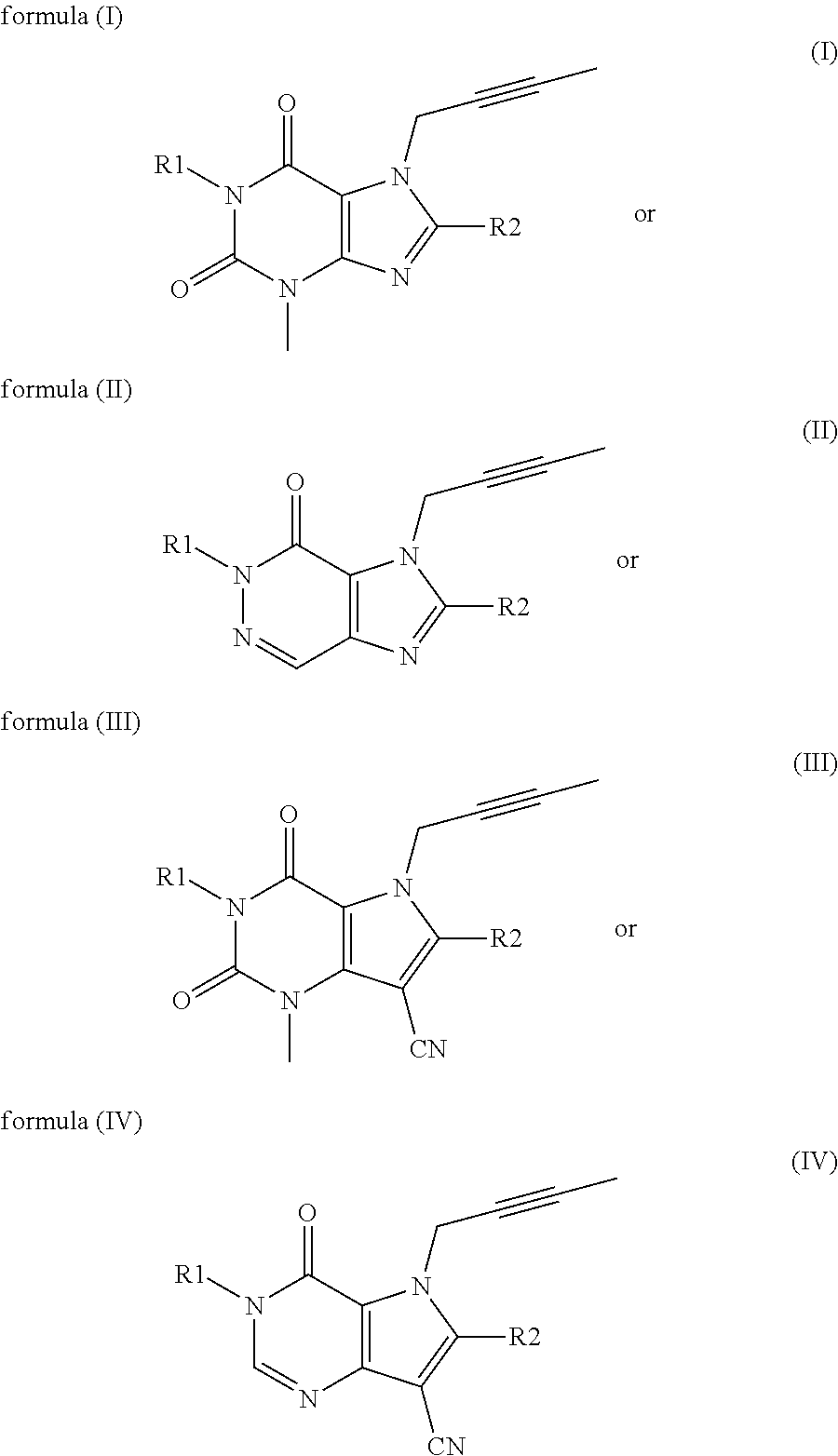
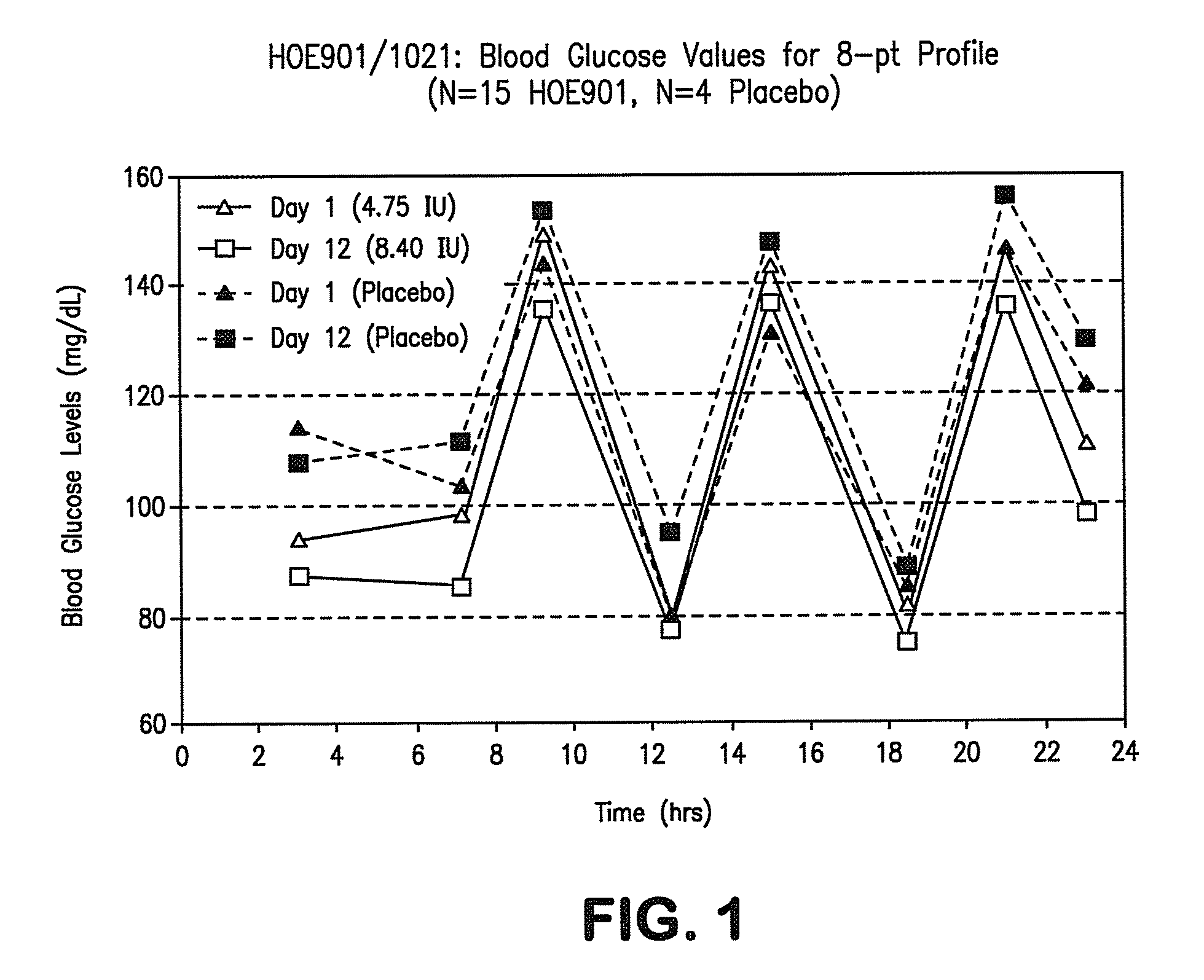
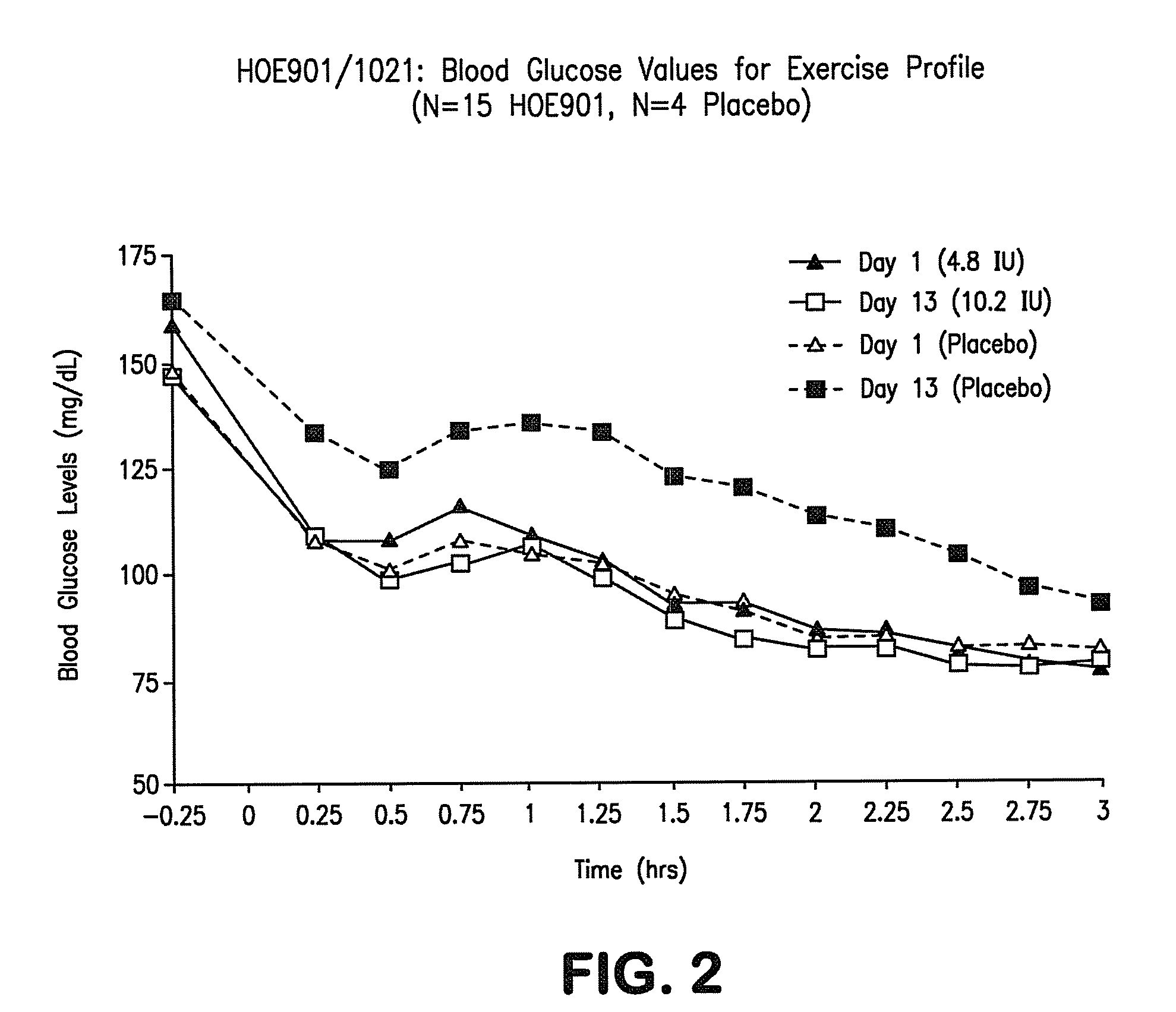
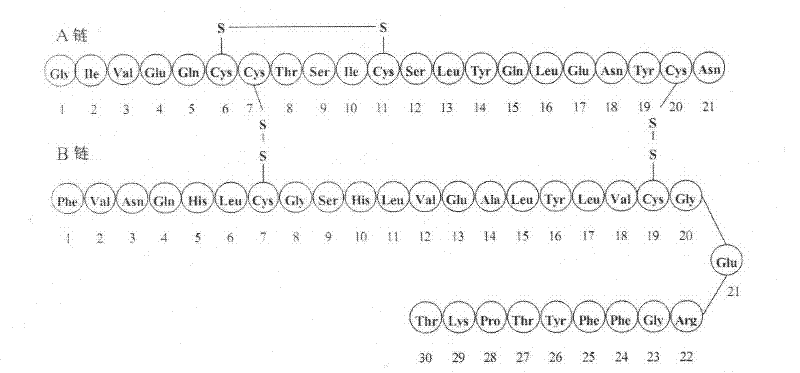
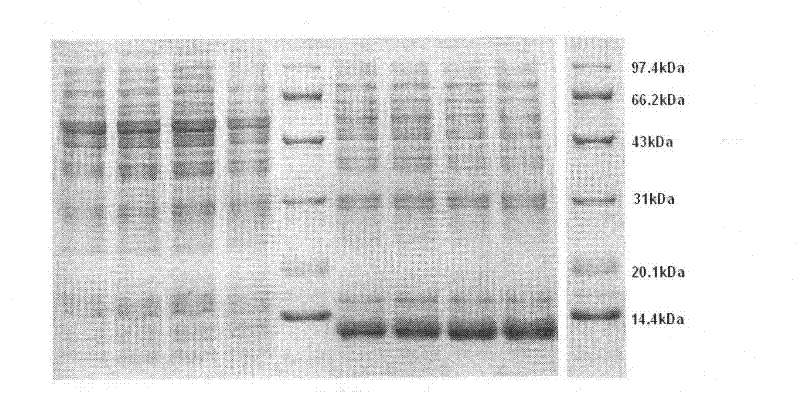
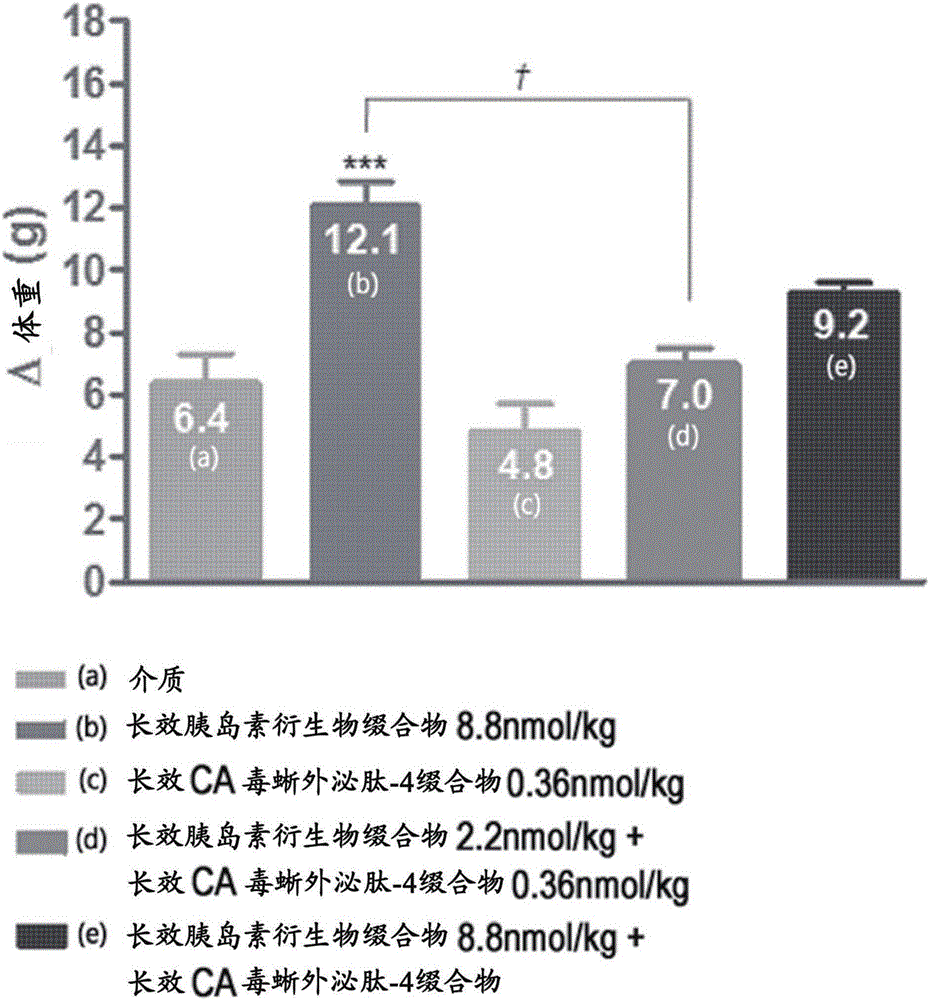
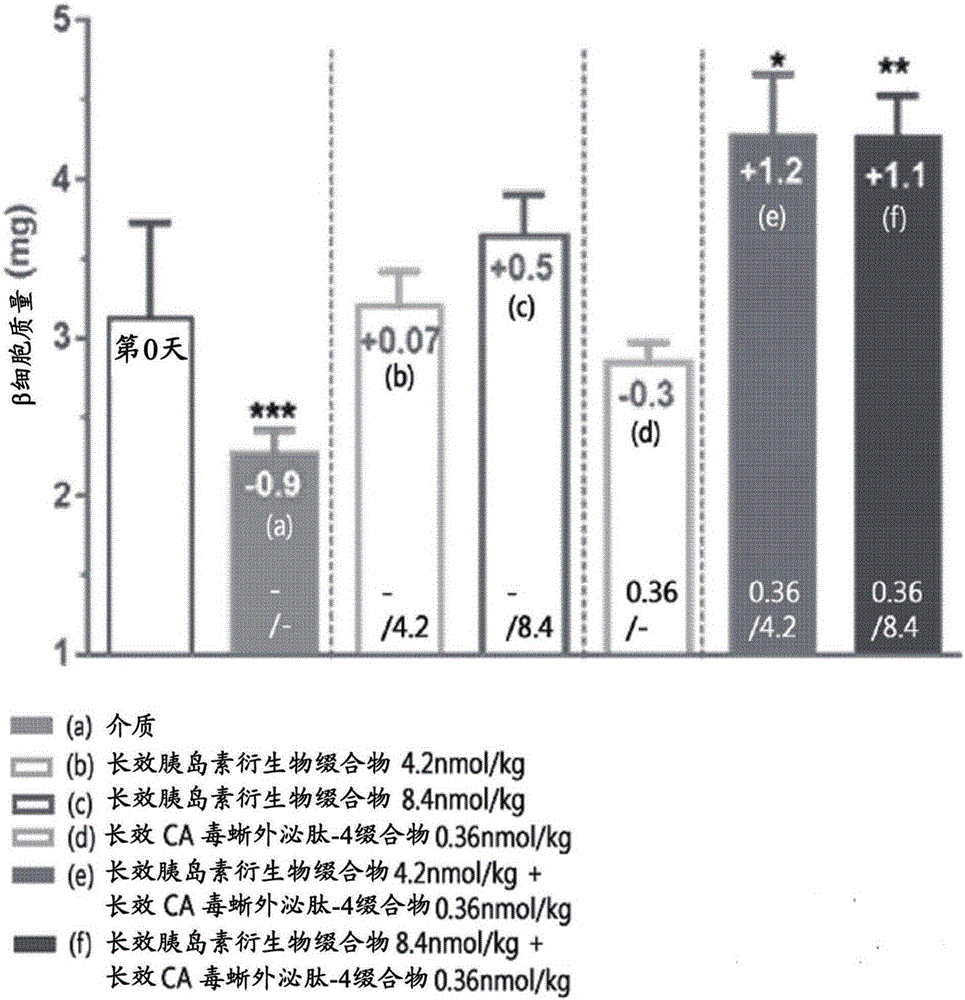
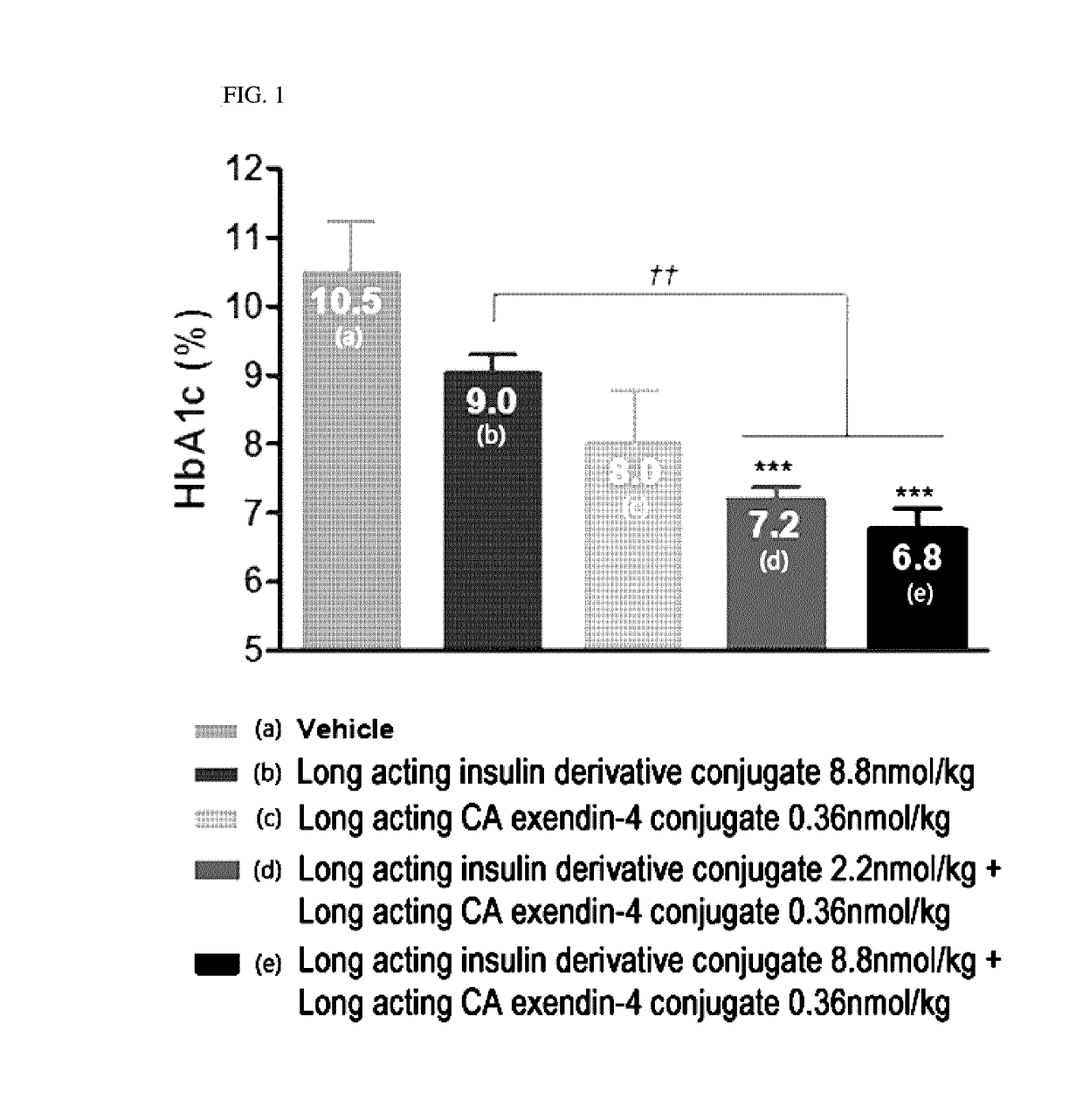
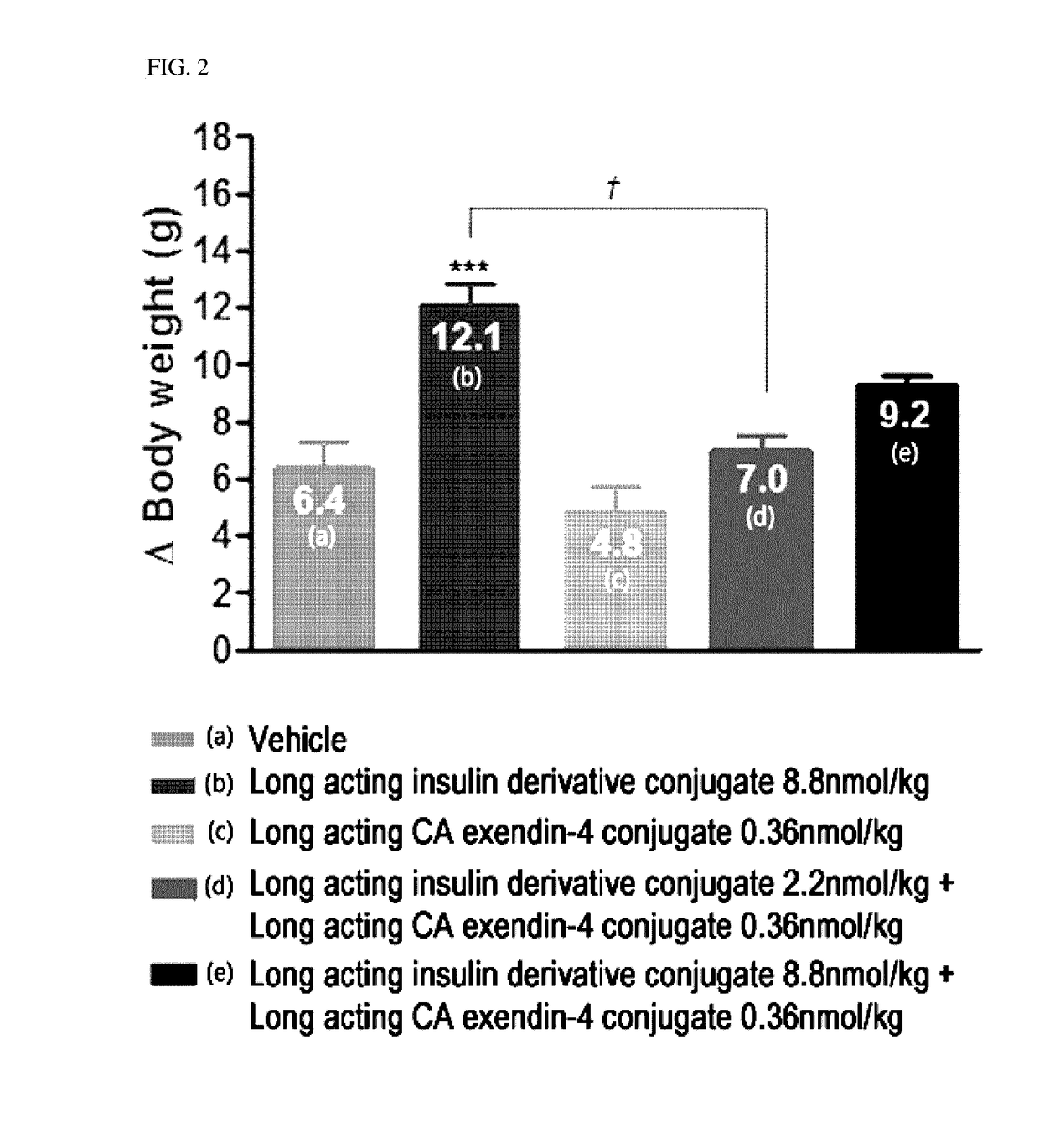
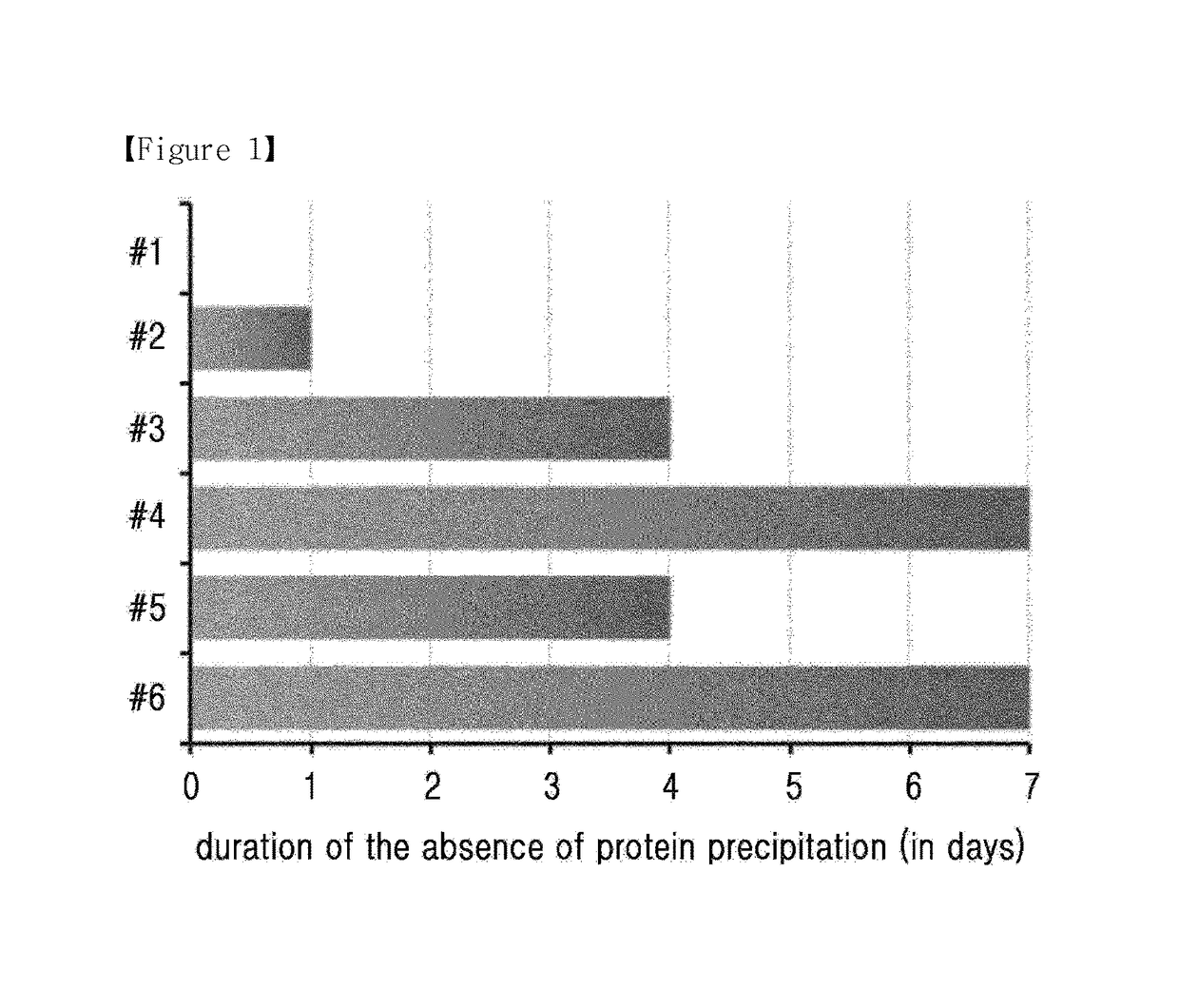
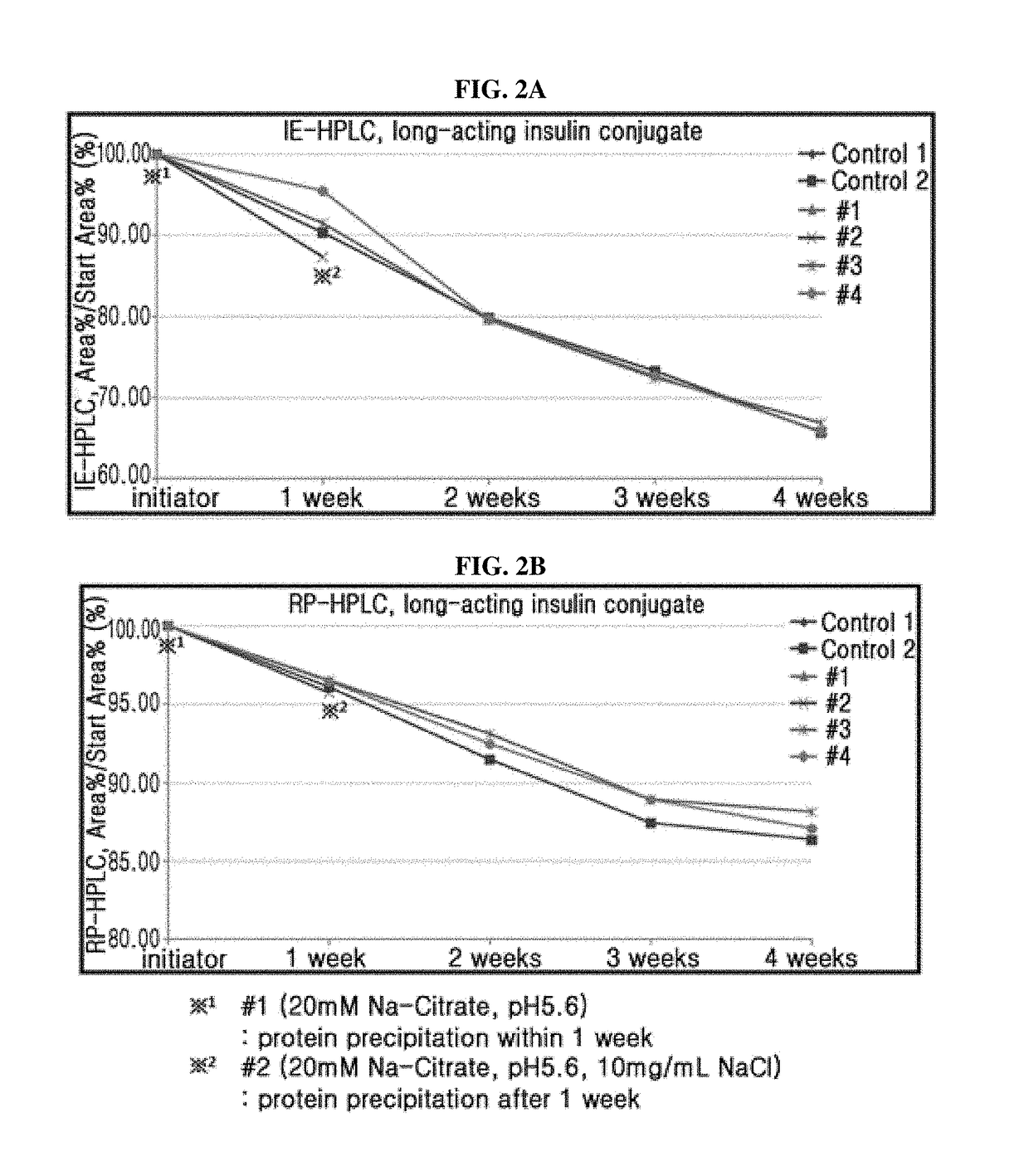
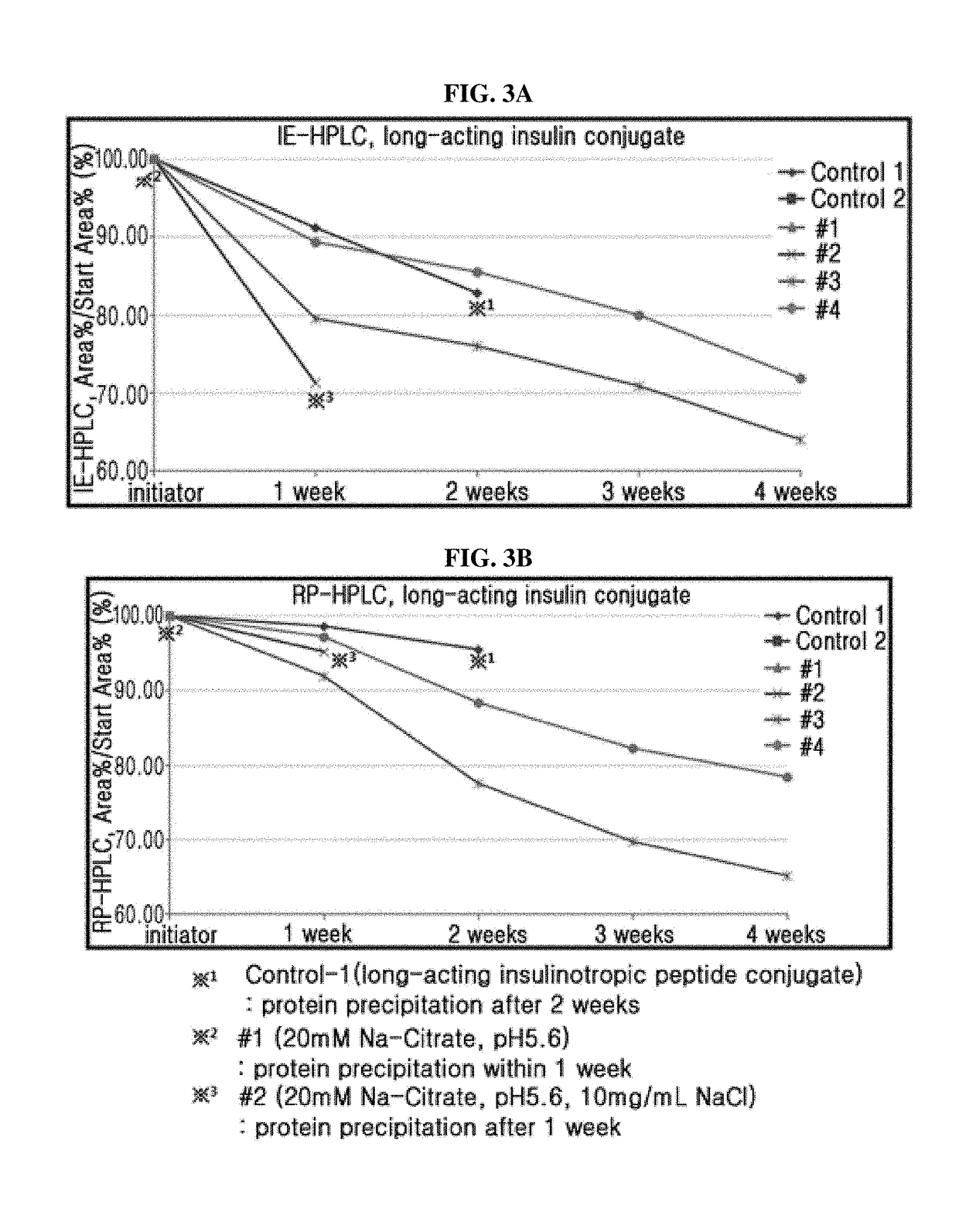
Patents
Literature
62 results about "Long acting insulin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
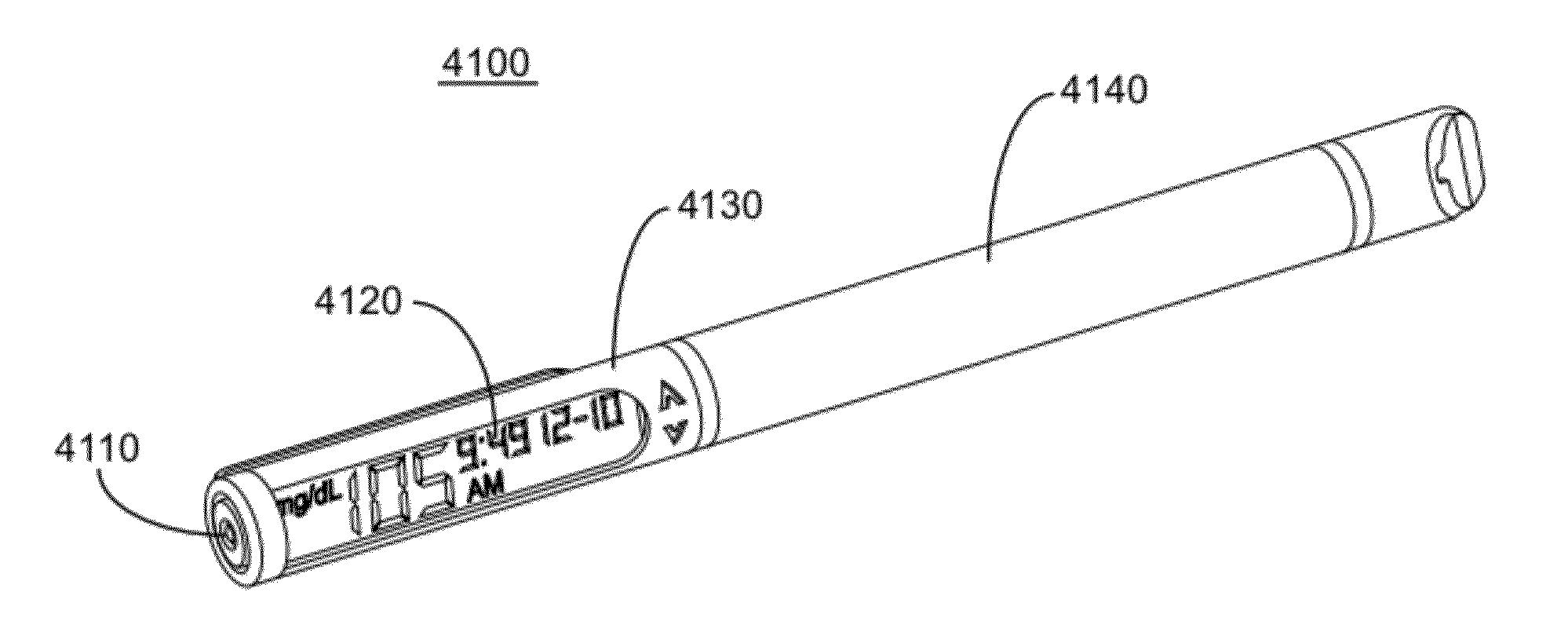
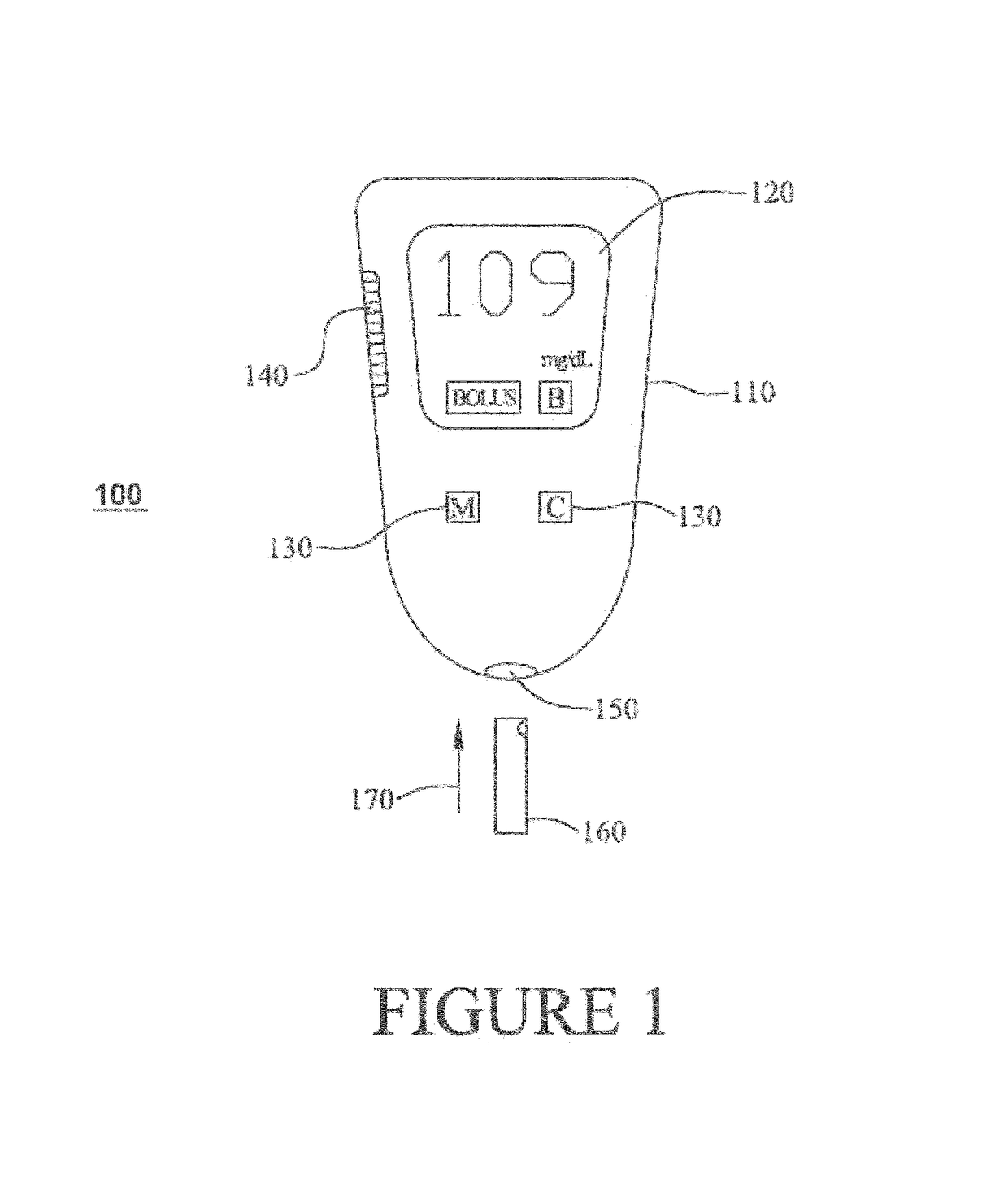
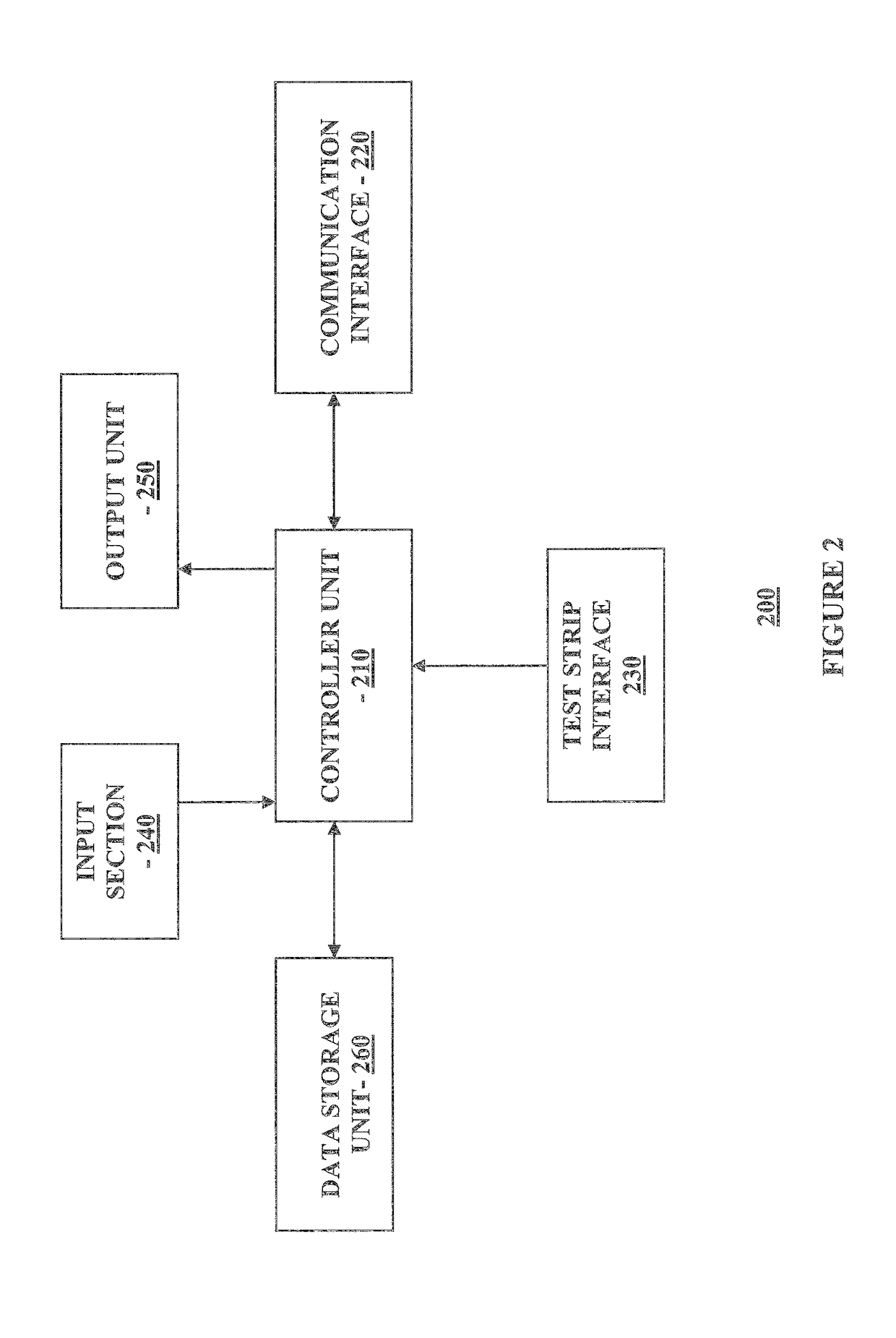
Multi-Function Analyte Monitor Device and Methods of Use
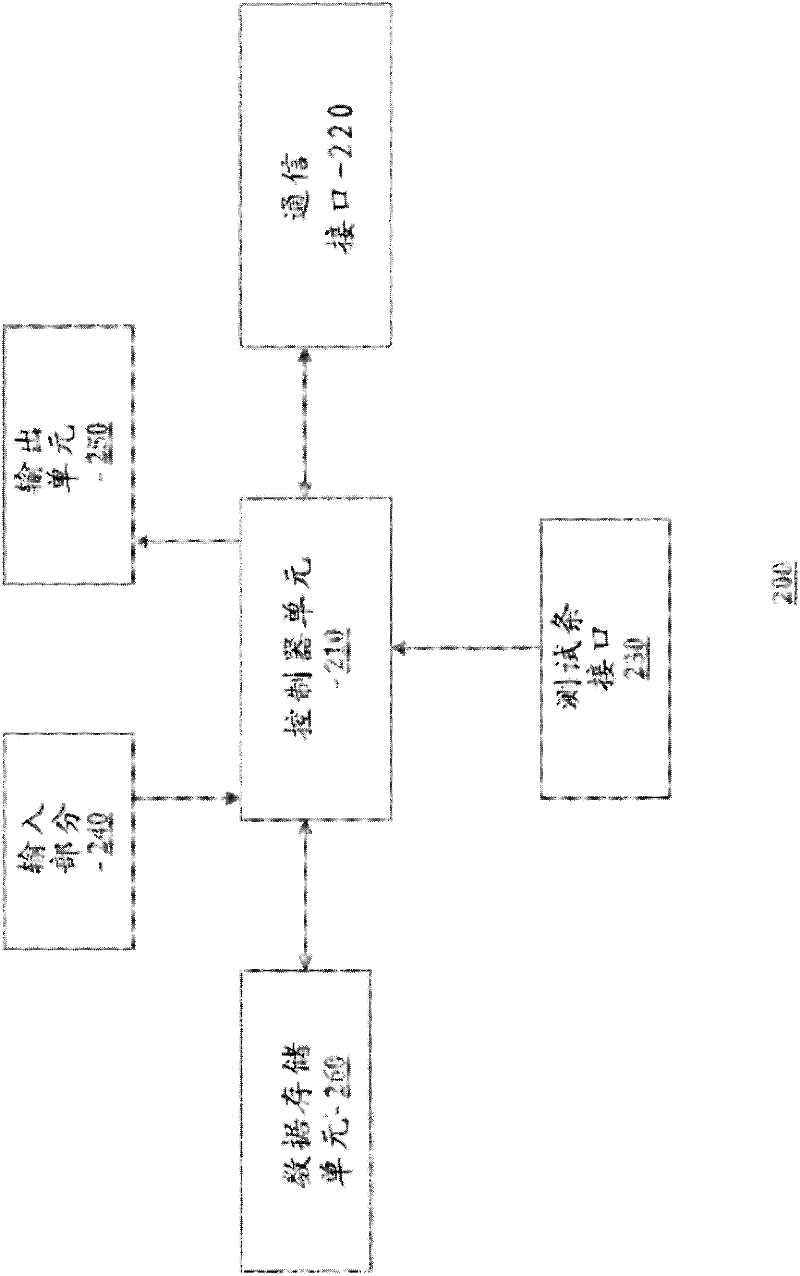
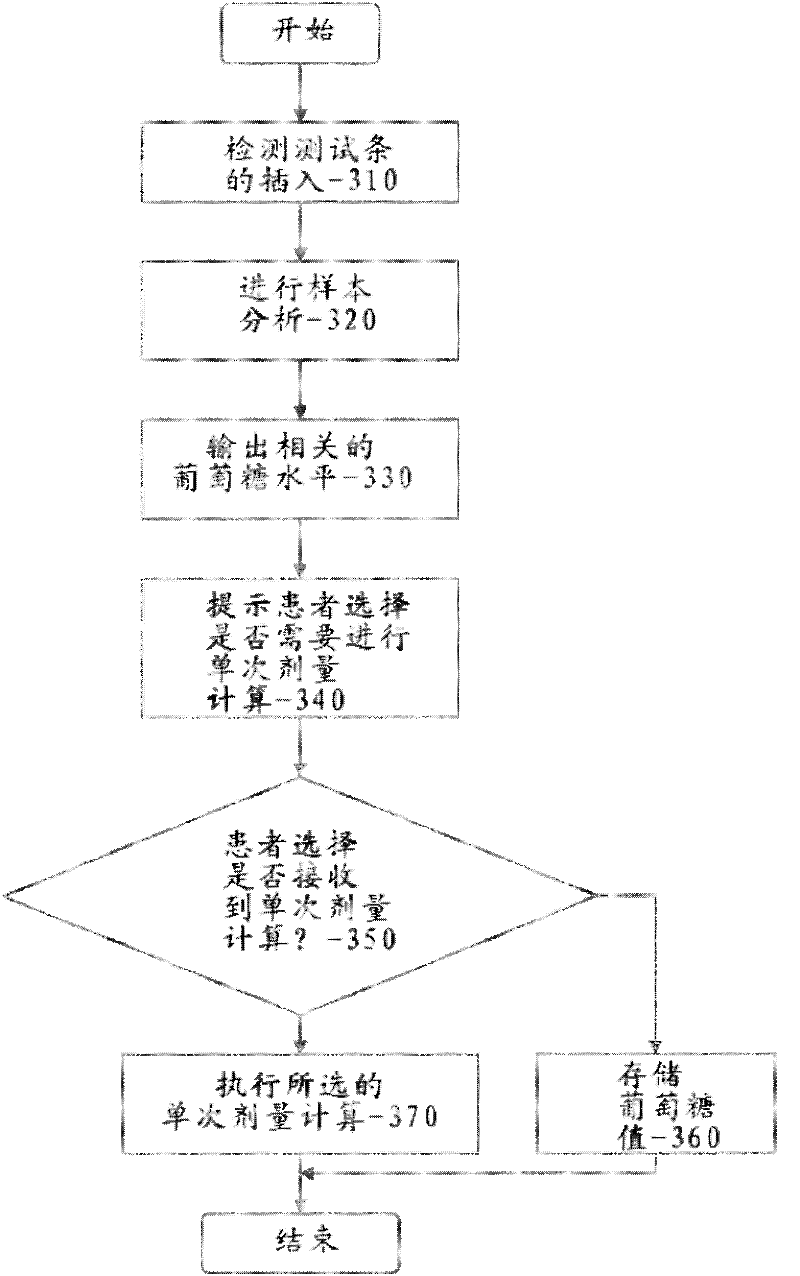
Methods, systems and devices for detecting an analyte sample, determining an analyte concentration associated with the detected analyte sample, storing the determined analyte concentration and a time associated with the determined analyte concentration, retrieving two or more stored analyte concentrations, and determining an adjusted dose level based at least in part on a current dose level and data associated with the two or more retrieved analyte concentrations are provided. For example, adjustments to dosage levels of long-acting insulin may be provided to assist in the management of diabetes and related conditions.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
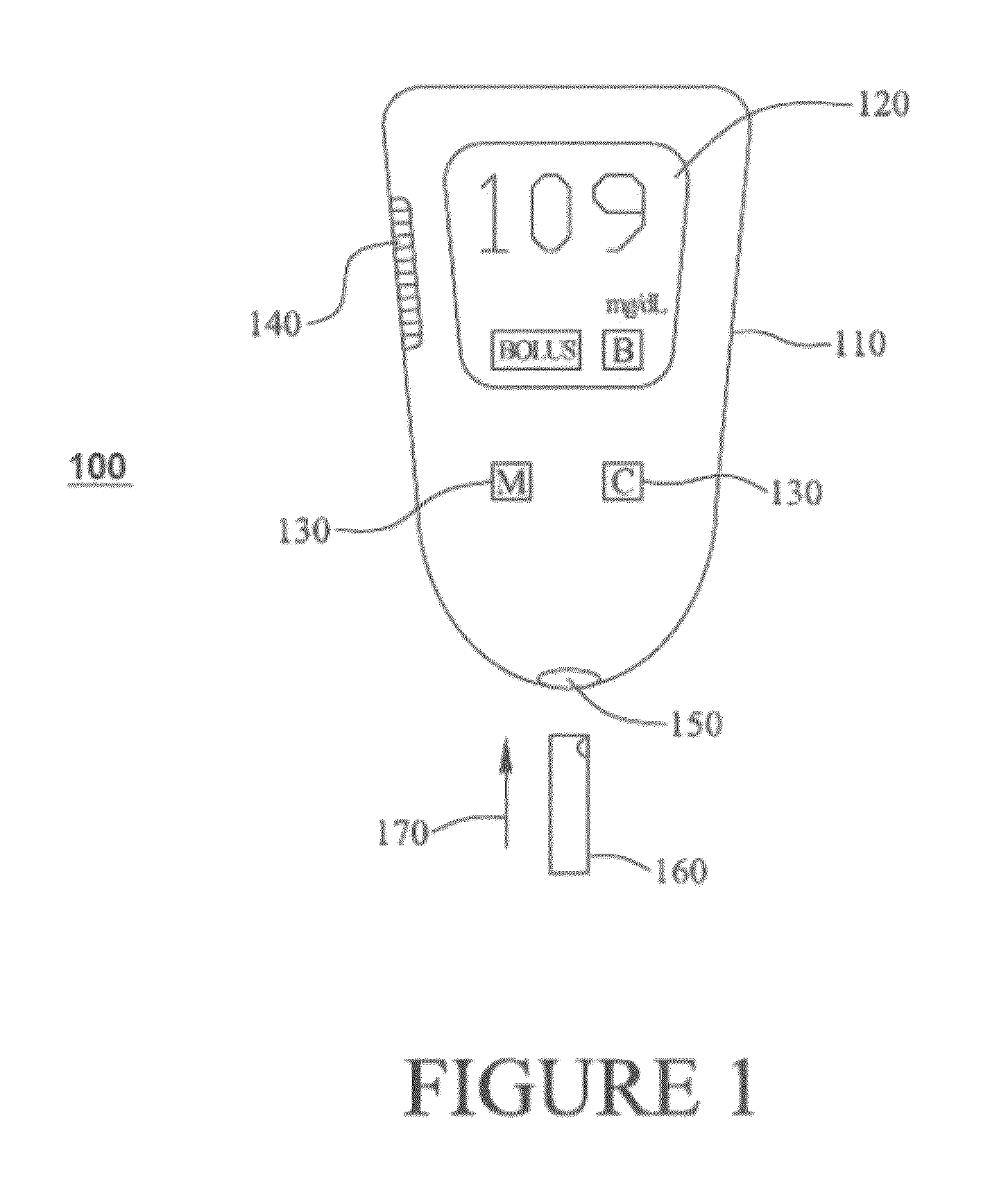
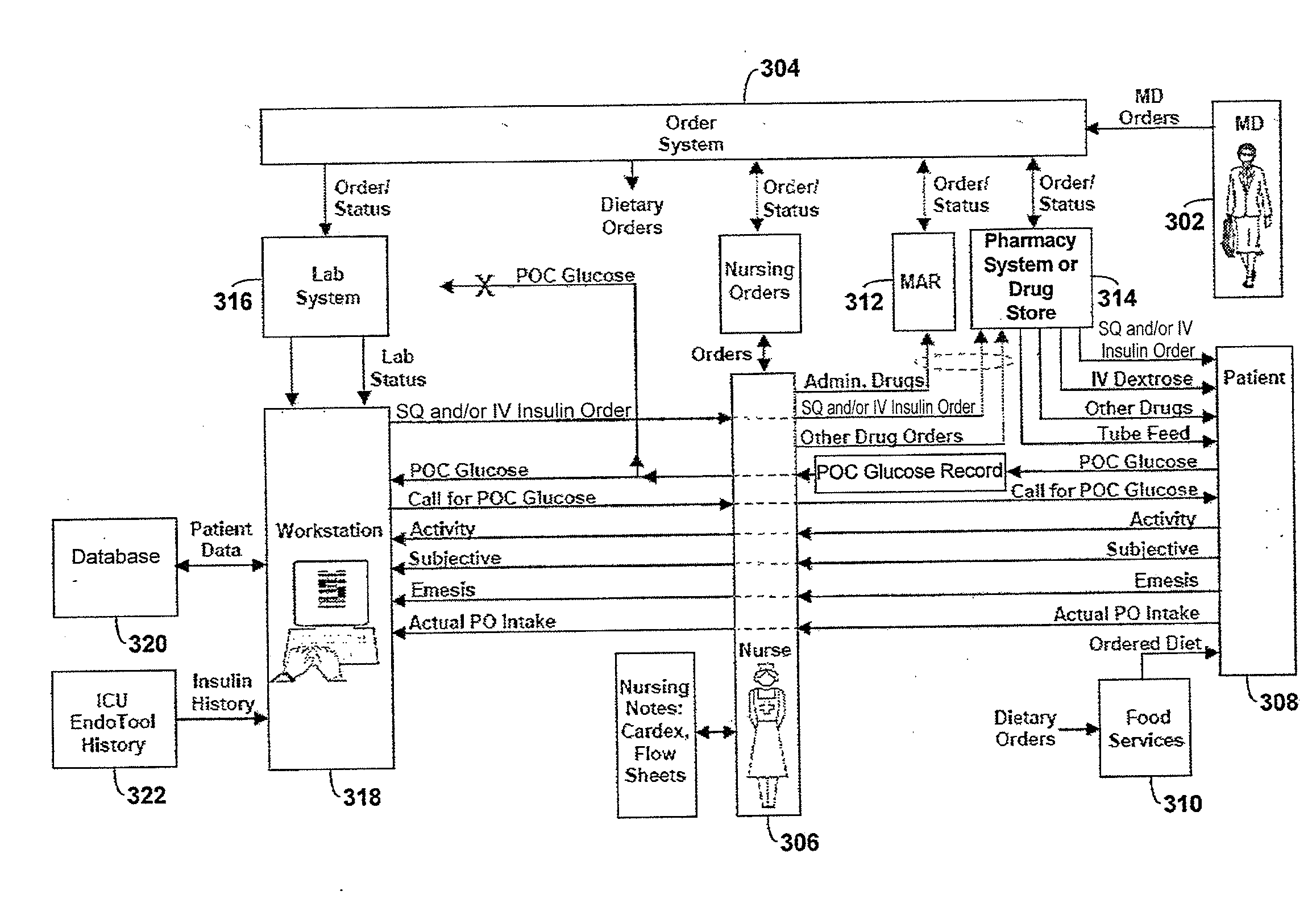
Systems and methods for determining insulin therapy for a patient
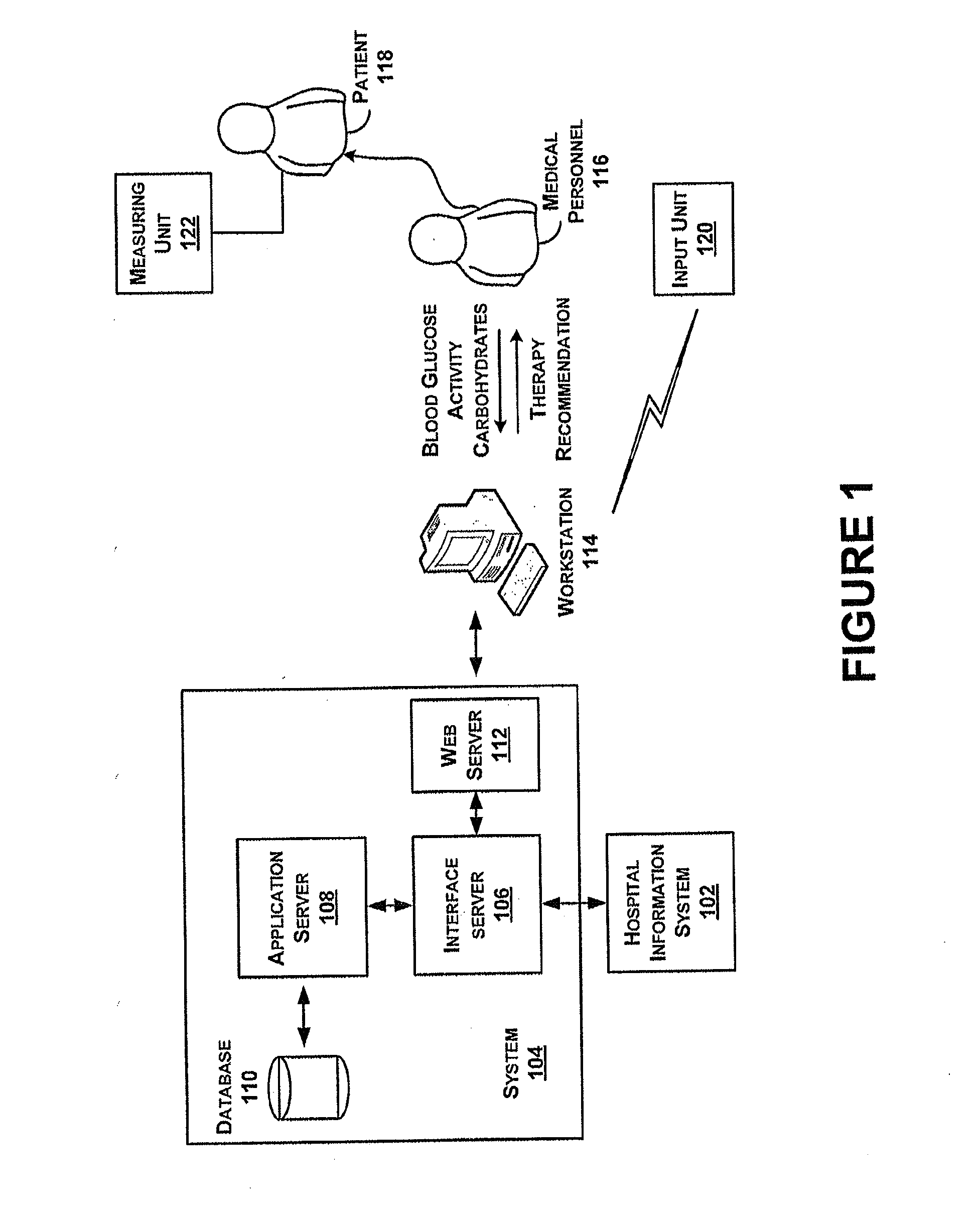
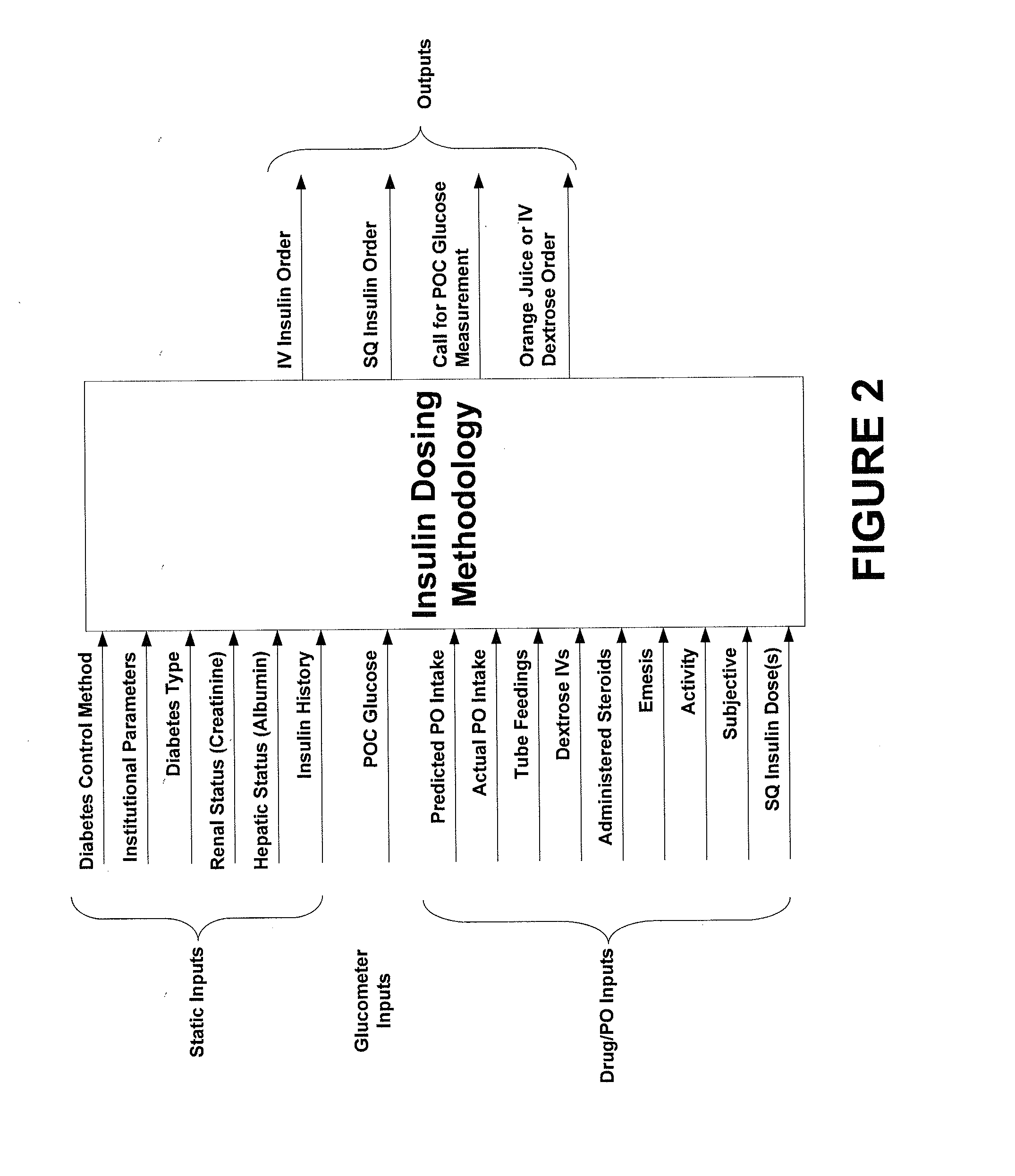
ActiveUS20130165901A1Data processing applicationsDrug and medicationsSubcutaneous insulinLong acting insulin
