Patents
Literature
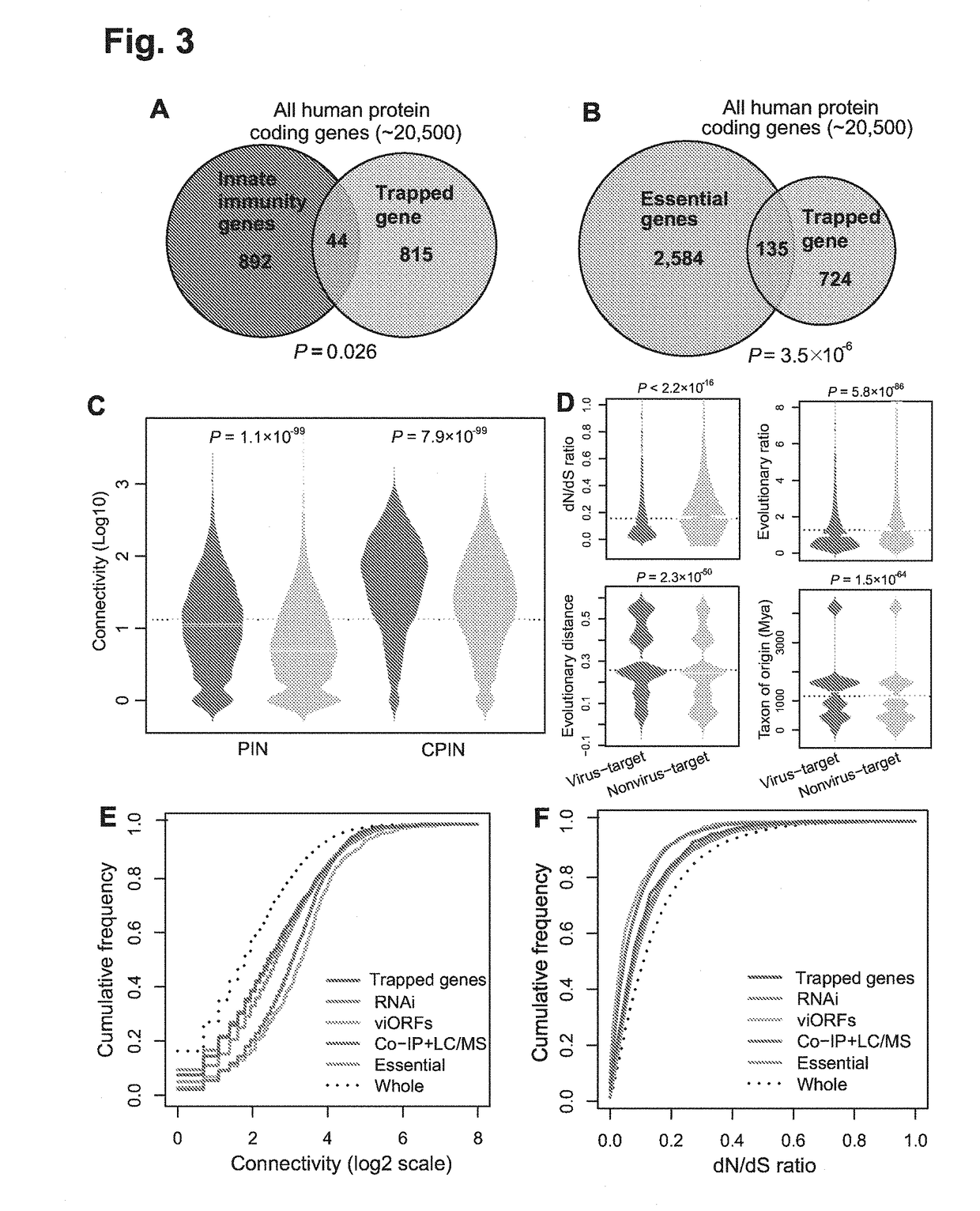
31 results about "Drugs identified" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
System and Methods for Pharmacogenomic Classification
InactiveUS20140222349A1Good statistical effectDataset can also become very largeBiostatisticsProteomicsGenomicsLearning machine
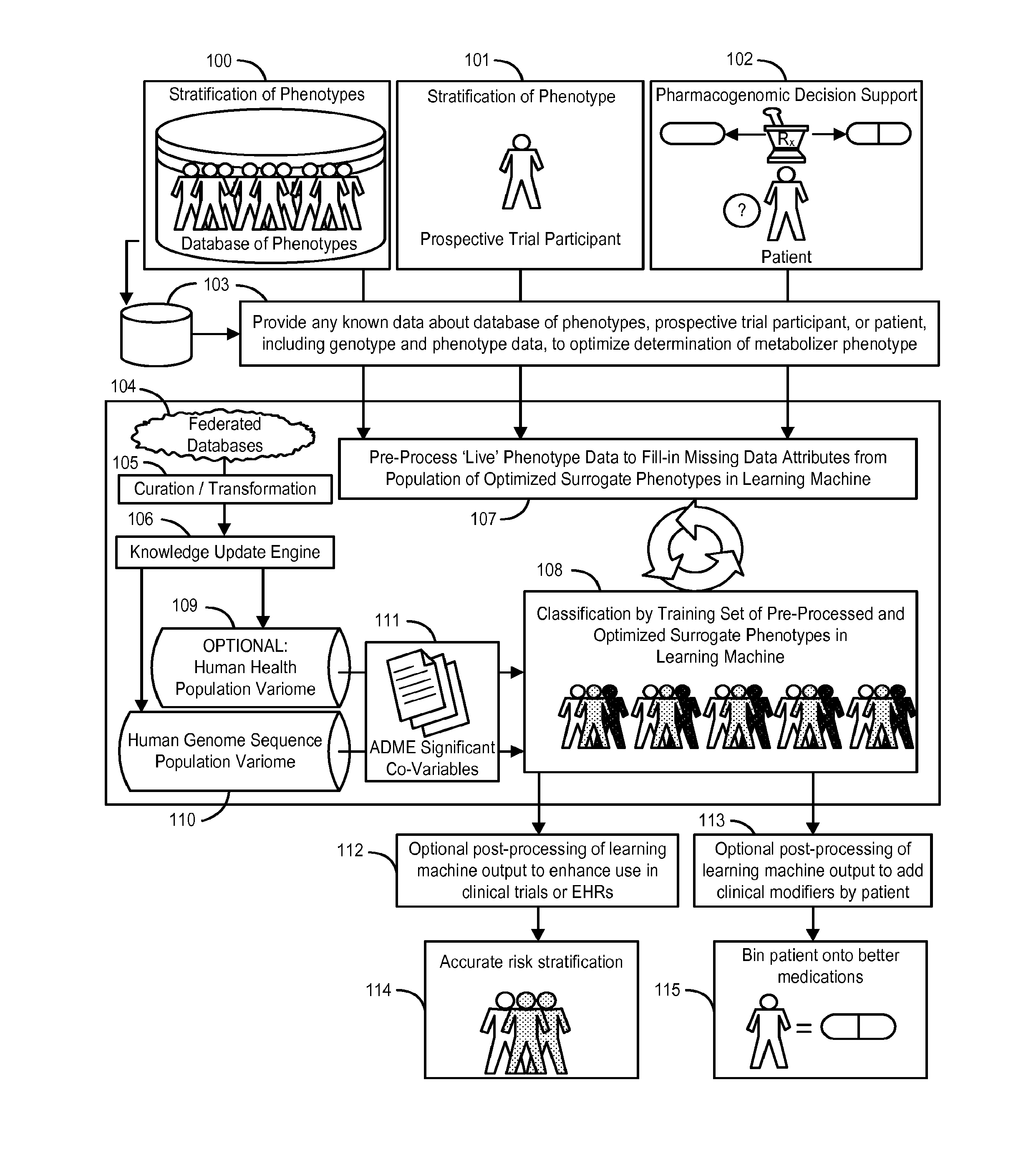
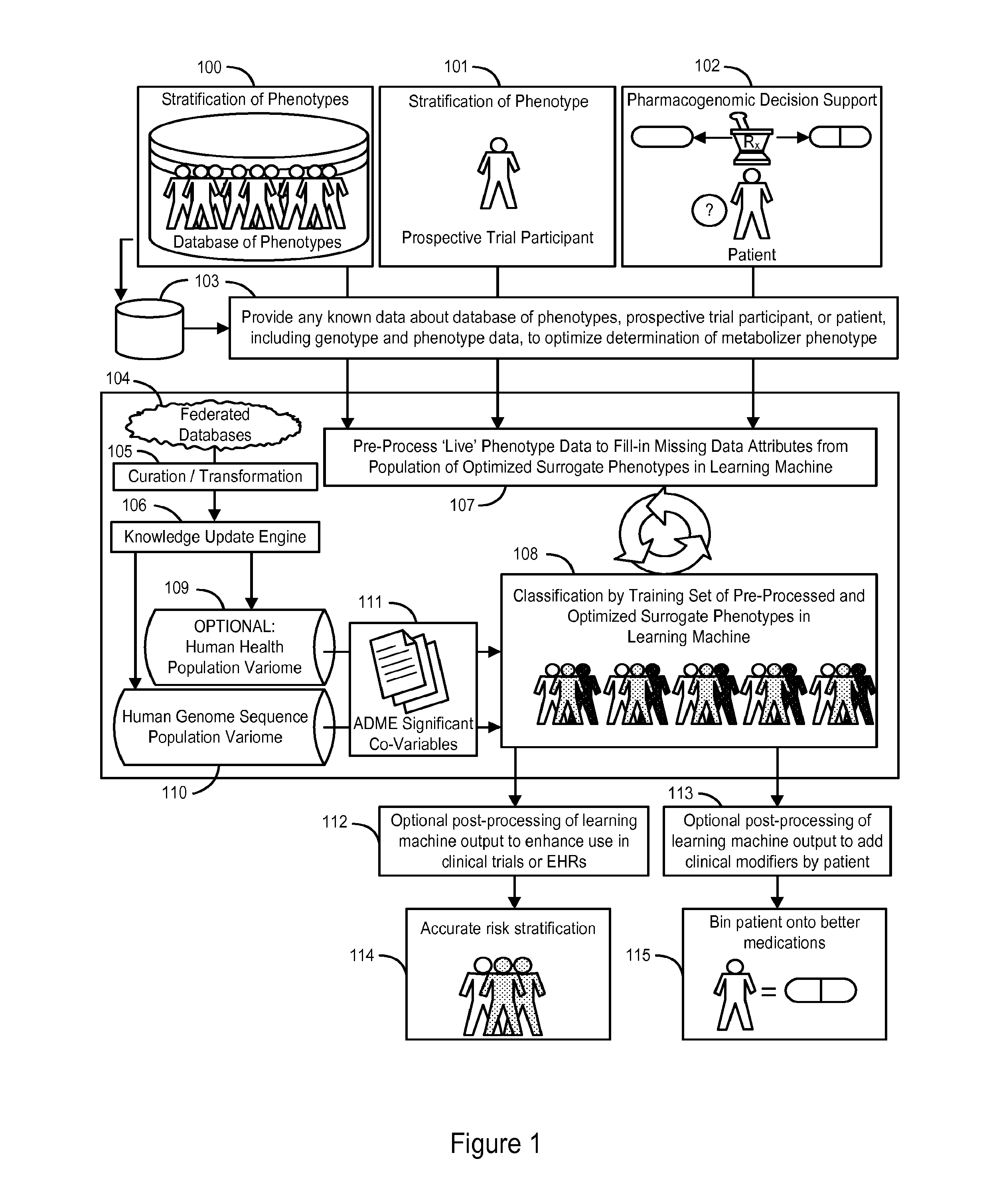
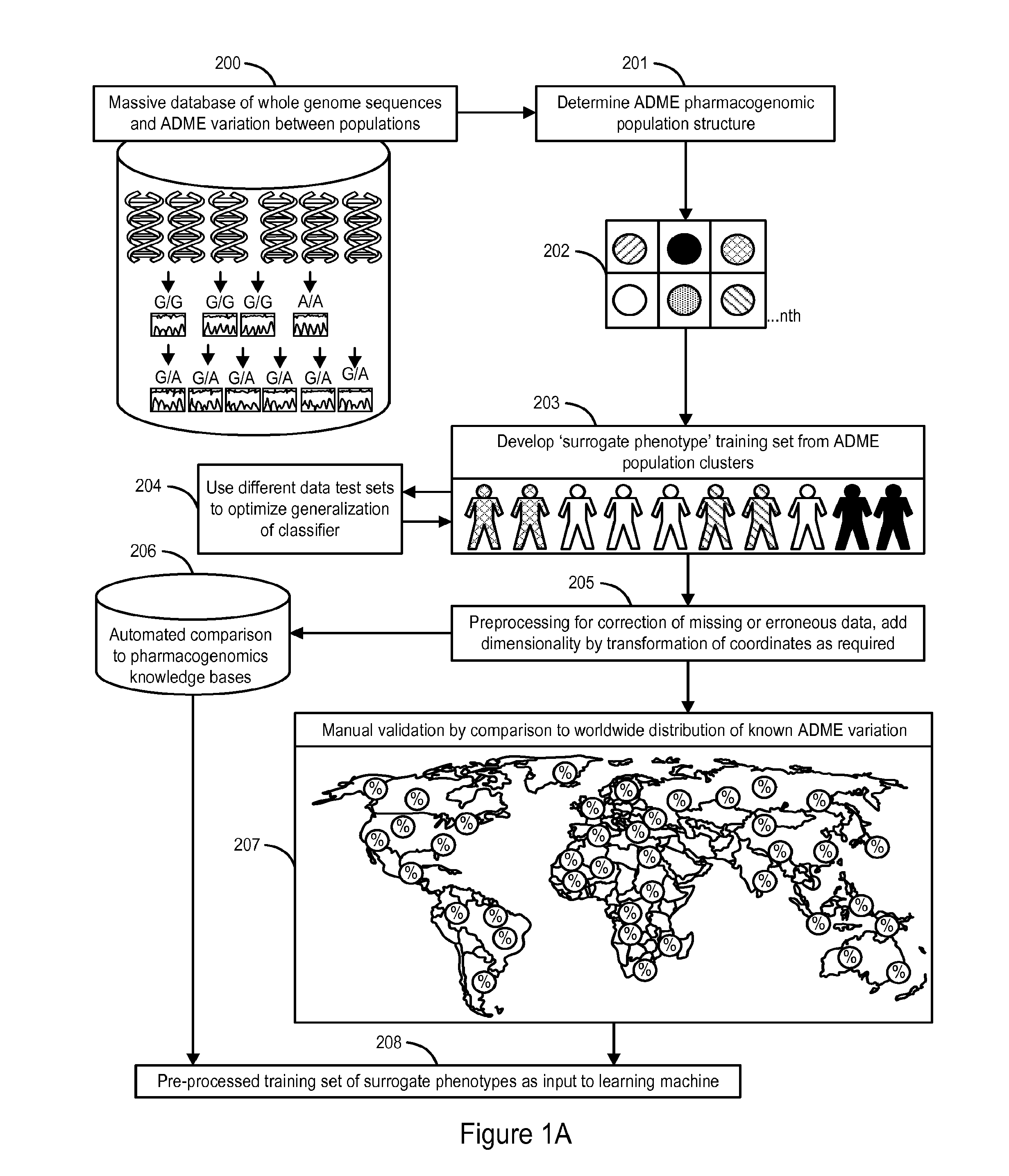
The invention provides a system and methods for the determination of the pharmacogenomic phenotype of any individual or group of individuals, ideally classified to a discrete, specific and defined pharmacogenomic population(s) using machine learning and population structure. Specifically, the invention provides a system that integrates several subsystems, including (1) a system to classify an individual as to pharmacogenomic cohort status using properties of underlying structural elements of the human population based on differences in the variations of specific genes that encode proteins and enzymes involved in the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) of drugs and xenobiotics, (2) the use of a pre-trained learning machine for classification of a set of electronic health records (EHRs) as to pharmacogenomic phenotype in lieu of genotype data contained in the set of EHRs, (3) a system for prediction of pharmacological risk within an inpatient setting using the system of the invention, (4) a method of drug discovery and development using pattern-matching of previous drugs based on pharmacogenomic phenotype population clusters, and (5) a method to build an optimal pharmacogenomics knowledge base through derivatives of private databases contained in pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies and academic research centers without the risk of exposing raw data contained in such databases. Embodiments include pharmacogenomic decision support for an individual patient in an inpatient setting, and optimization of clinical cohorts based on pharmacogenomic phenotype for clinical trials in drug development.
Owner:ASSUREX HEALTH INC
