Patents
Literature
46 results about "Glycerol synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
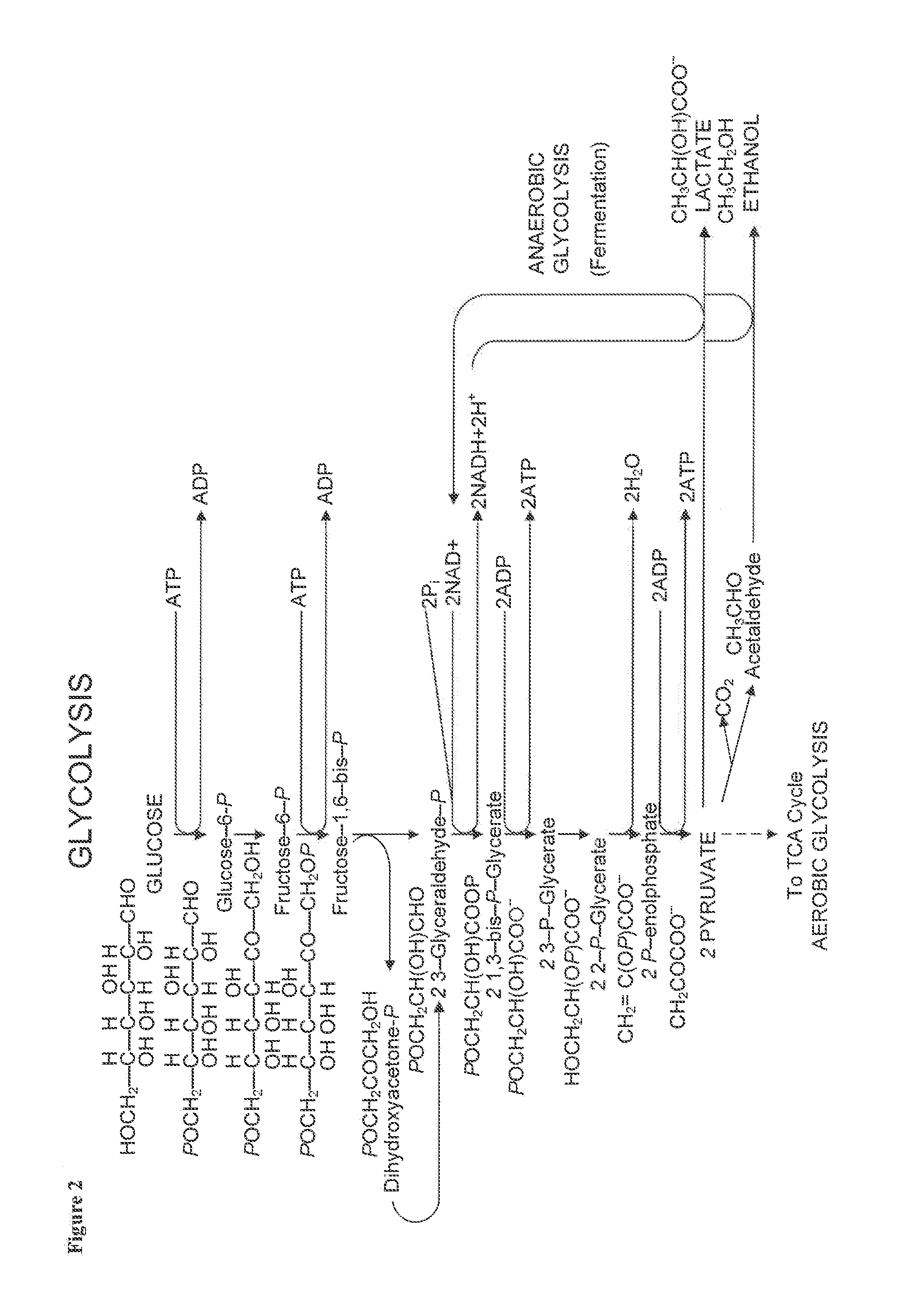
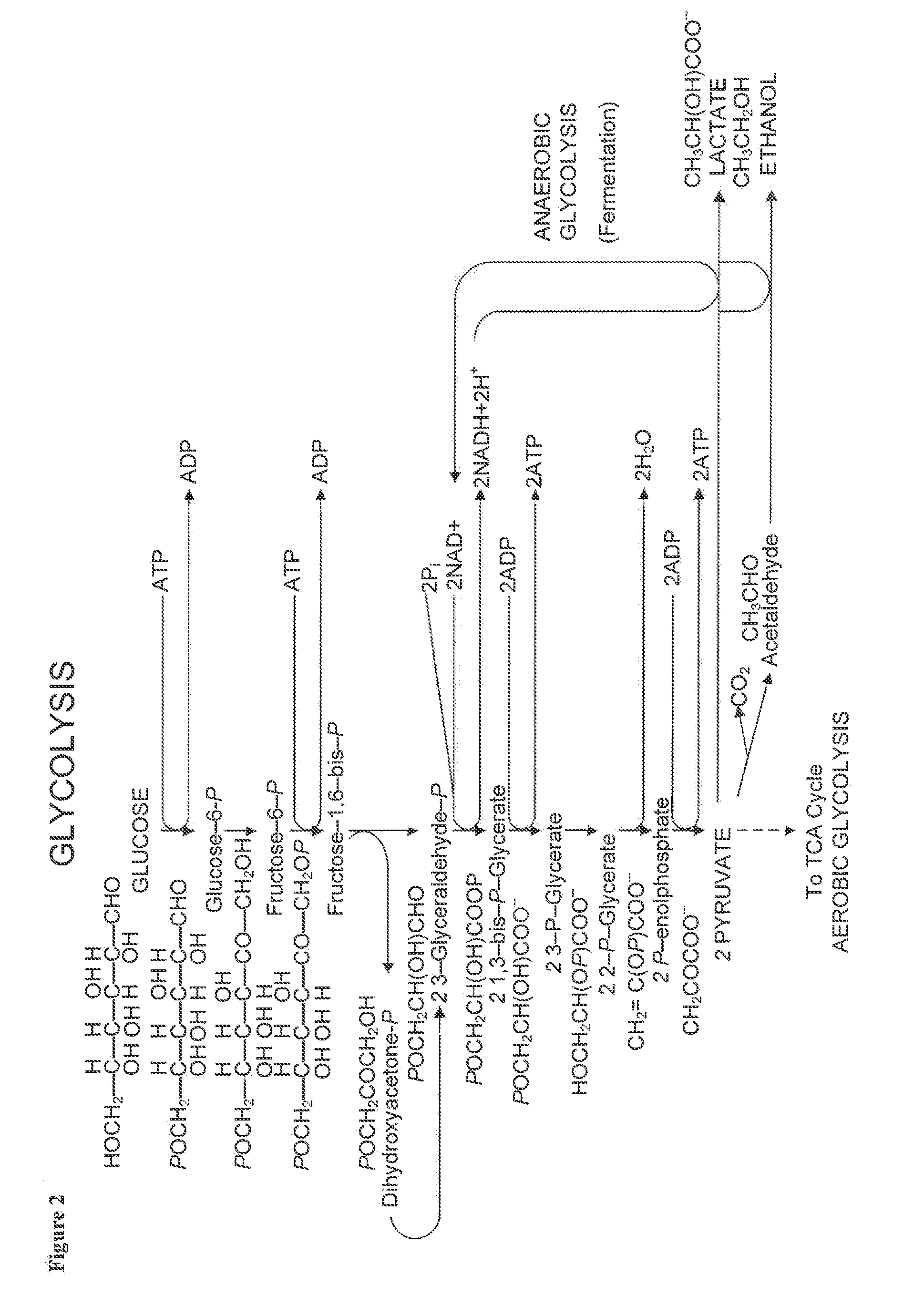
However, several experiments, which used stable isotopes to track the glycerol in liver and bloodstream, showed that 65% of the glycerol backbone of triglyceride flowing through the bloodstream is actually synthesised in the liver. Therefore, glycerol 3-phosphate synthesis in liver was discovered.
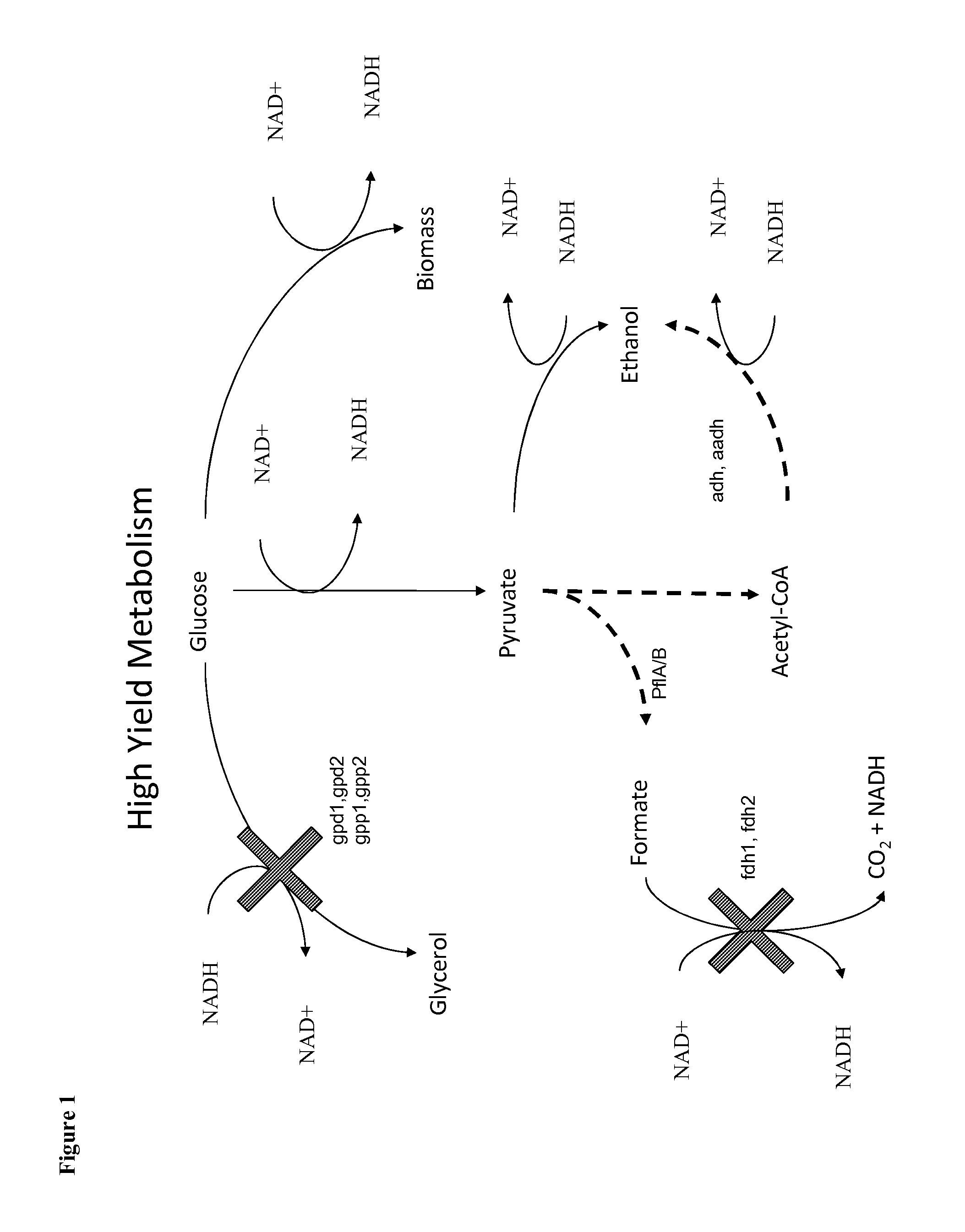
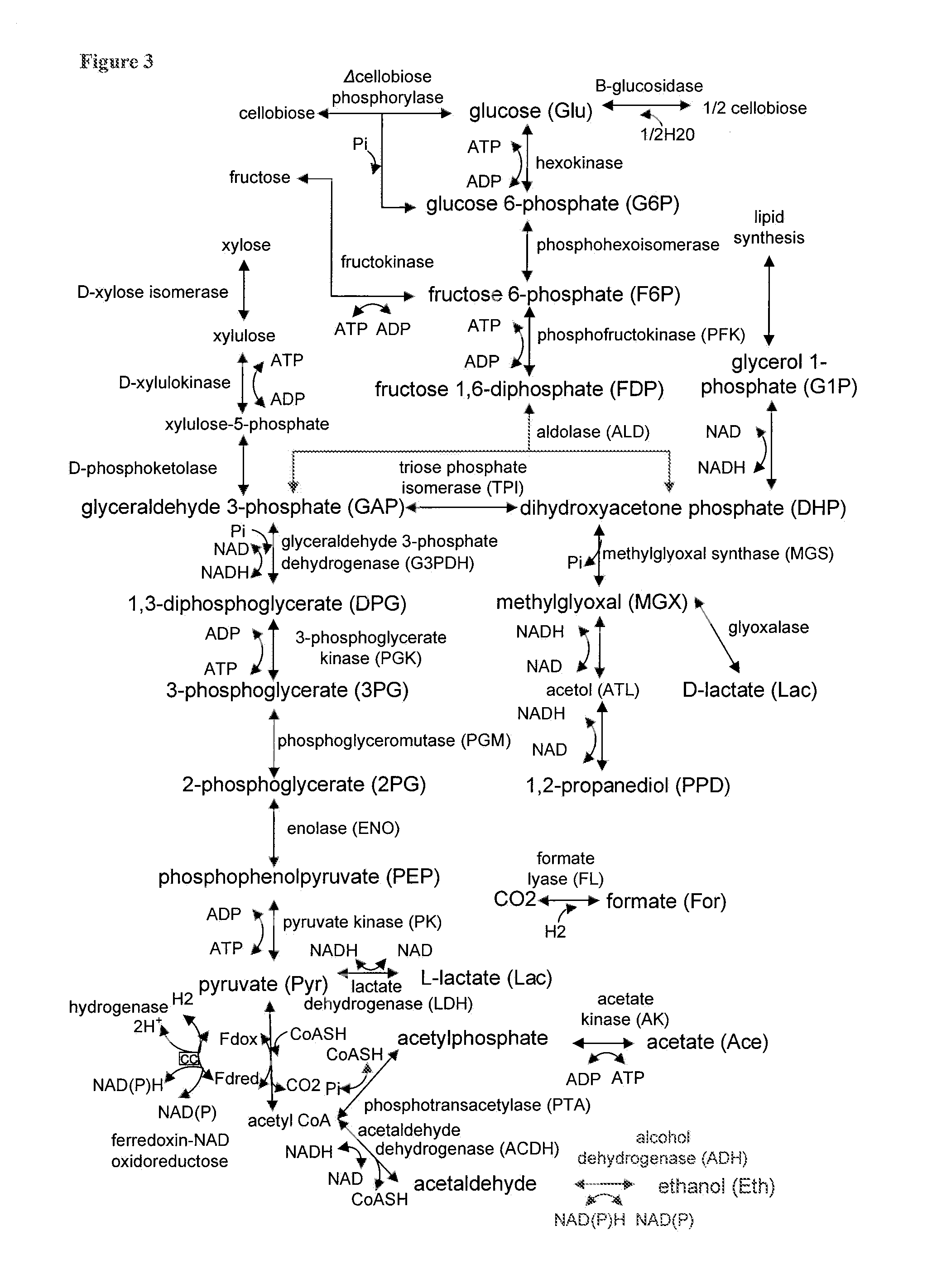
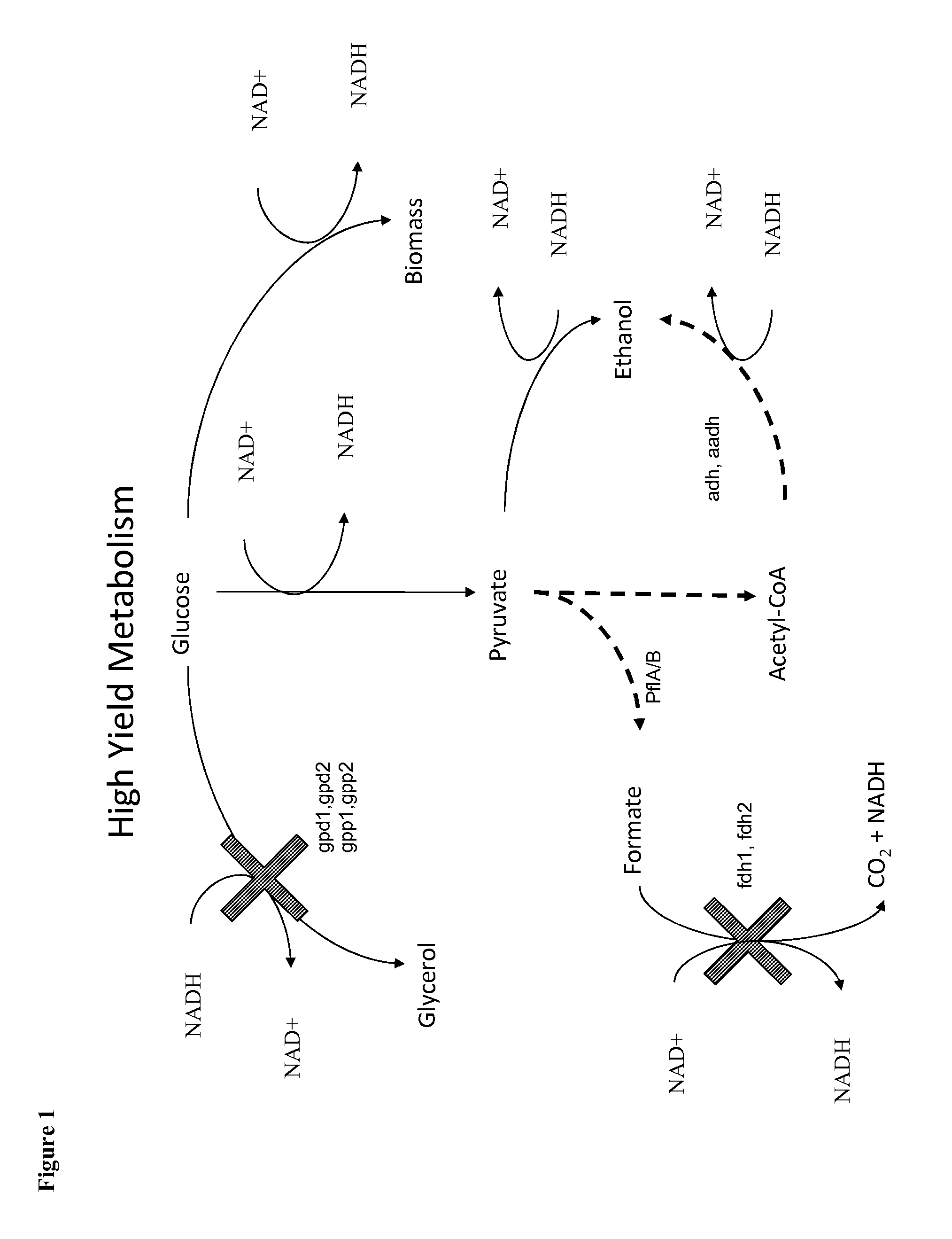
Methods for the improvement of product yield and production in a microorganism through the addition of alternate electron acceptors
ActiveUS8956851B2Reduce formationSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationBiotechnologyHeterologous
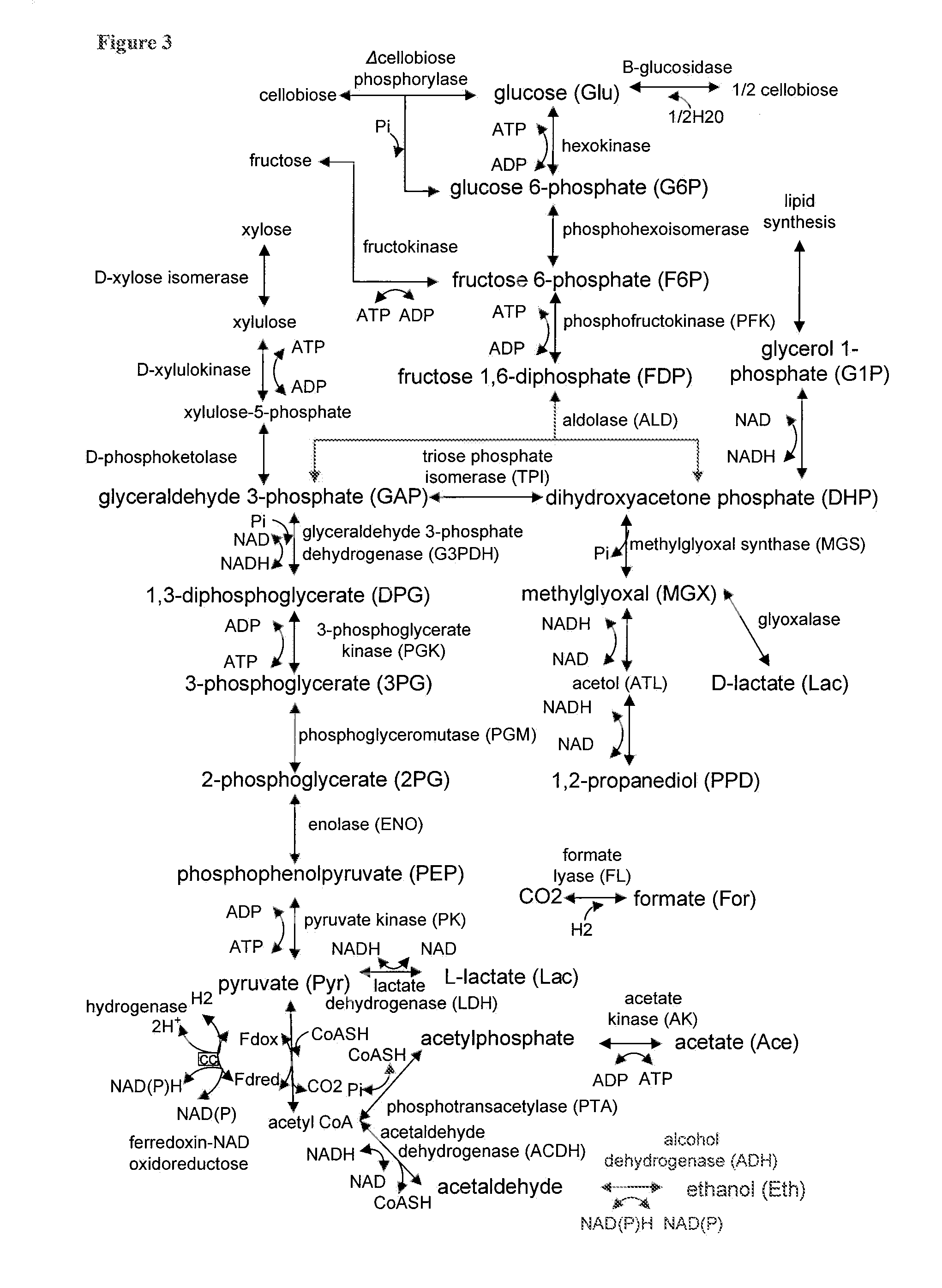
The present invention provides for novel metabolic pathways to reduce or eliminate glycerol production and increase product formation. More specifically, the invention provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising a deletion of one or more native enzymes that function to produce glycerol and / or regulate glycerol synthesis and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to convert a carbohydrate source, such as lignocellulose, to a product, such as ethanol, wherein the one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated, or downregulated. The invention also provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising one or more heterologous enzymes that function to regulate glycerol synthesis and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to convert a carbohydrate source to ethanol, wherein said one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated or downregulated.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
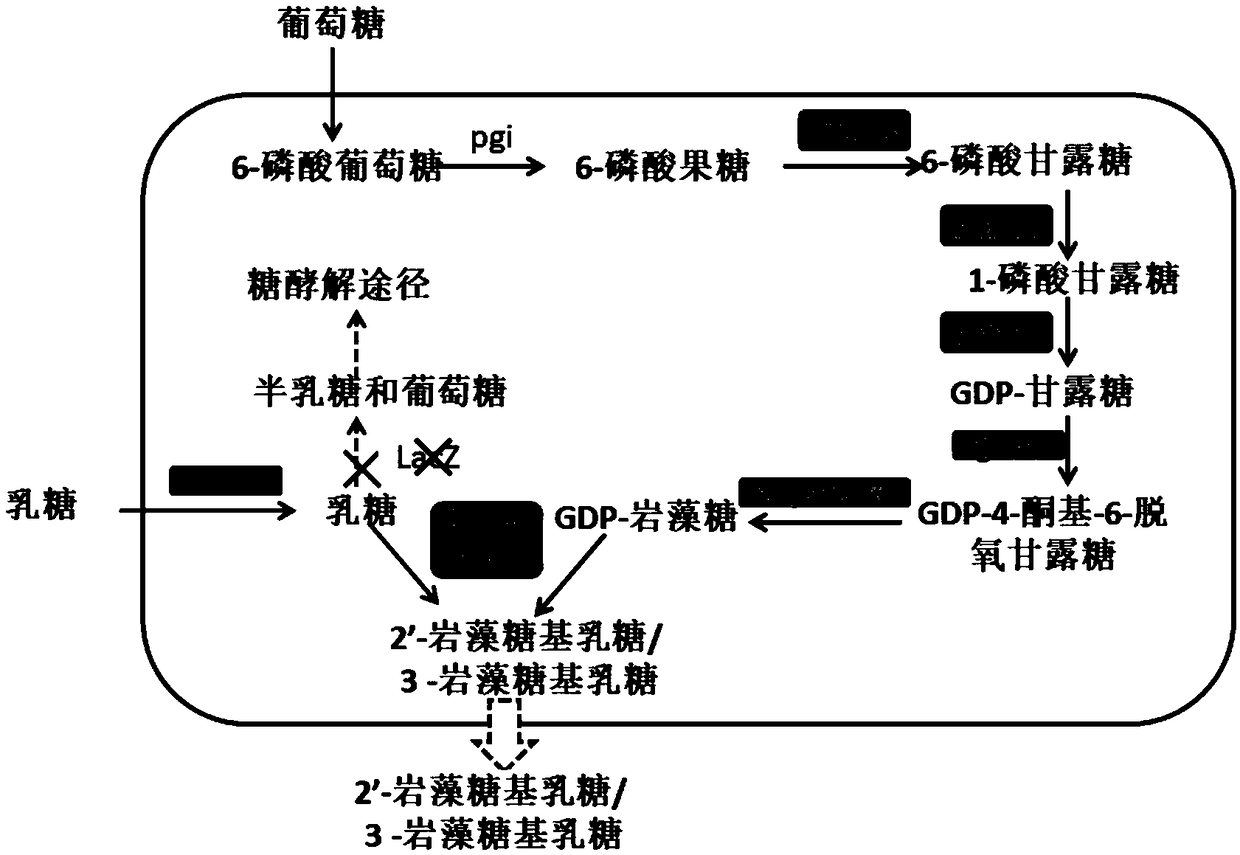
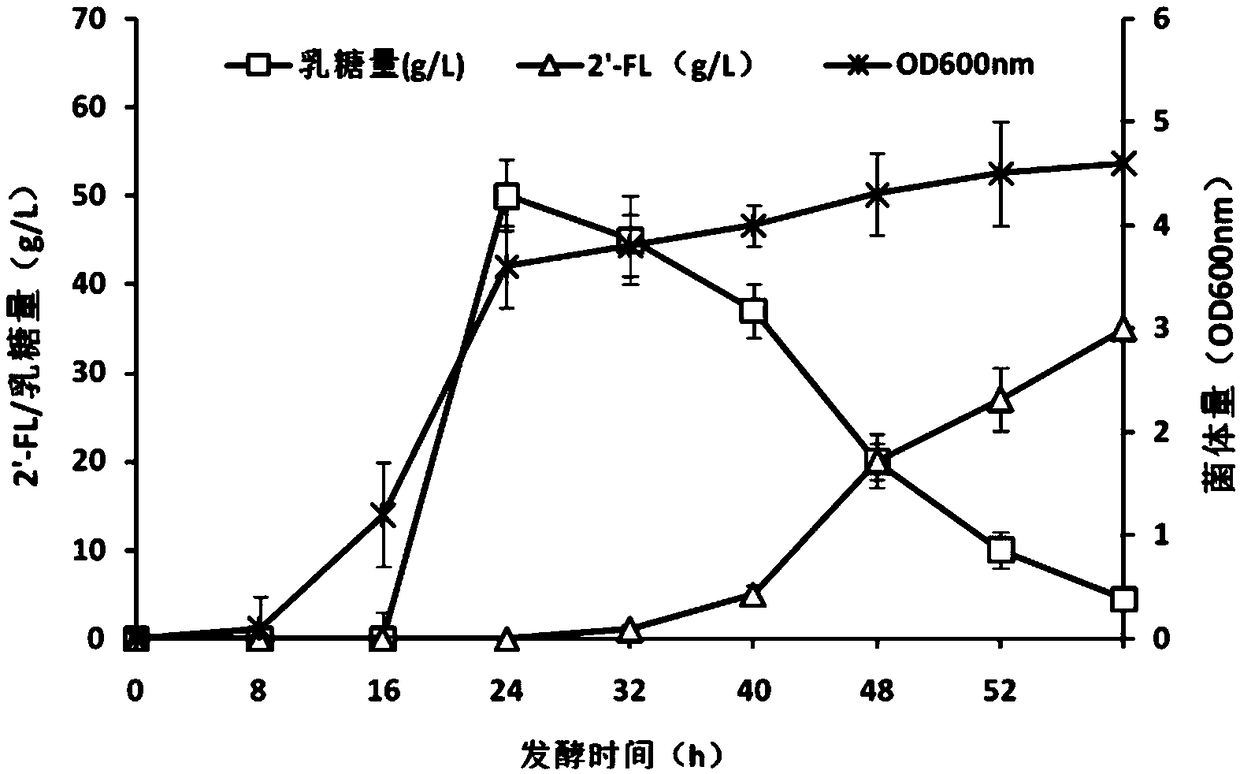
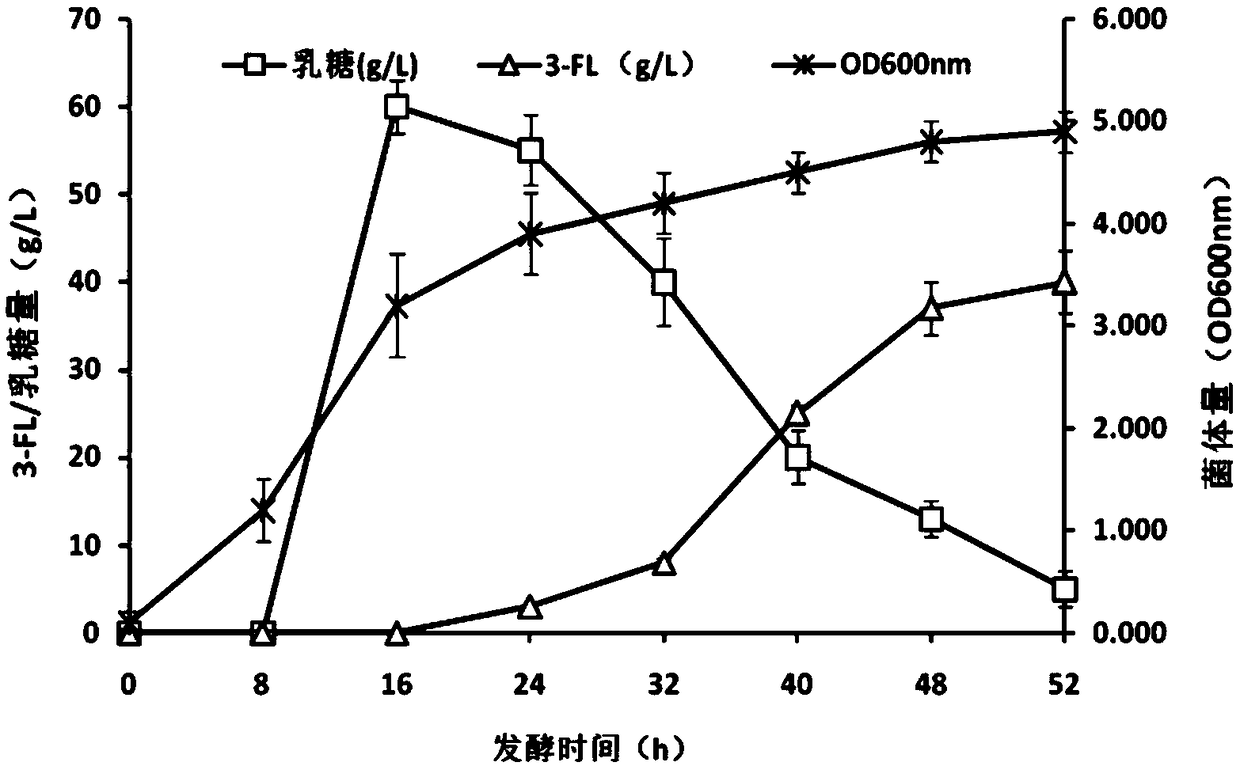
Recombinant expression plasmid vector for producing fucose-based lactose, metabolic engineering bacteria, and production method
The invention relates to a recombinant expression plasmid vector for producing fucose-based lactose, metabolic engineering bacteria, and a production method and belongs to the fields of metabolic engineering, food fermentation and the like. In the invention, genes for encoding GDP-mannose-6-dehydrogenase, GDP-fucose synthetase, lactose permease, and alpha-1,2-fucose transferase or alpha-1,3-fucosetransferase, which are required in a de-novo synthesis route of the fucose-based lactose, are expressed in corynebacterium glutamicum, so that recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is