Vaccine adjuvant for treating autoimmune diseases and application thereof
A technology for immune diseases and new uses, applied in the field of vaccine adjuvants for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, can solve the problems of ineffective prevention of diabetes and other problems, and achieve the effect of simple and easy treatment, lower titer, and simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030]The invention provides a method for preparing polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer microspheres loaded with antigen polypeptides, comprising the steps of:
[0031] S1: Dissolve polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer in dichloromethane to obtain a dichloromethane solution dissolved with polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer; wherein, the mass of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer and the volume of dichloromethane The ratio is (10 ~ 60) mg: (1 ~ 10) mL;
[0032] S2: Dissolving the antigenic polypeptide in ultrapure water to obtain an aqueous solution in which the antigenic polypeptide is dissolved; wherein, the ratio of the mass of the antigenic polypeptide to the volume of water is (0.05-50) mg: (1-100) μL;
[0033] S3: Mix the dichloromethane solution in which the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer is dissolved and the aqueous solution in which the antigenic polypeptide is dissolved, and then sonicate in an ice bath for 1 to 20 minutes, and the ultrasonic...
Embodiment 1
[0039] This example provides a method for preparing polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer microspheres loaded with antigen polypeptides, including steps:
[0040] S1: Dissolve 30 mg of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer in 1 mL of dichloromethane to obtain a dichloromethane solution in which polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer is dissolved;
