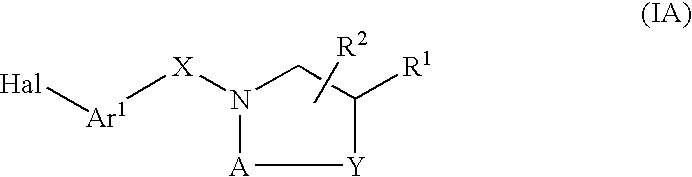
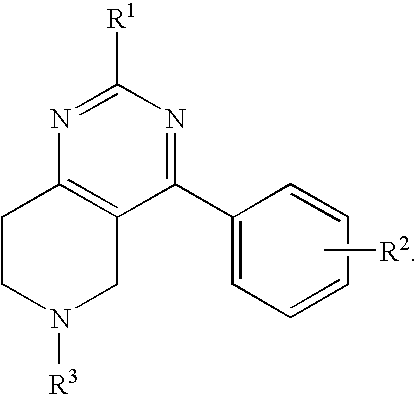
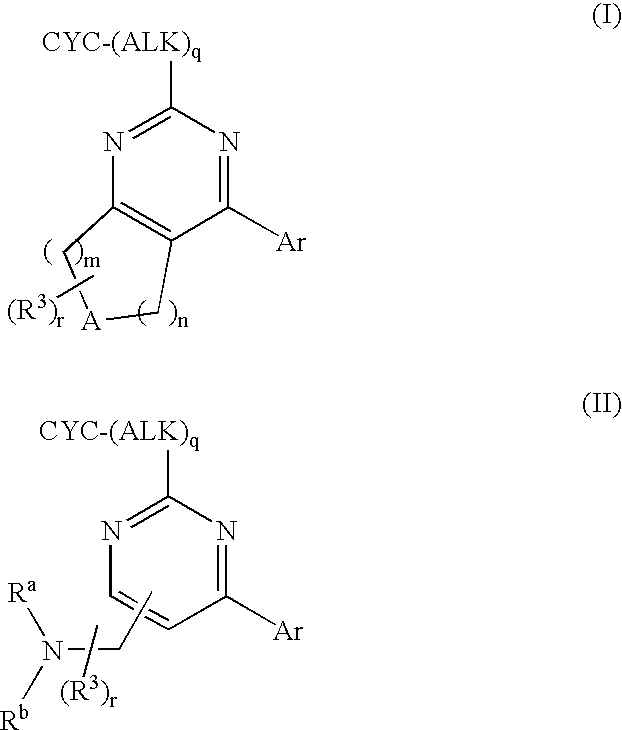
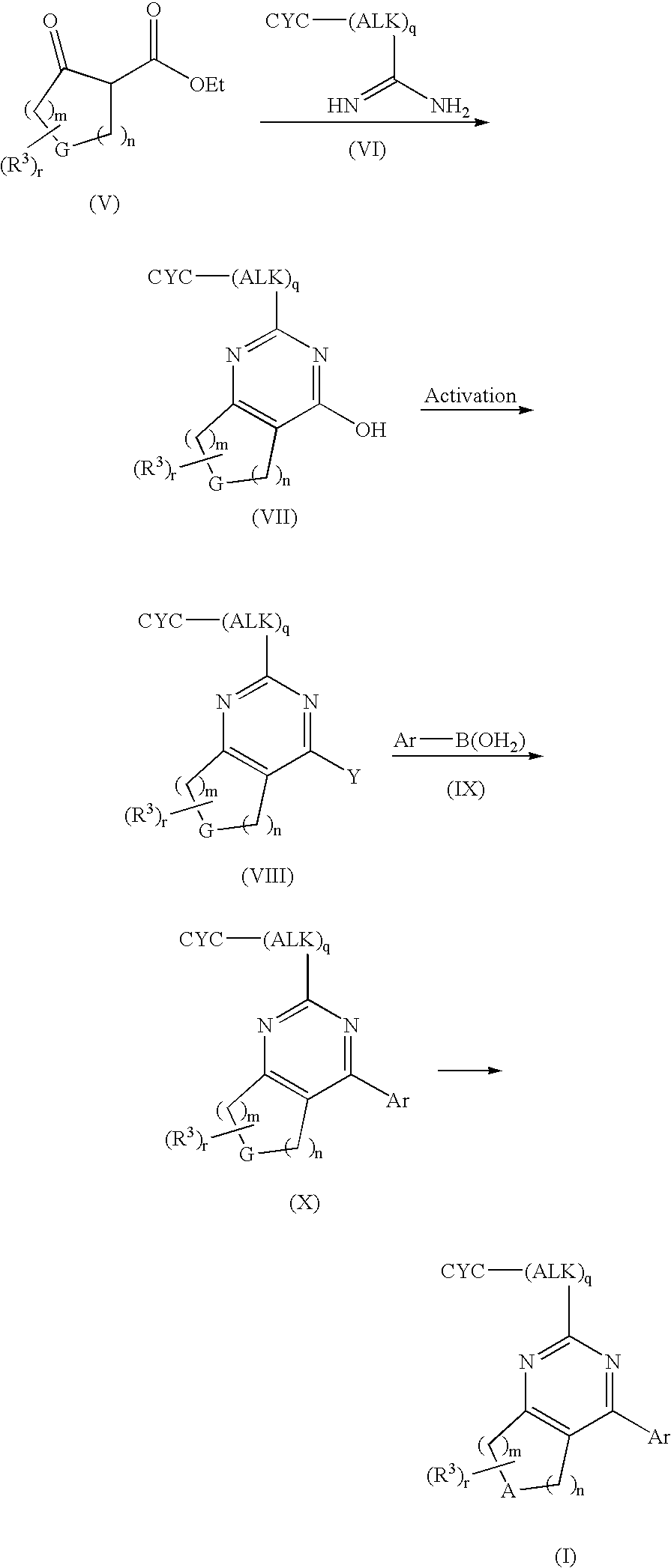
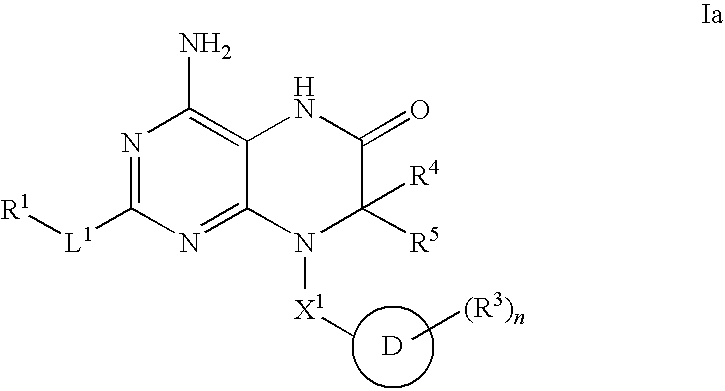
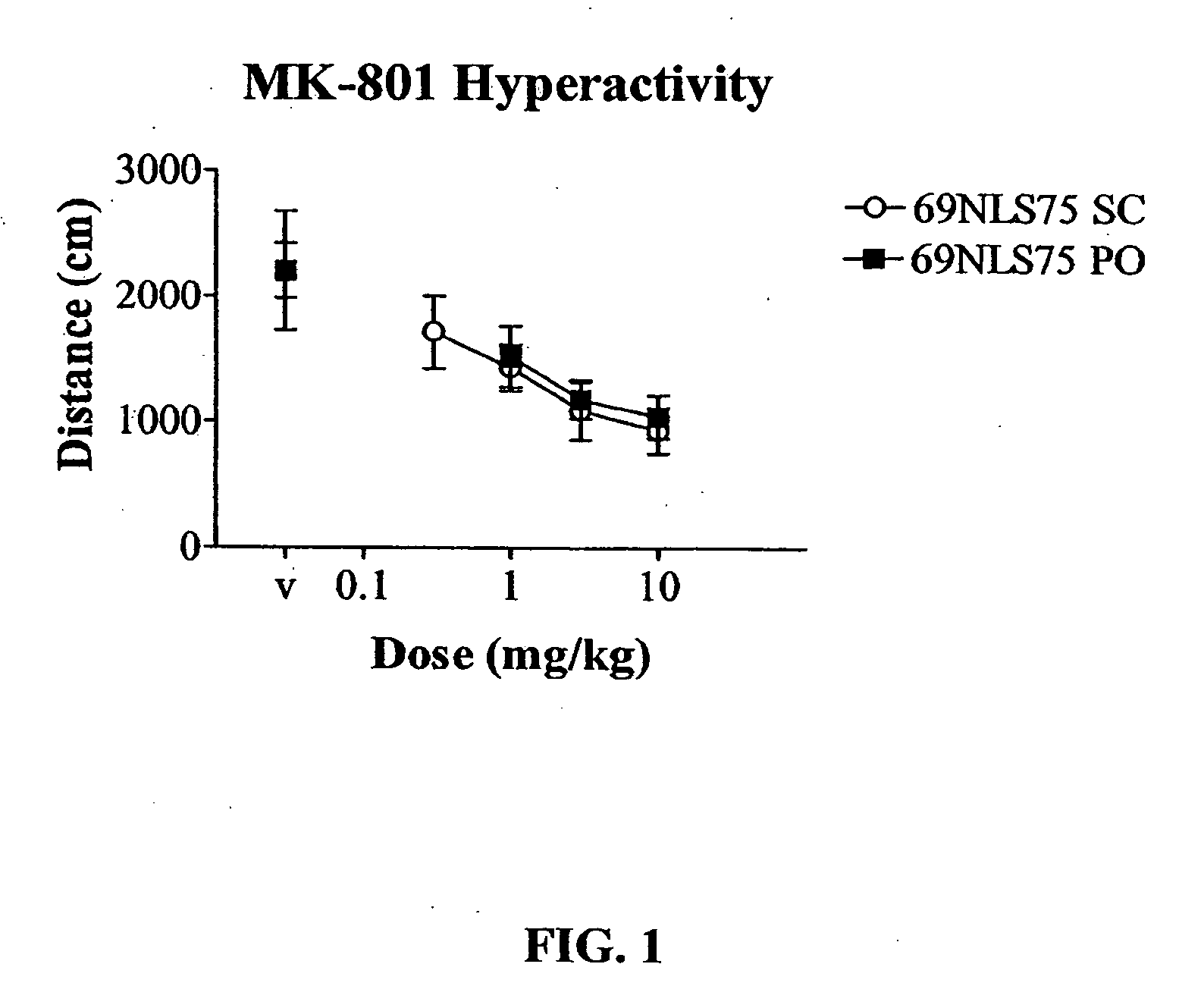
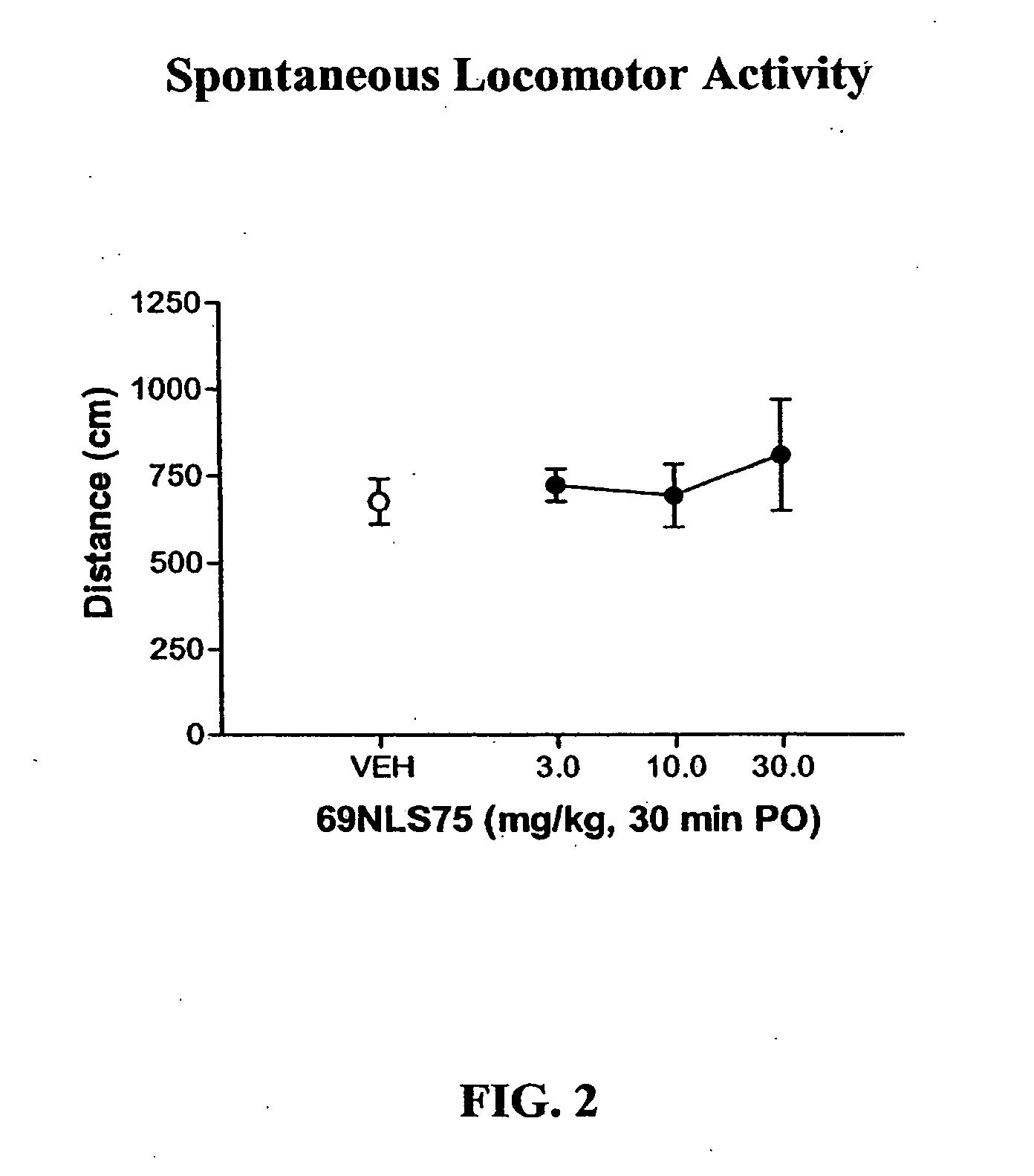
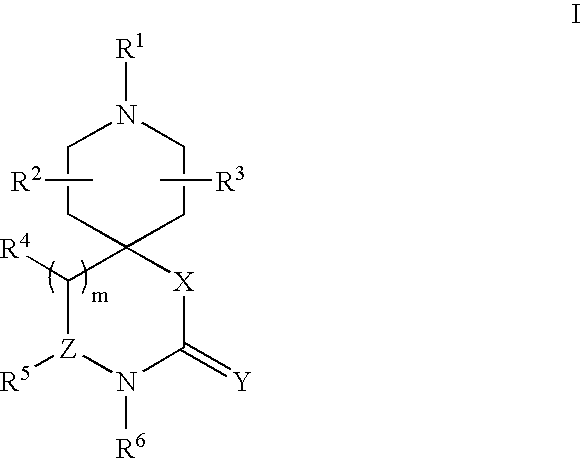
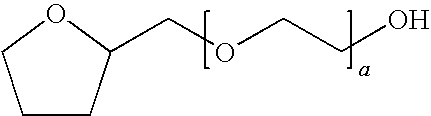
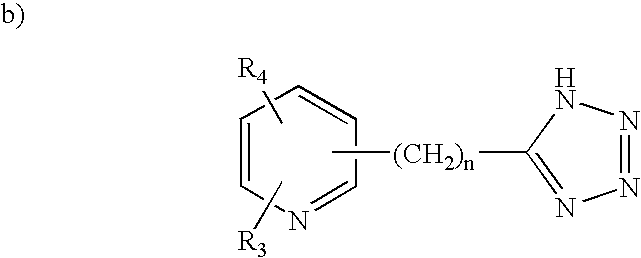
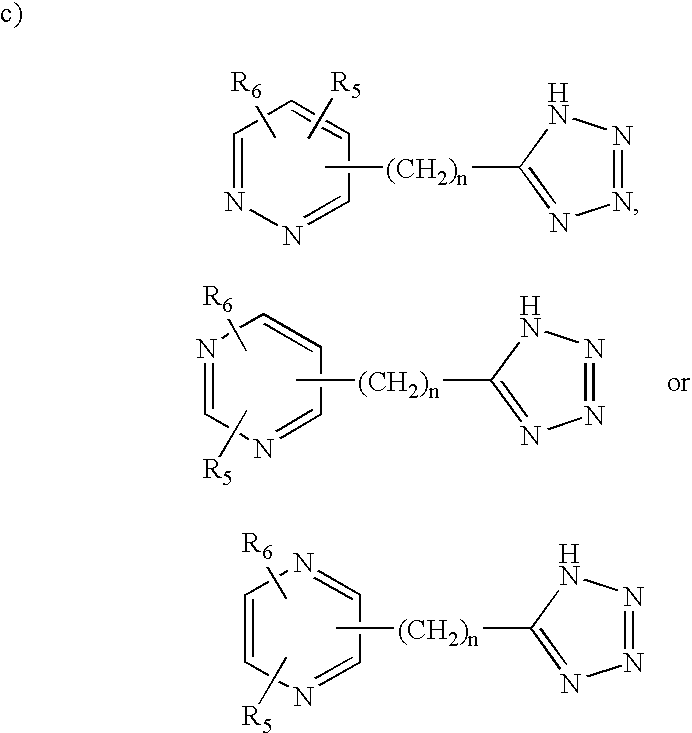
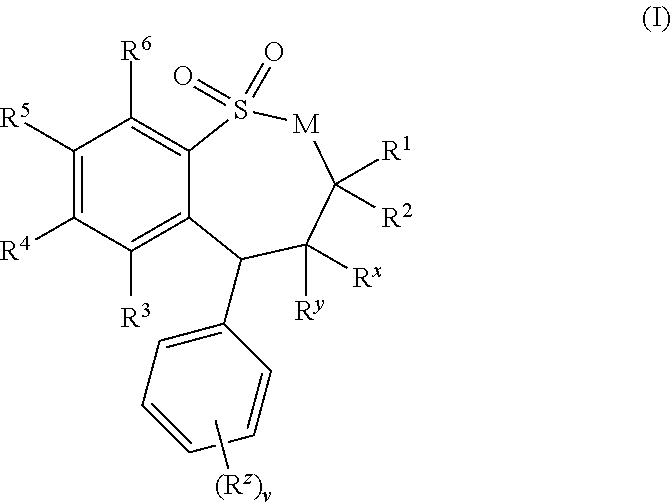
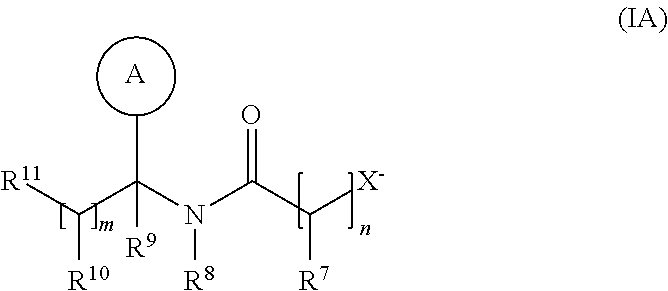
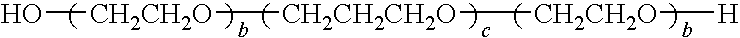Patents
Literature
571 results about "Receptor modulator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A receptor modulator, or receptor ligand, is a type of drug which binds to and modulates receptors. They are ligands and include receptor agonists and receptor antagonists, as well as receptor partial agonists, inverse agonists, and allosteric modulators.
