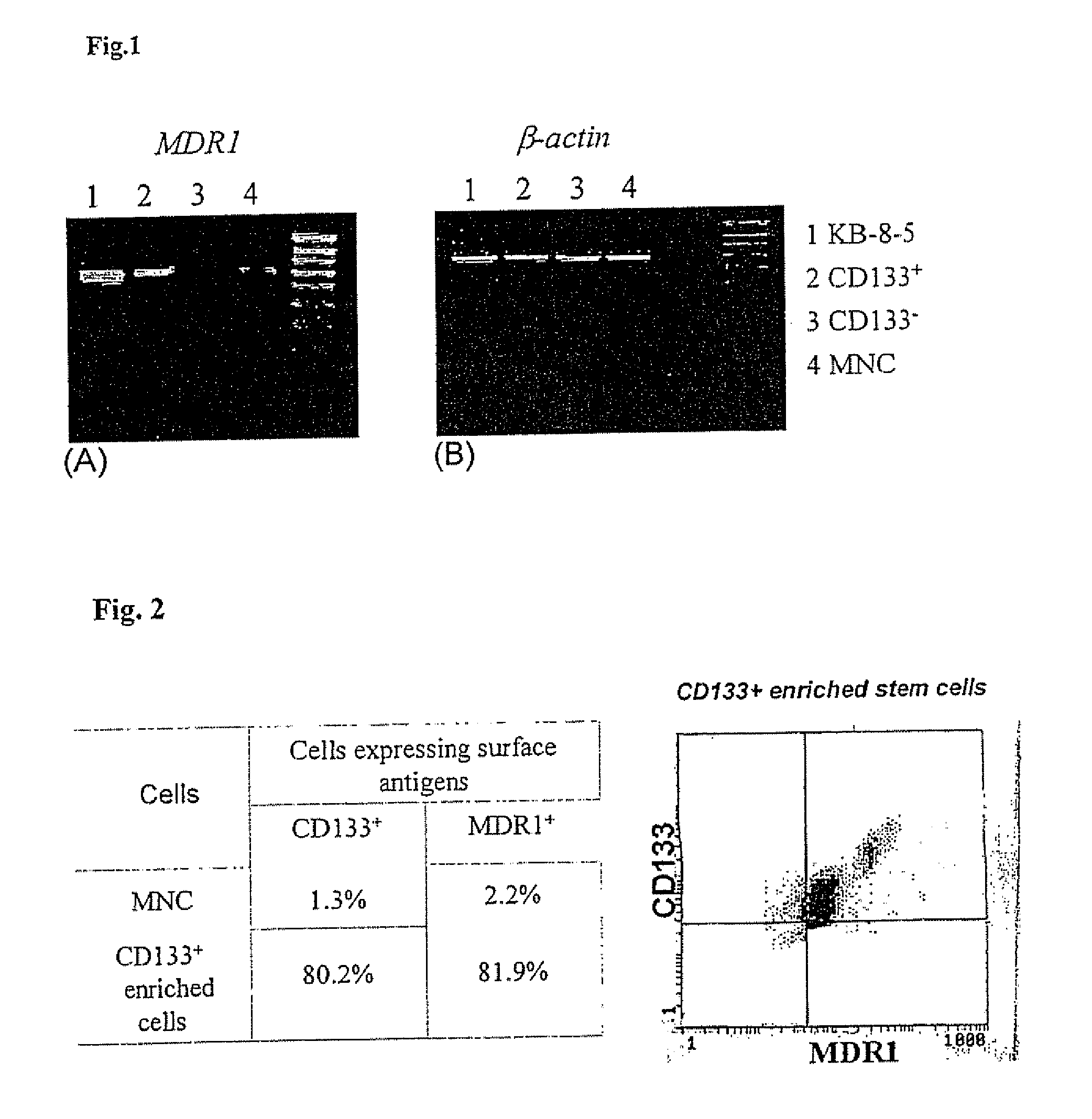
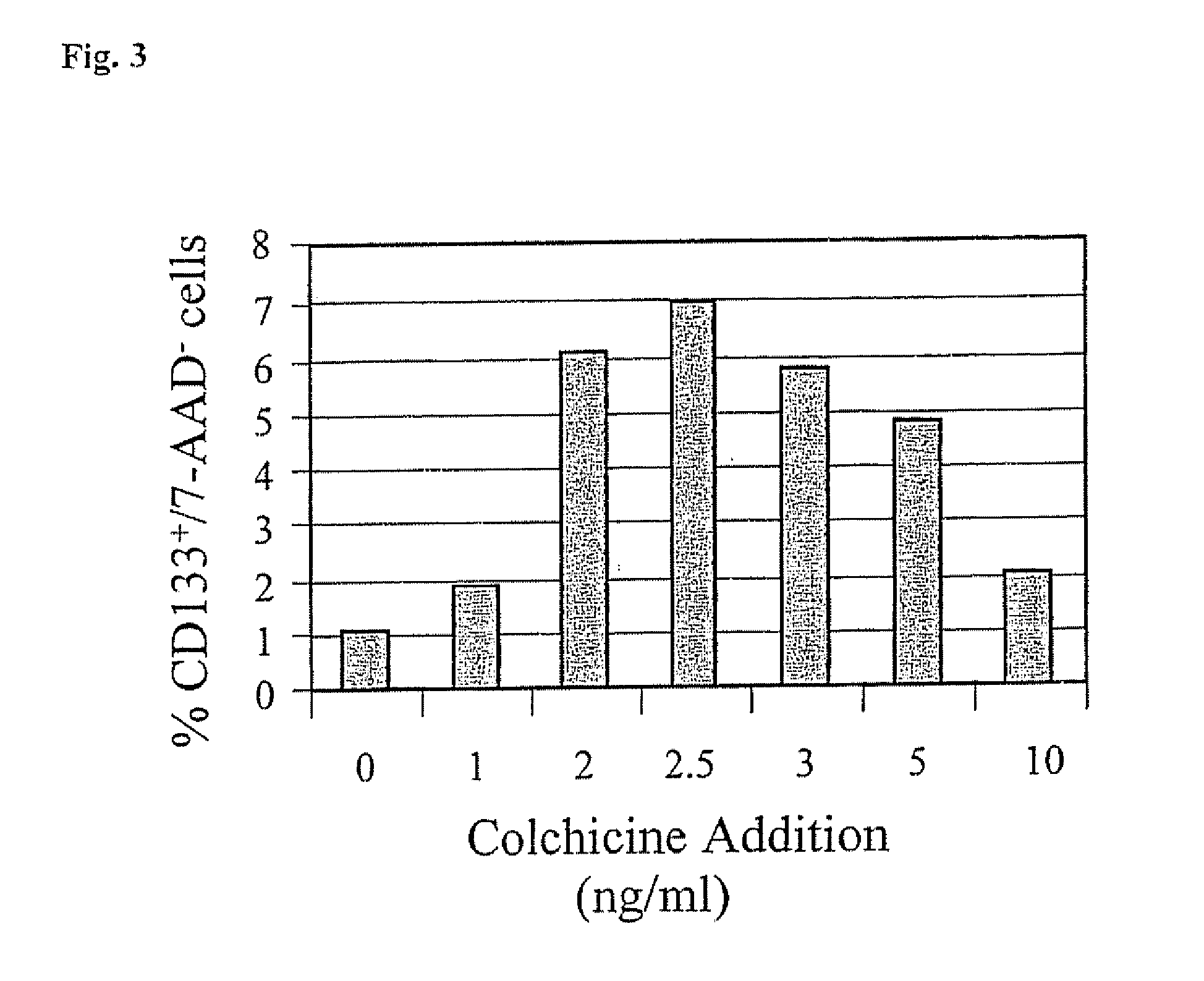
Patents
Literature
197 results about "Transporter gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gene, transporter: A gene that allows drugs to enter cells or, in some cases, acts to keep them out. Transporter genes may account for discrepancies in the way drugs such as antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and chemotherapy agents work in different people.
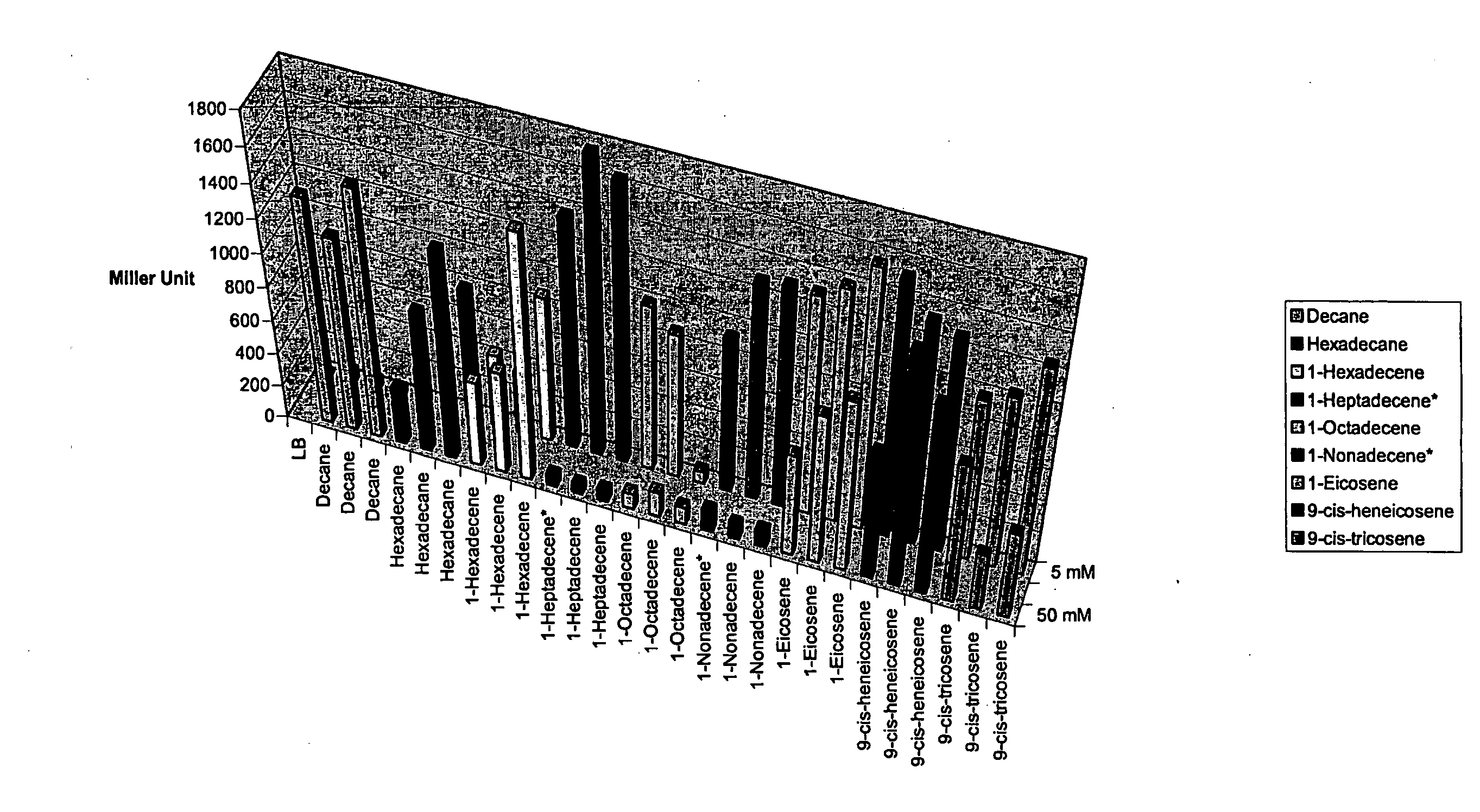
Methods and Compositions for Identification of Hydrocarbon Response, Transport and Biosynthesis Genes
InactiveUS20080293060A1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiosynthetic genesResponse element
Disclosed is a method using an alkane response element (ARE) from, e.g., Acinetobacter spp. to (i) identify and clone hydrocarbon biosynthesis genes, (ii) identify and clone hydrocarbon transporter genes (iii) identify and clone hydrocarbon response genes. Screening cells were developed that expressed a transcriptional activator, e.g., alkR, and included a reporter gene, e.g., GFP operatively linked to an ARE promoter, e.g., the alkM promoter. The cells were transformed with libraries from organisms capable of hydrocarbon biosynthesis. Transformed cells that expressed the reporter gene harbored library-derived genes involved in one or more of the above-mentioned processes; and these genes were isolated from the cells using standard molecular biology techniques. Additional systems were designed wherein screening cells also expressed a gene identified in the original screen, e.g., an additional hydrocarbon pathway gene, e.g., an enhancer.
