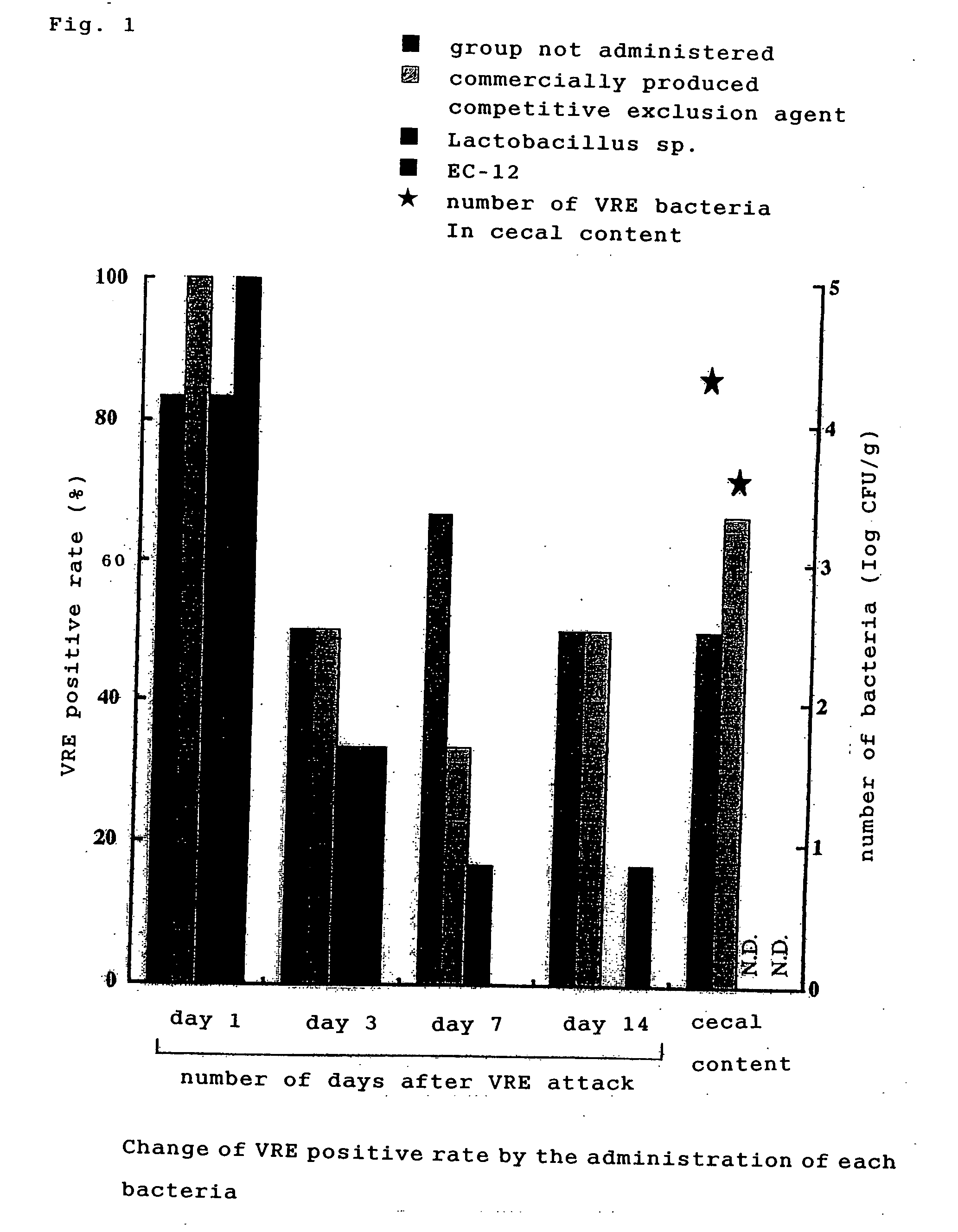
The present invention is to provide an agent for preventing and treating drug-resistant bacterial infection for livestock / fowls or fish and shellfish, using particular microbial agents as active components, without using synthetic antibacterial substances or antibiotics, and a method for preventing and treating its infection. By using lactic acid bacteria, their dead bacteria or treated substances thereof, or Mygasphaera elsdenii as active components, for an agent for preventing and treating drug-resistant bacterial infection for livestock / fowls or fish and shellfish carrying or being infected by drug-resistant bacteria such as Vancomycin, particularly by using Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium as lactic acid bacteria, the above mentioned object was resolved.
Owner:USHIDA KAZUNARI +4
Antimicrobial peptide gene of portunus trituberculatus and clone method
InactiveCN101508992AReduce savingsQuality improvementFermentationAnimals/human peptidesAquaculture industryComplete sequence
The invention provides a Portunus trituperculatus antibacterial peptide gene and a cloning method thereof. The Portunus trituperculatus crustin antibacterial peptide gene cDNA is 565nt except poly A, and contains 5' non-coding region (5' UTR) of 75nt, a reading frame of 330nt, and 3' non-coding region (3' UTR) of 160nt, wherein the sequence number of GenBank is FJ467931. The method successfully clones complete sequence of Portunus trituperculatus crustin cDNA, can construct pronucleus or eucaryon gene engineering strain through a gene engineering mode, efficiently express recombinant protein with physiological activity, and can be produced in scale. As a feed immunity additive, the gene can replace certain antibiotics in the traditional feed for seaculture industry, thereby realizing green culture, reducing and even eliminating accumulation of the antibiotics in aquatic products, and improving quality of the aquatic products; the gene can also be used as an effective substitute of certain drug resistance antibiotics for the medicine of preventing and treating drug resistance bacteria in seaculture.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Polypeptide capable of inhibiting and killing multiple medicine-resisting bacteria
ActiveCN104072583AAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
The invention relates to polypeptide capable of inhibiting and killing bacteria, and in particular relates to multiple medicine-resisting bacteria. The polypeptide is remarkable in effect of killing or inhibiting methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis, klebsiella pneumoniae, baumanii and / or escherichia coli. The invention further relates to a composition with the defined polypeptide, and an application of the defined polypeptide and the composition thereof in preparation of medicines and in killing or inhibiting of multiple in-vitro medicine-resisting bacteria.
Owner:冯小荣 +2
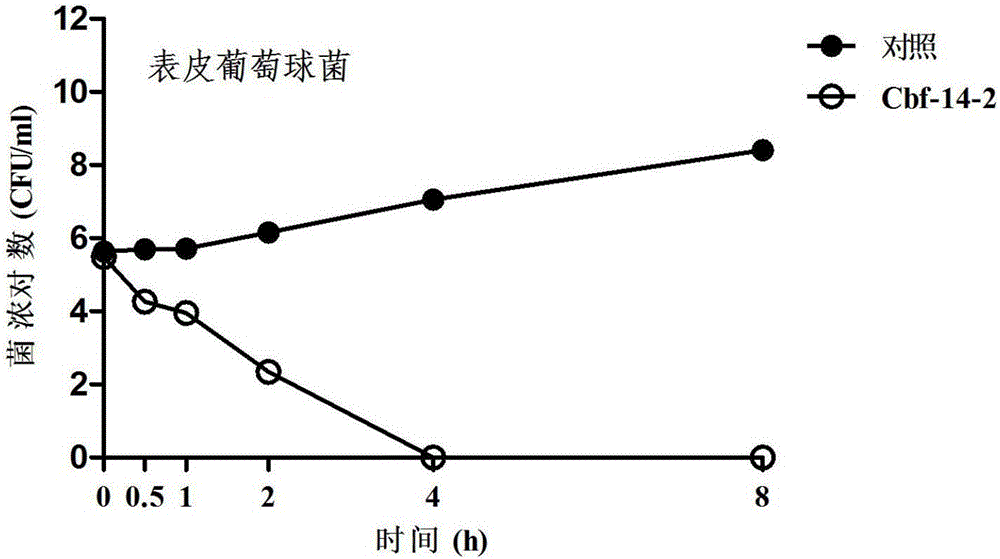
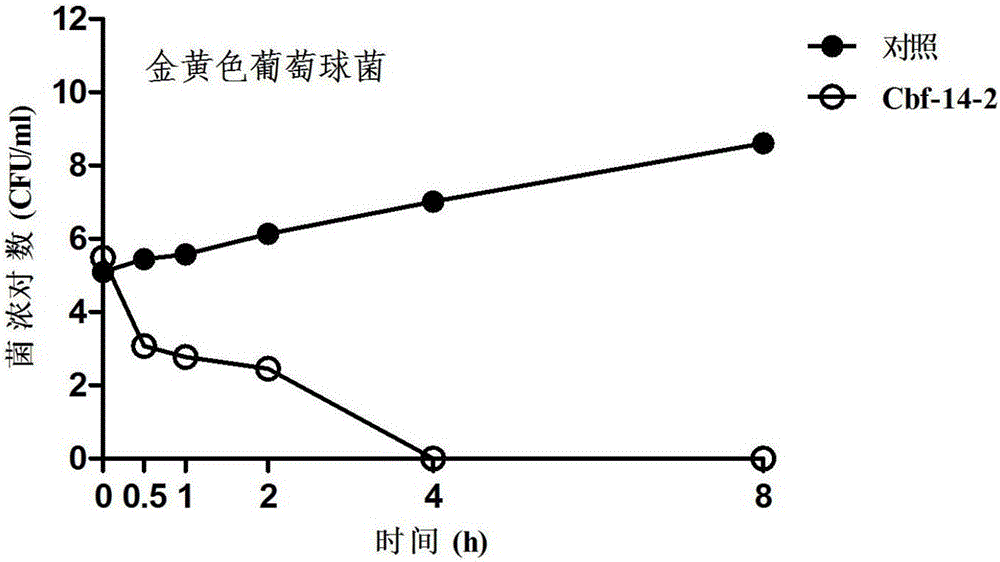
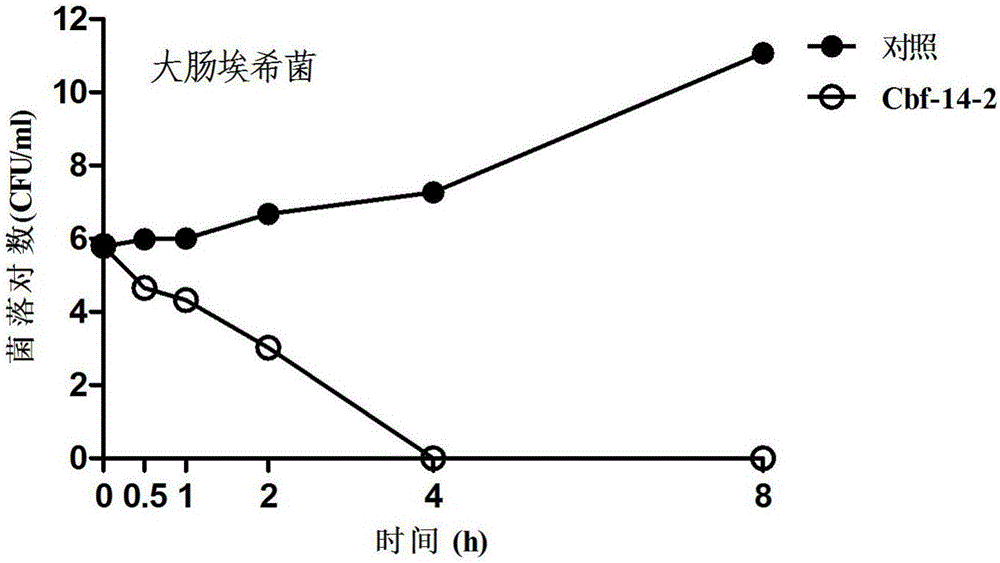
Anti-drug resistant infection polypeptide Cbf-14-2 and application thereof