In example methods and systems described, insulin therapy for a patient can be determined. At least one of a short-acting subcutaneous insulin dosage recommendation, a correction subcutaneous insulin dosage recommendation, an intravenous insulin dosage recommendation, a recommended amount of carbohydrates to be administered to the patient, or combinations thereof, can be determined. In addition, information indicating a confirmation of a nutrition intake for the patient, and a long-acting insulin-on-board for the patient can be received, and based on this information, a required long-acting subcutaneous or intravenous insulin dosage for the patient can be determined. The short-acting subcutaneous or intravenous insulin dosage recommendation can be adjusted based, at least in part, on a difference between the long-acting insulin-on-board and the required long-acting subcutaneous or intravenous insulin dosage.
Owner:MONARCH MEDICAL TECH
Potentiation of glucose elimination
InactiveUS20070020191A1Improve efficiencyEffective controlPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsInsulin activityPostprandial Hypoglycemia
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
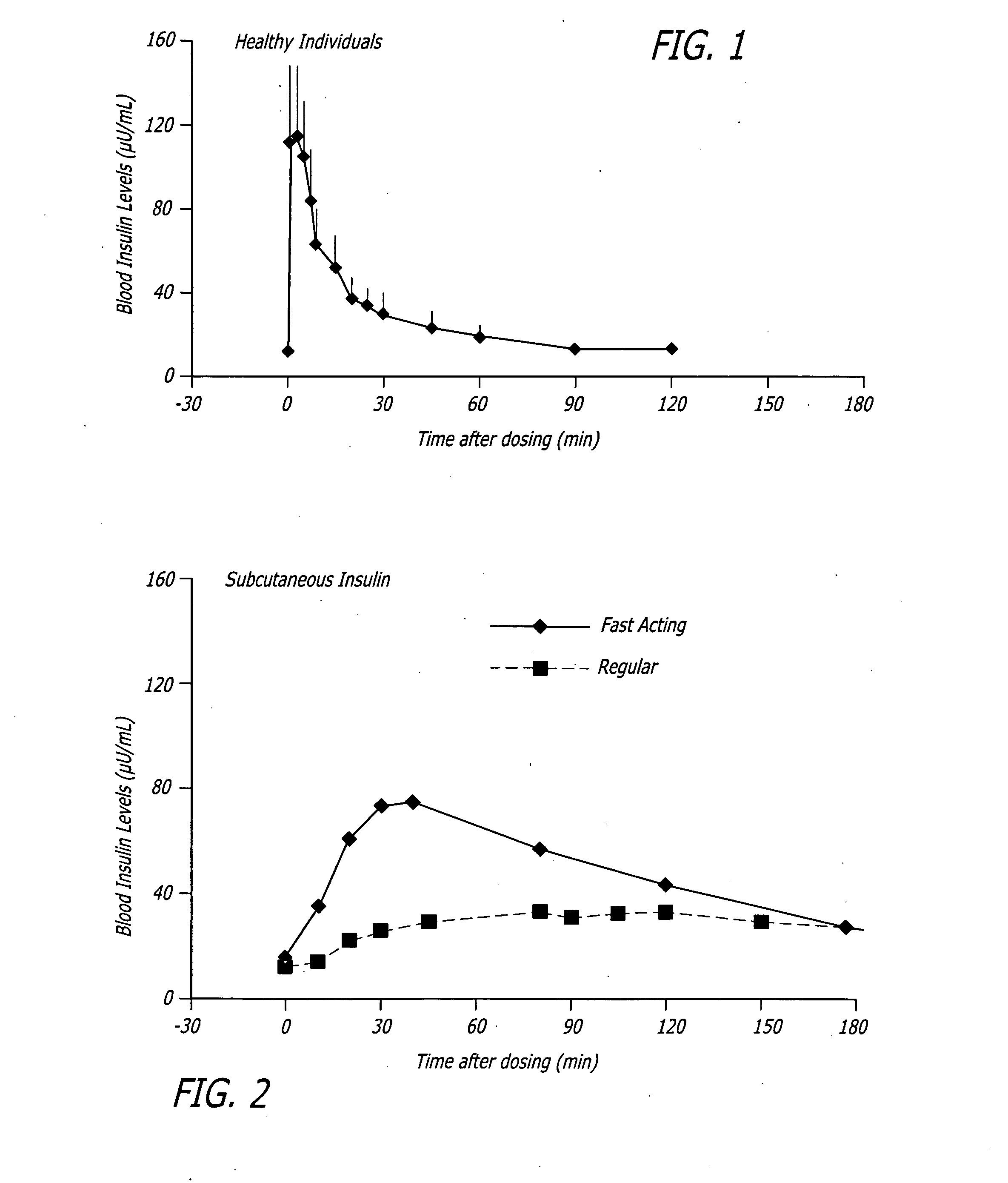
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS20080039368A1Increase speedReduce the amount of solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
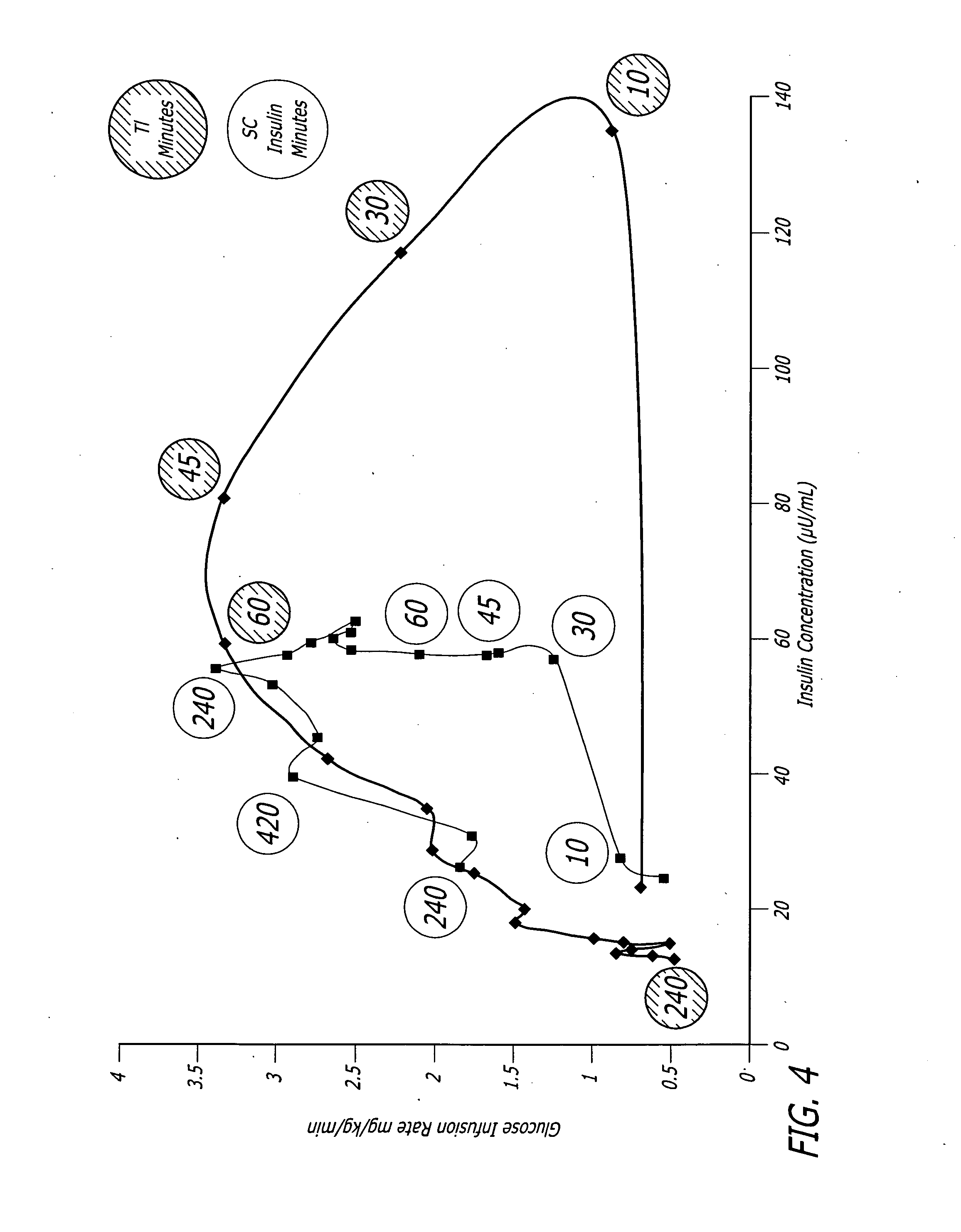
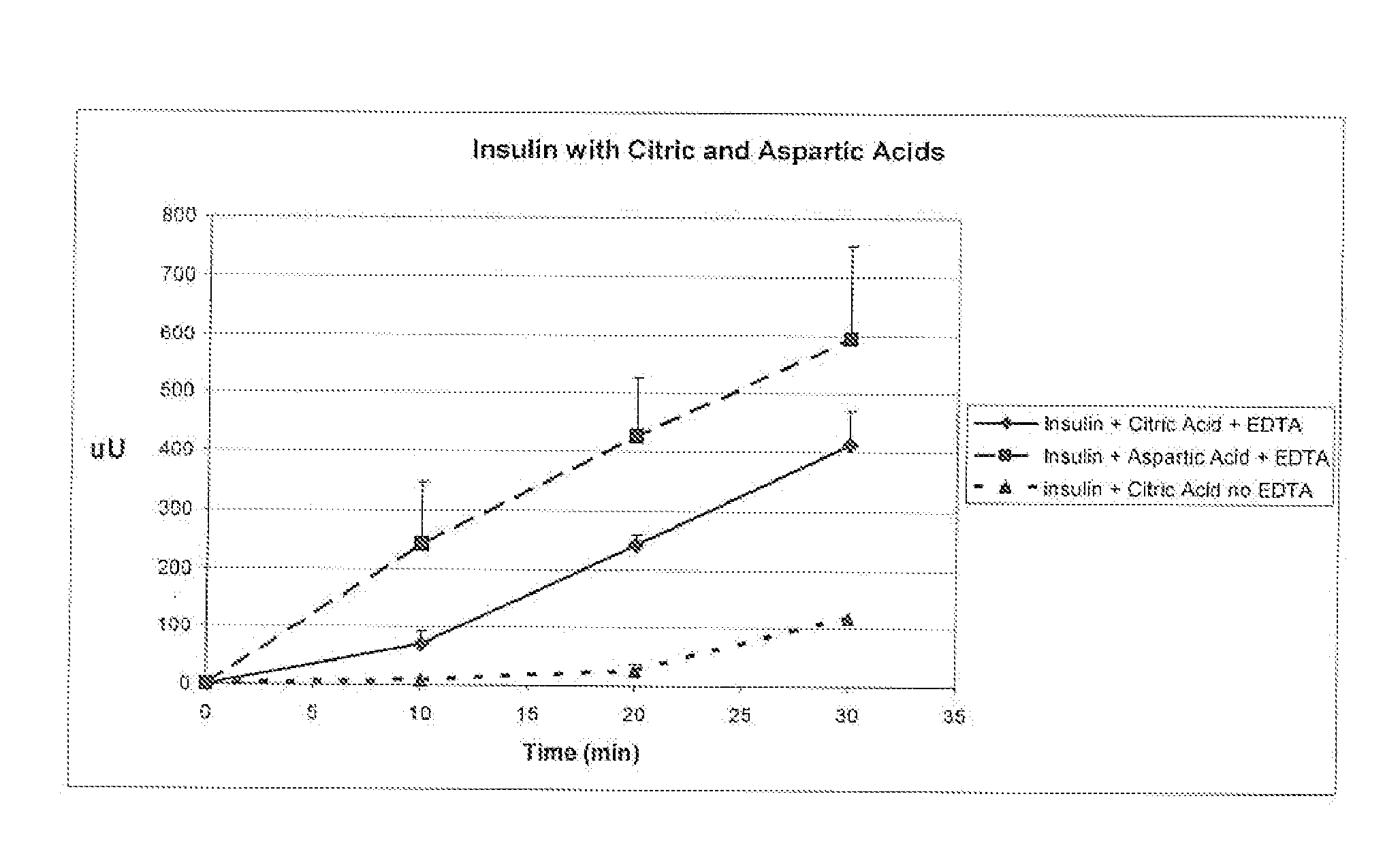
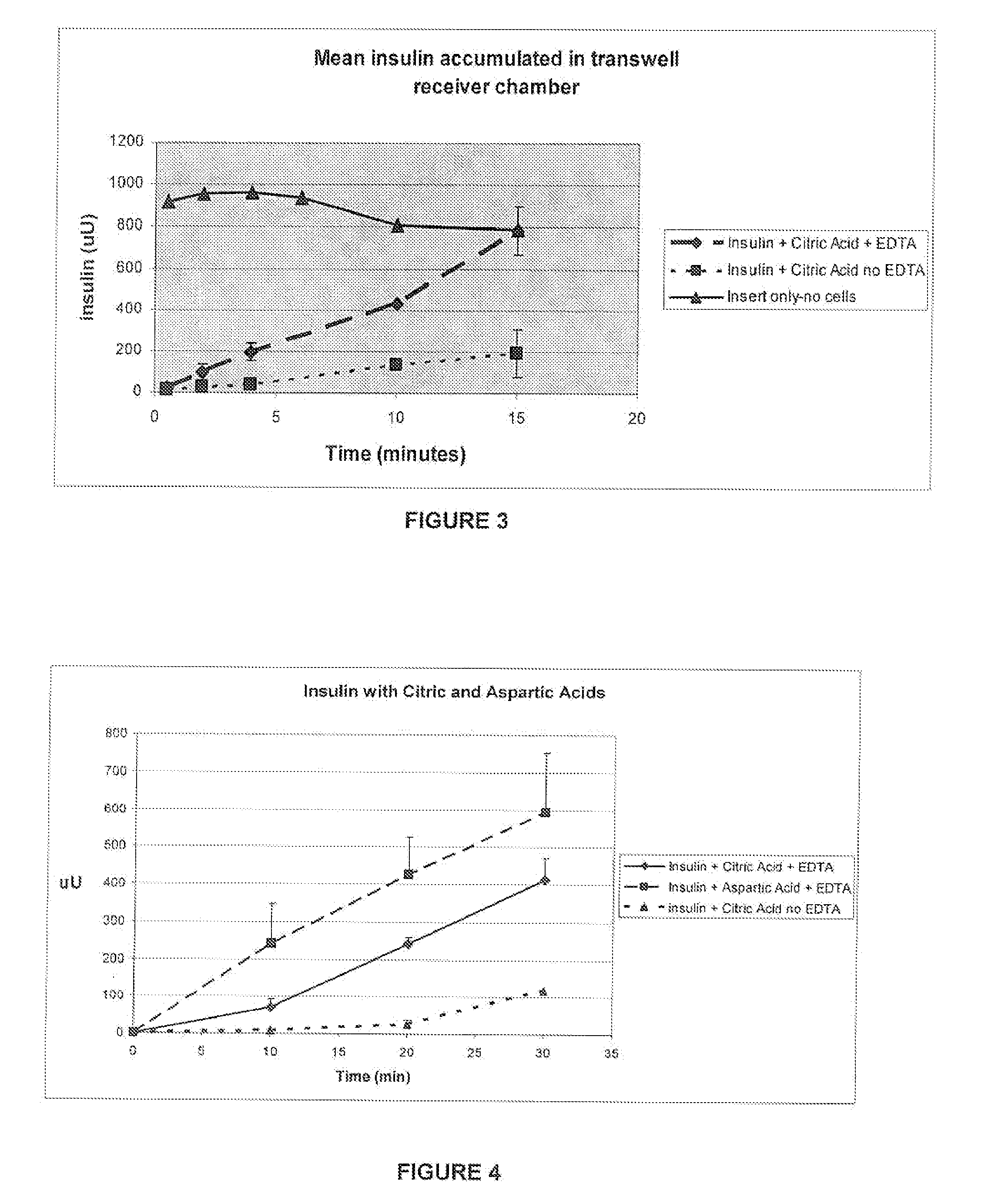
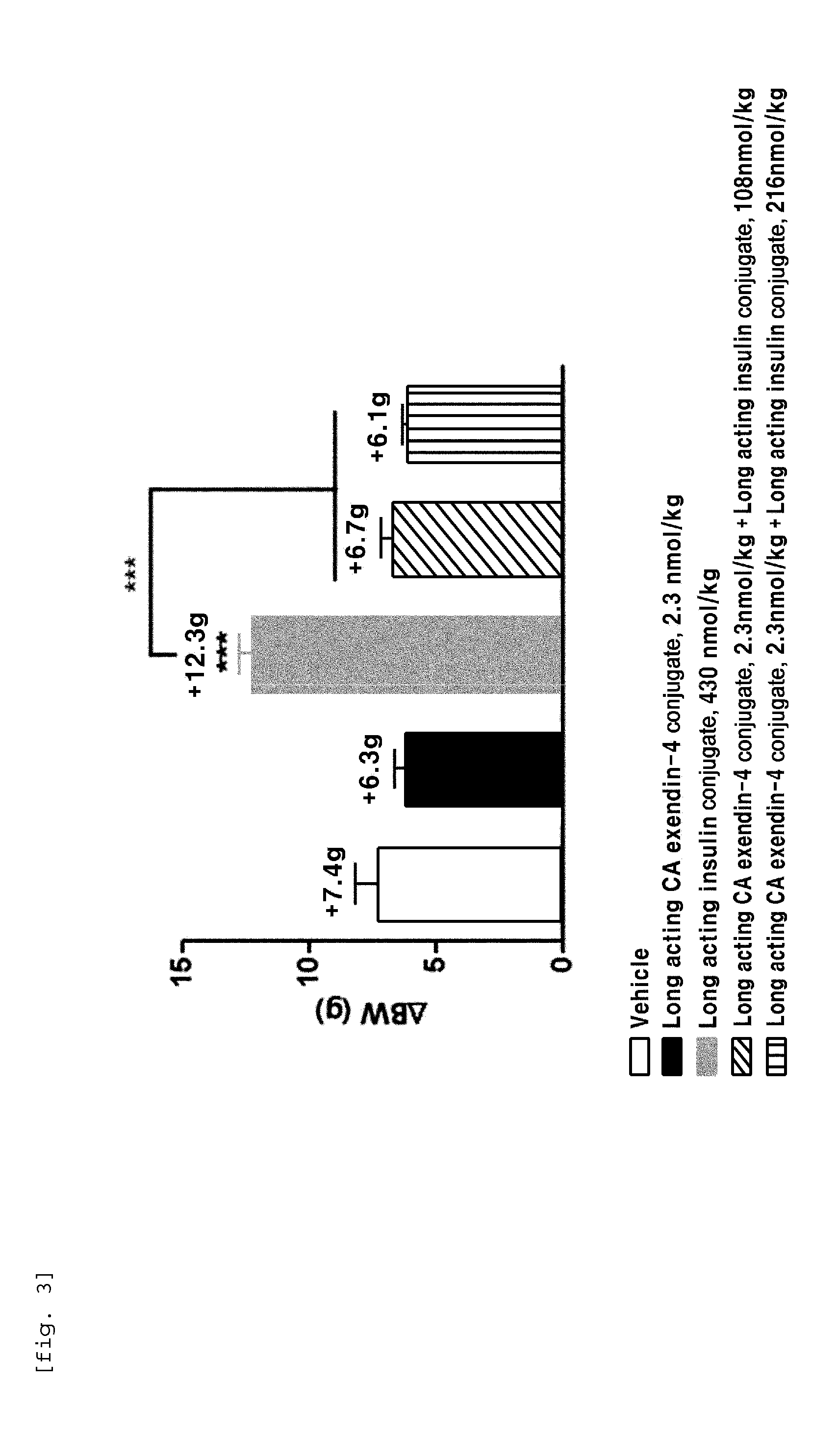
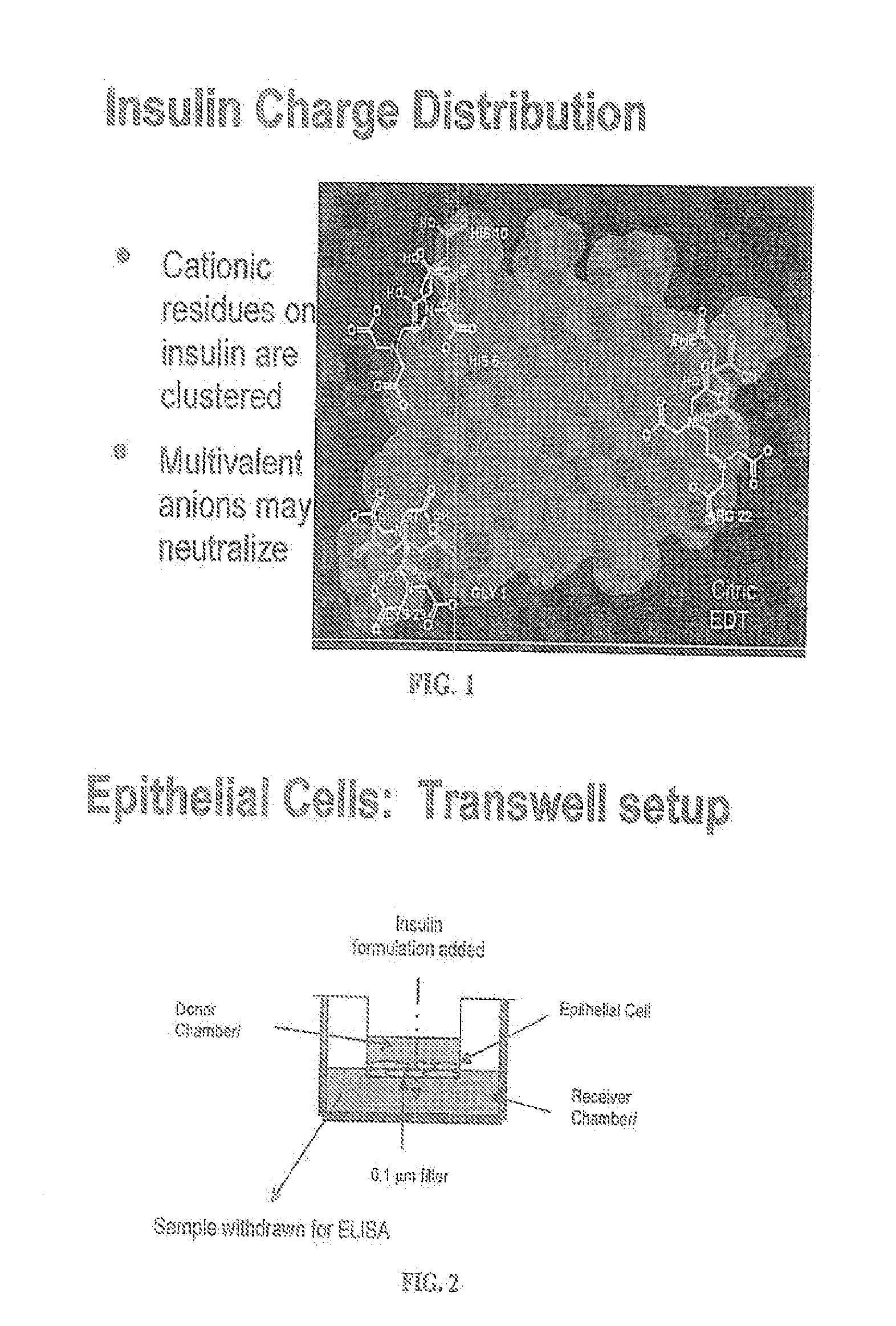
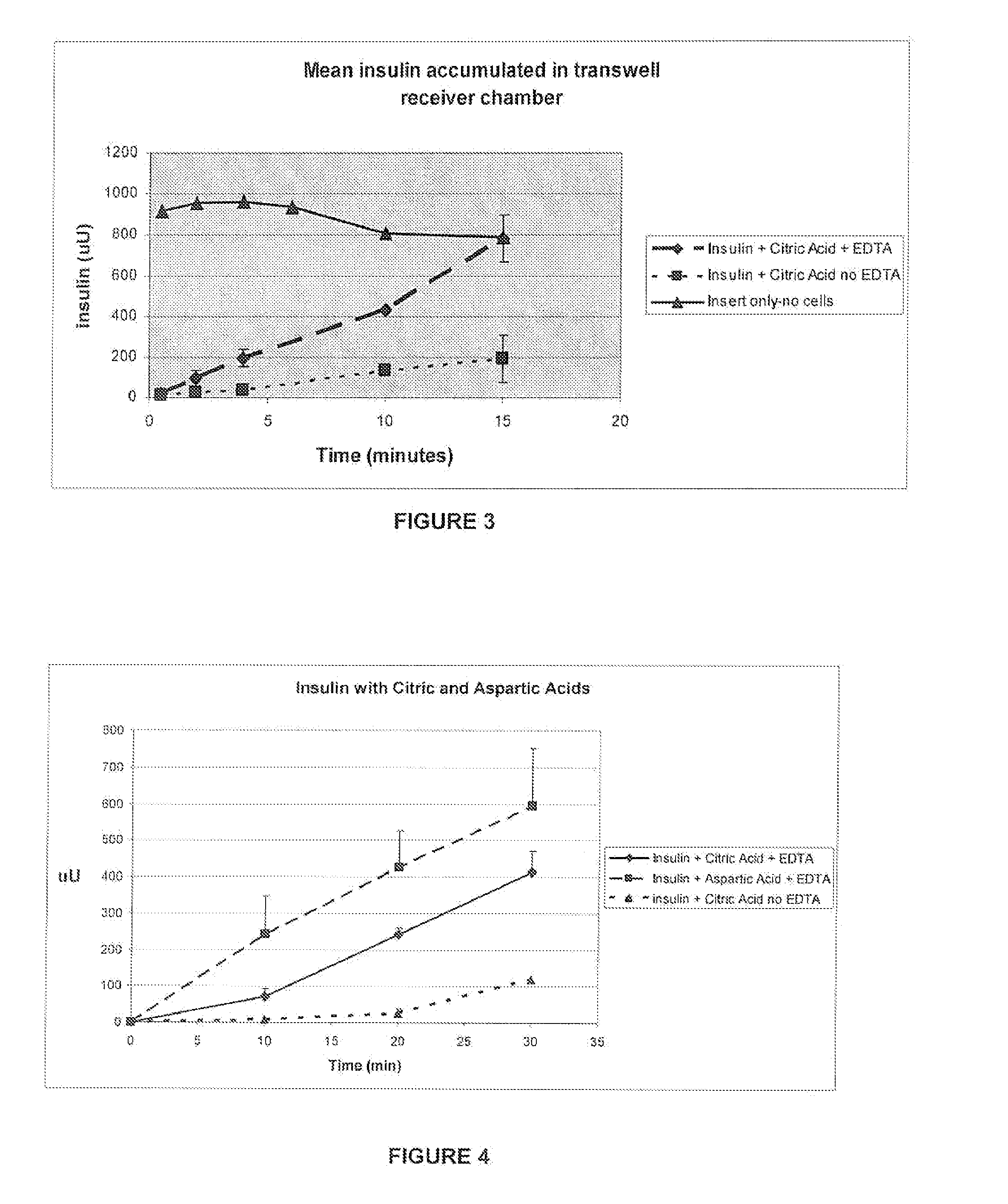
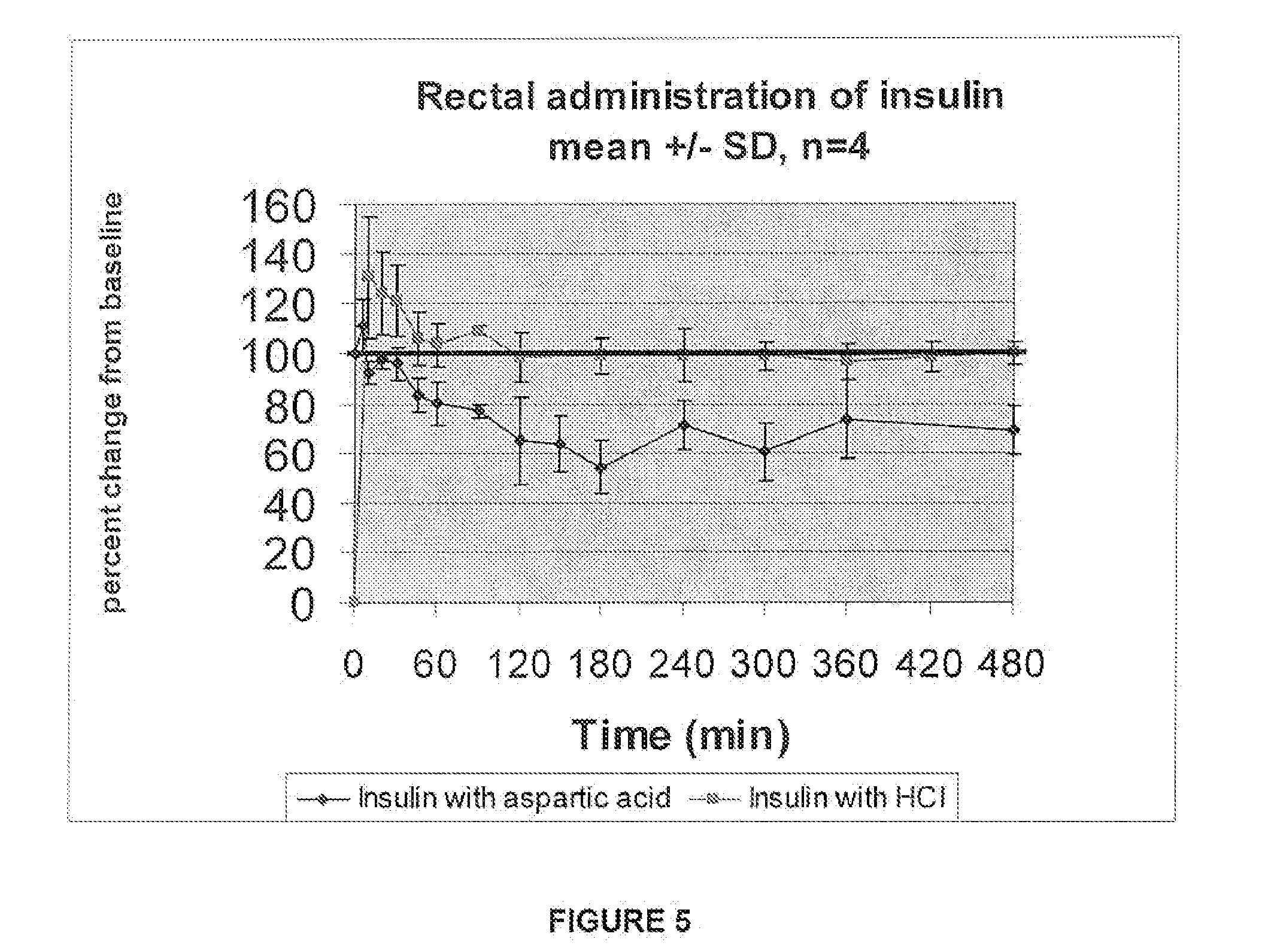
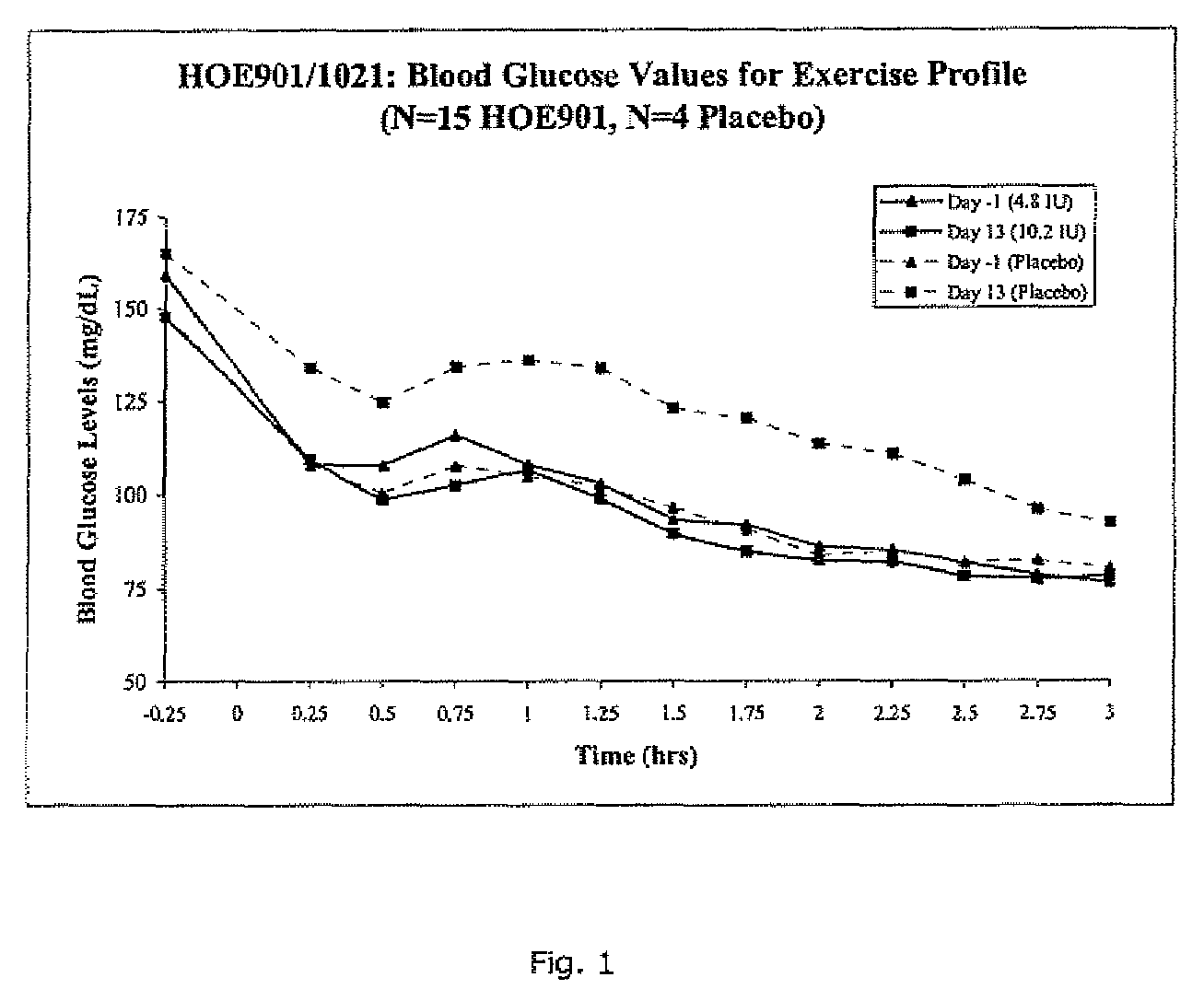
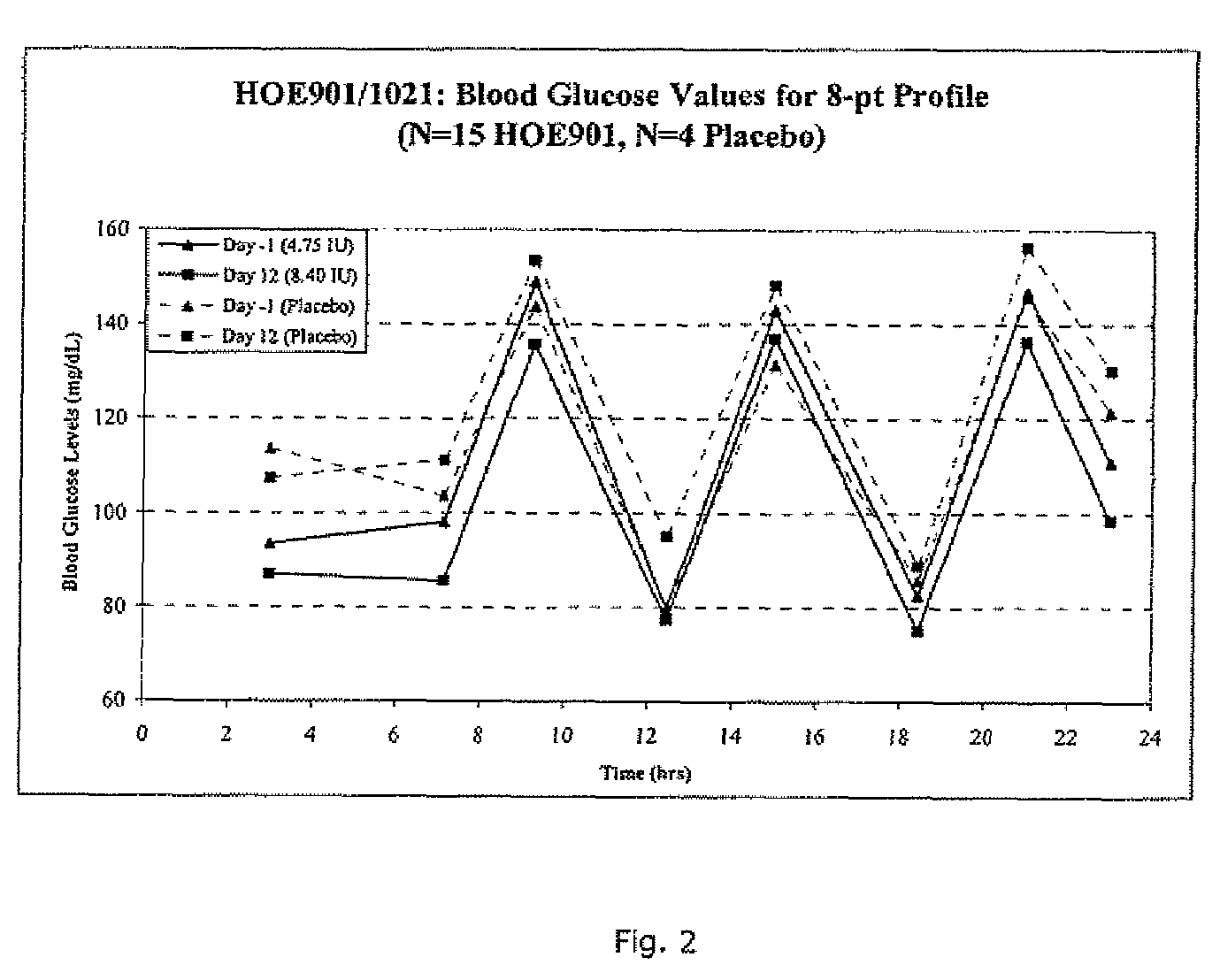
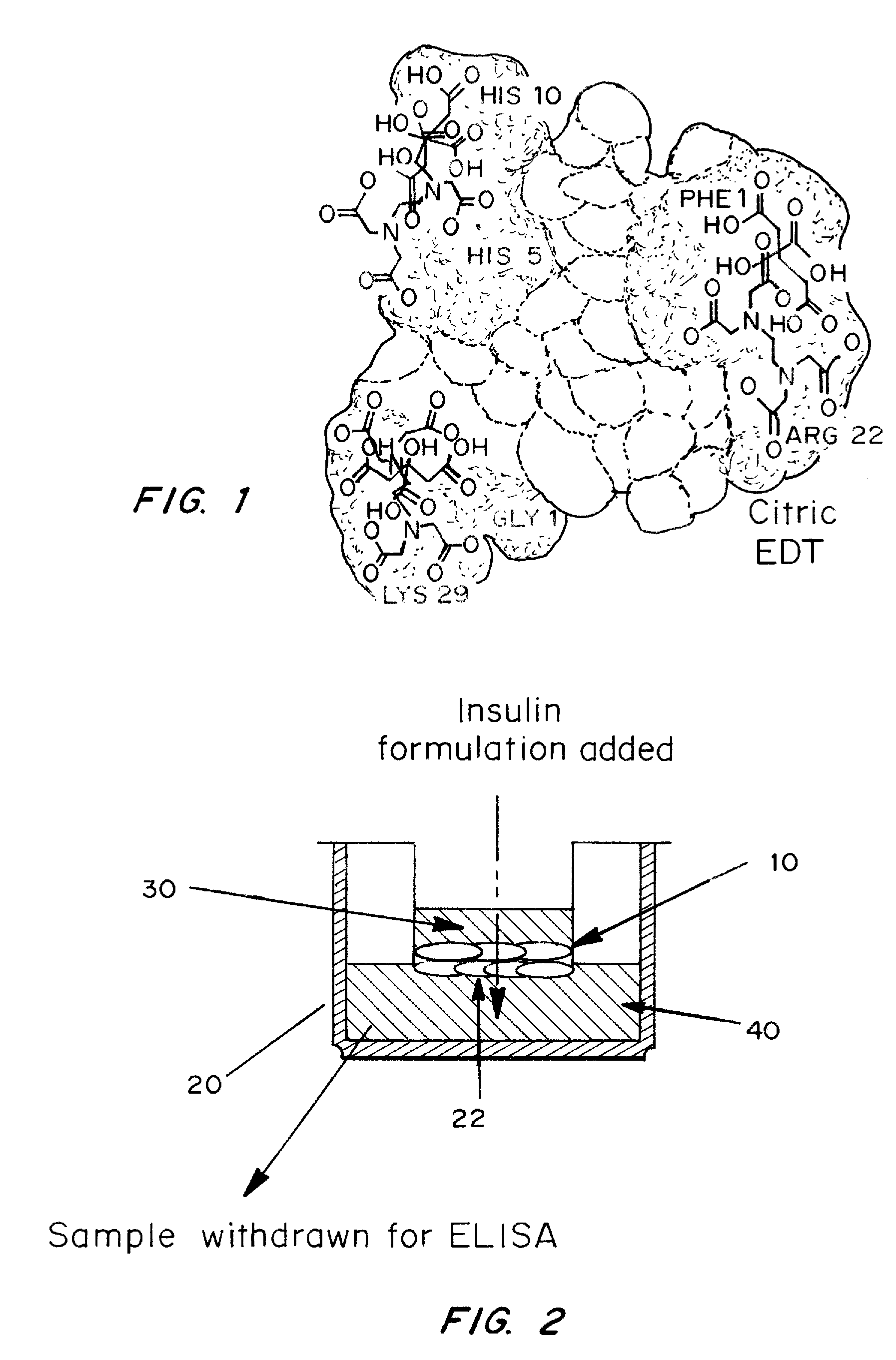
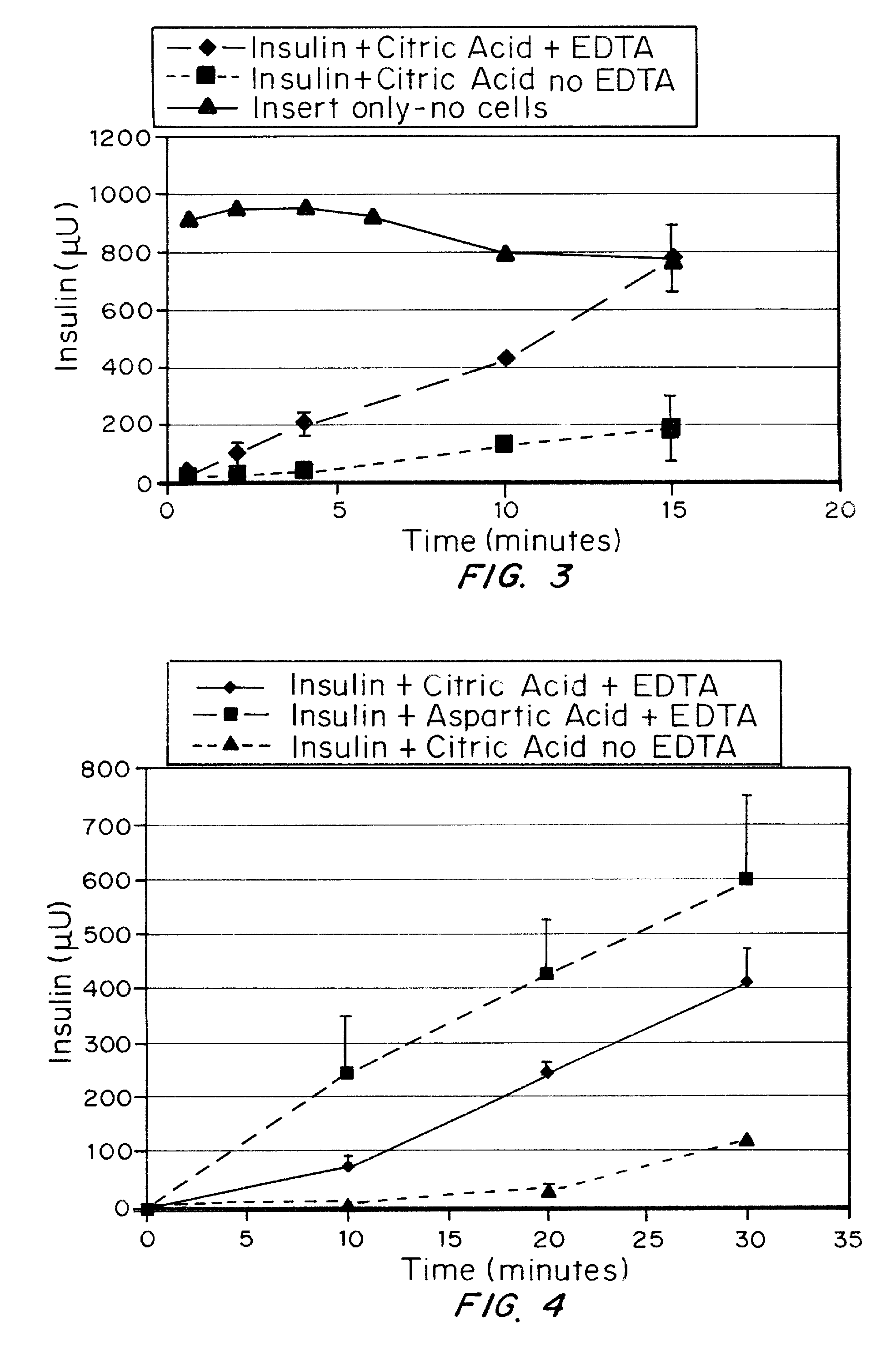
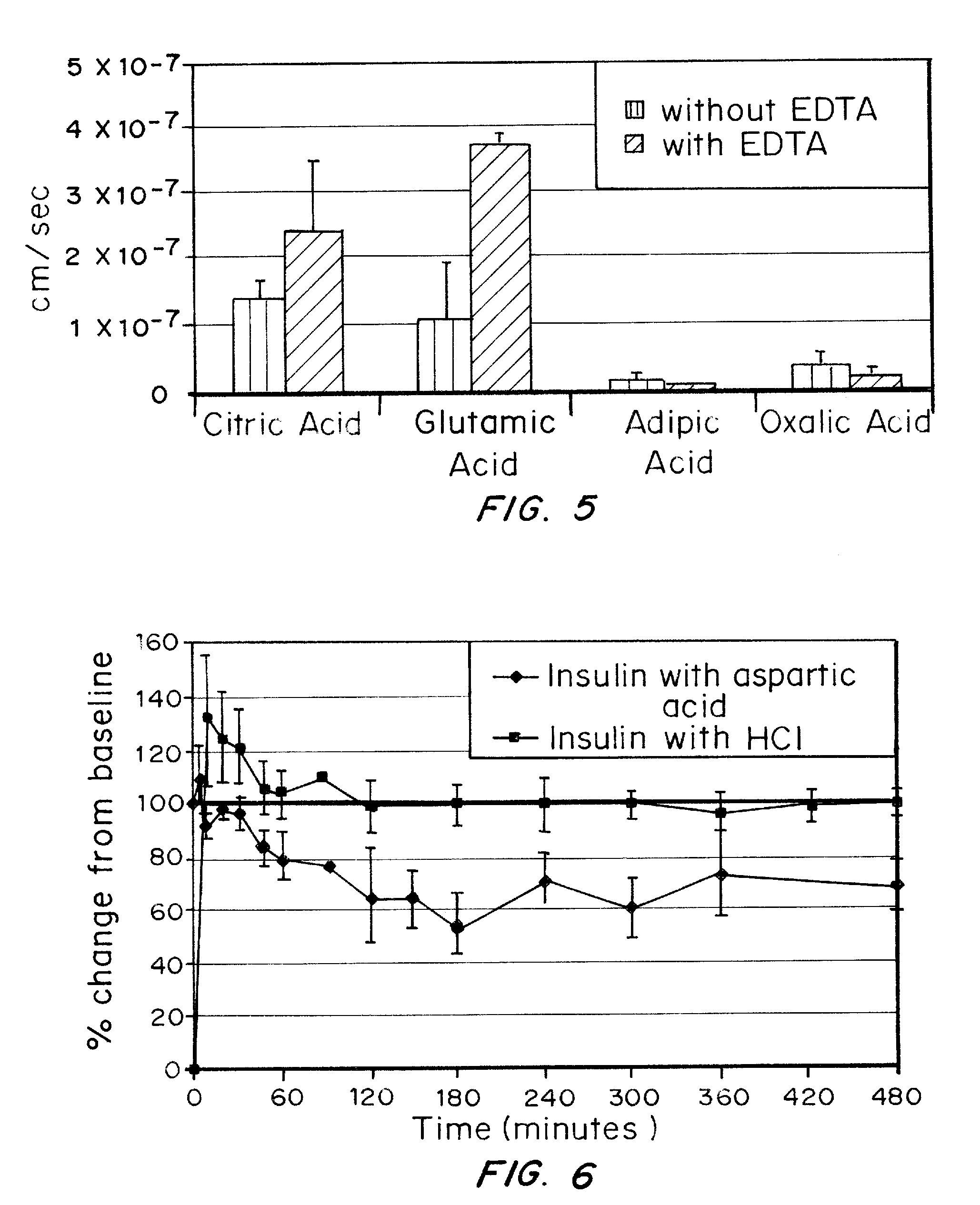
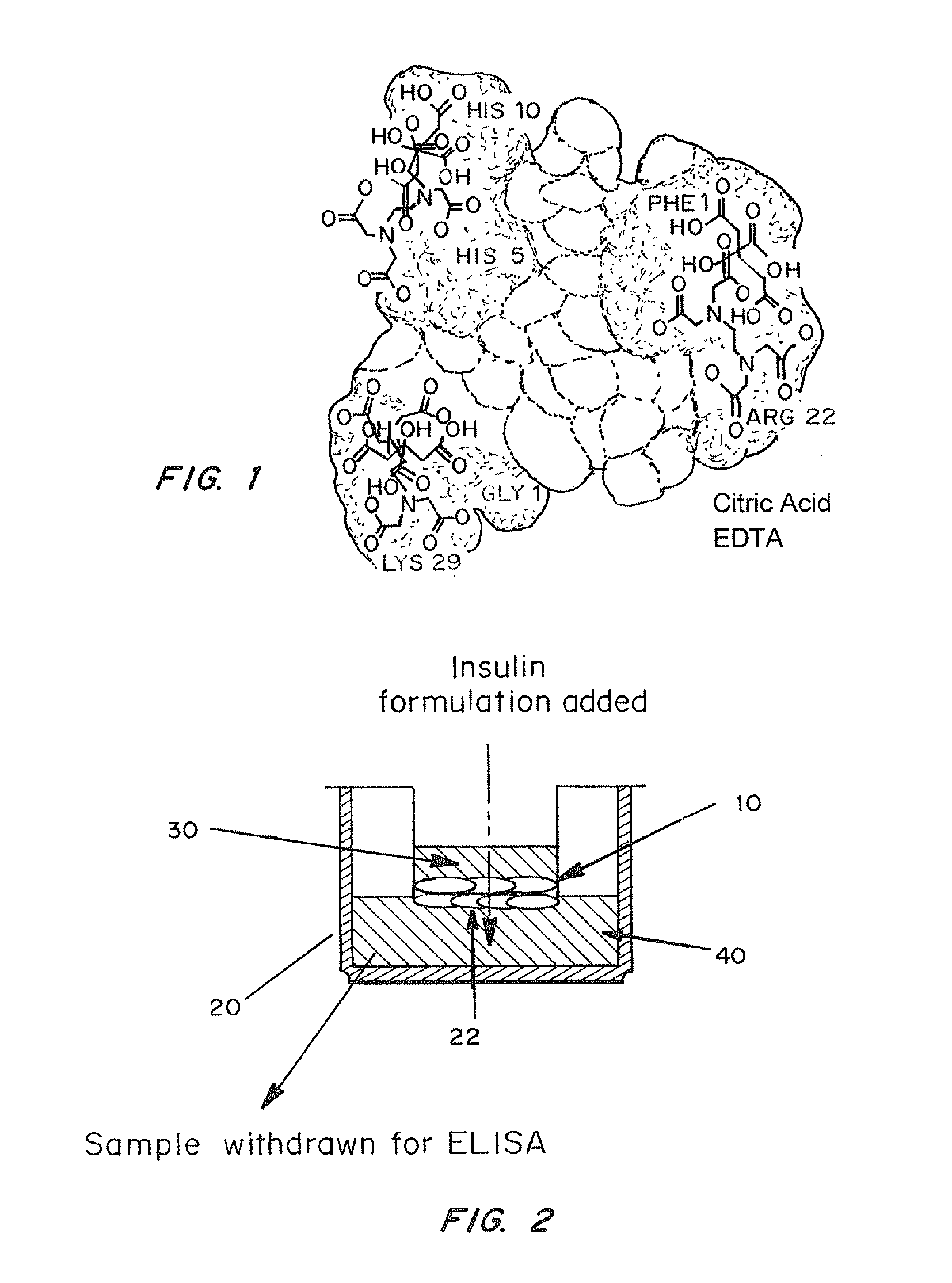
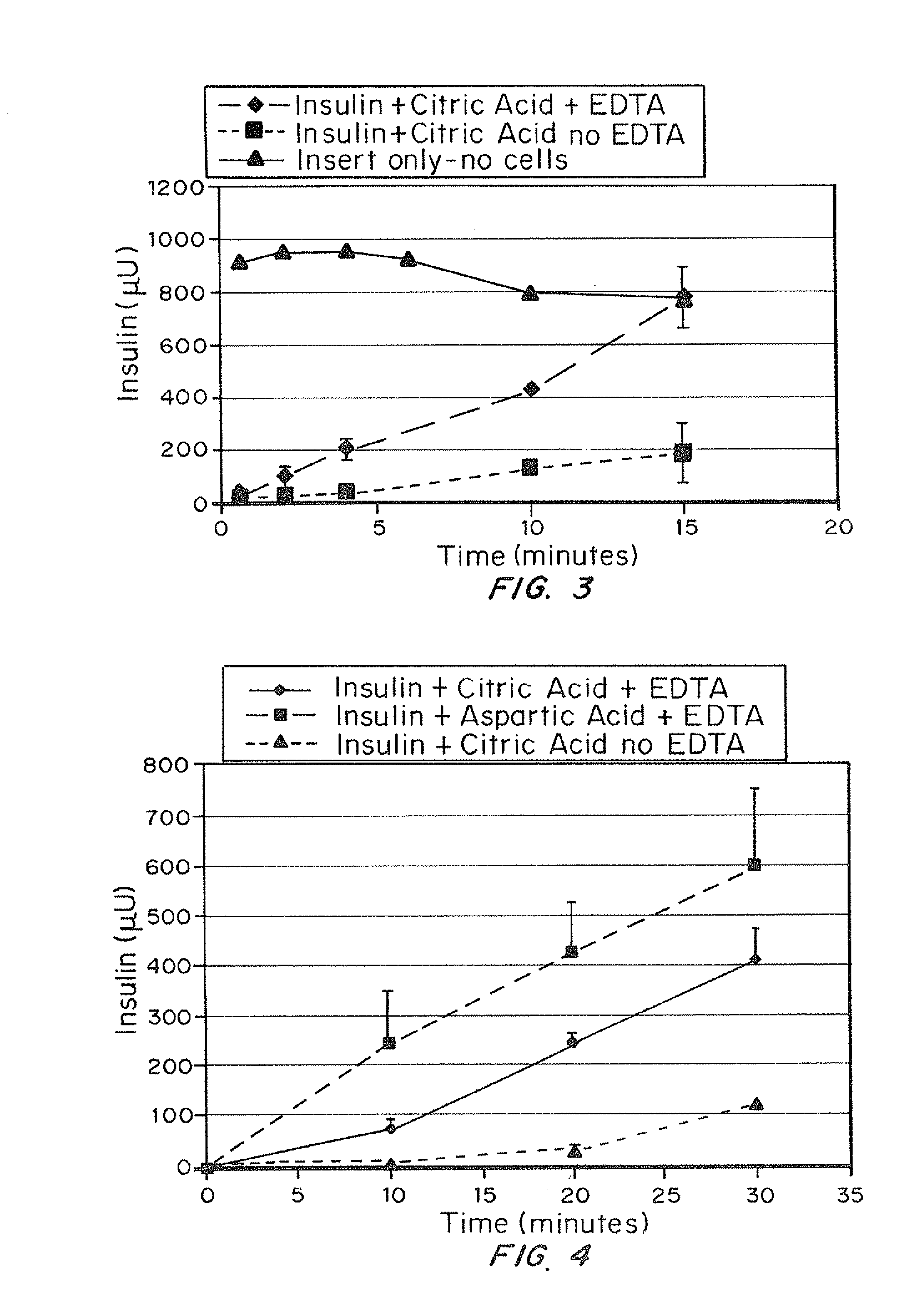
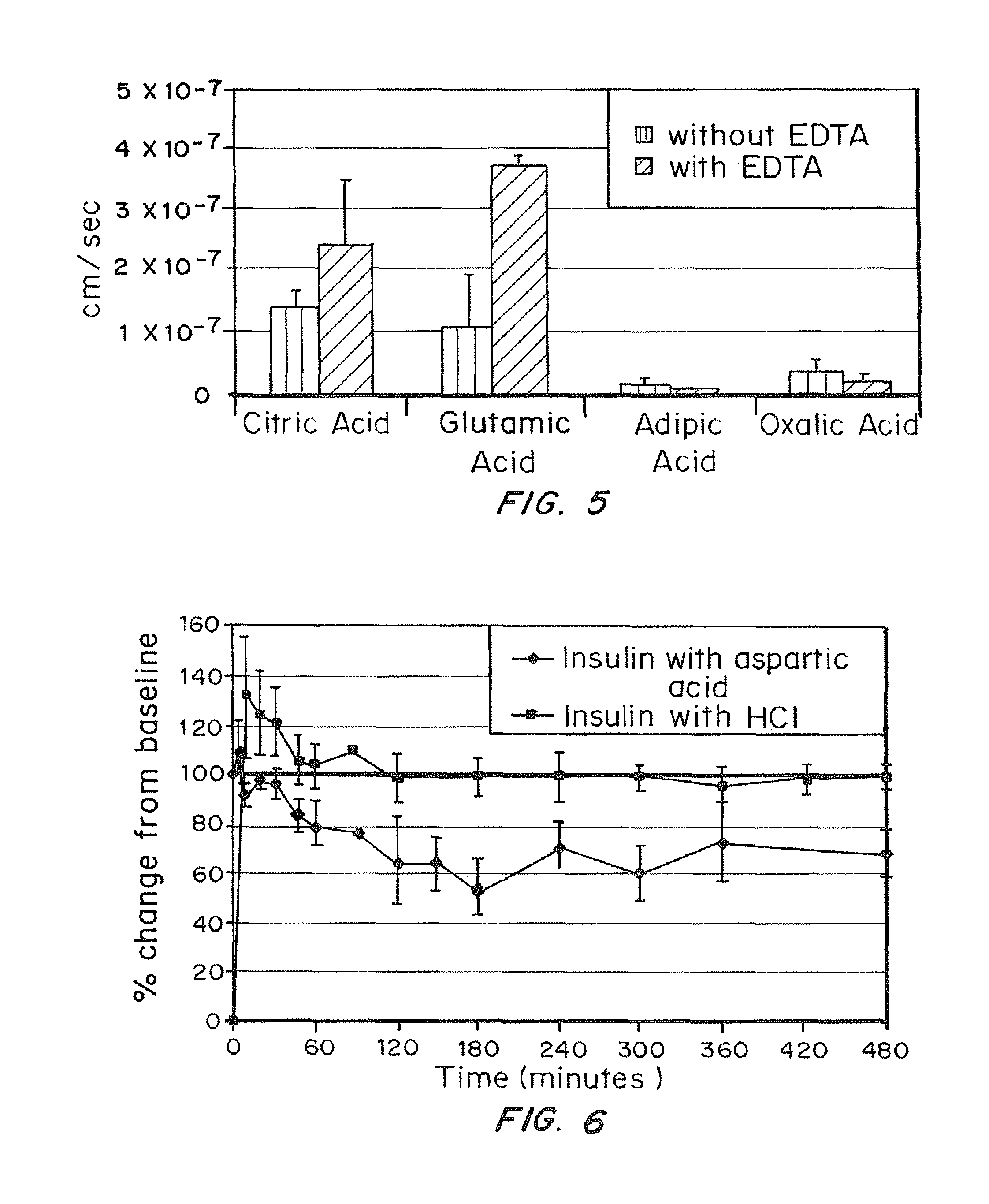
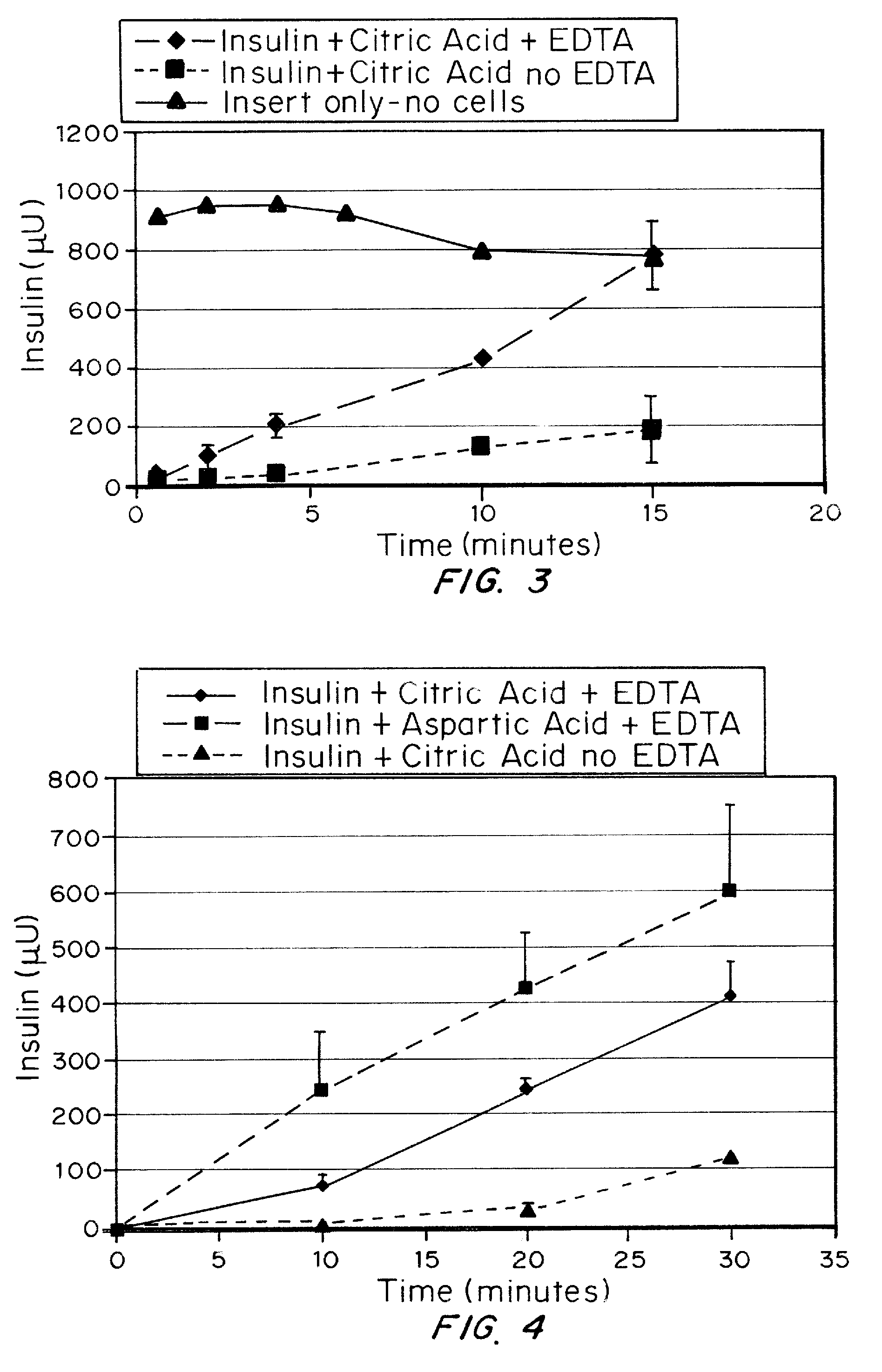
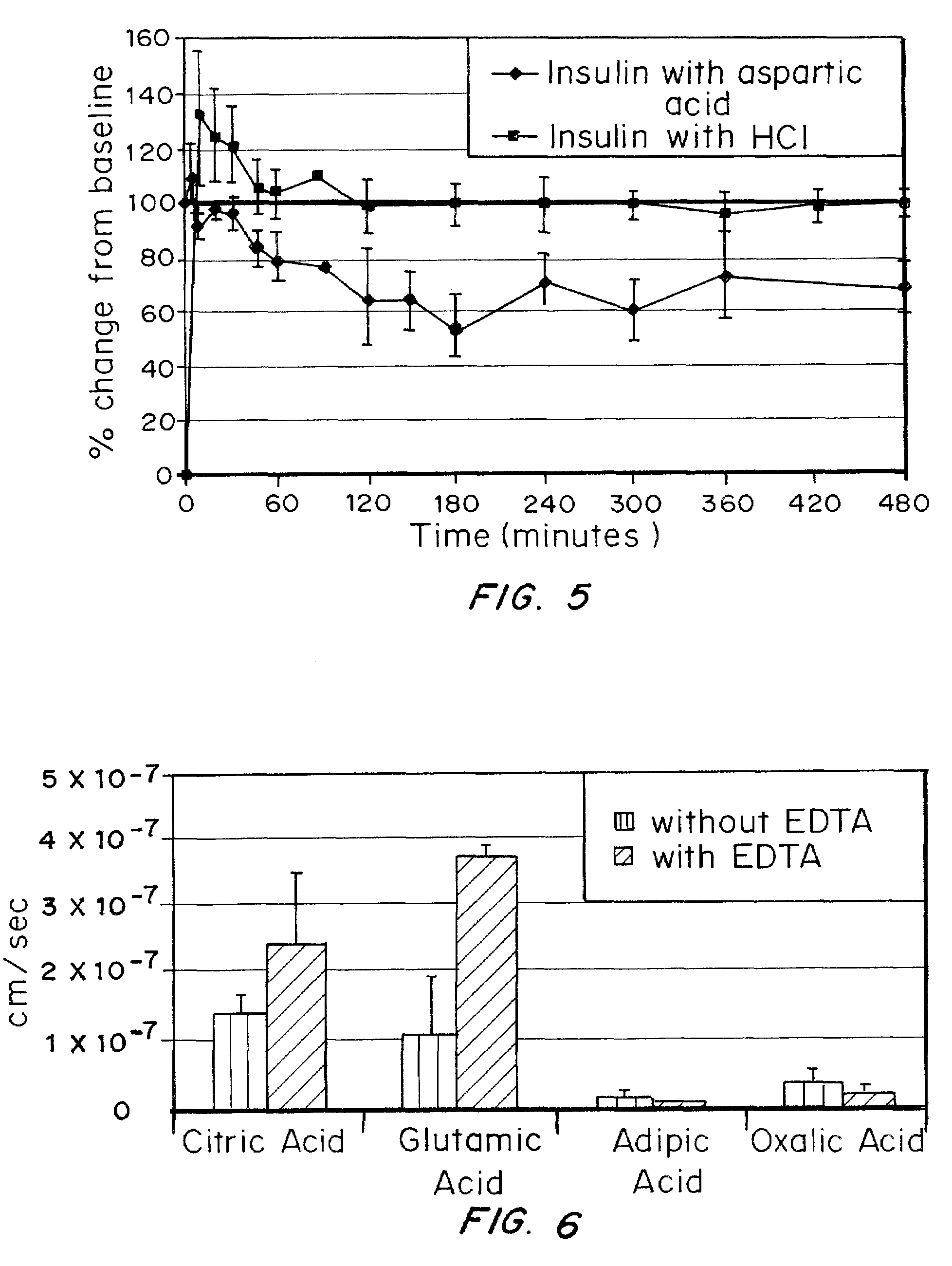
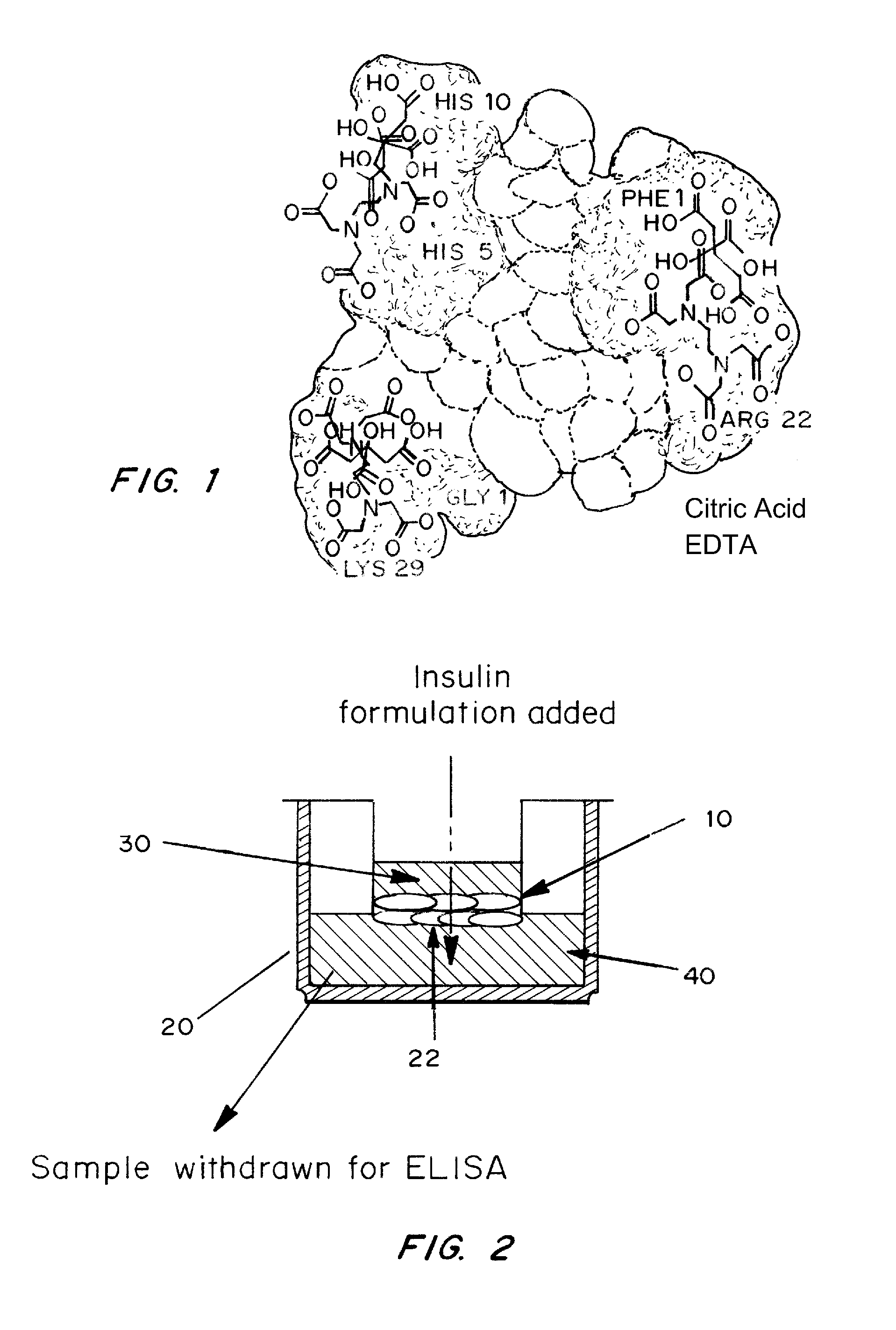
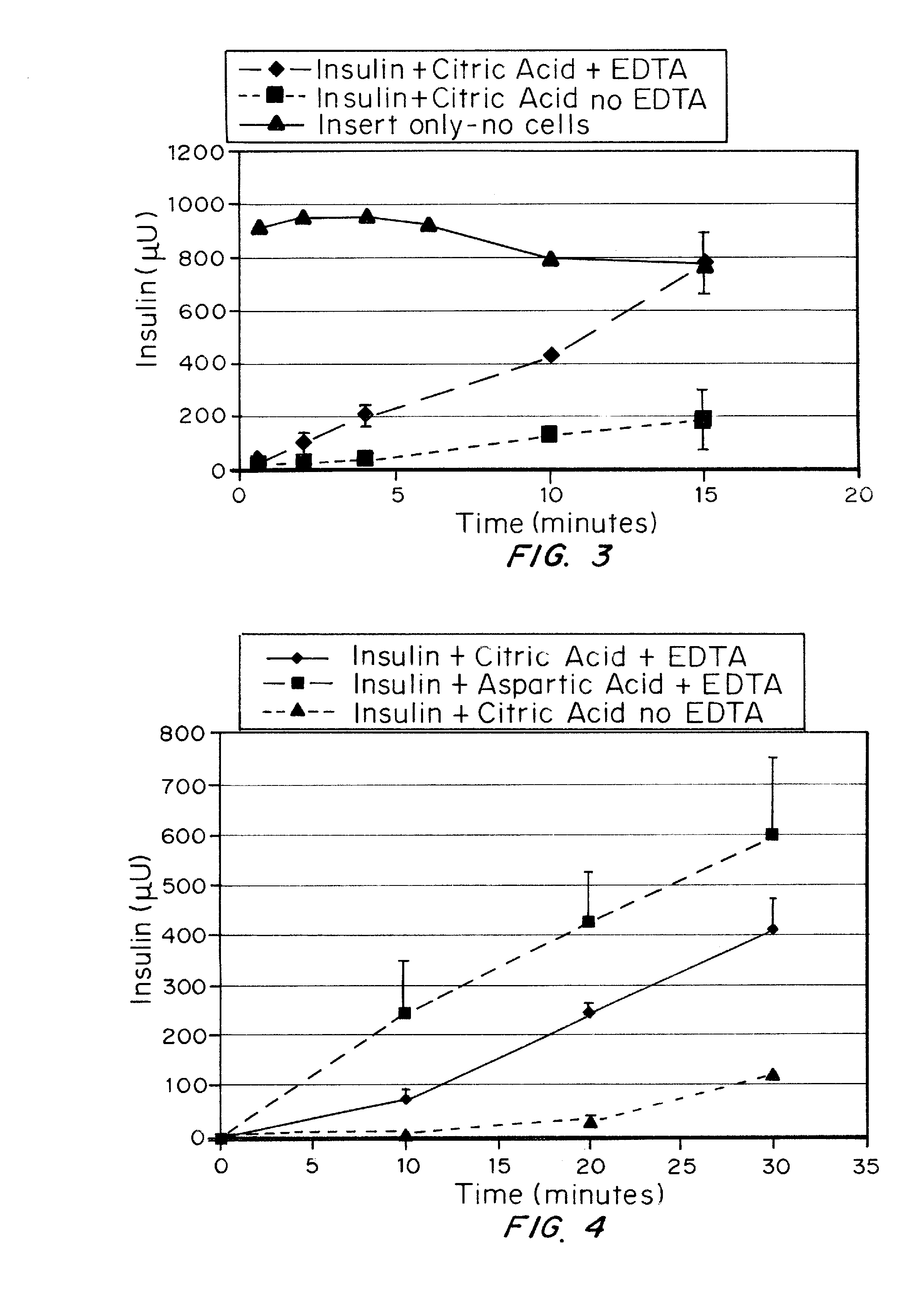
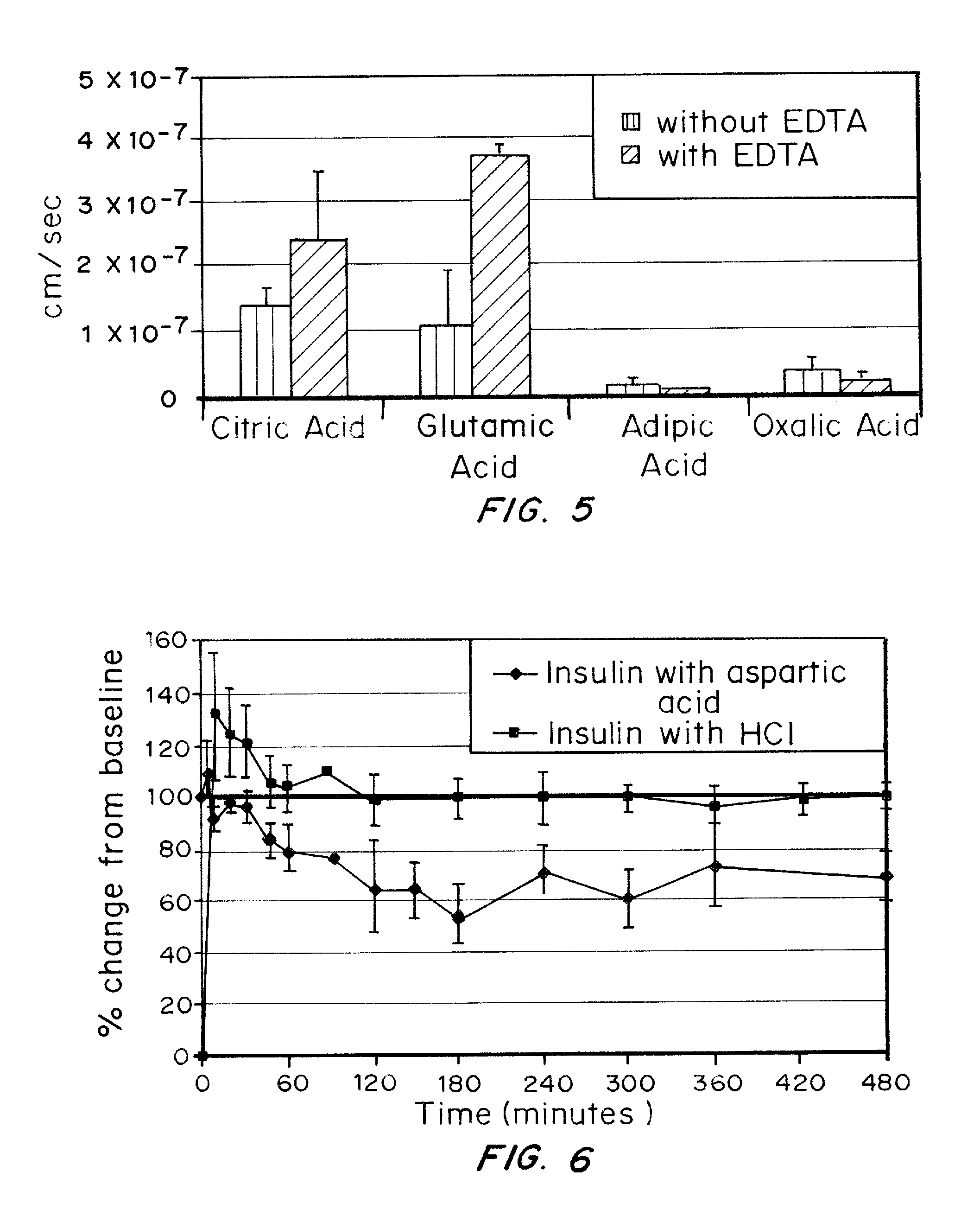
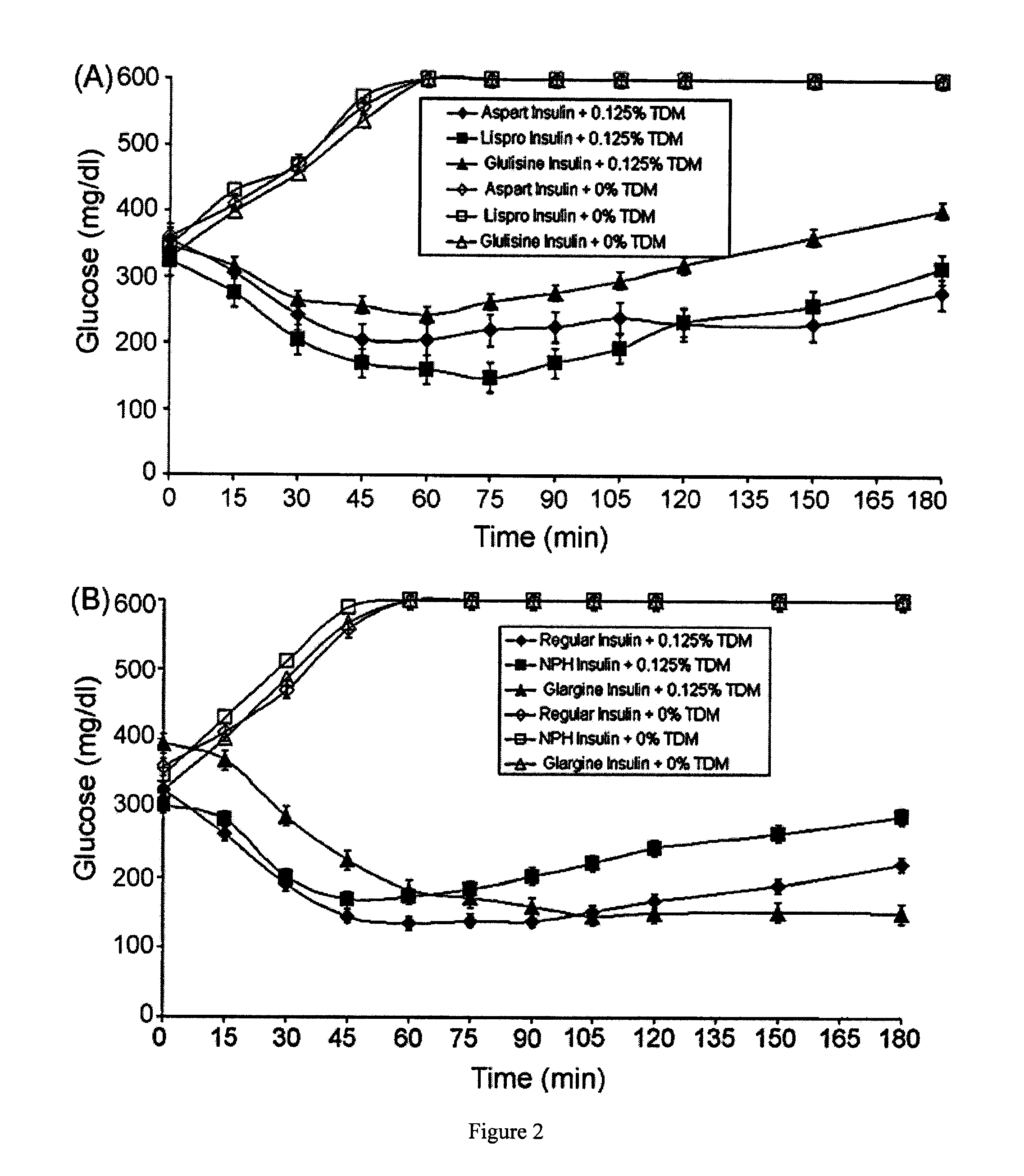
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate, the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, maleic, succinic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Diabetes therapy