constructed toachieve synthesis of 2'-fucose-based lactose or 3'-fucose-based lactose. In addition, by over-expression of the genes for encoding phosphomannose isomerase, phosphomannose mutase, and mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase in the corynebacterium glutamicum, high yield of the fucose-based lactose is achieved. According to the method, the engineering bacteria can synthesize the fucose-based lactose by means of glucose or glycerol, has advantages of high growth speed and good safety, and has significant industrial potential.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Methods for the Improvement of Product Yield and Production in a Microorganism Through the Addition of Alternate Electron Acceptors
The present invention provides for novel metabolic pathways to reduce or eliminate glycerol production and increase product formation. More specifically, the invention provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising a deletion of one or more native enzymes that function to produce glycerol and / or regulate glycerol synthesis and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to convert a carbohydrate source, such as lignocellulose, to a product, such as ethanol, wherein the one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated, or downregulated. The invention also provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising one or more heterologous enzymes that function to regulate glycerol synthesis and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to convert a carbohydrate source to ethanol, wherein said one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated or downregulated.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Clean process for using glycerin to synthesize epichlorohydrin
InactiveCN102617514ARealize mutual resource utilizationLow costOrganic chemistryPhosphorus compoundsO-Phosphoric AcidWater chlorination
The invention relates to a clean process for using glycerin to synthesize epichlorohydrin, belonging to the technical field of epichlorohydrin. HCl gas and dilute phosphoric acid are produced via hydrolysis of POCl3, and the dilute phosphoric acid produced via the hydrolysis of POCl3 is concentrated into concentrated phosphoric acid. The produced HCl gas is used for chlorination of glycerin to produce dichloro glycerin and byproduct water. The produced dichloro glycerin and lime milk or KOH solution are mixed for saponification to produce epichlorohydrin and saponification wastewater containing CaCl2 or KCl. The saponification wastewater is subjected to multi-effect evaporation and concentration, and the produced neutral condensate water is applied