ActiveCN106543271ALow hemolytic activityLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial peptidesAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to the technical field of polypeptide drugs in biochemistry, in particular to a polypeptide and application thereof. An unnatural amino acid is introduced according to an antimicrobial peptide Cbf-14 to obtain the polypeptide Cbf-14-2 having the high inhibiting activity on drug-resistant bacteria. An amino acid sequence of the antibacterial polypeptide is shown as SEQ ID: NO:1. An in-vitro antibacterial activity research shows that the polypeptide Cbf-14-2 has a more remarkable killing effect on clinic drug-resistant bacteria compared with a parent peptide Cbf-14. An in-vivo bacteremia model research shows that the polypeptide Cbf-14-2 can remarkably improve the survival rate of a rat suffering from bacteremia, the weight of the rat suffering from the bacteremia is protected, the bacterium concentration of the polypeptide in blood is reduced, and meanwhile the polypeptide has the very good treating effect on lung tissue infection inflammation caused by drug-resistant strains. The polypeptide Cbf-14-2 has very small toxicity to mammalian cells.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
Compounds for the treatment of multi-drug resistant bacterial infections
The present invention relates to compounds that demonstrate antibacterial activity, processes for their preparation, pharmaceutical compositions containing them as the active ingredient, to their use as medicaments and to their use in the manufacture of medicaments for use in the treatment of bacterial infections in warm-blooded animals such as humans. In particular this invention relates to compounds useful for the treatment of bacterial infections in warm-blooded animals such as humans, more particularly to the use of these compounds in the manufacture of medicaments for use in the treatment of bacterial infections in warm-blooded animals such as humans.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Composition for treatment of drug resistant bacterial infections and a method of treating drug resistant bacterial infections
The invention provides a novel composition useful in the treatment of resistant bacterial infections, said composition comprising an extract obtained from Azadiracta indica or Melia azadirachta and an effective amount of an antibiotic or chemotherapuetic antibacterial drug. Further, the invention provides a method for the treatment of resistant bacterial infections. The invention also provides a process for the preparation of the composition of the invention.
Owner:DABUR INDIA LTD
Application of polypeptide RK12 in preparation of medicine for treating acne
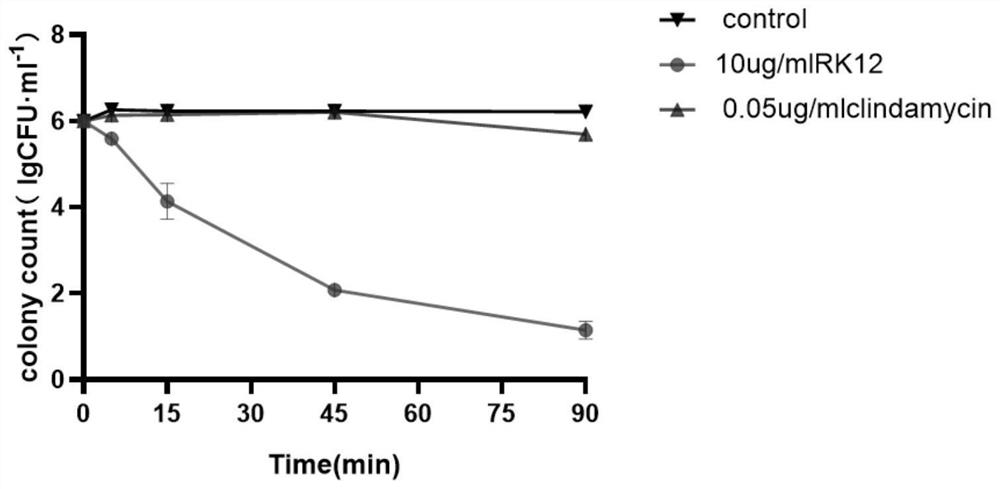
ActiveCN114209808ALimit drug resistanceInterference synthesisPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticBacillus acnesTreatment acne
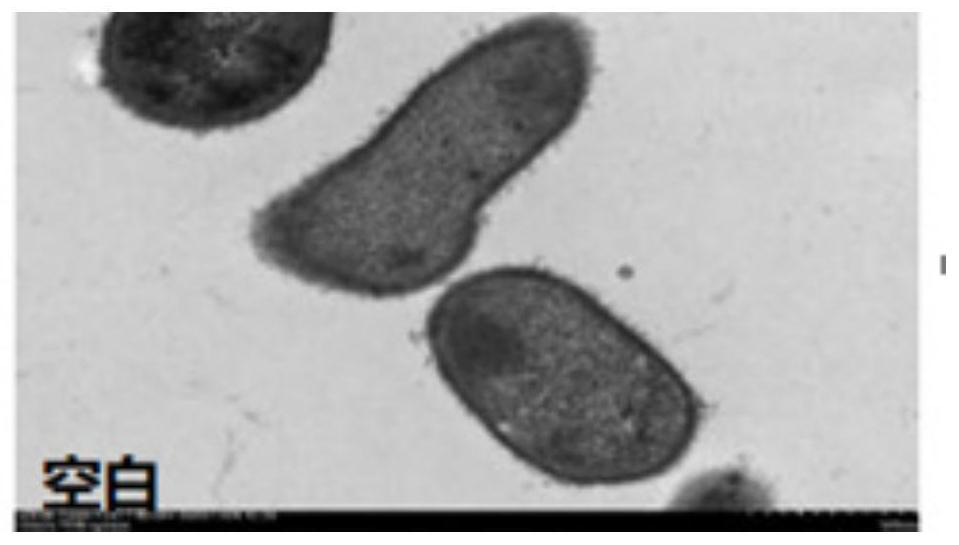
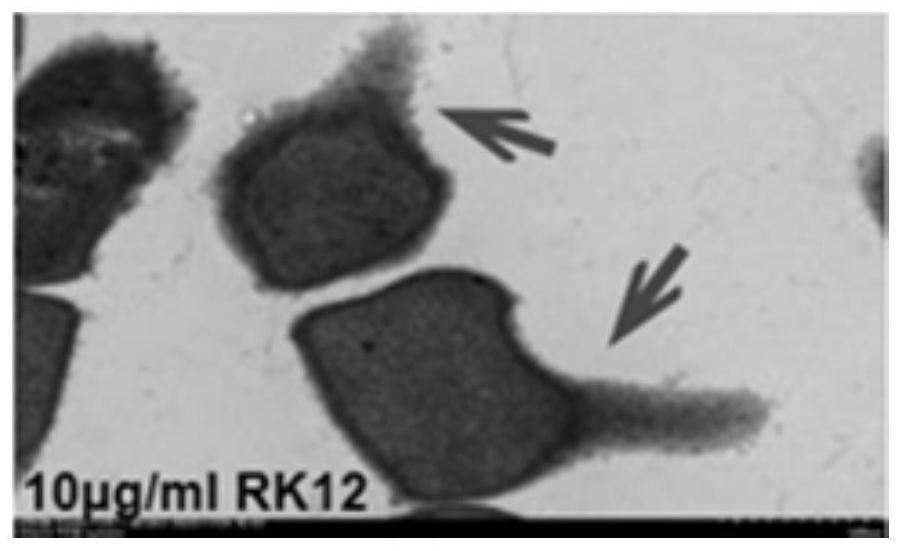
The invention provides application of polypeptide RK12 in preparation of a medicine for treating acne. The new application of the polypeptide RK12 is used for preparing the medicine for treating the acne, the polypeptide RK12 has a remarkable inhibition effect on propionibacterium acnes and clindamycin-resistant propionibacterium acnes, and compared with antibiotics, the polypeptide RK12 is low in drug resistance, has concentration and time dependence, and has a good application prospect in preparation of medicines for treating the acne and the clindamycin-resistant propionibacterium acnes. The research result of an in-vitro antibacterial spectrum experiment also proves that the composition can rapidly inhibit the growth of propionibacterium acnes and clindamycin-resistant propionibacterium acnes, the research result of an in-vitro anti-inflammatory experiment also proves that the composition has an obvious anti-inflammatory effect, and the composition is not easy to generate drug-resistant bacteria due to an antibacterial mechanism different from that of antibiotics. According to the new strategy and thought for treating acne provided by the invention, the antibacterial action mechanism is helpful for clinically limiting the influence of antibiotic resistance.
