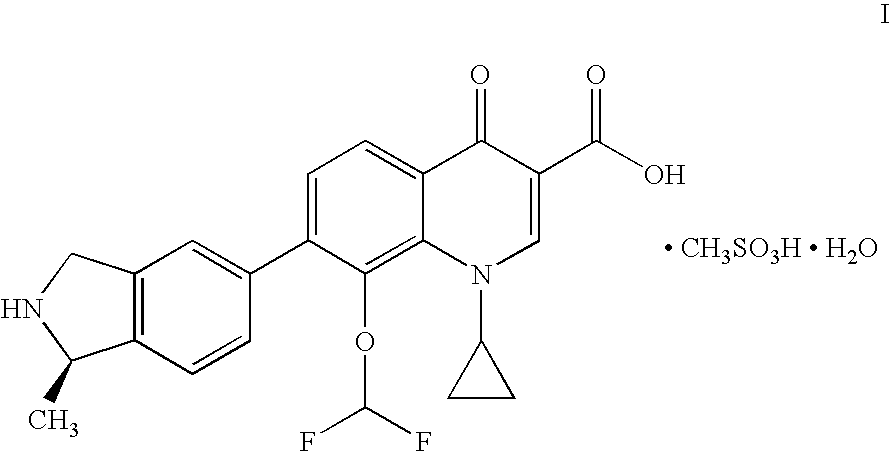
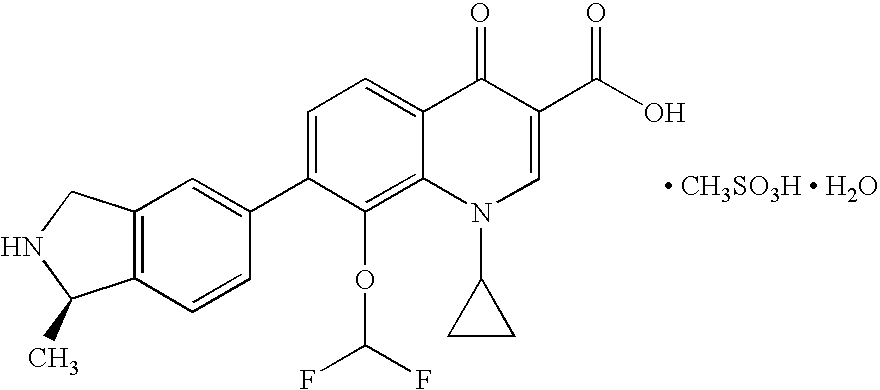
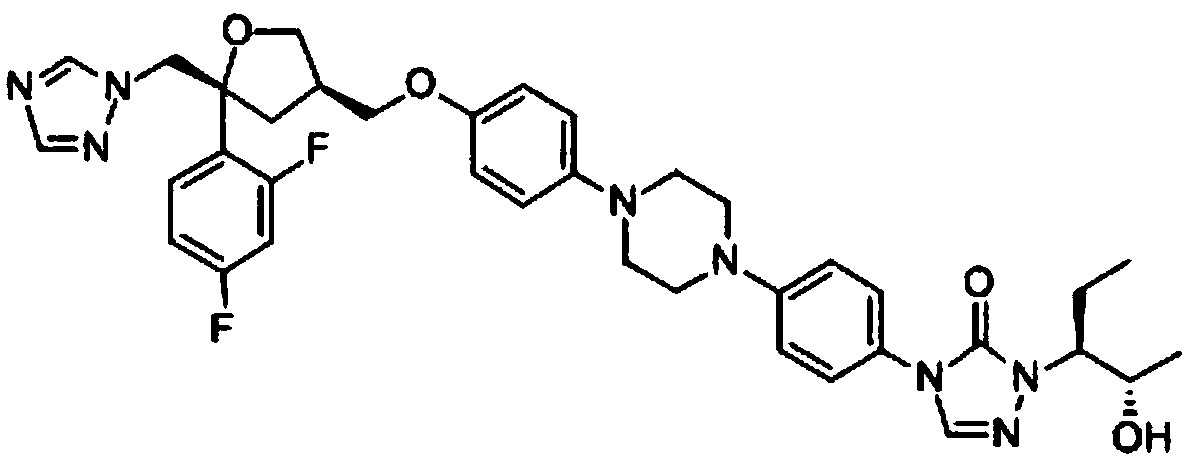
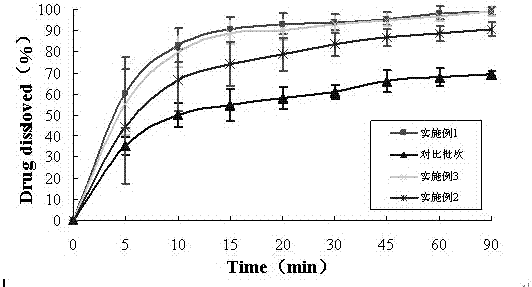
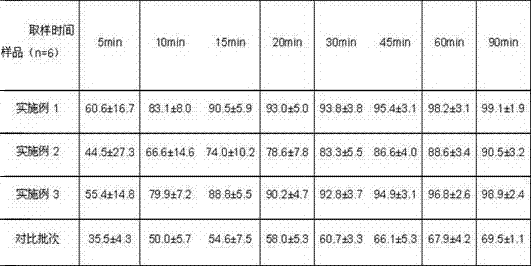
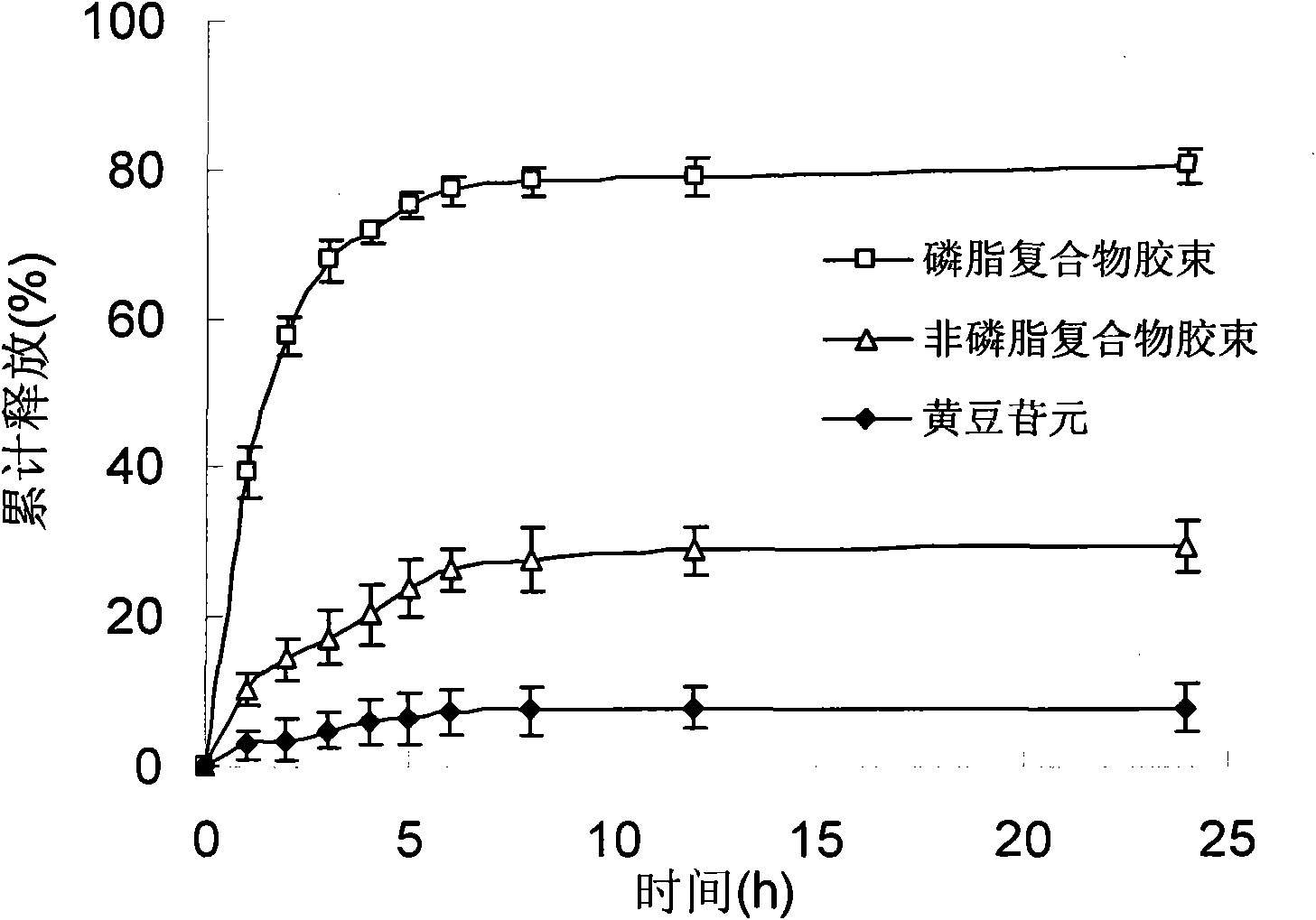
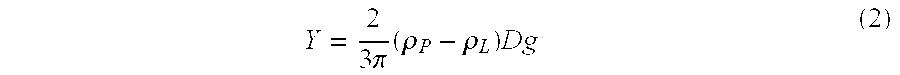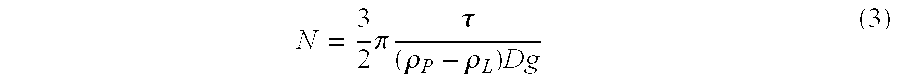Patents
Literature
59 results about "OralSuspension" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oral suspension formulation
An aqueous pharmaceutical suspension for oral administration of a drug, which suspension maintains its content uniformity for prolonged period.
Owner:UNILAB PHARMATECH
Oral suspension formulation
InactiveUS20030191192A1Grittiness decreaseImprove bioavailabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideOral suspensionsOral medication
An aqueous pharmaceutical suspension for oral administration of a drug, which suspension maintains its content uniformity for prolonged period.
Owner:UNILAB PHARMATECH
Injection containing burufen
InactiveCN101069681AReduce solubilitySlow absorptionOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticSolubilityIbuprofen Injection
The present invention provides an injection preparation containing ibuprofen and its preparation method. Said invention provides the concrete steps of its preparation method. Said ibuprofen injection preparation has high solubility and bioavailability, and its product quality is stable.
Owner:汪洪湖
Injection containing ketoprofen and preparation method thereof
The present invention provides one kind of injection containing ketoproten and its preparation process, and features that the injection contains ketoproten, alkaline assistant and stuffing in the molar ratio between ketoproten and alkaline assistant of 1 to 1, and the weight ratio between ketoproten and stuffing of 1 to 0-10. The injection containing ketoproten is superior to traditional orally taken ketoproten preparation, and has new administration way, high product quality, high bioavailability and fast acting.