for preparation of the lime milk or KOH solution. The concentrated phosphoric acid is subjected to reaction with the CaCl2 or the KCl in the concentrated saponification wastewater to produce a phosphate fertilizer or a phosphorus / potassium composite fertilizer. Byproduct hydrochloric acid is applied for hydrolysis of POCl3. The hydrolysis of POCl3, glycerin chlorination, saponification of dichloro glycerin and treatment of saponification wastewater are integrated in one system, and intermediates and byproducts in the process can be utilized as mutual resources.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Limiting yeast-produced trehalose in fermentation
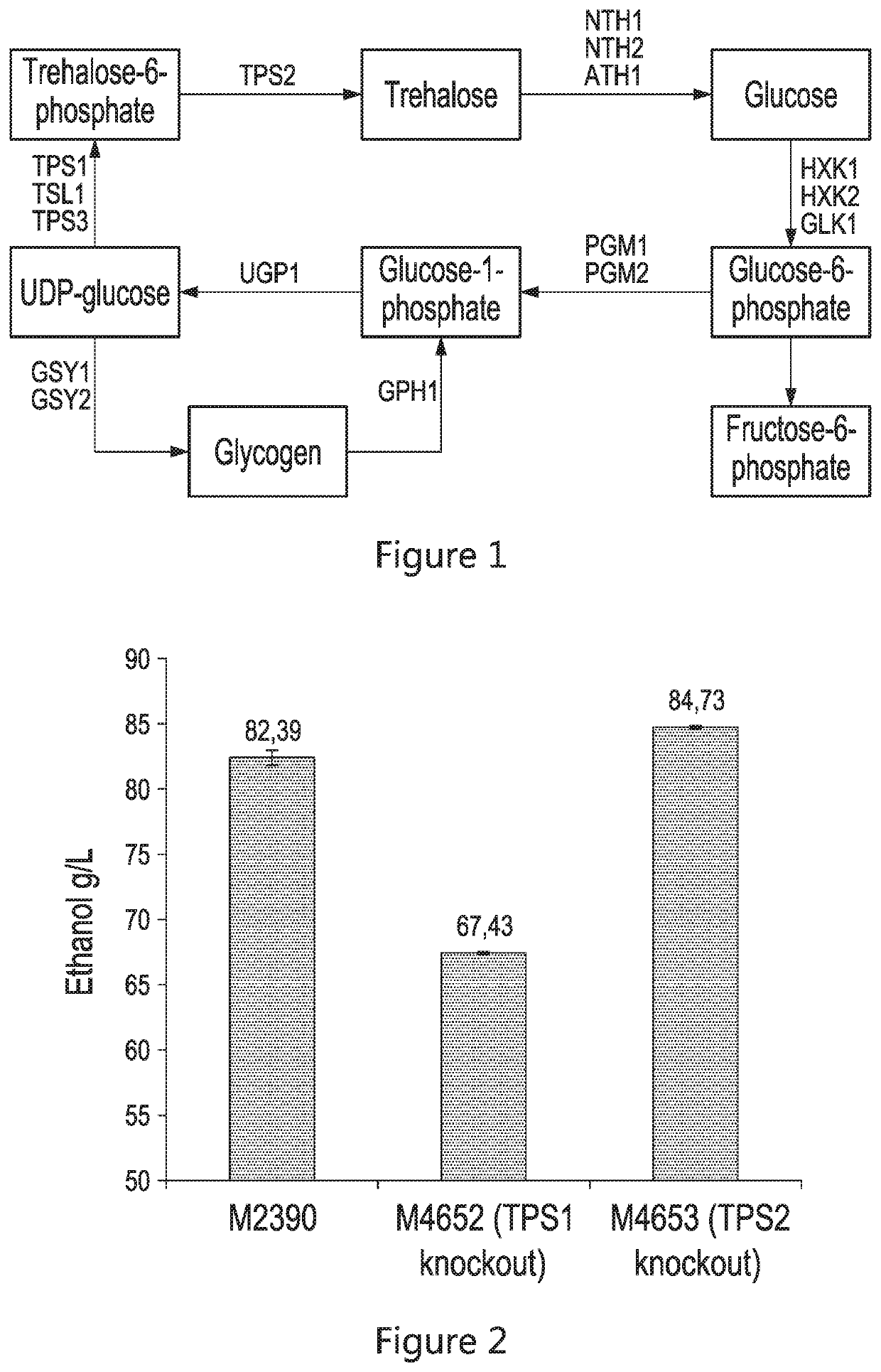
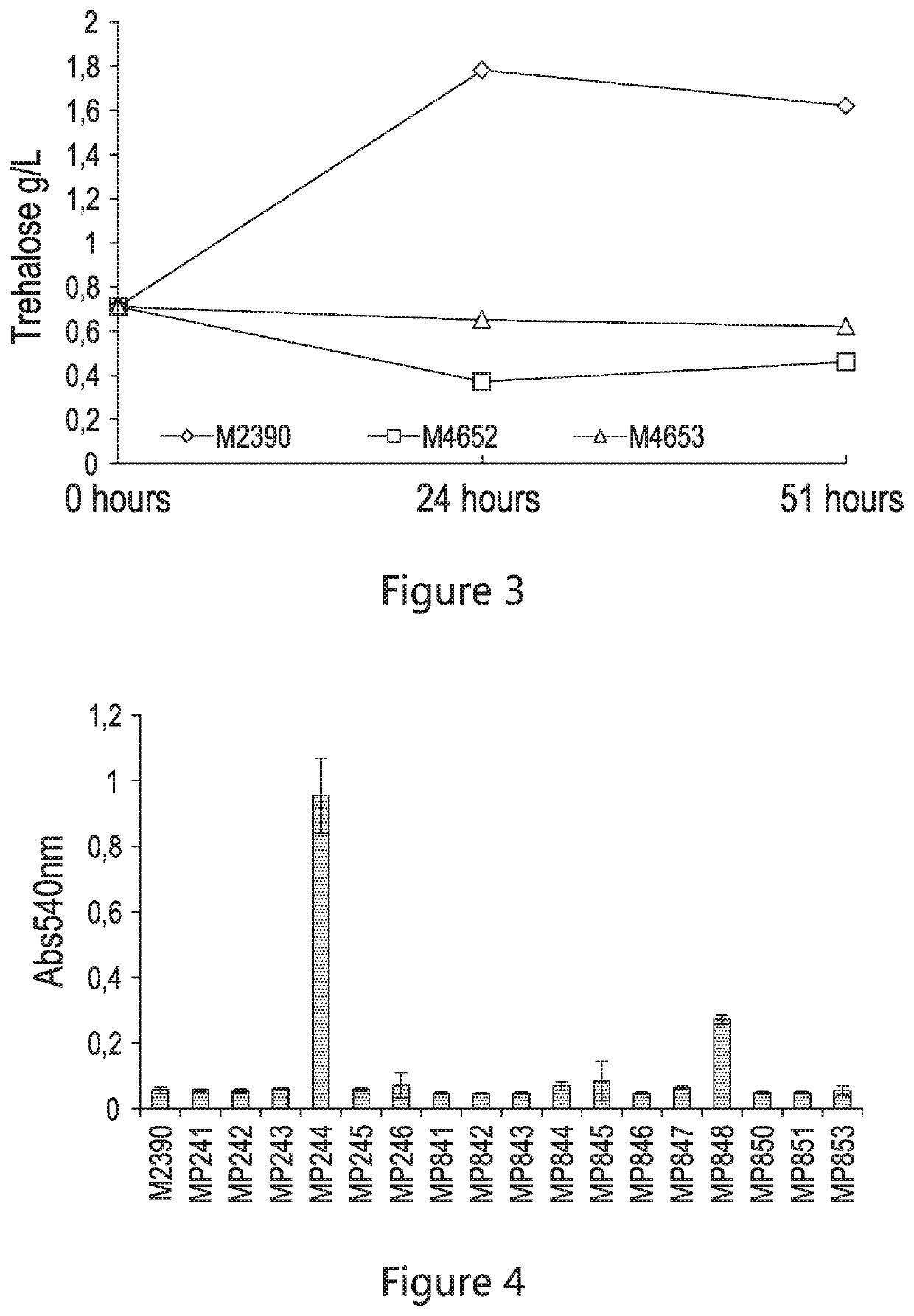
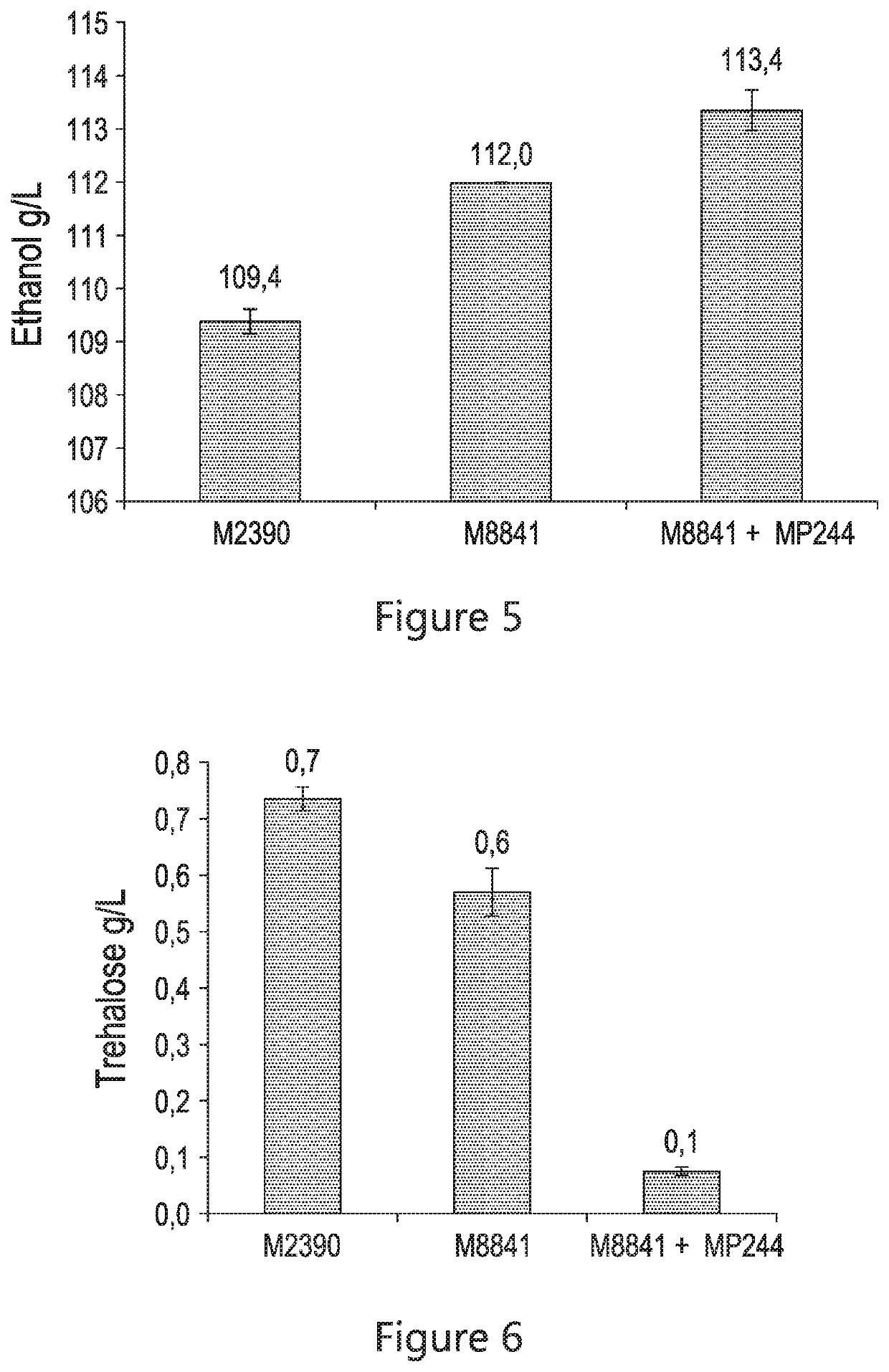
The present disclosure relates to recombinant yeast host cells having (i) a first genetic modification for reducing the production of one or more native enzymes that function to produce glycerol or regulating glycerol synthesis and / or allowing the production of an heterologous glucoamylase and (ii) a second genetic modification for reducing the production of one or more native enzymes that function to produce trehalose or regulating trehalose synthesis and / or allowing the expression of an heterologous trehalase. The recombinant yeast host cells can be used to limit the production of (yeast-produced) trehalose (particularly extracellular trehalose) during fermentation and, in some embodiments, can increase the production of a fermentation product (such as, for example, ethanol).
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
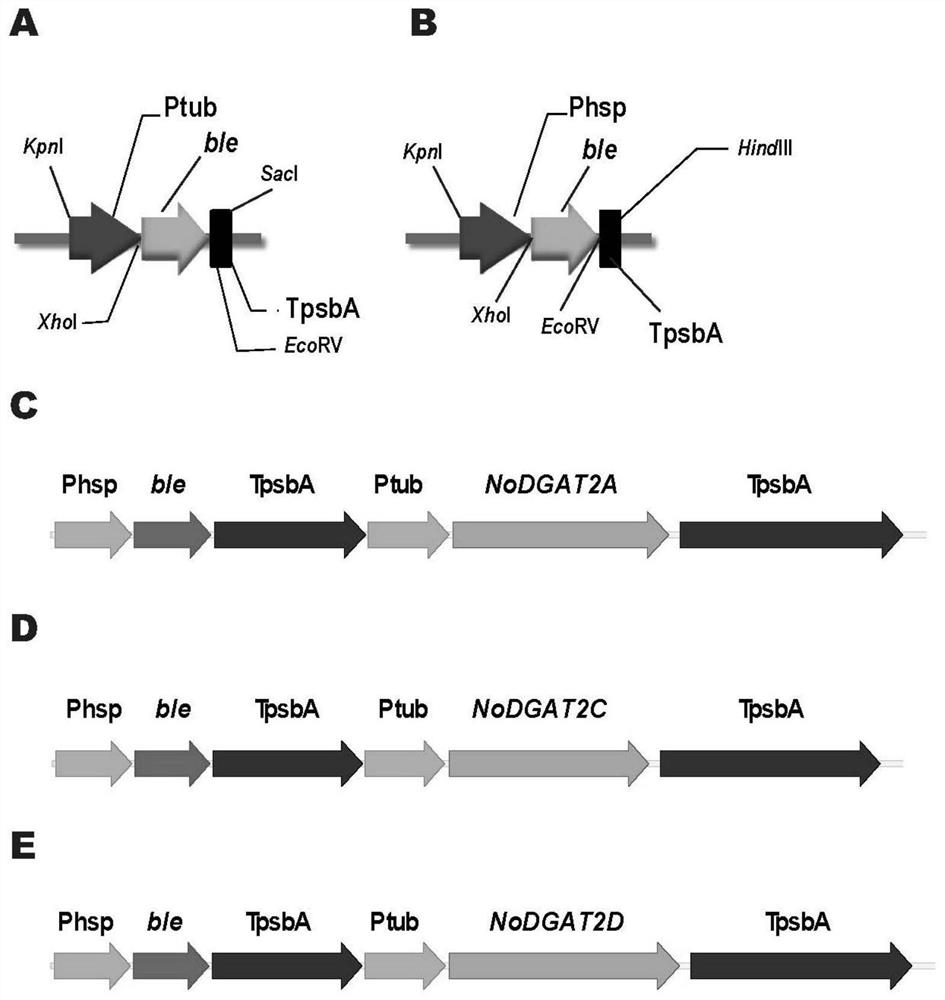
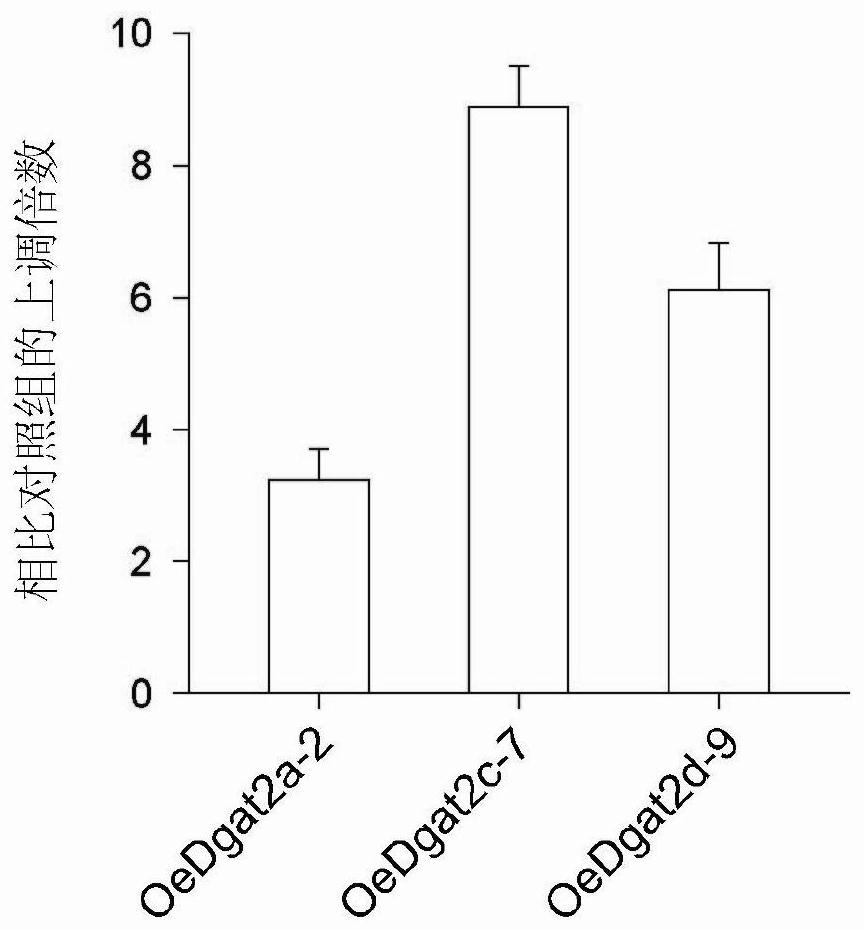
Gene having triacylglycerol synthesis function, and applications thereof
ActiveCN105255912AImprove synthesis abilityImprove oil qualityFungiTransferasesBiological bodyNucleotide
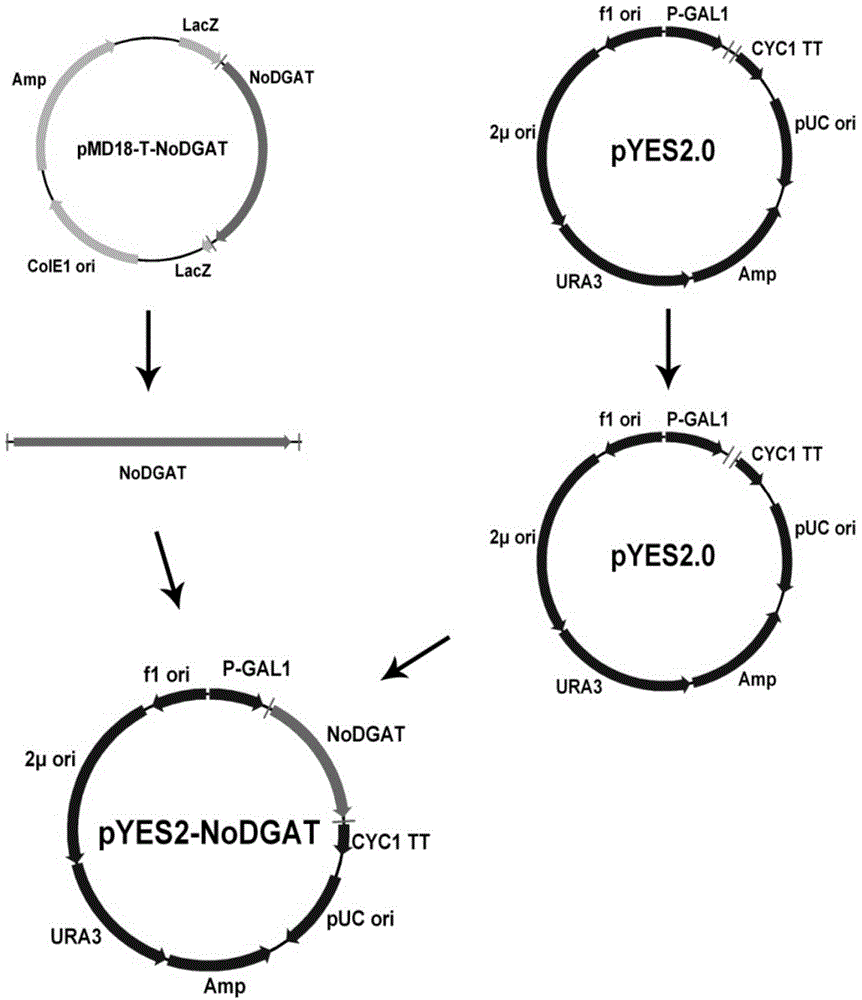
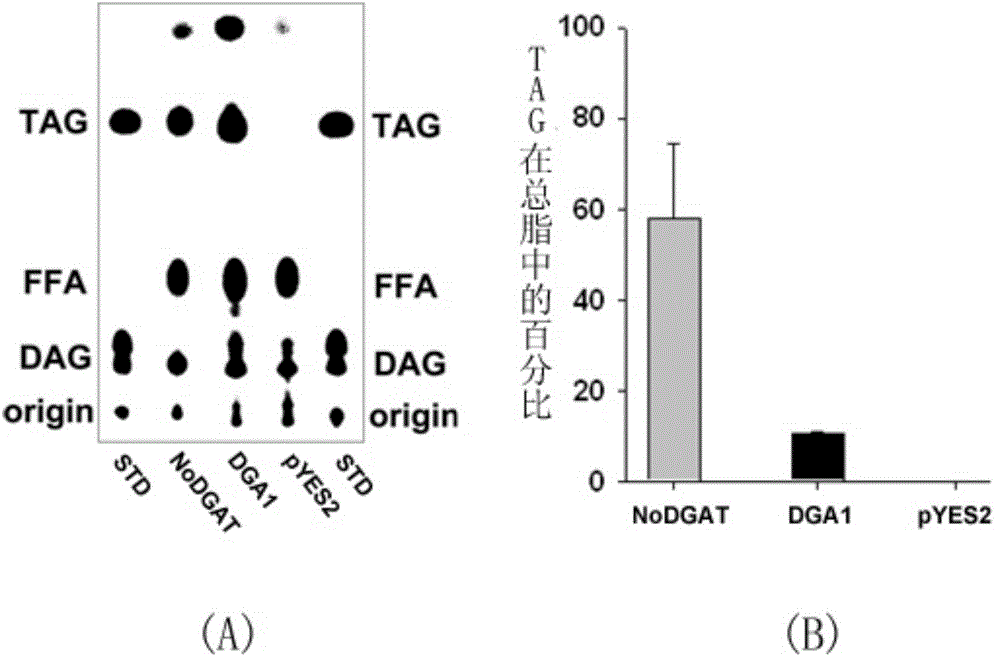
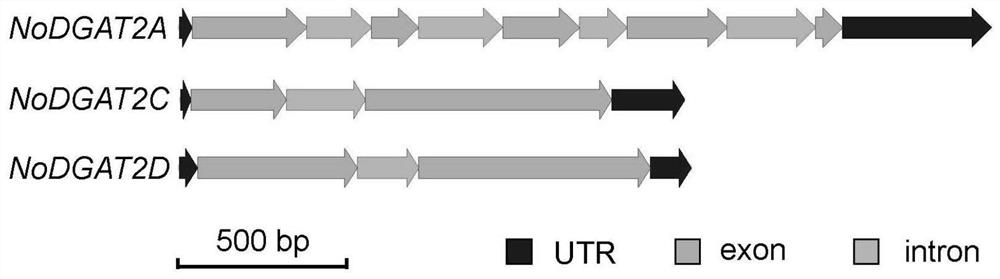
The present invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a gene having a triacylglycerol (TAG) synthesis function, and applications thereof, wherein the gene is the following nucleotide sequence: 1) the gene is base sequence represented by SEQ ID NO1; or, 2) the gene is the DNA sequence sharing more than or equal to 95% of homology with the nucleic acid sequence limited by the sequence 1 in the sequence list and encoding the same biological function protein. According to the present invention, the gene having the TAG synthesis function is the diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) gene isolated from Nannochloropsis, and has important application values in the improvement of the TAG content in the organism.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