Owner:成都佩德生物医药有限公司
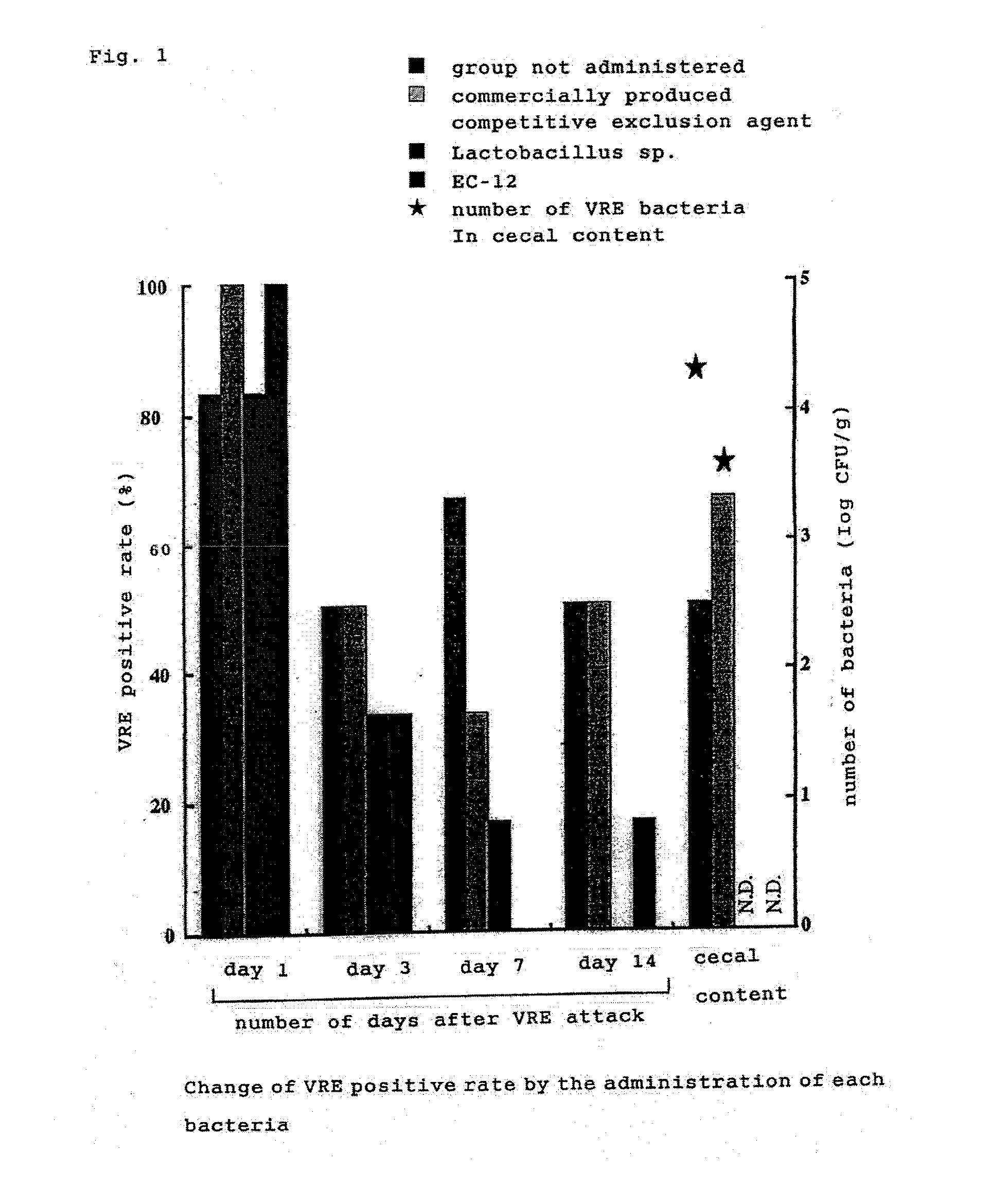
Preventing agent against drug-resistant bacterial infection
InactiveUS20060067923A1Avoid bacterial infectionAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicrobial agentAntibiotic Y
The present invention is to provide an agent for preventing and treating drug-resistant bacterial infection for livestock / fowls or fish and shellfish, using particular microbial agents as active components, without using synthetic antibacterial substances or antibiotics, and a method for preventing and treating its infection. By using lactic acid bacteria, their dead bacteria or treated substances thereof, or Mygasphaera elsdenii as active components, for an agent for preventing and treating drug-resistant bacterial infection for livestock / fowls or fish and shellfish carrying or being infected by drug-resistant bacteria such as Vancomycin, particularly by using Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium as lactic acid bacteria, the above mentioned object was resolved.
Owner:COMBI CORP
Compositions for treating drug resistant bacteria and biofilm
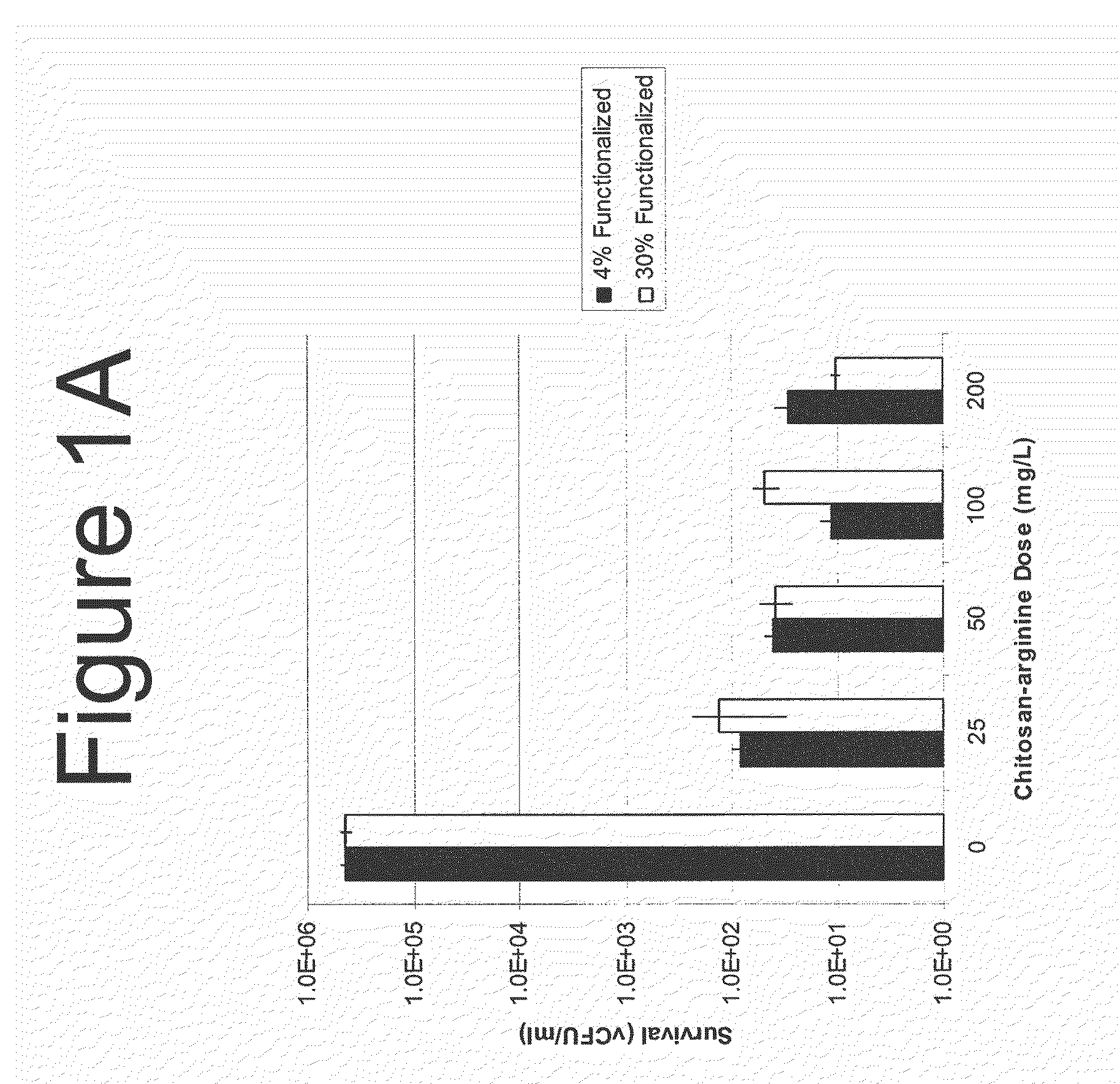
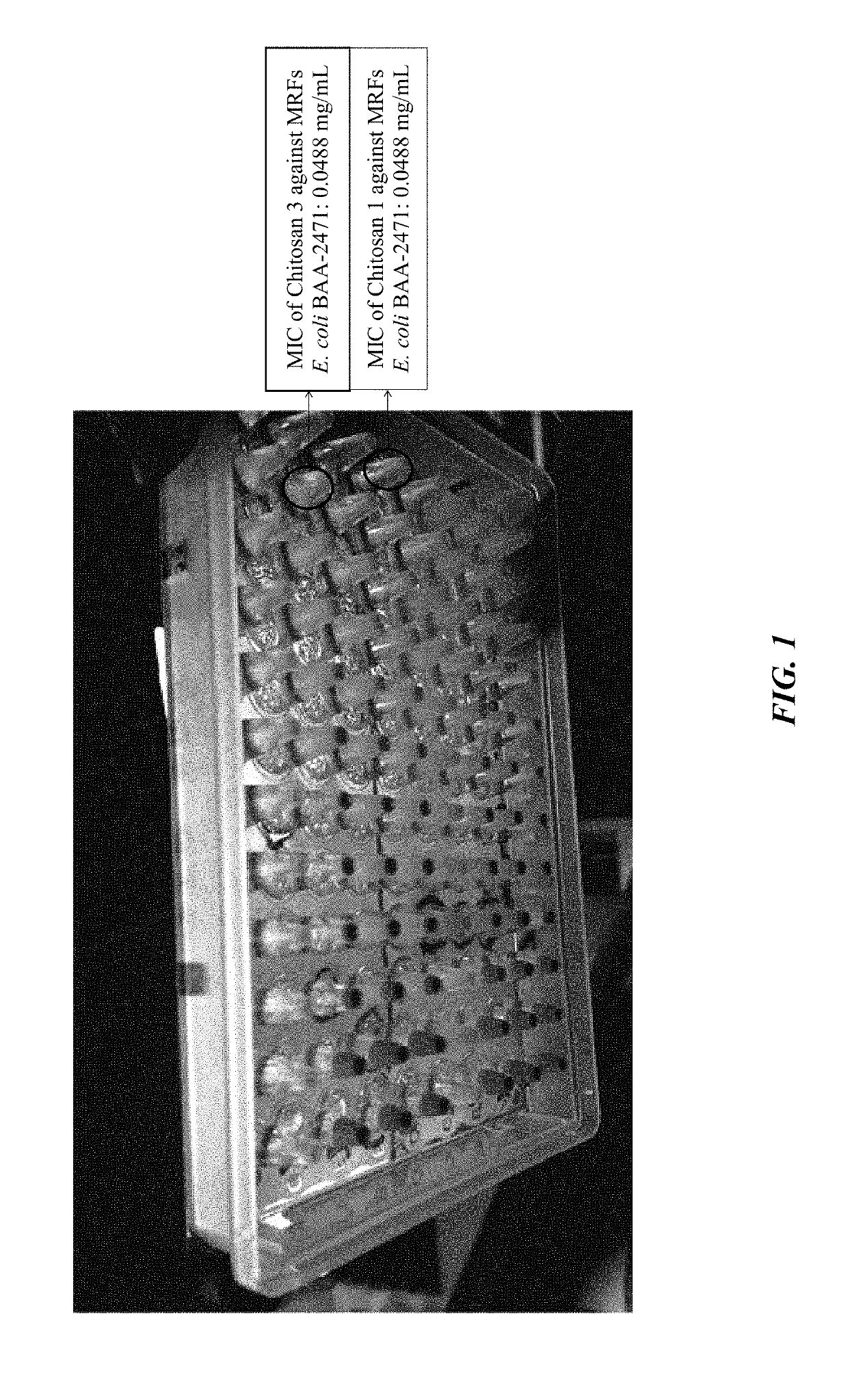
A broad-based remediation mechanism against MRFs and alternative fecal indicators such as multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, including nanotechnology formulations and methodologies that may be used to develop novel mitigation strategies against certain drug resistant bacterial strains. The current invention relates to mitigation of drug resistant bacteria, for example in hospitals and in food animals, and to the identification. The invention uses hybrid nanomaterials comprising oligo-chitosan and zinc oxide formulated as nanoparticles and micelles. The invention also relates to the treatment of multi-drug resistant biofilms which mimic in vivo conditions. The inventors unexpectedly found unique properties of very small oligomers of chitosan that effectively mitigate MRF and alternative resistant strain-induced illnesses without compromising the balance of the beneficial flora in the physiological and ecological microenvironments. The combination of chitosan with zinc oxide demonstrated synergistic and unexpected effects in treating multi-drug resistant pathogens.