Owner:汪洪湖
Palatable oral suspension and method
InactiveUS7175856B2Reduce and minimize solubilityReduces and masks bitter tasteAntibacterial agentsBiocideOral suspensionsSolubility
A drug formulation in the form of a dry powder is provided which when mixed with water forms a palatable oral suspension substantially free of bitter taste, the dry powder being formed of a drug, preferably des-quinolone, which in solution has a bitter taste, and a pH modifying agent which is preferably an alkaline material such as L-arginine, where upon mixing the dry-powder in water causes the drug to have reduced solubility or precipitate in-situ to form a palatable oral suspension essentially free of bitter taste.An oral suspension, methods for making same and a method for masking the bitter taste of drugs employing one or more pH modifying agents are also provided.
Owner:TOYAMA CHEM CO LTD
Oral azithromycin resin suspension and its preparing method
ActiveCN1985842AMask bitternessGreat tasteAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAzithromycinOrganic acid
The present invention discloses a kind of oral azithromycin resin suspension and its preparation process, and aims at making the suspension possess good taste. The oral azithromycin resin suspension consists of in each 100 ml azithromycin 0.25-4.0 g, ion exchange resin 0.5-8.0 g and water for the rest. Its preparation process includes the following steps: mixing azithromycin, inorganic acid and / or organic acid and pure water; adding ion exchange resin to obtain mixed liquid; preparing suspension medium with suspending agent, surfactant and pure water; adding metal ion complexing agent, preservative, corrective and colorizing agent; adding the mixed liquid. The present invention is superior to available technology in that the oral azithromycin resin suspension has the bitter of azithromycin masked by the ion exchange resin and thus good taste.
