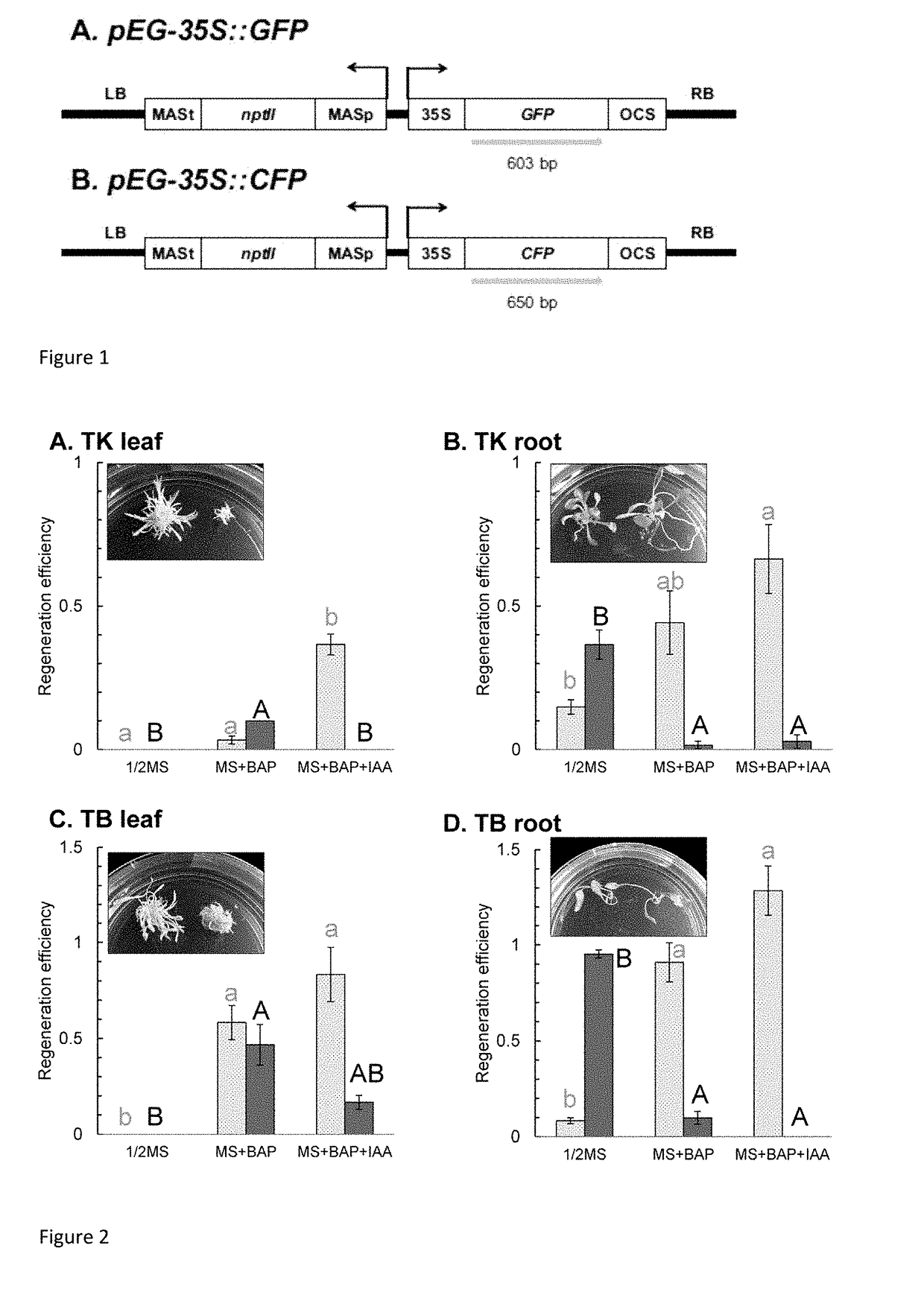
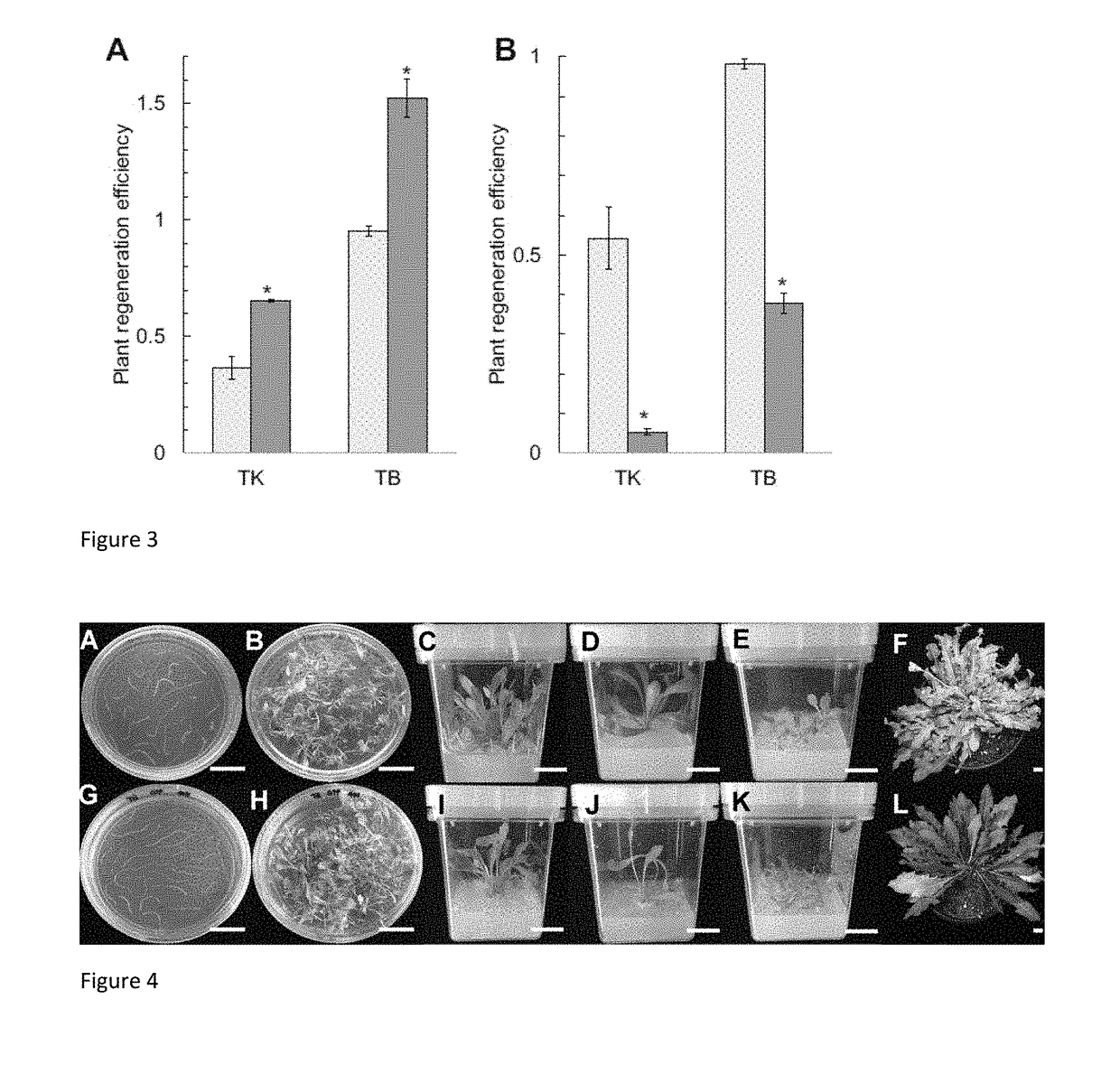
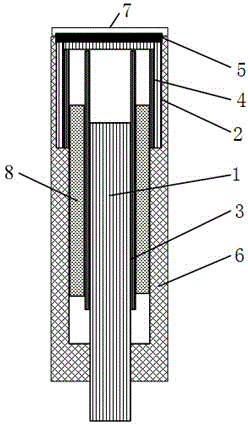
Patents
Literature
82 results about "Root cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for comprehensively verifying design rule checking runsets
InactiveUS6732338B2Extraction of informationComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer architectureDesign rule checking
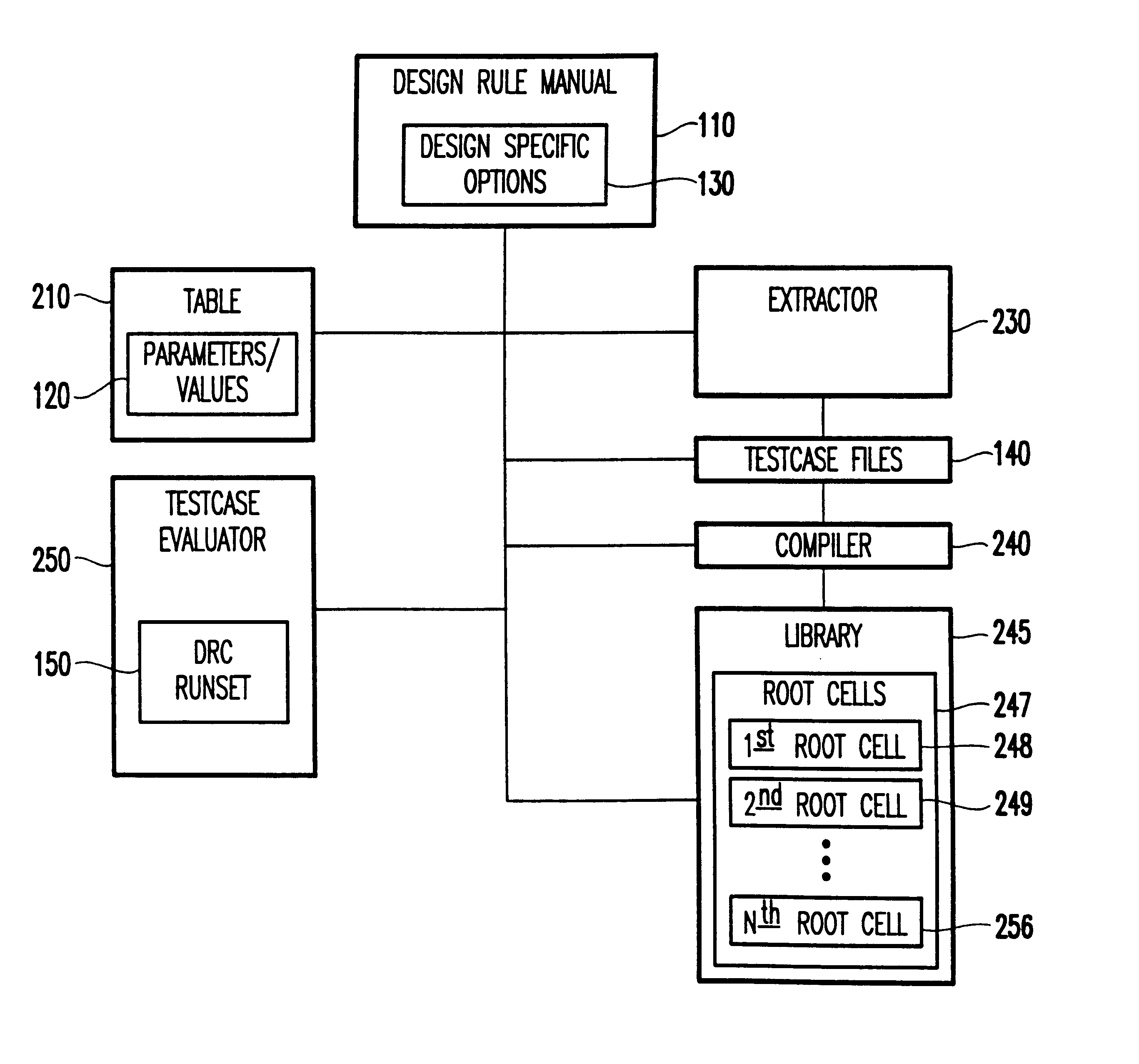
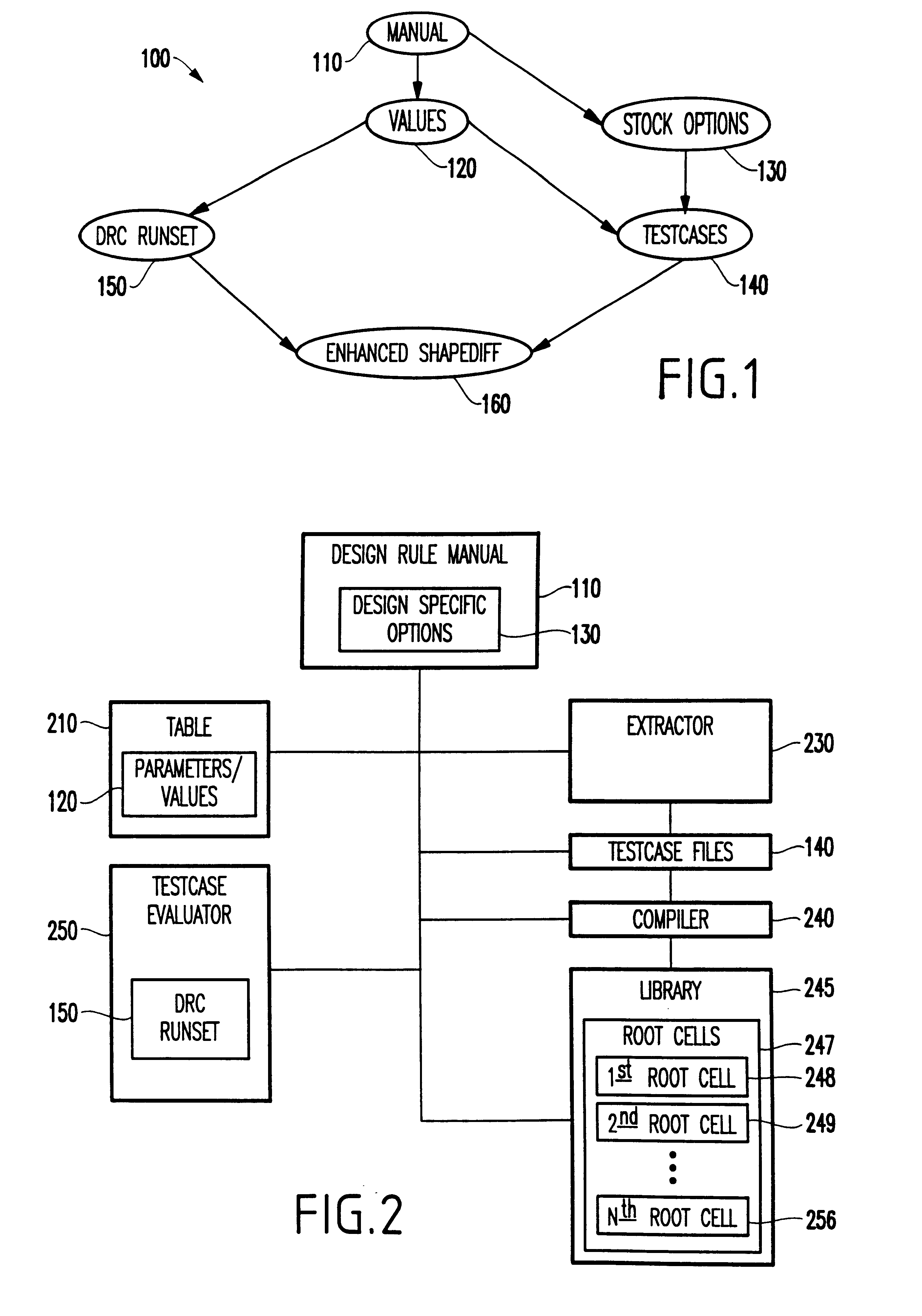
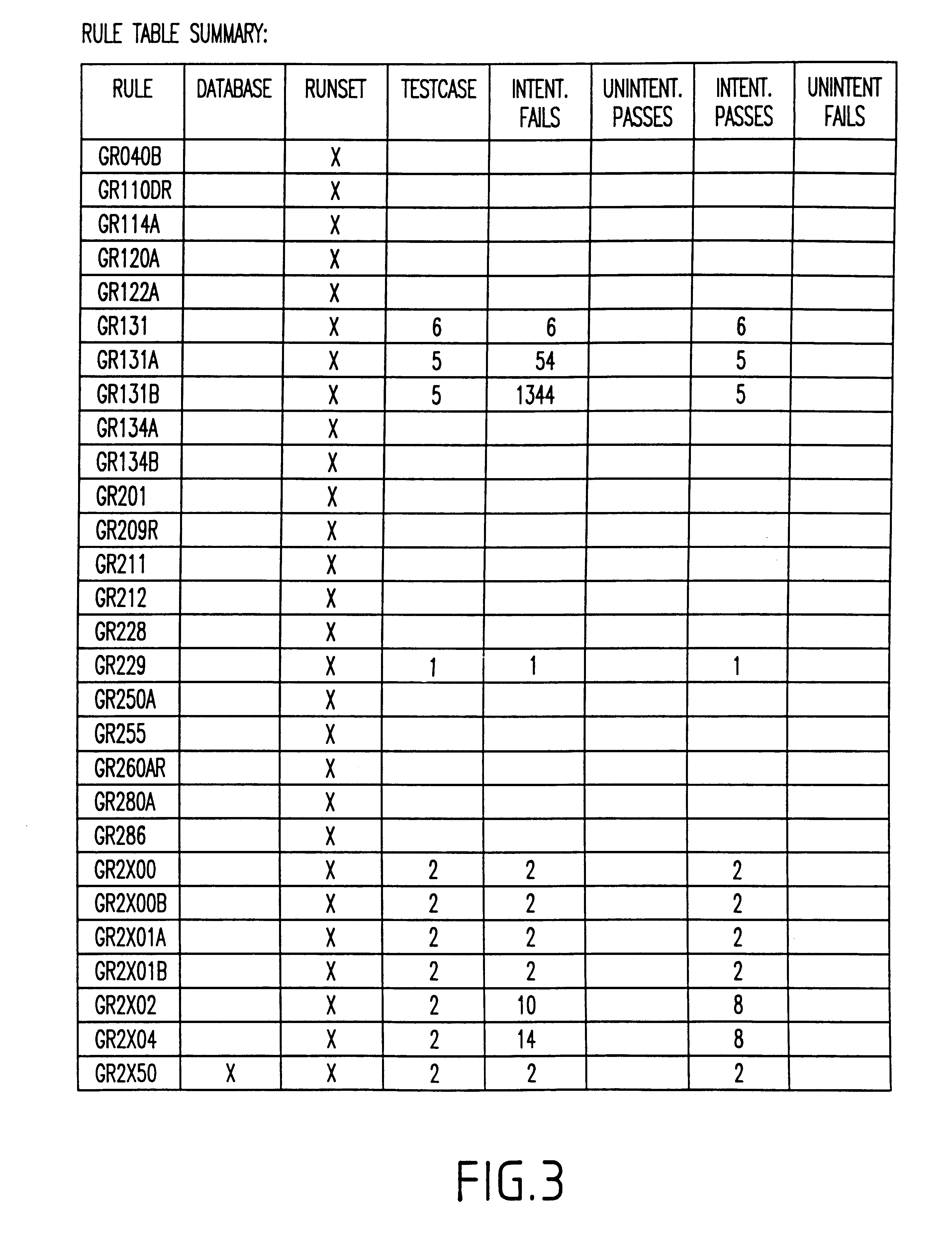
A system and method for automatically creating testcases for design rule checking comprises first creating a table with a design rule number, a description, and the values from a design rule manual. Next, any design specific options are derived that affect the flow of the design rule checking, including back end of the line stack options. Then, the design rule values and any design specific options (including back end of the line stack options) are extracted into testcases. Next, the testcases are organized such that there is one library with a plurality of root cells, further comprising one root cell for checking all rules pertaining to the front end of the line, and another root cell for checking design specific options including back end of the line stack options. Finally, the DRC runset is run against the testcases to determine if the DRC runset provides for design rule checking.