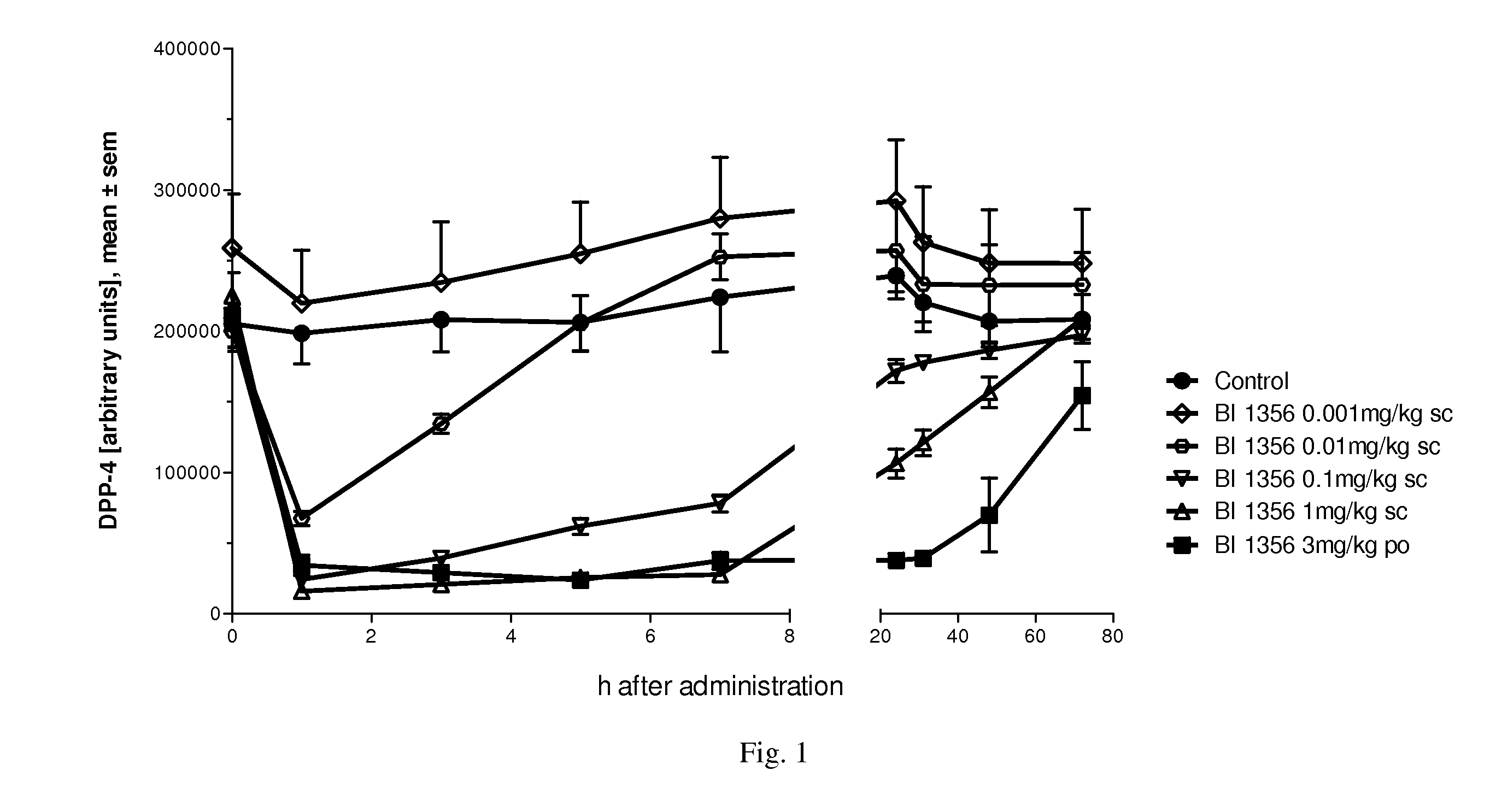
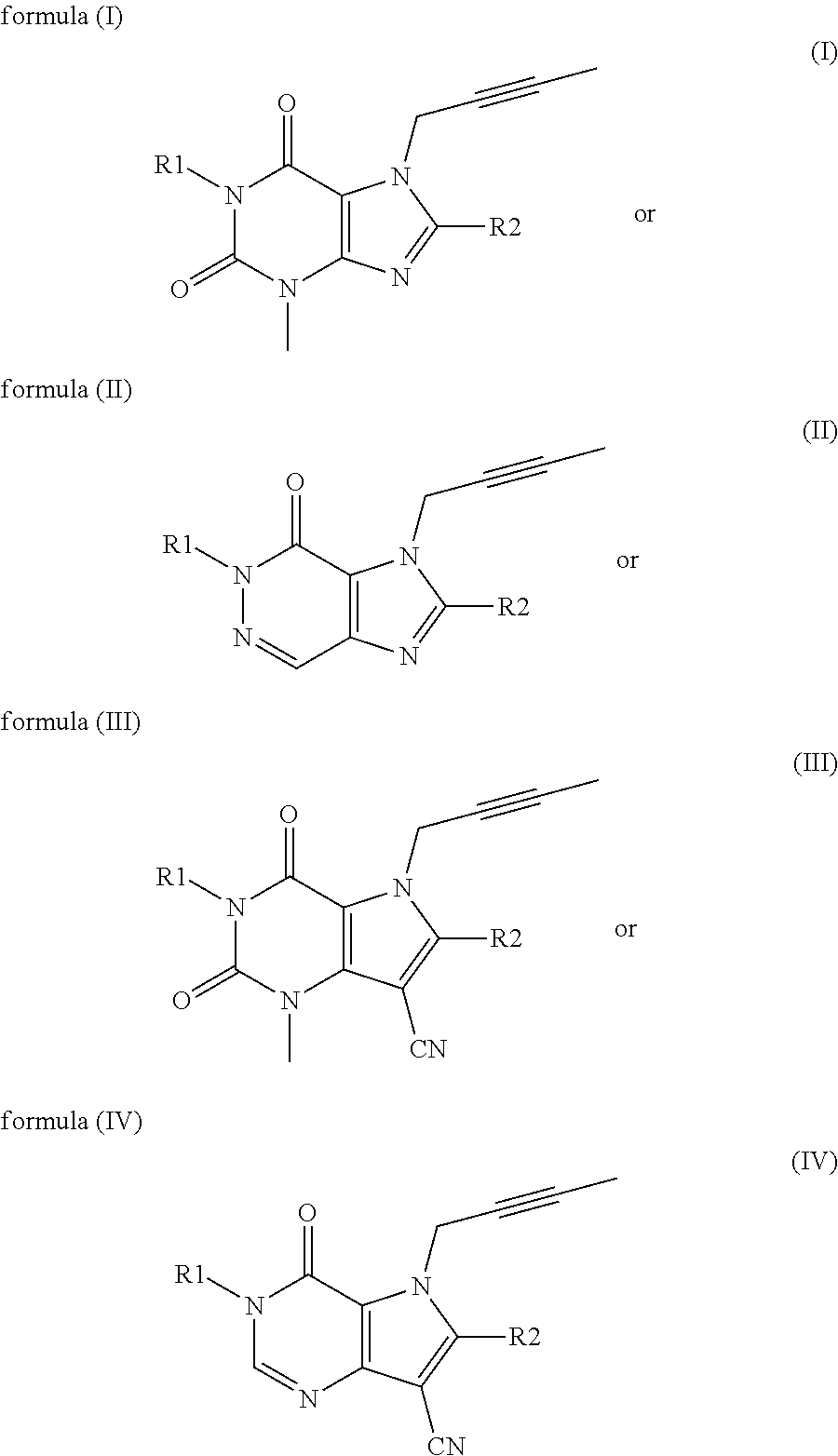
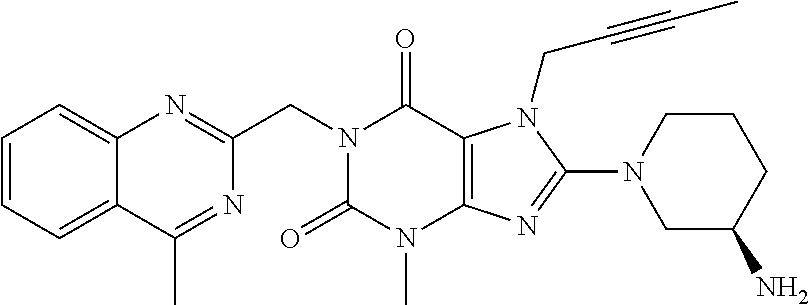
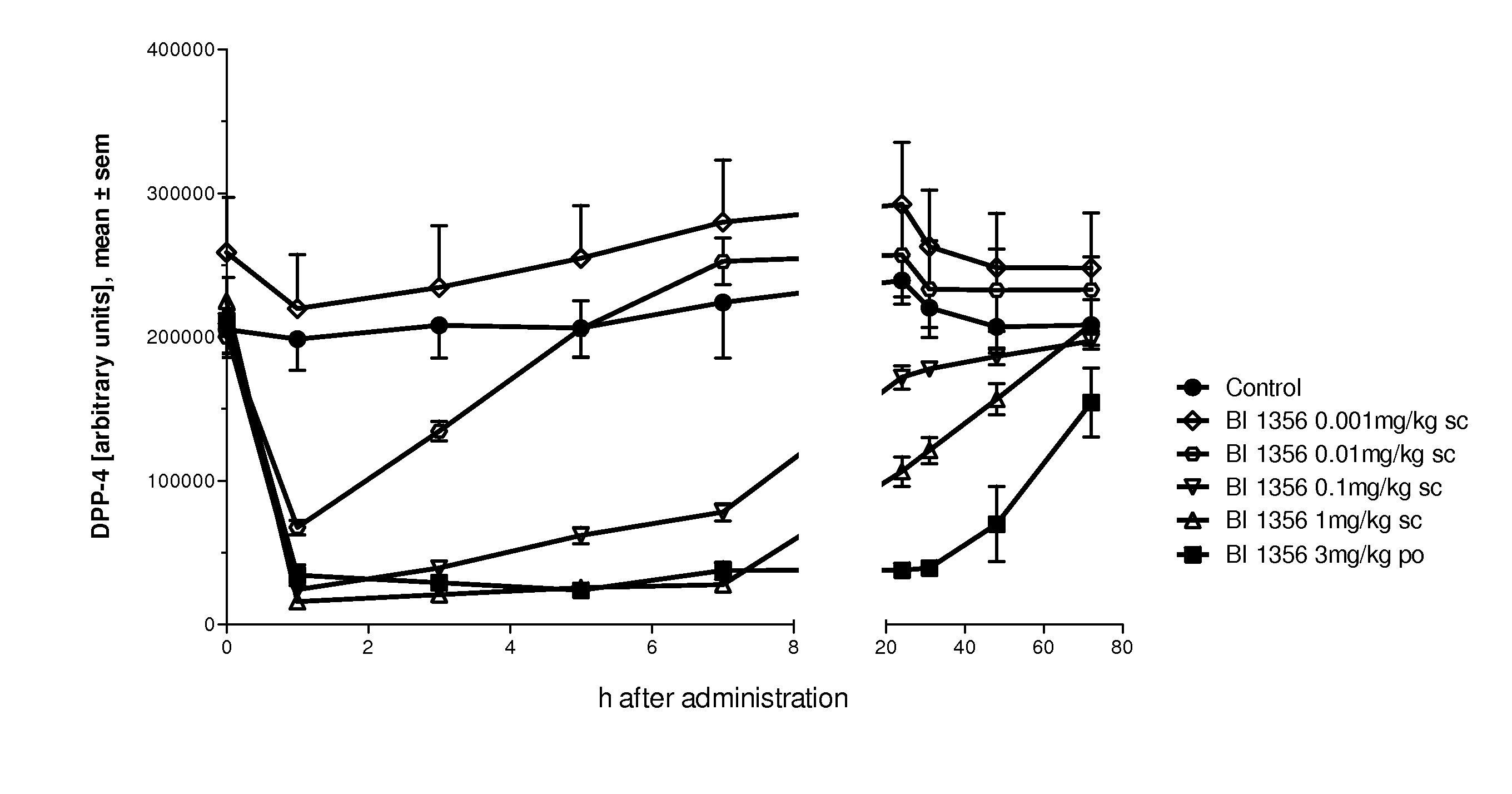
The present invention relates to methods for treating and / or preventing metabolic diseases comprising the combined administration of a DPP-4 inhibitor and a long-acting insulin. The invention further relates to a DPP-4 inhibitor for subcutaneous or transdermal use.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Multifunctional analyte testing device and method thereof
Methods, systems and devices for detecting an analyte sample, determining an analyte concentration associated with the detected analyte sample, retrieving stored one or more dose determination information and associated analyte concentration associated with the retrieved one or more dose determination information, and determining a current dose level based at least in part on the determined analyte concentration and the retrieved prior dose determination information, where the determined current dose level includes a predetermined type of medication classification are provided. For example, dosage determination of fast or rapid acting insulin, long acting insulin, intermediate acting insulin, or one or more combinations may be provided to assist in the management of diabetes and related conditions.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
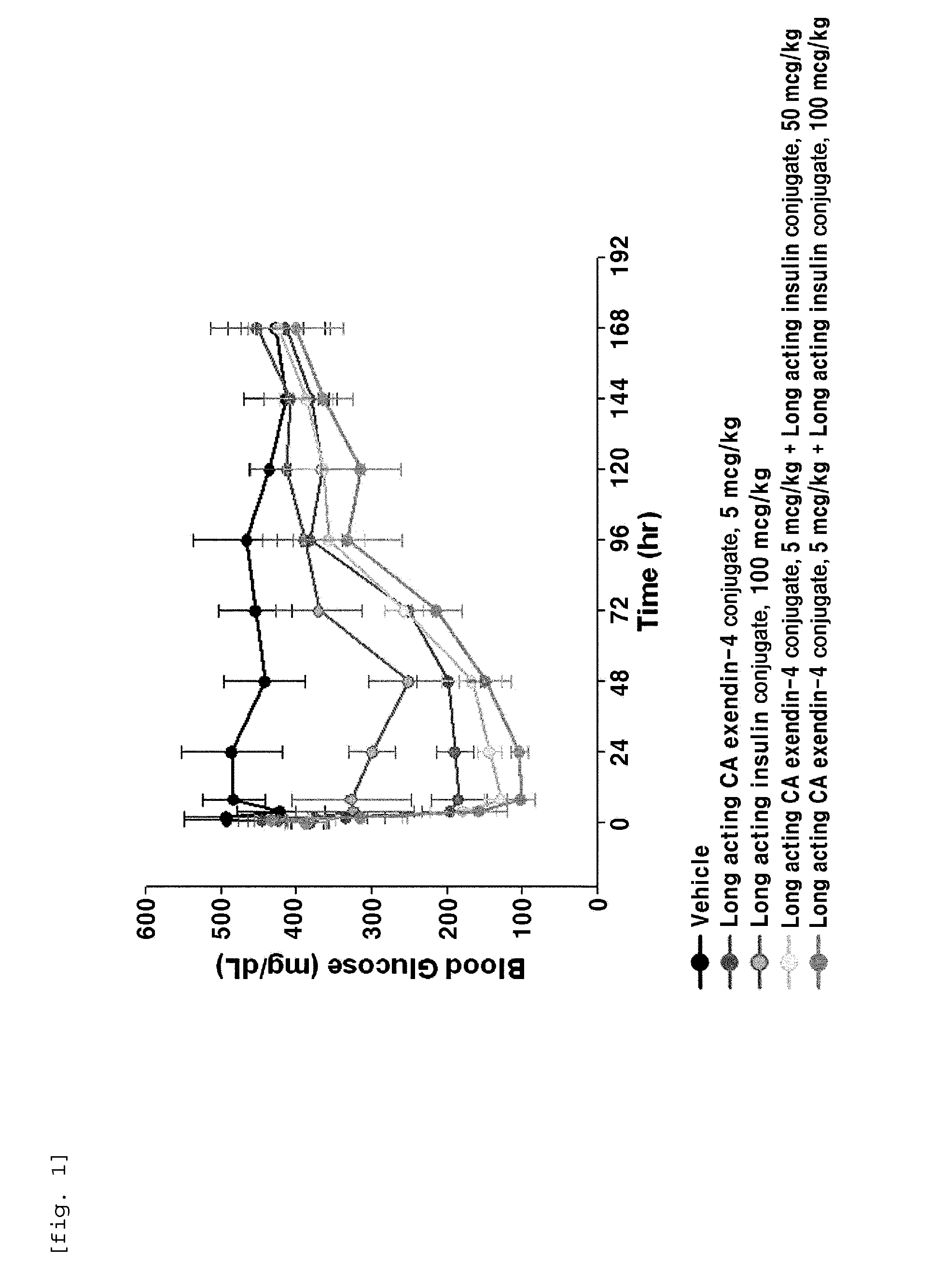
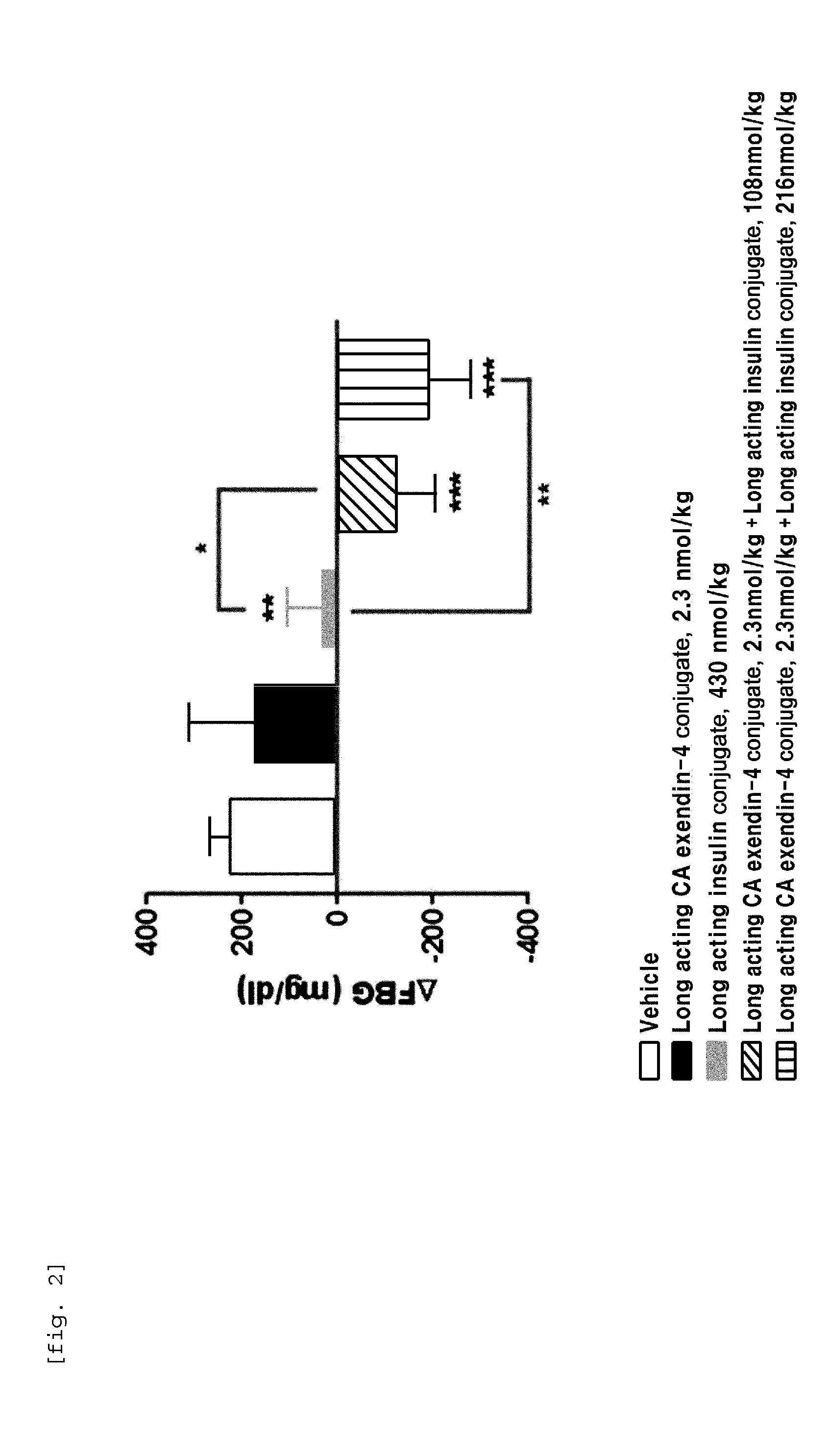
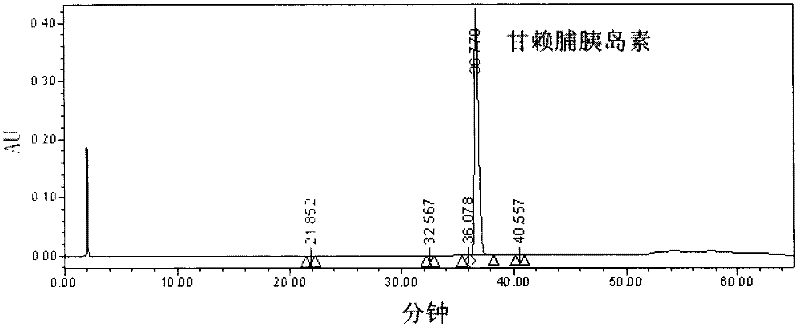
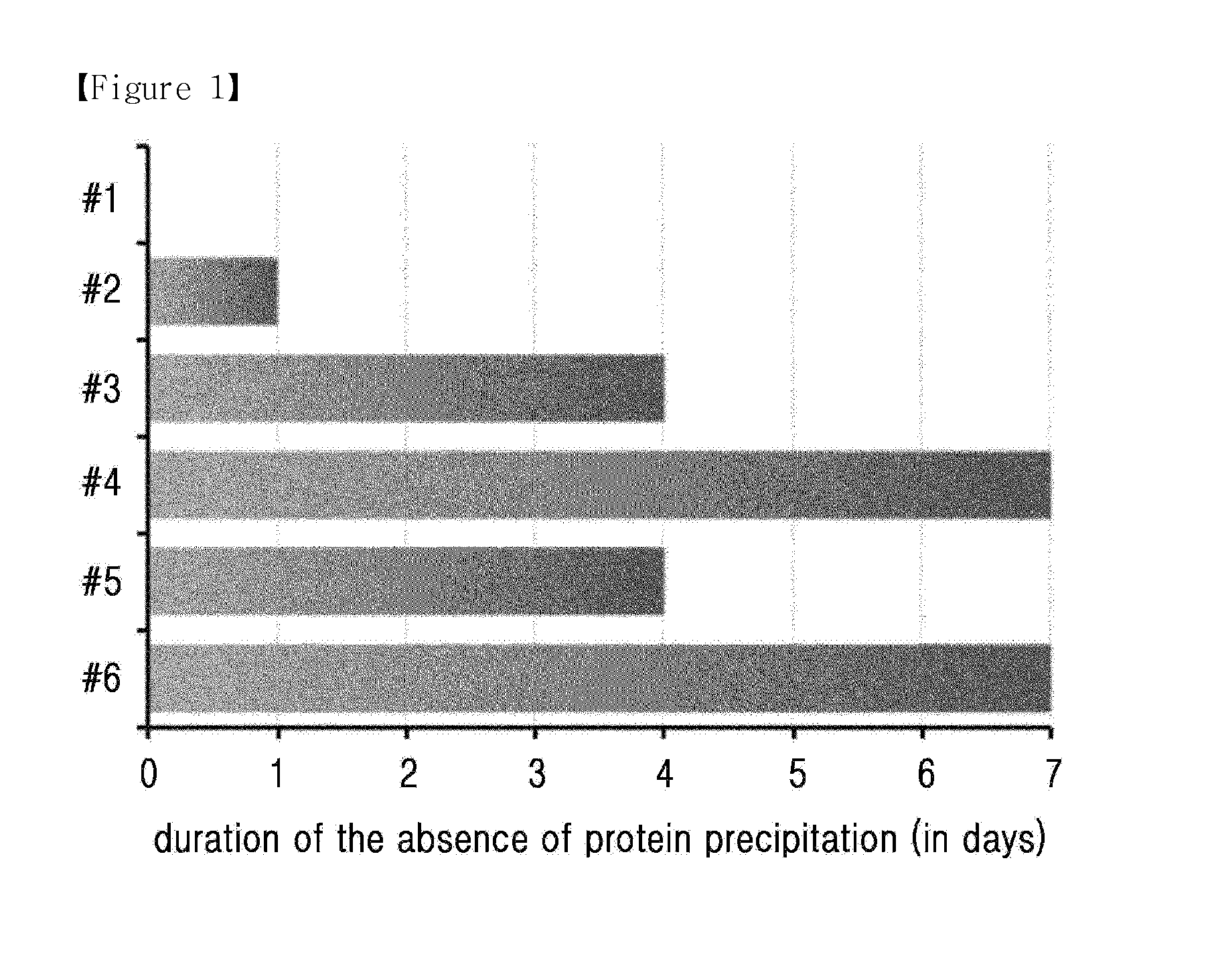
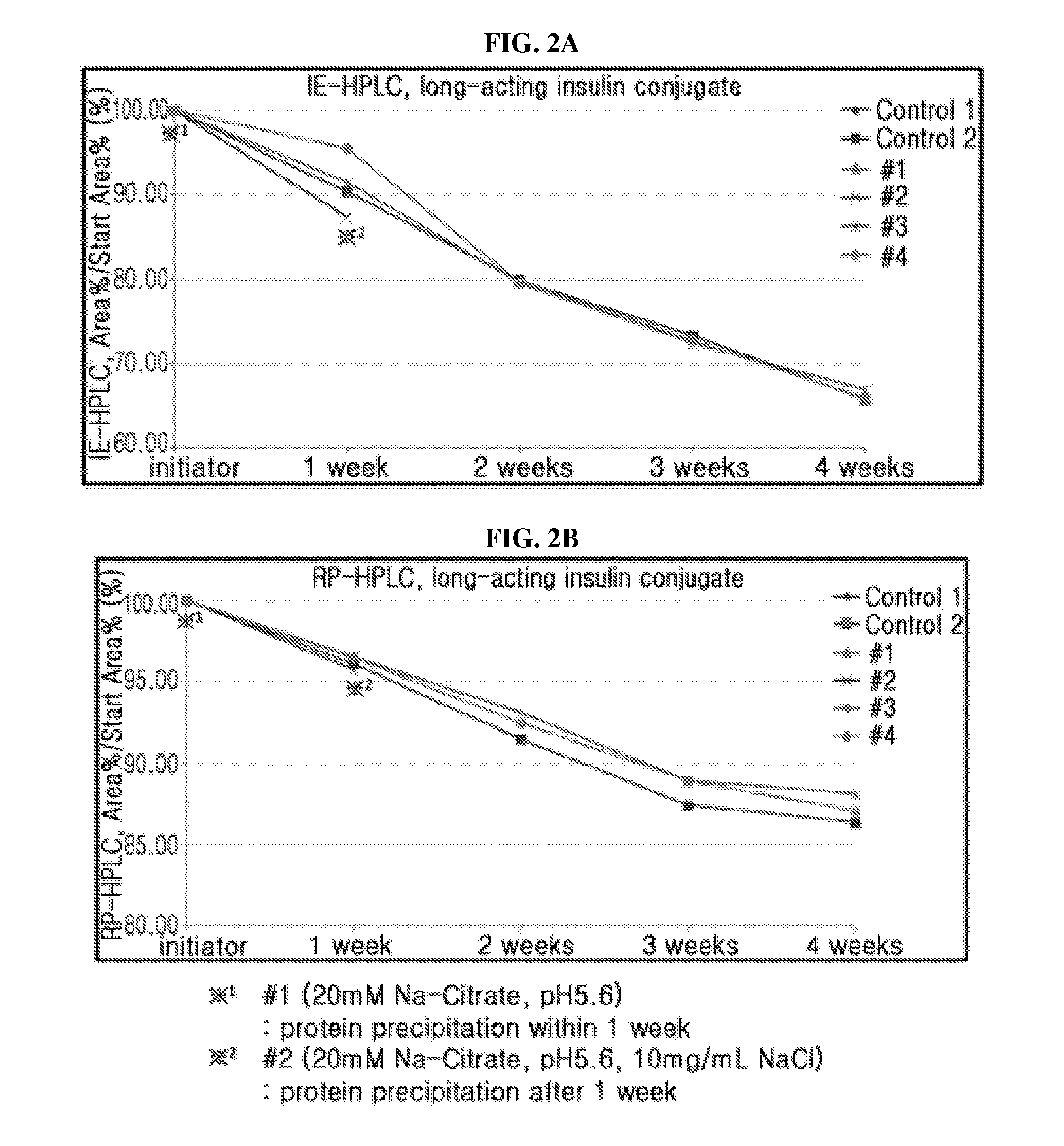
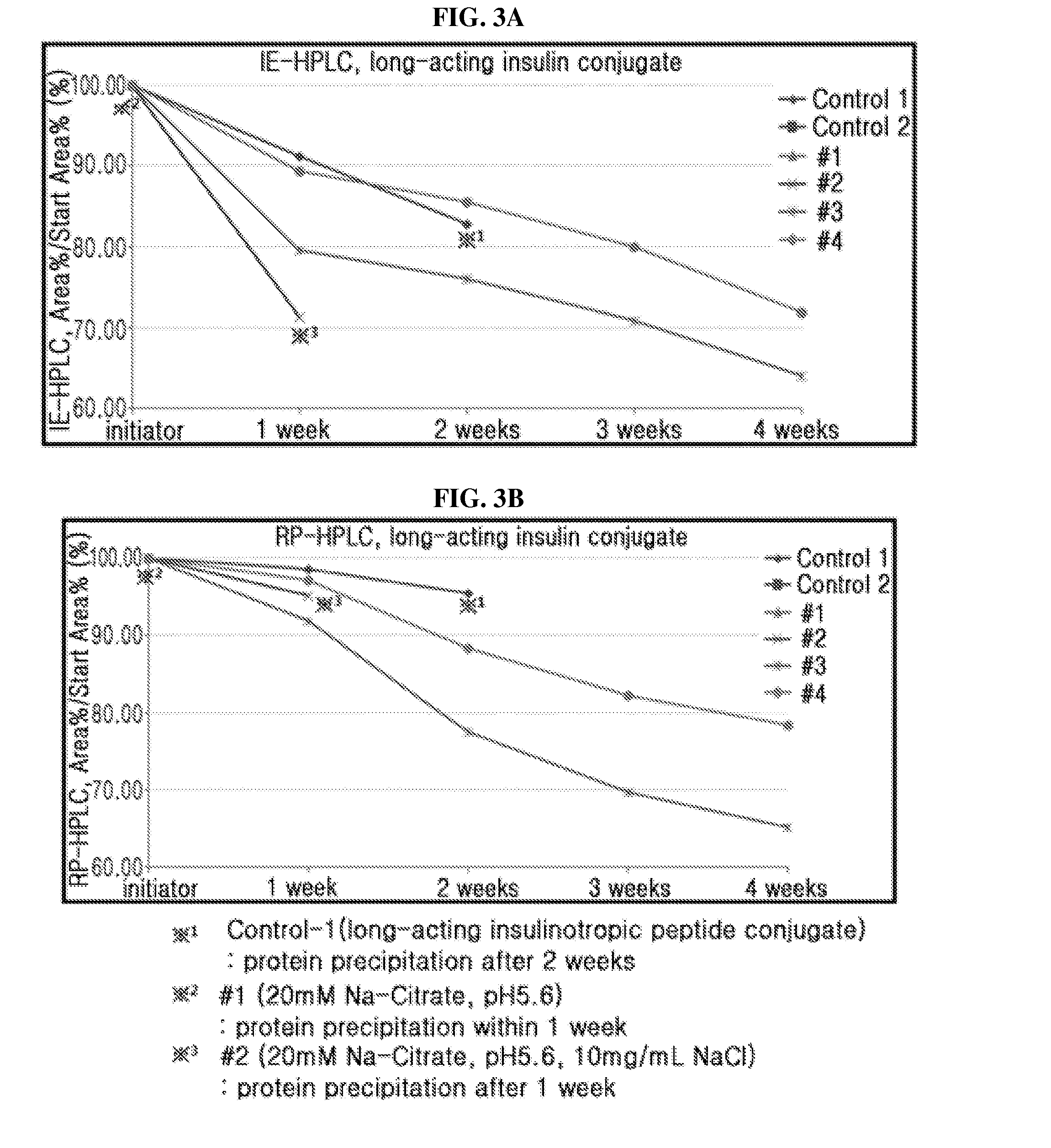
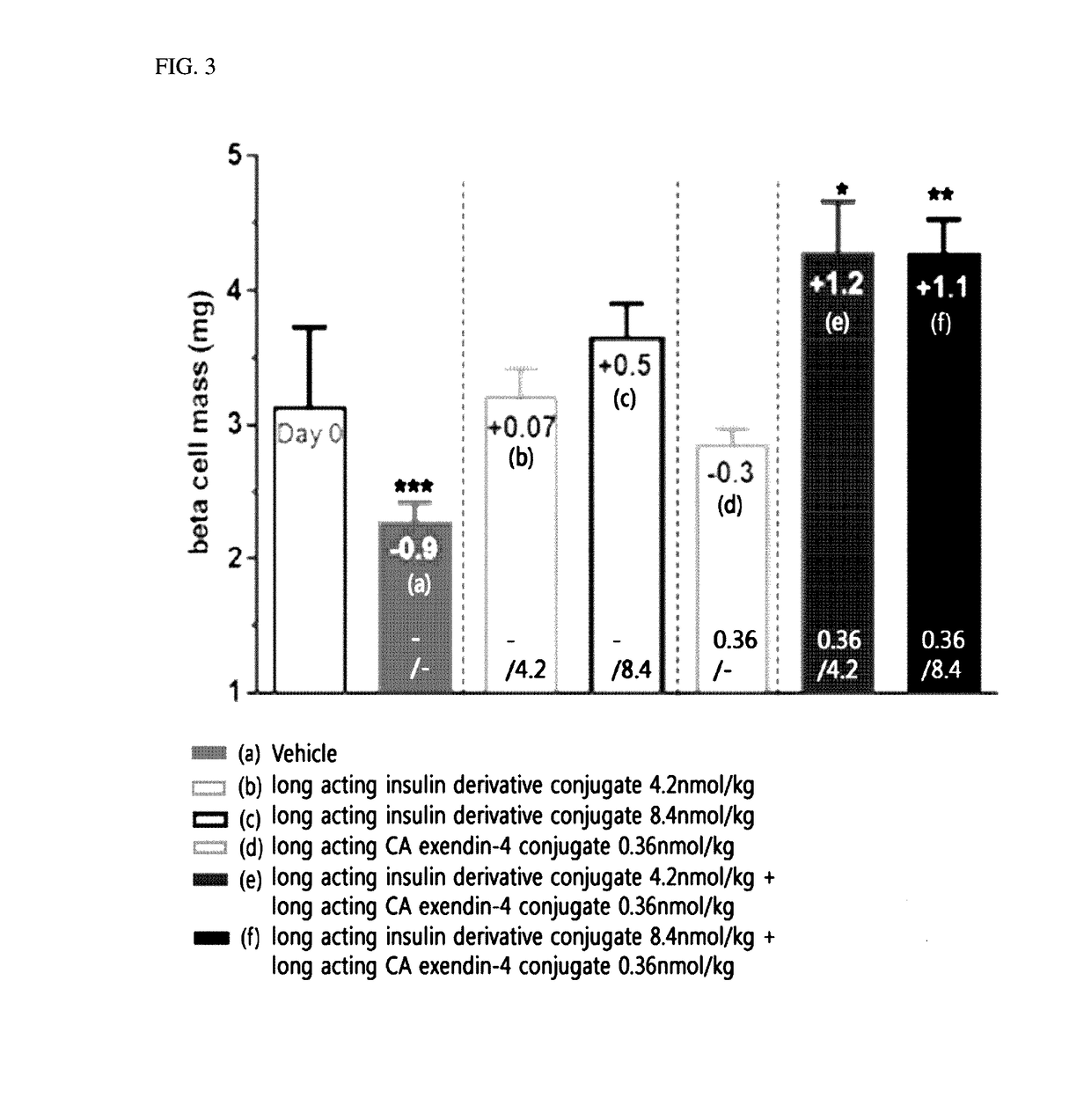
Composition for treating diabetes comprising long-acting insulin conjugate and long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate
ActiveUS20140120120A1Good treatment effectImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderIn vivoWeight gain