Owner:SINOPHARM ZHIJUN (SHENZHEN) PHARMA CO LTD
Oral suspension of prednisolone acetate
Owner:TARO PHARMA
Azithromycin dosage forms with reduced side effects
ActiveUS20050123627A1Reduce gastrointestinal side effectsAntibacterial agentsBiocideOral suspensionsGLYCERYL MONOBEHENATE
An oral dosage form comprising azithromycin and an effective amount of an alkalizing agent. Preferably, said oral dosage form comprises an effective amount of an alkalizing agent and an azithromycin multiparticulate wherein said multiparticulate comprises azithromycin, a mixture of glyceryl monobehenate, glyceryl dibehenate and glyceryl tribehenate, and a poloxamer. Typically, the oral dosage form includes any suitable oral dosing means such as a powder for oral suspension, a unit dose packet or sachet, a tablet or a capsule. Additionally disclosed is an oral suspension comprising azithromycin, an effective amount of an alkalizing agent and a vehicle. Preferably, the azithromycin is in multiparticulate form wherein said multiparticulate comprises azithromycin, a mixture of glyceryl monobehenate, glyceryl dibehenate and glyceryl tribehenate, and a poloxamer. Also disclosed is a method for reducing gastrointestinal side effects, associated with administering azithromycin to a mammal, comprising contiguously administering azithromycin and an effective amount of alkalizing agent to said mammal wherein the frequency of gastrointestinal side effects is lower than that experienced by administering an equal dose of azithromycin without said alkalizing agent. Further disclosed is a method of treating a bacterial or protozoal infection in a mammal in need thereof comprising contiguously administering to said mammal a single dose of an oral dosage form wherein said oral dosage form comprises azithromycin and an effective amount of an alkalizing agent. Additionally disclosed are azithromycin multiparticulates comprising azithromycin, a surfactant; and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:PFIZER INC
Dexibuprofen effervescent tablet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101077339AEasy to takeFast absorptionOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticEffervescent tabletFiller Excipient
The present invention provides one kind of effervescent dextro brufen tablet and its preparation process, and features that the effervescent dextro brufen tablet contains dextro brufen 1 weight portions, alkaline cosolvent 0-100 weight portions, acid disintegrant 1-8 weight portions, alkaline disintegrant 2-15 weight portions, stuffing 0-15 weight portions, adhesive 0.1-12 weight portions, corrective 0.01-0.5 weight portion, and lubricant 0.1-2 weight portions. Its preparation process includes the steps of mixing, pelletizing and tabletting. The effervescent dextro brufen tablet is superior to traditional orally taken dextro brufen preparation, can dissolve in water to form tasty solution, and has easy taking, high bioavailability, fast acting and other advantages.
Owner:汪洪湖
Cefixime oral administration mixed suspension and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101721363AGreat tasteFix stability issuesAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLiquid mediumDispersed media
Owner:SINOPHARM ZHIJUN (SHENZHEN) PHARMA CO LTD
Dexibuprofen granule and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101077343ATake fastEasy to takeOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticFiller ExcipientOralSuspension
The present invention discloses one kind of dextro brufen granule and its preparation process, and features that the dextro brufen granule contains dextro brufen 1 weight portions, alkaline cosolvent 0-100 weight portions, stuffing 0.1-100 weight portions, adhesive 0.1-12 weight portions, corrective 0.01-0.5 weight portion, and lubricant 0.1-2 weight portions. Its preparation process includes the steps of mixing, pelletizing and packing. The effervescent dextro brufen tablet is superior to traditional orally taken dextro brufen preparation, can dissolve in water to form tasty solution, and has easy taking, high bioavailability, fast acting and other advantages.
Owner:蚌埠丰原涂山制药有限公司
Oral lurasidone suspension and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104606133AQuality improvementGreat tasteOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderOral suspensionsPreservative
The invention discloses an oral lurasidone suspension and a preparation method thereof. The lurasidone suspension is a pharmaceutical composition which comprises lurasidone or salt thereof, a suspending aid, a wetting agent, a pH regulator, a preservative, a sweetening agent and a corrigent, wherein the particle size range of the lurasidone or salt thereof is 0.1-20 microns. The prepared oral suspension has the characteristics of being stable in quality and favorable in taste, facilitates dose distribution, and is beneficial to the acceptance of schizophrenia patients, simple in preparation method and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA HAINAN
Composition and preparation method and preparation thereof
InactiveCN110812365AImprove stabilityControlled release rateOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderOral suspensionsCaplet Dosage Form
The invention discloses a composition as well as a preparation method and a preparation thereof. The composition of the present invention includes nicotinamide mononucleotide, an ion exchange resin, acoating material, and a plasticizer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing the drug-loaded resin particles, and coating the drug-loaded resin particles. The coated drug-loaded resin particles are mixed with other auxiliary materials to prepare corresponding dosage forms, such as oral suspension, tablets, capsules, granules, cream, ointment, facial masks and the like. Thecomposition is simple in production process, easy to amplify and produce, capable of effectively improving the stability of nicotinamide mononucleotide, accurate in dosage, lasting in effect and stable in curative effect.
Owner:明特奇点医疗科技(北京)有限公司
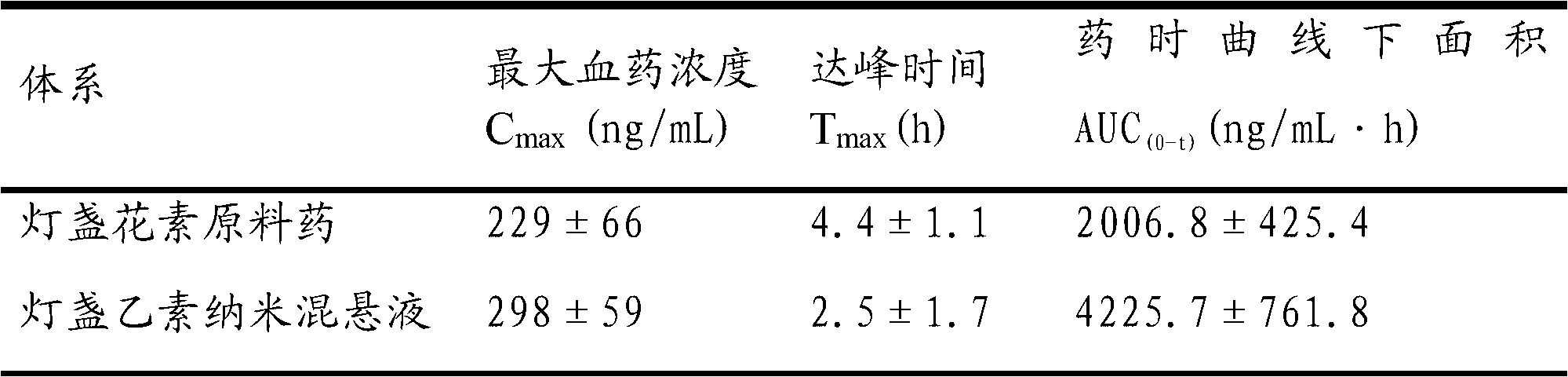
Scutellarin nanosuspension and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103006556AImprove solubilityImprove oral bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryOral suspensionsSolubility
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical preparations, and relates to a scutellarin nanosuspension and a preparation method thereof. The scutellarin nanosuspension is prepared from a stabilizer and scutellarin in a weight ratio of (1:1)-(10:1). The preparation method is implemented through dissolving the scutellarin into an alkaline solution and then adding the obtained mixture into an acid solution containing the stabilizer, so that due to the solubility difference of the scutellarin in the acid solution and the alkaline solution, the scutellarin is oversaturated and then crystallized by separating; and carrying out homogenization on the obtained product by using a high-pressure micro jet homogenizer so as to obtain the scutellarin nanosuspension, wherein the particle size of the scutellarin nanosuspension is 100-500 nm, and the polydispersity index is 0.1-0.5. The scutellarin nanosuspension and preparation method thereof disclosed by the invention have the significant advantages that the nanosuspension improves the solubility of the scutellarin and increases the oral bioavailability of the scutellarin; the scutellarin nanosuspension can be solidified through freeze drying or spray drying, and applied to dosage forms such as tablets, capsules, granules, oral suspensions and the like; and the scutellarin nanosuspension is simple in preparation process, and convenient for industrial production.