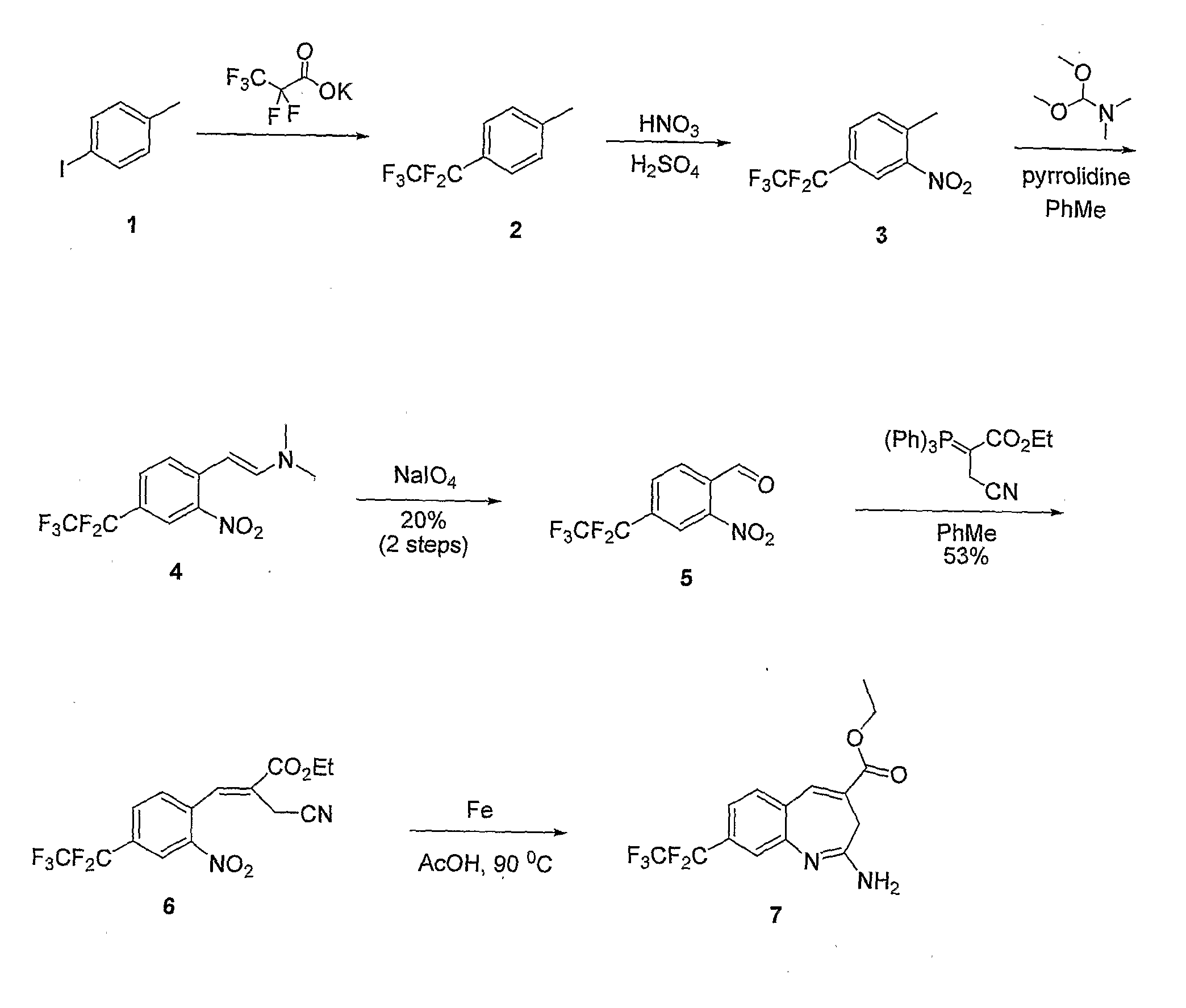
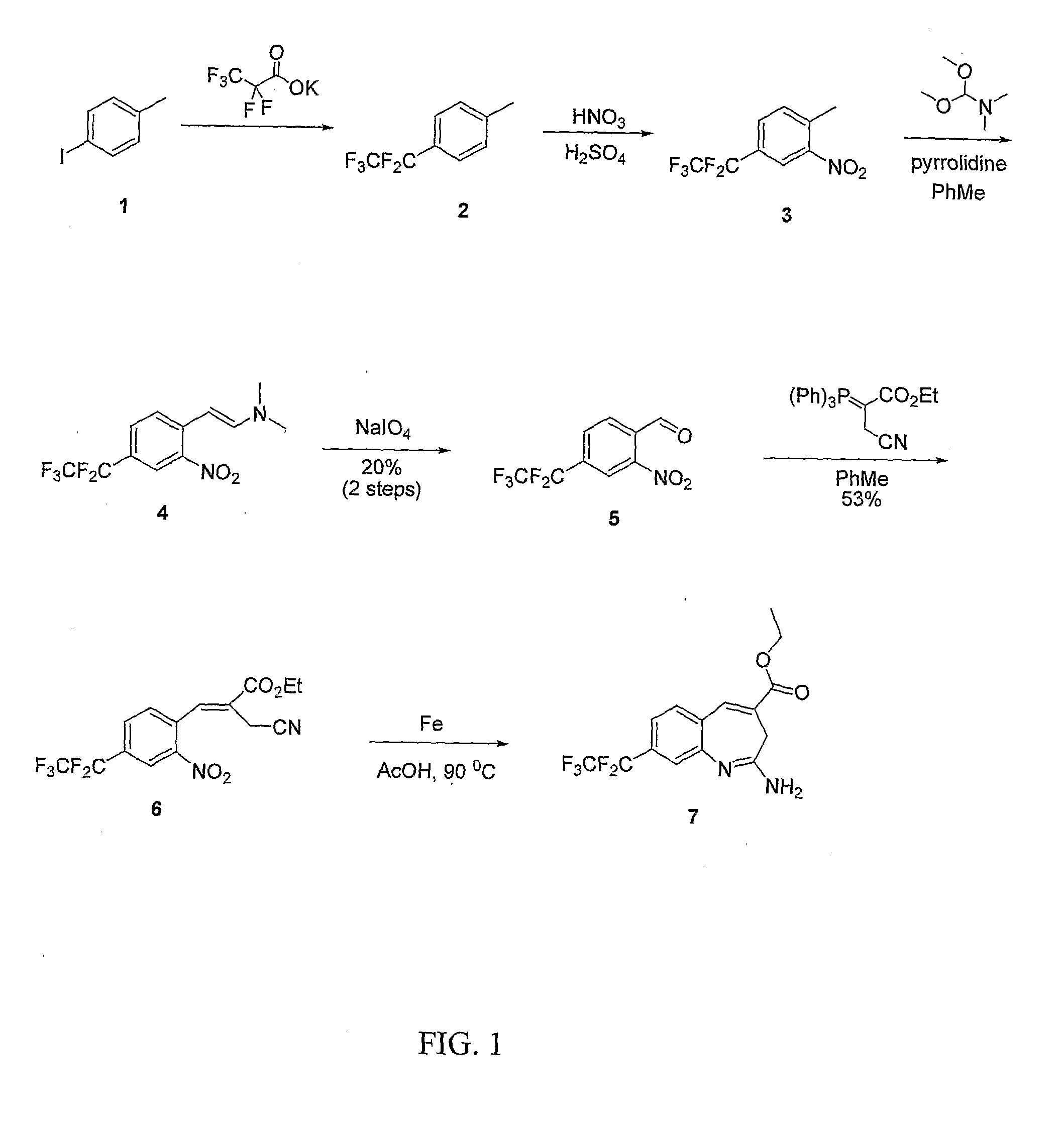
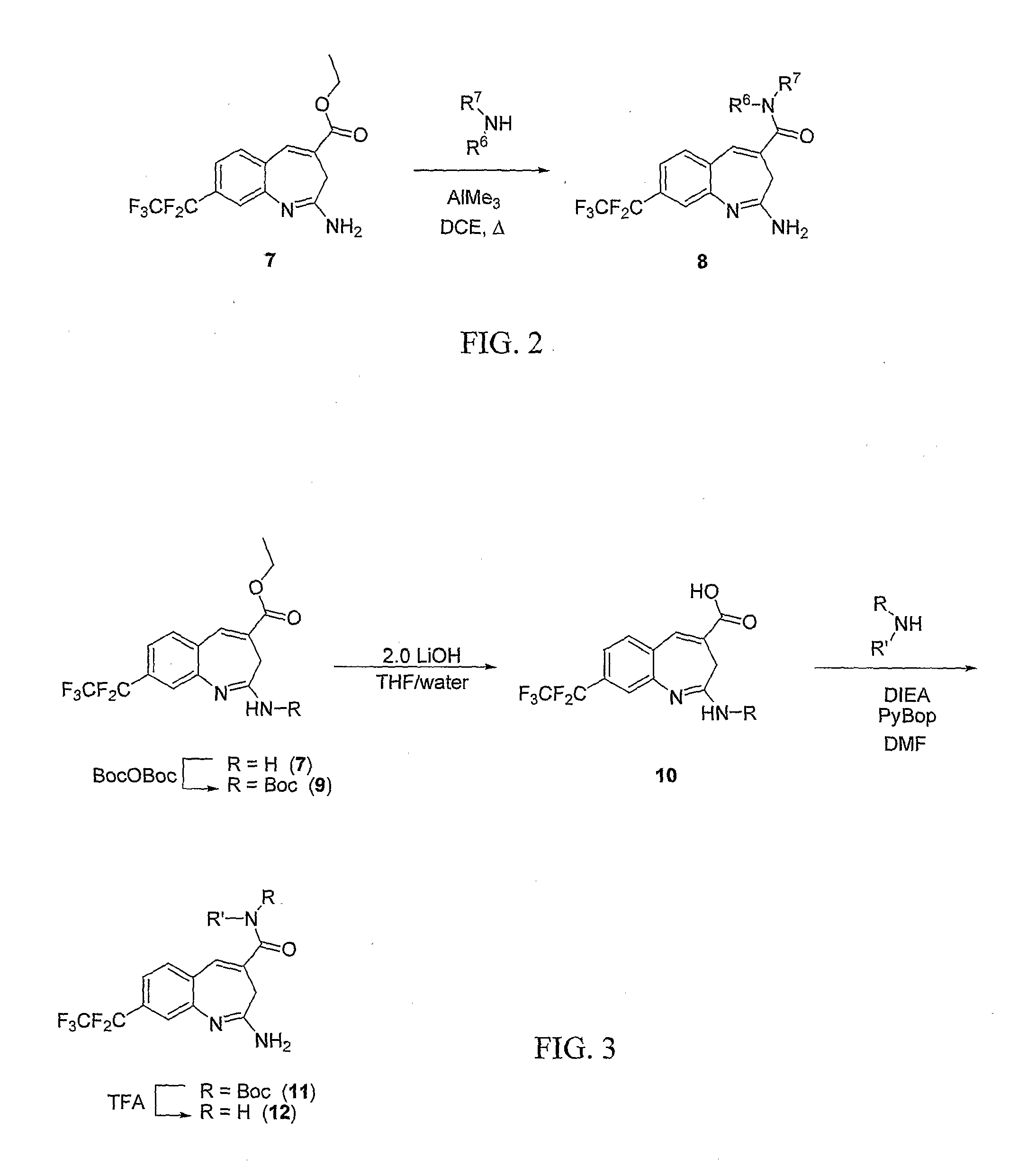
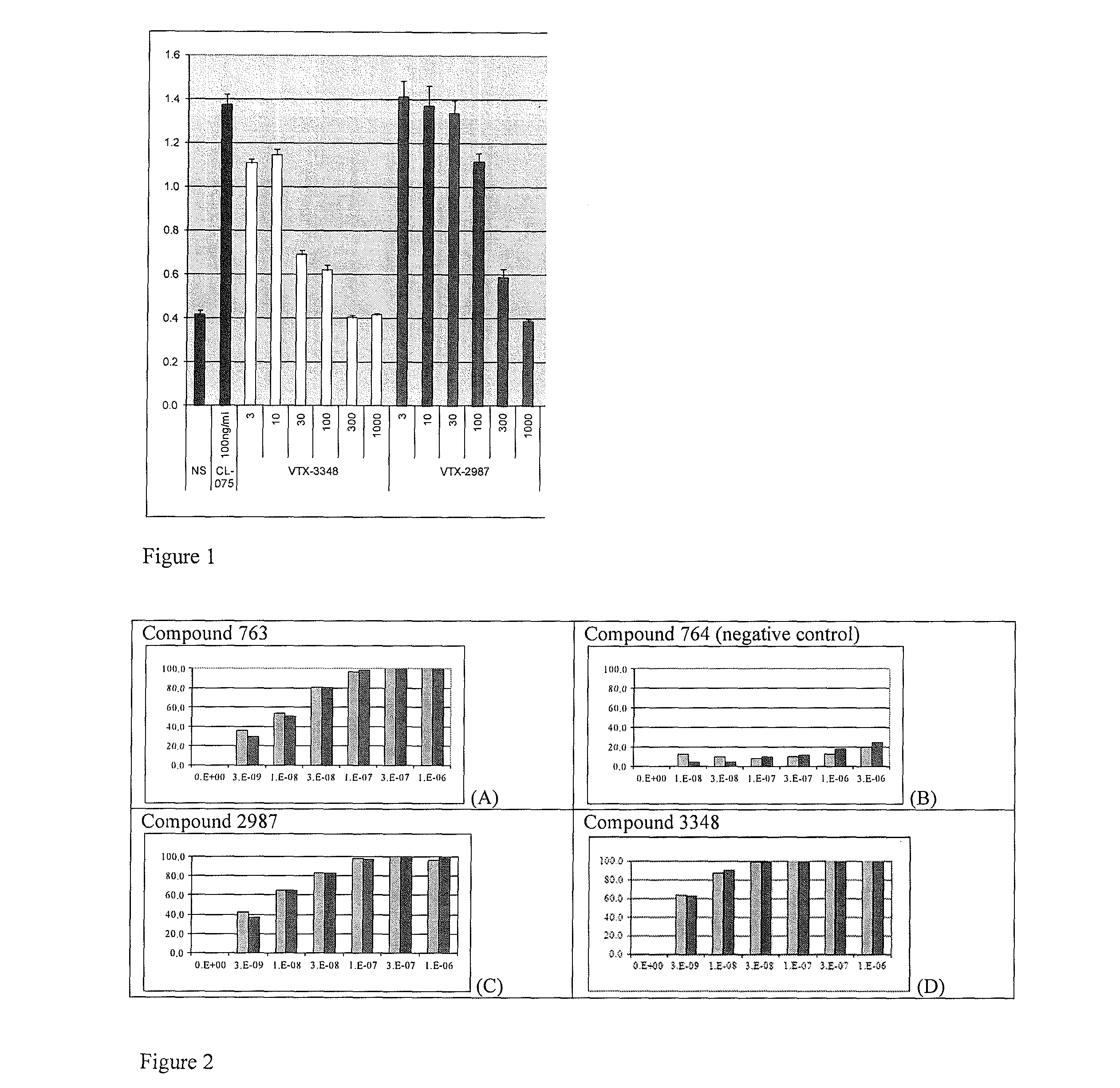
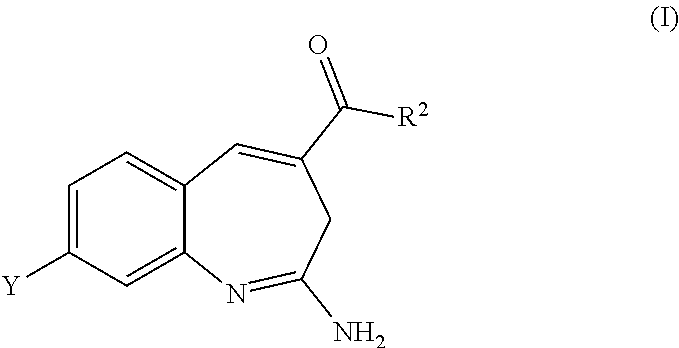
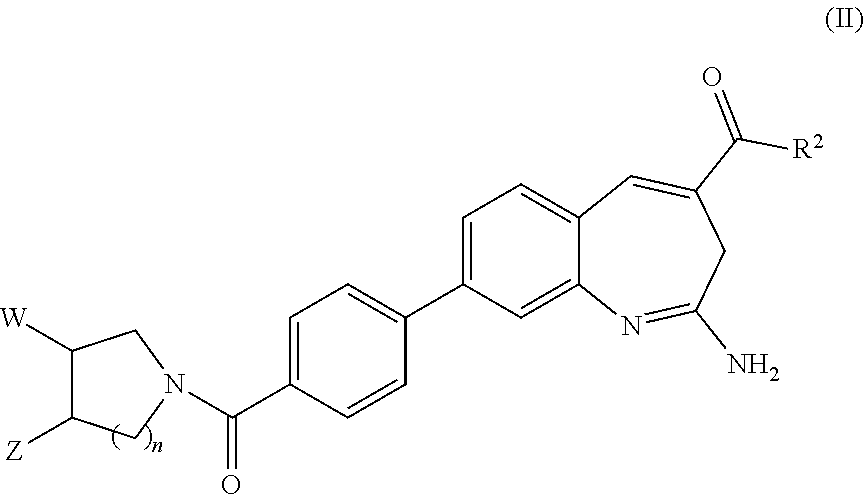
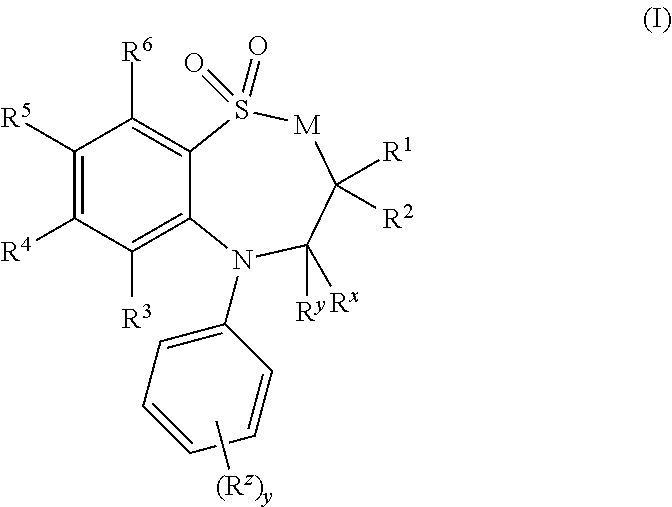
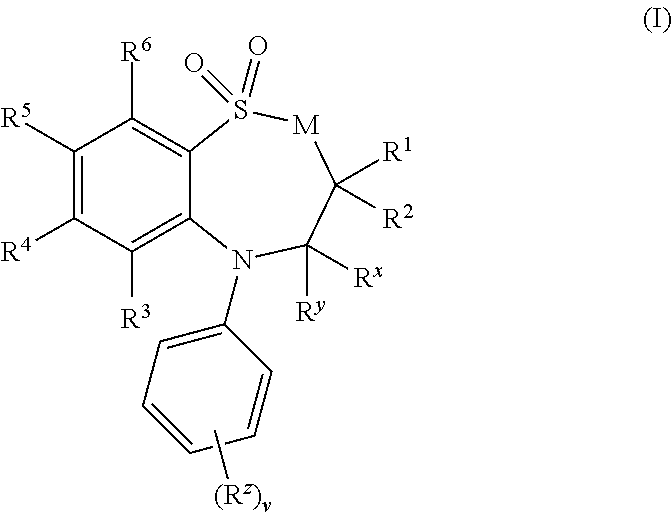
8-Substituted Benzoazepines as Toll-Like Receptor Modulators
Provided are compositions and methods useful for modulation of signaling through the Toll-like receptors TLR7 and / or TLR8. The compositions and methods have use in the treatment of autoimmunity, inflammation allergy, asthma, graft rejection, graft versus host disease, infection, sepsis, cancer and immunodeficiency.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA
Substituted Benzoazepines As Toll-Like Receptor Modulators
Provided are compositions and methods useful for modulation of signaling through the Toll-like receptors TLR7 and / or TLR8. The compositions and methods have use in treating or preventing disease, including cancer, autoimmune disease, fibrotic disease, cardiovascular disease, infectious disease, inflammatory disorder, graft rejection, or graft-versus-host disease.