Owner:IBM CORP
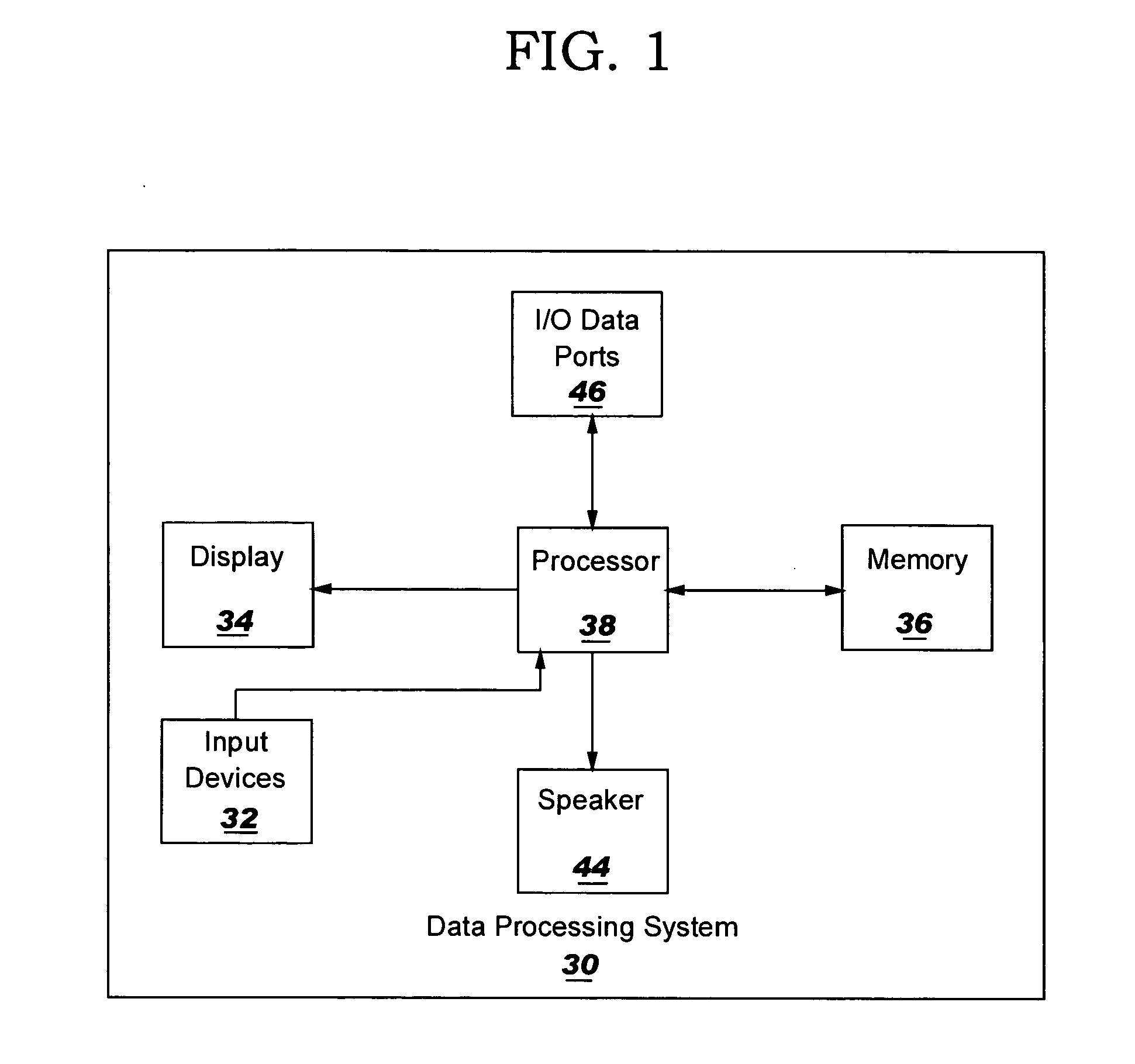
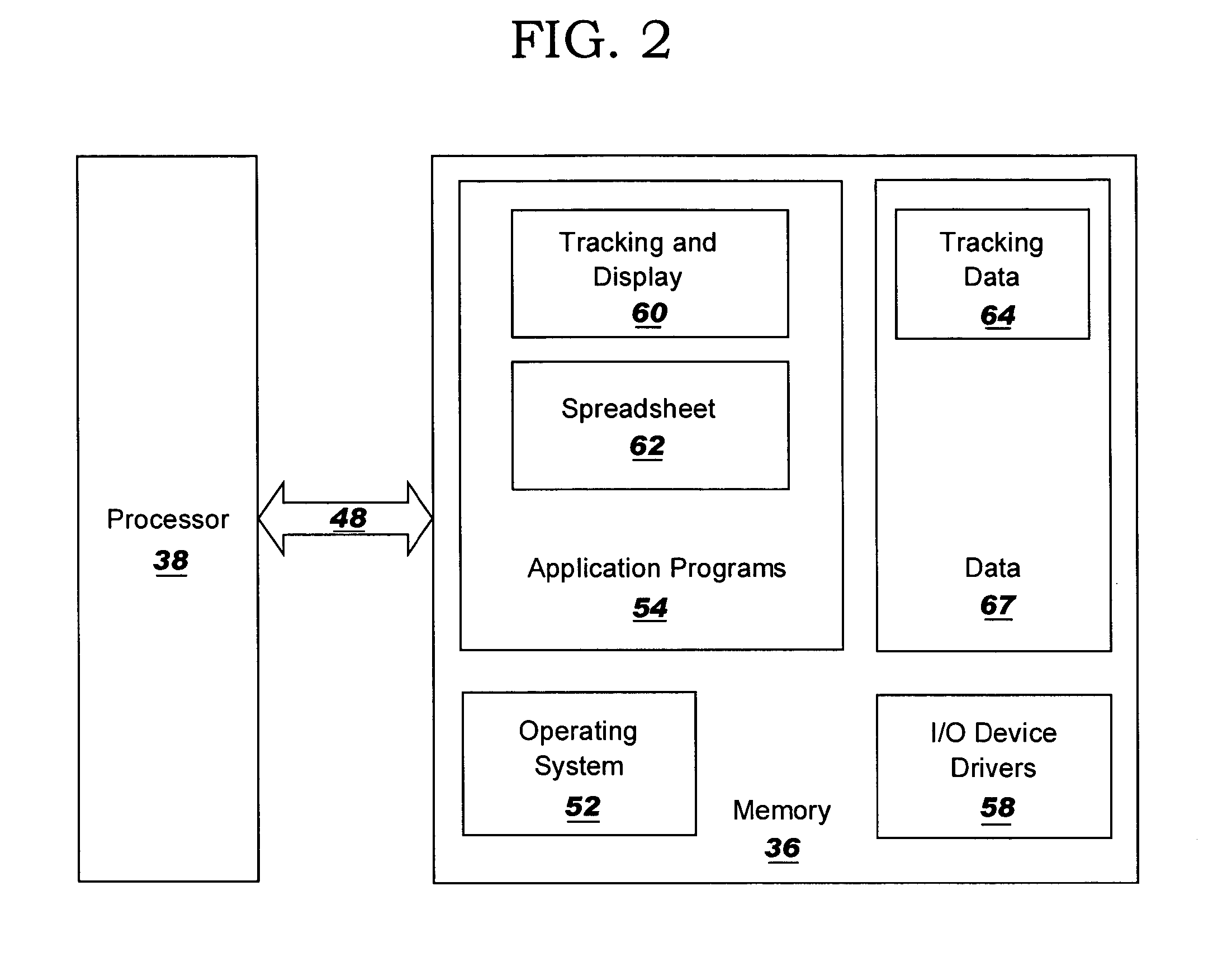
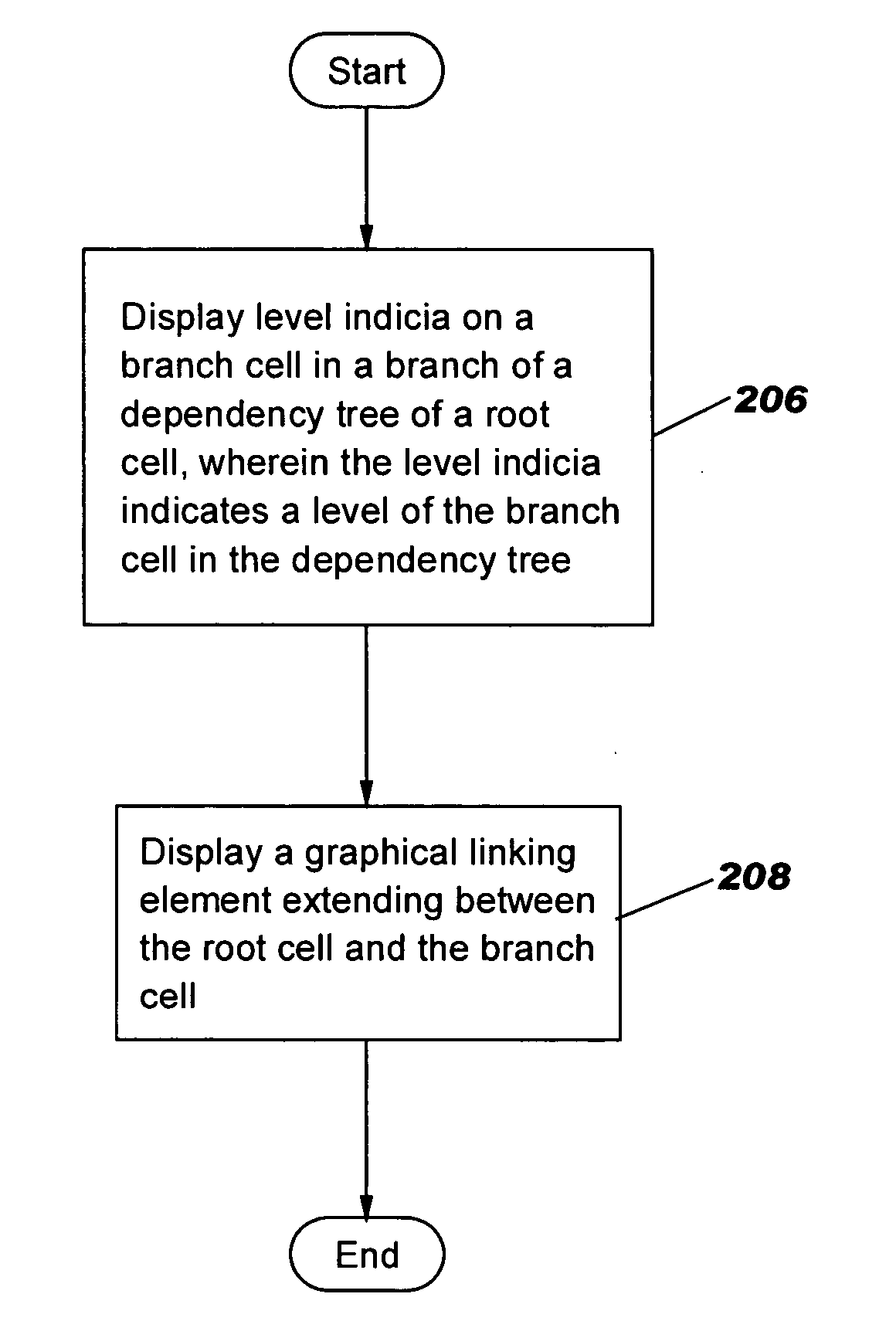
Methods, systems and computer program products for facilitating visualization of interrelationships in a spreadsheet
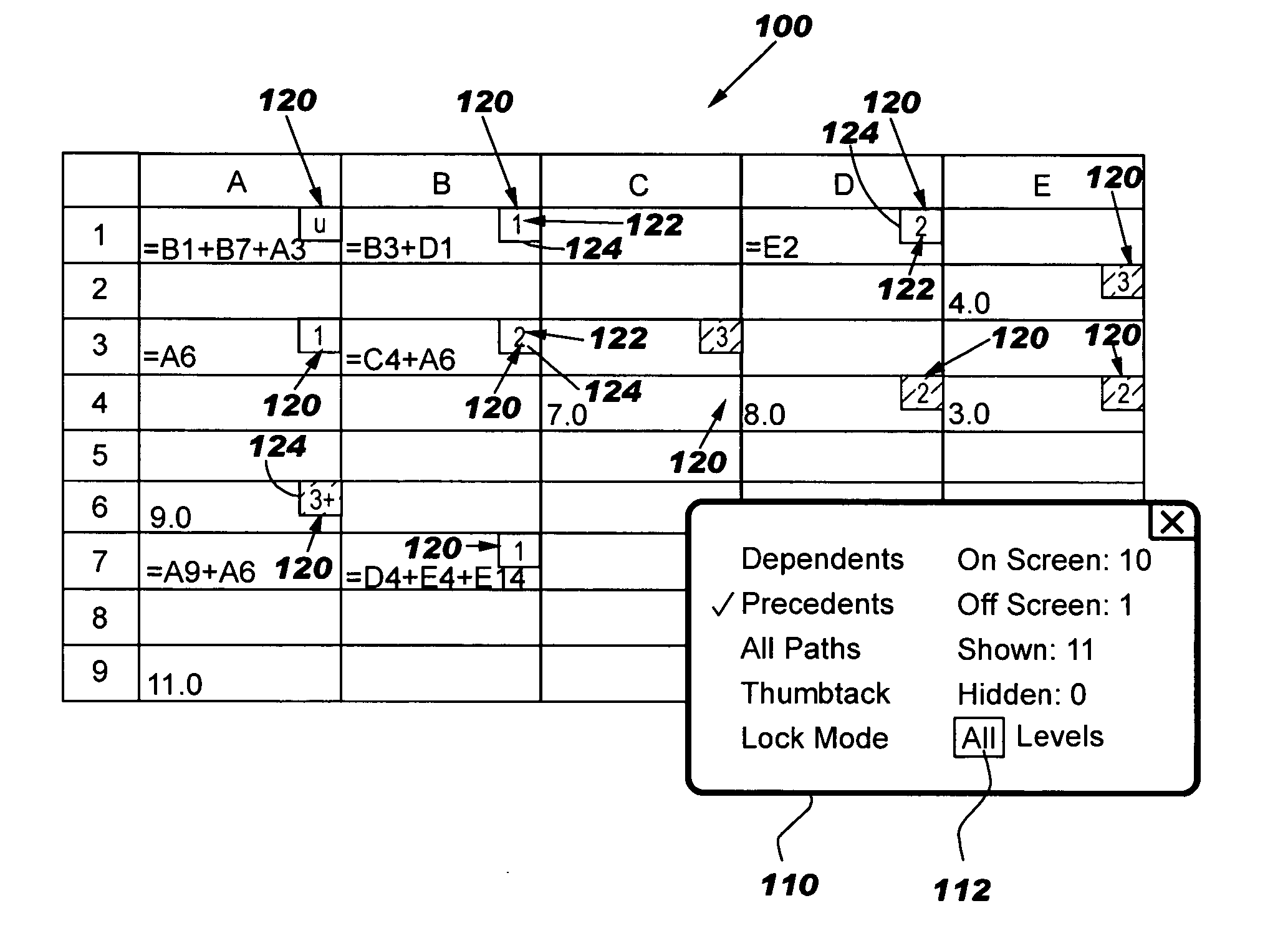
Methods, systems and computer program products are provided for visually indicating relationships among cells in a spreadsheet. Each of a first graphical linking element extending between cells in a first branch of a dependency tree of a root cell and a second graphical linking element extending between cells in a second branch of the dependency tree of the root cell is independently displayed and hidden.