Owner:LS9 INC +1
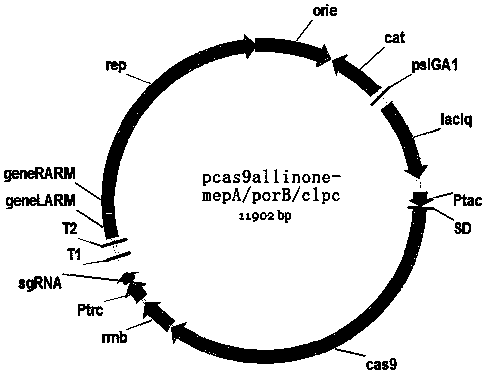
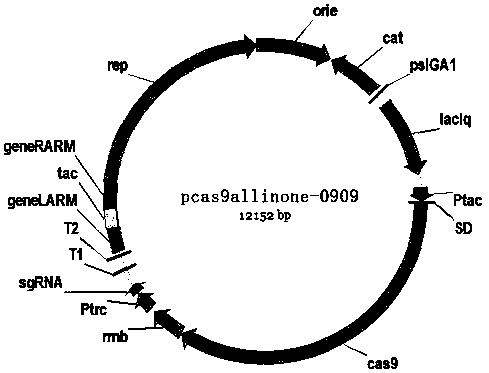
Caco-2 cell model for CRISPR/CAS9-mediated drug transporter targeted knockout and method thereof
The invention discloses a caco-2 cell model for CRISPR / CAS9-mediated drug transporter targeted knockout and a method thereof. The method is used for non-diagnostic or therapeutic purposes and comprises the following steps: designing sgRNA with target specificity for P-gp, BCRP and MRP2 transporters and constructing a sgRNA expression vector, wherein a sequence of the designed sgRNA is shown as SEQID NO. 1-6 in a sequence table; respectively designing P-gp, BCRP and MRP gene single knockout and pairwise combination double knockout by utilizing CRISPR / CAS9, co-transfecting a caco-2 cell with anhCas9 plasmid and performing monoclonal expansion culture to obtain the caco-2 cell model for transporter gene targeting. The caco-2 cell model obtained by the method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the mutual interference among different transporters is effectively eliminated, and a more specific and more sensitive cell model is provided for drug transport research.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
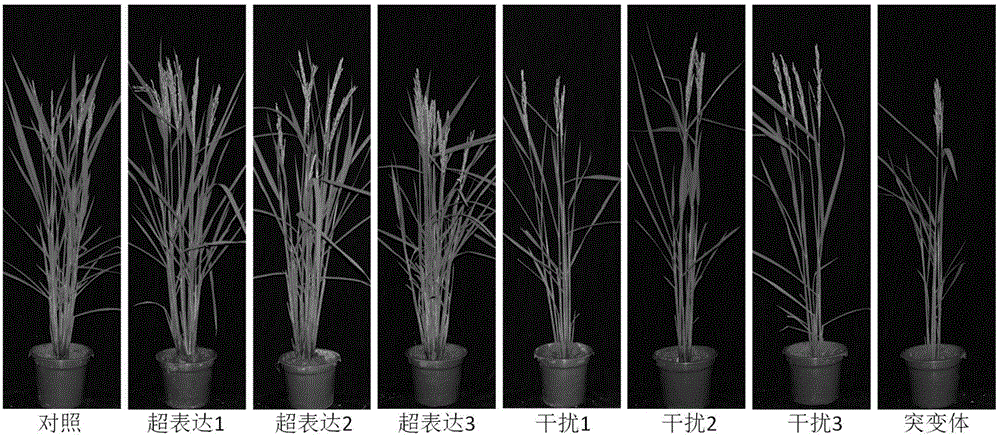
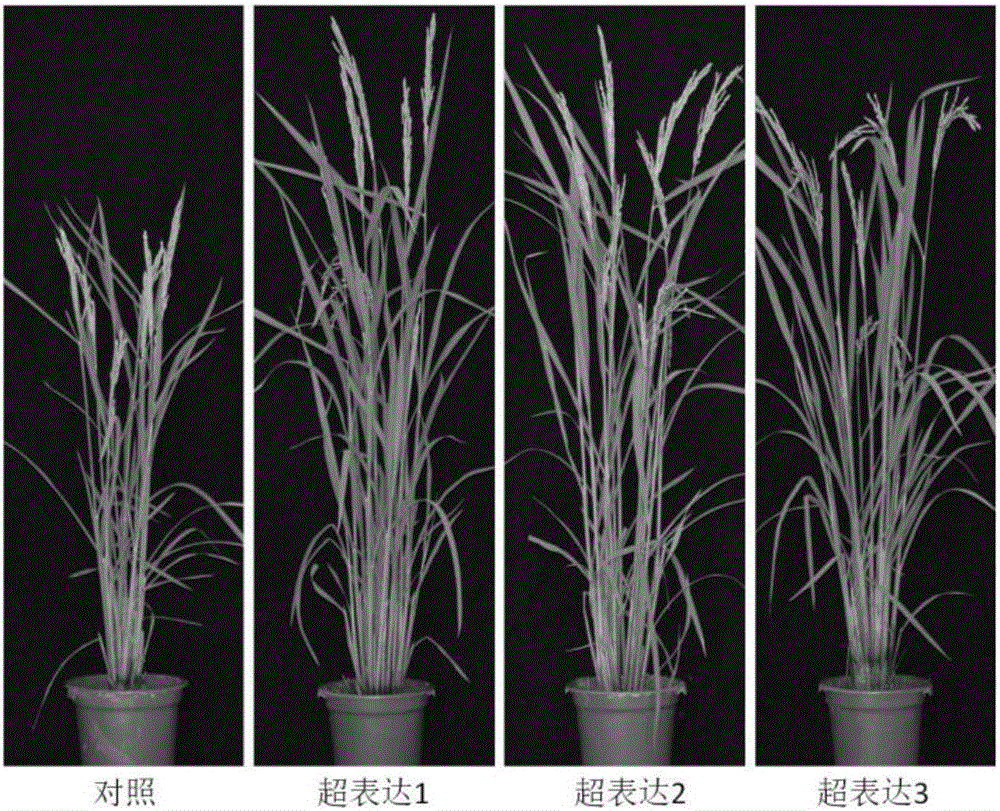
Gene OsPTR10 for improving nitrogen utilization efficiency and yield of rice and applications of gene OsPTR10
ActiveCN106119262AImprove utilization efficiencyIncrease the number of tillersMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesPlant genetic engineeringMutant
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering, and provides a rice nitrogen transporter gene OsPTR10, wherein the protein sequence of the rice nitrogen transporter gene OsPTR10 is shown as SEQ ID No.1, and the cDNA sequence of the rice nitrogen transporter gene OsPTR10 is shown as SEQ ID No.2. According to the rice nitrogen transporter gene OsPTR10, through the excessive expression of the OsPTR10 gene, the normal efficiency in absorbing nitrogenous fertilizer of the rice is improved, the content of soluble protein of plants is increased, further, the tiller number is increased, the ear length and filling grain number are increased, and finally, the yield is improved; through the RNAi technology, the expression quantity of the OsPTR 10 gene is reduced, and the functions of the gene are verified in the OsPTR10 target gene mutant. The gene has the significant application values on the aspects of the statement on the influences of the nitrogen element on the growth and development of the plants and on the aspects of the efficient utilization for the nitrogen fertilizer of the rice and the improvement on the yield of the rice.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF BIOENG
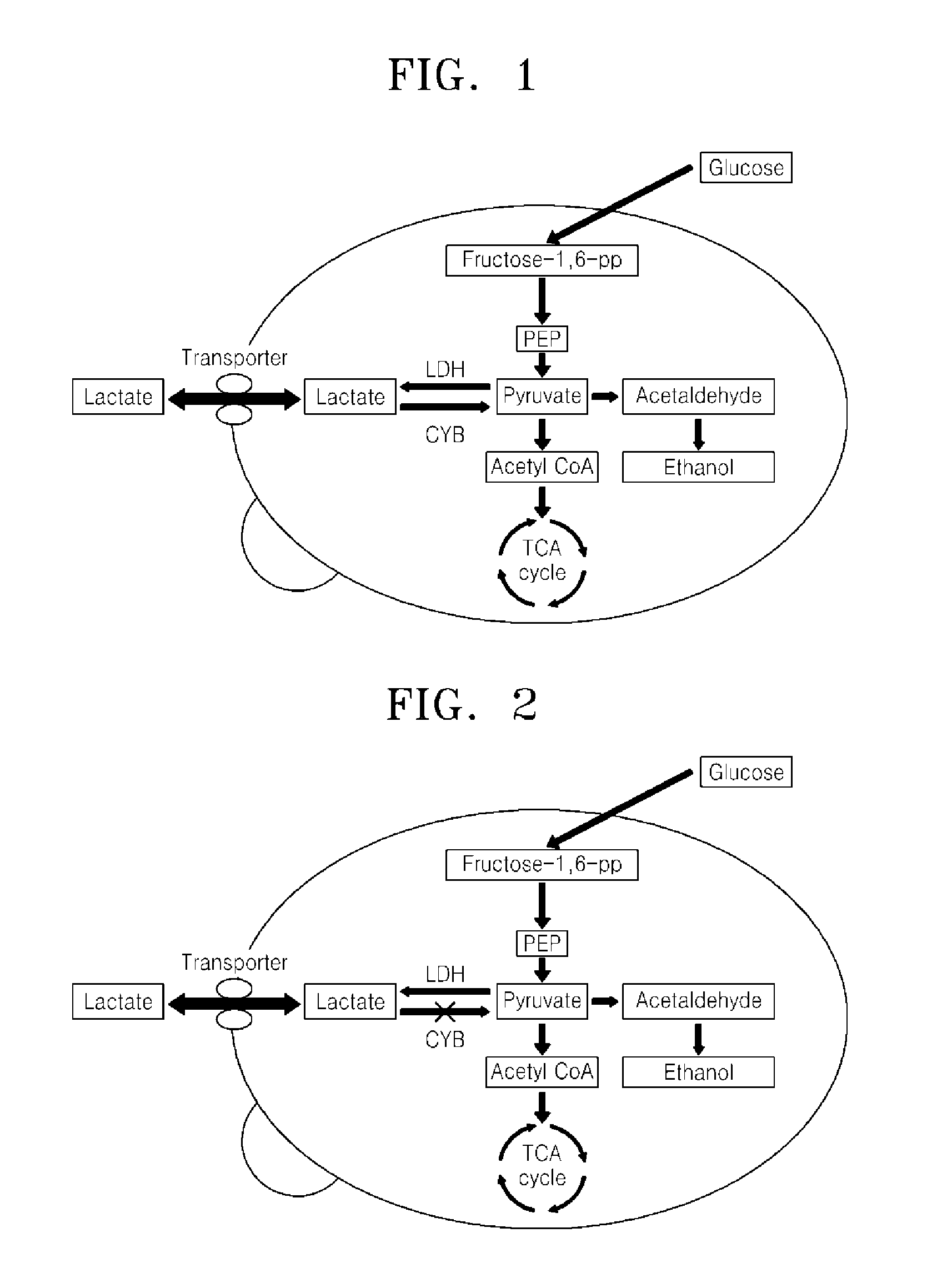
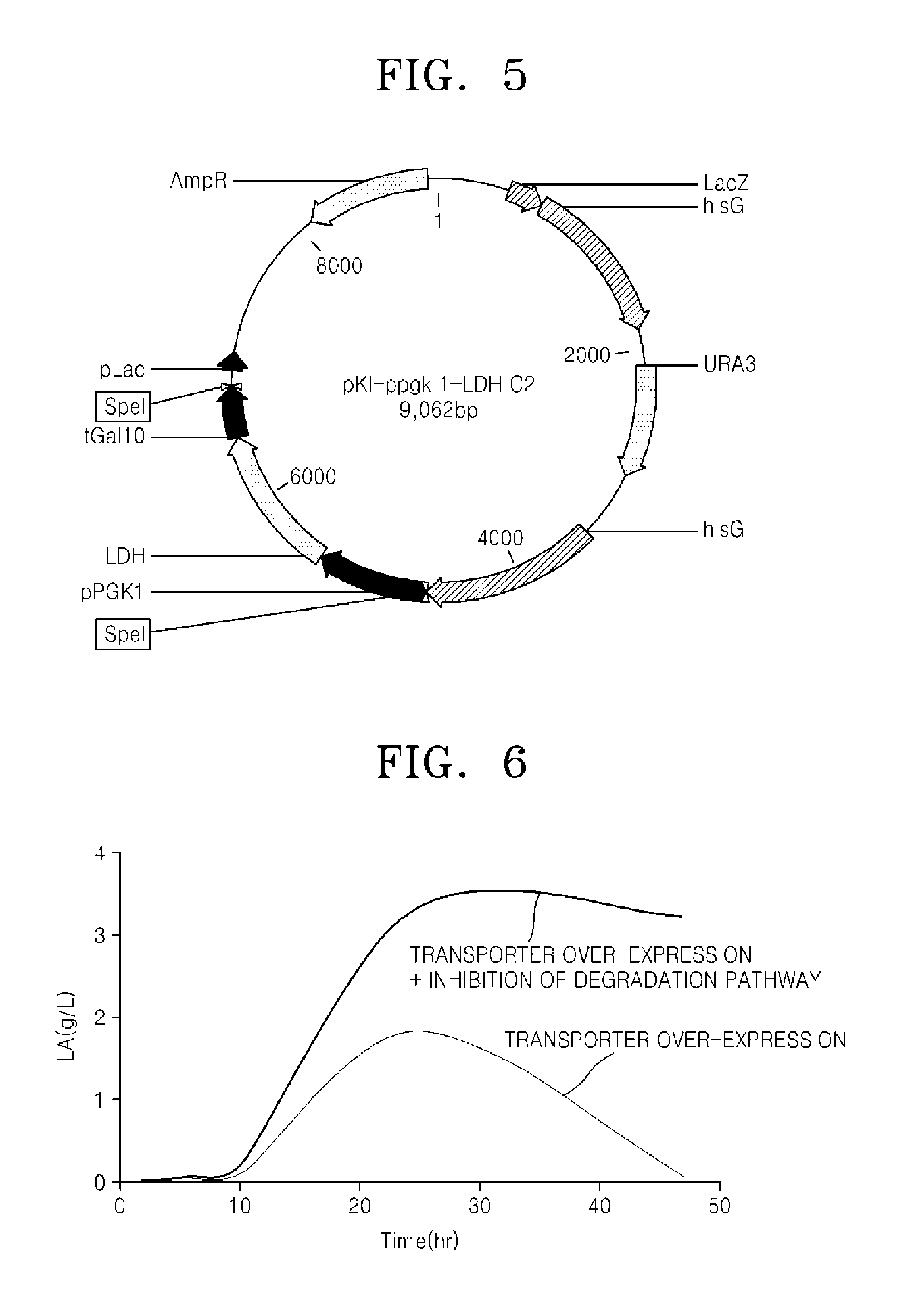
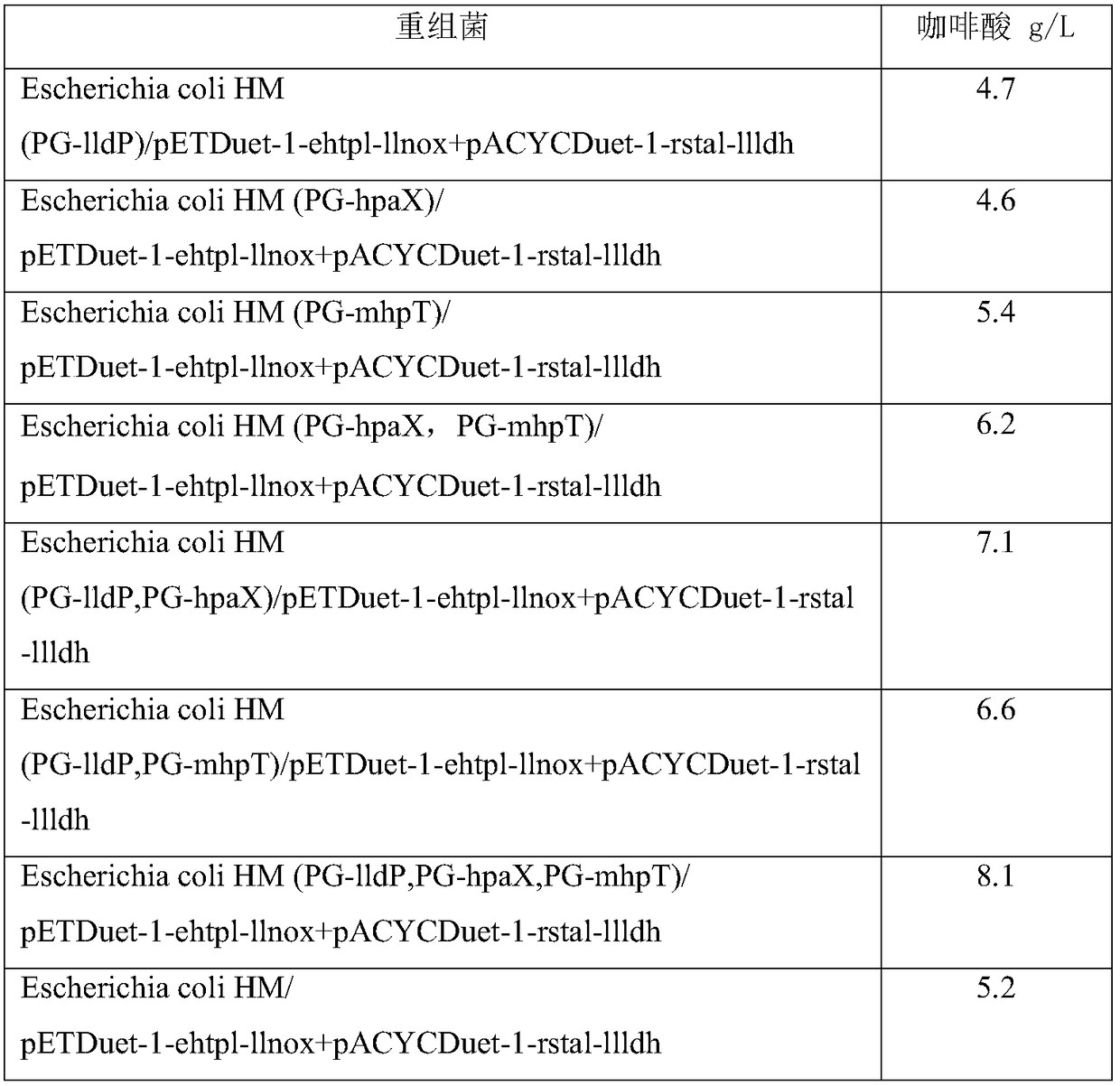
Microorganism over-expressing lactic acid transporter gene and having inhibitory pathway of lactic acid degradation, and method of producing lactic acid using the microorganism
A recombinant microorganism comprising a lactic acid (LA) transporter, wherein the expression of the LA transporter in the recombinant microorganism is increased relative to a parent microorganism, and a method of producing lactic acid using same.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Application of nitrate radical transporter gene OsNRT1.8 in rice breeding
ActiveCN106337055AEnhanced tillering abilityIncrease productionPlant peptidesFermentationGrowth plantNitrogen
The invention discloses application of a nitrate radical transporter gene OsNRT1.8 in rice breeding and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering. The protein encoding amino acid sequence of the gene OsNRT1.8 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and a cDNA sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. By establishing rice gene OsNRT1.8 overexpression plant and a gene OsNRT1.8 interference plant, it is found that normal rice tiller number and spike number of each plant can be increased by improving gene OsNRT1.8 expression. Therefore, the gene OsNRT1.8 can be used for increasing rice yield in rice breeding. The gene OsNRT1.8 has an important application value on the aspects of elaboration about nitrogen influence on plant growth and development and improvement of rice plant type.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF BIOENG
Aspergillus niger strain efficiently producing malic acid, construction method and application
ActiveCN111218408AIncreased purification process costsImprove efficiencyFungiTransferasesHexokinaseBatch fermentation
The invention relates to an Aspergillus niger gene engineering strain efficiently producing malic acid. The Aspergillus niger gene engineering strain is an Aspergillus niger gene engineering strain which knocks out a citric acid transporter gene cexA, and overexpresses a glucose transporter gene mstC, a hexokinase gene hxkA, a phosphofructokinase gene pfkA, and a pyruvate kinase gene pkiA which are derived from Aspergillus niger. The efficiency for producing malic acid of the Aspergillus niger gene engineering strain is significantly improved, the output on the eighth day through fed-batch fermentation in a fermentation tank reaches 195.72-210 g / L, a conversion rate of malic acid to glucose reaches 1.59-1.64 mol / mol, and a fermentation cycle is shorter by one day compared with a starting strain, namely the fermentation cycle is shortened from original 9 days to 8 days. An excellent strain for the preparation of malic acid by microbial fermentation methods is provided.
Owner:南京昊禾生物科技有限公司
Malic acid transporter gene GmALMT1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a malic acid transporter gene GmALMT1 and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the malic acid transporter gene GmALMT1 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. An amino acid sequence of an encoded protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The GmALMT1 gene provided by the invention can be used for regulating soybean root tip malic acid secretion.