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA +1
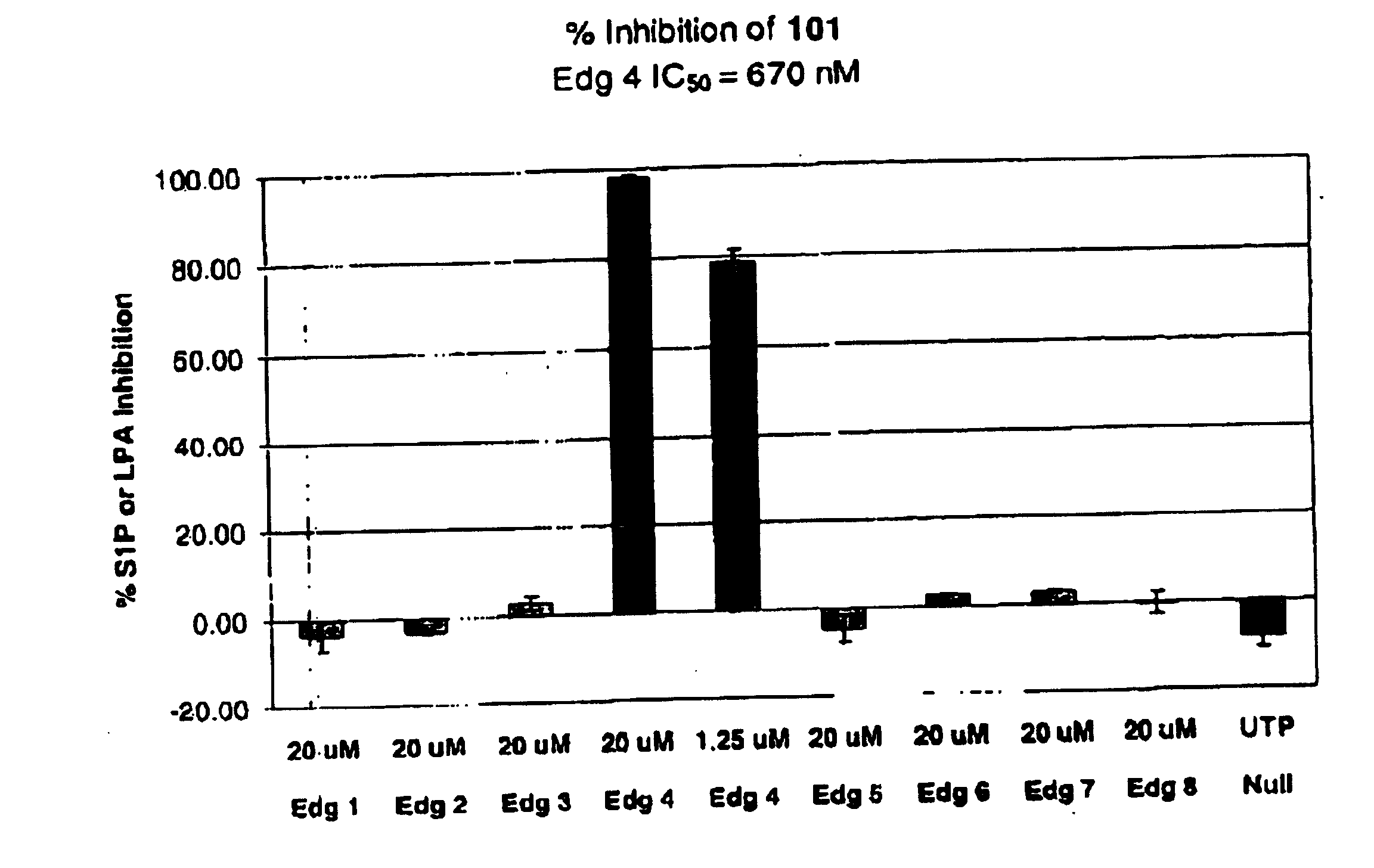
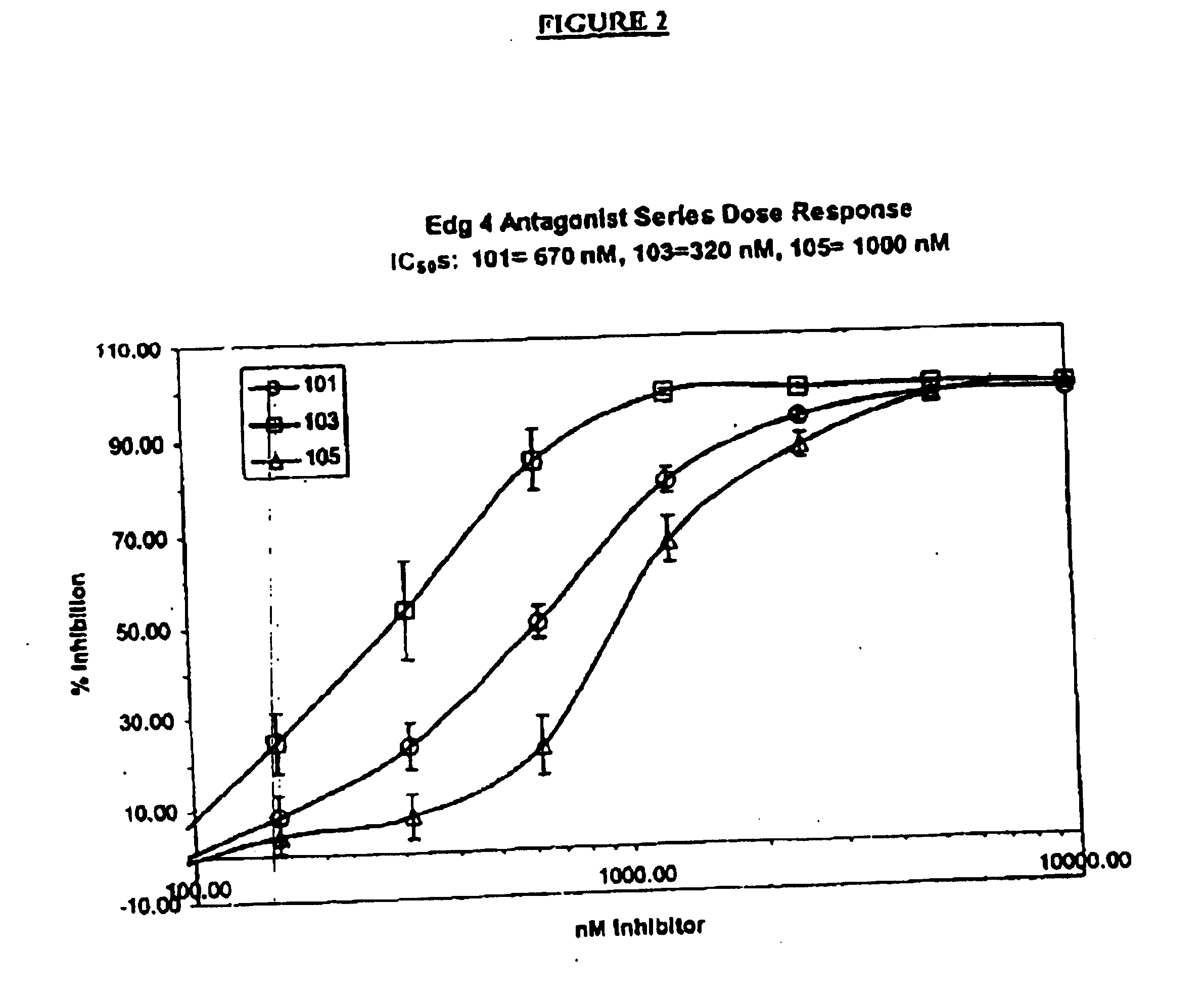
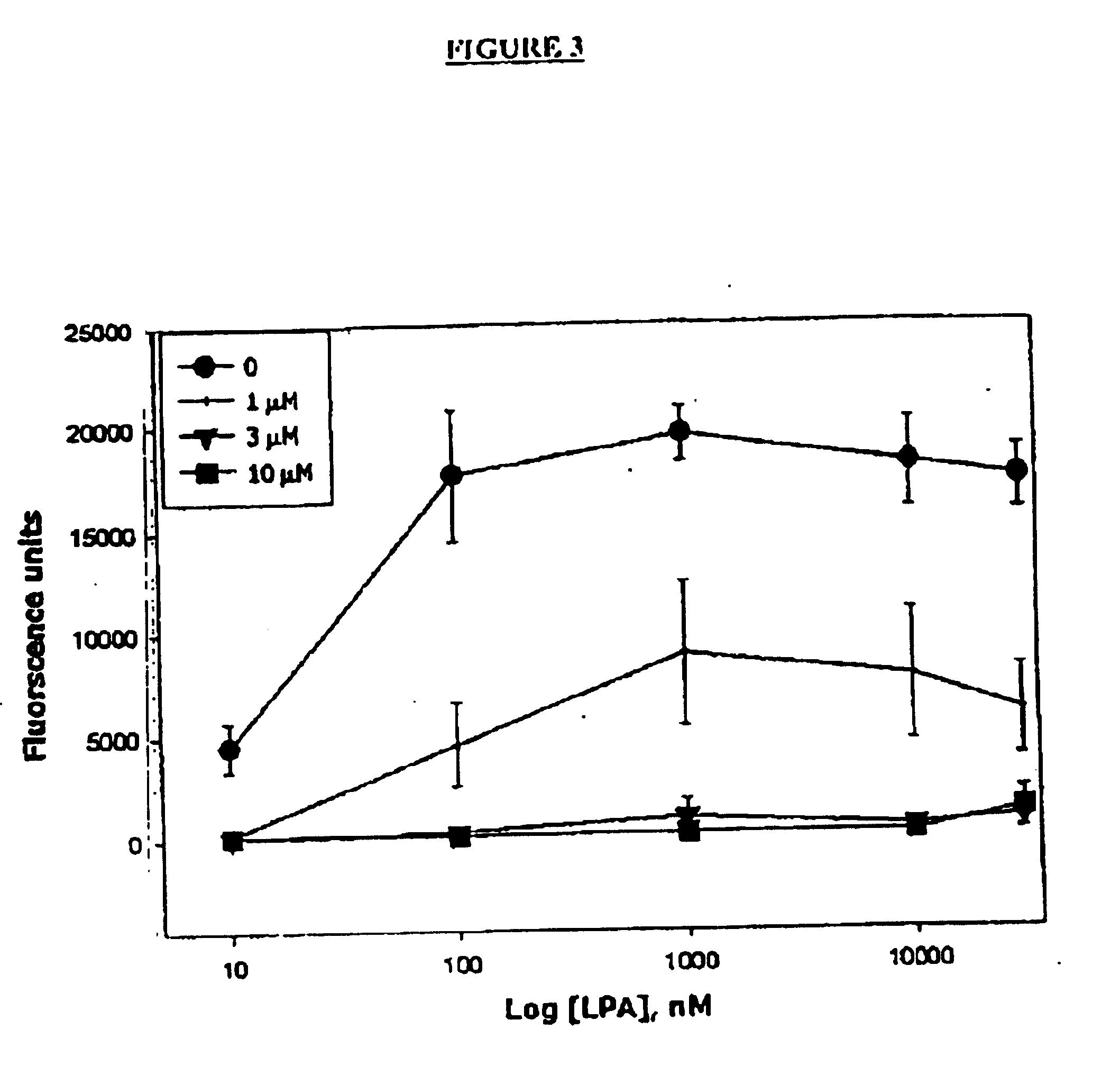
Methods of treating conditions associated with an EDG-4 receptor
InactiveUS20050113283A1Modulating biological activityBiocideAmide active ingredientsDrug biological activityReceptor modulator
The present invention provides a method of modulating an Edg-4 receptor mediated biological activity in a cell. A cell expressing the Edg-4 receptor is contacted with a modulator of an Edg-4 receptor sufficient to modulate the Edg-4 receptor mediated biological activity. In another aspect, the present invention provides a method for modulating an Edg-4 receptor mediated biological activity in a subject. A therapeutically effective amount of a modulator of the Edg-4 receptor is administered to the subject.
