Pneumatic valve interface for use in microfluidic structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
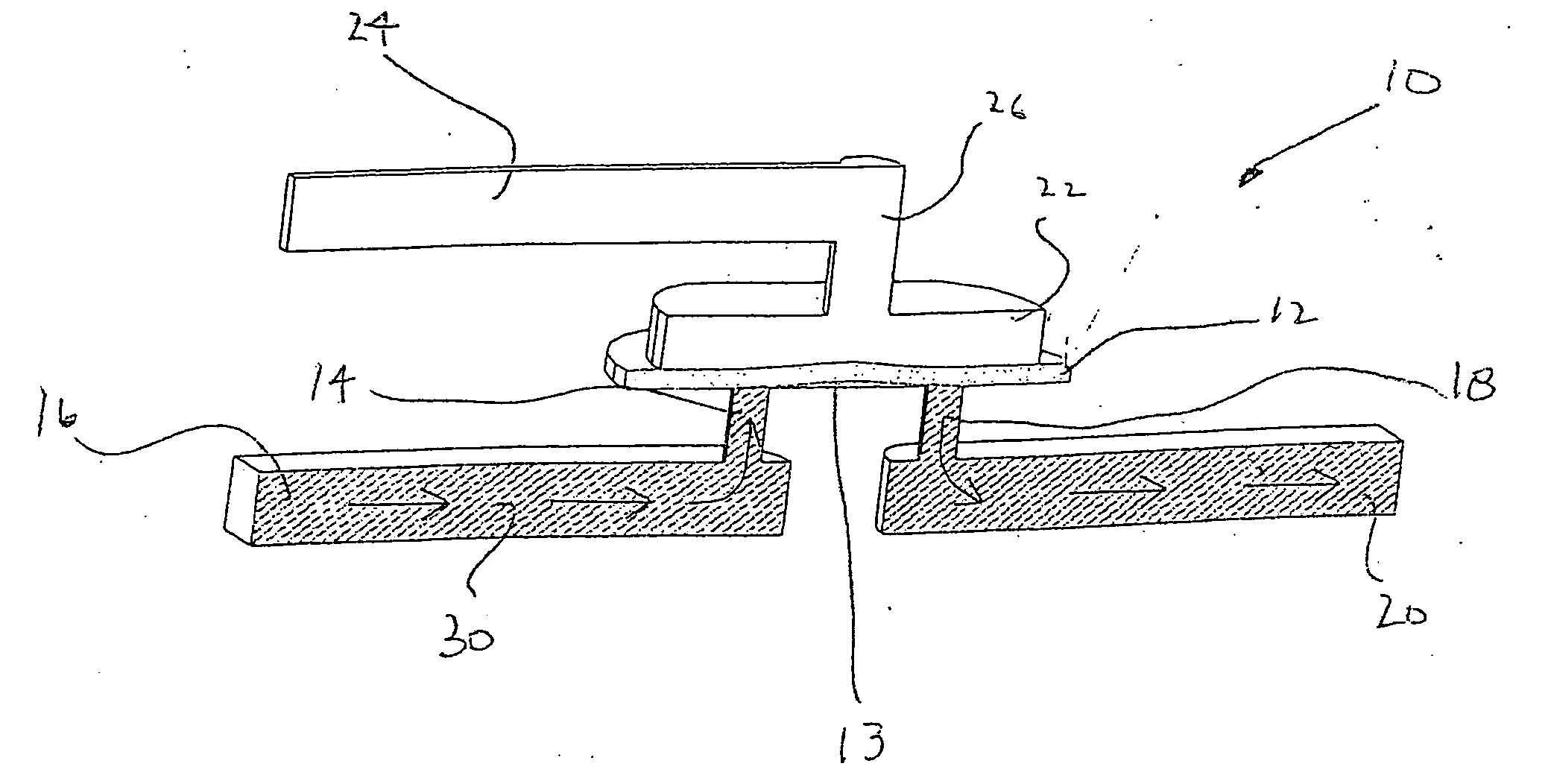
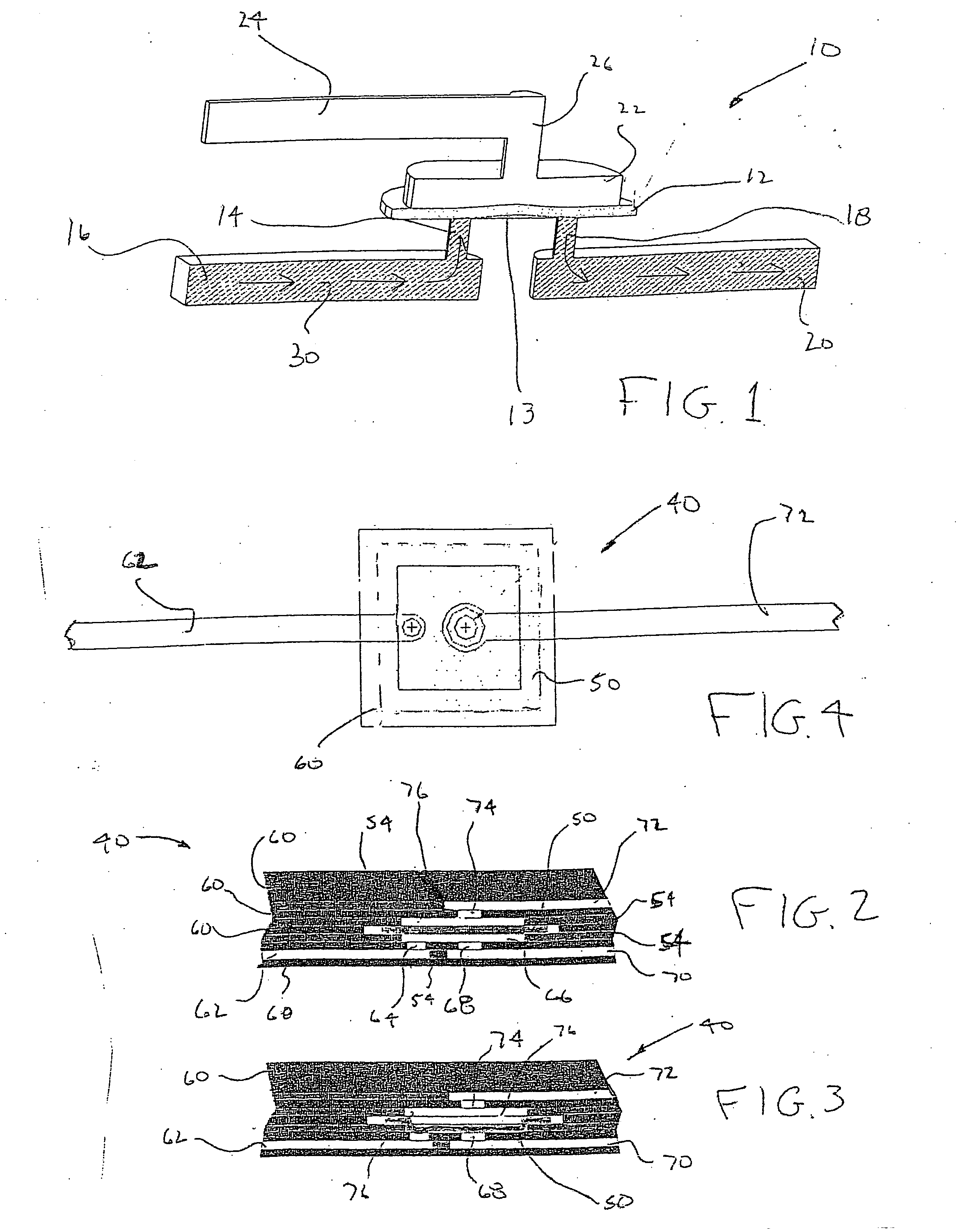
[0028] A basic zero dead volume valve according to the present invention is shown in FIG. 1. Referring now to FIG. 1, a valve generally indicated at 10 consists of a membrane layer 12 which covers a flat surface 13 coupled to an input channel 14, which is connected to a flow channel 16 and also an output channel 18 connected to a flow channel 20. Above layer 12 is an air chamber 22 which is coupled to a pneumatic source 24 by a short air channel 26. In operation, zero dead volume valve 10 works as follows: a liquid 30 enters channel 16 and travels into channel 14 where it contacts membrane layer 12. Under atmospheric conditions within air chamber 22, membrane lines flat against surface or seat 13, causing liquid 30 to stop in channel 14. However, if the fluid pressure within channel 14 exceeds the elastic force contained in membrane 13, membrane 13 will bulge out into chamber 22, allowing liquid 30 to pass under membrane 13 and flow out through channel 18 and into channel 20, as sho...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| air pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com