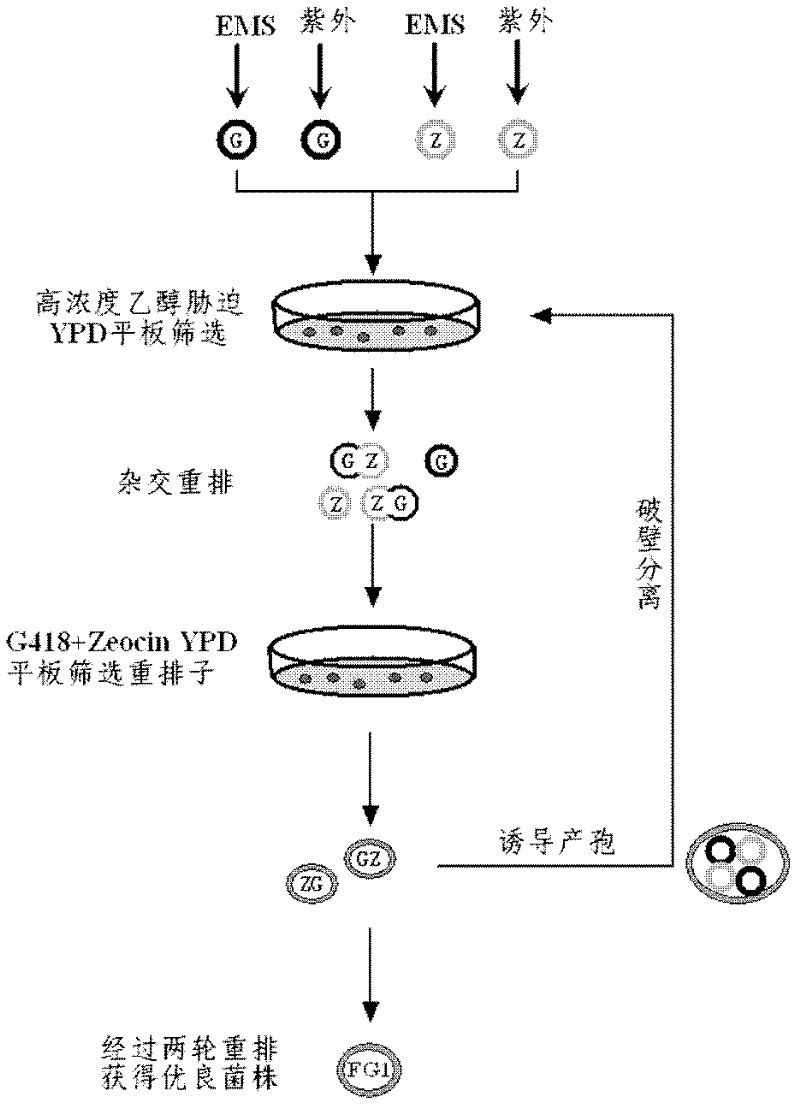
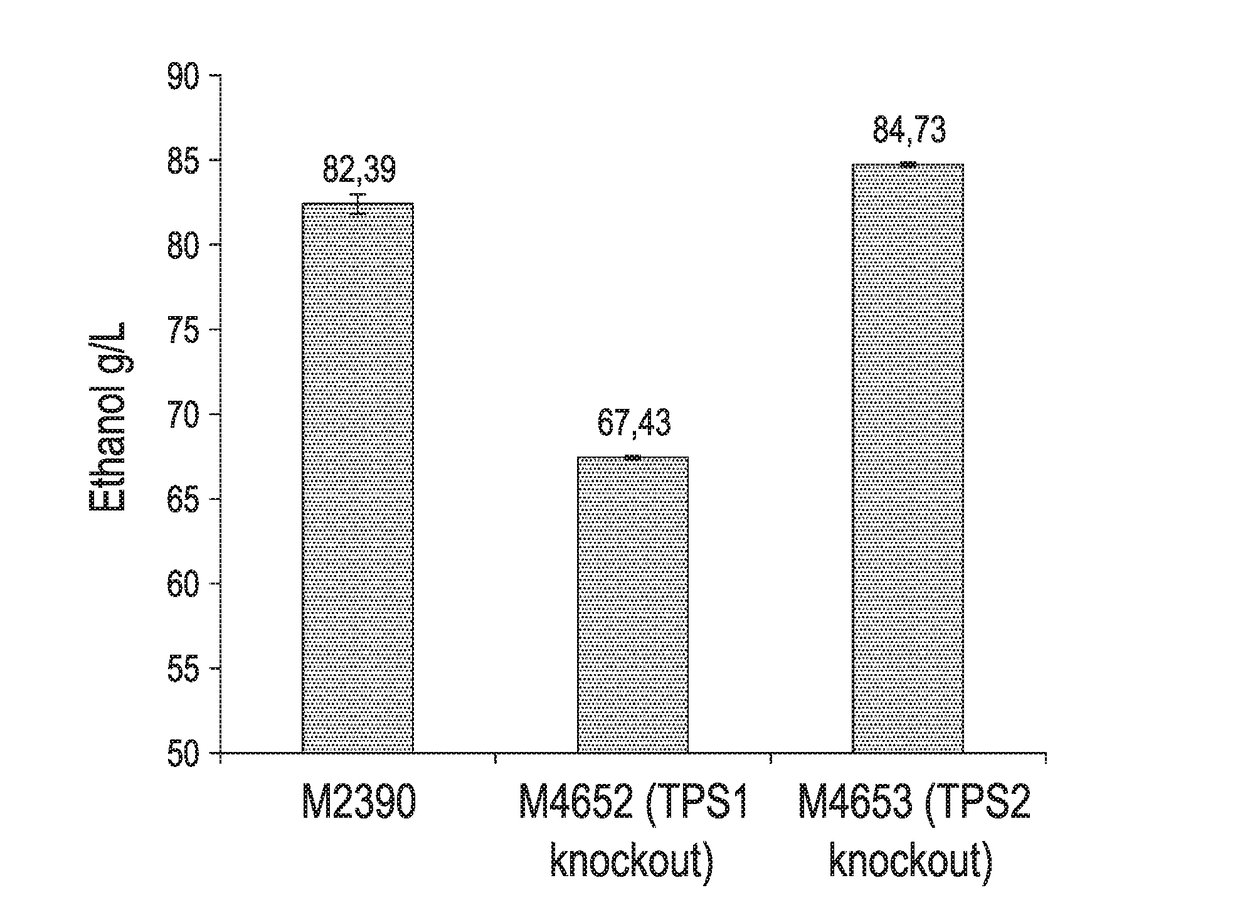
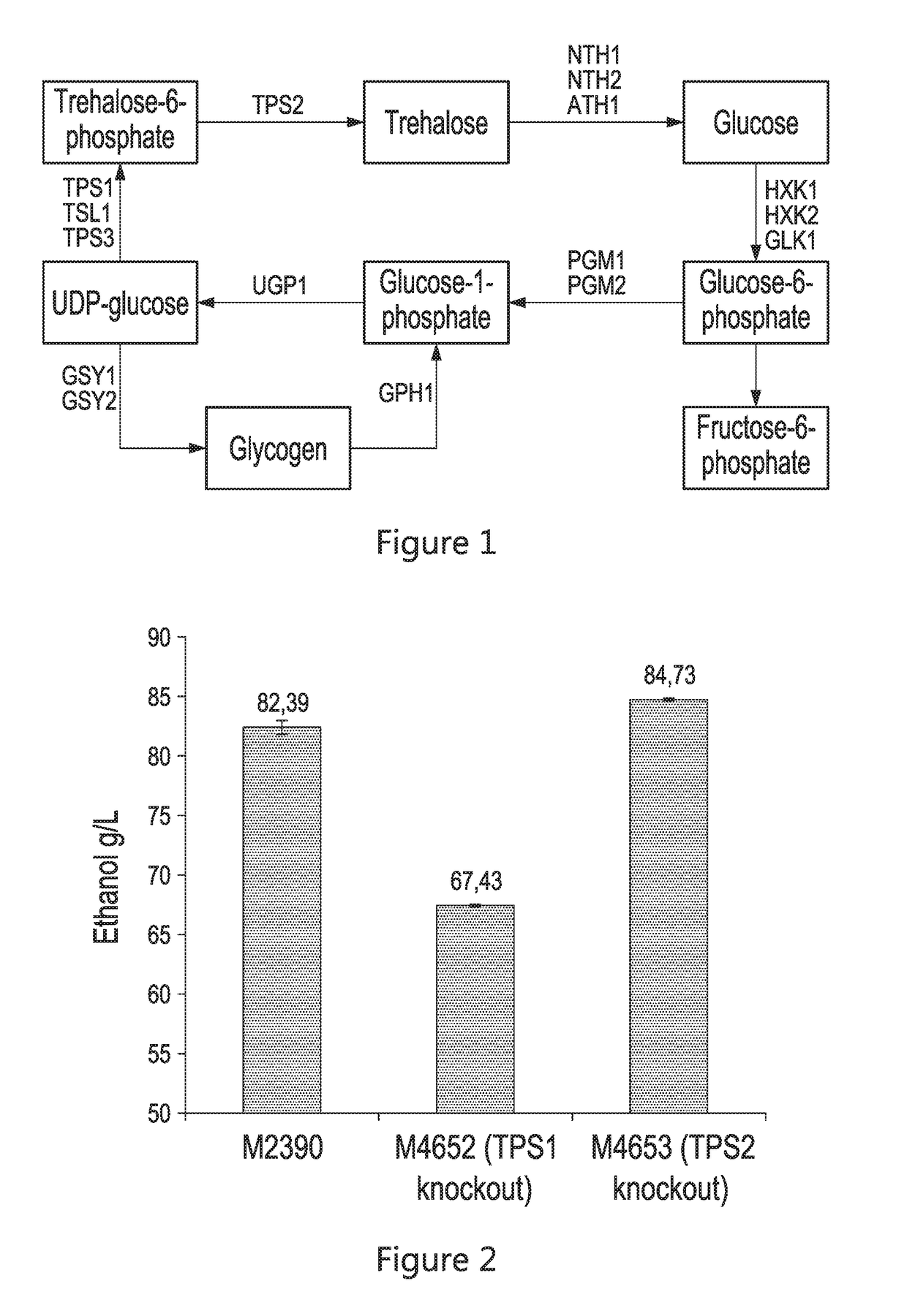
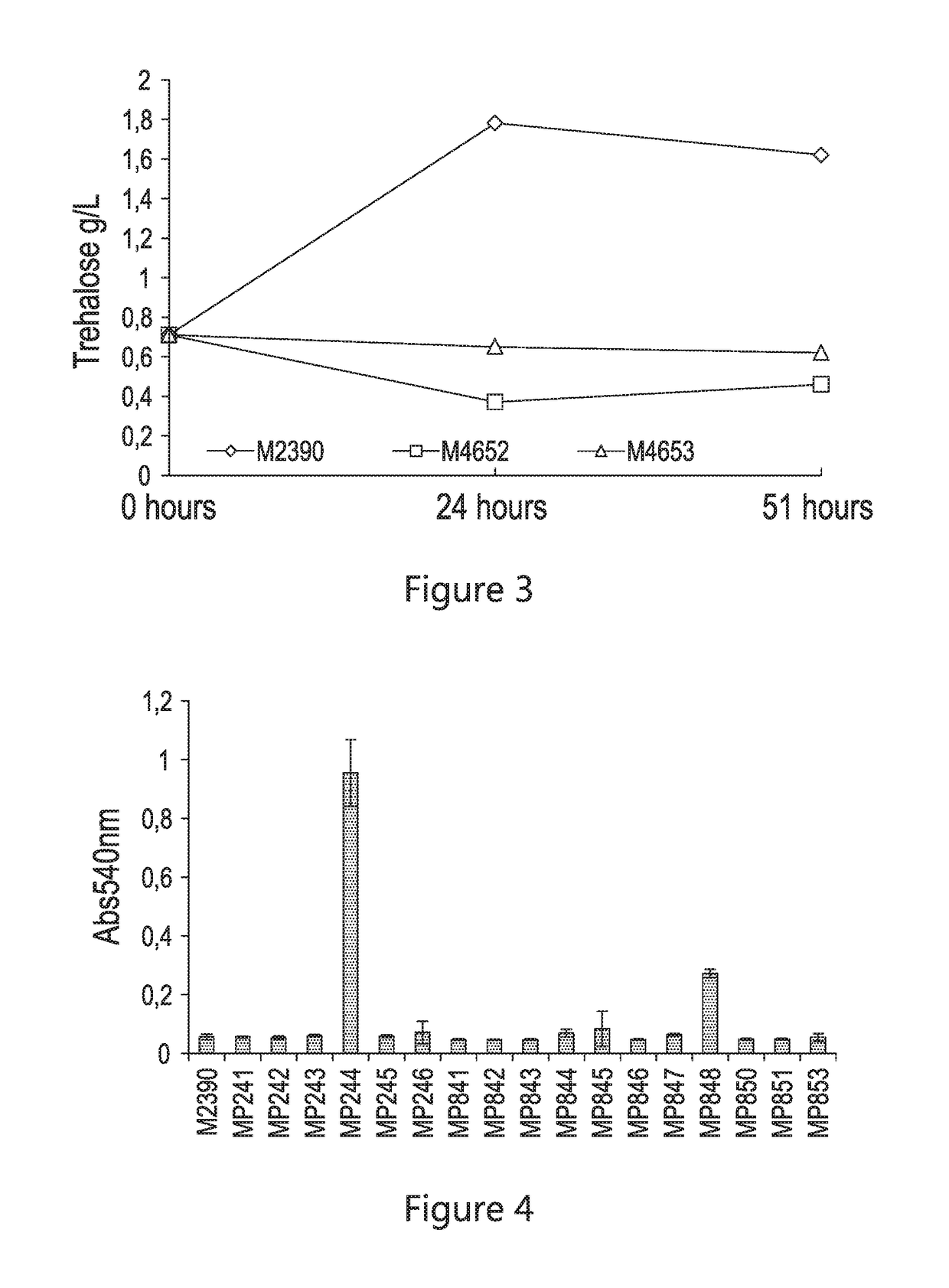
Industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with low glycerol synthesis and high alcohol tolerance and application thereof
InactiveCN102329743AImprove alcohol toleranceImprove patienceFungiMutant preparationGlycerol synthesisHigh Gravity
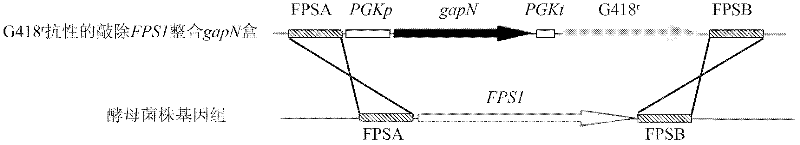
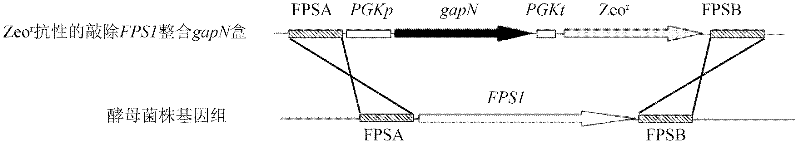
The invention provides an industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with low glycerol synthesis and high alcohol tolerance, namely Saccharomyces cerevisiae FG1. The strain was collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection in Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China, on August 1, 2011, and the collection number is CCTCC No: M2011274. The invention provides an excellent industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strain with few byproducts and high alcohol tolerance and application thereof, and a method for improving various production properties of the industrial strain, namely the combination of genetic and metabolic engineering and complete genome rearrangement. By the method, various production properties of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain such as conversion rate of sugar alcohol, tolerance, fermentation rate and the like can be improved; the improved strain can be used for fermentation production of industrial high-gravity alcohol, the energy consumption is reduced, and the production cost is reduced; and the method can also be used for improving the properties of other industrial microorganisms.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Limiting yeast-produced trehalose in fermentation
The present disclosure relates to recombinant yeast host cells having (i) a first genetic modification for reducing the production of one or more native enzymes that function to produce glycerol or regulating glycerol synthesis and / or allowing the production of an heterologous glucoamylase and (ii) a second genetic modification for reducing the production of one or more native enzymes that function to produce trehalose or regulating trehalose synthesis and / or allowing the expression of an heterologous trehalase. The recombinant yeast host cells can be used to limit the production of (yeast-produced) trehalose (particularly extracellular trehalose) during fermentation and, in some embodiments, can increase the production of a fermentation product (such as, for example, ethanol).