Owner:MANIV ENERGY CAPITAL
Substituted benzoazepines as toll-like receptor modulators
ActiveUS20110118235A1Efficient modulationAntibacterial agentsBiocideTLR8Graft versus host disease induction
Provided are compositions and methods useful for modulation of signaling through the Toll-like receptors TLR7 and / or TLR8. The compositions and methods have use in treating or preventing disease, including cancer, autoimmune disease, infectious disease, inflammatory disorder, graft rejection, and graft-verses-host disease.
Owner:ARRAY BIOPHARMA +1
Methods of using diaminopyrimidine P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptor modulators for treatment of respiratory and gastrointestinal diseases
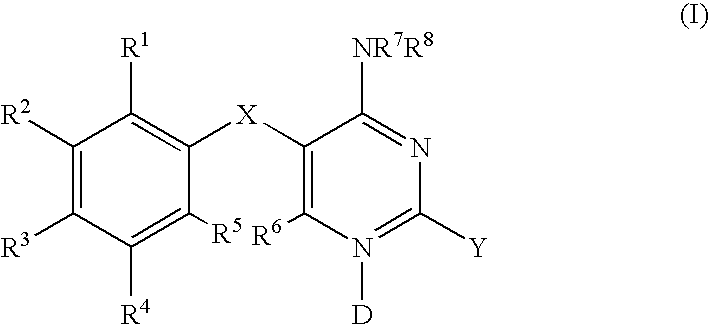
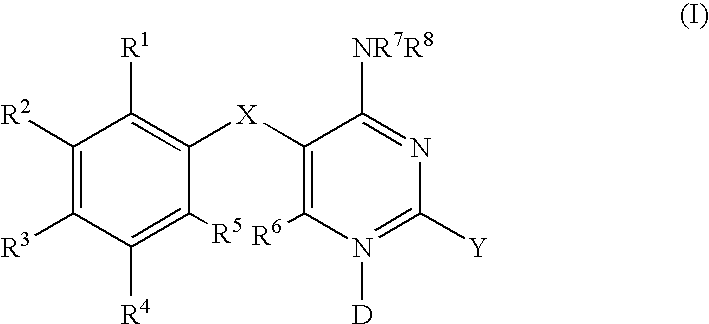
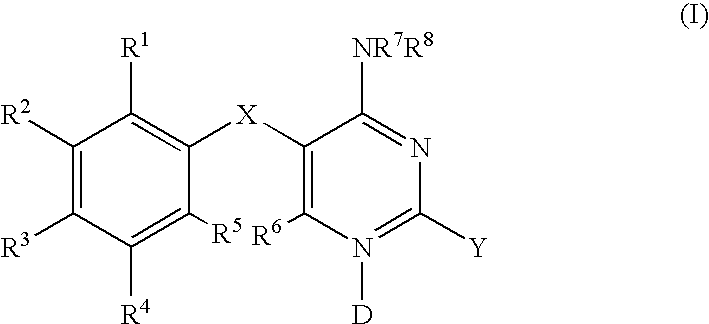
Methods for treating respiratory and gastrointestinal diseases mediated by a P2X3 and / or a P2X2 / 3 receptor antagonist, the methods comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of a compound of formula (I): or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein D, X, Y, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7 and R8 are as defined herein.
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
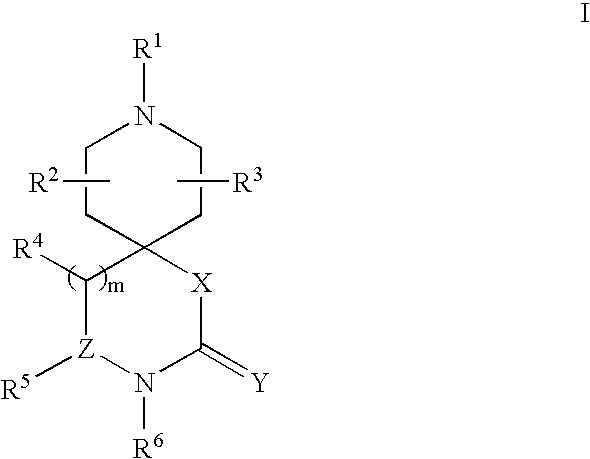
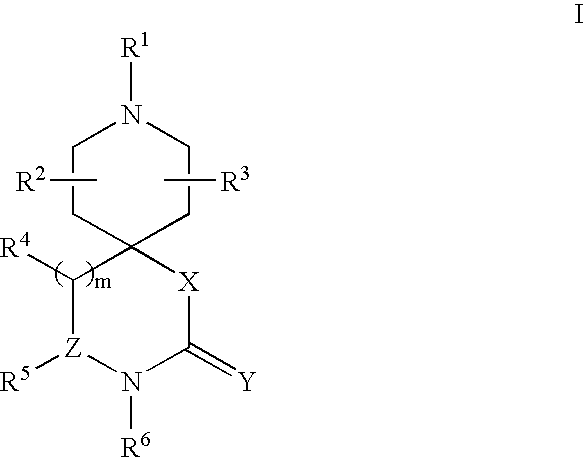
Spiroazacyclic compounds as monoamine receptor modulators
The present invention relates to 1-oxa-3,8-diaza-spiro[4.5]decan-2-one compounds as monoamine receptor modulators; compositions comprising the same; methods of inhibiting an activity of a monoamine receptor with said compounds; methods of treating a disease condition associated with a monoamine receptor using said compounds; and methods for identifying a subject suitable for treatment using said compounds.
Owner:ACADIA PHARMA INC
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor modulators
The present invention is directed to a compound of formula (I), or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, solvate hydrate or stereoisomer thereof, which is useful in treating or preventing disorders mediated by a peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) such as syndrome X, type II diabetes, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, obesity, coagaulopathy, hypertension, arteriosclerosis, and other disorders related to syndrome X and cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Method for screening taste-modulating compounds
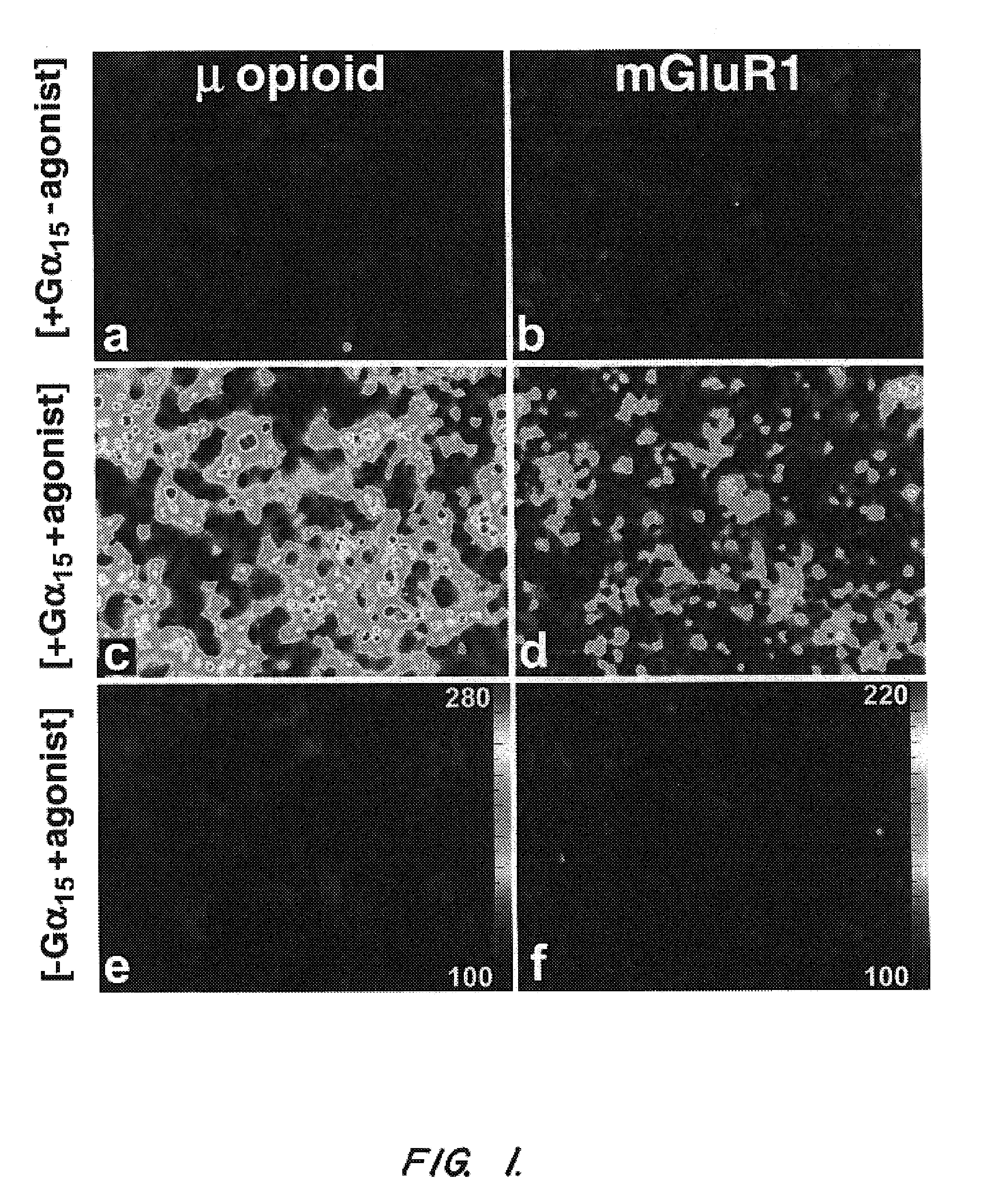
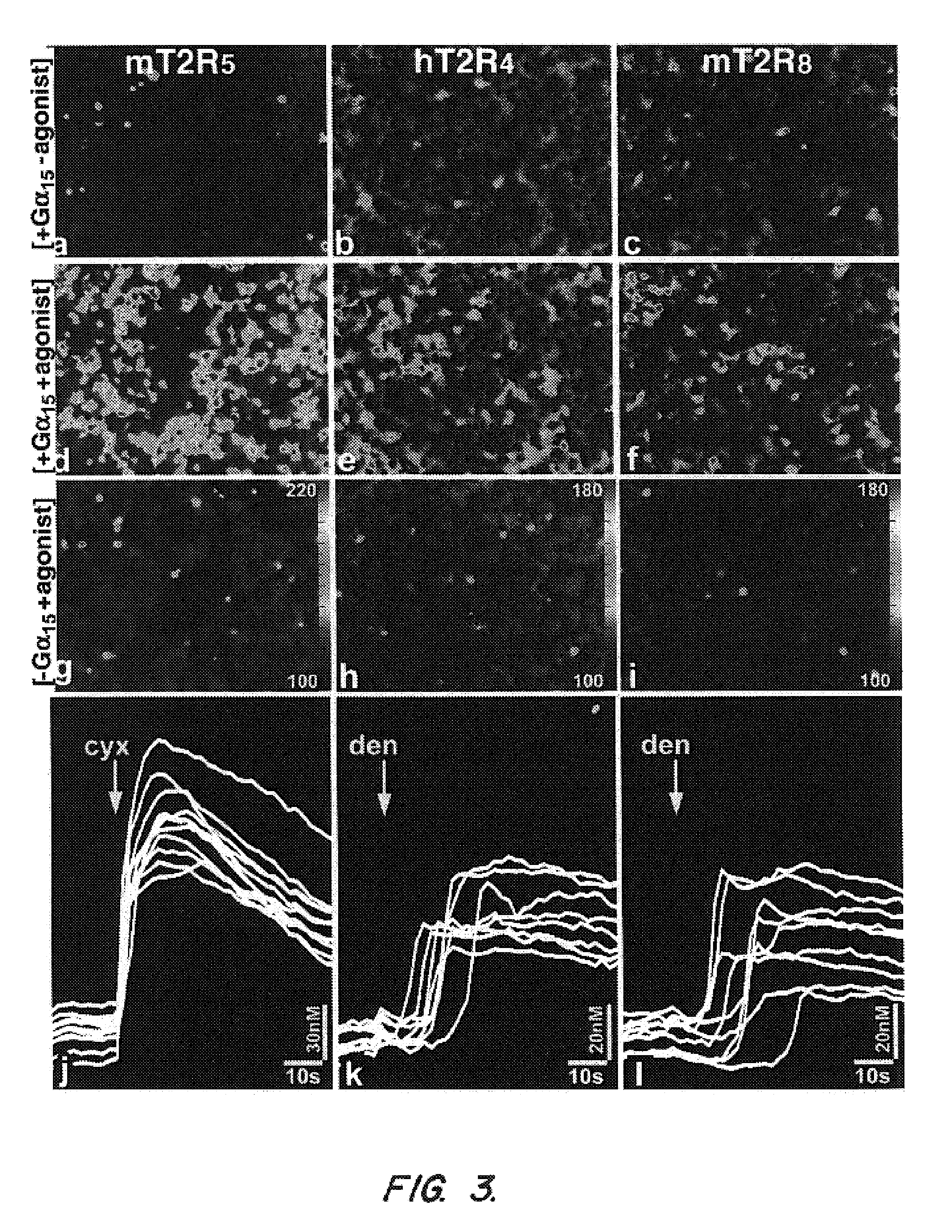