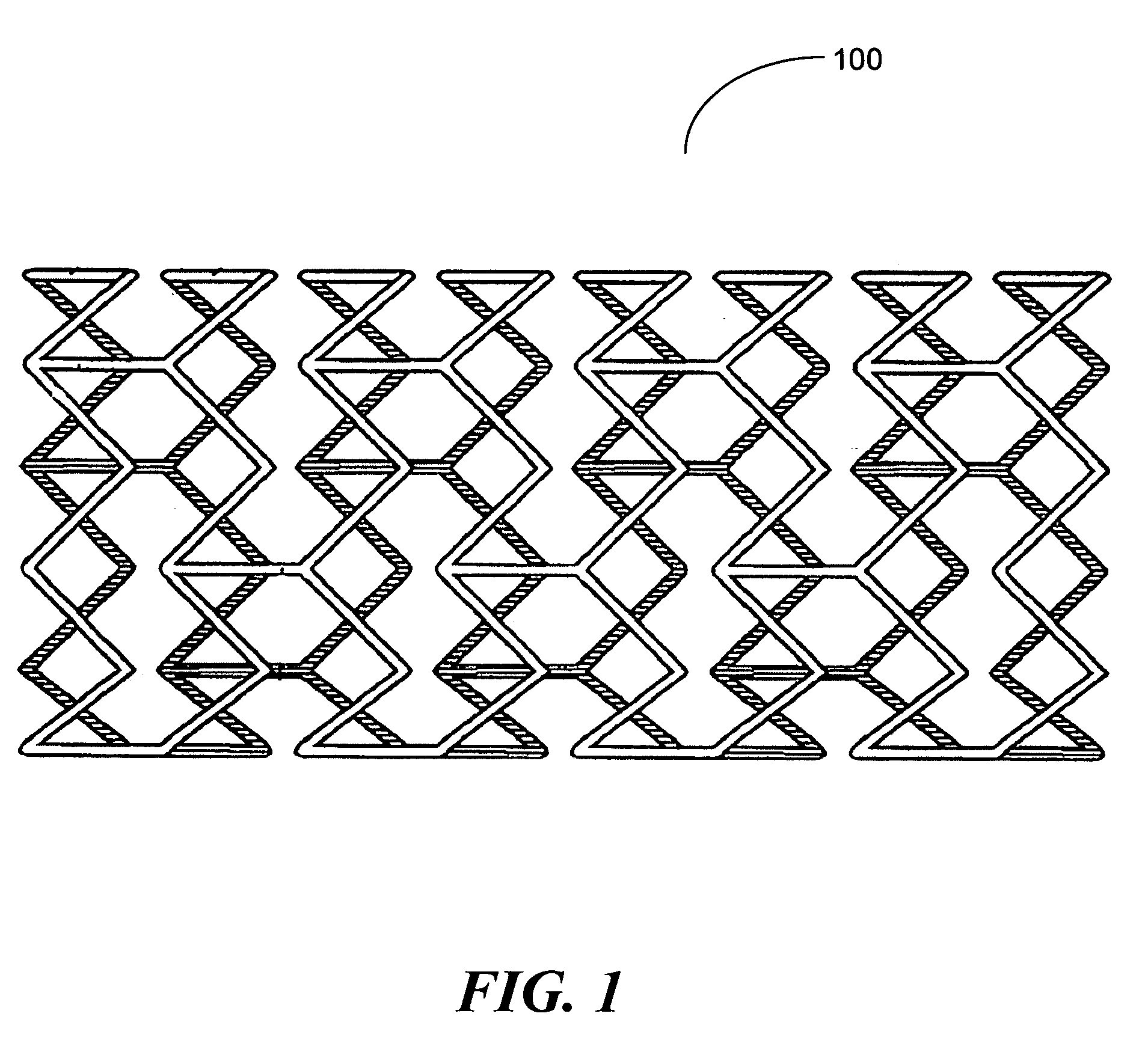
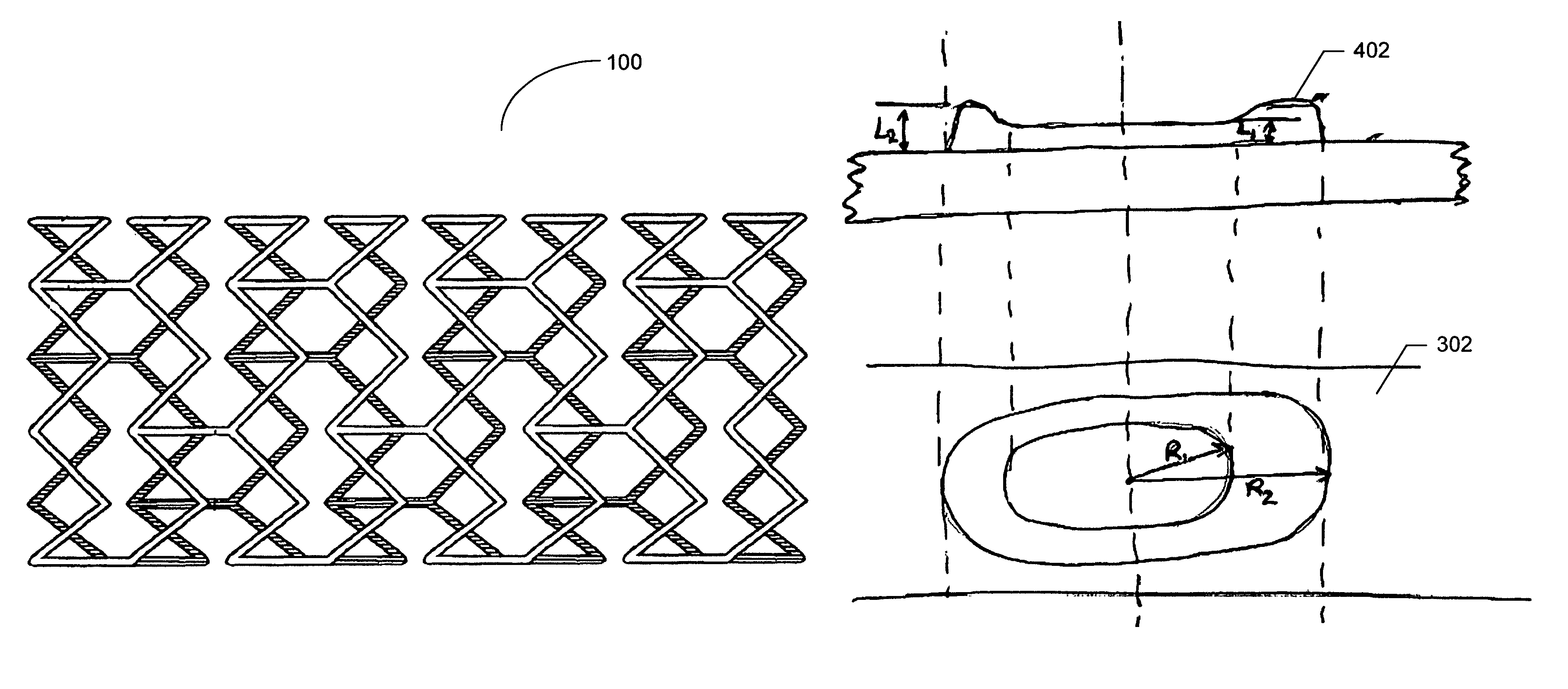
Device with engineered surface architecture coating for controlled drug release
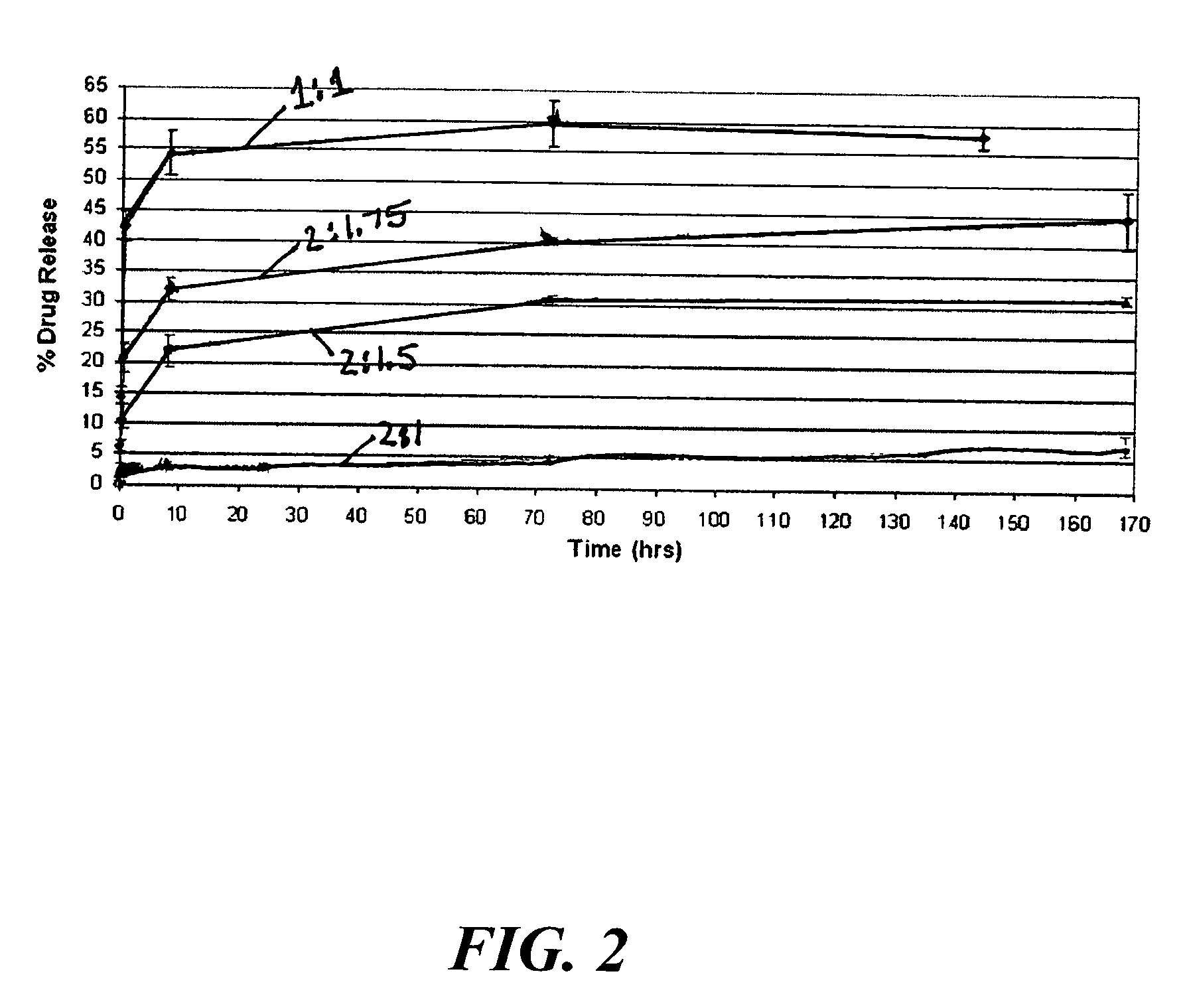
In one embodiment of the present invention a coating topology, or engineered surface architecture that may be referred to as a microdroplet deposited engineered surface architecture is provided. A plurality of drops are placed on the stent with the purpose, of building up individual units of coating material on the outer stent surface. This architecture results in a coating that uses less material, i.e., polymer, solvent, medicine, while at the same time providing for better, and determinable, drug kinetics, approaching 100% delivery and better mechanical operation of the coating binding to the stent.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
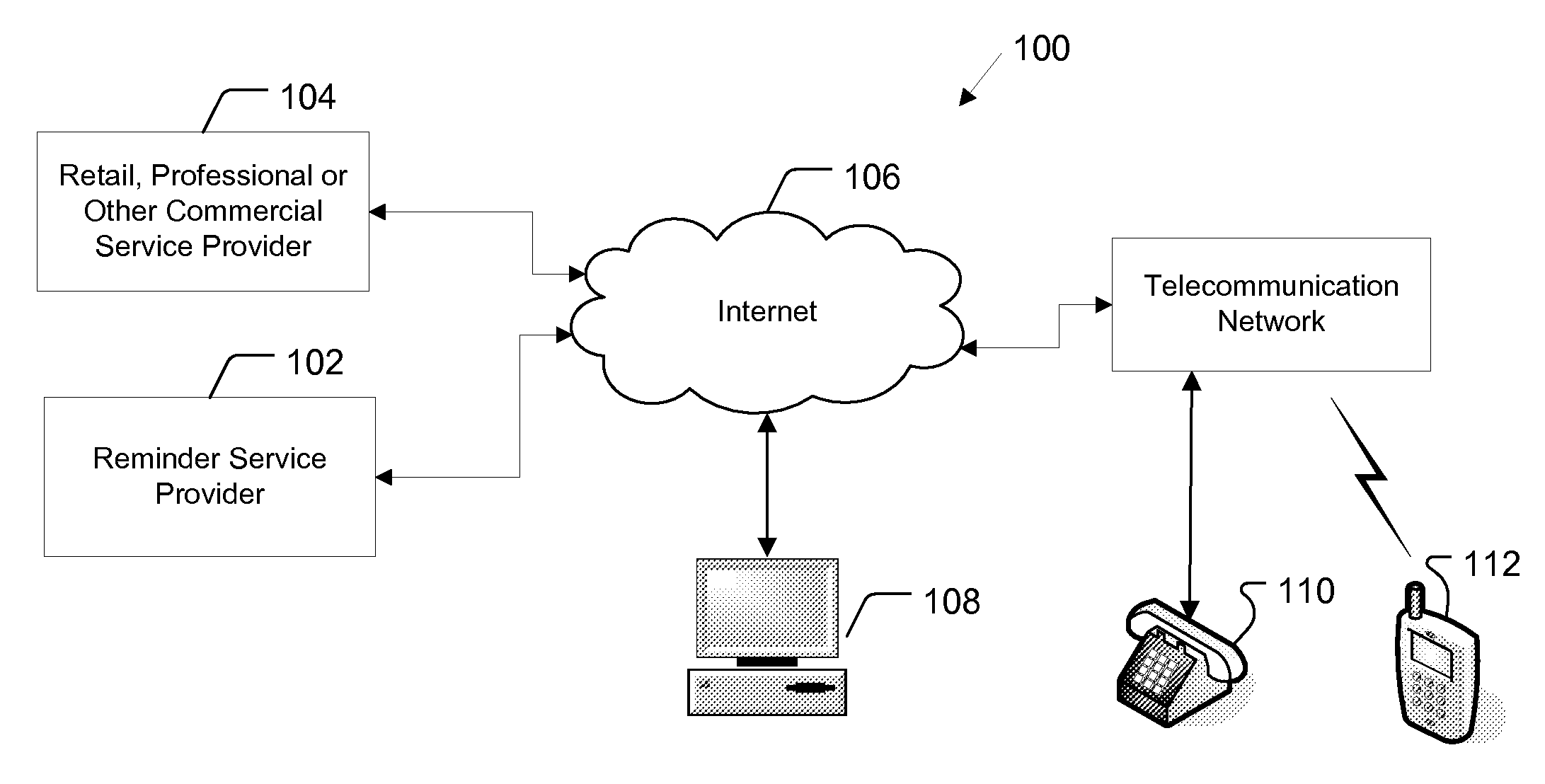
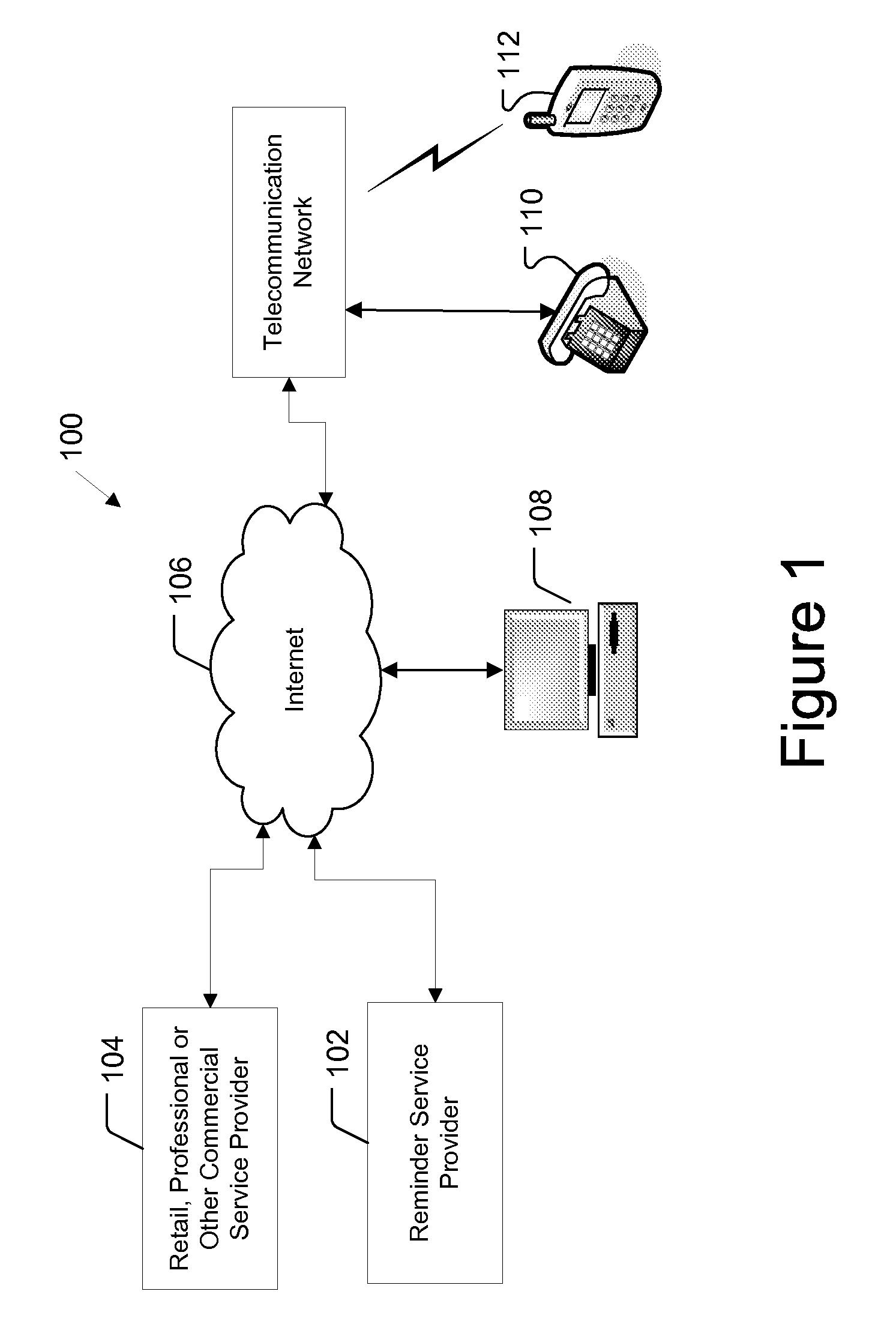
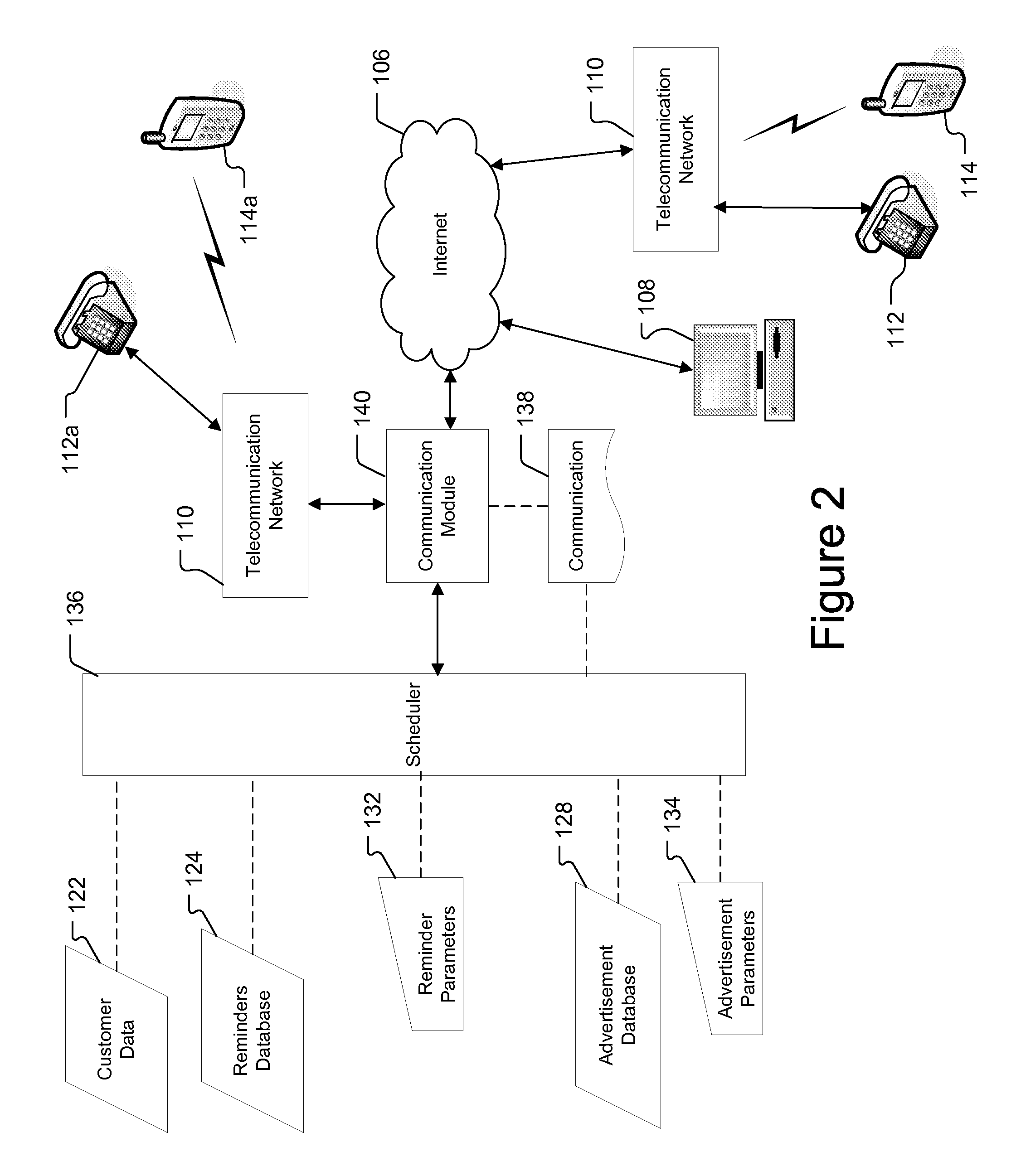
Reminder Notification System and Method
InactiveUS20080293392A1Special service for subscribersSignalling system detailsMobile Telephone NumberComputer science
A system and method of providing medication reminder notifications to a plurality of users is provided. In one embodiment, the method comprise storing data of mobile telephone number for each of the plurality of users in a memory, storing medication data in association with each of the plurality of users in a memory that comprises information identifying one or more medications of the user. The method may further include storing notification schedule data in association with each user in a memory that comprises information for determining one or more times for providing a medication reminder notification that comprises a reminder to take a medication, determining medication content for a medicine reminder notification based, at least in part, on the medication data in association with that user; and transmitting one or more medication reminder notifications, that include the determined medication content, to the mobile telephone number(s) destinations associated with each user according to the notification schedule data associated with the user.