Owner:MACAU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ibuprofen oral suspension and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101991531AGuaranteed accuracyWon't settleOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticIbuprofen Oral SuspensionCellulose
The invention provides an ibuprofen oral suspension comprising the following ingredients based on the concentration: ibuprofen of 20 to 40 g / L and dispersion cellulose of 13 to 30 g / L. The preparation method of ibuprofen oral suspension comprises the following steps: (1) heating glycerine, adding a preservative; (2) adding the dispersion cellulose into water, then dispersing uniformly; (3) mixing pure water with a wetting agent; (4) thoroughly mixing a sweetener, a flavouring agent and the preservative solution which is prepared in the first step with the suspension system which is obtained in the second step; (5) mixing a micronized ibuprofen with the dispersion solution which is obtained in the third step uniformly, then adding the mixture obtained therein into the mixture obtained in the fourth step, and then stirring at high speed and simultaneously infusing nitrogen to obtain an ibuprofen oral suspension. The ibuprofen oral suspension provided by the invention is a thixotropic colloid comprising ibuprofen particles which are arranged evenly, and is characterized in that the ibuprofen oral suspension can be changed to a low-viscosity liquid by shaking before taking, the problem of common suspension which has high viscosity and agglomeration after placing for a long time is improved, the accuracy of dosage is ensured and the stability of the ibuprofen oral suspension is good.
Owner:武汉人福药业有限责任公司
Avian decoquinate oral suspension and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102008435AOvercome the shortcomings of uneven mixing and insufficient absorptionEasy to useSolution deliveryAntiparasitic agentsOral suspensionsOrganic solvent
The invention relates to an avian decoquinate oral suspension and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of veterinary drug preparations. The avian decoquinate oral suspension comprises the following components per 100ml: 5-15g of decoquinate, 0.5-10g of surfactant, 0.1-2g of binding agent, 0.1-2g of stabilizer and 100ml of volume-metered solvent. The avian decoquinate oral suspension overcomes the defects of nonuniform stirring of premixed preparation and insufficient absorption, and can be clinically used only by dilution so that the use method is simple and convenient; and in addition, the organic solvent of the avian decoquinate oral suspension is low in content, the cost of unit preparation is effectively reduced, and the problems of high preparation cost and difficult popularization and application of the traditional preparation are solved.
Owner:QILU ANIMAL HEALTH PROD
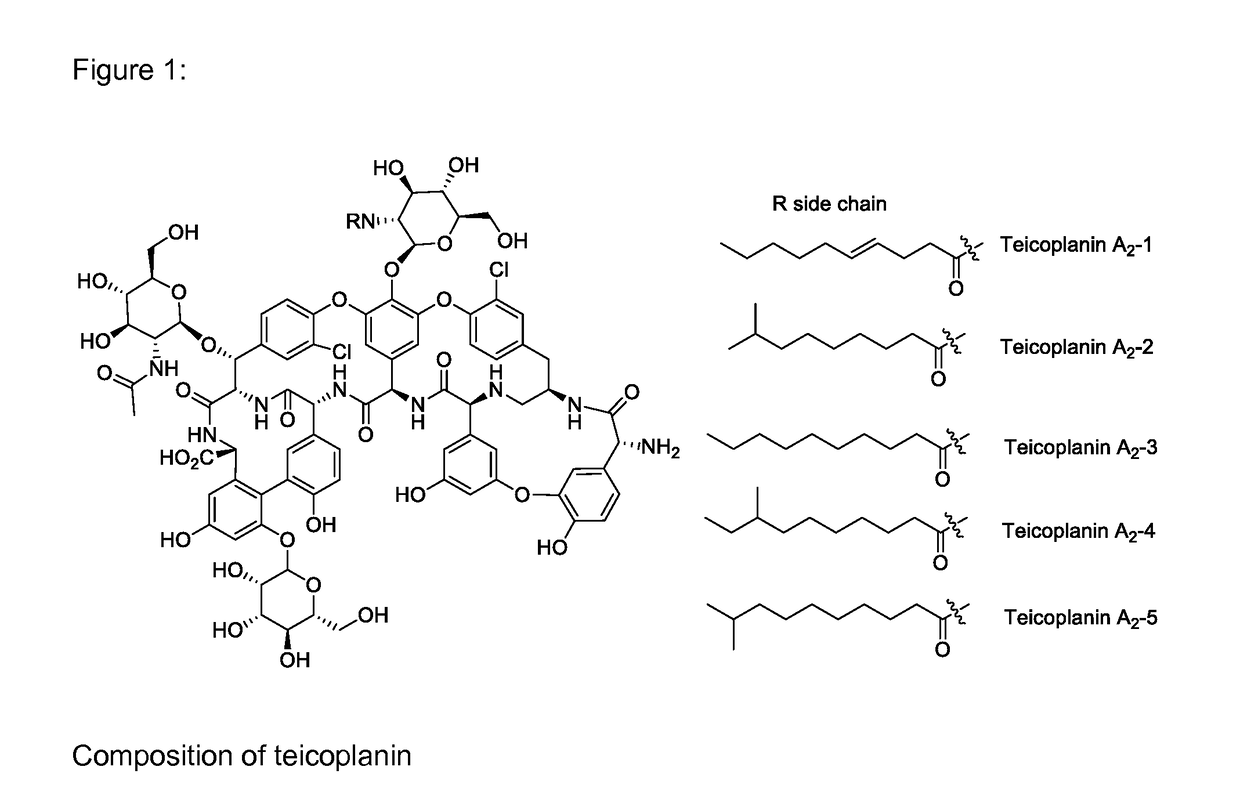
Methods for producing an oralsuspension of teichoplanin or teichoplanin analogs
InactiveUS20170065671A1Great tasteImprove stabilityPowder deliveryDispersion deliveryOralSuspensionChemistry
A stable suspension of teicoplanin and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable additives and method for preparation wherein the teicoplanin is mixed with an aqueous or non aqueous suspension base and pharmaceutically acceptable additives and wherein the teicoplanin is milled to obtain a homogeneously dispersed suspension.
Owner:MAHER ILLYA KEITH
Oral suspension comprising telmisartan
ActiveUS20140364473A1Improve subjective overall impressionIncrease contact timeOrganic active ingredientsBiocideOral suspensionsAlcohol sugars
A pharmaceutical solution with a pH value of 10 or higher contains an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, where one or more sugar alcohols are present up to a total concentration of 40 wt. % to 70 wt. %.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Stable non-dihydrate azithromycin oral suspensions
InactiveCN1822858ALow viscosityHigh viscosityOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsOral suspensionsOralSuspension
This invention relates to a powder for oral suspension, and an oral suspension made there from, which comprises non-dihydrate azithromycin and an azithromycin conversion stabilizing excipient, wherein said excipient reduces the conversion of the form of azithromycin, when placed in suspension, to another form of azithromycin. This invention further relates to a method for reducing the conversion of a form of non-dihydrate azithromycin, in an oral suspension, by adding a surface tension reducing excipient that reduces the surface tension of the aqueous vehicle. Furthermore, this invention relates to a method for reducing the conversion of a non-dihydrate azithromycin, in an unflavored oral suspension, by raising the viscosity of the oral suspension, and in a flavored oral suspension by lowering the viscosity of the oral suspension.