Owner:IBM CORP
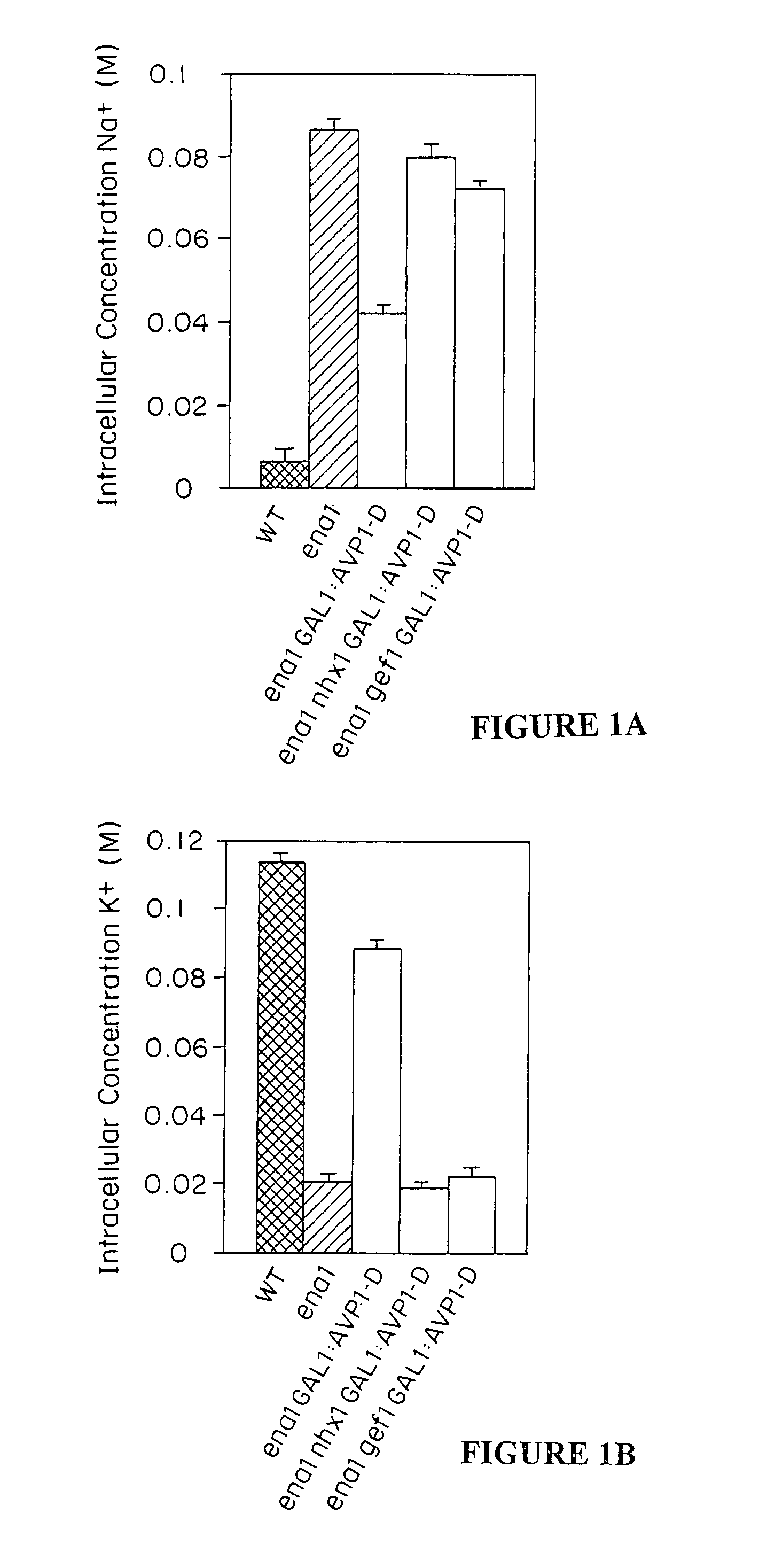
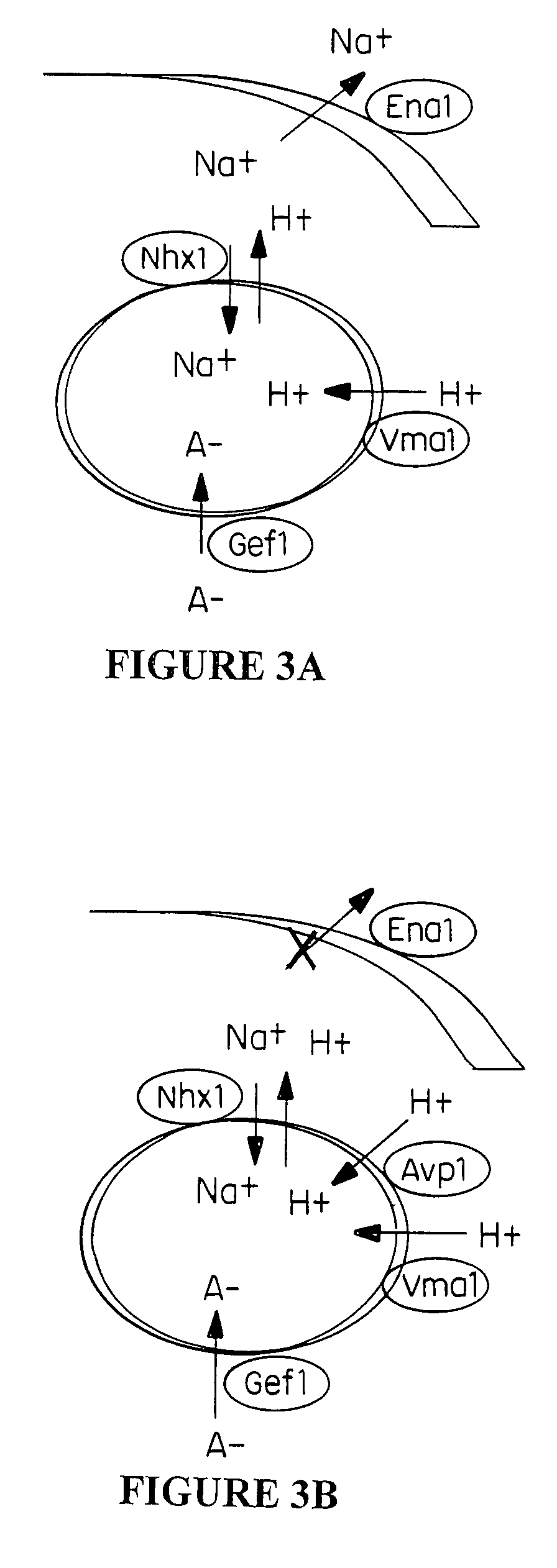
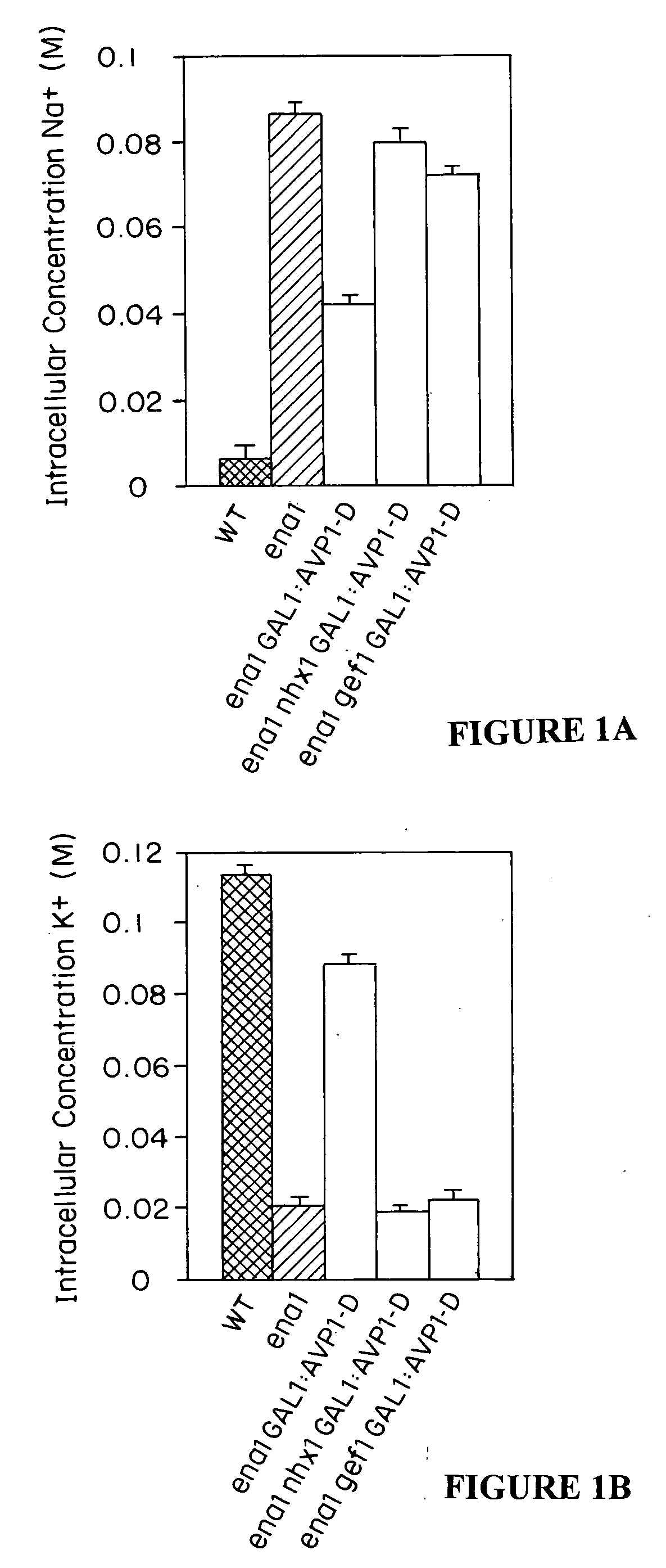
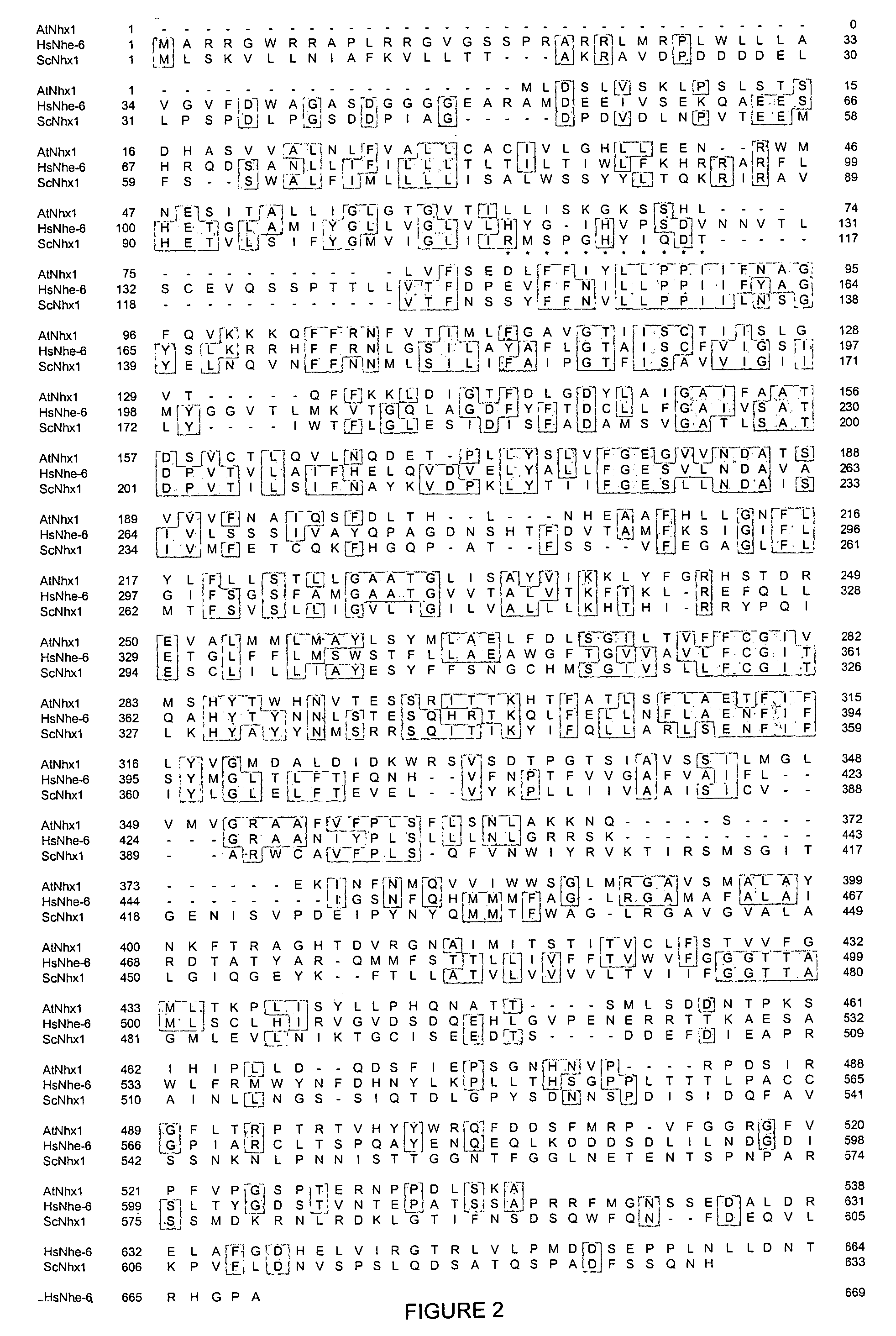
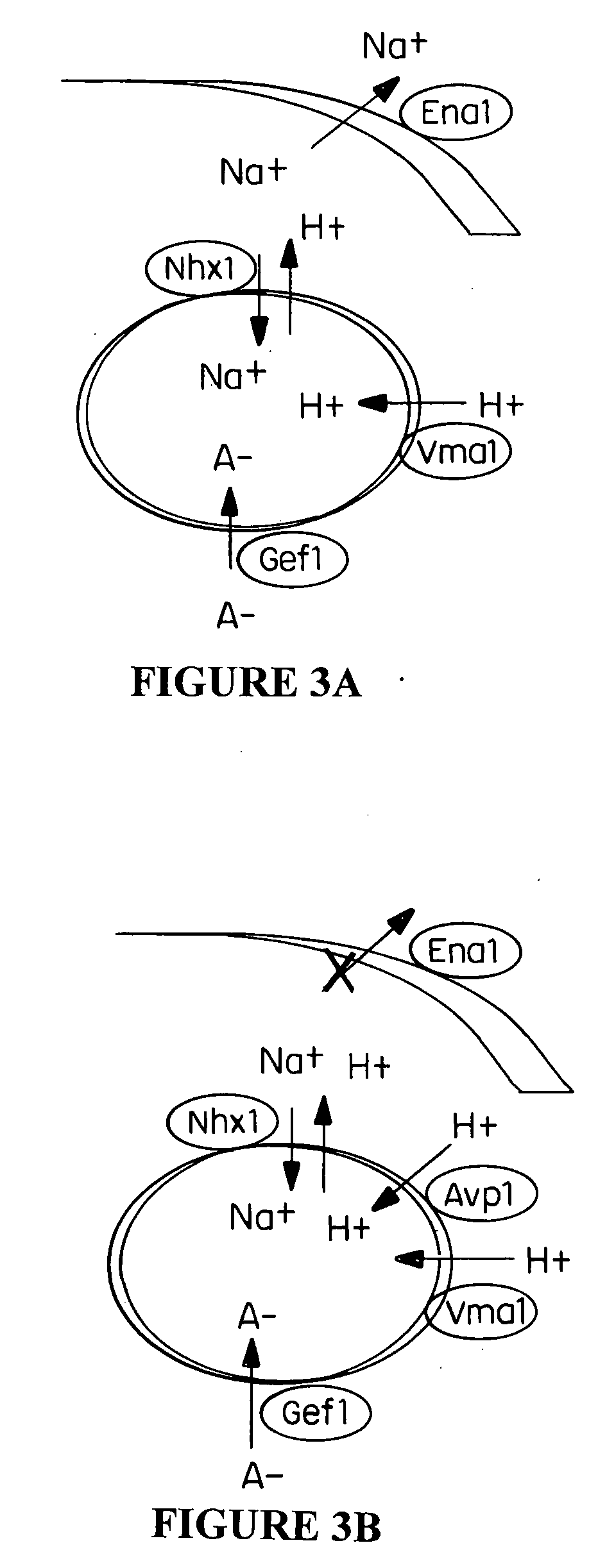
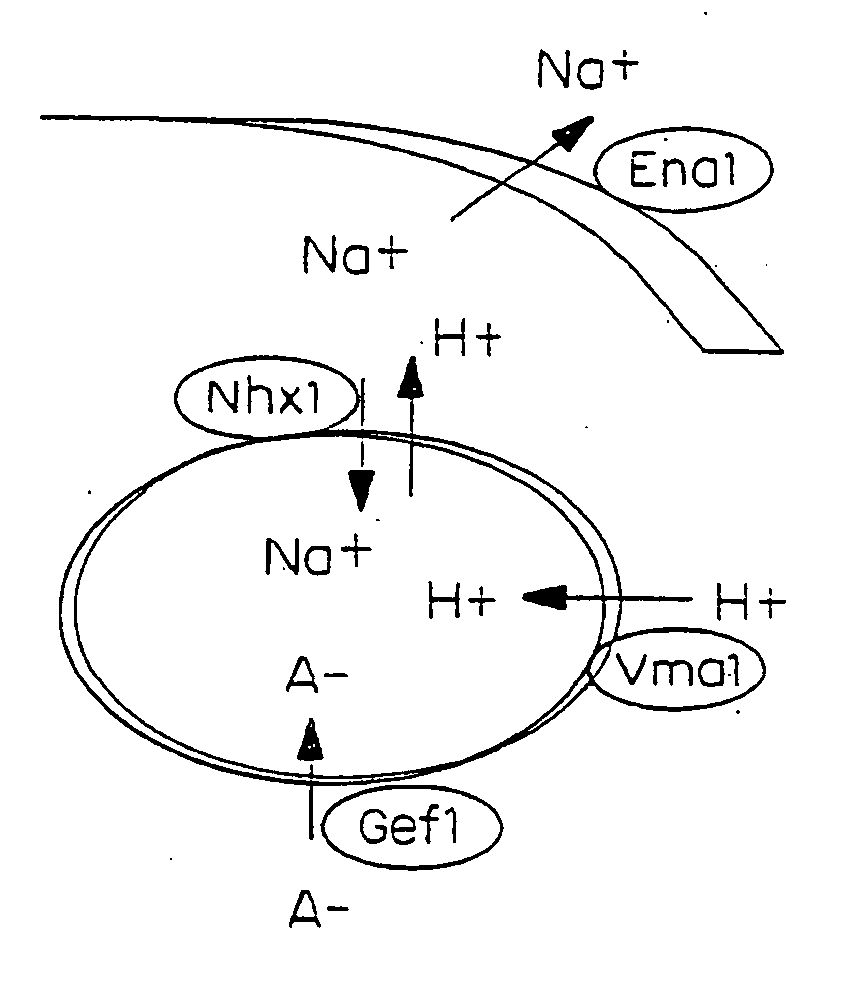
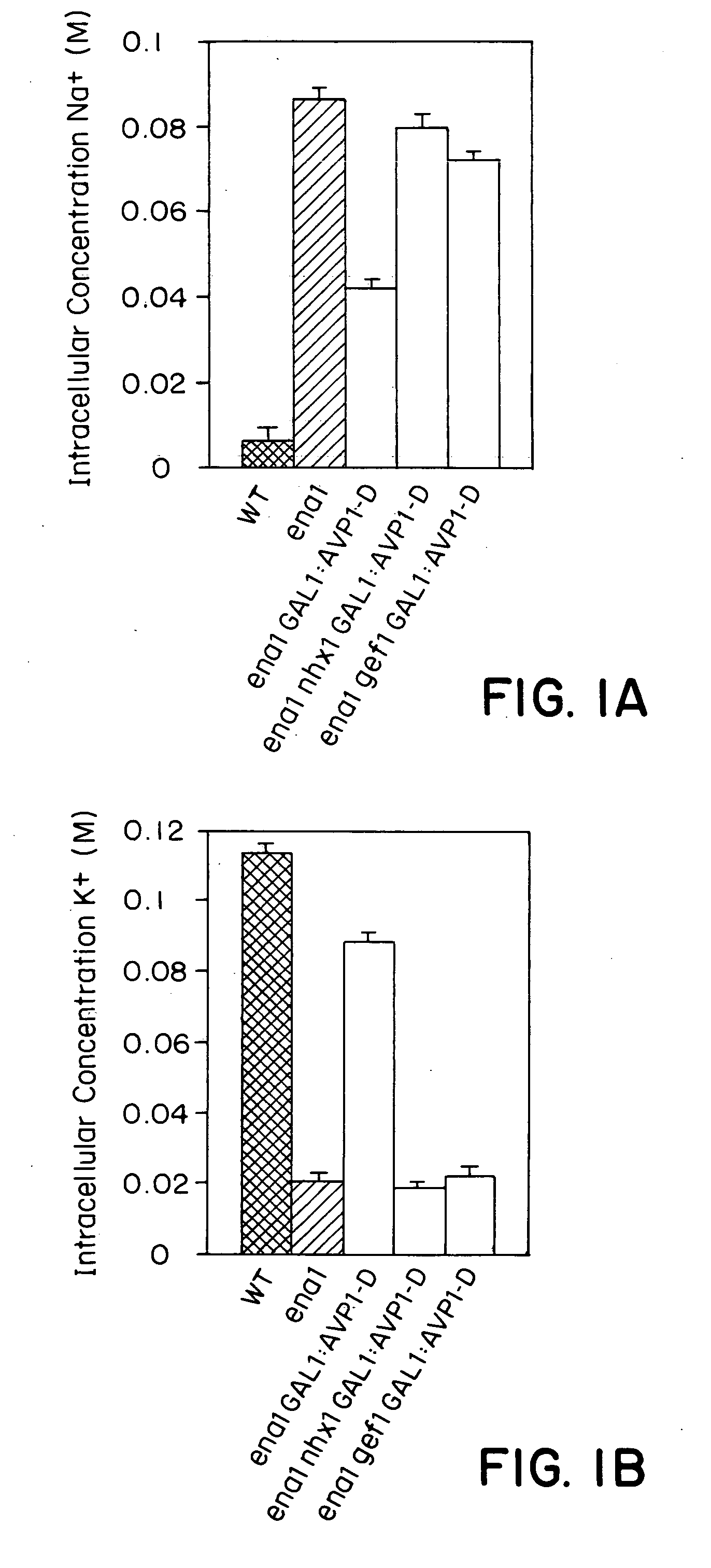
Plant cells and plants overexpressing vacuolar proton pyrophosphatases
InactiveUS8058515B2Increase planting yieldIncrease in sizeBryophytesClimate change adaptationHalotoleranceLeaf cell
The present invention relates to a transgenic plant, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which increases expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. Also encompassed by the present invention are transgenic progeny and seeds of the transgenic plants described herein. Progeny transgenic plants grown from seed are also described. Plant cells (e.g., root cells, stem cells, leaf cells) comprising exogenous nucleic acid which increases expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant cells are also the subject of the present invention. Also encompassed by the present invention are methods of making a transgenic plant described herein. The present invention also relates to a method of increasing the yield of a plant, a method of making a plant which is larger than its corresponding wild type plant, and a method of producing a transgenic plant with increased salt tolerance.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