Owner:STROTHER DANE A
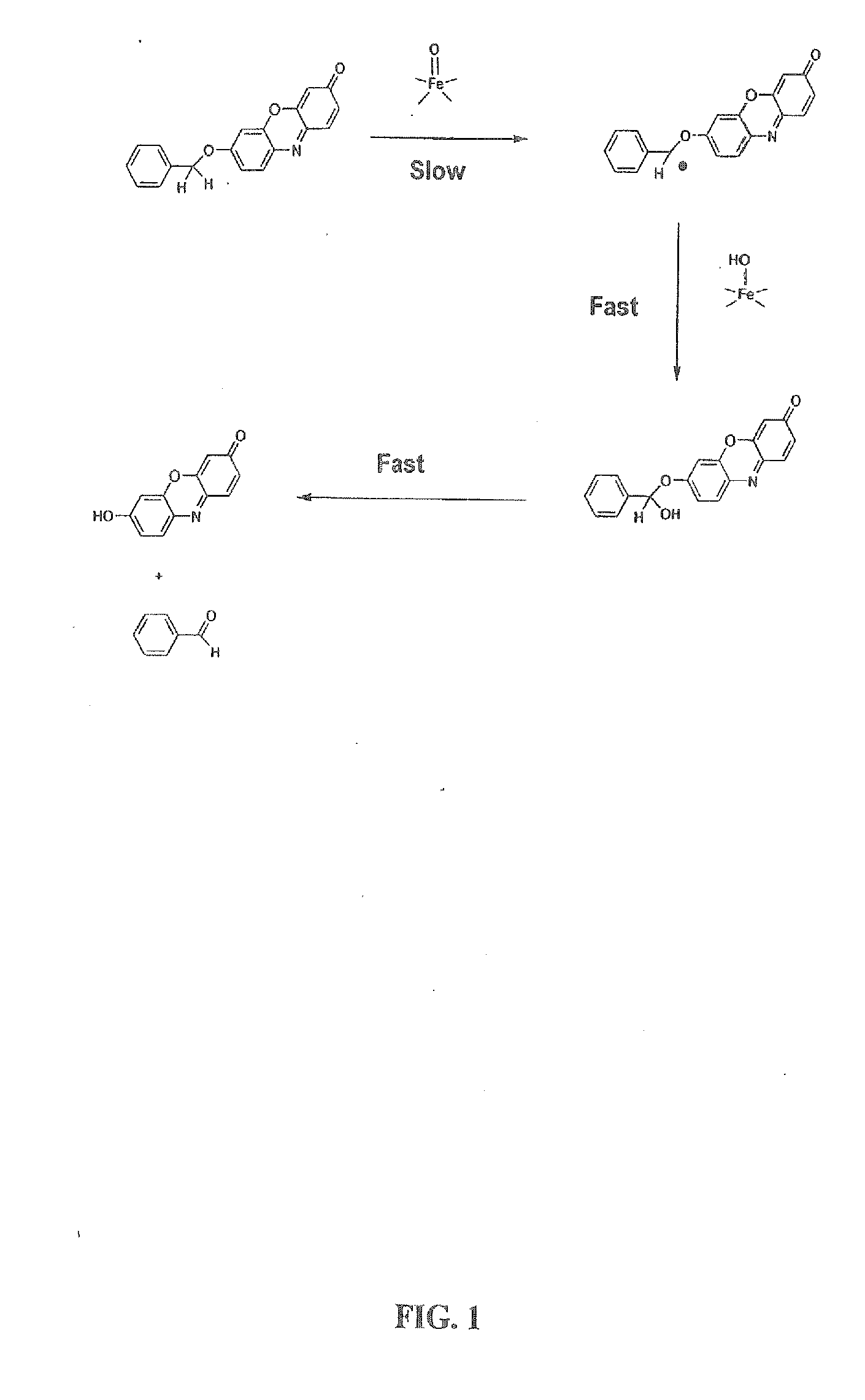
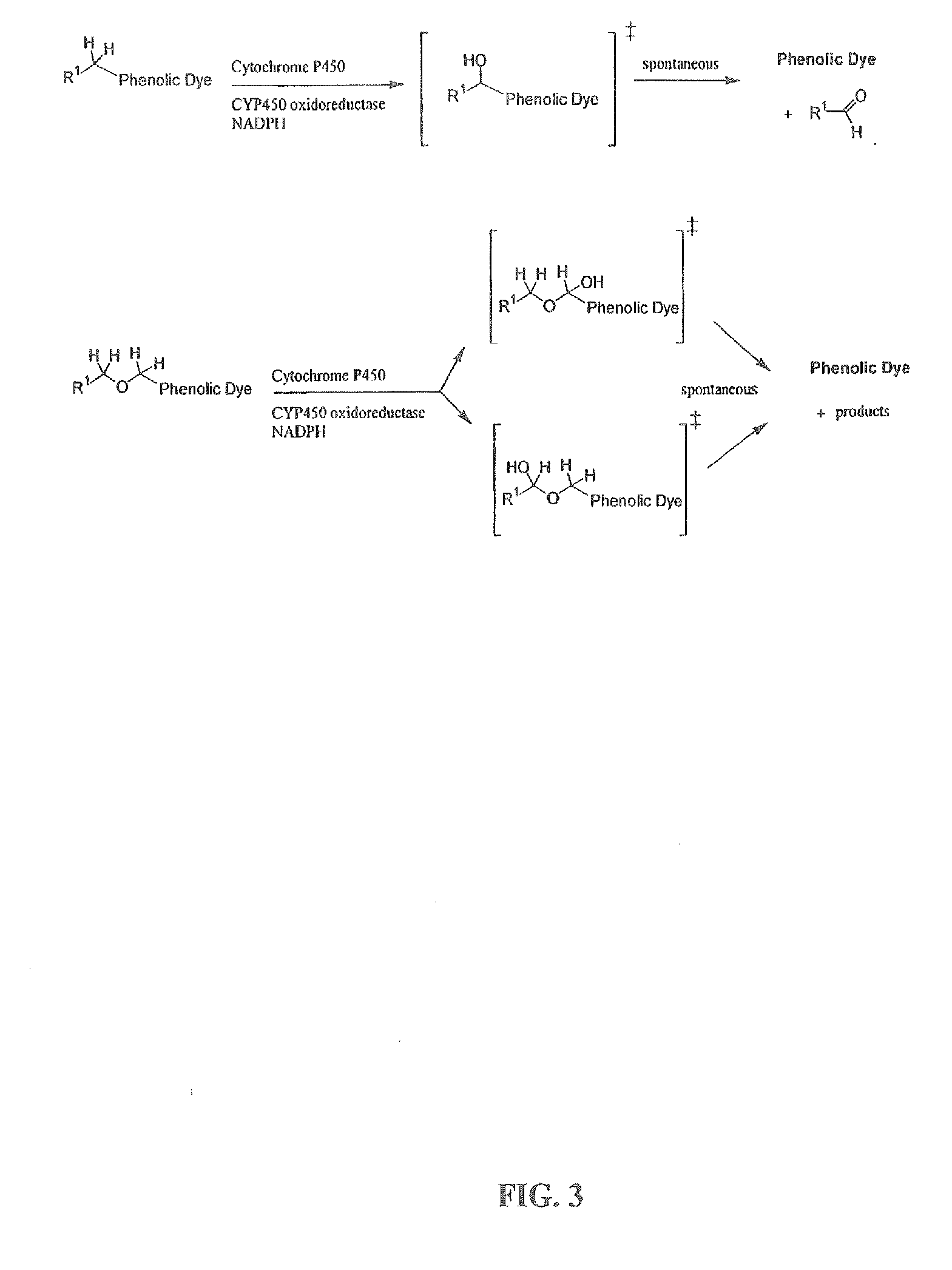
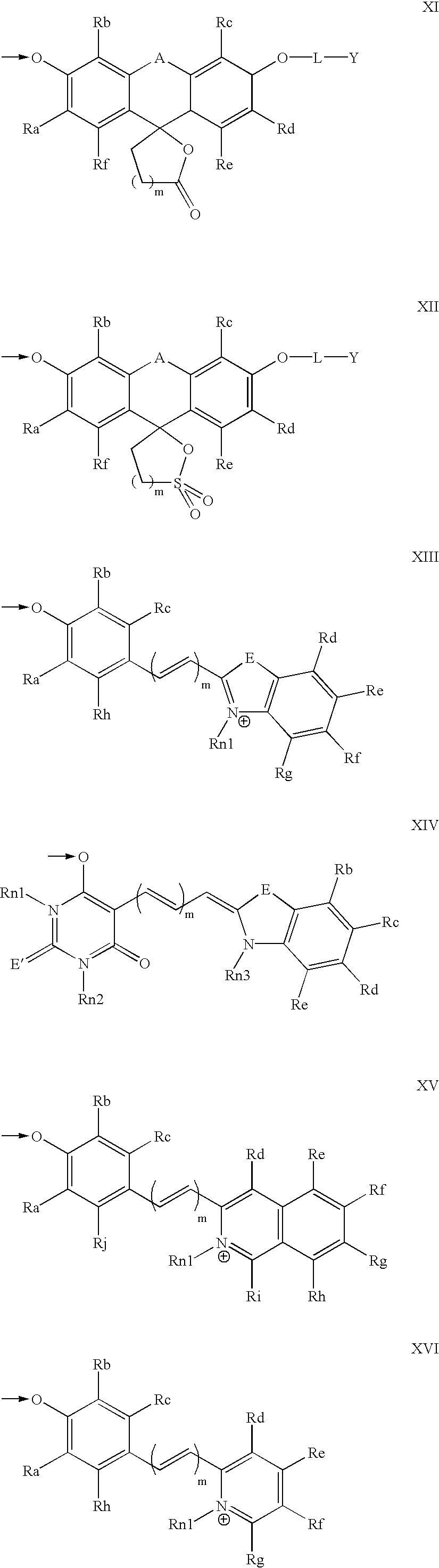
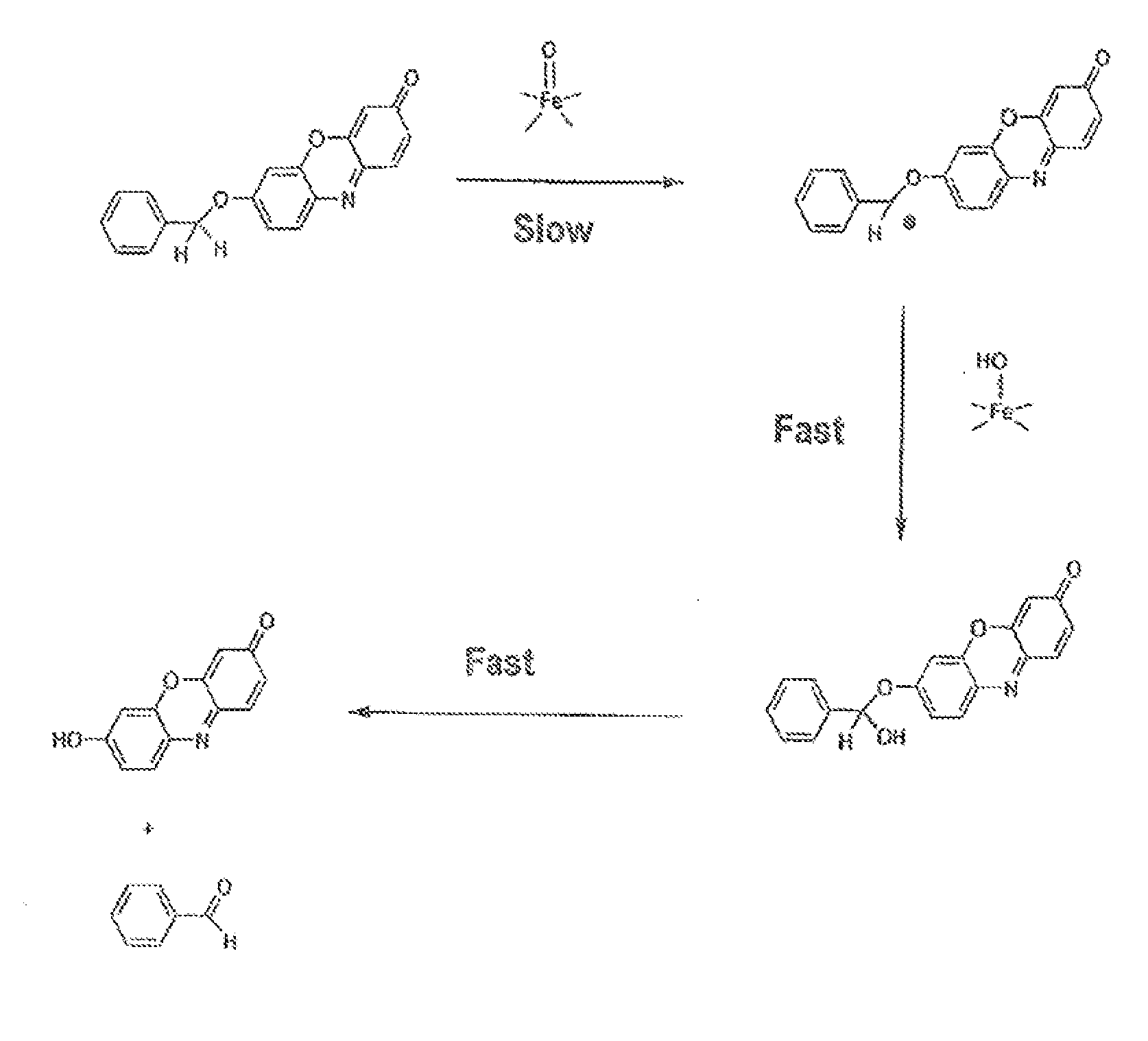
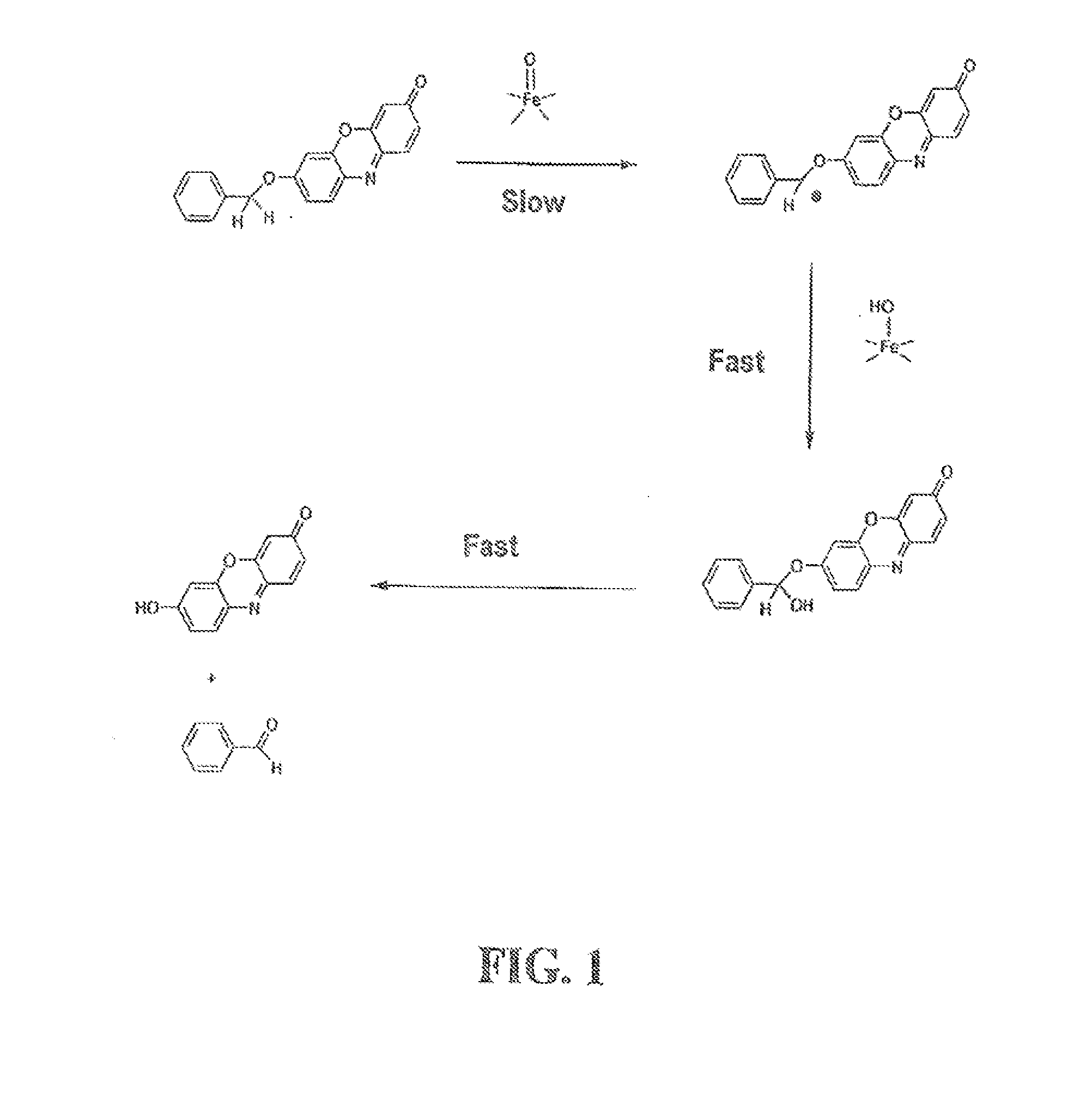
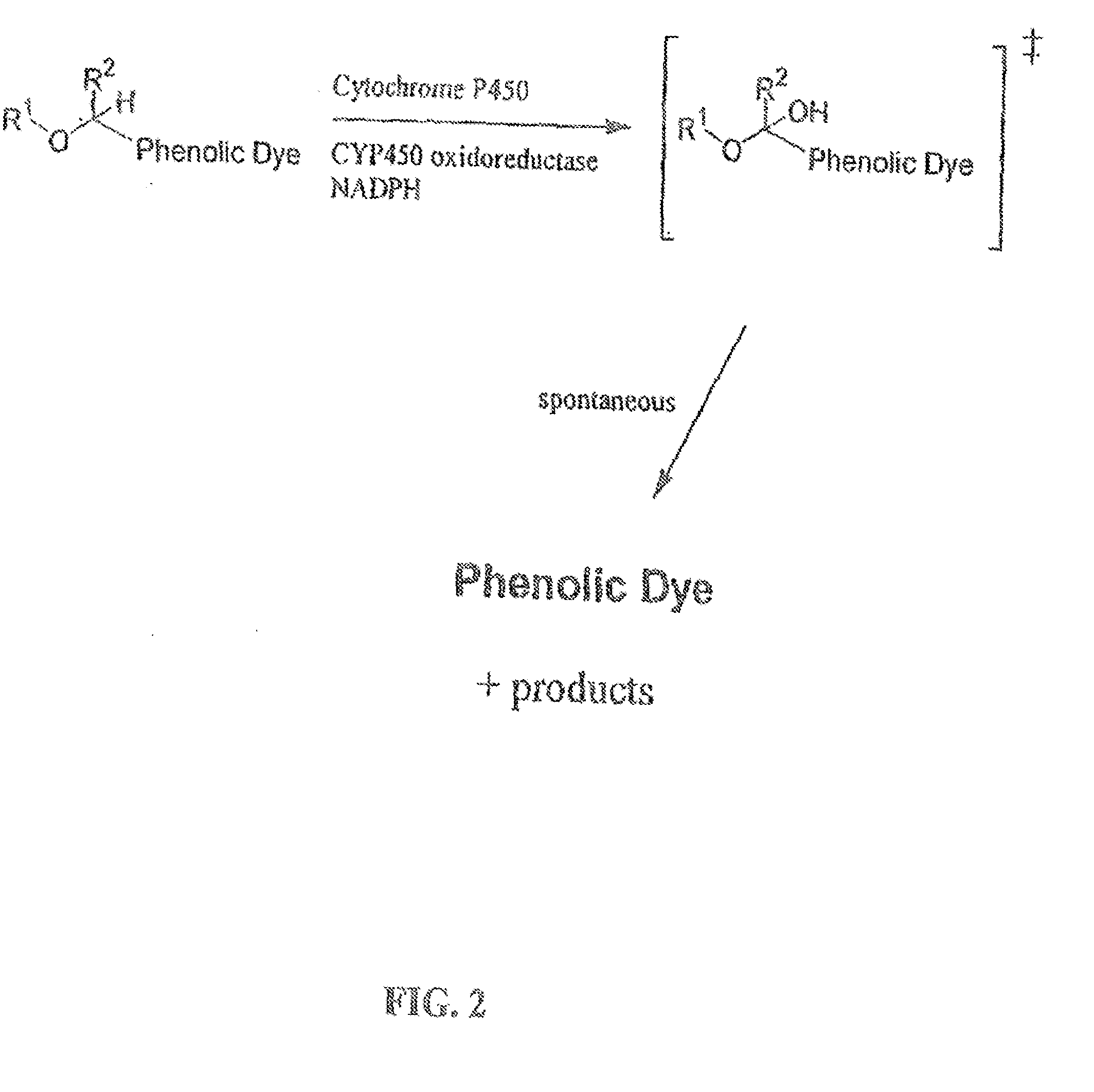
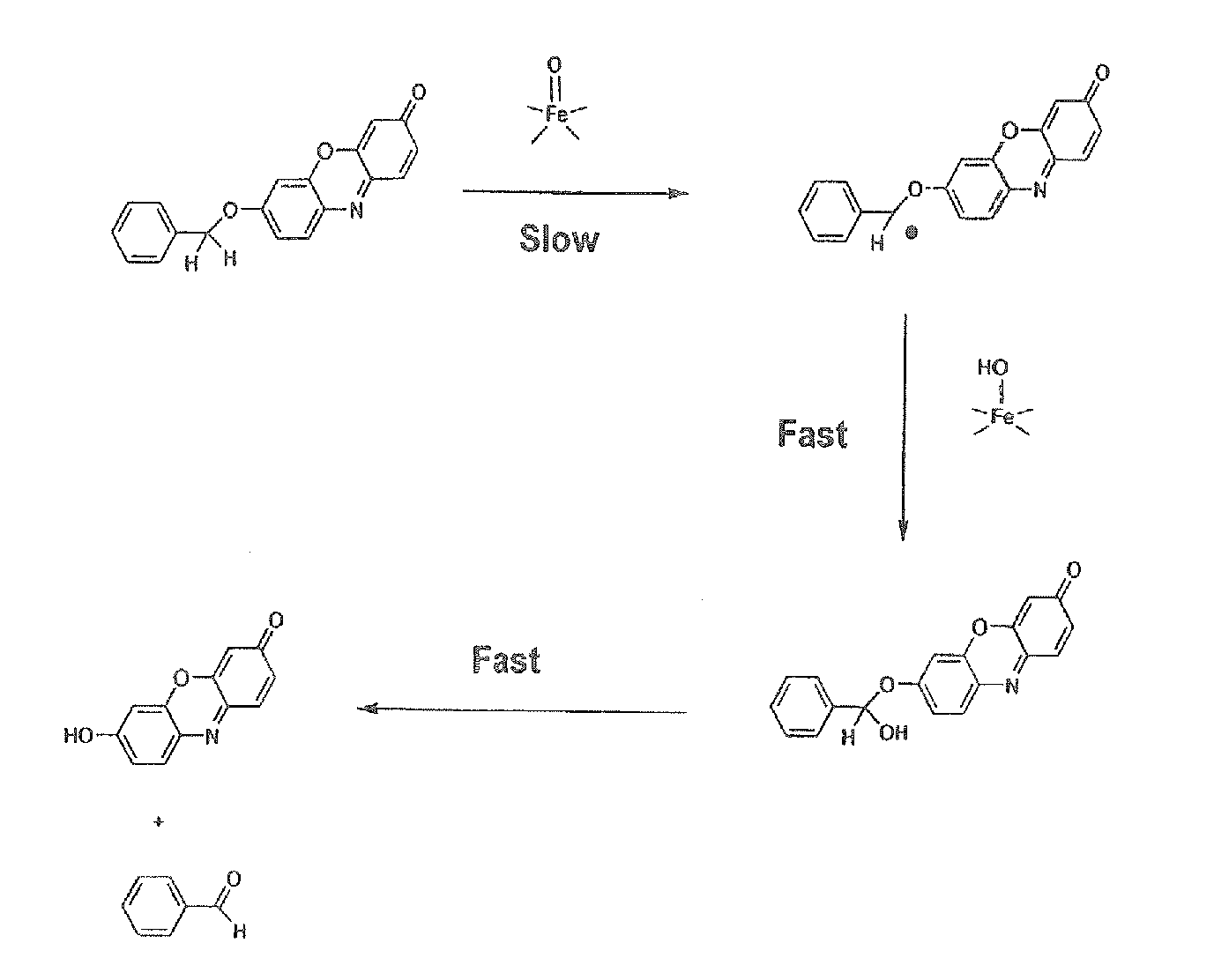
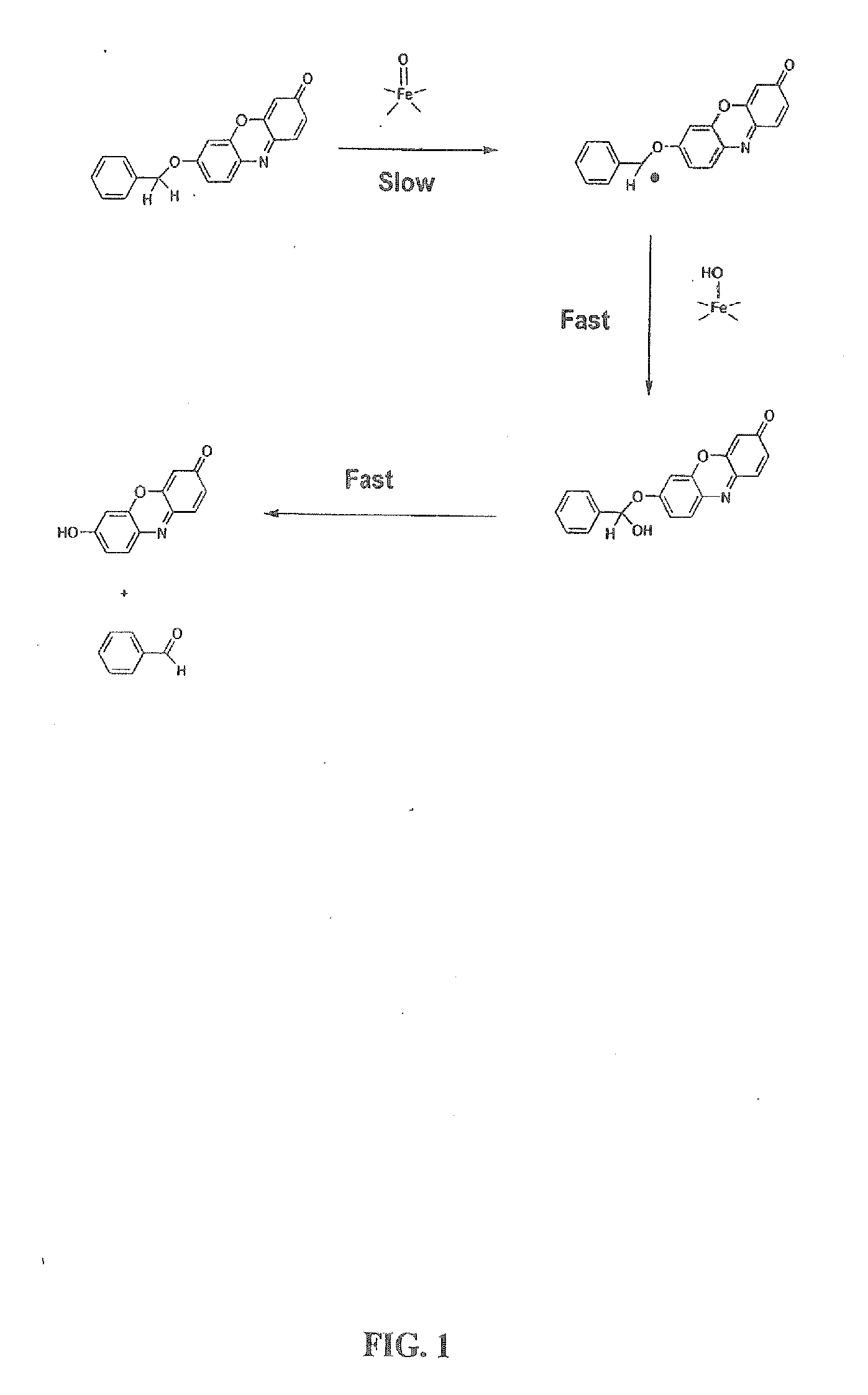
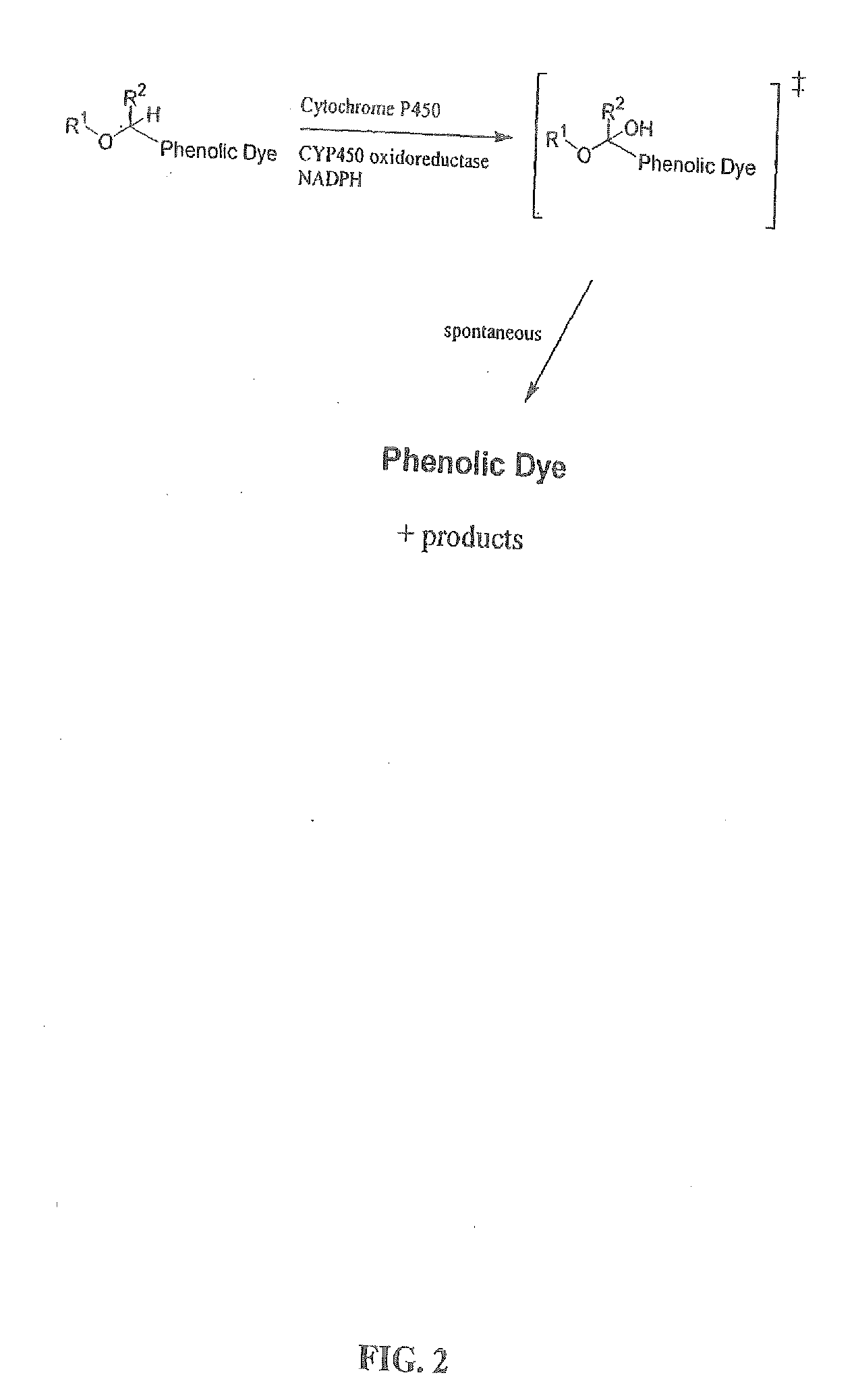
Optical molecular sensors for cytochrome p450 activity
The invention provides a compound, useful as an optical probe or sensor of the activity of at least one cytochrome P450 enzyme, and methods of using the compound to screen candidate drugs, and candidate drugs identified by these methods. The optical probe of the invention is a compound having the generic structure Y-L-Q, wherein Y is selected from the group consisting of Q as herein defined, saturated C1-C20 alkyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 alkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, C1-C20 cycloalkyl, C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 cycloalkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl; L is selected from the group of (—OCR2H)p—, wherein for each p, all R2 are separately selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, saturated C1-C20 alkyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 alkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, C1-C20 cycloalkyl, C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 cycloalkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and p is a positive integer no greater than twelve; and Q is a chemical moiety that gives rise to optical properties in its hydroxy or hydroxylate, phenol or phenoxide form that are different from the optical properties that arise from its ether form. Most preferably, p is one, R2 is hydrogen, and Q is the ether form of a phenoxide fluorophore.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
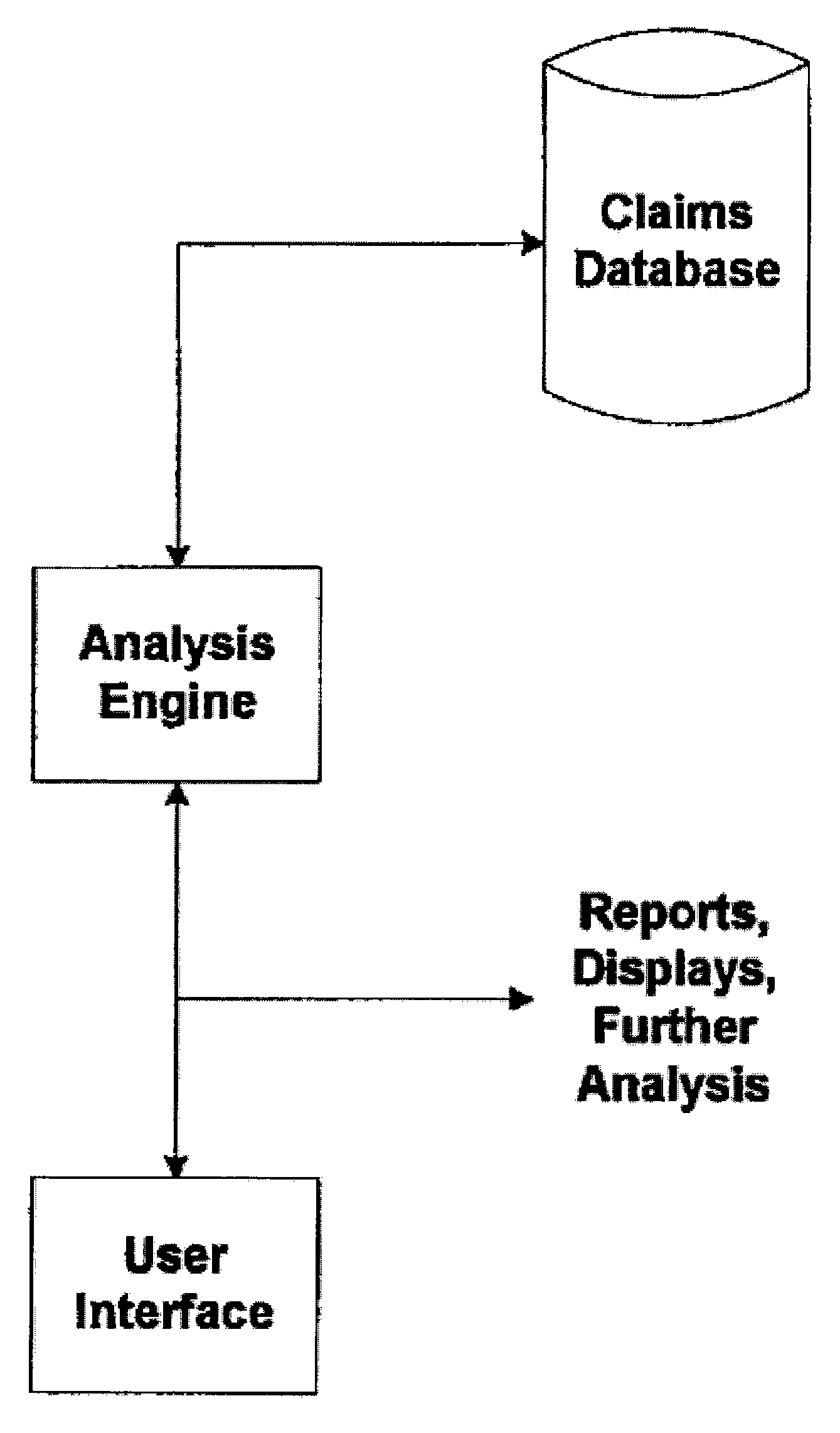
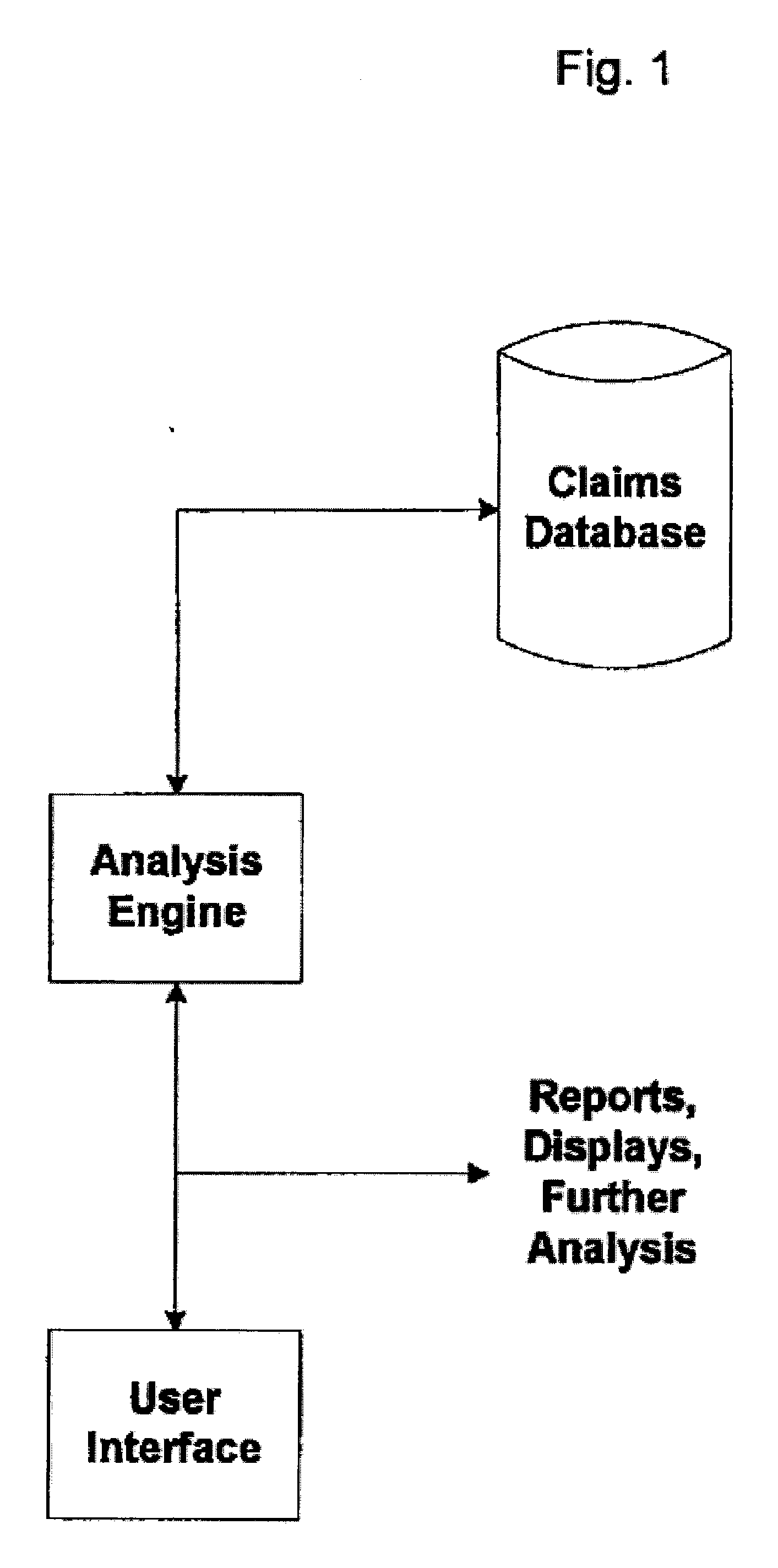
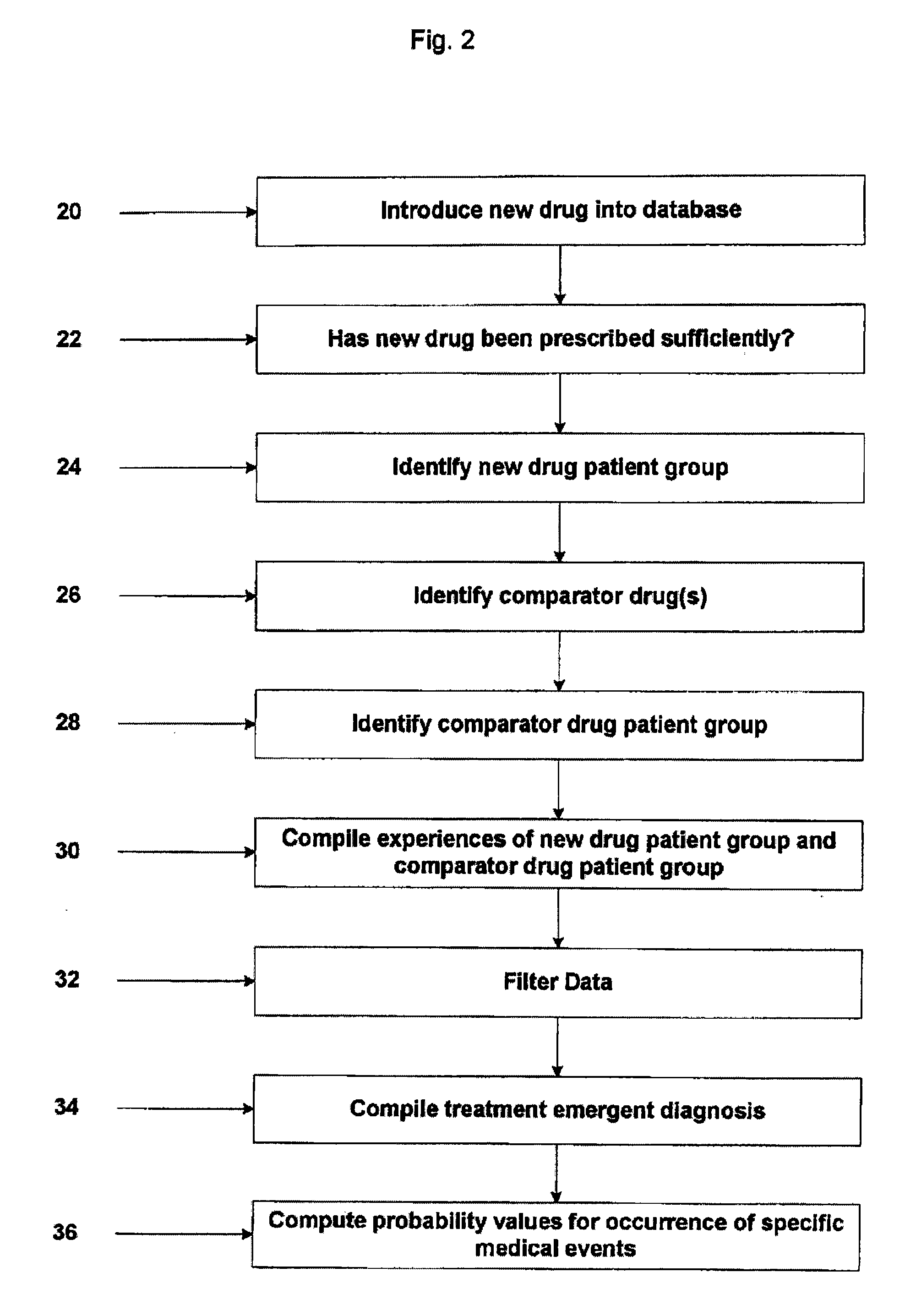