The present invention relates to a composition for the prevention or treatment of diabetes comprising a long-acting insulin conjugate and a long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate, and a therapeutic method for the treatment of diabetes, and more particularly, concurrent administration of the long-acting insulin conjugate and the long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate inhibits weight gain caused by insulin treatment, and vomiting and nausea caused by insulinotropic peptide treatment, and reduces the required dose of insulin, thereby remarkably improving drug compliance. Moreover, each of the long-acting insulin conjugate and the long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate of the present invention is prepared by linking insulin or insulinotropic peptide with an immunoglobulin Fc region via a non-peptidyl linker, thereby showing improved in-vivo duration of efficacy and stability.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Rapid Acting and Long Acting Insulin Combination Formulations
InactiveUS20080039365A1Promote absorptionAct quicklyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is decreased so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Method for reducing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in prediabetic patients and patients with type 2 diabetes
ActiveUS7405196B2Reduce riskReduce elevated blood lipid valuePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMortality rateDiabetic patient
This invention relates to a method of reducing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in a prediabetic or Type 2 Diabetes patient population. The method comprises administering an effective dosage of a long acting insulin, preferably insulin glargine, to a prediabetic or Type 2 Diabetes patient.
Owner:AVENTISUB LLC
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS7718609B2Increase speedReduce the amount of solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed in which the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS8084420B2Short durationImprove blood sugar controlPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastInsulin injection