Owner:嘉兴卓十生物科技有限公司
Streptomyces calculus genetically engineered bacterium and constructing method and application thereof
ActiveCN105441373ASolve problems caused by supplyLittle hinderedBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEconomic benefitsMicrobiology
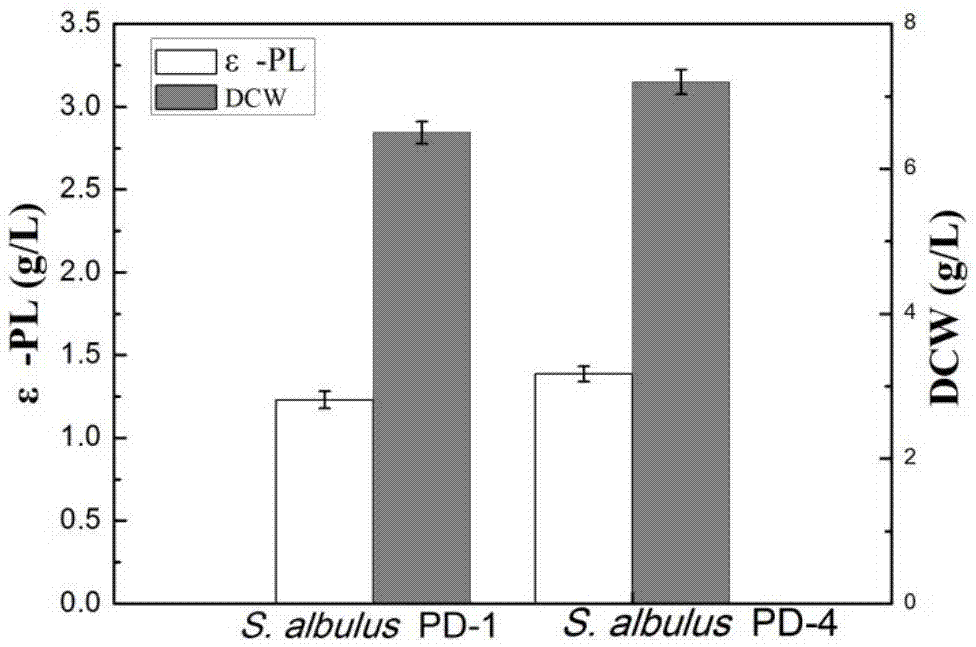
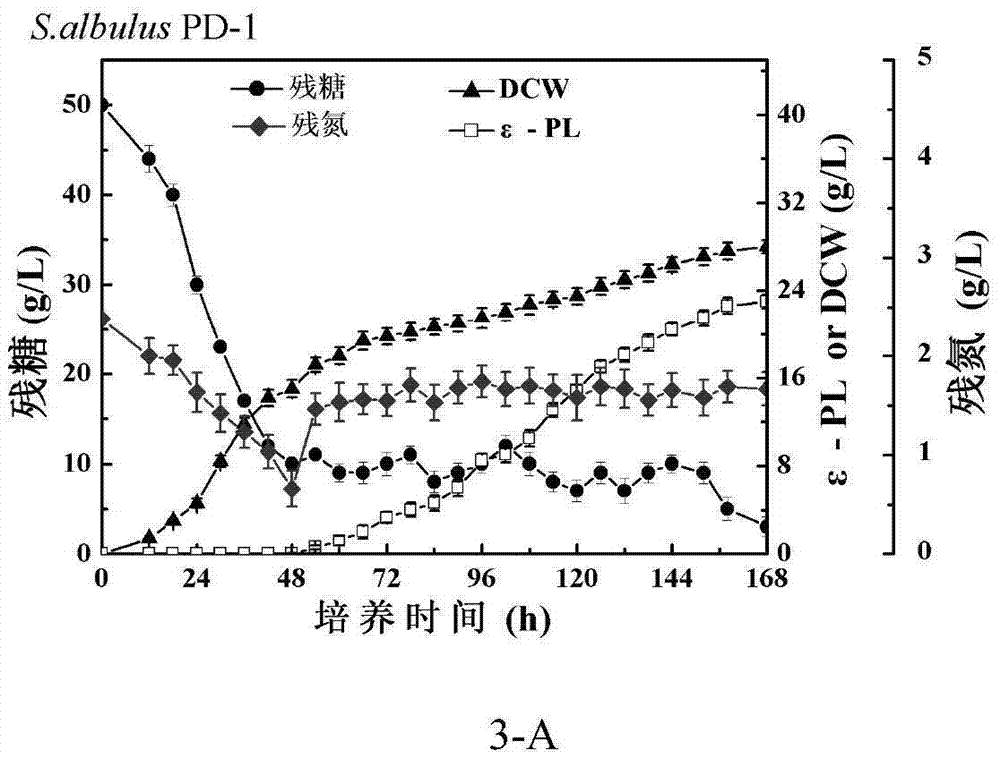
The invention discloses a streptomyces calculus genetically engineered bacterium PD-4. An ammonium transporter gene amtB from an S.albulus PD-1 genome is subjected to overexpression, and polylysine (epsilon-poly-L-lysine, epsilon-PL) synthesis ability higher than that of streptomyces albus S.albulus PD-1 is achieved. The sequence of the ammonium transporter gene is shown as SEQ ID No:1. The invention further discloses a construction method and fermentation verification of the recombinant strain. By means of efficient expression of amtB, limitations caused by defects of ammonium transporters are eliminated, and the rate of a nitrogen source in fermentation liquid utilized by S.albulus PD-4 is increased, so that the yield of epsilon-PL is increased, production cost is reduced, and huge economic benefits are brought.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Epilepsy medication recommendation method and system
PendingCN111462921AHigh control rateShorten the timeBiostatisticsProteomicsAntiepileptic drugMetabolic enzymes
The invention provides an epilepsy medication recommendation method and system, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine and data processing. According to the invention, deep sequencing is carried out on an antiepileptic drug metabolic enzyme gene, a transporter gene and a drug action target gene, related coding gene polymorphic sites are screened, a Bayesian accumulation regression treemodel and random forest regression are utilized to obtain a personalized medication scheme depending on individual genes, and a subset with high treatment effect is identified, so that clinical medication is guided in a targeted manner, the epilepsy control rate is improved, adverse reactions are reduced, the time for doctors and patients to explore the optimal treatment scheme is shortened, the diagnosis and treatment efficiency is improved, and the method has good practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
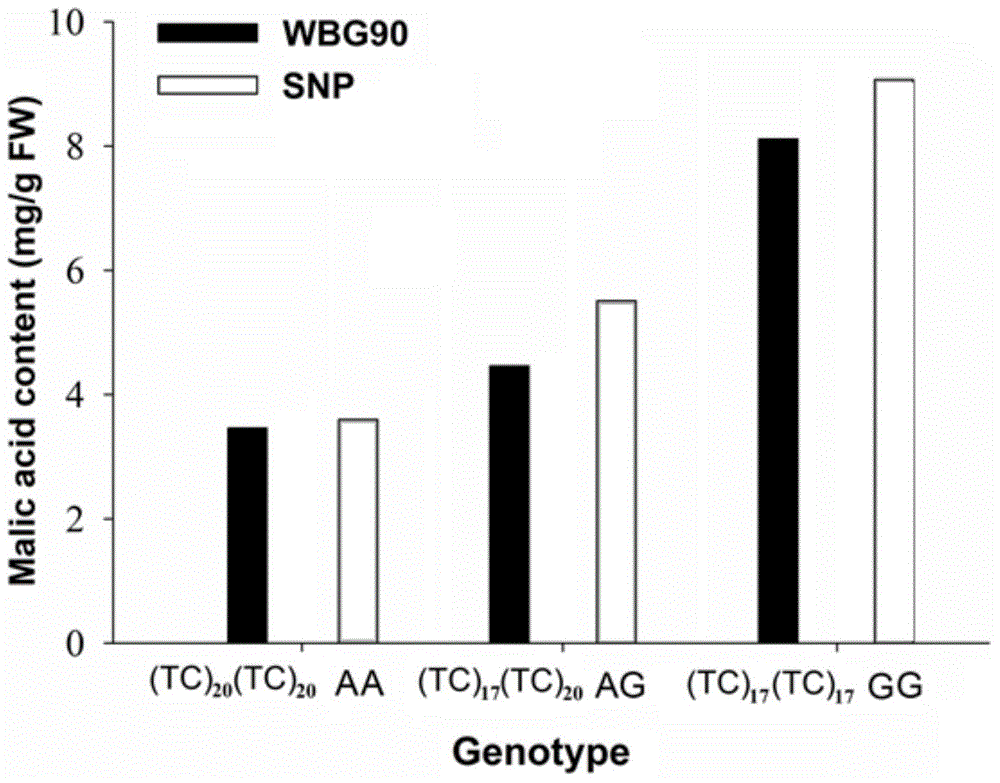
Malic acid transporter gene for controlling organic acid content in apple pulp and application of transporter gene
ActiveCN104561046AThe result is accurateImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyTransgene
The invention discloses a malic acid transporter gene for controlling organic acid content in apple pulp and application of the transporter gene, and relates to the field of apple molecule genetic breeding. The sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and the sequence of encoded protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The application is as follows: (1) designing a molecular marker according to the sequence for marker screening in breeding; and (2) detecting and screening related acidity screening phenotypes according to the expression quantity of the gene or the sequence subtype of a transcript, or improving or reducing the expression quantity of the gene by virtue of a transgenic method so as to acquire expected pulp acidity characters. The organic acid transporter gene disclosed by the invention can be used for determining pulp acidity; on the basis of the assembling result of RNA-Seq and the annotation result of a whole genome frame diagram, the obtained gene is more accurate; and the gene can be screened at the early stage of apple breeding, so that breeding time can be saved, and meanwhile screening efficiency can be improved.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
