Preparation and application of L-amino acid deaminase mutant
An amino acid and deaminase technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as low yield, achieve high catalytic activity, improve production capacity, and be easy to popularize and apply.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
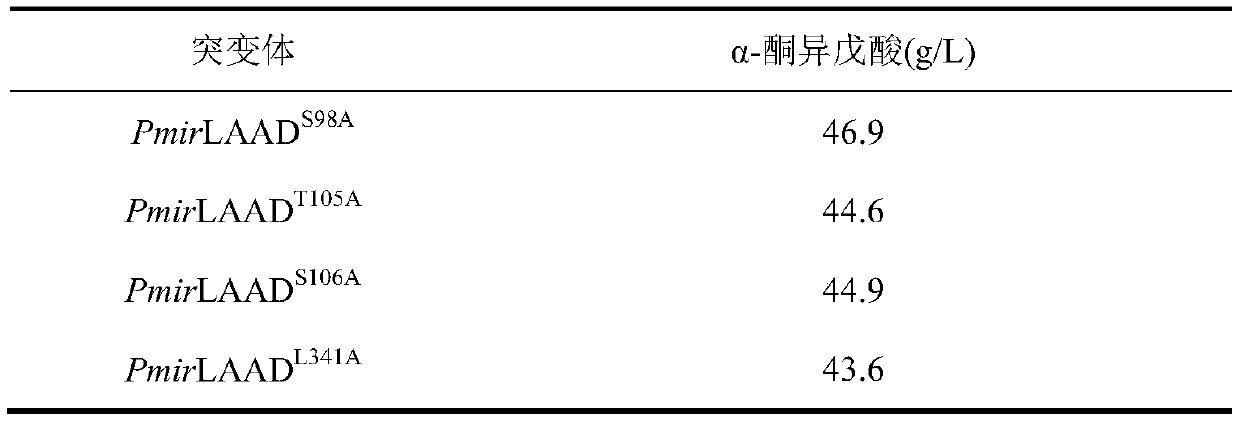
[0036] Example 1: Construction and screening of single mutants
[0037] (1) Mutant construction: primers for the 98th, 105th, 106th, and 341st mutation sites were designed, as shown in Table 1, and constructed by whole-plasmid PCR.
[0038] Table 1 Mutation primer sequence
[0039]
[0040]Construct the reaction PCR amplification system: PrimSTAR enzyme 0.5 μL, 5×PrimeSTAR Buffer 10 μL, dNTP 4 μL, two primers for each mutation site 1 μL, template (nucleotide sequence of pmirLAAD) 4 μL, water 32.5 μL; the reaction conditions are : ① 94°C for 3 minutes; ② 98°C for 10s; ③ 55°C for 30s; ④ 72°C for 3 minutes; ⑤ Cycle ② to ④ 29 times;
[0041] Incubate the above reaction system at 37°C for 3 hours to digest the plasmid template (digestion system: DpnI 0.5 μL, the above reaction PCR product 45 μL, 10×T Buffer 5 μL), and the digested product obtained after digestion is introduced into E. coli BL21 by chemical transformation method Competent cells, specific steps of chemical trans...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2: Construction and screening of double, triple and quadruple mutants
[0055] (1) double mutation mutant construction: in the mutant PmirLAAD S98A On the basis of the mutation primers T105A-S and T105A-A, S106A-S and S106A-A, L341A-S and L341A-A, double mutation mutants were constructed respectively; in the mutant PmirLAAD T105A On the basis of the mutation primers S106A*-S and S106A*-A, L341A-S and L341A-A, double mutation mutants were constructed respectively; in the mutant PmirLAAD S106A On the basis of mutation primers L341A-S and L341A-A (Table 3); carry out double mutation mutant construction by whole plasmid PCR, for specific implementation, refer to step (1) in Example 1, and prepare 6 double mutation mutants Body PmirLAAD S98A / T105A 、PmirLAAD S98A / S106A 、PmirLAAD S98A / L341A 、PmirLAAD T105A / S106A 、PmirLAAD T105A / L341A 、PmirLAAD S106A / L341A .