Owner:PFIZER PRODS ETAT DE CONNECTICUT
Eltrombopag oral suspension and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109893503AGood physical and chemical stabilitySedimentation volume ratio is highOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryOral suspensionsCarboxymethyl cellulose
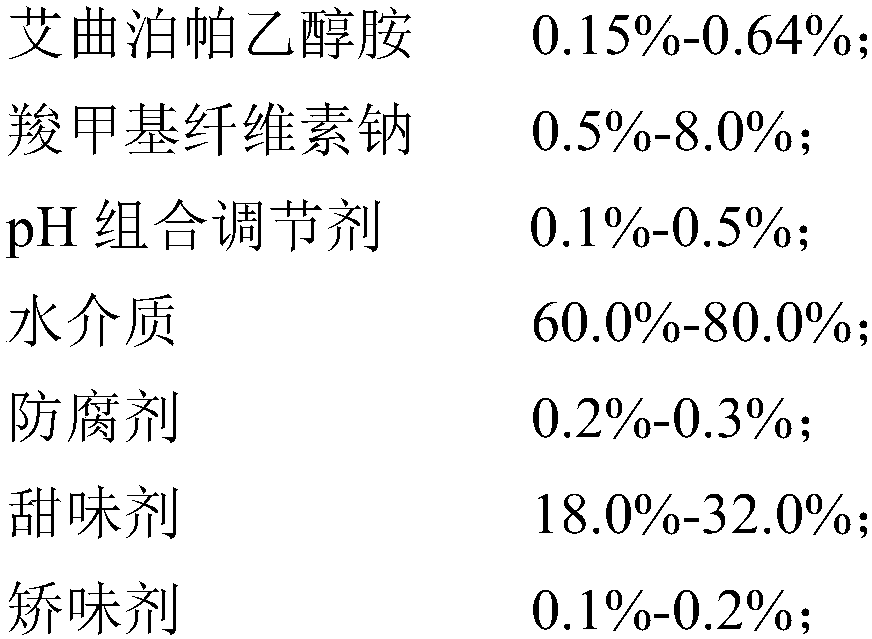
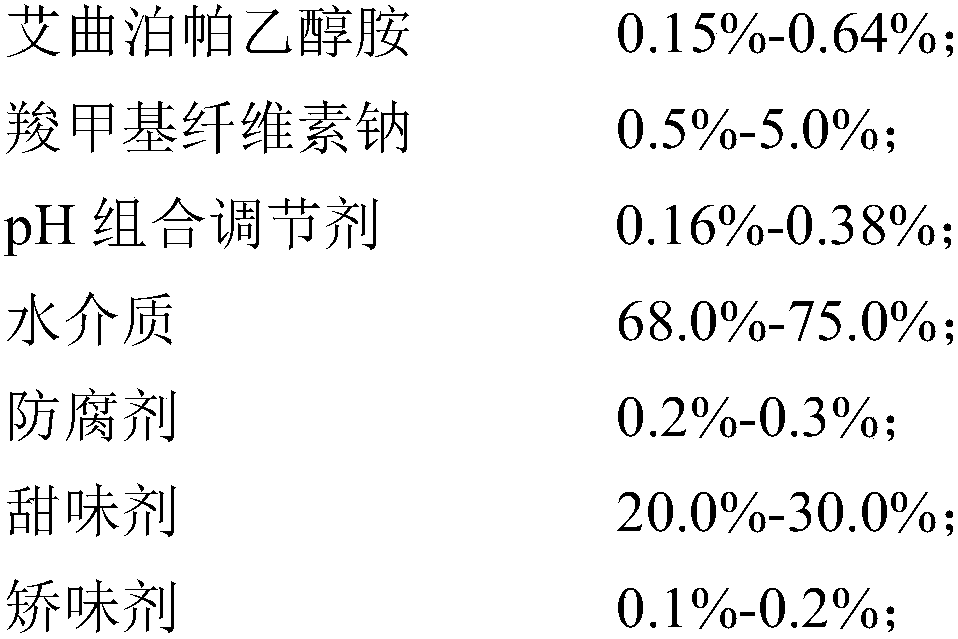
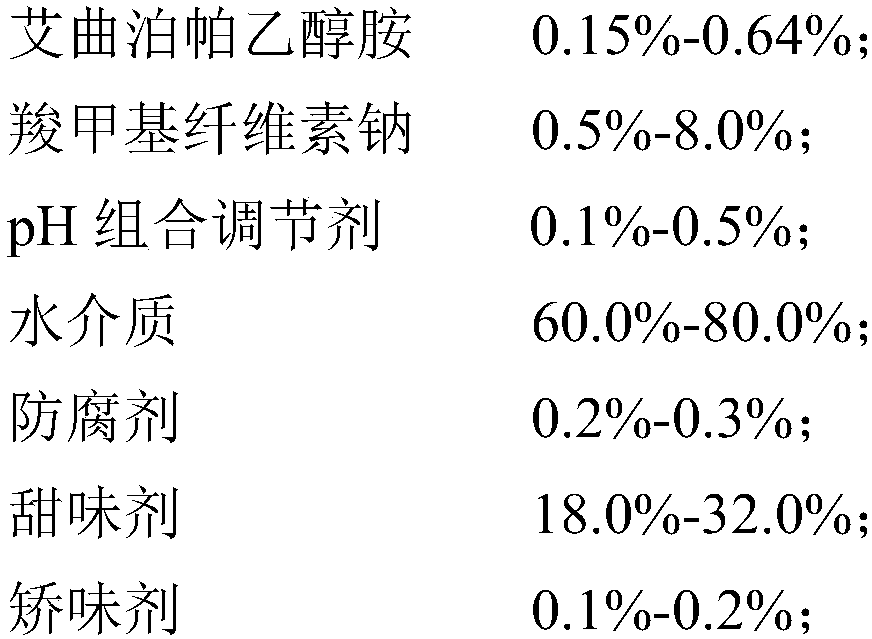
The invention discloses an eltrombopag oral suspension. The eltrombopag oral suspension is prepared from the following components: 0.15%-0.64% of eltrombopag ethanolamine, 0.5%-8.0% of carboxymethyl cellulose, 0.1%-0.5% of a PH combination regulator, 60.0%-80.0% of an aqueous medium, 0.2%-0.3% of a preservative, 18.0%-32.0% of a sweetening agent and 0.1%-0.2% of a corrigent. The eltrombopag oral suspension overcomes the defects of low solubility, difficulty in dissolution, multiple specifications and complex production process of eltrombopag, and a new dosage form selection is provided; and apreparation method of the eltrombopag oral suspension is simple and feasible and has reproducibility, and the eltrombopag oral suspension with the quality meeting the requirements can be consistentlyproduced.