The invention provides nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for a novel family of taste transduction G-protein coupled receptors, antibodies to such receptors, methods of detecting such nucleic acids and receptors, and methods of screening for modulators of taste transduction G-protein coupled receptors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
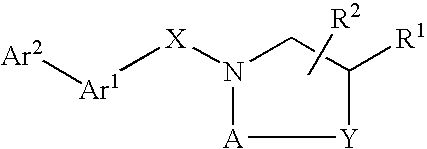
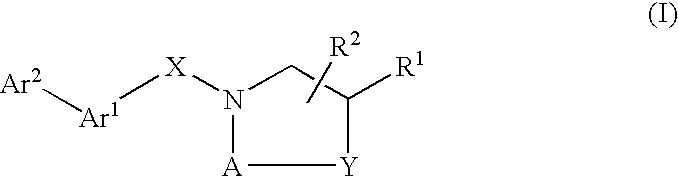
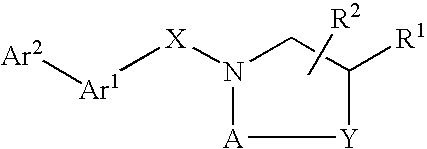
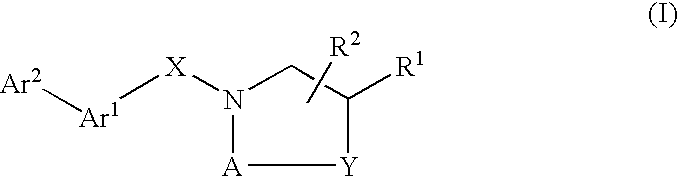
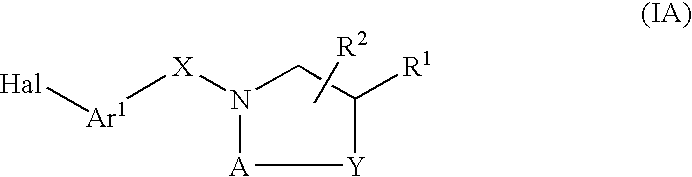
Compounds which modulate the CB2 receptor
Compounds are provided which bind to and are agonists, antagonists or inverse agonists of the CB2 receptor, the compounds having the general formulawherein, R1, R2, A, Y, X, Ar1 and Ar2 have the meanings given in the specification, and the preparation and use thereof. The compounds are valuable CB2 receptor modulators.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
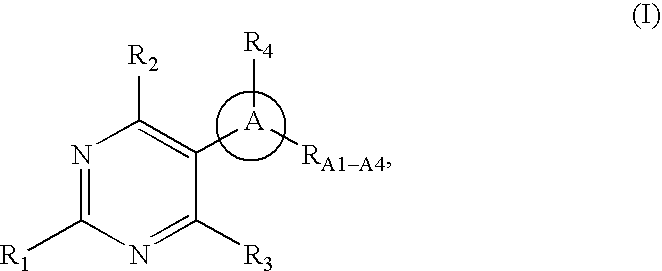
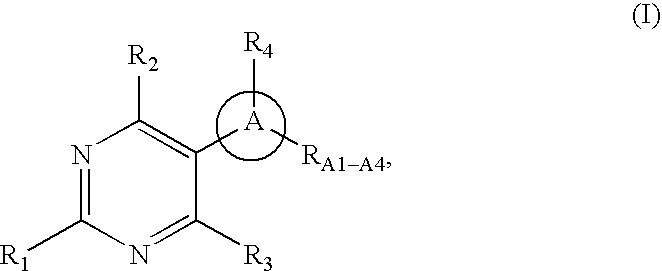
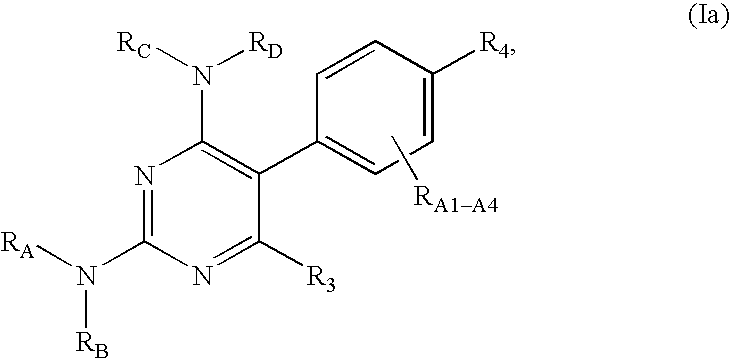
Pyrimidine compounds as serotonin receptor modulators
Certain pyrimidine-containing compounds are serotonin receptor modulators useful in the treatment of serotonin-mediated diseases.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
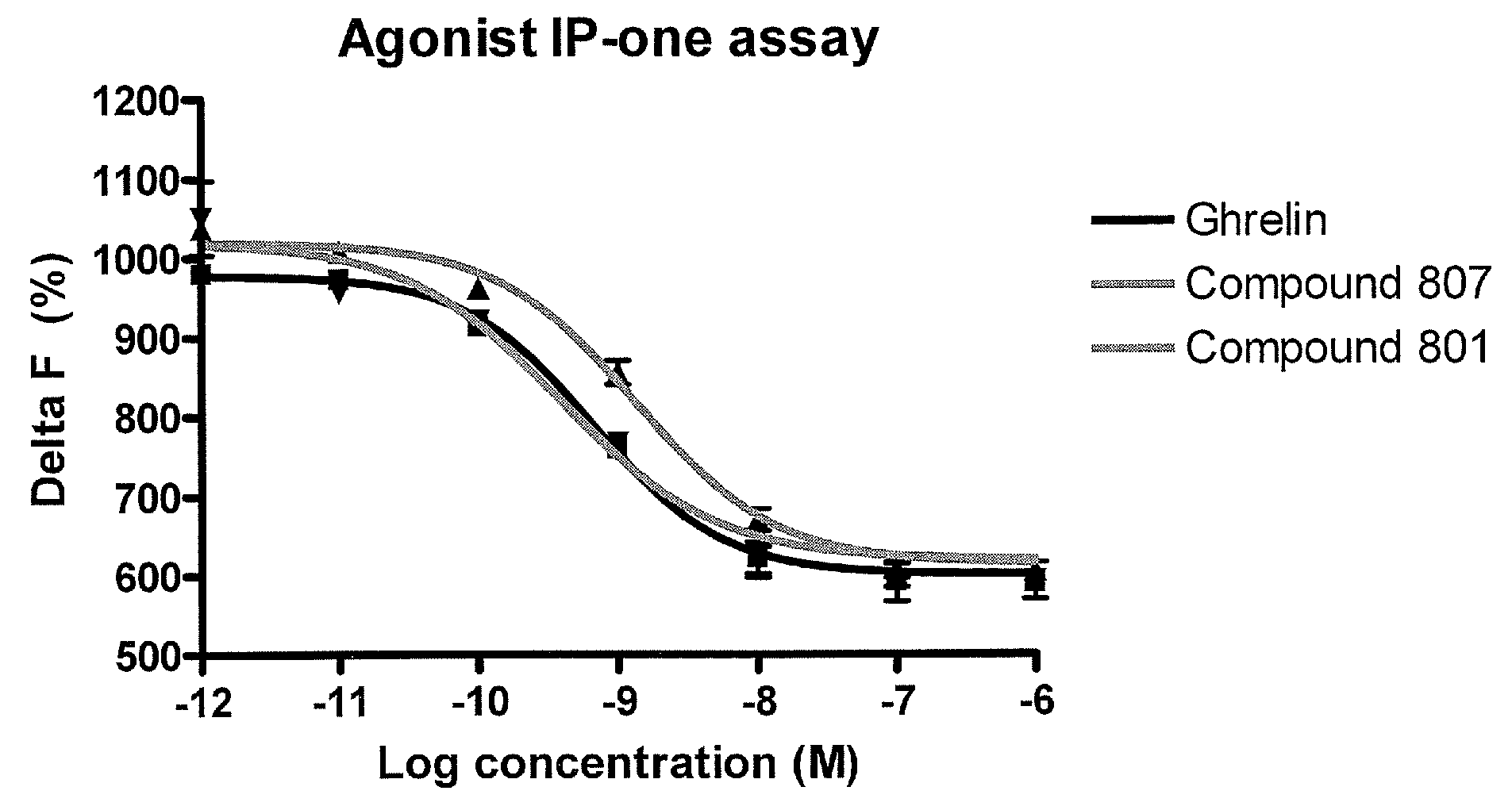
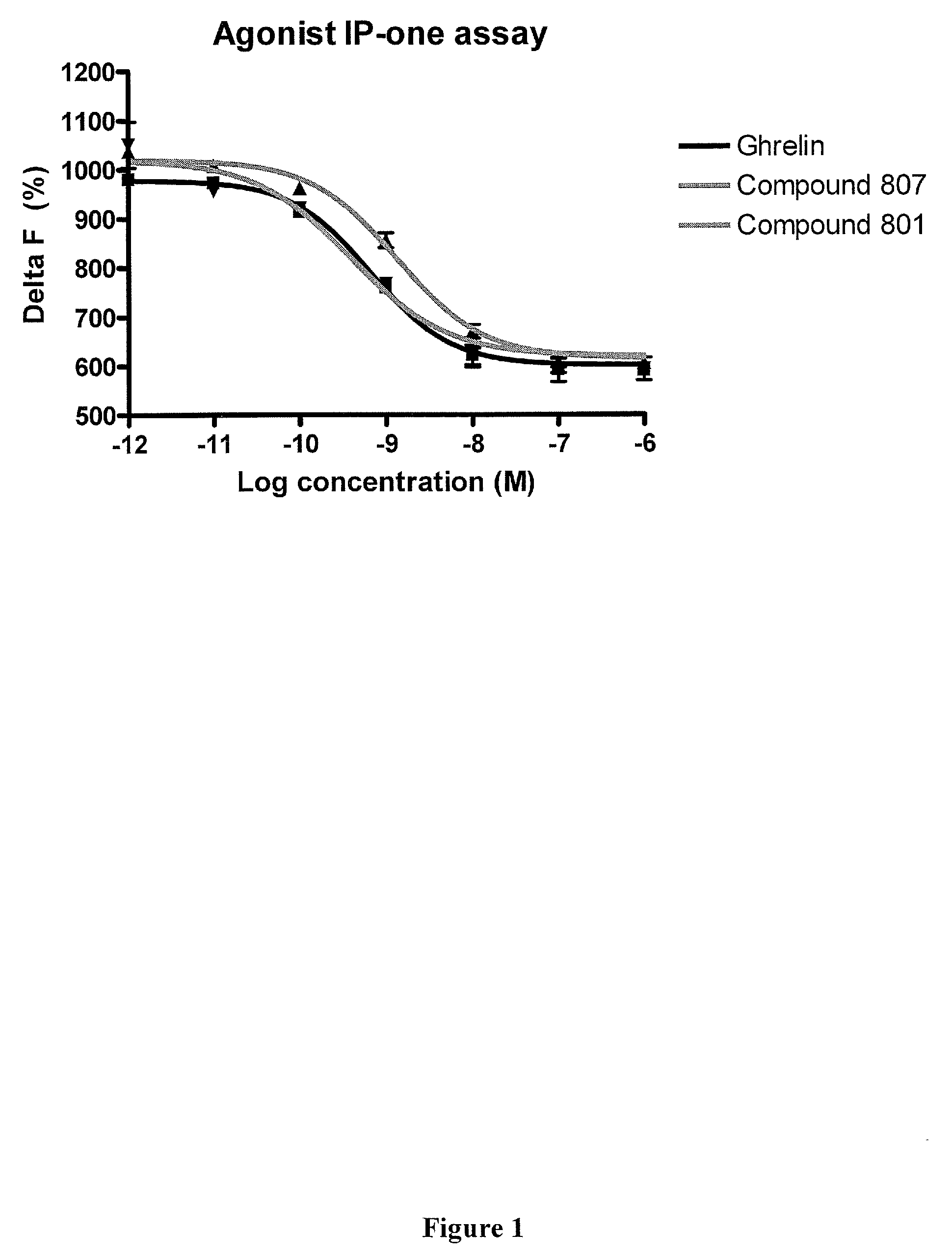
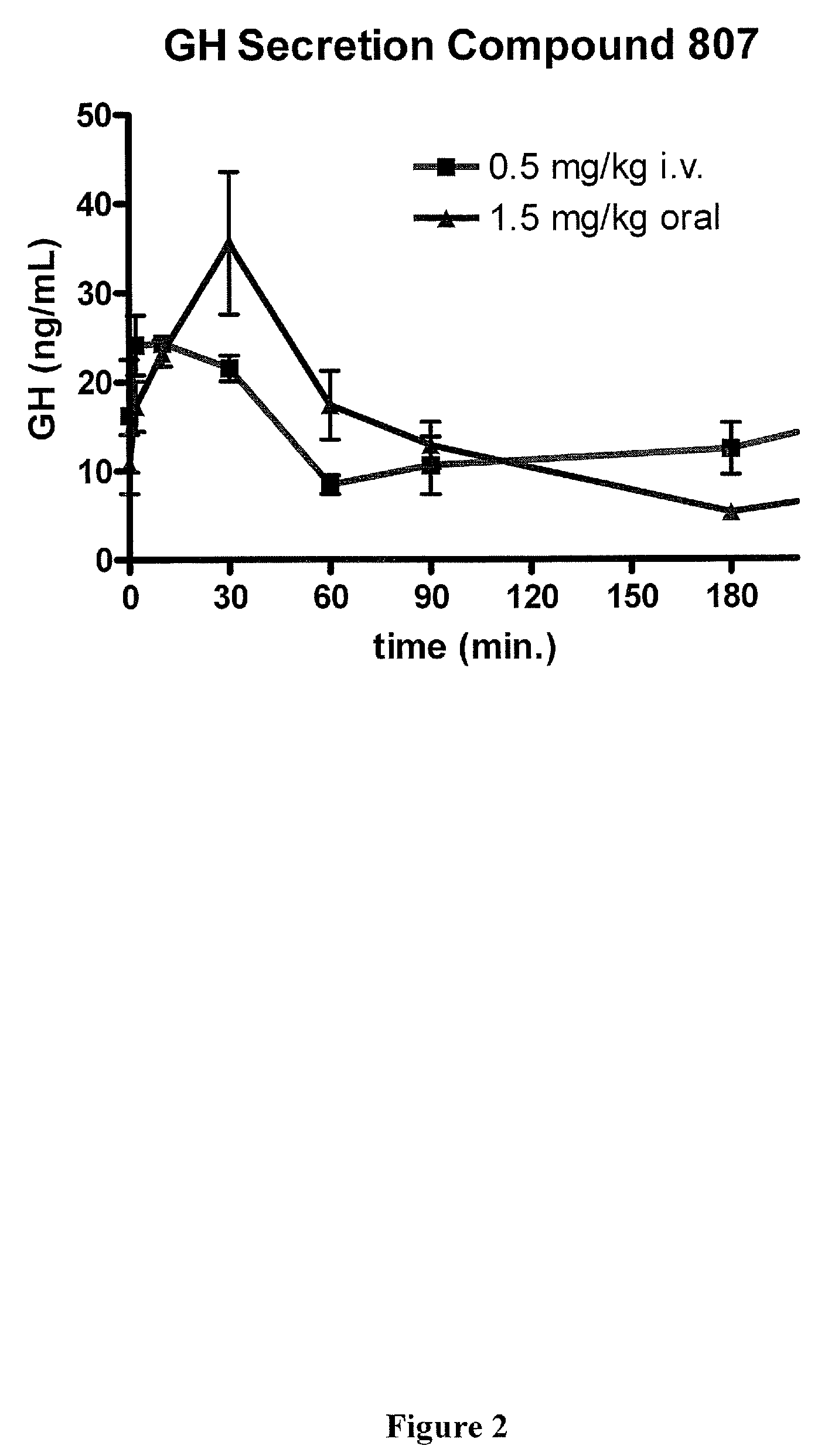
Macrocyclic ghrelin receptor modulators and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20080194672A1Reduced and dysfunctional gastrointestinal motilityInhibit gastrointestinal motilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSomatotropic hormonePharmaceutical Substances
The present invention provides novel conformationally-defined macrocyclic compounds that can function as selective modulators of the ghrelin receptor (growth hormone secretagogue receptor, GHS-R1a and subtypes, isoforms and variants thereof). Methods of synthesizing the novel compounds are also described herein. These compounds are useful as agonists of the ghrelin receptor and as medicaments for treatment and prevention of a range of medical conditions including, but not limited to, metabolic and / or endocrine disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, cardiovascular disorders, obesity and obesity-associated disorders, central nervous system disorders, bone disorders, genetic disorders, hyperproliferative disorders and inflammatory disorders.