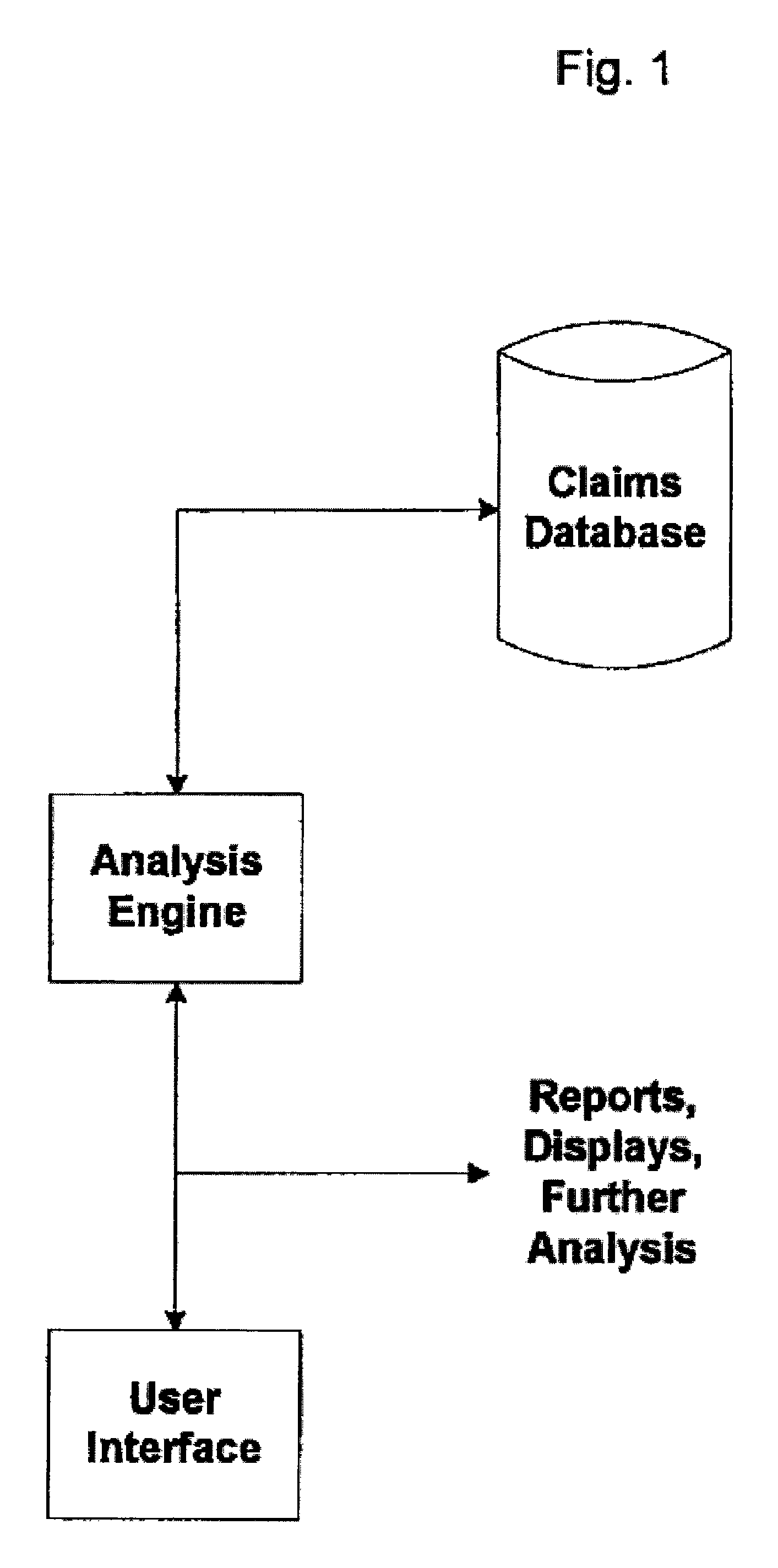
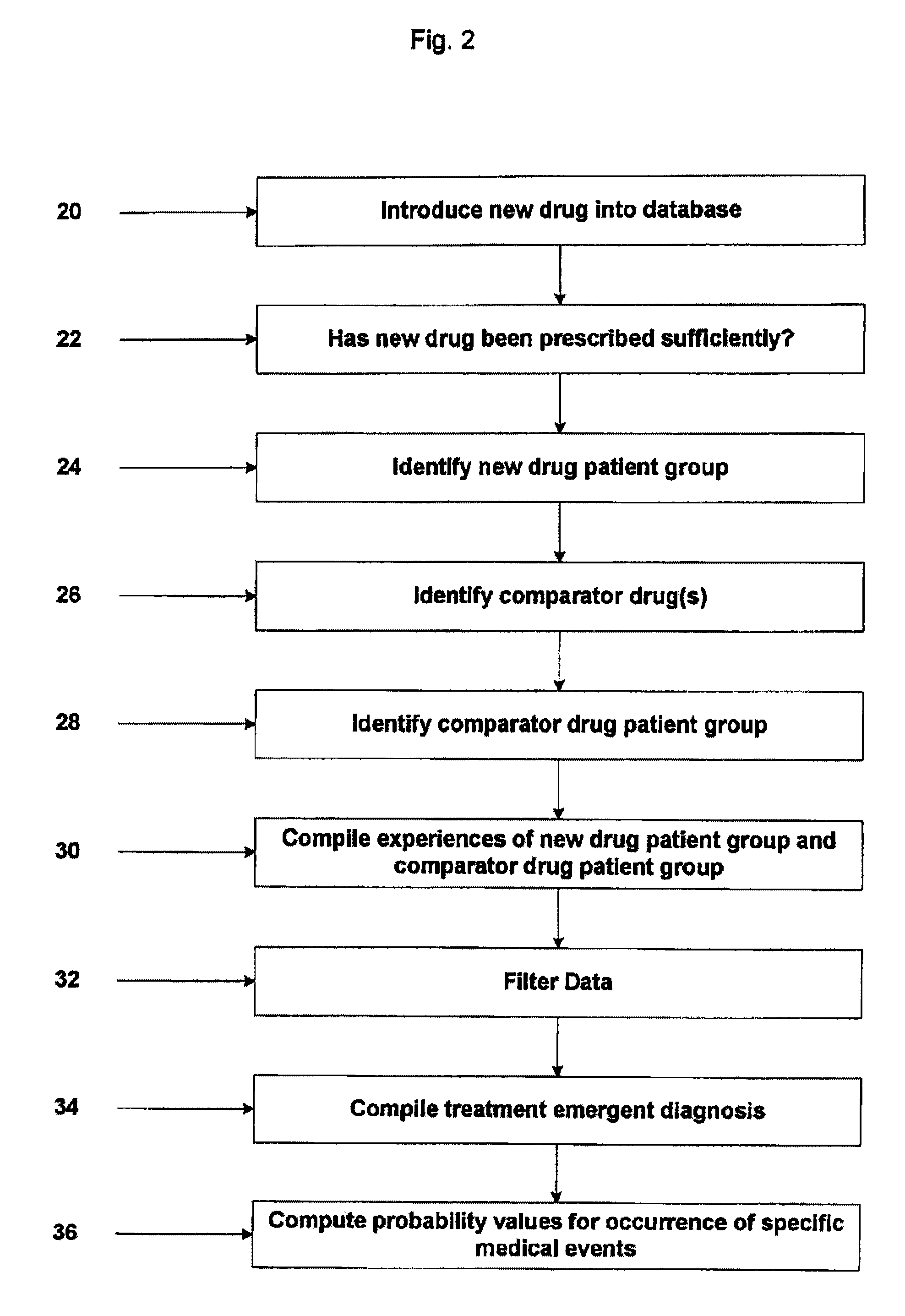
System and Method for Early Identification of Safety Concerns of New Drugs
ActiveUS20070174086A1Improved drug safety analysisMedical data miningData processing applicationsDiagnostic programLaboratory test
A system and method for identifying safety concerns regarding a drug identify a first group of patients that have received the drug from a database of healthcare claims and extract one or more medical events that the first group of patients have experienced from the database. The system and method also identify a second group of patients that have received a comparator drug in the database and extract one or more medical events that the second group of patients have experienced. The medical events of the first group are compared to the medical events of the second group to determine at least one common occurrence therebetween. The common occurrence(s) is then filtered based upon one or more user defined outcomes, each including at least one diagnosis, procedure or therapeutic classification; non-medical criteria; and / or patient laboratory test data.
Owner:OPTUMINSIGHT
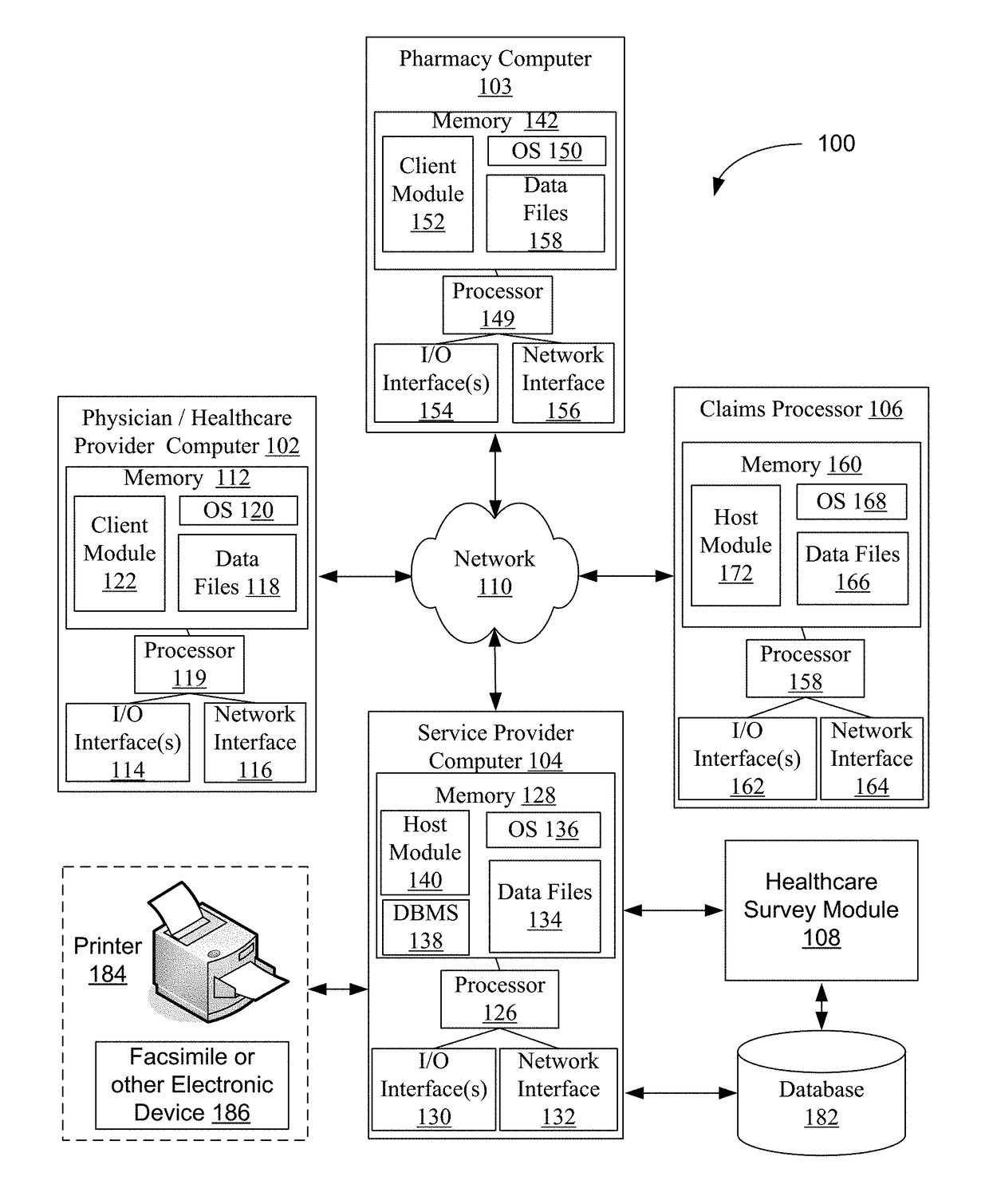
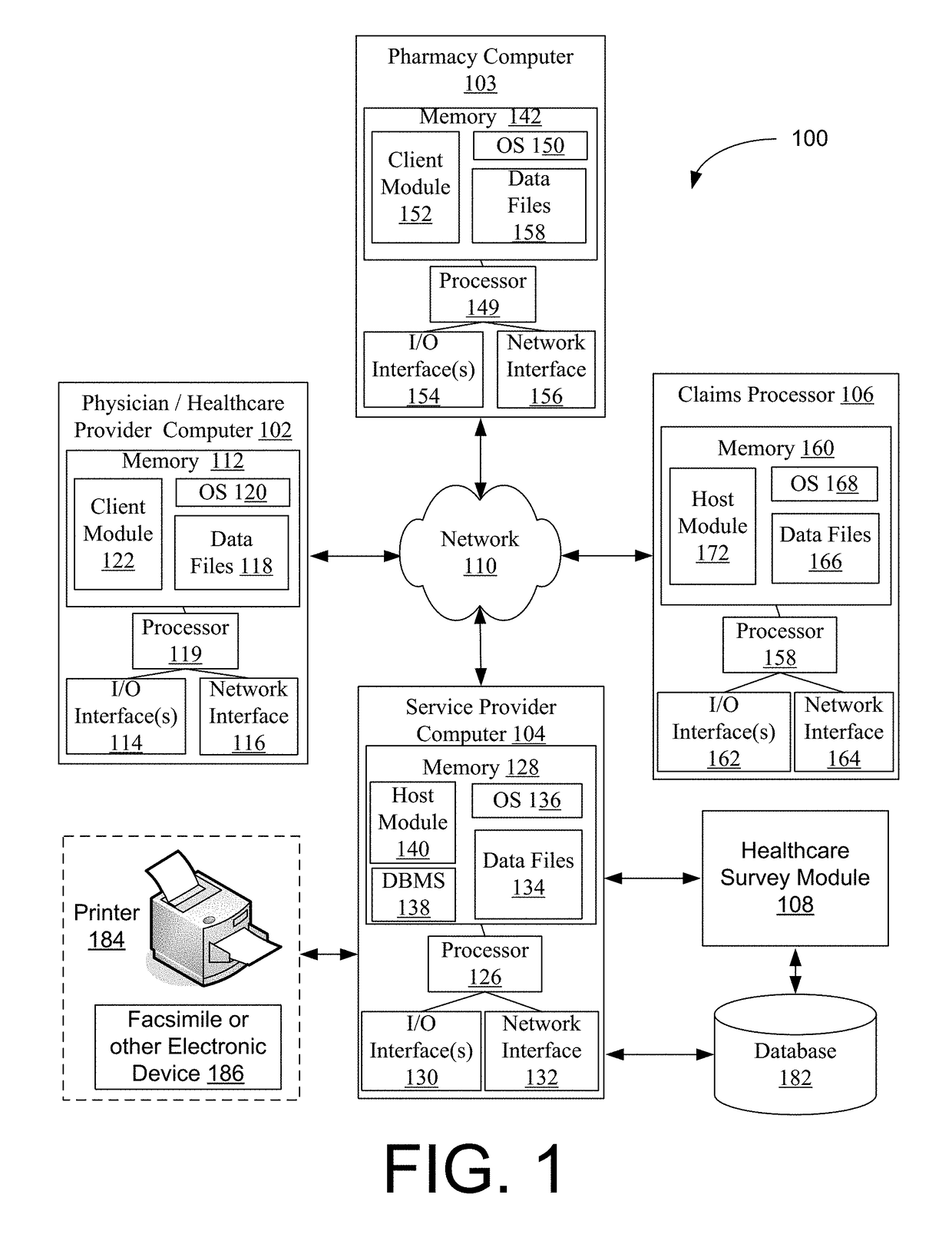
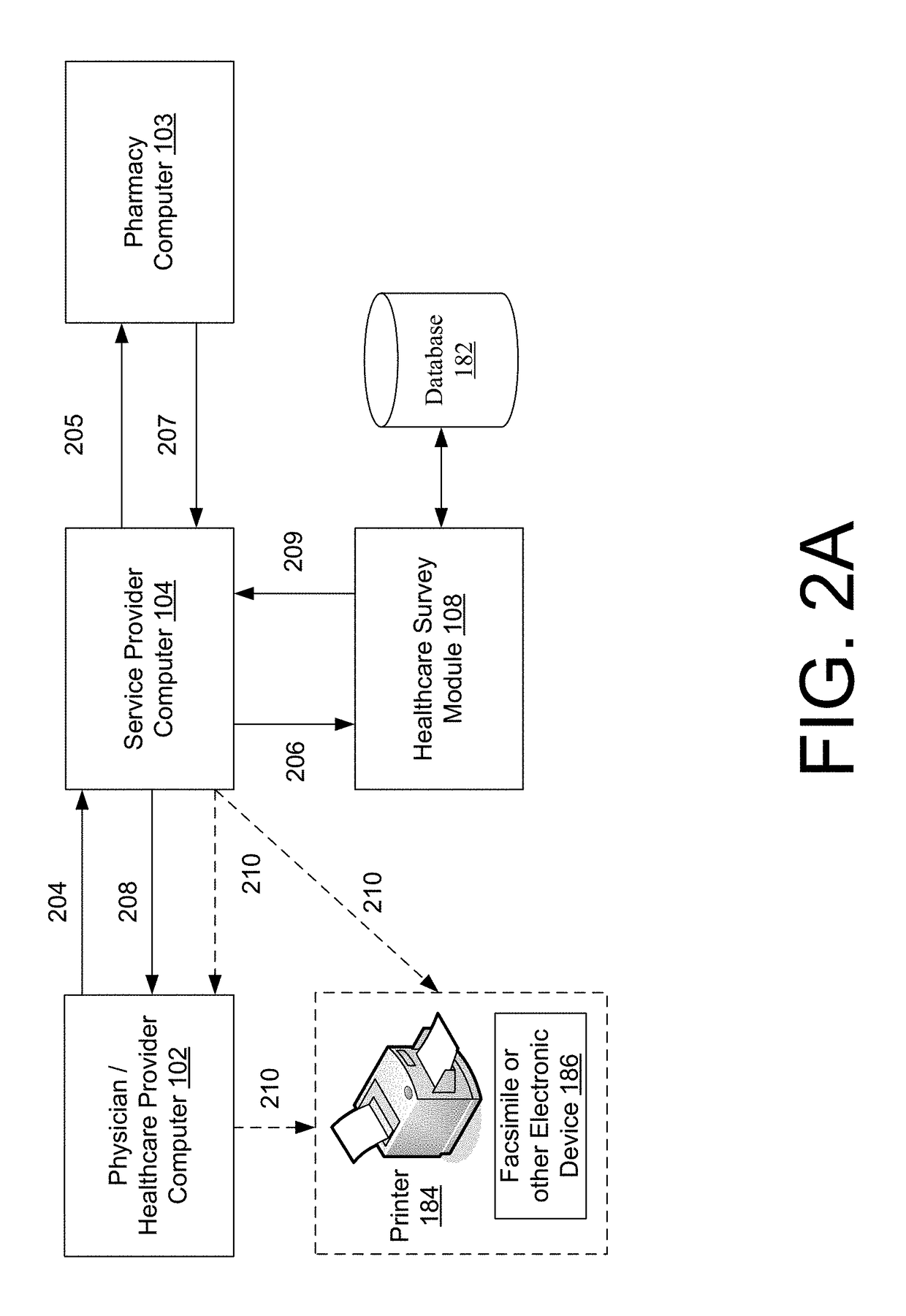
Systems and methods for a healthcare network survey solution
Systems and methods are provided for a healthcare network survey solution. The systems and methods may include receiving a healthcare transaction from a remote computer, where the healthcare transaction identifies at least one of a drug, product, or service for a patient; determining that the healthcare transaction is eligible for a survey based upon an analysis of the drug, product, or service identified in the healthcare transaction request; selecting the eligible healthcare transaction for the survey based at least in part upon a random selection process; and delivering a survey request to a survey recipient associated with the healthcare transaction, where the survey request includes at least a transaction identifier for identifying the survey.