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Preparation and application of modified peptide
ActiveCN110950932AEfficient killingPromote healingAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial actionWound dressing
The invention relates to a preparation method of a modified peptide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: covalently coupling a polypeptide with a photosensitizer through three glycines (GGG), wherein the conjugate has a relatively strong antibacterial effect (the antibacterial rate) of 50%, and can effectively kill most microorganisms including drug-resistant bacteria under illumination, and the sterilization rate reaches 99.999%. The conjugate has the effects of preventing infection and promoting healing on cut wounds of mice. The compound is simple in preparation method, relatively high in yield and convenient to store, can be used for preparing products such as antibacterial reagents and antibacterial drugs, and has a good application prospect in the fields of clinicaltreatment of local infection and wound dressing.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
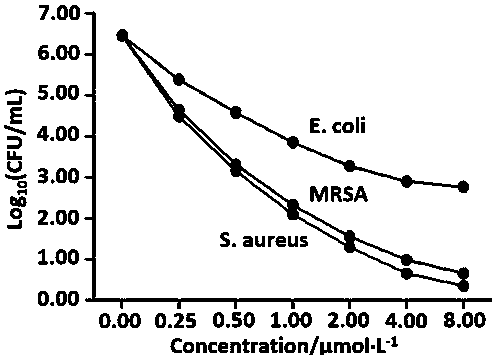
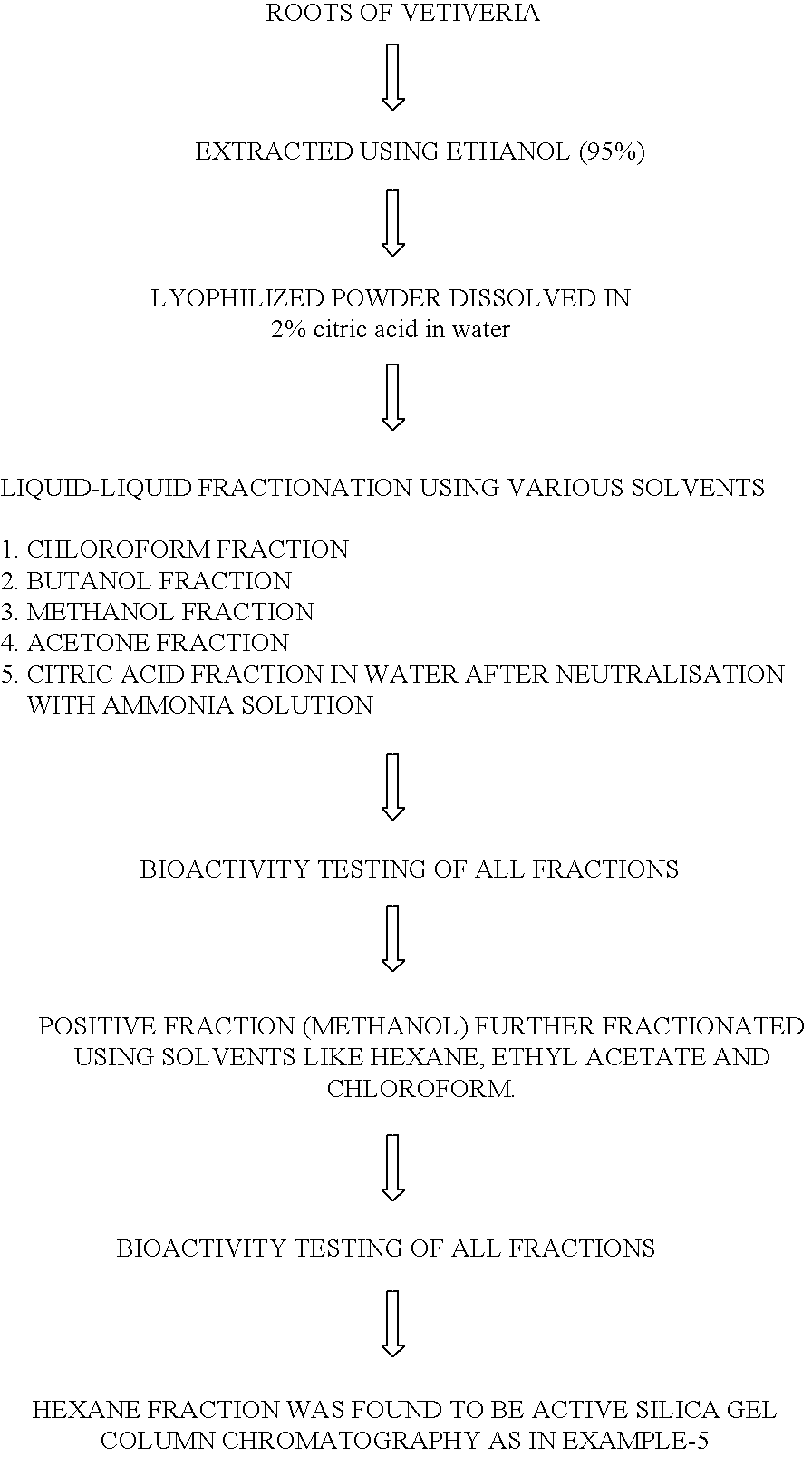
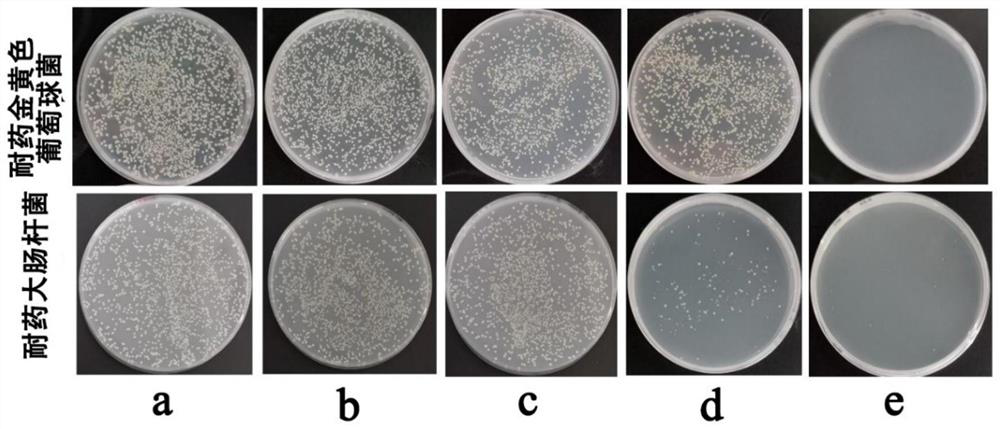
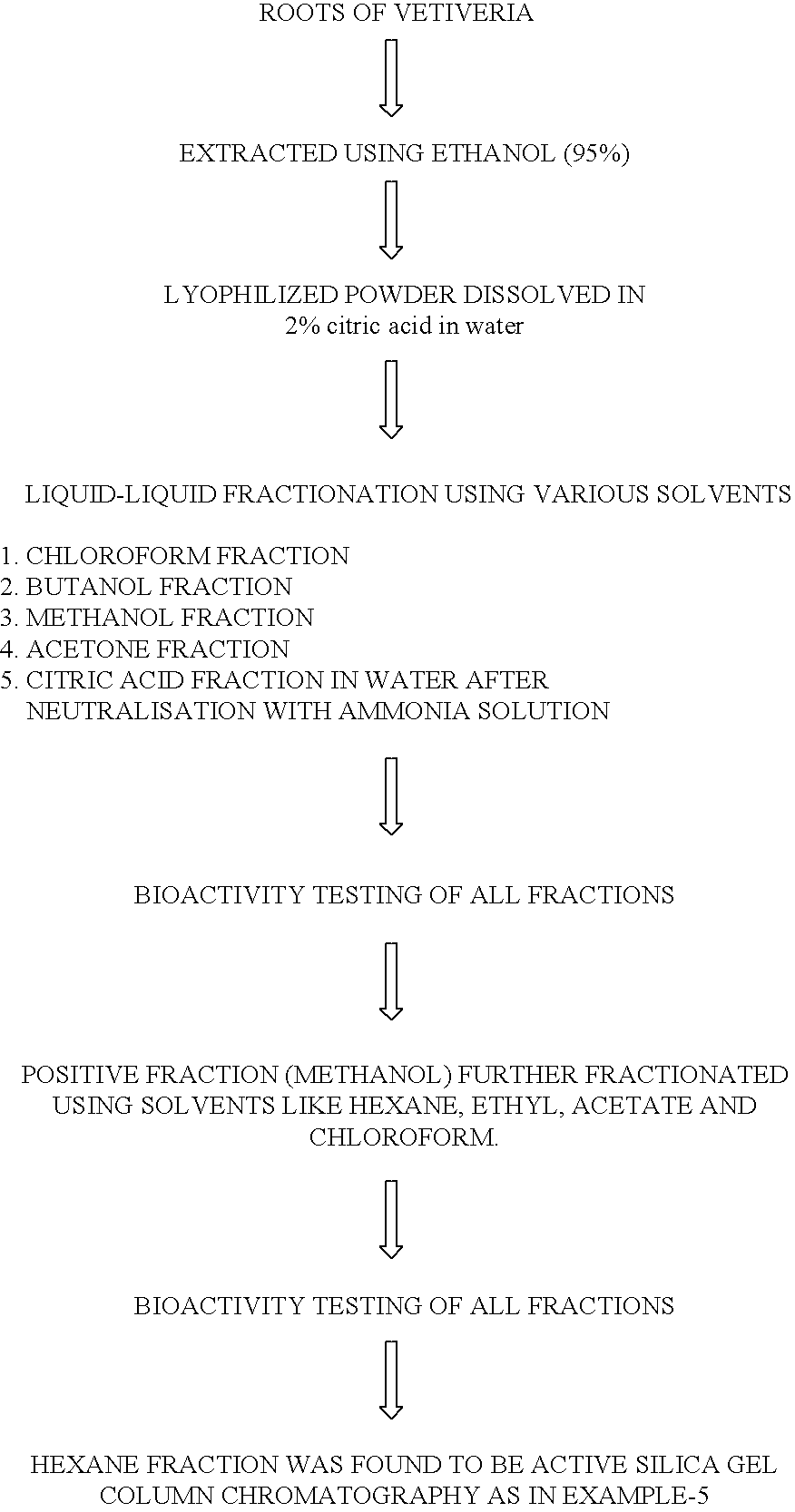
Bioactive hexane fraction from Vetiveria zizanioides
The present invention relates a hexane bioactive fraction and obtained from the roots of an aromatic plant named Vetiveria zizanioides commonly found in India for inhibiting the growth of drug resistant bacterial infections in humans and animals; also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the bioactive extract with other additives for inhibiting the growth of drug resistant bacterial infections in humans and animals and a process for the isolation of said bioactive extract