Owner:WUHAN WUYAO SCI & TECH
Stable non-dihydrate azithromycin oral suspensions
This invention relates to a powder for oral suspension, and an oral suspension made there from, which comprises non-dihydrate azithromycin and an azithromycin conversion stabilizing excipient, wherein said excipient reduces the conversion of the form of azithromycin, when placed in suspension, to another form of azithromycin.This invention further relates to a method for reducing the conversion of a form of non-dihydrate azithromycin, in an oral suspension, by including at least one cyclodextrin in said oral suspension.
Owner:JOHNSON BARBARA A +1
Posaconazole orally taken suspension and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107625729AThe process steps are simpleShort process timeOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsSolventChemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and specifically relates to a posaconazole orally taken suspension and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is used for preparing a posaconazole orally taken suspension compound on the basis of a micro-crystallizing technology. The posaconazole orally taken suspension compound comprises the following components in parts by weight: 30-50 parts of posaconazole, 160-402 parts of additives, solvent and aqueous medium, wherein the solvent is one or more of glycerinum, ethanol in volume percentage of 95%, absolute ethyl alcohol, propylene glycol and polyethylene glycol 100 / 400. According to the invention, the posaconazole orally taken suspension is prepared through the micro-crystallizing technology; according to the method, the solubility difference of the drug in different solvents is utilized to quickly and uniformly separate out the main drug particles under low-temperature and strong stirring conditions, the grainsize of the main drug particles is small and the distribution is concentrated; and the required grain size is further achieved by adopting the micro-crystallizing technology, the processing steps aresimple, the processing time is shorter, the process is convenient and quick, no high-temperature operation exists in the whole process, the active ingredients are free from decomposing risk, the product impurities are few and the quality is effectively guaranteed.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAPONT PHARMA
A perampanel dry suspension and a preparing method thereof
InactiveCN107536805AImprove solubilityImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryOral suspensionsSolubility
The invention relates to a perampanel dry suspension and a preparing method thereof. According to the perampanel dry suspension, a medicine active component that is perampanel and a carrier matrix areprepared into a perampanel solid dispersion. The perampanel dry suspension is prepared from 0.2-1% of perampanel, 20-40% of the carrier matrix, 60-80% of a filler, 0.2-2% of a suspending aid, 0.1-1%of a glidant, 0.2-2% of a corrective and 0.1-1% of an opacifying agent, wherein the perampanel and the carrier matrix are prepared into the perampanel solid dispersion firstly and then the solid dispersion is mixed with other auxiliary materials. The perampanel solid dispersion is prepared by utilizing a solid dispersion technique, and is further prepared into the perampanel dry suspension, thus achieving the objective of increasing solubility and bioavailability of the perampanel. In addition, the dry suspension can overcome problems that administration of tablets is difficult, and oral suspensions are inconvenient to carry and trouble in administration, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG POLY PHARMA +1