Owner:MCKESSON CORPORATION
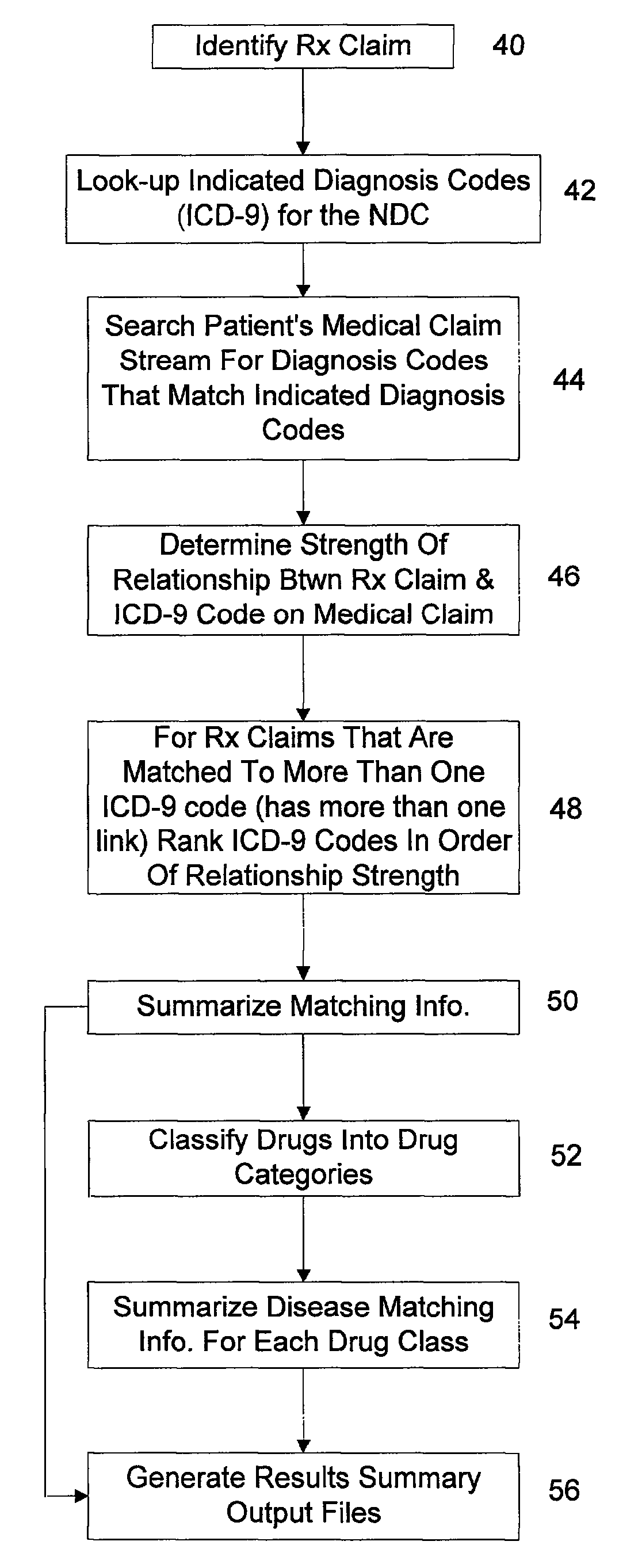
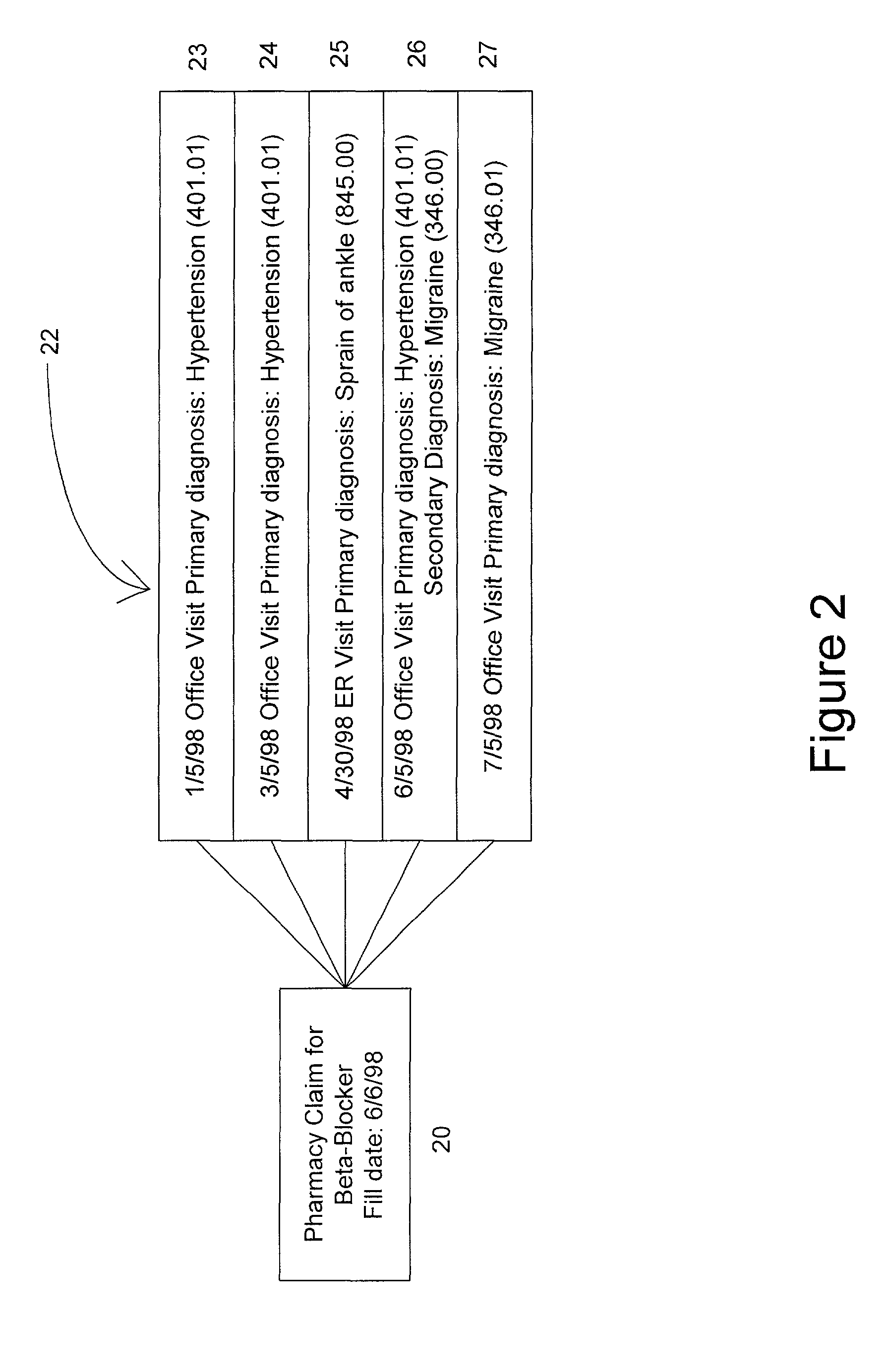
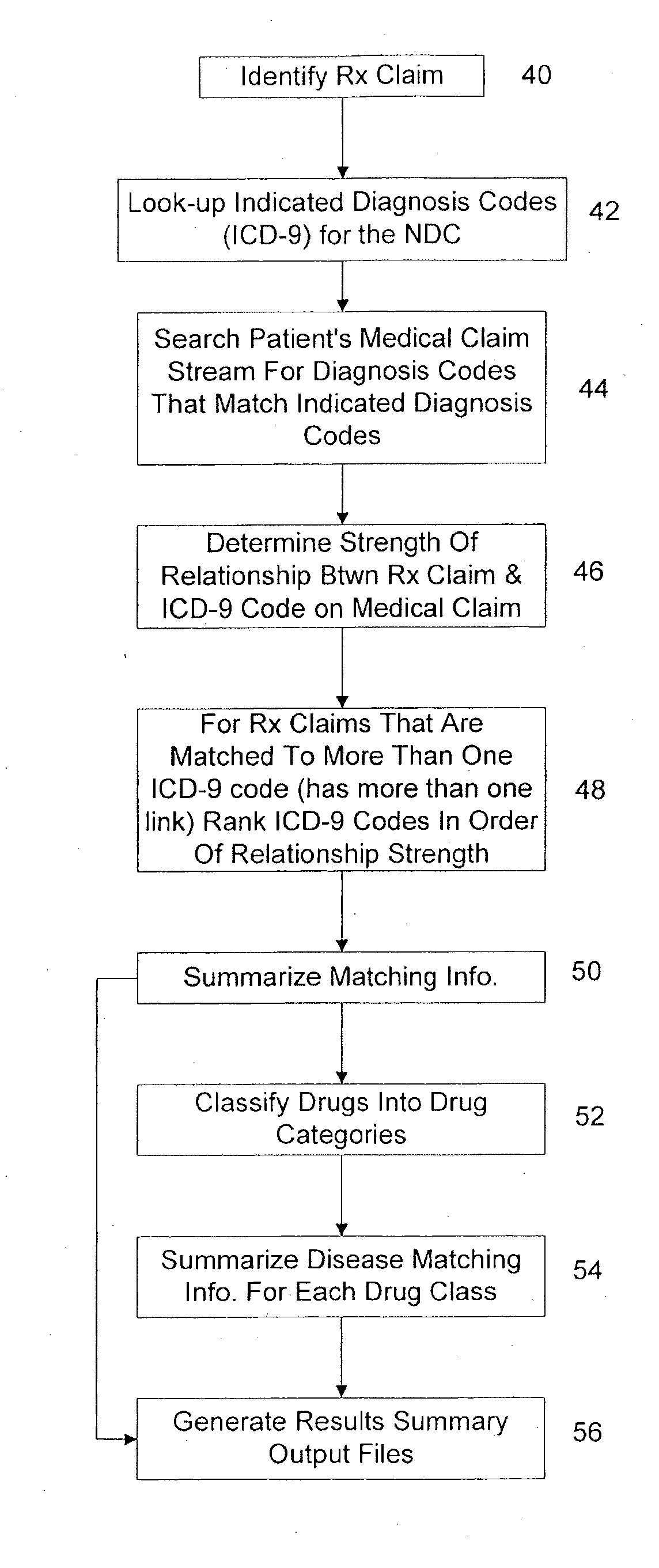
System and method of drug disease matching
A computer implemented system and method for matching drugs and diseases and generating a weighted relationship between the matched drugs and diseases. The system stores a quantity of patient medical history billing records identifiable as patient prescription claim records and medical claim records. The system also stores a grouping of drug codes and groupings of diagnosis codes. The system is configured to match drugs identified in a specific patient's prescription claim records with diseases identified in the patient's medical claims. The system generates a weighted relationship between the matched drugs and diseases by calculating a link weight in accordance with a preprogrammed formula for each occurrence of the diagnosis codes identified in the patient's medical claims that is identified as associated with the disease identified and the drug upon which the query is being processed. The link weight provides a statistical match association value to each of the matched diseases.
Owner:OPTUMINSIGHT
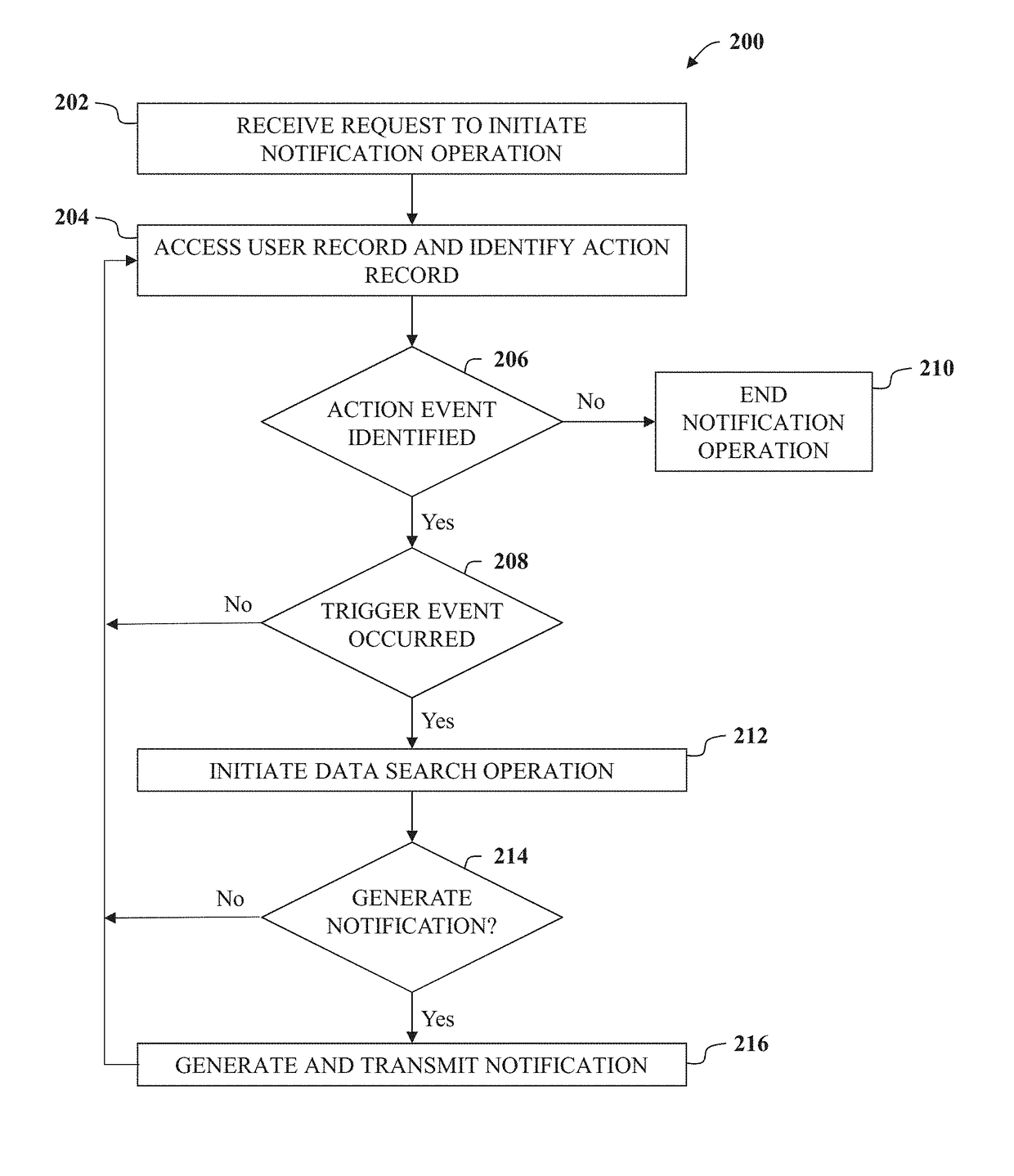
System, method, and non-transitory computer-readable storage media for displaying information on mobile devices
A networked computer system for displaying information to a user via a mobile computing device is described herein. The networked computer system includes a database including a list of user pharmacy account records and a server computer. The server computer is programmed to receive a request to display a notification message to a user including a corresponding user ID, access the database, and identify a user pharmacy account record associated with the received user ID. The server computer determines an action record associated with the determined pharmaceutical drug including action event, and initiates a data search operation associated with the action event data. The server computer generates a notification message as a function of the outcome of the data search operation, and generates and transmits a signal including the notification message to the mobile computing device.
Owner:WALMART APOLLO LLC
System and method for early identification of safety concerns of new drugs
ActiveUS7856362B2Improved drug safety analysisMedical data miningData processing applicationsLaboratory testComparator
A system and method for identifying safety concerns regarding a drug identify a first group of patients that have received the drug from a database of healthcare claims and extract one or more medical events that the first group of patients have experienced from the database. The system and method also identify a second group of patients that have received a comparator drug in the database and extract one or more medical events that the second group of patients have experienced. The medical events of the first group are compared to the medical events of the second group to determine at least one common occurrence therebetween. The common occurrence(s) is then filtered based upon one or more user defined outcomes, each including at least one diagnosis, procedure or therapeutic classification; non-medical criteria; and / or patient laboratory test data.
Owner:OPTUMINSIGHT
System and method of drug disease matching
Owner:OPTUMINSIGHT
Method and device for predicting drug susceptibility state and storage medium
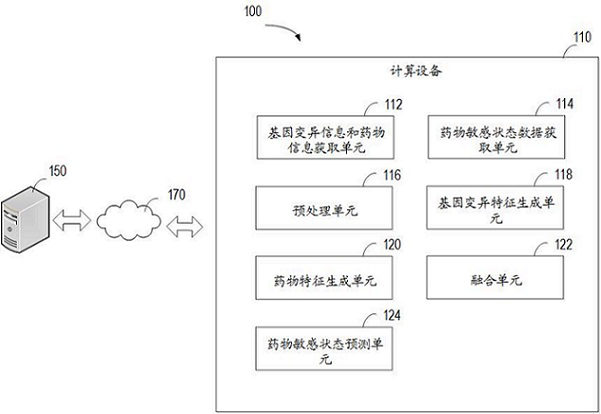
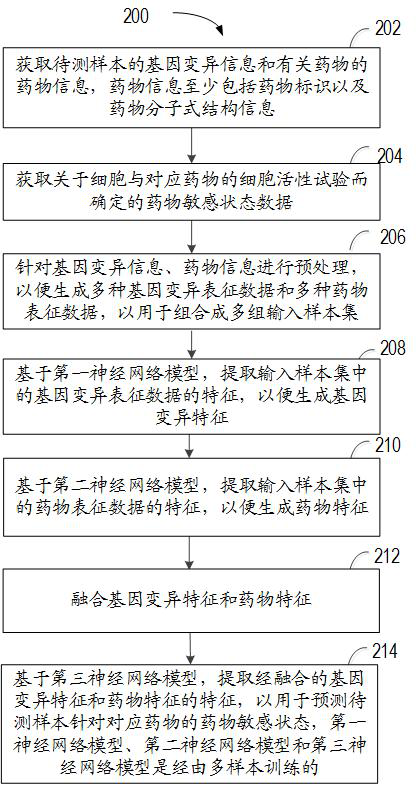
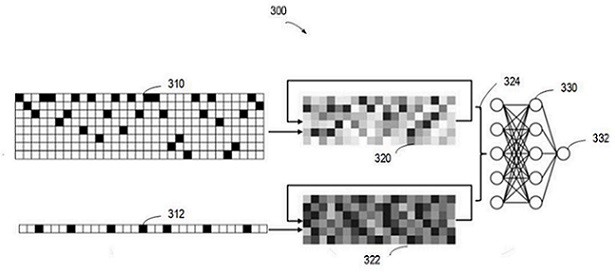
The invention relates to a method for predicting a drug susceptibility state, computing equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring gene variation information of a to-be-detected sample and drug information of related drugs; acquiring drug susceptibility state data determined by a cell viability test about the cells and the corresponding drugs; preprocessing the gene variation information and the drug information so as to generate a plurality of gene variation characterization data and a plurality of drug characterization data for combining into a plurality of groups of input sample sets; generating gene variation features based on a first neural network model; generating drug features based on a second neural network model; and based on a third neural network model, extracting the fused gene variation features and drug features to predict the drug susceptibility state of the to-be-detected sample for the corresponding drug. According to the method and device, the drug susceptibility can be accurately predicted, and the method has good versatility.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGIMED CO LTD +1
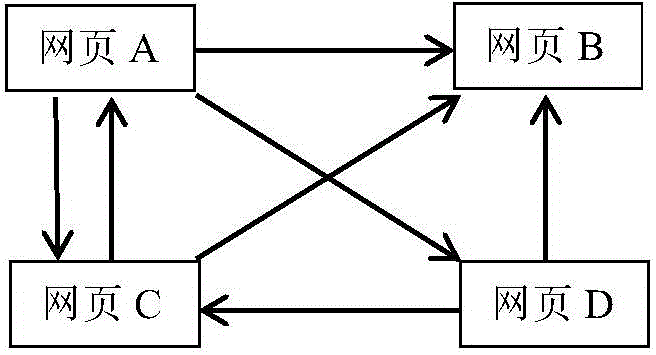
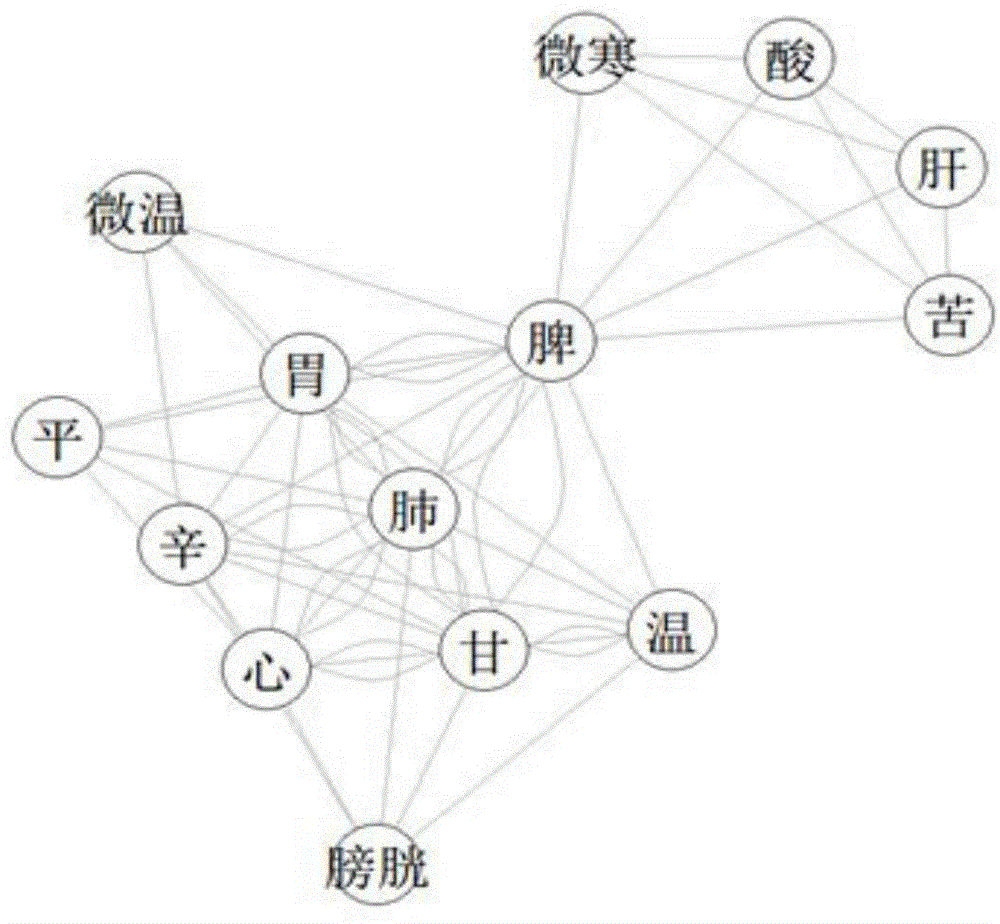
Prescription drug property quantifying method and system based on weighted PageRank algorithm
ActiveCN104933320AAdvance the pace of modernizationAccurate sortingSpecial data processing applicationsPagerank algorithmDrugs prescriptions
The invention provides a prescription drug property quantifying method and system based on a weighted PageRank algorithm. The quantifying method and system are beneficial for improving the accuracy of a drug property PR value. The method includes the steps that drug properties of all drugs in a prescription are decomposed to determine the drug properties of the prescription and weights of the drug properties; the drug properties of the prescription serve as drug property nodes in a network link structure, and according to interaction among the different drug properties, a network link structure graph among the drug property nodes is built; according to the determined weights of the drug properties, the weighted PageRank algorithm is used for iterating the drug property nodes to determine the drug property PR value. The prescription drug property quantifying method and system are suitable for the technical field of drug property quantifying.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Optical molecular sensors for cytochrome P450 activity
The invention provides a compound, useful as an optical probe or sensor of the activity of at least one cytochrome P450 enzyme, and methods of using the compound to screen candidate drugs, and candidate drugs identified by these methods. The optical probe of the invention is a compound having the generic structure Y-L-Q, wherein Y is selected from the group consisting of Q as herein defined, saturated C1-C20 alkyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 alkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, C1-C20 cycloalkyl, C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 cycloalkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl; L is selected from the group of (-OCR<2>H)p-, wherein for each p, all R<2 >are separately selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, saturated C1-C20 alkyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 alkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, C1-C20 cycloalkyl, C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 cycloalkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and p is a positive integer no greater than twelve; and Q is a chemical moiety that gives rise to optical properties in its hydroxy or hyrdoxylate, phenol or phenoxide form that are different from the optical properties that arise from its ether form. Most preferably, p is one, R<2 >is hydrogen, and Q is the ether form of a phenoxide fluorophore.
Owner:AUROA BIOSCI CORP
Methods and systems for class-flexible drug dispensing and electronic billing
InactiveUS20130151003A1Low costEasy to useFinanceDigital data processing detailsDrug dispensingDrug identifying
Presented are automated “class-flexible” drug dispensing systems, which include an automated drug dispensing machine. The automated machine has a multiplicity of drug cartridges and dispenses appropriate drugs on command from cartridges to fill a prescription. The system also has a user interface to input prescription information and class of trade information for each particular prescription to be filled. Further, it has an electronic storage medium with drug identifying information for the drug in each of the multiplicity of cartridges and the inventory of the drug in each cartridge. In addition, the system includes an electronic billing system that includes prescription information and the drug “class of trade” information. The billing system uses this information to create an electronic billing entry. Also presented are drug distribution systems to reduce overall drug costs from manufacturer to end user.
Owner:GILLUM RANDOLPH ROYAL
Medicine ejection apparatus and control method thereof
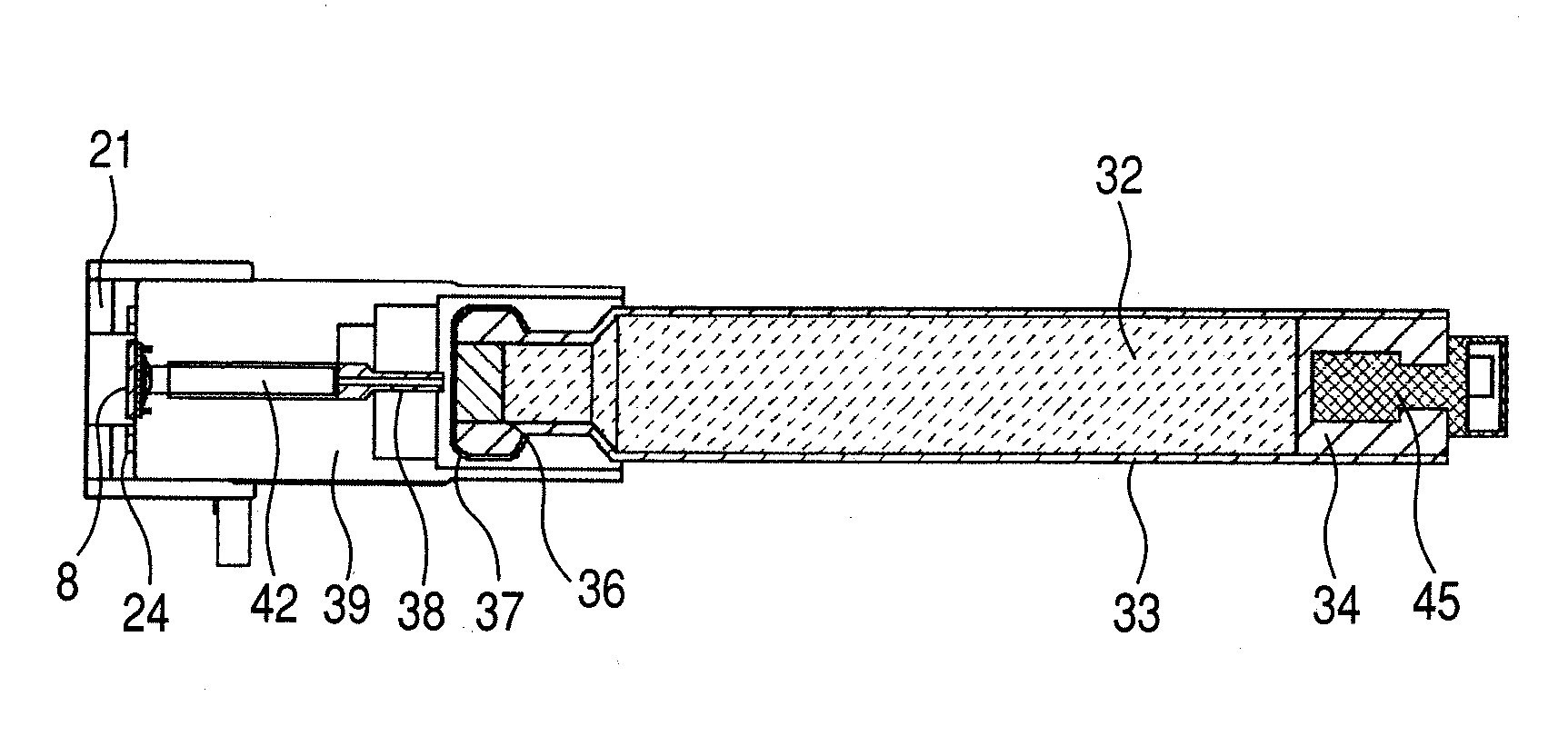
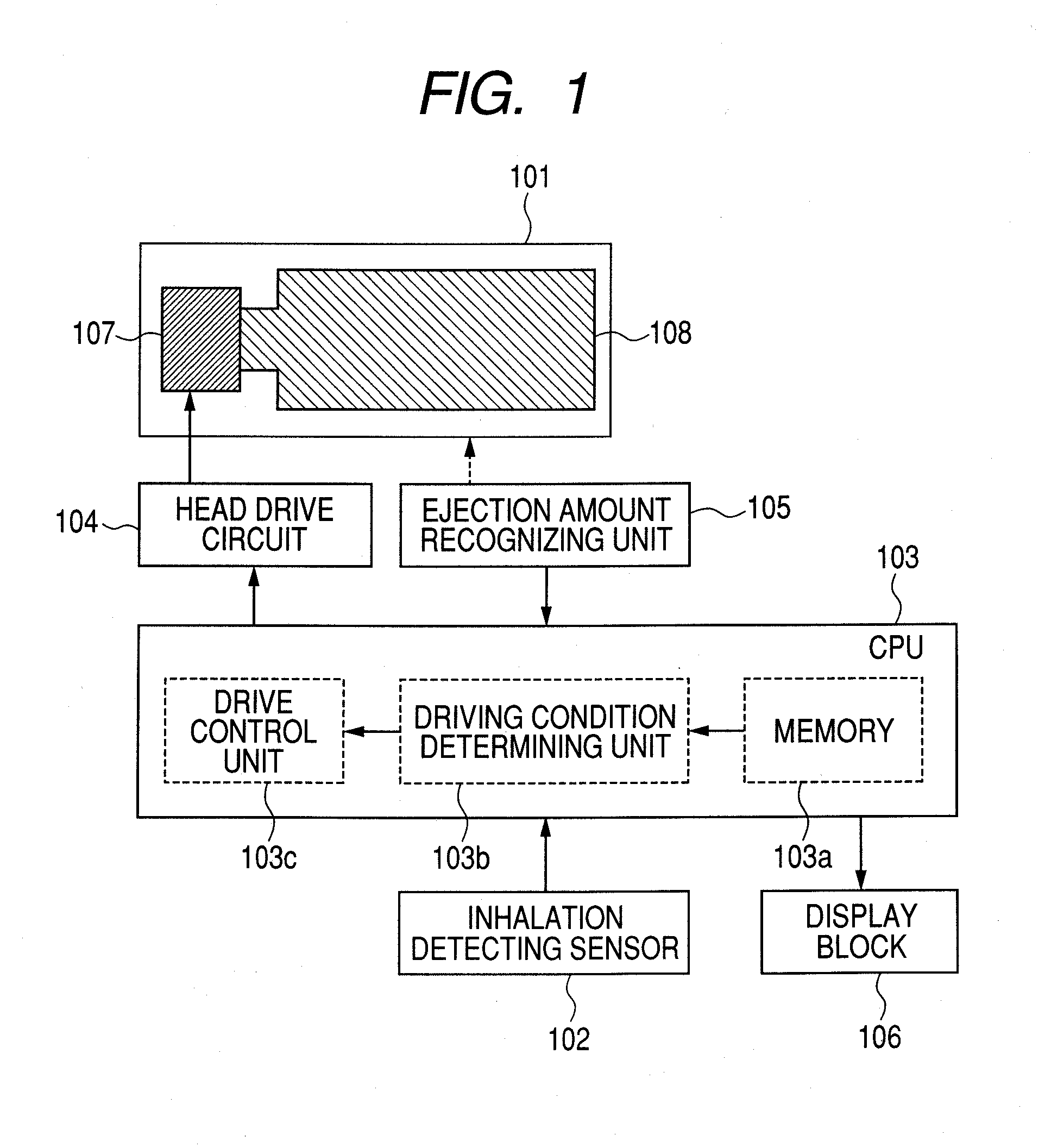
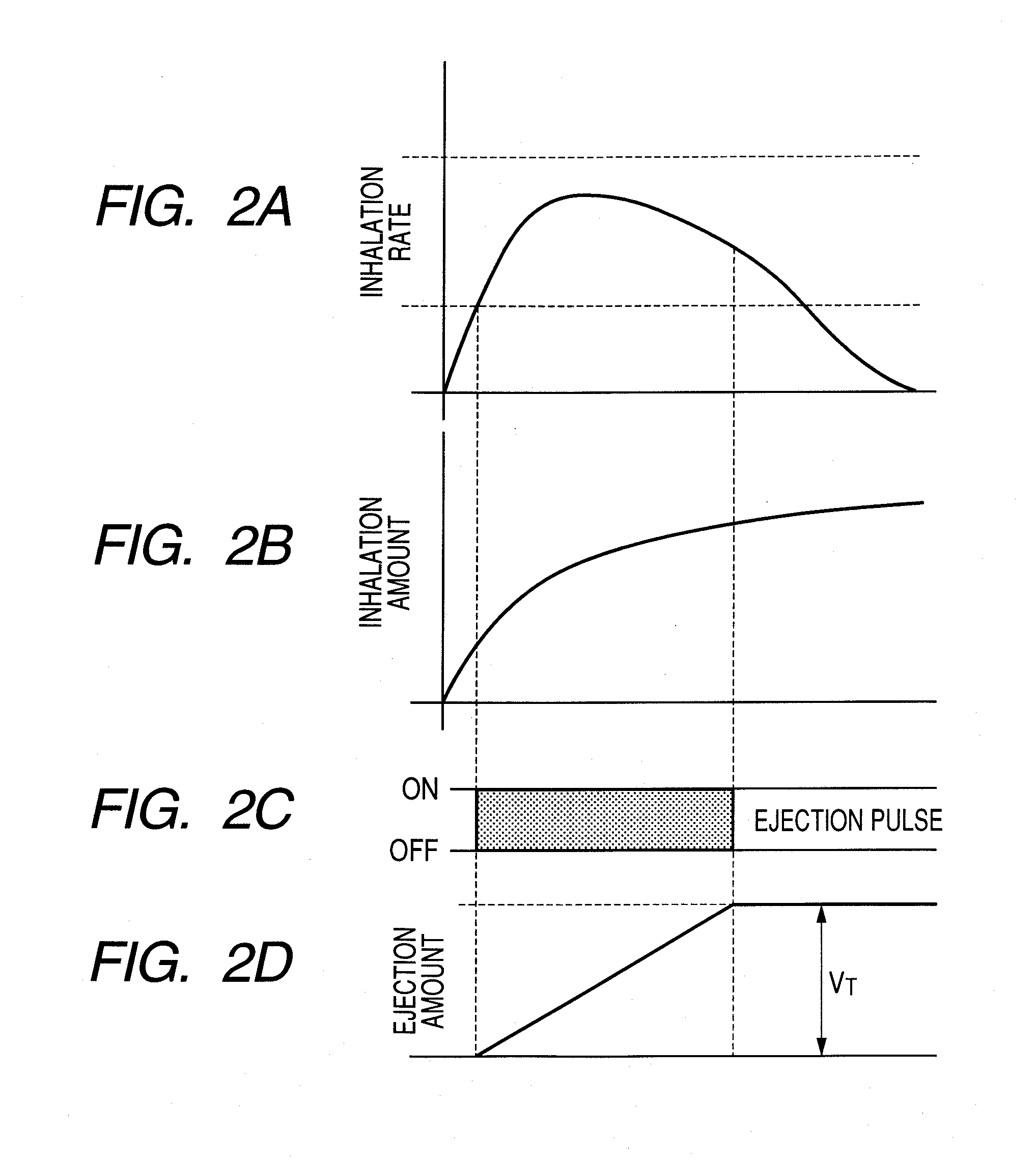
InactiveUS20100275916A1Liquid surface applicatorsRespiratory device testingEngineeringBiomedical engineering
A medicine ejection apparatus which ejects a medicine for medicating a user comprises; a medicine ejecting unit which has an element that generates energy for ejecting the medicine, a drive control unit which controls a drive start and a drive stop of the element, and an ejection amount determining unit which determines a total amount of a medicine that is ejected from the medicine ejecting unit after the element performs a drive stop, the drive control unit enabling the element to perform driving so as to eject an amount of medicine calculated from difference between the set ejection amount and the total amount of medicine when the total amount of medicine determined by the ejection amount determining unit does not reach the set ejection amount.