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Traditional Chinese medicine for treating rhagadia
InactiveCN102940678AIncreased secretion of hormonesGood solvent propertiesDermatological disorderPlant ingredientsMedicinal herbsSafflowers
The invention relates to traditional Chinese medicines and particularly relates to a traditional Chinese medicine for treating rhagadia. The traditional Chinese medicine is characterized by being prepared from the following medicinal materials: 350 g of angelica, 350 g of safflower and 350 g of fresh licorice, or 350 g of angelica, 350 g of safflower, 350 g of fresh licorice, 100 g of white vinegar prepared by brewing with pure grains, and 20 g of hydrous glycerol; and glycerol vinegar is synthesized by the 100g of white vinegar, prepared by brewing with pure grains, and the 20g of hydrous glycerol and is used for external painting. According to the traditional Chinese medicine for treating the rhagadia, provided by the invention, the problem of rhagadia caused by reasons is solved, the preparation method is simple, and the traditional Chinese medicine is mainly used for treating the rhagadia of hands and feet caused by various reasons, can directly enter a nidus, and is easily operated.
Owner:XIAN FUAN INNOVATION CONSULTATION
Method for synthesizing glycerol carbonate from glycerol
InactiveCN102952110AImprove conversion rateLess impuritiesOrganic chemistryO-Phosphoric AcidPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing glycerol carbonate, wherein glycerol and urea are used as raw materials and lewis acid salt is used as a catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding the glycerol, the urea and sodium sulfate into a four-mouth bottle provided with a condensing pipe, a stirrer, a thermometer and a point thermometer; heating to a molten material of 100 DEG C and keeping the vacuum degree at 0.3 KPa; reacting for 5-8 hours at the temperature of 100-180 DEG C under the condition of high-speed stirring; removing a small amount of solid impurity from a product through vacuum filtration to obtain rough glycerol carbonate; removing the glycerol from the rough glycerol carbonate through vacuum distillation to obtain glycerol carbonate with higher purity; and neutralizing and removing ammonia gas produced in the reaction process through a rotary vane oil pump and an absorption bottle filled with diluted phosphoric acid so as to improve the conversion rate of the glycerol. The method has the advantages of capability of improving the conversion rate of the glycerol, non-toxic reaction raw materials, high conversion rate of the glycerol, less impurity, simple process, easiness in subsequent separation and purification and capability of recycling the separated glycerol.
Owner:PANJIN KELONG FINE CHEM
Glycerol-3- phosphoric desaturase gene relating with glycerol synthesis and uses thereof
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
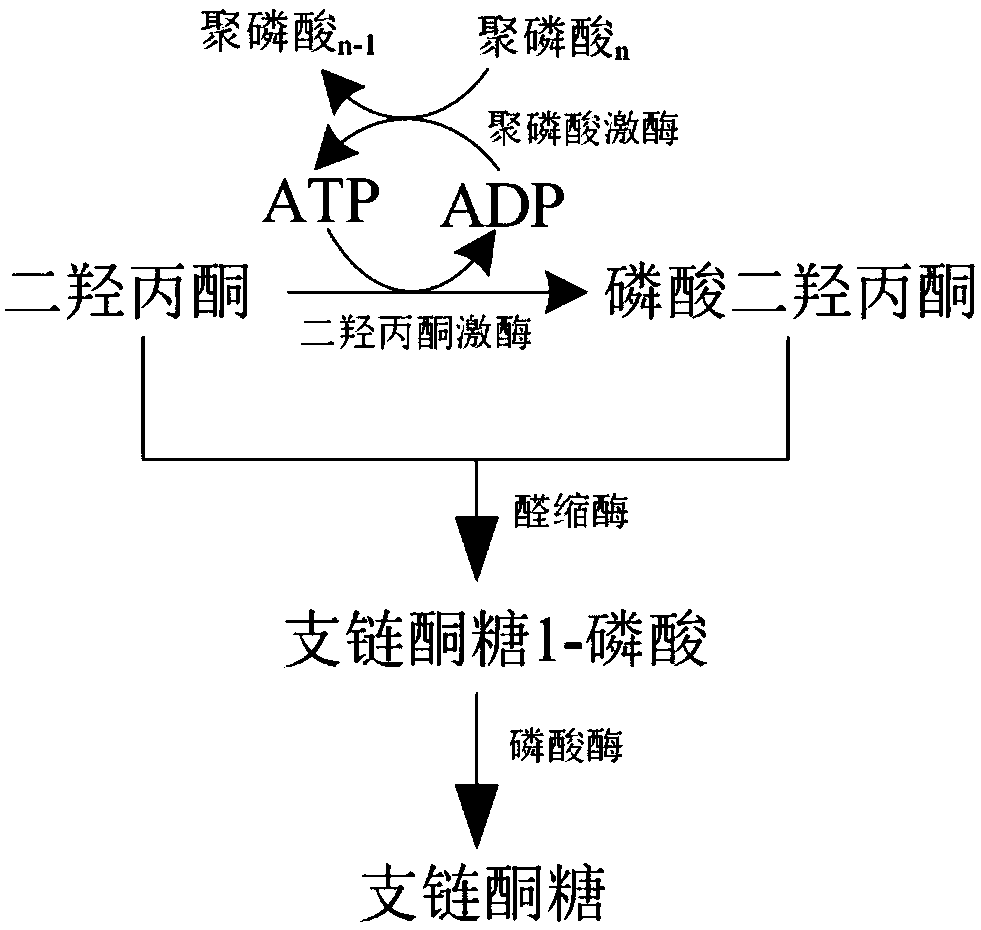
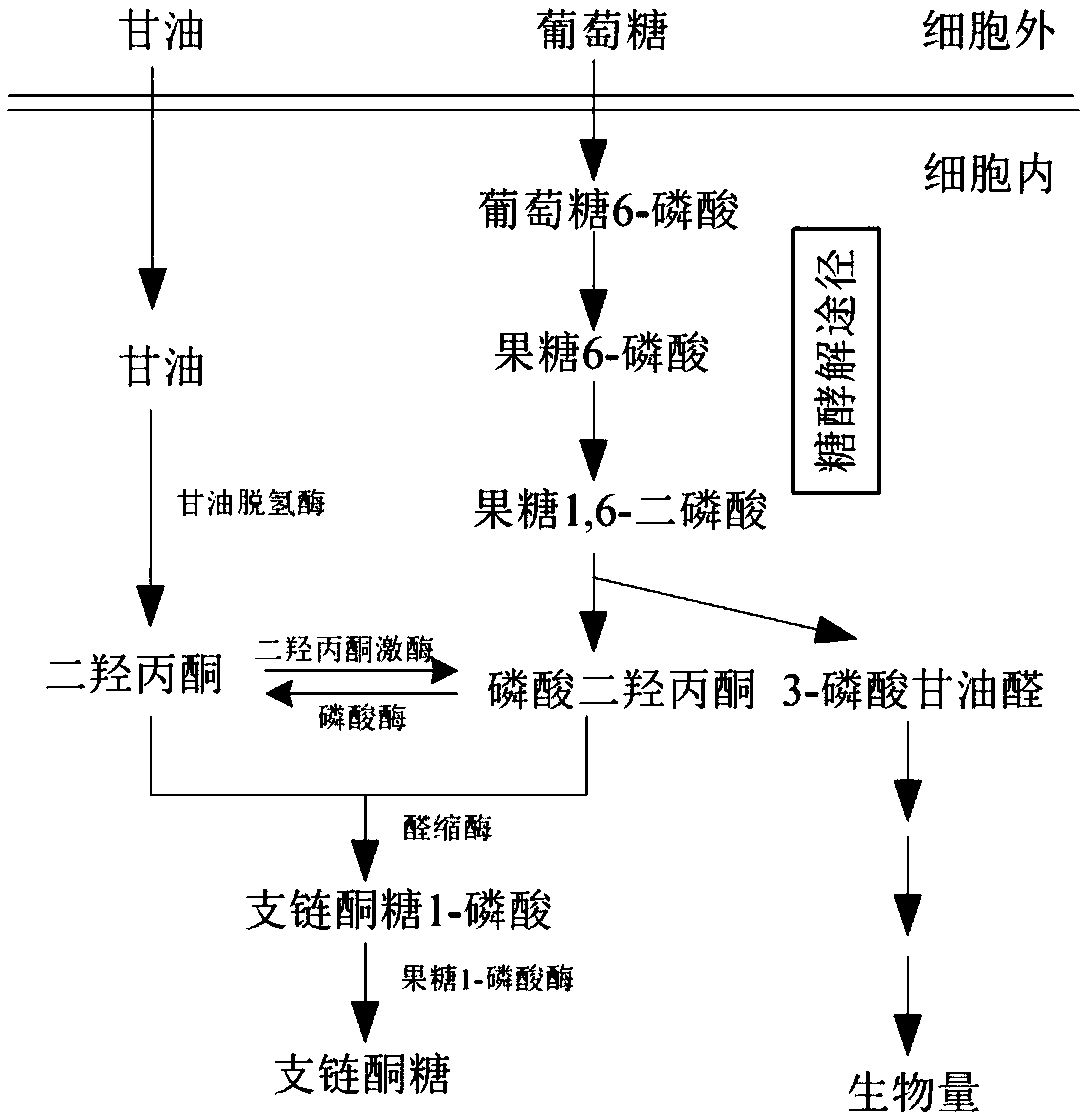
Biological synthesis method of branched ketose
The invention discloses a branched ketose method. According to the invention, the new function of known aldolase is provided, wherein the aldolase can catalyze an aldol condensation reaction between dihydroxyacetone phosphate and dihydroxyacetone to synthesize branched ketose, so that the invention discloses a method for synthesizing branched ketose by constructing an in-vitro multi-enzyme cascadereaction system to catalyze dihydroxyacetone on the basis, and the conversion rate is 90%; the invention also discloses a construction method of a corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing branched ketose, wherein the branched ketose is synthesized by fermenting a cheap substrate glucose or glycerol with the obtained recombinant strain, and the yield reaches 36.3 g / L; and compared with the existing chemical method for synthesizing branched ketose, the branched ketose synthesis method provided by the invention has the advantages of cheap substrate, environmental friendliness,high product synthesis efficiency, single product and convenience in separation, has industrial application potential, and provides a basis for synthesis of 4-hydroxymethylfurfural.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for synthesis of acrolein from glycerol
InactiveUS8143454B2Increase partial pressureHigh yieldCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationAcroleinMedicinal chemistry
The invention provides a technology for producing acrolein from glycerol while maintaining high reagent partial pressures, which leads to higher yield. The invention more particularly relates to a method for producing acrolein from glycerol that comprises the intermediate step of forming glycerol and acrolein cyclic acetals.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Preparation method and application of bacilli for efficiently metabolizing glycerol
ActiveCN108588108AIncrease metabolic rateIncrease consumption rateStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisGlycerol
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and microorganism, and particularly relates to a preparation method and application of bacilli for efficiently metabolizing glycerol. According to the method, a molecular biology technology is used; a transcription inhibition factor gene ccpC is knocked out in bacillus licheniformis to obtain a bacillus licheniformis engineering strain WX-02 delta ccpC with the ccpC being deleted, and the glycerol metabolizing speed of the bacillus licheniformis is obviously improved. The glycerol consumption speed of the WX-02 delta ccpC in different culture mediums is at least improved by 18.38 percent through being compared with that of an original bacterium of the bacillus licheniformis; the improvement value can reach 32.67 percent tothe highest degree. When the strain is used in a poly gamma-glutamic acid fermentation culture medium, the yield of the poly gamma-glutamic acid can be obviously improved and is at least improved by10.7 percent; the improvement value can reach 17.4 percent to the highest degree. The result shows that the genetic engineering transformation method has important effect on improving the glycerol metabolizing effect; the efficiency of synthesizing bio-based chemicals by the glycerol is improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Gene with triacylglycerol synthesis function and application of gene in rational regulation of content or saturation degree of oil-producing microalgae triacylglycerol
The invention belongs to the biological technical field, and relates to a gene with a triacylglycerol (TAG) synthesis function and the application of the gene in increase of the TAG content and rational regulation of the saturation degree of microalgae TAG. The gene is a base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO 1, a base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO 2 or a base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO 3, and aDNA sequence which is homologous with the base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO 1, the base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO 2 or the base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO 3 by 95 percent or above and encodes identical biological functional protein. The gene disclosed by the invention comprises three DGAT (diacylglycerol acyltransferase) genes separated from nannochloropsis. The obtained gene is used for rationally regulating the content and the saturation degree of TAG. Biodiesel, a health care product, a medicine and the like have demands for saturation degree of intracellular triglyceride to different extents.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Catalyst for synthesizing glycerol carbonate from glycerol, method for producing the catalyst and method for synthesizing glycerol carbonate from glycerol using the catalyst
ActiveUS8921261B2Activity economicEconomic efficiencyOrganic chemistryCatalyst activation/preparationGlycerolNitrogen
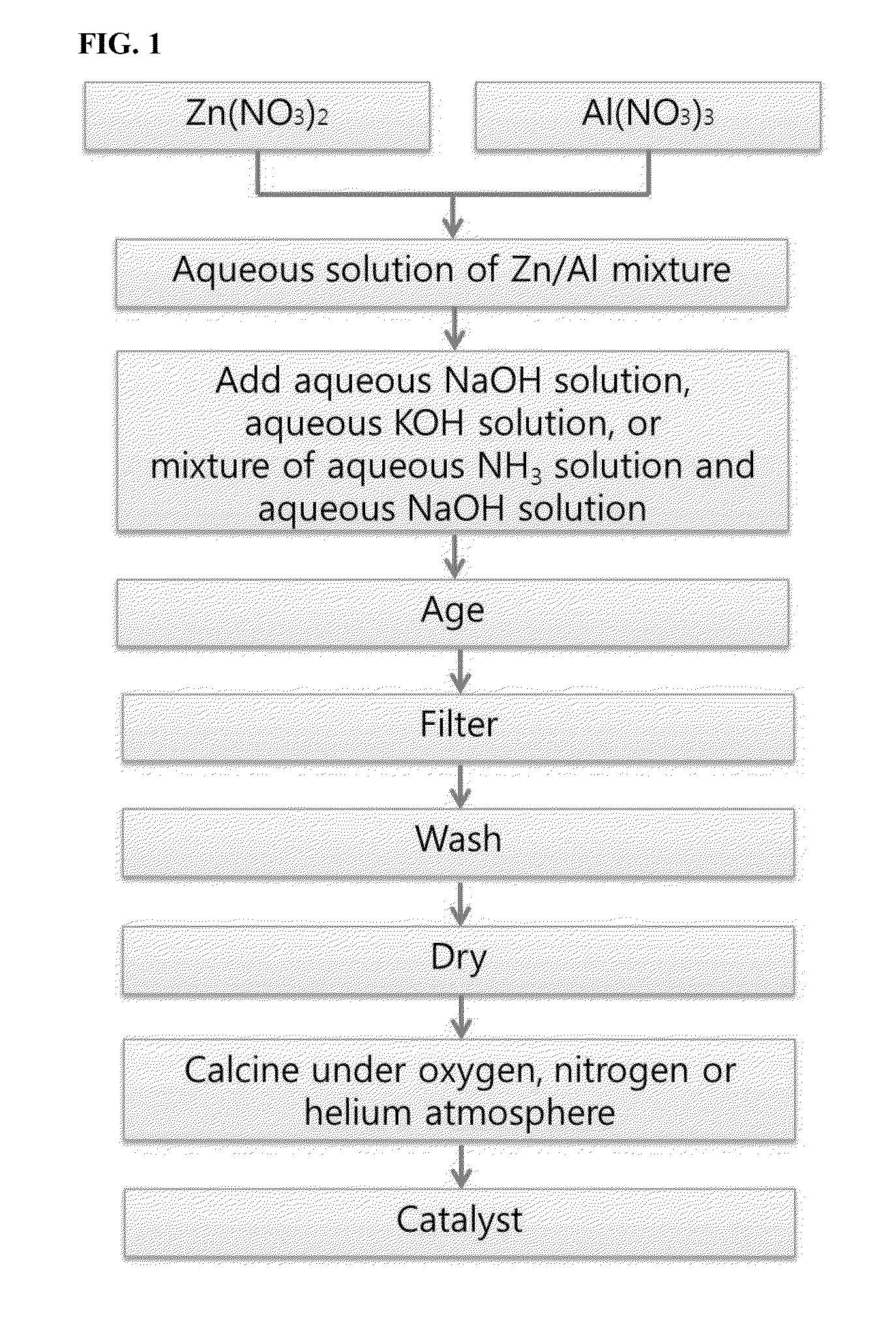
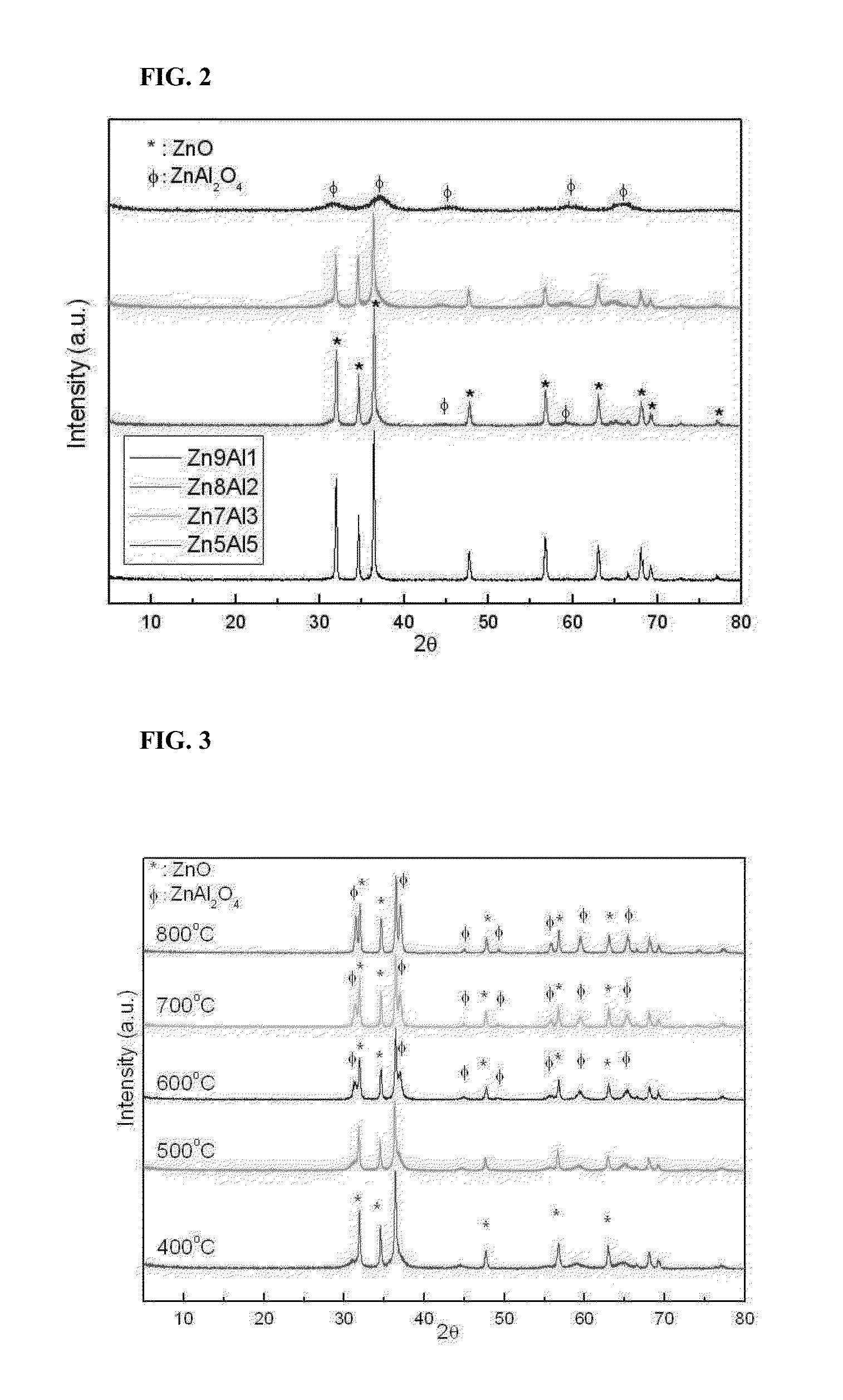
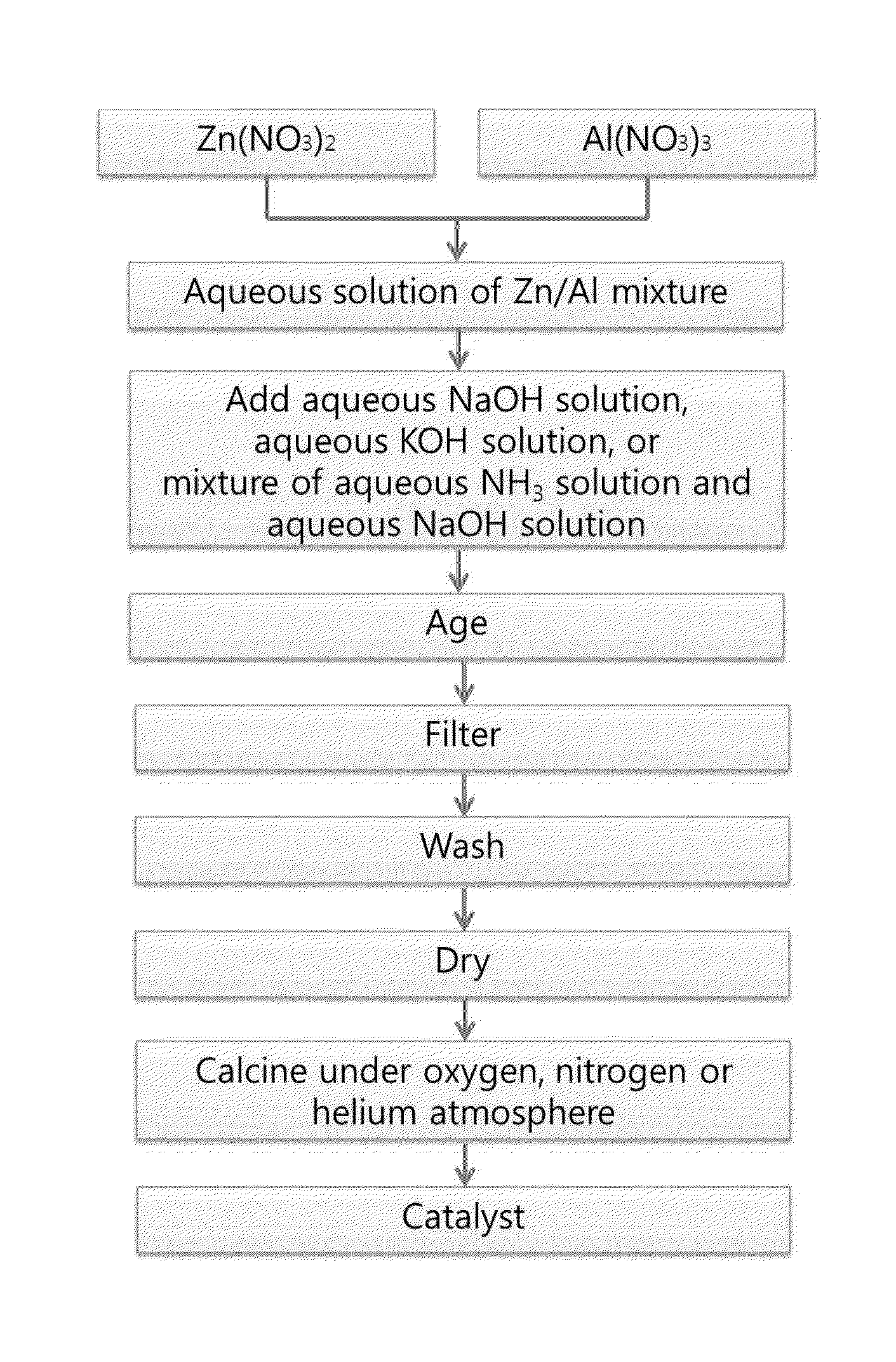
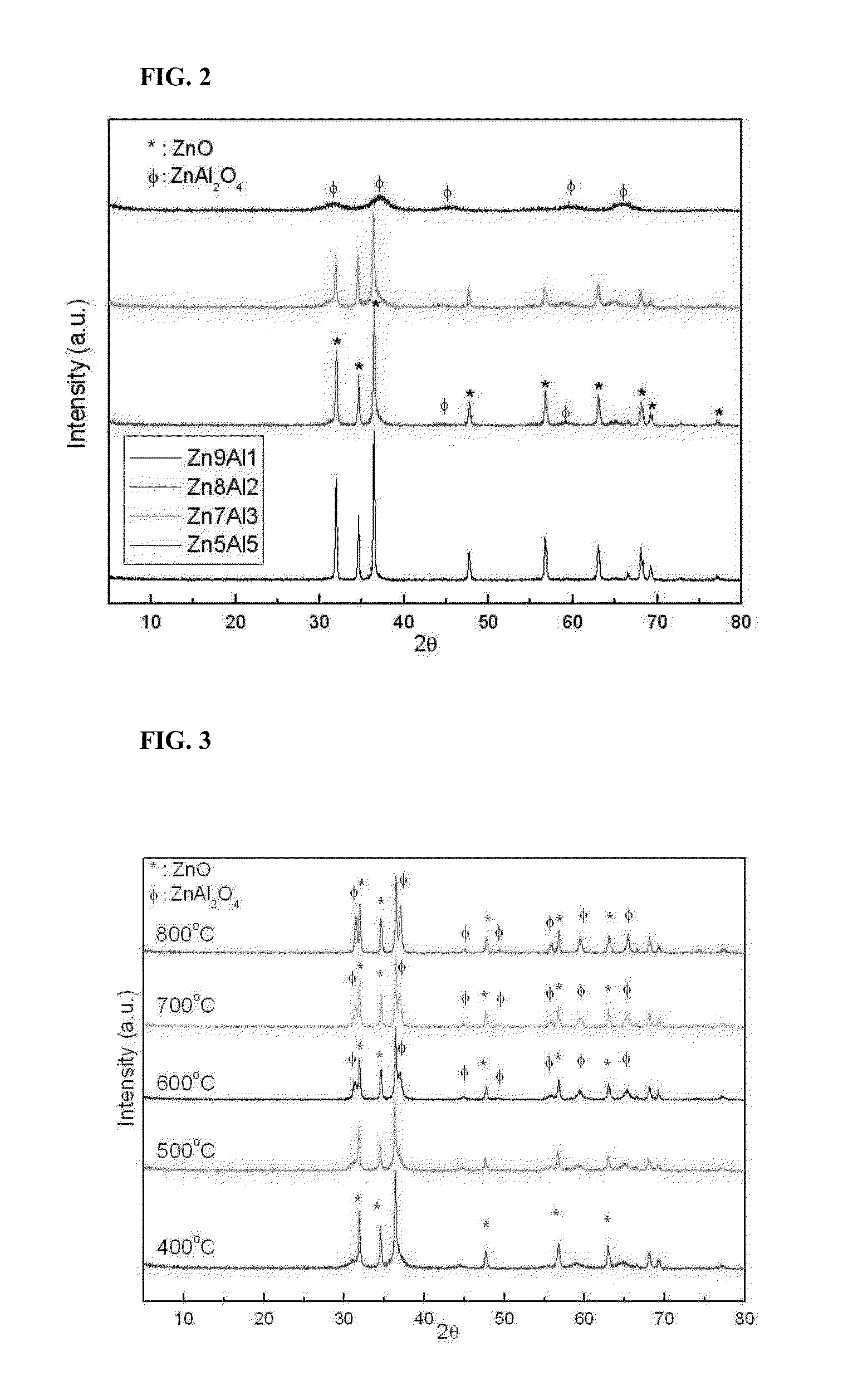
Disclosed are a catalyst for synthesizing glycerol carbonate from glycerol and a method for producing the catalyst. The method includes adding an aqueous NaOH solution, an aqueous KOH solution, or a mixture of an aqueous NH4(OH) solution and an aqueous NaOH solution to an aqueous solution of a mixture of zinc nitrate and aluminum nitrate, aging the mixture, filtering and washing the aged mixture to obtain a solid, and calcining the solid under an oxygen, nitrogen or helium atmosphere. The use of the catalyst enables the synthesis of glycerol carbonate from glycerol and urea with high conversion rate, selectivity and yield. Further disclosed is a method for synthesizing glycerol carbonate from glycerol using the catalyst.
Owner:KOREA INST OF IND TECH
Catalyst for synthesizing glycerol carbonate from glycerol, method for producing the catalyst and method for synthesizing glycerol carbonate from glycerol using the catalyst
ActiveUS20130267715A1Increase conversion rateHigh yieldOrganic chemistryCatalyst activation/preparationPtru catalystZinc nitrate
Disclosed are a catalyst for synthesizing glycerol carbonate from glycerol and a method for producing the catalyst. The method includes adding an aqueous NaOH solution, an aqueous KOH solution, or a mixture of an aqueous NH4(OH) solution and an aqueous NaOH solution to an aqueous solution of a mixture of zinc nitrate and aluminum nitrate, aging the mixture, filtering and washing the aged mixture to obtain a solid, and calcining the solid under an oxygen, nitrogen or helium atmosphere. The use of the catalyst enables the synthesis of glycerol carbonate from glycerol and urea with high conversion rate, selectivity and yield. Further disclosed is a method for synthesizing glycerol carbonate from glycerol using the catalyst.
Owner:KOREA INST OF IND TECH
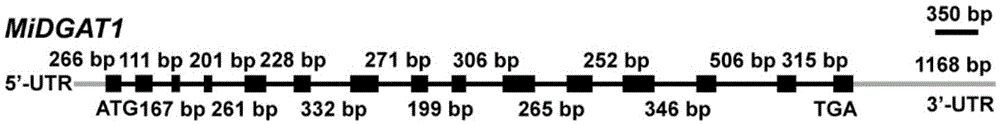
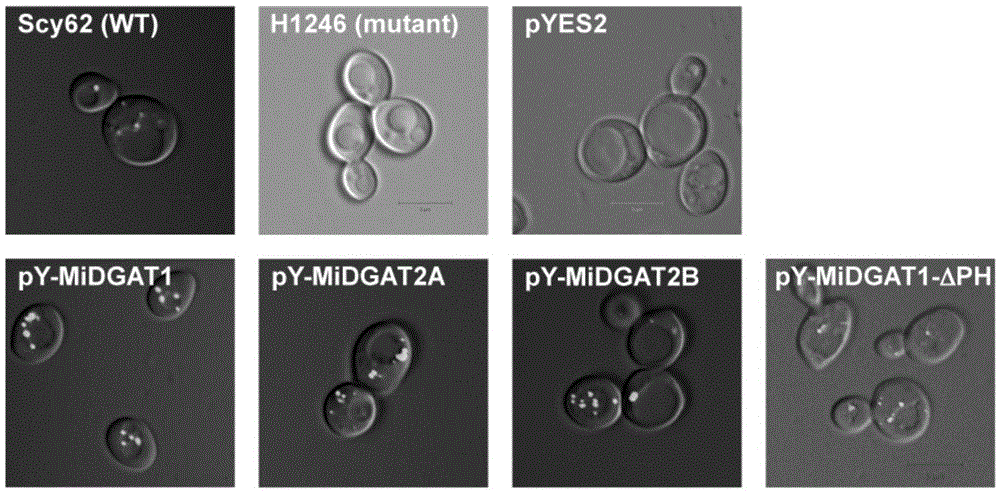
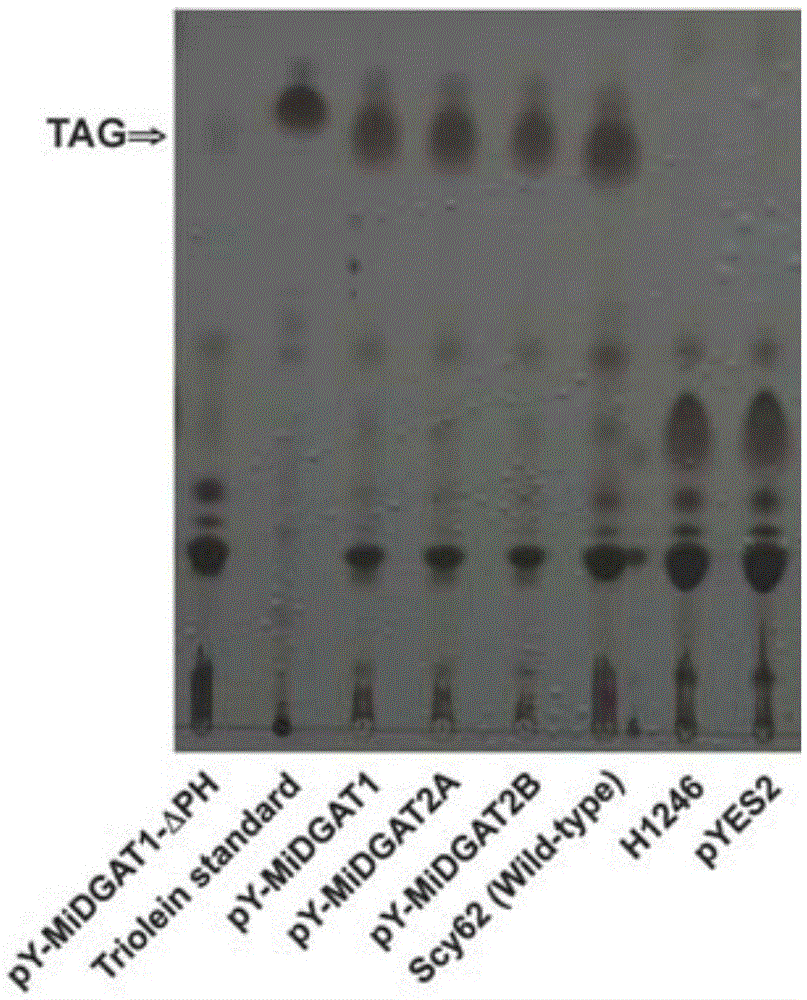
Polypeptide for improving triacylglycerol synthesizing capability of MiDGAT1 in beer yeast and application of polypeptide
ActiveCN105132391AEasy to synthesizeEnhanced ability to synthesize TAGAcyltransferasesFermentationBiologyGene
The invention relates to polypeptide for improving the triacylglycerol synthesizing capability of MiDGAT1 in beer yeast and application of the polypeptide. Particularly, a new DGAT gene is obtained through cloning and named MiDGAT1, a new PH structural domain sequence is obtained, it is found through a gene functional complementation experiment that proteins coded by MiDGAT1 and MiDGAT1-deltaPH have the TAG synthesizing capability, however, it is found through a semi-quantitative thin-layer chromatography method that the content of TAG synthesized through MiDGAT1 yeast is much higher than that synthesized through MiDGAT1-deltaPH yeast, and therefore it is proved that the PH structural domain sequence can improve the capability of the MiDGAT1 in synthesizing the TAG in the yeast, and the improving function of the PH structural domain sequence is obviously higher than that of a PH structural domain sequence in the prior art. Accordingly, MiDGAT1 containing a PH structural domain can be expressed in crops such as oilseeds to obviously increase the yield of triacylglycerol.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Gene producing glycerin candida NAD+ depending- glycerin3- glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and clone thereof