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
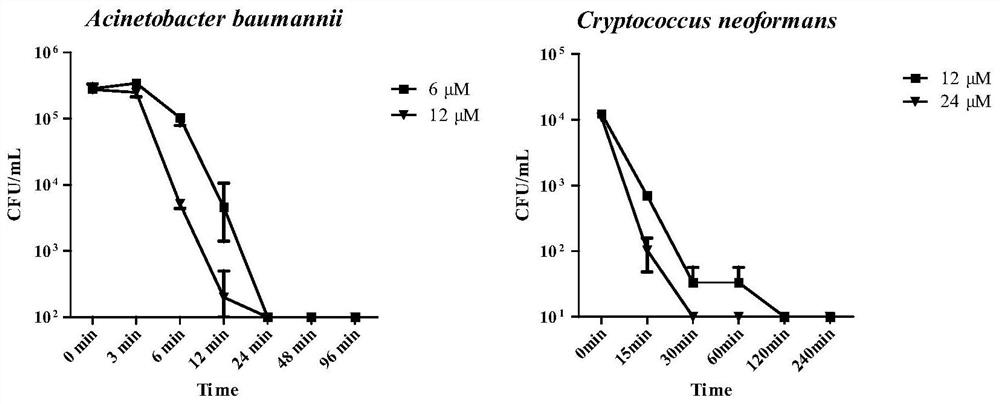
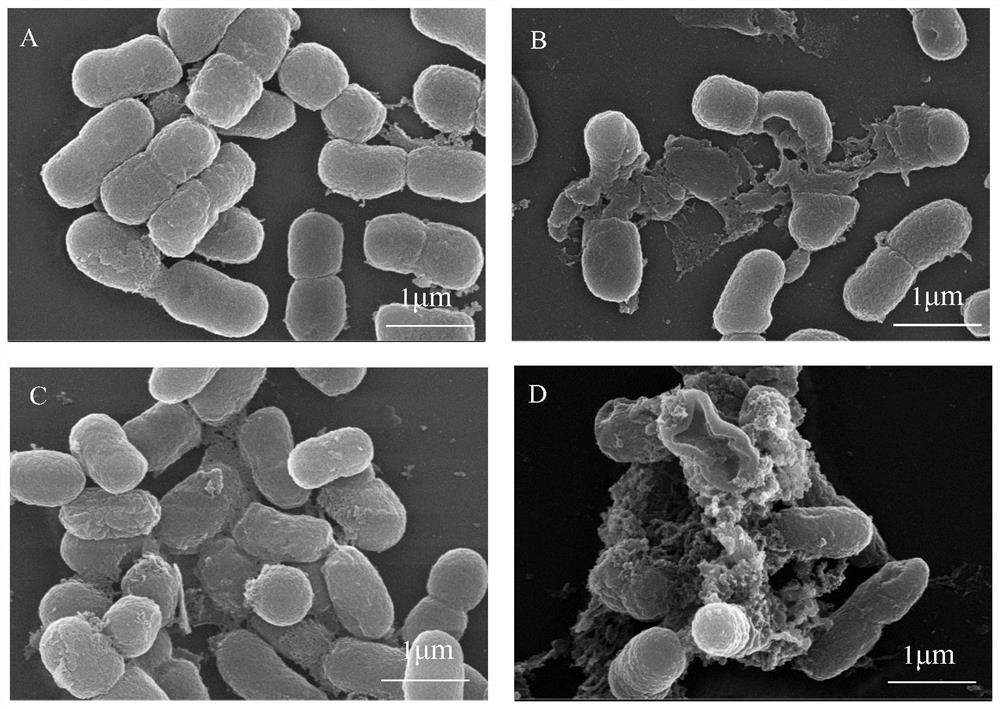
Antibacterial peptide Scybaumancin105-127 and application thereof
ActiveCN113121666AGood water solubilityBroad spectrum antibacterialAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacillus acnesPropionibacterium acnes
The invention discloses an antibacterial peptide Scybaumancin105-127 and application thereof, the antibacterial peptide is found in Scylla paramamosain for the first time, the molecular formula of the antibacterial peptide is C106H188N36O28S3, and the amino acid sequence of the antibacterial peptide is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The antibacterial peptide Scybaumancin105-127 disclosed by the invention has good antibacterial activity on acinetobacter baumannii, shigella flexneri, escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, cryptococcus neoformans, listeria monocytogenes, enterococcus faecium and propionibacterium acnes, and has no cytotoxicity on normal cells. The antibacterial peptide Scybaumancin105-127 has high antibacterial activity, safety and non-toxic, also has relatively strong antibacterial activity on clinical drug-resistant bacteria, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Glycopeptides compounds with anti-resistance bacterial activity, preparation method and application thereof
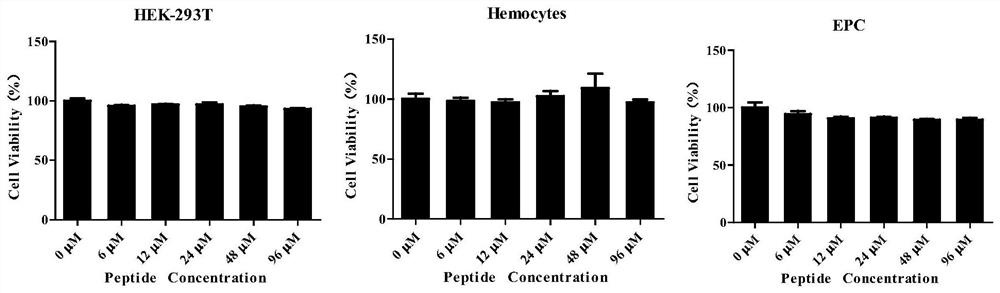
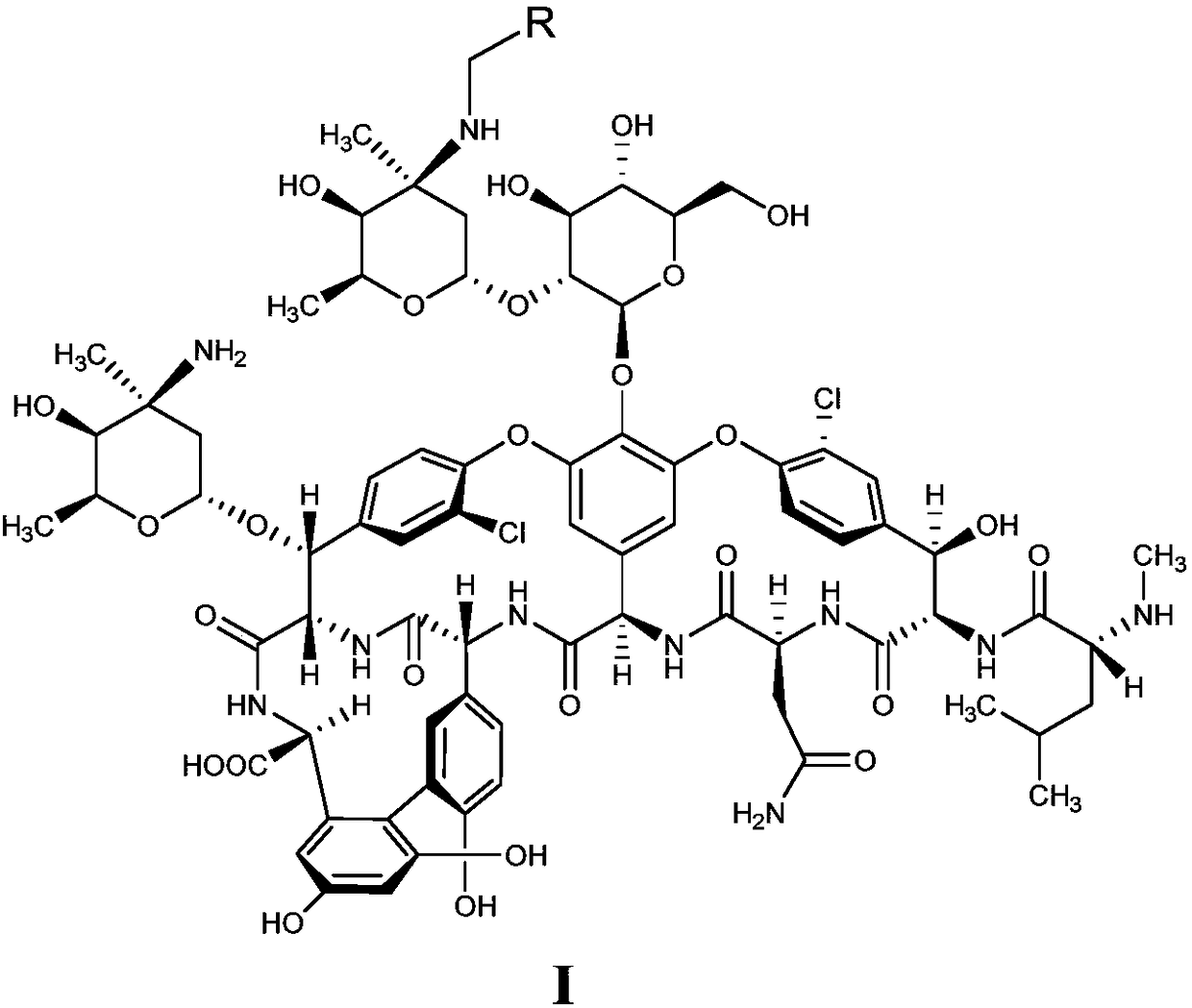
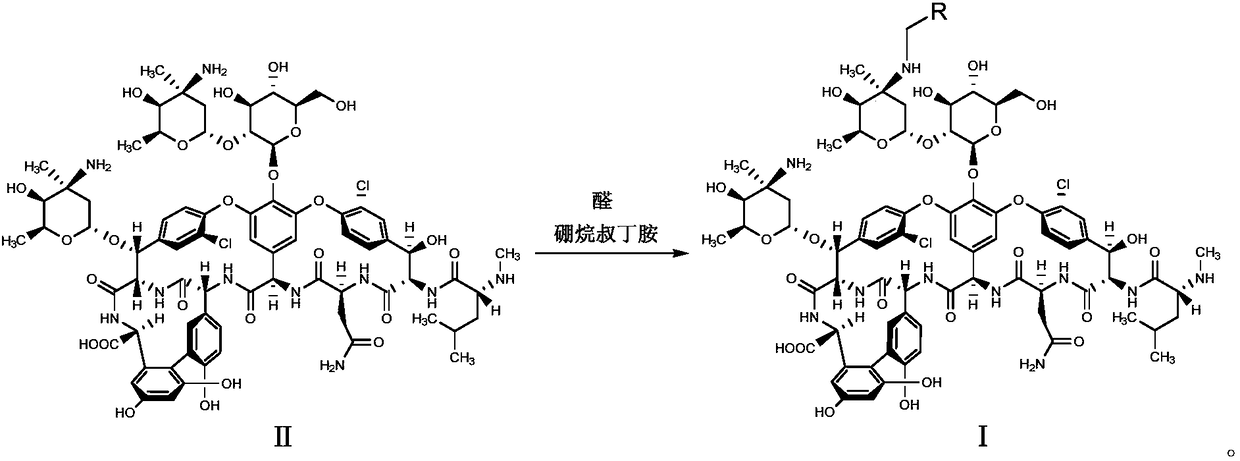
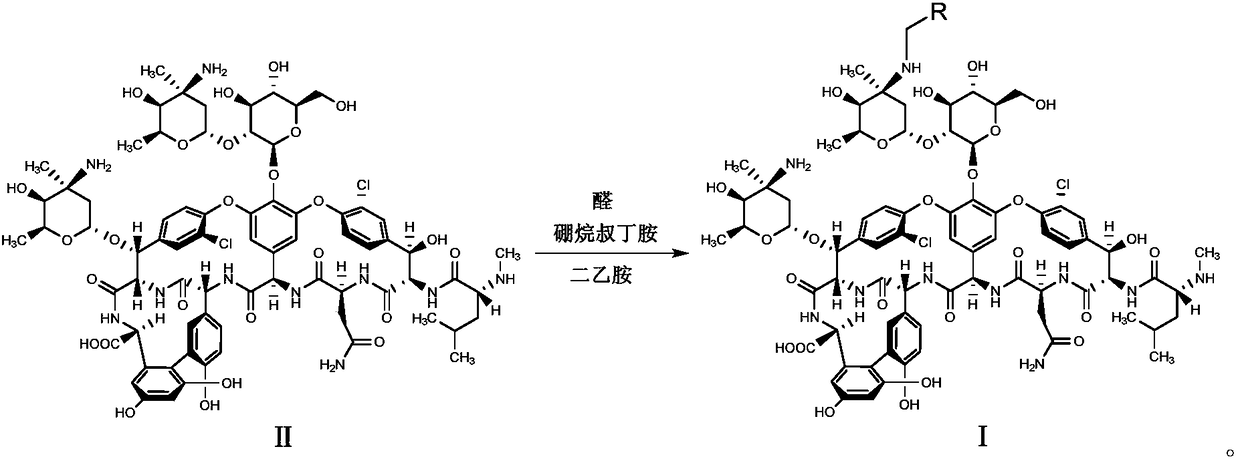
ActiveCN108409837AImprove securityStrong inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsInorganic non-active ingredientsDiseaseOritavancin
The invention discloses a group of glycopeptides compounds with anti-resistance bacterial activity. The glycopeptides compounds in accordance with a general formula (I) are as shown in the following specification. The invention further provides a preparation method and an application for the above glycopeptides compounds. Through testing, compared with