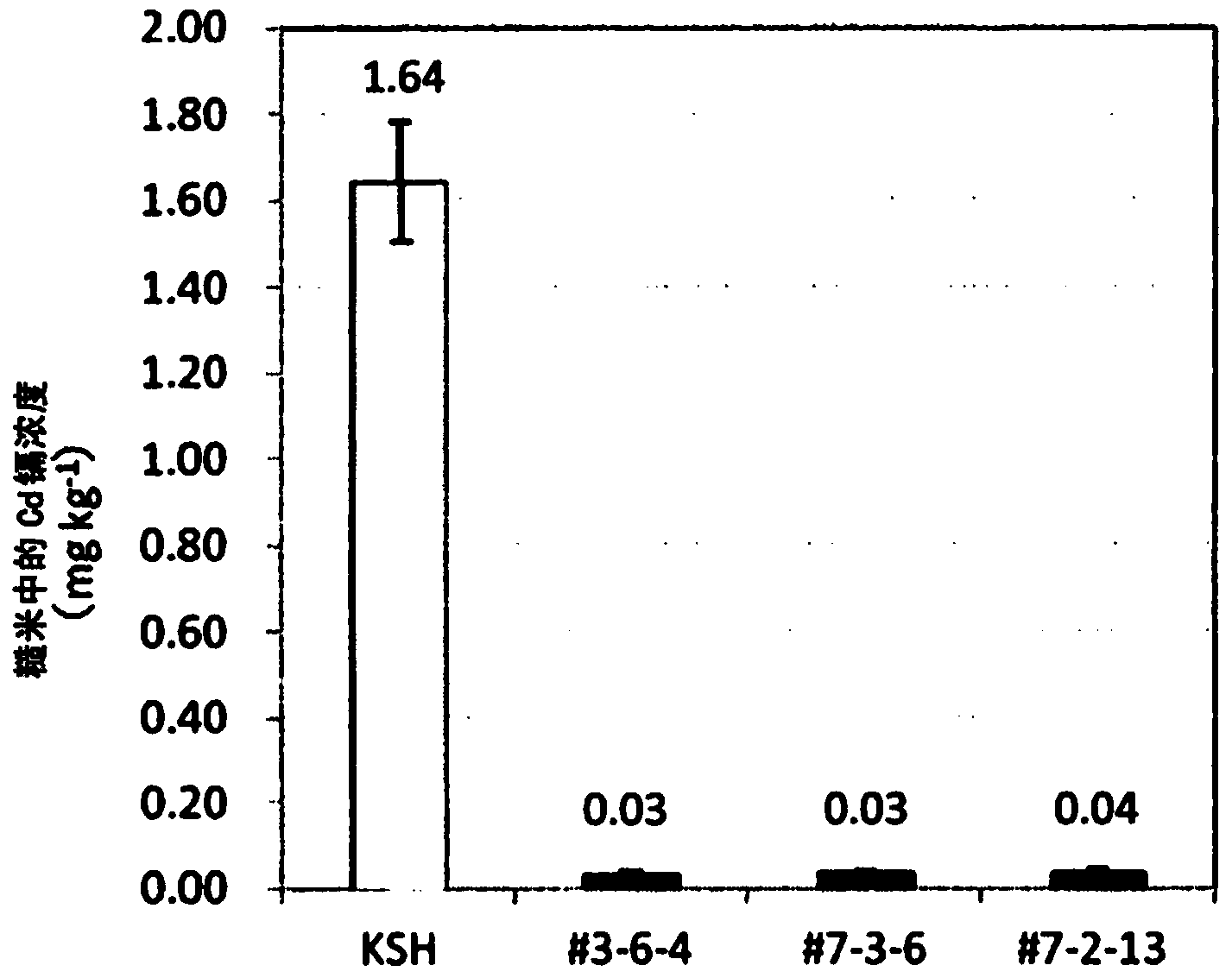
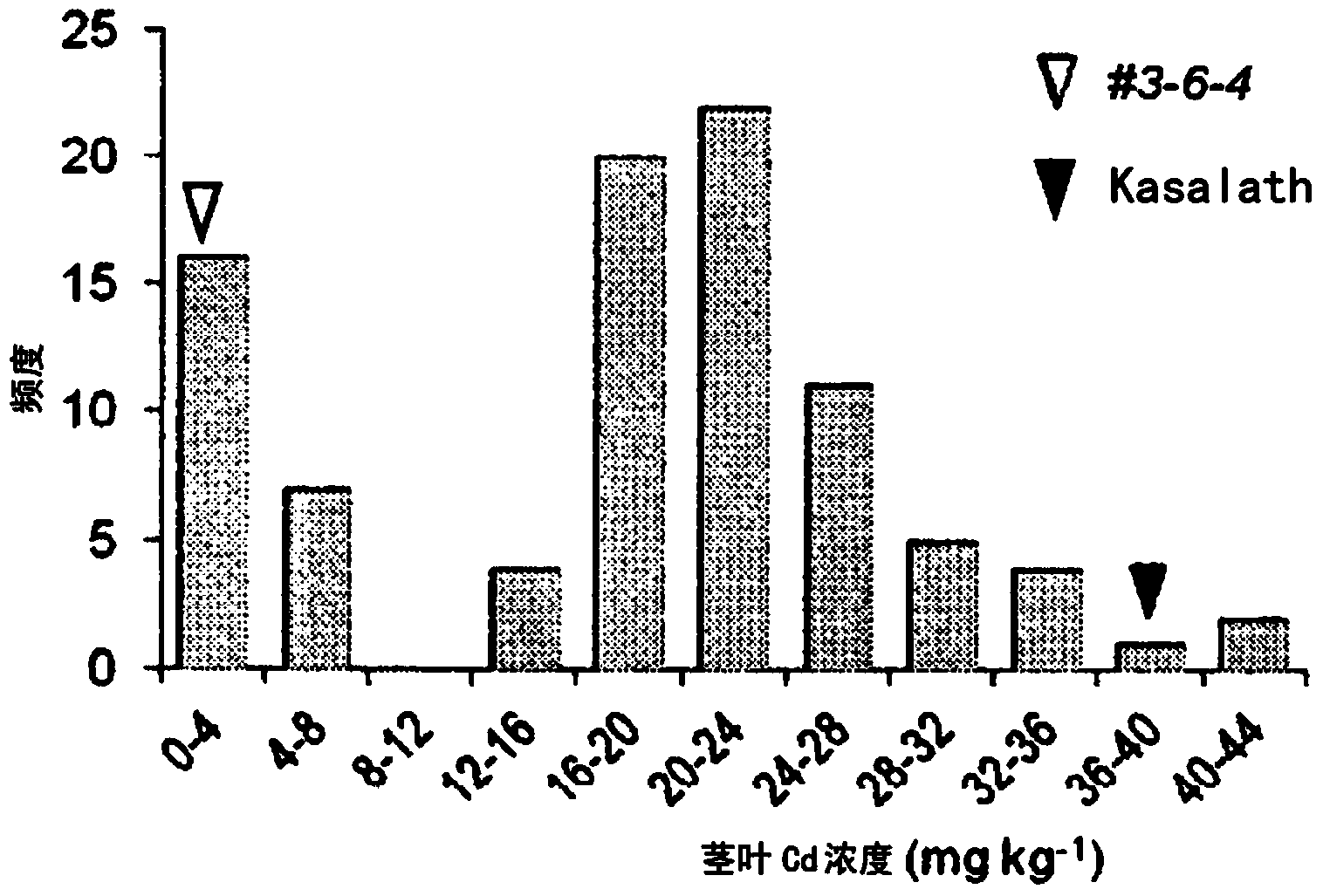
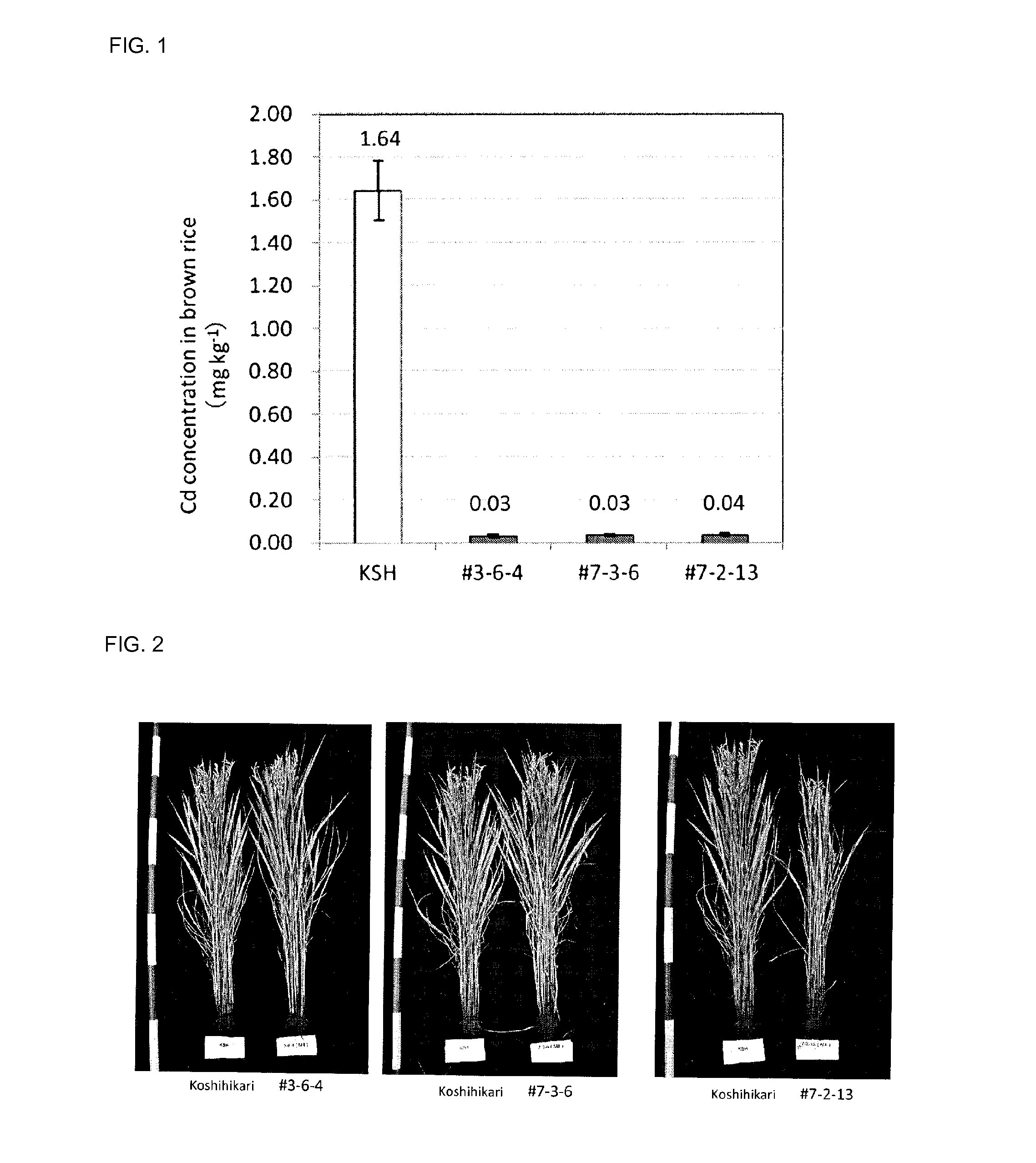
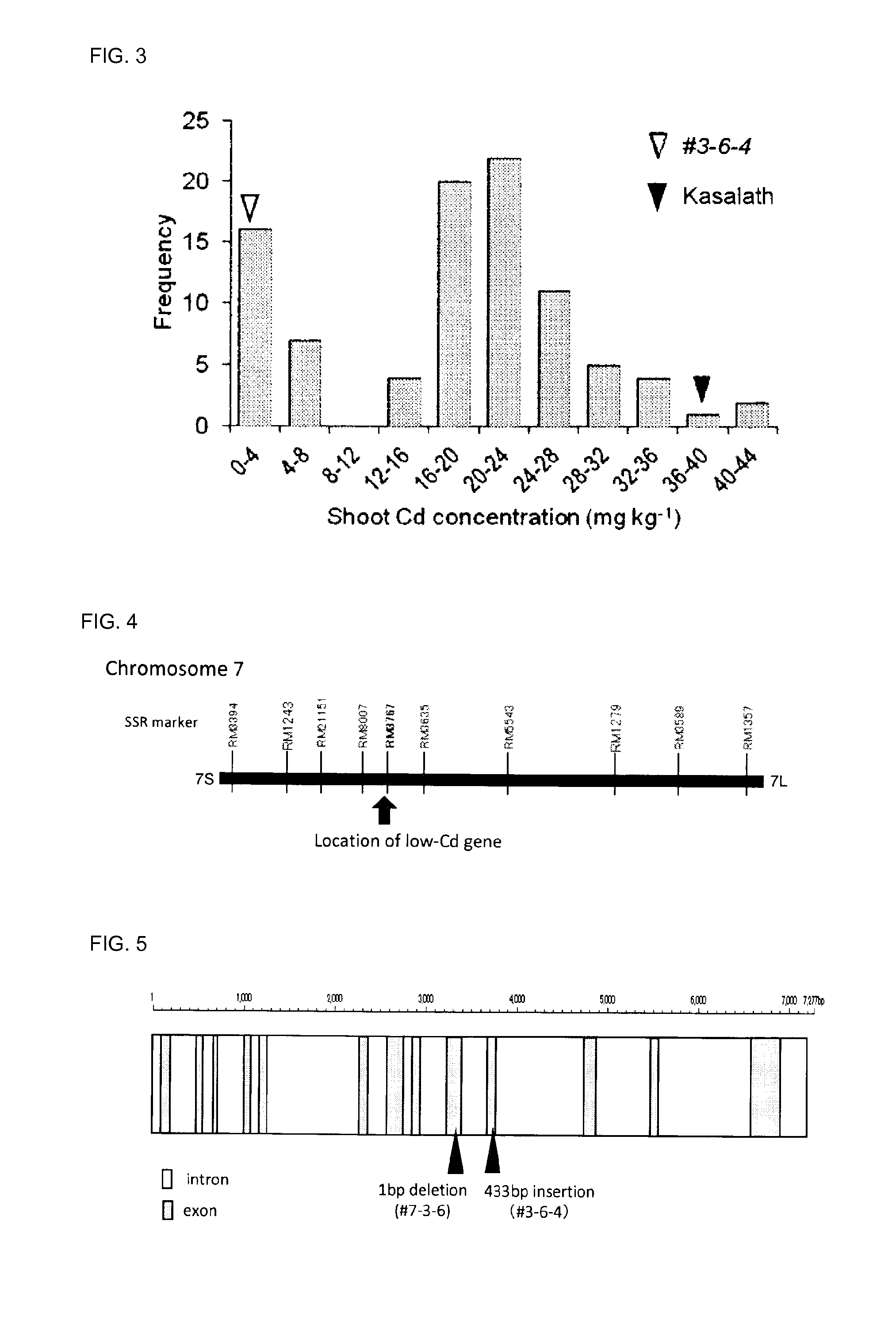
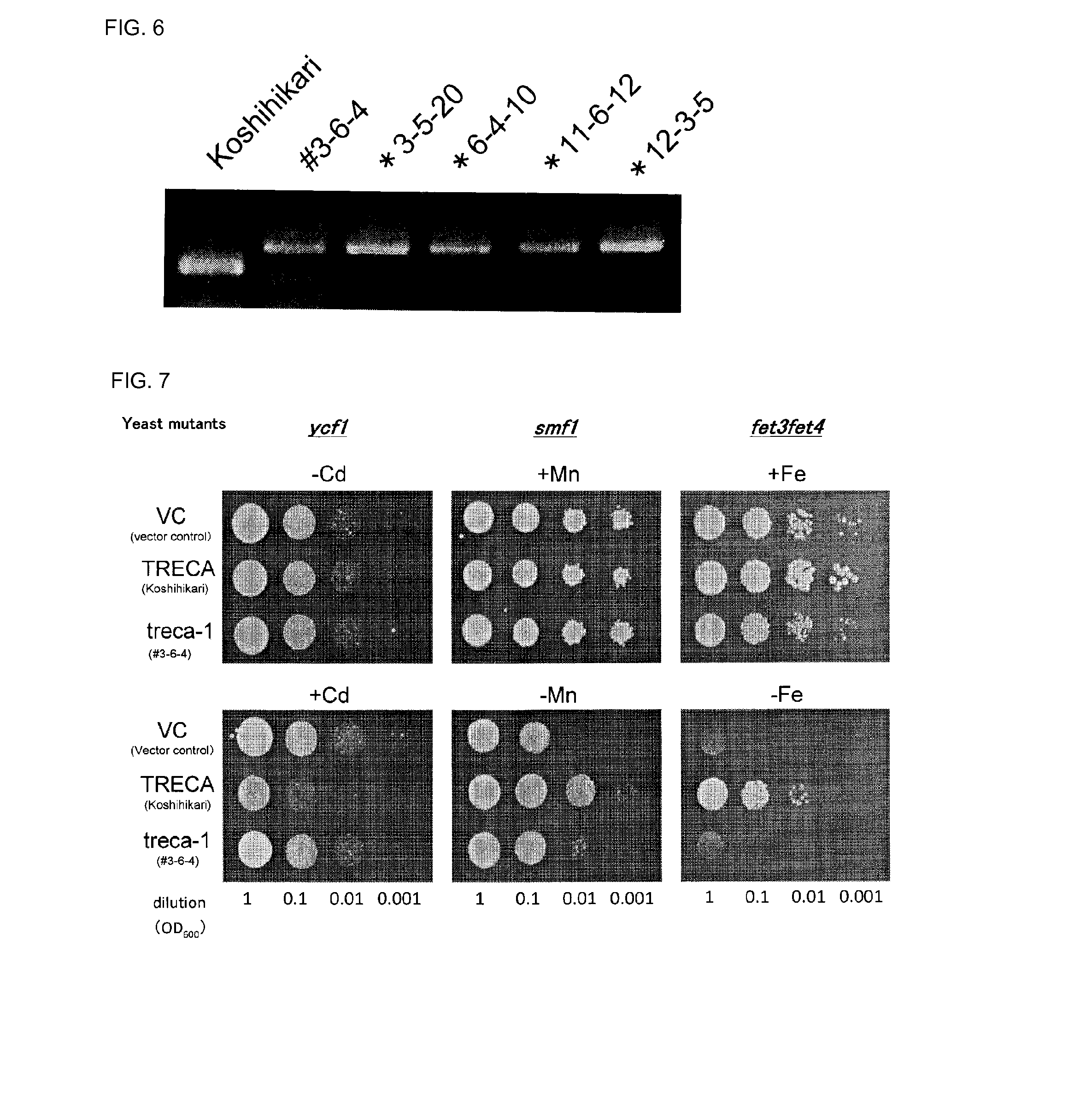
Cadmium absorption regulation gene, protein, and rice plant having reduced cadmium absorption
ActiveCN103917646AImprove practicalityEfficient screeningRecombinant DNA-technologyPlant peptidesRice plantsA-DNA
Provided are: a transporter gene involved in the promotion or inhibition of the absorption of Cd by a root; a mutant gene of the transporter gene; a transporter protein of the transporter gene; a rice plant of which the absorption of Cd is reduced; and a method for selecting and growing a rice plant of which the absorption of Cd is reduced. A gene encoding a transporter protein involved in the regulation of the absorption of cadmium, which comprises a DNA nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2; a gene encoding a transporter protein involved in the regulation of the absorption of cadmium, which comprises a DNA nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 3; a gene encoding a transporter protein involved in the regulation of the absorption of cadmium, which comprises a DNA nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 4; and a transporter protein involved in the regulation of the absorption of cadmium, which comprises an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:NAT INST FOR AGRO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
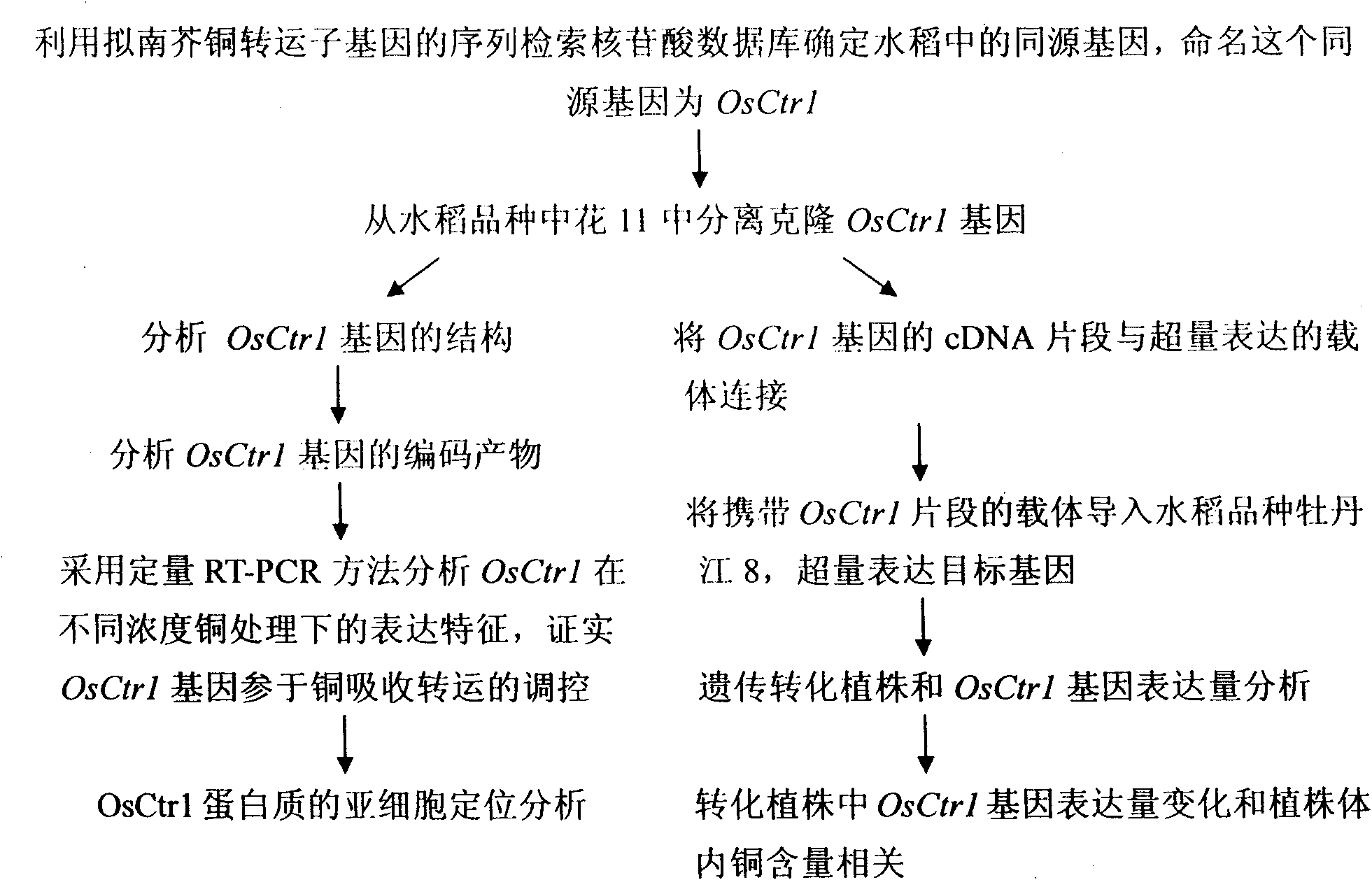
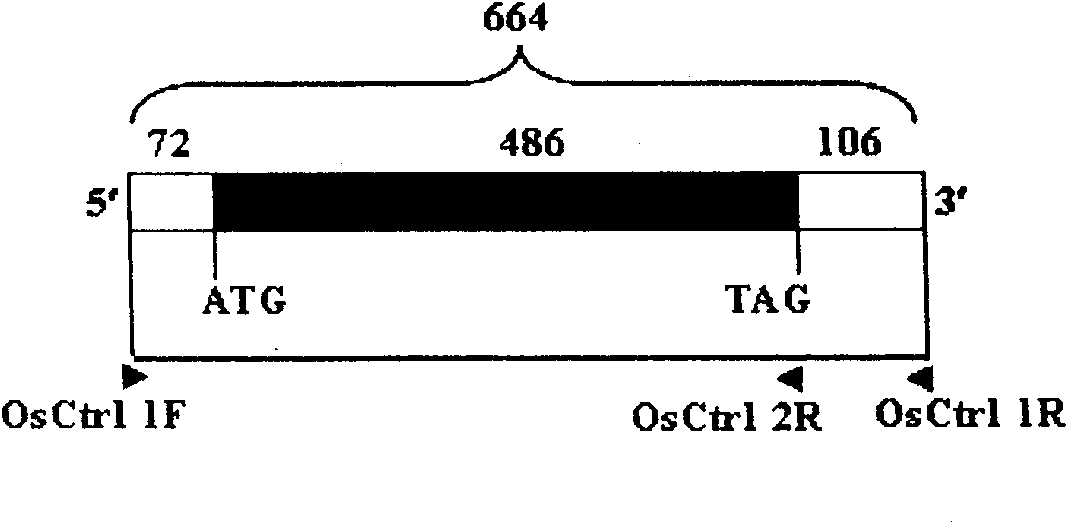
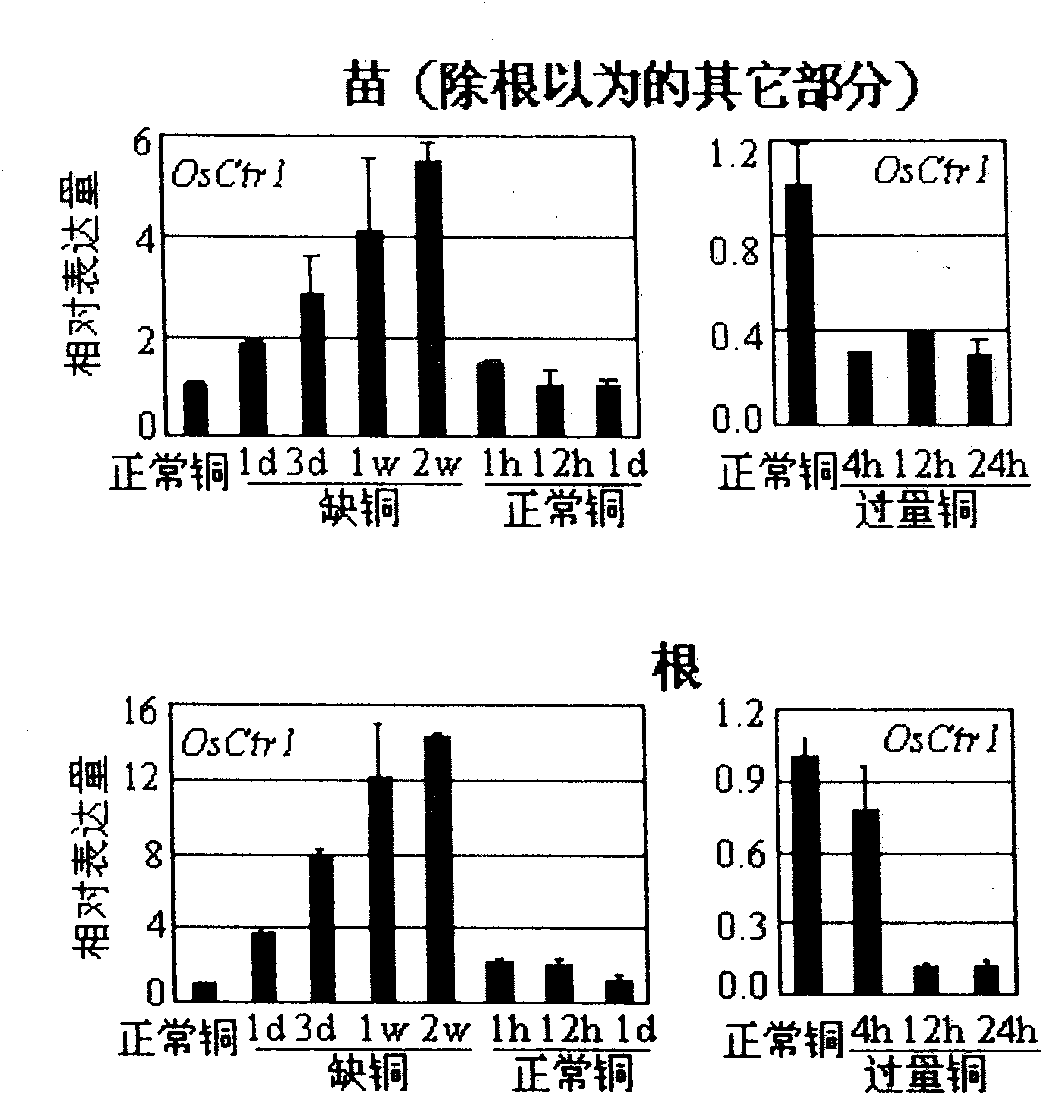
Oryza sativa copper transporter gene OsCtr1 and application thereof in remediation of copper contaminated soil and water body
InactiveCN101942447AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified riceBiology
The invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering, in particular to isolation, cloning and function verification of DNA fragments containing Oryza sativa copper transporter gene OsCtr1. The OsCtr1 encodes a copper transporter protein, and can enhance the copper absorption and accumulation capability of Oryza sativa. The segment and the extraneous adjustment sequence thereof are directly transported into the Oryza sativa, thereby obviously enhancing the copper absorption and accumulation capability of the transgenic Oryza sativa with excessive OsCtr1 expression. The Oryza sativa with excessive OsCtr1 expression can be planted to reduce the content of copper in soil and surrounding water body and remedy the copper pollution in the soil and the water body.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
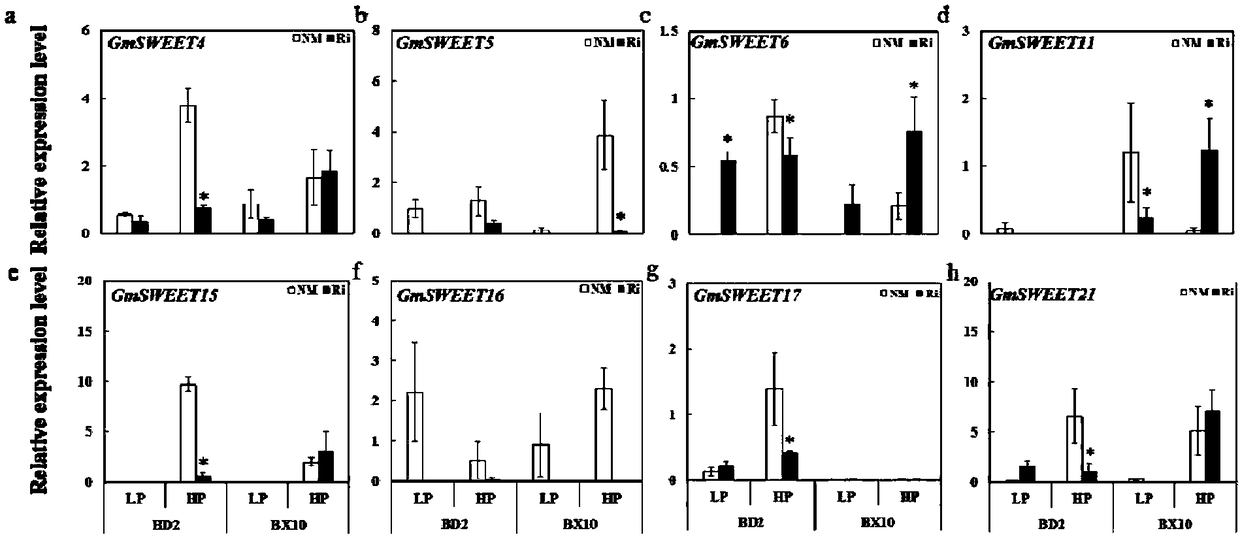
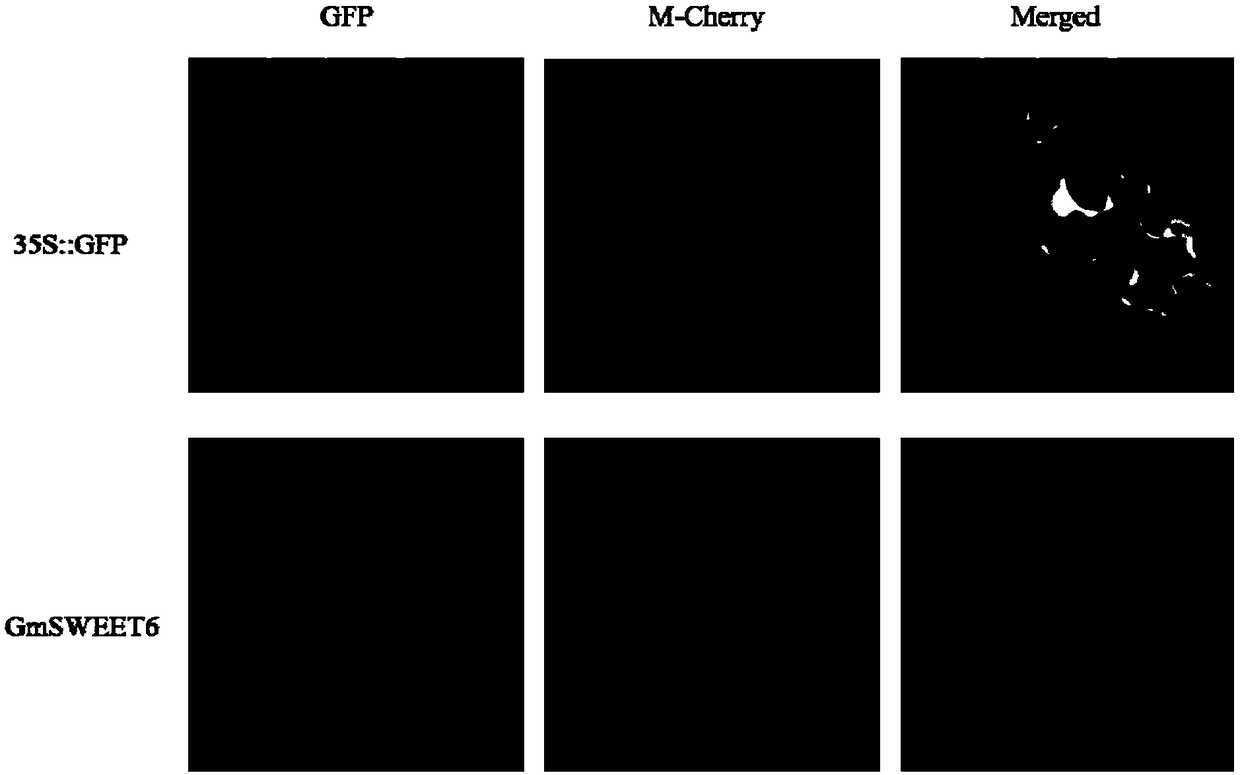
Application of important gene GmSWEET6 of soybean sucrose transporter
ActiveCN108467868AGood regulationRegulating absorbencyPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
The invention discloses application of an important gene GmSWEET6 of a soybean sucrose transporter and relates to the fields of plant genetic engineering and biotechnologies. According to a real-timefluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method, the sucrose transporter gene GmSWEET6 with mycorrhiza induced expression is identified in soybeans. The expression of the gene is regulated by mycorrhiza fungus infection. Under mycorrhiza fungus inoculation conditions, over-expressed or interference expressed GmSWEET6 in transgenic soybean plants has an effect of regulating plant growth and phosphorus absorption and has a significant influence on beneficial symbiosis of the soybeans and arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi, which has significance for explaining biological functions of the SWEET genes in symbiosis of leguminous crops and the mycorrhiza fungi so as to regulate beneficial symbiosis between plants and the mycorrhiza fungi.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
