Industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with low glycerol synthesis and high alcohol tolerance and application thereof
A strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a technology for Saccharomyces cerevisiae, applied in the directions of fermentation, fungi, microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve the problems of decreased tolerance, increased synthesis of by-products, decreased ethanol production, etc., and achieves reduced production costs and high alcohol content. Durability, the effect of reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: Acquisition of Industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae Glycerol Metabolism Engineering Strains
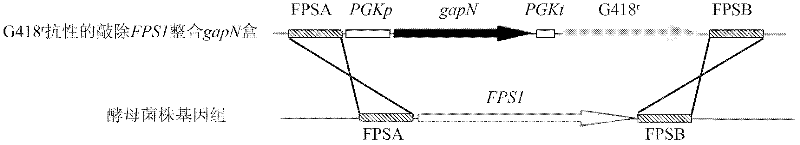
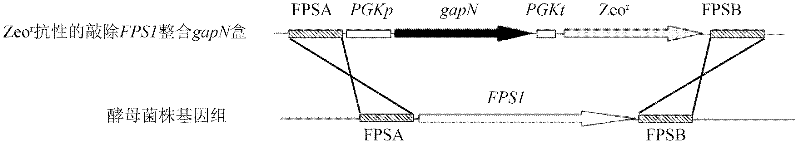
[0027] 1. Obtaining the haploid starting strain
[0028] After the industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae Z87 was activated by YPD at 30°C, it was transferred into the sporulation medium and cultured at 26°C for 3-7 days. When the ascospore formation was observed under a microscope, the bacterial cells were collected, washed twice with normal saline, and then added with 700 μL Tris-HCl (pH8.0, 0.01mol / L), 200 μL 100 mg / mL helicase solution and 100 μL 0.1mol / L mercaptoethanol , 120r / min at 30°C for 16h to rupture the ascus wall and release spores. Treat the vegetative cells at 58°C for 15 minutes to kill the vegetative cells, collect the spores by centrifugation, spread them on a YPD plate, incubate at 30°C for 2-3 days, pick a single colony, and verify the sporulation after activation on the YPD slant. Somatic strains.
[0029]The strains to be tested and the standard...
Embodiment 2
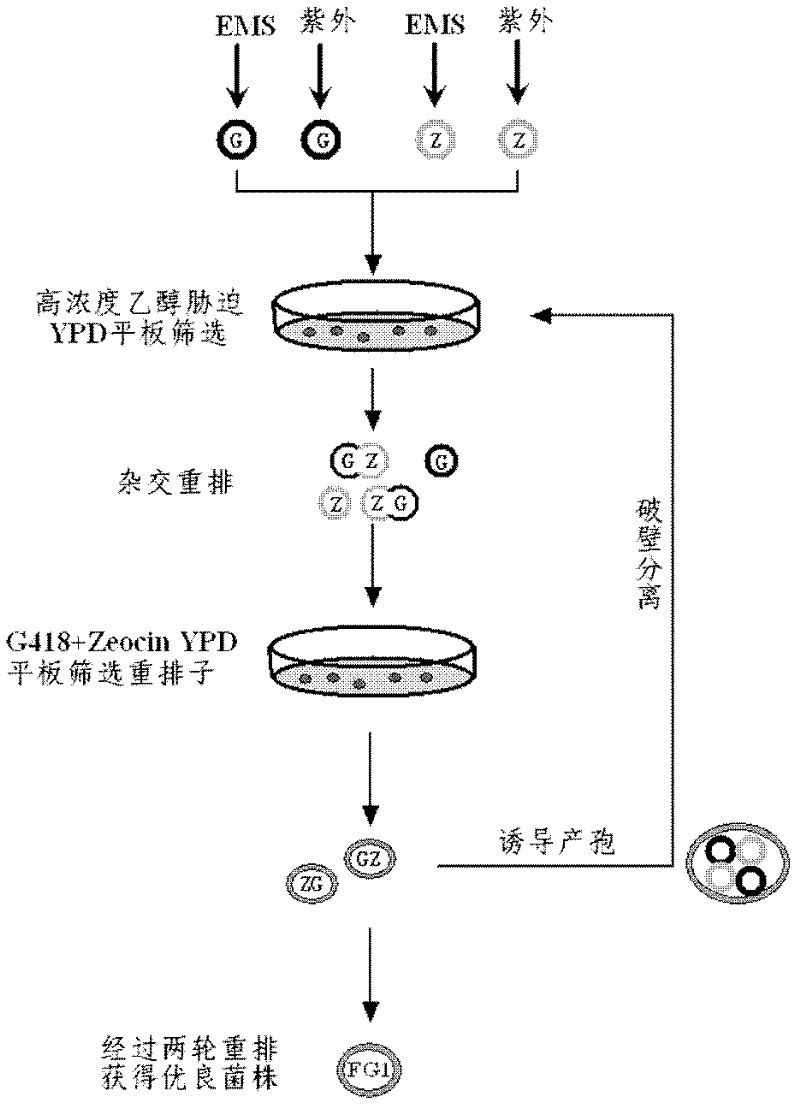
[0037] Embodiment 2: Implement whole genome rearrangement on genetically engineered strains
[0038] Such as image 3 The shown process implements whole genome rearrangement, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0039] 1. Treat genetically engineered haploid strains YFG1 (MAT a, fps1Δ::PGKp-gapN) and YFG2 (MAT α, fps1Δ::PGKp-gapN) with 1% (v / v) EMS mutagen for 30-120 minutes respectively Add 5% (w / v) sodium thiosulfate to remove EMS contamination every 30min, collect the bacterial cells by centrifuging at 4000rpm for 5min, wash twice with normal saline, apply gradient dilution to a YPD plate containing 8% (v / v) ethanol, Cultivate at 30°C for 3 days, and pick a vigorously growing single colony;
[0040] 2. Under the ultraviolet lamp with a distance of 40cm and a power of 15w, carry out ultraviolet induction on genetically engineered haploid strains YFG1 (MAT a, fps1Δ::PGKp-gapN) and YFG2 (MAT α, fps1Δ::PGKp-gapN) Change, every 1min samples were diluted and coated with 8%...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: Determination of production performance of engineering strains
[0045] 1. Growth determination under high-concentration ethanol stress conditions
[0046] Use YPD liquid medium containing 0% and 10% (v / v) ethanol to cultivate the starting strain Z87, the control strain Y12, the genetically engineered strain YFG12, and the genetically engineered rearrangement FG1 at 30°C, and take samples at different times to measure the dry weight of the strains, and calculate The maximum specific growth rate of the strain. Such as Figure 4 As shown, under the YPD culture condition containing 0% ethanol, there was no significant difference in the growth of the four strains, and the lag period was about 0.4h; under the YPD culture condition containing 10% (v / v) ethanol, the four strains lagged The average period was extended to about 10 hours, and the genetically engineered rearrangement FG1 grew the fastest, and the maximum specific growth rate was 11.4% higher than t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com