a second-generation glycopeptides pharmaceutical oritavancin, the glycopeptides antibiotic compounds have the higher inhibitory activity to endurance strains, especially MRSA or VRE. Through further testing, the most of the glycopeptides compounds have the higher safety than the oritavancin, and can be used for preparing pharmaceuticals for treating or preventing various diseases, such as skin and soft tissue infection, cephalomeningitis, sepsis, pneumonia, arthritis, peritonitis, bronchitis, and empyema, caused by bacterial infection.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +1
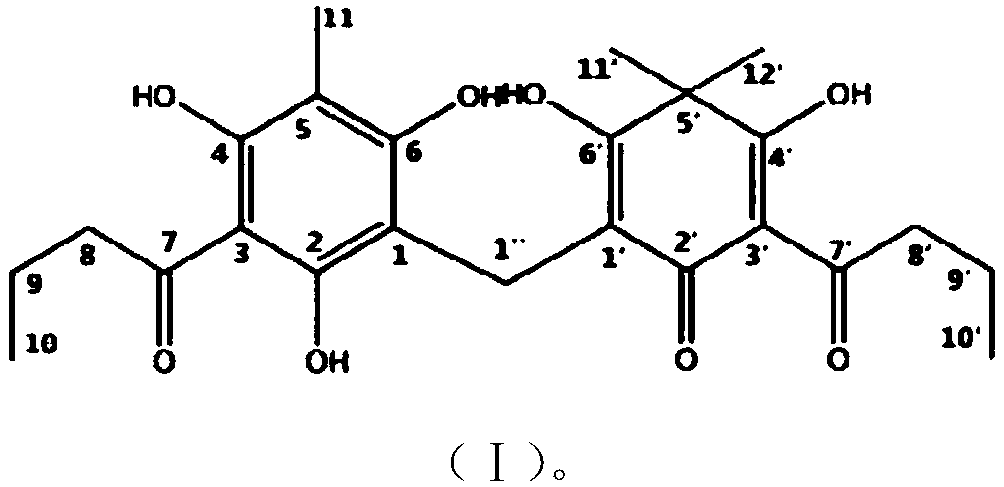
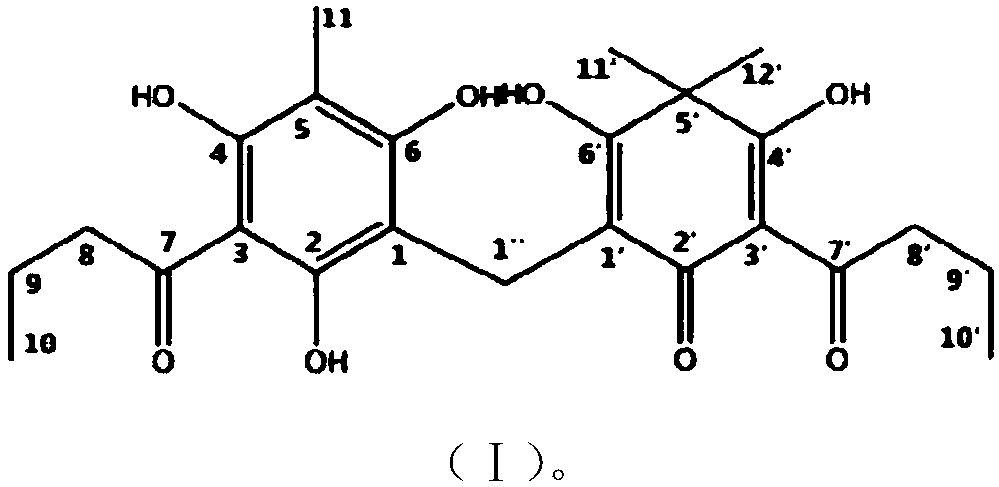
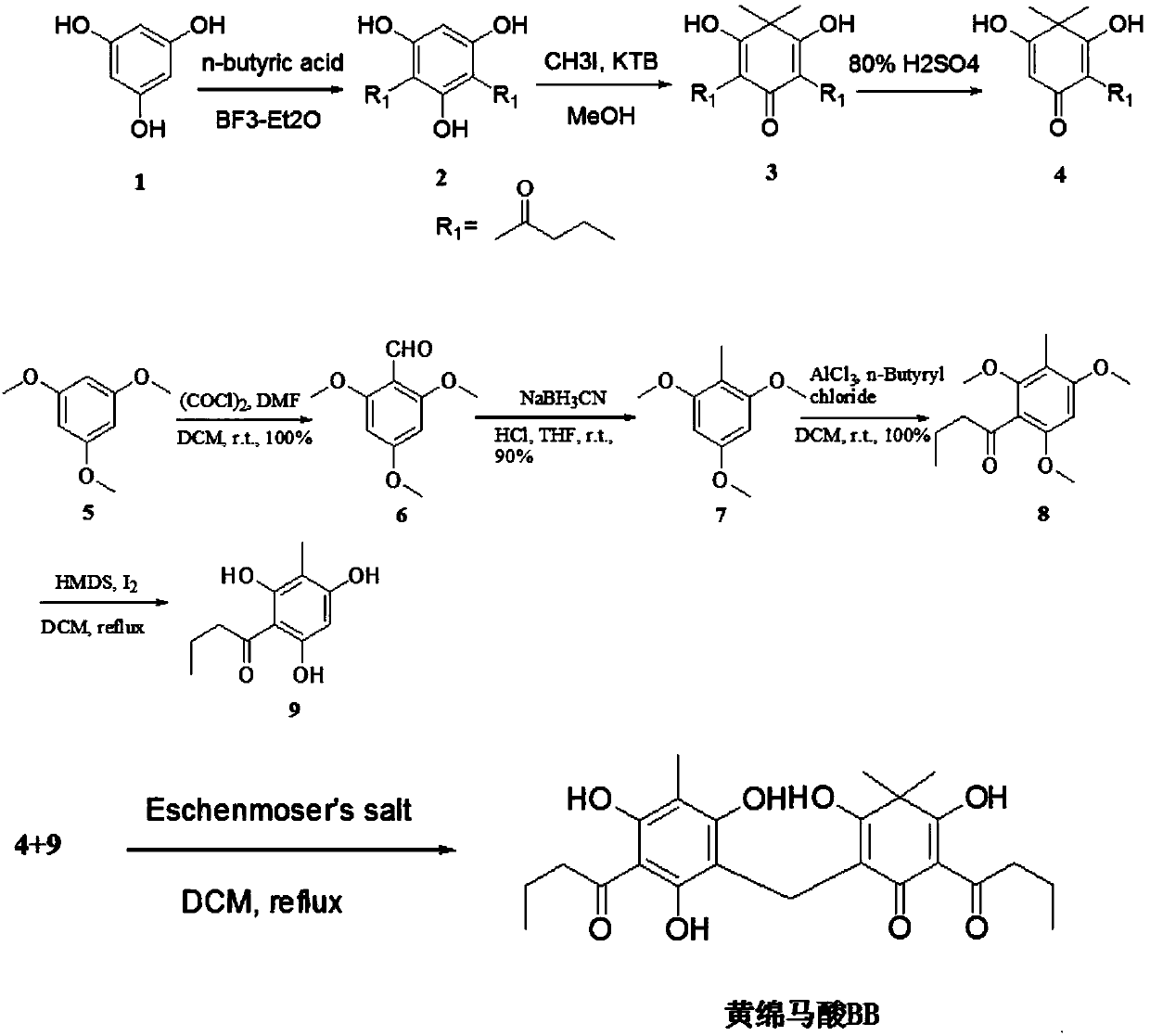
Dryopteris fragrans phloroglucinol compound flavaspidic acid BB and antibacterial application thereof
ActiveCN107837247AFill in the lack of applicationsImprove anti-bacterial abilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsChemical synthesisResistant bacteria
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine and discloses an antibacterial application of a Dryopteris fragrans phloroglucinol compound flavaspidic acid BB. The invention provides the flavaspidic acid BB obtained by the chemical synthesis method. The flavaspidic acid BB has good antibacterial effects, effectively fills in the application deficiency of the antibacterial natural compound and provides an effective antibacterial solution for drug-resistant bacteria. The experimental results show that the compound has a strong antibacterial effect and good curative effects especially on drug-resistant bacteria.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
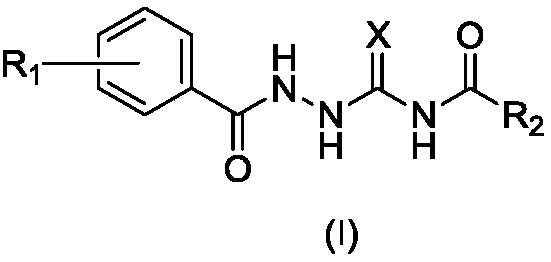
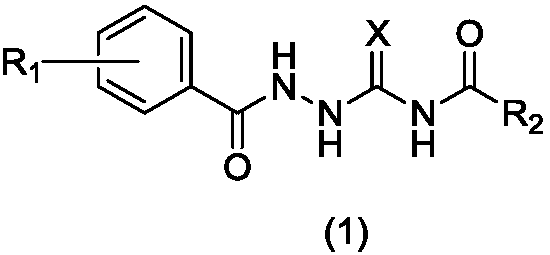
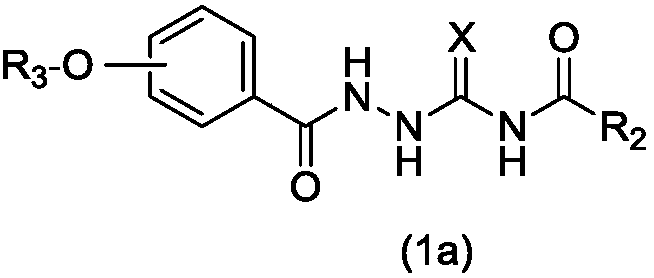
1-substituted benzoyl-4-fatty acylsemicarbazide derivative, preparation method thereof, and use thereof as antibacterial medicine
InactiveCN110272364AEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidisOxygen
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibacterial medicines, and relates to a 1-substituted benzoyl-4-fatty acylsemicarbazide derivative, a preparation method thereof, and a use thereof as an antibacterial medicine. The compound is represented by formula (I); and in the formula (I), R1 is selected from hydrogen, a hydroxyl group, a C1-C8 alkyl group, a C1-C8 alkoxy group, an arylmethoxy group and a halogenated arylmethoxy group, R2 is selected from hydrogen, a C1-C8 alkyl group and a halogenated C1-C8 alkyl group, and X is selected from sulfur and oxygen. The 1-substituted benzoyl-4-fatty acylsemicarbazide derivative of the present invention has a strong inhibition effect on Gram-positive bacteria, especially methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), and can be used for preparing novel drug-resistant bacteria medicines.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Production and use of high expression, high purity, high activity gene recombinant human lysozyme
A high-expression, high-purity and high-activity gene-recombinant human lysozyme, its preparing process and the medical composition of antibiotic and the said human lysozyme for treating bacterial and fungus infection, drug-resistant bacteria infection, and the sequela caused by gram-negative bacteria infection are disclosed.
Owner:长春奇龙生物技术研究所 +2
Anti-drug-resistant bacterial infection polypeptide cbf-14 and its use
ActiveCN103435686BStrong inhibitory activityLow production costAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine and in particular relates to an antibacterial polypeptide. Part of active amino acids of the antibacterial polypeptide of Cathelicidin family is mutated based on the antibacterial polypeptide of Cathelicidin family, and then the antibacterial polypeptide with high inhibitory activity to penicilin-resistant bacterium is obtained by solid phase chemical synthesis. The result of pharmacodynamic tests shows that the antibacterial polypeptide provided by the invention has good in vitro antibacterial activity and is applicable to treating diseases about drug-resistant bacterial infection.