An injectable formulation containing a rapid acting insulin and a long acting insulin has been developed. The pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting insulin, remains soluble when they are mixed together. Preferably, the formulation is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal and basal insulin for up to 24 hours, and does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast, rapid, or very rapid acting insulin. Alternatively, by adjusting the ratio of rapid to long acting insulin, the long acting insulin may be shortened to a 12 hour formulation, and re-administered to the patient at dinner time, providing a safe and effective basal insulin level until morning. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
InactiveUS7713929B2Rapid acting insulin isPromote absorptionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed in which the pH of the rapid acting insulin is decreased so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Diabetes therapy
ActiveUS9149478B2Shorten the progressSlow onsetSenses disorderNervous disorderDiabetes mellitusDiabetes Therapy
The present invention relates to methods for treating and / or preventing metabolic diseases comprising the combined administration of a DPP-4 inhibitor and a long-acting insulin. The invention further relates to a DPP-4 inhibitor for subcutaneous or transdermal use.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Rapid acting and long acting insulin combination formulations
ActiveUS20090137455A1Short durationImprove blood sugar controlPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
An injectable formulation containing a combination of a rapid acting insulin and a long acting insulin has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is adjusted so that the long acting insulin, e.g. insulin glargine, remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for up to 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. Alternatively, through adjustment of the ratio of rapid acting insulin to long acting insulin, the long acting insulin may be shortened to a 12 hour formulation. This rapid and long acting blend is re-administered to the patient at dinner time, providing a safe and effective basal insulin level until morning. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
