Method for preparation of active form of long-acting insulin analogue conjugate by using clostripain
A technology of insulin analogs and long-acting insulin, applied in the direction of insulin, biochemical equipment and methods, albumin peptide, etc., can solve the problems that are difficult to apply to large-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0092] Embodiment 1: the construction of the insulin expression vector and bacterial strain of fusion ABD
[0093] Human insulin is synthesized as preproinsulin, the presequence is cleaved in the endoplasmic reticulum, and the proinsulin is processed in the Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum to form mature insulin. Based on this fact, proinsulin was designed to produce recombinant insulin by expressing proinsulin protein in Escherichia coli and then removing the C chain by trypsin treatment. In order to improve the expression efficiency and purification efficiency of proinsulin in Escherichia coli, a fusion tag was inserted into the N-terminus, and codon optimization was performed.
[0094]Theoretically, the number of sites that an albumin binding domain (ABD) can be fused to insulin is four. However, the N-terminus of the A chain is a position important for insulin activity and was therefore excluded from fusion positions. Although the N-terminus of the B chain is important fo...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Example 2: Construction of Insulin Analogues Fused with ABD with Modified Insulin Amino Acid Sequence
[0105] In order to produce insulin using recombinant Escherichia coli, a method of converting proinsulin into an active form by using trypsin is necessary. However, trypsin cleaves dibasic amino acids with high efficiency, and also cleaves single amino acids such as lysine (Lys) or arginine (Arg), which makes it difficult to produce the desired active form of insulin. In addition, the ABD sequence also includes many lysine (Lys) and arginine (Arg) residues, which makes it difficult to further produce the desired ABD-fused insulin with activity by using trypsin.
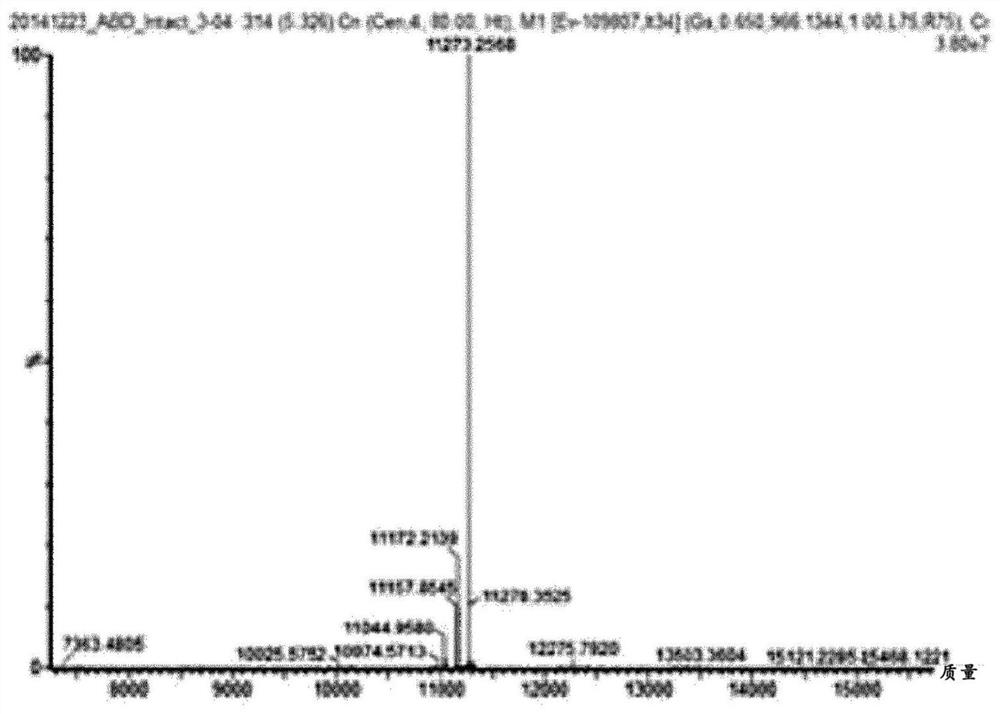
[0106] For this reason, clostripain was used as an enzyme capable of replacing trypsin in order to induce conversion into the active form. In this case, when clostripain reacts with ABD-fused insulin, the arginine (Arg) at position 22 of the insulin B chain is cleaved. To solve this problem, position 22 of ...