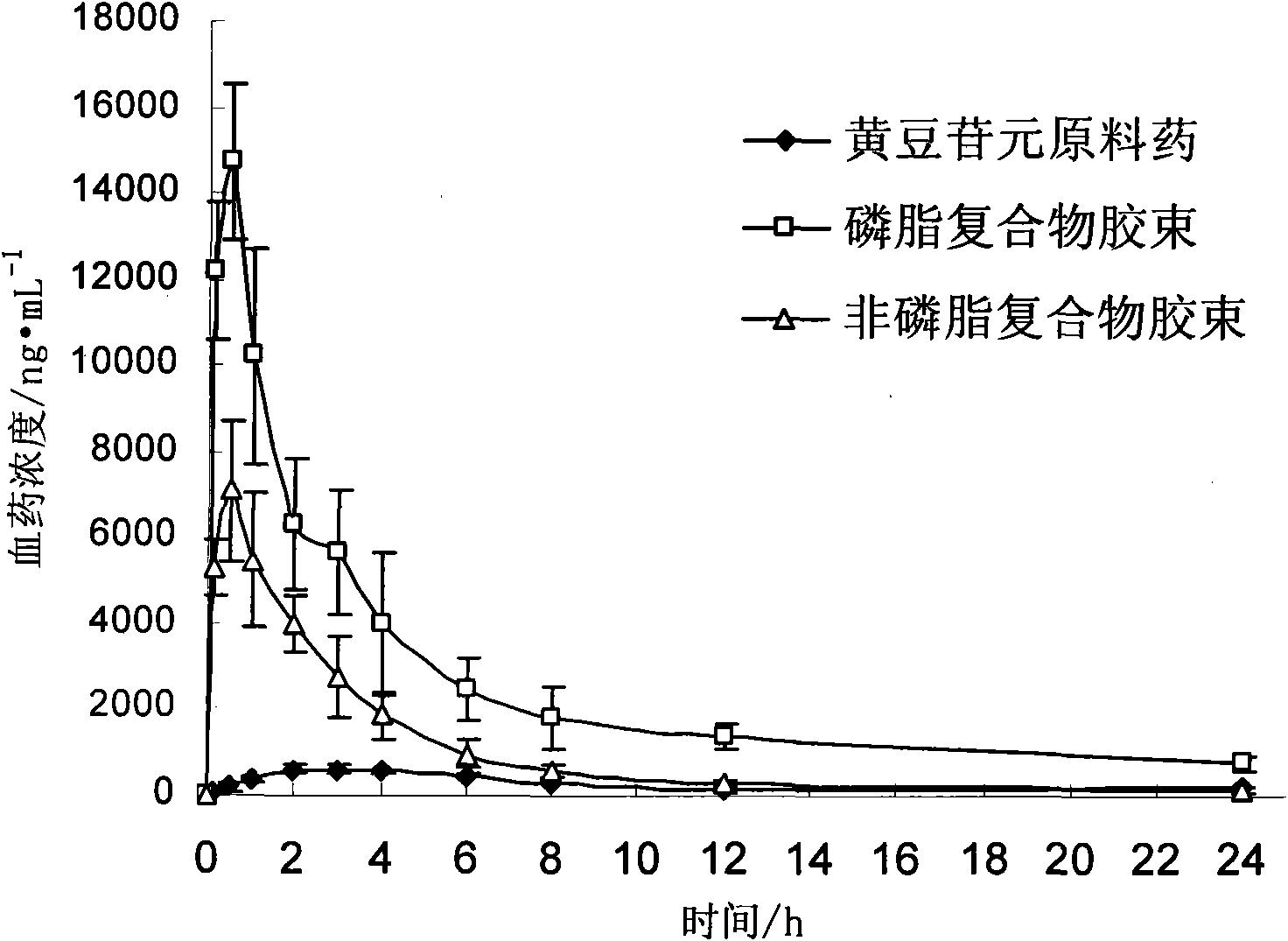
Daidzein micelles and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102058528AImprove bioavailabilityIncrease route of administrationOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryFreeze-dryingDaidzein
The invention relates to daidzein micelles and a preparation method thereof. The daidzein micelles contain 1 part of daidzein, 12 to 30 parts of phospholipid and 1 to 25 parts of additive. The preparation method comprises: preparing a daidzein and phospholipid composite, namely, adding daidzein and 50 to 95 percent of phospholipid into an organic solvent, heating the solution to 40 to 60 DEG C, refluxing under reduced pressure, keeping temperature and stirring for 2 to 10 hours, recovering the organic solvent, drying and crushing to obtain the daidzein and phospholipid composite; and preparing daidzein micelles from the phospholipid composite, namely, dissolving the daidzein and phospholipid composite, the rest phospholipid and the additive in an organic solvent, subjecting the solution to rotary evaporation to form a film, and hydrating at 40 to 60 DEG C to obtain daidzein micelle suspension with opalescence. The average particle size of the daidzein micelles is less than 50 nanometers. The daidzein micelles can be further prepared into oral or injection preparations including capsules, oral mixed suspension, oral liquid, injection, injection freeze-dried powder injection.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
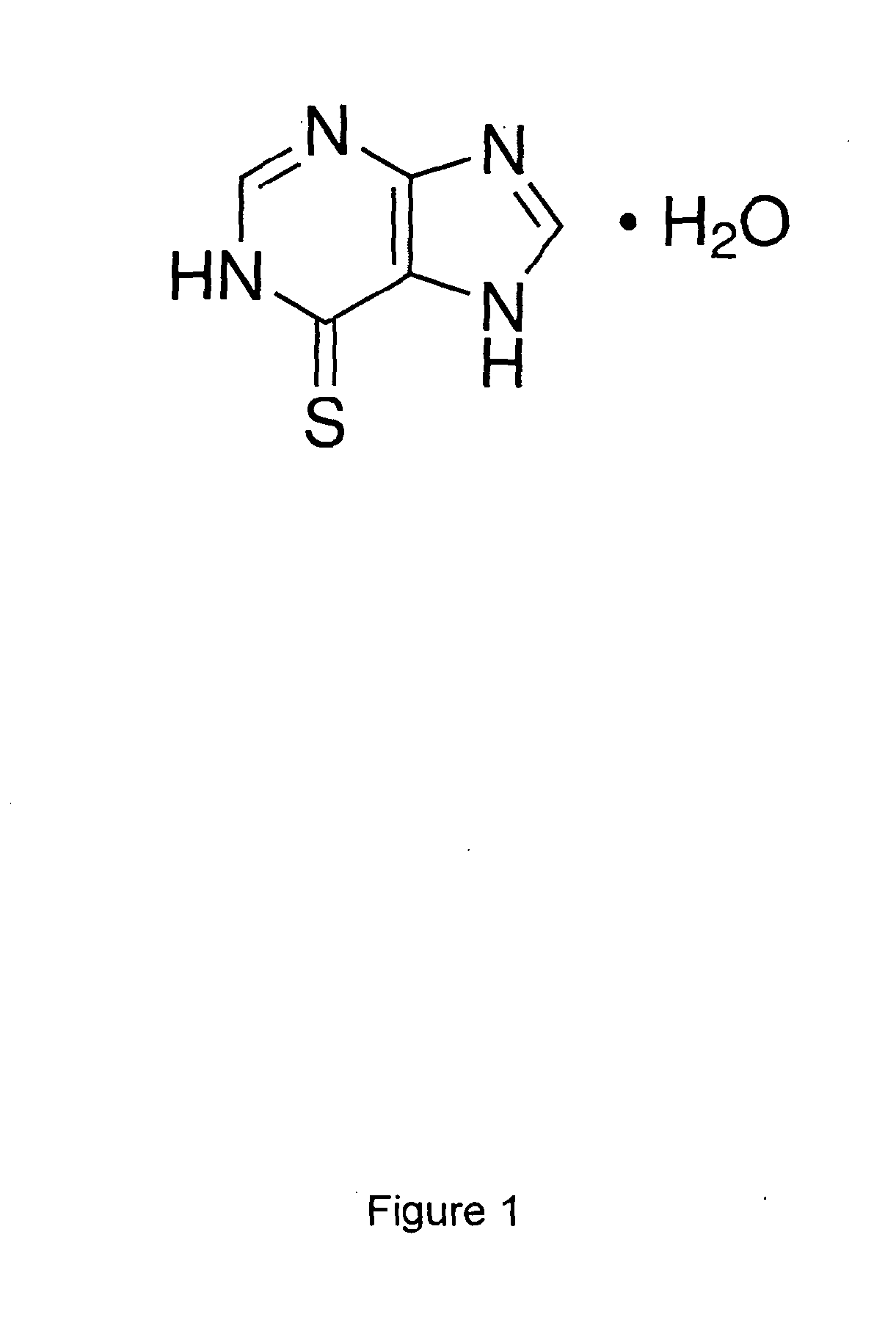
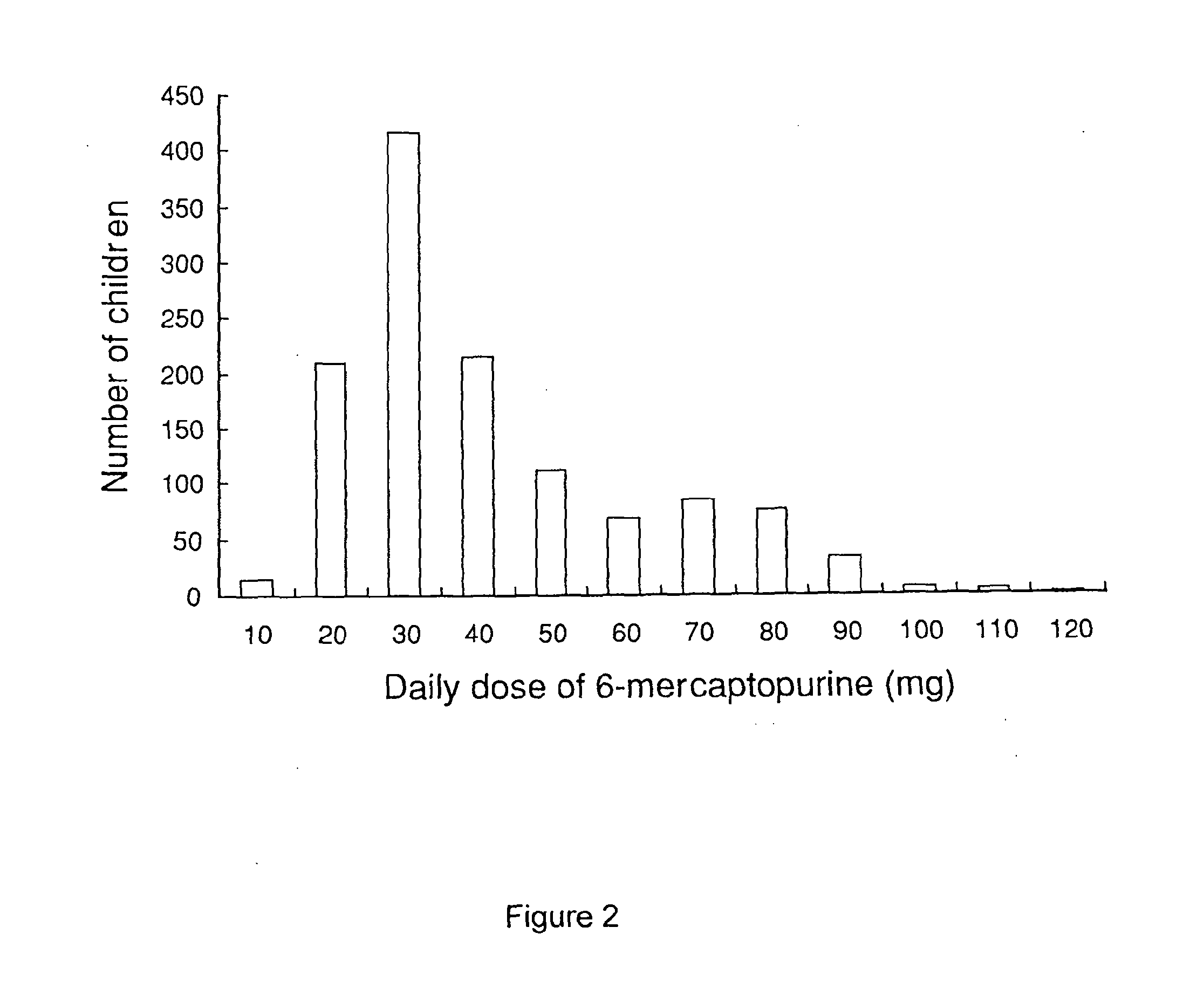
Oral Suspension
InactiveUS20140294972A1Accurate measurementImprove accuracyPowder deliveryBiocideOral suspensionsIntrathecal
A liquid pharmaceutical composition for use in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) comprising 6-mercaptopurine or a salt, hydrate or solvate thereof and a pharmaceutically-acceptable excipient, wherein the composition is a suspension for oral administration, a kit of parts for the accurate dosing and administration of the liquid pharmaceutical composition, and a method for the treatment of ALL in a human patient comprising administration of a therapeutically effective amount of the liquid pharmaceutical composition.
Owner:NOVA BIO PHARMA TECH LTD
Active carbon oral suspension liquid, preparing method and its use
InactiveCN1943595APromote absorptionReduce absorptionCarbon active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsOral suspensionsGlycerol
The invention provides an active carbon oral suspension for absorbing poison being through oral poisoning and preparation thereof, and said suspension comprising active carbon powder 15%-25%(w / v), glycerine 60%-80%(v / v) and right amount of water , its relative density is 1.15-1.25, pH value is 4.5-6.5,settling volume ratio is no lower than 0.90. Active carbon oral suspension described hereinabove can also be added propylene 2%-5%(v / v). Also can adding sucrose 5%-10%(w / v)and citric acid 0.2%-1% (w / v). Additionally said invention relates to application of said oral suspension in absorbing poison being through oral poisoning.
Owner:北京云威科技有限公司
Riluzole sustained-release oral-administration suspension
InactiveCN111437256AStable blood concentrationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSuspending AgentsDrug administration