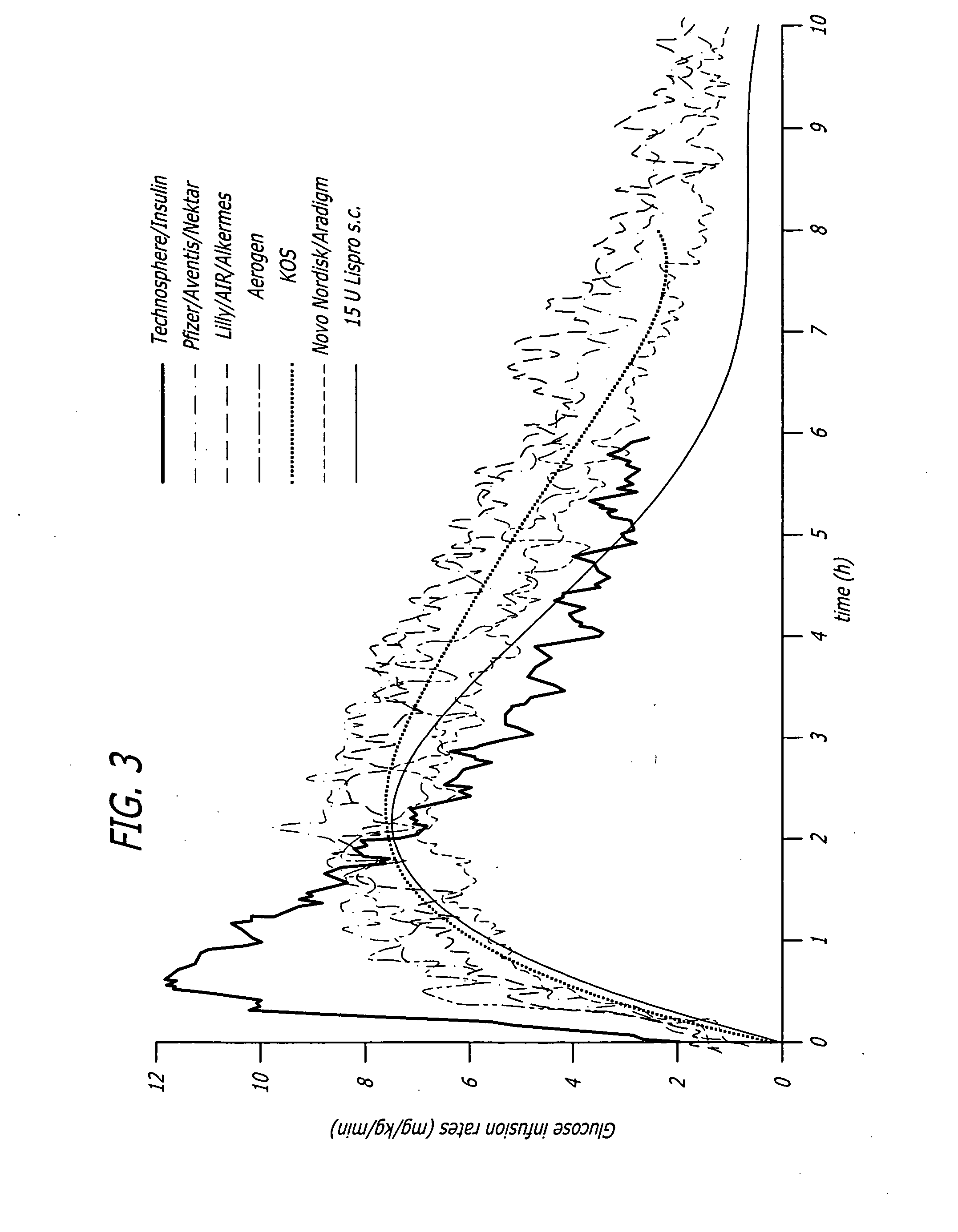
Rapid Acting Insulin Analogues
InactiveUS20110021423A1Promote formationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineInsulin B Chain
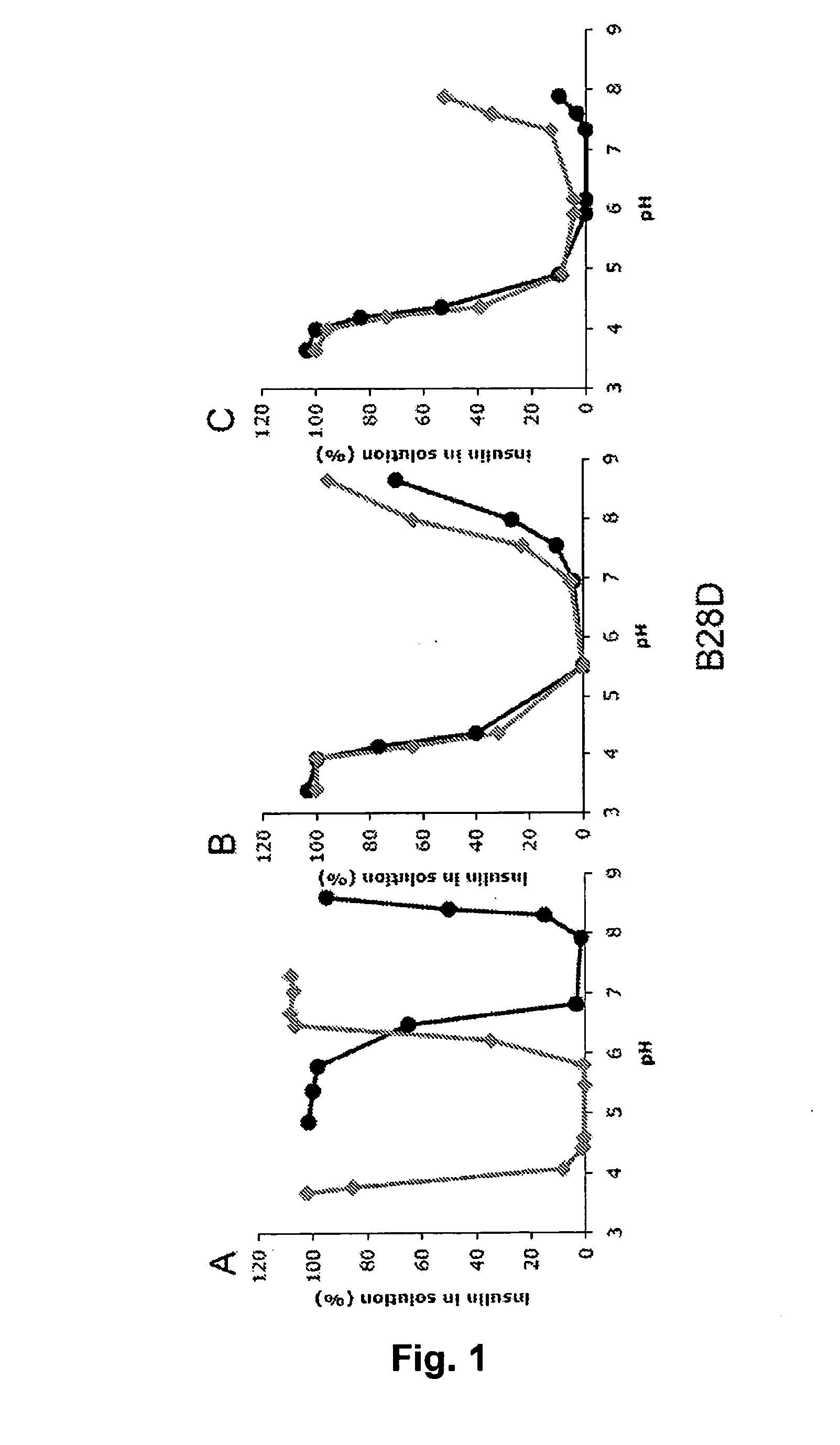
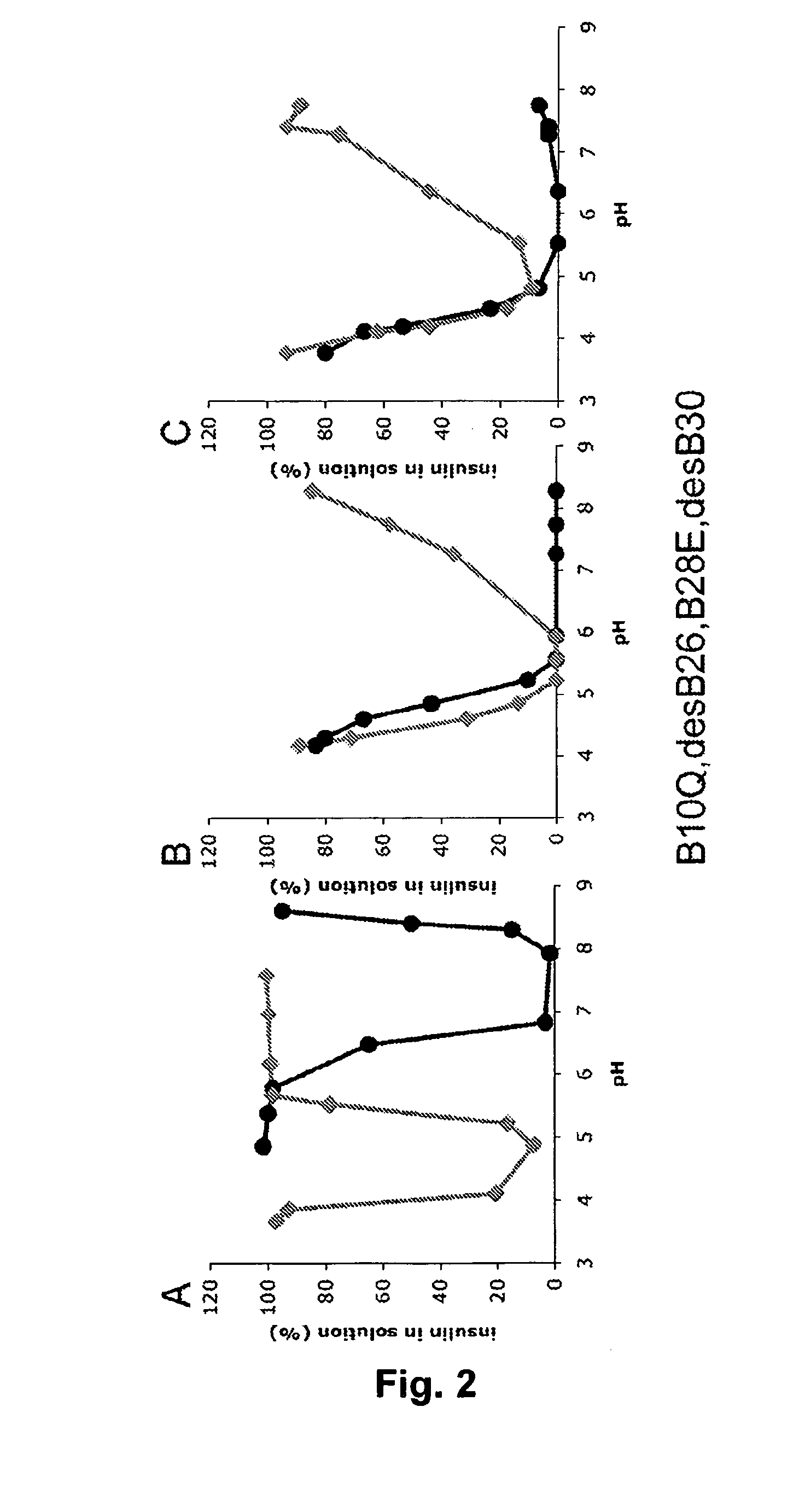
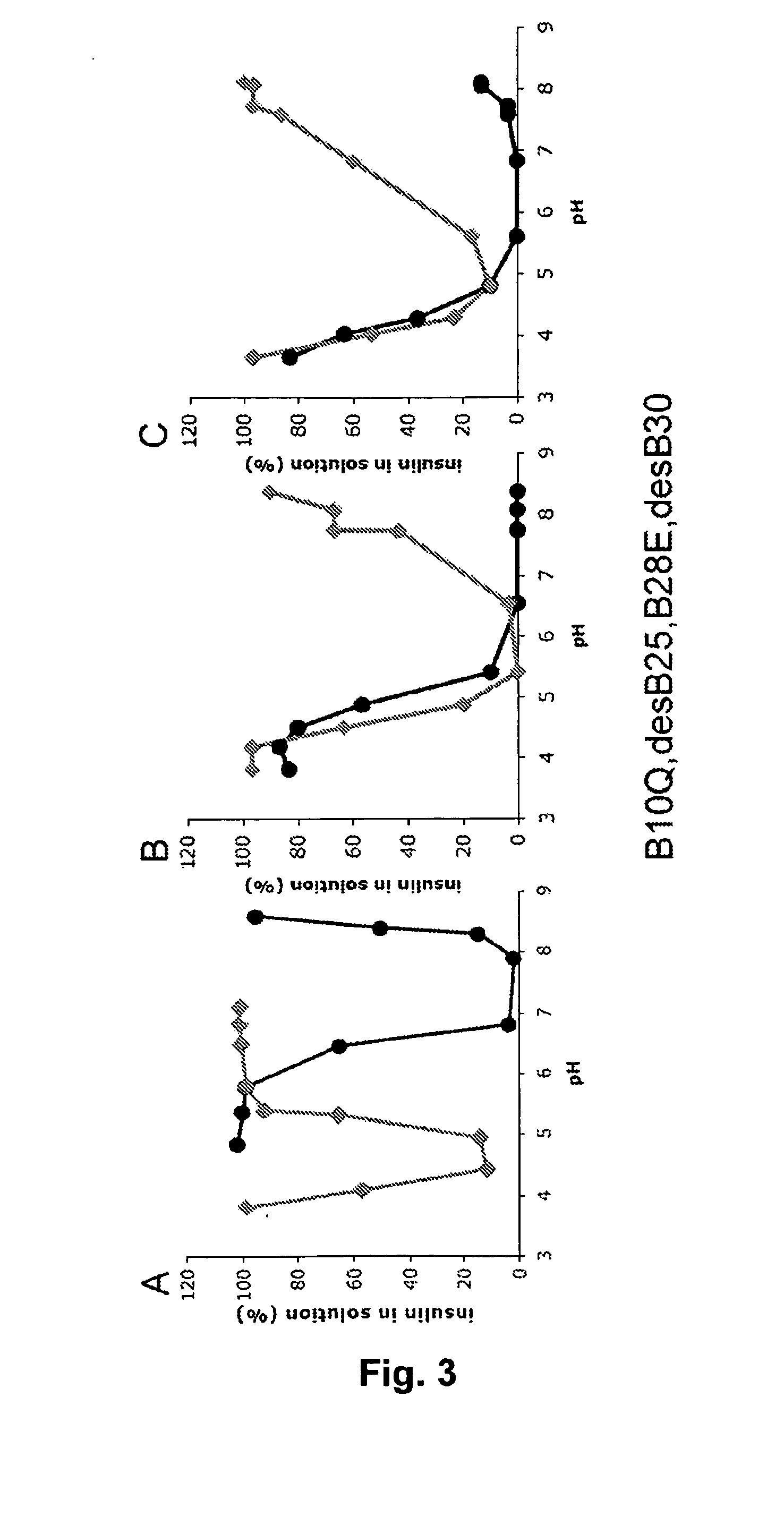
The invention is related to fast acting insulin analogues which can form soluble mix-tures (pre-mixed or self-mixed) with long acting insulin analogues. The fast action is achieved through monomerizing substitutions / deletions in the C-terminus of the B-chain of human insulin and the mixability with long acting insulin analogues is achieved through a substitution of the Zn-binding His in position B10 of human insulin with a Gln amino acid residue. In one embodiment the invention is related to fast acting insulin analogues in which at least one of the natural amino acid residues in position B22-B30 in the human B-chain has been substituted with another amino acid residue having the effect of promoting formation of the monomeric form of insulin, the His amino acid residue in position 10 in the B-chain is substituted with a Gln and wherein further one or more of the amino acid residues in position B22-B30 optionally have been deleted.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Method for reducing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in prediabetic patients and patients with type 2 diabetes
InactiveUS7977310B2Add additional massFunction increasePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineMortality rate
This invention relates to a method of reducing cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in a prediabetic or Type 2 Diabetes patient population. The method comprises administering an effective dosage of a long acting insulin, preferably insulin glargine, to a prediabetic or Type 2 Diabetes patient.
Owner:AVENTISUB LLC
Long-acting insulin or insulin analogue conjugate
ActiveUS20180161448A1Increase compliance of administrationEliminate side effectsVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifeIn vivo
