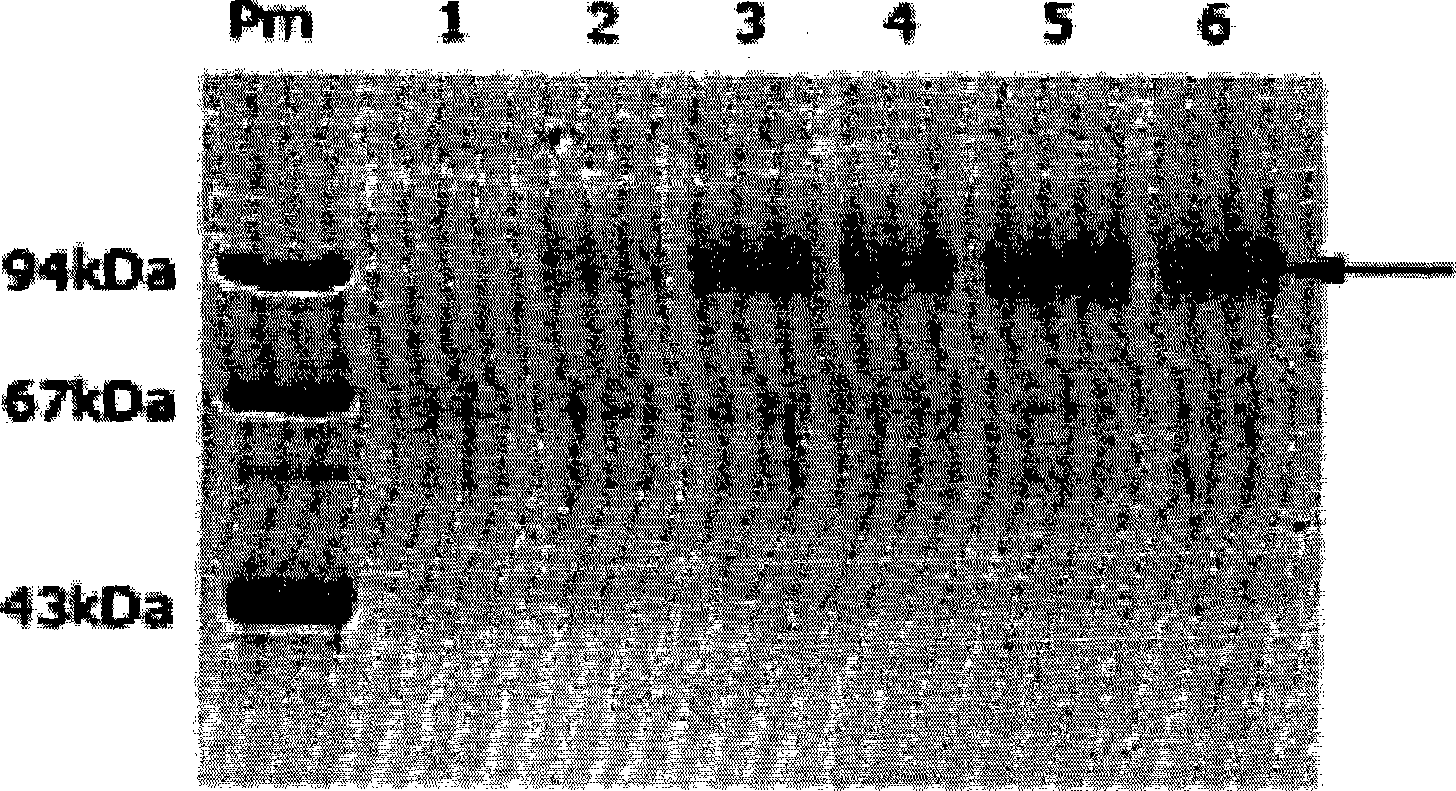Method for improving expression level of recombinant protein in kluyveromyces
A Kluyveromyces and protein technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, recombinant DNA technology, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems such as the unclear function of the Kluyveromyces lactis HAP1 gene, and achieve reduced production costs, The effect of increasing the amount of expression and expanding the scale of production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
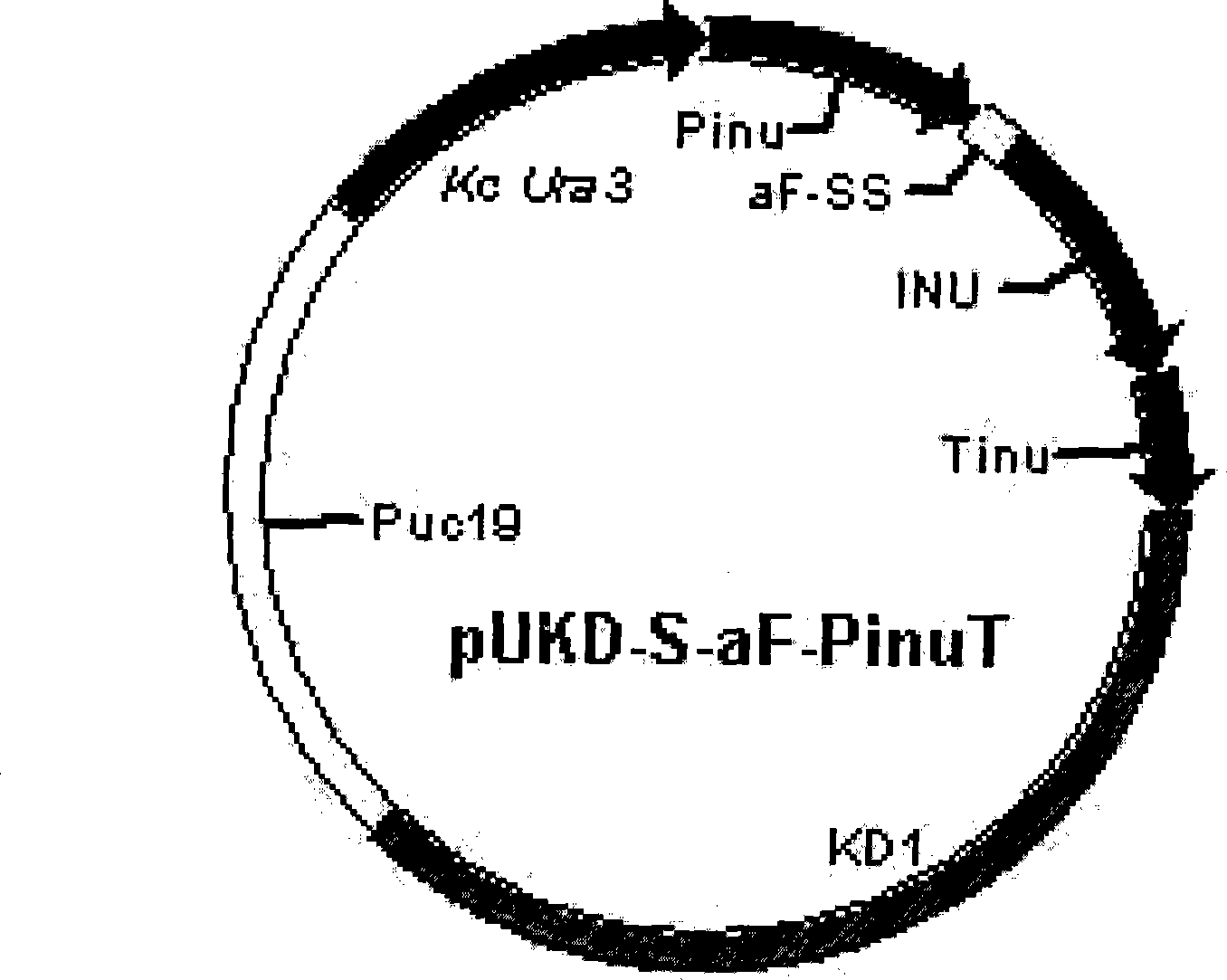
[0033] Example 1 Construction of Kluyveromyces chickpea inulinase gene expression plasmid pUKD-S-αF-PinuT
[0034] ①. Construction of Kluyveromyces chickpea inulinase gene expression cassette
[0035] First, using the total DNA of Kluyveromyces chickpea Y179 as a template, and using P1 and P2, P5 and P6 as primers, respectively, the promoter of Kluyveromyces chickpea exoinulinase gene was amplified by PCR technology. The DNA fragment of the subregion, the coding region of the inulinase gene and the DNA fragment of the terminator region, and then using the pPIC9K plasmid as a template and P3 and P4 as primers, the α-Factor signal peptide DNA fragment was amplified by PCR technology. Carry out the corresponding restriction endonuclease treatment according to the restriction enzyme site designed for each fragment, and the three restriction fragments obtained are connected with the plasmid pBS_SK which has undergone double restriction enzyme digestion treatment with EcoR1 and HindIII ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Construction of engineering strain K1-WT / pUKD-S-αF-PinuT and engineering strain klhap1Δ / pUKD-S-αF-PinuT expressing Kluyveromyces lactis gene.