Owner:OCERA THERAPEUTICS INC
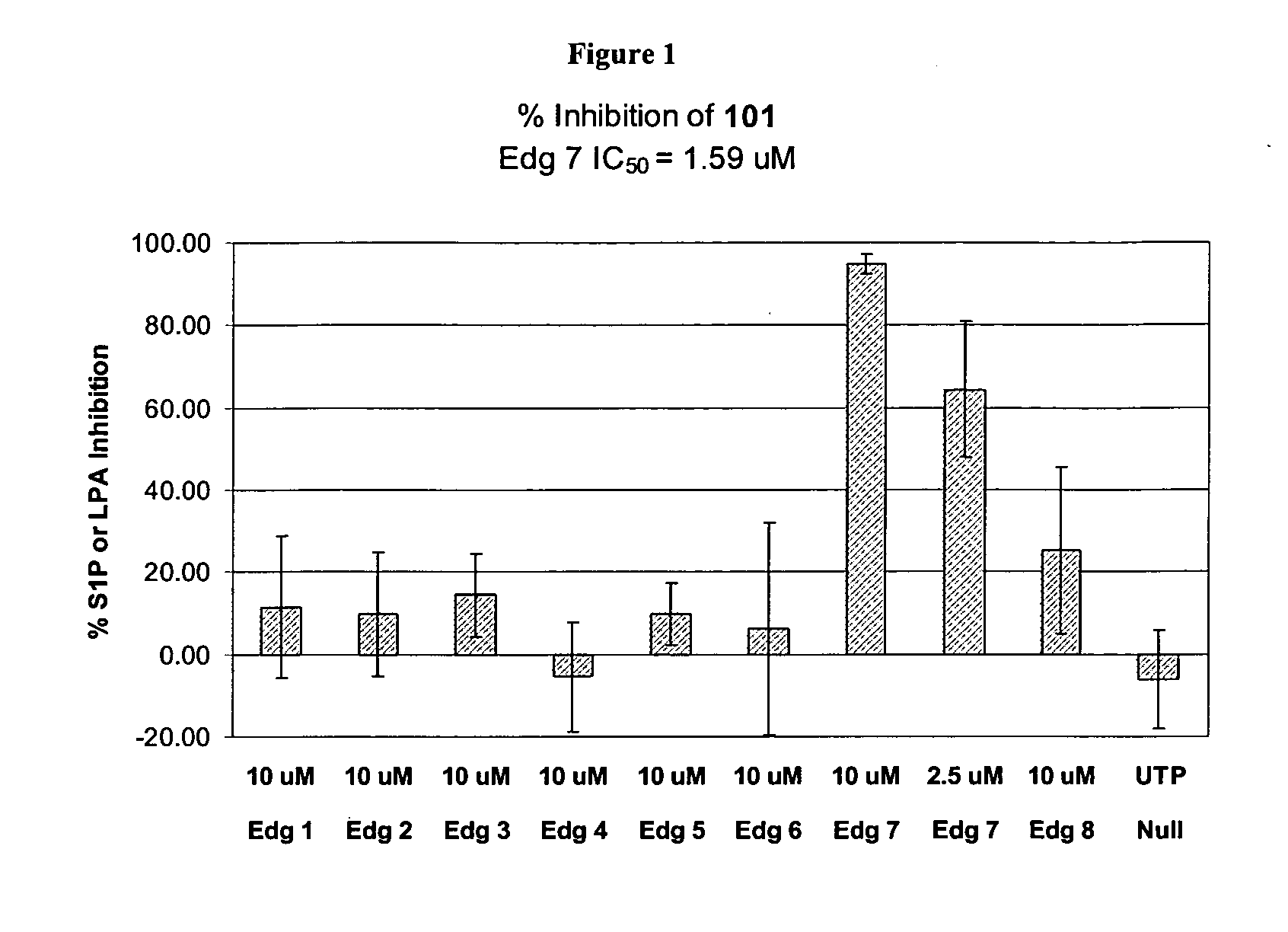
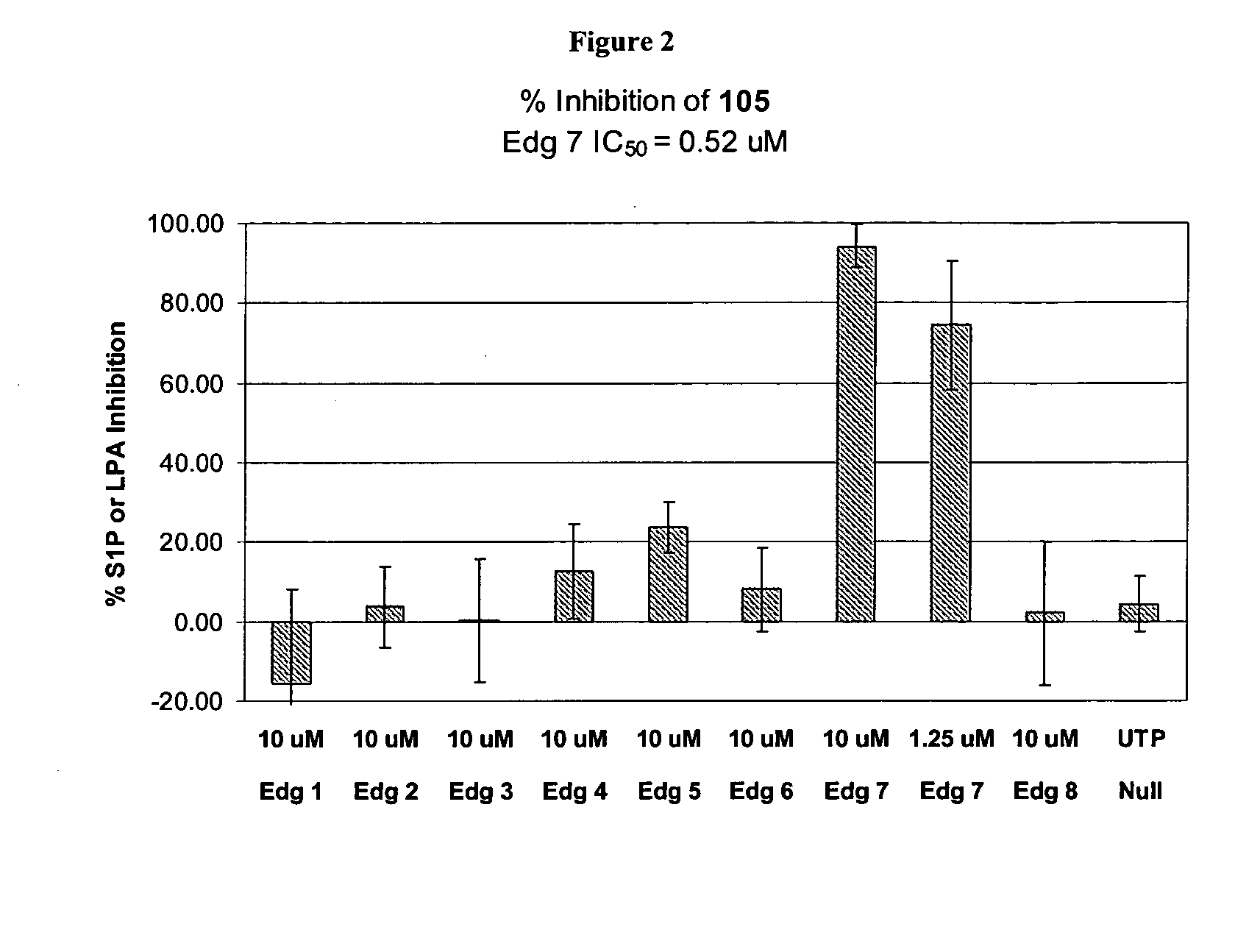
Methods of treating conditions associated with an Edg-7 receptor
InactiveUS20050261298A1Modulating biological activityEfficient modulationBiocideAnimal repellantsDrug biological activityEdg-7 Receptor
In one aspect, the present invention provides a method for modulating an Edg-7 receptor mediated biological activity in a cell. A cell expressing the Edg-7 receptor is contacted with a modulator of the Edg-7 receptor which is capable of modulating an Edg-7 receptor mediated biological activity. In another aspect, the present invention provides a method for modulating an Edg-7 receptor mediated biological activity in a subject. A therapeutically effective amount of a modulator of the Edg-7 receptor is administered to the subject.
Owner:MANIV ENERGY CAPITAL
Modulators of toll-like receptors
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
Spiroazacyclic compounds as monoamine receptor modulators
The present invention relates to spiroazacyclic compounds as monoamine receptor modulators; compositions comprising the same; methods of inhibiting an activity of a monoamine receptor with said compounds; methods of treating a disease condition associated with a monoamine receptor using said compounds; and methods for identifying a subject suitable for treatment using said compounds.
Owner:ACADIA PHARMA INC
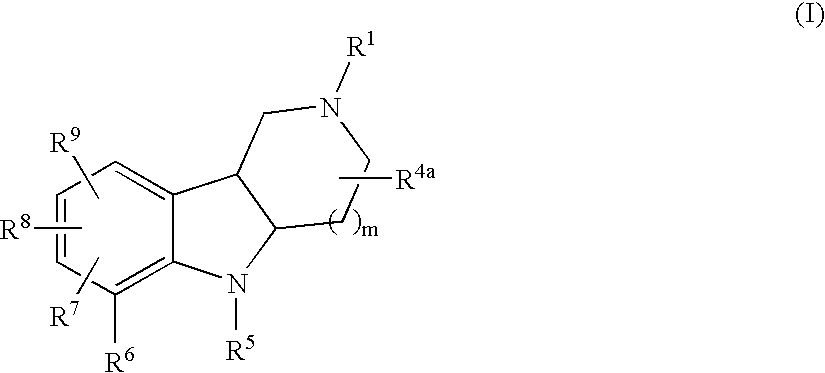
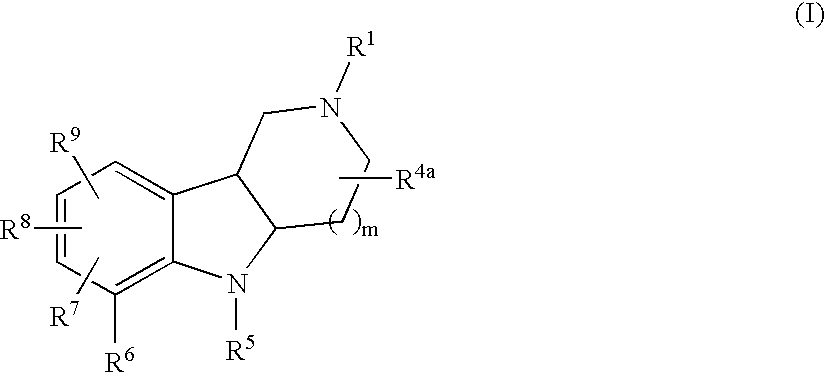
Substituted tricyclic gamma-carbolines as serotonin receptor agonists and antagonists
The present invention is directed to novel compounds represented by structural Formula (I):or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein R1, R4a, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9,and m, are defined herein. The invention is also concerned with pharmaceutical formulations comprising these novel compounds as active ingredients and the use of the novel compounds and their formulations in the treatment of certain central nervous system disorders. The compounds of this invention are serotonin receptor modulators, in particular 5HT2C receptor agonists and antagonists, and are useful in the control or prevention of central nervous system disorders including obesity, anorexia, bulemia, depression, anxiety, psychosis, schizophrenia, migraine, addictive behavior, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and sexual disorders.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Pharmaceutical Compositions of a 5-HT2A Serotonin Receptor Modulator Useful for the Treatment of Disorders Related Thereto
The present invention relates to certain pharmaceutical compositions of a 5-HT2A serotonin receptor modulator and methods for preparing pharmaceutical composition related thereto. The pharmaceutical compositions are useful in the treatment of platelet aggregation, coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, transient ischemic attack, angina, stroke, atrial fibrillation, reducing the risk of blood clot formation, asthma or symptoms thereof, agitation or a symptom, behavioral disorders, drug induced psychosis, excitative psychosis, Gilles de la Tourette's syndrome, manic disorder, organic or NOS psychosis, psychotic disorder, psychosis, acute schizophrenia, chronic schizophrenia, NOS schizophrenia and related disorders, sleep disorders, diabetic-related disorders, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and the like.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
Spiroazacyclic compounds as monoamine receptor modulators
The present invention relates to spiroazacyclic compounds as monoamine receptor modulators; compositions comprising the same; methods of inhibiting an activity of a monoamine receptor with said compounds; methods of treating a disease condition associated with a monoamine receptor using said compounds; and methods for identifying a subject suitable for treatment using said compounds.
Owner:ACADIA PHARMA INC
Pharmaceutical combination comprising an ibat inhibitor and a bile acid binder
InactiveUS20150031637A1Reduce generationEliminate the effects ofOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsDipeptidyl peptidaseEnzyme inhibitor
Owner:ALBIREO
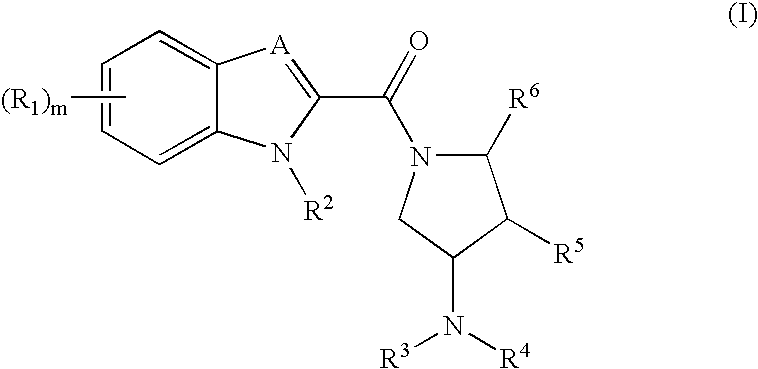
Indoles and benzoimidazoles as histamine H4 receptor modulators
Benzoimidazole and indole compounds are described, which are useful as H4 receptor modulators. Such compounds may be used in pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of disease states, disorders, and conditions mediated by H4 receptor activity, such as allergy, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and pruritis.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Human G protein-coupled receptors and modulators thereof for the treatment of metabolic-related disorders
InactiveUS6902902B2Lower Level RequirementsBiocideCompound screeningDyslipidemiaCoronary heart disease
The present invention relates to methods of identifying whether a candidate compound is a modulator of a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). In preferred embodiments, the GPCR is human. In other preferred embodiments, the GPCR is coupled to Gi and lowers the level of intracellular cAMP. In other preferred embodiments, the GPCR is expressed endogenously by adipocytes. In further preferred embodiments, the GPCR inhibits intracellular lipolysis. In other further preferred embodiments, the GPCR is a nicotinic acid receptor. The present invention also relates to methods of using a modulator of said GPCR. Preferred modulator is agonist. Agonists of the invention are useful as therapeutic agents for the prevention or treatment of metabolic-related disorders, including dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, stroke, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes.
Owner:ARENA PHARMA
Pharmaceutical combination comprising an ibat inhibitor and a bile acid binder
InactiveUS20170182115A1Reduce generationEliminate the effects ofOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsDipeptidyl peptidasePancreatic hormone
The present invention relates to a combination comprising a substance with inhibiting effect on the ileal bile acid transport system (I BAT) and at least one other active substance selected from an IBAT inhibitor; an enteroendocrine peptide or enhancer thereof; a dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor; a biguanidine; an incretin mimetic; a thiazolidinone; a PPAR agonist; a HMG Co-A reductase inhibitor; a bile acid binder; and a TGR5 receptor modulator; wherein the IBAT inhibitor compound and the at least one other active substance are adminstered simultaneously, sequentially or separately.