The present invention relates to insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate, and a use thereof, wherein the insulin and / or insulin analogue have improved in vivo durability and stability by linking the same with an Fe region of immunoglobulin. The insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate of the present invention show an in vivo activity similar to that of insulin. In addition, the insulin and / or insulin analogue conjugate of the present invention are long-acting formulations of insulin and / or the analogue thereof, in which serum half-life is remarkably increased, and therefore, the present invention provides remarkable insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate, which do not induce hypoglycemia, a drawback of insulin treatment.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Long-acting colloidal insulin formulation and its preparation
InactiveUS20090110742A1Easy injectionEasy to fillPowder deliveryNanotechTolerabilityLong acting insulin
The invention relates to injectable long-acting insulin formulations for the treatment of types I and II diabetes in humans and animals.The essential object of the invention is to provide an injectable long-acting insulin formulation in the form of a colloidal suspension which is stable, which has a good local tolerance and toxicity compatible with the chronic treatment of diabetics, and which maintains a substantial hypoglycemic effect extending over at least 24 hours after a single administration, e.g. by the subcutaneous route.To achieve this object, the invention relates to a stable aqueous colloidal formulation of insulin-laden nanoparticles of at least one poly(Leu-block-Glu) in which the pH is between 5.8 and 7.0, the osmolarity O (in mOsmol) . . . : 270≦O≦800, and the viscosity v (in mPa.s) is low, namely v≦40. The nanoparticles of poly(Leu-block-Glu) have a mean hydrodynamic diameter Dh such that: 15≦Dh≦40.The invention relates to an antidiabetic drug based on this long-acting insulin formulation and injectable using needles of gauge 29G, 30G or 31G.