ABC transporter PgPDR2 gene and encoding protein and application of ABC transporter gene PgPDR2
The invention discloses a PgPDR2 (panax ginseng pleiotropic drug resistance) gene related to regulation of transport and accumulation of ginsenosides, as well as an encoding protein and an application of the PgPDR2 gene. A sequence of the ABC (ATP-binding cassette) PgPDR2 gene is shown as SEQ ID No. (sequence identification number) 1, and the sequence of the encoding protein of the ABC PgPDR2 gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 2. The research finds that PgPDR2 gene expression has tissue specificity and is related to the accumulation of the ginsenosides. The research preliminarily indicates that the PgPDR2 gene has functions of promoting synthesis, the transport and the accumulation of the ginsenosides. Panax ginseng or other plants can be screened or improved through the PgPDR2 gene or derivatives of the PgPDR2 gene to obtain excellent plant varieties with high ginsenoside content. Also, panax ginseng transgenic cells or plants can be adopted to produce ginsenoside monomers such as protopanaxadiol, Rb, Re, Rh2, Rg2 and Rg3.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
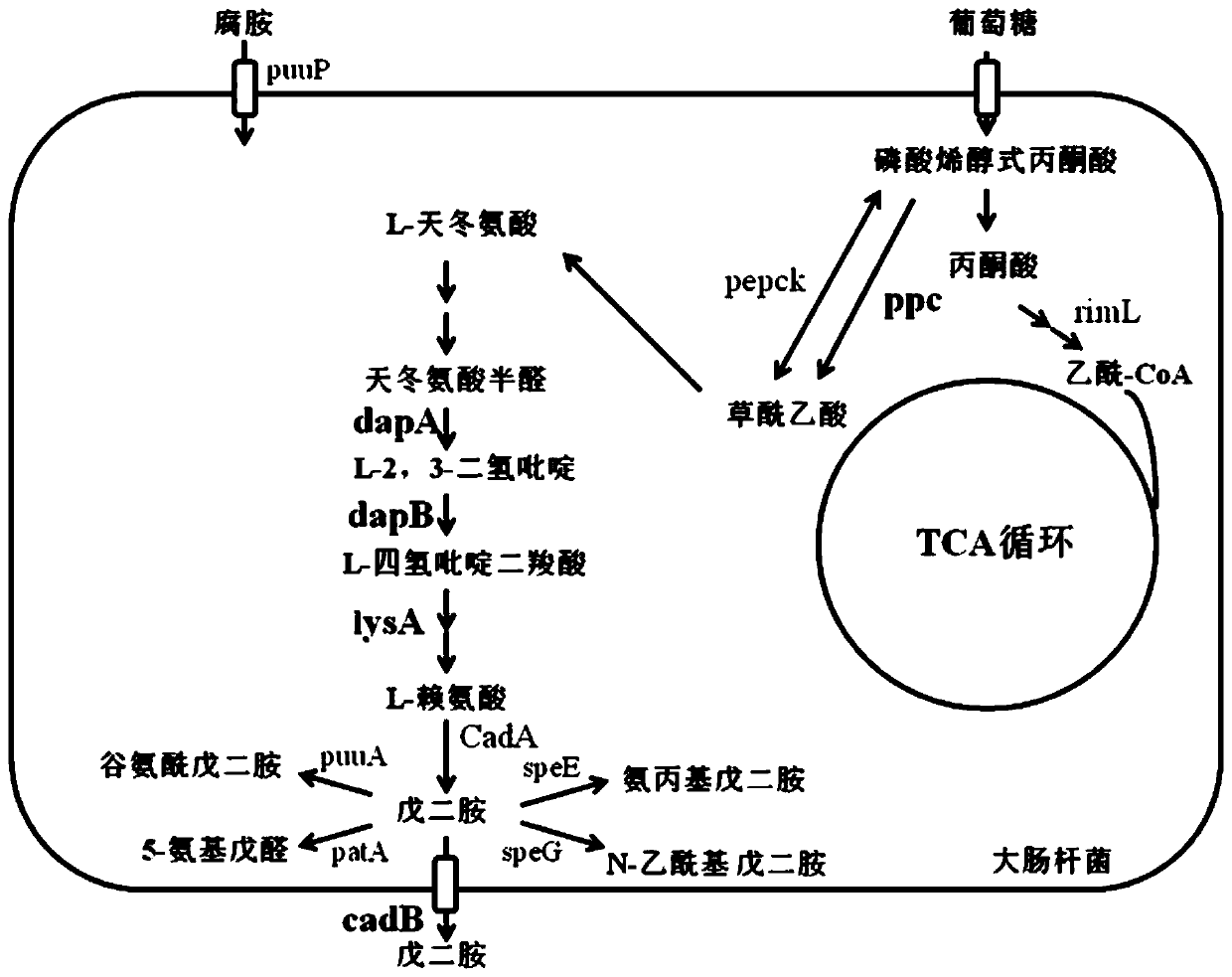
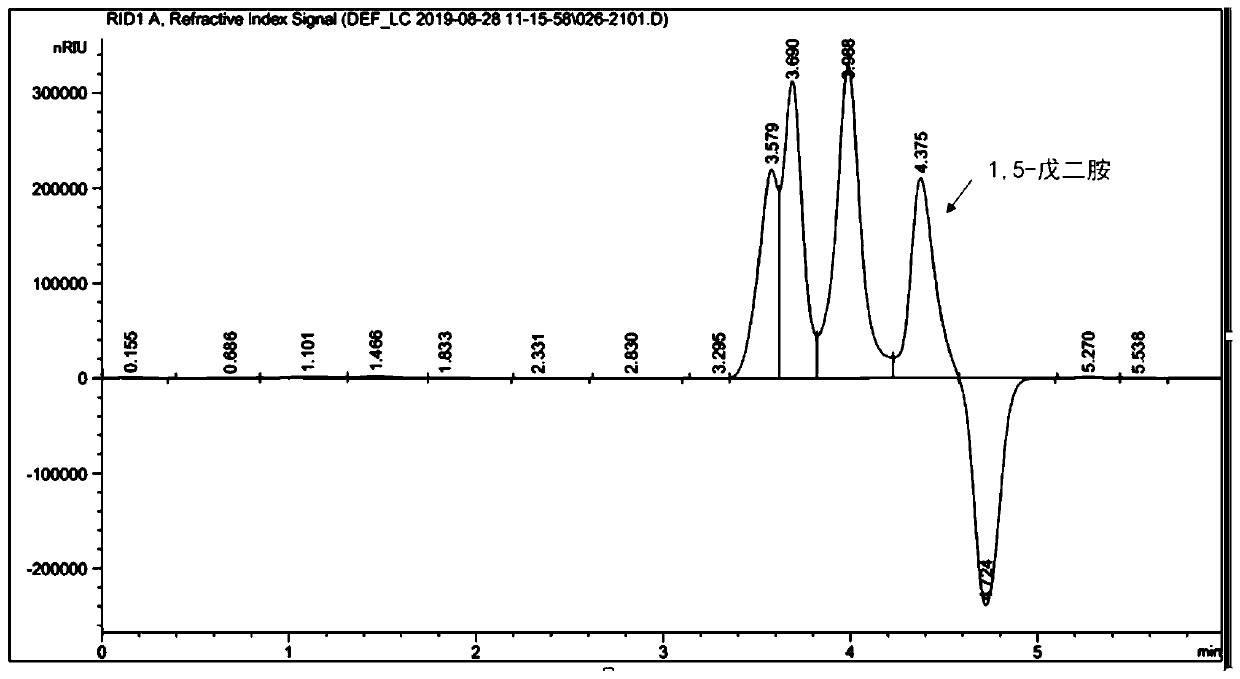
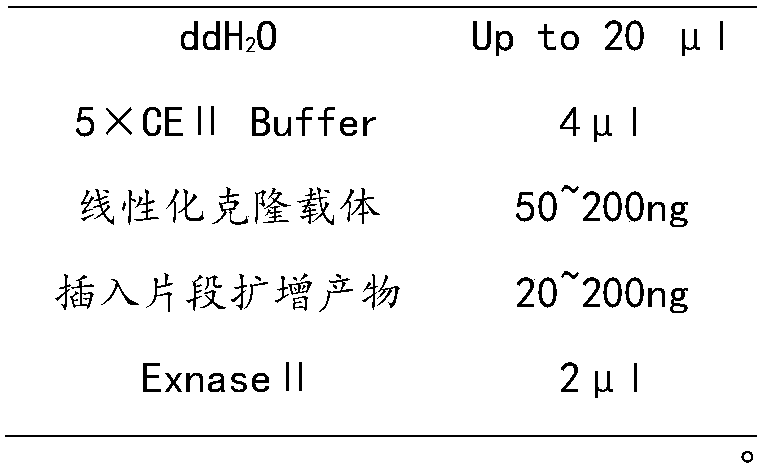
Bioconversion method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine
PendingCN110699394AIncrease usageIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and relates to a bioconversion method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine. The method can increase the yield of 1,5-pentanediamine bymodifying a metabolic pathway of Escherichia coli. The method specifically comprises the following steps: selecting an Escherichia coli strain, firstly, knocking out a 1,5-pentanediamine degradation pathway; secondly, adding a synthetic precursor,namely lysine, of 1,5-pentanediamine; thirdly, overexpressing a transporter gene and finally directly fermenting the Escherichia coli strain DFC1002 to produce 1,5-pentanediamine. After the metabolic pathway of Escherichia coli is modified, themethod can produce 1,5-pentanediamine with high yield.The method is simple and easy to implement, has high yield of 1,5-pentanediamine, few by-products, and good repeatability, and is suitable for industrialization.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Cadmium absorption regulatory gene, protein and cadmium absorption-inhibiting rice plant
InactiveUS20140259233A1Reduce cadmium absorptionValid choiceSugar derivativesDepsipeptidesNucleotideAmino acid
Provided are a transporter gene involved in the promotion or inhibition of Cd absorption by roots, a mutant gene thereof and a transporter protein thereof, as well as a rice plant in which Cd absorption is inhibited and a method for selecting and raising a Cd absorption-inhibiting rice plant, which are a gene encoding a transporter protein involved in the regulation of cadmium absorption, which contains the DNA nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2, a gene encoding a transporter protein involved in the regulation of cadmium absorption, which contains the DNA nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:3, a gene encoding a transporter protein involved in the regulation of cadmium absorption, which contains the DNA nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:4, and a transporter protein involved in the regulation of cadmium absorption, which contains the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1.