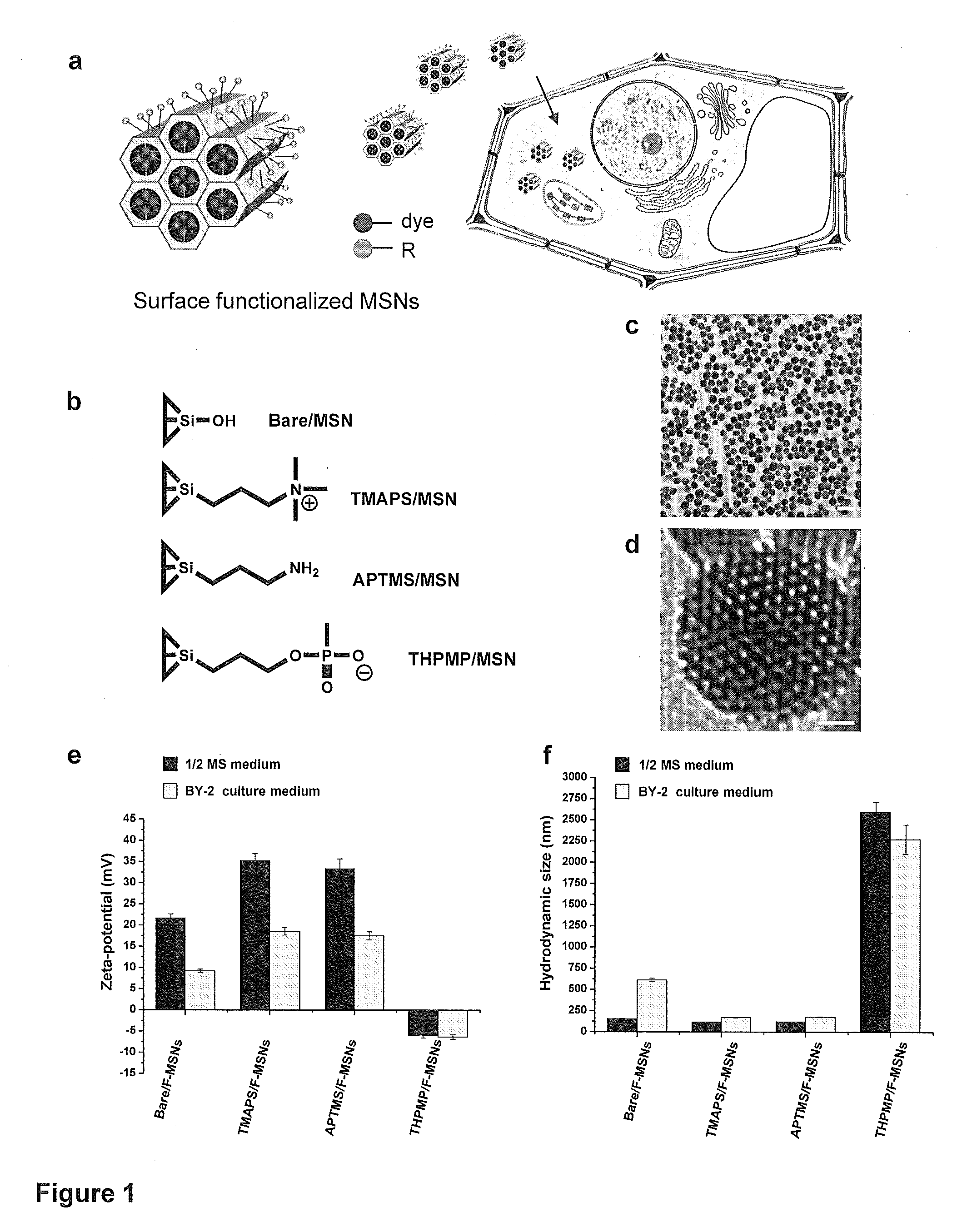
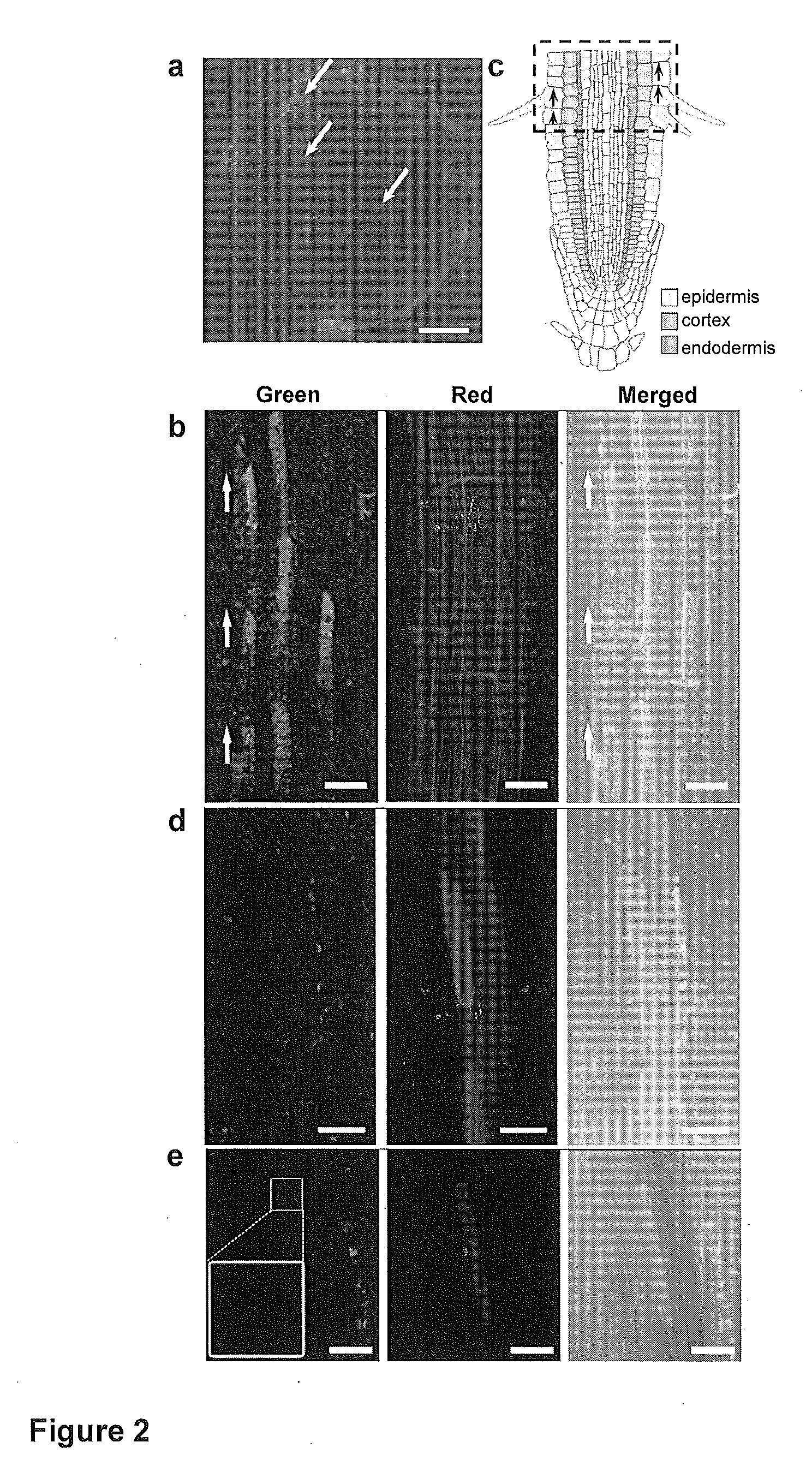
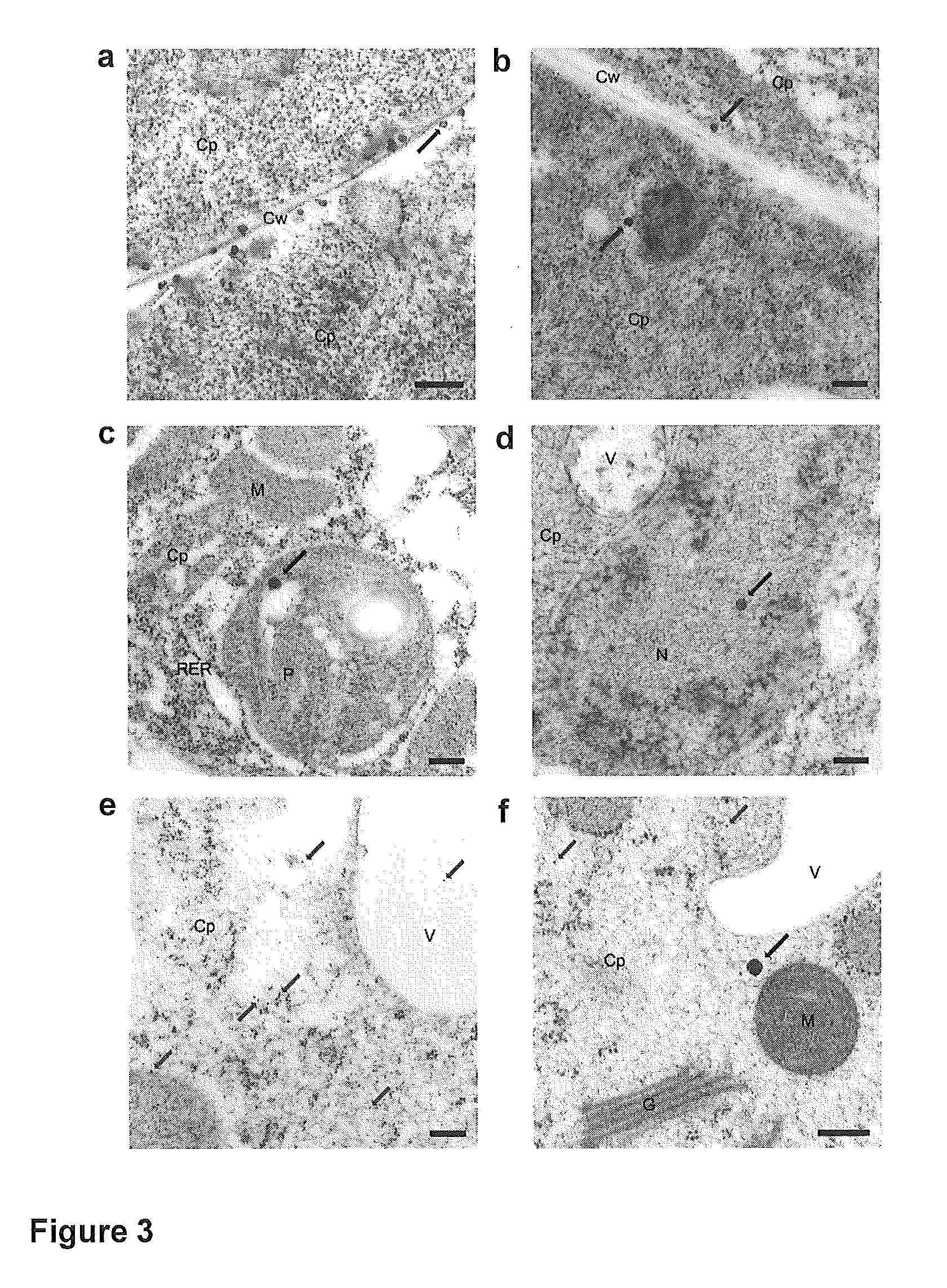
Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-mediated delivery of DNA into arabidopsis root
InactiveUS20130185823A1MicroorganismsOther foreign material introduction processesGerm layerGene delivery
Transient gene expression is a powerful tool for plant genomics studies. Recently, the use of nanomaterials has drawn great interest. Delivery with mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) has many advantages. We used surface-functionalized MSNs to deliver and express foreign DNA in Arabidopsis thaliana root cells without the aid of particle bombardment. Gene expression was detected in the epidermis layer and in the more inner cortex and endodermis root tissues. This method is superior to the conventional gene-gun method to deliver DNA, which delivers the gene to the epidermis layer only. Less DNA is needed for the MSN method. Our system is the first use of nanoparticles to deliver DNA to plants with good efficiency and without external aids. MSNs, with multifunctionality and the capability of cargo delivery to plant cells as we demonstrated, provide a versatile system for biomolecule delivery, organelle targeting, and even agriculture, such as improved nutrient uptake.