Owner:CANON KK
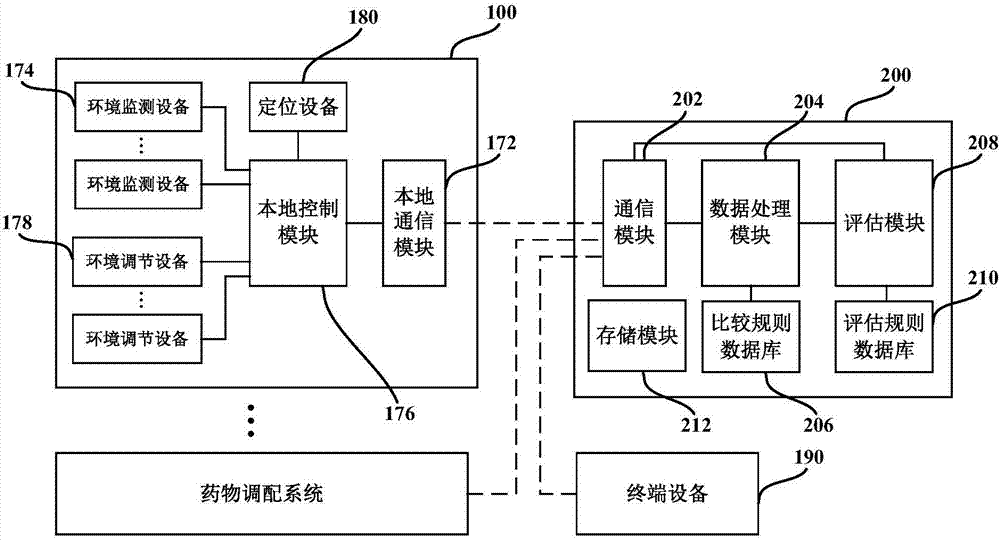
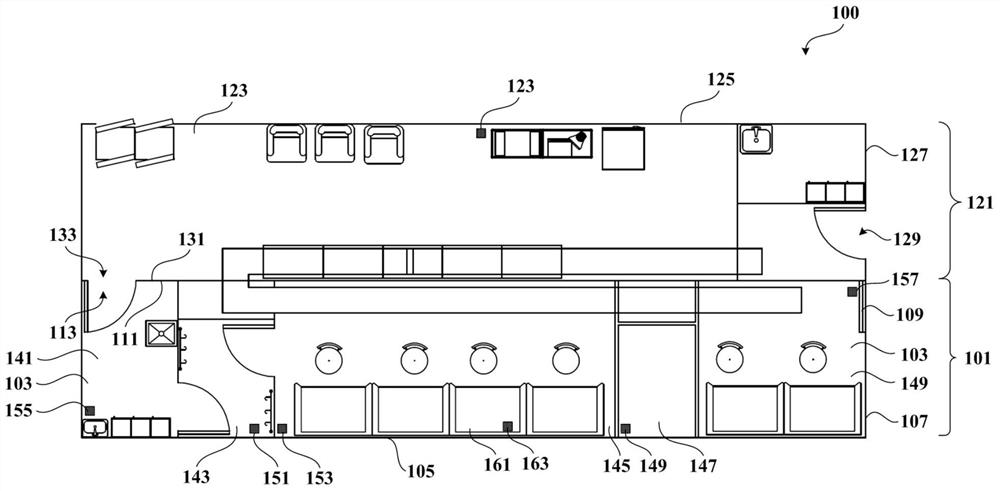
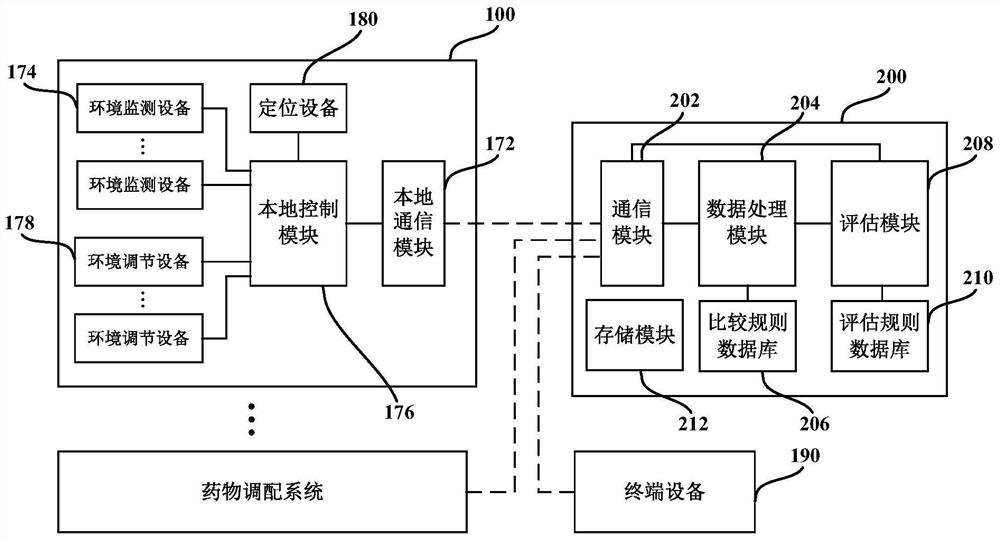
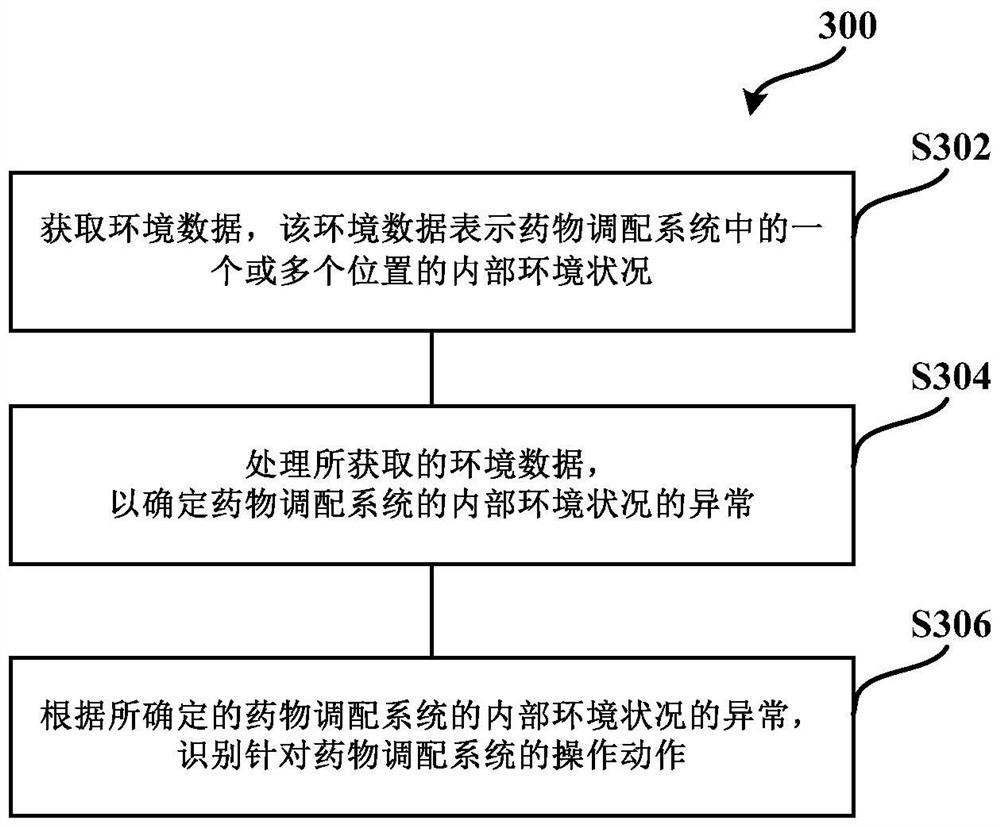
Medicine allocation system, and method and device for monitoring medicine allocation system
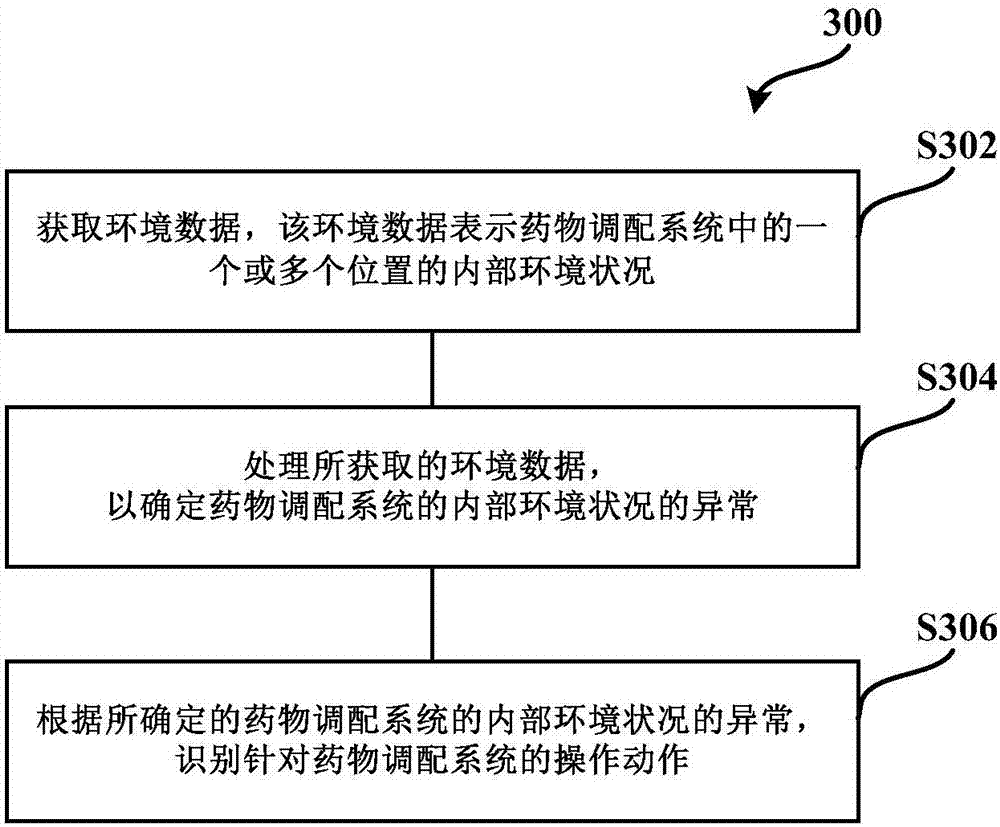
The invention discloses a method and device for monitoring a medicine allocation system. The medicine allocation system includes at least one environment monitoring device for monitoring an internal environment condition of the medicine allocation system. The method for monitoring the medicine allocation system includes: acquiring environment data, wherein the environment data expresses an internal environment condition at one or more positions in the medicine allocation system; processing the acquired environment data so as to determine abnormality of the internal environment condition of the medicine allocation system; and determining an operation action for the medicine allocation system according to the determined abnormality of the internal environment condition of the medicine allocation system.
Owner:BAXTER CHINA INVESTMENT
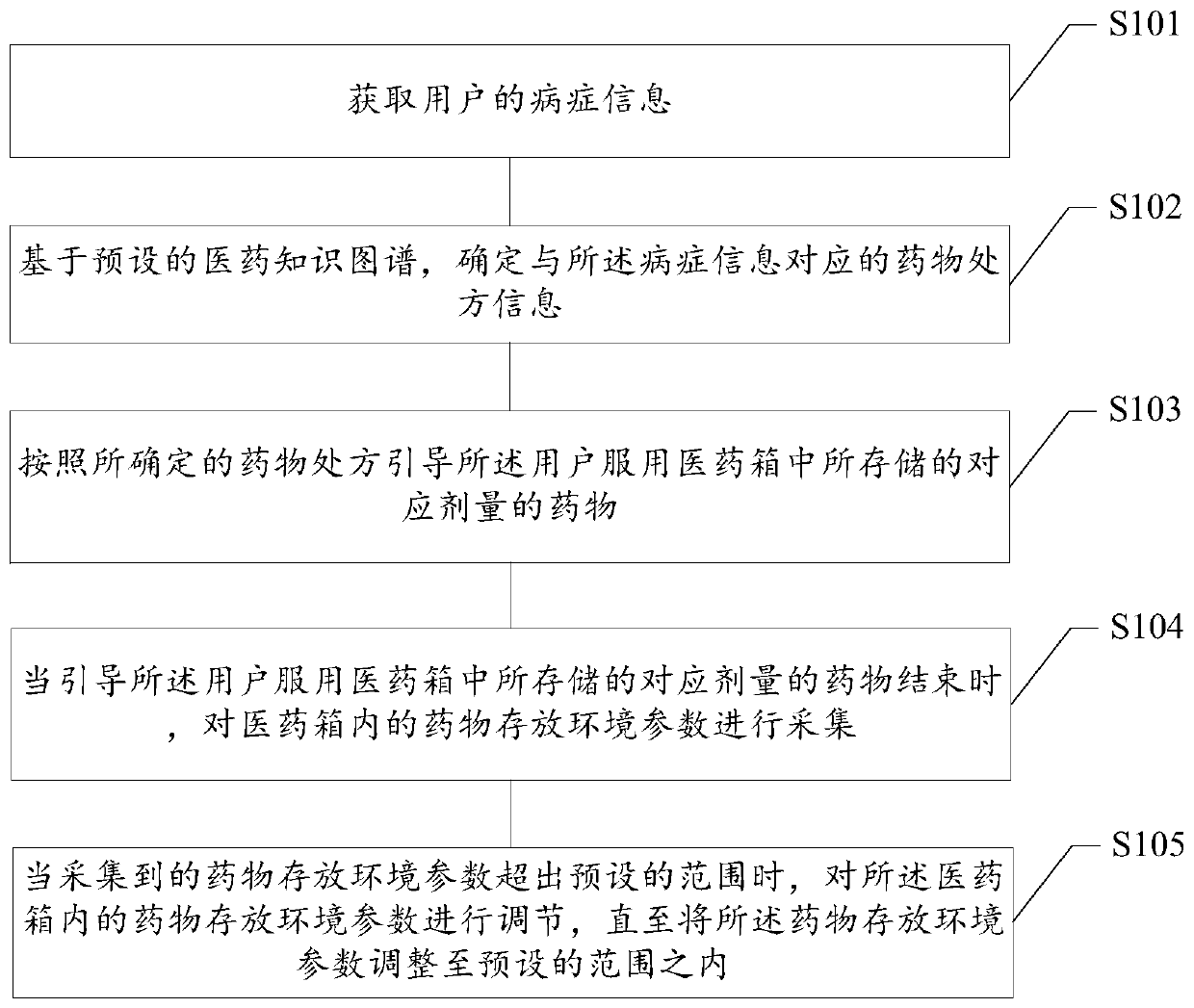
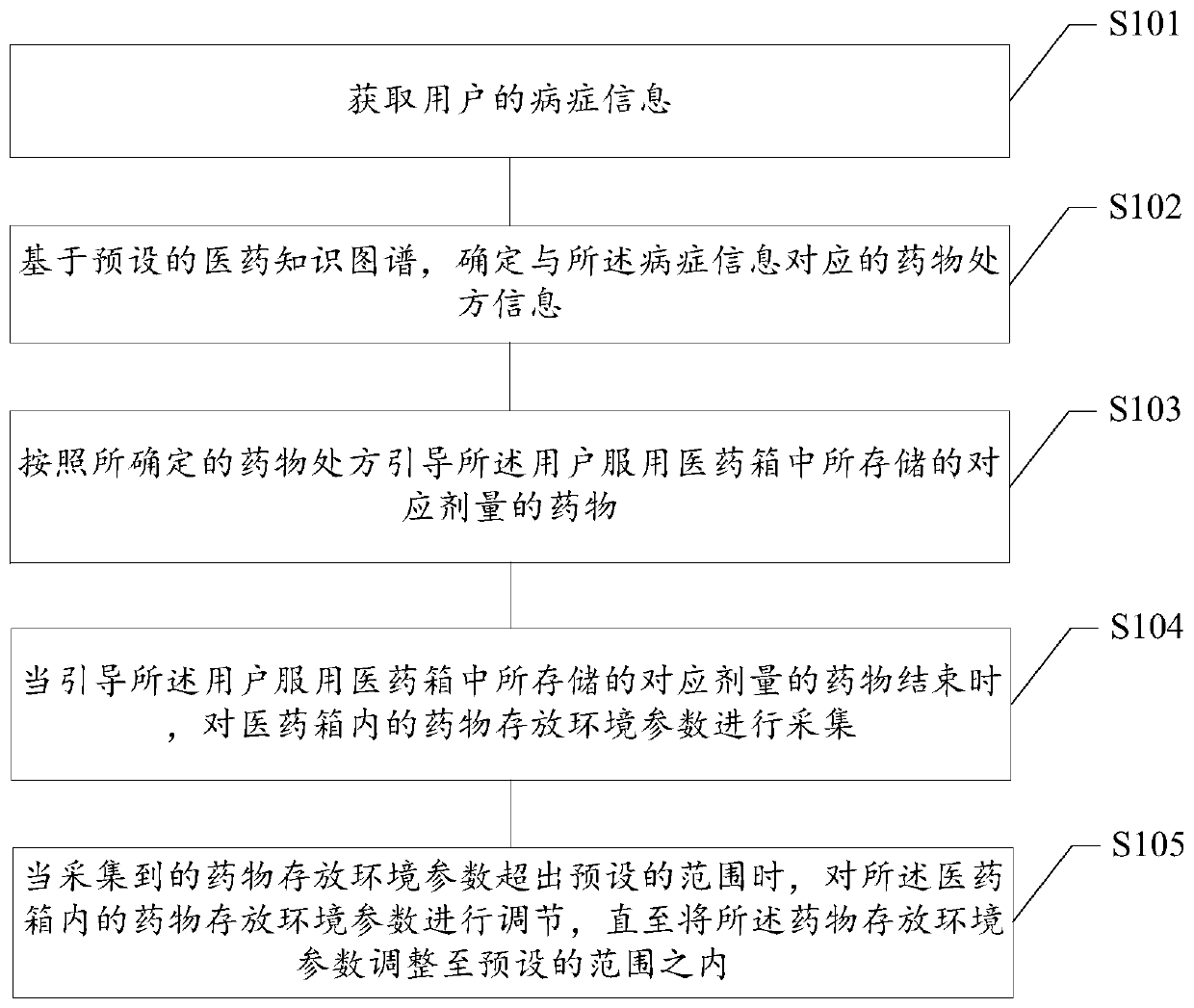
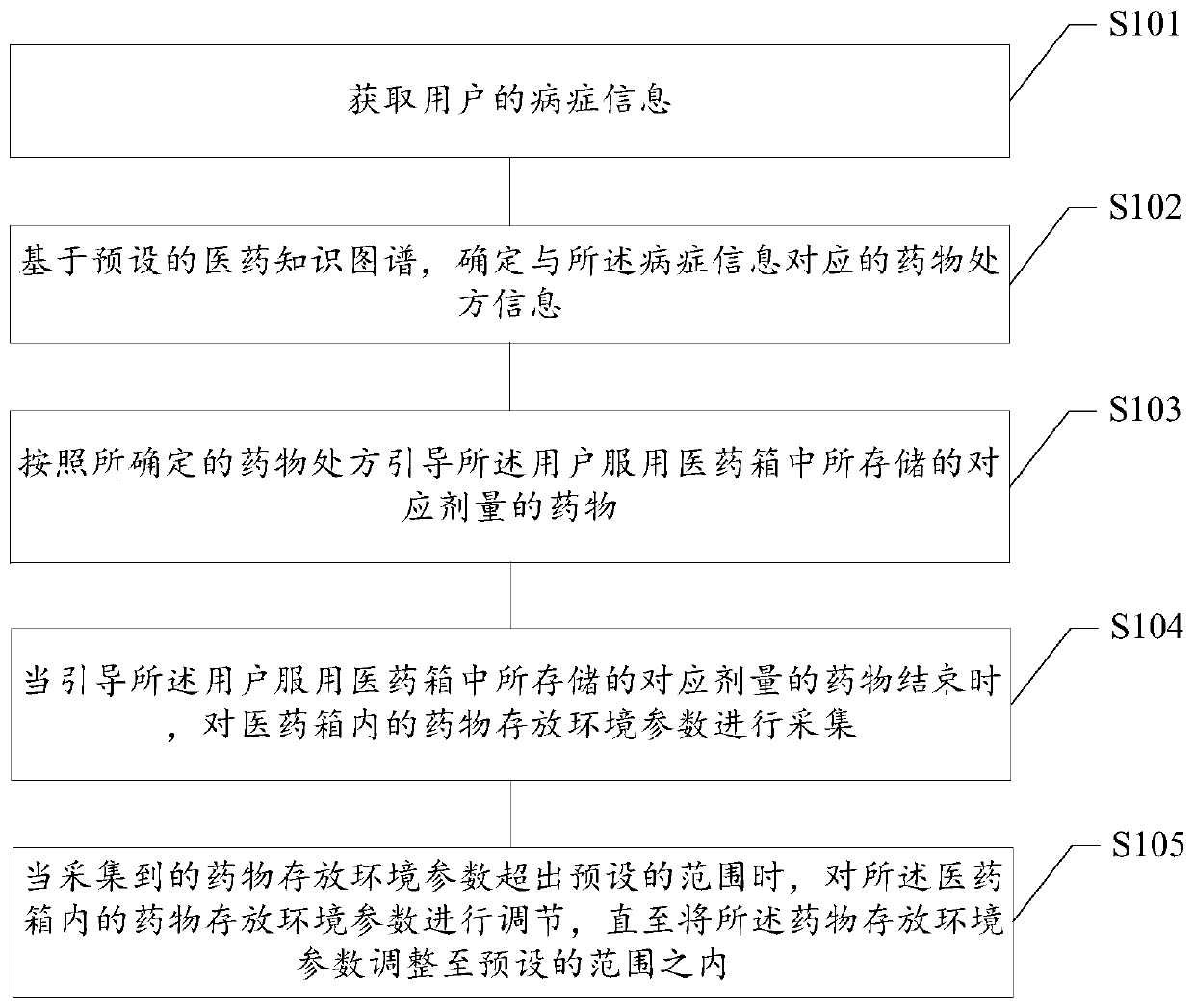
Medicine taking management method based on medical kit, readable storage medium and terminal
PendingCN109979561AHigh degree of intelligenceDrug and medicationsMedical knowledgeEmergency medicine
The invention provides a medicine taking management method based on a medical kit, a readable storage medium and a terminal. The medicine taking management method comprises the steps of acquiring symptom information of a user; based on a preset medical knowledge graph, determining medicine prescription information which corresponds with the symptom information; and according to the determined medicament prescription, guiding the user to take a corresponding dosage of the medicine which is stored in the medical kit. The medicine taking management method, the readable storage medium and the terminal can improve an intelligence degree in medicine taking management of the medical kit, thereby improving user experience.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
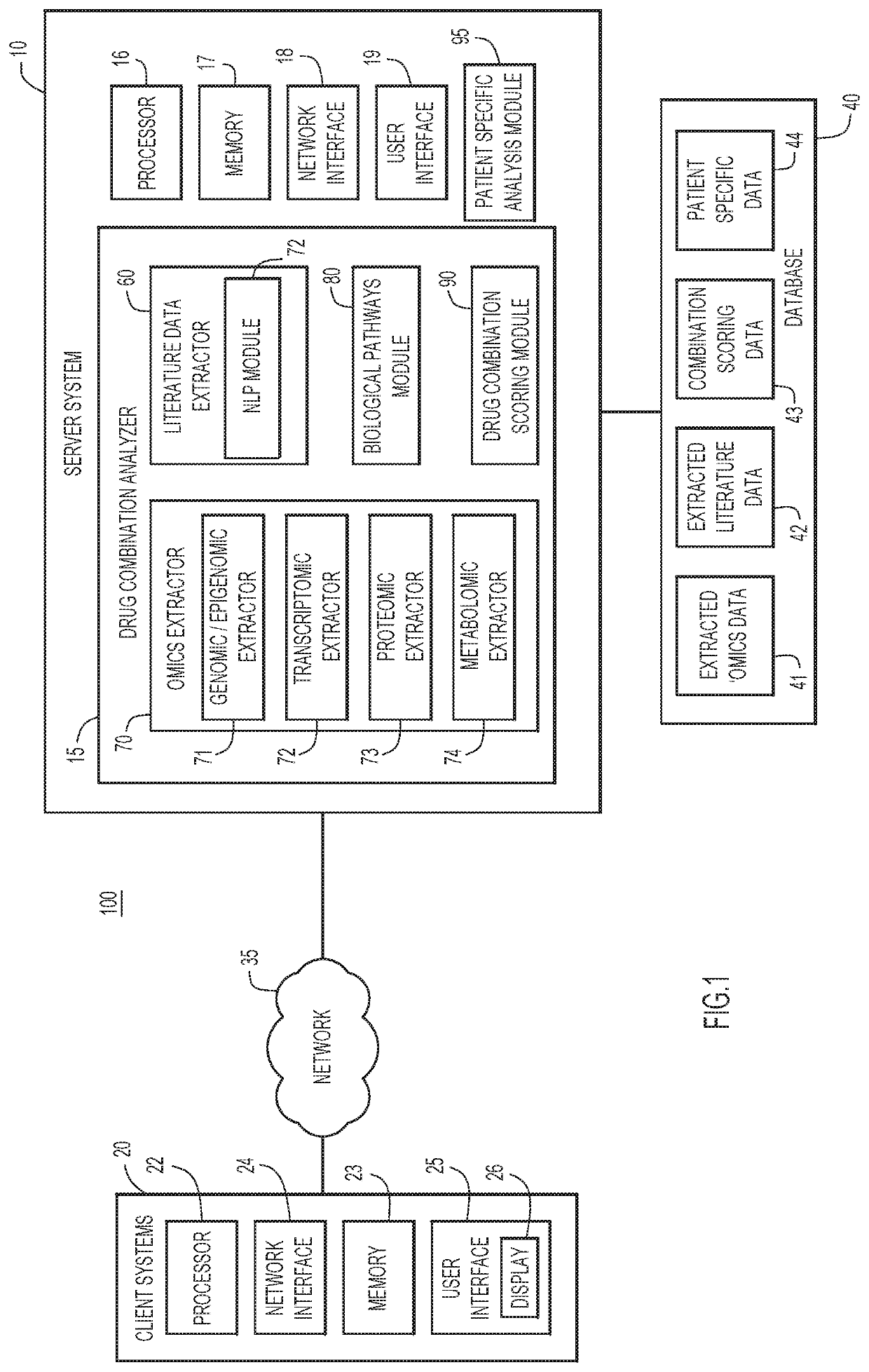
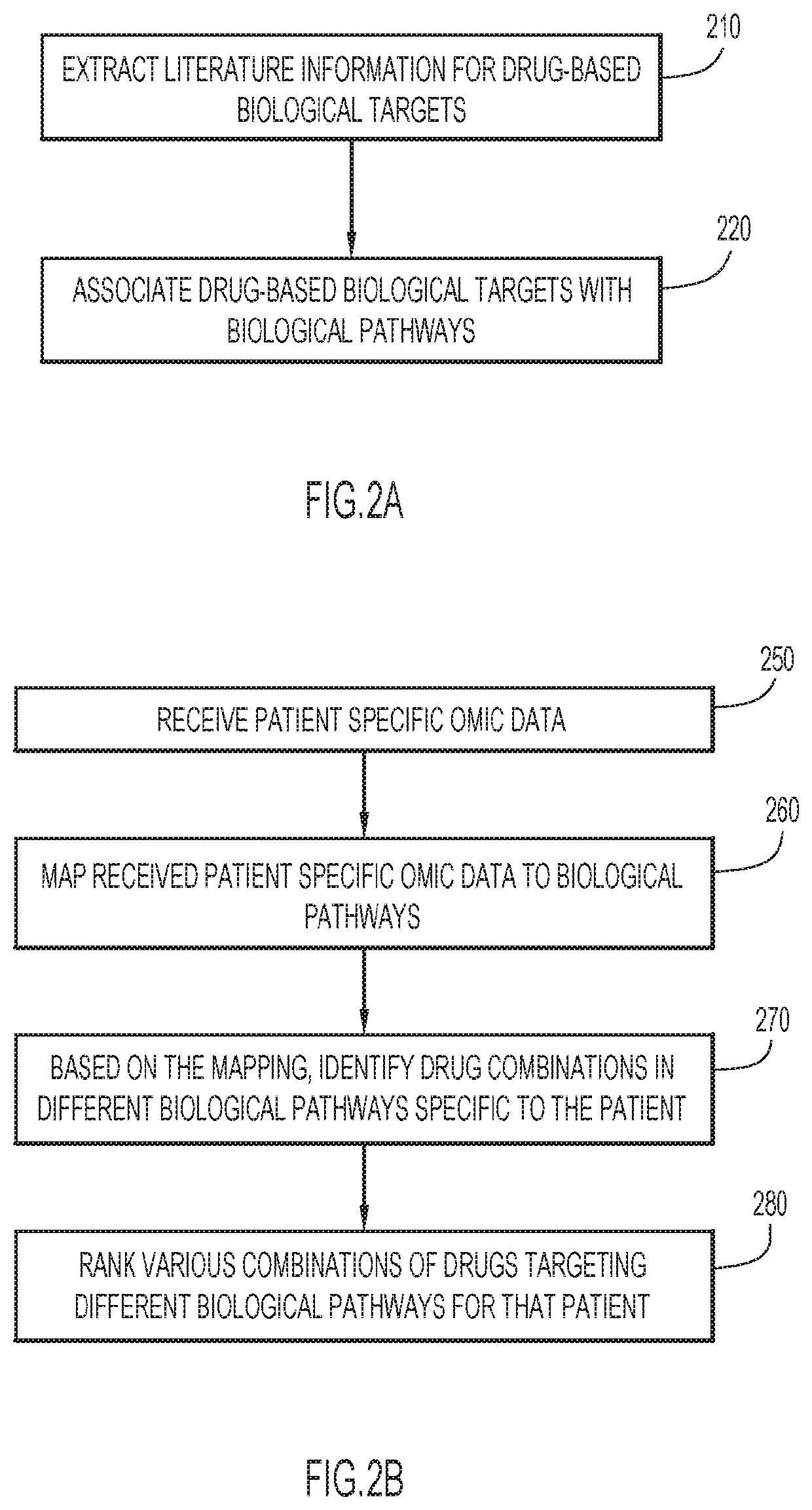
Automated techniques for identifying optimal combinations of drugs
PendingUS20200222538A1Improve performanceConvenient treatmentDrug and medicationsData visualisationPharmaceutical drugOmics data
Techniques are provided for administering combination of drug treatments to a patient. Information is analyzed pertaining to individual drug treatments from structurally or functionally defined drugs, drugs with unknown functions, and corresponding effects, wherein the information includes omic data including genes, transcripts, proteins, as well as experimental data from published documents. One or more combinations of drug treatments are identified with combined effects producing a positive result, wherein the positive result is directed to a specific aspect of patient health. The identified combination of drug treatments are administered to a patient.
Owner:IBM CORP
Optical Molecular Sensors for Cytochrome P450 Activity
The invention provides a compound, useful as an optical probe or sensor of the activity of at least one cytochrome P450 enzyme, and methods of using the compound to screen candidate drugs, and candidate drugs identified by these methods. The optical probe of the invention is a compound having the generic structure Y-L-Q, wherein Y is selected from the group consisting of Q as herein defined, saturated C1-C20 alkyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 alkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, C1-C20 cycloalkyl, C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 cycloalkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl; L is selected from the group of (—OCR2H)p—, wherein for each p, all R2 are separately selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, saturated C1-C20 alkyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 alkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, C1-C20 cycloalkyl, C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 cycloalkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and p is a positive integer no greater than twelve; and Q is a chemical moiety that gives rise to optical properties in its hydroxy or hydroxylate, phenol or phenoxide form that are different from the optical properties that arise from its ether form. Most preferably, p is one, R2 is hydrogen, and Q is the ether form of a phenoxide fluorophore.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Optical molecular sensors for cytochrome P450 activity