InactiveCN101157931AExpand genetic resourcesImprove stress resistanceOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringOpen reading framePhosphate
Glycerol fermentation by candida glycerinogenes NAD+ depends on glycerine-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and clone thereof and pertains to the microorganism molecular biology field. The invention relates to a new gene order SEQID NO.1. a degenerate primer PCR method and a reverse PCR method are adopted to clone rate-limiting enzyme NAD+ depending glycerine-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and lateral regulation sequence thereof from genome DNA of glycerine-producing candida mycoderma WL2002-5-59 which is produced by glycerine. The total length of the gene is 4900bp and a start codon ATG is at 2082bp while a stop codon TAA is at 3246bp. The sequence has no intron but has an 1167bp complete open reading frame which encodes 388 amino acids. The gene has homology as high as 60 percent with saccharomyces cerevisia GPD1 gene and 70 percent with Angus pichia yeast GPD gene. The clone of the gene expands gene resource of microorganism anti-osmotic pressure stress research and lays a foundation for research on molecular mechanism of glycerine-producing candida mycoderma producing glycerine with high yield.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
High-purity tripolyglycerol monolaurate and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111233637ALarge scale preparationEfficient preparationAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsFood additivePolyester
The invention provides high-purity tripolyglycerol monolaurate and a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of food biology. The preparation method comprises four steps of polyglycerol synthesis, tripolyglycerol purification, tripolyglycerol laurate synthesis and tripolyglycerol monolaurate purification. According to the method provided by the invention, lipase 435 is used as a catalyst, tripolyglycerol and lauric acid are used as raw materials to synthesize tripolyglycerol monolaurate, molecular distillation and ethyl acetate / water extraction methods are combined, tripolyglycerol polyesters are firstly removed, and then tripolyglycerol is separated, so that large-scale rapid preparation of high-purity tripolyglycerol monolaurate is realized. The method provided by the invention realizes efficient, low-toxicity, rapid and high-purity large-scale preparation of the multifunctional food additive tripolyglycerol monolaurate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION
Polyglycerol-10 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107235830AHigh purityEase of industrial productionEther separation/purificationEther preparation from oxiranesDistillationGlycerol
The invention relates to the field of polyglycerol synthesis, in particular to polyglycerol-10 and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of polyglycerol-10 comprises the following steps: (1) a crude polyglycerol product is prepared from glycerol and glycidol through a polymerization reaction in presence of an acid catalyst; (2) the polymerization reaction product is neutralized, a neutralization product is distilled by molecular distillation equipment, and the obtained heavy constituent is polyglycerol-10, wherein the heavy constituent condensing surface set by the molecular distillation equipment is at the temperature of 85 DEG C or higher, the light constituent condensing surface is at the temperature of 65-90 DEG C, and the heavy constituent condensing surface is higher than the light constituent condensing surface. With adoption of the method, the polyglycerol-10 product with higher purity is prepared with high yield by means of molecular distillation, and the method is beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:GUANGDONG HEJI BIOTECH CO LTD
Fermentative glycerol-free ethanol production
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Catalyst for the production of acrylic acid from glycerol
ActiveCN109304163BOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A microalgal triacylglycerol synthesis regulation gene and its application
InactiveCN103589737BReduced neutral fat contentIncreased neutral fat contentMicroorganism based processesAlgae/lichens peptidesChlamydomonas reinhardtiiNucleotide
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Pseudomonas putida enolase gene cloning method and application
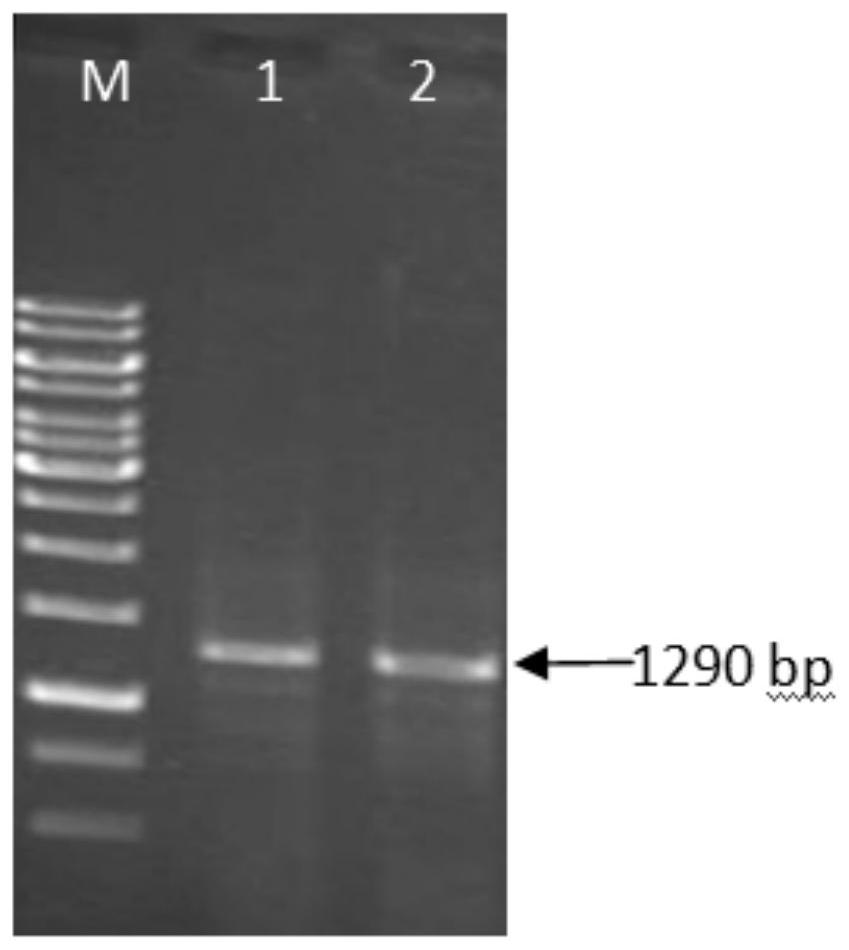
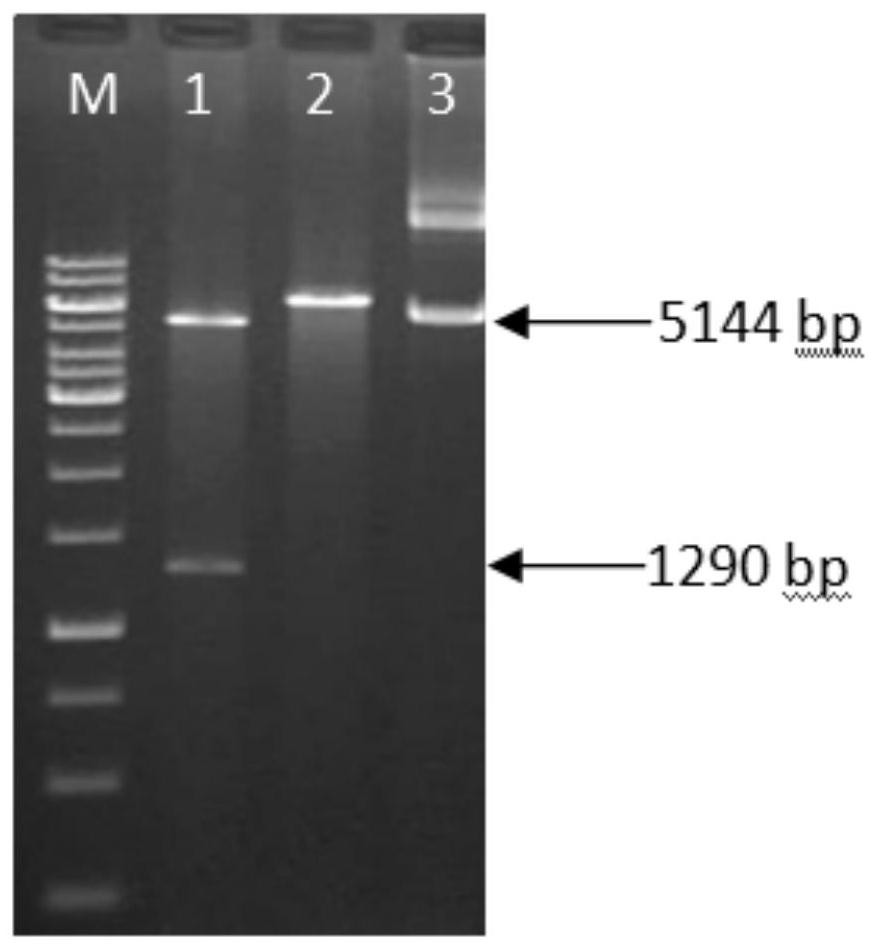
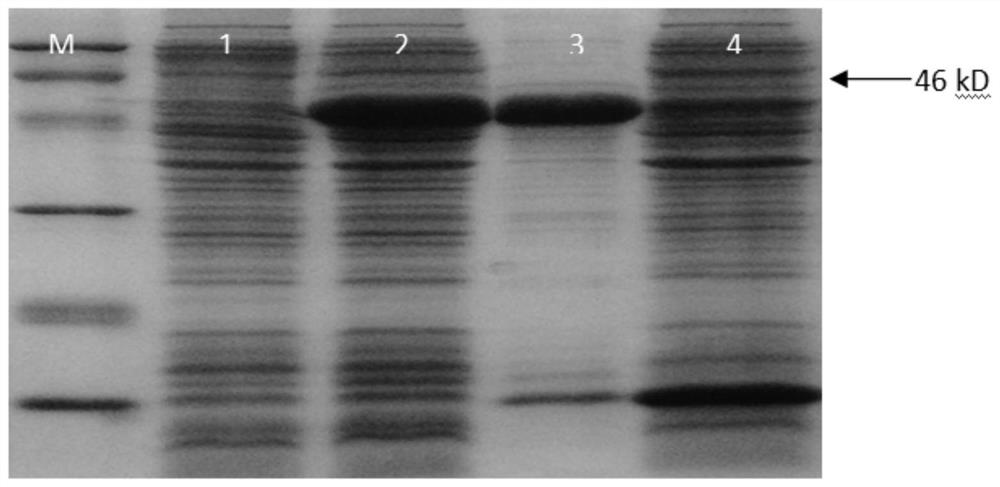
The invention discloses a pseudomonas putida enol enzyme gene cloning method and application. In order to solve the problem that PHA synthase is relatively weak in tolerance in crude glycerol, a primer is added from a pseudomonas putida enol enzyme genome for successful amplification to obtain a 1290bp fragment, a vector pET28a-Eno is successfully constructed through enzyme digestion connection, and after enzyme digestion and sequencing verification are correct, the vector pET28a-Eno is transformed into escherichia coli BL21 to obtain expression recombinant bacteria. The concentration and temperature of IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside) under two conditions of induced expression of recombinant bacteria are optimized, so that the Eno inclusion body successfully expresses a large amount of soluble expression. The method has important significance for synthesizing the PHA by using the biodiesel byproduct glycerol with low price, solving the environmental problem caused by excessive accumulation of the biodiesel byproduct and reducing the production cost of the PHA.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Genes with triacylglycerol synthesis function and their application in rational regulation of triacylglycerol content or saturation in oleaginous microalgae