Owner:ACAD SINIC +1
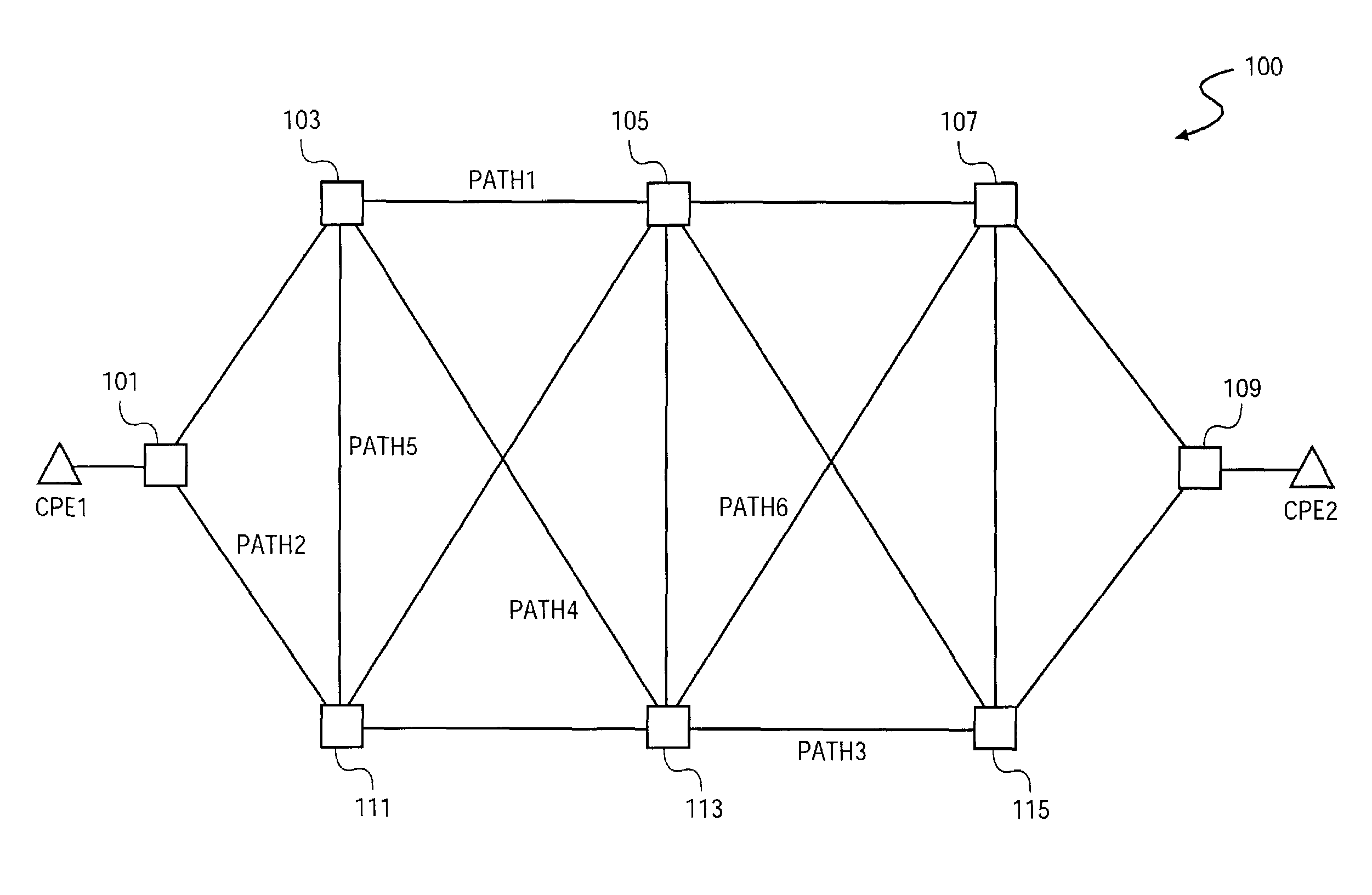
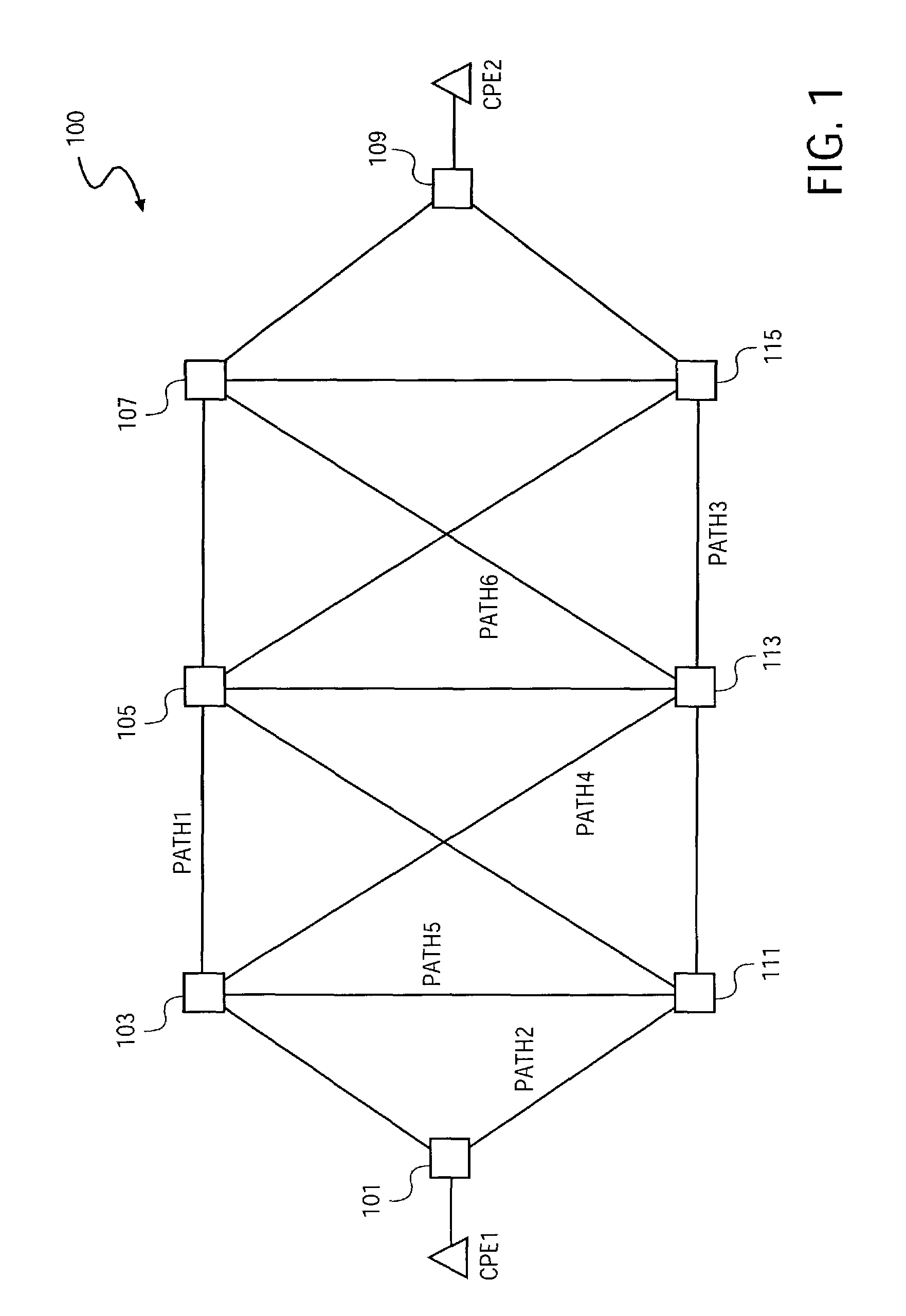
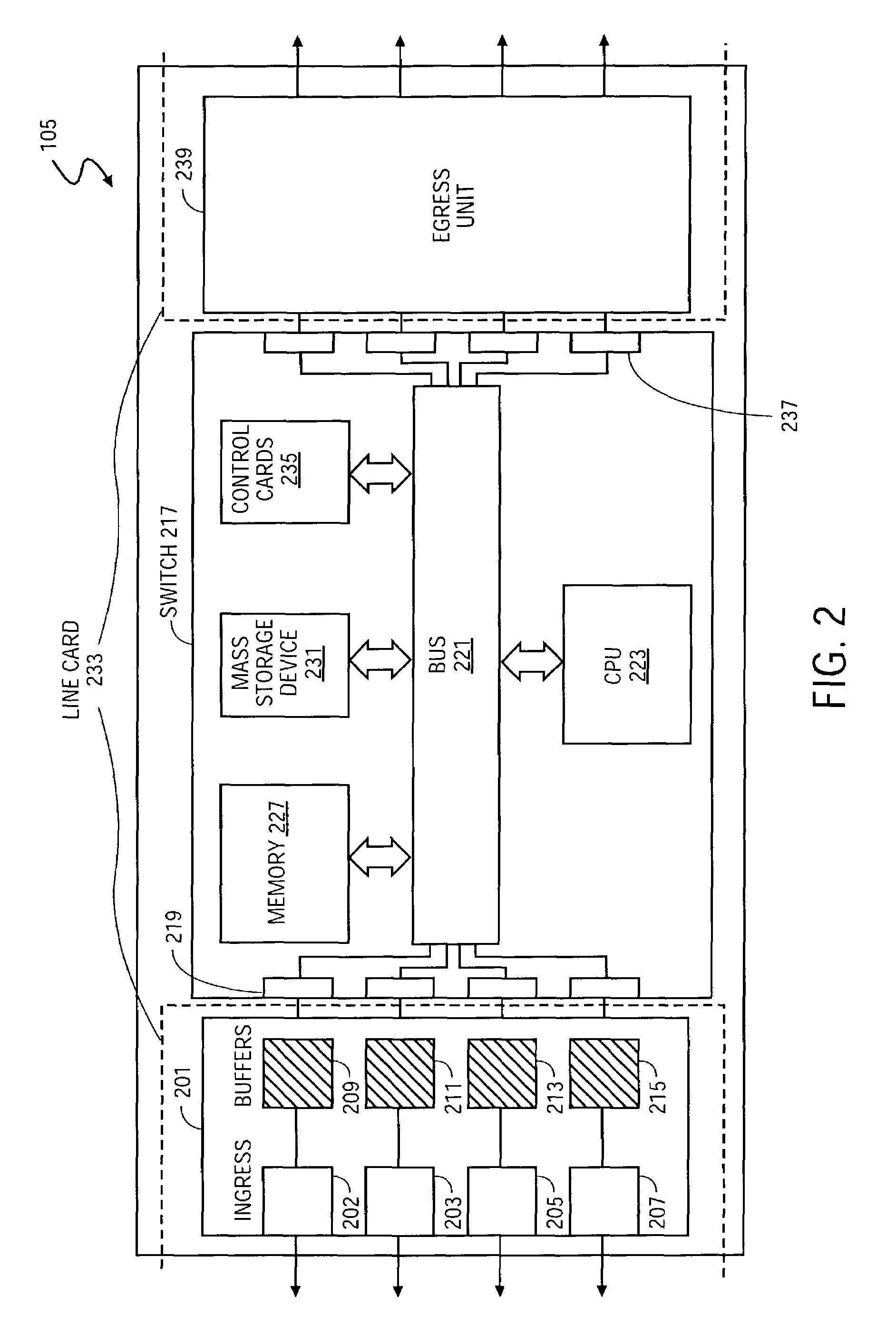
System and method to multicast guaranteed and best-effort traffic in a communications network
InactiveUS7450503B1Special service provision for substationError preventionTraffic capacityClass of service
A system and method to multicast guaranteed and best-effort traffic in a communications network are disclosed. According to one embodiment, incoming traffic is separated into unicast traffic and multicast traffic. Each root cell of the multicast traffic is classified based on multiple corresponding classes of service. Each root cell is then stored into a root cell buffer of multiple root cell buffers within an egress memory, each root cell buffer being associated with a corresponding class of service. According to one embodiment, each root cell is retrieved from the corresponding root cell buffer within the egress memory according to the associated class of service. Each root cell is then stored in a corresponding replication queue of multiple replication queues based on its associated class of service, with predetermined replication parameters assigned to each replication queue. Each root cell is subsequently replicated according to one or more associated replication parameters to obtain multiple leaf cells for each replicated root cell. According to one embodiment, the unicast traffic is multiplexed with the replicated leaf cells of the multicast traffic to obtain egress arrival cells. Each egress arrival cell is then stored hierarchically into a queuing buffer of multiple queuing buffers within a queuing memory according to queuing parameters corresponding to each egress arrival cell.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods, systems and computer program products for facilitating visualization of interrelationships in a spreadsheet
InactiveUS8745483B2Text processingSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsTheoretical computer science
Methods, systems and computer program products are provided for visually indicating relationships among cells in a spreadsheet. Each of a first graphical linking element extending between cells in a first branch of a dependency tree of a root cell and a second graphical linking element extending between cells in a second branch of the dependency tree of the root cell is independently displayed and hidden.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for clonal expression in plants
ActiveUS20060085871A1Reduce cell concentrationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant cellGene product
The present invention provides systems and methods for generating clonal root lines, clonal root cell lines, clonal plant cell lines, and clonal plants and for expressing gene products in such cell lines and plants. According to certain of the inventive methods, a viral vector containing a polynucleotide of interest operably linked to a promoter is introduced into a plant or portion thereof. Plant material (e.g., leaf portions) containing the viral vector are used to generate clonal root lines, e.g., by contacting them with A. rhizogenes so as to form hairy roots. The hairy roots are derived from single ancestral cells and are therefore clonal. These clonal root lines contain the viral vector and express the polynucleotide of interest. Clonal root cell lines, clonal plant cell lines, and clonal plants are obtained from the clonal roots. According to certain other inventive methods, a viral vector containing a polynucleotide of interest operably linked to a promoter is introduced into cells of a plant cell line (e.g., pre-existing or newly derived) that is maintained in culture. Clonal plant cell lines that express the polynucleotide of interest are obtained, e.g., by successive rounds of enrichment until a population of cells exhibiting stable expression is obtained. Clonal plants whose cells contain the viral vector are obtained from the clonal plant cell lines using standard methods. The invention provides clonal root lines, clonal root cell lines, clonal plant cell lines, and clonal plants generated using the inventive methods.
Owner:IBIO
Method for preparing nano-level notoginseng root powder
InactiveCN102085224AImprove broken rateReduce lossesPowder deliveryAntipyreticMetallurgyAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a method preparing nano-level notoginseng root powder, and belongs to the field of processing materials. The method comprises the followings steps of: performing crushing, impurity removal, air drying and grinding of notoginseng root by ultramicro crushing technology to obtain notoginseng root powder, adding water into the notoginseng root powder while stirring at a high speed to obtain suspension, screening the suspension by a 1,000-mesh steel screen, and collecting and performing low-temperature drying to obtain the finished product. The method for preparing the nano-level notoginseng root powder has the advantages that: the operating method is simple, the broken wall rate of notoginseng root cells is over 90 percent, the effective ingredients are easily dissolved into water, and bioavailability and absorptivity are high.