The invention provides a compound, useful as an optical probe or sensor of the activity of at least one cytochrome P450 enzyme, and methods of using the compound to screen candidate drugs, and candidate drugs identified by these methods. The optical probe of the invention is a compound having the generic structure Y-L-Q, wherein Y is selected from the group consisting of Q as herein defined, saturated C1-C20 alkyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 alkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, C1-C20 cycloalkyl, C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 cycloalkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl; L is selected from the group of (—OCR2H)p—, wherein for each p, all R2 are separately selected from the group consisting of a hydrogen atom, saturated C1-C20 alkyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 alkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkenyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 alkynyl, C1-C20 cycloalkyl, C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, substituted saturated C1-C20 cycloalkyl, substituted unsaturated C1-C20 cycloalkenyl, aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl, substituted heteroaryl, and p is a positive integer no greater than twelve; and Q is a chemical moiety that gives rise to optical properties in its hydroxy or hydroxylate, phenol or phenoxide form that are different from the optical properties that arise from its ether form. Most preferably, p is one, R2 is hydrogen, and Q is the ether form of a phenoxide fluorophore.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
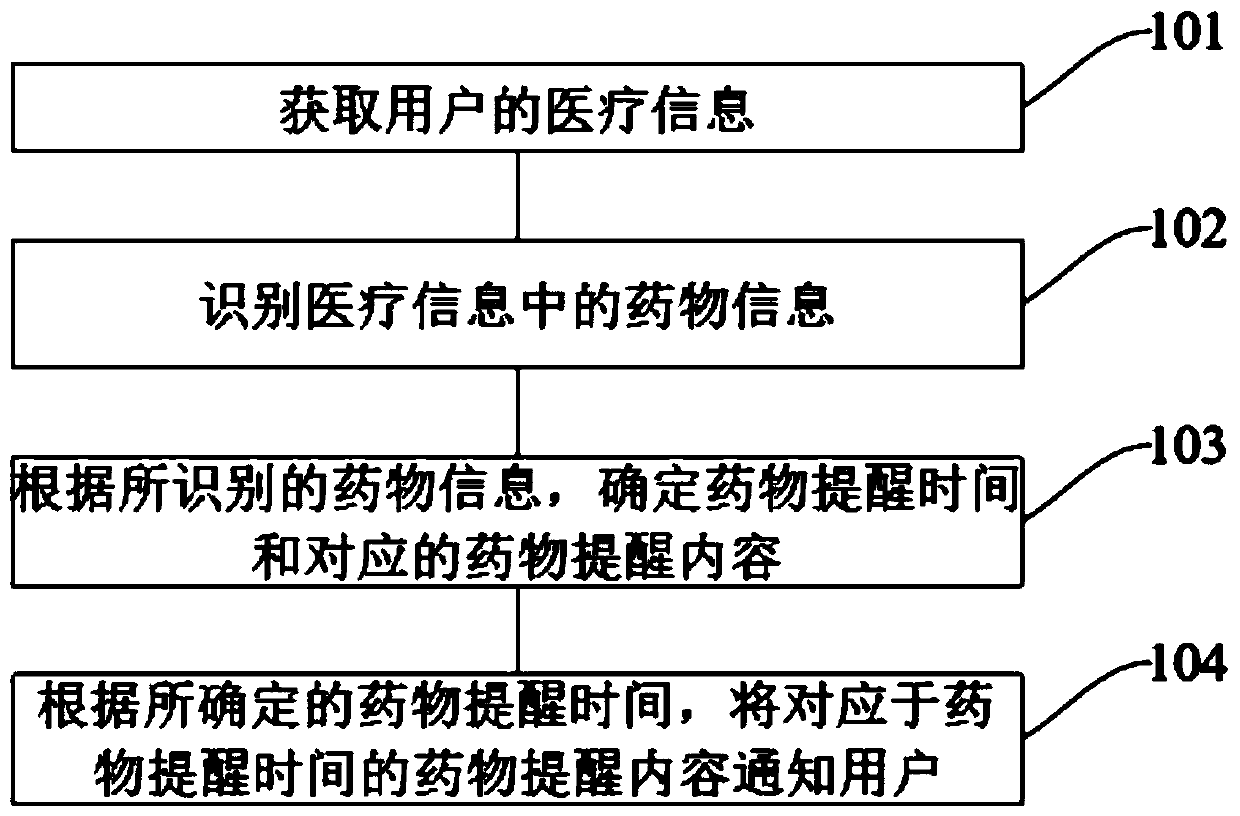
Information interaction method and device and computer-readable storage medium
InactiveCN110782963ATake medicine on timeDrug and medicationsAlarmsMedication informationPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses an information interaction method and device and a computer-readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps that the medical information of a user is acquired; drug information in the medical information is identified; drug reminder time and corresponding drug reminder content are acquired according to the identified drug information; and according to the determineddrug reminder time, a user is notified of the drug reminder content corresponding to the drug reminder time. In the application, when the set medicine reminder time is reached, the user can be notified on time, and the drug reminder content can be notified to the user, and especially middle-aged and elderly users, so as to help the middle-aged and elderly users to take a medicine on time.
Owner:AISPEECH CO LTD
Medication adherence monitoring device
ActiveUS11193925B2Promotes quick releaseAvoid lostComponent separationSurgeryPharmaceutical drugEmergency medicine
A Self Monitoring And Reporting Therapeutics, SMART® composition, method apparatus and system are provided which flexibly provide options, by combining different embodiments of the device with different embodiments of the composition, the ability to conduct definitive medication adherence monitoring over the short term (Acute Medication Adherence Monitoring, immediately up to an hour or so after taking a medication), intermediate term (Intermediate Medication Adherence Monitoring, IMAM, an hour or so to a day or so after taking a medication), and longer term (Chronic Medication Adherence Monitoring, CMAM, a day to several days after taking a medication).
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
A weighted pagerank algorithm-based method and system for quantifying drug attributes of prescriptions
ActiveCN104933320BAdvance the pace of modernizationAccurate sortingSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionPagerank algorithm
The invention provides a weighted PageRank algorithm-based method and system for quantifying drug attributes of prescriptions, which helps to improve the accuracy of PR values of drug attributes. The method includes: decomposing the drug attributes of each drug in the prescription, determining the drug attributes of the prescription and the weights of the drug attributes; using the drug attributes in the prescription as drug attribute nodes in the network link structure, and according to different drug attributes According to the interaction between the drug attribute nodes, the network link structure diagram between the drug attribute nodes is constructed; according to the determined weight of the drug attribute, the weighted PageRank algorithm is used to iterate the drug attribute nodes to determine the PR value of the drug attribute. The invention is applicable to the technical field of medicine attribute quantification.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
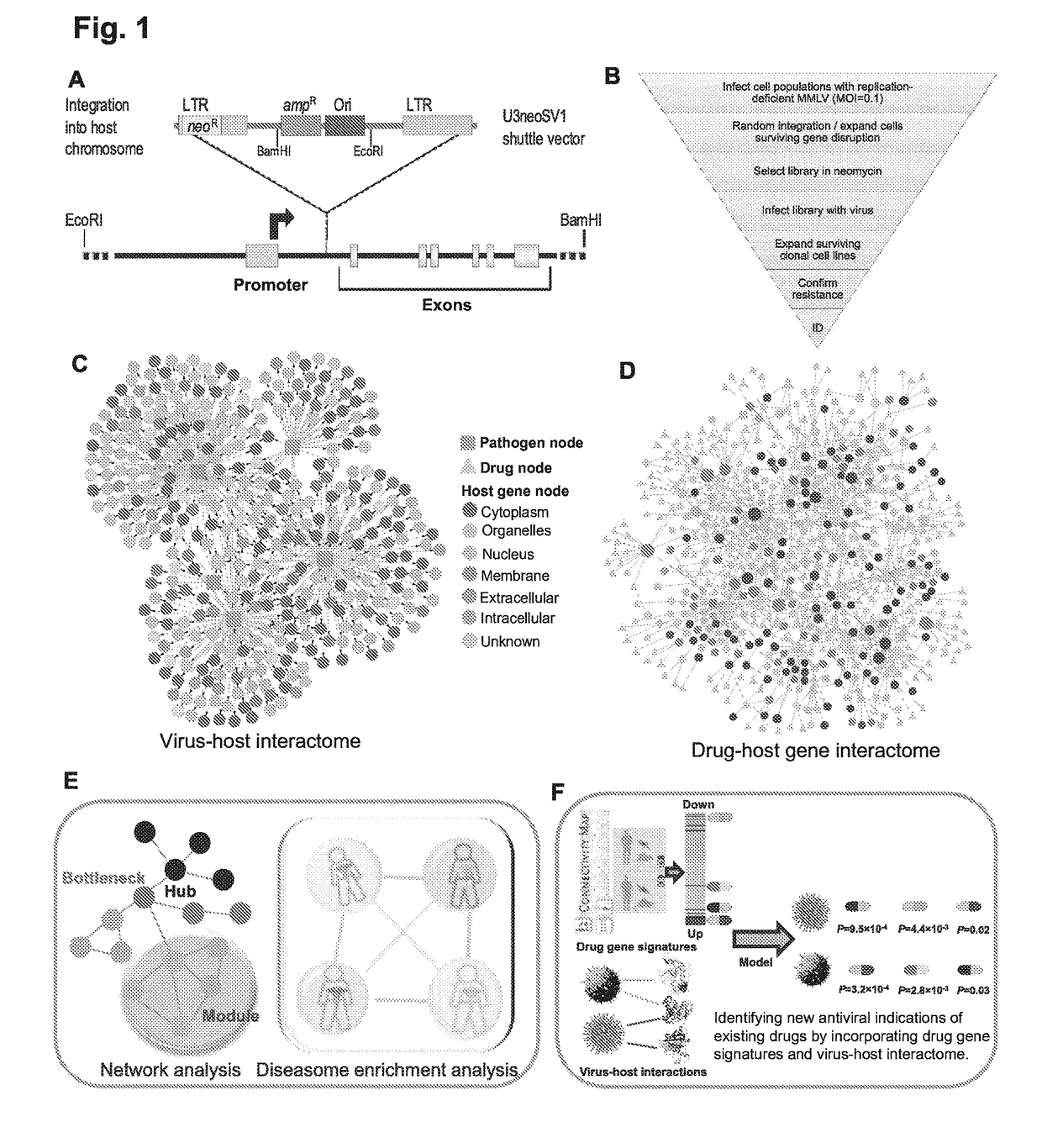
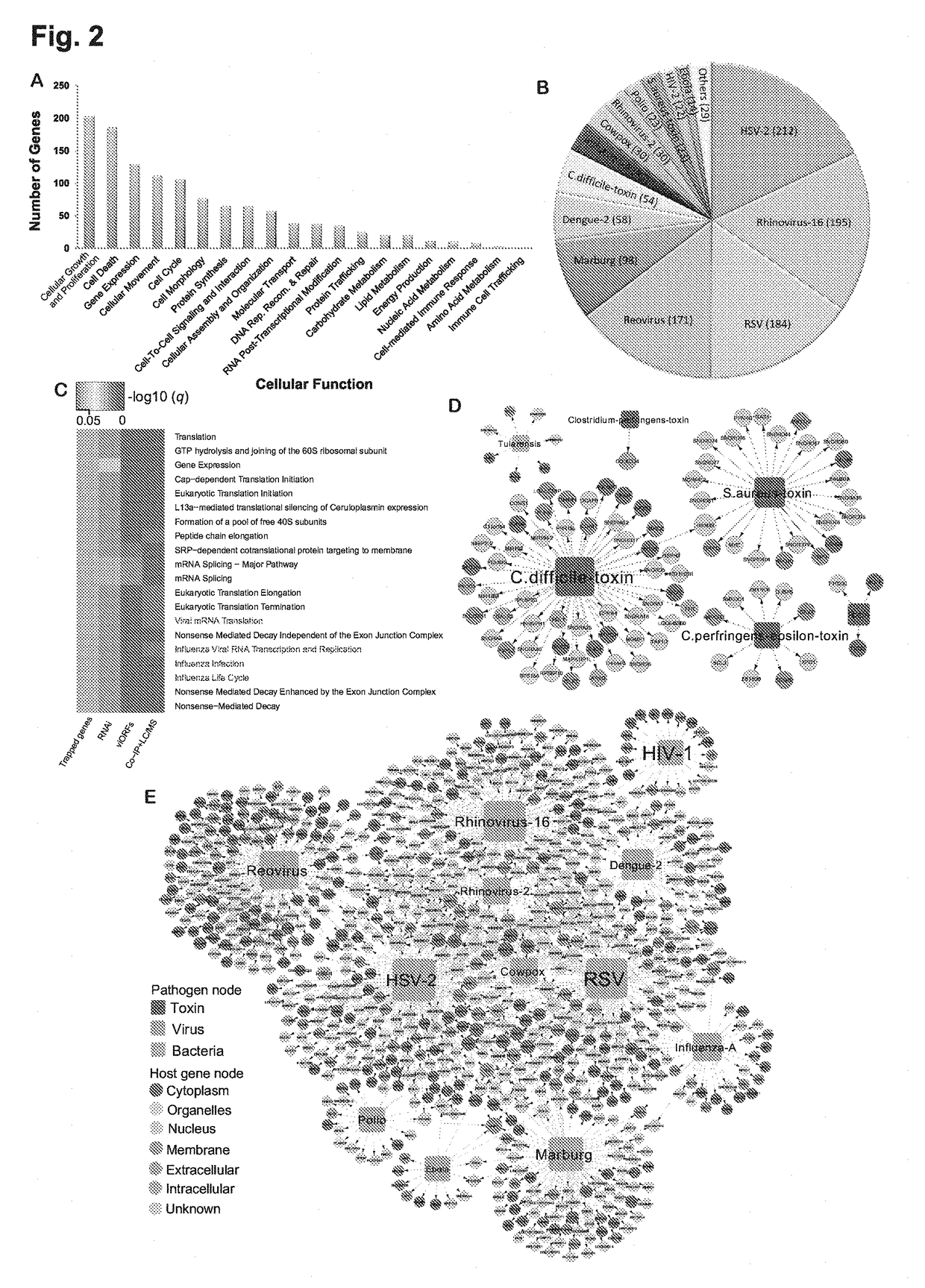
Identification of cellular antimicrobial drug tablets through interactome analysis
InactiveUS20170364630A1Good pharmacokinetics profileEnhance the imageAntibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntimicrobial drugDrug target
A method of identifying a promising cellular antiviral or bacterial toxin drug target is described including: 1) providing a plurality of potential antiviral or bacterial toxin drug targets; 2) generating an interactome including the potential drug targets using a systems-biology computational method; and 3) analyzing the interactome to identify one or more promising antiviral or bacterial toxin drug targets. New indications for older drugs identified using this method are also described.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
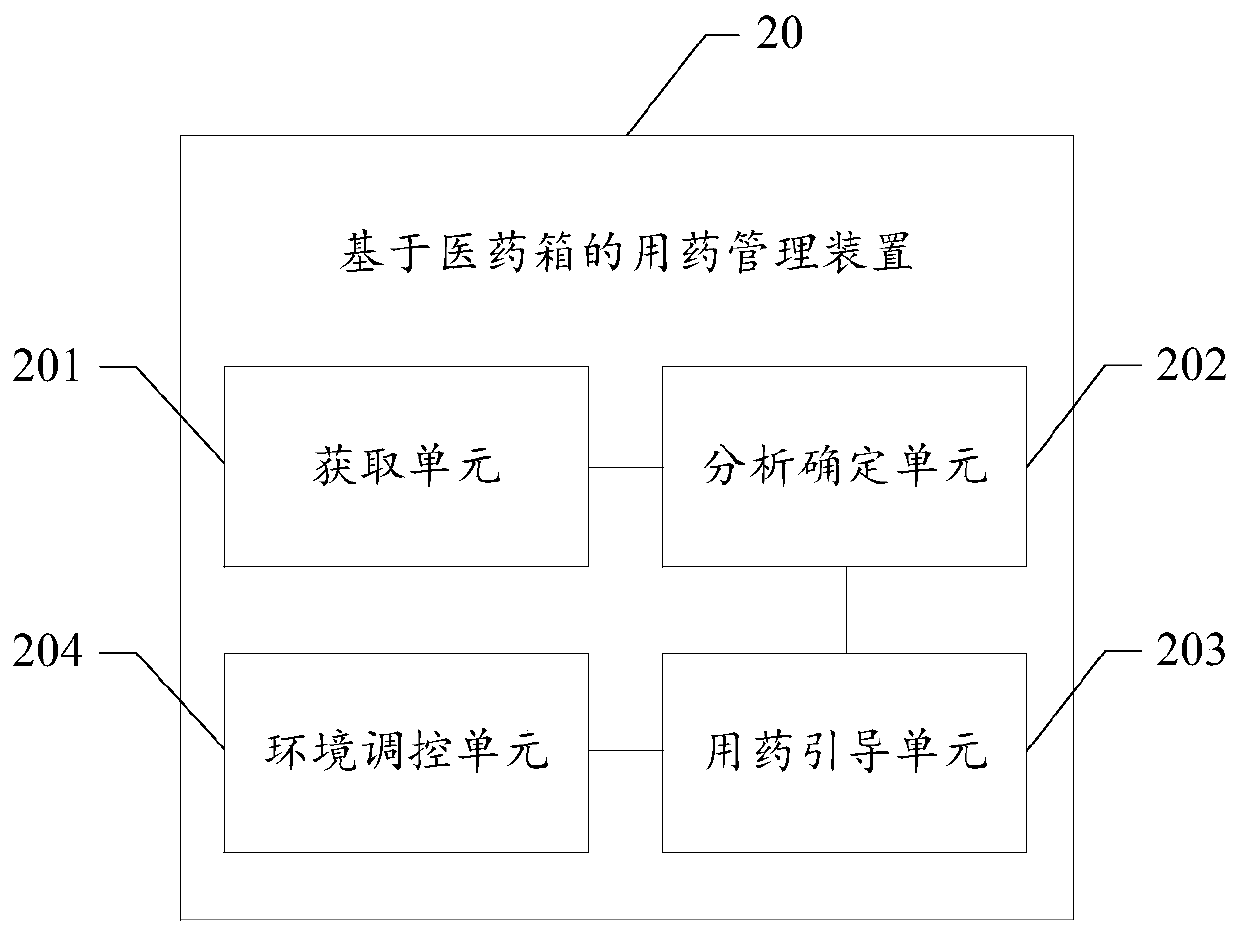
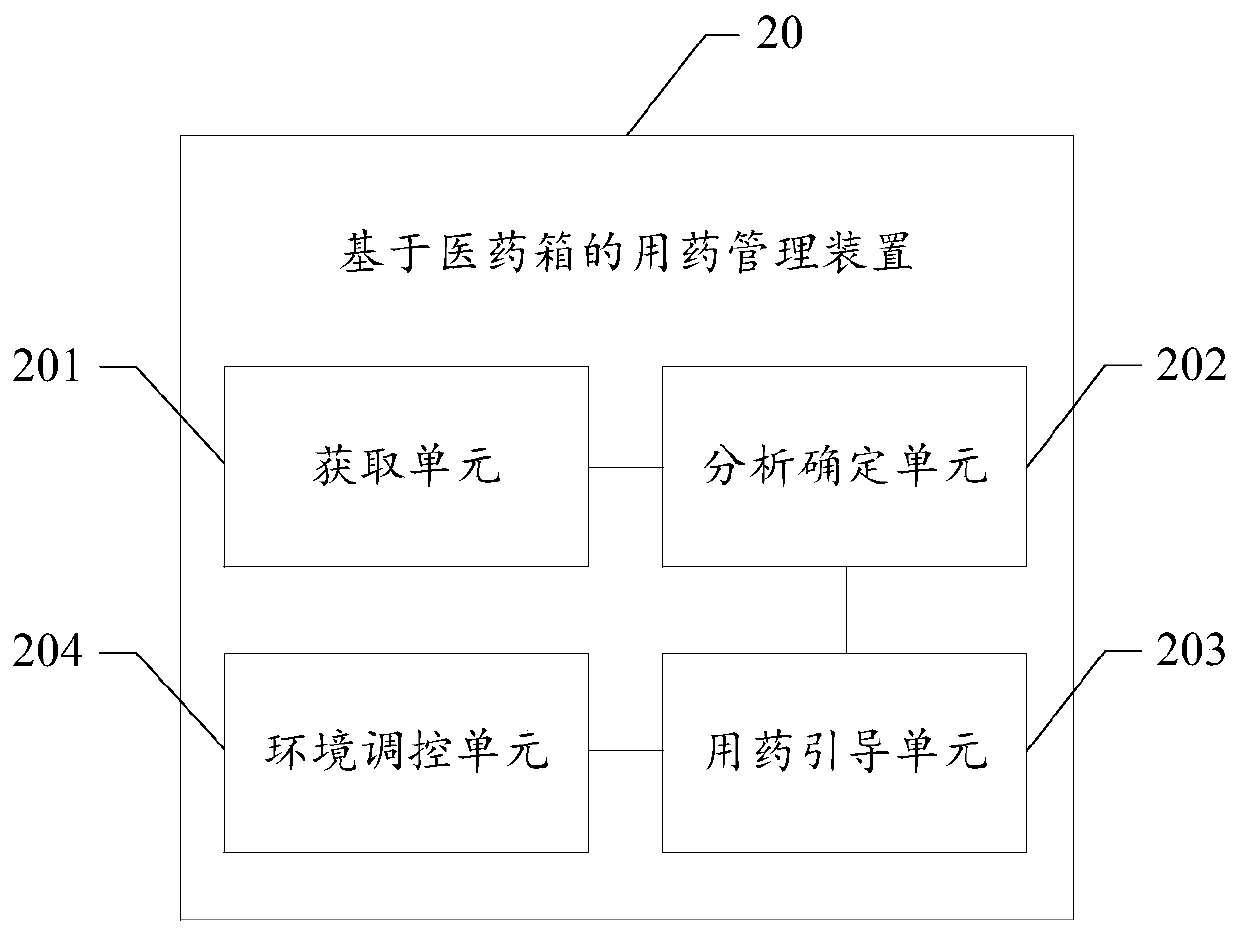
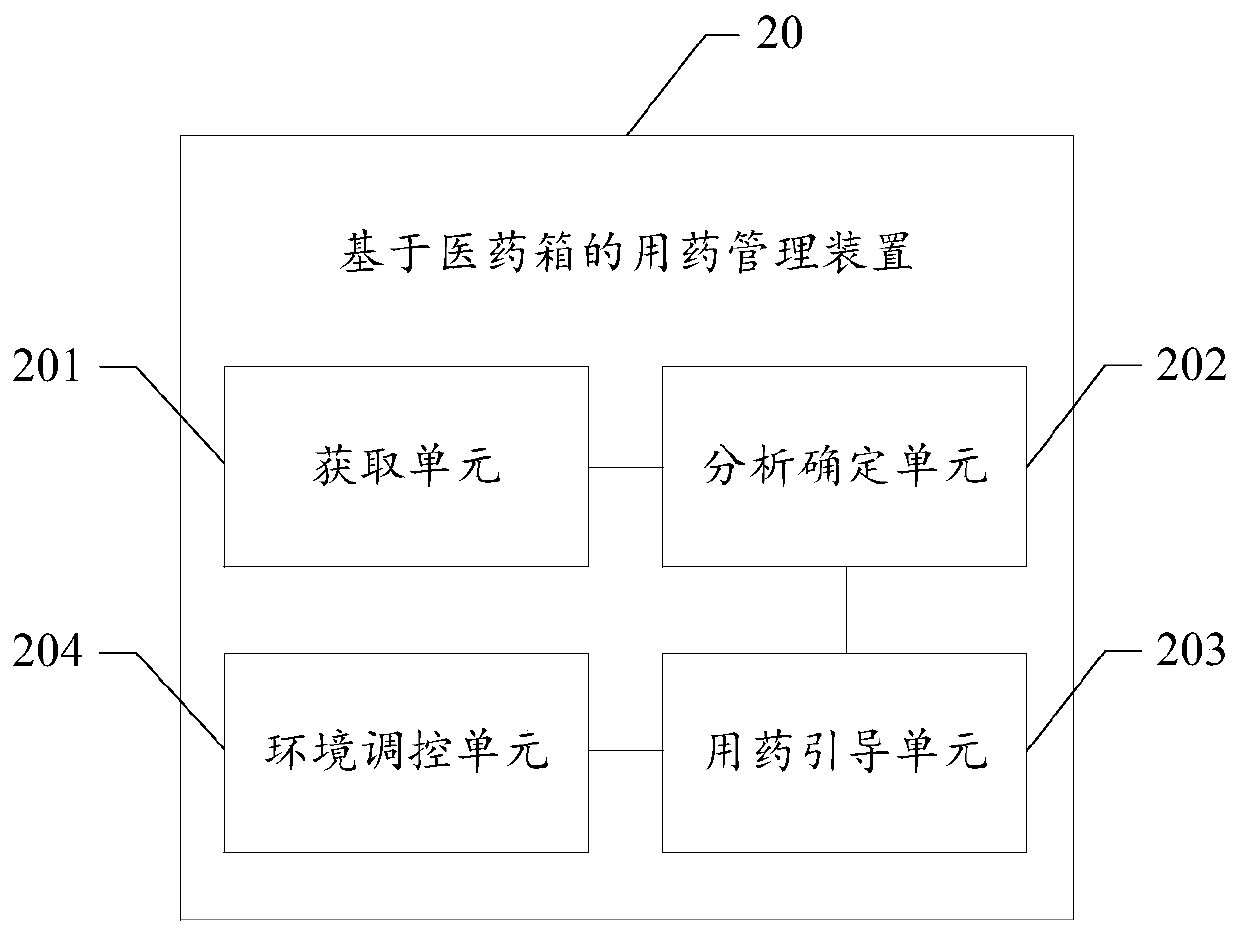
Medicine taking management device for medical kit