Owner:NANJING YINGHAIYUE BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
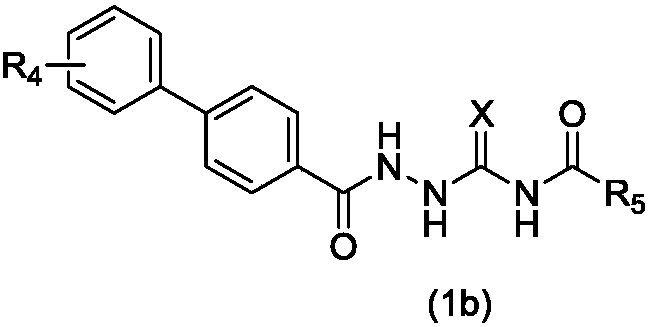
1-substituted benzoyl-4-fatty acyl semicarbazide derivative, preparation method and application thereof as antibacterial agent
ActiveCN108456157AEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsOrtho positionMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
The invention belongs to the technical field of antibacterial agents, and relates to a 1-substituted benzoyl-4-fatty acyl semicarbazide derivative, a preparation method and application thereof as an antibacterial agent. The compound is shown in a formula (I), wherein R1 is selected from hydrogen, hydroxyl, C1-C3 alkyls, C1-C8 alkoxyls, C3-C6 cycloalkyl oxyls, non-substitute or halogenated phenylsC1-C3 alkoxyls, phenyls, C1-C3 alkylbenzene, halogeno benzene, and the substitution site of R1 is selected from ortho-position or meta-position or para-position; R2 is selected from non-substitute orhalogenated C1-C8 alkyls, non-substitute or halogenated C3-C6 naphthenic bases and non-substitute or halogenated phenyl C1-C3 alkyls; X is selected from sulfur or oxygen. The 1-substituted benzoyl-4-fatty acyl semicarbazide derivative has the high inhibiting effect on drug-resistance bacteria including gram-positive bacteria, in particular to methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) and vancomycin resistant enterococcus (VRE), and can be used for preparing novel drug resistance bacterium drugs. The formula is shown in the description.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
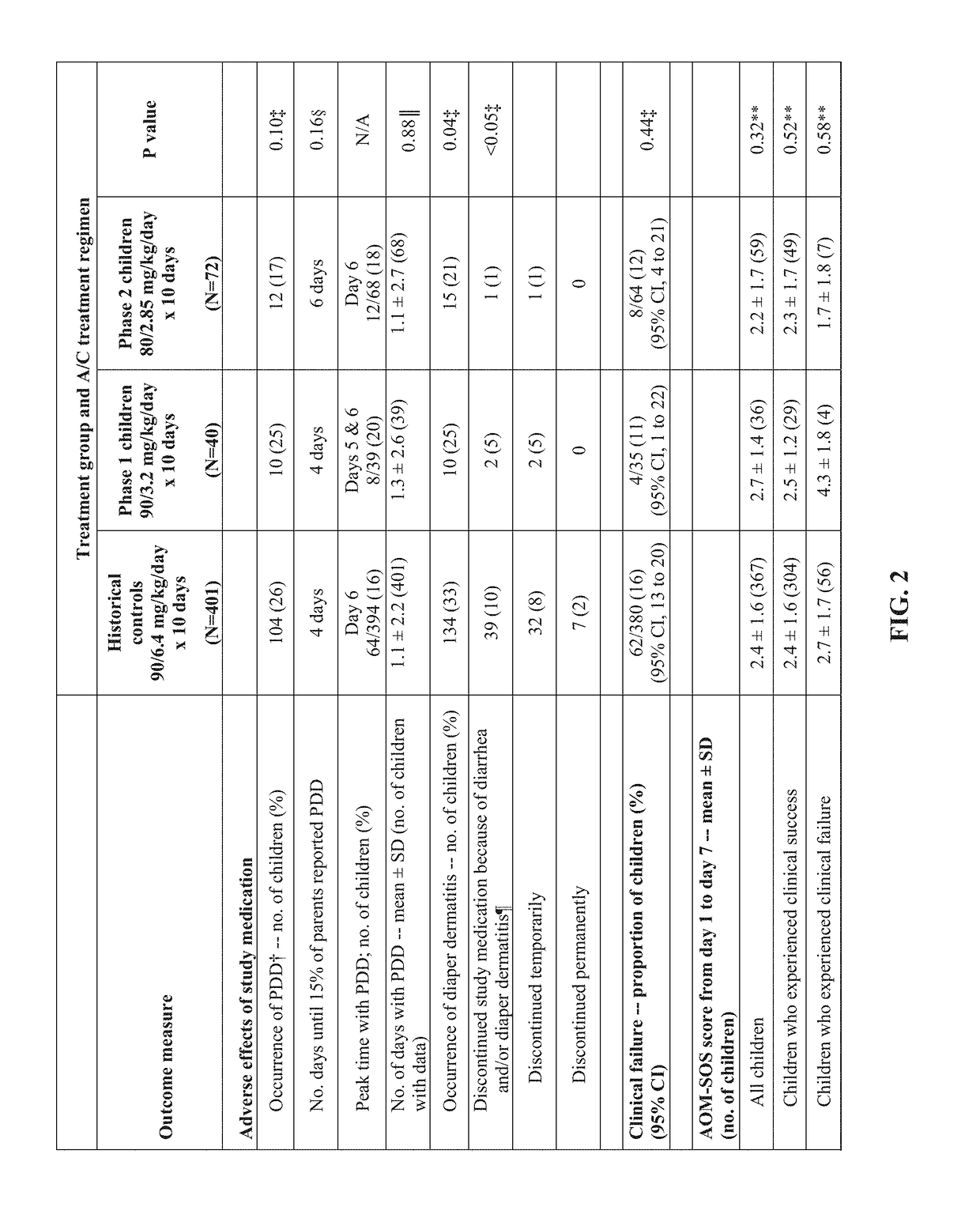
Pediatric oral suspension formulations of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium and methods for using same
InactiveUS20180235941A1Reduce amountReduce the amount requiredAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderOral suspensionsOralSuspension
The invention is directed to a pediatric oral suspension composition containing amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium where the clavulanate potassium is present in an amount equal to or less than about 21.5 mg / 5 mL, and a method of treating bacterial infections by providing between about one to about fourteen dosage days of the composition. Also disclosed are methods of treating a patient comprising administering amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium to the patient in dosages of at least about 80 mg / kg / day of the amoxicillin and from about 1.66 mg / kg / day to about 2.84 mg / kg / day of the clavulanate potassium. The methods are useful for treating pediatric otitis media, treating a drug resistant bacterial infection, or treating beta-lactamase producing Haemophilus influenzae or Moraxella catarrhalis in a patient under 24 months of age.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
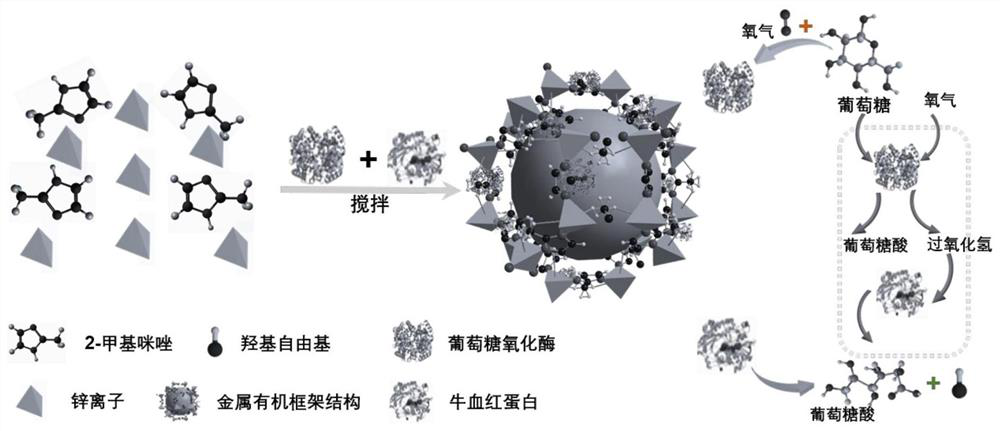
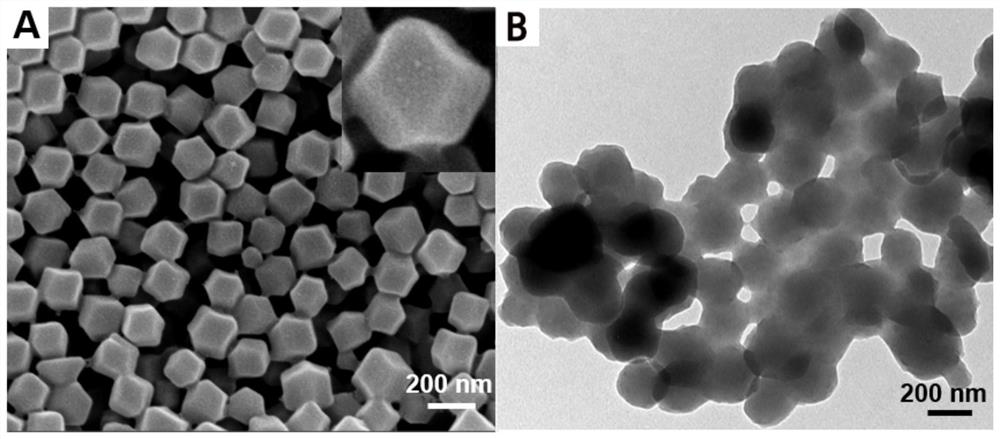
Glucose oxidase and hemoglobin loaded nanoreactor as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113262296AReduce energy supplyImprove antibacterial propertiesAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano-material preparation and bacterial infection resistance, and relates to a glucose oxidase and hemoglobin loaded nano-reactor and a preparation method and an application thereof, the structure of the nano-reactor is a zeolite imidazate skeleton structure simultaneously loading glucose oxidase and hemoglobin, and the nano-reactor can be applied to bacterial infection resistance, and particularly, bacterial infection of wounds of diabetics can be controlled, and wound healing is promoted; the nano-reactor has good biocompatibility and environmental friendliness, is more remarkable in antibacterial effect, can achieve a good antibacterial effect without adding exogenous hydrogen peroxide, has a remarkable bactericidal effect on methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamase, and can efficiently promote the wound healing caused by multi-drug-resistant bacterial infection of the diabetics, and the market prospect is extremely wide.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV +1
Bioactive hexane fraction from Vetiveria zizanioides
The present invention relates a hexane bioactive fraction and obtained from the roots of an aromatic plant named Vetiveria zizanioides commonly found in India for inhibiting the growth of drug resistant bacterial infections in humans and animals; also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the bioactive extract with other additives for inhibiting the growth of drug resistant bacterial infections in humans and animals and a process for the isolation of said bioactive extract
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com