Embodiment 3
[0112] Example 3: Expression of insulin analogs fused to ABD
[0113] In order to express an ABD-fused insulin analog, each recombinant E. coli strain was inoculated in 100 mL of LB medium, cultured with shaking at 37° C. for 16 hours, and the culture was used as a seed culture. 2L of LB medium was added to a 7L fermenter (New Brunswick BioFlo), sterilized, and then inoculated with the seed culture. The culture was carried out at a temperature of 35° C., an air flow rate of 3 vvm, and a stirring speed of 1,000 rpm, and the pH during the culture was maintained at 6.8 with ammonia water and phosphoric acid. At the time point when the carbon source was depleted in the medium, feeding was started and protein expression was simultaneously induced with IPTG. After induction of expression, culture was carried out for 10 hours, and the recombinant strain was recovered using a centrifuge.
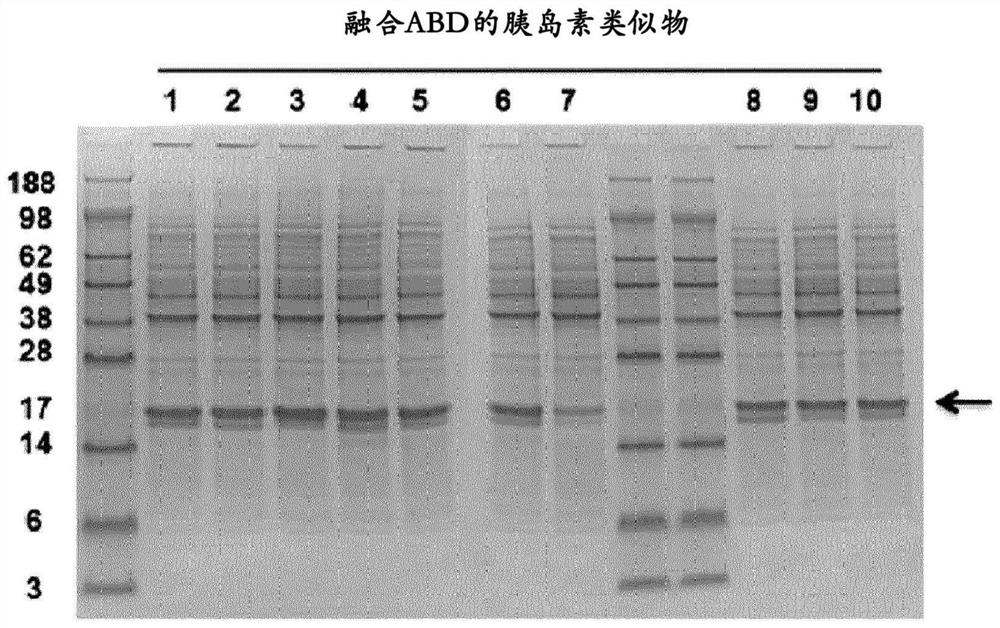
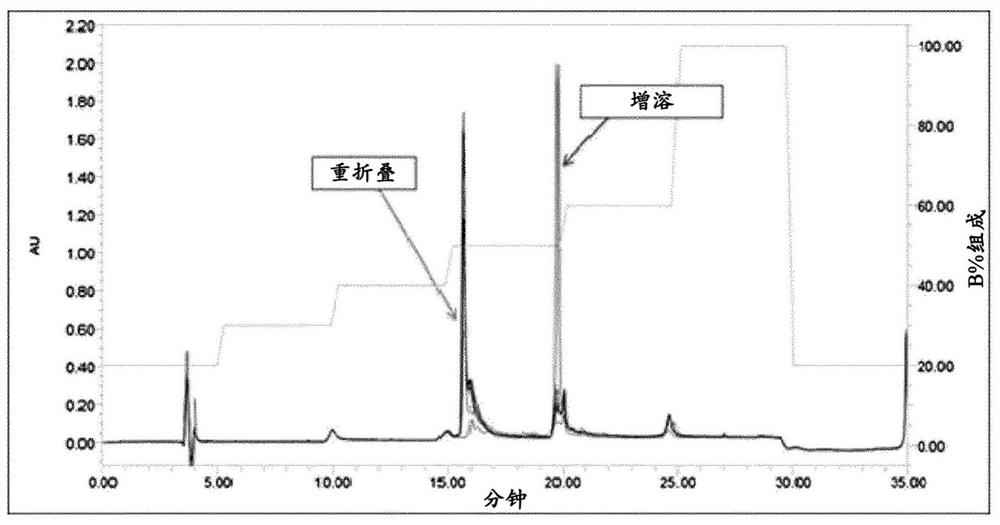
[0114] Insulin analogues fused to ABD were expressed as inclusion bodies in E. coli strains, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com