The invention provides a medicine taking management device for a medical kit. The medicine taking management device comprises the components of an acquiring unit which is suitable for acquiring disease information of a user; an analysis determining unit which is suitable for determining medicine prescription information that corresponds with the disease information based on a preset medicine knowledge graph; and a medicine taking guiding unit which is suitable for guiding the user to take the corresponding-dosage medicine stored in the medical kit according to a determined medicine prescription. The medicine taking management device can improve medicine taking management intelligent degree of the medical kit and further improves user experience.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
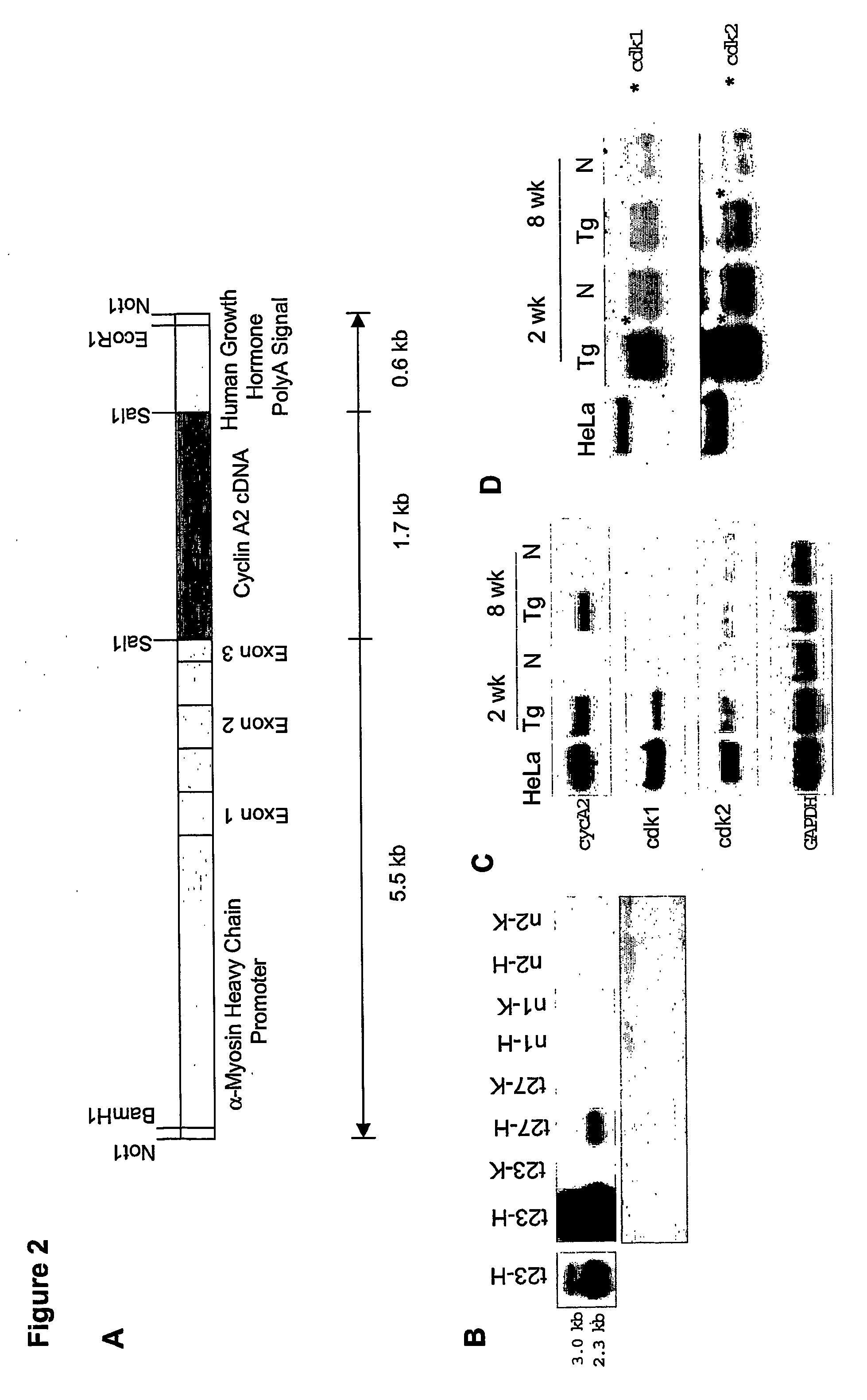
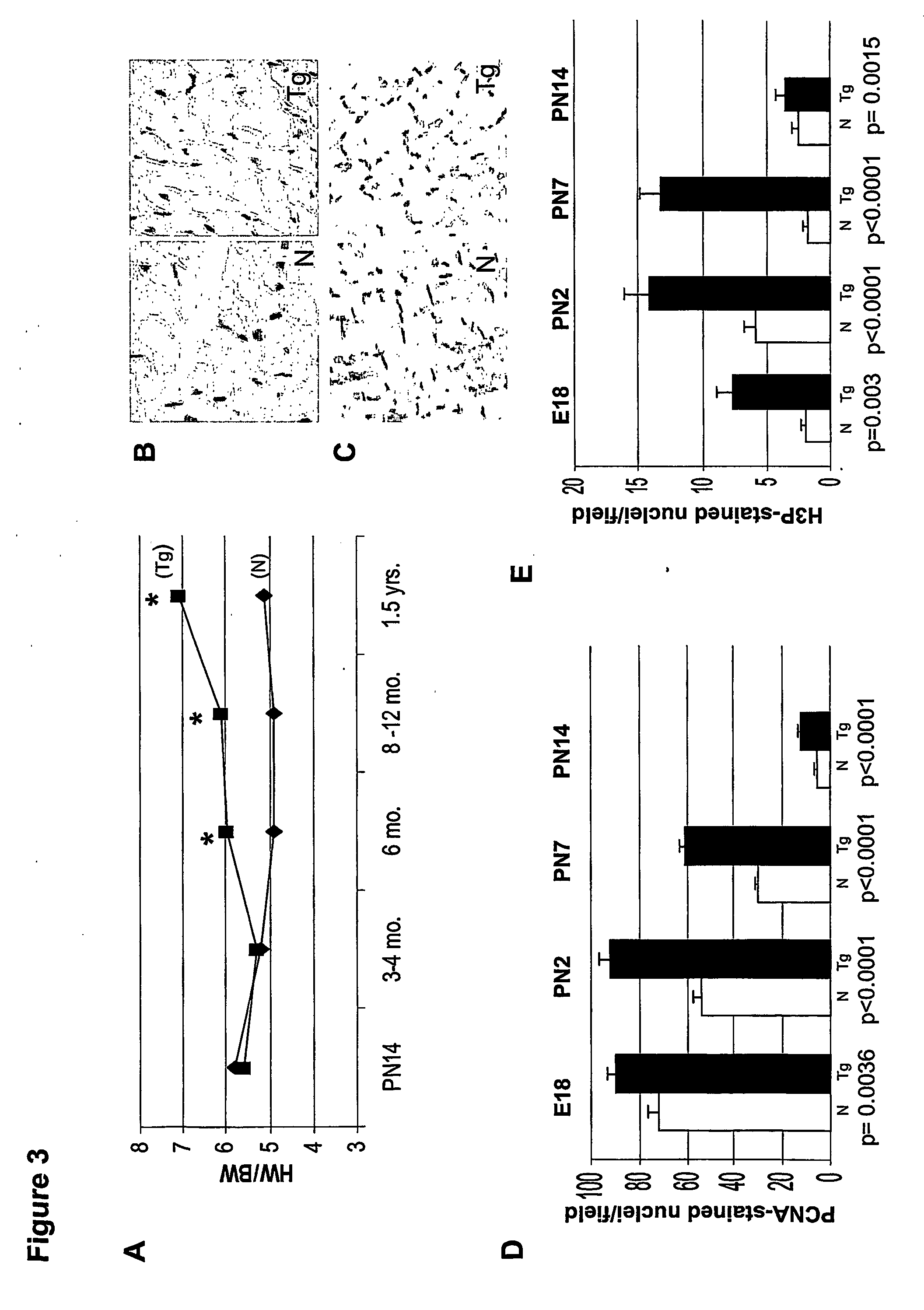
Compositions and methods for treating and preventing heart tissue degeneration, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070014766A1Altered cell divisionMyocardial injuryPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsProgenitorScreening method
The present invention provides methods for promoting generation of heart tissue, and for treating and preventing heurt tissue degeneration. Additionally, the present invention provides a therapeutic composition comprising a cyclin-associated agent, and a kit comprising the composition. The present invention further provides a heart tissue tell, a sidepopulation progenitor tell, and a stem tell in which cyclin is augmented. Also provided are tell lins comprising these tells, screening methods using the tell lins, and drugs identified by these methods. The present invention further provides in vitro systems for use in screening candidate drugs for at least one cardiotoxic effect and / or for synergy with cyclin in the treatment and prevention of heart tissue degeneration. Finally, the present invention provides use of a cyclin-associated agent in the generation of heart tissue, and use of a cyclin associated agent in the treatment or prevention of heart tissue degeneration.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Device with engineered surface architecture coating for controlled drug release
In one embodiment of the present invention a coating topology, or engineered surface architecture that may be referred to as a microdroplet deposited engineered surface architecture is provided. A plurality of drops are placed on the stent with the purpose, of building up individual units of coating material on the outer stent surface. This architecture results in a coating that uses less material, i.e., polymer, solvent, medicine, while at the same time providing for better, and determinable, drug kinetics, approaching 100% delivery and better mechanical operation of the coating binding to the stent.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Drug compounding system and method and device for monitoring drug compounding system
The present application discloses a method and device for monitoring a drug compounding system. The drug compounding system has at least one environmental monitoring device for monitoring internal environmental conditions of the drug compounding system. The method of monitoring a drug compounding system includes: acquiring environmental data representing internal environmental conditions at one or more locations in the drug compounding system; processing the acquired environmental data to determine anomalies in the internal environmental conditions of the drug compounding system; And according to the determined abnormality of the internal environment of the drug compounding system, determine an operation action for the drug compounding system.
Owner:BAXTER CHINA INVESTMENT
Identification of Candida albicans essential fungal specific genes and use thereof in antifungal drug discovery
InactiveUS7129341B1Prevent adverse side effectsEffective amountSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntifungal drugCandida famata
The invention relates to the identification and disruption of essential fungal specific genes isolated in the yeast pathogen Candida albicans namely CaKRE5, CaALR1, and CaCDC24 and to the use thereof in antifungal diagnosis and as essential antifungal targets in a fungal species for antifungal drug discovery. More specifically, the invention relates to the CaKRE5, CaALR1, and CaCDC24 genes, to their use to screen for antifungal compounds and to the drugs identified by such.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Method and system for intelligent positioning and management of medicines in medicine cabinets
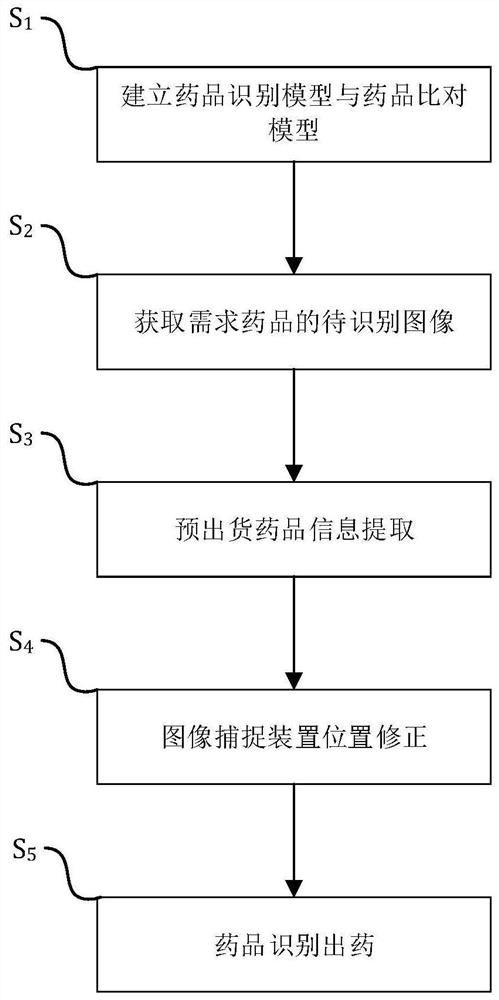
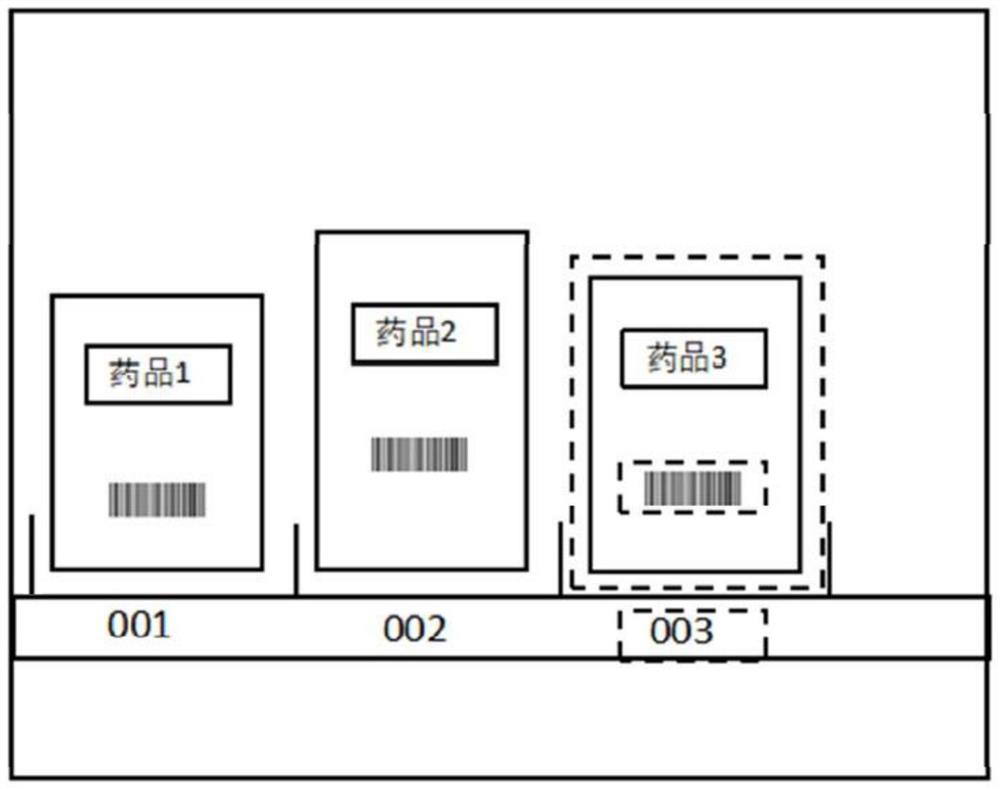
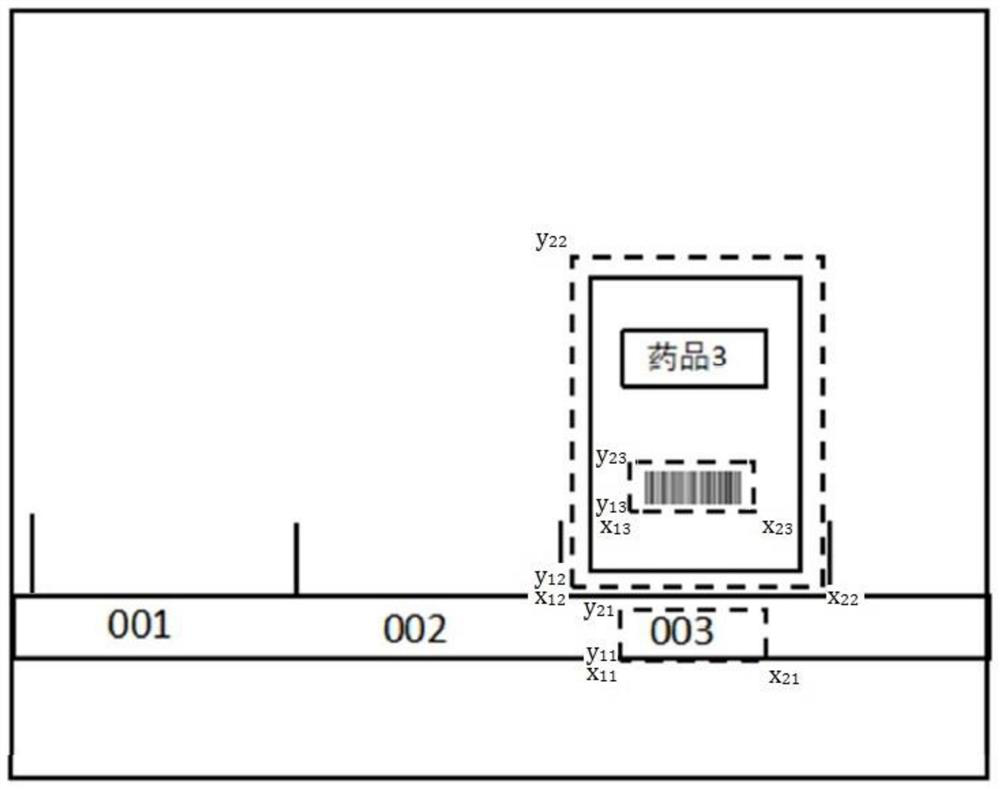
ActiveCN109472297BPrevent missellingImprove management efficiencyImage enhancementGeometric image transformationImage detectionDrug identification
A medicine cabinet drug intelligent positioning management method and system in the field of pharmaceutical retail technology, comprising the following steps: S 1 , establish a drug identification model and a drug comparison model; S 2 , to obtain the image to be recognized of the required drug; S 3 , Pre-shipment drug information extraction; S 4 , image capture device position correction; S 5 , the drug identifies the drug. The invention uses the image detection technology to match the customer's expected medicines with the medicines to be shipped, prevents wrong selling of medicines, and improves the safety of selling medicines; at the same time, it can update the medicine information in the medicine cabinet in real time, improve the management efficiency of medicines in the medicine cabinet, and reduce the management cost. cost.
Owner:陕西鑫泉通道网络科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com