Owner:NAT INST FOR AGRO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
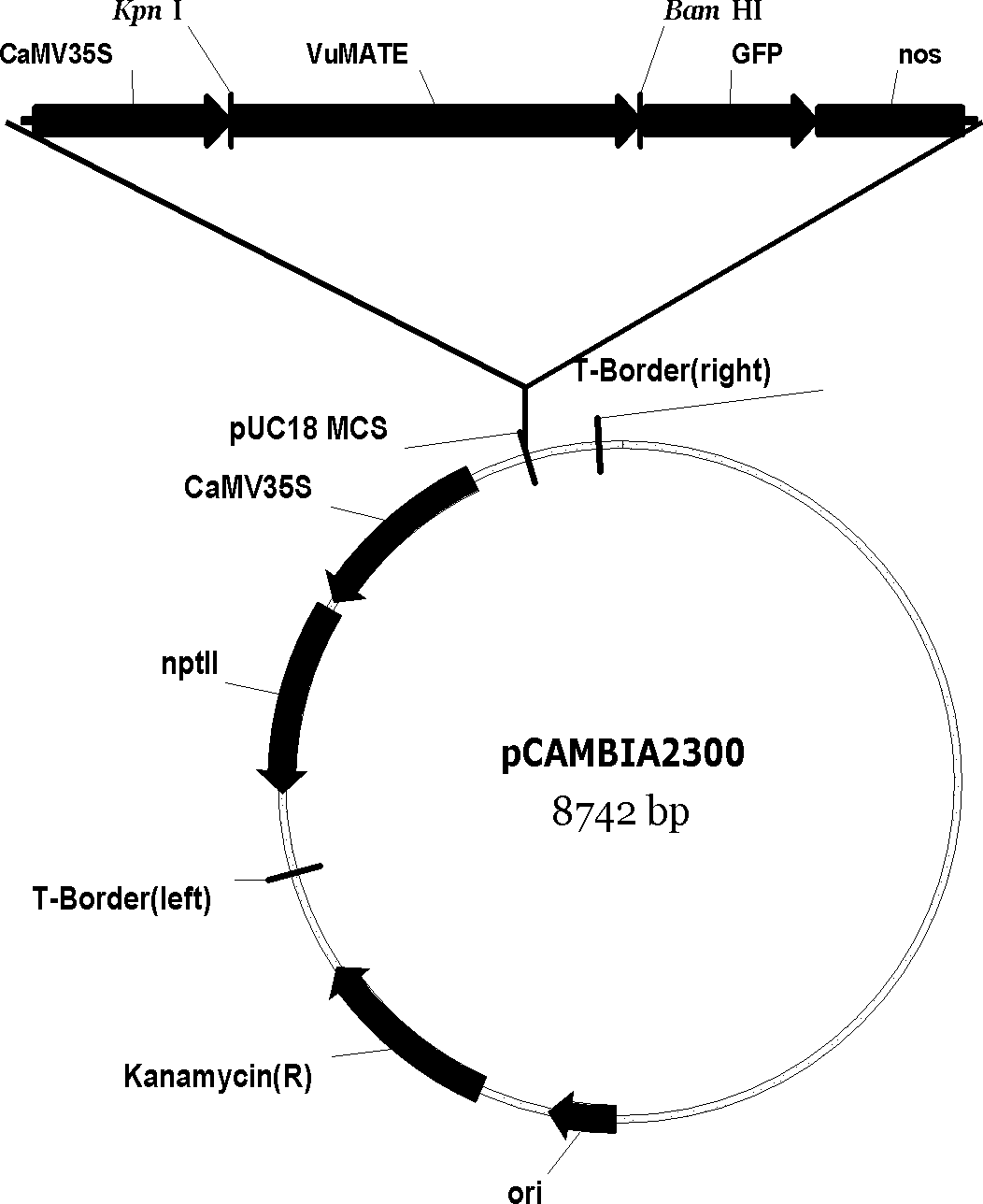
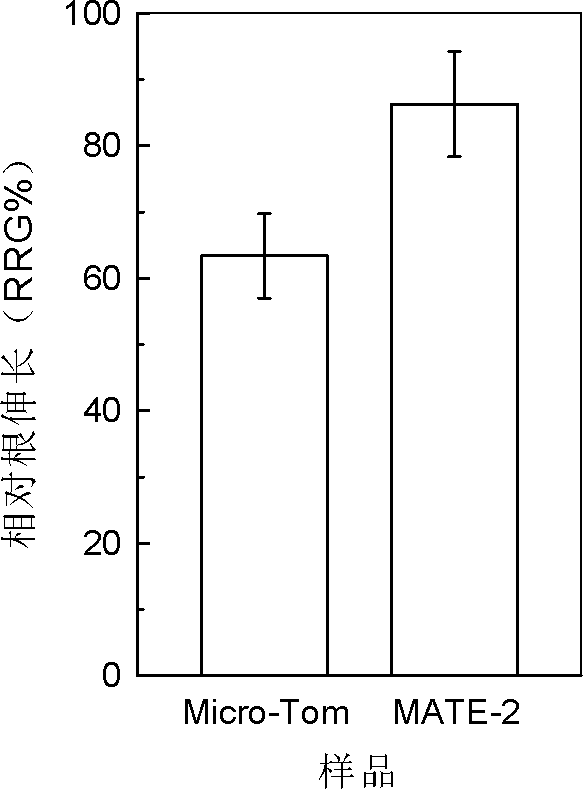
Snailflower citric acid transporter gene VuMATE and use thereof
InactiveCN102154318AIncrease aluminum resistanceImprove secretion capacityFermentationHorticulture methodsNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a snailflower citric acid transporter gene VuMATE, which has a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1. The invention also discloses a method for breeding an aluminum-tolerance transgenic crop, which comprises the following steps: 1) selecting the snailflower citric acid transporter gene VuMATE having the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1; 2) constructing a constitutive type expression transgenic vector; and 3) and breeding the transgenic crop, namely infecting leaf disc of tomatoes Micro-Tom with Agrobacterium rhizogenes EHA105 into which the pseudo-rigid-body model (pRBM) vector is transferred, co-culturing the transgenic plant, selecting, differentiating and rooting to obtain transgenic tomatoes MATE-2. The snailflower citric acid transporter gene VuMATE disclosed by the invention can be used for plant transgenosis for improving the aluminum tolerance of the crop.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Tobacco cadmium transporter gene NtHMA2, and cloning method and application thereof
The invention discloses a tobacco cadmium transporter gene NtHMA2, and a cloning method and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the tobacco cadmium transporter gene NtHMA2 is disclosed as SEQ ID:No.1, and the coded amino acid sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID:No.2. The invention also discloses a cloning method of the tobacco cadmium transporter gene NtHMA2, which comprises the following steps: A. determining the NtHMA2 gene sequence; B. extracting tobacco RNA (ribonucleic acid), and carrying out reverse transcription to obtain a first chain cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid); C. designing and synthesizing specific primers according to the NtHMA2 gene sequence, and carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by using the cDNA as the template; D recycling and purifying the PCR product; E. connecting the purified product with the vector, and transforming competent cells; and F. screening positive clone, carrying out PCR amplification on the positive clone, and sequencing. By regulating the expression of the tobacco cadmium transporter gene NtHMA2, the method can lower the operation rate of cadmium being transported from the tobacco root to leaves, thereby lowering the chromium content of the tobacco and providing a gene resource for green high-quality tobacco.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Method For Selectively Expanding, Selecting And Enriching Stem/Progenitor Cell Populations
InactiveUS20090298045A1Error detection/correctionDead animal preservationIntestinal structureProgenitor
A method of producing stem / progenitor cells from human or animal origin. A population, from an embryonic, fetal or adult source, preferably from bone marrow, blood, fat, muscle, heart, intestine, kidney, liver, lung, pancreas, skin or neural tissues, that includes stem / progenitor cells, is treated with one or more first cytostatic or cytotoxic agents to which the stem / progenitor cells are less sensitive than the other cells of the population. Preferably, the agent(s) selectively deplete(s) from the population cells that are negative with respect to expressing a transporter gene of the first agent(s) while sparing cells that are positive with respect to expressing that gene. Preferably, the population also is treated with one or more cytokines and / or growth factors.
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES
Method for quantitative determination of multi-drug resistance in tumors
InactiveUS20050147978A1Reliable diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthQuantitative determination
The invention relates to a method for determining, whether a cell of interest is resistant to an active substance to which it is exposed, e.g. during cancer chemotherapy. The method comprises the quantitative analysis of the expression of at least 5 ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter genes within a sample, treated in the same manner using a DNA micro-array.
Owner:EPPENDORF ARRAY TECH SA
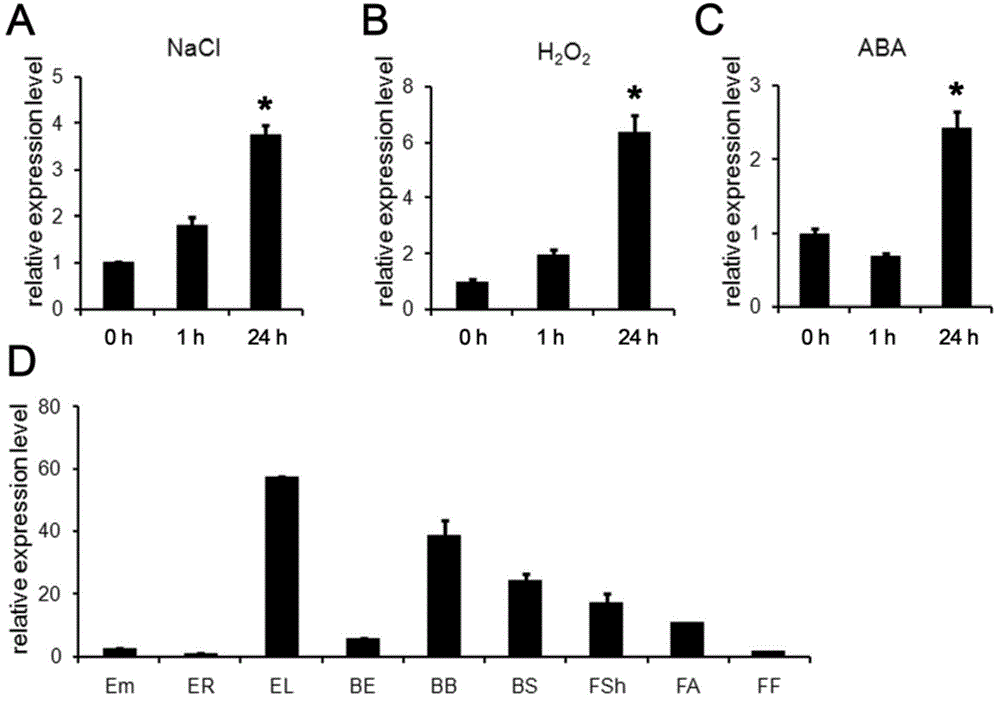
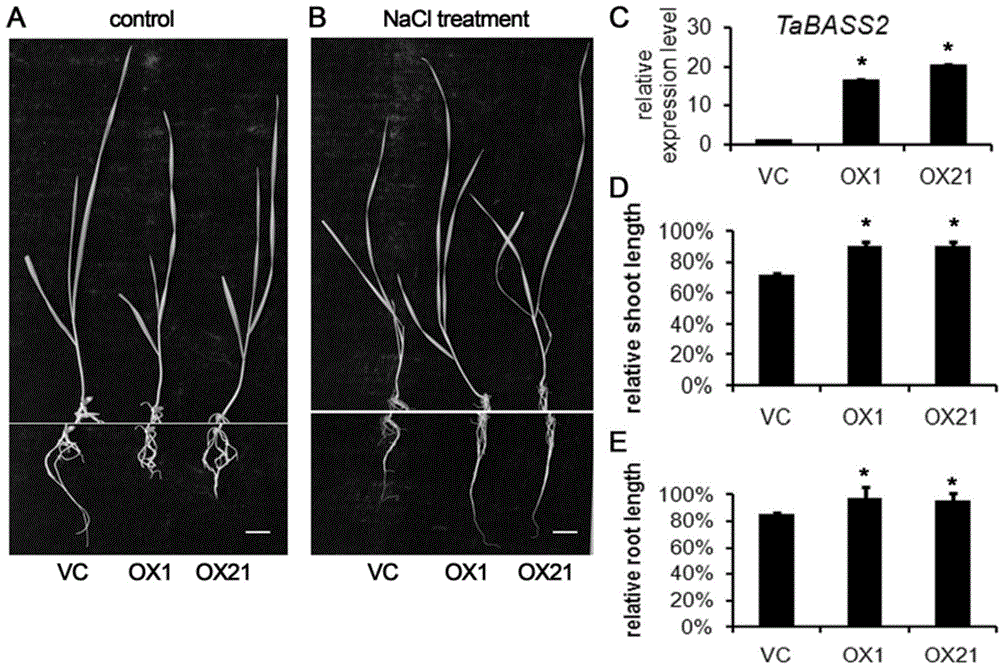
Wheat salt-tolerant gene TaBASS2 and application thereof
InactiveCN104561053AImprove salt toleranceGain salt toleranceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologySalt Tolerant Plants