[0049] Plasmid pUKD-S-αF-PinuT was used to transform Kluyveromyces lactis MW179-1D strain and HAP1 gene-deficient strain MW179-1D hap1Δ, respectively, using LiAc transformation method. The sequence of Kluyveromyces lactis HAP1 gene is SEQ1.ID.NO 1.
[0050] ① Inoculate a single colony into 3ml liquid YEPD medium and culture with shaking at 30°C for 16-18 hours.
[0051] ②Dilute the culture into 50ml liquid YEPD to make the initial OD 600 =0.2, culturing with shaking at 30℃ for 3-5 hours, OD 600 = 0.4-0.6.
[0052] ③ Collect the cells by centrifugation at 5K for 5 minutes.
[0053] ④ Discard the culture medium, suspend the cells in 25ml sterile water, and centrifuge as above.
[0054] ⑤ Discard the water, suspend the cells with 1ml of 0.1mol / L LiAc, and transfer to a sterile 1.5ml centrifuge tube.
[0055] ⑥ Pellet the cell...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Kluyveromyces lactis engineering bacteria K1-WT / pUKD-S-αF-PinuT and klhap1Δ / pUKD-S-αF-PinuT fermentation culture and inulinase expression analysis
[0061] ①Put K1-WT / pUKD-S-αF-PinuT and klhap1Δ / pUKD-S-αF-PinuT engineering strains of Kluyveromyces lactis into 3ml selective SD liquid medium, respectively, in a shaker at 30℃ and 250rpm After being cultured in medium overnight, it is used as seed solution. The components of the selective SD liquid medium are: 0.67% YNB, 2% glucose, 0.002% uracil and 0.002% methionine.
[0062] ②Put the seed solution into a 150ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 25ml of liquid YEPD medium at a ratio of 1:25, and cultivate for 120 hours in a shaker at 30°C and 250rpm. The components of the liquid YEPD medium are: 1% yeast extract, 2% peptone and 2% glucose.
[0063] ③Aspirate fermentation broth samples every 24 hours, centrifuge at 5000 rpm for 5 min to precipitate the bacteria, and take the supernatant to analyze the expressed product inul...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com