Owner:ALBIREO
Compounds Which Modulate The CB2 Receptor
Compounds are provided which bind to and are agonist, antagonists or inverse agonists of the CB2 receptor, the compounds having the general formula (I) wherein R1, R2, R3, X and Ar have the meanings given in the specification, and the preparation and use thereof. The compounds are valuable CB2 receptor modulators, and are useful for treating inflammation. Those compounds which are agonists are additionally useful for treating pain.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Pyrimidine derivatives as ghrelin receptor modulators
The present invention is related to compounds of formula (I), or a therapeutically suitable salt or prodrug thereof, the preparation of the compounds, compositions containing the compounds and the use of the compounds in the prevention or treatment of disorders regulated by ghrelin including anorexia, cancer cachexia, eating disorders, age-related decline in body composition, weight gain, obesity, and diabetes mellitus.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Compounds Which Modulate The CB2 Receptor
Compounds are provided which bind to and are agonists, antagonists or inverse agonists of the CB2 receptor, the compounds having the general formula wherein, R1, R2, A, Y, X, Ar1 and Ar2 have the meanings given in the specification, and the preparation and use thereof. The compounds are valuable CB2 receptor modulators.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
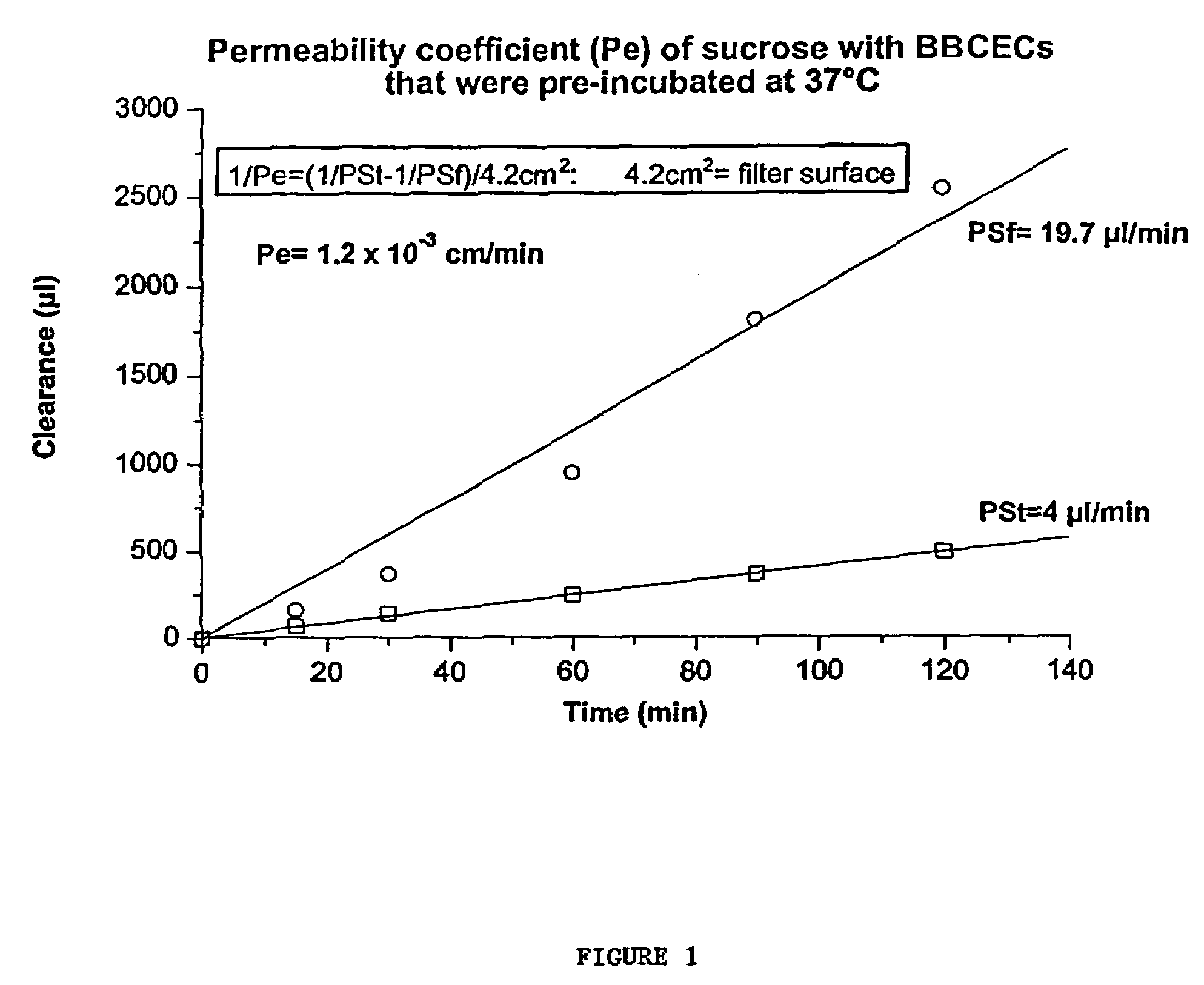
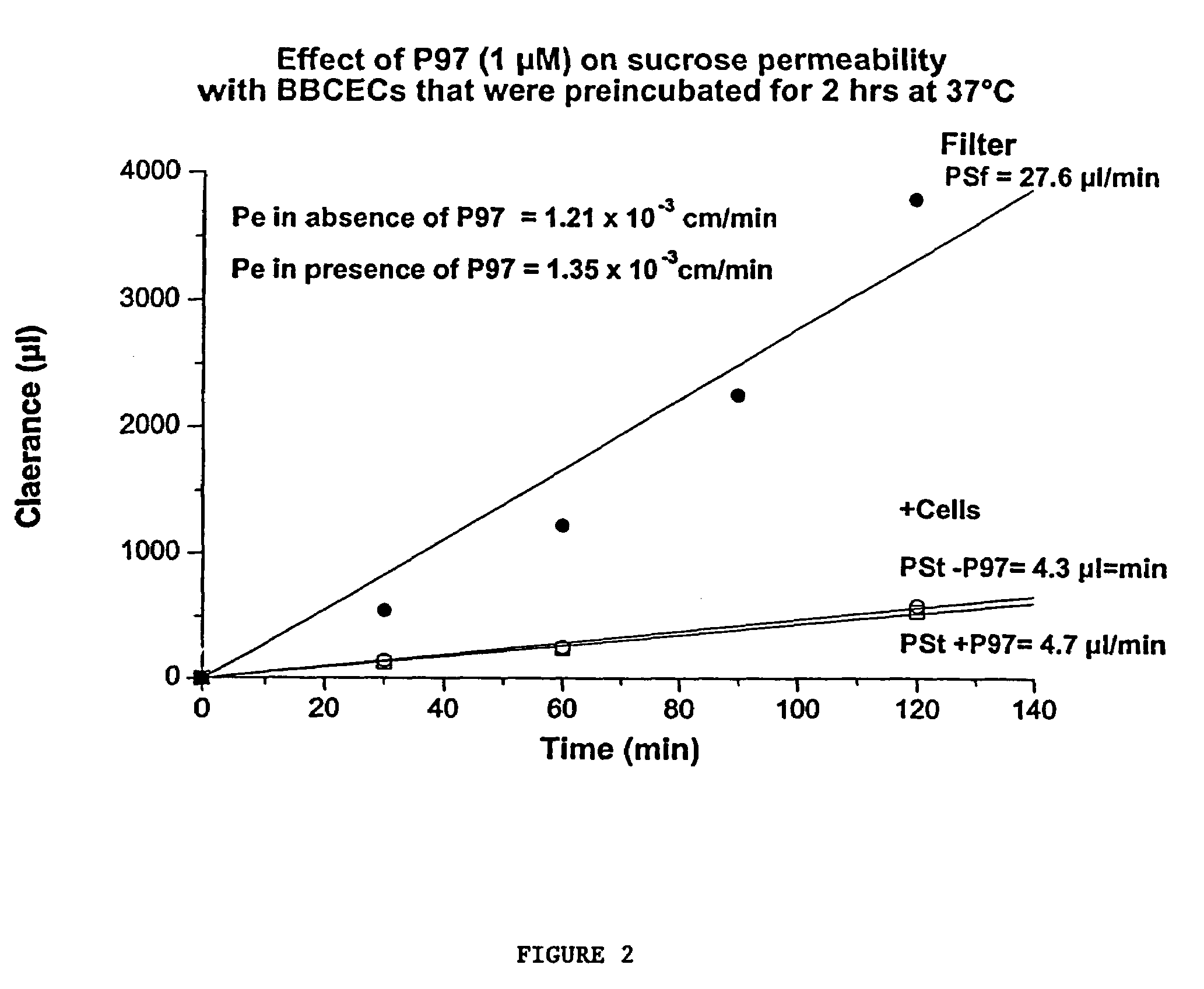
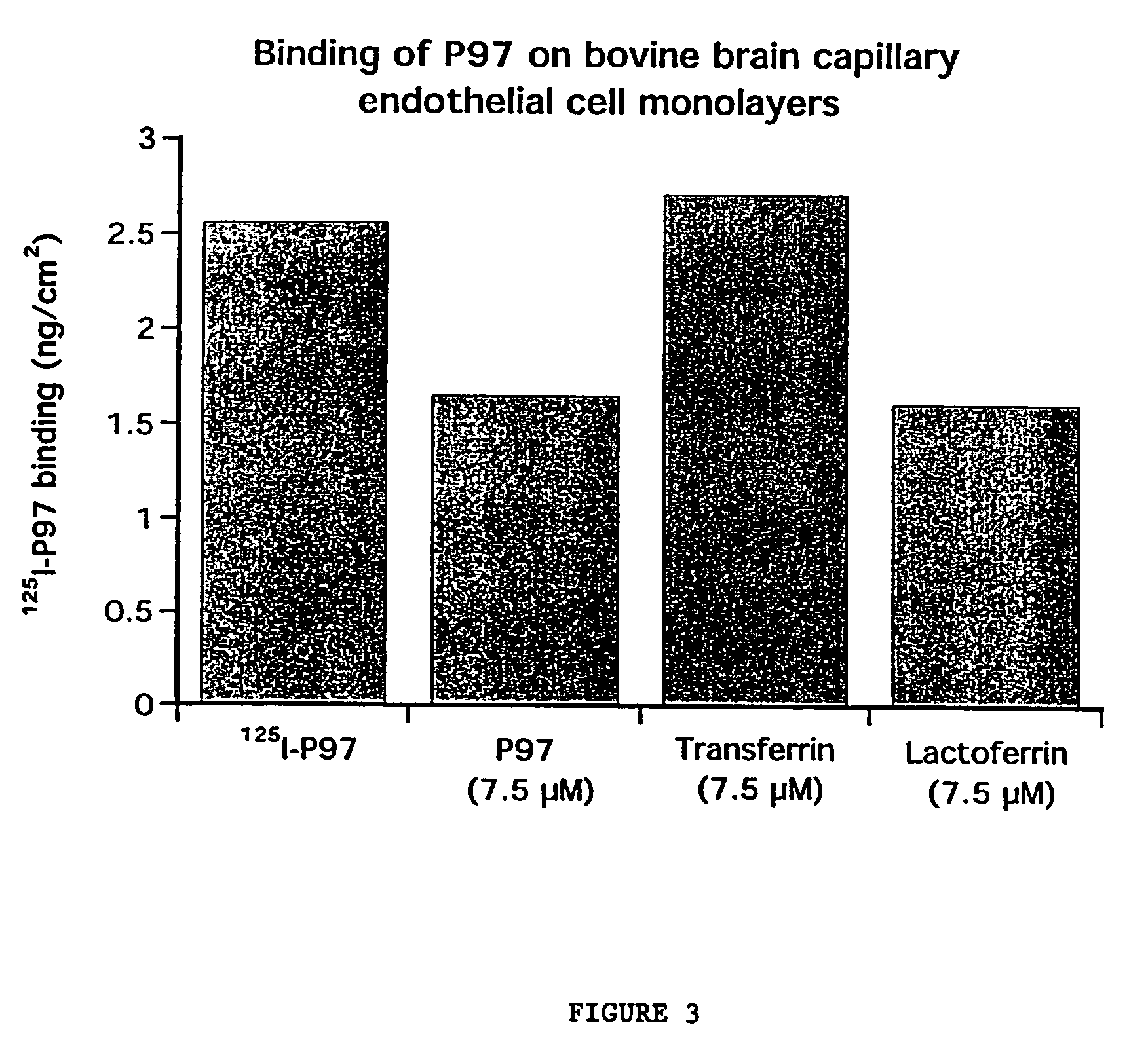
Compositions for modulating blood-brain barrier transport
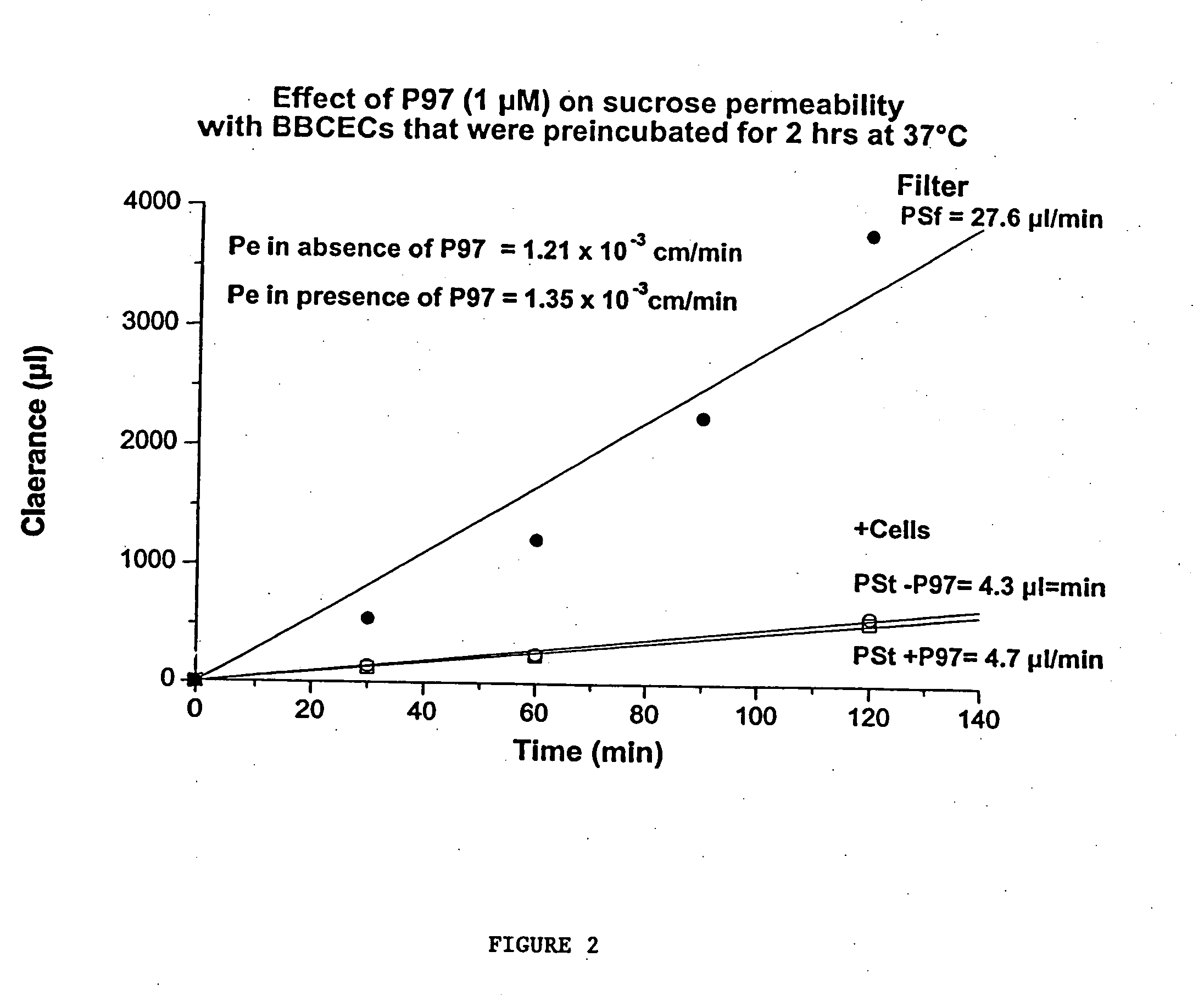
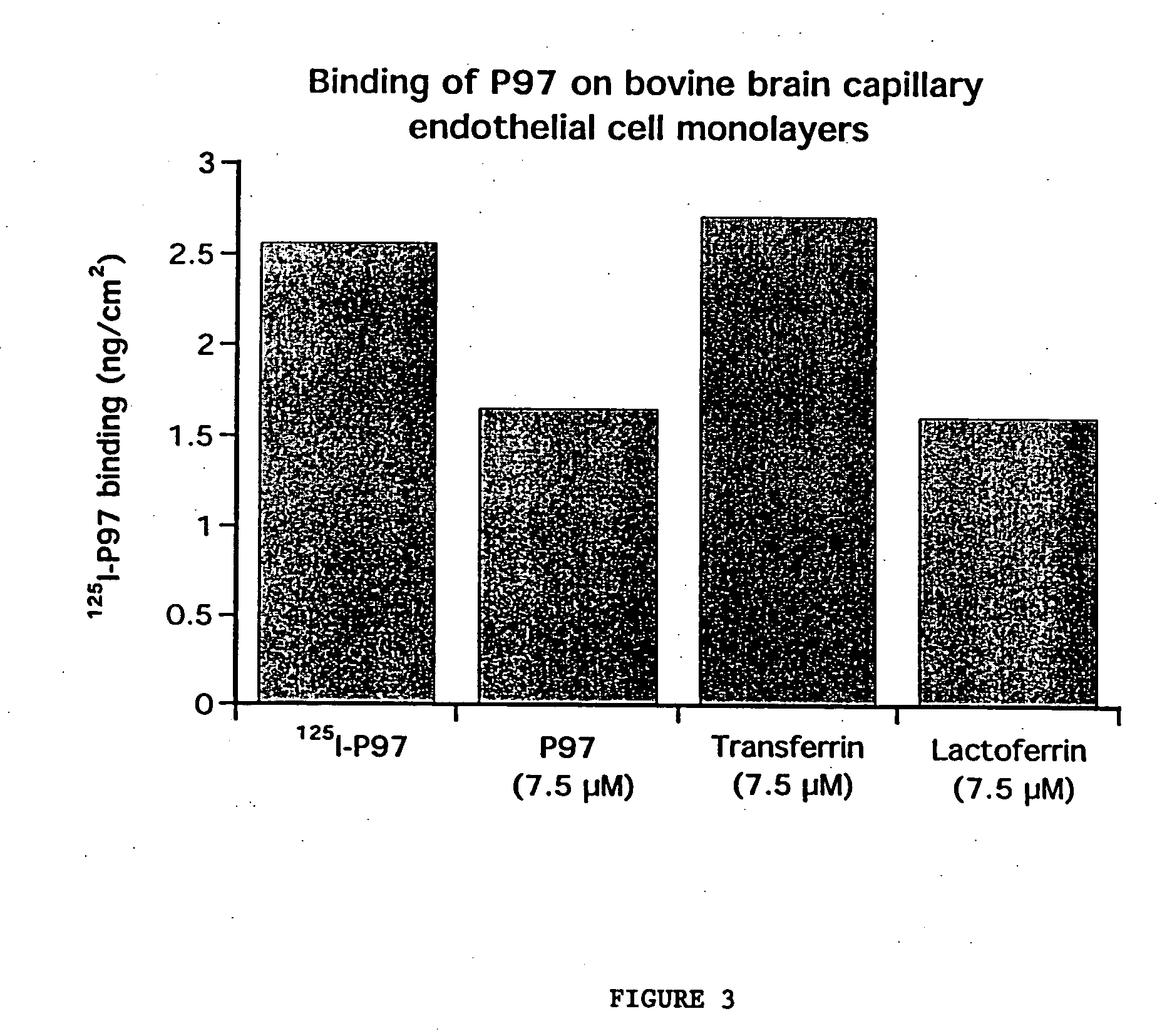
InactiveUS7700554B2Reducing a neurological side-effectReceive treatment wellOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderActive agentLysosome
This invention provides conjugates of therapeutic or active agents with melanotransferrin or with other ligands of a melanotransferrin receptor, melanotransferrin receptor modulators, and related compositions and methods for modulating blood-brain barrier transport by providing methods of screening and selecting such conjugates, ligands, and modulators in vitro and in vivo, and methods of use of such conjugates, modulators and ligands in diagnosis and the treatment of diseases, including particularly diseases of the central nervous system or lysosomal storage diseases.
