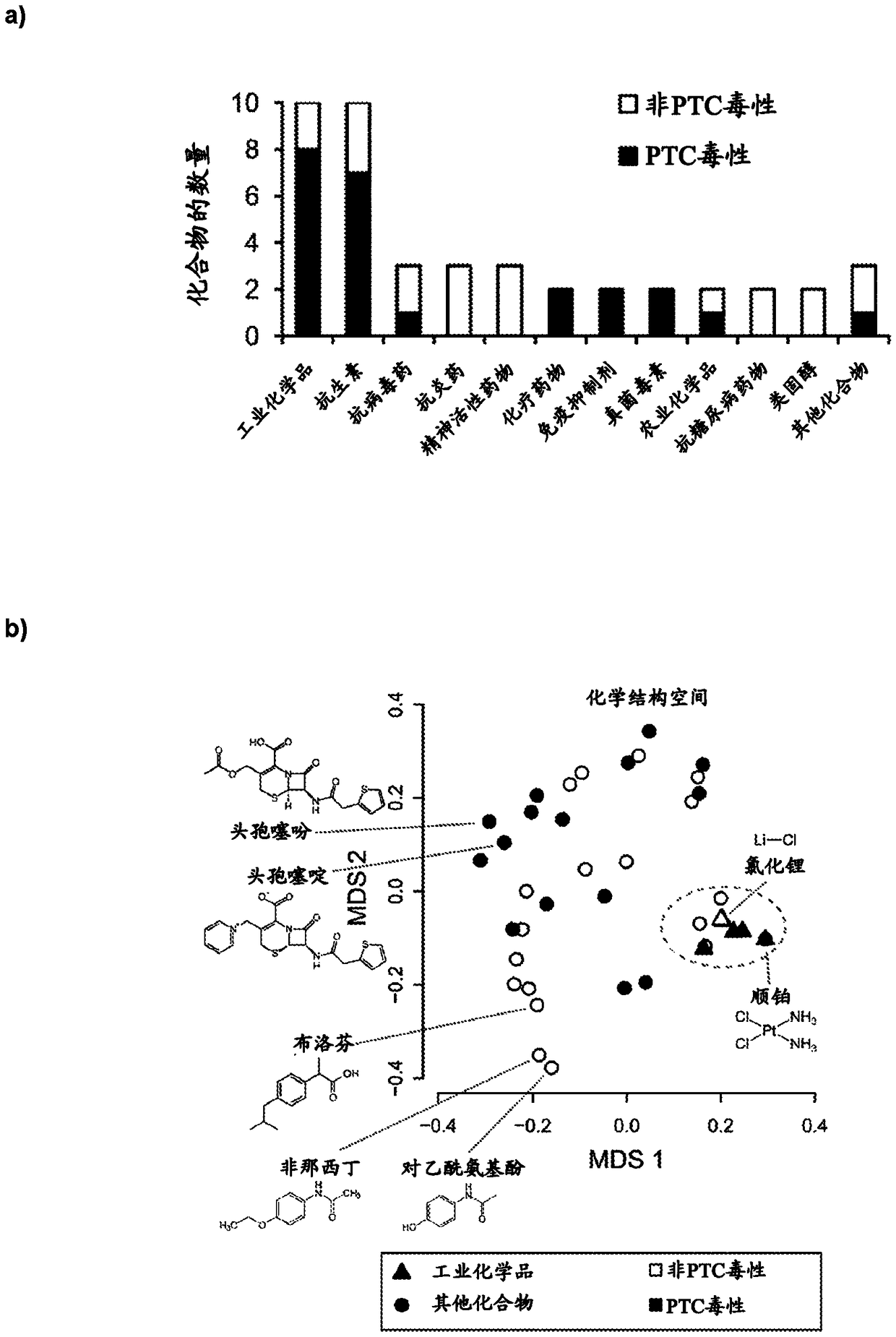
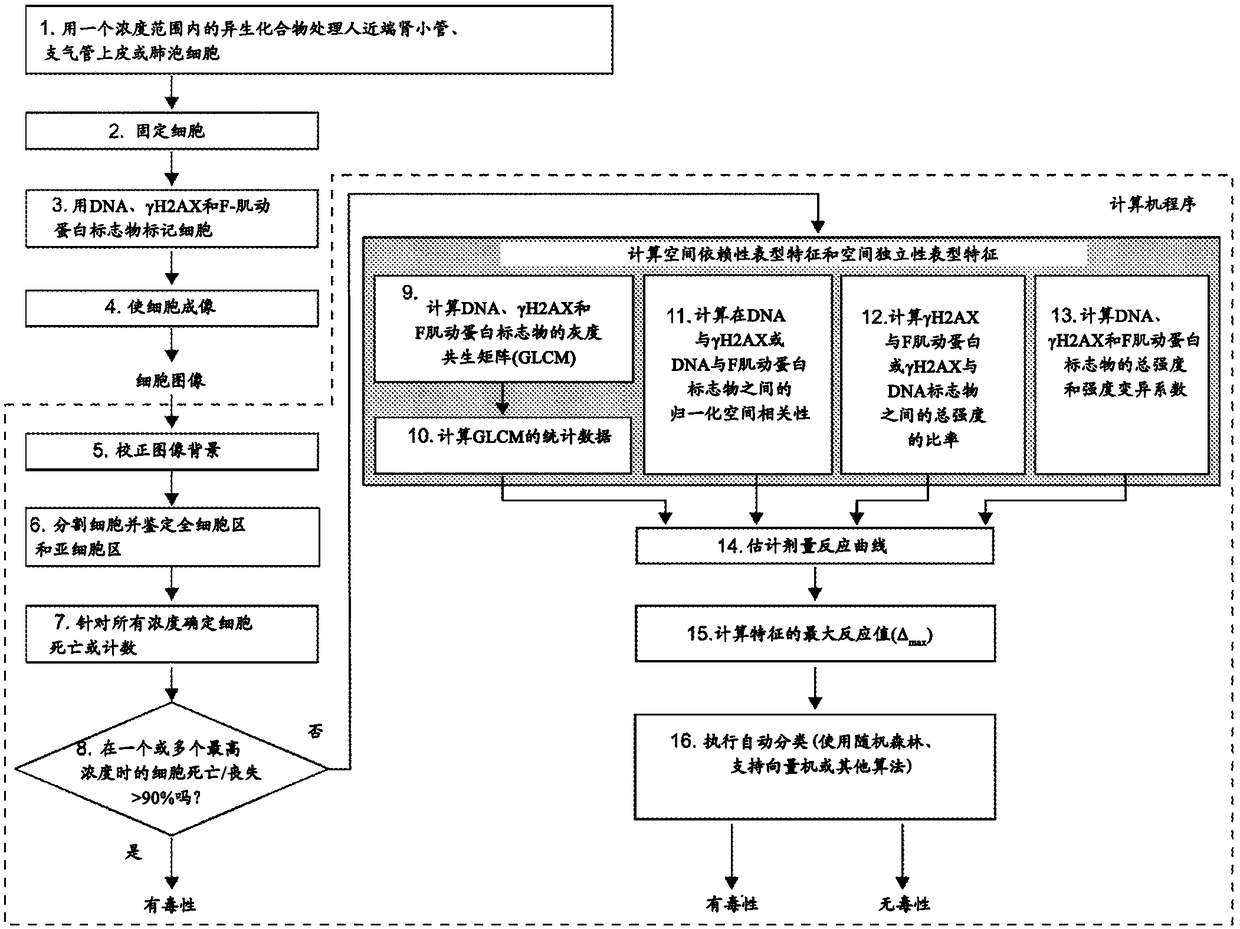
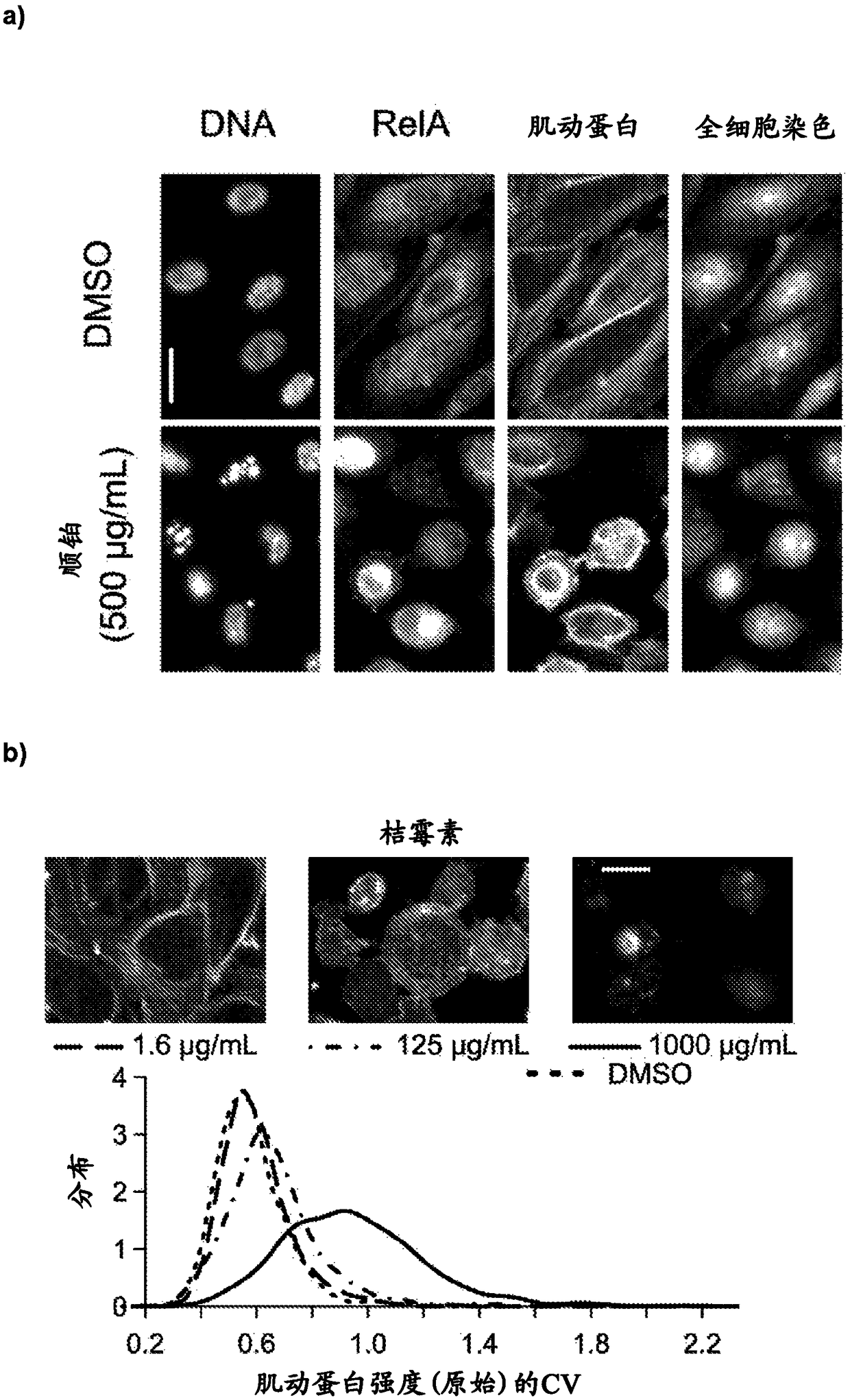
High-throughput imaging-based methods for predicting cell-type-specific toxicity of xenobiotics with diverse chemical structures
A cell-type technology, applied in the field of predicting the in vivo cell-specific toxicity of compounds, which can solve the problems of poor performance and non-evaluation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0136] Reference Compounds for Nephrotoxicity Studies
[0137] For the HPTC-A dataset (DNA / RelA / Actin / WCS), we used 44 xenogeneic compounds. The "PTC toxicity" group had 24 nephrotoxicants known to damage human proximal tubular cells (PTC), and the "non-PTC toxic" group had 12 nephrotoxicants and 8 non-nephrotoxicants that were unknown to injure PTC (regarding most compounds). Details of PTC toxicity can be found in our reports (Li et al., Mol Pharm11:1982–1990(2014); Kandasamy et al., Sci Rep.doi:10.1038 / srep12337(2015)). For HPTC-B and HK-2 dataset (DNA / γH2AX / Actin / WCS), using 42 compounds (excluding lead acetate and hydrocortisone). Compounds were dissolved in DMSO at a stock concentration of 50 mg / mL, or as A stock concentration of 10 mg / mL was dissolved in water. A complete list of reference compounds along with their sources, solvents, and known human renal and hepatotoxicity is provided in Table 1.
[0138] Table 1: Reference nephrotoxic compounds.
[0139]
[014...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com