Owner:周亚强
Method of balancing path delay of clock tree in integrated circuit (IC) layout
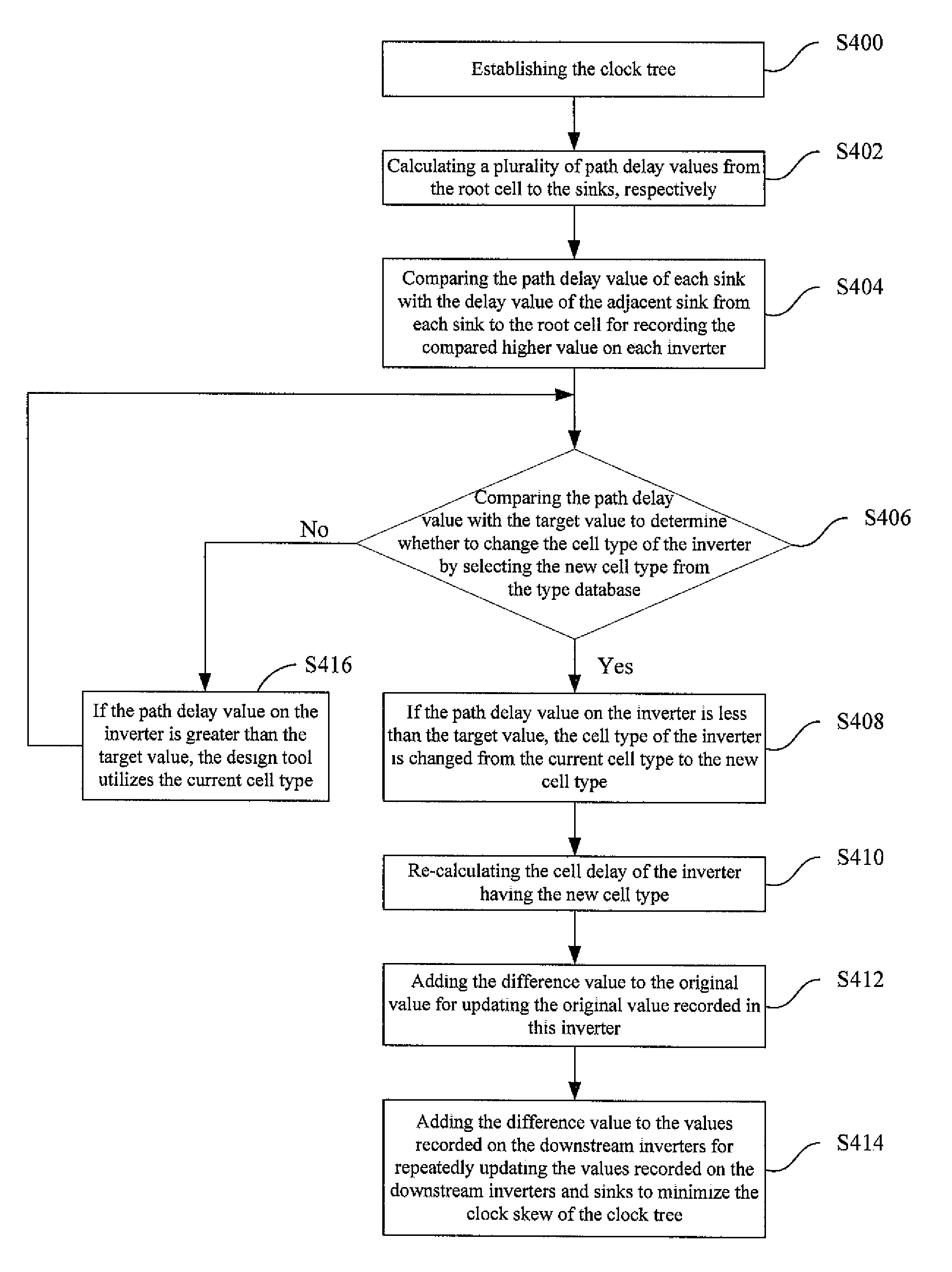
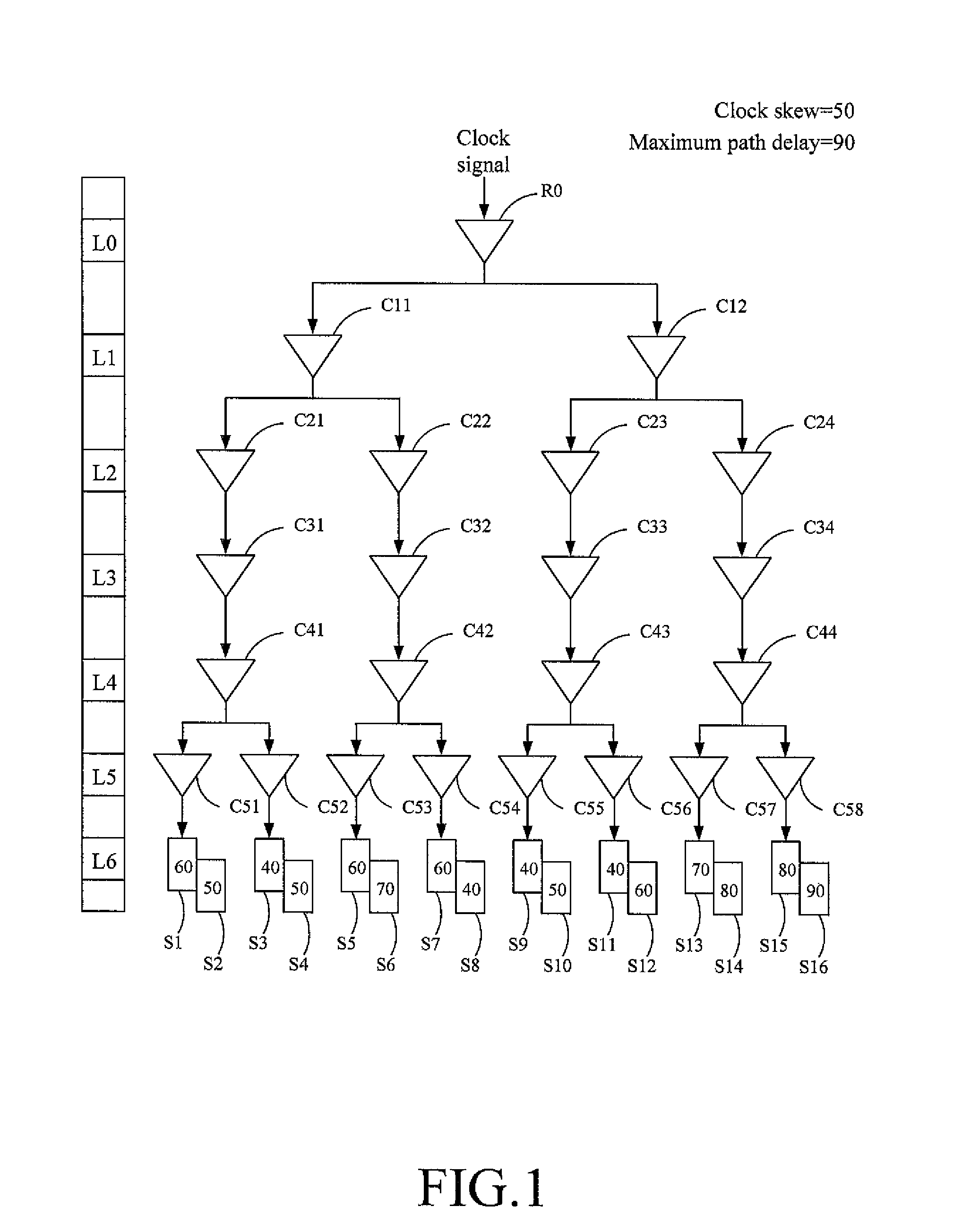
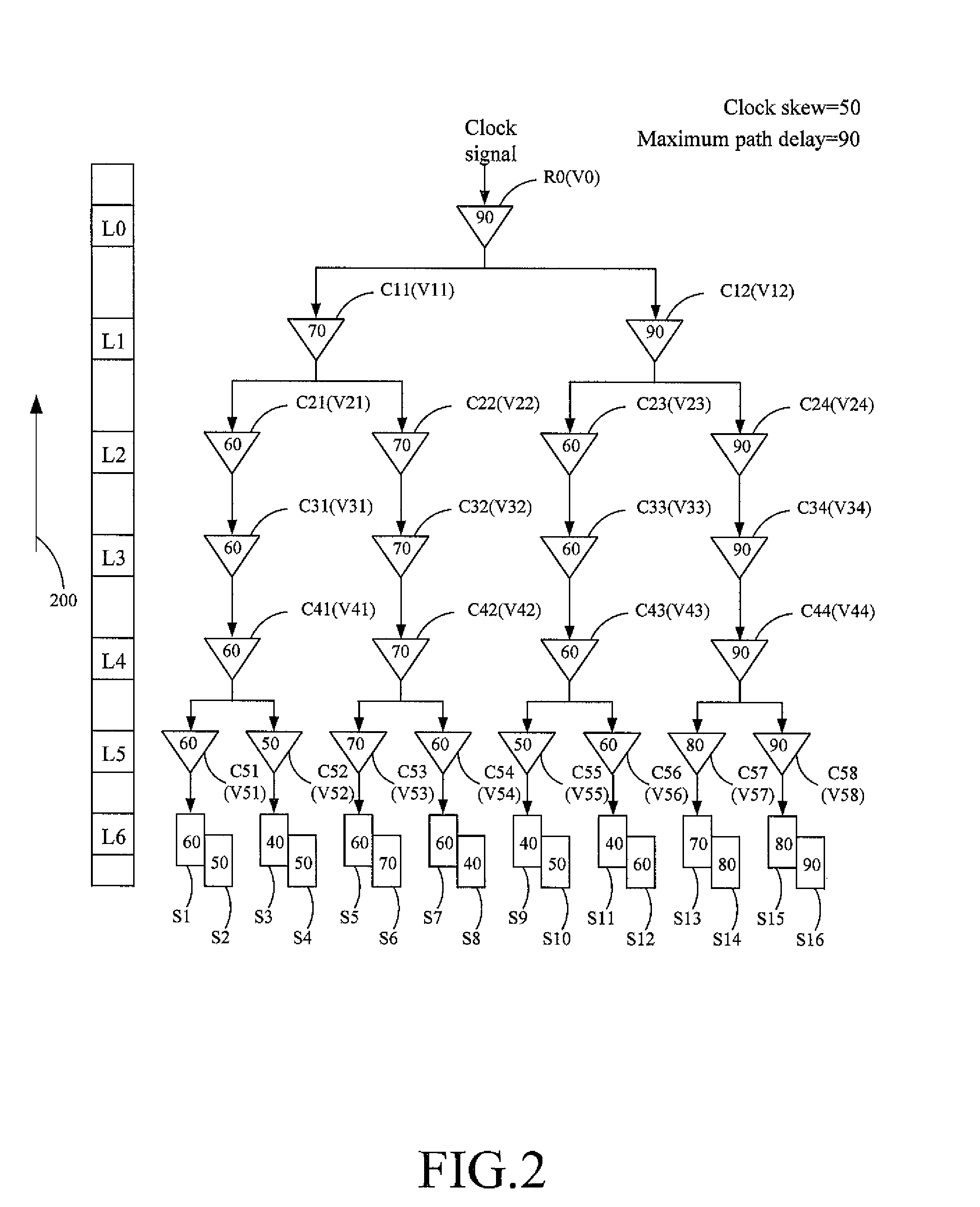
InactiveUS20090064067A1Effectively minimize the clock skewMinimizing clock skew of the clock treeGenerating/distributing signalsComputer aided designCurrent cellClock tree
A method of balancing the path delay of a clock tree for minimizing clock skew of the clock tree in the IC layouts is described. The method includes the following steps: (a) A design tool calculates a plurality of path delay values from the root cell to each sink via some of the inverters, wherein the maximum one of the path delay values recorded on the sinks serves as a target value, respectively; (b) The design tool compares the path delay value of each sink with the delay value of the adjacent sink from each sink to the root cell for recording the compared higher value on each inverter until the higher compared values are recorded, respectively, in the inverters and the root cell; (c) The design tool compares the path delay value on each inverter with the target value from the root cell to the sinks to determine whether to change the cell type of the inverter from a current cell type to a new cell type by selecting the new cell type from the type database; (d) The design tool adds the difference value to the original value for updating the original value recorded in this inverter; and (e) The design tool adds the difference value to the values recorded on the downstream inverters relative to the inverter for repeatedly updating the values recorded on the downstream inverters and sinks to minimize the clock skew of the clock tree.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
Proton transporters and uses in plants
InactiveUS20050262598A1Increase planting yieldIncreased flower sizeBryophytesClimate change adaptationPlant cellWild type
The present invention relates to a transgenic plant which is tolerant to a salt, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. Also encompassed by the present invention are transgenic progeny and seeds of the transgenic plants described herein. Progeny transgenic plant grown from seed are also described. The present invention also relates to a construct comprising an AVP1 gene operably linked to a chimeric promoter designed to overexpress AVP1 or designed to down regulate endogenous pyrophosphatase. Plant cells (e.g., root cells, stem cell, leaf cells) comprising exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant cell are also the subject of the present invention. Also encompassed by the present invention are methods of making a transgenic plant described herein. Transgenic plants produced by the methods of making a transgenic plant as described herein are also a subject of the present invention. The present invention also relates to a method of bioremediating soil, a method of increasing the yield of a plant, a method of making a plant which is larger than its corresponding wild type plant, and a method of producing a transgenic plant which grows in salt water comprising introducing into one or more cells of a plant nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. The transgenic plants of the present invention can also be used to produce double transgenic plants which are tolerant to a salt.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
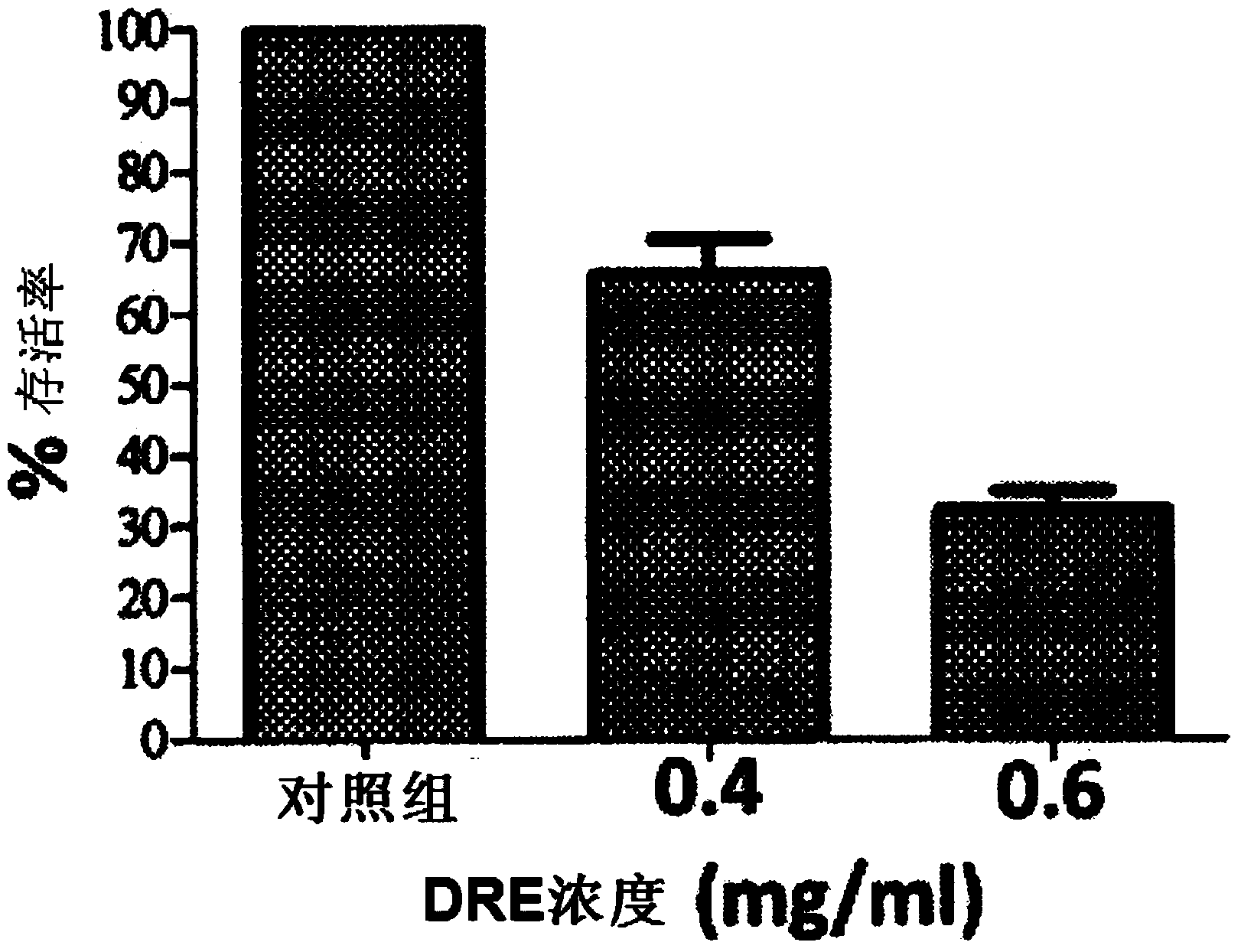
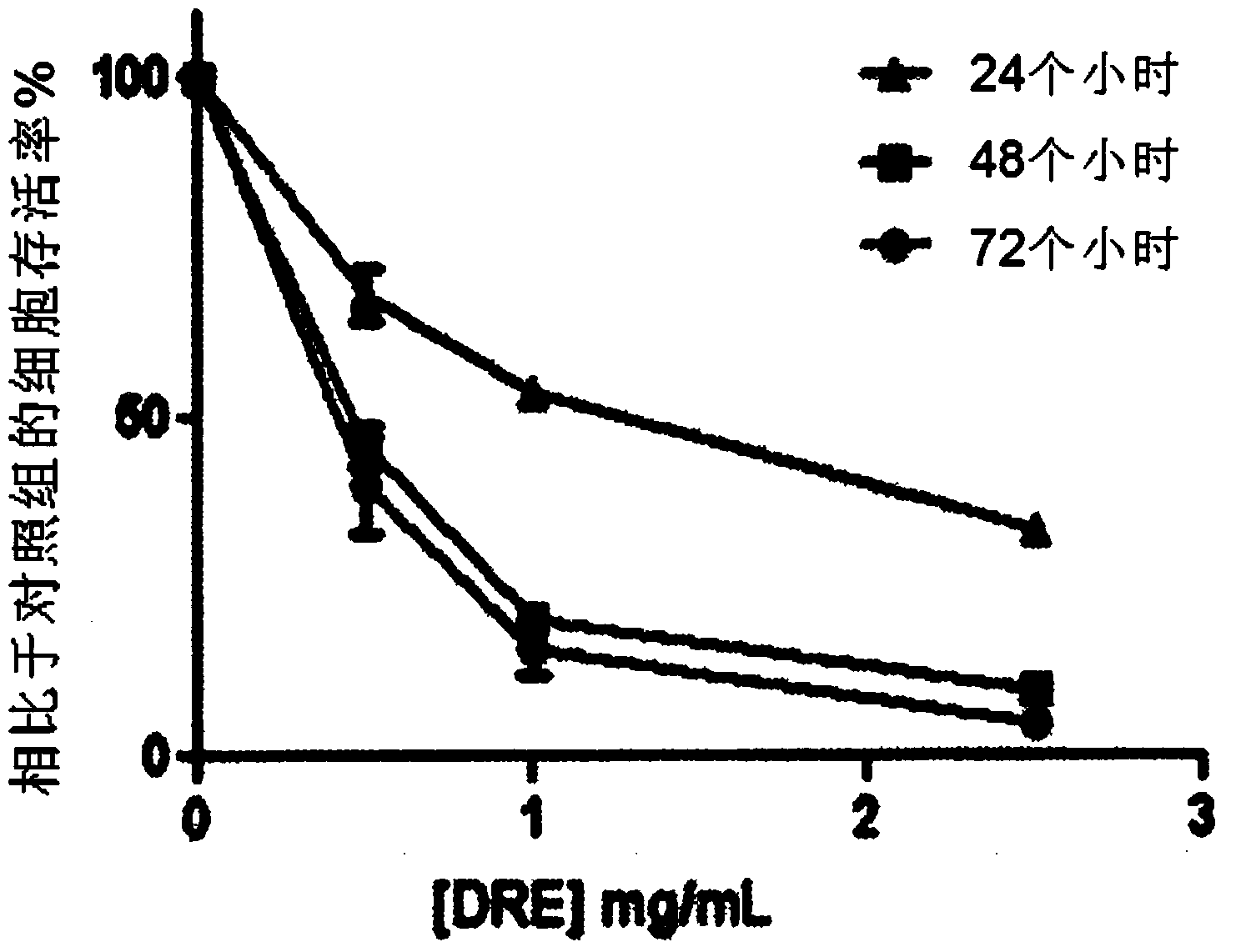
Medicament containing taraxacum plant root extract for treatment or prevention of cancer, and method for preparing same
The present invention relates to an improved method for preparing a medicament comprising a Taraxacum plant root extract for the treatment or prevention of a cancer. In one aspect, the method comprises freezing Taraxacum plant root to obtain a frozen root stock, said freezing step being selected to effect at least partial disruption of one or more root cells; dry grinding the frozen root stock to obtain a ground root powder, wherein during said dry grinding step the frozen root stock is maintained at a grinding temperature below about 40°C; steeping the ground root powder with a solvent to obtain a suspension having a liquid extract portion and a solid particle portion; and separating the liquid extract portion from the solid particle portion to provide a separated liquid extract for use in the medicament.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR
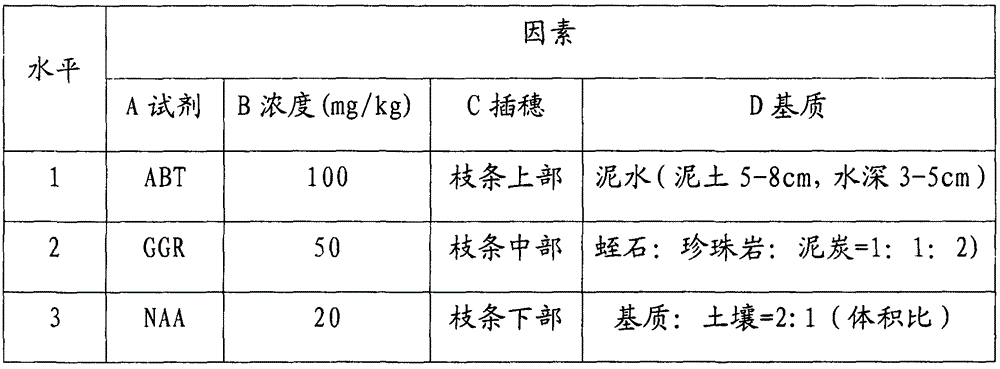
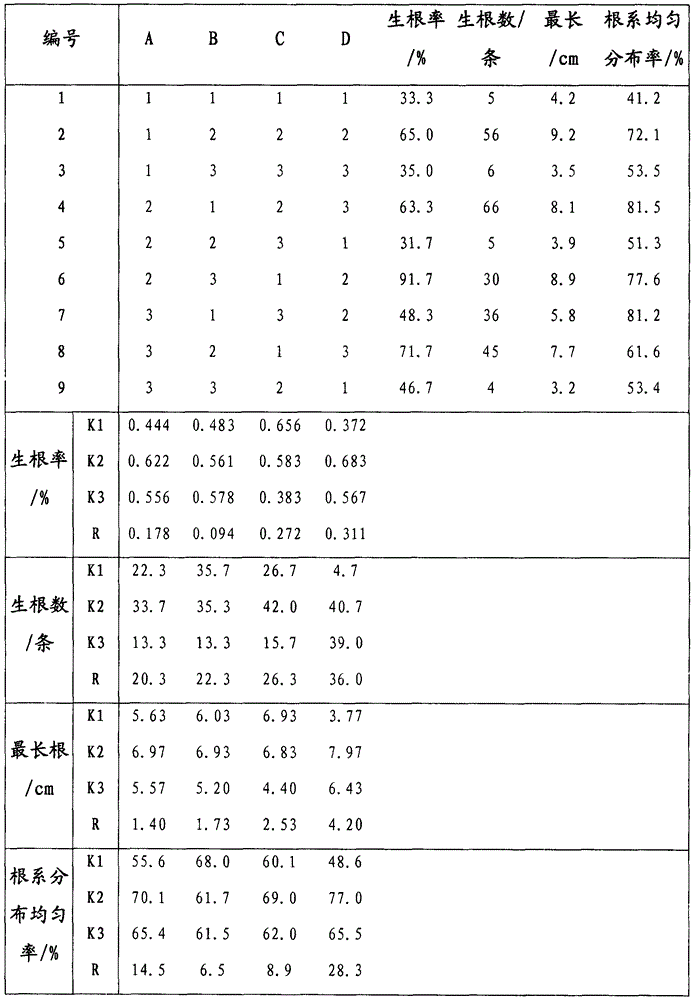
Rose red hibiscus cutting propagation technique
InactiveCN105724215AEasy to operateIncrease vitalityCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationDiseasePorosity
The invention discloses a rose red hibiscus cutting propagation technique. The technique comprises the following steps of 1 branch selecting, 2 cutting shoot making, 3 cutting shoot processing, 4 cutting medium preparing, 5 cutting performing, 6 cutting managing and 7 plantlet transplanting. According to the rose red hibiscus cutting propagation technique, operation is easy, and the cultivated and selected cutting shoots are high in life vigor and sufficient in stored nutrition; a medium and the cutting shoots are processed through disinfection and disinsectization, and therefore infection and harm of diseases and pests to the cutting shoots can be avoided; GGR processing is performed, and in the appropriate root dipping time, formation and differentiation of root primordium cells and division and growth of root cells are stimulated; the compactness, porosity, nutritional ingredients and humidity of the prepared medium are suitable for growth of root systems of cutting seedlings; not only is the cutting survival rate of rose red hibiscus high, but also the cutting and managing labor force is reduced.
Owner:杭州天景水生植物园有限公司
Cyclocarya paliurus cutting seedling growing method
InactiveCN105393771AGood physical propertiesStrong Survival RatePlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsNutrient solutionObserved Survival