Owner:HORIZON ORPHAN LLC
Pharmaceutical combination comprising an ibat inhibitor and a bile acid binder
InactiveUS20130236541A1Maximal bile acid binding capacityDecrease needed doseOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDipeptidyl peptidaseAldose reductase inhibitor
The present invention relates to a combination comprising a substance with inhibiting effect on the ileal bile acid transport system (I BAT) and at least one other active substance selected from an IBAT inhibitor; an enteroendocrine peptide or enhancer thereof; a dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor; a biguanidine; an incretin mimetic; a thiazolidinone; a PPAR agonist; a HMG Co-A reductase inhibitor; a bile acid binder; and a TGR5 receptor modulator; wherein the IBAT inhibitor compound and the at least one other active substance are administered simultaneously, sequentially or separately.
Owner:ALBIREO
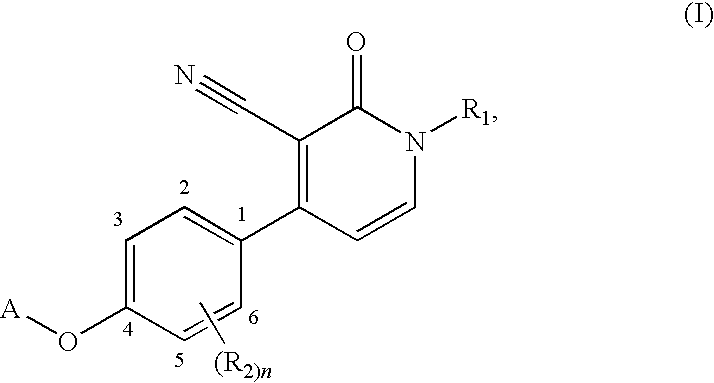
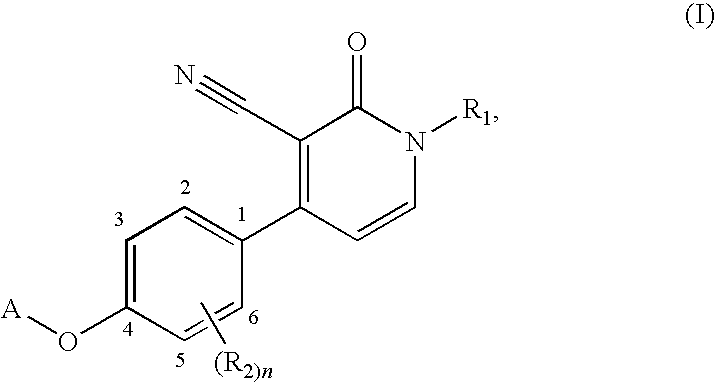
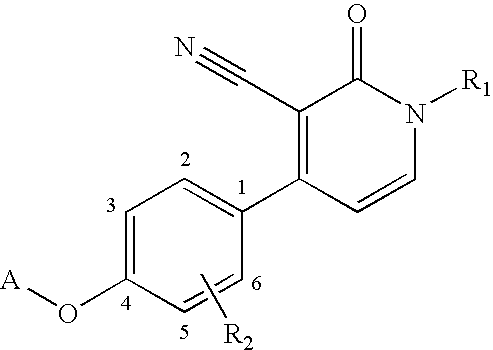
1,4-disubstituted 3-cyano-pyridone derivatives and their use as positive mglur2-receptor modulators
The present invention relates to novel compounds, in particular novel pyridinone derivatives according to Formula (I) including any stereochemically isomeric form thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a solvate thereof, wherein all radicals are defined in the application and claims. The compounds according to the invention are positive allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate receptors subtype 2 (“mGluR2”) which are useful for the treatment or prevention of neurological and psychiatric disorders associated with glutamate dysfunction and diseases in which the mGluR2 subtype of metabotropic receptors is involved. In particular, such diseases are central nervous system disorders selected from the group of anxiety, schizophrenia, migraine, depression, and epilepsy. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions and processes to prepare such compounds and such compositions, as well as to the use of such compounds for the prevention and treatment of such diseases in which mGluR2 is involved.
Owner:ADDEX PHARM SA +1
Compositions and methods for modulating blood-brain barrier transport
InactiveUS20070167365A1Receive treatment wellIncrease the amount addedNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsActive agentLysosomal enzyme defect
This invention provides conjugates of therapeutic or active agents with melanotransferrin or with other ligands of a melanotransferrin receptor, melanotransferrin receptor modulators, and related compositions and methods for modulating blood-brain barrier transport by, providing methods of screening and selecting such conjugates, ligands, and modulators in vitro and in vivo, and methods of use of such conjugates, modulators and ligands in diagnosis and the treatment of diseases, including particularly diseases of the central nervous system or lysosomal storage diseases.
Owner:HORIZON ORPHAN LLC
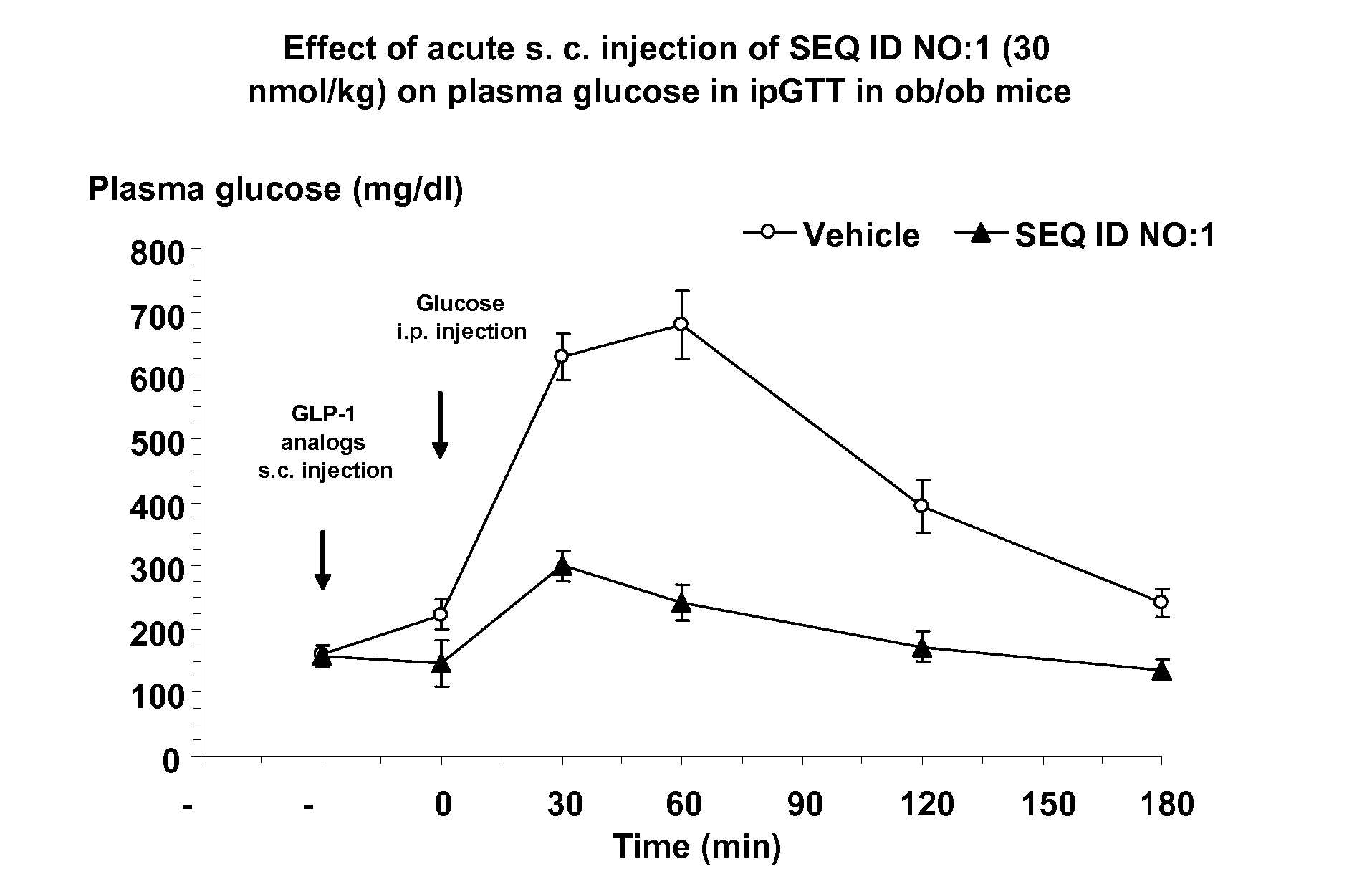
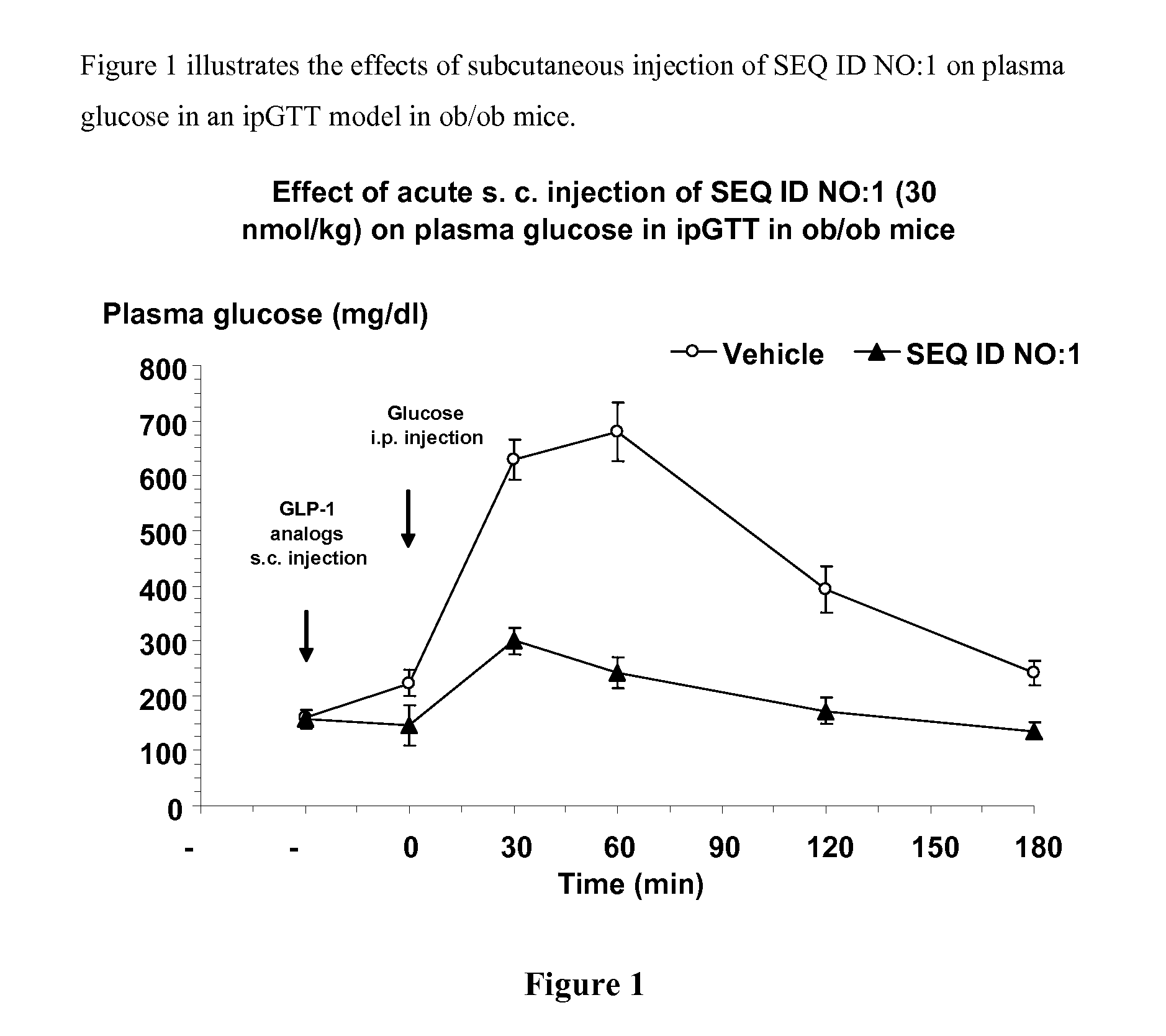
Human glucagon-like-peptide-1 modulators and their use in the treatment of diabetes related conditions
InactiveUS20070238669A1Improve the level ofNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsGlucagon-like peptide-1Drug biological activity
The present invention provides novel human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)-receptor modulators that have biological activity similar or superior to native GLP-1 peptide and thus are useful for the treatment or prevention of diseases or disorders associated with GLP activity. Further, the present invention provides novel, chemically modified compounds that not only stimulate insulin secretion in type II diabetics, but also produce other beneficial insulinotropic responses. These synthetic peptide GLP-1 receptor modulators exhibit increased stability to proteolytic cleavage making them ideal therapeutic candidates for oral or parenteral administration. The compounds of this invention show desirable pharmacokinetic properties and desirable potency in efficacy models of diabetes.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com