[0056] Table 3 double mutant mutation primer sequence
[0057]
[0058] (2) Screening of double-mut...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Embodiment 3: Determination of kinetic parameters and product inhibition constants of parental enzymes and mutants
[0067] In order to evaluate the mutants, the present invention has determined the mutant parent PmirLAAD WT and mutant PmirLAAD M1 、PmirLAAD M2 、PmirLAAD M3 、PmirLAAD M4 Kinetic parameters at 25 °C.
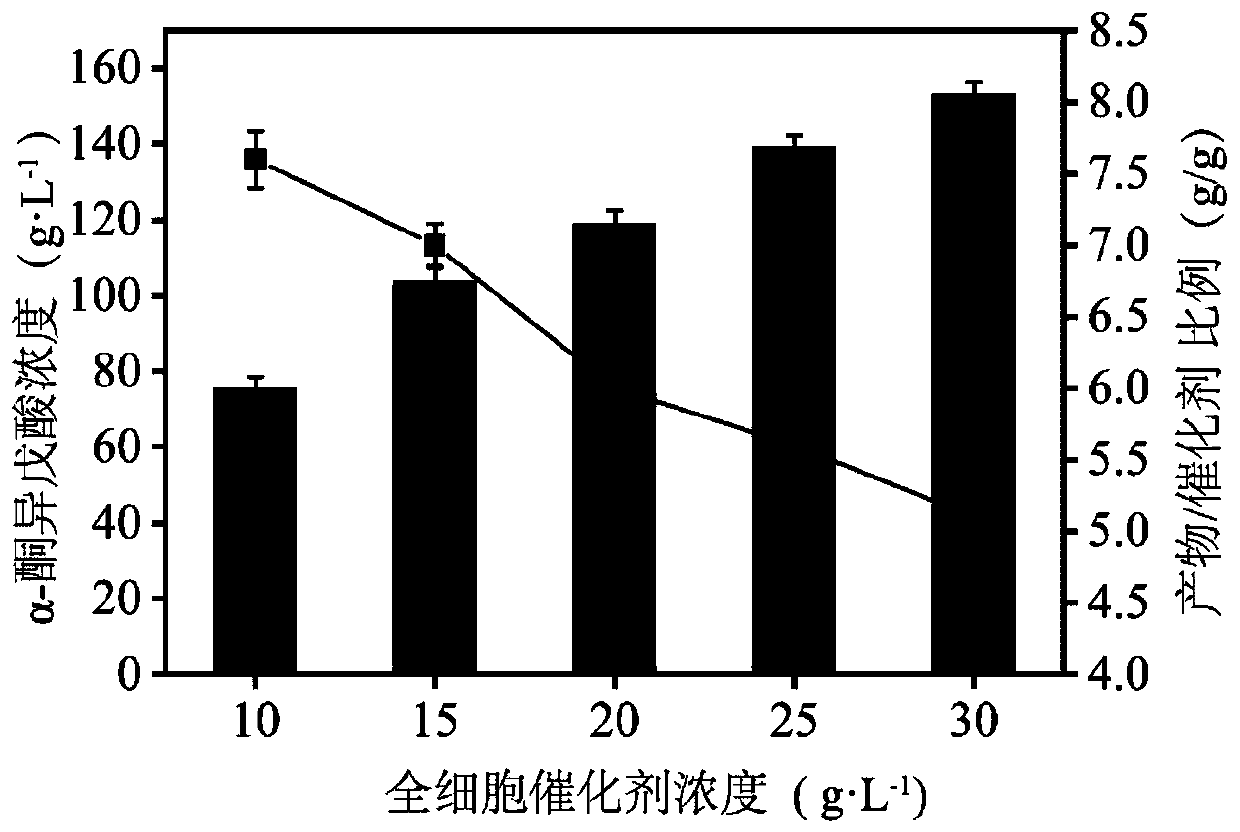
[0068] k cat / K m Calculated by measuring the initial rate of α-ketoisovaleric acid produced by the hydrolysis of different concentrations of L-valine substrate at 25°C. The product inhibition constant of the parental enzyme and the mutant was determined by the assay of the product inhibition constant in the transformation process, and the PmirLAAD WT Parental enzyme strains and mutant strains were added to the reaction solution with wet cells at a final concentration of 10g / L, and 60mM L-valine was used as a substrate, and 10-100mM α-ketoisovaleric acid was added to the transformation system. Measure the initial reaction rate V after reacting for ab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com