The invention discloses a Cyclocarya paliurus cutting seedling growing method comprising the following steps: 1, cuttingwood selecting; 2, cuttingwood processing; 3, cuttingwood planting; 4, post-planting management; the method uses specially prepared matrix, and the matrix has excellent physicochemical performance so as to provide good environment conditions for cuttingwood growth; nitration soup immersion and electric field alternative repeatedly treatment are carried out for the cuttingwood root, thus enhancing root cell splitting and differentiation capability, and improving growth vitality and anti adversity performance of the cuttingwood; combining with matrix effect and post-planting management, the novel method can largely improve cuttingwood survival rate, and the seedling is tidy and prosperous in growth vigor, thus reducing incubation time for 7-10 days when compared with same specification cutting seedlings; the method is suitable for large-area popularization plantation, and very strong in market competitiveness.
Owner:全椒县香妃农业专业合作社
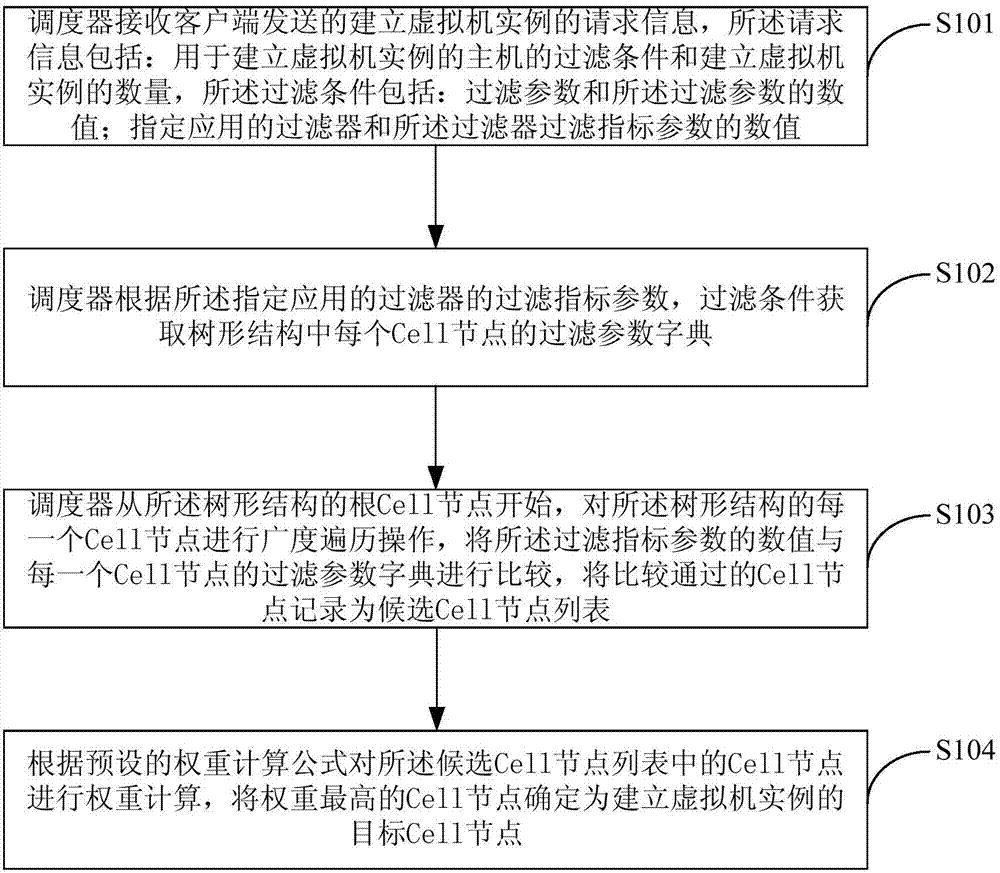
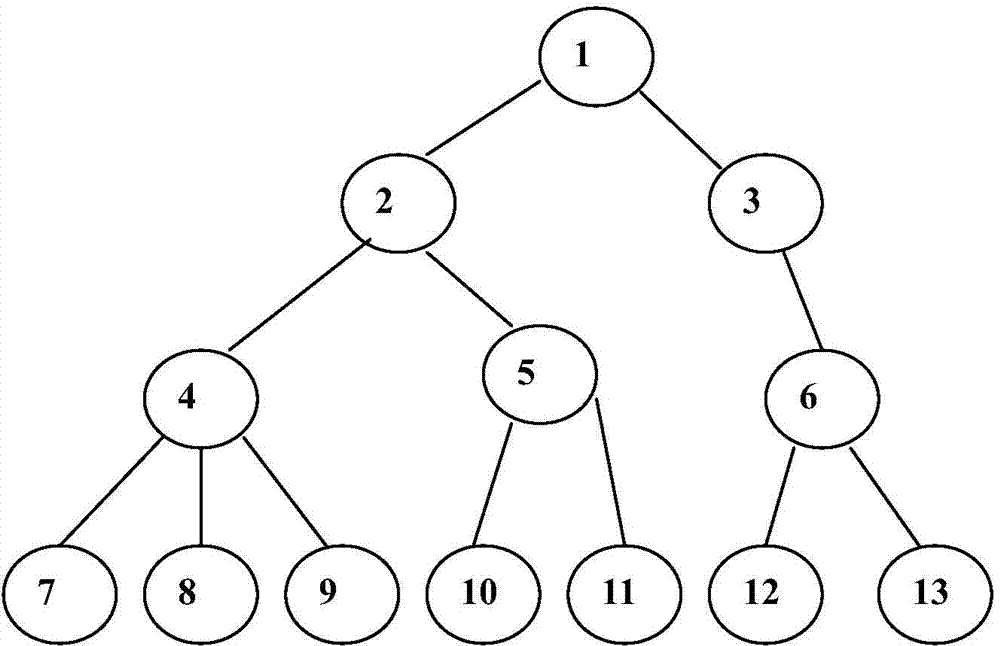
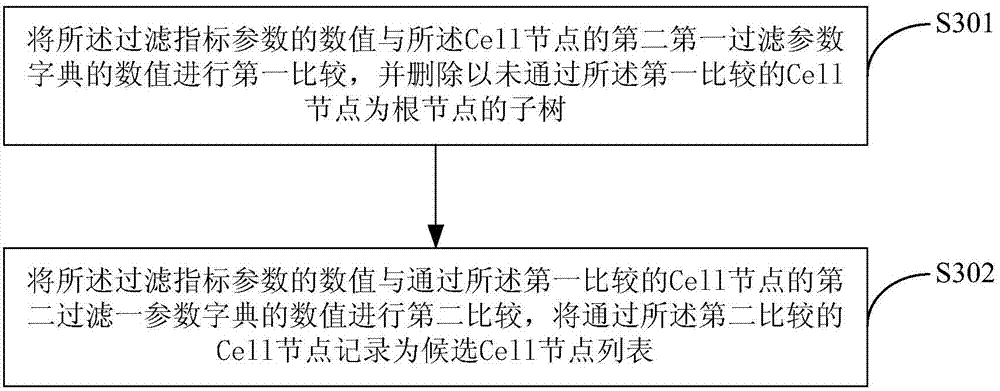
Scheduling method and system for Cell nodes through OpenStack cloud computing management platform
The invention is applicable to the field of cloud service and provides a scheduling method and system for Cell nodes through an OpenStack cloud computing management platform. The method includes the steps that a scheduler receives request information sent by a client and used for establishing virtual machine instances; the scheduler obtains a filtration parameter dictionary of each Cell joint in a tree structure according to filtration index parameters of a filter designated to be applied; the scheduler makes a comparison between numerical values of the filtration index parameters and the filtration parameter dictionary of each Cell joint from the root Cell nodes of the tree structure, and the Cell nodes passing the comparison are recorded into a candidate Cell node list; weight calculation is carried out on the Cell nodes in the candidate Cell node list according to a preset weight calculation formula, and the Cell nodes with the highest weights are determined as target Cell nodes for establishing the virtual machine instances. According to the method and system, the optimal Cell nodes can be rapidly and efficiently selected for establishing the virtual machine instances.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Herbicide-resistant taraxacum kok-saghyz and taraxacum brevicorniculatum
InactiveUS20170314033A1Promote generationImprove scalabilityTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionTaraxacum brevicorniculatumHerbicide resistance
The invention provides the genetically manipulated herbicide-resistant rubber producing dandelion plants and seed of said plants. Another aspect of the invention comprises progeny plants, or seeds, or regenerable parts of plants and seeds of the genetically manipulated herbicide-resistant dandelion plants. Applicants have further found that use of root cells for transformation and other optimized protocols enable quick transformation with high plant regeneration. Further, Applicants have developed the first transformation / regeneration protocol that is successful without the addition of hormone treatment.
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
Soil moisture meter
ActiveCN104089854AReflect the state of water absorptionSurface/boundary effectPlant rootsEngineering
The invention relates to a soil moisture meter. A cylindrical fiber bundle is attached to inner side walls of the top and upper part of a sealing cavity; a semipermeable membrane layer is attached to the inner side wall of the cylindrical fiber bundle; humidity-sensitive ink is arranged on the top of the cylindrical fiber bundle; the top of the sealing cavity is made of breathable transparent plastic; a columnar fiber bundle is arranged in the sealing cavity and extends from the upper half part of the inner cavity of the sealing cavity to exterior of the sealing cavity; the columnar fiber bundle in the sealing cavity is not contacted with the cylindrical fiber bundle; another semipermeable membrane is attached to the outer side of the columnar fiber bundle and goes beyond the top of the columnar fiber bundle to reach the top of the cylindrical fiber bundle; a saline ion solution with osmotic pressure is fed between the first part of the semipermeable membrane and the inner wall of the sealing cavity. The soil moisture is monitored through difference of the osmotic pressure in root cells and osmotic pressure of the outside, and the plant root water absorption conditions can be really and sensitively reflected. The soil moisture meter is simple in structure and low in cost and is suitable for monitoring the soil moisture in a large-area crop cultivation process.
Owner:HANGZHOU BAIBAN BIO TECH
High-yield planting method for grapes
InactiveCN106234142AIncrease stressImprove developmentFertilising methodsCultivating equipmentsRoot cellTip growth
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural planting and particularly relates to a high-yield planting method for grapes. The high-yield planting method comprises the first step of seedling selecting, the second step of selecting and soil preparation, the third step of planting, the fourth step of pruning and the fifth step of water and fertilizer management. By means of deep trench fertilization, it is guaranteed that long-term nutrition is provided for grape growing, optimal seedlings are selected, the stress of the seedlings is improved, and activity of root cells is promoted, growing of root systems is promoted, the survival rate of the seedlings is increased, planting lands are optimized and treated, the fertility of soil is improved, growth of the grapes is guaranteed, organic fertilizer is sprayed to the grapes, stem tip growth of the grapes is promoted, the mature period of the grapes is advanced, and the yield of the grapes is effectively increased.