The invention belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical preparations and discloses a Riluzole sustained-release oral-administration suspension. The Riluzole sustained-release oral-administration suspension is used for simultaneously solving problems in smooth release of drugs and compliance of drug administration of people suffering from dysphagia such as the elderly and children. The disclosed sustained-release suspension is prepared through dispersing Riluzole sustained-release microspheres in a solution containing a diluent, a flavoring agent, a suspending agent, a preservative and apH buffering agent, wherein the Riluzole sustained-release microspheres are prepared through dissolving Riluzole in an aqueous dispersion of ethyl cellulose and carrying out spray drying. Compared with common tablets, capsules and oral-administration suspensions on the market at present, the Riluzole sustained-release oral-administration suspension disclosed by the invention has the advantages that drug release is smooth, the number of times of drug administration is reduced, the quality is stable, the mouth feel is good, the compliance of drug administration is high, and the Riluzole sustained-release oral-administration suspension is applicable to the people suffering from the dysphagia such as the elderly and the children.
Owner:BEIJING VENTUREPHARM BIOTECH
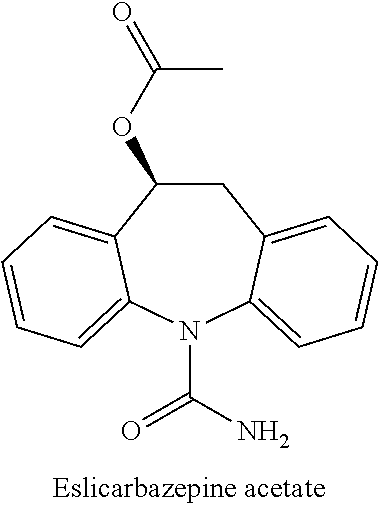
Oral Suspension Formulations of Esclicarbazepine Acetate
InactiveUS20130040939A1Minimize formationLimited chemical stabilityBiocideNervous disorderOral suspensionsOralSuspension
Owner:BIAL PORTELA & CA SA
Low-dose non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug composition and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses a low-dose non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug composition and a preparation process thereof, belonging to the technical field of drugs. The drug composition contains low-dose non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other auxiliary materials which are suitable for the drug composition and include oral suspensions, granules, tablets and capsules. Submicron diclofenac is obtained by taking diclofenac as a model drug and adopting the high pressure homogenization technology, thus increasing in vitro dissolution and improving the bioavailability. The drugs are used at the lowest effective dose so that the duration of the drugs in vivo is the shortest, thus reducing the risk of severe cardiovascular events and gastrointestinal problems accompanying high-dose non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and improving the compliance of patients.
Owner:苏州朗易生物医药研究有限公司
Dexibuprofen granule and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101077343BTake fastEasy to takeOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticFiller ExcipientOralSuspension
The present invention discloses one kind of dextro brufen granule and its preparation process, and features that the dextro brufen granule contains dextro brufen 1 weight portions, alkaline cosolvent 0-100 weight portions, stuffing 0.1-100 weight portions, adhesive 0.1-12 weight portions, corrective 0.01-0.5 weight portion, and lubricant 0.1-2 weight portions. Its preparation process includes thesteps of mixing, pelletizing and packing. The effervescent dextro brufen tablet is superior to traditional orally taken dextro brufen preparation, can dissolve in water to form tasty solution, and has easy taking, high bioavailability, fast acting and other advantages.
Owner:蚌埠丰原涂山制药有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com