The invention discloses a wheat salt-tolerant gene pyruvic acid transporter gene, and particularly relates to an allene oxide reductase gene TaBASS2 and a plant expression vector containing the gene TaBASS2. The invention further discloses an application of the gene TaBASS2 in cultivation of salt-tolerant plants, especially wheat. An experiment proves that the salt tolerance of a transgenic plant prepared by transgene transformation disclosed by the invention is obviously improved; and a foundation is laid for wide application of the gene in cultivation of a new variety of salt-tolerant crops.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
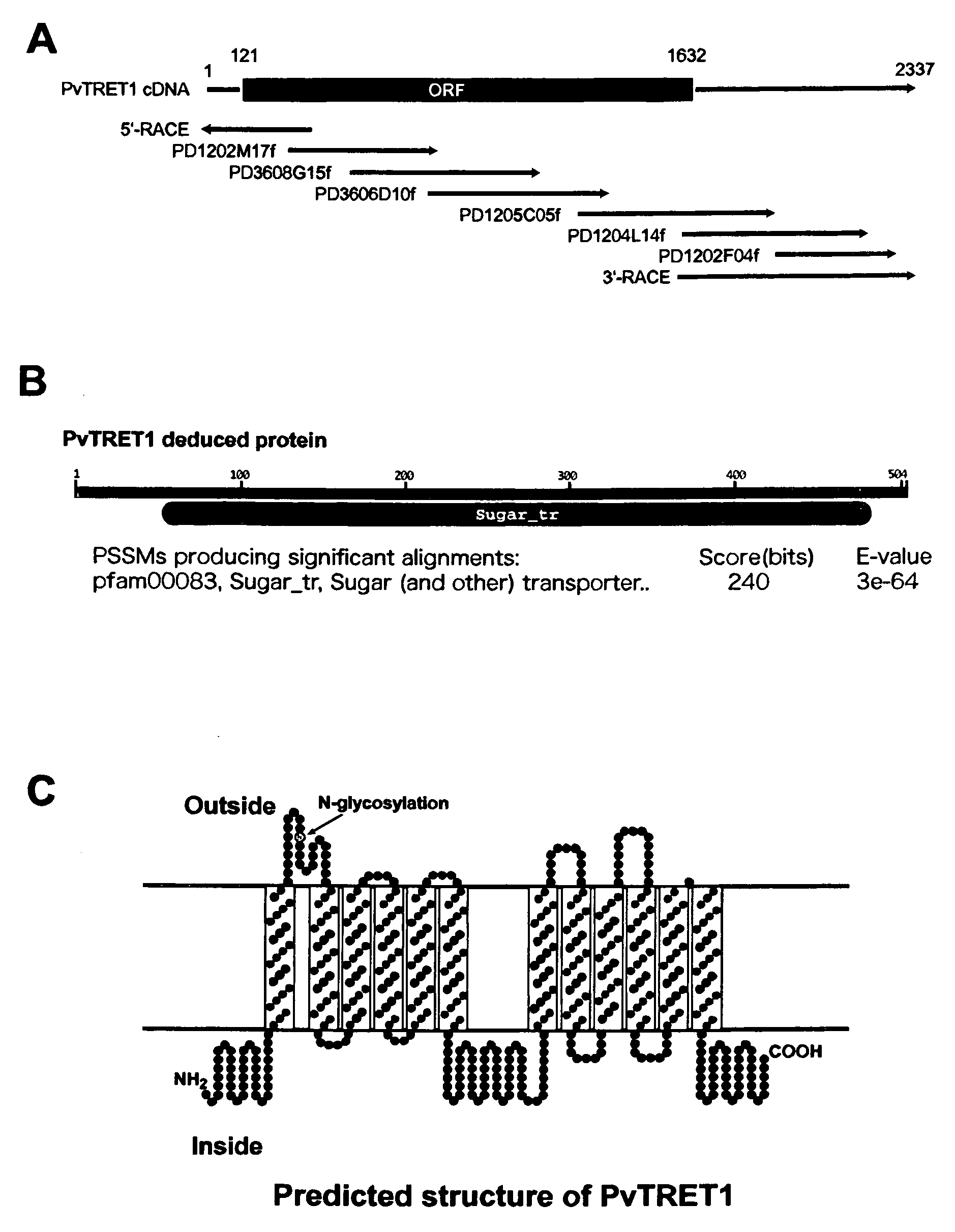
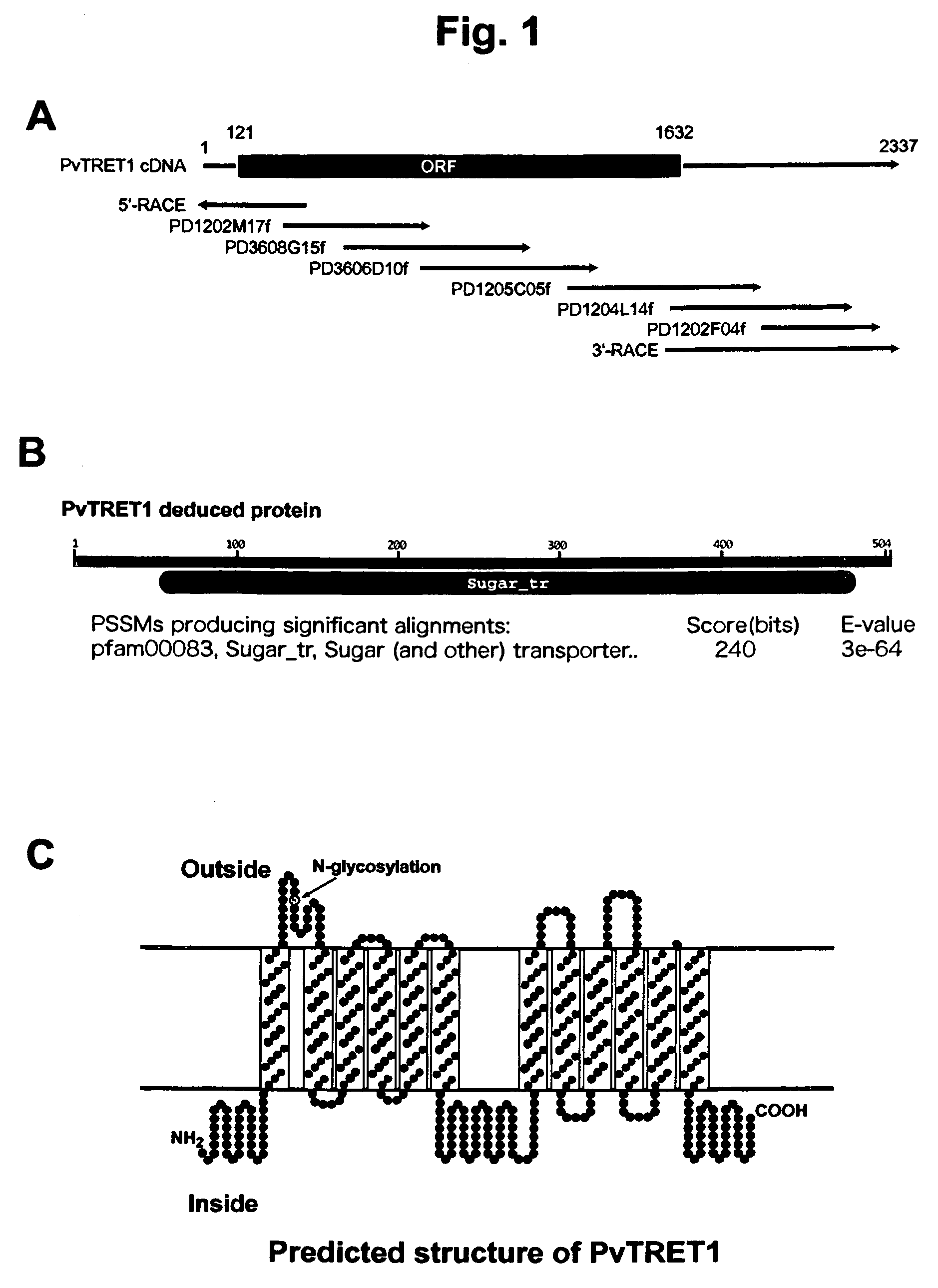
Trehalose transporter gene and method of introducing trehalose into cells
InactiveUS20090111176A1Allows trehalose uptake easily into cellsSugar derivativesArtificial cell constructsConcentration gradientMembrane potential
There are provided trehalose transporter gene and a method of introducing trehalose into cells by using the gene. Candidates for the trehalose transporter genes were searched in P. vanderplanki EST, resulting in being obtained cDNA designated as Tret1. Tret1 encodes a 504 amino acid protein with 12 trans-membrane structures. Tret1 expression was induced by desiccation stress and predominant in the fat body. Functional expression of TRET1 in Xenopus oocytes showed that transport activity was specific for trehalose and independent of extracellular pH and electrochemical membrane potential. The direction of transport of TRET1 was reversible depending on the concentration gradient of trehalose. Apparent Km and Vmax of TRET1 for trehalose were extraordinarily high values. These results indicate that TRET1 is a facilitated, high-capacity trehalose-specific transporter. Tret1 is widespread in insects. Furthermore, TRET1 conferred trehalose permeability upon cells including those of vertebrates as well as insects.
Owner:KIKAWADA TAKAHIRO +5
Antibiotic Resistance Conferrred by a Plant Abc Transporter Gene when Expressed in Transgenic Plants
InactiveUS20080250527A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesAntibiotic resistanceArabidopsis thaliana
The use of selectable marker genes, such as the kanamycin resistance encoding neomycin phosphotransferase (nptII), has been invaluable in transgenic plant production. The subject invention provides a new selectable marker gene, an Arabidopsis thaliana ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter, Atwbc19 and methods of using the gene for the identification of transgenic plants. Since ABC transporters are endogenous to plants, there should be less controversy using Atwbc19, as a selectable marker in transgenic plants with regards to concerns of horizontal gene transfer.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Microorganism over-expressing lactic acid transporter gene and having inhibitory pathway of lactic acid degradation, and method of producing lactic acid using the microorganism
A recombinant microorganism comprising a lactic acid (LA) transporter, wherein the expression of the LA transporter in the recombinant microorganism is increased relative to a parent microorganism, and a method of producing lactic acid using same.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Engineering bacterium, and application thereof in production of caffeic acid
ActiveCN108949652AEasy to produceRaw materials are easy to getCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaL-Lactate dehydrogenaseCaffeic acid
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium, and an application thereof in the production of caffeic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The engineering bacterium providedby the invention is a recombinant bacterium capable of producing caffeic acid at a low cost; the recombinant bacterium can simultaneously express four enzymes which are tyrosine phenol lyase, tyrosine ammonia lyase, L-lactate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase respectively; and the recombinant bacterium knocks out a phenolic substance-decomposing gene, and can achieve enhanced expression of any one or more of a lactic acid transporter gene, a catechol transporter gene and a coenzyme synthesis-related gene. The engineering bacterium has the advantages of realization of the efficient production ofcaffeic acid, simple process, few impurities and great industrial application values.
Owner:卓虹超源生物科技(郑州)有限公司
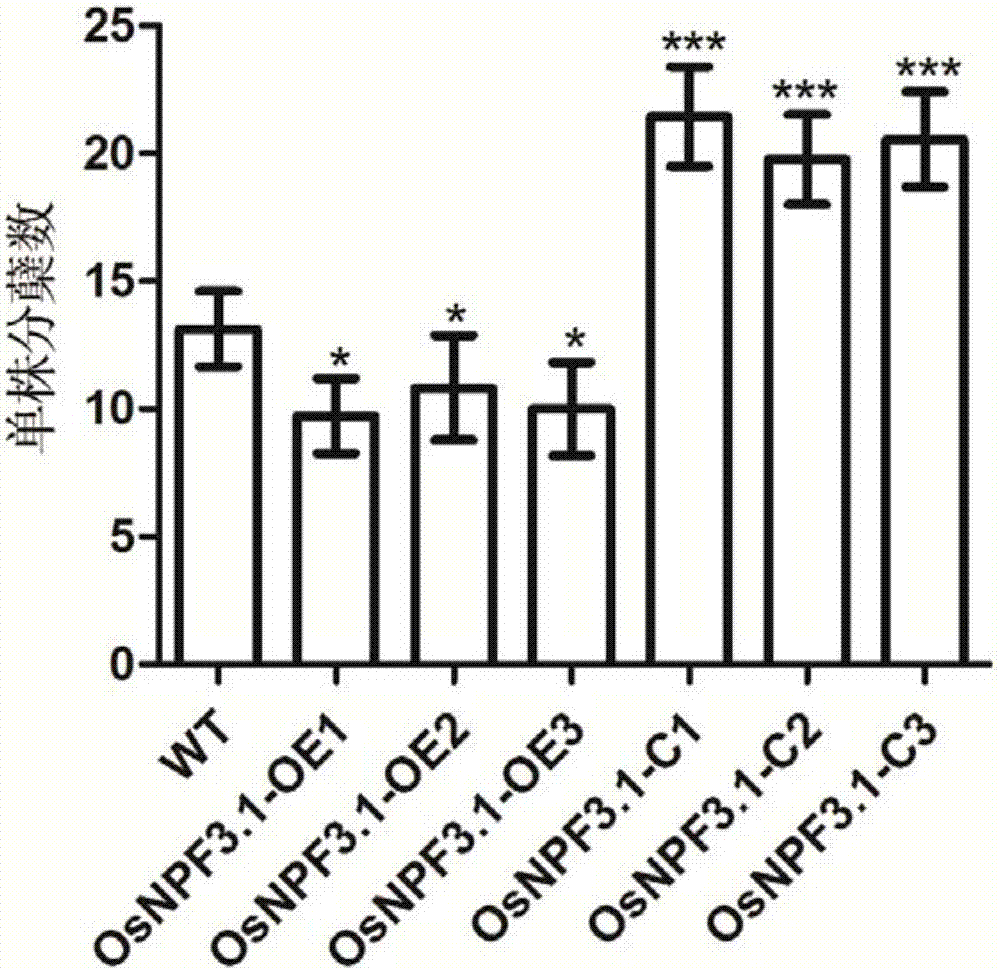
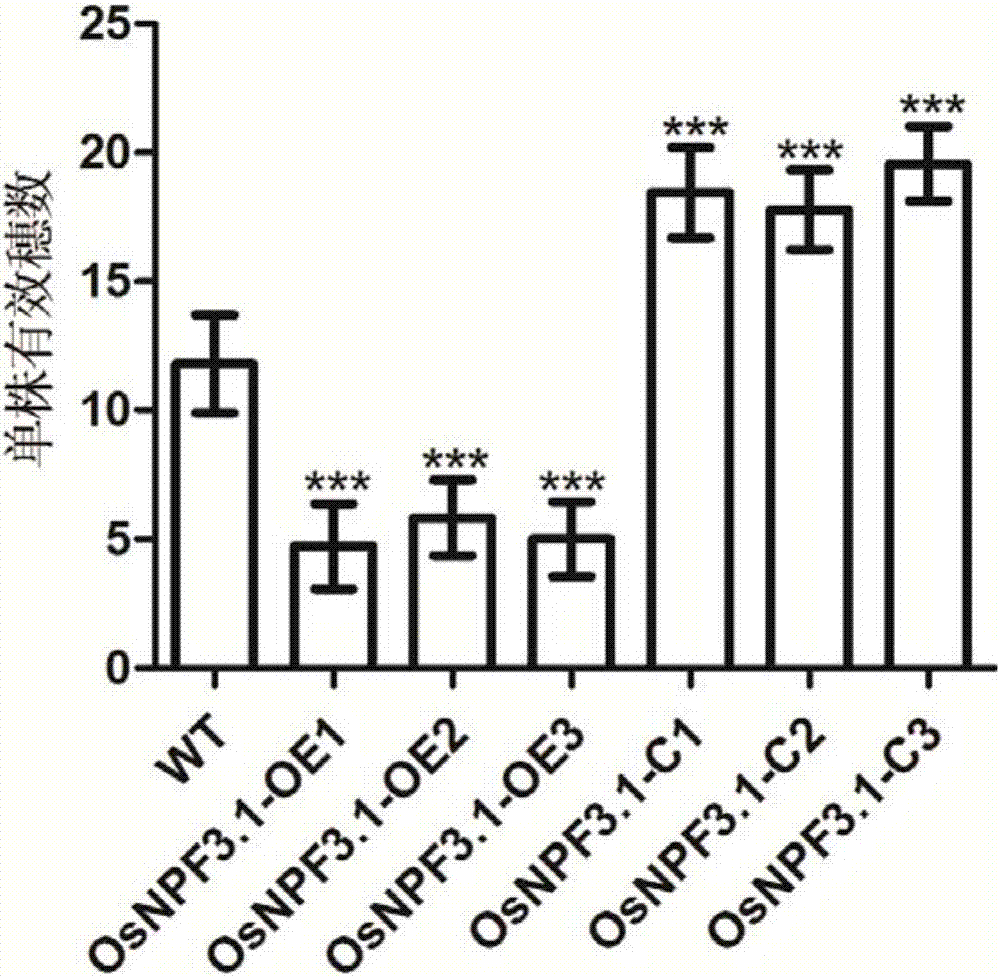
Application of gibberellin transporter gene OsNPF3.1 in increasing paddy rice output
ActiveCN107987140ADecreased tillering abilityIncrease productionPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringPlant genetic engineeringGibberellin
