Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol as well as building and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
The technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and yeast strain is applied in the field of bioengineering, which can solve the problem of not simultaneously regulating key genes of higher alcohol metabolism, and achieve the effects of broad market prospects, improved expression, and overcoming inconsistency in flavor.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with high ester yield and low yield of higher alcohol
[0049] The starting strain CICC32315 used in this example. The Escherichia coli DH5a was purchased from Takara Company. The YPD medium is a universal complete medium, and the solid medium contains 2% imported agar powder.
[0050] Based on the yeast genome data in Genebank and the integrated plasmid sequence, the following primers were designed.
[0051] The primers used in the present embodiment of table 1
[0052]
[0053]
[0054] Note: The underlined part is the restriction site.
[0055] The PCR amplification system used in the present embodiment of table 2
[0056]
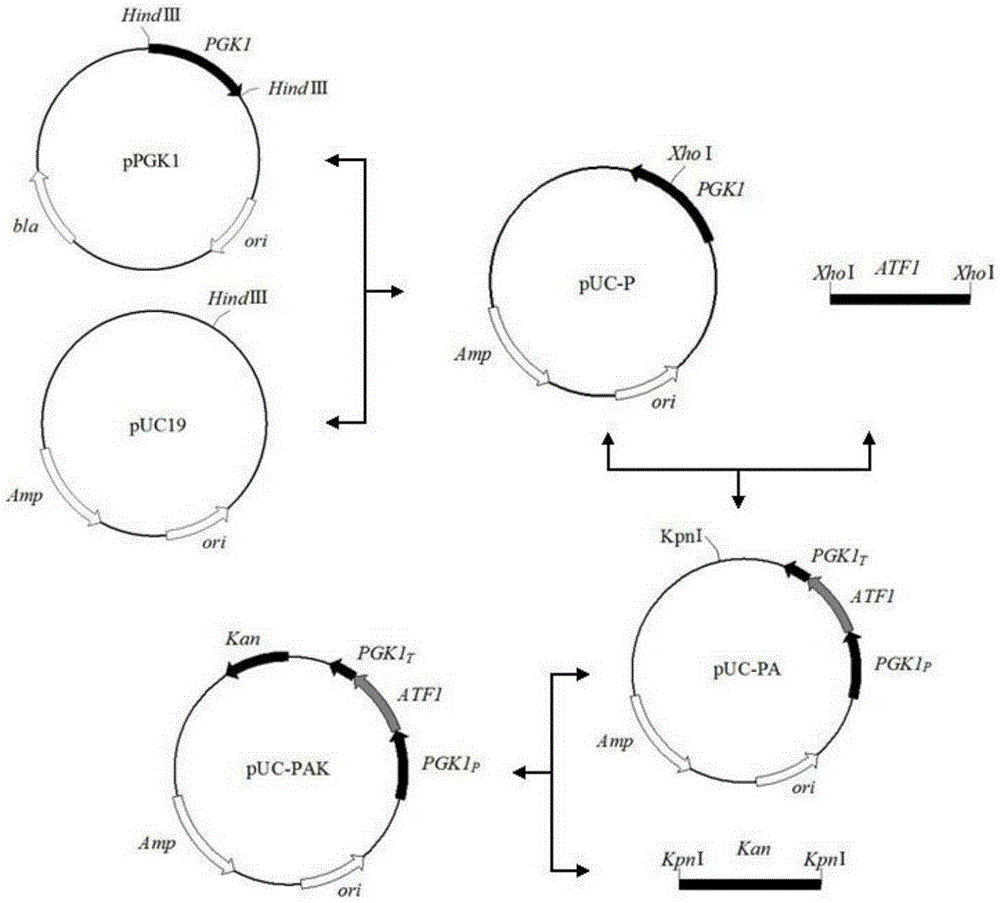
[0057] (1) Construction of recombinant plasmid pUC-PAK
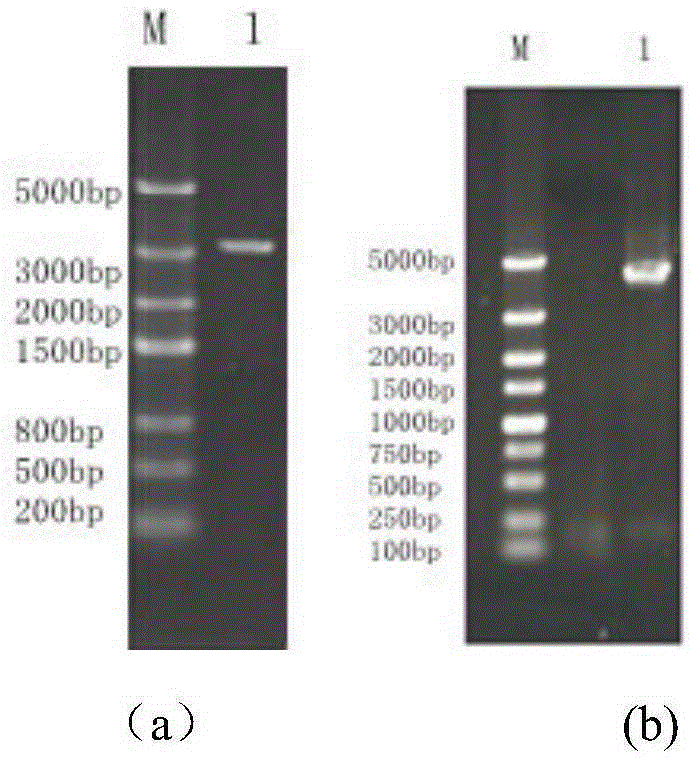
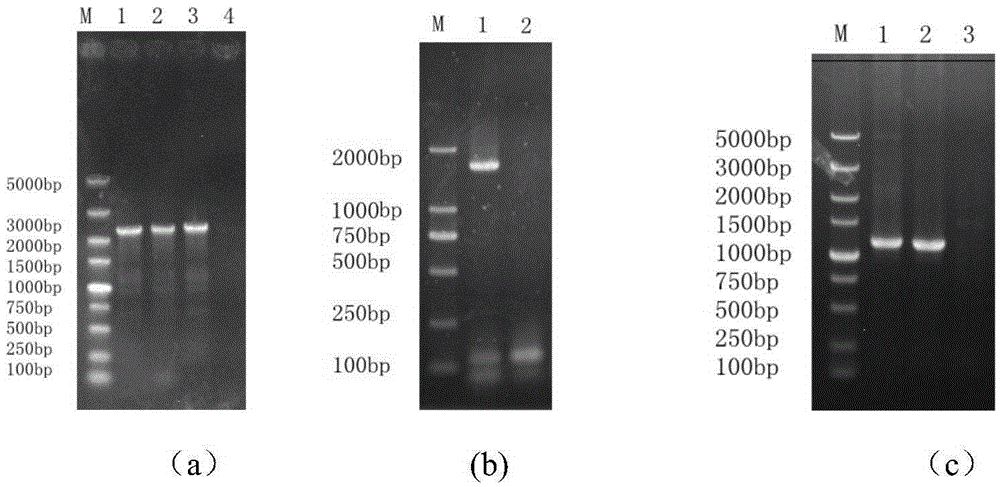
[0058] The construction process of the recombinant plasmid pUC-PAK is as follows: figure 1 shown;
[0059] Plasmid pPGK1 and carrier plasmid pUC19 were digested with restriction endonuclease HindIII respectively, and the di...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2: Fermentation experiment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high ester yield and low yield of higher alcohol
[0076] (1) Corn thick mash fermentation experiments of recombinant strains and starting strains
[0077] The recombinant strain and the starting strain were subjected to corn mash fermentation experiments at the same time, the fermentation process roadmap: corn flour→soaking→liquefaction→saccharification→cooling→inoculation→fermentation→steaming wine→measurement indicators;
[0078] Process conditions:
[0079] Soaking conditions: 60670°C, soaking for 20 minutes; liquefaction conditions: 85690°C, adding high-temperature-resistant α-amylase, liquefying for 90 minutes; saccharification conditions: 55660°C, adding glucoamylase, saccharifying for 20 minutes;
[0080] Ingredients: corn flour 60g, water 130mL, high temperature resistant α-amylase 2×10 4 U / mL, 30μL, glucoamylase 1×10 5 U / mL, 90μL, 7.5×10 2 U / mL acid protease 1.2mL; nutrient salt 1mL...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com