Plant disease-resistant protein BjMYB9 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
A disease-resistant protein and gene-encoding technology, applied in plant genetic improvement, botany equipment and methods, applications, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Molecular cloning of embodiment 1, BjMYB9
[0032] 1. Plants and growth conditions
[0033] Plants Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) (ecotype Col-0), Nicotiana.benthamiana and Brassica juncea were grown at 22°C (light) / 19°C (dark) and 16h light / 8h dark cycle conditions . Arabidopsis was used for stable genetic transformation, Nicotiana.benthamiana was used for transient expression, and Brassica juncea was used for construction of cDNA library and endogenous gene expression analysis experiments.
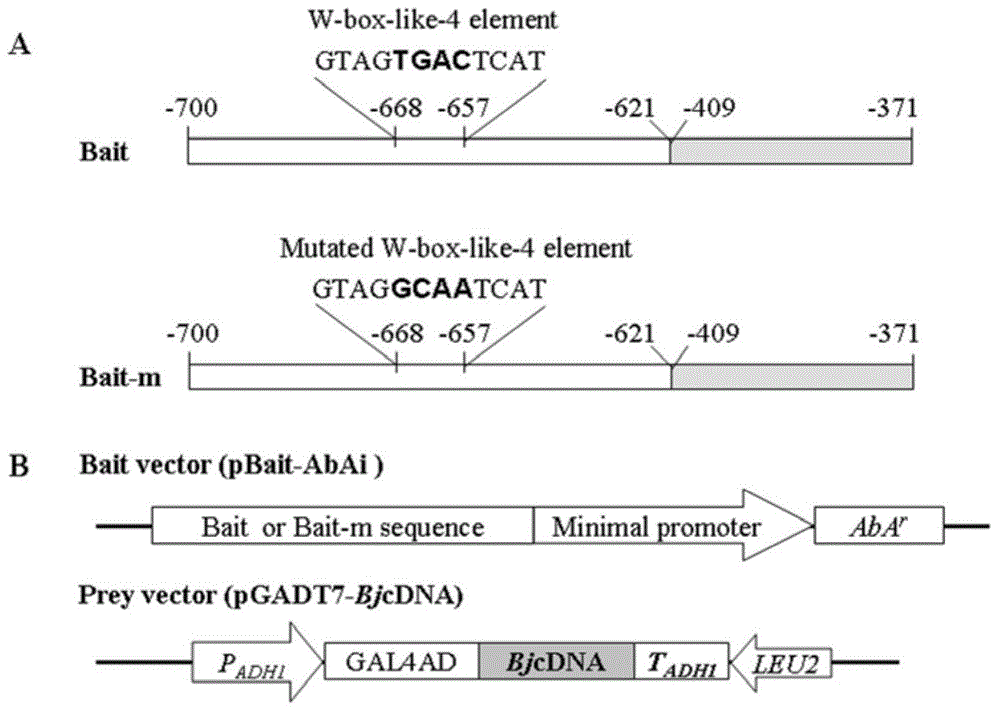
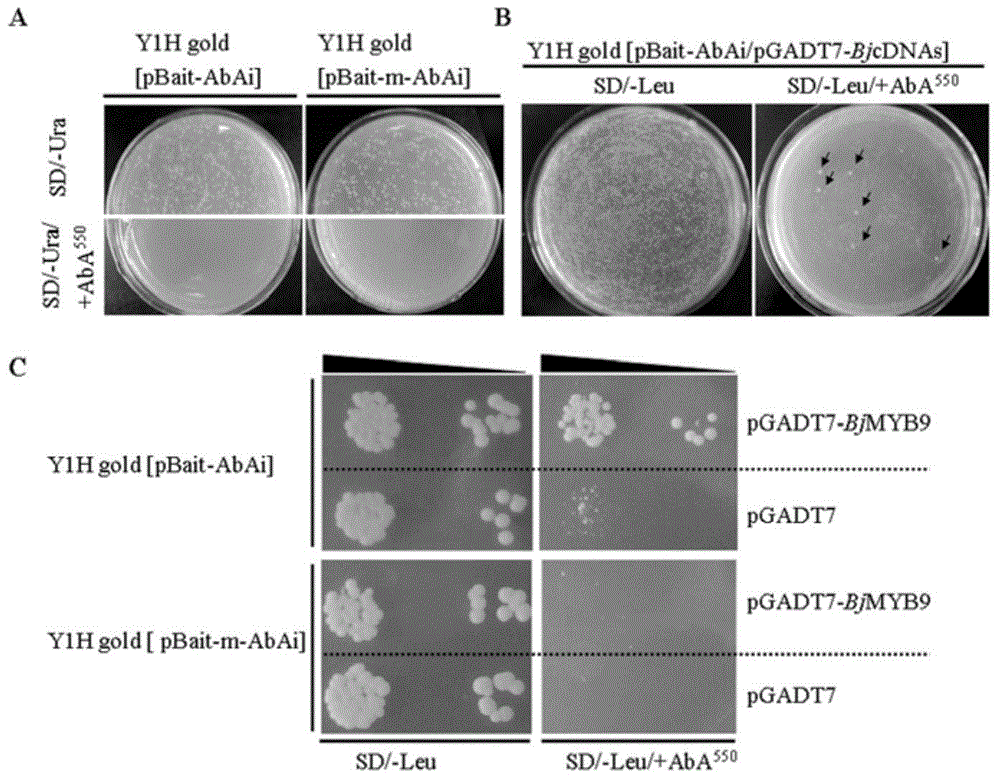
[0034] 2. Screening of transcription factors interacting with W-box-like-4 elements by yeast one-hybrid assay
[0035] The mustard seedlings were sprayed with 200 μg / ml fungal elicitor (hexa-Nacetyl-chitohexaose) (Raventos et al., 1995) on the leaves, and the leaves were quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen at 12, 24, 48 and 72 hours after treatment. Leaf samples taken at different time periods were mixed and total RNA was extracted to construct a mustard cDNA library. The vector used...