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing acrylic acid from glycerin
ActiveCN109304162BOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
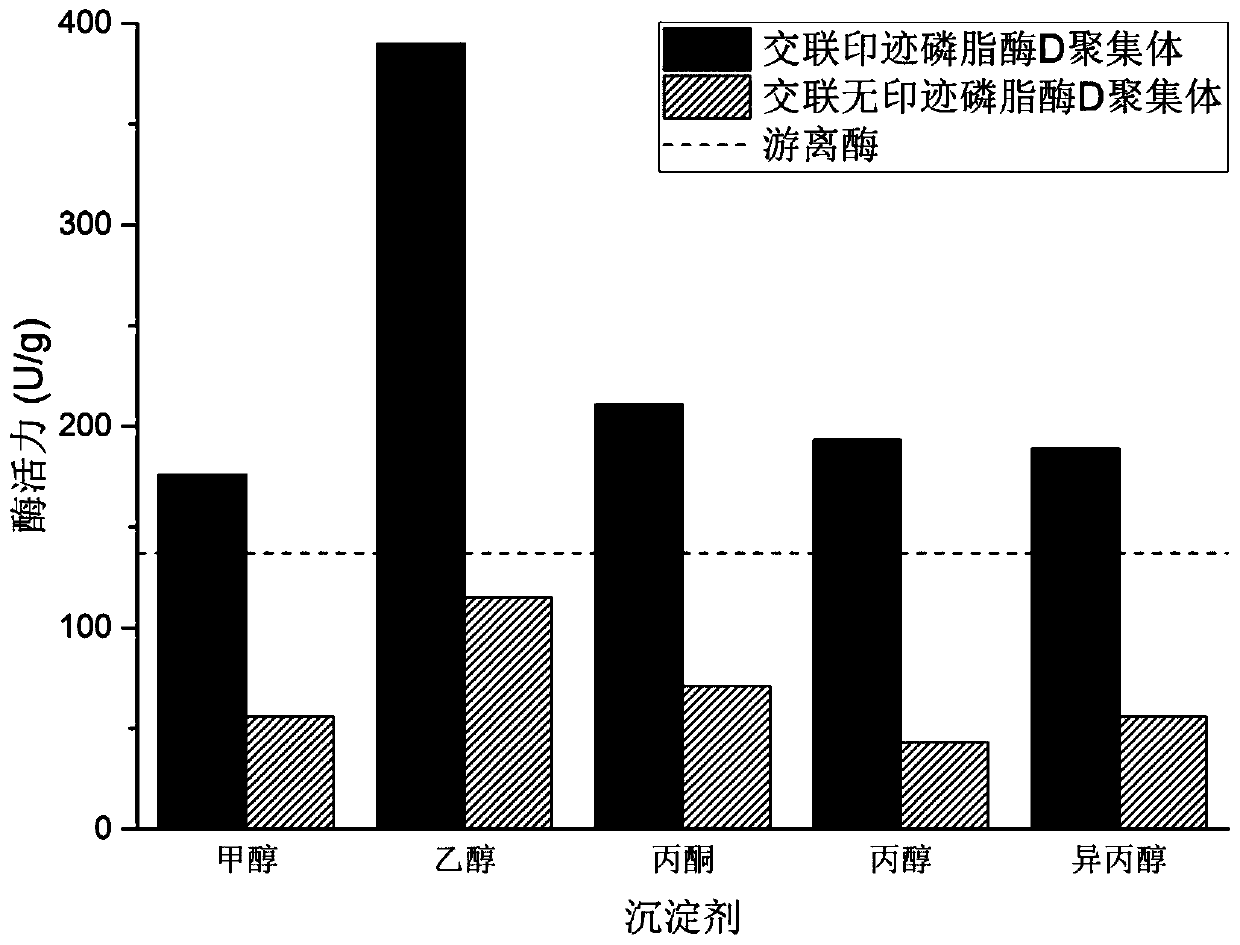
A method for immobilizing phospholipase d to improve the activity of phosphatidylglycerol synthesis
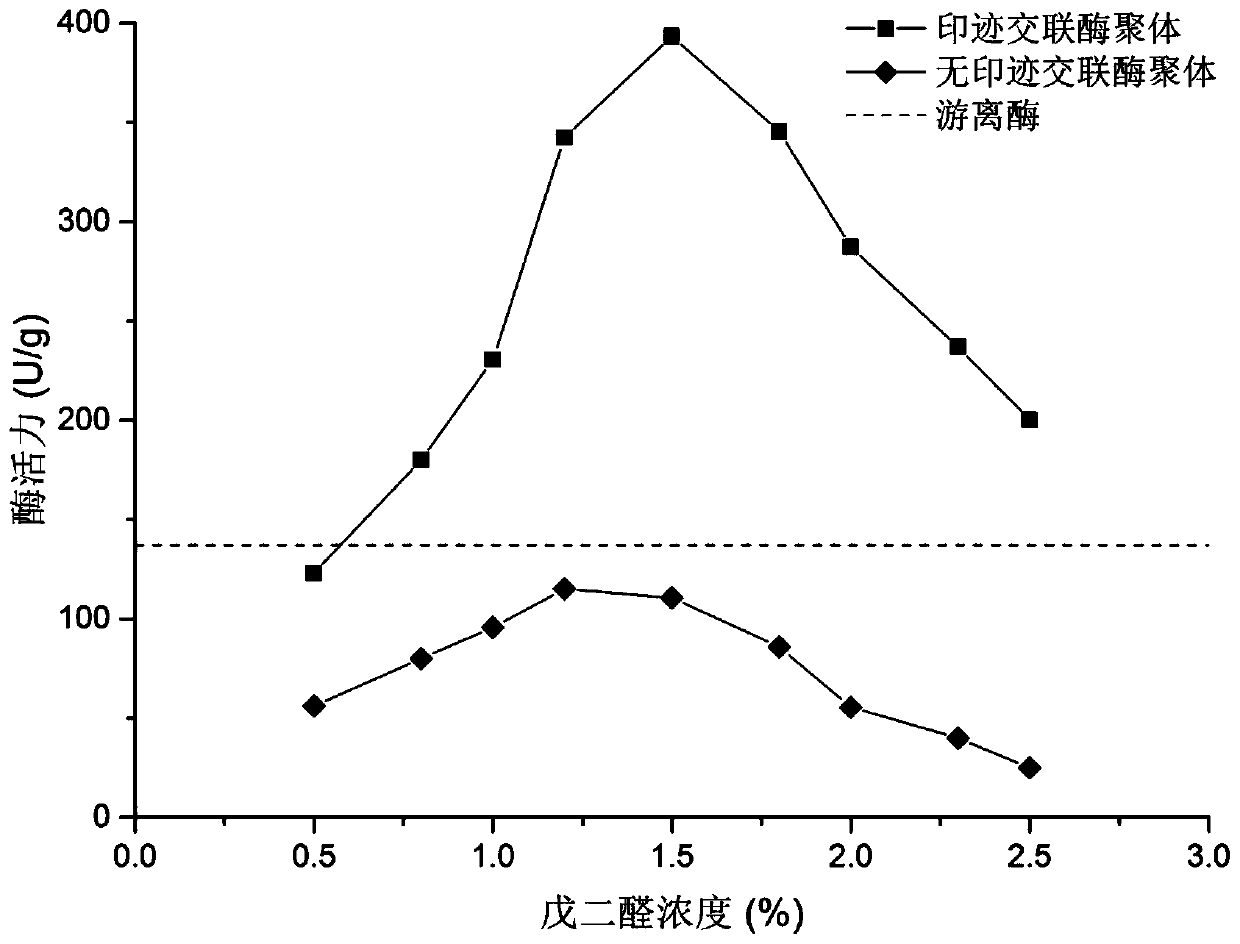
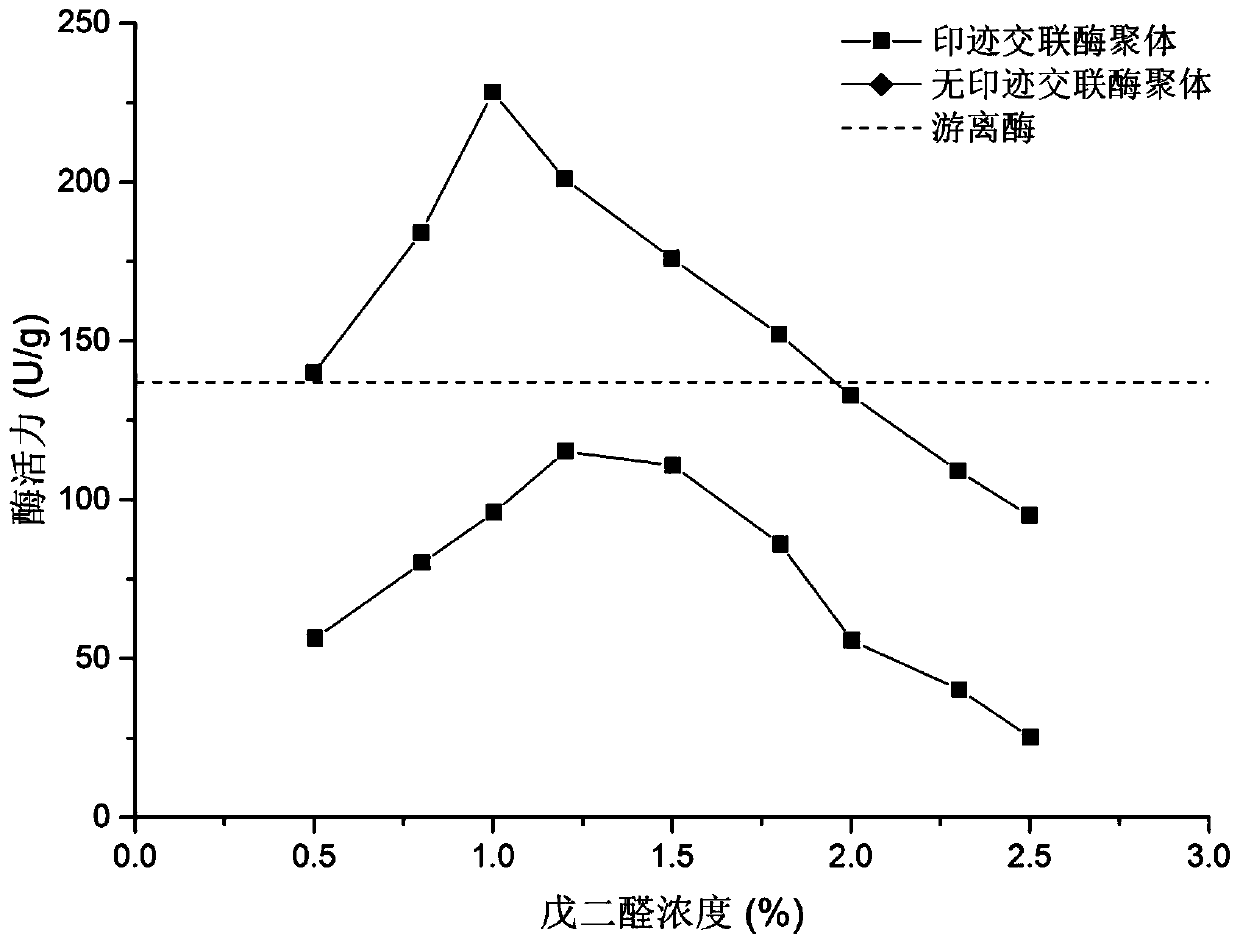
ActiveCN106947753BPersistence of imprinted featuresIncrease enzyme activityHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierPhosphatidylglycerol synthesisPhospholipin
The invention provides a method for immobilizing phospholipase D to improve the reaction activity of phosphatidylglycerol synthesis. The method is carried out according to the following steps: step 1, adding the imprinted substrate to the phospholipase D solution for coordination to obtain the enzyme-substrate Complex solution (imprinted enzyme); step 2, adding a precipitating agent to precipitate the enzyme-substrate complex to obtain a mixed solution containing enzyme-substrate complex aggregates; step 3, adding a water-soluble cross-linking agent to the mixed solution after precipitation Perform a cross-linking reaction to obtain cross-linked enzyme-substrate complex aggregates; step 4, wash the cross-linked enzyme-substrate complex aggregates, and obtain cross-linked imprinted phospholipase D aggregates after removing the substrate. In the method of the present invention, after the imprinting action between the phospholipase D molecule and the substrate molecule is completed, the precipitation method is used to "fossilize" the "superactivated" structure of the enzyme molecule, and then add an appropriate water-soluble cross-linking agent to carry out cross-linking of the enzyme molecule , achieving intermolecular cross-linking and intramolecular cross-linking of "superactivated" structural enzyme molecules to form cross-linked imprinted phospholipase D aggregates.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
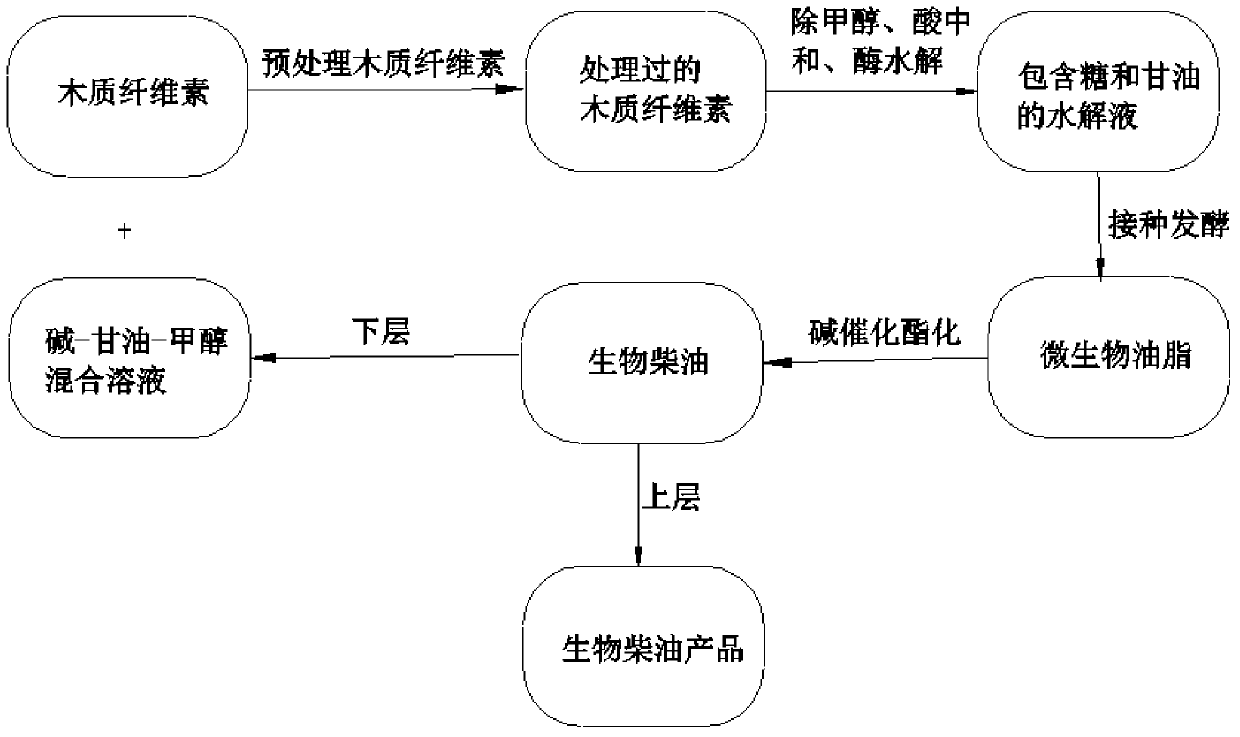
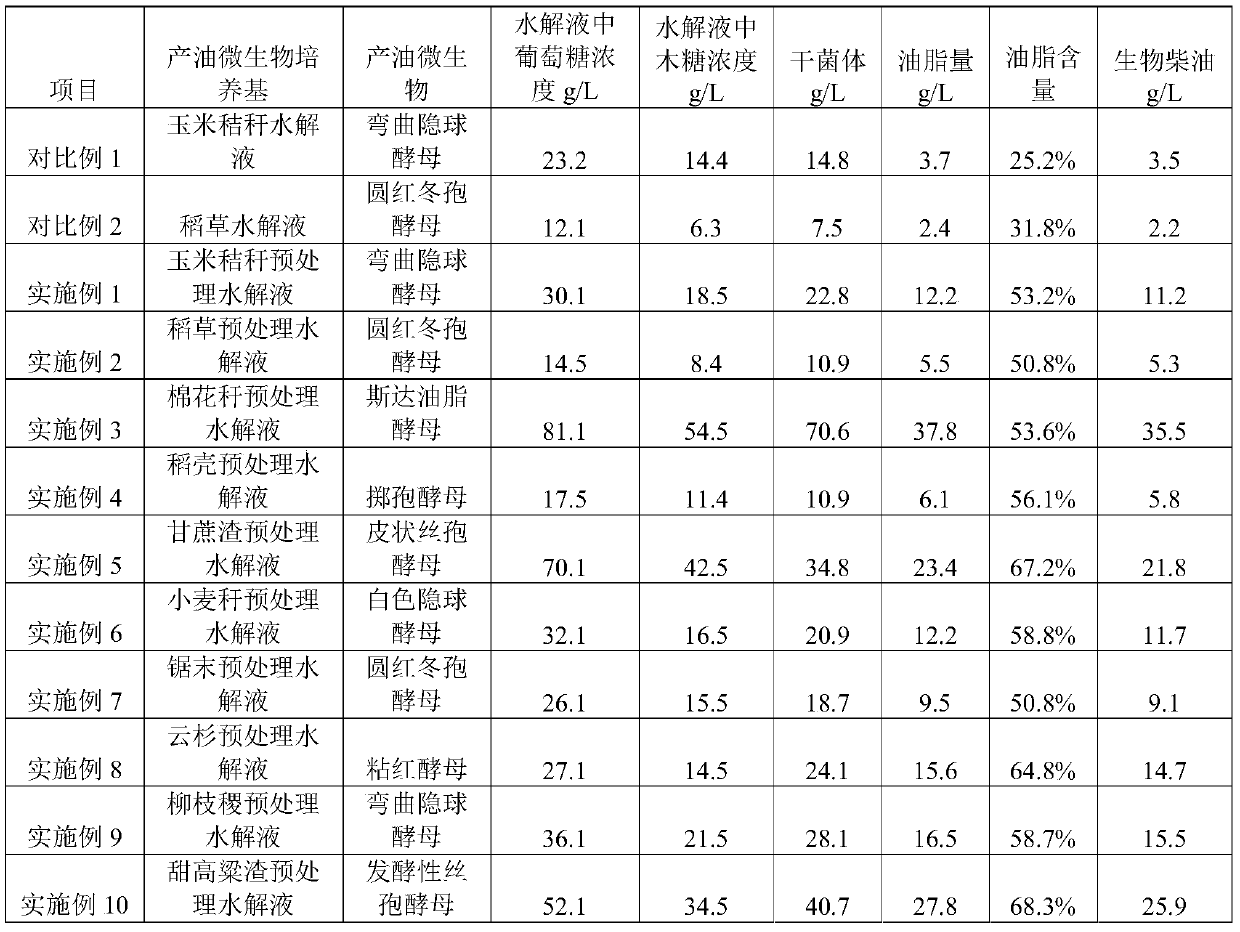
A kind of method utilizing lignocellulosic raw material to produce biodiesel
ActiveCN105695524BIncrease productionAchieve cycleFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningMicrobial oilCellulose
The invention is suitable for the field of biomass energy, and provides a method for producing biodiesel by means of a lignocellulose material. The method comprises the steps that pretreatment is conducted on the lignocellulose material through an alkali-glycerin-methanol mixed solution produced in the process that the biodiesel is prepared by conducting single-step base catalysis transesterification on microbial lipid; after in-situ evaporation is conducted on the raw material, and methanol is subjected to condensation recovery, water is added to reach the proper solid-to-liquid ratio, after acid neutralization is conducted, an appropriate number of enzymes are added for hydrolysis, solid-liquid separation is conducted, and hydrolysate is obtained; oleaginous yeast is introduced and synthesizes lipid by means of carbohydrates and glycerin in the hydrolysate; microbial thalli containing oil are collected, intracellular lipid is extracted, the biodiesel is prepared through single-step base catalysis transesterification, n-hexane is added for extraction, the biodiesel is obtained on the upper layer, the alkali-glycerin-methanol solution is obtained on the lower layer, and the alkali-glycerin-methanol solution is recycled for pretreating lignocellulose. According to the method for producing the biodiesel by means of the lignocellulose material, strong alkali, by-product glycerin and methanol are used for pretreating the lignocellulose; meanwhile, the glycerin further serves as a carbon source of oleaginous microorganisms to be subjected to in-situ integration recycling, the cost is greatly reduced, and the significant economic benefit is achieved.
Owner:江西碳金科技有限公司
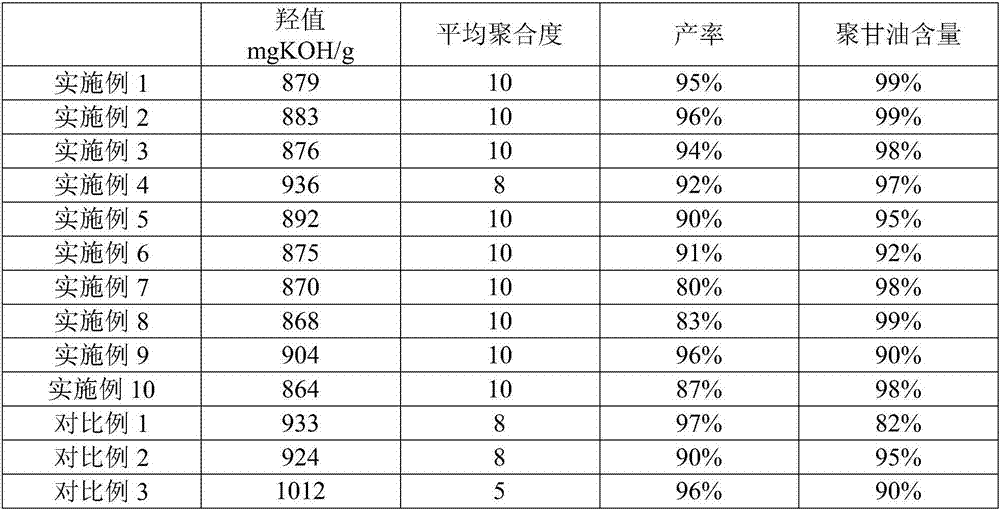
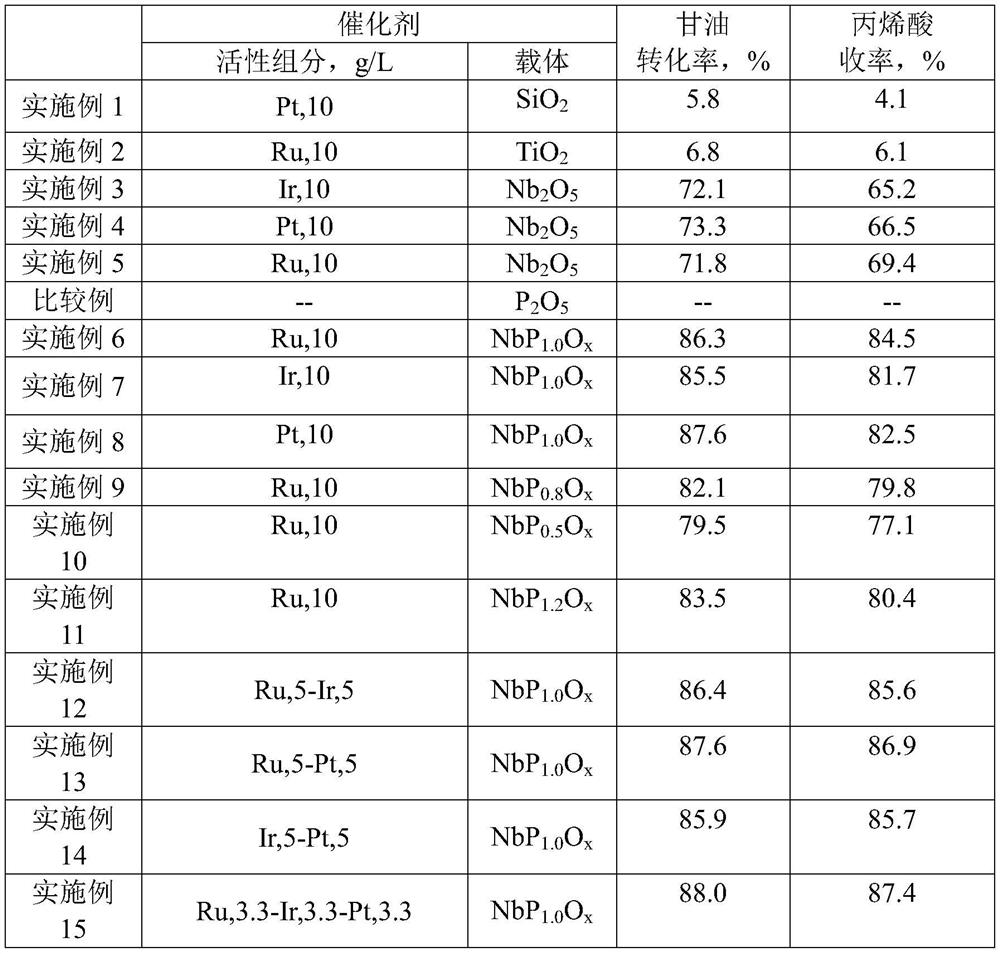
One-step method for synthesizing acrylic acid from glycerol
ActiveCN109305909BOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The present invention relates to a method for synthesizing acrylic acid from glycerol in one step, which mainly solves the problem of low yield of acrylic acid in the process of synthesizing acrylic acid from glycerin in the prior art. The method for synthesizing acrylic acid by adopting glycerol in one step includes raw materials containing glycerin and raw materials containing oxygen and Catalyst contact, glycerin dehydration reaction produces acrolein, and acrolein is further oxidized to acrylic acid; The catalyst includes a carrier and an active component, and the active component includes at least one technical solution selected from Ir, Pd and Au, The technical problem is better solved, and it can be used in the industrial production of acrylic acid synthesized from glycerin.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com