Owner:铜仁市万山区米贡山高效农业科技有限公司
Method for producing ginsenoside and polysaccharide by cell culture method
InactiveCN102634477AIncrease collection ratePromote growth and reproductionSteroidsPlant cellsBiotechnologyPectinase
The invention discloses a method for producing ginsenoside and polysaccharide by a cell culture method. According to the method, the root cell culture of perennial ginsengs is utilized and an enzymatic technology is adopted to shorten the cell culture cycle to produce the ginsenoside and the polysaccharide. The method adopts the cell culture method to culture and produce ginseng plant cells and then the ginsenoside and the polysaccharide are extracted. Cellulose is added when seed cells are collected to increase the collection rate of the seed cells by 5-10%. During the culture of the seed cells, growth hormone and pectinase are added to induce the histocytes to accelerate growth and reproduction and the culture cycle can be shortened by 1 / 4 to 1 / 6, so that the infection rate during the culture process is effectively reduced and the production yield is increased. The method is simple and stable in process and the enzymatic technology is utilized to shorten the cell culture cycle and improve the yield, thus the method is applicable to industrial production.
Owner:江西中天医药生物有限公司
Fast hymen Yegenerating repair medicine
InactiveCN101020046AIncrease elasticityImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic effectAmino acid
The fast hymen regenerating and repairing medicine is prepared with hemoglobin 15-30 weight portions, lecithin 10-20 weight portions, amino acid 15-25 weight portions, albumin glue 2-10 weight portions, notoginseng 2-10 weight portions, saffron 1-8 weight portions, protein 5-15 weight portions, cellulose 10-20 weight portions, and free coagulase 5-15 weight portions. The present invention is used in the local targeting process to provide hymen root cell with nutritious components and active growth elements, to activate cells for division and regeneration and to regenerate hymen. The present invention has excellent treating effect.
Owner:闫娜
Bacterial agent for resurrecting trees, and application thereof
InactiveCN107593770APromote the absorption of nutrientsInhibition of disease growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDiseaseBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses a bacterial agent for resurrecting trees, and an application thereof. The bacterial agent which is used immediately is prepared through a preparation method comprising the following steps: taking a clean plastic container, adding 100-150 kg of groundwater, adding 800-1000 g of Bacillus licheniformis, Paenibacillus kribbensis and Streptomyces microflavus composite bacteria,10-20 g of naphthaleneacetic acid powder, 1000-1500 g of amino acid powder and 500-800 g of amino oligosaccharin powder, and fully stirring all above materials for 10 min to prepare the bacterial liquid for resurrecting trees. The bacterial agent can repair root decay, root trauma, root atrophy, root deformity, root aging and other diseases of the trees, and also can purify soil surrounding the root system, inhibit the disease growth of soil, decompose animal and plant residues and heavy metal residues in the soil, activate the growth of root cells and promote the nutrient absorption of the root system.
Owner:河南中麦生物科技有限公司
Vacuolar pyrophosphatases and uses in plants
InactiveUS20080104733A1Improve toleranceLarge plant sizeClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesWild typePlant cell
The present invention relates to a transgenic plant which is tolerant to a salt, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. The present invention also relates to a transgenic plant with increased Pi uptake, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. Also encompassed by the present invention are transgenic progeny and seeds of the transgenic plants described herein. Progeny transgenic plant grown from seed are also described. Plant cells (e.g., root cells, stem cell, leaf cells, flower cells, fruit cells and seed cells) comprising exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant cell are also the subject of the present invention. Also encompassed by the present invention are methods of making a transgenic plant described herein. Transgenic plants produced by the methods of making a transgenic plant as described herein are also a subject of the present invention. The present invention also relates to a method of bioremediating soil, a method of increasing the yield of a plant, a method of making a plant which is larger than its corresponding wild type plant, a method of producing a transgenic plant which grows in salt water, and a method of producing a transgenic plant with increased Pi uptake. The transgenic plants of the present invention can also be used to produce double transgenic plants which are tolerant to a salt, or have increased Pi uptake.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
Single-cell clamping method and single-cell position regulating device
InactiveCN103131664ARealize position controlRealize the clamping effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluid viscosityControl cell
The invention provides a single-cell clamping method and a single-cell position regulating device. The method is that in the regulating operation process of cells, fluid pressure and fluid viscosity force between clamping tubes are used for clamping the cells, the cells are wrapped and clamped to move in a non-contacting mode through the movement of the clamping tubes, and so that the position regulation of the cells is achieved. The device comprises two cell clamping tubes, two soft micro tubes, a control unit and a micropump unit which supplies the needed flow to the cell clamping tubes. Each cell clamping tube is connected with the micropump unit through the soft micro tubes, and the two cell clamping tubes are installed on the control unit and are distributed on two sides of the cells. The single-cell clamping method and the single-cell position regulating device can be suitable for the cells with different shapes and different sizes, the three-dimensional position regulation of the cells is achieved, mechanical damage to the cells can be avoided, and the single-cell clamping method and the single-cell position regulating device are beneficial to improving the success rate of cell experiment operation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Snow lotus flavone active ingredient production method by cultivating acaleph snow lotus trichome
InactiveCN1520719AProtect environmentQuality improvementSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationRhizobium rhizogenesBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention is the process of culturing Saussurea involucrata hairy root with Saussurea involucrata hairy root cell line and liquid and producing Saussurea involucrata flavone compound. The process includes the following steps: culturing green cotyledon of three days age in caespitose seedling culture medium to inducing caespitose seedling; culturing single plant with the caespitose seedling in seedling growing and strengthening culture medium; culturing in root inducing culture medium to obtain seedling with satus root; cutting the foliage into explant, dark culturing the explant and transforming with mediating rooting agrobacterium to inducing rooting; re-culturing the foliage with hairy root in screening culture medium; cutting root tip of selected anti-Km root line with positive mannopine test for expanding culture; drying, crushing, separating and extracting the cultured material to prepare Saussurea involucrata flavone compound.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
FoMV-mediated GFP-ATG8 expression vector and application thereof
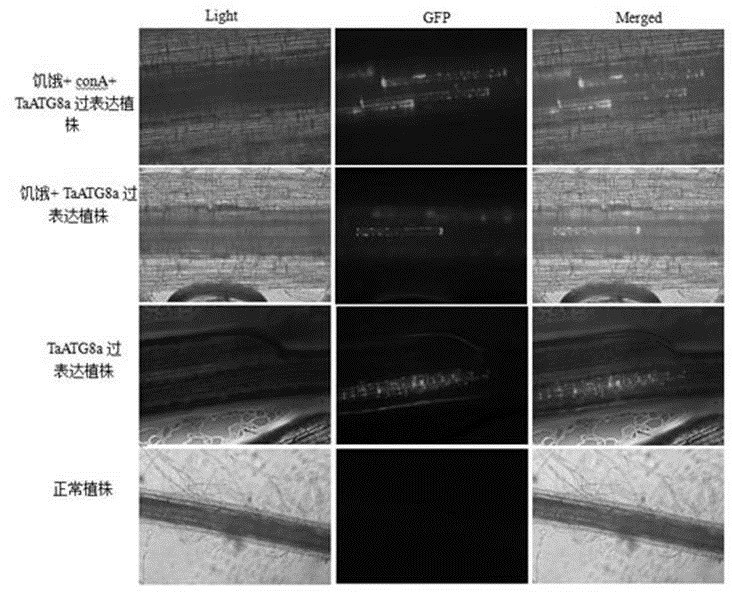
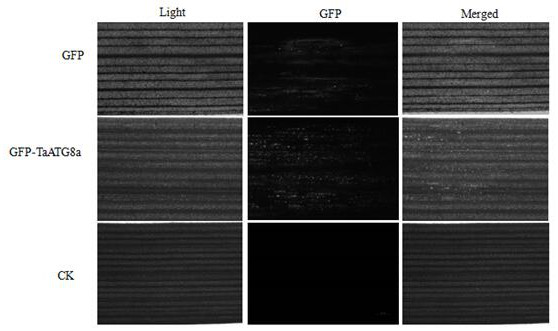
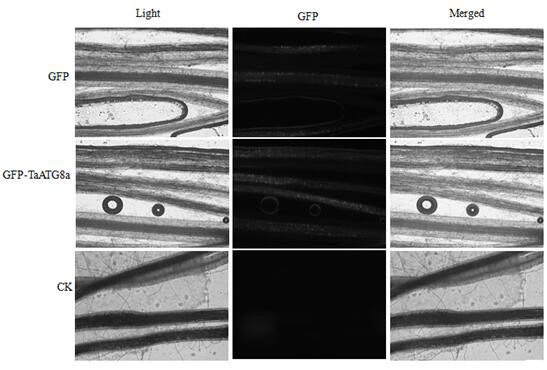
PendingCN112430619AEasy to operateSuitable for gene function researchHydrolasesPlant peptidesBiotechnologyAutophagosome
The invention constructs a FoMV-mediated GFP-ATG8 expression vector and application thereof. A method takes TaATG8a as a target for monitoring autophagy, a VOX technology based on FoMV is adopted forexpressing GFP-TaATG8a fusion protein on a wheat plant, the expression situation and subcellular localization situation of the fusion protein in leaves and root tissues are observed through fluorescence, and a technical platform for monitoring the autophagy level on a wheat living plant with overexpression GFPTaATG8 as the target is established. The platform is successfully applied to observationof representation autophagosomes and autophagovesicles in leaf epidermis, mesophyll cells and root cells under hunger and drug treatment, and the invention shows that the vector can be applied to autophagy level monitoring and autophagy function research in the wheat growth and development process or the environmental factor response process. Research results provide technical support for deep exploration of autophagy regulation and control mechanisms and physiological functions of important crop wheat.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
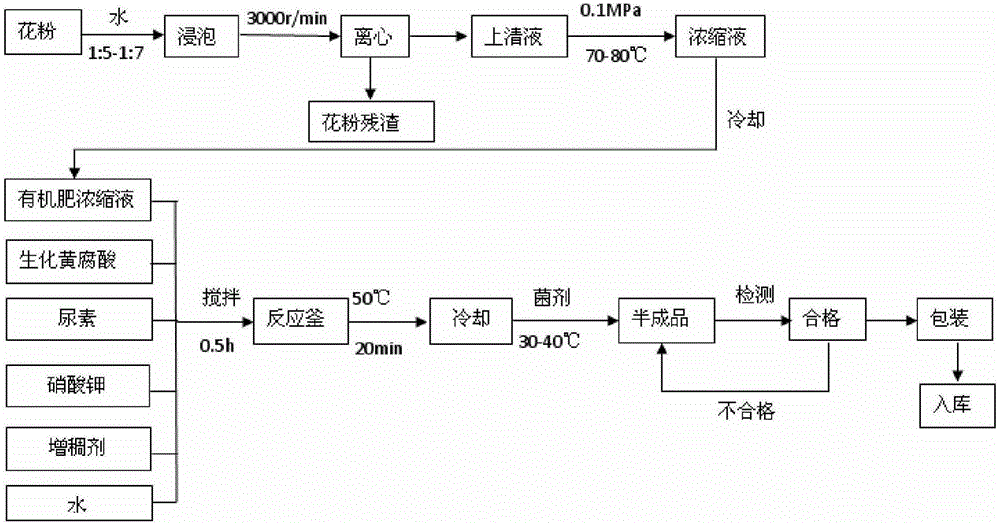
Water-soluble bio-organic fertilizer and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of fertilizers and particularly relates to a water-soluble bio-organic fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The water-soluble bio-organic fertilizer is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 3-8% of a water-soluble organic fertilizer extract concentrated solution, 35-45% of biochemical fulvic acid, 3-8% of a potassium fertilizer, 5-10% of a nitrogen fertilizer, 0.1-0.3% of a preservative, 0.05-0.15% of a thickening agent, 0.1-0.3% of a defoaming agent, 0.5-1.5% of a biological agent and the balance of water. The water-soluble bio-organic fertilizer prepared by using the preparation method is suitable for all agricultural production and crops and is beneficial to increment of water-soluble organic matter content of soil, promotion of root growth of the crops, promotion of the absorption and utilization of roots to the fertilizer, activation of demands of root cells to nutrient elements including N, P, K and the like, regulation of nutrient balance and improvement of root resistance after being used.
Owner:CHENGDU NEWSUN CROPSCI
Method for transforming root cell of Cymbidium
InactiveCN101278652AProtect resourcesStrong stress resistanceBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationSeedlingCymbidium
The invention provides a method for transforming the rhizosphere cells of Chinese orchid; the method utilizes organic planting material for inducing the rhizosphere cells of Chinese orchid to be transformed from nutrition type cells to embryonic type cells under natural condition. The method includes the following steps: (1) the preparation of the planting material; (2) the disposal of deserted orchid root; (3) the mutation of the rhizosphere cells; (4) material replacement and transplantation for a new seedling. The orchid seedling cultivated by the method of the invention has strong anti-adversity ability, can comprehensively guarantee the accuracy and entireness of gene inheritance; the sprout, seedling formation and flower bearing of the orchid seedling are identical with that of the maternal natural plant. Meanwhile, the method follows nature, which has advanced concept, convenient material taking and simple operation, thus having important significance for protecting the Chinese orchid resource, developing precious varieties and facilitating Chinese orchid to enter numerous households in advance.
Owner:刘开宁
Leafy-vegetable growth rate promoting device based on high-voltage pulsed electric field
InactiveCN107926679APromote growthChange permeabilityAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsLow voltageNutrient solution
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Heavy metal harm reducing magnetization slow-release fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105541469APromote photosynthesisPromote growth and developmentCalcareous fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserPhosphatePotassium
The present invention discloses a heavy metal harm reducing magnetization slow-release fertilizer and a preparation method thereof, the magnetization slow-release fertilizer comprises the following parts by weight of raw materials: 200-240 parts of rapeseed cake powder, 24-26 parts of calcium ammonium nitrate, 30-35 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 160-180 parts of bagasse, 15-20 parts of actinolite powder, 7-9 parts of zinc sulfate powder, 70-80 parts of fly ash, 45-55 parts of pyrite ash, 20-24 parts of tapioca starch, 4-6 parts of calcium acetate, 10-12 parts of a complex biological agent and proper amount of water; the magnetization slow-release fertilizer is prepared in inorganic and organic mixing manner, can effectively improve the nutrient content of the fertilizer, through double magnetization of the fertilizer and activation of the actinolite powder and other raw materials, crop root superoxide dismutase and catalase activity can be significantly improved, oxidative stress caused by residual heavy metals in soil can be eliminated, the integrity of root cell membranes can be maintained, plant tolerance to heavy metals can be enhanced, plants can be prevented from harm and harm to plants can be reduced.
Owner:ANHUI HUACHUANG MODERN AGRI TECH
Greenhouse planting method of wild chive
InactiveCN108551795AIncrease productionQuality improvementSuperphosphatesBulb cultivationTime processingRoot cell
The invention relates to the technical field of vegetable introduction planting, and discloses a greenhouse planting method of wild chive. The method comprises greenhouse establishing, chive processing, chive planting, chive managing, common sage herb planting and joint management; the yield and quality of the wild chive are significantly improved, the annual acre yield of the wild chive reaches 6439 kg, and the annual acre yield of common sage herb reaches 1127 kg; leaves and fibrous roots are cut, the generation of newly borne leaves and the fibrous roots is promoted to prevent the slow germination of the leaves and roots after the transplanting is conducted due to the fact that the leaves and the fibrous roots do not adapt to a greenhouse environment, high-temperature short-time processing is conducted after plant division is conducted to kill residual pathogenic bacteria and insect eggs on the roots, stimulation on root cells is generated to enhance the environmental adaptation capability and cell division capability, the chive is placed in root promoting liquid to be soaked immediately after high-temperature processing is conducted to prevent the deterioration and rotten of cells at the incision positions of the fibrous roots, the activity of the cells is improved to accelerate the generating and growing of the fibrous roots, and the rooting percentage of the wild chive is improved.
Owner:HUOSHAN XINYUAN ECOLOGICAL AGRI CO LTD
Efficient slow-release fertilizer for Vulpia myuros on beach saline land and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105294291ARich pore sizeRich hydrophobicityFertilizer mixturesSodium metasilicatePolyvinyl alcohol
The invention belongs to the field of slow-release fertilizer, and specifically discloses an efficient slow-release fertilizer for Vulpia myuros on beach saline land. The fertilizer is characterized by including the following components by weight: micron glass fiber, water-soluble nano silica, graystone fiber, alginic acid, weathered coal polyvinyl alcohol complex, ammonium phosphate humic acid, compound microbial inoculant, sodium metasilicate, eucalyptus oil, sepiolite micropowder, potassium feldspar powder, alginate propylene glycol, fermented bran, organic fermented cow dung, fermented vermicompost rich in active substances, hydroxymethyl cellulose, and a proper amount of water. The invention uses weathered coal grafted alginic acid as a basic coating material; and materials in different sizes are added in the coating material, so as to enrich the pore size, hydrophobicity and adsorbability of the coating material, and improve the regulation of fertilizer efficiency. The efficient slow-release fertilizer can realize protection of root cells of Vulpia myuros on beach saline land, promote the absorption and utilization of different nutrition materials in environment, and reach efficient cultivation.
Owner:HEFEI YONGSHENG CULTIVATION CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com