Novel process for genetic engineering preparation of insulin and insulin analogs
A technology for insulin and insulin precursors, applied in the field of bioengineering, which can solve the problems of complex preparation methods of final products, mismatched disulfide bonds, and low expression of gene recombination methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
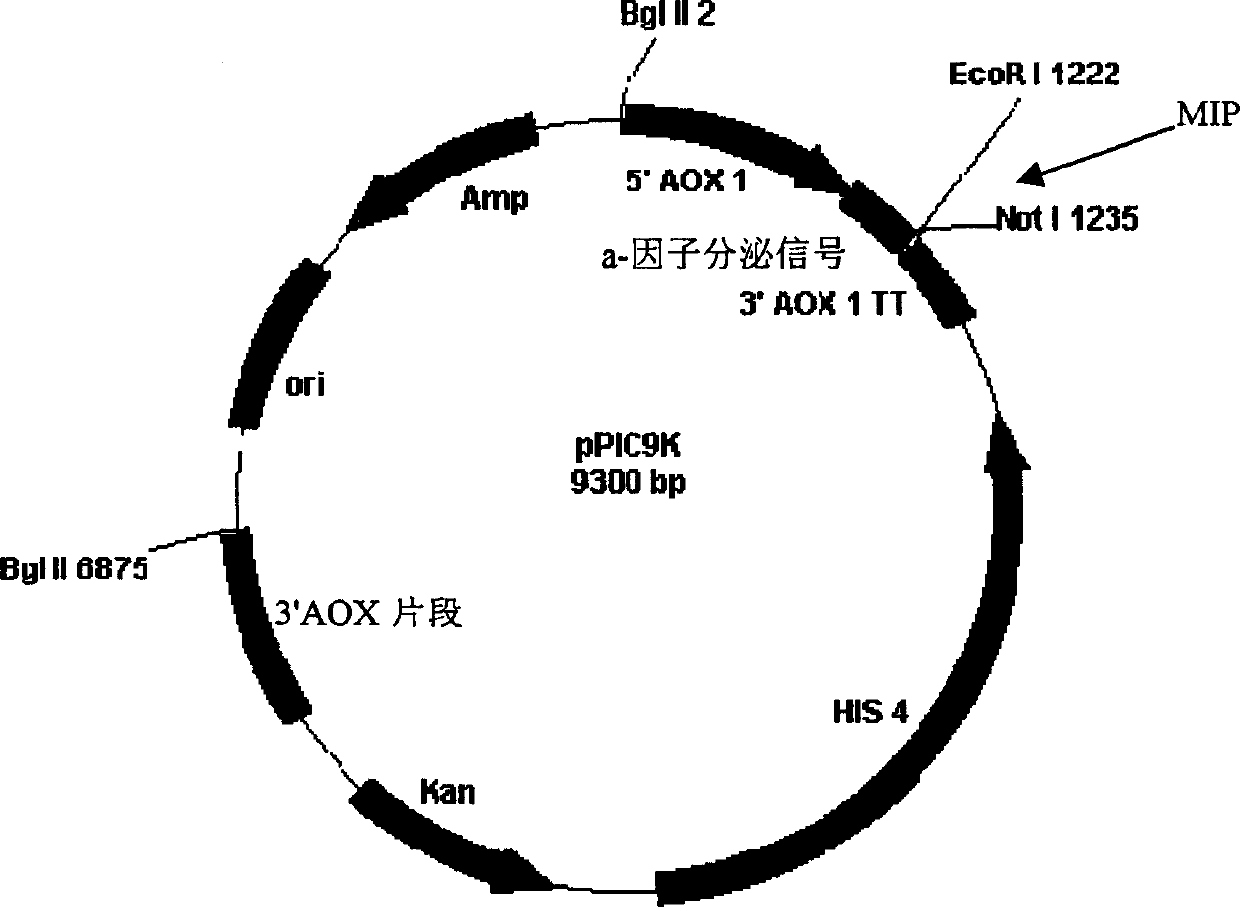
[0077] Construction of expression vector
[0078] The codon usage of P. pastoris is basically similar to that of S. cerevisiae, but there are some differences in individual amino acids such as Glu [Zhao, X., Huo, K.K. and Li, Y.Y.(2000). Synonymous codon usage in Pichia pastoris Sheng Wu Gong Cheng XueBao16(3):308-11.]. Chemical synthesis of monomeric insulin B following the codon preference of P. pastoris 27 K-DTrI precursor gene fragment (Fig. 1A).
[0079] Chemically synthesize code B by the same method 1 A B 27 K-DTrI (Fig. 1B) and (DesB 1 )B 27 DNA of K-DTrI (Fig. 1C). Similar to S.cerevisiae, a suitable prepro-leader is helpful for the secretion and expression of insulin precursors in P.pastoris, and the chemically synthesized DNA fragments are cloned into the EcoRI and NotI sites of the pPIC9K plasmid (Invitrogen Company) to form α- Mating factor leader-EAEAYVEFK-MIP expression framework. Among them, the EA-rich spacer peptide (such as EAEAYVEFK, SEQ ID NO: 9) i...
Embodiment 2
[0082] Plasmid transformation and screening of MIP expression strains
[0083] 3ug of pPIC9K / B linearized with Bgl II 27 K-DtrI plasmid electrotransformed Pichia pastoris GS115 (his4) (purchased from NRRL, deposit number NRRL Y-15851, US6,730,499), 0.4cm electric shock cup, 2.4KV, 5.3ms, two consecutive electric shocks, transformed yeast cells Painted MD board. Plasmid pPIC9K / B 27 After K-DtrI is linearized with Bgl II, after entering yeast cells, part of it will be re-circularized and integrated into the chromosome through single-point insertion to obtain Mut+ phenotype transformants, and the other part of the linear plasmid will be integrated into the chromosome through substitution to obtain Muts expression. Type transformants, during which multi-copy insertion integration will spontaneously form. Pick 1,500 single clones from the MD plate, culture them in 2ml of YPD medium at 30°C for 24 hours, take 2μL and spot them on YPD plates containing 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 mg / ml of G4...