Owner:FLAMEL TECHNOLOGIES
Long-acting insulin or insulin analogue conjugate
ActiveUS10894089B2Increase compliance of administrationEliminate side effectsVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsIntravenous gammaglobulinHypoglycemia
The present invention relates to insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate, and a use thereof, wherein the insulin and / or insulin analogue have improved in vivo durability and stability by linking the same with an Fc region of immunoglobulin. The insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate of the present invention show an in vivo activity similar to that of insulin. In addition, the insulin and / or insulin analogue conjugate of the present invention are long-acting formulations of insulin and / or the analogue thereof, in which serum half-life is remarkably increased, and therefore, the present invention provides remarkable insulin and / or an insulin analogue conjugate, which do not induce hypoglycemia, a drawback of insulin treatment.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Insulin analogue having quick response and stability under acidic condition and preparation thereof
ActiveCN102199206AQuick effectProtect capillariesPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical formulationInsulin Analogue
The invention relates to an isulin analogue having quick response and stability under acidic condition, and a medicinal composition and a medicinal preparation thereof. Asparagine (Asn) at the A 21 position of the chain A of the isulin analogue is mutated into glycine (Gly), the isulin analogue can be mixed with a long-acting isulin analogue such as insulin glargine to form a premixed preparationwith two functions of quick-acting sugar reduction and stable long-acting sugar reduction, and the problems that the conventional natural insulin (of pigs, cows and human) and quick-acting isulin analogues are unstable in the acidic environment, and the conventional isulin premixed preparation is not clarified and needed to be introduced with a foreign protein (such as protamine) serving as a slow release preparation so as to easily cause immune reaction, and is needed to be injected twice each day, namely in the morning and evening are solved, so that the safety of the preparation is higher.
Owner:GAN&LEE PHARMA
Liquid formulation of long-acting insulin and insulinotropic peptide
ActiveUS20150190528A1Good storage stabilityMaintain activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderHigh concentrationAlcohol sugars
The present invention relates to a liquid formulation of a combination of long-acting insulin and insulinotropic peptide, comprising insulin which is a physiologically active peptide, insulinotropic peptide, and albumin-free stabilizer, wherein the stabilizer comprises a buffer, a sugar alcohol, a non-ionic surfactant, and an isotonic agent; and a method for preparing the liquid formulation. The liquid formulation of the present invention does not contain a human serum albumin and potentially toxic factors to the body, and thus it has excellent storage stability for insulin conjugate and insulinotropic peptide conjugate at high concentration, without a risk of viral contamination.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Long-acting insulin analogue preparations in soluble and crystalline forms
InactiveUS20130085101A1Enhances receptor-binding selectivityDecrease absolute affinity for IGF-1ROrganic active ingredientsBacteriaInsulin A ChainPharmaceutical formulation
A pharmaceutical formulation comprises an insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof, wherein the insulin analogue or a physiologically acceptable salt thereof contains an insulin A-chain sequence that contains paired Histidine substitutions at A4 and A8, and optionally a substitution at A21. The formulation further contains a pharmaceutically acceptable buffer containing at least about 4 zinc ions per 6 insulin analogue molecules. The formulation forms a long-acting zinc-dependent subcutaneous depot upon subcutaneous injection. In a zinc-free formulation, the insulin analogue monomer exhibits decreased affinity for the Insulin-like Growth Factor receptor and at least 20% of the affinity for the insulin receptor of the same species, in comparison to an otherwise identical insulin or insulin analogue that does not contain the HisA4 and HisA8 substitutions.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Composition for treating diabetes and containing long-acting insulin analog conjugate and long-acting insulin secretion peptide conjugate
PendingCN106559984AImprove complianceSmall dosePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide effectInsulin secretion
The present invention relates to a composition for preventing or treating diabetes and containing long-acting insulin analog and long-acting insulin secretion peptide conjugates, and a method for treating diabetes. More specifically, the composition can remarkably improve compliance by inhibiting weight gain caused by the administration of insulin, inhibiting emesis and nausea phenomena caused by the administration of an insulin secretion peptide and reducing the dose of insulin through the concomitant administration of the long-acting analog conjugate and the long-acting insulin secretion peptide conjugate. In addition, the present invention relates to: a pharmaceutical composition for alleviating the side effects of pancreatic beta cells in a patient with diabetes, and containing a long-acting insulin analog conjugate and a long-acting insulin secretion peptide conjugate; and a method for alleviating the side effects of pancreatic beta cells in a patient with diabetes. The method comprises a step of administering the composition. The composition, the pharmaceutical composition and the method are characterized in alleviation of side effects such as pancreatic beta cell dysfunction, pancreatic beta cell reduction, lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity, which are caused by the progression of diabetes.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Composition for treating diabetes comprising long-acting insulin analogue conjugate and long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate
ActiveUS20170143802A1Good treatment effectImprove in duration of efficacyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSide effectWeight gain
The present invention relates to a composition for the prevention or treatment of diabetes including a long-acting insulin conjugate and a long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate, and a method for treating diabetes. More specifically, combination administration of the long-acting analogue conjugate and the long-acting insulinotropic peptide conjugate inhibits weight gain due to administration of insulin, and vomiting and nausea due to administration of the insulinotropic peptide, and also reduces the required doses of insulin, thereby remarkably improving drug compliance. In addition, the present invention relates to administering a pharmaceutical composition for reducing side effects of pancreatic beta cells in diabetic patients, including a long-acting insulin analogue conjugate and a long-acting insulinotropic peptide analogue conjugate, and to a method for reducing side effects of pancreatic beta cells in diabetic patients, including the step of administering the composition. Specifically, the present invention is characterized in reducing side effects such as abnormality in the function of pancreatic beta cells associated with the development of diabetes, reduction in the pancreatic beta cell mass, lipotoxicity, or glucotoxicity.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
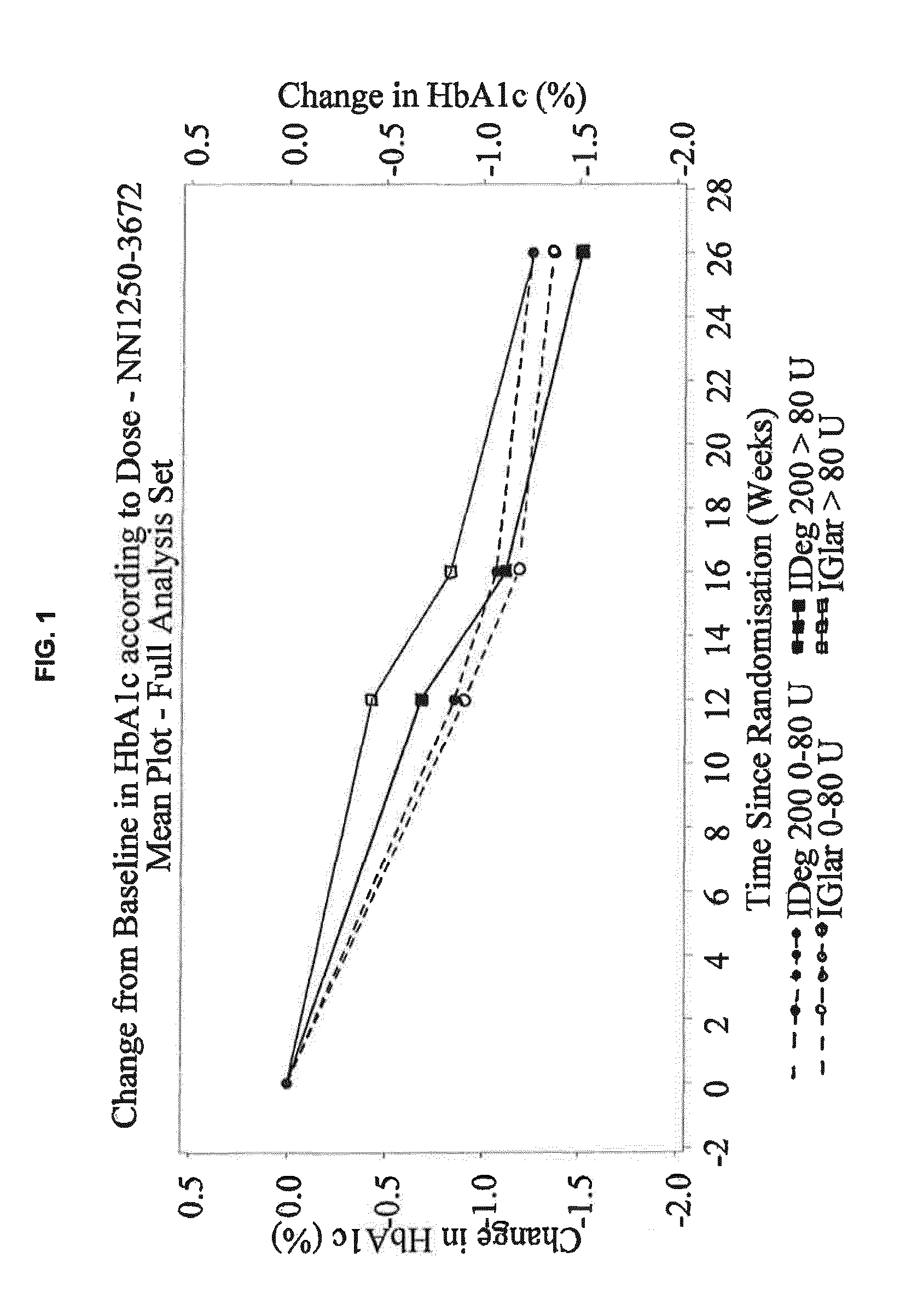
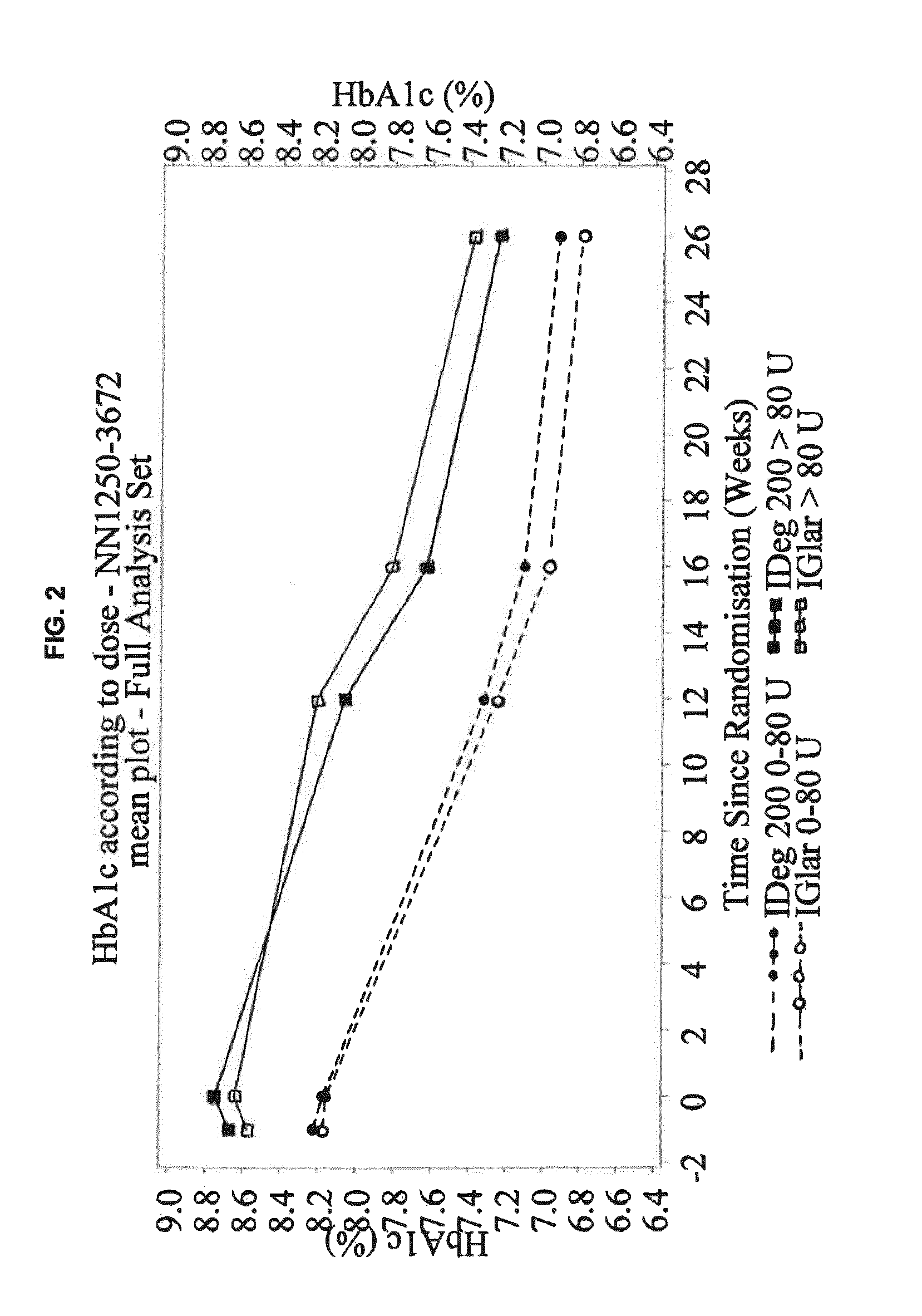
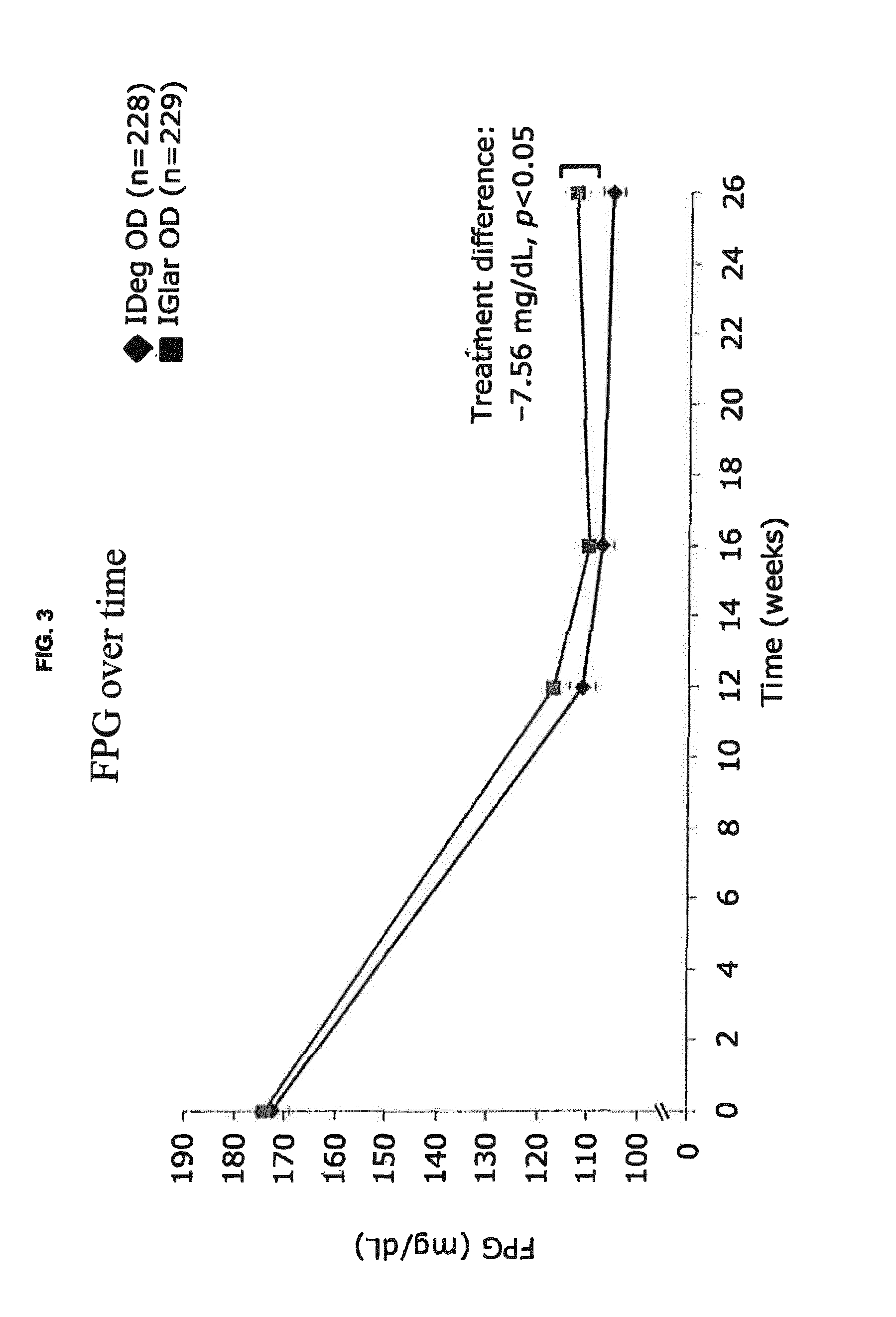
Dosing Regimen
InactiveUS20160296602A1Good hypoglycemic effectReduce riskPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDosing regimenCvd risk
The present invention relates to a long acting insulin analogue for use in reducing the risk of hypoglycaemia in a patient suffering from diabetes and requiring high amounts of delivered insulin, wherein the long acting insulin analogue is administered to said patient and in an amount of greater than 80 U / administration.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Liquid formulation of long-acting insulin conjugate
ActiveUS20150196643A1No risk of viral contaminationGood storage stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAlcohol sugarsNon ionic
The present invention relates to a liquid formulation of long-acting insulin conjugate, comprising a pharmaceutically effective amount of a long-acting insulin conjugate, wherein a physiologically active peptide, which is an insulin, is linked to an immunoglobulin Fc region; and an albumin-free stabilizer, wherein the stabilizer comprises a buffer, a sugar alcohol, a non-ionic surfactant, and an isotonic agent, and a method for preparing the formulation. For preventing microbial contamination in multiple uses, a preservative can be added to the formulation. The liquid formulation of the present invention does not comprise a human serum albumin and potentially hazardous factors to body, and thus it has excellent storage stability for insulin conjugate without a risk of viral infection.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Method for administration of insulin and pharmaceutical composition thereof
InactiveUS20120035103A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderLong acting insulinInsulin analog
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions including alkylglycosides admixed with at least one of fast-acting and long-acting insulin analogs for treatment of disorders, such as diabetes.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Preparation method of insulin
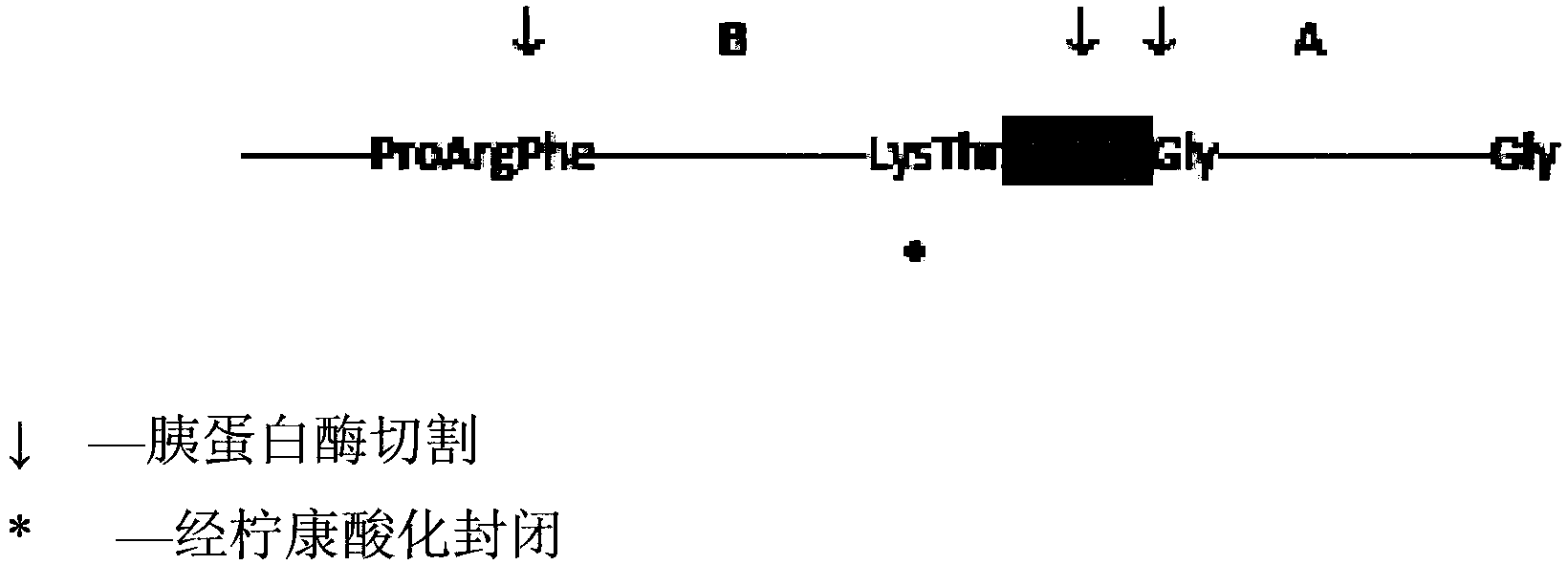
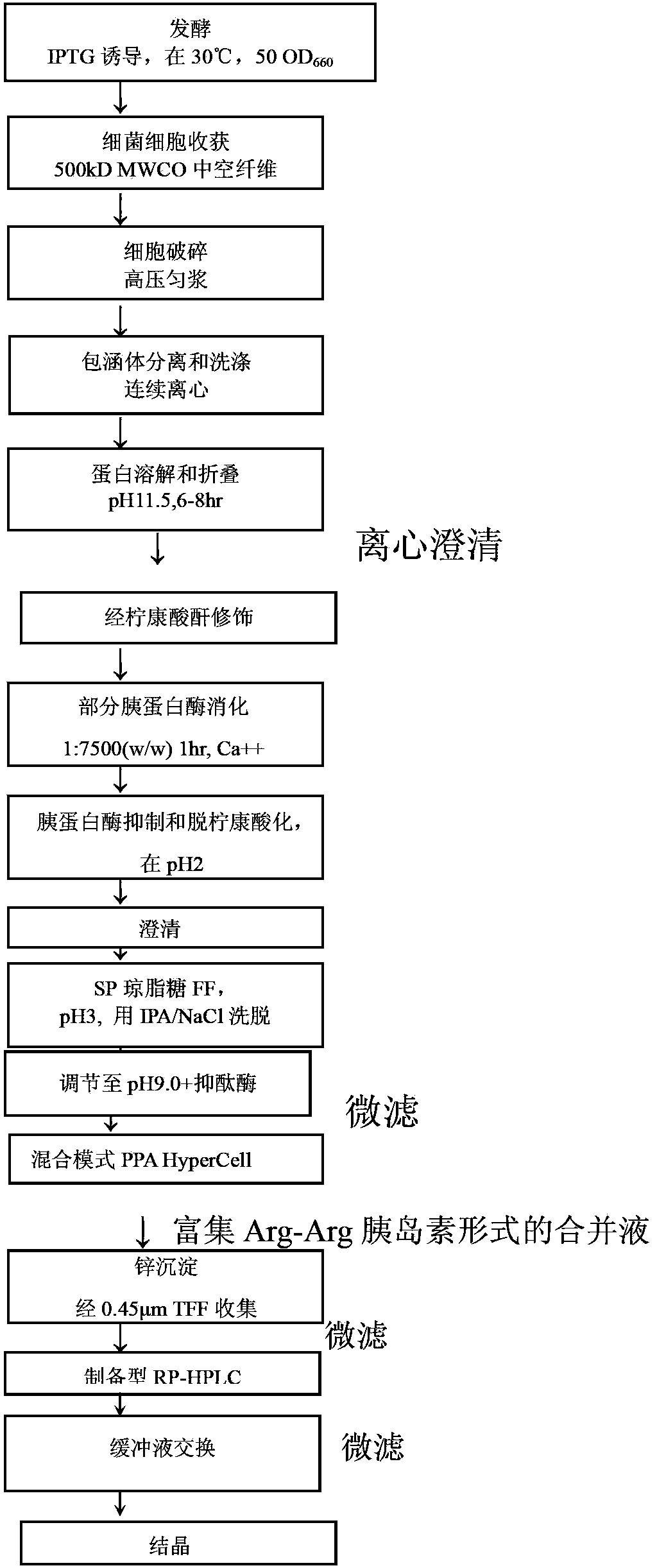
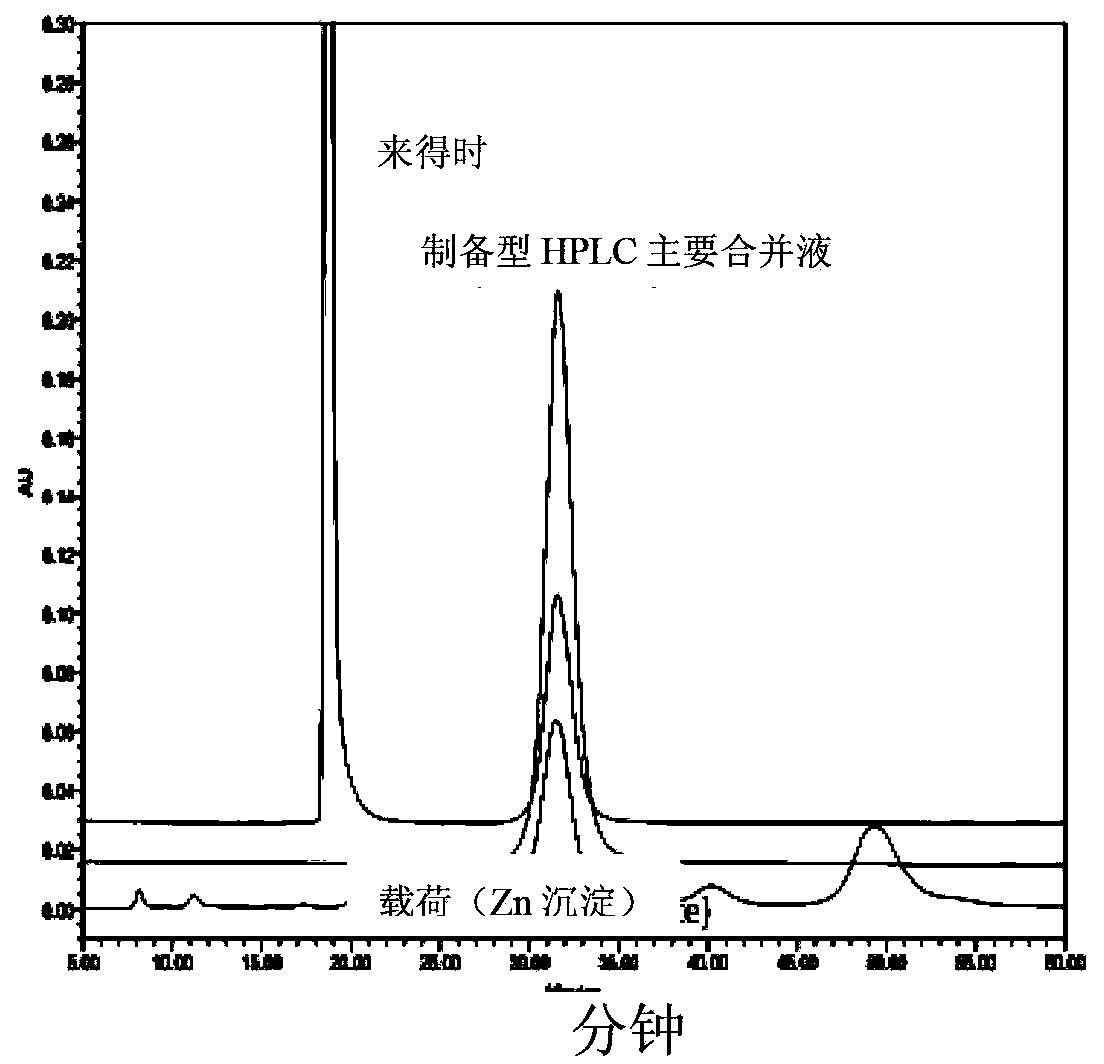
The invention provides a preparation method of insulin, relates to a method for transforming an insulin precursor into an active insulin compound, preferably a method for improving long-acting insulin; and particularly provides a method, wherein lysine residues in Arg-Arg precursor insulin can be reversibly closed, and parenzyme can cut the reversibly closed Arg-Arg precursor insulin.
Owner:VALIN TECH
Liquid formulation of long-acting insulin and insulinotropic peptide
ActiveUS9833516B2Good storage stabilityMaintain activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderHigh concentrationAlcohol sugars
The present invention relates to a liquid formulation of a combination of long-acting insulin and insulinotropic peptide, comprising insulin which is a physiologically active peptide, insulinotropic peptide, and albumin-free stabilizer, wherein the stabilizer comprises a buffer, a sugar alcohol, a non-ionic surfactant, and an isotonic agent; and a method for preparing the liquid formulation. The liquid formulation of the present invention does not contain a human serum albumin and potentially toxic factors to the body, and thus it has excellent storage stability for insulin conjugate and insulinotropic peptide conjugate at high concentration, without a risk of viral contamination.
Owner:HANMI PHARMA
Multi-function analyte monitor device and methods of use
Methods, systems and devices for detecting an analyte sample, determining an analyte concentration associated with the detected analyte sample, storing the determined analyte concentration and a time associated with the determined analyte concentration, retrieving two or more stored analyte concentrations, and determining an adjusted dose level based at least in part on a current dose level and data associated with the two or more retrieved analyte concentrations are provided. For example, adjustments to dosage levels of long-acting insulin may be provided to assist in the management of diabetes and related conditions.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com