[0041] S2: Dissolving 1 mg of the antigenic polypeptide in 100 μL of ultrapure water to obtain an aqueous solution in which the antigenic polypeptide is dissolved;
[0042] S3: Mix the dichloromethane solution in which the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer is dissolved and the aqueous solution in which the antigenic polypeptide is dissolved, and then sonicate in an ice bath for 1 min, and the power of the sonication is 30W, to obtain oil-in-water (w / o) colostrum; , the mass ratio of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer to antigenic polypeptide is 1:0.20;
[0043] S4: After mixing the oil-in-water colostrum and the pol...
Embodiment 2
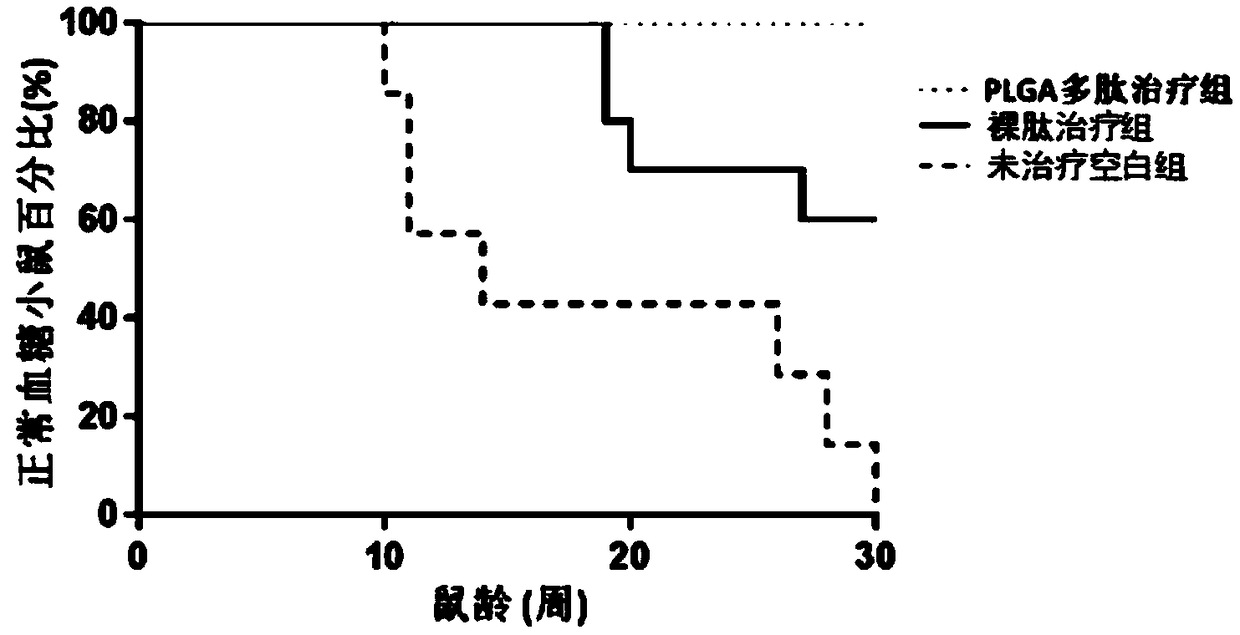
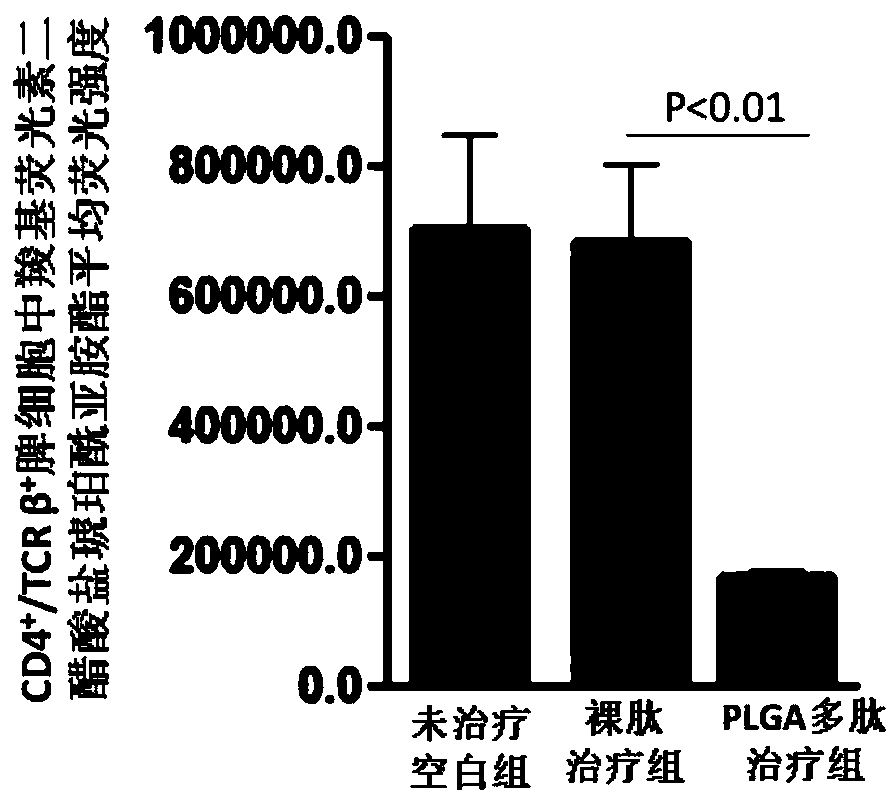
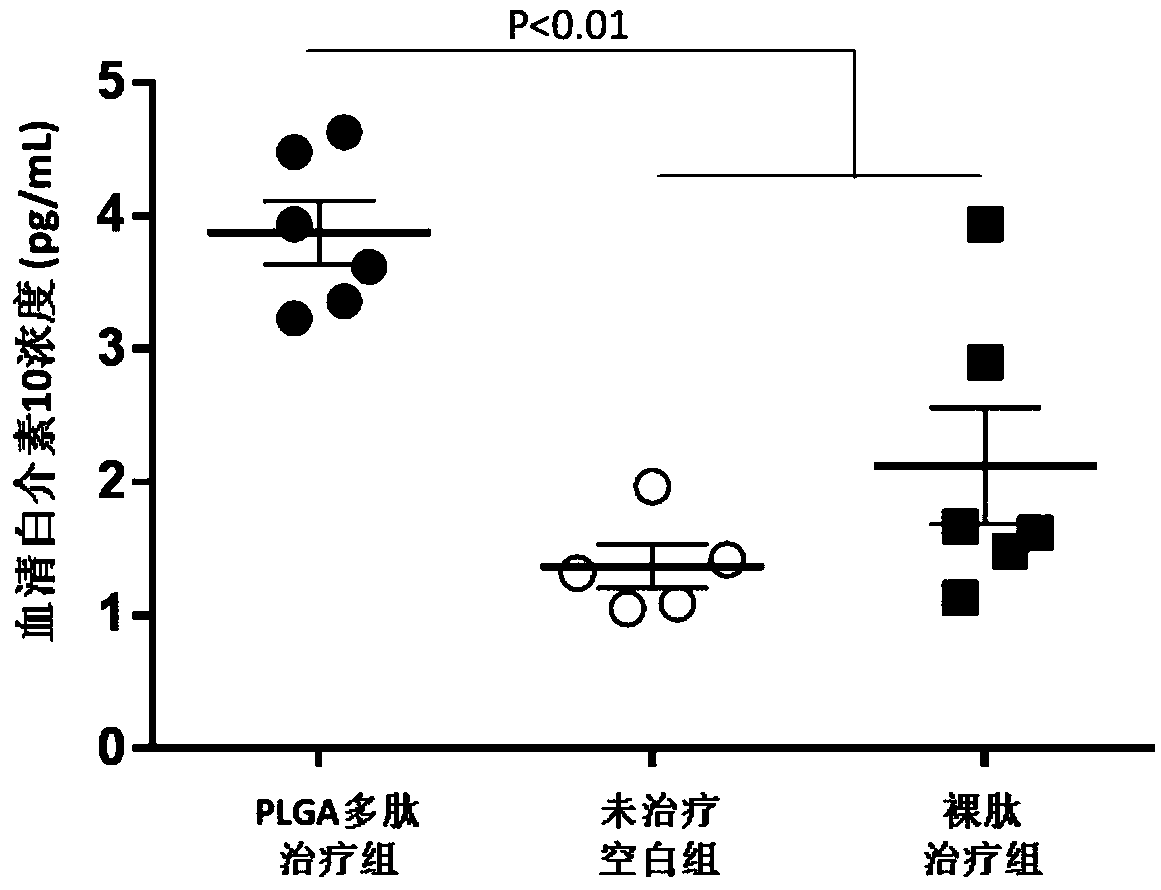
[0047] The polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer microspheres loaded with antigen polypeptide prepared in Example 1 of the present invention were subcutaneously injected into spontaneous type 1 diabetes model mice (non-obese diabetic, NOD mice), and the curative effect was tested.
[0048] 1. Experimental method
[0049] Weaned female non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice were randomly divided into three groups, and there was no statistical difference among the three groups of mice. After normal body weight and blood sugar measurements, the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer microspheres loaded with antigen polypeptide prepared in Example 1 of the present invention (PLGA polypeptide treatment group) were injected subcutaneously, once a week, 100 μg each time, 4 times in total, And a naked peptide treatment group (injection of the same amount of antigen polypeptide) and an untreated blank group (injection of the same amount of phosphate saline, ie PBS solution) were set up. Aft...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com