Embodiment 2
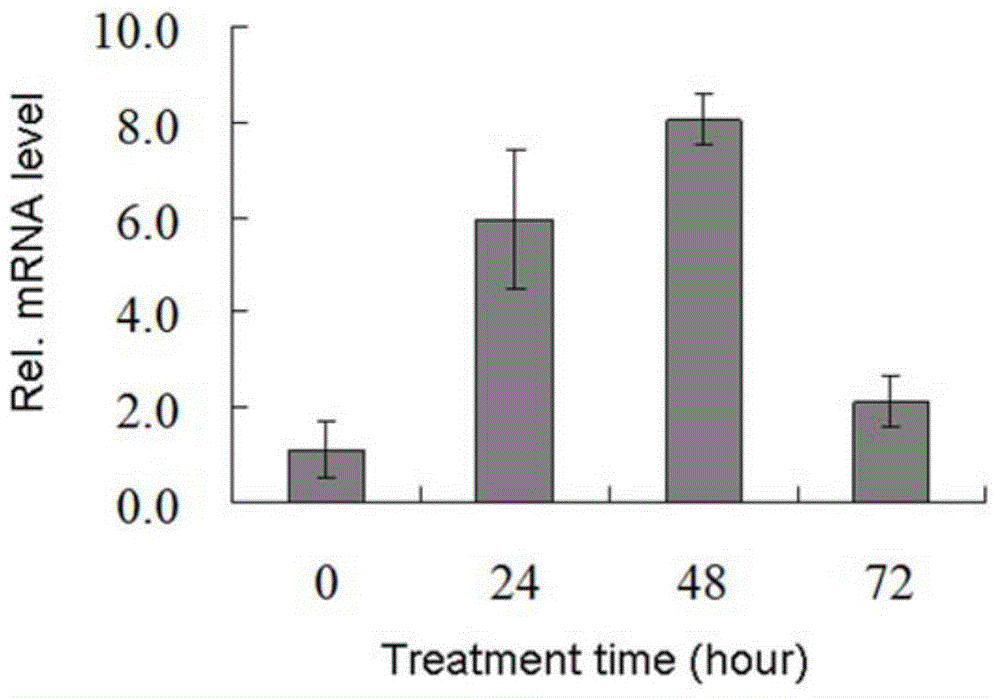
[0039] Example 2, real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis of RNA expression of BjMYB9 gene induced by fungal elicitor
[0040] 1. Material handling
[0041] Leaves of mustard (Brassica juncea) seedlings were sprayed with 200 μg / ml fungal elicitor (hexa-Nacetyl-chitohexaose), and samples were taken at 24, 48, 72 h after treatment and 0 h of the control (untreated), quickly frozen and ground in liquid nitrogen, and used The plant total RNA extraction kit from TIANGEN company extracts the total RNA of mustard, and treats it with DNAase without RNAase contamination to remove the contamination of genomic DNA in the RNA. The first strand of cDNA was synthesized with RNA reverse transcription kit from TIANGEN Company. The first strand of reverse transcription product cDNA was used for real-time quantitative PCR analysis.
[0042] 2. Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
[0043] Real-time quantitative PCR was carried out using SYBR Green Premix (Tiangen Company,...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3, BjMYB9 resistance to Botrytis cinerea phenotype detection
[0046] 1. Genetic transformation of Arabidopsis Col-0 by BjMYB9
[0047] The BjMYB9 cDNA was amplified using the primer pair BjMYB9-F2 / BjMYB9-R (see Table 1 for the sequence), sequenced correctly and cloned into the BamH I and Sal I sites of the pCAMBIA1307 vector to obtain the plasmid pCAMBIA1307-BjMYB9 driven by the 35S promoter. Arabidopsis was transformed using the flower apex method and mediated by Agrobacterium EHA 105 (Clough and Bent, 1998). Positive transgenic lines were detected by PCR using primers BjMYB9-F2 / BjMYB9-R. Three independent positive transgenic lines of the T2 generation were screened again in MS medium containing 40 μg / ml hygromycin, and then transplanted into the soil. They were inoculated with Botrytis cinerea when they were about 4 weeks old.
[0048] 2. Cultivation of Botrytis cinerea (B.cinerea) and inoculation treatment of Arabidopsis
[0049] Botrytis cinerea (B. cine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com