Embodiment 3
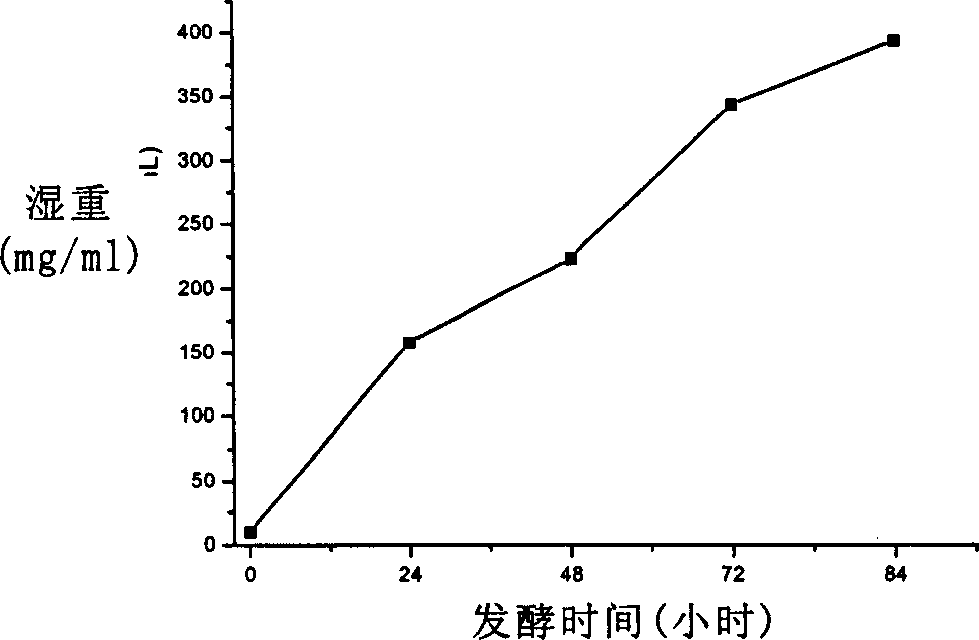
[0086] 2L scale fermentation
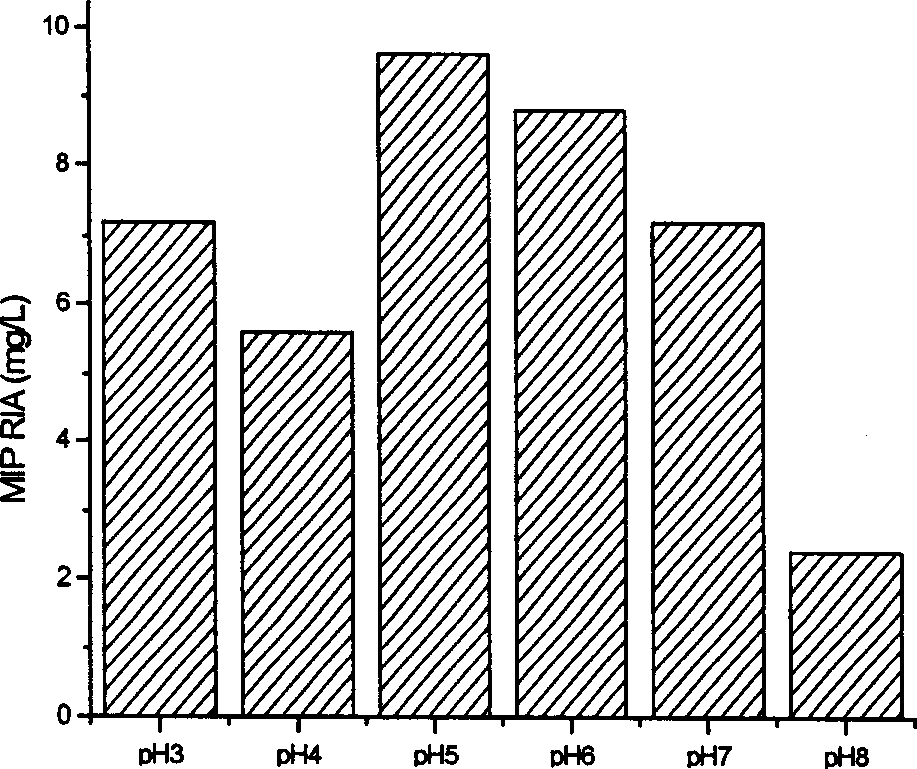
[0087] High-density fermentation is an effective means to obtain a large amount of heterologous protein from methanol yeast. Methanol yeast can grow in a simple inorganic salt medium. Harmful products such as alcohol and acetic acid are rarely produced during the fermentation process, so it is suitable for large-scale high-density fermentation . The pH value of the fermentation broth has a significant impact on the growth state of the cells and the stability of the secreted protein. The pH range of the fermentation was preliminarily optimized by shaking table experiments to be 4.5-6.5, and the optimal pH value was 5 (Figure 3).
[0088] Each liter of basic inorganic salt medium (basal salt medium, BSM) contains: 50ml glycerol, 26.7mlH 3 PO 4 , 0.93g CaSO 4 2H 2 O, 18.2 g K 2 SO 4 , 14.9 g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O), and 4.13 g KOH, autoclaved with NH 4 OH to adjust the pH value.
[0089] The formula of trace element solution (PTM1) is 1L containin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com