The invention discloses an application of a gibberellin transporter gene OsNPF3.1 in increasing the paddy rice output, and belongs to the field of plant gene engineering. The amino acid sequence of OsNPF3.1 coded protein is represented by SEQ ID No.1, and the cDNA sequence is represented by SEQ ID No.2. By constructing a paddy rice OsNPF3.1 gene over-expression plant and an OsNPF3.1 gene mutant plant, people find that by losing the expression of OsNPF3.1 gene, the tiller number and effective spike number of normal paddy rice are increased, filled grain number and output of a single plant are increased, and the output of a single paddy rice plant is reduced by increasing the expression of OsNPF3.1 gene. OsNPF3.1 gene can be used to increase the paddy rice yield. OsNPF3.1 gene has an important application value in aspects such as influence of nitrogen in plant growth, paddy rice plant type improvement, and the like.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF BIOENG
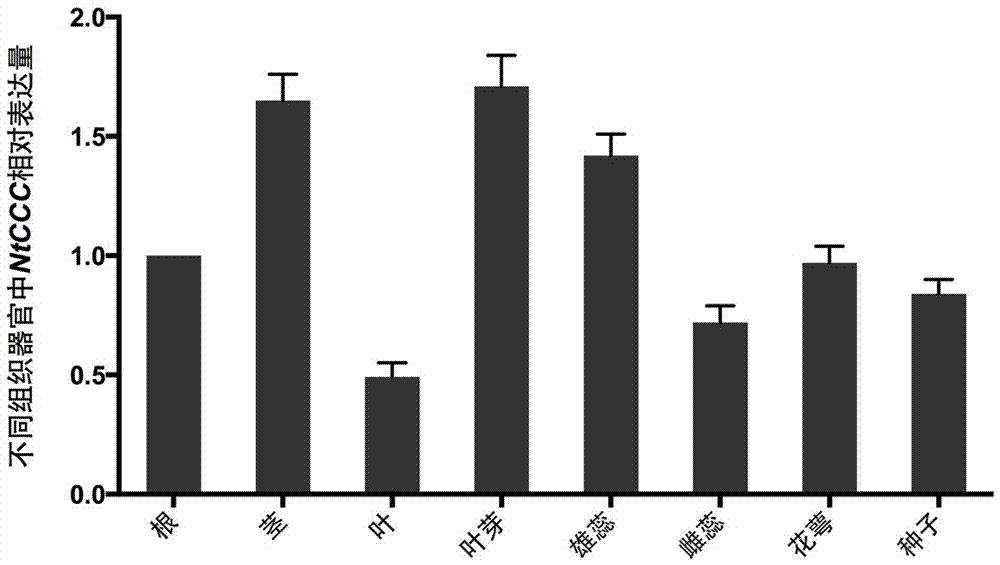
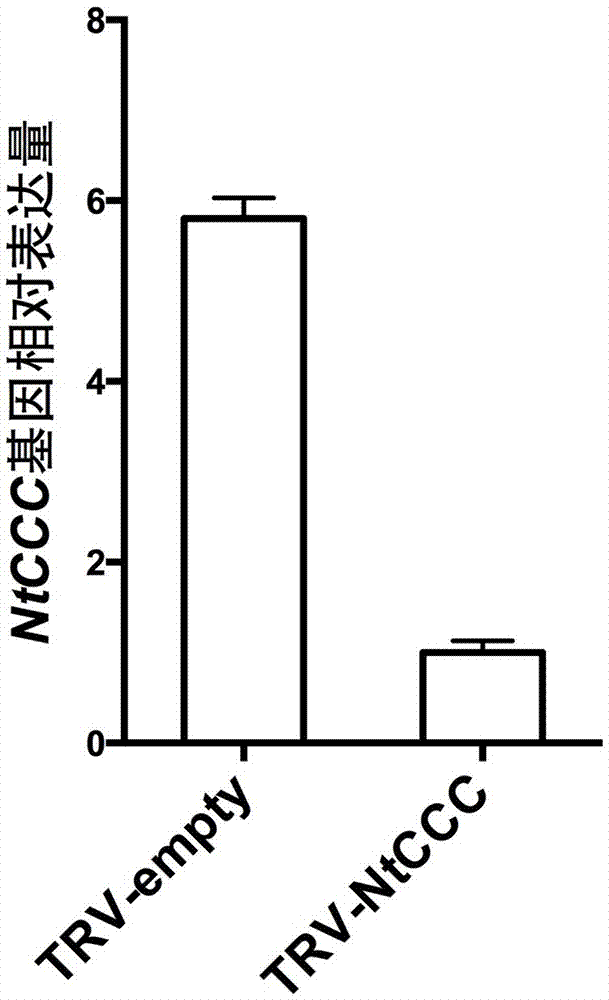
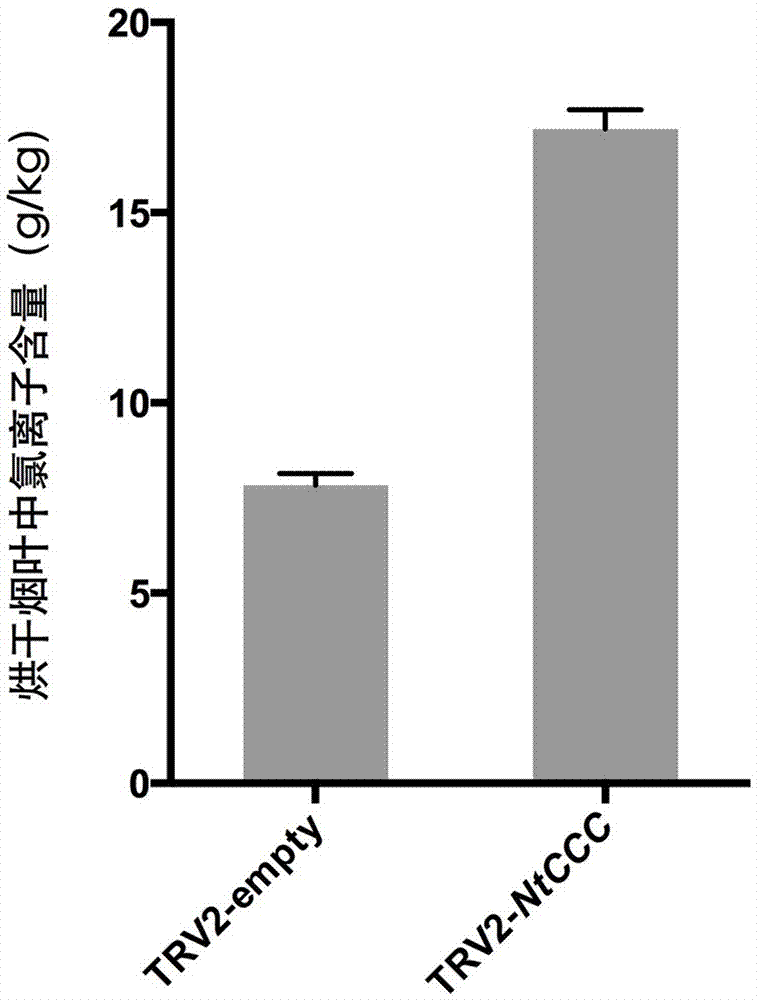
NtCCC (nicotiana tabacum cation/chloride cotransporter) and application thereof
The invention relates to nicotiana tabacum chloride transport related genes, in particular to an application of an NtCCC (nicotiana tabacum cation / chloride cotransporter) in improvement of saline-alkali soil. The contransporter is related to chloride transport and has a base sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, wherein nucleotides at 5-477 sites are specific nucleic acid fragments. The NtCCC is a key regulator in nicotiana tabacum chloride metabolism, is found to be expressed in all tissue of nicotiana tabacum through real-time PCR and has higher expression in stems and leafbuds of nicotiana tabacum. Gene silenced plants with increased chloride content can be obtained through VIGS (virus-induced gene silence) or NtCCC knockout, making breeding of the nicotiana tabacum with higher chloride content possible, and a new technological approach is provided for adaptation of the nicotiana tabacum to different planting environments and improvement of saline-alkali soil.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
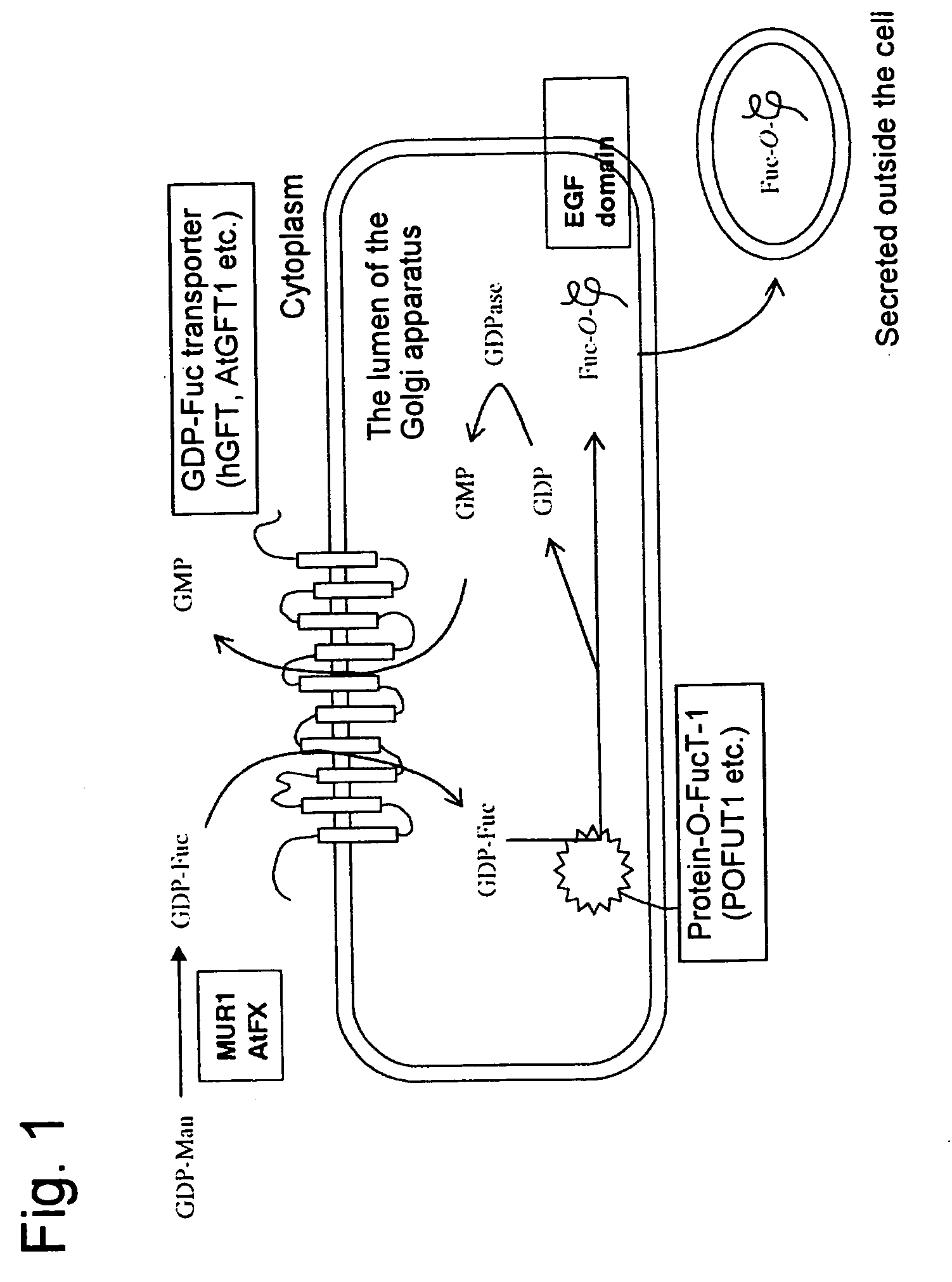
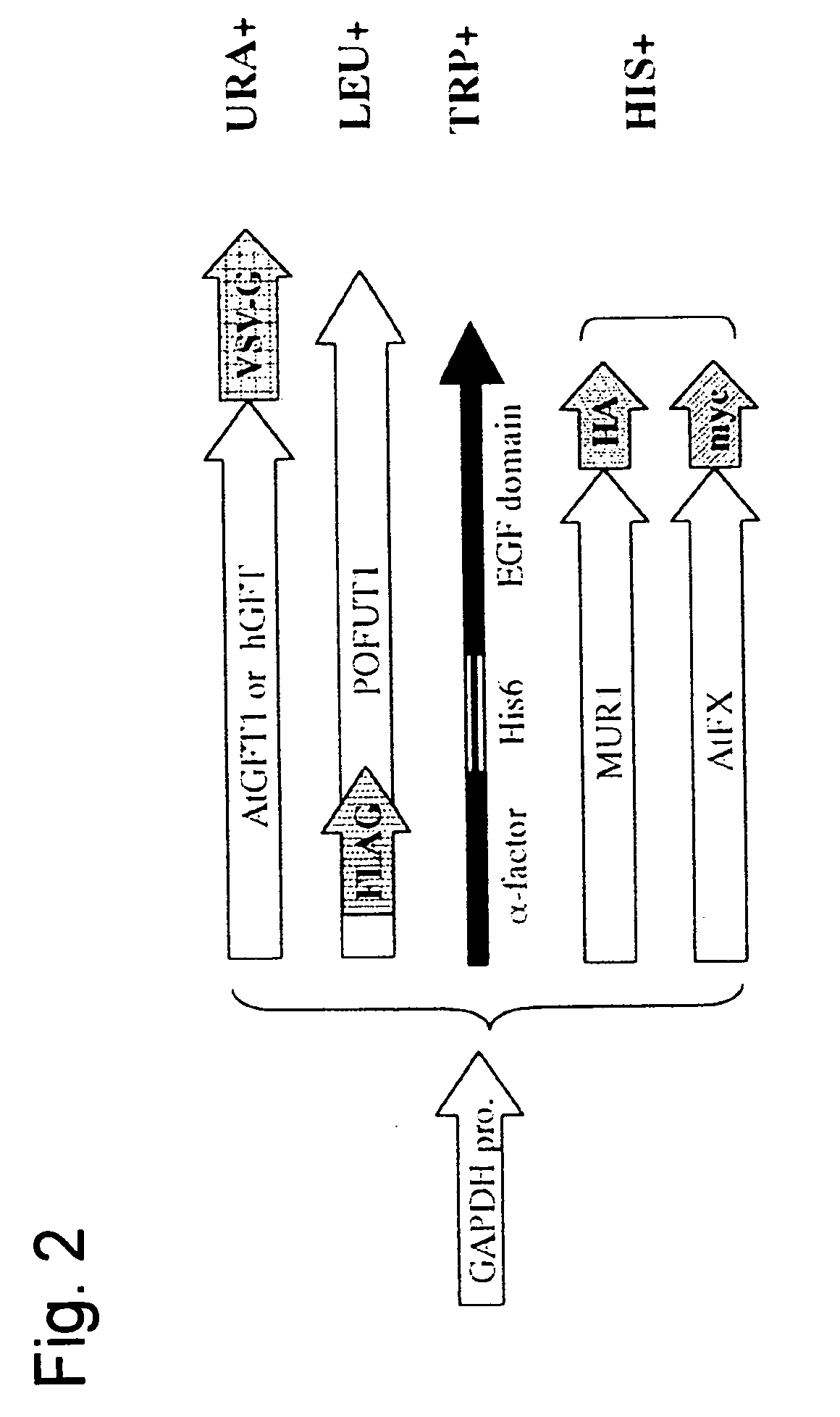
Yeast transformant into which genes associated with synthesis system of O-fucosylated protein are introduced
InactiveUS20060099680A1Efficient production of O-fucosylatedFungiSugar derivativesFucosylationEnzyme Gene
An object of the present invention is to provide a means for producing O-fucosylated protein in large quantities, a means for searching for new genes associated with the synthesis system of O-fucosylated protein or the proteins expressed by the genes, and a means for elucidating the functions thereof. According to the present invention, a yeast transformant characterized in that the genes associated with the synthesis system of O-fucosylated protein are a GDP-fucose synthase gene, a GDP-fucose transporter gene, a fucosyltransferase gene, and a fucose receptor gene is provided.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Kit and method for detecting genes related to individualized medication for depression
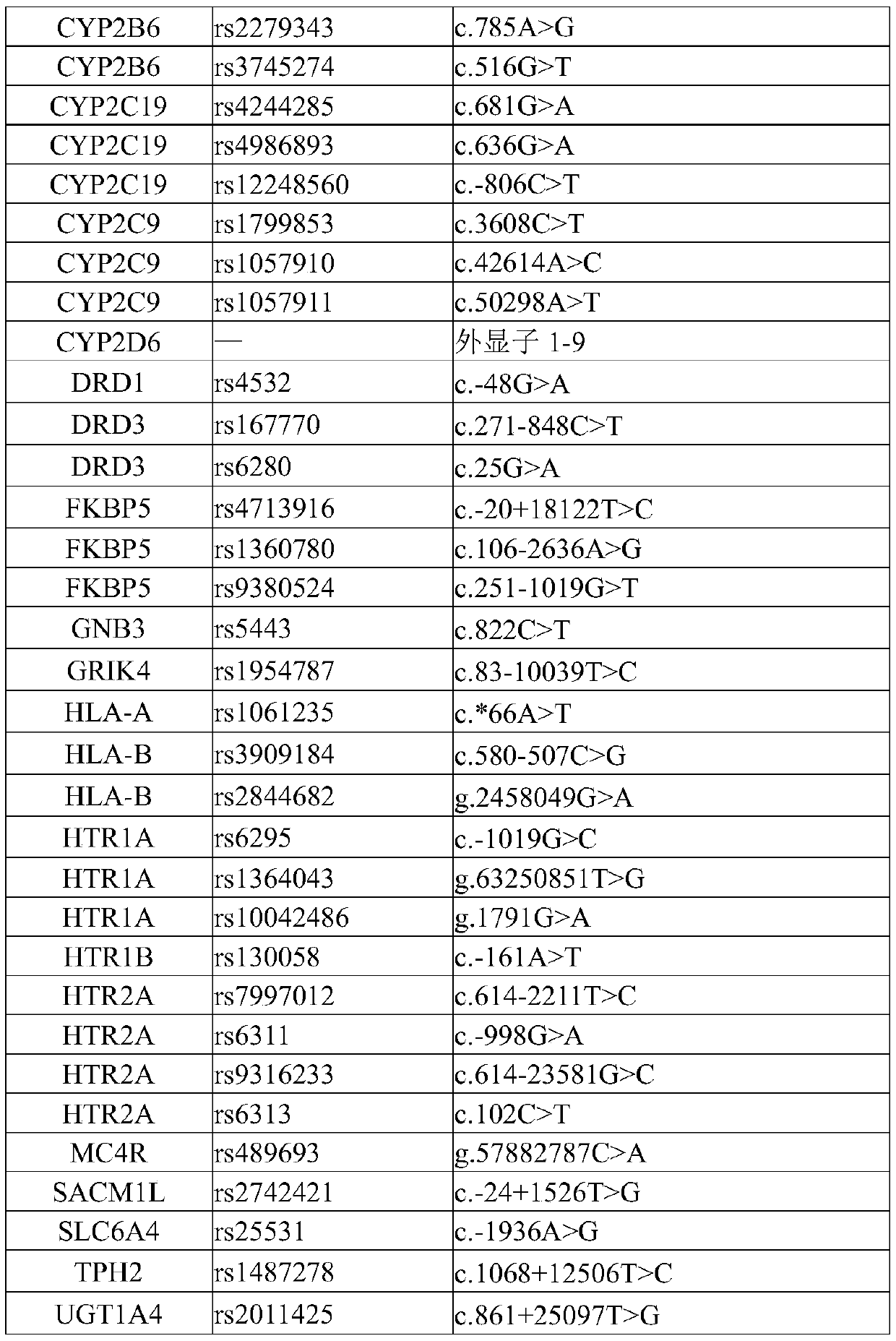
PendingCN110157793APredict efficacyPredictive reactivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDrug metabolismNucleotide
The invention discloses a primer group, a kit and a detection method for detecting genes related to individualized medication for depression. The primer group is selected from nucleotide sequences inSEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.154. The detection kit covers eight major categories of clinical first-line and second-line antidepressant efficacy-related genes, and relates to drug metabolism, target spots and transporter gene loci, and detection is conducted comprehensively and accurately. Accordingly, aiming at part of patients suffering from treatment-refractory depression, gene detection related to the therapeutic effect of antidepressant synergistic drugs is added, and powerful support is provided for selection of therapeutic schedules of the treatment-refractory depression.
Owner:广州海思医疗科技有限公司
Recombined corynebacterium glutamicum as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108085287ANo effect on growth rateHigh expressionBacteriaHydrolasesForeign proteinIon Channel Protein
The invention provides recombined corynebacterium glutamicum, can be used for effectively solving the technical problem that the conventional corynebacterium glutamicum is low in foreign protein expression quantity. The peptidoglycan endonucleases gene mepA, cytomembrane surface anion protein gene porB and endoproteinase gene clpC in the corynebacterium glutamicum are knocked out, meanwhile ACB transporter gene Ncg10909 are over expressed. Moreover the invention further provides a preparation method for the recombined corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com